Page 1

Virus TI Series
Parameter Reference Manual
Page 2

Page 3

Enjoy making waves.
Page 4

Page 5

Table Of Contents
11 Oscillators
Oscillator 1 (Classic)
Oscillator 1 (HyperSaw)
Oscillator 1 (WaveTable)
Oscillator 1 (Wavetable PWM Oscillator)
Tips for auditioning the Wavetables
Oscillator 1 (Simple Grain Table)
Oscillator 1 (Complex Grain Table Oscillator)
Oscillator 1 (Simple Formant Table Oscillator)
Oscillator 1 (Complex Formant Table Oscillator)
Oscillator 2 (Classic)
Oscillator 2 (HyperSaw)
Oscillator 2 (WaveTable)
Oscillator 2 (Simple Grain Table)
Oscillator 2 (Complex Grain Table Oscillator)
Oscillator 2 (Simple Formant Table Oscillator)
Oscillator 2 (Complex Formant Table Oscillator)
Oscillator 2 (Wavetable PWM Oscillator)
Common
Sub Oscillator
Noise
Ring Modulator
TABLE OF CONTENT
37 Filters
Saturation
Filter-1
Filter-2
Common
43 Envelopes
Filter Envelope
Amp Envelope
Page 6

PARAMETER REFERENCE MANUAL6
45 Mod Matrix Parameters
47 Modulator Parameters
LFO 1
LFO 2
LFO 3
LFO 1 Destinations
LFO 2 Destinations
LFO 3 Destination
53 Arpeggiator Parameters
55 Effect Parameters
Delay
Reverb
Low EQ
Mid EQ
High EQ
Distortion
Characters
Chorus
Phaser
Frequency Shifter and Ring Modulator
Ring Modulator
Frequency Shifter
Vocoder
Vocoder Parameters on Mod Matrix
Input Follower
Input Ring Modulator
71 Common
Unison
Velocity Map
Inputs
Categories
Soft Knob
Page 7

79 Multi Mode Parameters
Multi Patch
Bank
Program
Volume
Panorama
MIDI Channel
Output
Transpose
Detune
Priority
Master Clock
Init Volume
Low Key
High Key
Hold Pedal
Volume RX
Prog Change
Patch Volume
Tempo
TABLE OF CONTENT
87 Cong Menu Parameters
MIDI
MIDI Dump RX
MIDI Dump TX
Inputs
Audio Clock
Global Soft Knob settings
Global Tuning
Random Patch Generator (PG)
95 System Settings
Switches
User Interface
Mem Protect
Page 8

PARAMETER REFERENCE MANUAL8
Legal Notice
© Copyright 2009 Kemper Digital GmbH. All rights reserved.
This manual, as well as the software and hardware described in it, is furnished under license and may be
used or copied only in accordance with the terms of such license. The content of this manual is furnished for
informational use only, is subject to change without notice and should not construed as a commitment by
Kemper Digital GmbH.
Kemper Digital GmbH assumes no responsibility or liability for any errors or inaccuracies that may appear in
this book. Except as permitted by such license, no part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a
retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, recording, by smoke
signals or otherwise without the prior written permission of Kemper Digital GmbH.
Virus is a trademark of Kemper Digital GmbH. All other trademarks contained herein are the property of their
respective owners. All features and specications subject to change without notice.
www.access-music.de
support@access-music.de
Page 9

Sound
Parameters
Page 10

PARAMETER REFERENCE MANUAL10
Page 11

OCILLATOR
Oscillators
The Virus TI has a total of ve internal sound-generation sources: Three main oscillators, a sub-oscillator and
a noise generator.
Several different oscillator modes are available, each with its own distinct characteristics, including: Classic
(as in previous Virus models), HyperSaw (up to 9 layered, detunable Saw waves), WaveTable (smoothly interpolated, additive waves with optional PWM), Grain Table and Formant Table (which both work by applying
granular audio techniques to the wavetables).
Oscillator 1 (Classic)
Mode •
Classic, HyperSaw, WaveTable etc.: Selects the basic type of oscillator.
Shape •
Spectral Wave ... Sawtooth ... Pulse: Waveform mix. At minimum, you will only hear one of the 64 spectral
waves, at dead centre you will hear a pure Sawtooth, at maximum a pure Pulse wave. Set intermediate values for different mixtures (these are displayed as percentages).
Modulation destination “Osc1 Shape”.
Wave Select / Pulse Width •
Two distinct functions, depending on the value of the Shape parameter (see below): If Shape is anywhere
below centre, Waveselect/PW will select a spectral wave. If Shape is set to “Sawtooth” or above, the Waveselect/PW knob will control pulse width instead...
Sine, Triangle, Waves 3 to 64: Spectral Wave function. Modulation destination “Osc1WaveSelect“. or 50.0%
to 100%: Pulse width function. Modulation destination “Osc1PulseWidth“.
Semitone •
-48 to +48 semitones: Adjust the pitch of oscillator 1 in semitones. Modulation destination “Osc1Pitch“.
Key Follow •
-64 to +31, Norm, +33 to +63: How much the pitch of oscillator 1 follows the keyboard (i.e. MIDI note
number). Press both Value buttons at the same time for normal tuning (Norm).
Page 12

PARAMETER REFERENCE MANUAL12
Balance •
-64 to +63: Adjusts the relative levels of oscillator 1 and oscillator 2 (including FM), whereby -64 is oscillator 1 only and +63 is oscillator 2 only. Note that this parameter is mirrored in the oscillator 2 menu. Modulation destination “Osc Balance”.
Oscillator 1 (HyperSaw)
This information only applies to oscillator 1 in HyperSaw mode
Mode •
Classic, HyperSaw, WaveTable etc.: Selects the basic type of oscillator.
Density •
1.0 to 9.0: The number of sawtooth waves used. The volumes are cross-faded for completely smooth transitions. Modulation destination “Osc1 Shape“.
Spread •
0 to 127: Detuning of individual sawtooth waves within the HyperSaw. Modulation destination “Osc1
PulseWidth”.
Semitone •
-48 to +48 semitones: Adjust the pitch of oscillator 1 in semitones. Modulation destination “Osc1Pitch“.
Key Follow •
-64 to +31, Norm, +33 to +63: How much the pitch of oscillator 1 follows the keyboard (i.e. MIDI note
number). Press both VALUE buttons at the same time for normal tuning (Norm).
Balance •
-64 to +63: Adjusts the relative levels of oscillator 1 and oscillator 2 (including FM), whereby -64 is oscillator 1 only and +63 is oscillator 2 only. Note that this parameter is mirrored in the oscillator 2 menu. Modulation destination “Osc Balance”.
Sync •
Off, On: Switches oscillator 1 Sync off/on.
Unlike Classic oscillators where oscillator 2 can be synchronized to oscillator 1, HyperSaws are always synchronized to their own internal sync oscillator. In HyperSaw mode, FM Amount controls a frequency offset
Page 13

OCILLATOR
parameter instead, controlling how much higher the pitch of the oscillator is than its master. To differentiate
this function from standard oscillator synchronization, it is called Sync.
Modulation destination “Osc2 FM Amount”.
About HyperSaw and SubOscillators : Similarly, HyperSaw oscillators also have their own integrated sub
oscillators - up to 9 square waves tuned an octave below the main oscillator, one for each saw wave.. To differentiate these from the Classic sub oscillator, they are called HyperSub. The sub oscillator volume control
cross-fades between the main HyperSaw oscillator and its HyperSub.About HyperSaw and SubOscillators.
Similarly, HyperSaw oscillators also have their own integrated sub oscillators - multiple square waves tuned
an octave below the main oscillator. To differentiate these from the Classic sub oscillator, they are called HyperSub.
Sync Frequency •
0 to 127: Adjust the frequency of the internal sync oscillator. If sync is set to off, this parameter will be not
available.
Oscillator 1 (WaveTable)
Mode •
Classic, HyperSaw, WaveTable etc.: Selects the basic type of oscillator.
Index •
0 to 127: This determines the playback position within the currently selected Wavetable. Each of the 128
available values represents either a particular wave or the interpolation of the two nearest waves. Modulating
the Index of a wavetable with an LFO or Envelope will often result in a highly-dynamic variation in the timbre
of a sound, impossible via any other means.
Table •
Sine ... Domina7rix: Selects one of many wavetables.
Interpolation •
Use this parameter to determine how smoothly the different waves in the current Wavetable are blended into
each other as the Wavetable Index of the respective oscillator is swept.
Since the number of waves differs with each Wavetable, the result of this will depend on which table you
have selected.
Each Wavetable refers to a selection of different original waves, through which the oscillator can sweep in realtime. At the default (0) setting of Interpolation, each of the 128 positions of the Wavetable Index represent
Page 14

PARAMETER REFERENCE MANUAL14
a unique mix of the two nearest waves, resulting in a smooth morphing of the timbre as you sweep the Index
position.
With Interpolation at zero position, the waves are blended as smoothly as possible, with the mid-point
between each wave representing a 50/50 mix of the two nearest waves. As you increase the value, an increasingly large “dead-zone” is created between each of the original waves, and the blend rate is increased
accordingly until, at the maximum value (127), a stepping effect is achieved.
The net result is a very different characteristic from when the waves are blended smoothly, in two very important ways: rstly, that slow LFO modulations of Wavetable Index will generally result in a somewhat rhythmic
effect that is difcult to achieve by other means, and secondly, the original waves will be presented much
more distinctly, and may often appear much brighter as a result (not that they are, mind - it’s just that pinpointing the exact value out of 128 possibilities at which a wave is not blended with any other, can be rather
tricky!)
Interpolation is also available as a destination in the Mod Matrix (Osc1/2 Interpolation).
Semitone •
-48 to +48 semitones: Adjust the pitch of oscillator 1 in semitones. Modulation destination “Osc1Pitch“.
Key Follow •
-64 to +31, Norm, +33 to +63: How much the pitch of oscillator 1 follows the keyboard (i.e. MIDI note
number). Press both VALUE buttons at the same time for normal tuning (Norm).
Balance •
-64 to +63: Adjusts the relative levels of oscillator 1 and oscillator 2 (including FM), whereby -64 is oscillator 1 only and +63 is oscillator 2 only. Note that this parameter is mirrored in the oscillator 2 menu.
Modulation destination “Osc Balance”.
Oscillator 1 (Wavetable PWM Oscillator)
The WavePWM oscillator takes two instances of the same wavetable, and phase-shifts them against each
other to achieve an effect reminiscent of the traditional pulsewidth modulation of a pulse wave oscillator.
Mode •
Classic, HyperSaw, WaveTable etc.: Selects the basic type of oscillator.
Index •
This determines the playback position within the currently selected Wavetable. Each of the 128 available values represents either a particular wave or the interpolation of the two nearest waves. Modulating the Index of
Page 15

OCILLATOR
a wavetable with an LFO or Envelope will often result in a highly-dynamic variation in the timbre of a sound,
impossible via any other means.
This parameter can be modulated via the Mod Matrix and the LFO’s - please select Wavetable 1/2 Index
from the list of available destinations
Please note that Table 0 (Sine) contains only a sine wave, and as such, the Index parameter will have no effect on it.
Wavetable •
Selects the current Wavetable - each being a unique collection of different waves from which all manner of
different timbres may be achieved.
PulseWidth •
At zero position, all the even-numbered harmonics are cancelled out, creating a hollow sound similar to a
50% pulse wave - when the value reaches 127, the whole wave is almost entirely cancelled out, resulting in
a much thinner sound.
This parameter can be modulated via the Mod Matrix and the LFO’s - please select Osc1/2 Pulse Width
from the list of available destinations
Detune •
As with traditional PWM, much of the fun comes from modulating the pulsewidth by an LFO, which creates
the characteristic warmth of detuned oscillators - the Detune parameter creates this effect automatically,
with no further modulation assignments.
Interpolation •
Use this parameter to determine how smoothly the different waves in the current Wavetable are blended into
each other as the Wavetable Index of the respective oscillator is swept.
Semitone •
-48 to +48 semitones: Adjust the pitch of oscillator 1 in semitones. Modulation destination “Osc1Pitch“.
Key Follow •
-64 to +31, Norm, +33 to +63: How much the pitch of oscillator 1 follows the keyboard (i.e. MIDI note
number). Press both VALUE buttons at the same time for normal tuning (Norm).
Balance •
-64 to +63: Adjusts the relative levels of oscillator 1 and oscillator 2 (including FM), whereby -64 is oscillator 1 only and +63 is oscillator 2 only. Note that this parameter is mirrored in the oscillator 2 menu.
Page 16

