Page 1

ES4624-SFP/ES4626-SFP
L3 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
1
www.edge-core.com
Page 2

Preface
ES4624-SFP/ES4626-SFP L3 Gigabit Ethernet Switch is a high performance routing
switch released by Edge-Core that can be deployed as an aggregation device for
enterprise and campus networks.ES4624-SFP/ES4626-SFP L3 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
support a variety of network interfaces from 100Mb, 1000Mb to 10 GB Ethernet.
We are providing this manual for your better understanding, use and maintenance of
the ES4624-SFP/ES4626-SFP L3 Gigabit Ethernet Switch. We strongly recommend you
to read through this manual carefully before installation and configuration to avoid
possible malfunction or damage to the switch. Furthermore, we sincerely hope our
products and services satisfy you.
2
Page 3

Content
CHAPTER 1 SWITCH MANAGEMENT.......................................................................... 17
1.1 MANAGEMENT OPTIONS........................................................................................... 17
1.1.1 Out-Of-Band Management.............................................................................. 17
1.1.2 In-band Management...................................................................................... 20
1.1.3 Management Via Telnet .................................................................................. 20
1.1.4 Management Via HTTP................................................................................... 23
1.2 MANAGEMENT INTERFACE ........................................................................................ 25
1.2.1 CLI Interface ................................................................................................... 25
1.2.2 Configuration Modes....................................................................................... 26
1.2.3 Configuration Syntax....................................................................................... 29
1.2.4 Shortcut Key Support...................................................................................... 30
1.2.5 Help Function.................................................................................................. 30
1.2.6 Input Verification ............................................................................................. 31
1.2.7 Fuzzy Match Support ...................................................................................... 31
1.3 WEB MANAGEMENT ................................................................................................. 32
1.3.1 Main Page....................................................................................................... 32
1.3.2 Module Front Panel......................................................................................... 32
CHAPTER 2 BASIC SWITCH CONFIGURATION.......................................................... 34
2.1 COMMANDS FOR BASIC SWITCH CONFIGURATION ...................................................... 34
2.1.1 Commands for Basic Configuration ................................................................ 34
2.2 MONITOR AND DEBUG COMMAND.............................................................................. 48
2.2.1 Ping................................................................................................................. 48
2.2.2 Ping6............................................................................................................... 48
2.2.3 Telnet .............................................................................................................. 49
2.2.4 SSH ................................................................................................................ 51
2.2.5 Traceroute....................................................................................................... 55
2.2.6 Traceroute6..................................................................................................... 55
2.2.7 Show............................................................................................................... 56
2.2.8 Debug ............................................................................................................. 62
2.2.9 System log ...................................................................................................... 62
2.3 CONFIGURATE SWITCH IP ADDRESSES...................................................................... 67
2.3.1 Switch IP Addresses Configuration Task List .................................................. 67
2.3.2 Commands For Configuring Switch IP ............................................................ 68
2.4 SNMP CONFIGURATION ........................................................................................... 69
2.4.1 Introduction To SNMP ..................................................................................... 69
3
Page 4

2.4.2 SNMP Configuration Task List......................................................................... 72
2.4.3 Commands for SNMP ..................................................................................... 74
2.4.4 Typical SNMP Configuration Examples........................................................... 84
2.4.5 SNMP Troubleshooting ................................................................................... 85
2.5 SWITCH UPGRADE ................................................................................................... 86
2.5.1 Switch System Files........................................................................................ 86
2.5.2 BootROM Upgrade ......................................................................................... 86
2.5.3 FTP/TFTP Upgrade......................................................................................... 89
2.5.4 FTP/TFTP Configuration Examples ................................................................ 97
2.5.5 FTP/TFTP Troubleshooting........................................................................... 101
2.6 SECURITY FEATURE CONFIGURATION...................................................................... 103
2.6.1 Security Feature Introduction ........................................................................ 103
2.6.2 Security Feature Configuration ..................................................................... 103
2.6.3 Commands for Security Feature ................................................................... 105
2.6.4 Security Feature Example............................................................................. 108
2.7 JUMBO CONFIGURATION......................................................................................... 109
2.7.1 Jumbo Introduction ....................................................................................... 109
2.7.2 Jumbo Configuration Task Sequence............................................................ 109
2.7.3 Jumbo Command.......................................................................................... 109
2.8 SFLOW CONFIGURATION......................................................................................... 109
2.8.1 sFlow introduction ......................................................................................... 109
2.8.2 sFlow Configuration Task ...............................................................................11 0
2.8.3 Commands for sFlow ..................................................................................... 111
2.8.4 sFlow Examples.............................................................................................116
2.8.5 sFlow Troubleshooting...................................................................................116
2.9 TACACS+ CONFIGURATION ....................................................................................117
2.9.1 TACACS+ Introduction ...................................................................................117
2.9.2 TACACS+ Configurations...............................................................................117
2.9.3 Commands for TACACS+ ..............................................................................118
2.9.4 Typical TACACS+ Scenarios......................................................................... 120
2.9.5 TACACS+ Troubleshooting ........................................................................... 120
2.10 WEB MANAGEMENT ............................................................................................. 121
2.10.1 Switch Basic Configuration ......................................................................... 121
2.10.2 SNMP Configuration ................................................................................... 121
2.10.3 Switch upgrade ........................................................................................... 124
2.10.4 Monitor And Debug Command.................................................................... 127
2.10.5 Switch Maintenance.................................................................................... 128
2.10.6 Telnet server configuration .......................................................................... 129
4
Page 5

2.10.7 Telnet server user configuration .................................................................. 129
2.10.8 Telnet security IP......................................................................................... 129
CHAPTER 3 PORT CONFIGURATION........................................................................131
3.1 INTRODUCTION TO PORT ........................................................................................ 131
3.2 PORT CONFIGURATION........................................................................................... 131
3.2.1 Network Port Configuration........................................................................... 131
3.2.2 VLAN Interface Configuration ....................................................................... 140
3.2.3 Network Management Port Configuration ..................................................... 142
3.3 PORT MIRRORING CONFIGURATION......................................................................... 145
3.3.1 Introduction to Port Mirroring......................................................................... 145
3.3.2 Port Mirroring Configuration Task List ........................................................... 146
3.3.3 Commands for Mirroring Configuration ......................................................... 146
3.3.4 Device Mirroring Troubleshooting ................................................................. 147
3.4 PORT CONFIGURATION EXAMPLE............................................................................ 148
3.5 PORT TROUBLESHOOTING...................................................................................... 148
3.6 WEB MANAGEMENT ............................................................................................... 149
3.6.1 Ethernet port configuration............................................................................ 149
3.6.2 Physical port configuration............................................................................ 149
3.6.3 Bandwidth control ......................................................................................... 150
3.6.4 Vlan interface configuration........................................................................... 150
3.6.5 Allocate IP address for L3 port ...................................................................... 151
3.6.6 L3 port IP addr mode configuration............................................................... 151
3.6.7 Port mirroring configuration........................................................................... 151
3.6.8 Mirror configuration ....................................................................................... 151
3.6.9 Port debug and maintenance ........................................................................ 152
3.6.10 Show port information ................................................................................. 152
CHAPTER 4 PORT CHANNEL CONFIGURATION ..................................................... 153
4.1 INTRODUCTION TO PORT CHANNEL ......................................................................... 153
4.2 PORT CHANNEL CONFIGURATION TASK LIST ............................................................ 154
4.3 COMMANDS FOR PORT CHANNEL............................................................................. 155
4.3.1 debug lacp .................................................................................................... 155
4.3.2 port-group ..................................................................................................... 155
4.3.3 port-group mode ........................................................................................... 156
4.3.4 interface port-channel ................................................................................... 157
4.3.5 show port-group ............................................................................................ 157
4.4 PORT CHANNEL EXAMPLE ...................................................................................... 161
4.5 PORT CHANNEL TROUBLESHOOTING....................................................................... 164
5
Page 6

4.6 WEB MANAGEMENT ............................................................................................... 164
4.6.1 LACP port group configuration...................................................................... 164
4.6.2 LACP port configuration................................................................................ 165
CHAPTER 5 VLAN CONFIGURATION........................................................................ 166
5.1 VLAN CONFIGURATION.......................................................................................... 166
5.1.1 Introduction to VLAN..................................................................................... 166
5.1.2 VLAN Configuration Task List ....................................................................... 167
5.1.3 Commands For Vlan Configuration............................................................... 169
5.1.4 Typical VLAN Application .............................................................................. 174
5.2 GVRP CONFIGURATION ......................................................................................... 176
5.2.1 Introduction to GVRP .................................................................................... 176
5.2.2 GVRP Configuration Task List....................................................................... 176
5.2.3 Commands for GVRP ................................................................................... 177
5.2.4 Typical GVRP Application ............................................................................. 180
5.2.5 GVRP Troubleshooting ................................................................................. 182
5.3 DOT1Q-TUNNEL CONFIGURATION............................................................................ 183
5.3.1 Dot1q-tunnel Introduction.............................................................................. 183
5.3.2 Dot1q-tunnel Configuration ........................................................................... 184
5.3.3 Commands for Dot1q-Tunnel Configuration.................................................. 184
5.3.4 Typical Applications Of The Dot1q-tunnel ..................................................... 186
5.3.5 Dot1q-tunnel Troubleshooting ....................................................................... 187
5.4 VLAN-TRANSLATION CONFIGURATION..................................................................... 187
5.4.1 VLAN-translation Introduction ....................................................................... 187
5.4.2 VLAN-translation Configuration..................................................................... 188
5.4.3 Commands for VLAN-Translation Configuration ........................................... 188
5.4.4 Typical application of VLAN-translation......................................................... 190
5.4.5 VLAN-translation Troubleshooting ................................................................ 191
5.5 DYNAMIC VLAN CONFIGURATION ........................................................................... 191
5.5.1 Dynamic VLAN Introduction .......................................................................... 191
5.5.2 Dynamic VLAN Configuration ....................................................................... 192
5.5.3 Typical Application Of The Dynamic VLAN ................................................... 199
5.5.4 Dynamic VLAN Troubleshooting ................................................................... 200
5.6 VOICE VLAN CONFIGURATION................................................................................ 200
5.6.1 Voice VLAN Introduction ............................................................................... 200
5.6.2 Voice VLAN Configuration............................................................................. 201
5.6.3 Typical Applications Of The Voice VLAN....................................................... 204
5.6.4 Voice VLAN Troubleshooting ........................................................................ 205
6
Page 7

CHAPTER 6 MAC TABLE CONFIGURATION.............................................................206
6.1 INTRODUCTION TO MAC TABLE............................................................................... 206
6.1.1 Obtaining MAC Table .................................................................................... 206
6.1.2 Forward or Filter............................................................................................ 208
6.2 COMMANDS FOR MAC ADDRESS TABLE CONFIGURATION .......................................... 209
6.2.1 mac-address-table ........................................................................................ 209
6.2.2 show mac-address-table............................................................................... 210
6.3 TYPICAL CONFIGURATION EXAMPLES ...................................................................... 210
6.4 TROUBLESHOOTING ................................................................................................211
6.5 MAC ADDRESS FUNCTION EXTENSION ....................................................................211
6.5.1 MAC Address Binding....................................................................................211
CHAPTER 7 MSTP CONFIGURATION........................................................................ 219
7.1 MSTP INTRODUCTION............................................................................................ 219
7.1.1 MSTP Region................................................................................................ 219
7.1.2 Port Roles ..................................................................................................... 221
7.1.3 MSTP Load Balance ..................................................................................... 221
7.2 MSTP CONFIGURATION TASK LIST.......................................................................... 221
7.3 COMMANDS FOR MSTP ......................................................................................... 225
7.3.1 abort.............................................................................................................. 225
7.3.2 exit ................................................................................................................ 225
7.3.3 instance vlan ................................................................................................. 226
7.3.4 name............................................................................................................. 226
7.3.5 revision-level ................................................................................................. 227
7.3.6 spanning-tree ................................................................................................ 227
7.3.7 spanning-tree format..................................................................................... 228
7.3.8 spanning-tree forward-time ........................................................................... 228
7.3.9 spanning-tree hello-time................................................................................ 229
7.3.10 spanning-tree link-type p2p......................................................................... 229
7.3.11 spanning-tree maxage................................................................................. 230
7.3.12 spanning-tree max-hop ............................................................................... 230
7.3.13 spanning-tree mcheck................................................................................. 231
7.3.14 spanning-tree mode .................................................................................... 231
7.3.15 spanning-tree mst configuration.................................................................. 231
7.3.16 spanning-tree mst cost................................................................................ 232
7.3.17 spanning-tree mst port-priority .................................................................... 233
7.3.18 spanning-tree mst priority............................................................................ 233
7.3.19 spanning-tree portfast ................................................................................. 234
7
Page 8

7.3.20 spanning-tree digest-snooping.................................................................... 234
7.3.21 spanning-tree tcflush (global mode)............................................................ 235
7.3.22 spanning-tree tcflush (port mode) ............................................................... 235
7.4 MSTP EXAMPLE.................................................................................................... 236
7.5 MSTP TROUBLESHOOTING .................................................................................... 241
7.5.1 Commands for Monitor And Debug ............................................................... 241
7.6 WEB MANAGEMENT ............................................................................................... 245
7.6.1 MSTP field operation..................................................................................... 245
7.6.2 MSTP port operation..................................................................................... 246
7.6.3 MSTP global control...................................................................................... 247
7.6.4 Show MSTP setting....................................................................................... 249
CHAPTER 8 QOS AND PBR CONFIGURATION.........................................................250
8.1 QOS CONFIGURATION............................................................................................ 250
8.1.1 Introduction to QoS ....................................................................................... 250
8.1.2 QoS Configuration Task List.......................................................................... 255
8.1.3 Commands for QoS ...................................................................................... 259
8.1.4 QoS Example................................................................................................ 268
8.1.5 QoS Troubleshooting .................................................................................... 271
8.2 PBR CONFIGURATION............................................................................................ 276
8.2.1 Introduction to PBR....................................................................................... 276
8.2.2 PBR configuration ......................................................................................... 276
8.2.3 PBR examples .............................................................................................. 277
CHAPTER 9 L3 FORWARD CONFIGURATION..........................................................278
9.1 LAYE R 3 INTERFACE............................................................................................... 278
9.1.1 Introduction to Layer 3 Interface ................................................................... 278
9.1.2 Layer 3 Interface Configuration Task List ...................................................... 278
9.1.3 Commands for Layer 3 Interface................................................................... 279
9.2 IP CONFIGURATION................................................................................................ 279
9.2.1 Introduction to IPv4, IPv6.............................................................................. 279
9.2.2 IP Configuration ............................................................................................ 281
9.2.3 IP Configuration Examples............................................................................ 296
9.2.4 IP Troubleshooting ........................................................................................ 300
9.3 IP FORWARDING .....................................................................................................311
9.3.1 Introduction to IP Forwarding.........................................................................311
9.3.2 IP Route Aggregation Configuration Task ......................................................311
9.3.3 Commands for IP Route Aggregation.............................................................311
9.4 URPF................................................................................................................... 312
8
Page 9

9.4.1 URPF Introduction ........................................................................................ 312
9.4.2 URPF Operation Mechanism ........................................................................ 312
9.4.3 URPF Configuration Task Sequence............................................................. 312
9.4.4 Commands For URPF .................................................................................. 313
9.4.5 URPF Troubleshooting.................................................................................. 314
9.5 ARP ..................................................................................................................... 315
9.5.1 Introduction to ARP....................................................................................... 315
9.5.2 ARP Configuration Task List.......................................................................... 315
9.5.3 Commands for ARP Configuration ................................................................ 316
CHAPTER 10 DHCP CONFIGURATION...................................................................... 319
10.1 INTRODUCTION TO DHCP..................................................................................... 319
10.2 DHCP SERVER CONFIGURATION .......................................................................... 320
10.2.1 DHCP Sever Configuration Task List .......................................................... 320
10.2.2 Commands for DHCP Server Configuration................................................ 322
10.3 DHCP RELAY CONFIGURATION............................................................................. 330
10.3.1 DHCP Relay Configuration Task List........................................................... 331
10.3.2 Commands for DHCP Relay Configuration ................................................. 332
10.4 DHCP CONFIGURATION EXAMPLE ........................................................................ 334
10.5 DHCP TROUBLESHOOTING .................................................................................. 337
10.5.1 Commands for Monitor and Debug ............................................................. 337
10.6 WEB MANAGEMENT ............................................................................................. 340
10.6.1 DHCP server configuration ......................................................................... 340
10.6.2 DHCP debugging ........................................................................................ 345
CHAPTER 11 SNTP CONFIGURATION.......................................................................347
11.1 INTRODUCTION TO SNTP ..................................................................................... 347
11.2 COMMANDS FOR SNTP........................................................................................ 348
11.2.1 sntp server .................................................................................................. 348
11.2.2 sntp poll ....................................................................................................... 348
11.2.3 debug sntp .................................................................................................. 349
11.2.4 show sntp .................................................................................................... 349
11.3 TYPICAL SNTP CONFIGURATION EXAMPLES .......................................................... 349
11.4 WEB MANAGEMENT.............................................................................................. 350
11.4.1 SNMP/NTP server configuration ................................................................. 350
11.4.2 Request interval configuration..................................................................... 350
11.4.3 Time difference............................................................................................ 350
11.4.4 Show SNTP................................................................................................. 351
CHAPTER 12 PREVENT ARP, ND SPOOFING CONFIGURATION............................352
9
Page 10

12.1 OVERVIEW........................................................................................................... 352
12.1.1 ARP ( Address Resolution Protocol)............................................................ 352
12.1.2 ARP Spoofing.............................................................................................. 352
12.1.3 How to prevent void ARP/ND Spoofing for our Layer 3 Switch ................... 352
12.2 PREVENT ARP, ND SPOOFING CONFIGURATION..................................................... 353
12.2.1 Prevent ARP, ND Spoofing Configuration Task List..................................... 353
12.3 COMMANDS FOR PREVENTING ARP, ND SPOOFING............................................... 354
12.3.1 ip arp-security updateprotect....................................................................... 354
12.3.2 ipv6 nd-security updateprotect .................................................................... 354
12.3.3 ip arp-security learnprotect.......................................................................... 355
12.3.4 ipv6 nd learnprotect .................................................................................... 355
12.3.5 ip arp-security convert................................................................................. 355
12.3.6 ipv6 nd-security convert .............................................................................. 356
12.3.7 clear ip arp dynamic.................................................................................... 356
12.3.8 clear ipv6 nd dynamic ................................................................................. 356
12.4 PREVENT ARP, ND SPOOFING EXAMPLE............................................................... 356
CHAPTER 13 ROUTING PROTOCOL......................................................................... 359
13.1 ROUTING PROTOCOL OVERVIEW........................................................................... 359
13.1.1 Routing Table .............................................................................................. 360
13.2 IP ROUTING POLICY............................................................................................. 361
13.2.1 Introduction To Routing Policy..................................................................... 361
13.2.2 IP Routing Policy Configuration Task List.................................................... 363
13.2.3 Commands for Routing Policy..................................................................... 367
13.2.4 Configuration Examples.............................................................................. 379
13.2.5 Troubleshooting .......................................................................................... 380
13.3 STATI C ROUTE..................................................................................................... 383
13.3.1 Introduction to Static Route......................................................................... 383
13.3.2 Introduction to Default Route ...................................................................... 383
13.3.3 Static Route Configuration Task List............................................................ 384
13.3.4 Commands for Static Route ........................................................................ 384
13.3.5 Configuration Examples.............................................................................. 388
13.4 RIP..................................................................................................................... 389
13.4.1 Introduction to RIP ...................................................................................... 389
13.4.2 RIP Configuration Task List......................................................................... 391
13.4.3 Commands for RIP ..................................................................................... 397
13.4.4 RIP Examples ............................................................................................. 412
13.4.5 RIP Troubleshooting.................................................................................... 415
13.5 RIPNG ................................................................................................................ 421
10
Page 11

13.5.1 Introduction to RIPng .................................................................................. 421
13.5.2 RIPng Configuration Task List ..................................................................... 422
13.5.3 Commands For RIPng ................................................................................ 426
13.5.4 RIPng Configuration Examples ................................................................... 431
13.5.5 RIPng Troubleshooting................................................................................ 433
13.6 OSPF................................................................................................................. 437
13.6.1 Introduction to OSPF .................................................................................. 437
13.6.2 OSPF Configuration Task List ..................................................................... 440
13.6.3 Commands for OSPF.................................................................................. 444
13.6.4 OSPF Example ........................................................................................... 465
13.6.5 OSPF Troubleshooting................................................................................ 474
13.7 OSPFV3............................................................................................................. 483
13.7.1 Introduction to OSPFv3............................................................................... 483
13.7.2 OSPFv3 Configuration Task List ................................................................. 486
13.7.3 Commands for OSPFV3 ............................................................................. 490
13.7.4 OSPFv3 Examples...................................................................................... 500
13.7.5 OSPFv3 Troubleshooting............................................................................ 503
13.8 BGP ................................................................................................................... 510
13.8.1 BGP Introduction......................................................................................... 510
13.8.2 BGP Configuration Task List ....................................................................... 514
13.8.3 Commands for BGP.................................................................................... 526
13.8.4 Configuration Examples of BGP ................................................................. 567
13.8.5 BGP Troubleshooting .................................................................................. 581
13.9 MBGP4+ ............................................................................................................ 592
13.9.1 MBGP4+ Introduction.................................................................................. 592
13.9.2 MBGP4+ Configures Mission List ............................................................... 592
13.9.3 MBGP4+ Examples..................................................................................... 593
13.9.4 MBGP4+ Troubleshooting........................................................................... 594
CHAPTER 14 IGMP SNOOPING ................................................................................. 595
14.1 INTRODUCTION TO IGMP SNOOPING..................................................................... 595
14.2 IGMP SNOOPING CONFIGURATION TASK ............................................................... 595
14.3 COMMANDS FOR IGMP SNOOPING ....................................................................... 597
14.3.1 ip igmp snooping vlan ................................................................................. 597
14.3.2 ip igmp snooping vlan immediate-leave ...................................................... 597
14.3.3 ip igmp snooping vlan l2-general-querier .................................................... 597
14.3.4 ip igmp snooping vlan limit.......................................................................... 598
14.3.5 ip igmp snooping vlan mrouter-port interface .............................................. 598
14.3.6 ip igmp snooping vlan mrpt ......................................................................... 599
11
Page 12

