Accton Technology Accton Fast etherHub 3500 System 12mi SNMP, Accton Fast etherHub 3500 System 12i User Manual
Page 1

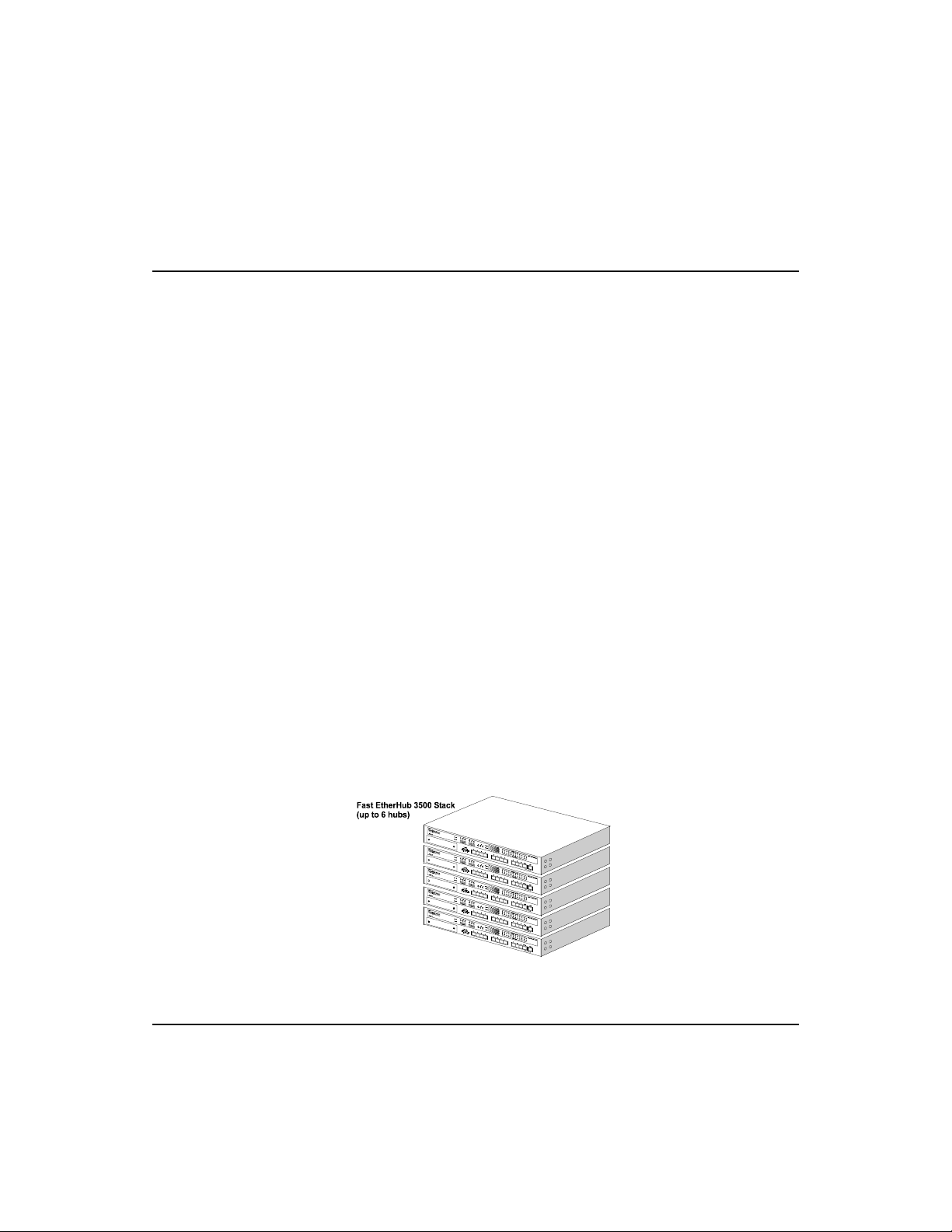
Fast EtherHub 3500 System
&INO<GG<ODJI<I?2N@MN$PD?@
♦ #<NO"OC@M%P=D
♦ #<NO"OC@M%P=HD0+*-
Page 2

Installation and User’s Guide
Fast EtherHub 3500 System
Intelligent
Fast Ethernet Stackable Hub
with 12 100BASE-TX Ports;
including SNMP Management Support
Page 3

Copyright (c) 1996 by Accton Technology Corporation. All rights reserved.
No part of this document may be copied or reproduced in any form or by any means without the prior written
consent of Accton Technology Corporation.
Accton makes no warranties with respect to this documentation and disclaims any implied warranties of
merchantability, quality, or fitness for any particular purpose. The information in this document is subject to change
without notice. Accton reserves the right to make revisions to this publication without obligation to notify any person
or entity of any such changes.
Before operating this product, please review the statements on electomagnetic emission interference and safety
compliance in Appendix D.
International Headquarters
No. 1 Creation Road III,
Science-based Industrial Park
Hsinchu 300, Taiwan, R.O.C.
Phone: 886-3-5770-270
FAX: 886-3-5770-267
BBS: 886-3-5770-654
Internet: support@accton.com.tw
Accton, EtherHub, SmartWatch, SmartExtender and AccView and are trademarks or registered trademarks of
Accton Technology Corporation. Other trademarks or brand names mentioned herein are trademarks or registered
trademarks of their respective companies.
EH3512I-TX
EH3512M-TX
E1296-R01
150136-101
USA Headquarters
1962 Zanker Road
San Jose, CA 95112
Phone: 408-452-8900
FAX: 408-452-8988
BBS: 408-452-8828
FAST FAX: 408-452-8811
Page 4

Package Checklist
Package Contents
Carefully unpack the contents of the package and verify them
against the checklist given below. This checklist applies to all
the Fast EtherHub 3500 Series models unless otherwise specified.
æ Fast EtherHub-12i
Intelligent Fast Ethernet Stackable Hub with 12 100BASE-TX Ports
(Model No. EH3512I-TX)
or Fast EtherHub-12mi SNMP
Intelligent Fast Ethernet Stackable Hub with 12 100BASE-TX Ports;
including SNMP Managment Support
(Model No. EH3512M-TX)
Two mounting brackets
æ
æ Four rubber foot pads
æ One AC power cord
æ One 20 cm FlexBus 3500 stack cable
æ Installation manual
æ Owner registration card
Please inform your dealer immediately should there be any
wrong, missing, or damaged parts.
If possible, retain the carton, including the original packing
materials. Use them again to repack the unit in case there is a
need to return it for repair.
To qualify for product updates and product warranty
@
registration, fill in the
to Accton Technology Corporation.
Package Contents i
Owner Registration Card and return it
Page 5

Quick Installation
Accton’s Fast EtherHub 3500 models each contain 12 Fast
Ethernet (100BASE-TX) RJ-45 ports, one MDI daisy- chain port,
and one slot for an optional connection using 1 00BAS E -TX
(10BASE-T), 100BASE-T4 or 100BASE-FX.
The smart design built into the front display panel and
configure options provide a friendly interface that simplifies
installation and network troubleshooting. If you are already
familiar with basic network operations, you should be able to
install this hub as described below:
1. Unpack the Fast EtherHub 3500 unit.
2. Find a location close to the network devices you need to
connect, and within easy reach of an electrical outlet.
These hubs are suitable for
desktop or rack mounting
Attach PCs to the station ports
Attach each hub in the stack
with FlexBus 3500 stack cable
3. Mount the hub on a desktop or any other flat surface. If you
are installing multiple hubs, you can stack them on top of
each other (after attaching the foot pads), or install them in a
standard EIA 19-inch rack.
4. Connect any devices that use a standard network interface
to the RJ-45 (MDI-X) station ports (e.g., a workstation,
server or router). Use 100
pair (UTP) or 100
W shielded twisted-pair (STP) cable. Also
W Category 5 unshielded twisted-
be sure that the length of any twisted-pair connection does
not exceed 100 meters. (Refer to Chapter 2 for a more
detailed description of calculating the maxim u m cable length
permitted between two end nodes.)
5. If you are stacking multiple hubs, connect the FlexBus 3500
stack cable between the “
adjacent hubs. Run a simple chain starting at the
the top hub in the stack, and ending at the
Out” and “In” backplane ports on
Out port on
In port on the
bottom hub in the stack. No more than 6 hubs can be
connected via the backplane bus.
Quick Installation iii
Page 6

Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
e
s
o
n
k
s
k
t
Attach each hub to one of th
backplane segment
Use the SmartExtender Module t
interconnect different segments i
the stac
Or interconnect the stack’
segments by attaching the daisychain port to a switch, or the
station ports to a router
Attach to the extended networ
via the daisy-chain por
6. Connect each hub to one of the 3 Fast Ethernet segments
embedded in the backplane bus using either on-board
configuration (Chapter 4) or optional network management
software (e.g., AccView/Open). You can leave a hub isolated
from the backplane if required for your network environment
(e.g., to restrict network access for the attached user group).
However, you should be careful to structure your network
connections so that nodes which communicate frequently are
located in the same segment. (Factory default is Segment 1.)
7. Bridge the different backplane segments in the Fast Ethernet
3500 stack by running a connection from the optional
100BASE-TX extender module on this hub to any station
port on another hub in the stack that has been assigned to a
different segment. Remember that devices connected to the
switching port exist in a separate segment (and unless also
connected to the FlexBus management channel) cannot be
controlled by a management agent in the stack. When
connecting a hub to the expansion port, the maximum cable
length is 100 meters.
8. If you do not have any available SmartExtender Modules,
the different segments in a Fast EtherHub 3500 stack can
also be combined into an interconnected network by running
a cable from the hubs’ daisy-chain ports (i.e., using port
12MDI on hubs attached to the different segments) to a
network interconnection device such a switch; or by running
a cable from the hubs’ station ports (i.e., using ports on hubs
attached to different segments) to a router.
9. You can also attach the overall stack to a network intercon-
nection device via the daisy-chain port (when connecting to
a switch) or via a station port (when connecting to a router).
Run straight-through twisted-pair cable from the hub to the
other device. When attaching to a switch, run cable from the
MDI daisy-chain port on this hub to any (MDI-X) station
port on the switch (or vice versa).
Note: When using the 12MDI daisy-chain port, remember that port
12X cannot be used.
iv Quick Installation
Page 7

Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
Or attach to the extended
network via the SmartExtender
Module
The SmartExtender Module can
be used to attach to another
network device that uses a
different media type
Attach the SmartExtender Module
to a hub, switch, bridge or router
Transmission speed is automatically
set for any connection made to the
SmartExtender Module
Transmission mode automatically
configured for the connected device
only if it supports auto-negotiation
Use half duplex for a
shared collision domain
10. If an optional SmartExtender Module is installed in the
expansion port, it can be used to make a bridged connection
from this hub to another network device using 100BASE- TX
(10BASE-T), 100BASE-T4 or 100BASE-FX media types.
When connecting a node to the expansion port, the maximum cable length is 100 meters for twisted-pair cable, and 2
kilometers for fiber. (Refer to Chapter 2 for a more detailed
description of calculating the maximum length permitted for
fiber optic cable.)
You can use the extender module to bridge this hub to
another Ethernet or Fast Ethernet hub or stack; or to attach it
to a network interconnection device, such as a switch, bridge
or router. However, when using the expansion port to cascade
to other networking devices outside the stack, note that the
maximum cascade length should be limited to 7 devices.
For integrating legacy networks, the 100BASE-TX extender
module provides for connection via either 100BASE-TX or
10BASE-T. All 100BASE entender modules use auto-sensing
to set the transmission speed at 10 or 100 Mbps. In other words,
this module can correctly set the transmission speed for the
attached device, even if it does not support auto-negotiation.
The extender modules, except for 100BASE-T4, support both
half-duplex and full-duplex communications. However, for
this hub to correctly set the transmission mode, the attached
device must also support auto-negotiation. If auto-negotiation
fails, the transmission mode defaults to half duplex. If this
setting is not suitable, then the transmission mode must be
manually configured via on-board configuration (Chapter 4)
or optional network management software (e.g ., AccView/Open).
To reactivate auto-negotiation, just unplug a connection from
the port on the hub and plug it in again. Remember that fullduplex mode can o n l y be used f o r a d e d ic a t ed l in k, such as t h a t
provided by the SmartExtender Module. When connecting to a
shared collision domain (i.e., another hub) set the transmission
mode for half duplex.
Quick Installation v
Page 8

Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
Difference in connecting to the
extended network via the daisychain port or SmartExtenter Module
Check your connections
The Fast EtherHub 3500 stack can be connected to a larger
network using any device such as a switch, bridge or router.
Depending on your network configuration, you may attain
better performance by making a direct connection from the
daisy-chain port (or a station port) on this hub to an
interconnection device. Making a connection from an
extender module may introduce slightly more delay.
11. Verify network communications by ensuring that -
• you have made all the necessary connections
• you can access any connected resources
• the hub’s indicators are functioning properly
If you encounter any problems in installing the Fast EtherHub
3500 system, refer to Chapter 2 for a detailed description of
installation procedures, or to Appendix A for help in
troubleshooting.
vi Quick Installation
Page 9

About this Guide
This guide is designed for the experienced network installer.
It describes how to install and o pe rate A ccton ’s Fast EtherHub
3500 system. After reading this manual, you should be able to
use the front display panel and configure options to manage all
your network connections.
This manual covers the following topics:
Chapter 1 -
Chapter 2 -
Chapter 3 -
Chapter 4 -
Chapter 5 -
Appendices - Troubleshooting, cable assignments, and product specifications.
Product Overview
Brief description of Fast Ethernet, followed by a description of
this hub and a summary of its important features and
specifications.
Installing the System
Installing a Fast EtherHub 3500 and making basic network
connections. Also includes a description of significant
components on the hub including ports and indicators.
Setting up Network Connections
Shows sample network configurations for a local area network.
Configuring the System
Describes how to manage the system via the on-board
configuration program.
Hardware Reference
Detailed description of indicator panel and ports.
About this Guide vii
Page 10

Contents
Chapter 1: Product Overview 1-1
Introduction to Fast Ethernet 1-1
Brief Description of the Fast EtherHub 3500 System 1-1
Distinguishing Factors of Fast EtherHub 3500 System 1-5
Basic Features of Fast EtherHub 3500 System 1-6
Data Switching with the SmartExtender Modules 1-9
Switching Technology 1-9
Configuration Options for the SmartExtender Modules 1-9
Switching Methods 1-10
Chapter 2: Installing the System 2-1
Pre-Installation Requirements 2-1
Hardware Installation 2-2
Stacking Hubs without a Rack 2-2
Mounting Hubs in a Rack 2-3
Connecting the Hub System 2-4
Making a Connection via an MDI-X Station Port 2-4
Connecting to the Stack’s Backplane 2-5
Making a Connection via the MDI Daisy-Chain Port 2-6
Connecting to a SmartExtender Module 2-6
Installing a Backup Power Supply 2-11
Powering on the Hub 2-12
Diagnostic Tests 2-12
Hot Remove 2-13
Configuring a Manageable Stack 2-14
Installing an SNMP Backup Agent 2-14
Verifying Port Status 2-15
Verifying System Operation 2-15
Contents ix
Page 11

Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
Chapter 3: Setting up Network Connections 3-1
Special Architecture Used for the Fast EtherHub 3500 Stack 3-1
Multi-Segment Architecture 3-1
FlexBus Management Link 3-2
Hub ID Setting 3-2
Using Management Agents 3-2
Port Backup Function 3-4
Security Features 3-4
Sample Network Configurations 3-5
Attaching the Stack to One Segment 3-5
Attaching the Stack to Multiple Segments 3-6
Isolating Specific Hub Connections 3-7
Isolating Each Hub 3-8
Extending the Network with Alternate Connections 3-9
Linking the Stack to a Management Station 3-10
Interconnecting the Segments 3-11
Connecting Remote Stacks 3-12
Operating in the Novell NetWare IPX Environment 3-13
Operating in the TCP/IP Environment 3-14
Connecting to the Network Backbone 3-15
Chapter 4: Configuring the System 4-1
Making the Connections Required for System Configuration 4-1
Direct Connection 4-2
Network Connection 4-2
Local In-Band Telnet Connection 4-3
Local In-Band Network Connection 4-3
Remote Connection 4-4
Configuring the Fast EtherHub Site 4-4
Configuring the Remote Site 4-4
Remote Configuration Methods 4-4
Accessing the Configuration Management Program 4-5
Configuring Your System with the On-board Program 4-5
Using the Fast EtherHub 3500 System Configuration Program 4-7
System Configuration Program for the Fast EtherHub-12i 4-8
Configuring the SmartExtender Port 4-9
x Contents
Page 12

Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
Sys t e m Co n fig u r a tion P r o g r am f o r the 1 2 mi a n d S tack 4-11
Exiting the Configuration Program 4-12
Restarting the Agent 4-13
Displaying System Information 4-14
Configuring the SNMP Agent 4-15
Configuring SNMP Communities 4-16
Configuring IP Trap Managers 4-17
Configuring IPX Trap Managers 4-18
Changing the Segment Configuration 4-19
Configuring Hub Parameters 4-21
Configuring Port Parameters 4-25
Defining Backup Ports 4-29
Port Intrusion Control 4-30
Downloading System Software via a TFTP Server 4-32
Xmodem Download 4-34
Changing User Passwords 4-35
Console Lockout 4-36
Segment Statistics 4-37
Hub Statistics 4-38
Port Statistics 4-39
Chapter 5: Hardware Reference 5-1
Indicator Panel 5-2
Power Indicator 5-2
SmartExtender Module Indicator 5-2
Interhub 5-3
SNMP 5-4
Segment Indicators 5-4
Management Agent Indicators 5-5
Hub ID Indicator 5-5
Serial 5-6
Terminator 5-7
Isolation 5-7
Utilization Indicators 5-7
Collision Indicators 5-8
Port Status Indicators 5-10
Diagnostic Test Indicators 5-11
Contents xi
Page 13

Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
Network Connections 5-13
Station Ports 5-13
Daisy-Chain Port 5-13
Serial Port 5-14
Rear Panel Components 5-15
Power Supply Modules 5-15
FlexBus Ports 5-16
In 5-16
Out 5-16
Appendix A: Troubleshooting A-1
Diagnosing Hub Indicators A-1
System Diagnostics A-2
Power and Cooling Problems A-2
Installation A-2
Physical Configuration A-4
System Integrity A-4
Appendix B: Pin Assignments B-1
RJ-45 Port B-1
DB9 Serial Port Pin Description B-2
Hub’s 9-Pin Serial Port to PC’s 9-Pin COM Port B-3
Hub’s 9-Pin Serial Port to PC’s 25-Pin DTE Port B-4
Hub’s 9-Pin Serial Port to Modem’s 25-Pin DCE Port B-5
Appendix C: Product Specifications C-1
Product Specifications C-1
Appendix D: Regulatory Standards D-1
EMI Warning D-1
FCC Class A Certification D-1
Voluntary Control Council for Interference (VCCI-1) D-2
EN55022 Declaration of Conformance D-3
CE Mark Declaration of Conformance D-3
Safety Compliance D-4
xii Contents
Page 14

Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
Underwriters Laboratories Compliance Statement D-4
Sicherheitshinweise D-5
Appendix E: Product Support Services E-1
Product Registration E-1
Problem Report E-1
Hardware Repair Service E-1
Software Update and Upgrade Service E-2
Bulletin Board Service (BBS) E-2
Interactive Fast Fax (U.S.A. office) E-3
Technical Support E-3
Limited Warranty E-4
Customer Remedies E-4
Return Process E-5
Accton Offices E-6
Ordering Information E-7
Glossary
Index
Contents xiii
Page 15

Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
List of Figures
Figure 2-1 Stacking Hubs without a Rack 2-2
Figure 2-2 Mounting Hubs Using a Mounting Rack 2-3
Figure 3-1 Attaching All Hubs in Stack to One Segment 3-5
Figure 3-2 Attaching Hubs in Stack to Three Segments 3-6
Figure 3-3 Linking Part of the Stacked Hubs to a Segment 3-7
Figure 3-4 Stacked Hubs Not Linked to a Segment 3-8
Figure 3-5 Linking Stacked Hubs to Unmanaged Hubs 3-9
Figure 3-6 Linking Stacked Hubs to an NMS 3-10
Figure 3-7 Linking Segments in a Stacked System 3-11
Figure 3-8 Connecting Remote Stacks 3-12
Figure 3-9 Syst e m Ap p l i e d i n Nov e ll Ne t W a r e I P X E n viro n men t 3-13
Figure 3-10 System Applied in TCP/IP Environment 3-14
Figure 3-11 Connecting to the Network Backbone 3-15
Figure 4-1 Main Configuration Menu (12i only) 4-8
Figure 4-2 Confi guration Menu for Extender Module (12i only) 4-9
Figure 4-3 Main Configuration Menu 4-11
Figure 4-4 Screen Messages for System Resart 4-13
Figure 4-5 System Information Menu 4-14
Figure 4-6 SNMP Configuration Menu 4-15
Figure 4-7 SNMP Communities Menu 4-16
Figure 4-8 IP Trap Managers Menu 4-17
Figure 4-9 IPX Trap Managers Menu 4-18
Figure 4-10 Segment Configuration Menu 4-19
Figure 4-11 Hub Configuration: Hub Selection Menu 4-21
Figure 4-12 Hub Configuration Menu 4-22
Figure 4-13 Hub ID Configuration Menu 4-24
Figure 4-14 Port Configuration: Port Selection Menu 4-25
Figure 4-15 Port Configuration Menu 4-26
Figure 4-16 SEM Port Configuration Menu 4-27
Figure 4-17 Port Backups Menu 4-29
Figure 4-18 Port Intrusion Control: Hub Selection Menu 4-30
Figure 4-19 Port Intrusion Control Menu 4-31
Figure 4-20 TFTP Download Menu 4-32
Figure 4-21 Xmodem Download Menu 4-34
Figure 4-22 User Passwords Menu 4-35
Figure 4-23 Console Lockout Menu 4-36
Figure 4-24 Segment Statistics Window 4-37
xiv Contents
Page 16

Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
Figure 4-25 Hub Statistics: Hub Selection Menu 4-38
Figure 4-26 Hub Statistics Window 4-38
Figure 4-27 Port Statistics: Port Selection Menu 4-39
Figure 4-28 Port Statistics Menu 4-40
Figure 4-29 SEM Port Statistics Menu 4-42
Figure 5-1 Front Panel of EtherHub-12mi 5-1
Figure 5-2 Indicators for EtherHub-12mi 5-2
Figure 5-3 Rear Panel 5-15
Figure B-1 RJ-45 Connector (on the Hub Side) B-1
Figure B-2 DB9 Serial Port (on the Hub Side) B-2
List of Tables
Table 2.1 Calculating the Power Budget for Fiber Optics 2-8
Table 2.2 Power Budget for Common Guage Fiber Optics 2-9
Table 2.3 Diagnostic Test Functions 2-13
Table 2.4 Checking Key LED Indicators 2-15
Table 2.5 Maximum Cable Length 2-16
Table 4.1 Configuration Options in Main Menu (12i only) 4-9
Table 4.2 Confi g urat i o n O p tion s for E x tend e r M o d u le (1 2 i o n l y) 4-10
Table 4.3 Main Configuration Menu 4-12
Table 4.4 System Information Menu 4-14
Table 4.5 SNMP Configuration Menu 4-15
Table 4.6 SNMP Communities Menu 4-16
Table 4.7 IP Trap Managers Menu 4-17
Table 4.8 IPX Trap Managers Menu 4-18
Table 4.9 Segment Configuration Menu 4-20
Table 4.10 Hub Configuration Menu 4-23
Table 4.11 Port Configuration Menu 4-26
Table 4.12 SEM Port Configuration Menu 4-28
Table 4.13 Port Backups Menu 4-30
Table 4.14 Port Intrusion Control Menu 4-31
Table 4.15 TFTP Download Menu 4-33
Table 4.16 Xmodem Download Menu 4-34
Table 4.17 User Passwords Menu 4-35
Table 4.18 Console Lockout Menu 4-36
Table 4.19 Segment Statistics Menu 4-37
Table 4.20 Hub Statistics Menu 4-39
Table 4.21 Port Statistics Menu 4-41
Contents xv
Page 17

Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
Table 4.22 SEM Port Statistics Menu 4-42
Table 5.1 Power Indicator 5-2
Table 5.2 SmartExtender Module Indicator 5-2
Table 5.3 SmartExtender Module Indicators 5-3
Table 5.4 Interhub Indicator 5-3
Table 5.5 SNMP Indicator 5-4
Table 5.6 Management Agent Indicators 5-5
Table 5.7 Hub Indicators 5-6
Table 5.8 Serial Indicator 5-6
Table 5.10 Terminator Indicator 5-7
Table 5.11 Isolation Indicator 5-7
Table 5.12 Utilization Indicators 5-7
Table 5.13 Collision Indicators 5-8
Table 5.14 Partition/Disable Indicators 5-9
Table 5.15 Link/Traffic Indicators 5-10
Table 5.16 Diagnostic Indicators 5-11
Table 5.17 Diagnostic Results 5-12
Table B.1 RJ-45 Pin Assignments B-1
Table B.2 DB9 Port Pin Assignments B-2
Table B.3 Full-Pin Connection from
Hub’s 9-Pin Serial Port to PC’s 9-Pin COM Port B-3
Table B.4 Three-Pin Connection from
Hub’s 9-Pin Serial Port to PC’s 9-Pin COM Port B-3
Table B.5 Full-Pin Connection from
Hub’s 9-Pin Serial Port to PC’s 25-Pin DTE Port B-4
Table B.6 Three-Pin Connection from
Hub’s 9-Pin Serial Port to PC’s 25-Pin DTE Port B-4
Table B.7 Hub’s 9-Pin Serial Port to
Modem’s 25-Pin DCE Port Pin Assignments B-5
Table E.1 Parameters for SmartExtender Modules E-7
T
xvi Contents
Page 18

Chapter 1: Product Overview
Introduction to Fast Ethernet
Standard 10 Mbps Ethernet has served well for past generations
of 80286 and 80386 machines performing simple file transfers.
However, with the inevitable growth in corporate network size
and the introduction of fully-functional 32-bit PC architectures,
and operating systems running complex applications, 10 Mbps
Ethernet has become a serious bottleneck.
With the recent flood of choices for upgrading media
bandwidth, 100 Mbps Fast Ethernet has become the most
popular choice because of its low cost, compatibility with
existing Ethernet applications, and the fact that it can run on top
of an installed base of twisted-pair cabling.
Moreover, by using a dual-speed switch (10 or 100 Mbps),
Fast Ethernet can be easily integrated into an existing 10 Mbps
Ethernet environment with no need for protocol translation or
changes to network software. It also includes specifications for
a media-independent interface (MII), which permits a switched
connection to any of the 100BASE-T sublayers; i.e., 100BASETX (10BASE-T), 100BASE-FX or 100BASE-T4.
Brief Description of the Fast EtherHub 3500 System
The EtherHub 3500 System is a powerful and innovative LAN
network enhancement and management product series. Each
component in the system supports a Fast Ethernet m u lti- segment
bus architecture that enhances traffic management and network
bandwidth utilization. This system offers the network manager
a wide range of flexible configuration options, allowing you to
increase your network’s bandwidth tenfold or more. In addition,
the entire installation can be monitored and controlled via SNMP
protocol through any network management station.
Product Overview 1-1
Page 19

Full Connectivity
Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
Moreover, the Fast EtherHub 3500 System provides advanced
network security features including “Intrusion Protection”
which ensures that only designated workstations are able to
transmit packets onto the network. Management access via the
out-of-band serial port or in-band via telnet is also password
protected.
The basic components of this network system include:
• Provides 12 RJ-45 (MDI-X) 100BASE-TX Fast Ethernet
(shielded) station ports for connecting devices to the network
using straight-through shielded or unshielded twisted-pair
cable (100
W Cat 5 UTP or 100WSTP)
• 1 RJ-45 (MDI) daisy-chain port for connection to a switching
hub, eliminating the need for crossover cables
• 1 slot for optional SmartExtender Modules which provide a
connection to 100BASE-TX (10BASE-T), 100BASE-T4 or
100BASE-FX via a switching port
• A multi-segment bus architecture that enhances traffic
management and network bandwidth utilization
• 2 FlexBus ports for connecting to other hubs in a Fast
EtherHub 3500 stack via FlexBus 3500 stack cable
• On-board management via the RS232 serial port connected
directly to a terminal, or to a local or remote computer (that
provides a standard RS232 port)
The specific components are the:
Fast EtherHub-12i
Intelligent Fast Ethernet Stackable Hub with 12 100BASE-TX Ports
The Fast EtherHub-12i conforms to the IEEE 802.3u repeater
specification. It also serves as an intelligent hub which collects
port statistics and records events for system administration. Basic
configuration is provided by the on-board configuration program.
1-2 Product Overview
Page 20

Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
This hub can be used in a stand-alone configuration to form a
simple Fast Ethernet LAN networking 2 to 12 computers using
the RJ-45 station ports. Further network expansion can be
achieved using the embedded tri-segment backplane, the MDI
daisy-chain port, or one of the optional SmartExtender Modules.
Moreover, when stacked with other intelligent hubs through the
FlexBus ports and connected to the Fast EtherHub-12mi SNMP
management device, it can be monitored and controlled through
in-band or out-of-band channels.
Fast EtherHub-12mi SNMP
Intelligent Fast Ethernet Stackable Hub with 12 100BASE-TX Ports;
including SNMP Managment Support
This model conforms to both the IEEE 802.3u repeater
specification and the Simple Network Management Protocol
(SNMP). It not only functions as a 12-port Fast Ethernet
repeater, but also provides an on-board SNMP-based network
management agent for monitoring and controlling various
network components. It can monitor up to 6 intelligent hubs
connected to the same stack (including itself) through the
FlexBus port connection. This Fast EtherHub provides SNMP
management for the connected stack via various Management
Information Bases (MIBs), including MIB II, repeater MIB, and
Accton’s private MIB.
SmartExtender Module -
• 100BASE-TX (EM3551-TX)
Provides two RJ-45 ports, both of which can be connected to
10BASE-T or 100BASE-TX media types. Transmission
speed is automatically set to 10 or 100 Mbps via autosensing, and half or full duplex via auto-negotiation.
• 100BASE-T4 (EM3551-T4)
Provides two RJ-45 ports for 100BASE-T4 connection.
Transmission speed is automatically set to 10 or 100 Mbps
Product Overview 1-3
Page 21

Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
via auto-sensing. Transmission mode for 100BASE-T4 is
fixed at half duplex.
• 100BASE-FX (EM3551-FX-SC or EM3551-FX-ST)
Provides two SC or ST type connectors for 100BASE-FX
connection. Transmission mode is automatically set to half
or full duplex via auto-negotiation. Transmission speed is
fixed at 100 Mbps.
Power Module Power Module (EM3550-PWR)
Slide-in power module for use in the slots on the back of hub.
When using two modules, the load is shared equally between
both, reducing the chance of failure, but still providing backup
power in case either module should fail.
In-Band Network Managment Software AccView/Open (SW6102)
This Windows-based network management software package
analyzes and displays data received from the Fast EtherHub
3500 system. This package allows the network supervisor to
access information from and set parameters for any hub in stack
by transmiting commands to the appropriate management agent.
AccView should be installed on the network management
station designated to manage the Fast EtherHub 3500 stack.
The workstation may communicate with the stack via a network
connection or from a remote site using SLIP run over TCP/IP.
If segmented architecture is used, the network management
station should be connected to the same segment as the SNMP
management agent (i.e., Fast EtherHub-12mi).
The minimal configuration for network management station
includes a 386 workstation with 10MB of available space on
the hard drive, 2 MB on-board memory, a VGA display, and
Windows version 3.1 or higher.
1-4 Product Overview
Page 22

Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
Distinguishing Factors of Fast EtherHub 3500 System
This system provides the following key features:
• Provides multi-segment architecture allowing the network to
be split into three segments
• Supports fault-tolerant configuration by allowing port link
backup and agent backup
• Supports management functions via SNMP
• Supports on-board management (using Accton’s proprietary
Fast EtherHub 3500 System Configuration Program), and full
software configurable in-band manag ement using the optional
AccView/Open (network manag ement software)
• The on-board management agents support nearly any network
environment by providing m anag ement options via SNMP/IP,
SNMP/IPX and SNMP/Ethernet
• Provides extensive security features including port intrusion
protection, as well as password protection for out-of-band
access or in-band telnet access
• Supports redundant power supply
Product Overview 1-5
Page 23

Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
Basic Features of Fast EtherHub 3500 System
In addition to all the features mentioned above, the sy stem provides:
Basic Repeater Functions
• Repeats all incoming frames to the connected segment
• Automatically partitions and reconnects devices which
experience excessive collisions
• Jabber lockup protection provided by disabling any port that
receives 64 Kbytes of continues data, and re-enabling the port
after the condition improves
Outstanding Performance
Extensive Management
Capabilities
• Total bandwidth of up to 300 Mbps
• The backplane contains 3 separate Ethernet segments, and
a high-speed management channel
• Manages up to 6 concentrators using the FlexBus stack cable
• An extensive indicator panel for reporting network activity,
and unit configuration, and for facilitating problem diagnosis
• Menu-driven configuration program can be accessed via a
local or remote terminal connection to the hub’s serial port
• The Fast EtherHub model with the SNMP agent supports
in-band network manag ement using optional network
management software such as Accton’s AccView/Open (not
included with this package) to monitor and control a stacked
system
• Provides one serial 9-pin RS232 port for out-of-band or
remote in-band network management
• BOOTP support for dynamic address assignment
• Flash ROM on board the Fast EtherHub-12m i models for
easily updating the SNMP agent
1-6 Product Overview
Page 24

Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
• Firmware update supported for the Fast EtherHub-12mi
models via out-of-band Xmodem file transfer through the
serial port, or in-band TFTP file transfer over the network
Networking Flexibility
(via SmartExtender Modules)
Easy Installation
• One slot supports optional slide-in network extender
modules for connection to 10BASE-T, 100BASE-TX,
100BASE-T4 or 100BASE-FX (on a separate segment)
• Transparent bridging (between stack and external device) via
optional network extender modules
• Uses adaptive cut-through switching (which dynamically
cha n g e s b e t w e e n fr a gme n t f re e c u t -thr o u gh and store-andforward depending on the CRC error rate)
• 100BASE-TX SmartExtender module automatically senses
transmission speed (at 100 Mbps or 10 Mbps)
• 100BASE-TX and 100BASE-FX SmartExtender modules
support two interface modes: full duplex or half duplex —
auto-negotiates transmission mode for full duplex and half
duplex (if same feature is supported by attached device);
otherwise can be manually configured
• Automatically learns MAC addresses to build the routing
information database
• Automatically filters local traffic
• Transparent to all higher level protocols
• Flexible installation for desktop or rack (standard 19” size)
• Plug-and-play
• Self-diagnostics
• Automatic polarity detection and correction permits
automatic recovery due to wiring errors
• Automatic ID assignment and auto-terminator setting for
auto-configuration
Product Overview 1-7
Page 25

Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
• Adapts to universal wide range voltage power
(i.e., 100V AC to 240V AC
10%, 50~60 3Hz)
• Provides a slot for an optional backup power supply
Complete Standards
Conformance
• Conforms to IEEE 802.3u Class I repeater specification
and 100BASE-TX standard (i.e., 100 Mbps Fast Ethernet)
• Optional SmartExtender Modules conform to relevant IEEE
specifications and standards for respective media types
• Supports MIB II, Repeater MIB, Ethernet MIB, and
Accton’s private MIB
• Conforms to Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
1-8 Product Overview
Page 26

Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
Data Switching with the SmartExtender Modules
Switching Technology
The SmartExtender Modules that plug into the expansion slot
on the front panel of the Fast Ethernet 3500 series use advanced
switching techniques to provide a high-speed network
backbone. Each extender module acts as a two-port Ethernet
switch which effectively partitions the stack from the backbone.
The module scans the destination address from the packet
header, searches the routing table provided for the incoming
port and forwards the packet only if required, often before fully
received. A learning function stores the address and corresponding segment identifier of each incoming and outgoing
packet in a routing table. This information is subsequently
used to filter packets whose destination address is on the same
segment as the source address. This confines network traffic to
its respective domain, reducing the overall load on the network.
Configuration Options for the SmartExtender Modules
Only the 100BASE-TX and
100BASE-FX media support
full-duplex operation.
The SmartExtender Modules can be connected to either a
subnetwork, or directly to a server or key workstation. In
addition to partitioning an overloaded network, they provide a
connection between legacy 10BASE-T networks and the newer
generation 100BASE-TX, and can be configured to operate in
either full-duplex or half-duplex data transfer mode to support
the interconnection requirements of other high-speed devices.
These modules perform adaptive cut-through switching,
which is capable of instantly forwarding or filtering a packet
according to the destination address scanned from the packet
header. This technique transmits packets with near-z ero latency .
Product Overview 1-9
Page 27

Switching Methods
Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
As a device functioning on the media access control (MAC)
layer, the extender modules are protocol independent, and
therefore compatible with IEEE802.3, IEEE802.3u, TCP/IP,
NetWare, DECnet and XNS protocols. They can provide a
connection between conventional 10BASE-T and high-speed
100BASE-TX networks; or can serve as a 2-port bridge in a
100BASE-TX or 100BASE-FX environment. Moreover, where
traditional 100BASE-TX networks restrict the maximum
distance between end-nodes to 205 meters, these modules break
down this barrier. By breaking your network into smaller and
more manageable segments, each linked to the larger network
with a SmartExtender Module, the maximum distance for
communications between end-nodes is unlimited (depending on
the specific timing requirements of your network applications).
Traditional bridges and routers use a switching method called
store-and-forward in which the entire frame must be received
before performing a table look-up for the destination node and
forwarding the packet to the corresponding port. As a result,
each packet experiences a hefty delay. It may be necessary to
use store-and-forward when a lot data errors are occurring over
the network, or when connecting to very slow devices.
Compared to this “conservative” mode of operation, fragmentfree cut-through switching significantly reduces packet
transmission delay by picking the destination address out of the
header as soon as the first full 64 bytes has been received. This
technique directs the frame to the appropriate segment long
before the full packet has been received. It also cleans up the
data stream by preventing runts from being passed along,
thereby improving data reliability.
Although fragment-free cut-though switching is recommended
as the fastest method for most applications, store and forward is
also supported by the SmartExtender Modules to guarantee
1-10 Product Overview
Page 28

Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
flawless performance. To ensure that you can manage any kind
of network load, the extender modules provide adaptive cut-
through switching based on Accton’s smart algorithm. This
method dynamically changes the way it handles data based on
the current error rate. This switching strategy start at fragmentfree for a clean to moderately dirty data environment, and
changes to store-and-forward for a highly contentious
environment. By using this method, the SmartExtender
Modules deliver the best networking performance under any
environment.
Moreover, in addition to using adaptive switching to optimize
throughput, these modules also support back pressure to
eliminate frame loss after their buffers fill by “blocking”
unwanted traffic from being passed onto a segment.
Product Overview 1-11
Page 29

Chapter 2: Installing the System
This chapter describes how to install the Fast EtherHub unit
and establish network connections. You may install this hub
on any level surface (e.g., a table or shelf) or in a standard
equipment rack. However, please take note of the following
minimum site requirements before you begin.
Pre-Installation Requirements
Before you start actual hardware installation, make sure you
can provide the right operating environment, including power
requirements, sufficient physical space, and proximity to other
network devices that are to be connected. Verify the following
installation requirements:
• Power requirements: 100 to 240 VAC (± 10%) at 50 to 60
Hz (± 3Hz). The hub’s power supply automatically adjusts
to accept the input voltage level.
• The hub should be located in a cool dry place, with at least
10 cm. of space at the front and back for ventilation.
• Place the switch out of direct sunlight, and away from heat
sources or areas with a high amount of electromagnetic
interference.
• If you intend to mount the hub on a rack, make sure you have
the mounting screws, brackets, bolts and nuts, and the right
tools.
• Be sure the network cables and connectors needed for
installation are available.
Installing the System 2-1
Page 30
Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
Hardware Installation
This hub is suitable for desktop or rack-mount installation. A
good location is at the center of all the devices you want to link,
close to a collapsed backbone, and near a power outlet.
These hubs can be stacked with other hubs using a mounting rack or
F
Stacking Hubs without a Rack
directly on top of one another. Refer to the sections on
Hubs without a Rack
these methods.
If you don’t want to stack the hub with other hubs now, or you plan to
use the hub in a stand-alone configuration, go to the section on
Connecting the Hub System
or
Mounting Hubs in a Rack
.
Stacking
for a description of
If you need to install a
redundant power module,
refer to
Installing a Backup
Power Supply
and complete that procedure
before stacking the hub.
on page 2-11,
The hub can be stacked anywhere there is a sufficiently large
flat space, such as on a table or desktop.
1. Stick the self-adhesive rubber foot pads (that come with this
package) on each of the 4 hollow spaces located on the
bottom of the first hub.
2. Place the first hub on a firm and flat surface in the area
where you want the stack to be installed.
3. Attach the rubber feet on each hub before stacking them.
They cushion the hub against shock/vibrations and provide
space between each hub for ventilation.
Figure 2-1 Stacking Hubs without a Rack
2-2 Installing the System
Page 31

Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
Mounting Hubs in a Rack
If you need to install a
redundant power module,
refer to
Installing a Backup
Power Supply
and complete that procedure
before stacking the hub.
on page 2-11,
Please comply with the following instructions to ensure that
your hub is securely mounted in the rack.
1. Use an standard EIA 19-inch rack.
2. Use a Phillips (i.e., cross-head) screwdriver to attach the
3. Position the hub in the rack by lining up the holes in the
brackets to the sides of the hub.
brackets with the appropriate holes on the rack, and then use
the supplied screws to mount the hub in the rack.
Figure 2-2 Mounting Hubs Using a Mounting Rack
Installing the System 2-3
Page 32

Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
configuration.
Connecting the Hub System
Remember to label all your
connections at both ends of the
cable to facilitate troubleshooting
or future changes to network
The Fast EtherHub has 12 RJ-45 shielded ports (i.e.,
100BASE-TX) that support connections to 100 Mbps Fast
Ethernet. Ports 1 - 12 (MDI-X) allow you to connect to devices
such as a workstation, server or router. While Port 12 (MDI)
lets you easily cascade to a compatible switch (i.e., connecting
from MDI to MDI-X ports on either device).
This hub also provides an expansion slot for plugging in
optional SmartExtender Modules. These modules support a
single connection to 100BASE-TX (10BASE-T), 100BASE-T4
or 100BASE-FX. They provide a convenient way to attach to
devices which use an alternate media type (e.g., linking fiber
optic cable to a remote device).
The transmission speed for ports on the optional 100BASE-TX
SmartExtender Module is automatically set at 10 or 100 Mbps to
match the operating speed of the attached device. Moreover, the
transmission mode of the ports on the optional 100BASE-TX and
100BASE-FX extender modules is automatically set at full or
half duplex to match the optimum capability of the attached
device.
Making a Connection via an MDI-X Station Port
You can connect an RJ-45 station port on the hub to any device
that uses a standard LAN interface such as a workstation or
server, or also to a network interconnection device such as a
bridge or router (depending on the port type implemented).
1. Prepare the network devices you wish to network. Make
sure you have installed suitable 100BASE-TX network
interface cards before making a connection to any of the
hub’s station ports. You also need to prepare straightthrough 100
W Category 5 shielded or unshielded twisted-pair
cables with RJ-45 plugs at both ends.
2-4 Installing the System
Page 33

I
Notes:
Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
2. Connect one end of the cable to the RJ-45 port of the network
interface card, and the other end to any available (MDI-X)
station port on the hub. Just remember that if you use Port
12MDI-X, the daisy-chain port (12MDI) cannot be used. When
inserting an RJ-45 plug, be sure the tab on the plug click s into
position to ensure that it is properly seated. Using the hub in a
stand-alone configuration, you can network up to 12 nodes.
Do not plug a phone jack connector into the RJ-45 port. This may
damage the switch. Instead, use only twisted-pair cables with RJ-45
connectors that conform with FCC standards.
1. Make sure each twisted-pair cable does not exceed 100 meters.
2. We advise using Category 5 cable for all network connections to
avoid any confusion or inconvenience in the future when you
upgrade attached devices to Fast Ethernet.
3. You may also connect a device to the switching port located on
hub’s front panel if required. However, be sure you use a
SmartExtender Module that meets your communication requirements.
Refer to
4. To facilitate troubleshooting, label all network cables to indicate the
attached device and location.
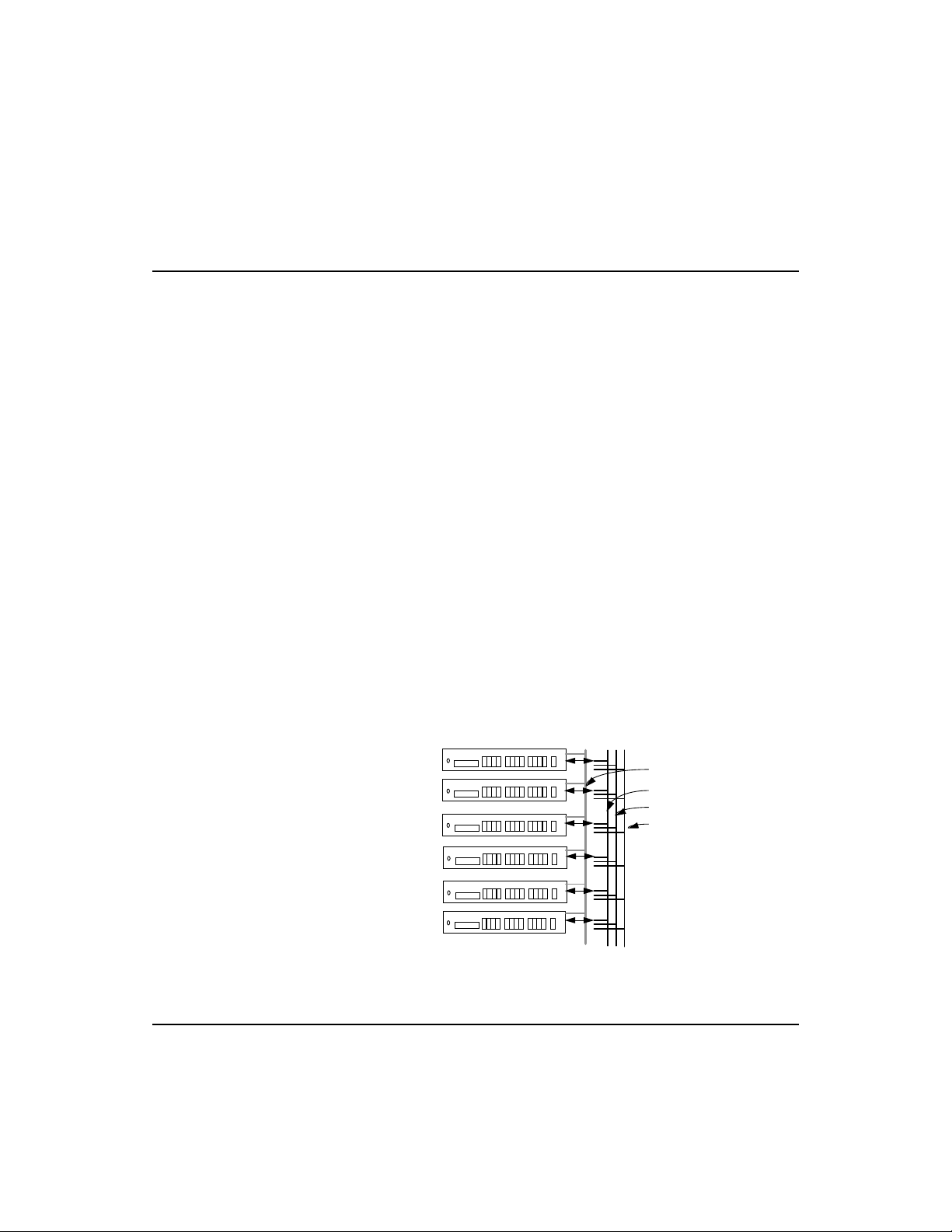
Connecting to the Stack’s Backplane
SmartExtender Module
in Chapter 1 for more details.
Plug one end of the FlexBus 3500 stack cable (provided with
the base package) in the
end to the
In port of the next hub. Repeat this step for each hub
in the stack. Form a simple chain starting at the
first hub and ending at the
FlexBus Ports in Chapter 5 for related information.
Out port of the top hub and the other
Out port on the
In port on the last hub. Refer to
F
Hubs in a stack can only be grouped into segments through the
FlexBus 3500 stack cable. You should therefore use the FlexBus ports to
make Out to In connections in a stack.
Hubs in a stack can only be managed by the network management
agent through the stack cable. In a managed stack, you should therefore
use the stack ports to make Out to In connections, and include a
management agent (i.e., a Fast EtherHub-12mi) in the chain.
You can also cascade hubs using the daisy-chain port (Port 12MDI).
However, hubs cascaded using the daisy-chain port cannot be managed by
the management agent. See the next section for details.
Installing the System 2-5
Page 34

The Fast EtherHub 3500 hubs
are Class I repeaters. Class I
repeaters cannot be cascaded
to another repeater in the same
collision domain.
The daisy-chain port can only
be cascaded to another device
which breaks up the collision
domain (e.g., an Ethernet
switch).
Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
Making a Connection via the MDI Daisy-Chain Port
Stackable Fast Ethernet hubs are generally restricted to Class I
repeater types due to the timing requirements for passing traffic
and management data across the stack’s backplane. Although
Class I repeaters cannot be cascaded to another device in the
same collision domain via the daisy-chain port, more powerful
interconnection options are provided via the hub’s backplane
and optional SmartExtender Modules.
The daisy-chain port can only be cascaded to another device
which breaks up the collision domain (e.g., an Ethernet switch).
Notes:
Prepare straight-through 100
W Category 5 shielded or
unshielded twisted-pair cables with RJ-45 plugs at both ends.
Connect one end of the cable to the
12MDI port on this hub,
and the other end to a standard MDI-X station port on the other
device. Remember that when using the daisy-chain port
12MDI), station port (12MDI-X) cannot be used. When inserting
(
an RJ-45 plug, be sure the tab on the plug clicks into position
to ensure that it is properly seated.
1. Make sure the twisted-pair cable does not exceed 100 meters.
2. To connect to a switch, you may also run straight-through twistedpair cabling from a station port on this hub to a crossover port on
the switch. However, if you must connect to a switch via station
ports at both ends of the cable, use crossover cabling.
Connecting to a SmartExtender Module
The Fast Ethernet 3500 Series includes a network expansion
slot on the front panel that supports connection to 100BASE-TX
(10BASE-T), 100BASE-T4 or 100BASE-FX. Each
SmartExtender Module acts as a two-port switch that can
forward and filter data frames at line speed. One port is
connected to the hub’s internal repeater bus, while the other
port (on the hub’s front panel) can be used to connect the hub to
any compatible network device. The optional extender modules
include:
2-6 Installing the System
Page 35