PARAMETER REFERENCE MANUAL16
Hint: If you do not make use of either the PulseWidth or Detune parameters, switch back to Wavetable mode
to save on DSP and increase polyphony!
Tips for auditioning the Wavetables
As with the majority of the Wavetable content, it is advisable to audition them at relatively low pitch (we suggest setting Oscillator Semitone to -24). This is because the lowest audible frequency (the fundamental) in
any table is always pitched to middle C3, but in many of the brighter-sounding tables, the fundamental plays
little part in the overall timbre, and the upper harmonics (often where all the action is) can be very difcult to
perceive at high pitch, or are simply ltered out altogether.
Since there are many differences between the tables in terms of their spectral dynamics, it is a good idea
to audition them all in a variety of different ways. Simply sweeping through the Index by hand is one way,
but can give very misleading impressions as to the usefulness of the table. Try rst with a slow LFO (triangle
wave) and then a fast envelope sweep in both directions to get a better idea of what the table may or may
not be good for.
Remember, for those tables with several contrasting waves, subtle modulation is often the key.
Don’t forget to try them all with different settings of the new Interpolation parameter.
Oscillator 1 (Simple Grain Table)
The remaining oscillator modes all make use of a new technology for the Virus TI, called Grain Table. The
basic idea behind this technology, is to take the existing wavetables, and apply similar techniques as
those used in some granular sampling and pitch-shifting algorithms to open up a whole new world of
possibilities. Each of the two main types: Grain Table and Formant Table are presented in both Simple
and Complex formats. In each case, the Simple mode offers fewer parameters, and a higher polyphony
than Complex, with the values of parameters common to each mode remaining constant.
It’s important to note that the characteristics of the Grain Table and Formant Table oscillators are quite
different to those of traditional “granular” sampling/synthesis techniques, which tend to be associated with other-worldly “clouds” of sound. In the Virus TI, we have instead employed the technology to
achieve a very musical result which should prove every bit as useful as the other oscillator types in all
manner of musical projects.
Mode •
Classic, HyperSaw, WaveTable etc.: Selects the basic type of oscillator.
Page 17

OCILLATOR
Index •
Determines the playback position within the currently selected Wavetable. Each of the 128 available values
represents either a particular wave or the interpolation of the two nearest waves. Modulating the Index of a
wavetable with an LFO or Envelope will often result in a highly-dynamic variation in the timbre of a sound,
impossible via any other means.
This parameter can be modulated via the Mod Matrix and the LFO’s - please select ‘Wavetable 1/2 Index’
from the list of available destinations
Please note that Table 0 (Sine) contains only a sine wave, and as such, the Index parameter will have no effect on it.
Wavetable •
Selects the current Wavetable - each being a unique collection of different waves from which all manner of
different timbres may be achieved.
Formant Shift •
Use this parameter to sweep the pitch of the formants in the wavetable by +/- 64 semitones. The effect is
reminiscent of oscillator sync, and can be useful for both extreme lead sounds (try broad sweeps!), as well
as subtle timbral variations.
The movement within a wavetable will still be recognisable as you sweep through the Index points, but you
will notice a very different character to the same table as played by the standard Wavetable oscillator.
A useful property of the Simple version is that the fundamental frequency can always be heard, no matter
where you set Formant Shift.
This parameter can be modulated via the Mod Matrix and the LFO’s - please select Osc1/2 Formant from
the list of available destinations.
Hint: Use the Simple modes where possible if polyphony is a concern - they eat a lot less DSP power than
the ‘Complex’ modes.
Interpolation •
Use this parameter to determine how smoothly the different waves are blended you sweep the index parameter.
Semitone •
-48 to +48 semitones: Adjust the pitch of oscillator 1 in semitones. Modulation destination “Osc1Pitch“.
Key Follow •
-64 to +31, Norm, +33 to +63: How much the pitch of oscillator 1 follows the keyboard (i.e. MIDI note
number). Press both VALUE buttons at the same time for normal tuning (Norm).
Page 18

PARAMETER REFERENCE MANUAL18
Balance •
-64 to +63: Adjusts the relative levels of oscillator 1 and oscillator 2 (including FM), whereby -64 is oscillator 1 only and +63 is oscillator 2 only. Note that this parameter is mirrored in the oscillator 2 menu.
Oscillator 1 (Complex Grain Table Oscillator)
Here we have the purest application of the Grain Table technology - and a very powerful oscillator indeed.
Mode •
Classic, HyperSaw, WaveTable etc.: Selects the basic type of oscillator.
Index •
Determines the playback position within the currently selected Wavetable. Each of the 128 available values
represents either a particular wave or the interpolation of the two nearest waves. Modulating the Index of a
wavetable with an LFO or Envelope will often result in a highly-dynamic variation in the timbre of a sound,
impossible via any other means.
This parameter can be modulated via the Mod Matrix and the LFO’s - please select Wavetable 1/2 Index
from the list of available destinations.
Please note that Table 0 (Sine) contains only a sine wave, and as such, the Index parameter will have no effect on it.
Wavetable •
Selects the current wavetable - each being a unique collection of different waves from which all manner of
different timbres may be achieved.
Formant Shift •
Use this parameter to sweep the pitch of the formants in the wavetable by +/- 64 semitones. The effect is
reminiscent of oscillator ‘sync’, and can be useful for both extreme lead sounds, as well as subtle timbral
variations.
At 12 o’clock position, the sound will be identical to that of the standard Wavetable oscillator. As you sweep
through the other values you will hear a fascinating shift in the spectra of harmonics, and a very different
character to the same wavetable played by the standard Wavetable oscillator.
In contrast to the Simple version, the fundamental frequency is shifted along with the rest of the wave, resulting in a more dramatic effect.
This parameter can be modulated via the Mod Matrix and the LFO’s - please select Osc1/2 Formant from
the list of available destinations.
Page 19

OCILLATOR
Formant Spread •
By adjusting the spread of the formants, a very complex effect is achieved - something like an unholy alliance between a sub-oscillator and a sync-sweep could be one way of describing it, although the depth of
the effect is highly-dependent on the current value of Formant Shift.
For an effective demonstration, try sweeping from 0 (default) through to 127, with Formant Shift set at 12
o’clock position.
This parameter can be modulated via the Mod Matrix and the LFO’s - please select Osc1/2 Spread from the
list of available destinations.
Local Detune •
Use this parameter to achieve the effect of two detuned oscillators an octave apart. Note that this parameter
is most effective when Formant Spread is set to a relatively low value.
Interpolation •
Use this parameter to determine how smoothly the different waves are blended you sweep the index parameter.
Semitone •
-48 to +48 semitones: Adjust the pitch of oscillator 1 in semitones. Modulation destination “Osc1Pitch“.
Key Follow •
-64 to +31, Norm, +33 to +63: How much the pitch of oscillator 1 follows the keyboard (i.e. MIDI note
number). Press both VALUE buttons at the same time for normal tuning (Norm).
Balance •
-64 to +63: Adjusts the relative levels of oscillator 1 and oscillator 2 (including FM), whereby -64 is oscillator 1 only and +63 is oscillator 2 only. Note that this parameter is mirrored in the oscillator 2 menu.
Hint: Use the ‘Simple’ modes where possible if polyphony is a concern - they eat a lot less DSP power than
the ‘Complex’ modes
Oscillator 1 (Simple Formant Table Oscillator)
The Simple Formant Table oscillator is similar in concept to the Simple Grain Table oscillator, only with one
crucial difference: the formants remain xed as you play up and down the keys. This effectively turns the
oscillator into a kind of lterbank, comprising up to 256 resonant bandpass lter poles, whereby the cutoff of
each pole is determined by the harmonics in the current wavetable index.
Page 20

PARAMETER REFERENCE MANUAL20
Mode •
Classic, HyperSaw, WaveTable etc.: Selects the basic type of oscillator.
Index •
Determines the playback position within the currently selected Wavetable. Each of the 128 available values
represents either a particular wave or the interpolation of the two nearest waves. Modulating the Index of a
wavetable with an LFO or Envelope will often result in a highly-dynamic variation in the timbre of a sound,
impossible via any other means.
This parameter can be modulated via the Mod Matrix and the LFO’s - please select Wavetable 1/2 Index
from the list of available destinations
Please note that Table 0 (Sine) contains only a sine wave, and as such, the Index parameter will have no effect on it.
Wavetable •
Selects the current Wavetable - each being a unique collection of different waves from which all manner of
different timbres may be achieved.
Formant Shift •
Use this parameter to sweep the pitch of the formants in the wavetable by +/- 64 semitones. The effect is
reminiscent of oscillator ‘sync’, and can be useful for both extreme lead sounds, as well as subtle timbral
variations.
The movement within a wavetable will still be recognisable as you sweep through the Index points, but you
will notice a very different character to the same table as played by the standard Wavetable oscillator.
A useful property of the Simple version is that the fundamental frequency can always be heard, no matter
where you set Formant Shift.
This parameter can be modulated via the Mod Matrix and the LFO’s - please select Osc1/2 Formant from
the list of available destinations.
Interpolation •
Use this parameter to determine how smoothly the different waves are blended you sweep the index parameter.
Semitone •
-48 to +48 semitones: Adjust the pitch of oscillator 1 in semitones. Modulation destination “Osc1Pitch“.
Page 21

OCILLATOR
Key Follow •
-64 to +31, Norm, +33 to +63: How much the pitch of oscillator 1 follows the keyboard (i.e. MIDI note
number). Press both VALUE buttons at the same time for normal tuning (Norm).
Balance •
-64 to +63: Adjusts the relative levels of oscillator 1 and oscillator 2 (including FM), whereby -64 is oscillator 1 only and +63 is oscillator 2 only. Note that this parameter is mirrored in the oscillator 2 menu.
Hint: Use the ‘Simple’ modes where possible if polyphony is a concern - they eat a lot less DSP power than
the ‘Complex’ modes!
Oscillator 1 (Complex Formant Table Oscillator)
Similar to the Simple version, the Complex Formant Table oscillator keeps the formants at a xed pitch as
you play up and down the keys. It also introduces the additional parameters found in the Complex Grain
oscillator.
Mode •
Classic, HyperSaw, WaveTable etc.: Selects the basic type of oscillator.
Index •
Determines the playback position within the currently selected Wavetable. Each of the 128 available values
represents either a particular wave or the interpolation of the two nearest waves. Modulating the Index of a
wavetable with an LFO or Envelope will often result in a highly-dynamic variation in the timbre of a sound,
impossible via any other means.
This parameter can be modulated via the Mod Matrix and the LFO’s - please select Wavetable 1/2 Index
from the list of available destinations
Please note that Table 0 (Sine) contains only a sine wave, and as such, the Index parameter will have no effect on it.
Wavetable •
Selects the current Wavetable - each being a unique collection of different waves from which all manner of
different timbres may be achieved.
Formant Shift •
Use this parameter to sweep the pitch of the formants in the wavetable by +/- 64 semitones. The effect is
reminiscent of oscillator ‘sync’, and can be useful for both extreme lead sounds, as well as subtle timbral
variations.
Page 22