14.3.7 ip igmp snooping vlan query-interval........................................................... 599
14.3.8 ip igmp snooping vlan query-mrsp .............................................................. 599
14.3.9 ip igmp snooping vlan query-robustness..................................................... 600
14.3.10 ip igmp snooping vlan suppression-query-time ......................................... 600
14.4 IGMP SNOOPING EXAMPLE.................................................................................. 601
14.5 IGMP SNOOPING TROUBLESHOOTING .................................................................. 603
14.5.1 Commands for Monitor And Debug............................................................. 603
CHAPTER 15 MULTICAST VLAN................................................................................ 607
15.1 INTRODUCTIONS TO MULTICAST VLAN.................................................................. 607
15.2 MULTICAST VLAN CONFIGURATION TASK.............................................................. 607
15.3 COMMANDS FOR MULTICAST VLAN...................................................................... 608
15.3.1 multicast-vlan .............................................................................................. 608
15.3.2 multicast-vlan association<vlan-list>........................................................... 608
15.4 EXAMPLES OF MULTICAST VLAN.......................................................................... 609
CHAPTER 16 IPV4 MULTICAST PROTOCOL ............................................................ 611
16.1 IPV4 MULTICAST PROTOCOL OVERVIEW.................................................................611
16.1.1 Introduction to Multicast ...............................................................................611
16.1.2 Multicast Address........................................................................................ 612
16.1.3 IP Multicast Packet Transmission................................................................ 613
16.1.4 IP Multicast Application ............................................................................... 613
16.2 PIM-DM ............................................................................................................. 614
16.2.1 Introduction to PIM-DM ............................................................................... 614
16.2.2 PIM-DM Configuration Task List.................................................................. 615
16.2.3 Commands for PIM-DM .............................................................................. 616
16.2.4 PIM-DM Configuration Examples................................................................ 618
16.2.5 PIM-DM Troubleshooting ............................................................................ 619
16.3 PIM-SM.............................................................................................................. 622
16.3.1 Introduction to PIM-SM ............................................................................... 622
16.3.2 PIM-SM Configuration Task List .................................................................. 623
16.3.3 Commands for PIM-SM............................................................................... 626
16.3.4 PIM-SM Configuration Examples ................................................................ 635
16.3.5 PIM-SM Troubleshooting............................................................................. 637
16.4 DVMRP.............................................................................................................. 646
16.4.1 Introduction to DVMRP ............................................................................... 646
16.4.2 Configuration Task List................................................................................ 647
16.4.3 Commands for DVMRP............................................................................... 649
16.4.4 DVMRP Configuration Examples ................................................................ 652
12
Page 13

16.4.5 DVMRP Troubleshooting............................................................................. 652
16.5 ECSCM.............................................................................................................. 657
16.5.1 Introduction to ECSCM ............................................................................... 657
16.5.2 ECSCM Configuration Task List .................................................................. 658
16.5.3 Commands for ECSCM............................................................................... 661
16.5.4 ECSCM Configuration Examples ................................................................ 666
16.5.5 ECSCM Troubleshooting............................................................................. 667
16.6 IGMP ................................................................................................................. 669
16.6.1 Introduction to IGMP ................................................................................... 669
16.6.2 Configuration Task List................................................................................ 671
16.6.3 Commands for IGMP .................................................................................. 673
16.6.4 IGMP Configuration Example...................................................................... 678
16.6.5 IGMP Troubleshooting ................................................................................ 679
CHAPTER 17 IPV6 MULTICAST PROTOCOL ............................................................683
17.1 PIM-DM6............................................................................................................ 683
17.1.1 Introduction to PIM-DM6 ............................................................................. 683
17.1.2 PIM-DM Configuration Task List.................................................................. 684
17.1.3 Commands for PIM-DM6 ............................................................................ 685
17.1.4 PIM-DM Typical Application ........................................................................ 689
17.1.5 PIM-DM Troubleshooting ............................................................................ 690
17.2 PIM-SM6............................................................................................................ 693
17.2.1 Introduction to PIM-SM6 ............................................................................. 693
17.2.2 PIM-SM Configuration Task List .................................................................. 694
17.2.3 Commands for PIM-SM............................................................................... 697
17.2.4 PIM-SM Typical Application......................................................................... 705
17.2.5 PIM-SM Troubleshooting............................................................................. 707
17.3 MLD ................................................................................................................... 716
17.3.1 Introduction to MLD..................................................................................... 716
17.3.2 MLD Configuration Task List ....................................................................... 717
17.3.3 Commands for MLD.................................................................................... 718
17.3.4 MLD Typical Application.............................................................................. 724
17.3.5 MLD Troubleshooting.................................................................................. 725
17.4 MLD SNOOPING .................................................................................................. 727
17.4.1 MLD Snooping Introduction......................................................................... 727
17.4.2 MLD Snooping Configuration Task.............................................................. 728
17.4.3 Commands For MLD Snooping Configuration ............................................ 729
17.4.4 MLD Snooping Examples............................................................................ 736
17.4.5 MLD Snooping Troubleshooting.................................................................. 739
13
Page 14

CHAPTER 18 ACL CONFIGURATION......................................................................... 740
18.1 INTRODUCTION TO ACL........................................................................................ 740
18.1.1 Access-list................................................................................................... 740
18.1.2 Access-group .............................................................................................. 740
18.1.3 Access-list Action and Global Default Action ............................................... 741
18.2 ACL CONFIGURATION........................................................................................... 741
18.2.1 ACL Configuration Task Sequence.............................................................. 741
18.2.2 Commands for ACL..................................................................................... 754
18.3 ACL EXAMPLE ..................................................................................................... 772
18.4 ACL TROUBLESHOOTING...................................................................................... 773
18.4.1 Command for Monitor And Debug............................................................... 773
18.5 WEB MANAGEMENT ............................................................................................. 777
18.5.1 Numeric standard ACL configuration........................................................... 777
18.5.2 Delete numeric IP ACL................................................................................ 778
18.5.3 Configure the numeric extended ACL ......................................................... 778
18.5.4 Configure and delete the standard ACL name ............................................ 779
18.5.5 Configure extended ACL name configuration.............................................. 780
18.5.6 Firewall configuration .................................................................................. 780
18.5.7 ACL port binding.......................................................................................... 781
CHAPTER 19 802.1X CONFIGURATION .................................................................... 782
19.1 INTRODUCTION TO 802.1X .................................................................................... 782
19.2 802.1X CONFIGURATION TASK LIST....................................................................... 783
19.3 COMMANDS FOR 802.1X ...................................................................................... 787
19.3.1 aaa enable .................................................................................................. 787
19.3.2 aaa-accounting enable................................................................................ 787
19.3.3 dot1x accept-mac........................................................................................ 788
19.3.4 dot1x eapor enable ..................................................................................... 788
19.3.5 dot1x enable ............................................................................................... 789
19.3.6 dot1x macfilter enable................................................................................. 789
19.3.7 dot1x max-req ............................................................................................. 789
19.3.8 dot1x max-user ........................................................................................... 790
19.3.9 dot1x port-control ........................................................................................ 790
19.3.10 dot1x port-method..................................................................................... 791
19.3.11 dot1x re-authenticate................................................................................. 791
19.3.12 dot1x re-authentication.............................................................................. 792
19.3.13 dot1x timeout quiet-period......................................................................... 792
19.3.14 dot1x timeout re-authperiod ...................................................................... 792
14
Page 15

19.3.15 dot1x timeout tx-period.............................................................................. 793
19.3.16 radius-server accounting host ................................................................... 793
19.3.17 radius-server authentication host .............................................................. 794
19.3.18 radius-server dead-time ............................................................................ 794
19.3.19 radius-server key ...................................................................................... 795
19.3.20 radius-server retransmit ............................................................................ 795
19.3.21 radius-server timeout ................................................................................ 796
19.4 802.1X APPLICATION EXAMPLE ............................................................................. 797
19.5 802.1X TROUBLESHOOTING ................................................................................. 797
19.5.1 Command for Monitor and debug ............................................................... 798
19.6 WEB MANAGEMENT ............................................................................................. 804
19.6.1 RADIUS client configuration........................................................................ 804
19.6.2 802.1X configuration ................................................................................... 806
CHAPTER 20 VRRP CONFIGURATION......................................................................810
20.1 INTRODUCTION TO VRRP..................................................................................... 810
20.2 CONFIGURATION TASK LIST ...................................................................................811
20.3 COMMANDS FOR VRRP ....................................................................................... 813
20.3.1 advertisement-interval................................................................................. 813
20.3.2 circuit-failover.............................................................................................. 813
20.3.3 debug vrrp................................................................................................... 814
20.3.4 disable......................................................................................................... 814
20.3.5 enable ......................................................................................................... 815
20.3.6 interface ...................................................................................................... 815
20.3.7 preempt-mode............................................................................................. 815
20.3.8 priority ......................................................................................................... 816
20.3.9 router vrrp ................................................................................................... 816
20.3.10 show vrrp .................................................................................................. 816
20.3.11 virtual-ip..................................................................................................... 817
20.4 TYPICAL VRRP SCENARIO ................................................................................... 818
20.5 VRRP TROUBLESHOOTING .................................................................................. 819
20.6 WEB MANAGEMENT ............................................................................................. 819
20.6.1 Create VRRP Number................................................................................. 819
20.6.2 Configure VRRP Dummy IP........................................................................ 819
20.6.3 Configure VRRP Port.................................................................................. 820
20.6.4 Activate Virtual Router................................................................................. 820
20.6.5 Configure Preemptive Mode For VRRP ...................................................... 820
20.6.6 Configure VRRP priority.............................................................................. 820
20.6.7 Configure VRRP Timer interval ................................................................... 821
15
Page 16

20.6.8 Configure VRRP Interface Monitor.............................................................. 821
20.6.9 Configure Authentication Mode For VRRP.................................................. 821
CHAPTER 21 MRPP CONFIGURATION...................................................................... 823
21.1 MRPP INTRODUCTION ......................................................................................... 823
21.1.1 Conception Introduction .............................................................................. 823
21.1.2 MRPP Protocol Packet Types ..................................................................... 824
21.1.3 MRPP Protocol Operation System.............................................................. 825
21.2 MRPP CONFIGURATION TASK LIST ....................................................................... 826
21.3 COMMANDS FOR MRPP ...................................................................................... 827
21.3.1 clear mrpp statistics .................................................................................... 827
21.3.2 control-vlan ................................................................................................. 827
21.3.3 debug mrpp................................................................................................. 828
21.3.4 enable ......................................................................................................... 828
21.3.5 fail-timer ...................................................................................................... 829
21.3.6 hello-timer ................................................................................................... 829
21.3.7 mrpp enable ................................................................................................ 830
21.3.8 mrpp ring..................................................................................................... 830
21.3.9 node-mode.................................................................................................. 830
21.3.10 primary-port............................................................................................... 831
21.3.11 secondary-port .......................................................................................... 831
21.3.12 show mrpp ................................................................................................ 831
21.3.13 show mrpp statistics.................................................................................. 832
21.4 MRPP TYPICAL SCENARIO.................................................................................... 832
21.4.1 MRPP typical scenario 1............................................................................. 832
21.4.2 MRPP typical scenario 2............................................................................. 834
21.4.3 MRPP typical scenario 3............................................................................. 837
21.5 MRPP TROUBLESHOOTING .................................................................................. 840
CHAPTER 22 CLUSTER CONFIGURATION............................................................... 842
22.1.1 Introduction to cluster network management .............................................. 842
22.1.2 Cluster Network Management Configuration Sequence ............................. 842
22.1.3 Commands for cluster................................................................................. 844
22.1.4 Examples of Cluster Administration ............................................................ 850
22.1.5 Cluster Administration Troubleshooting....................................................... 851
16
Page 17

Chapter 1 Switch Management
1.1 Management Options
After purchasing the switch, the user needs to configure the switch for network
management. ES4624-SFP/ES4626-SFP Switch provides two management options:
in-band management and out-of-band management.
1.1.1 Out-Of-Band Management
Out-of-band management is the management through Console interface. Generally,
the user will use out-of-band management for the initial switch configuration, or when
in-band management is not available. For instance, the user must assign an IP address
to the switch via the Console interface to be able to access the switch through Telnet.
The procedures for managing the switch via Console interface are listed below:
Step 1: setting up the environment:
Connect with serial port
Fig 1-1 Out-of-band Management Configuration Environment
As shown in Fig 1-1, the serial port (RS-232) is connected to the switch with the
serial cable provided. The table below lists all the devices used in the connection.
Device Name Description
PC machine Has functional keyboard and RS-232,with terminal emulator
installed,such as HyperTerminal included in Windows
9x/NT/2000/XP.
Serial port cable One end attach to the RS-232 serial port, the other end to
the Console port.
ES4624-SFP/ES462 Functional Console port required.
17
Page 18

6-SFP
Step 2: Entering the HyperTerminal
Open the HyperTerminal included in Windows after the connection established. The
example below is based on the HyperTerminal included in Windows XP.
1) Click Start menu - All Programs -Accessories -Communication - HyperTerminal.
Fig 1-2 Opening HyperTerminal
2) Type a name for opening HyperTerminal, such as “Switch”.
Fig 1-3 Opening HyperTerminal
3) In the “Connecting using” drop-list, select the RS-232 serial port used by the PC, e.g.
COM1, and click “OK”.
18
Page 19
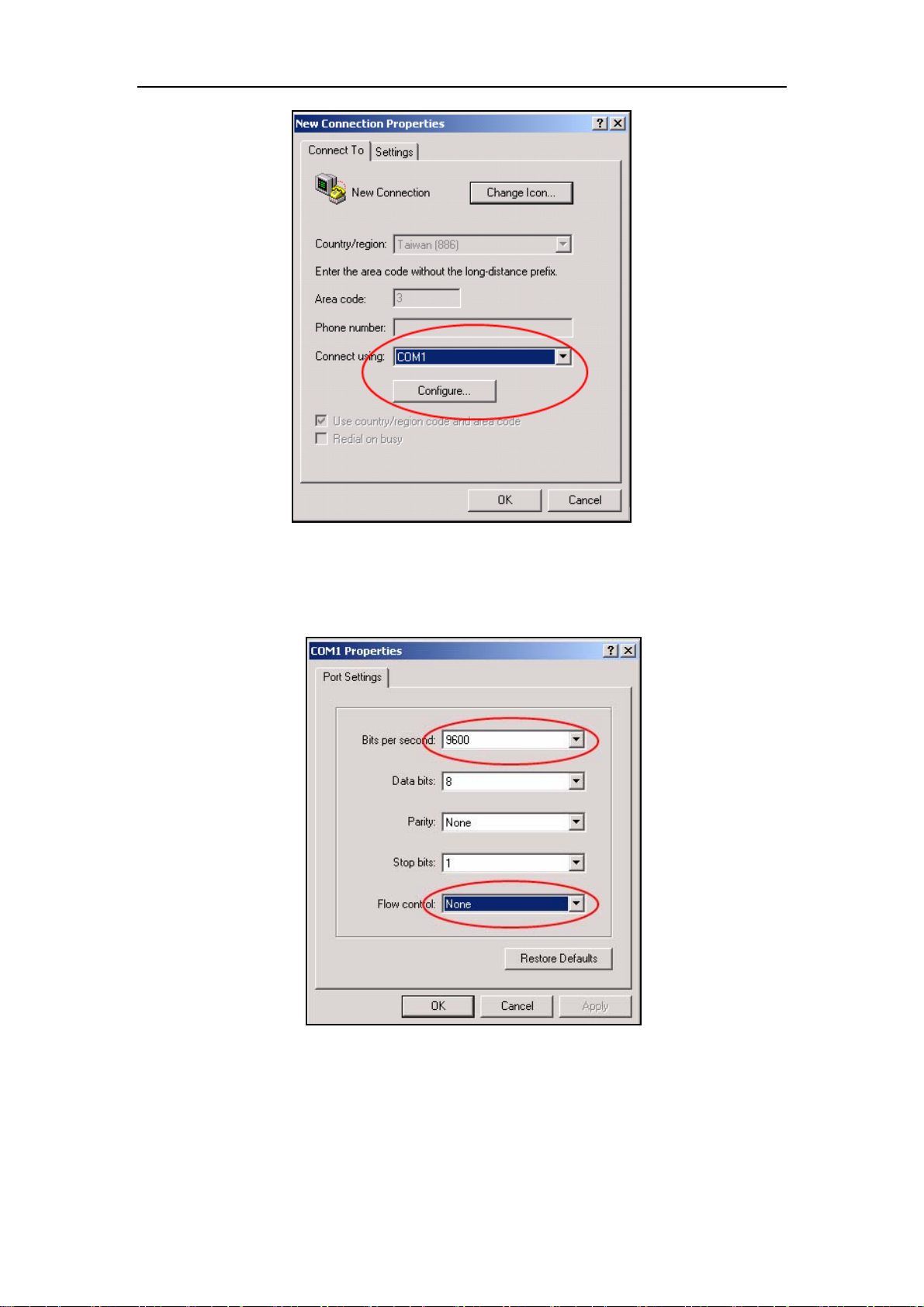
Fig 1-4 Opening HyperTerminal
4) COM1 property appears, select “9600” for “Baud rate”, “8” for “Data bits”, “none” for
“Parity checksum”, “1” for stop bit and “none” for traffic control;or,you can also click
“Restore default” and click “OK”.
Fig 1-5 Opening HyperTerminal
Step 3 :Entering switch CLI interface
Power on the switch, the following appears in the HyperTerminal windows, that is the
CLI configuration mode for ES4624-SFP/ES4626-SFP Switch.
ES4624-SFP Management Switch
19
Page 20

Copyright (c) 2001-2006 by Accton Technology Corporation.
All rights reserved.
Reset chassis ... done.
Testing RAM...
134,217,728 RAM OK.
Initializing...
Attaching to file system ... done.
Loading nos.img ... done.
Starting at 0x10000...
Current time is WED APR 20 09: 37: 52 2005
ES4624-SFP Switch Operating System, Software Version ES4624-SFP 1.1.0.0,
Copyright (C) 2001-2006 by Accton Technology Corporation
http: //www.edge-core. com.
ES4624-SFP Switch
24 Ethernet/IEEE 802.3 interface(s)
Press ENTER to start session
The user can now enter commands to manage the switch. For a detailed description
for the commands, please refer to the following chapters.
1.1.2 In-band Management
In-band management refers to the management by login to the switch using Telnet.
In-band management enables management of the switch for some devices attached to
the switch. In the case when in-band management fails due to switch configuration
changes, out-of-band management can be used for configuring and managing the switch.
1.1.3 Management Via Telnet
To manage the switch with Telnet, the following conditions should be met:
1) Switch has an IP address configured
20
Page 21