I
Retain the face plate for
possible future use.
I The SmartExtender
Modules and not hot-swappable.
Be sure the hub is powered off
when installing these modules
Avoid running your cables near
equipment that may generate
electromagnetic interference.
Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
10BASE-T - EM3551-TX SmartExtender Module
100BASE-TX - EM3551-TX SmartExtender Module
100BASE-T4 - EM3551-T4 SmartExtender Module
100BASE-FX - EM3551-FX-ST SmartExtender Module
EM3551-FX-SC SmartExtender Module
Note: The EM3551-TX automatically adjust s to 10 or 100 Mbps using
auto-sensing. Refer to
The SmartExtender Modules are not hot-swappable. Be sure you
power off the hub before installing any of these modules.
Installing a SmartExtender Module - If you need to install an
SmartExtender Module
in Chapter 1.
extender module, take the following steps:
1. Disconnect power to the hub.
2. Remove the face plate on the expansion slot (or a previously
installed SmartExtender Module) by removing the two
screws with a Phillips (i.e., cross-head) screwdriver.
3. Before opening the package that contains the extender
module, touch the bag to the hub casing to discharge any
potential static electricity.
4. Remove the module from the anti-static shielded bag.
5. Holding the module level, gently push it all the way into the
expansion slot, ensuring that it firmly engages with the
connector.
6. If you are sure the module is properly mated with the
connector, replace the retainer screws to secure the module
in the expansion slot.
7. Run corresponding media type between the extender module
and the target device.
Connecting Twisted-pair Cabling - For the 100BASE-TX and
100BASE-T4 modules, prepare Category 5 straight-through
twisted-pair cables with RJ-45 plugs at both ends. When
connecting the module directly to an end-node device (e.g., a
workstation or file server), a bridge or router, run cable from the
MDI-X port on the SmartExtender Module to the target device.
However, when connecting the module to a hub or switch,
Installing the System 2-7
Page 36
Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
cable length (kilometers)
c dB/km
loss per kilometer of cable
connect one end of the cable to the MDI port on the extender
module, and the other end to the MDI-X port on the target
device (or vice versa). When inserting an RJ-45 plug, be sure
the tab on the plug clicks into position to ensure that it is
properly seated. Note that as a general rule, the length of any
twisted-pair cable should not exceed 100 meters.
Connecting Fiber Optic Cabling - For the 100BASE-FX module,
prepare fiber optic cable with SC or ST connectors at both
ends. When connecting the module directly to an end-node
device (e.g., workstation or file server), run cable from the Rx
(Tx) port on the module to the Tx (Rx) port on the target
device. Also, when daisy-chaining SmartExtender Modules,
make similar connections between the current module and the
next device in the stack. When inserting a cable, be sure the tab
on the plug clicks into position, to ensure that it is properly
seated. Note that as a general rule, the length of fiber optic
cable should not exceed 2 kilometers. However, power
budgeting must be considered when calculating the maximum
cable length for your specific environmen t (as describ ed later in
this chapter).
Distance Limit and Power Loss in Fiber Optics - When using fiber
optic cabling, the maximum leng th between two hubs can be up
to 2 kilometers. However, you m ust consider power loss when
calculating the actual length of cable that can be used with your
system. You can calculate power loss with the following formula:
(p dB - i dB)
m =
c dB/km
Table 2.1 Calculating the Power Budget for Fiber Optics
2-8 Installing the System
Variable Description
m
p dB power budget
i dB intervening devices
(e.g., patch cables and splices)
Page 37

Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
Gauge of Fiber Cable
Power Budget
Note: To determine the power loss incurred by intervening dev ices and
specific cable type, inquire with the manufacturer. The power budget
depends on the gauge of cable as shown below.
50/125 mm
62.5/125 mm
Table 2.2 Power Budget for Common Guage Fiber Optics
9.2 dB
13 dB
For a sample calculation, assume the following v alues:
• cable gauge - 62.5/125 mm, which means a 13 dB power budget,
• 2 patch panels along the path, each with 1.5 dB power loss,
• 1 splice with 1 dB power loss, and
• inherent power loss in the cable is 4 dB/km
The maximum cable leng th is therefore:
13 dB - 4 dB
m =
4 dB/km
When the 100BASE-FX link is set for the full-duplex
I
= 2.25 km
communications (i.e., a dedicated connection), cable length
should not exceed 2 kilometers. However, when the link is set
for half-duplex communications (i.e., a shared collision domain),
cable length should not exceed 412 meters (IEEE 802.3u).
Note: Even though your calculations for power loss may indicate a longer
permissible length based on signal strength (as seen in the preceeding
example), we advise remaining w ithin the recommended limits.
Maximum Segment Length
- In contrast to cascading devices
through repeater ports, cascading through the SmartExtender
Module breaks up the collision domain. The number of devices
that can be cascaded is therefore theoretically unlimited.
However, in practice, the length of a cascade (even one passing
through switching ports, as implemented in the extender
modules) may be limited by the time-out requirements of the
particular applications running over the network. Considering
these delay factors, the IEEE 802.1D standard (i.e., RFC for
MAC bridges) recommends restricting the number of
interconnection devices between any two nodes to seven.
Installing the System 2-9
Page 38

Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
Setting the Communication Mode - The 100BASE-TX and
100BASE-FX SmartExtender Modules both support half and
full-duplex communications. The hub uses auto-negotiation to
determine the transmission mode for any new connection made
to these modules. However, if a connected device does not also
support auto-negotiation, and a link cannot be established using
half duplex (i.e., the last state tested by auto-negotiation), then
you must manually set the transmission mode for the concerned
port to full or half duplex via on-board configuration (Chapter
4) or using optional network management software.
Bridging Functions - The SmartExtender Modules form a
separate segment (i.e., collision domain) from the rest of the
ports in the stack. They therefore provide fully transparent
bridging functions which automatically learns node addresses
required to filter and forward traffic based on the destination
address (i.e., traffic is filtered if the destination address is in the
local collision domain, or forwarded if the destination is in
another segment).
Note: Devices connected to the SmartExtender M odule exist in a
separate segment, and cannot be controlled by a management agent in
the stack.
Switching Functions -
commonly found on an Ethernet switch. The scheme used to
process data packets is automatically adjusted to optimize
system performance. Fragment-free cut-through or store-andforward processing may be used depending on the current error
rate. (Refer to
Data Switching with the SmartExtender Modules in
Chapter 1 for a detailed discussion of these processing
methods.)
In addition to the features listed above, the extender modules
also use back pressure to eliminate frame loss when its buffers
fill, by “slowing” the traffic received from end stations or
segments connected directly to this port.
2-10 Installing the System
These modules also provide functions
Page 39

SEM
SEM
This stack has been fully
RJ-45RJ-45
RJ-45
SEG3
SEG1
SEG2
interconnected using two
extender modules.
Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
Interconnecting Stack Segments - Hubs can be completely
isolated from the stack, or can be attached to any of the three
available segments embedded in the backplane. When attached
to a segment (i.e., common collision domian), the hub can
communicate with all other devices attached to that segment.
(Refer to the discussion on
and to
Configuring Hub Parameters in Chapter 4.)
Mult-Segment Architecture in Chapter 3,
A Fast EtherHub stack can be split into three separate (isolated)
segments. The best way to interconnect these different segments
is to con n e ct a (1 0 0 BASE-TX) SmartExtender Module to a
repeater port on a hub in a different segment, using an MDI to
MDI-X connection. Two extender modules can be used in this
way to connect all three segments
You can also make a direct connection between extender
modules (i.e., similar media types) that exist in two different
segments in the stack. However, this approach is not only more
costly, but also entails a slightly higher transit delay for trafffic
passing between the segments.
The last alternative is to connect different segments via a Fast
Ethernet switch or router. Because this is the most expensive
approach, we do not advise it unless you already have a suitable
interconnection device available.
Installing a Backup Power Supply
If you need to install a backup power module, take these steps:
1. Remove the face plate on the optional power bay (or a
previously installed power module) by turning the two
retaining knobs on the rear panel counterclockwise.
2. Holding the module level, gently push it all the way into the
empty bay, ensuring that it firmly engages with the connector.
3. After you are sure the module is properly seated in the bay,
tighten the retaining knobs to secure it in place.
4. Connect power to the backup power supply. Use separate
AC circuits to provide optimal backup capability.
Note: Leave at least 12 inches clearance in the back of the hub (or
stack) to facilitate system maintenance (e.g., removing power modules).
Installing the System 2-11
Page 40

Powering on the Hub
I
Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
1. Plug one end of the power cord into a power outlet, and the
other end into the power socket at the rear of the hub (in that
order for reasons of safety). Then plug in the backup power
module if you purchased this option. For reliable backup,
connect the backup power module to a separate AC circuit.
2. Check the LED indicator marked PWR1 (or PWR2) on the
front panel to see if it is on. The unit will automatically
select the setting that matches the connected input voltage.
Therefor e, n o a d d i ti o n a l a d ju s tments are necessary when
connecting it to any input voltage within the range marked
on the rear panel.
3. The hub performs a self-diagnostic test upon power-on.
(Note that this test takes about 15 seconds to complete.) For
details about the system self-diagnostic test, refer to the
following section.
The unit supports a "hot remove" feature which permits you to
connect/disconnect network cables without powering off the hub and
without disrupting the operation of the hubs in stack. However, when
changing SmartExtender Modules or power supply modules, first
disconnect power to the concerned hub.
Diagnostic Tests
Upon power on, the system performs an internal self-diagnostic
test of major hub components. If any component fails during
the test, the hub will try to complete the diagnostic procedure.
Otherwise, the system will hang. For related information, refer
to
Diagnostics Test Indicators in Chapter 5.
2-12 Installing the System
Page 41

Hot Remove
Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
The following table shows the components to be tested.
Test Function/Component
Fast EtherHub-12i Fast EtherHub-12mi
Boot ROM All tests listed for Fast EtherHub-12i
Hub Configuration EEPROM
RAM for Repeater Board CPU Console I/O
Repeater Information Base SRAM Flash ROM for SNMP Firmware
Repeater Interface Controller EEPROM for Stack Configuration
Routing Table for Internal SEM Port DRAM Buffer for Management Program
Input Queue for Internal SEM Port Management Bus Output Buffer
Output Queue for Internal SEM Port Management Bus Input Buffer
Routing Table for External SEM Port Network Interface Controller
Input Queue for External SEM Port
Output Queue for External SEM Port
Table 2.3 Diagnostic Test Functions
and then the following tests:
The Fast EtherHub 3500 System supports “hot remove”
capability that allows you to connect/disconnect hubs or media
connectors from the system with minimal disruption to the
network. You can remove any network cabling without
affecting traffic passing across the internal repeater bus.
However, if the FlexBus 3500 stack cable is disconnected at
any point in the stack, or is not properly terminated, all Ethernet
and management traffic passing across the stack’s backplane
will be disrupted.
When changing modules in the expansion slot or changing power
I
supply modules, first disconnect power to the concerned hub.
Installing the System 2-13
Page 42

Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
Configuring a Manageable Stack
To manage the stack with the on-board configuration program
or any optional network management software, the stack must
include an EtherHub-12mi (i.e., a unit with an SNMP agent).
Moreover, the network management station must be able to
access the segment containing the management agent.
You should also consider adding a backup SNMP agent to
provide greater management reliability for critical applications.
The procedures required to install a backup agent is described
below.
Installing an SNMP Backup Agent
The on-board configuration
program only provides access
to the private MIB. To gain full
SNMP functionality, you must
use optional network
management software (e.g.,
AccView/Open).
Just add the backup agent(s) to the stack and let the system
automatically choose the Master agent and the Slave agent
based on longest up-time. The
chosen as the primary agent will turn ON . The
will turn ON for all other hubs (attached to the same segment)
that contain SNMP agents.
Note: If you attach SNMP agents to separate segments, be sure they
are assigned unique IP addresses via on-board configuration (as
described under
Master indicator on the device
Backup indicator
Changing the Segment Configuration
in Chapter 4).
2-14 Installing the System
Page 43

Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
LED
State
Indication
LinkOnPort has established a valid network connection.
Traffic
Blinking
Traffic is traversing the port.
Tx/Rx1Blinking
Traffic is traversing the port.
1001On
Communications have been set to a speed of 100 Mbps.
FDX1On
Communications have been set to full-duplex mode.
Verifying Port Status
Check each connection by viewing the port status indicators
listed below. (For a more detailed description on these
indicators, refer to Chapter 5.)
1 - The indicators appear on the front of the SmartExtender Module.
Table 2.4 Checking Key LED Indicators
If the Link status indicator is not functioning properly, or you
experience any other difficulties in setting up the switch, refer
to Appendix A.
Verifying System Operation
Verify that all attached devices have a valid connection. The
hub monitors link status for each port. If any device is properly
connected to the hub and transmitting a link beat signal, the
Link indicator lights for the corresponding port. If the Link
indicator fails to light when you connect a device to the hub,
check the following items -
• Be sure the media cable is properly attached to the connected
device and the hub. Verify that the cable connector snaps
into place when attached.
• See if the media cable is functioning properly by using it for
another port and attached device that displays valid
indications when connected to the network.
Installing the System 2-15
Page 44

Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
• Verify that you have not exceeded the specified limits for any
attached media type as summarized in the following table:
Media Type Maximum Length (meters)
Twisted Pair 100
Fiber Opitc 412 (at half duplex)
2000 (at full duplex)
Table 2.5 Maximum Cable Length
• If a computer is attached to the hub, verify that its adapter
card is functioning properly by trying it in another computer
that has been successfully connected to the network.
• When using the 100BASE-TX or 100BASE-FX
SmartExtender Module, both sides of each connection must
use the same transmission mode (i.e., full or half duplex). If
the device connected to the hub operates at full duplex but
does not support auto-negotiation, then you m ust manually set
the transmission mode with the configure button. (Refer to
section on
Communication Mode earlier in this chapter.)
If you still can’t resolve the problem, please refer to
Troubleshooting in Appendix A.
2-16 Installing the System
Page 45

Chapter 3: Setting up Network Connections
Special Architecture Used for the Fast EtherHub 3500 Stack
Multi-Segment Architecture
The Fast EtherHub 3500 system supports multi-segment
configuration through the FlexBus cabling. Three Ethernet
segments (i.e., separate collision domains) are embedded in the
hub’s FlexBus port (i.e., the stack’s backplane). You can
choose to attach a hub to one of these segments, or to leave it
isolated except for the management channel. Nodes attached to
a specific segment (e.g., Segment 1) can only communicate
with nodes attached to the same segment (unless the segments
are interconnected with a device such as an Ethernet switch).
This type of architecture makes the system more flexible,
provides better traffic load sharing and data protection,
improves network bandwidth utilization, and simplifies
troubleshooting.
Carefully plan your network setup to make this architecture
work well for your system. Form a common domain for
devices that need to frequently communicate with each other
by attaching them to the same segment. In this way you can
arrange network resources to balance traffic and thereby
increase overall network efficiency.
To combine the segments into an interconnected network (while
at the same time retaining the higher effective bandwidth and
segment integrity provided by the multi-segment architecture),
attach each segment to a switch or similar interconnection device,
such as one of Accton’s Fast Ethernet Switches.
Setting Up Network Connections 3-1
Page 46

Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
FlexBus 3500 Management Link
The management link in a chain of cascaded hubs must be
connected to manage the stack as a single unit. This means that
only hubs connected using the FlexBus can be controlled by an
SNMP management agent (i.e., Fast EtherHub-12mi). At most, 6
hubs can be managed and linked together using the FlexBus
connection.
Hub ID Setting
In a stacked system, each hub should have a unique ID number
to identify itself. Each hub automatically sets an ID number if
attached to an SNMP management agent through the FlexBus port
(i.e., Fast EtherHub-12mi). When a new hub is inserted in the
stack, the next available hub identifier is assigned to the new hub
(i.e., the identifier numbers are not changed for previously
configured hubs). When the stack includes a management agent,
you can also set hub IDs using the on-board configuration
program. Refer to
information.
Configuring Hub Parameters in Chapter 4 for more
Using Management Agents
The Fast EtherHub-12mi SNMP includes an SNMP management
agent. To add SNMP functionality to the entire stack, this hub
type must be included in the stack. To provide in-band access to
the agent you must also attach your network management station
to a the segment that includes the management agent.
3-2 Setting Up Network Connections
Page 47

The on-board configuration
program only provides access
to the private MIB. To gain full
SNMP functionality, you must
use optional network
management software (e.g.,
AccView/Open).
Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
Multiple Agents
You may include multiple agents in a stack. To provide a failsafe backup management agent, include it in the same segment
with the Master agent. You may also use several active agents
in the same stack. However, they must be attached to different
segments and have unique IP addresses.
SNMP Backup Agent
The Fast EtherHub 3500 system supports a backup function for
the management agent. This special function allows the stack to
have two or more SNMP network management agents attached
to the same segment, wherein one agent is configured as the
Master agent and the other(s) as a Slave (i.e., Backup) agent.
The agent in slave mode behaves as a Fast EtherHub-12i. But if
the Master agent fails, the Slave agent takes over its functions
using the latest data mirrored from the Master, including its IP
address. Note that to manage the stack out-of-band after the
Slave has assumed control, you must plug your PC or modem
into the Serial port of the Slave agent. If you are using optional
network management software, just ensure that your network
management station can access the new control agent via its
current network connection.
Note: Placing redundant agents in a segment will cause the system to
set the agent with longest up-time as the Master, and the other(s) as a
slave. If more than one slave exists in a segment, the slave higher up in
the FlexBus chain will be chosen to function as the Master if it fails.
Setting Up Network Connections 3-3
Page 48

Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
Port Backup Function
The Fast EtherHub 3500 system supports a port backup
function (i.e., a redundant link). A hub system can have up to
18 pairs of redundant links. These links are configurable using
the in-band or out-of-band management program. When a
primary link fails, the secondary (i.e., backup) link
automatically takes over.
Notes:
1. To prevent traffic from looping, the primary port is enabled and the
backup port disabled. If the system is functioning normally, the Link
indicator for the primary port and the Partition indicator for the
backup port will be on.
2. It is common practice to attach these links to the same physical
device (e.g., two separate adapter cards on a critical server).
However, to provide more flexibility, this is not enforced by the
configuration program.
Security Features
Intrusion Protection
Any repeater port on the hub can be configured with a preferred
source address. If an unauthorized intruder is detected, the
network management station can be notified, or a trap can be
sent and the port disabled.
3-4 Setting Up Network Connections
Page 49
Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
SEG. LINK 1
SEG. LINK 2
SEG. LINK 3
Sample Network Configurations
The Fast EtherHub 3500 series stackable hubs are designed to
provide flexibility in configuring network connections. This
hub can be used as a simple stand-alone hub or connected to
other network interconnection devices in various configurations.
This section includes sample applications, most of which take
advantage of the multi-segment architecture. Pay attention to
the examples that illustrate how to segment a hub stack. This
procedure can extend network bandwidth up to 300 Mbps.
Attaching the Stack to One Segment
You can attach all the hubs in a stacked system to the same
segment. In this example, a stacked system using the FlexBus
port connection is connected to segment 1.
Putting all hubs in the same segment groups all nodes attached
to the stack in a single collision domain. All Ethernet frames
transmitted by any node are seen by every other node in the
stack. For a heavily loaded network, you can significantly
improve performance by configuring the stack into separate
segments as shown in the next example.
SEGMENT 1
SEGMENT 1
SEGMENT 1
SEGMENT 1
SEGMENT 1
SEGMENT 1
ID1
ID2
ID3
ID4
ID5
ID6
EtherHub3500
EtherHub3500 HUB
EtherHub3500 HUB
EtherHub3500 HUB
EtherHub3500 HUB
EtherHub3500 HUB
MANAGEMENT
CHANNEL
FlexBus 3500 Cable
Figure 3-1 Attaching All Hubs in Stack to One Segment
Setting Up Network Connections 3-5
Page 50

Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
Attaching the Stack to Multiple Segments
This example shows 3 independent Ethernet LANs in a stacked
system. Hubs 1 and 2 are attached to segment 1, while hubs 3
and 4 are attached to segment 2, and hubs 5 and 6 are attached
to segment 3.
This configuration serves to both balance the network load and
improve performance. Using three separate segments provides
300 Mbps of Ethernet bandwidth to the overall stack. Moreover,
using a segmented configuration serves to confine the effects of
heavy loading or network problems to a single segment.
EtherHub3500 AGENT
SEGMENT 1
SEGMENT 1
SEGMENT 2
SEGMENT 2
SEGMENT 3
SEGMENT 3
ID 1
ID 2
ID 3
ID 4
ID 5
ID 6
EtherHub3500 HUB
EtherHub3500 HUB
EtherHub3500 HUB
EtherHub3500 HUB
EtherHub3500 HUB
MANAGEMENT
CHANNEL
SEG. LINK 1
SEG. LINK 2
SEG. LINK 3
FlexBus 3500 Cable
Figure 3-2 Attaching Hubs in Stack to Three Segments
Traffic in each segment is restricted to that segment and cannot pass
F
to another segment without a device such as a SmartExtender Module
or one of Accton’s Fast Ethernet Switches to link them.
3-6 Setting Up Network Connections
Page 51
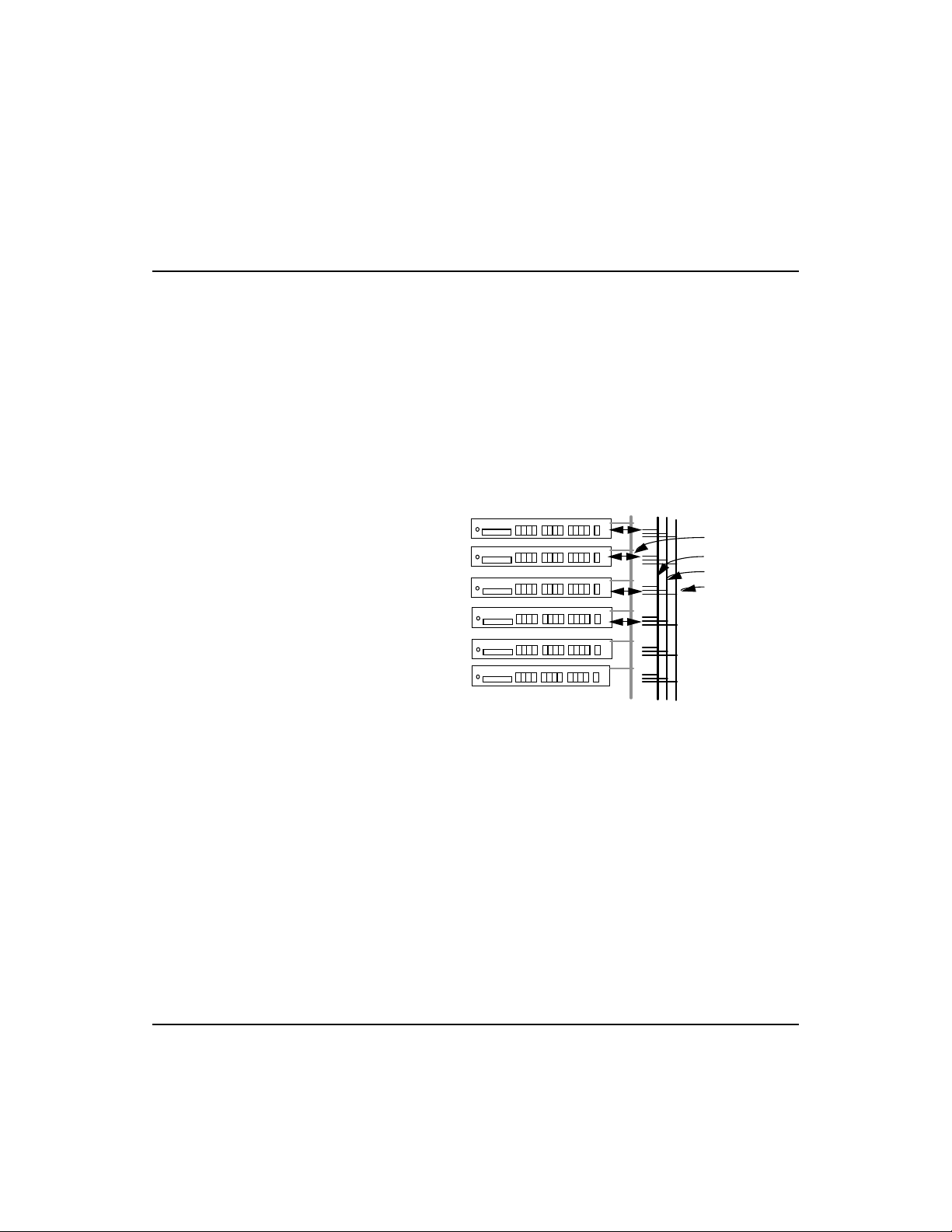
Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
EtherHub3500 AGENT
FlexBus 3500 Cable
Isolating Specific Hub Connections
You can interconnect or isolate the hubs in a stack using a
multi-segment configuration. In a stacked system, some hubs
may be connected to a segment while others are isolated (not
attached to any segment). In this example, hubs 1 and 2 are
attached to segment 1, while hubs 3 and 4 are attached to
segment 2. However, hubs 5 and 6 are not connected to any
segment. These hubs form isolated segments. With careful
planning, you can restrict access for specific user groups to
required connections only.
F
SEGMENT 1
SEGMENT 1
SEGMENT 2
SEGMENT 2
ISOLATED
ISOLATED
ID 1
ID 2
ID 3
ID 4
ID 5
ID 6
EtherHub3500 HUB
EtherHub3500 HUB
EtherHub3500 HUB
EtherHub3500 HUB
EtherHub3500 HUB
MANAGEMENT
CHANNEL
SEG. LINK 1
SEG. LINK 2
SEG. LINK 3
Figure 3-3 Linking Part of the Stacked Hubs to a Segment
When hubs are isolated, they cannot communicate with any other
device in the stack via the FlexBus.
Setting Up Network Connections 3-7
Page 52

FlexBus 3500 Cable
F
Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
Isolating Each Hub
In this example, each hub in the stack is an independent
segment (i.e., isolated collision domain). Hubs 2 to 6 are not
connected to any of the 3 segments embedded in the FlexBus
3500 cable.
ID 1
ID 2
ID 3
ID 4
ID 5
ID 6
Figure 3-4 Stacked Hubs Not Linked to a Segment
If the Fast EtherHub-12mi is isolated from the backplane (i.e., not
attached to any of the 3 segments), the stack can still be managed
with the out-of-band configuration program via the management
channel embedded in the FlexBus 3500 cable.
EtherHub3500 AGENT
EtherHub3500 HUB
EtherHub3500 HUB
EtherHub3500 HUB
EtherHub3500 HUB
EtherHub3500 HUB
MANAGEMENT
CHANNEL
SEG. LINK 1
SEG. LINK 2
SEG. LINK 3
3-8 Setting Up Network Connections
Page 53

Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
Extending the Network with Alternate Connections
You can extend your network by connecting any of the hubs in
a stacked system to other compatible hubs via the
SmartExtender Module. In the diagram below, a stand-alone
hub is connected to hub 3 in the stacked system using the
extender module. However, remember that the Fast EtherHub
3500 Agent can only manage hubs connected to it through the
FlexBus connection.
EtherHub3500 AGENT
SEGMENT 1
SEGMENT 1
SEGMENT 2
SEGMENT 2
SEGMENT 3
SEGMENT 3
ID 1
ID 2
ID 3
ID 4
ID 5
ID 6
EtherHub3500 HUB
EtherHub3500 HUB
EtherHub3500 HUB
EtherHub3500 HUB
EtherHub3500 HUB
MANAGEMENT
CHANNEL
SEG. LINK 1
SEG. LINK 2
SEG. LINK 3
EtherHub3500
FlexBus 3500 Cable
Figure 3-5 Linking Stacked Hubs to Unmanaged Hubs
via the SmartExtender Module
Setting Up Network Connections 3-9
Page 54

Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
Linking the Stack to a Management Station
In a stacked system, connect the in-band management workstation
to the same segment that the management agent is attached to. In
this example, the management agent is attached to segment 1.
Thus, the in-band management workstation (e.g., a PC running
AccView/Open) should also be connected to segment 1.
SEGMENT 1
SEGMENT 1
SEGMENT 2
SEGMENT 2
SEGMENT 3
ACCVIEW
AccView Station
(Segment 1)
SEGMENT 3
Figure 3-6 Linking Stacked Hubs to a Network Management Station
EtherHub 3500 AGENT
EtherHub3500 HUB
EtherHub3500 HUB
EtherHub3500 HUB
EtherHub3500 HUB
EtherHub3500 HUB
FlexBus 3500 Cable
MANAGEMENT
CHANNEL
SEG. LINK 1
SEG. LINK 2
SEG. LINK 3
3-10 Setting Up Network Connections
Page 55

Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
Interconnecting the Segments
The 3 segments within a stacked system can be combined into an
interconnected network using the SmartExtender Modules. For
example, you can connect all the segments in the stack using just
two extender modules as shown below. Using this approach, you
provide a higher bandwidth by using three separate collision
domains, but still permit stations to communicate with nodes in
other segments, as required.
SEGMENT 1
SEGMENT 1
Inter-Segment Link
SEGMENT 2
SEGMENT 2
Inter-Segment Link
SEGMENT 3
SEGMENT 3
Figure 3-7 Linking Segments in a Stacked System
ETHERHUB3500 AGENT
ETHERHUB3500 HUB
ETHERHUB3500 HUB
ETHERHUB3500 HUB
ETHERHUB3500 HUB
ETHERHUB3500 HUB
ACCVIEW
AccView Station
FlexBus 3500 Cable
Setting Up Network Connections 3-11
Page 56

Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
Connecting Remote Stacks
Fast EtherHub stacks can be connected by using the
SmartExtender Modules. For example, you can connect two
stacks by running a cable from the extender module in one stack
to any station port in a remote stack. When using twisted-pair
cable, the maximum cable length is 100 meters. Also note that
when you connect directly to a repeater bus in this manner, the
transmission mode is limited to half duplex.
You can connect stacks over an even greater distance if you run
fiber optic cable between SmartExtender Modules in both stacks.
When you connect to switching ports at both ends of the cable, the
transmission mode is automatically set to full duplex, allowing
you can run a fiber optic link up to 2 kilometers. However, if you
must operate at half duplex, then the maximum separation
between stacks is 412 meters .
STACK 1
ETHERHUB3500 HUB
STACK 1
Remote Stack Link
STACK 2
STACK 2
Remote Stack Link
STACK 3
STACK 3
ETHERHUB3500 HUB
(Up to 100 meters with twisted-pair cable)
ETHERHUB3500 HUB
ETHERHUB3500 HUB
(Up to 2 kilometers with fiber optic cable)
ETHERHUB3500 HUB
ETHERHUB3500 HUB
Figure 3-8 Connecting Remote Stacks
3-12 Setting Up Network Connections
FlexBus 3500 Cable
Page 57
Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
Operating in the Novell NetWare IPX Environment
If you’re using Novell NetWare server as your Network
Operating System, you can have up to 3 LAN adapters installed
in the File Server. With this type of setup, the network is
perceived as logically divided into different collision domains,
but the File Server is still accessible by all nodes. As shown in
the following figure, three LAN adapters installed in a NetWare
server are each connected to a hub in the stack with IPX
Protocol bound to each adapter.
The first adapter is attached to segment 1 with IPX network
number 102; the second adapter is attached to segment 2 with
IPX network number 103; and the third one is connected to
segment 3 with IPX network number 104.
SEGMENT 1
SEGMENT 1
EtherHub 3500 Agent
EtherHub 3500 Hub
IPX net number=102
SEGMENT 1
SEGMENT 2
SEGMENT 2
SEGMENT 3
SEGMENT 3
EtherHub 3500 Hub
EtherHub 3500 Hub
EtherHub 1500 Hub
EtherHub 1500 Hub
IPX net number=103
SEGMENT 2
IPX net number=104
SEGMENT 3
NOVELL NetWare Server
Figure 3-9 System Applied in Novell NetWare IPX Environment
Setting Up Network Connections 3-13
Page 58
Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
Operating in the TCP/IP Environment
In TCP/IP Internet environment, gateways are used to improve
performance and regulate network traffic by confining most
network activity to their respective local network, and still
maintain communication links among LANs of the same or
different architectures. You can implement an IP subnet
gateway if you have an IP network address (e.g., 140.20.0.0).
For example, in a Fast EtherHub 3500 system (as shown in the
figure below), you can attach three LAN adapters to your
subnet gateway using a UNIX server. Perform the following
steps.
Assign IP addresses from 140.20.1.1 ~ 140.20.1.254 to nodes on
segment 1, and set their subnet mask to 255.255.255.0.
Assign IP addresses from 140.20.2.1 ~ 140.20.2.254 to nodes on
segment 3, and set their subnet mask to 255.255.255.0.
Assign IP addresses from 140.20.3.1 ~ 140.20.3.254 to nodes on
segment 2, and set their subnet mask to 255.255.255.0.
Assign IP address 140.20.1.10 to the first adapter, 140.20.2.20 to the
second adapter, and 140.20.3.30 to the third one.
SEGMENT 1
SEGMENT 1
SEGMENT 2
SEGMENT 2
SEGMENT 3
SEGMENT 3
EtherHub 3500 Agent
EtherHub 3500 Hub
EtherHub 3500 Hub
EtherHub 3500 Hub
EtherHub 3 500 Hub
EtherHub 3500 Hub
SubnetMask = 255.255.255.0 for all segments
SEGMENT 1
SEGMENT 2
IP = 140.20.2.20
IP =140.20.3.30
SEGMENT 3
IP = 140.20.1.10
NOVELL NetWare Server,
Unix Server(e.g., SCO Unix)
Figure 3-10 System Applied in TCP/IP Environment
3-14 Setting Up Network Connections
Page 59

Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
Connecting to the Network Backbone
The stack can be connected to the network backbone by attaching
it to a device such as a Fast Ethernet switch. The following figure
shows a direct connection from the stack’s daisy-chain port to a
100BASE-TX switch which is serving as collapsed network
backbone.
SEGMENT 1
SEGMENT 1
SEGMENT 2
SEGMENT 2
ETHERHUB3500 AGENT
ETHERHUB3500 HUB
ETHERHUB3500 HUB
ETHERHUB3500 HUB
ACCVIEW
AccView Station
SEGMENT 3
SEGMENT 3
Collapsed Backbone
ETHERHUB3500 HUB
ETHERHUB3500 HUB
Fast Ethernet Switch
FlexBus 3500 Cable
Links to Network
Figure 3-11 Connecting to the Network Backbone
Setting Up Network Connections 3-15
Page 60

Chapter 4: Configuring the System
Making the Connections Required for System Configuration
The Fast EtherHub 3500 series provides a menu-driven
configuration program. This program can be accessed by
making a connection to the serial port on the front of the hub
(using a terminal or a computer running a terminal emulation
program). Moreover, when configuring the Fast EtherHub- 12mi,
you can Telnet into the hub from any computer attached to the
network, or call into the hub from a remote computer using a
modem connection.
The Fast EtherHub-12mi also provides an on-board
management program based on Simple Network Management
Protocol (SNMP). This agent allows you to manage the hub
(and connected stack) from any PC attached to the network
with optional in-band network management software (e.g.,
AccView/Open). This kind of software provides advanced
management functions using a straight-forward graphical
interface. You can even use this kind of software to control
these hubs over a remote modem connection by running SLIP
protocol over TCP/IP.
This chapter describes how to perform basic configuration, and
manage the overall stack, via:
• Direct connection - making a local connection via the hub’s
serial port to the on-board menu-driven configuration program.
• Network connection - Telneting over the network to the on-
board menu-driven configuration program; or making a
network connection to the SNMP agent using optional
network management software (e.g., AccView/Open).
Configuring the System 4-1
Page 61

Direct Connection
Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
• Remote connection - making a modem connection via the
hub’s serial port to the on-board menu-driven configuration
program; or using SLIP over TCP/IP from a remote site to
access the hub with optional network management software.
The F ast Ethe r Hub-12i does not
include a management agent.
Configuration options for this
model are therefore limited to
direct connection only.
Moreover, configuration via the
management port on this model
is limited to this hub only (i.e.,
the attached stack cannot be
managed with this model).
F
Network Connection
Attach a VT100 compatible terminal, or a PC running a
terminal emulatio n p r o gram, to t h e DB9 s e r ia l p o rt on the front
of any Fast EtherHub 3500 model. Use a null modem connection
that complies with the wiring assignments provided in
Appendix B.
When attaching to a PC, set terminal emulation type to VT100,
specify the port used by your PC (i.e., COM 1~4), and then set
communications to 8 data bits, 1 stop bit, no parity, and 9600 bps.
Set flow control to “none,” and be sure the modem is configured
to generate Data Set Ready (DSR) signals.
The Fast EtherHub-12i can only be managed via a direct connection,
or via a Fast EtherHub-12mi unit located in the same stack.
To access the on-board management agent on the Fast
EtherHub-12mi, connect a PC to any available port on the
stacked system. If proper network interconnections are
available, you can access the management agent from anywhere
in the attached network. However, if the stack segments are not
interconnected, you must connect to the segment containing the
SNMP management agent.
4-2 Configuring the System
Page 62

Before accessing a hub
using a Telnet connection, be
sure you have already set the
agent’s IP address via the onboard configuration program or
boot protocol.
Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
Local In-Band Telnet Connection
Prior to accessing the hub via an in-band Telnet connection,
you must first configure it with a valid IP address, subnet mask,
and default gateway using an out-of-band connection or boot
protocol. (Refer to
Using the Fast EtherHub 3500 Configuration Program
later in this chapter.) After configuring the hub’s IP param eters,
you can Telnet into its on-board menu-driven configuration
program from anywhere within the attached network.
Local In-Band Network Connection
If you want to use optional network management software (e.g.,
Accton’s AccView/Open) to configure the Fast EtherHub 3500
System, then first set up your Network Management Station
(NMS). The in-band NMS is the personal computer used to run
your network management software.
Before accessing a hub
using in-band management
software, be sure you have
already set the agent’s IP
address via the on-board
configuration program or
boot protocol.
F
If proper network connections are available, you can access the
on-board management agent from anywhere in the attached
network. However, prior to accessing the Fast EtherHub-12mi
via in-band management software, you must first configure the
hub with a valid IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway
using a direct connection or boot protocol.
Accton provides optional Windows-based network management
software called AccView/Open. Any PC running the AccView/
Open program can serve as your in-band network management
station. You may purchase this package through your Accton
dealer. A l so n o t e th a t th e A c c Vi e w / O p e n F a s t E t h e rHub 3500
Manager module can be easily integrated into most third-party
management platforms.
After completing hardware installation, configure the hub using the
out-of-band program or optional in-band network management
software (e.g., AccView/Open). Refer to the following sections for
details on on-board configuration. Refer to the appropriate manual
for information on optional in-band management software.
Configuring the System 4-3
Page 63

Remote Connection
Connect your modem and PC
at the remote site . D ia l in to th e
management agent, and remotely
configure the hub using the onboard configuration program; or
directly attach to the network via
a SLIP connection and perform
configuration or management
functions using in-band network
management software.
Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
If you want to use a remote PC to configure either of the Fast
EtherHub-12mi models via modem connections, at the remote
site make sure the modem’s baud rate is 9600 and that the AT
command set is supported.
Configuring the Fast EtherHub Site
Connect the hub’s DB9 serial port to the modem’s serial port
using standard serial cabling. (Refer to Appendix B for pin
assignments). For most modems, which use a 25-pin port, you
will have to provide an RS232 cable with a 9-pin connector on
one end and a 25-pin connection on the other end. You do not
have to set the modem com munication parameters at the hub’s
site, because the hub will automatically configure it to autoanswer mode. Just set it to force Data Set Ready (DSR) signals.
Configuring the Remote Site
At the remote site, connect the PC’s COM port (COM 1~4) to
the modem’s serial port. Set terminal emulation type to VT100,
specify the port used by your PC (i.e., COM 1~4), and then set
communications to 8 data bits, 1 stop bit, no parity, and 9600 bps.
Also be sure you set the flow control to “none.”
Remote Configuration Methods
Remote On-Board - If you establish a remote connection as
described in the previous section, you can use the on-board
management functions on the Fast EtherHub-12mi via a
terminal emulation program. See the section on
EtherHub 3500 System Configuration Program
more information. However, note that the on-board
configuration functions only provide access to the hub’s private
MIB. To access the full range of SNMP management
functions, you must use optional network management software
(e.g., AccView/Open).
4-4 Configuring the System
Using the Fast
later in this chapter for
Page 64

Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
Before accessing a hub using
in-band management software
from a remote site, be sure you
have already set the hub’s serial
IP address via the on-board
configuration program or boot
protocol.
Remote In-Band - You can also make a remote network
connection to the Fast EtherHub-12mi via the serial port using
SLIP protocol over TCP/IP. Using this kind of connection, you
can manage the hub or other attached network devices using inband network management software. Note that the system
functions similar to a router when you use IP protocol over a
SLIP link to the serial port, providing direct access to all
attached network resources (depending on y o ur assigned user
privileges).
Note: The winsocket used by both Windows 95 and Windows NT
include the SLIP protocol.
Accessing the Configuration Management Program
There are two methods for configuring the EtherHub 3500
system - using the on-board configuration program, or using
network management software (e.g., AccView/Open). Contact
your Accton dealer for more information on AccView/Open.
Configuring Your System with the On-board Program
On-board configuration requires a terminal or a computer
running a terminal emulation program as your working
platform. There are three valid connection types to the hub:
• Onsite connection
The workstation, normally within the vicinity of the hub, is
directly connected to the serial port on the hub.
• Telnet connection
The workstation is connected to a remote Fast EtherHub
3500 hub via a networked Telnet connection.
• Modem connection
The workstation is connected to a remote Fast EtherHub
3500 hub via modems.
Configuring the System 4-5
Page 65

When telneting into the hub, be
sure the telnet application has
disabled Windows cursor control.
If you are using Microsoft Telnet,
this can be accomplished by
selecting “VT100 Arrows” from the
Terminal Options menu.
Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
The physical setup and connections required for on-board
management are described in greater detail at the beginning of
this chapter. To open the Fast EtherHub 3500 System
Configuration Program, do the following:
1. Activate the Fast EtherHub 3500 System Configuration
Program from a local console, via Telnet, or via modem
connection as described below.
From a local console -
Be sure you have already run a cable from your terminal or
PC’s Com port to the serial port on the target hub as described
earlier in this chapter. When connecting a PC to the hub, use
a terminal emulation package to connect to the specific Com
port that is attached to the hub. Configure the connection for
9600 baud, 8 data bits, no parity bits, 1 stop bit, and no flow
control. Also be sure the modem is configured to force DSR
signals. Then open the connection.
From a telnet connection -
Telnet into the target hub using its assigned IP address.
From a remote modem connection -
Be sure you have attached a modem to both your local PC
and the remote hub as described earlier in this chapter. Use
a terminal emulation package to connect to the Com port
that is attached to the modem. Configure the connection for
9600 baud, 8 data bits, no parity bits, and 1 stop bit. Then
dial in to the hub.
If the screen is blank, press the
until the the login screen appears. If diagnostic messages
indicate a failure, refer to
Once the connection has been properly established, the login
screen for the on-board configuration program should appear.
4-6 Configuring the System
<Enter> key several times
Troubleshooting in Appendix A.
Page 66

Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
2. The login procedure for the Fast EtherHub-12i configuration
program requires a password only. Access priviledges are
Read/Write, and the default password is “admin.”
When logging into the Fast EtherHub-12mi configuration
program, you must provide both a user name and password.
The default user names are “admin” and “guest.” The
Administrator account has read/write access, and the Guest
has read-only access. For initial configurations, the
password is blank. Just press the
<Enter> key.
Admin i s tr a to r i s t h e h ighest pr ivilege l e vel in the Fast
EtherHub-12mi configuration program. The ad ministrat o r
should define a password, record it and put it in a safe place.
If you have not already done so, select the
User Passwords
field under the Configuration Panel and enter a password.
The configuration parameters you can access after logging
into the system are described in the following section.
Using the Fast EtherHub 3500 System Configuration Program
Accton provides a proprietary, user-friendly, menu driven onboard configuration program (i.e., the Fast EtherHub 3500
System Configuration Program). The configuration program
differs for the Fast EtherHub-12i and the Fast EtherHub-12mi.
The connection types allowed and options provided by this
configuration program are summarized below:
• The Fast EtherHub-12i is designed as a manageable hub,
without an on-board SNMP agent. Therefore, when an
SNMP agent (i.e., the Fast EtherHub-12mi) is connected to
this hub via the backplane bus, its management port will be
disabled, and configuration must be carried out using the
agent. However, if this hub is not connected to an agent, you
can configure it by making a direct connection to the
management port.
Configuring the System 4-7
Page 67

Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
• When configuring a Fast EtherHub-12mi or the connected
stack, you can use a direct connection to the managment
port, use a Telnet connection from a networked computer, or
use a standard modem connection from a remote computer.
System Configuration Program for the Fast EtherHub-12i
With this program you can carry out basic configuration on
the attached hub, such as setting the hub ID, connecting to the
required backplane segment, or configuring the SmartExtender
Module. Set up a direct connection to the hub, and enter the
password “admin” (if you have not yet changed the password).
The following menu will be displayed after logging on.
**************************************************
* Accton
**************************************************
Status
------ Hub ID : 1
Segment : 1
Isolate : OFF
Command
------------ h = Set hub ID
s = Set segment
e = Set SEM status
c = Change password
w = Write values into EEPROM
i = Change isolation status
q = Exit
Fast EtherHub-12i *
Enter command :
Figure 4-1 Main Configuration Menu (12i only)
Note: Input options for the selected item are displayed at the bottom of
the interface screen.
4-8 Configuring the System
Page 68

Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
Field
Description
Command
Set hub ID
Press “h” to set the hub identifier to any value from 1 ~ 6. When stacked with
a management agent, note that all hub identifiers are automatically configured.
Set Segment
Press “s” to attach the hub to backplane segment 1 ~ 3.
Set SEM status
Press “e” to display the menu for the SmartExtender Module. Refer to the
following table for a description of the configuration options for this module.
Change password
Press “c” to change the password. Passwords can be up to 5 characters long
and are case sensitive.
Write values to EEPROM
Press “w” to write all configuration changes to nonvolatile memory. You must
save your changes, or they will be lost the next time you restart the system.
Change isolation status
You can isolate the hub from the backplane, or reattach it to the backplane.
Exit
Press “q” to quit the cofiguration menu and return to the command prompt.
Accton
Menu selections are briefly described in the following table.
Table 4.1 Configuration Options in Main Menu (12i only)
Configuring the SmartExtender Module
To configure the SmartExtender Module, press “e”. The
following menu will be displayed.
***********************************************
*
***********************************************
SEM Status
--------- Duplex : negotiated full-duplex
Forward : adaptive cut-through
Back Pressure : disable
===============================
Command
------ d = Set duplex mode
m = Set forward mode
b = Set back pressure
r = Return to Main Menu
Fast EtherHub-12i *
Enter command :
Figure 4-2 Configuration Menu for SmartExtender Module (12i only)
Note: Input options for the selected item are displayed at the bottom of
the interface screen.
Configuring the System 4-9
Page 69

Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
The current settings for the extender module are displayed in
the status field. Menu selections are briefly described in the
following table.
Field Description
Command Set duplex Press “d” to set the transmission mode to half-duplex, full-duplex or auto-
negotiation. All Fast EtherHubs are set to auto-negotiation when powered up.
Any changes to transmission mode will be lost if the power to the hub is reset.
Set forward mode Press “f” to set the frame forwarding mode to adaptive cut-through or store &
forward.
Set back pressure Press “b” to enable or disable back pressure.
Return to Main Menu Press “r” to return to the Main Menu.
Table 4.2 Configuration Options for SmartExtender Module (12i only)
4-10 Configuring the System
Page 70

Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
System Configuration Program for the Fast EtherHub-12mi and Stack
With this program you can define system parameters, manage
and control stacked hubs and associated ports, and monitor
network conditions. Set up a management connection to the
hub, and enter a user name and password. User names are
“admin” (read/write access) or “guest” (read access). No
password is configured for the default configuration. The
following menu will be displayed after logging on.
Main Menu
=========
Exit
Restart System System Information ...
Configuration Panels:
SNMP Configuration ... Port Intrusion Control ...
Segment Configuration ... TFTP Download ...
Hub Configuration ... Xmodem Download ...
Port Configuration ... User Passwords ...
Port Backups ... Console Lockout ...
Statistics Panels:
Segment Statistics ... Port Statistics ...
Hub Statistics ...
Exit this User Interface program.
Use arrow keys to move. <Enter> to confirm.
<Ctrl+E> to exit this program.
Figure 4-3 Main Configuration Menu
Note: Input options for the selected item are displayed at the bottom of
the interface screen. For items which require you to choose an option,
follow your input by pressing the [Enter] key. Use <Ctrl+L> to scroll
through an options list, <Ctrl+T> to move to an upper level menu, or
<Ctrl+E> to close the configuration program.
Configuring the System 4-11
Page 71

Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
To select a configuration item, use the arrow keys to position
the cursor (i.e., the highlighted box), and then press the [Enter]
key. Configuration items followed by dots (...) open up another
menu screen. Menu selections are briefly described in the
following table.
Field Description
Main Exit Exits the program and returns to the operating system.
Restart System Restarts the on-board management agent.
System Information Identifies the system.
Configuration SNMP Configuration Configures communities, as well as IP and IPX trap managers.
Segment Configuration Configures IP, IPX and SNMP parameters for each segment.
Hub Configuration Isolates/attaches a hub, or sets the hub’s segment;
defines attached segment for Network Management Module, and sets bootup option;
also sets protocol status for SNMP/IP, SNMP/IPX and SNMP/Ethernet.
Port Configuration Disables/enables a port, shows link and partition state, as well as allowing you to
set the communication mode to full or half-duplex for the SmartExtender Module.
Port Backups Sets up to 18 pairs of backup ports. Each pair contains a master and slave port.
The slave port is normally disabled. When master port fails, the system disables
the master port and enables the slave port to maintain the link.
Port Intrusion Control Sets the authorized entry address, and defines response for detected intrusion.
TFTP Download Downloads new version of firmware to update your system (via in-band).
Xmodem Download Downloads new version of firmware to update your system (via on-board program).
User Passwords Defines password for administrator and guest.
Console Lockout Sets the time the system will wait without receiving any keyboard input before
logging you off the configuration program.
Statistics Segment Statistics Displays network performance for each hub segment.
Hub Statistics Displays network performance for each hub.
Port Statistics Displays network performance for each port.
Table 4.3 Main Configuration Menu
Exiting the Configuration Program
Use the Exit command under the Main Menu to close the
configuration program. Note that this command and <Ctrl+E>
have the same effect.
4-12 Configuring the System
Page 72
Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
-
Restarting the Agent
Use the Restart System command under the Main Menu to reset
the agent and all devices managed by the agent. The hardware
configuration for the agent and system tests are displayed on
the management console, similar to the messages shown in the
following example.
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION:
--------------------EPROM size: 128KB (configured)
Flash ROM size: 512KB
EEPROM size: 8KB
DRAM size: 4MB
no SRAM detected
SRAM size: 0KB
Input FIFO: 1024 bytes
Output FIFO: 1024 bytes
SYSTEM TESTS:
------------Console I/O test...
!"#$%&’()*+,
./0123456789:;<=>?@ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ
[\]^_‘abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz{|}~
Flash ROM test...
Checksum test passed
EEPROM header test...
Checksum test passed
DRAM test...
Address ripple test passed
Walking 0 test passed
Walking 1 test passed
Refresh test passed
SRAM test...
No SRAM detected
Output FIFO testing OK ! SIZE 1024 bytes
Input FIFO testing OK ! SIZE 1024 bytes
SYSTEM TESTS COMPLETED
----------------------
Figure 4-4 Screen Messages for System Resart
Configuring the System 4-13
Page 73

Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
Displaying System Information
Use the System Information command to display and modify
general information about the EtherHub stack, or for quick
system identification. View a description of the system similar
to that displayed in the following example:
System Information
Return to Previous Panel
System Description : Accton Fast EtherHub 3500 System
System Object ID : 1.3.6.1.4.1.2.6.37
System Up Time : 602343 (0 day 1 hr 40 min 23 sec)
System Name : R&D Stack
Contact : Mark Spitz
Location : 2nd floor
Return to previous panel.
Use arrow keys to move. <Enter> to confirm.
<Ctrl+T> to return to Main Menu.
Figure 4-5 System Information Menu
Menu items are briefly described in the following table.
Field Description
System Description Model name of the EtherHub unit
System Object ID Object identifier as defined in MIB II
System Up Time Length of time the EtherHub management agent has been running
System Name Name assigned to the EtherHub system
Contact Contact person for the system
Location Specifies area or location where the system is located
Table 4.4 System Information Menu
4-14 Configuring the System
Page 74

Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
Configuring the SNMP Agent
When using SNMP-based network management software (e.g.,
the optional AccView/Open package), you must specify basic
parameters that control management access to the system. Use
the SNMP Configuration menu to display the following screen:
parameters:
SNMP Configuration
Return to Previous Panel
Send Authentication Fail Trap : YES
SNMP Communities ...
IP Trap Managers ...
IPX Trap Managers ...
Display or work with IPX trap managers.
Use arrow keys to move. <Enter> to confirm.
<Ctrl+T> to return to Main Menu.
Figure 4-6 SNMP Configuration Menu
Menu items are briefly described in the following table.
Field Description
Send Authentication Fail Trap Issue a trap message if anyone attempts to access the configuration program without
the proper user name and password.
SNMP Communities The community strings authorized for SNMP or trap management access. All
community strings used for IP and IPX Trap Managers must be listed in this table.
IP Trap Managers IP management stations selected to receive trap messages from the system.
IPX Trap Managers IPX management stations selected to receive trap messages from the system.
Table 4.5 SNMP Configuration Menu
Configuring the System 4-15
Page 75

Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
Configuring SNMP Communities
Access to the hub’s on-board management agent via in-band
management software is controlled with community strings.
Use the SNMP Communities command to edit community
strings and access rights as shown below:
SNMP Communities
Return to Previous Panel
Community Name Access Status
1. public READ ONLY ENABLED
2. xray READ/WRITE ENABLED
3. READ ONLY DISABLED
4. READ ONLY DISABLED
5. READ ONLY DISABLED
Return to previous panel.
Use arrow keys to move. <Enter> to confirm.
<Ctrl+T> to return to Main Menu.
Figure 4-7 SNMP Communities Menu
Menu items are briefly described in the following table.
Field Description
Community Name A community entry authorized for management access.
Access Management access is restricted to Read Only or Read/Write.
Status The current entry can be ENABLED or DISABLED.
Table 4.6 SNMP Communities Menu
4-16 Configuring the System
Page 76

Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
Configuring IP Trap Managers
When the hub experiences an unusual event, a message is
issued to all listed network managers. Networks compliant
with Internet Protocol (IP) can pass trap messages to IP Trap
Managers as shown below:
IP Trap Managers
Return to Previous Panel
IP Address Community Name Status
1. 203.70.236.106 public ENABLED
2. 0.0.0.0 public DISABLED
3. 0.0.0.0 public DISABLED
4. 0.0.0.0 public DISABLED
5. 0.0.0.0 public DISABLED
Return to previous panel.
Use arrow keys to move. <Enter> to confirm.
<Ctrl+T> to return to Main Menu.
Figure 4-8 IP Trap Managers Menu
Menu items are briefly described in the following table.
Field Description
IP Address IP address of the trap receiver. (Use dotted decimal notation.)
Community Name The community string required for trap access.
Status The current entry can be ENABLED or DISABLED.
Table 4.7 IP Trap Managers Menu
Configuring the System 4-17
Page 77

Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
Configuring IPX Trap Managers
When the hub experiences an unusual event, a message is
issued to all listed network managers. Networks compliant
with Internetwork Packet Exchange (NetWare IPX) protocol
can pass trap messages to IPX Trap Managers as shown below:
IPX Trap Managers
Return to Previous Panel
IPX Address Community Name Status
1. 00-00-13-52:00-00-00-00-E8-90 public ENABLED
2. 00-00-00-00:00-00-00-00-00-00 public DISABLED
3. 00-00-00-00:00-00-00-00-00-00 public DISABLED
4. 00-00-00-00:00-00-00-00-00-00 public DISABLED
5. 00-00-00-00:00-00-00-00-00-00 public DISABLED
Return to previous panel.
Use arrow keys to move. <Enter> to confirm.
<Ctrl+T> to return to Main Menu.
Figure 4-9 IPX Trap Managers Menu
Menu items are briefly described in the following table.
Field Description
IPX Address IPX address of the trap receiver. (Provide dotted decimal notation with both the network and MAC
address components.)
Community Name The community string required for trap management access.
Status The status of the current entry can be set to ENABLED or DISABLED.
Table 4.8 IPX Trap Managers Menu
4-18 Configuring the System
Page 78
Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
Changing the Segment Configuration
When accessing the EtherHub system with in-band tools such
as SNMP, Telnet or TFTP, you must configure the hub to use
IP, IPX or SNMP over Ethernet protocols. Use the Segment
Configuration menu to display the following screen:
Segment Configuration
Return to Previous Panel
Segment 1 Segment 2 Segment 3
Segment Name : R&D
IP Configuration :
IP Address : 203.70.236.1 203.70.236.2 203.70.236.3
Subnet Mask : 255.255.255.0 255.255.255.0 255.255.255.0
Gateway IP : 203.70.236.254 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0
Serial IP : 203.70.236.9 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0
Save to EEPROM Save to EEPROM Save to EEPROM
IPX Frame Type : IPX 802.2 FRAME IPX 802.2 FRAME IPX 802.2 FRAME
Internal IPX Network : AC-B3-00-56 AC-B3-00-56 AC-B3-00-56
IP Protocol : ENABLED ENABLED ENABLED
IPX Protocol : DISABLED DISABLED DISABLED
SNMP Over Ethernet : DISABLED DISABLED DISABLED
IP configuration of segment 1 saved to EEPROM and enabled!
Use arrow keys to move. <Enter> to confirm.
<Ctrl+T> to return to Main Menu.
Figure 4-10 Segment Configuration Menu
Configuring the System 4-19
Page 79
Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
Menu items are briefly described in the following table.
Field Description
Segment Name A name you can assign to the segment.
IP Configuration The hub system may be run on SNMP protocol over UDP/IP transport protocol. In this
environment, all systems on the Internet, such as network interconnection devices and
Network Management Stations (e.g., the PC running AccView) are assigned an IP address.
When accessing the hub from a remote site, you will also have to assign an IP address to
the management port.
IP Address IP address of the segment you’re managing.
Subnet Mask Subnet mask of the agent you’ve selected. This mask identifies the host address bits used
for routing to specific subnets.
Gateway IP Gateway used in passing trap messages from the hub agent to the management station.
Serial IP IP address used to access the on-board configuration program via an out-of-band SLIP
connection to the management port.
Save to EEPROM This command saves the IP address for the selected segment in nonvolatile memory, and
makes it effective immediately.
IPX Frame Type The selected format used on the LAN; i.e., this type is that used by the IPX network where
the hub is installed. If the specified frame type is not detected, the hub will automatically
detect the current type. (Values: 802.3, Ethernet II, SNAP, 802.2)
Internal IPX Network This address is composed of Net Number which identifies the IPX network number for the
connected slot.
IP Protocol Protocol suite selection.
IPX Protocol Protocol suite selection.
SNMP over Ethernet Protocol suite selection.
Table 4.9 Segment Configuration Menu
4-20 Configuring the System
Page 80

Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
Configuring Hub Parameters
Use the Hub Configuration menu under the Configuration
Panel to configure any hub in the stack. This menu is used to
configure the repeater and management modules. Use the
following menu to select the required hub, or to change the
numeric identifier for any hub in stack.
Hub Configuration: Hub Selection Menu
Return to Previous Panel
Hub 1 Configuration ...
Hub 2 Configuration ...
Hub 3 Configuration ...
Hub 4 Configuration ...
Hub 5 Configuration ...
Hub 6 Configuration ...
Hub ID Configuration ...
Display or work with hub ID configuration.
Use arrow keys to move. <Enter> to confirm.
<Ctrl+T> to return to Main Menu.
Figure 4-11 Hub Configuration: Hub Selection Menu
Configuring the System 4-21
Page 81

Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
Hub Configuration
To configure a hub, select it from the list shown above. The
following Hub Configuration menu will appear, allowing you to
set parameters for the base repeater unit or the network
management module.
Hub Configuration
Return to Previous Panel
Hub ID : 1 Position : 1
Name : H/W Group Type : EH3512M-TX
Segment : 1 H/W Ver : 0
Status : ATTACHED
Power 1 : OPERATIONAL
Power 2 : NOT PRESENT
Network Management Module (NMM) :
Status : PRIMARY H/W Ver : 4
Segment : 1 F/W Ver : 1.09
Bootup Option : NORMAL
Physical Address : 00-04-AC-B3-00-31
F/W Ver : 1.05
Return to previous panel.
Use arrow keys to move. <Enter> to confirm.
<Ctrl+T> to return to Main Menu.
Figure 4-12 Hub Configuration Menu
4-22 Configuring the System
Page 82

Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
Menu items are briefly described in the following table.
Board Field Description
(Repeater Unit) Hub ID Hub identifier within the stack. (Up to 6 hubs may be connected via the FlexBus
management channel.)
Name Any user-defined name for the selected hub.
Status The hub may be isolated from the backplane or attached to the backplane.
Segment Attach the hub to a specified segment (1 ~ 3). The segment indicator will light up to
show that it has been connected to the specified stack segment.
Power 1 Shows status of power module in Slot 1 as Operational, Not Present, or Failed.
Power 2 Shows status of power module in Slot 2 as Operational, Not Present, or Failed.
Position The physical position in the stack.
Type Indicates hub type as EH3512I-TX or EH3512M-TX.
H/W Ver Indicates the current hardware version number of the repeater board.
F/W Ver Indicates the current firmware version number of the repeater board.
Network Status Defines the status of the Network Management Module as Primary or Backup.
Management Segment The backplane segment the NMM is attached to. Note that the management agent
does not have to be attached to the same segment as the repeater unit.
Module (NMM) Bootup Option Specifies bootup method as -
NORMAL - Use on-board ROM code and default IP address.
TFTP DOWNLOAD - Get system code from TFTP server (and use default IP
address).
BOOTP GET IP - Get IP address from server (and use on-board ROM code).
BOOTP DOWNLOAD - Get IP address and system code from server. Image is
stored in temporary memory.
NO BOOTP TFTP REQUEST - Do not issue BOOTP request. Wait for download
via out-of-band.
BOOTP UPGRADE FIRMWARE - Get IP address and system code from server.
Image is stored in nonvolatile memory, and BOOTP option reset to NORMAL. Note
that this is the only in-band option that places the image in nonvolatile memory.
H/W Ver Indicates the current hardware version number for the managment board.
F/W Ver Indicates the current firmware version number for the managment board.
Physical Address MAC address of the management agent.
Table 4.10 Hub Configuration Menu
Configuring the System 4-23
Page 83

Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
Hub ID Configuration
To change the numeric hub identifier, select Hub ID
Configuration from the Hub Configuration: Hub Selection
Menu shown above. The following Hub ID Configuration
menu will appear. After changing a hub identifier, verify the
change with the “Enable Above Settings” command.
Hub ID Configuration
Return to Previous Panel
Position Hub ID
1. 1
2. 2
3. 3
4. 4
5. 5
6. 6
Enable Above Settings
Return to previous panel.
Use arrow keys to move. <Enter> to confirm.
<Ctrl+T> to return to Main Menu.
Figure 4-13 Hub ID Configuration Menu
4-24 Configuring the System
Page 84
Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
Configuring Port Parameters
Use the Port Configuration menu under the Configuration
Panel to configure the ports for any hub in the stack. Select the
port type for the required hub from the following menu.
Port Configuration: Port Selection Menu
Return to Previous Panel
Select port to get configuration
Hub ID | Port ID
----------+----------------------- 1 | 1 through 12 SEM
2 | 1 through 12 SEM
3 | 1 through 12 SEM
4 | 1 through 12 SEM
5 | 1 through 12 SEM
6 | 1 through 12 SEM
Display or work with hub 1 ports 1 through 12 configuration.
Use arrow keys to move. <Enter> to confirm.
<Ctrl+T> to return to Main Menu.
Figure 4-14 Port Configuration: Port Selection Menu
Configuring the System 4-25
Page 85
Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
Field
Description
Hub ID
Hub identifier within the stack.
Position
The physical position in the stack (as determined by its position from the top of the FlexBus chain).
Port ID
Numeric identifier 1~12 or SEM (i.e., SmartExtender Module).
Name
User-defined name for selected port.
Type
Connection type for the repeater Ports 1~12 is 100BASE-TX.
Admin Status
Any port may be set by the operator to ENABLED or DISABLED.
Oper Status
Reflects the port’s actual status as ENABLED or DISABLED.
Link State
Indicates if the port has a valid connection to an external device.
Partition
Indicates if the port is partitioned
. (Refer to Partition/Disable Indicators in Chapter 5 for a more
detailed description of the reasons a port may be partitioned.)
Configuring Repeater Ports
If you select the repeater port type (i.e., 1 through 12), the Port
Configuration Menu will open. This menu displays the ID and
stack position of the selected hub, and also allows you to
enable/disable any repeater port in the selected hub.
Port Configuration
Return to Previous Panel
Hub ID : 1 Position : 1
Port ID Name Type Admin Status Oper Status Link State Partition
1. 100BASE-TX ENABLED ENABLED DOWN NOT PART
2. 100BASE-TX ENABLED DISABLED DOWN NOT PART
3. 100BASE-TX ENABLED ENABLED DOWN NOT PART
4. 100BASE-TX ENABLED ENABLED DOWN NOT PART
5. 100BASE-TX ENABLED ENABLED DOWN NOT PART
6. 100BASE-TX ENABLED ENABLED DOWN NOT PART
7. 100BASE-TX ENABLED ENABLED DOWN NOT PART
8. 100BASE-TX ENABLED ENABLED DOWN NOT PART
9. 100BASE-TX ENABLED ENABLED DOWN NOT PART
10. Steve 100BASE-TX ENABLED ENABLED UP NOT PART
11. 100BASE-TX ENABLED ENABLED DOWN NOT PART
12. 100BASE-TX ENABLED ENABLED DOWN NOT PART
Return to previous panel.
<Ctrl+T> to return to Main Menu.
Use arrow keys to move. <Enter> to confirm.
Figure 4-15 Port Configuration Menu
Menu items are briefly described in the following table.
1
1
1 - If the port is set to ENABLED by the administrator, but used as a backup port, Admin Status and Oper Status will differ.
Table 4.11 Port Configuration Menu
4-26 Configuring the System
Page 86

Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
Configuring the SmartExtender Module
If you select the SmartExtender Module (i.e., SEM), the SEM
Port Configuration Menu will open. This menu allows you to
configure various communication parameters for this module.
SEM Port Configuration
Return to Previous Panel
Hub ID : 1 Position : 1
Port ID : SEM
Name : Uplink Link State : UP
Type : 100BASE-TX Speed : 10M
Admin Status : ENABLED Oper Status : ENABLED
Duplex Mode : HALF-DUPLEX Duplex In Use : HALF-DUPLEX
Back Pressure : DISABLED
Forwarding Mode : STORE AND FORWARD
Forwarding In Use : STORE AND FORWARD
Return to previous panel.
Use arrow keys to move. <Enter> to make changes.
<Ctrl+T> to return to Main Menu.
Figure 4-16 SEM Port Configuration Menu
Configuring the System 4-27
Page 87

Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
Admin Status
Any port may be set by the operator to ENABLED or DISABLED.
Menu items are briefly described in the following table.
Field Description
Hub ID Hub identifier within the stack.
Position The physical position in the stack (as determined by its position from the top of the FlexBus chain).
Port ID Identifies this port as the SmartExtender Module.
Name User-defined name for selected port.
Link State Indicates if the port has a valid connection to an external device.
Type Connection types for the SmartExtender Module include 100BASE-TX (10BASE-T), 100BASE-T4,
100BASE-FX.
Speed The 100BASE-TX module relies on auto-detection to set the speed at 10 or 100 Mbps, while the
100BASE-T4 and 100BASE-FX modules are fixed at 100 Mbps.
1
Oper Status
Duplex Mode The extender module for 100BASE-TX (10BASE-T) and 100BASE-FX can be set to half or full duplex.
Duplex In Use Displays the actual duplex mode in use based on the results of auto-negotiation.
Back Pressure When the internal buffers on this port begin to fill, it can be configured to signal the connected
Forwarding Mode The scheme by which frames are processed and forwarded through this module can be set to
Forwarding In Use Indicates the actual forwarding mode in use based on the current error rate.
1 - If the port is set to ENABLED by the administrator, but used as a backup port, Admin Status and Oper Status will differ.
1
Reflects the port’s actual status as ENABLED or DISABLED.
device to slow transmission by setting this field to ENABLED.
Adaptive Cut-through or Store and Forward.
Table 4.12 SEM Port Configuration Menu
4-28 Configuring the System
Page 88

Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
Defining Backup Ports
Use the Port Backups menu under the Configuration Panel to
define up to 6 master/slave port pairs. If the connection to the
master port fails, the slave port will automatically take over.
For greater reliability, primary and secondary ports should be
located on different hubs. Use the following menu to specify
and activate port backup pairs.
Port Backups
Return to Previous Panel
Backup Set Primary Port Secondary Port Action
1. Hub: 1 Port: 1 Hub: 1 Port: 1 INACTIVE
2. Hub: 1 Port: 4 Hub: 1 Port: 1 INACTIVE
3. Hub: 1 Port: 1 Hub: 1 Port: 1 INACTIVE
4. Hub: 1 Port: 1 Hub: 1 Port: 1 INACTIVE
5. Hub: 1 Port: 1 Hub: 1 Port: 2 INACTIVE
6. Hub: 1 Port: 2 Hub: 1 Port: 1 INACTIVE
Return to previous panel.
Use arrow keys to move. <Enter> to make changes.
<Ctrl+T> to return to Main Menu.
Figure 4-17 Port Backups Menu
Menu items are briefly described in the following table.
Field Description
Backup Set Identifier for up to 18 backup port pairs.
Primary Port Pair member serving as the primary link.
Hub Hub ID for the master port.
Port Port identifier for the master port.
Secondary Port Pair member serving as the backup link.
Hub Hub ID for the slave port.
Port Port identifier for the slave port.
Action Each backup pair can be set to ACTIVE or INACTIVE.
BACKUP is displayed if the primary port is not currently linked.
STAND-BY is displayed if the backup port is not currently linked.
Table 4.13 Port Backups Menu
Configuring the System 4-29
Page 89

Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
Port Intrusion Control
Use the Port Intrusion Control menu under the Configuration
Panel to restrict access for any port to an authorized source
address. Select the required hub from the following menu.
Port Intrusion Control: Hub Selection Menu
Return to Previous Panel
Hub 1 Port Intrusion Control ...
Hub 2 Port Intrusion Control ...
Hub 3 Port Intrusion Control ...
Hub 4 Port Intrusion Control ...
Hub 5 Port Intrusion Control ...
Hub 6 Port Intrusion Control ...
Return to previous panel.
Use arrow keys to move. <Enter> to confirm.
<Ctrl+T> to return to Main Menu.
Figure 4-18 Port Intrusion Control: Hub Selection Menu
4-30 Configuring the System
Page 90
Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
Use the Port Intrusion Control Menu to define the MAC
address for the device authorized to access a port, and set the
response type, as shown in the following example.
Port Intrusion Control
Return to Previous Panel
Hub ID : 1 Position : 1
Port ID Authorized Address Intrusion Action
1. 00-00-00-00-00-00 INACTIVE
2. 00-00-00-00-00-00 INACTIVE
3. 00-00-00-00-00-00 INACTIVE
4. 00-00-00-00-00-00 INACTIVE
5. 00-00-00-00-00-00 INACTIVE
6. 00-00-00-00-00-00 INACTIVE
7. 00-00-00-00-00-00 INACTIVE
8. 00-00-00-00-00-00 INACTIVE
9. 00-00-00-00-00-00 INACTIVE
10. 00-00-E8-90-1B-73 WARNING & DISABLE
11. 00-00-00-00-00-00 INACTIVE
12. 00-00-00-00-00-00 INACTIVE
Return to previous panel.
Use arrow keys to move. <Enter> to make changes.
<Ctrl+T> to return to Main Menu.
Figure 4-19 Port Intrusion Control Menu
Menu items are briefly described in the following table.
Field Description
Hub ID Hub identifier within the stack.
Position The physical p o s it i o n i n t h e st ack (as d e t e rmined by its position from the top of the FlexBus chain).
Port Selects any station port (1~12) on the hub.
Authorized Address Defines the MAC address that is authorized to attach to this port.
Intrusion Action Response to a detected intrusion can be set to:
INACTIVE - no action taken,
WARNING - trap message is issued to the management station, or
WARNING & DISABLE - trap message is issued and port is disabled.
Note: If a port is disabled by an unauthorized intrusion attempt, it must be manually re-enabled
using the Oper Status field in the Port Configuration menu.
Table 4.14 Port Intrusion Control Menu
Configuring the System 4-31
Page 91

Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
Downloading System Software via a TFTP Server
Use the TFTP Download command under the Configuration
Panel to download firmware updates into the hub. You may
upgrade firmware from a server attached to the local network,
or remotely via a serial link using TFTP over SLIP.
Specify the IP address for the TFTP server, the filename, and
the download mode. The download file should be a binary file
from Accton; otherwise the agent will not accept it. Also be
sure that you have already set the required bootup option for the
target hub under the Hub Configuration menu.
Download status is indicated by messages at the bottom of the
screen. Firmware is first loaded into a temporary buffer. If you
selected download for permanent use, it will then be transferred
to nonvolatile memory. After you download the firmware, the
agent will be reset and you will have to log back into the configuration program again. The following screen shows an
example of the TFTP download menu.
TFTP Download
Return to Previous Panel
Download Server IP : 203.70.236.12
Download Filename : acc110.bin
Download Mode : PERMANENT
Start TFTP Download
Return to previous panel.
Use arrow keys to move. <Enter> to confirm.
<Ctrl+T> to return to Main Menu.
Figure 4-20 TFTP Download Menu
4-32 Configuring the System
Page 92

Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
Menu items are briefly described in the following table.
Field Description
Download Server IP IP address of a TFTP server. (TFTP stands for Trivial File Transfer Protocol.)
Download Filename The *.bin file to download.
Download Mode You can download to permanent flash ROM or temporary storage in RAM (for test purposes).
However, if you download to temporary memory, this firmware will be lost upon power off. To
update new agent firmware for permanent use, it must be downloaded to flash ROM.
Start TFTP Download Initiates download process.
Table 4.15 TFTP Download Menu
Configuring the System 4-33
Page 93
Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
Xmodem Download
Use the Xmodem Download menu under the Configuration
Panel to download firmware to the hub. The Xmodem protocol
is used to transfer binary files over a PC connection (i.e., using
terminal emulation or modem access software).
Specify the download mode and select Process Download.
Open the file transfer utility in your terminal emulation or
modem access program, specify the filename, and then start file
transfer. When tran sf e r ri n g files fro m you c o mputer, b e s u r e you
specify “Send” or “Upload” file. The file should be a binary file
from Accton; otherwise the agent will not accept it. Also be
sure that you have already set the required bootup option for the
target hub under the Hub Configuration menu.
File transfer status is indicated by messages at the bottom of the
screen. Firmware is first loaded into a temporary buffer. If you
selected download for permanent use, it will then be transferred
to nonvolatile memory . After y ou finish transfering the firm ware,
the agent will be reset and you will have to log back into the
configuration program again. The following screen shows an
example of the Xmodem Download menu.
Xmodem Download
Return to Previous Panel
Download Mode : TEMPORARY
Process Download
Return to previous panel.
Use arrow keys to move. <Enter> to confirm.
<Ctrl+T> to return to Main Menu.
Figure 4-21 Xmodem Download Menu
Menu items are briefly described in the following table.
Field Description
Download Mode You can download to permanent flash ROM or temporary storage in RAM (for test purposes only).
Process Download Initiate the file transfer process.
Table 4.16 Xmodem Download Menu
4-34 Configuring the System
Page 94

Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
Changing User Passwords
The on-board configuration program includes two fixed user
types, including Admin and Guest. The access privilege is
Read/Write for administrator and Read Only for guest. The
default user names are “admin” and “guest,” without passwords.
The administrator is the only user with write access for agent
parameters. You should therefore assign a password to
administrator as soon as possible, and store it in a safe place.
The User Passwords menu is shown below.
User Passwords
Return to Previous Panel
User Type User Name Password
Admin : admin pluto
Guest : guest
Return to previous panel.
Use arrow keys to move. <Enter> to confirm.
<Ctrl+T> to return to Main Menu.
Figure 4-22 User Passwords Menu
Menu items are briefly described in the following table.
Field Description
User Type There are only two fixed user types - Admin and Guest. The respective access rights are
Read/Write and Read Only.
User Name The login name required for access to the management agent. (not case sensitive)
Password The password that must be provided with the user name to access the system. (not case sensitive)
Table 4.17 User Passwords Menu
Configuring the System 4-35
Page 95

Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
Console Lockout
This function instructs the configuration program to
automatically lock the console if no keyboard input is detected
for the defined delay time. The Console Lockout menu is
shown below.
Console Lockout
Return to Previous Panel
Status : ON
Delay Time : 20 Minutes
Return to previous panel.
Use arrow keys to move. <Enter> to confirm.
<Ctrl+T> to return to Main Menu.
Figure 4-23 Console Lockout Menu
Menu items are briefly described in the following table.
Field Description
Status The console lockout feature can be turned on or off.
Delay Time The delay time for console lockout can set for any value in the range of 0 ~ 99 minutes.
Table 4.18 Console Lockout Menu
4-36 Configuring the System
Page 96
Screen statistics are not
automatically refreshed from the
agent. Select
to update the displayed values.
The values displayed have been
accumulated since the last
system reboot or counter reset.
Refresh Statistics
Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
Segment Statistics
Displays statistics for the stack’s segments. These values can
be used to indicate the approximate load balance in your stack.
If the loading is severly unbalanced, you may consider
adjusting your network connections or segment assignments.
The Segment Statistics window is shown below.
Segment Statistics
Return to Previous Panel
Refresh Statistics
Segment 1 Segment 2 Segment 3
Frames : 19271 0 0
Bytes : 3767321 0 0
Collisions : 57 0 0
Alignment Errors : 0 0 0
CRC Errors : 0 0 0
Total Errors : 0 0 0
Symbol Errors : 0 0 0
Return to previous panel.
Use arrow keys to move. <Enter> to confirm.
<Ctrl+T> to return to Main Menu.
Figure 4-24 Segment Statistics Window
Displayed items are briefly described in the following table.
Field Description
Refresh Statistics Fetch the current statistics stored in the agent’s counters.
Frames Number of frames passing through this device.
Bytes Number of bytes passing through this device.
Collisions Number of simultaneous node transmissions detected by this device.
Alignment Errors Number of mis-synchronized data packets detected by this device.
CRC Errors Number of Ethernet Cyclic Redundancy Check errors detected by this device.
Total Errors Total number of errors, including FCS, alignment, FramesTooLong, ShortEvents,
LateEvents, Jabber, and DataRateMismatches detected on this device.
Symbol Errors Number of symbol errors (i.e., code-group errors including collision artifacts or transmission
errors). Note that these errors are unique to 100 Mbps analog signals.
Table 4.19 Segment Statistics Menu
Configuring the System 4-37
Page 97
Screen statistics are not
automatically refreshed from the
agent. Select
to update the displayed values.
The values displayed have been
accumulated since the last
system reboot or counter reset.
Refresh Statistics
Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
Hub Statistics
Displays statistics for any hub in the stack. Select the required
hub from the following menu.
Hub Statistics: Hub Selection Menu
Return to Previous Panel
Hub 1 Statistics ...
Hub 2 Statistics ...
Hub 3 Statistics ...
Hub 4 Statistics ...
Hub 5 Statistics ...
Hub 6 Statistics ...
Return to previous panel.
Use arrow keys to move. <Enter> to confirm.
<Ctrl+T> to return to Main Menu.
Figure 4-25 Hub Statistics: Hub Selection Menu
Hub statistics can be used to check on the general health of
your hardware and network connections. If any of the error
indications are extremely high (e.g., collisions or CRC errors),
you should take appropriate measure to resolve the problem.
Hub Statistics
Return to Previous Panel
Refresh Statistics
Hub ID : 1 Position : 1
Frames : 20116
Bytes : 3860016
Collisions : 64
Alignment Errors : 0
CRC Errors : 0
Total Errors : 0
Symbol Errors : 0
Return to previous panel.
Use arrow keys to move. <Enter> to confirm.
<Ctrl+T> to return to Main Menu.
Figure 4-26 Hub Statistics Window
4-38 Configuring the System
Page 98

Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
Displayed items are briefly described in the following table.
Field Description
Hub ID Hub identifier within the stack.
Position The physical position in the stack (as determined by its position from the top of the FlexBus chain).
Frames Number of frames passing through this device.
Bytes Number of bytes passing through this device.
Collisions Number of simultaneous node transmissions detected by this device.
Alignment Errors Number of mis-synchronized data packets detected by this device.
CRC Errors Number of Ethernet Cyclic Redundancy Check errors detected by this device.
Total Errors Total number of errors, including FCS, alignment, FramesTooLong, ShortEvents, LateEvents,
Jabber, and DataRateMismatches detected on this device.
Symbol Errors Number of symbol errors (i.e., code-group errors including collision artifacts or transmission errors).
Note that these errors are unique to 100 Mbps analog signals.
Table 4.20 Hub Statistics Menu
Port Statistics
Displays statistics for any port in the stack. Select the required
port from the following menu.
Port Statistics: Port Selection Menu
Return to Previous Panel
Select port to get statistics
Hub ID | Port ID
---------+------------------------------------------------ 1 | 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 SEM
2 | 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 SEM
3 | 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 SEM
4 | 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 SEM
5 | 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 SEM
6 | 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 SEM
Return to previous panel.
Use arrow keys to move. <Enter> to confirm.
<Ctrl+T> to return to Main Menu.
Figure 4-27 Port Statistics: Port Selection Menu
Configuring the System 4-39
Page 99

Screen statistics
are not
automatically
refreshed from the
agent. Select
Refresh Statistics
to update the
displayed values.
The values
displayed have
been accumulated
since the last
system reboot or
counter reset.
Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
Statistics for Repeater Ports
Statistics for repeater ports covers a wide range of Ethernet
variables. If any of the error indications are extremely high,
there may be a problem with the port, the attached device, or
the network cabling. (The
System Diagnostics section in Appendix
A provides help on troubleshooting.) The Port Statistics
window is shown below.
Port Statistics
Return to Previous Panel
Refresh Statistics
Hub ID : 1 Position : 1
Port ID : 10
Readable Frames : 20524 Late Events : 0
Readable Octets : 3904366 Data Rate Mismatches : 0
FCS Errors : 0 Auto Partitions : 0
Alignment Errors : 0 Total Errors : 0
Frames Too Long : 0 LSA Changes : 1
Short Events : 0 Last Source Address : 00-00-E8-90-1B-73
Runts : 2 Symbol Errors : 0
Collisions : 65
Return to previous panel.
Use arrow keys to move. <Enter> to confirm.
<Ctrl+T> to return to Main Menu.
Figure 4-28 Port Statistics Menu
4-40 Configuring the System
Page 100

Fast EtherHub 3500 System User’s Guide
Displayed items are briefly described in the following table.
Field Description
Hub ID Hub identifier within the stack.
Position The physical position in the stack (as determined by its position from the top of the FlexBus chain).
Port ID Port identifier on the hub.
Readable Frames Number of good frames received.
Readable Octets Number of good octets received.
FCS Errors Number of Frame Control Sequence errors.
Alignment Errors Number of mis-synchronized data packets detected by this device.
Frames Too Long Number of times frame length has exceeded the maximum allowable size (i.e., 1518 bytes).
Short Events Number of short fragments.
Runts Number of fragments (that were too long to qualify as short events).
Collisions Number of simultaneous node transmissions detected by this device.
Late Events Number of frames where a collision occurred late in the transmission.
Data Rate Mis. Number of frames for which the data rate does not match the local frequency.
Auto Partitions Number of times this port has been automatically partitioned due to jabber.
Total Errors Total number of errors, including FCS, alignment, FramesTooLong, ShortEvents, LateEvents,
Jabber, and DataRateMismatches detected on this device.
LSA Changes Number of times the source address has changed.
Last Source Addr. Last source address.
Symbol Errors Number of symbol errors (i.e., code-group errors including collision artifacts or transmission errors).
Note that these errors are unique to 100 Mbps analog signals.
Table 4.21 Port Statistics Menu
Configuring the System 4-41
 Loading...
Loading...