PARAMETER REFERENCE MANUAL22
The movement within a wavetable will still be recognisable as you sweep through the Index points, but you
will notice a very different character to the same table as played by the standard Wavetable oscillator.
In contrast to the Simple version, the fundamental frequency is shifted along with the rest of the wave, resulting in a more dramatic effect.
This parameter can be modulated via the Mod Matrix and the LFO’s - please select Osc1/2 Formant from
the list of available destinations.
Formant Spread •
By adjusting the spread of the formants, a very complex effect is achieved - something like an unholy alliance between a sub-oscillator and a sync-sweep could be one way of describing it, although the depth of
the effect is highly-dependent on the current value of Formant Shift.
For an effective demonstration, try sweeping from 0 (default) through to 127, with Formant Shift set at 12
o’clock position!
This parameter can be modulated via the Mod Matrix and the LFO’s - please select Osc1/2 Spread from the
list of available destinations.
Local Detune •
Use this parameter to achieve the effect of two detuned oscillators an octave apart - note that this parameter is most effective when Formant Spread is set to a relatively low value.
Interpolation •
Use this parameter to determine how smoothly the different waves are blended you sweep the index parameter.
Semitone •
-48 to +48 semitones: Adjust the pitch of oscillator 1 in semitones. Modulation destination “Osc1Pitch“.
Key Follow •
-64 to +31, Norm, +33 to +63: How much the pitch of oscillator 1 follows the keyboard (i.e. MIDI note
number). Press both VALUE buttons at the same time for normal tuning (Norm).
Balance •
-64 to +63: Adjusts the relative levels of oscillator 1 and oscillator 2 (including FM), whereby -64 is oscillator 1 only and +63 is oscillator 2 only. Note that this parameter is mirrored in the oscillator 2 menu.
Hint: Use the ‘Simple’ modes where possible if polyphony is a concern - they eat a lot less DSP power than
the ‘Complex’ modes!
Page 23

Oscillator 2 (Classic)
Mode •
Classic, HyperSaw, WaveTable etc.: Selects the basic type of oscillator.
Shape •
As in oscillator 1. Modulation destination “Osc2Shape“.
Wave Select / Pulse Width •
As in oscillator 1. Modulation destination “Osc2WaveSelect“ or “Osc2PulseWidth“.
Semitone •
As in oscillator 1. Modulation destination “Osc2Pitch“.
OCILLATOR
Key Follow •
As in oscillator 1.
Balance •
Mirrors the Balance parameter in the oscillator 1 page.
Detune •
0 to 127: Fine-tunes oscillator 2 upwards. Modulation destination “Osc2Detune“.
FM Mode •
Species the source of FM modulation:
Mode Meaning
Pos Triangle Unipolar triangle wave from oscillator 1
Triangle Bipolar triangle wave from oscillator 1
Wave The selected wave from oscillator 1
Noise The Noise signal
In L, In L+R, In R One or both of the Audio inputs (see rear panel)
Page 24

PARAMETER REFERENCE MANUAL24
FM Amount •
0 to 127: The intensity of frequency modulation. Modulation destination “Osc2 FM Amount“.
FiltEnv>Pitch •
>-64 to +63: How much the lter envelope modulates the pitch of oscillator 2. This was implemented in previous Virus models to facilitate sync sweeps, and has been retained for compatibility reasons.
Modulation destination “FiltEnv>Osc2 Pitch“.
Sync •
Off, On: Activates/deactivates oscillator synchronization. Whenever oscillator 1 starts a new cycle, oscillator 2 resets its phase).
FiltEnv>FM •
-64 to +63: Controls how much lter envelope is applied to FM Amount. This was implemented in previous
Virus models to facilitate FM sweeps, and has been retained for compatibility reasons.
Modulation destination “FiltEnv>FM Amt“.
Oscillator 2 (HyperSaw)
Mode •
Classic, HyperSaw, WaveTable etc.: Selects the basic type of oscillator.
Density •
1.0 to 9.0: The number of sawtooth waves used. The volumes are cross-faded for completely smooth transitions. Modulation destination “Osc2 Shape“.
Spread •
0 to 127: Nominal detuning between individual waves in the HyperSaw. Modulation destination “Osc2
PulseWidth“.
Semitone •
As in oscillator 1. Modulation destination “Osc2 Pitch“.
Page 25

Key Follow •
As in oscillator 1.
Balance •
Mirrors the Balance parameter in the oscillator 1 page.
Detune •
0 to 127: Fine-tunes oscillator 2 upwards. Modulation destination “Osc2 Detune“.
FiltEnv>Pitch •
As in Classic mode.
Sync Frequency •
0 to 127: Adjust the frequency of the internal sync oscillator.
OCILLATOR
Modulation destination “Osc2 FM Amount”.
Oscillator 2 (WaveTable)
Mode •
Classic, HyperSaw, WaveTable etc.: Selects the basic type of oscillator.
Index •
1 to 127: This determines the playback position within the currently selected Wavetable. Each of the 128
available values represents either a particular wave or the interpolation of the two nearest waves. Modulating
the Index of a wavetable with an LFO or Envelope will often result in a highly-dynamic variation in the timbre
of a sound, impossible via any other means.
Table •
Sine ... Domina7rix: Selects one of many wavetables.
Interpolation •
Use this parameter to determine how smoothly the different waves are blended you sweep the index parameter.
Page 26
PARAMETER REFERENCE MANUAL26
Semitone •
As in oscillator 1. Modulation destination “Osc2 Pitch“.
Key Follow •
As in oscillator 1.
Balance •
Mirrors the Balance parameter in the oscillator 1 page
Detune •
0 to 127: Fine-tunes oscillator 2 upwards. Modulation destination “Osc2 Detune“.
FM Mode •
Species the type of FM. Note that the FM modes available in Wavetable mode are different from those
available in Classic mode
Value Meaning
FreqMod Analog-style FM i.e. true frequency modulation.
PhaseMod DX7-style FM i.e. phase modulation.
FM Amount •
0 to 127: Controls the intensity of frequency modulation. Modulation destination “Osc2 FM Amount”.
FiltEnv>Pitch •
-64 to +63: How much the lter envelope modulates the pitch of oscillator 2. This was implemented in previous Virus models to allow (especially) sync sweeps without using up precious space in the modulation
matrix, and has been retained for compatibility reasons. Note that oscillator 2 in WaveTable mode does not
feature Sync. Modulation destination “FiltEnv>Osc2 Pitch“.
FiltEnv>FM •
>-64 to +63: Controls how much lter envelope is applied to FM Amount. Modulation destination
“FiltEnv>FM“.
Oscillator 3 Mode/Wave •
Value The waveform of oscillator 3
Off Deactivates oscillator 3. All other oscillator 3 parameters will be invisible.
Page 27
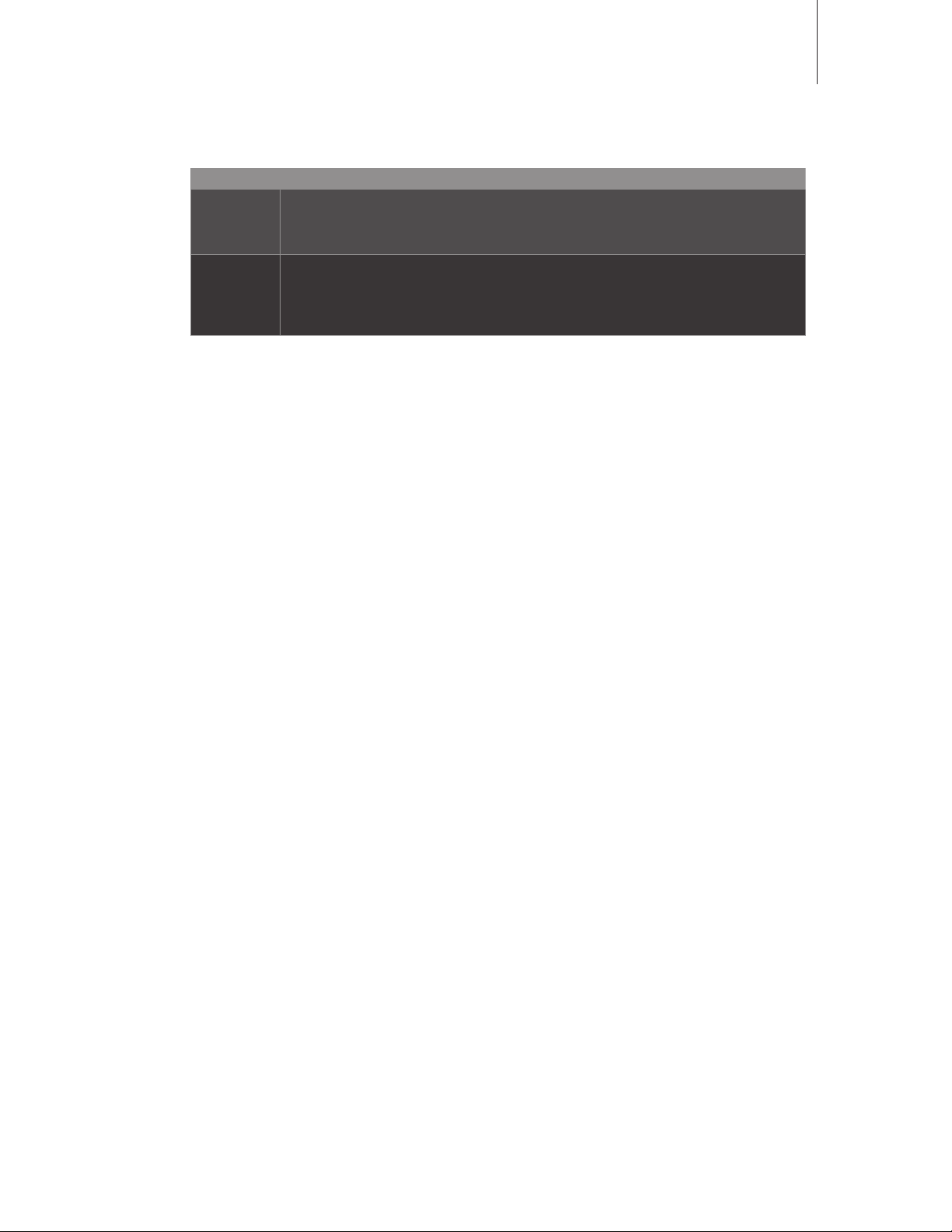
Value The waveform of oscillator 3
OCILLATOR
lave Oscillator 3 will follow oscillator 2. The mixture of waveforms i.e. HAPE and any modulation
aw, Pulse,
ine, Triangle,
Wave 3 to
Wave 64
applied to oscillator 2 will also apply to oscillator 3. The values of “emitone” and “Detune” (see
below) are ignored.
Oscillator3 waveform. Note that if “Pulse” is selected here, its pulse width will follow that of
oscillator 2.
Semitone •
-48 to +48: The pitch of oscillator 3. If Slave mode is selected, this value will be ignored and oscillator 3 pitch
will track oscillator 2 pitch.
Modulation destination “Osc3 Pitch“.
Volume •
0 to 127: The level of oscillator 3 when switched on. See “Mode/Wave” above.
Modulation destination “Osc3 Volume”.
Detune •
0 to -127: Fine-tunes oscillator 3 downwards. Ignored if Slave mode (see “Mode/ Wave” above) is selected.
Modulation destination “Osc3 Detune“.
Oscillator 2 (Simple Grain Table)
Mode •
Classic, HyperSaw, WaveTable etc.: Selects the basic type of oscillator.
Index •
Determines the playback position within the currently selected Wavetable. Each of the 128 available values
represents either a particular wave or the interpolation of the two nearest waves. Modulating the Index of a
wavetable with an LFO or Envelope will often result in a highly-dynamic variation in the timbre of a sound,
impossible via any other means.
Page 28