2) The host IP address (Telnet client) and the switch’s VLAN interface IP address is
in the same network segment.
3) If not 2), Telnet client can connect to an IP address of the switch via other
devices, such as a router.
ES4624-SFP/ES4626-SFP Switch is a Layer 3 switch that can be configured with
several IP addresses. The following example assumes the shipment status of the switch
where only VLAN1 exists in the system.
The following describes the steps for a Telnet client to connect to the switch’s VLAN1
interface by Telnet.
Fig 1-6 Manage the switch by Telnet
Step 1: Configure the IP addresses for the switch
First is the configuration of host IP address. This should be within the same network
segment as the switch VLAN1 interface IP address. Suppose the switch VLAN interface
IP address 10.1.128.251/24. Then, a possible host IP address is 10.1.128.252/24. Run
“ping 10.1.128.251” from the host and verify the result, check for reasons if ping failed.
The IP address configuration commands for VLAN1 interface are listed below.
Before in-band management, the switch must be configured with an IP address by
out-of-band management (i.e. Console mode), The configuration commands are as
follows (All switch configuration prompts are assumed to be “switch” hereafter if not
otherwise specified):
Switch>
Switch>en
Switch#config
Switch(Config)#interface vlan 1
Switch(Config-If-Vlan1)#ip address 10.1.128.251 255.255.255.0
Switch(Config-If-Vlan1)#no shutdown
21
Page 22
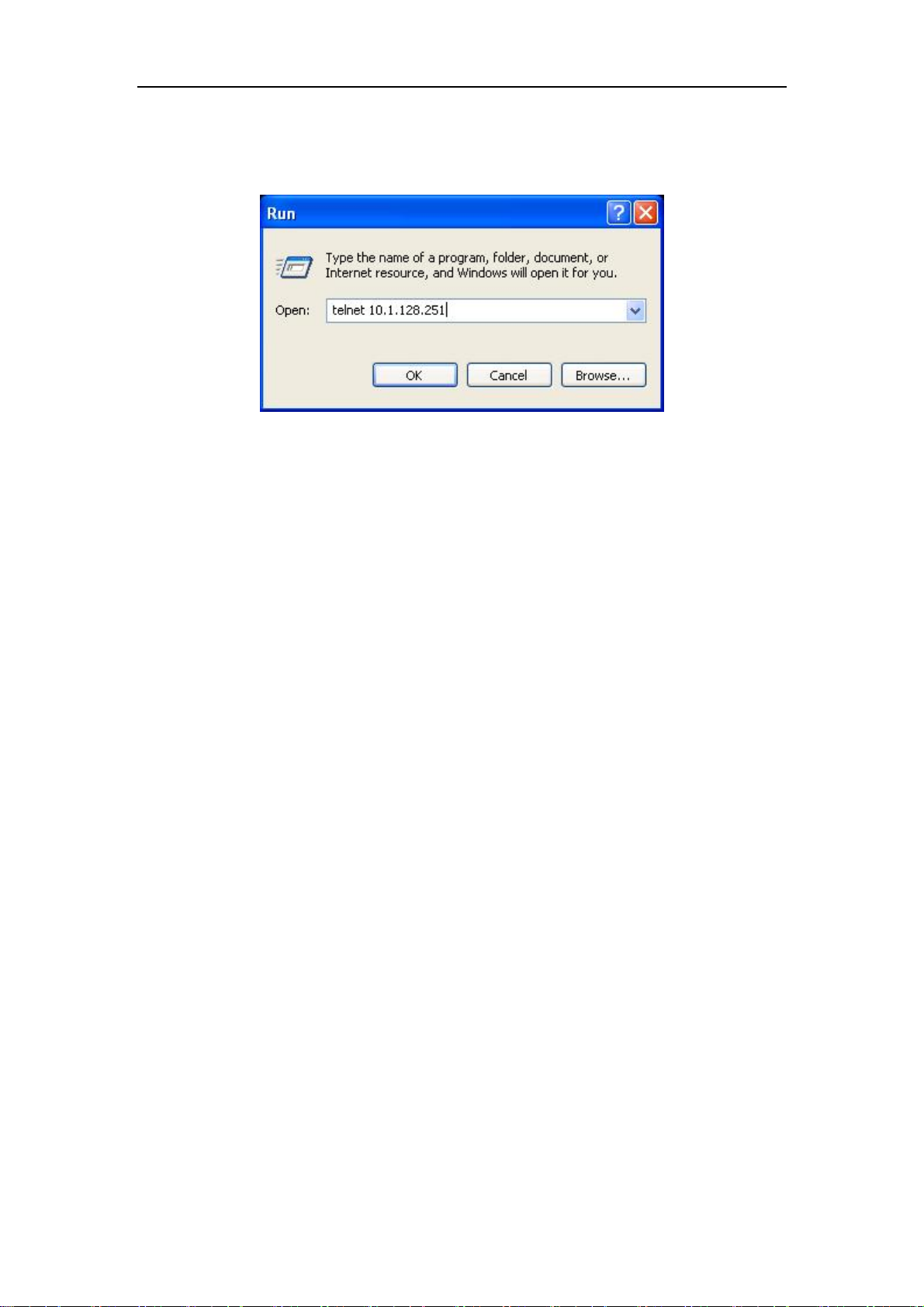
Step 2: Run Telnet Client program.
Run Telnet client program included in Windows with the specified Telnet target.
Fig 1-7 Run telnet client program included in Windows
When accessing a switch with IPv6 address, it is recommended to use the Firefox
browser with 1.5 or later version. For example, if the IPv6 address of the switch is
“3ffe:506:1:2::3”, enter the switch address at the address bar: http://[3ffe:506:1:2::3],
where the address should be in the square brackets.
Step 3: Login to the switch
Login to the Telnet configuration interface. Valid login name and password are
required, otherwise the switch will reject Telnet access. This is a method to protect the
switch from unauthorized access. As a result, when Telnet is enabled for configuring and
managing the switch, username and password for authorized Telnet users must be
configured with the following command:
username <user> password {0|7} <password>.
Assume an authorized user in the switch has a username of “test”, and password of
“test”, the configuration procedure should like the following:
Switch
>en
Switch#config
Switch(Config)#username test password 0 test
Enter valid login name and password in the Telnet configuration interface, Telnet
user will be able to enter the switch’s CLI configuration interface. The commands used in
the Telnet CLI interface after login is the same as that in the Console interface.
22
Page 23

Fig 1-8 Telnet Configuration Interface
1.1.4 Management Via HTTP
To manage the switch via HTTP, the following conditions should be met:
1) Switch has an IP address configured
2) The host IP address (HTTP client) and the switch’s VLAN interface IP address
are in the same network segment;
3) If 2) is not met, HTTP client should connect to an IP address of the switch via
other devices, such as a router.
Similar to management via Telnet, as soon as the host succeeds to ping an IP
address of the switch and to type the right login password, it can access the switch via
HTTP. The configuration list is as below:
Step 1: Configure the IP addresses for the switch and start the HTTP function on the
switch.
For configuring the IP address on the switch through out-of-band management, see
the relevant chapter.
To enable the WEB configuration, users should type the CLI command ip http
server in the global mode as below:
Switch
Switch#config
Switch(Config)#ip http server
>en
23
Page 24
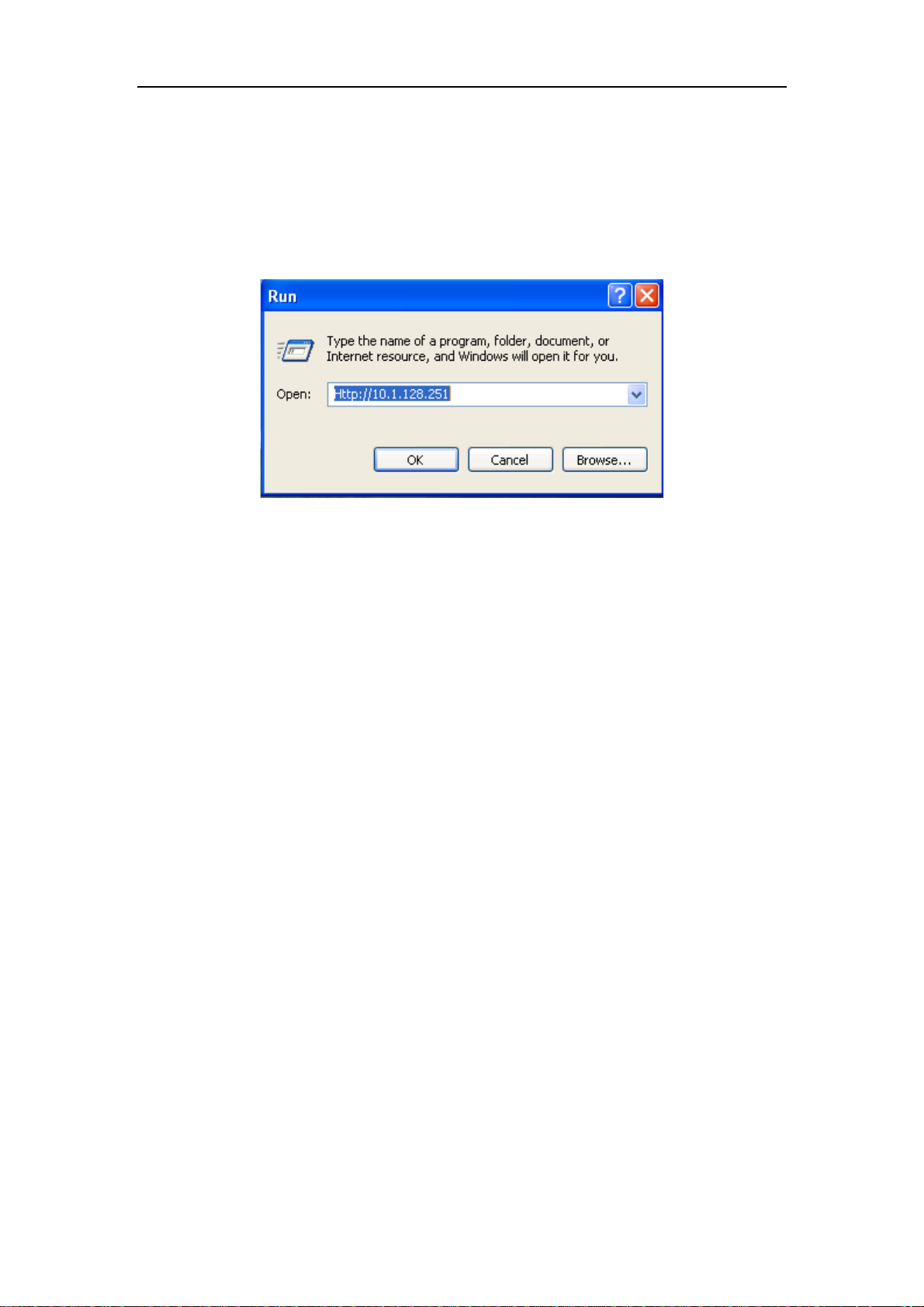
Step 2: Run HTTP protocol on the host.
Open the Web browser on the host and type the IP address of the switch.Or run
directly the HTTP protocol on the Windows. For example, the IP address of the switch is
“10.1.128.251”.
Fig 1-9 Run HTTP Protocol
Step 3: Logon to the switch
To logon to the HTTP configuration interface, valid login user name and password
are required; otherwise the switch will reject HTTP access. This is a method to protect
the switch from the unauthorized access. Consequently, in order to configure the switch
via HTTP, username and password for authorized HTTP users must be configured with
the following command in the global mode:
username <username> password <show_flag> <password>.
Suppose an authorized user in the switch has a username as “test”, and password
as “test”. The configuration procedure is as below:
Switch
>en
Switch#config
Switch(Config)# username test password 0 test
The Web login interface is as below:
24
Page 25

Fig 1-10 Web Login Interface
Input the right username and password, and then the main Web configuration
interface is shown as below.
Fig 1-11 Main Web Configuration Interface
1.2 Management Interface
1.2.1 CLI Interface
25
Page 26
CLI interface is familiar to most users. As aforementioned, out-of-band management
and Telnet login are all performed through CLI interface to manage the switch.
CLI Interface is supported by Shell program, which consists of a set of configuration
commands. Those commands are categorized according to their functions in switch
configuration and management. Each category represents a different configuration mode.
The Shell for the switch is described below:
z Configuration Modes
z Configuration Syntax
z Shortcut keys
z Help function
z Input verification
z Fuzzy match support
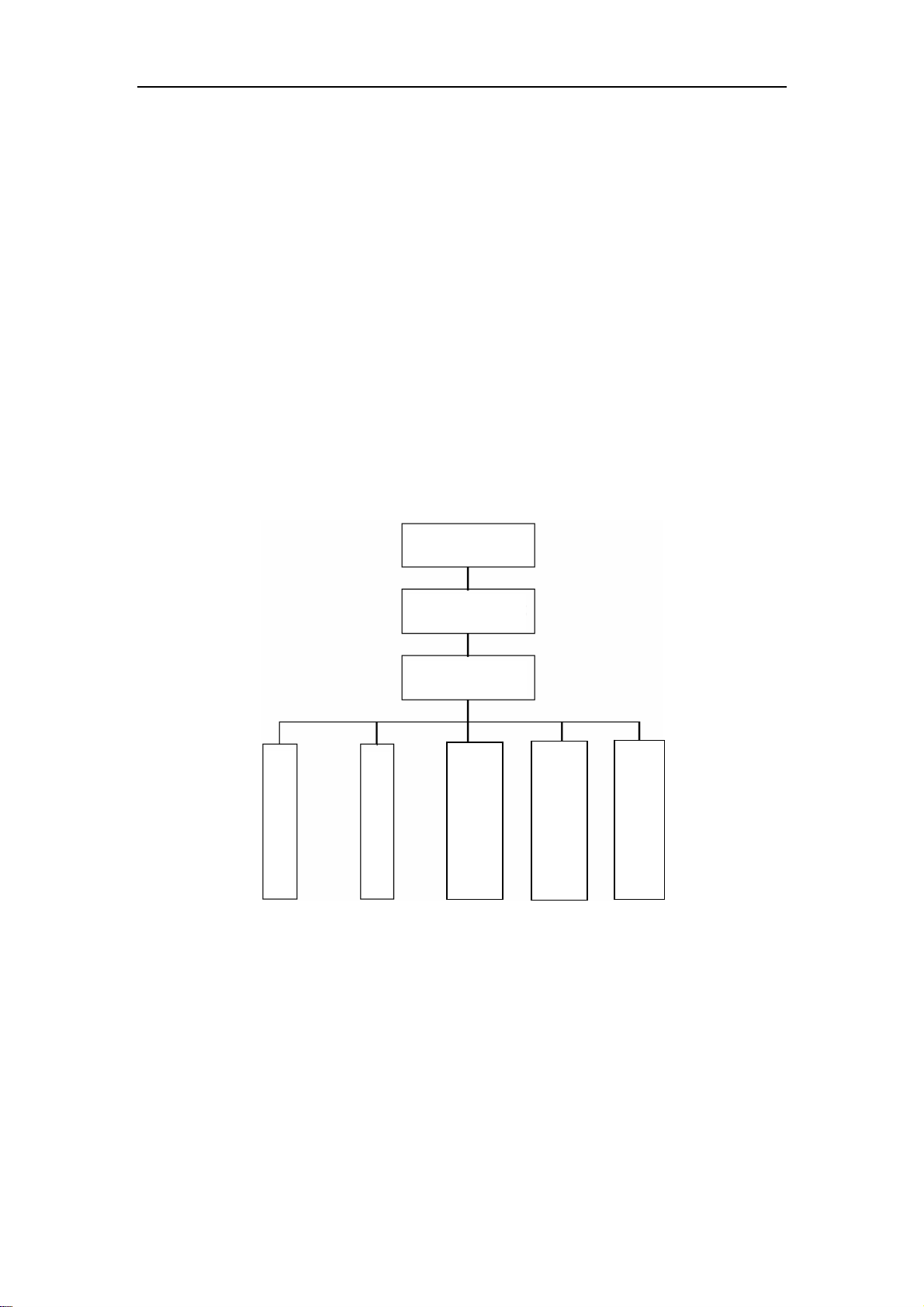
1.2.2 Configuration Modes
Interface Mode
1.2.2.1 User Mode
User Mode
Admin Mode
Global Mode
Vlan Mode
DHCP address pool
configuration mode
Fig 1-12 Shell Configuration Modes
Route configuration
mode
ACL configuration
mode
On entering the CLI interface, entering user entry system first. If as common user, it
is defaulted to User Mode. The prompt shown is “Switch>“, the symbol “>“ is the prompt
for User Mode. When disable command is run under Admin Mode, it will also return to
the User Mode.
Under User Mode, no configuration to the switch is allowed, only clock time and
version information of the switch can be queries.
26
Page 27

1.2.2.2 Admin Mode
To Admin Mode sees the following: In user entry system, if as Admin user, it is
defaulted to Admin Mode. Admin Mode prompt “Switch#” can be entered under the User
Mode by running the enable command and entering corresponding access levels admin
user password, if a password has been set. Or, when exit command is run under Global
Mode, it will also return to the Admin Mode. ES4624-SFP/ES4626-SFP Switch also
provides a shortcut key sequence "Ctrl+z”, this allows an easy way to exit to Admin Mode
from any configuration mode (except User Mode).
Under Admin Mode, when disable command is run, it will return to User Mode. When
exit command is run, it will exit the entry and enter user entry system direct. Next users
can reenter the system on entering corresponding user name and password.
Under Admin Mode, the user can query the switch configuration information,
connection status and traffic statistics of all ports; and the user can further enter the
Global Mode from Admin Mode to modify all configurations of the switch. For this reason,
a password must be set for entering Admin mode to prevent unauthorized access and
malicious modification to the switch.
1.2.2.3 Global Mode
Type the config command under Admin Mode will enter the Global Mode prompt
“Switch(Config)#”. Use the exit command under other configuration modes such as
Interface Mode, VLAN mode will return to Global Mode.
The user can perform global configuration settings under Global Mode, such as MAC
Table, Port Mirroring, VLAN creation, IGMP Snooping start, GVRP and STP, etc. And the
user can go further to Interface Mode for configuration of all the interfaces.
1.2.2.4 Interface Mode
Use the interface command under Global Mode can enter the interface mode
specified. ES4624-SFP/ES4626-SFP Switch provides three interface type: VLAN
interface, Ethernet port and port-channel, and accordingly the three interface
configuration modes.
Interface
Entry Prompt Operates Exit
Type
VLAN
Interface
Ethernet Port Type interface
Type interface
vlan <Vlan-id>
command under
Global Mode.
ethernet
Switch(Config-IfVlanx)#
Switch(Configethernetxx)#
27
Configure
switch IPs, etc
Configure
supported
Use the exit
command to
return to
Global Mode.
Use the exit
command to
Page 28

<interface-list>
command under
Global Mode.
port-channel Type interface
port-channel
<port-channel-nu
mber> command
under Global
Mode.
Switch(Config-ifport-channelx)#
duplex mode,
speed, etc.
of Ethernet
Port.
Configure
port-channel
related
settings such
as duplex
mode, speed,
etc.
return to
Global Mode.
Use the exit
command to
return to
Global Mode.
1.2.2.5 VLAN Mode
Using the vlan <vlan-id> command under Global Mode can enter the corresponding
VLAN Mode. Under VLAN Mode the user can configure all member ports of the
corresponding VLAN. Run the exit command to exit the VLAN Mode to Global Mode.
1.2.2.6 DHCP Address Pool Mode
Type the ip dhcp pool <name> command under Global Mode will enter the DHCP
Address Pool Mode prompt “Switch(Config-<name>-dhcp)#”. DHCP address pool
properties can be configured under DHCP Address Pool Mode. Run the exit command to
exit the DHCP Address Pool Mode to Global Mode.
1.2.2.7 Route Mode
Routing
Protocol
RIP
Routing
Protocol
OSPF
Entry Prompt Operates Exit
Type router
rip
command
under
Global
Mode.
Type router
Switch(Config-Router-Rip)# Configure
RIP protocol
parameters.
Switch(Config-Router-Ospf)# Configure
Use the
“exit”
command to
return to
Global
Mode.
Use the
Routing
Protocol
ospf
command
under
Global
28
OSPF
protocol
parameters.
“exit”
command to
return to
Global
Page 29

Mode. Mode.
1.2.2.8 ACL Mode
ACL type Entry Prompt Operates Exit
Standard IP
ACL Mode
Extended IP
ACL Mode
Type
access-list ip
command
under Global
Mode.
Type
access-list ip
command
under Global
Mode.
Switch(Config-Std-Nacla)#
Switch(Config-Ext-Naclb)#
Configure
parameters
for
Standard
IP ACL
Mode
Configure
parameters
for
Extended
IP ACL
Mode
Use the “exit”
command to
return to
Global Mode.
Use the “exit”
command to
return to
Global Mode.
1.2.3 Configuration Syntax
ES4624-SFP/ES4626-SFP Switch provides various configuration commands.
Although all the commands are different, they all abide by the syntax for
ES4624-SFP/ES4626-SFP Switch configuration commands. The general commands
format of ES4624-SFP/ES4626-SFP Switch is shown below:
cmdtxt <variable> { enum1 | … | enumN } [option]
Conventions: cmdtxt in bold font indicates a command keyword; <variable> indicates a
variable parameter; {enum1 | … | enumN } indicates a mandatory parameter that should
be selected from the parameter set enum1~enumN; and the square bracket ([ ]) in
[option] indicate an optional parameter. There may be combinations of “< >“, “{ }” and
“[ ]” in the command line, such as [<variable>],{enum1 <variable>| enum2}, [option1
[option2]], etc.
Here are examples for some actual configuration commands:
z show calendar, no parameters required. This is a command with only a keyword
and no parameter, just type in the command to run.
z vlan <vlan-id>, parameter values are required after the keyword.
z duplex {auto|full|half}, user can enter duplex half, duplex full or duplex auto for this
29
Page 30

command.
z snmp-server community <string>{ro|rw}, the followings are possible:
snmp-server community <string> ro
snmp-server community <string> rw
1.2.4 Shortcut Key Support
ES4624-SFP/ES4626-SFP Switch provides several shortcut keys to facilitate user
configuration, such as up, down, left, right and Blank Space. If the terminal does not
recognize Up and Down keys, ctrl +p and ctrl +n can be used instead.
Key(s) Function
Back Space Delete a character before the cursor, and the cursor moves back.
Up “↑” Show previous command entered. Up to ten recently entered
commands can be shown.
Down “↓” Show next command entered. When use the Up key to get
previously entered commands, you can use the Down key to
return to the next command
Left “←” The cursor moves one character to
the left.
Right “→” The cursor moves one character to
the right.
Ctrl +p The same as Up key “↑”.
Ctrl +n The same as Down key “↓”.
Ctrl +b The same as Left key “←”.
Ctrl +f The same as Right key “→”.
Ctrl +z Return to the Admin Mode directly from the other configuration
modes ( except User Mode).
Ctrl +c Break the ongoing command process, such as ping or other
command execution.
Tab When a string for a command or keyword is entered, the Tab can
be used to complete the command or keyword if there is no
You can use the Left and
Right key to modify an
entered command.
conflict.
1.2.5 Help Function
There are two ways in ES4624-SFP/ES4626-SFP Switch for the user to access help
information: the “help” command and the “?”.
30
Page 31