PARAMETER REFERENCE MANUAL28
Wavetable •
Selects the current Wavetable - each being a unique collection of different waves from which all manner of
different timbres may be achieved.
Formant Shift •
Use this parameter to sweep the pitch of the formants in the wavetable by +/- 64 semitones. The effect is
reminiscent of oscillator sync, and can be useful for both extreme lead sounds (try broad sweeps!), as well
as subtle timbral variations.
Interpolation •
Use this parameter to determine how smoothly the different waves are blended you sweep the index parameter.
Semitone •
-48 to +48 semitones: Adjust the pitch of oscillator 1 in semitones. Modulation destination “Osc1Pitch“.
Key Follow •
-64 to +31, Norm, +33 to +63: How much the pitch of oscillator 1 follows the keyboard (i.e. MIDI note
number). Press both VALUE buttons at the same time for normal tuning (Norm).
Balance •
-64 to +63: Adjusts the relative levels of oscillator 1 and oscillator 2 (including FM), whereby -64 is oscillator 1 only and +63 is oscillator 2 only. Note that this parameter is mirrored in the oscillator 2 menu.
Oscillator 2 (Complex Grain Table Oscillator)
Mode •
Classic, HyperSaw, WaveTable etc.: Selects the basic type of oscillator.
Index •
Determines the playback position within the currently selected Wavetable. Each of the 128 available values
represents either a particular wave or the interpolation of the two nearest waves. Modulating the Index of a
wavetable with an LFO or Envelope will often result in a highly-dynamic variation in the timbre of a sound,
impossible via any other means.
Page 29

OCILLATOR
Wavetable •
Selects the current wavetable - each being a unique collection of different waves from which all manner of
different timbres may be achieved.
Formant Shift •
Use this parameter to sweep the pitch of the formants in the wavetable by +/- 64 semitones. The effect is
reminiscent of oscillator ‘sync’, and can be useful for both extreme lead sounds, as well as subtle timbral
variations.
Formant Spread •
By adjusting the spread of the formants, a very complex effect is achieved - something like an unholy alliance between a sub-oscillator and a sync-sweep could be one way of describing it, although the depth of
the effect is highly-dependent on the current value of Formant Shift.
Local Detune •
Use this parameter to achieve the effect of two detuned oscillators an octave apart. Note that this parameter
is most effective when Formant Spread is set to a relatively low value.
Interpolation •
Use this parameter to determine how smoothly the different waves are blended you sweep the index parameter.
Semitone •
-48 to +48 semitones: Adjust the pitch of oscillator 1 in semitones. Modulation destination “Osc1 Pitch“.
Key Follow •
-64 to +31, Norm, +33 to +63: How much the pitch of oscillator 1 follows the keyboard (i.e. MIDI note
number). Press both VALUE buttons at the same time for normal tuning (Norm).
Balance •
-64 to +63: Adjusts the relative levels of oscillator 1 and oscillator 2 (including FM), whereby -64 is oscillator 1 only and +63 is oscillator 2 only. Note that this parameter is mirrored in the oscillator 2 menu.
Page 30

PARAMETER REFERENCE MANUAL30
Oscillator 2 (Simple Formant Table Oscillator)
Mode •
Classic, HyperSaw, WaveTable etc.: Selects the basic type of oscillator.
Index •
Determines the playback position within the currently selected Wavetable. Each of the 128 available values
represents either a particular wave or the interpolation of the two nearest waves. Modulating the Index of a
wavetable with an LFO or Envelope will often result in a highly-dynamic variation in the timbre of a sound,
impossible via any other means.
Wavetable •
Selects the current Wavetable - each being a unique collection of different waves from which all manner of
different timbres may be achieved.
Formant Shift •
Use this parameter to sweep the pitch of the formants in the wavetable by +/- 64 semitones. The effect is
reminiscent of oscillator ‘sync’, and can be useful for both extreme lead sounds, as well as subtle timbral
variations.
Interpolation •
Use this parameter to determine how smoothly the different waves are blended you sweep the index parameter.
Semitone •
-48 to +48 semitones: Adjust the pitch of oscillator 1 in semitones. Modulation destination “Osc1Pitch“.
Key Follow •
-64 to +31, Norm, +33 to +63: How much the pitch of oscillator 1 follows the keyboard (i.e. MIDI note
number). Press both VALUE buttons at the same time for normal tuning (Norm).
Balance •
-64 to +63: Adjusts the relative levels of oscillator 1 and oscillator 2 (including FM), whereby -64 is oscillator 1 only and +63 is oscillator 2 only. Note that this parameter is mirrored in the oscillator 2 menu.
Page 31

OCILLATOR
Oscillator 2 (Complex Formant Table Oscillator)
Mode •
Classic, HyperSaw, WaveTable etc.: Selects the basic type of oscillator.
Index •
Determines the playback position within the currently selected Wavetable. Each of the 128 available values
represents either a particular wave or the interpolation of the two nearest waves. Modulating the Index of a
wavetable with an LFO or Envelope will often result in a highly-dynamic variation in the timbre of a sound,
impossible via any other means.
Wavetable •
Selects the current Wavetable - each being a unique collection of different waves from which all manner of
different timbres may be achieved.
Formant Shift •
Use this parameter to sweep the pitch of the formants in the wavetable by +/- 64 semitones. The effect is
reminiscent of oscillator ‘sync’, and can be useful for both extreme lead sounds, as well as subtle timbral
variations.
Formant Spread •
By adjusting the spread of the formants, a very complex effect is achieved - something like an unholy alliance between a sub-oscillator and a sync-sweep could be one way of describing it, although the depth of
the effect is highly-dependent on the current value of Formant Shift.
Local Detune •
Use this parameter to achieve the effect of two detuned oscillators an octave apart - note that this parameter is most effective when Formant Spread is set to a relatively low value.
Interpolation •
Use this parameter to determine how smoothly the different waves are blended you sweep the index parameter.
Semitone •
-48 to +48 semitones: Adjust the pitch of oscillator 1 in semitones. Modulation destination “Osc1 Pitch“.
Page 32

PARAMETER REFERENCE MANUAL32
Key Follow •
-64 to +31, Norm, +33 to +63: How much the pitch of oscillator 1 follows the keyboard (i.e. MIDI note
number). Press both VALUE buttons at the same time for normal tuning (Norm).
Balance •
-64 to +63: Adjusts the relative levels of oscillator 1 and oscillator 2 (including FM), whereby -64 is oscillator 1 only and +63 is oscillator 2 only. Note that this parameter is mirrored in the oscillator 2 menu.
Oscillator 2 (Wavetable PWM Oscillator)
Mode •
Classic, HyperSaw, WaveTable etc.: Selects the basic type of oscillator.
Index •
This determines the playback position within the currently selected Wavetable. Each of the 128 available values represents either a particular wave or the interpolation of the two nearest waves. Modulating the Index of
a wavetable with an LFO or Envelope will often result in a highly-dynamic variation in the timbre of a sound,
impossible via any other means.
Wavetable •
Selects the current Wavetable - each being a unique collection of different waves from which all manner of
different timbres may be achieved.
PulseWidth •
At zero position, all the even-numbered harmonics are cancelled out, creating a hollow sound similar to a
50% pulse wave - when the value reaches 127, the whole wave is almost entirely cancelled out, resulting in
a much thinner sound.
Detune •
As with traditional PWM, much of the fun comes from modulating the pulsewidth by an LFO, which creates
the characteristic warmth of detuned oscillators - the Detune parameter creates this effect automatically,
with no further modulation assignments.
Interpolation •
Use this parameter to determine how smoothly the different waves are blended you sweep the index parameter.
Page 33

OCILLATOR
Semitone •
-48 to +48 semitones: Adjust the pitch of oscillator 1 in semitones. Modulation destination “Osc1 Pitch“.
Key Follow •
-64 to +31, Norm, +33 to +63: How much the pitch of oscillator 1 follows the keyboard (i.e. MIDI note
number). Press both VALUE buttons at the same time for normal tuning (Norm).
Balance •
-64 to +63: Adjusts the relative levels of oscillator 1 and oscillator 2 (including FM), whereby -64 is oscillator 1 only and +63 is oscillator 2 only. Note that this parameter is mirrored in the oscillator 2 menu.
Common
The Common pages contain parameters which affect more than one oscillator at the same time.
Initial Phase •
Value Meaning
Off The phase angle (see glossary) of each oscillator is reset to a random value at the start of each note.
1 to 127 The phase angle of oscillator 1 is xed at 0°, oscillator 2 phase is shifted forward, oscillator 3 phase is
This closely emulates the “free-running” oscillators found in real analogue synthesizers.
shifted backwards by the same amount. Because it ensures that the “click”at the start of notes always
sound the same, setting the Initial Phase to a value other than Off is particularly useful for percussive
sounds.
Modulation destination “Osc Initial Phase”.
Key Mode •
Value Meaning
Poly Polyphonic
Mono 1 Monophonic, multi-trigger, full portamento
Mono 2 Monophonic, multi-trigger, legato portamento
Mono 3 Monophonic, single-trigger, full portamento
Mono 4 Monophonic, single-trigger, legato portamento
Page 34

PARAMETER REFERENCE MANUAL34
Value Meaning
Hold Polyphonic. Notes are held until they are all released and a new note is played.
Osc Volume •
-64 to -63: Determines the total level of all oscillators and input signals (but not Noise or Ring Modulator) immediately before entering the lters. Note: The value 0 is unity gain i.e. already maximum volume - positive
values control Saturation intensity only.
Modulation destination “OscVolume“.
Portamento •
Off, 1 to 127: Determines how slowly the pitch of notes glides from one to the next. The actual effect of portamento depends on the KeyMode.
Modulation destination “Portamento”.
Punch •
>0 to 127: Enhances the percussive effect of short Attack times in the amplier envelope. At higher values,
Punch becomes a noticeable “snap” at the start of each note.
Modulation destination “Punch Intensity”.
FiltEnv>Sync Frequency •
-64 to +63: Controls how much lter envelope is applied to. Only visible if at least one of the oscillators is in
HyperSaw mode.
Sync Offset. Analogous to FiltEnv>FM in the other oscillator models. If oscillators 1 and 2 are both HyperSaws, this parameter modulates the Sync Offset of both oscillators at the same time. Note that it will not
effect oscillator 1 if SYNC is not active.
Modulation destination “FiltEnv>FM/Sync”.
Sync Frequency •
0 to 127: The frequency offset of the audible HyperSaw with
Only visible if at least one oscillator is in HyperSaw mode. Directly accessible from the panel via FM Amount.
respect to its own internal “master” oscillator. Modulation destination “Osc2 FM Amount”.
Page 35

OCILLATOR
Sub Oscillator
An extra “slave” oscillator tuned an octave below its master oscillator. If oscillator 1 is in Classic mode, the
sub-oscillator is a Square or Triangle wave slaved to oscillator 1. If either oscillator 1 or 2 is in HyperSaw
mode, the sub oscillator is HyperSub instead
Volume •
0 to 127: Sub oscillator mix. In HyperSaw mode, this parameter crossfades between HyperSaw and HyperSub.
Modulation destination “SubOscVolume“.
Shape •
Square, Triangle: Selects the sub oscillator waveform.
Not available if oscillator 1 is in HyperSaw or WaveTable mode.
Noise
Volume •
Off, 1 to 127: The level of noise. If set to Off, the Color parameter will not be visible.
Modulation destination “Osc Noise Vol“.
Color •
-64 to +63: Adjusts the noise frequency range. Negative values are darker, positive ones are brighter. A value
of 0 is standard “white noise”.
Modulation destination “Osc Noise Color“.
Ring Modulator
The Ring Modulator creates additional frequencies (the sum and difference) by multiplying the oscillator 1
and 2 signals. It cannot be active in Split Mode.
Page 36

PARAMETER REFERENCE MANUAL36
Volume •
Off, 1 to 127: The output level of the ring modulator. Independent of Osc Volume.
Modulation destination “Ring Modulator“.
Page 37

FILTER
Filters
The Virus TI has two multimode lters that can be congured in series, parallel or split (i.e. separate left and
right channels with differing signal sources).
Saturation
Type Meaning
Off No saturation. Note that positive OC VOLUME values will still control “analog”
Light, oft, Medium, Hard,
Digital
Wave haper inusoidal waveshaping. Can cause drastic changes to a waveform comparable
Rectier Full wave rectication. Inverts half of the signal, thus distorting the sound.
Bit Reducer Bit depth reduction. Generates digital quantization noise similar to early samplers.
Rate Reducer ample rate reduction. Generates digital aliasing similar to early samplers.
Rate+Follow Rate reduction with Key Follow.
Low Pass imple low pass lter.
Low+Follow Low Pass with Key Follow.
High Pass imple high pass lter.
High+Follow High Pass with Key Follow.
saturation if an Analog lter model is selected.
Four different distortion curves.
to linear FM. Note that the Wave haper already starts to take effect at low
OC VOLUME (i.e. negative values).
Osc Volume / Saturation •
-64 to -63:Because the OSC VOLUME knob also controls saturation, this parameter changes its name depending on the value. Please remember that some saturation types (especially Wave Shaper) already take
effect below the central position.
Page 38

PARAMETER REFERENCE MANUAL38
Filter-1
Cutoff •
0 to 127: Filter 1 threshold frequency.
Modulation destination “Filter1 Cutoff”.
Resonance •
0 to 127: Accentuation of the lter 1 Cutoff frequency. The actual effect of resonance depends on the selected Mode (see below).
Modulation destination “Filter1 Resonance”.
Env Amount •
0 to 127: The amount of lter envelope applied to lter 1 Cutoff. Note that this effect can be inverted.
Modulation destination “Filter 1 Env Amount”.
Mode •
Filter Mode Meaning
Low Pass LP. Allows frequencies below the cutoff point to pass through i.e rejects those above the
High Pass HP. Allows frequencies above the cutoff point to pass through i.e. rejects those below the
Band Pass BP. Allows frequencies close to the cutoff point to pass through i.e. simultaneously rejects
Band top B. Rejects frequencies close to the cutoff point i.e. allows frequencies above or below the
Analog 1 .. 4 Pole Emulation of a classic analog cascade (or ladder) lter, but with a variable number of
cutoff point
cutoff point
those above and below the cutoff point
cutoff point to pass through. Note that Resonance effectively narrows this band, making the
effect actually more subtle.
poles. In this mode, the aturation Type is ignored - it is replaced by MiniMoog™ style lter
saturation. This type is interesting for experimentation, often yielding surprising results when
the resonance is set very high.
Page 39

FILTER
About the Analog 1pole..4pole lter modes: In addition to the classic Virus lters, famous for their smooth,
musical character, the Virus TI Snow offers an analog-style lter, inspired by the ‘ladder’ cascade array of
the Minimoog synthesizer. However, where the original offered only a 4-pole lowpass, we have provided the
option to choose between 1 and 4 poles on a single lter. In fact, by using Filter 2 as well, it’s possible to
achieve a 5 or even 6 pole cascade lter! Embedded saturation and resonance that can be pushed all the
way to self-oscillation ensure a very convincing analog character.
Tip: Please be aware that when using the Analog lter, the polyphony for that Part will be reduced by up to
50%.
Key Follow •
-64 to +63: How much cutoff follows the MIDI note and pitch bender.
Env Polarity •
Positive, Negative: The effect of Env Amount on lter 1 can be inverted by setting this parameter to Negative.
Filter-2
Cutoff •
0 to 127 or -64 to +63: Filter 2 threshold frequency. If Cutoff Link is active, lter 2 cutoff becomes a bipolar
offset to lter 1 instead of an absolute value.
Modulation destination “Filter2 Cutoff”.
Resonance •
0 to 127: Accentuation of the lter 2 Cutoff frequency. The actual effect of resonance depends on the selected Mode (see below).
Modulation destination “Filter2 Resonance”.
Env Amount •
0 to 127: Filter 2 envelope amount i.e. the amount of lter envelope applied to its cutoff. Note that this can
be inverted by changing the polarity.
Modulation destination “Filter2 Env Amount”.
Page 40

PARAMETER REFERENCE MANUAL40
Mode •
Mode Meaning
Low Pass LP. Allows frequencies below the cutoff point to pass through i.e rejects those above the cutoff
High Pass HP. Allows frequencies above the cutoff point to pass through i.e. rejects those below the cutoff
Band Pass BP. Allows frequencies close to the cutoff point to pass through i.e. simultaneously rejects those
Band top B. Rejects frequencies close to the cutoff point (within a certain “band”) i.e. allows frequencies
point.
point.
above and below the cutoff point.
above or below the cutoff point to pass through. Note that Resonance effectively narrows this
band, making the effect less obvious.
Note that lter 2 does not offer “analog” modes.
Key Follow •
0 to 127: How much cutoff 2 follows the MIDI note and pitch bender.
Modulation destination “Filter2 Key Follow”.
Env Polarity •
Positive, Negative: The effect of Env Amount on lter 2 cutoff can be inverted by setting this parameter to
Negative.
Common
Routing •
Mode Meaning
erial 4 The lters are routed in series, with 2 poles each.
erial 6 The lters are routed in series, lter 1 has 4 poles and lter 2 has 2 poles.
Parallel 4 The lters are routed in parallel with 2 poles each.
Page 41

Mode Meaning
FILTER
plit Mode The lters are also routed in parallel with 2 poles each, but each lter receives a different set of
signals: Oscillator 1 and the sub-oscillator are sent to lter 1, oscillator 2 (including FM), oscillator 3
and noise are sent to lter 2. The ring modulator is disabled.
There is no difference between Serial 4 and Serial 6 if one of the “analog” lter modes is selected .
Filter Balance •
-64 to +63: Put as simply as possible, this is the relative contribution of each lter to the overall output of the
lter section. Actually a complex set of cross-fades, but the result is highly intuitive: At 64 you can only hear
the output of Filter 1. At 0, both lters contribute equally. At +63 you can only hear the output of Filter 2.
Cutoff Link •
Position Meaning
Off The lter 1 CUTOFF knob only affects lter 1.
On The upper CUTOFF knob also controls lter 2. The lower knob (CUTOFF 2) becomes a bipolar (64 to
+63) offset to lter 1 cutoff instead of an independant value.
Key Follow Base •
C-2 to G8: The pivot-note for Key Follow. Notes below and above this point will be affected by Key Follow.
Pan Spread •
0 to 127: The stereo width of the Split mode signal i.e. the relative levels of the left and right signals. Pan
Spread also applies to Unison sounds, and is therefore mirrored in the Master edit menu. Modulation destination “Pan Spread“.
Only visible here in Split mode (see “Routing” above).
Page 42

PARAMETER REFERENCE MANUAL42
Page 43

ENVELOPE
Envelopes
Note that the lter envelope generator can also be used for other purposes by setting Filter Envelope as
source in the Matrix.
Filter Envelope
Attack •
0 to 127: The time it takes for the lter envelope to rise from 0 to maximum.
Decay •
0 to 127: The time it takes to fall from maximum to the Sustain level (see below).
Sustain •
0 to 127: The nominal level after the Decay.
Sustain Slope •
-64 to +63: Negative values cause the sustain phase to decay to zero, positive values cause it to rise to
maximum.
Release •
0 to 127: Starts as soon as a note is released - the time it takes to fall from the current level to zero.
Amp Envelope
Attack •
0 to 127: The time it takes for the amplier envelope to rise from 0 to maximum.
Accessible from the panel via the lower ATTACK knob.
Page 44

PARAMETER REFERENCE MANUAL44
Decay •
0 to 127: The time it takes to fall from maximum to the Sustain level (see below).
Sustain •
0 to 127: The nominal level after the Decay.
Sustain Slope •
-64 to +63: Negative values cause the sustain phase to decay to zero, positive values cause it to rise to
maximum.
Release •
0 to 127: The time it takes to fall from the current level to zero after the note is released.
Accessible from the panel via the amp RELEASE knob.
Page 45

MOD MATRIX PARAMETER
Mod Matrix Parameters
The MOD menu contains all the parameters for the LFOs (Low Frequency Oscillators) and the Modulation
Matrix. You can use a wide variety of modulators to apply dynamic changes to the sound, such as vibrato or
tremolo effects, automated sweeps etc.
The modulation matrix is used for custom control routing. Six sources can be routed to three destinations
each. Available sources include the internal envelopes and LFOs as well as most MIDI controllers, channel
pressure (aftertouch) etc.. The list of destinations includes almost every Single Mode parameter in the Virus.
The information below applies to any slot in the matrix.
Source •
Off, Pitch Bend ... Random: Species the modulation source (envelopes, LFOs, MIDI controllers etc.). This
source can be simultaneously routed to a maximum of three destinations per slot.
Amount •
-64 to +63: Modulation amount for the specied destination. The range is bipolar so that modulation can be
inverted, and amounts are internally doubled so that unipolar destinations can be modulated over their entire
range (i.e. 128 values). The Amount itself can be controlled by another modulation source - modulation destination is e.g. “Slot4 Amount2”.
• Destination
Off ... Wavetable 2 Index: Species a destination parameter.
Page 46

PARAMETER REFERENCE MANUAL46
Page 47

MODULATOR PARAMETER
Modulator Parameters
The MOD menu contains all the parameters for the LFOs (Low Frequency Oscillators) and the Modulation
Matrix. You can use a wide variety of modulators to apply dynamic changes to the sound, such as vibrato or
tremolo effects, automated sweeps etc.
Traditionally, LFOs (low frequency oscillators) are used for cyclic modulation e.g. vibrato, tremolo etc.. Alternatively, two of the three LFOs in the Virus can serve as simple envelopes, so the label “Modulators” seems
more appropriate than “LFOs” for this section.
Note that each LFO in the Virus has a different set of preset destinations, and that LFO3 allows just one destination to be selected.
LFO 1
Cloc • k
Value Meaning
Off LFO1 is not synchronized.
1/64 ... 16/1 LFO1 rate is synchronized to the Clock, expressed as a fraction of one bar in 4/4 time.
Ra • te
0 to 127: The speed of LFO1 when not synchronized (see “Clock” above).
Modulation destination “LFO1 Rate“.
Shap • e
Sine, Triangle, Sawtooth, Square, S&H, S&G, Waves 3 to 64: Species the LFO waveform.
Co • ntour
-64 to +63: Continuous control over LFO waveform.
Modulation destination “LFO1 Contour“
Page 48

PARAMETER REFERENCE MANUAL48
HAPE Negative Positive
ine to Triangle to quare
Triangle to falling aw to rising aw
aw concavity convexity
quare pulse width <50% pulse width >50%
&H --- ---
&G --- ---
3 to 64 zoom into wave ---
Mode •
Mode Meaning
Poly Each voice has its own LFO, and these are slightly detuned against each other.
Mono All voices share a common LFO. Only applies if the parameters Envelope Mode and Trigger Phase
(see below) are both set to “Off”.
Envelope • Mode
Value Meaning
Off tandard (cyclic) LFO mode.
On The LFO effectively becomes an additional Envelope. LFOs in Envelope Mode are unipolar and stop
after completing exactly one cycle. The start/nish point within the wave can be specied via Trigger
Phase...
Trigger • Phase
Off, 1 to 127: When set to Off, LFO1 runs freely i.e. its phase is not reset by every note played (except in Envelope Mode). All other values set the starting point within the wave.
Page 49