Access to Help Usage and function
Help Under any command line prompt, type in “help” and press Enter will
get a brief description of the associated help system.
“?” 1. Under any command line prompt, enter “?” to get a command list of
the current mode and related brief description.
2. Enter a “?” after the command keyword with a embedded space. If the
position should be a parameter, a description of that parameter type,
scope, etc, will be returned; if the position should be a keyword, then
a set of keywords with brief description will be returned; if the output
is “<cr>“, then the command is complete, press Enter to run the
command.
3. A “?” immediately following a string. This will display all the
commands that begin with that string.
1.2.6 Input Ve rification
Returned Information: success
All commands entered through keyboards undergo syntax check by the Shell.
Nothing will be returned if the user entered a correct command under corresponding
modes and the execution is successful.
Returned Information: error
Output error message Explanation
Unrecognized command or illegal
parameter!
Ambiguous command At least two interpretations is possible basing on
Invalid command or parameter The command is recognized, but no valid
This command is not exist in current
mode
Please configure precursor
command "*" at first !
The entered command does not exist, or there
is error in parameter scope, type or format.
the current input.
parameter record is found.
The command is recognized, but this command
can not be used under current mode.
The command is recognized, but the
prerequisite command has not been configured.
syntax error : missing '"' before the
end of command line!
Quotation marks are not used in pairs.
1.2.7 Fuzzy Match Support
ES4624-SFP/ES4626-SFP switch shell support fuzzy match in searching command
31
Page 32

and keyword. Shell will recognize commands or keywords correctly if the entered string
causes no conflict.
For example:
1) For command “show interfaces status ethernet 1/1”, typing “sh in status e 1/1” will
work
2) However, for command “show running-config”, the system will report a “> Ambiguous
command!” error if only “show r” is entered, as Shell is unable to tell whether it is
“show run” or “show running-config”. Therefore, Shell will only recognize the
command if “sh ru” is entered.
1.3 Web Management
1.3.1 Main Page
ES4624-SFP/ES4626-SFP switch routing switch provides HTTP web management
function and users can configure and monitor the status of the switch through the web
interface.
To manage the switch through web browser use the following steps:
Configure valid IP address, mask and confirm gateway for the switch.
1) Configure web user management and its password
2) Connect to the switch using the web browser. Enter the username and password to
proceed to web management.
1.3.2 Module Front Panel
When entering username, password and passing authentication, you will see the
following web management main page. On the left of the management page is the main
management menu and on the right of the page system information and command
parameter are displayed. Click the main menu link to browse other management links
and to display configuration and statistic information.
32
Page 33

Fig 1-13 Module Front Panel
33
Page 34

Chapter 2 Basic Switch Configuration
2.1 Commands for Basic Switch Configuration
Basic switch configuration includes commands for entering and exiting the admin
mode, commands for entering and exiting interface mode, for configuring and displaying
the switch clock, for displaying the version information of the switch system, etc.
Command Explanation
Normal User Mode/ Admin Mode
enable
disable
Admin Mode
config [terminal] Enter global mode from admin mode
Various Modes
Exit
Admin Mode
calendar set <HH:MM:SS>
<YYYY.MM.DD>
Show version Display version information of the switch
set default Restore to the factory default
The User uses enable command to step into
admin mode from normal user mode. The
disable command is for exiting admin mode.
Exit current mode and enter previous mode,
such as using this command in global mode
to go back to admin mode, and back to
normal user mode from admin mode
Set system date and time
Flash Memory
Write
Reload Hot reset the switch
Save current configuration parameters to
Flash Memory
2.1.1 Commands for Basic Configuration
2.1.1.1 authentication login
Command: authentication login {local | radius | local radius | radius local}
no authentication login
Function: Configure the authentication mode and priority on Telnet Server for remote
login users; the “no authentication login” command restores to the default login
34
Page 35

authentication mode.
Default: Default login authentication mode is local.
Command mode: Global mode
Usage guide: When using authentication modes combinations, the mode at the first of
the queue is with the highest priority which receding accordingly. When a user passes
authentication mode with higher priority, the login will be granted without proceeding to
other modes with lower priority. It is to be noted that to login in only one authentication
mode is required. When using radius authentication, the AAA function must be enabled
and radius server be configured.
Example: Configure the remote login authentication mode to radius
Switch(Config)#authentication login radius
2.1.1.2 calendar set
Command: calendar set <HH> <MM> <SS> {<DD> <MON> <YYYY> | <MON> <DD>
<YYYY>}
Function: Set system date and time.
Parameter: <HH> <MM> <SS> is the current time, and the valid scope for HH is 0 to 23,
MM and SS 0 to 59; <DD> <MON> <YYYY> or <MON> <DD> <YYYY> is the current
date, month and year or the current year, month and date, and the valid scope for YYYY
is 1970~2100, MON meaning month, and DD between 1 to 31.
Command mode: Admin Mode
Default: upon first time start-up, it is defaulted to 2001.1.1 0: 0: 0.
Usage guide: The switch can not continue timing with power off, hence the current date
and time must be first set at environments where exact time is required.
Example: To set the switch current date and time to 2002.8.1 23: 0: 0:
Switch# calendar set 23 0 0 august 1 2002
2.1.1.3 config
Command: config [terminal]
Function: Enter Global Mode from Admin Mode.
Parameter: [terminal] indicates terminal configuration.
Command mode: Admin Mode
Example: Switch#config
2.1.1.4 debug ssh-server
Command: debug ssh-server
no debug ssh-server
Function: Display SSH server debugging information; the “no debug ssh-server”
35
Page 36

command stops displaying SSH server debugging information.
Default: This function is disabled by default.
Command mode: Admin Mode
2.1.1.5 dir
Command: dir
Function: Display the files and their sizes in the Flash memory.
Command mode: Admin Mode
Example: Check for files and their sizes in the Flash memory.
Switch#dir
boot.rom 329,828 1900-01-01 00: 00: 00 --SH
boot.conf 94 1900-01-01 00: 00: 00 --SH
nos.img 2,449,496 1980-01-01 00: 01: 06 ----
startup-config 2,064 1980-01-01 00: 30: 12 ----
2.1.1.6 enable
Command: enable
Function: Enter Admin Mode from User Mode.
Command mode: User Mode
Usage Guide: To prevent unauthorized access of non-admin user, user authentication is
required (i.e. Admin user password is required) when entering Admin Mode from User
Mode. If the correct Admin user password is entered, Admin Mode access is granted; if 3
consecutive entry of Admin user password are all wrong, it remains in the User Mode.
Set the Admin user password under Global Mode with “enable password” command.
Example:
Switch>enable
password: ***** (admin)
Switch#
2.1.1.7 enable password
Command: enable password [8] <password>
no enable password
Function: Configure the password used for enter Admin Mode from the User Mode,
The “no enable password” command deletes this password
Parameter: password is the configured code. Encryption will be performed by entering 8.
Command mode: Global Mode
Default: This password is empty by system default
Usage Guide: Configure this password to prevent unauthorized entering Admin Mode. It
36
Page 37

is recommended to set the password at the initial switch configuration. Also, it is
recommended to exit Admin Mode with “exit” command when the administrator needs to
leave the terminal for a long time.
Example: Set the Admin user password to “admin”.
Switch(Config)#enable password 8 admin
2.1.1.8 exec-timeout
Command: exec-timeout <minutes > [<seconds>]
no exec-timeout
Function:Configure the timeout of exiting admin mode. The “no exec-timeout”
command restores the default value.
Parameters: < minute > is the time value shown in minute and ranges between
0~35791.<seconds> is the time value shown in seconds and ranges between 0~2147483
Command mode:Global mode
Default:Default timeout is 10 minutes.
Usage guide: To secure the switch, as well to prevent malicious actions from
unauthorized user, the time will be count from the last configuration the admin had made,
and the system will exit the admin mode at due time. It is required to enter admin code
and password to enter the admin mode again. The timeout timer will be disabled when
the timeout is set to 0.
Example: Set the admin mode timeout value to 6 minutes
Switch(Config)#exec-timeout 6
2.1.1.9 exit
Command: exit
Function: Quit current mode and return to it’s previous mode.
Command mode: All Modes
Usage Guide: This command is to quit current mode and return to it’s previous mode.
Example: Quit global mode to it’s previous mode
Switch(Config)#exit
Switch#
2.1.1.10 help
Command: help
Function: Output brief description of the command interpreter help system.
Command mode: All configuration modes.
Usage Guide: An instant online help provided by the switch. Help command displays
information about the whole help system, including complete help and partial help. The
37
Page 38

user can type in ? any time to get online help.
Example:
Switch>help
enable -- Enable Admin mode
exit -- Exit telnet session
help -- help
show -- Show running system information
2.1.1.11 hostname
Command: hostname <hostname>
Function: Set the prompt in the switch command line interface.
Parameter <hostname> is the string for the prompt, up to 30 characters are allowed.
Command mode: Global Mode
Default: The default prompt is ES4624-SFP/ES4626-SFP switch.
Usage Guide: With this command, the user can set the CLI prompt of the switch
according to their own requirements.
Example: Set the prompt to “Test”.
Switch(Config)#hostname Test
Test(Config)#
2.1.1.12 ip host
Command: ip host <hostname> <ip_addr>
no ip host <hostname>
Function: Set the mapping relationship between the host and IP address; the “no ip
host” parameter of this command will delete the mapping.
Parameter: <hostname> is the host name, up to 15 characters are allowed; <ip_addr>
is the corresponding IP address for the host name, takes a dot decimal format.
Command mode: Global Mode
Usage Guide: Set the association between host and IP address, which can be used in
commands like “ping <host>“.
Example: Set IP address of a host with the hostname of “taiwan” to 200.121.1.1.
Switch(Config)#ip host beijing 200.121.1.1
2.1.1.13 ipv6 host
Command: ipv6 host <hostname> <ipv6_addr>
no ipv6 host <hostname>
Function: Configure the mapping relationship between the IPv6 address and the host;
the “no ipv6 host <hostname>” command deletes this mapping relationship
38
Page 39

Parameter : <hostname> is the name of the host,containing max 15
characters;<ipv6_addr> is the IPv6 address corresponding to the host name.
Command Mode: Global Mode
Usage Guide: Configure a fixed corresponding relationship between the host and the
IPv6 address, applicable in commands such as “traceroute6 <host>”, etc.
Example: Set the IPv6 address of the host named beijing to 2001:1:2:3::1
Switch(Config)#ipv6 host beijing 2001:1:2:3::1
2.1.1.14 ip http server
Command: ip http server
no ip http server
Function: Enable Web configuration; the “no ip http server” command disables Web
configuration
Command mode: Global mode
Usage guide: Web configuation is for supplying a interface configured with HTTP for the
user, which is straight and visual, esay to understand. This command functions equal to
selection [2] of the main menu in Setup mode to configure the Web Server.
Example: Enable Web Server function and enable Web configurations.
Switch(Config)#ip http server
2.1.1.15 login
Command: login
no login
Function: login enable password authentication ,no login command cancels the login
configuration
Command mode: Global mode
Default: no login by default
Usage guide: By using this command, users have to enter the password set by
password command to enter normal user mode with console; no login cancels this
restriction
Example: Enable password
Switch(Config)#login
2.1.1.16 language
Command: language {chinese|english}
Function: Set the language for displaying the help information.
Parameter: Chinese for Chinese display; English for English display.
Command mode: Admin Mode
39
Page 40

Default: The default setting is English display.
Usage Guide: ES4624-SFP/ES4626-SFP switch provides help information in two
languages, the user can select the language according to their preference. After the
system restart, the help information display will revert to English.
2.1.1.17 login local
Command:login local
no login
Function: Login enables local user name and password identification, no login cancels
login local configuration.
Command Mode: Global Mode
Default: System Default is no login.
Usage Guide: The command enable the user access in common mode of shell, types in
user name and password configured by username command, and then can access in
common user mode through level configured by the command. No login cancels login
local configuration.
Notice: Executing the command, it insures that priority of one user is 15, if it uses
username command configuration to login. Only this can ensure that the user accesses
from common mode to admin mode and modify system configuration after the user pass
the shell login identification. If there is no user of priority 15, the user can not access in
admin and global mode.
Example: Enable local use password identification
Switch(Config)#login local
2.1.1.18 password
Command: password <password>
no password
Function: Configure the password used for enter normal user mode on the console. The
“no password” command deletes this password
Parameter: password is the configured code. Encryption will be performed by entering 8
Command mode: Global mode
Default: This password is empty by system default
Usage guide: When both this password and login command are configured, users have
to enter the password set by password command to enter normal user mode on console
Example:Switch(Config)#password 8 test
Switch(Config)#login
2.1.1.19 ping
40
Page 41

Command: ping [<ip-addr> | <host>|vrf|]
Function: The switch send ICMP packet to remote devices to verify the connectivity
between the switch and remote devices.
Parameter: <ip-addr> is the target host IP address for ping, in dot decimal format.
<host> is the target host name for ping.
<vrf>VPN Routing/Forwarding instance.it is usefull only when VR is
configured.
Default: Send 5 ICMP packets of 56 bytes each, timeout in 2 seconds.
Command mode: Admin Mode
Usage Guide: When the user types in the ping command and press Enter, the system
will provide an interactive mode for configuration, and the user can choose all the
parameters for ping.
Example:
Default parameter for ping.
Switch#ping 10.1.128.160
Type ^c to abort.
Sending 5 56-byte ICMP Echos to 10.1.128.160, timeout is 2 seconds.
...!!
Success rate is 40 percent (2/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 0/0/0 ms
As shown in the above example, the switch pings a device with an IP address of
10.1.128.160, three ICMP request packets sent without receiving corresponding reply
packets (i.e. ping failed), the last two packets are replied successfully, the successful rate
is 40%. The switch represent ping failure with a “.”, for unreachable target; and ping
success with “!” , for reachable target.
Switch#ping
VRF name:
Target IP address: 10.1.128.160
Repeat count [5]: 100
Datagram size in byte [56]: 1000
Timeout in milli-seconds [2000]: 500
Extended commands [n]: n
Displayed information Explanation
VRF name: VPN Routing/Forwarding instance
Target IP address: Target IP address
Repeat count [5] Packet number, the default is 5
Datagram size in byte [56] ICMP packet size the default is 56 bytes
Timeout in milli-seconds [2000]: Timeout (in milliseconds,) the default is 2
seconds.
41
Page 42

Extended commands [n]: Whether to change the other options or not
2.1.1.20 ping6
Command: ping6 [<dst-ipv6-address> | host <hostname> | src < src-ipv6-address >
{<dst- ipv6-address > | host <hostname>} ]
Function: Verify the accessibility of the network
Parameter: <dst- ipv6-address > is the destination IPv6 address,< src-ipv6-address >
is the source IPv6 address,<hostname> is the host name of the remote host,containing
no more than 30 characters.
Default: None
Command Mode: User Mode
Usage Guide: Ping6 followed by IPv6 address is the default configuration. Ping6 function
can configure the parameters of the ping packets on users’ demands. When the
ipv6-address is the local link address, a vlan interface name is needed to be specified.
When specifying source IPv6 address, the sent icmp query packets will use specified
source IPv6 address as the source address of the ping packets.
Example:
(1) Default parameters of the ping6 program
Switch>ping6 2001:1:2::4
Type ^c to abort.
Sending 5 56-byte ICMP Echos to 2001:1:2::4, timeout is 2 seconds.
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/320/1600 ms
(2) Specify source IPv6 address when using ping6
switch>ping6 src 2001:1:2::3 2001:1:2::4
Type ^c to abort.
Sending 5 56-byte ICMP Echos to 2001:1:2::4, using src address 2001:1:2::3, timeout is
2 seconds.
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/1/1 ms
(3) Modify ping6 parameter with the help of the ping6 program
switch>ping6
Target IPv6 address:fe80::2d0:59ff:feb8:3b27
Output Interface: vlan1
Use source address option[n]:y
Source IPv6 address: fe80::203:fff:fe0b:16e3
Repeat count [5]:
Datagram size in byte [56]:
42
Page 43

Timeout in milli-seconds [2000]:
Extended commands [n]:
Type ^c to abort.
Sending 5 56-byte ICMP Echos to fe80::2d0:59ff:feb8:3b27, using src address
fe80::203:fff:fe0b:16e3, timeout is 2 seconds.
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/4/16 ms
Displayed Information Explanation
ping6 Run ping6 function
Target IPv6 address Destination IPv6 address
Output Interface Name of Vlan interface,required to be
specified when destination address is a
local link address
Use source IPv6 address [n]: Use source IPv6 address, not used by
default
Source IPv6 address Source IPv6 IP address
Repeat count[5] Number of ping packets to be sent,5 by
default
Datagram size in byte[56] Size of Ping packet,56 by default
Timeout in milli-seconds[2000] Permitted delay time, 2 seconds by default
Extended commands[n] Configuration of extended parameter, not
applied by default
! Indicate the network is accessible
. Indicate the network is inaccessible
Success rate is 100 percent (8/8),
round-trip min/avg/max = 1/1/1 ms
Statistic information,indicating that ping
packets has succeeded in arriving in 100%
without any packet lost
2.1.1.21 reload
Command: reload
Function: Warm reset the switch.
Command mode: Admin Mode
Usage Guide: The user can use this command to restart the switch without power off.
2.1.1.22 service password-encryption
Command: service password-encryption
43
Page 44

no service password-encryption
Function: Encrypt system password. The “no service password-encryption” command
cancels the encryption
Command mode: Global mode
Default: no service password-encryption by system default
Usage guide: The current unencrypted passwords as well as the coming passwords
configured by password, enable password and username command will be encrypted by
executed this command. no service password-encryption cancels this function however
encrypted passwords remain unchanged.
Example: Encrypt system passwords
Switch(Config)#service password-encryption
2.1.1.23 service terminal-length
Command: service terminal-length <0-512>
no service terminal-length
Function: Configure the columns of characters displayed in each screen on terminal
(vty). The “no service terminal-length” command cancels the screen shifting operation.
Parameter: Columns of characters displayed on each screen of vty, ranging between
0-512.
Command mode: Global mode
Usage guide: Configure the columns of characters displayed on each screen of the
terminal. The columns of characters displayed on each screen on the telent.ssh client
and the Console will be following this configuration.
Example: Set the number of vty threads to 20.
Switch(Config)#service terminal-length 20
2.1.1.24 set default
Command: set default
Function: Reset the switch to factory settings.
Command mode: Admin Mode
Usage Guide: Reset the switch to factory settings. That is to say, all configurations made
by the user to the switch will disappear. When the switch is restarted, the prompt will be
the same as when the switch was powered on for the first time.
Note: After the command, “write” command must be executed to save the operation. The
switch will reset to factory settings after restart.
Example:
Switch#set default
Are you sure? [Y/N] = y
44
Page 45

Switch#write
Switch#reload
2.1.1.25 setup
Command: setup
Function: Enter the Setup Mode of the switch.
Command mode: Admin Mode
Usage Guide: ES4624-SFP/ES4626-SFP switch provides a Setup Mode, in which the
user can configure IP addresses, etc.
2.1.1.26 terminal length
Command: terminal length <0-512>
terminal no length
Function: Set columns of characters displayed in each screen on terminal; the “terminal
no length” cancels the screen switching operation and display content once in all.
Parameter: Columns of characters displayed in each screen, ranging between 0-512 (0
refers to non-stop display)
Command mode: Admin mode
Default: Default columns is 25
Usage guide: Set columns of characters displayed in each screen on terminal, so that
the-More-message will be shown when displayed information exceeds the screen. Press
any key to show information in next screen. 25 columns by default
Example: Configure treads in each display to 20
Switch#terminal length 20
2.1.1.27 terminal monitor
Command: terminal monitor
terminal no monitor
Function: Copy debugging messages to current display terminal; the “terminal no
monitor” command restores to the default value
Command mode: Admin mode
Usage guide: Configures whether the current debugging messages is displayed on this
terminal. If this command is configured on telnet or ssh clients, debug messages will be
sent to that client. The debug message is displayed on console by default
Example: Switch#terminal monitor
2.1.1.28 traceroute
Command: traceroute {<ip-addr> | host <hostname> }[hops <hops>] [timeout
45
Page 46