MODULATOR PARAMETER
• Key Follow
Off, 1 to 127: How much LFO1 rate is affected by MIDI note number. Note that Key Follow does not apply
when LFOs are in Envelope Mode or are synchronized to the Clock).
LFO 2
All edit parameters for LFO2 are the same as those for LFO1.
LFO 3
The edit parameters for LFO3 are the same as those for LFO1, except that Contour, Envelope Mode and
Trigger Phase are not available in LFO3.
LFO 1 Destinations
Osc1 • Pitch
-64 to +63: How much LFO1 modulates oscillator 1 pitch.
Modulation destination “LFO1>Osc1 Pitch“.
Osc1+2 Pitch •
-64 to +63: How much LFO1 modulates the pitch of all oscillators, controlling the other two values in this
page at the same time.
Osc2 Pitch •
-64 to +63: How much LFO1 modulates oscillator 2 pitch. Note that oscillator 3 automatically follows any
pitch modulation applied to oscillator 2.
Modulation destination “LFO1>Osc2 Pitch“.
• Pulse Width
-64 to +63: How much LFO1 modulates the pulse width of both main oscillators.
Modulation destination “LFO1>Pulse Width”.
Page 50

PARAMETER REFERENCE MANUAL50
• Resonance
-64 to +63: How much LFO1 modulates the resonance of both lters.
Modulation destination “LFO1>Resonance“.
• Filter Gain
-64 to +63: How much LFO1 modulates the total level of all signals before entering the lters.
Modulation destination “LFO1>Filter Gain“.
• Assign Target
Off, Amp Env Attack ... WaveTable 2 Index: Select from a list of available destinations for LFO1.
Amount •
-64 to +63: How much LFO1 modulates the Target parameter.
Modulation destination “LFO1 Assign Amt“.
LFO 2 Destinations
• Cutoff 1
-64 to +63: How much LFO2 modulates lter 1 cutoff frequency. Like automating the CUTOFF knob when
Cutoff Link is switched off.
Modulation destination “LFO2>Cutoff1“.
Cutoff 1+2 •
-64 to +63: How much LFO2 modulates lter 1 and lter 2 cutoff frequencies simultaneously, controlling the
other two values in this page.
Cutoff 2 •
-64 to +63: How much LFO2 modulates lter 2 cutoff frequency. Like automating the CUTOFF 2 knob.
Modulation destination “LFO2>Cutoff2“.
• Shape 1+2
-64 to +63: How much LFO2 modulates the shapes of oscillators 1 and 2 simultaneously.
Page 51

MODULATOR PARAMETER
Modulation destination “LFO2>Shape“.
• FM Amount
-64 to +63: How much LFO2 modulates the amount of frequency modulation.
Modulation destination “LFO2>FM Amount“.
Pano • rama
-64 to +63: How much LFO2 modulates the position of the signal across the stereo outputs. Modulation
destination “LFO2>Panorama“.
• Assign Target
Off, Amp Env Attack ... WaveTable 2 Index: Selects one of the many possible destinations for LFO2.
Amount •
-64 to +63: How much LFO2 modulates the specied Assign Target (see above).
Modulation destination “LFO2 Assign Amt“.
LFO 3 Destination
• Fade In
0 to 127: The amount of LFO3 can be faded in after each note is played: 0 = instantaneous, 127 = about 40
seconds. Particularly useful for delayed vibrato effects etc..
Assign Target •
Value Meaning
Osc1 Pitch Oscillator 1 pitch.
Osc1+2 Pitch The pitch of all oscillators.
Osc2 Pitch Oscillator 2 pitch. Note that oscillator 3 automatically follows any pitch modulation applied
Osc1 Pulse Width The pulse width of oscillator 1.
to oscillator 2.
Page 52

PARAMETER REFERENCE MANUAL52
Value Meaning
Osc1+2 Pulse
Width
Osc2 Pulse Width The pulse width of oscillator 2.
ync Phase When ync is switched on, this denes the absolute phase of oscillator 2 each time it
The pulse width of both oscillators at the same time.
is reset by oscillator 1. Modulating ync Phase can cause effects similar to pulse width
modulation, thus giving the (typically rather cold) sync-sounds more warmth.
Unlike LFO1 and LFO2, LFO3 has only one modulation slot, offering a choice of one of targets above.
Amount •
0 to 127: How much LFO3 modulates the selected target. Note that, unlike the other LFOs, this is a unipolar
parameter.
Modulation destination “LFO3 Assign Amt“.
Page 53

ARPEGGIATOR PARAMETER
Arpeggiator Parameters
ARP is short for Arpeggiator, a clocked processor that normally takes a chord and outputs individual notes,
one after the other. The Arpeggiator in your Virus also features repeated chords, preset and custom rhythmic
patterns, shufe, innite hold etc.
Mode •
Mode Meaning
Off No arpeggiation. No other arpeggiator parameters will be visible.
Up Ascending notes, starting with the lowest note.
Down Descending notes, starting with the highest note.
Up+Down Ascending then descending notes, starting with the lowest note.
As Played In the same order as received MIDI notes.
Random Random note order, random octave (see Octaves parameter below).
Chord Plays all entered notes at the same time.
Octaves •
1 to 4: Notes can be successively transposed up an octave at the start of each new arpeggio cycle. The
value here is equal to the number of cycles before the arpeggio reverts to its original pitch - so a value of 1
means no transposition.
Pattern •
User, 2 to 64: Selects the arpeggiator pattern. A “User” pattern can be created for each program using Virus Control. As well as positions and lengths, most patterns contain extra velocity data for added rhythmic
effect. To apply velocity data, set the Velocity parameters or use the modulation matrix with Velocity as the
source.
Modulation destination “Arp Pattern”.
Page 54

PARAMETER REFERENCE MANUAL54
Resolution •
1/128 to 1/2: The Arpeggiator’s rate expressed as a fraction of a bar in 4/4 time. The minimum rate is therefore one complete arpeggio every 4/4 bar. The standard setting is 1/16 (i.e. 16 beats per bar), and normally
does not need to be changed. The actual rate is determined by the Tempo parameter.
• Note Length
-64 to +63: Scales the lengths (hold time) of all notes. Negative values shorten the notes, positive values
lengthen them. The audible effect of this parameter is highly dependant upon the envelope settings.
Modulation destination “Arp Note Length“.
• Swing Factor
Off, 50.2% to 75.0%: Affects the position (in time) of every other 16th note. At 66% the rhythm is “full swing”
i.e. triplets. The values 16C, 16D, 16E and 16F are the same as those in Apple Logic (a popular sequencer
program).
Modulation destination “Arp Swing“.
Hold •
Value Meaning
Off The arpeggio stops as soon as all notes are released.
On The arpeggio continues after notes are released. Playing new notes after releasing all previous ones
resets the arpeggio (i.e. the original notes disappear). Note that releasing a Hold pedal will stop the
arpeggio until new notes are played.
Page 55

EFFECT PARAMETER
Effect Parameters
‘Effect’ is the generic term used to describe a process which affects the sound of a patch at the output
stage. Traditionally, the output of an instrument, such as a keyboard or guitar, was sent through an external
device, like a chorus or delay unit in order to add an extra dimension to the sound. The Virus TI Snow offers
several such effects internally, and per Part - far more convenient than the 20+ external devices this would
have required otherwise! Furthermore, each of these effects can be modulated by the same sources as the
synth engine, which allows the effects to become an integral part of any sound, and a powerful synthesis
tool in their own right.
The Virus TI Snow offers multiple effects per patch which all can be used at the same time.
Delay
Mode •
Value Meaning
Off No Delay effect.
imple Delay tandard delay effect, the left and right channels have the same nominal delay
Ping Pong 2:1 ... Ping Pong 8:7 The left and right channels have different delay times, indicated by the ratio.
Pattern 1+1 ... Pattern 5+5 The left and right channels can have different delay times. Pattern modes
• Send
Dry, 1 to 126, Wet: Effect send - actually a crossfade i.e. the overall level remains fairly constant (the dry signal is faded out at higher values).
Modulation destination “Delay Send“.
Clo • ck
Off, 1/64 ... 3/4: Synchronized delay rate expressed as a 4/4 bar division.
times.
are always synchronized to the Clock. The TIME / COLOR knob controls the
Coloration parameter.
Page 56

PARAMETER REFERENCE MANUAL56
Delay • Time
0.0 ms to 693.6 ms: Non-synchronized delay expressed in milliseconds. This values is used if Clock (see
above) is set to Off.
Modulation destination “Delay Time”.
• Feedback
0 to 127: For repeated delays. Determines how much of the output signal is fed back into delay input, affecting the number of audible repeats.
Modulation destination “Delay Feedback“.
Coloration •
-64 to +63: Applies progressive ltering within the feedback path (see “Feedback” above). Negative values
make repeats successively mellower, whereas positive values make them brighter. Modulation destination
“Delay Coloration”. The Delay effect has its own dedicated LFO for modulating the delay time. Note that this
can cause interesting pitch modulation and stereo effects.
Mod Rate •
0 to 127: The speed of the delay LFO.
Modulation destination “Delay Mod Rate“.
Mod Depth •
0 to 127: The amount of modulation applied to Delay Time by the delay’s own LFO. Note that the left and
right channels are affected differently, so this parameter can be used to create stereo effects.
Modulation destination “Delay Mod Depth”.
Mod Shape •
Sine, Triangle, Sawtooth, Square, S&H, S&G: The delay LFO’s waveform. Use S&G for “tape echo” type effects.
Reverb
In the signal path, delay and reverb are routed in series i.e. the dry signal plus any delay is sent to the reverb
input.
Page 57

EFFECT PARAMETER
Mode •
Value Meaning
Off No effect. All other parameters will not be visible.
Reverb tandard reverb effect with predelay (see “Predelay” parameter below).
Feedback 1 Reverb effect with a feedback loop in the pre-delay line, thus allowing multiple reverb tails.
Feedback 2 The same as Feedback 1, except that the rst reverb tail appears immediately.
Type •
Ambience, Small Room, Large Room, Hall: Different types of room simulations, in order of size. This parameter affects the so-called “early reections”.
Send •
Dry, 1 to 126, Wet: Effect send. Actually a cross-fade between dry and wet - the overall level remains fairly
constant.
Modulation destination “Reverb Send”.
Clock •
Off, 1/64 ... 3/4: Used to synchronize Predelay to the Clock (see “Predelay” below). Expressed as a 4/4 bar
division.
• Time
0 to 127: The length of the reverb tail. Modulation destination “Reverb Time”.
Dam • ping
0 to 127: For simulating different surface materials by progressively removing higher frequencies. Carpets
and drapes etc. tend to absorb a lot of high frequencies, while tiled oors and walls do not.
Modulation destination “Reverb Damping”.
• Coloration
-64 to +63: Post-EQ for the reverb signal. Negative values are mellower, positive values are brighter.
Modulation destination “Reverb Coloration”.
Page 58

PARAMETER REFERENCE MANUAL58
Pre • delay
0.0 ms to 300.4 ms: The time between the original signal and the reverb signal, expressed in milliseconds.
This can be fed back for multiple reverb tails.
Modulation destination “Reverb Predelay“.Only visible if the Clock parameter is set to Off (see above).
Feed • back
0 to 127: How much of the reverb signal is fed back into it’s own input. The repeat rate is determined by the
Predelay parameter (see “Predelay” above).
Modulation destination “Reverb Feedback”. Only visible in Feedback 1 or Feedback 2 modes.
Low EQ
Frequency •
32 to 458: Low shelf (1 pole) cutoff frequency in Hertz.
Gain •
-16 dB to +16 dB: Low shelf cut or boost.
Mid EQ
Frequency •
19 Hz to 24.0 kHz: Centre frequency of the MID EQ. Values above 10,000 are given in kHz.
Modulation destination “EQ Mid Frequency”.
Q-Factor •
0.28 to 15.4: Bandwidth around the centre frequency. Low values are wider, high values are narrower. For
wah-wah effects, set very high Q-Factor and Gain values, then modulate “EQ Mid Frequency”.
Modulation destination “EQ Mid Q-Factor”.
Page 59