<timeout> ]
Function: This command is tests the gateway passed in the route of a packet from the
source device to the target device. This can be used to test connectivity and locate a
failed sector.
Parameter: <ip-addr> is the target host IP address in dot decimal format. <hostname>
is the hostname for the remote host. <hops> is the maximum gateway number allowed
by Traceroute command. <timeout> Is the timeout value for test packets in milliseconds,
between 100 -10000.
Default: The default maximum gateway number is 16, timeout in 2000 ms.
Command mode: Admin Mode
Usage Guide: Traceroute is usually used to locate the problem for unreachable network
nodes.
2.1.1.29 traceroute6
Command: traceroute6 {<ipv6-addr> | host <hostname> }[hops <hops>] [timeout
<timeout> ]
Function: This command is for testing the gateways passed by the data packets from
the source device to the destination device, so to check the accessibility of the network
and further locating the network failure.
Parameter: <ipv6-addr> is the IPv6 address of the destination host,shown in colonned
hex notation;<hostname> is the name of the remote host;<hops> is the max number of
the gateways the traceroute6 passed through,ranging between 1-255;<timeout> is the
timeout period of the data packets,shown in millisecond and ranging between
100~10000.
Default: Default number of the gateways pass by the data packets is 16, and timeout
period is defaulted at 2000 ms
Command Mode: Admin Mode
Usage Guide: Traceroute6 is normally used to locate destination network inaccessible
failures.
Example:
Switch# traceroute6 2004:1:2:3::4
Relevant Command:ipv6 host
2.1.1.30 cli username
Command:cli username <username> [privilege < privilege >] [ password (0|7)
<password>]
no cli username <username>
Function: Configure shell user and priority shell by logging in user name and password.
46
Page 47

Parameter: Username is the user name, privilege is the highest level executed by the
user, level is 1 to 15, default is 1, and password is user password, if input option 7 on
password setting, the password is encrypted; if input option 0, the password is not
processed.
Command Mode: Global Mode
Usage Guide: Currently there are two priorities 1 and 15 of registered commands in
system. The command of priority 1 often registers in common user mode and admin
mode. The command of priority 15 registers in other modes, except for common user
mode. The command configures user, priority and password. After executing login local
command, it can control that users must use configured user name and password to
access common user mode of shell. Only the user of priority 15 can access admin mode
by enable command. If the priority of identified user by login local is less than 15, the
user can not access in admin mode, other than common user mode.
Notice: The user can log in use name and priority after the command configures, before
login local command is executed (Enable username and password), it insures that priority
of one user is maximum 15, so that users could log in by this username and access in
admin mode and global mode to modify system configuration, otherwise, users only
access in common mode, not admin mode to take the users effect.
Example: Configure an administrator user admin, priority is 15, configure two common
users, priority is 1, and enable local user name and password identification.
Switch(Config)#cli username admin privilege 15 password 0 admin
Switch(Config)#cli username user1 privilege 1 password 7 user1
Switch(Config)#cli username user2 password 0 user2
Switch(Config)#login local
2.1.1.31 username password
Command: username <user_name> password <show_flag> <pass_word>
no uername <user_name>
Function: Configure username and password for logging on the switch; the “no
username <user_name>“ command deletes the user.
Parameter: <user_name> is the username. It can’t exceed 16 characters; <show_flag>
can be either 0 or 7. 0 is used to display unencrypted username and password, whereas
7 is used to display encrypted username and password; <pass_word> is password. It
can’t exceed 16 characters;
Command mode: Global Mode
Default: The username and password are null by default.
Usage Guide: This command can be used to set the username for logging on the switch
and set the password as null.
47
Page 48

Example: Set username as “admin” and set password as “admin”
Switch(Config)#username admin password 0 admin
2.1.1.32 username nopassword
Command: username <user_name> nopassword
Function: Set the username for logging on the switch and set the password as null.
Parameter: <user_name> is the username. It can’t exceed 16 characters.
Command mode: Global Mode
Usage Guide: This command is used to set the username for logging on the switch and
set the password as null.
Example: Set username as “admin” and set password as null.
Switch(Config)#username admin nopassword
2.1.1.33 write
Command: write
Function: Save the currently configured parameters to the Flash memory.
Command mode: Admin Mode
Usage Guide: After a set of configuration with desired functions, the setting should be
saved to the Flash memory, so that the system can revert to the saved configuration
automatically in the case of accidentally powered off or power failure. This is the
equivalent to the copy running-config startup-config command.
2.2 Monitor and Debug Command
When the users configures the switch, they will need to verify whether the
configurations are correct and the switch is operating as expected, and in network failure,
the users will also need to diagnostic the problem. ES4624-SFP/ES4626-SFP switch
provides various debug commands including ping, telnet, show and debug, etc. to help
the users to check system configuration, operating status and locate problem causes.
2.2.1 Ping
Ping command is mainly used for sending ICMP query packet from the switches to
remote devices, also for check the accessibility between the switch and the remote
device. Refer to the Ping command chapter in the Command Manual for explanations of
various parameters and options of the Ping command.
2.2.2 Ping6
48
Page 49

Ping6 command is mainly used by the switch to send ICMPv6 query packet to the
remote equipment, verifying the accessibility between the switch and the remote
equipment. Options and explanations of the parameters of the Ping6 command please
refer to Ping6 command chapter in the command manual.
2.2.3 Telnet
2.2.3.1 Introduction To Telnet
Telnet is a simple remote terminal protocol for remote login. Using Telnet, the user
can login to a remote host with its IP address of hostname from his own workstation.
Telnet can send the user’s keystrokes to the remote host and send the remote host
output to the user’s screen through TCP connection. This is a transparent service, as to
the user, the keyboard and monitor seems to be connected to the remote host directly.
Telnet employs the Client-Server mode, the local system is the Telnet client and the
remote host is the Telnet server. ES4624-SFP/ES4626-SFP switch can be either the
Telnet Server or the Telnet client.
When ES4624-SFP/ES4626-SFP switch is used as the Telnet server, the user can
use the Telnet client program included in Windows or the other operation systems to login
to ES4624-SFP/ES4626-SFP switch, as described earlier in the In-band management
section. As a Telnet server, ES4624-SFP/ES4626-SFP switch allows up to 5 telnet client
TCP connections.
And as Telnet client, using telnet command under Admin Mode allows the user to
login to the other remote hosts. ES4624-SFP/ES4626-SFP switch can only establish TCP
connection to one remote host. If a connection to another remote host is desired, the
current TCP connection must be dropped.
2.2.3.2 Telnet Configuration Task List
1. Configuring Telnet Server
2. Telnet to a remote host from the switch.
1. Configuration of Telnet Server
Command Explanation
Global Mode
ip telnet server
no ip telnet server
telnet-server securityip <ip-addr> Configure the secure IP address to
Enable the Telnet server function in the
switch: the “no ip telnet server”
command disables the Telnet function.
49
Page 50

no telnet-server securityip <ip-addr> login to the switch through Telnet: the
“no telnet-server securityip
<ip-addr>“ command deletes the
authorized Telnet secur e address.
Admin Mode
Display debug information for Telnet
monitor
no monitor
2. Telnet to a remote host from the switch
Command Explanation
Admin Mode
telnet [<ip-addr>] [<port>]
client login to the switch; the “no
monitor” command disables the
debug information.
Login to a remote host with the
Telnet client included in the switch.
2.2.3.3 Commands for Telnet
2.2.3.3.1 telnet
Command: telnet {<ip-addr> | <ipv6-addr> | host <hostname>} [<port>]
Function: Log on the remote host by Telnet
Parameter: <ip-addr> is the IP address of the remote host,shown in dotted decimal
notation;<ipv6-addr> is the IPv6 address of the remote host;<hostname> is the name of
the remote host,containing max 30 characters;<port> is the port number,ranging
between 0~65535.
Command Mode: Admin Mode
Usage Guide: This command is used when the switch is applied as Telnet client, for
logging on remote host to configure. When a switch is applied as a Telnet client, it can
only establish one TCP connection with the remote host. To connect to another remote
host, the current TCP connection must be disconnected with a hotkey “CTRL+ |”. To
telnet a host name, mapping relationship between the host name and the IP/IPv6
address should be previously configured. For required commands please refer to ip host
and ipv6 host. In case a host corresponds to both an IPv4 and an IPv6 addresses, the
IPv6 should be preferred when telneting this host name.
Example:
1) The switch Telnets to a remote host whose IP address is 20.1.1.1
Switch#telnet 20.1.1.1 23
2) The switch Telnets to a remote host whose IPv6 address is 3ffe:506:1:2::3
50
Page 51

Switch#telnet 3ffe:506:1:2::3
3) Configure the mapping relationship between the host name ipv6host and the IPv6
address 3ffe:506:1:2::3, and then telnet to host ipv6host
Switch#config
Switch(Config)# ipv6 host ipv6host 3ffe:506:1:2::3
Switch#telnet host ipv6host
2.2.3.3.2 ip telnet server
Command: ip telnet server
no ip telnet server
Function: Enable the Telnet server function in the switch: the “no ip ip telnet server”
command disables the Telnet function in the switch.
Default: Telnet server function is enabled by default.
Command mode: Global Mode
Usage Guide: This command is available in Console only. The administrator can use this
command to enable or disable the Telnet client to login to the switch.
Example: Disable the Telnet server function in the switch.
Switch(Config)#no ip telnet server
2.2.3.3.3 telnet-server securityip
Command: telnet-server securityip <ip-addr>
no telnet-server securityip <ip-addr>
Function: Configure the secure IP address of Telnet client allowed to login to the switch;
the “no telnet-server securityip <ip-addr>“ command deletes the authorized Telnet
secure address.
Parameter: <ip-addr> is the secure IP address allowed to access the switch, in dot
decimal format.
Default: no secure IP address is set by default.
Command mode: Global Mode
Usage Guide: When no secure IP is configured, the IP addresses of Telnet clients
connecting to the switch will not be limited; if a secure IP address is configured, only
hosts with the secure IP address is allowed to connect to the switch through Telnet for
configuration. The switch allows multiple secure IP addresses.
Example: Set 192.168.1.21 as a secure IP address.
Switch(Config)#telnet-server securityip 192.168.1.21
2.2.4 SSH
2.2.4.1 Introduction to SSH
51
Page 52

SSH (Secure Shell) is a protocol which ensures a secure remote access connection
to network devices. It is based on the reliable TCP/IP protocol. By conducting the
mechanism such as key distribution, authentication and encryption between SSH server
and SSH client, a secure connection is established. The information transferred on this
connection is protected from being intercepted and decrypted. The switch meets the
requirements of SSH2.0. It supports SSH2.0 client software such as SSH Secure Client
and putty. Users can run the above software to manage the switch remotely.
The switch presently supports RSA authentication, 3DES cryptography protocol and
SSH user password authentication etc.
2.2.4.2 SSH Server Configuration Task List
1. SSH Server Configuration
Command Explanation
Global Mode
ssh-server enable
no ssh-server enable
ssh-user <user-name> password {0|7}
<password>
no ssh-user <user-name>
ssh-server timeout <timeout>
no ssh-server timeout
ssh-server authentication-retires <
authentication-retires>
no ssh-server authentication-retries
Enable SSH function on the switch; the
“no ssh-server enable” command
disables SSH function.
Configure the username and password of
SSH client software for logging on the
switch; the “no ssh-user
<user-name>“ command deletes the
username.
Configure timeout value for SSH
authentication; the “no ssh-server
timeout” command restores the default
timeout value for SSH authentication.
Configure the number of times for
retrying SSH authentication; the “no
ssh-server authentication-retries”
command restores the default number of
times for retrying SSH authentication.
ssh-server host-key create rsa
modulus <moduls>
Admin Mode
monitor
no monitor
52
Generate the new RSA host key on the
SSH server.
Display SSH debug information on the
SSH client side; the “no monitor”
command stops displaying SSH debug
information on the SSH client side.
Page 53

2.2.4.3 Commands for SSH
2.2.4.3.1 ssh-server authentication-retries
Command: ssh-server authentication-retries < authentication-retries >
no ssh-server authentication-retries
Function: Configure the number of times for retrying SSH authentication; the “no
ssh-server authentication-retries” command restores the default number of times for
retrying SSH authentication.
Parameter: < authentication-retries > is the number of times for retrying authentication;
valid range is 1 to 10.
Command mode: Global Mode
Default: The number of times for retrying SSH authentication is 3 by default.
Example: Set the number of times for retrying SSH authentication to 5.
Switch(Config)#ssh-server authentication-retries 5
2.2.4.3.2 ssh-server enable
Command: ssh-server enable
no ssh-server enable
Function: Enable SSH function on the switch; the “no ssh-server enable” command
disables SSH function.
Command mode: Global Mode
Default: SSH function is disabled by default.
Usage Guide: In order that the SSH client can log on the switch, the users need to
configure the SSH user and enable SSH function on the switch.
Example: Enable SSH function on the switch.
Switch(Config)#ssh-server enable
2.2.4.3.3 ssh-server host-key create rsa
Command: ssh-server host-key create rsa [modulus < modulus >]
Function: Generate new RSA host key
Parameter: modulus is the modulus which is used to compute the host key; valid range
is 768 to 2048. The default value is 1024.
Command mode: Global Mode
Default: The system uses the key generated when the ssh-server is started at the first
time.
Usage Guide: This command is used to generate the new host key. When SSH client
logs on the server, the new host key is used for authentication. After the new host key is
generated and “write” command is used to save the configuration, the system uses this
key for authentication all the time. Because it takes quite a long time to compute the new
53
Page 54

key and some clients are not compatible with the key generated by the modulus 2048, it
is recommended to use the key which is generated by the default modulus 1024.
Example: Generate new host key.
Switch(Config)#ssh-server host-key create rsa
2.2.4.3.4 ssh-server timeout
Command: ssh-server timeout <timeout>
no ssh-server timeout
Function: Configure timeout value for SSH authentication; the “no ssh-server timeout”
command restores the default timeout value for SSH authentication.
Parameter: <timeout> is timeout value; valid range is 10 to 600 seconds.
Command mode: Global Mode
Default: SSH authentication timeout is 180 seconds by default.
Example: Set SSH authentication timeout to 240 seconds.
Switch(Config)#ssh-server timeout 240
2.2.4.3.5 ssh-user
Command: ssh-user <username> password {0|7} <password>
no ssh-user <username>
Function: Configure the username and password of SSH client software for logging on
the switch; the “no ssh-user <user-name>“ command deletes the username.
Parameter: <username> is SSH client username. It can’t exceed 16 characters;
<password> is SSH client password. It can’t exceed 8 characters; 0|7 stand for
unencrypted password and encrypted password.
Command mode: Global Mode
Default: There are no SSH username and password by default.
Usage Guide: This command is used to configure the authorized SSH client. Any
unauthorized SSH clients can’t log on and configure the switch. When the switch is a
SSH server, it can have maximum three users and it allows maximum three users to
connect to it at the same time.
Example: Set a SSH client which has “switch” as username and “switch” as password.
Switch(Config)#ssh-user switch password 0 switch
2.2.4.4 Typical SSH Server Configuration
Example 1:
Requirement: Enable SSH server on the switch, and run SSH2.0 client software
such as Secure shell client and putty on the terminal. Log on the switch by using the
username and password from the client.
54
Page 55

Configure the IP address, add SSH user and enable SSH service on the switch.
SSH2.0 client can log on the switch by using the username and password to configure
the switch.
Switch(Config)#interface vlan 1
Switch(Config-Vlan-1)#ip address 100.100.100.200 255.255.255.0
Switch(Config-Vlan-1)#exit
Switch(Config)#ssh-user test password 0 test
Switch(Config)#ssh-server enable
2.2.5 Traceroute
Trace route command is for testing the gateways through which the data packets
travels from the source device to the destination device, so to check the network
accessibility and locate the network failure.
Execution procedure of the Trace route command consists of: first a data packet with
TTL at 1 is sent to the destination address, if the first hop returns an ICMP error message
to inform this packet can not be sent (due to TTL timeout), a data packet with TTL at 2 will
be sent. Also the send hop may be a TTL timeout return, but the procedure will carries on
till the data packet is sent to its destination. These procedures is for recording every
source address which returned ICMP TTL timeout message, so to describe a path the IP
data packets traveled to reach the destination
2.2.6 Traceroute6
The Traceroute6 function is used on testing the gateways passed through by the
data packets from the source equipment to the destination equipment, to verify the
accessibility and locate the network failure. The principle of the Traceroute6 under IPv6 is
the same as that under IPv4, which adopts the hop limit field of the ICMPv6 and IPv6
header. First, Traceroute6 sends an IPv6 datagram (including source address,
destination address and packet sent time) whose HOPLIMIT is set to 1. When first route
on the path receives this datagram, it minus the HOPLIMIT by 1 and the HOPLIMIT is
now 0. So the router will discard this datagram and returns with a 「ICMPv6 time
exceeded」 message (including the source address of the IPv6 packet, all content in the
IPv6 packet and the IPv6 address of the router). Upon receiving this message, the
Traceroute6 sends another datagram of which the HOPLIMIT is increased to 2 so to
discover the second router. Plus 1 to the HOPLIMIT every time to discover another router,
the Traceroute6 repeat this action till certain datagram reaches the destination.
Traceroute6 Options and explanations of the parameters of the Traceroute6
55
Page 56

command please refer to traceroute6 command chapter in the command manual.
2.2.7 Show
show command is used to display information about the system , port and protocol
operation. This part introduces the show command that displays system information,
other show commands will be discussed in other chapters.
Admin Mode
show calendar Display current system clock
show debugging Display the debugging state
dir
show history
show memory Display content in specified memory area
show running-config
show startup-config
show interface
switchport[ethernet
<interface-list>]
show tcp
Display the files and the sizes saved in the
flash
Display the recent user input history
command
Display the switch parameter configuration
validating at current operation state.
Display the switch parameter configuration
written in the Flash Memory at current
operation state, which is normally the
configuration file applied in next time the
switch starts up
Display the VLAN port mode and the
belonging VLAN number of the switch as well
as the Trunk port information
Display the TCP connection status
established currently on the switch
show udp
show telnet login
show telnet user
Display the UDP connection status
established currently on the switch
Display the information of the Telnet client
which currently establishes a Telnet
connection with the switch
Display the information of all the Telnet clients
which are authorized to access the switch
through Telnet.
56
Page 57

Display the operation information and the
Show tech-support
show version
state of each task running on the switch. It is
used by the technicians to diagnose whether
the switch operates properly.
Display the version of the switch
2.2.7.1 Commands for Show
2.2.7.1.1 show calendar
Command: show calendar
Function: Display the system clock.
Command mode: Admin Mode
Usage Guide: The user can use this command to check system date and time so that
the system clock can be adjusted in time if inaccuracy occurs.
Example: Switch#show calendar
Current time is TUE AUG 22 11: 00: 01 2002
2.2.7.1.2 show debugging
Command: show debugging
Function: Display the debug switch status.
Usage Guide: If the user need to check what debug switches have been enabled, show
debugging command can be executed.
Command mode: Admin Mode
Example: Check for currently enabled debug switch.
Switch#show debugging
STP:
Stp input packet debugging is on
Stp output packet debugging is on
Stp basic debugging is on
2.2.7.1.3 show history
Command: show history
Function: Display the recent user command history,.
Command mode: Admin Mode
Usage Guide: The system holds up to 10 commands the user entered, the user can use
the UP/DOWN key or their equivalent (ctrl+p and ctrl+n) to access the command history.
Example:
57
Page 58

Switch#show history
enable
config
interface ethernet 1/3
enable
dir
show ftp
2.2.7.1.4 show memory
Command: show memory
Function: Display the contents in the memory.
Command mode: Admin Mode
Usage Guide: This command is used for switch debug purposes. The command will
interactively prompt the user to enter start address of the desired information in the
memory and output word number. The displayed information consists of three parts:
address, Hex view of the information and character view.
Example:
Switch#show memory
start address : 0x2100
number of words[64]:
002100: 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 *................*
002110: 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 *................*
002120: 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 *................*
002130: 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 *................*
002140: 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 *................*
002150: 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 *................*
002160: 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 *................*
002170: 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 *................*
2.2.7.1.5 show running-config
Command: show running-config
Function: Display the current active configuration parameters for the switch.
Default: If the active configuration parameters are the same as the default operating
parameters, nothing will be displayed.
Command mode: Admin Mode
Usage Guide: When the user finishes a set of configuration and needs to verify the
configuration, show running-config command can be used to display the current active
parameters.
Example: Switch#show running-config
58
Page 59

2.2.7.1.6 show ssh-server
Command: show ssh-server
Function: Display SSH state and users which log on currently.
Command mode: Admin Mode
Example:
Switch#show ssh-server
ssh-server is enabled
connection version state user name
1 2.0 session started test
2.2.7.1.7 show ssh-user
Command: show ssh-user
Function: Display the configured SSH usernames.
Parameter: Admin Mode
Example:
Switch#show ssh-user
test
2.2.7.1.8 show startup-config
Command: show startup-config
Function: Display the switch parameter configurations written into the Flash memory at
the current operation; those are usually also the configuration files used for the next
power-up.
Default: If the configuration parameters read from the Flash are the same as the default
operating parameter, nothing will be displayed.
Command mode: Admin Mode
Usage Guide: The show running-config command differs from show startup-config in
that when the user finishes a set of configurations, show running-config displays the
added-on configurations whilst show startup-config won’t display any configurations.
However, if write command is executed to save the active configuration to the Flash
memory, the displays of show running-config and show startup-config will be the
same.
2.2.7.1.9 show interface switchport
Command: show interface switchport [ethernet <interface-list>]
Function: Show the VLAN port mode, VLAN number and Trunk port messages of the
VLAN port mode on the switch.
Parameter: <interface-list> is the port number or port list, which could be any port
information existing in the switch
59
Page 60

Command mode: Admin mode
Example: Show VLAN messages of port ethernet 1/1.
Switch#show interface switchport ethernet 1/1
Ethernet1/1
Type :Universal
Mac addr num :-1
Mode :Access
Port VID :1
Trunk allowed Vlan :ALL
Displayed Information Description
Ethernet1/1 Corresponding interface number of the Ethernet
Type Current interface type
Mac addr num Number of interfaces with MAC address learning
ability
Mode :Access Current interface VLAN mode
Port VID :1 Current VLAN number the interface belongs
Trunk allowed Vlan :ALL VLAN permitted by Trunk.
2.2.7.1.10 show users
Command: show users
Function: Display all user information that can login the switch .
Usage Guide: This command can be used to check for all user information that can login
the switch.
Example:
Switch#show users
User level havePasword
admin 0 1
Online user info: user ip login time(second) usertype
2.2.7.1.11 show tcp
Command: show tcp
Function: Display the current TCP connection status established to the switch.
Command mode: Admin Mode
Example:
Switch#show tcp
LocalAddress LocalPort ForeignAddress ForeignPort State
0.0.0.0 23 0.0.0.0 0 LISTEN
0.0.0.0 80 0.0.0.0 0 LISTEN
60
Page 61

Displayed information Description
LocalAddress Local address of the TCP connection.
LocalPort Local pot number of the TCP connection.
ForeignAddress Remote address of the TCP connection.
ForeignPort Remote port number of the TCP connection.
State Current status of the TCP connection.
2.2.7.1.12 show udp
Command: show udp
Function: Display the current UDP connection status established to the switch.
Command mode: Admin Mode
Example:
Switch#show udp
LocalAddress LocalPort ForeignAddress ForeignPort State
0.0.0.0 161 0.0.0.0 0 CLOSED
0.0.0.0 123 0.0.0.0 0 CLOSED
0.0.0.0 1985 0.0.0.0 0 CLOSED
Displayed information Description
LocalAddress Local address of the udp connection.
LocalPort Local pot number of the udp connection.
ForeignAddress Remote address of the udp connection.
ForeignPort Remote port number of the udp connection.
State Current status of the udp connection.
2.2.7.1.13 show version
Command: show version<unit>
Parameter: where the range of unit is 1
Function: Display the switch version.
Default: The default value for <unit> is 1
Command mode: Admin Mode
Usage Guide: Use this command to view the version information for the switch, including
hardware version and software version.
Example:
Switch#show ver 1
ES4626-SFP Device, Apr 14 2005 11: 19: 29
Hardware version is 2.0, SoftWare version packet is ES4626-SFP _1.1.0.0, BootRom
version is ES4626-SFP _1.0.4
Copyright (C) 2001-2006 by Accton Technology Corporation..
All rights reserved.
61
Page 62

Last reboot is cold reset
Uptime is 0 weeks, 0 days, 0 hours, 28 minutes
2.2.8 Debug
All the protocols ES4624-SFP/ES4626-SFP switch supports have their
corresponding debug commands. The users can use the information from debug
commands for troubleshooting. Debug commands for their corresponding protocols
will be introduced in the later chapters.
2.2.9 System log
2.2.9.1 System Log Introduction
The system log takes all information output under it control, while making detailed
catalogue, so to select the information effectively. Combining with Debug programs, it will
provide a powerful support to the network administrator and developer in monitoring the
network operation state and locating the network failures.
The switch system log has following characteristics
z Log output from four directions (or log channels) of the Console, Telnet terminal
and monitor, log buffer zone, and log host.
z The log information is classified to four level of severities by which the
information will be filtered
z According to the severity level the log information can be auto outputted to
corresponding log channel.
2.2.9.1.1 Log Output Channel
So far the system log can be outputted the log information through four channels
z Through Console port to the local console
z Output the log information to remote Telnet terminal or monitor, this function is
good for remote maintenance
z Assign a proper log buffer zone inside the switch, for record the log information
permanently or temporarily
z Configure the log host, the log system will directly send the log information to
the log host, and save it in files to be viewed at any time
Among above log channels, users rarely use the console monitor, but will commonly
choose the Telnet terminal to monitor the system operation status. However information
outputted from these channels are of low traffic capacity and can not be recorded for later
62
Page 63

view. The other two channels---the log buffer zone and log host channel are two
important channels
SDRAM (Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory) and NVRAM (Non
Vulnerable Random Access Memory) is provided inside the switch as two part of the log
buffer zone, The two buffer zone record the log information in a circuit working pattern,
namely when log information need to be recorded exceeds the buffer size, the oldest log
information will be erased and replaced by the new log information, information saved in
NVRAM will stay permanently while those in SDRAM will lost when the system restarts or
encounter an power failure. Information in the log buffer zone is critical for monitoring the
system operation and detecting abnormal states.
Note: the NVRAM log buffer may not exist on some switches, which only
have the SDRAM log buffer zone
It is recommended to use the system log server. By configuring the log host
on the switch, the log can be sent to the log server for future examination
2.2.9.1.2 Format And Severity Of The Log Information
The log information format is compatible with the BSD syslog protocol, so we can
record and analyze the log by the systlog (system log protect session) on the
UNIX/LINUX, as well as syslog similar applications on PC.
The log information is classified into eight classes by severity or emergency
procedure. One level per value and the higher the emergency level the log information
has, the smaller its value will be. For example, the level of critical is 2, and warning is 4,
debugging is leveled at 7, so the critical is higher than warnings which no doubt is high
than debugging. The rule applied in filtering the log information by severity level is that:
only the log information with level equal to or higher than the threshold will be outputted.
So when the severity threshold is set to debugging, all information will be outputted and if
set to critical, only critical, alerts and emergencies will be outputted.
Follow table summarized the log information severity level and brief description.
Note: these severity levels are in accordance with the standard UNIX/LINUX syslog
Severity Value Description
emergencies 0
System is unusable
alerts 1
critical 2
errors 3
warnings 4
notifications 5
63
Action must be taken immediately
Critical conditions
Error conditions
Warning conditions
Normal but significant condition
Page 64

informational 6
debugging 7
Right now the switch can generate information of following four levels
z Restart the switch, mission abnormal, hot plug on the CHASSIS switch chips are
classified critical
z Up/down switch, topology change, aggregate port state change of the interface
are classified warnings
z Outputted information from the CLI command is classified informational
z Information from the debugging of CLI command is classified debugging
Log information can be automatically sent to corresponding channels with regard to
respective severity levels. Amongst the debugging information can only be sent to the
monitor. Those with the Informational level can only be sent to current monitor terminal,
such as the information from the Telnet terminal configuration command can only be
transmitted to the Telnet terminal. Warnings information can be sent to all terminal with
Informational messages
Debug-level messages
also saved in the SDRAM log buffer zone. And the critical information can be save both in
SDRAM and the NVRAM (if exists) besides sent to all terminals. To check the log save in
SDRAM and the NVRAM, we can use the show logging buffered command. To clear the
log save in NVRAM and SDRAM log buffer zone, we can use the clear logging command
2.2.9.2 System Log Configuration
2.2.9.2.1 System Log Configuration Task Sequence
1. Display and clear log buffer zone
2. Configure the log host output channel
1. Display and clear log buffer zone
Command Description
Admin Mode
show logging buffered [level { critical |
warnings} | range <begin-index>
<end-index>]
Show detailed log information in
the log buffer channel
clear logging { sdram | nvram } Clear log buffer zone information
2. Configure the log host output channel
Command Description
Global Mode
64
Page 65

logging {<ipv4-addr> | <ipv6-addr>} [ facility
<local-number> ] [level <severity>]
no logging {<ipv4-addr> |
<ipv6-addr>}[ facility <local-number>]
Enable the output channel of the
log host. The “no” form of this
command will disable the output
at the output channel of the log
host.
2.2.9.2.2 System Log Configuration Command
2.2.9.2.2.1 show logging buffered
Command: show logging buffered [level { critical | warnings} | range <begin-index>
<end-index>]
Function: This command displays the detailed information in the log buffer channel. This
command is not supported on low end switches
Parameter: <begin-index> is the index start value of the log message, the valid range is
1-65535,<end-index> is the index end value of the log message, the valid range is
1-65535.
Command Mode:Admin Mode
Default:No parameter specified indicates all the critical log information will be displayed.
Usage Guide:Warning and critical log information is saved in the buffer zone. When
displayed to the terminal, their display format should be: index ID time <level> module
ID [mission name] log information.
2.2.9.2.2.2 clear logging
Command: clear logging { sdram | nvram }
Function: This command is used to clear all the information in the log buffer zone.
Command Mode:Admin Mode
Usage Guide: When the old information in the log buffer zone is no longer concerned,
we can use this command to clear all the information
example:Clear all information in the log buffer zone sdram
Switch# clear logging sdram
2.2.9.2.2.3 logging host
Command: logging {<ipv4-addr> | <ipv6-addr>} [ facility <local-number> ] [level
<severity>]
no logging {<ipv4-addr> | <ipv6-addr>}[ facility <local-number> ]
Function: The command is used to configure the output channel of the log host. The
“no” form of this command will disable the output at the log host output channel
Parameter: <ipv4-addr> is the IPv4 address of the host,<ipv6-addr> is the IPv6
address of the host;<local-number> is the recording equipment of the host with a valid
65
Page 66

range of local0 ~ local7,which is in accordance with the facility defined in the
RFC3164;<severity> is the severity threshold of the log information severity level,The
rule of the log information output is explained as follows:only those with a level equal to
or higher than the threshold will be outputted. For detailed description on the severity
please refer to the operation manual.
Command Mode:Global Mode
Default: No log information output to the log host by default. The default recorder of the
log host is the local0, the default severity level is warnings
Usage Guide:Only when the log host is configured by the logging command, this
command will be available. We can configure many IPv4 and IPv6 log hosts.
Example 1:Send the log information with a severity level equal to or higher than warning
to the log server with an IPv4 address of 100.100.100.5, and save to the log recording
equipment local1
Switch(Config)# logging 100.100.100.5 facility local1 level warnings
Example 2:Send the log information with a severity level equal to or higher than
informational to the log server with an IPv6 address of 3ffe:506:1:2::3, and save to the log
recording equipment local1
Switch(Config)# logging 3ffe:506:1:2::3 facility local5 level informational
2.2.9.3 System Log Configuration Example
Example 1:When managing VLAN the IPv4 address of the switch is 100.100.100.1, and
the IPv4 address of the remote log server is 100.100.100.5. It is required to send the
log information with a severity equal to or higher than warnings to this log server and
save in the log record equipment local1
Configuration procedure:
Switch(Config)#interface Ethernet 0
Switch(Config-Ethernet0)#ip address 100.100.100.1 255.255.255.0
Switch(Config-Ethernet0)#exit
Switch(Config)#logging 100.100.100.5 facility local1 level warnings
Example 2:When managing VLAN the IPv6 address of the switch is 3ffe:506::1, and the
IPv4 address of the remote log server is 3ffe:506::4. It is required to send the log
information with a severity equal to or higher than critical to this log server and save the
log in the record equipment local7.
Configuration procedure
Switch(Config)#interface Ethernet 0
Switch(Config-Ethernet0)#ipv6 address 3ffe:506::1/64
66
Page 67

Switch(Config-Ethernet0)#exit
Switch(Config)#logging 3ffe:506::4 facility local7 level warnings
2.3 Configurate Switch IP Addresses
All Ethernet ports of ES4624-SFP/ES4626-SFP switch is default to Data Link layer
ports and perform layer 2 forwarding. VLAN interface represent a Layer 3 interface
function which can be assigned an IP address, which is also the IP address of the switch.
All VLAN interface related configuration commands can be configured under VLAN Mode.
ES4624-SFP/ES4626-SFP switch provides three IP address configuration methods:
& Manual
& BootP
& DHCP
Manual configuration of IP address is assign an IP address manually for the switch.
In BootP/DHCP mode, the switch operates as a BootP/DHCP client, send broadcast
packets of BootPRequest to the BootP/DHCP servers, and the BootP/DHCP servers
assign the address on receiving the request. In addition, ES4624-SFP/ES4626-SFP
switch can act as a DHCP server, and dynamically assign network parameters such as IP
addresses, gateway addresses and DNS server addresses to DHCP clients DHCP
Server configuration is detailed in later chapters.
2.3.1 Switch IP Addresses Configuration Task List
1. Manual configuration
2. BootP configuration
3. DHCP configuration
1. Manual configuration
Command Explanation
ip address <ip_address> <mask>
[secondary]
no ip address <ip_address> <mask>
Configure the VLAN interface IP address;
the “no ip address <ip_address> <mask>
[secondary]” command deletes VLAN
[secondary]
2. BootP configuration
Command Explanation
ip address bootp
no ip address bootp
interface IP address.
Enable the switch to be a BootP client and
obtain IP address and gateway address
through BootP negotiation; the no ip
67
Page 68

address bootp” command disables the
BootP client function.
3.DHCP
Command Explanation
ip address dhcp
no ip address dhcp
Enable the switch to be a DHCP client and
obtain IP address and gateway address
through DHCP negotiation; the “no ip
address dhcp-client” command disables
the DHCP client function.
2.3.2 Commands For Configuring Switch IP
2.3.2.1 ip address
Command: ip address <ip-address> <mask> [secondary]
no ip address [<ip-address> <mask>] [secondary]
Function: Set the IP address and mask for the specified VLAN interface; the “no ip
address <ip address> <mask> [secondary]” command deletes the specified IP
address setting.
Parameter: <ip-address> is the IP address in dot decimal format; <mask> is the subnet
mask in dot decimal format; [secondary] indicates the IP configured is a secondary IP
address.
Default: No IP address is configured upon switch shipment.
Command mode: Interface Mode
Usage Guide: A VLAN interface must be created first before the user can assign an IP
address to the switch.
Example: Set 10.1.128.1/24 as the IP address of VLAN1 interface.
Switch(Config)#interface vlan 1
Switch(Config-If-Vlan1)#ip address 10.1.128.1 255.255.255.0
Switch(Config-If-Vlan1)#exit
2.3.2.2 ip address bootp-client
Command: ip address bootp-client
no ip address bootp-client
Function: Enable the switch to be a BootP client and obtain IP address and gateway
address through BootP negotiation; the “no ip address bootp-client” command disables
68
Page 69

the BootP client function and releases the IP address obtained in BootP .
Default: BootP client function is disabled by default.
Command mode: Interface Mode
Usage Guide: Obtaining IP address through BootP, Manual configuration and DHCP are
mutually exclusive, enabling any 2 methods for obtaining IP address is not allowed. Note:
To obtain IP address via DHCP, a DHCP server or a BootP server is required in the
network.
Example: Get IP address through BootP.
Switch(Config)#interface vlan 1
Switch(Config-If-Vlan1)#ip address bootp-client
Switch (Config-If-Vlan1)#exit
2.3.2.3 ip address dhcp-client
Command: ip address dhcp-client
no ip address dhcp-client
Function: Enables the switch to be a DHCP client and obtain IP address and gateway
address through DHCP negotiation; the “no ip dhcp-client” command disables the
DHCP client function and releases the IP address obtained in DHCP. Note: To obtain IP
address via DHCP, a DHCP server is required in the network.
Default: the DHCP client function is disabled by default.
Command mode: Interface Mode
Usage Guide: Obtaining IP address by DHCP, Manual configuration and BootP are
mutually exclusive, enabling any 2 methods for obtaining an IP address is not allowed.
Example: Getting an IP address through DHCP.
Switch (Config)#interface vlan 1
Switch (Config-If-Vlan1)#ip address dhcp-client
2.4 SNMP Configuration
2.4.1 Introduction To SNMP
SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) is a standard network management
protocol widely used in computer network management. SNMP is an evolving protocol.
SNMP v1 [RFC1157] is the first version of SNMP which is adapted by vast numbers of
manufacturers for its simplicity and easy implementation; SNMP v2c is an enhanced
version of SNMP v1, which supports layered network management; SNMP v3
strengthens the security by adding USM (User-based Security Mode) and VACM
(View-based Access Control Model).
69
Page 70

SNMP protocol provides a simple way of exchange network management
information between two points in the network. SNMP employs a polling mechanism of
message query, and transmits messages through UDP (a connectionless transport layer
protocol). Therefore it is well supported by the existing computer networks.
SNMP protocol employs a station-agent mode. There are two parts in this structure:
NMS (Network Management Station) and Agent. NMS is the workstation on which SNMP
client program is running. It is the core on the SNMP network management. Agent is the
server software runs on the devices which need to be managed. NMS manages all the
managed objects through Agents. The switch supports Agent function.
The communication between NMS and Agent functions in Client/Server mode by
exchanging standard messages. NMS sends request and the Agent responds. There are
seven types of SNMP message:
z Get-Request
z Get-Response
z Get-Next-Request
z Get-Bulk-Request
z Set-Request
z Trap
z Inform-Request
NMS sends queries to the Agent with Get-Request, Get-Next-Request,
Get-Bulk-Request and Set-Request messages; and the Agent, upon receiving the
requests, replies with Get-Response message. On some special situations, like network
device ports are on Up/Down status or the network topology changes, Agents can send
Trap messages to NMS to inform the abnormal events. Besides, NMS can also be set to
alert to some abnormal events by enabling RMON function. When alert events are
triggered, Agents will send Trap messages or log the event according to the settings.
Inform-Request is mainly used for inter-NMS communication in the layered network
management.
USM ensures the transfer security by well-designed encryption and authentication.
USM encrypts the messages according to the user typed password. This mechanism
ensures that the messages can’t be viewed on transmission. And USM authentication
ensures that the messages can’t be changed on transmission. USM employs DES-CBC
cryptography. And HMAC-MD5 and HMAC-SHA are used for authentication.
VACM is used to classify the users’ access permission. It puts the users with the
same access permission in the same group. Users can’t conduct the operation which is
not authorized.
Introduction to MIB
The network management information accessed by NMS is well defined and
70
Page 71

organized in a Management Information Base (MIB). MIB is pre-defined information
which can be accessed by network management protocols. It is in layered and structured
form. The pre-defined management information can be obtained from monitored network
devices. ISO ASN.1 defines a tree structure for MID. Each MIB organizes all the available
information with this tree structure. And each node on this tree contains an OID (Object
Identifier) and a brief description about the node. OID is a set of integers divided by
periods. It identifies the node and can be used to locate the node in a MID tree structure,
shown in the figure below:
Fig 2-1 ASN.1 Tree Instance
In this figure, the OID of the object A is 1.2.1.1. NMS can locate this object through
this unique OID and gets the standard variables of the object. MIB defines a set of
standard variables for monitored network devices by following this structure.
If the variable information of Agent MIB needs to be browsed, the MIB browse
software needs to be run on the NMS. MIB in the Agent usually consists of public MIB
and private MIB. The public MIB contains public network management information that
can be accessed by all NMS; private MIB contains specific information which can be
viewed and controlled by the support of the manufacturers
MIB-I [RFC1156] is the first implemented public MIB of SNMP, and is replaced by
MIB-II [RFC1213]. MIB-II expands MIB-I and keeps the OID of MIB tree in MIB-I. MIB-II
contains sub-trees which are called groups. Objects in those groups cover all the
functional domains in network management. NMS obtains the network management
information by visiting the MIB of SNMP Agent.
The switch can operate as a SNMP Agent, and supports both SNMP v1/v2c and
SNMP v3. The switch supports basic MIB-II, RMON public MIB and other public MID
such as BRIDGE MIB. Besides, the switch supports self-defined private MIB.
Introduction to RMON
RMON is the most important expansion of the standard SNMP. RMON is a set of
71
Page 72