EFFECT PARAMETER
• Gain
-16dB to +16dB: Mid frequency cut or boost, in decibels.
Modulation destination “EQ Mid Gain”.
High EQ
Frequency •
1831 to 24.0: High shelf (1-pole) cutoff frequency in Hertz (values above 10,000 are given in kHz).
Gain •
-16 dB to +16 dB: High shelf cut or boost.
Distortion
Type •
Value Meaning
Off Distortion is disabled.
Light, oft,
Medium &
Hard
Digital Digital clipping. Can even turn a aw wave into a square wave.
Wave
haper
Rectier Full wave rectication with subsequent DC-compensation.
Bit
Reducer
Rate
Reducer
Four analog-style distortion curves with differing characteristics.
A sinusoidal waveshaper, the effect of which is often similar to linear FM. Note that the results of the
haper are highly dependant upon the signal level (see INTENITY below).
Variable reduction of bit-depth. For generating the digital quantization effects typical of early
samplers and digital synthesizers.
Variable reduction of sampling rate. For generating the aliasing effects typical of early samplers and
digital synthesizers.
Page 60

PARAMETER REFERENCE MANUAL60
Value Meaning
Low Pass ingle pole low pass lter for variable reduction of high frequencies. This effect is only included to
High Pass ingle pole high pass lter for variable reduction of low frequencies. Also included for compatibility
The choice of “Distortion” effects are similar those available in the FILTERS menu, but here they treat the signal as a whole, i.e. not each individual voice. The difference is particularly noticeable when playing chords.
Intensity •
0 to 127: Generally determines the amount of effect. In the two lter models (see “Low Pass” and “High
Pass” above), this is the cutoff frequency.
Modulation destination “Distortion Intensity“.
ensure compatibility with older programs (early Virus models did not feature a dedicated EQ section).
reasons.
Analog Boost
Analog Boost can be used to emulate the frequency response of various real analogue synthesizers. Note
that boosting bass frequencies will reduce the proportion of high frequencies in the resulting signal.
Intensity •
Off, 1 to 127: The degree of Analog Boost.
Modulation destination “Analog Boost Int“.
Frequency •
0 to 127: The frequency where Analog Boost is applied. Very high values will even boost mid-range frequencies.
Chorus
Typically, Chorus is a thickening effect caused by modulating a pair of very short delay lines via a dedicated
LFO, then mixing this with the original dry signal. In combination with Feedback, the Chorus effect in your
Virus is also capable of anging, ensemble, vibrato or resonator effects. Note that if the Mix parameter is set
to Off, the other parameters will not be visible in the menu.
Page 61

EFFECT PARAMETER
Mix •
Off, 1 to 127: Cross-fade between the dry and wet signal. Set this to 64 for maximum Chorus, or to 127 for
a vibrato effects. If set to Off, none of the other parameters in this menu will be visible.
Modulation destination “Chorus Mix“.
Delay •
0 to 127: The nominal delay time, modulated by a dedicated LFO (see “Mod Rate” etc. below). Very high
values result in a short but noticable stereo delay effect.
Modulation destination “Chorus Delay“.
Feedback •
-64 to +63: The amount of signal fed back into the Chorus input. The Feedback parameter is bipolar because positive and negative values have different tonal characteristics.
Modulation destination “Chorus Feedback“.
Mod Rate •
0 to 127: Modulation rate - the speed of the dedicated LFO.
Modulation destination “Chorus Mod Rate”.
Mod Depth •
0 to 127: How much the LFO modulates the Delay parameter.
Modulation destination “Chorus Mod Depth“.
Mod Shape •
Sine, Triangle, Sawtooth, Square, S&H, S&G: Selects the waveform used to modulate the Delay parameter.
Phaser
Typically, phasing is the classic “whoosh” effect originally achieved by running two tape machines in parallel,
then slightly changing the speed of one of them. The Virus phaser uses up to six “all-pass” lters to achieve
a very similar effect. In combination with Feedback, the Virus phaser is also capable of resonator, ensemble,
vibrato and anging effects. Note that if the Mix parameter is set to Off, the other parameters will not be visible in the menu.
Page 62

PARAMETER REFERENCE MANUAL62
Mix •
Off, 1 to 127: Cross-fade between the dry and wet signal. Set this to 64 for normal phasing (together with
zero Feedback - see below).
Modulation destination “Phaser Mix“.
Frequency •
0 to 127: The average frequency of resonant peaks (see Spread below). Modulation destination “Phaser Frequency“.
Feedback •
-64 to +63: The amount of signal fed back into the Phaser input, causing a resonance effect. The Feedback
parameter is bipolar because positive and negative values result in different tonal characteristics.
Modulation destination “Phaser Feedback“.
Mod Rate •
0 to 127: Modulation rate - the speed of the Phaser’s dedicated LFO (a triangle wave) used to modulate the
Frequency parameter (see above).
Modulation destination “Phaser Mod Rate“.
Mod Depth •
0 to 127: How much the Frequency parameter (see above) is modulated by the Phaser’s LFO.
Modulation destination “Phaser Mod Depth“.
Stages •
1 to 6: The number of all-pass lters used in the Phaser. This value affects the complexity of the phased signal.
Spread •
0 to 127: How far apart the resonant peaks between multiple stages are. Modulation destination
“Phaser Spread“.
Vocoder
Although available as “effect”, the Virus Vocoder actually replaces the entire lter section i.e. Vocoder and
normal lters cannot be used at the same time within a single program.
Page 63

EFFECT PARAMETER
The Virus vocoder has two banks of up to 32 bandpass lters: One to analyse the frequency spectrum of a
modulator audio signal, and the other to process a carrier signal (usually the internal oscillators) accordingly.
Mode •
Carrier ignal Meaning
Off The Vocoder is disabled, no other Vocoder parameters will be visible.
Oscillator The carrier is the entire oscillator section, including any noise.
Osc Hold Identical to “Osc” except that Hold mode is activated for the vocoder.
Noise The carrier is the noise signal only. The rest of the oscillator section is disabled
In L, In L+R, In R The carrier is one or both of the audio inputs.
Spread •
-64 to +63: Simultaneously controls Carrier Spread and Modulator Spread (see below).
Q-Factor •
-64 to +63: Simultaneously controls Carrier Q and Mod Q (see below), overriding those two parameters.
Only available if both lter SELECT buttons are active.
Carrier Spread •
-64 to +63: How far apart individual Carrier bands are. The standard value is +63 (100% i.e. full range),
negative values effectively invert the order of bands - great for special effects.
Modulation destination “Filter1 Key Follow“.
Carrier Q •
0 to 127: Quality (steepness) of the Carrier bands.
Modulation destination “Filter1 Resonance“.
Modulator Spread •
-64 to +63: How far apart individual Modulator bands are. The standard value is +63 (full range), negative
values effectively invert the order of bands.
Modulation destination “Filter2 Key Follow“.
Page 64

PARAMETER REFERENCE MANUAL64
Mod Q •
0 to 127: Quality (steepness) of the Modulator bands.
Modulation destination “Filter2 Resonance“.
Center Freq •
-64 to +63: Centre frequency of the Carrier bank.
Modulation destination “Filter1 Cutoff“.
Balance •
-64 to +63: Balance between the carrier and modulator signals. For pure vocoder signal, set this value to
<0>.
Modulation destination “Filter Balance“.
Mod Offset •
-64 to +63: Centre frequency offset of the modulator bank relative to the carrier bank.
Modulation destination “Filter2 Cutoff“.
Carrier Attack •
0 to 127: Attack time of the carrier’s own “envelope follower”. Together with Carrier Release, this is used to
smoothen the vocoded signal.
Carrier Release •
0 to 127: Release time of the carrier’s envelope follower. Together with Carrier Attack, this is used to
smoothen the vocoded signal.
Spectral Balance •
0 to 127: Balance between high and low frequencies in the vocoded signal. In effect, this parameter works
like a simple equalizer, determining the overall colour of the vocoder output. Higher values can improve the
clarity of speech.
Modulation destination “Filter Env Slope”.
Bands •
1 to 32: The number of lter bands used. The higher this number, the higher the quality (e.g. speech becomes more intelligible). Lower values are better for robot voices etc..
Modulation destination “Filter Env Release”.
Page 65

Vocoder Parameters on Mod Matrix
Vocoder Parameter Modulation Destination
Carrier Freq Cutoff 1
Mod Freq Offset Cutoff 2
Carrier Q Filter 1 Resonance
Modulator Q Filter 2 Resonance
Q Factor Filter 1 Resonance
Carrier pread Filter 1 Key Follow
Modulator pread Filter 2 Key Follow
pread Filter 1 Key Follow
Carrier Attack Filter Env Attack
EFFECT PARAMETER
Carrier Release Filter Env Decay
pectral Balance Filter Env lope
Bands Filter Env Release
Balance Filter Balance
Input Follower
A modulation signal is extracted from the level of the selected input (see “Input Select” below) and replaces
the lter envelope. To hear any effect, turn up ENV AMOUNT and/or use “Filter Envelope” as source in the
Matrix.
Input Select •
Value Meaning
Off The Input follower is not used. The other parameters in this page will not be visible.
Left, L+R , Right ignal source for the envelope follower.
Page 66

PARAMETER REFERENCE MANUAL66
Attack •
0 to 127: Accessible from the panel via the lter ATTACK knob. Reaction time to sudden peaks in the input
signal level. Used to regulate how smooth the resulting envelope will be.
Modulation destination “Filter Env Attack“.
Release •
0 to 127: Accessible from the panel via the lter DECAY knob. Reaction time to sudden drops in the input
signal level. Used to regulate how smooth the resulting envelope will be.
Modulation destination “Filter Env Decay“.
Sensitivity •
0% to 100%: Accessible from the panel via the lter SUSTAIN knob. Controls the sensitivity of the envelope
follower to its input signal (note that this parameter does not directly affect signal level). The standard value is
50%.
Modulation destination “Filter Env Sustain“.
Input Ring Modulator
The source specied by the Input Select parameter can be ring-modulated with the oscillator signal.
Mix •
Off, 1 to 63, Ringmod, 65 to 126, Input: “Off” means no input ring modulation, other values determine the
balance between the two signals: “1” is mostly the untreated oscillator signal, “Ringmod” is the ring-modulated signal only, and “Input” is the input signal only.
Page 67

COMMON
Common
The ‘Common’ parameters are those which determine the performance of the overall patch, for example
how the pitch bender will affect the pitch, how MIDI velocity will affect certain parameters, how the Soft
Knobs function etc.
In here you nd all paramters which do not belong to a specic section of sound engine.
• Tempo
63 bpm to 190 bpm: The Virus has an internal clock to which the LFOs, arpeggiator and delay/reverb can
be synchronized. The clock automatically slaves to any received MIDI clock signal, otherwise it adopts this
value.
Patch • Volume
0 to 127: Overall volume of a program, particularly useful for balancing levels between different programs
(or Parts when in Multi or Sequencer modes). Note that you may have to keep this value well below 127 to
avoid unwanted distortion, especially when playing many notes at the same time - 100 is a good starting
point. Patch Volume reacts to MIDI CC#7 (Channel Volume) as well as CC#11 (Expression).
Modulation destination “Patch Volume“.
• Panorama
-64 to +63: The position of the signal across the stereo outputs. Reacts to MIDI CC#10 (Panorama).
Modulation destination “Panorama“.
• Transpose
-64 to +63 semitones: Transposes the pitch of the entire program in semitones.
Modulation destination “Transpose“.
• Smooth Mode
Right from the very beginning, we have been applying a technique called “Adaptive Control Smoothing”
(ACS) in all their synthesizer models, thus avoiding the zipper noise that rapid changes (knob movements,
modulation) would otherwise cause.
Page 68