MIB definitions, used to define standard network monitor functions and interfaces,
enabling the communication between SNMP management terminals and remote monitors.
RMON provides a highly efficient method to monitor actions inside the subnets.
MID of RMON consists of 10 groups. The switch supports the most frequently used
group 1, 2, 3 and 9:
Statistics: Maintain basic usage and error statistics for each subnet monitored by
the Agent.
History: Record periodical statistic samples available from Statistics.
Alarm: Allow management console users to set any count or integer for sample
intervals and alert thresholds for RMON Agent records.
Event: A list of all events generated by RMON Agent.
Alarm depends on the implementation of Event. Statistics and History display some
current or history subnet statistics. Alarm and Event provide a method to monitor any
integer data change in the network, and provide some alerts upon abnormal events
(sending Trap or record in logs).
2.4.2 SNMP Configuration Task List
1. Enable or disable SNMP Agent server function
2. Configure SNMP community string
3. Configure IP address of SNMP management base
4. Configure engine ID
5. Configure user
6. Configure group
7. Configure view
8. Configuring TRAP
9. Enable/Disable RMON
1. Enable or disable SNMP Agent server function
Command Explanation
snmp-server
no snmp-server
Enable the SNMP Agent function on the
switch; the “no snmp-server” command
disables the SNMP Agent function on the
switch.
2. Configure SNMP community string
Command Explanation
snmp-server community <string>
{ro|rw}
no snmp-server community <string>
Configure the community string for the
switch; the “no snmp-server community
<string>“ command deletes the configured
72
Page 73

community string.
3. Configure IP address of SNMP management base
Command Explanation
snmp-server securityip {<ipv4-address>|
<ipv6-address>}
no snmp-server securityip
{<ipv4-address>| <ipv6-address>}
Configure the secure IPv4/IPv6 address
which is allowed to access the switch on
the NMS; the “no snmp-server securityip
{<ipv4-address>| <ipv6-address>}
“ command deletes configured secure
address.
snmp-server SecurityIP enable
snmp-server SecurityIP disable
Enable or disable secure IP address check
function on the NMS.
4. Configure engine ID
Command Explanation
snmp-server engineid < engine-string >
no snmp-server engineid <
engine-string >
Configure the local engine ID on the
switch. This command is used for SNMP
v3.
5. Configure user
Command Explanation
snmp-server user <user-string>
Add a user to a SNMP group. This
<group-string> [[encrypted] {auth
{md5|sha} <password-string>}]
command is used to configure USM for
SNMP v3.
no snmp-server user <user-string>
<group-string>
6. Configure group
Command Explanation
snmp-server group <group-string>
{NoauthNopriv|AuthNopriv|AuthPriv}
[[read <read-string>] [write
Set the group information on the switch.
This command is used to configure VACM
for SNMP v3.
<write-string>] [notify <notify-string>]]
no snmp-server group <group-string>
{NoauthNopriv|AuthNopriv|AuthPriv}
7. Configure view
Command Explanation
snmp-server view <view-string>
<oid-string> {include|exclude}
Configure view on the switch. This
command is used for SNMP v3.
no snmp-server view <view-string>
8. Configuring TRAP
Command Explanation
73
Page 74

snmp-server enable traps
no snmp-server enable traps
Command: snmp-server host
{<ipv4-addr>|<ipv6-addr>}
{v1|v2c|{v3
{NoauthNopriv|AuthNopriv|AuthPriv}}}
<user-string>
no snmp-server host
{<ipv4-addr>|<ipv6-addr>} {v1|v2c|{v3
{NoauthNopriv|AuthNopriv |AuthPriv}}}
<user-string>
9. Enable/Disable RMON
Command Explanation
rmon enable
no rmon enable
Enable the switch to send Trap message.
This command is used for SNMP v1/v2/v3.
Set the host IPv4/IPv6 address which is
used to receive SNMP Trap information.
For SNMP v1/v2, this command also
configures Trap community string; for
SNMP v3, this command also configures
Trap user name and security level.
Enable/disable RMON.
2.4.3 Commands for SNMP
2.4.3.1 rmon
Command: rmon enable
no rmon enable
Function: Enable RMON; the “no rmon enable” command disables RMON.
Command mode: Global Mode
Default: RMON is disabled by default.
Example 1: Enable RMON
Switch(config)#rmon enable
Example 2: Disable RMON
Switch(config)#no rmon enable
2.4.3.2 show snmp
Command: show snmp
Function: Display all SNMP counter information.
Command mode: Admin Mode
Example:
Switch#show snmp
0 SNMP packets input
74
Page 75

0 Bad SNMP version errors
0 Unknown community name
0 Illegal operation for community name supplied
0 Encoding errors
0 Number of requested variables
0 Number of altered variables
0 Get-request PDUs
0 Get-next PDUs
0 Set-request PDUs
0 SNMP packets output
0 Too big errors (Max packet size 1500)
0 No such name errors
0 Bad values errors
0 General errors
0 Get-response PDUs
0 SNMP trap PDUs
Displayed information Explanation
snmp packets input Total number of SNMP packet inputs.
bad snmp version errors Number of version information error
packets.
unknown community name Number of community name error
packets.
illegal operation for community name
supplied
Number of permission for community
name error packets.
encoding errors Number of encoding error packets.
number of requested variablest Number of variables requested by NMS.
number of altered variables Number of variables set by NMS.
get-request PDUs Number of packets received by “get”
requests.
get-next PDUs Number of packets received by “getnext”
requests.
set-request PDUs Number of packets received by “set”
requests.
snmp packets output Total number of SNMP packet outputs.
too big errors Number of “Too_ big” error SNMP
packets.
maximum packet size Maximum length of SNMP packets.
75
Page 76

no such name errors Number of packets requesting for
non-existent MIB objects.
bad values errors Number of “Bad_values” error SNMP
packets.
general errors Number of “General_errors” error SNMP
packets.
response PDUs Number of response packets sent.
trap PDUs Number of Trap packets sent.
2.4.3.3 show snmp status
Command: show snmp status
Function: Display SNMP configuration information.
Command mode: Admin Mode
Example:
Switch#show snmp status
Trap enable
RMON enable
Community Information:
V1/V2c Trap Host Information:
V3 Trap Host Information:
Security IP Information:
Displayed information Description
Community string Community string
Community access Community access permission
Trap-rec-address IP address which is used to receive Trap.
Trap enable Enable or disable to send Trap.
SecurityIP IP address of the NMS which is allowed
to access Agent
2.4.3.4 snmp-server community
Command: snmp-server community <string> {ro|rw}
snmp-server community <string>
Function: Configure the community string for the switch; the “no snmp-server
community <string>“ command deletes the configured community string.
Parameter: <string> is the community string set; ro|rw is the specified access mode to
MIB, ro for read-only and rw for read-write.
76
Page 77

Command mode: Global Mode
Usage Guide: The switch supports up to 4 community strings.
Example 1: Add a community string named “private” with read-write permission.
Switch(config)#snmp-server community private rw
Example 2: Add a community string named “public” with read-only permission.
Switch(config)#snmp-server community public ro
Example 3: Modify the read-write community string named “private” to read-only.
Switch(config)#snmp-server community private ro
Example 4: Delete community string “private”.
Switch(config)#no snmp-server community private
2.4.3.5 snmp-server
Command: snmp-server
no snmp-server
Function: Enable the SNMP proxy server function on the switch. The “no snmp-server”
command disables the SNMP proxy server function
Command mode: Global mode
Default: SNMP proxy server function is disabled by system default.
Usage guide: To perform configuration management on the switch with network manage
software, the SNMP proxy server function has to be enabled with this command.
Example: Enable the SNMP proxy server function on the switch.
Switch(Config)#snmp-server
2.4.3.6 snmp-server enable traps
Command: snmp-server enable traps
no snmp-server enable traps
Function: Enable the switch to send Trap message; the “no snmp-server enable traps”
command disables the switch to send Trap message.
Command mode: Global Mode
Default: Trap message is disabled by default.
Usage Guide: When Trap message is enabled, if Down/Up in device ports or of system
occurs, the device will send Trap messages to NMS that receives Trap messages.
Example 1: Enable to send Trap messages.
Switch(config)#snmp-server enable traps
Example 2: Disable to send Trap messages.
Switch(config)#no snmp-server enable trap
2.4.3.7 snmp-server host
77
Page 78

Command: snmp-server host {<ipv4-addr>|<ipv6-addr>} {v1|v2c|{v3
{NoauthNopriv|AuthNopriv|AuthPriv}}} <user-string>
no snmp-server host {<ipv4-addr>|<ipv6-addr>} {v1|v2c|{v3
{NoauthNopriv|AuthNopriv |AuthPriv}}} <user-string>
Function: As for the v1/v2c versions this command configures the IP address and trap
community character string of the network manage station receiving the SNMP Trap
message. And for v3 version, this command is used for receiving the network manage
station IP address and the Trap user name and safety level; the “no” form of this
command cancels this IP address.
Command Mode: Global Mode
Parameter: <ipv4-addr>|<ipv6-addr> is the IP address of the NMS managing station
which receives Trap message.
v1|v2c|v3 is the version number when sending the trap
NoauthNopriv|AuthNopriv|AuthPriv is the safety level v3 trap is applied, which may be
non encrypted and non authentication, non encrypted and authentication, encrypted and
authentication.
<user-string> is the community character string applied when sending the Trap
message at v1/v2, and will be the user name at v3
Usage Guide:The Community character string configured in this command is the default
community string of the RMON event group. If the RMON event group has no community
character string configured, the community character string configured in this command
will be applied when sending the Trap of RMON, and if the community character string is
configured, its configuration will be applied when sending the RMON trap.
Example:
Configure an IP address to receive Trap
Switch(config)#snmp-server host 1.1.1.5 v1 usertrap
Delete a Trap receiving IP address
Switch(config)#no snmp-server host 1.1.1.5 v1 usertrap
Configure a Trap receiving IPv6 address
Switch(config)#snmp-server host 2001:1:2:3::1 v1 usertrap
Delete a Trap receiving IPv6 address
Switch(config)#no snmp-server host 2001:1:2:3::1 v1 usertrap
2.4.3.8 debug snmp mib
Command: debug snmp mib
no debug snmp mib
Function:Enable the SNMP mib debugging; the " no debug snmp mib” command
disables the debugging
78
Page 79

Command Mode: Admin Mode
Usage Guide: When user encounters problems in applying SNMP, the SNMP debugging
is available to locate the problem causes.
Example: Switch#debug snmp mib
2.4.3.9 debug snmp keneral
Command: debug snmp keneral
no debug snmp keneral
Function:Enable the SNMP keneral debugging; the “no debug snmp keneral”
command disables the debugging function
Command Mode: Admin Mode
Usage Guide:When user encounters problems in applying SNMP, the SNMP debugging
is available to locate the problem causes.
Example: Switch#debug snmp keneral
2.4.3.10 show snmp engineid
Command: show snmp engineid
Function:Display the engine ID commands
Command Mode: Admin Mode
Example:
Switch#show snmp engineid
SNMP engineID:3138633303f1276c Engine Boots is:1
Displayed Information Explanation
SNMP engineID Engine number
Engine Boots Engine boot counts
2.4.3.11 show snmp group
Command: show snmp group
Function: Display the group information commands
Command Mode: Admin Mode
Example:
Switch#show snmp group
Group Name:initial Security Level:noAuthnoPriv
Read View:one
Write View:<no writeview specified>
Notify View:one
Displayed Information Explanation
Group Name Group name
79
Page 80

Security level Security level
Read View Read view name
Write View Write view name
Notify View Notify view name
<no writeview specified> No view name specified by the user
2.4.3.12 show snmp mib
Command: show snmp mib
Function: Display all MIB supported by the switch
Command Mode: Admin Mode
2.4.3.13 show snmp user
Command: show snmp user
Function:Display the user information commands
Command Mode: Admin Mode
Example:
Switch#show snmp user
User name: initialsha
Engine ID: 1234567890
Auth Protocol:MD5 Priv Protocol:DES-CBC
Row status:active
Displayed Information Explanation
User name User name
Engine ID Engine ID
Priv Protocol Employed encryption algorithm
Auth Protocol Employed identification algorithm
Row status User state
2.4.3.14 show snmp view
Command: show snmp view
Function:Display the view information commands.
Command Mode: Admin Mode
Example:
Switch#show snmp view
View Name:readview 1. -Included active
1.3. Excluded active
Displayed Information Explanation
View Name View name
80
Page 81

1.and1.3. OID number
Included The view includes sub trees rooted by
this OID
Excluded The view does not include sub trees
rooted by this OID
active State
2.4.3.15 snmp-server engineid
Command: snmp-server engineid < engine-string >
no snmp-server engineid < engine-string >
Function: Configure the engine ID; the “no" form of this command restores to the default
engine ID
Command Mode:Global mode
Parameter:<engine-string> is the engine ID shown in 1-32 digit hex characters
Default:Default value is the company ID plus local MAC address
Usage Guide:
Example: Set current engine ID to A66688999F
Switch(config)#snmp-server engineid A66688999F
Restore the default engine ID
Switch(config)#no snmp-server engineid A66688999F
2.4.3.16 snmp-server group
Command: snmp-server group <group-string>
{NoauthNopriv|AuthNopriv|AuthPriv} [[read <read-string>] [write
<write-string>] [notify <notify-string>]]
no snmp-server group <group-string> {NoauthNopriv|AuthNopriv|AuthPriv}
Function:This command is used to configure a new group; the “no” form of this
command deletes this group.
Command Mode: Global Mode
Parameter:<group-string > group name which includes 1-32 characters
NoauthNopriv Applies the non recognizing and non encrypting safety level
AuthNopriv Applies the recognizing but non encrypting safety level
AuthPriv Applies the recognizing and encrypting safety level
Name of readable view which includes 1-32 characters
Name of writable view which includes 1-32 characters
Name of trappable view which includes 1-32 characters
Usage Guide:There is a default view “v1defaultviewname” in the system. It is
recommended to use this view as the view name of the notification. If the read or write
81
Page 82

view name is empty, corresponding operation will be disabled.
Example:Create a group CompanyGroup, with the safety level of recognizing
andencrypting, the read viewname isreadview, and the writing is disabled.
Switch (Config)#snmp-server group CompanyGroup AuthPriv read readview
deletet group
Switch (Config)#no snmp-server group CompanyGroup AuthPriv
2.4.3.17 snmp-server SecurityIP enable
Command: snmp-server SecurityIP enable
snmp-server SecurityIP disable
Function: Enable/disable the safety IP address authentication on NMS manage station
Command Mode:Global Mode
Default:Enable the safety IP address authentication function
Example:
Disable the safety IP address authentication function
Switch(config)#snmp-server securityip disable
2.4.3.18 snmp-server view
Command: snmp-server view <view-string> <oid-string> {include|exclude}
no snmp-server view <view-string>
Function: This command is used to create or renew the view information; the “no" form
of this command deletes the view information
Command Mode:Global Mode
Parameter: <view-string> view name, containing 1-32 characters;
<oid-string>is OID number or corresponding node name, containing 1-255 characters.
include|exclude , include/exclude this OID
Usage Guide: The command supports not only the input using the character string of the
variable OID as parameter. But also supports the input using the node name of the
parameter
Example:
Create a view, the name is readview, including iso node but not including the iso.3 node
Switch (Config)#snmp-server view readview iso include
Switch (Config)#snmp-server view readview iso.3 exclude
Delete the view
Switch (Config)#no snmp-server view readview
2.4.3.19 snmp-server user
Command: snmp-server user <user-string> <group-string> [[encrypted] {auth
82
Page 83

{md5|sha} <password-string>}]
no snmp-server user <user-string> <group-string>
Function: Add a new user to an SNMP group; the "no” form of this command deletes this
user
Command Mode:Global Mode
Parameter: <user-string> is the user name containing 1-32 characters
<group-string> is the name of the group the user belongs to, containing 1-32 characters
encrypted use DES for the packet encryption
auth perform packet authentication
md5 packet authentication using HMAC MD5 algorithm
sha packet authentication using HMAC SHA algorithm
<password-string> user password,containing 1-32 character
Usage Guide: If the encryption and authentication is not selected, the default settings
will be no encryption and no authentication. If the encryption is selected, the
authentication must be done. When deleting a user, if correct username and incorrect
group name is inputted, the user can still be deleted.
Example: Add a new user tester in the UserGroup with an encryption safety level and
HMAC md5 for authentication, the password is hello.
Switch (Config)#snmp-server user tester UserGroup encrypted auth md5 hello
deletes an User
Switch (Config)#no snmp-server user tester UserGroup
2.4.3.20 snmp-server securityip
Command:snmp-server securityip {<ipv4-address>| <ipv6-address>}
no snmp-server securityip {<ipv4-address>| <ipv6-address>}
Function: Configure to permit to access security IPv4 or IPv6 address of the switch
NMS administration station; the “ no snmp-server securityip {<ipv4-address>|
<ipv6-address>}”command deletes configured security IPv4 or IPv6 address.
Command Mode: Global Mode
Parameter: <ipv4-address> is NMS security IPv4 address, point separated decimal
format
<ipv6-address> is NMS security IPv6 address, colon separated hex format.
Usage Guide: It is only the consistency between NMS administration station IPv4 or
IPv6 address and security IPv4 or IPv6 address configured by the command,
so it send SNMP package could be processed by switch, the command only
applies to SNMP.
Example:
Configure security IP address of NMS administration station
83
Page 84

Switch(config)#snmp-server securityip 1.1.1.5
Delete security IPv6 address
Switch(config)#no snmp-server securityip 2001::1
2.4.4 Typical SNMP Configuration Examples
Switch
1.1.1.9
NMS
1.1.1.5
Fig 2-2 Typical SNMP Configuration
The IP address of the NMS is 1.1.1.5; the IP address of the switch (Agent) is 1.1.1.9
Scenario 1: The NMS network administrative software uses SNMP protocol to obtain
data from the switch.
The configuration on the switch is listed below:
Switch(config)#snmp-server
Switch(Config)#snmp-server community private rw
Switch(Config)#snmp-server community public ro
Switch(Config)#snmp-server securityip 1.1.1.5
The NMS can use “private” as the community string to access the switch with read-write
permission, or use “public” as the community string to access the switch with read-only
permission.
Scenario 2: NMS will receive Trap messages from the switch (Note: NMS may have
community string verification for the Trap messages. In this scenario, the NMS uses a
Trap verification community string of “ectrap”).
The configuration on the switch is listed below:
Switch(config)#snmp-server
Switch(Config)#snmp-server host 1.1.1.5 ectrap
Switch(Config)#snmp-server enable traps
Scenario 3: NMS uses SNMP v3 to obtain information from the switch.
84
Page 85

The configuration on the switch is listed below:
Switch(config)#snmp-server
Switch (Config)#snmp-server user tester UserGroup encrypted auth md5 hello
Switch (Config)#snmp-server group UserGroup AuthPriv read max write max notify max
Switch (Config)#snmp-server view max 1 include
Scenario 4: NMS wants to receive the v3Trap messages sent by the switch.
The configuration on the switch is listed below:
Switch(config)#snmp-server
Switch(config)#snmp-server host 10.1.1.2 v3 AuthPriv tester
Switch(config)#snmp-server enable traps
2.4.5 SNMP Troubleshooting
When users configure the SNMP, the SNMP server may fail to run properly due to
physical connection failure and wrong configuration, etc. Users can troubleshoot the
problems by following the guide below:
z Good condition of the physical connection.
z Interface and datalink layer protocol is Up (use the “show interface” command),
and the connection between the switch and host can be verified by ping ( use
“ping” command).
z The switch enabled SNMP Agent server function (use “snmp-server” command)
z Secure IP for NMS (use “snmp-server securityip” command) and community
string (use “snmp-server community” command) are correctly configured, as any
of them fails, SNMP will not be able to communicate with NMS properly.
z If Trap function is required, remember to enable Trap (use “snmp-server enable
traps” command). and remember to properly configure the target host IP
address and community string for Trap (use “snmp-server host” command) to
ensure Trap message can be sent to the specified host.
z If RMON function is required, RMON must be enabled first (use “rmon enable”
command).
z Use “show snmp” command to verify sent and received SNMP messages; Use
“show snmp status” command to verify SNMP configuration information; Use
“debug snmp packet” to enable SNMP debug function and verify debug
information.
z If users still can’t solve the SNMP problems, Please contact our technical and
service center.
85
Page 86

2.5 Switch Upgrade
ES4624-SFP/ES4626-SFP switch provides two ways for switch upgrade: BootROM
upgrade and the TFTP/FTP upgrade under Shell.
2.5.1 Switch System Files
The system files includes system image file and boot file. The updating of the switch
is to update the two files by overwrite the old files with the new ones.
The system image files refers to the compressed files of the switch hardware drivers,
and software support program, etc, namely what we usually call the IMG update file. The
IMG file can only be saved in the FLASH with a defined name of nos.img
The boot file is for initiating the switch, namely what we usually call the ROM update
file ((It can be compressed into IMG file if it is of large size). The boot file can only be
saved in the ROM in which the file name is defined as boot.rom
The update method of the system image file and the boot file is the same. The
switch supplies the user with two modes of updating: 1. BootROM mode; 2. TFTP and
FTP update at Shell mode. This two update method will be explained in details in
following two sections.
2.5.2 BootROM Upgrade
There are two methods for BootROM upgrade: TFTP and FTP, which can be
selected at BootROM command settings.
Console cable
connection
cable
connection
Fig 2-3 Typical topology for switch upgrade in BootROM mode
The upgrade procedures are listed below:
Step 1:
As shown in the figure, a PC is used as the console for the switch. A console cable is
86
Page 87

used to connect PC to the management port on the switch. The PC should have
FTP/TFTP server software installed and has the image file required for the upgrade.
Step 2:
Press “ctrl+b” on switch boot up until the switch enters BootROM monitor mode. The
operation result is shown below:
ES4626-SFP Management Switch
Copyright (c) 2001-2004 by Accton Technology Corporation.
All rights reserved.
Reset chassis ... done.
Testing RAM...
134,217,728 RAM OK.
Loading BootROM...
Starting BootRom...
Attaching to file system ... done.
BootRom version: 1.0.4
Creation date: Jun 9 2006, 14: 54: 12
Attached TCP/IP interface to lnPci0.
[Boot]:
Step 3:
Under BootROM mode, run “setconfig” to set the IP address and mask of the switch
under BootROM mode, server IP address and mask, and select TFTP or FTP upgrade.
Suppose the switch address is 192.168.1.2/24, and PC address is 192.168.1.66/24, and
select TFTP upgrade, the configuration should like:
[Boot]: setconfig
Host IP Address: 10.1.1.1 192.168.1.2
Server IP Address: 10.1.1.2 192.168.1.66
FTP(1) or TFTP(2): 1 2
Network interface configure OK.
[Boot]:
87
Page 88

Step 4:
Enable FTP/TFTP server in the PC. For TFTP, run TFTP server program; for FTP, run
FTP server program. Before start downloading upgrade file to the switch, verify the
connectivity between the server and the switch by ping from the server. If ping succeeds,
run “load” command in the BootROM mode from the switch; if it fails, perform
troubleshooting to find out the cause. The following is the configuration for the system
update image file.
[Boot]: load nos.img
Loading...
entry = 0x10010
size = 0x1077f8
Step 5:
Execute “write nos.img” in BootROM mode. The following saves the system update
image file.
[Boot]: write nos.img
Programming...
Program OK.
[Boot]:
Step 6:
After successful upgrade, execute “run” command in BootROM mode to return to CLI
configuration interface.
[Boot]: run(or reboot)
Other commands in BootROM mode
1. DIR command
Used to list existing files in the FLASH.
[Boot]: dir
boot.rom 327,440 1900-01-01 00: 00: 00 --SH
boot.conf 83 1900-01-01 00: 00: 00 --SH
nos.img 2,431,631 1980-01-01 00: 21: 34 ----
startup-config 2,922 1980-01-01 00: 09: 14 ----
temp.image 2,431,631 1980-01-01 00: 00: 32 ----
2. CONFIG RUN command
Used to set the IMAGE file to run upon system start-up, and the configuration file to run
upon configuration recovery.
88
Page 89

[Boot]: config run
Boot File: [nos.img] nos1.image
Config File: [boot.conf]
2.5.3 FTP/TFTP Upgrade
2.5.3.1 Introduction To FTP/TFTP
FTP(File Transfer Protocol)/TFTP(Trivial File Transfer Protocol) are both file transfer
protocols that belonging to fourth layer(application layer) of the TCP/IP protocol stack,
used for transferring files between hosts, hosts and switches. Both of them transfer files
in a client-server model. Their differences are listed below.
FTP builds upon TCP to provide reliable connection-oriented data stream transfer
service. However, it does not provide file access authorization and uses simple
authentication mechanism(transfers username and password in plain text for
authentication). When using FTP to transfer files, two connections need to be established
between the client and the server: a management connection and a data connection. A
transfer request should be sent by the FTP client to establish management connection on
port 21 in the server, and negotiate a data connection through the management
connection.
There are two types of data connections: active connection and passive connection.
In active connection, the client transmits its address and port number for data
transmission to the sever, the management connection maintains until data transfer is
complete. Then, using the address and port number provided by the client, the server
establishes data connection on port 20 (if not engaged) to transfer data; if port 20 is
engaged, the server automatically generates some other port number to establish data
connection.
In passive connection, the client, through management connection, notify the server
to establish a passive connection. The server then creates its own data listening port and
informs the client about the port, and the client establishes data connection to the
specified port.
As data connection is established through the specified address and port, there is a
third party to provide data connection service.
TFTP builds upon UDP, providing unreliable data stream transfer service with no
user authentication or permission-based file access authorization. It ensures correct data
transmission by sending and acknowledging mechanism and retransmission of time-out
packets. The advantage of TFTP over FTP is that it is a simple and low overhead file
transfer service.
ES4624-SFP/ES4626-SFP switch can operate as either FTP/TFTP client or server.
89
Page 90

When ES4624-SFP/ES4626-SFP switch operates as a FTP/TFTP client, configuration
files or system files can be downloaded from the remote FTP/TFTP servers(can be hosts
or other switches) without affecting its normal operation. And file list can also be retrieved
from the server in ftp client mode. Of course, ES4624-SFP/ES4626-SFP switch can also
upload current configuration files or system files to the remote FTP/TFTP servers(can be
hosts or other switches). When ES4624-SFP/ES4626-SFP switch operates as a
FTP/TFTP server, it can provide file upload and download service for authorized
FTP/TFTP clients, as file list service as FTP server.
Here are some terms frequently used in FTP/TFTP.
ROM: Short for EPROM, erasable read-only memory. EPROM is repalced by FLASH
memory in ES4624-SFP/ES4626-SFP switch.
SDRAM: RAM memory in the switch, used for system software operation and
configuration sequence storage.
FLASH: Flash memory used to save system file and configuration file
System file: including system image file and boot file.
System image file: refers to the compressed file for switch hardware driver and software
support program, usually refer to as IMAGE upgrade file. In ES4624-SFP/ES4626-SFP
switch, the system image file is allowed to save in FLASH only.
ES4624-SFP/ES4626-SFP switch mandates the name of system image file to be
uploaded via FTP in Global Mode to be nos.img, other IMAGE system files will be
rejected.
Boot file: refers to the file initializes the switch, also referred to as the ROM upgrade file
(Large size file can be compressed as IMAGE file). In ES4624-SFP/ES4626-SFP switch,
the boot file is allowed to save in ROM only. ES4624-SFP/ES4626-SFP switch mandates
the name of the boot file to be boot.rom.
Configuration file: including start up configuration file and running configuration file. The
distinction between start up configuration file and running configuration file can facilitate
the backup and update of the configurations.
Start up configuration file: refers to the configuration sequence used in switch start up.
ES4624-SFP/ES4626-SFP switch start up configuration file stores in FLASH only,
corresponding to the so called configuration save. To prevent illicit file upload and easier
configuration, ES4624-SFP/ES4626-SFP switch mandates the name of start up
configuration file to be startup-config.
Running configuration file: refers to the running configuration sequence use in the
switch. In ES4624-SFP/ES4626-SFP switch, the running configuration file stores in the
RAM. In the current version, the running configuration sequence running-config can be
saved from the RAM to FLASH by write command or copy running-config
startup-config command, so that the running configuration sequence becomes the start
90
Page 91

up configuration file, which is called configuration save. To prevent illicit file upload and
easier configuration, ES4624-SFP/ES4626-SFP switch mandates the name of running
configuration file to be running-config.
Factory configuration file: The configuration file shipped with
ES4624-SFP/ES4626-SFP switch in the name of factory-config. Run set default and
write, and restart the switch, factory configuration file will be loaded to overwrite current
start up configuration file.
2.5.3.2 FTP/TFTP Configuration
The configurations of ES4624-SFP/ES4626-SFP switch as FTP and TFTP clients
are almost the same, so the configuration procedures for FTP and TFTP are described
together in this manual.
2.5.3.2.1 FTP/TFTP Configuration Task List
1. FTP/TFTP client configuration
Upload/download the configuration file or system file.
(1) For FTP client, server file list can be checked.
2. FTP server configuration
(1) Start FTP server
(2) Configure FTP login username and password
(3) Modify FTP server connection idle time
(4) Shut down FTP server
3. TFTP server configuration
(1) Start TFTP server
(2) Configure TFTP server connection idle time
(3) Configure retransmission times before timeout for packets without
acknowledgement
(4) Shut down TFTP server
1. FTP/TFTP client configuration
(1)FTP/TFTP client upload/download file
Command Explanation
Admin Mode
copy <source-url> <destination-url>
[ascii | binary]
(2)For FTP client, server file list can be checked.
Global Mode
FTP/TFTP client upload/download file
91
Page 92

For FTP client, server file list can be
dir <ftpServerUrl>
checked.
FtpServerUrl format looks like: ftp: //user:
password@IP Address
2. FTP server configuration
(1)Start FTP server
Command Explanation
Global Mode
Start FTP server, the “no ftp-server enable”
ftp-server enable
command shuts down FTP server and
no ftp-server enable
prevents FTP user from logging in.
(2)Modify FTP server connection idle time
Command Explanation
Global Mode
ftp-server timeout <seconds> Set connection idle time
3. TFTP server configuration
(1)Start TFTP server
Command Explanation
Global Mode
Start TFTP server, the “no ftp-server enable”
tftp-server enable
command shuts down TFTP server and
no tftp-server enable
prevents TFTP user from logging in.
(2)Modify TFTP server connection idle time
Command Explanation
Global Mode
tftp-server
Set maximum retransmission time within
retransmission-number <
timeout interval.
number >
(3)Modify TFTP server connection retransmission time
Command Explanation
Global Mode
tftp-server
Set maximum retransmission time within
retransmission-number <
timeout interval.
number >
92
Page 93

2.5.3.2.2 Commands for Switch Upgrade
2.5.3.2.2.1 copy(FTP)
Command: copy <source-url> <destination-url> [ascii | binary]
Function: Download files to the FTP client.
Parameter: <source-url> is the location of the source files or directories to be
copied;<destination-url> is the destination address to which the files or directories to be
copied;forms of <source-url> and <destination-url> vary depending on different
locations of the files or directories. ascii indicates the ASCII standard will be
adopted;binary indicates that the binary system will be adopted in the file transmission
(default transmission method).When URL represents an FTP address, its form should
be:
ftp://<username>:<password>@{<ipaddress>|<ipv6address>|<hostname> }/<filename>,a
mongst <username> is the FTP user name,<password> is the FTP user
password,<ipaddress>|<ipv6address> is the IPv4 or IPv6 address of the FTP
server/client,<hostname> is the name of the host mapping with the IPv6 address,it does
not support the file download and upload with hosts mapping with IPv4
addresses,<filename> is the name of the FTP upload/download file.
Special keywords of the filename
Keywords Source or destination addresses
running-config Running configuration files
startup-config Startup configuration files
nos.img System files
nos.rom System startup files
Command Mode: Admin Mode
Usage Guide: This command supports command line hints,namely if the user can enter
commands in following forms: copy <filename> ftp:// or copy ftp:// <filename> and
press Enter,following hints will be provided by the system:
ftp server ip/ipv6 address [x.x.x.x]/[x:x::x:x] >
ftp username>
ftp password>
ftp filename>
Requesting for FTP server address, user name, password and file name
Examples:
(1)Save images in the FLASH to the FTP server of 2004:1:2:3::6
Switch#copy nos.img ftp://username:password@2004:1:2:3::6/ nos.img
(2)Obtain system file nos.img from the FTP server 2004:1:2:3::6
93
Page 94

Switch#copy ftp:// username:password@2004:1:2:3::6/nos.img nos.img
(3)Save the running configuration files
Switch#copy running-config startup-config
Relevant Command: write
2.5.3.2.2.2 copy(TFTP)
Command: copy <source-url> <destination-url> [ascii | binary]
Function: Download files to the TFTP client
Parameter: <source-url> is the location of the source files or directories to be
copied;<destination-url> is the destination address to which the files or directories to be
copied;forms of <source-url> and <destination-url> vary depending on different
locations of the files or directories. ascii indicates the ASCII standard will be
adopted;binary indicates that the binary system will be adopted in the file transmission
(default transmission method).When URL represents an TFTP address, its form should
be: tftp://{<ipaddress>|<ipv6address>|<hostname> }/<filename>,amongst
<ipaddress>|<ipv6address> is the IPv4 or IPv6 address of the TFTP
server/client,<hostname> is the name of the host mapping with the IPv6 address,it does
not support the file download and upload with hosts mapping with IPv4
addresses,<filename> is the name of the TFTP upload/download file.
Special keyword of the filename
Keywords Source or destination addresses
running-config Running configuration files
startup-config Startup configuration files
nos.img System files
nos.rom System startup files
Command Mode: Admin Mode
Usage Guide: This command supports command line hints,namely if the user can enter
commands in following forms: copy <filename> tftp:// or copy tftp:// <filename> and
press Enter,following hints will be provided by the system:
tftp server ip/ipv6 address[x.x.x.x]/[x:x::x:x]>
tftp filename>
Requesting for TFTP server address, file name
Example:
(1)Save images in the FLASH to the TFTP server of 2004:1:2:3::6
Switch#copy nos.img tftp:// 2004:1:2:3::6/ nos.img
94
Page 95

(2)Obtain system file nos.img from the TFTP server 2004:1:2:3::6
Switch#copy tftp:// 2004:1:2:3::6/nos.img nos.img
(3)Save running configuration files
Switch#copy running-config startup-config
2.5.3.2.2.3 dir
Command: dir <ftp-server-url>
Function: Browse the file list on the FTP server.
Parameter : The form of < ftp-server-url > is :
ftp://<username>:<password>@{<ipv4address>|<ipv6address>},amongst <username> is
the FTP user name,<password> is the FTP user password,
{<ipv4address>|<ipv6address>} is the IPv4 or IPv6 address of the FTP server.
Command Mode: Global Mode
Example: Browse the list of the files on the server with the FTP client
Switch(Config)# dir ftp://user:password@IPv6 Address.
2.5.3.2.2.4 ftp-server enable
Command: ftp-server enable
no ftp-server enable
Function: Start FTP server, the “no ftp-server enable” command shuts down FTP
server and prevents FTP user from logging in.
Default: FTP server is not started by default.
Command mode: Global Mode
Usage Guide: When FTP server function is enabled, the switch can still perform ftp client
functions. FTP server is not started by default.
Example: enable FTP server service.
Switch#config
Switch(Config)# ftp-server enable
2.5.3.2.2.5 ftp-server timeout
Command: ftp-server timeout <seconds>
Function: Set data connection idle time
Parameter: < seconds> is the idle time threshold ( in seconds) for FTP connection, the
valid range is 5 to 3600.
Default: The system default is 600 seconds.
Command mode: Global Mode
Usage Guide: When FTP data connection idle time exceeds this limit, the FTP
95
Page 96

management connection will be disconnected.
Example: Modify the idle threshold to 100 seconds.
Switch#config
Switch(Config)#ftp-server timeout 100
2.5.3.2.2.6 show ftp
Command: show ftp
Function: display the parameter settings for the FTP server
Command mode: Admin Mode
Default: No display by default.
Example:
Switch#show ftp
Timeout : 600
Displayed information Description
Timeout Timeout time.
2.5.3.2.2.7 show tftp
Command: show tftp
Function: display the parameter settings for the TFTP server
Default: No display by default.
Command mode: Admin Mode
Example:
Switch#show tftp
timeout : 60
Retry Times : 10
Displayed information Explanation
Timeout Timeout time.
Retry Times Retransmission times.
2.5.3.2.2.8 tftp-server enable
Command: tftp-server enable
no tftp-server enable
Function: Start TFTP server, the “no ftp-server enable” command shuts down TFTP
server and prevents TFTP user from logging in.
Default: TFTP server is not started by default.
Command mode: Global Mode
Usage Guide: When TFTP server function is enabled, the switch can still perform tftp
96
Page 97

client functions. TFTP server is not started by default.
Example: enable TFTP server service.
Switch#config
Switch(Config)#tftp-server enable
2.5.3.2.2.9 tftp-server retransmission-number
Command: tftp-server retransmission-number <number>
Function: Set the retransmission time for TFTP server
Parameter: < number> is the time to re-transfer, the valid range is 1 to 20.
Default: The default value is 5 retransmission.
Command mode: Global Mode
Example: Modify the retransmission to 10 times.
Switch#config
Switch(Config)#tftp-server retransmission-number 10
2.5.3.2.2.10 tftp-server transmission-timeout
Command: tftp-server transmission-timeout <seconds>
Function: Set the transmission timeout value for TFTP server
Parameter: < seconds> is the timeout value, the valid range is 5 to 3600s.
Default: The system default timeout setting is 600 seconds.
Command mode: Global Mode
Example: Modify the timeout value to 60 seconds.
Switch#config
Switch(Config)#tftp-server transmission-timeout 60
2.5.4 FTP/TFTP Configuration Examples
Switch
10.1.1.2
computer
10.1.1.1
Fig 2-4 Download nos.img file as FTP/TFTP client
Scenario 1: The switch is used as FTP/TFTP client. The switch connects from one
97
Page 98

of its ports to a computer, which is a FTP/TFTP server with an IP address of 10.1.1.1; the
switch acts as a FTP/TFTP client, the IP address of the switch management VLAN is
10.1.1.2. Download “nos.img” file in the computer to the switch.
z FTP Configuration
Computer side configuration:
Start the FTP server software on the computer and set the username “Switch”, and
the password “switch”. Place the “12_30_nos.img” file to the appropriate FTP server
directory on the computer.
The configuration procedures of the switch is listed below:
Switch(Config)#inter vlan 1
Switch (Config-If-Vlan1)#ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
Switch (Config-If-Vlan1)#no shut
Switch (Config-If-Vlan1)#exit
Switch (Config)#exit
Switch#copy ftp: //Switch:switch@10.1.1.1/12_30_nos.img nos.img
With the above commands, the switch will have the “nos.img” file in the computer
downloaded to the FLASH.
z TFTP Configuration
Computer side configuration:
Start TFTP server software on the computer and place the “nos.img” file to the
appropriate TFTP server directory on the computer.
The configuration procedures of the switch is listed below:
Switch (Config)#inter vlan 1
Switch (Config-If-Vlan1)#ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
Switch (Config-If-Vlan1)#no shut
Switch (Config-If-Vlan1)#exit
Switch (Config)#exit
Switch#copy tftp: //10.1.1.1/12_30_nos.img nos.img
Scenario 2: The switch is used as FTP server. The switch operates as the FTP server
and connects from one of its ports to a computer, which is a FTP client. Transfer the
“nos.img” file in the switch to the computer and save as 12_25_nos.img.
The configuration procedures of the switch is listed below:
Switch (Config)#inter vlan 1
Switch (Config-If-Vlan1)#ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
Switch (Config-If-Vlan1)#no shut
98
Page 99

Switch (Config-If-Vlan1)#exit
Switch (Config)#ftp-server enable
Switch(Config)# username Switch password 0 Admin
Computer side configuration:
Login to the switch with any FTP client software, with the username “Admin” and
password “switch”, use the command “get nos.img 12_25_nos.img” to download
“nos.img” file from the switch to the computer.
Scenario 3: The switch is used as TFTP server. The switch operates as the TFTP server
and connects from one of its ports to a computer, which is a TFTP client. Transfer the
“nos.img” file in the switch to the computer.
The configuration procedures of the switch is listed below:
Switch(Config)#inter vlan 1
Switch (Config-If-Vlan1)#ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
Switch (Config-If-Vlan1)#no shut
Switch (Config-If-Vlan1)#exit
Switch (Config)#tftp-server enable
Computer side configuration:
Login to the switch with any TFTP client software, use the “tftp” command to download
“nos.img” file from the switch to the computer.
Scenario 4: The switch is used as FTP/TFTP client. The switch connects from one of its
ports to a computer, which is a FTP/TFTP server with an IP address of 10.1.1.1; several
switch user profile configuration files are saved in the computer. The switch operates as
the FTP/TFTP client, the management VLAN IP address is 10.1.1.2. Download switch
user profile configuration files from the computer to the switch FLASH.
z FTP Configuration
Computer side configuration:
Start the FTP server software on the computer and set the username “Switch”, and the
password “Admin”. Save “nos.img”, “boot.rom” and “startup-config” in the appropriate
FTP server directory on the computer.
The configuration procedures of the switch is listed below:
Switch (Config)#inter vlan 1
Switch (Config-If-Vlan1)#ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
Switch (Config-If-Vlan1)#no shut
Switch (Config-If-Vlan1)#exit
99
Page 100

Switch (Config)#exit
Switch#copy ftp: //Switch: Admin@10.1.1.1/nos.img nos.img
Switch#copy ftp: //Switch: Admin@10.1.1.1/boot.rom boot.rom
Switch#copy ftp: //Switch: Admin@10.1.1.1/startup-config startup-config
With the above commands, the switch will have the user profile configuration file in the
computer downloaded to the FLASH.
z TFTP Configuration
Computer side configuration:
Start TFTP server software on the computer and place “nos.img”, “boot.rom” and
“startup-config” to the appropriate TFTP server directory on the computer.
The configuration procedures of the switch is listed below:
Switch (Config)#inter vlan 1
Switch (Config-If-Vlan1)#ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
Switch (Config-If-Vlan1)#no shut
Switch (Config-If-Vlan1)#exit
Switch (Config)#exit
Switch#copy tftp: //10.1.1.1/ nos.img nos.img
Switch#copy tftp: //10.1.1.1/ boot.rom boot.rom
Switch#copy tftp: //10.1.1.1/ startup-config startup-config
Scenario 5: ES4624-SFP/ES4626-SFP switch acts as FTP client to view file list on the
FTP server.
Synchronization conditions: The switch connects to a computer by an Ethernet port, the
computer is a FTP server with an IP address of 10.1.1.1; the switch acts as a FTP client,
and the IP address of the switch management VLAN1 interface is 10.1.1.2.
z FTP Configuration
PC side:
Start the FTP server software on the PC and set the username “Switch”, and the
password “Admin”.
ES4624-SFP/ES4626-SFP switch:
Switch (Config)#inter vlan 1
Switch (Config-If-Vlan1)#ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
Switch (Config-If-Vlan1)#no shut
Switch (Config-If-Vlan1)#exit
Switch (Config)#dir ftp: //Switch: Admin@10.1.1.1
220 Serv-U FTP-Server v2.5 build 6 for WinSock ready...
331 User name okay, need password.
230 User logged in, proceed.
100
 Loading...
Loading...