PARAMETER REFERENCE MANUAL68
Bend Up •
-64 to +63 semitones: How much pitch bend is applied to the oscillators when the Pitch Bender (on a keyboard etc.) is at maximum.
Bend Down •
-64 to +63 semitones: How much pitch bend is applied when the Pitch Bender is at minimum.
• Bender Scale
Mode Meaning
Linear Pitch bend is directly proportional to the position of the Pitch Bender.
Exponential Pitch bend sensitivity is lower when the bender is close to its middle position, allowing for more
subtle control over pitch.
Unison
“Unison” means several instances of the same note at the same time. In the Virus, voices can be stacked
up, detuned against each other and spread across the stereo eld (see “Pan Spread” below) for a richer
sound. The trade-off is a reduction in polyphony.
Voices •
Off, Twin, 3 to 16: How many voices are used for each note. “Twin” is relatively efcient, only halving the
maximum polyphony while giving ne control over LFO phase (see below). If set to Off, no other Unison parameters will be visible except Pan Spread (see below).
Detune •
0 to 127: How much the stacked voices are detuned against each other.
Modulation destination “Unison Detune”.
Pan Spread •
0 to 127: The stereo width of the signal. As well as applying to Unison sounds, this parameter also applies to
any Parallel and Split mode sounds so it is still visible even if Voices (see above) is set to Off.
Modulation destination “Pan Spread“.
Page 69

COMMON
LFO Phase •
-64 to +63: How much the phases of all LFOs are shifted against each other. For making Unison sound even
more complex.
Modulation destination “Unison LFO Phase”.
Velocity Map
These pages give you access to several xed destinations for MIDI velocity data (i.e. how hard a key is
struck).
Volume •
-64 to +63: How much velocity affects the total volume of all internal sound generation sources.
Panorama •
-64 to +63: How much velocity affects panorama position.
FM Amount •
-64 to +63: How much velocity affects the amount of frequency modulation (FM) between oscillators 1 and
2. For HyperSaw oscillators, this affects Sync offset instead.
Osc 1 Shape •
-64 to +63: How much velocity affects oscillator 1 Shape. If oscillator 1 is in HyperSaw mode, this is the
Density parameter. If oscillator 1 is in WaveTable mode, this is the Index parameter.
Osc 2 Shape •
-64 to +63: How much velocity affects oscillator 2 Shape. If oscillator 2 is in HyperSaw mode, this is the
Density parameter. If oscillator 2 is in WaveTable mode, this is the Index parameter.
Pulse Width •
-64 to +63: How much velocity affects the pulse width of all main oscillators. For oscillators in HyperSaw
mode, this affects the Spread parameter.
Filter 1 Env Amount •
-64 to +63: How much velocity affects the envelope amount of lter 1.
Page 70

PARAMETER REFERENCE MANUAL70
Resonance 1 •
-64 to +63: How much velocity affects the resonance of lter 1.
Filter 2 Env Amount •
-64 to +63: How much velocity affects the envelope amount of lter 2.
Resonance 2 •
-64 to +63: How much velocity affects the resonance of lter 2.
Inputs
Mode •
Instead of using the internal oscillators, a signal from the external inputs can be treated using the Virus lters,
envelopes and effects.
Value Meaning
Off tandard setting i.e. the Virus oscillators are used as the basic source of sound.
Dynamic The source specied by Input elect (see below) is routed to the FILTER section, the envelopes
tatic The source specied by Input elect is routed to the FILTER section, but all envelopes are ignored.
Input Select •
Left, L+R, Right: Signal from the left, both or right inputs.
remain functional. This means you have to play a note to hear any sound. Although there is only one
audio source, each note has an independant envelope and lter.
The lter section effectively becomes “monophonic”.
Categories
Name Cat 1, Name Cat 2 •
Off, Acid ... Favourites 3: Select Category names. As certain sounds could conceivably belong to more than
one such category (e.g. Bass and Digital), two can be specied.
Page 71

COMMON
Programs are assigned one or two categories to make it easier to nd particular types (Lead, Pad, Drums
etc.) via the SEARCH function.
Soft Knob
As well as being used for editing, the three VALUE knobs below the display function as extra performance
controls called “Soft Knobs” for instant access to parameters that might otherwise not be directly available.
Function as... •
Off, Analog Boost Int ... Velo>Volume: Select from a list of Soft Knob destinations.
Tip: Instead of direct control, it is fairly common to specify a continuous controller (e.g. CC06 Data) here,
then use the same CC as source in the modulation matrix. This method not only lets you control a wider
range of destinations with the Soft Knobs, but also allows multiple destinations with variable ranges - complex morphing at the twist of a knob.
Name •
+3rds ... Width: Species a word that will appear above the VALUE knob - try to choose the most appropriate name for the overall effect of adjusting this knob.
Page 72

PARAMETER REFERENCE MANUAL72 PARAMETER REFERENCE MANUAL74 PARAMETER REFERENCE MANUAL76
Page 73

Page 74

Page 75

Page 76

Page 77

Multi
Parameters
Page 78

PARAMETER REFERENCE MANUAL78
Page 79

MULTI MODE PARAMETER
Multi Mode Parameters
In earlier Virus models, Multi mode programs consisted of multiple Parts, each one referencing a Single
program. The downside: Multi programs depended on the location of all their referenced Singles, so if you
changed any program while working in Single mode, Multi programs would change accordingly.
In the Virus TI Snow however, each of the 4 Parts actually contains the equivalent of a Single program. Parts
also require a few additional parameters (e.g. transposition, keyboard range) which are all accessed via
MULTI EDIT
Multi Patch
The Bank and Program parameters in the rst page are used to copy existing Singles into the current Part.
Part Enable
Off, On: Species whether the selected Part is active.
Bank
A to Z: Selects the bank from which a Single program is automatically copied into the current Part.
Program
0 to 127: Selects the Single program to be automatically copied into the current Part.
Volume
-64 to +63: Bipolar parameter for balancing levels between different Parts.
Page 80

PARAMETER REFERENCE MANUAL80
Panorama
-64 to +63: Stereo position of the Part. Overrides/overwrites the Single parameter of the same name.
MIDI Channel
01 to 16: The MIDI channel to which this Part will respond.
Output
Out1 L ... USB2 R: Sends this Part to the selected analogue or USB output.
Transpose
-48 to +48 semitones: Part transposition. Adds/subtracts from the Single parameter of the same name.
Detune
-64 to +63: Tunes all pitched elements (oscillators, lters) within a fairly narrow range.
Priority
Low, High: Species whether note-stealing will favour the current Part when all voices in the Virus have been
used up. The Virus TI has plenty of voices and applies a very clever note-stealing algorithm, so you should
seldom (or never) notice this happening.
Master Clock
63 bpm to 190 bpm: Species the tempo in Multi mode. Note: this is adopted by all Parts, ignoring individual Tempo values of the original Single Mode programs.
Page 81

MULTI MODE PARAMETER
Init Volume
Off, 1 to 127: Initializes MIDI volume (CC#7) for the current Part whenever this Multi program is selected. See
Volume RX below.
Low Key
C-2 to G8: The lowest MIDI note to which this Part will respond. If this is set higher than High Key (see below), the range between Low Key and High Key is disabled, and all notes outside this range are enabled.
High Key
C-2 to G8: The highest MIDI note to which this Part will respond. If this is set lower than Low Key (see
above), the range between Low Key and High Key is disabled, and all notes outside this range are enabled.
Hold Pedal
Disabled, Enabled: Species whether the Part will respond to MIDI CC#64 (usually a Sustain Pedal).
Volume RX
Disabled, Enabled: Species whether the Part will respond to MIDI CC#7 (Volume).
Prog Change
Disabled, Enabled: Species whether the Part will respond to MIDI Program Change messages. The global
“Program Change” parameter in the CONFIG menu is ignored.
Page 82

PARAMETER REFERENCE MANUAL82
Patch Volume
Quick access to the Patch Volume parameter, used for balancing levels between different programs.
Tempo
Quick access to the internal clock rate In Multi Mode, this controls the Master Clock parameter.
Page 83

MULTI MODE PARAMETER
Page 84

PARAMETER REFERENCE MANUAL84
Page 85

Conguration
Parameters
Page 86

PARAMETER REFERENCE MANUAL86
Page 87

CONFIG MENU PARAMETER
Cong Menu Parameters
This menu is opened by pressing the CONFIG button to the left of the display. It contains global parameters
that determine how the entire Virus works. Conguration data does not have to be explicitly stored.
MIDI
Global Channel
1 to 16: Species a MIDI channel used for SINGLE mode, as well as for switching between MULTI mode
programs via the MIDI message “Program Change”.
Soft Thru
Off, On: Species whether received MIDI data is also directly routed to (i.e. mirrored at) the MIDI out socket.
Before switching this parameter on, make sure there will be no MIDI loop in your system. This parameter has
no effect when working with Virus Control.
MIDI Device ID
1 to 16, Omni (17): Identication number for transmitting/receiving System Exclusive data (see glossary). To
allow SysEx communication between two devices, they must be set to the same device ID. If set to Omni,
the Virus will receive Sysex data with any ID, and transmit with ID = 17.
Arp Note Send
Off, On: Species whether the notes created by the arpeggiator will be sent to the MIDI output instead of the
original played notes.
MIDI Volume
Disabled, Enabled: Species whether MIDI CC#7 (volume) will be recognized.
Program Change
Disabled, Enabled: Species whether the MIDI message “Program Change” will switch Single programs. This
applies to programs in Single mode as well as PARTs in Multi or sequencer mode.
Page 88

PARAMETER REFERENCE MANUAL88
Multi Prog. Change
Disabled, Enabled: Species whether the MIDI message “Program Change” will switch the entire Multi Mode
program if received on the global MIDI channel.
MIDI Clock
Value Meaning
Internal ync Any received MIDI Clock will be ignored. An internally generated clock is used instead.
ync to External Received MIDI Clock will be recognized. This is the standard setting.
end Internally generated MIDI Clock is sent to the MIDI output.
MIDI Dump RX
Receive Dump
The Virus automatically recognizes the type of data appearing at its MIDI input. Whenever individual programs are received, they will appear in the Edit Buffer (see glossary), and must be explicitly stored. Therefore, the following options only apply when receiving entire bank.
Apart from the Snow, all Viruses so far had banks each holding 128 patches. To maintain compatibility,
the Snow uses 2 banks of each 64 patches to load a Bank Dump. Use Virus Control and the Virus Control
Center to overwrite specic patches, banks or ROM locations.
Value Meaning
Disable Program data arriving at the MIDI input will be ignored.
Enable Bank data (128 sounds) will be stored to the Bank from which it was originally dumped,
Force To Bank A+B Bank data is always stored in bank A and B
Force To Bank C+D Bank data is always stored in bank C and D
regardless of which bank is currently selected.
Force To Bank E+F Bank data is always stored in bank E and F
Force To Bank g*h Bank data is always stored in bank G and H
Page 89

Value Meaning
CONFIG MENU PARAMETER
To Edit Buffer Incoming bank data is not stored, but is treated as a series of individual programs. These
Verify Incoming bank data is compared with the memory in the Virus, after which a status
will appear sequentially in the edit buffer – useful for trying out sounds without having to
overwrite an entire bank.
message appears. Use this setting to check whether a bulk dump has been successful.
MIDI Dump TX
Transmit MIDI Dump
Transmits various types of system exclusive data to an external device e.g. a computer or another Virus.
Value Meaning
ingle Buffer The contents of the single Edit buffer i.e. the current ingle program (or Part without the
ingle Bank A All 128 programs in Bank A.
ingle Bank B All 128 programs in Bank B.
ingle Bank C All 128 programs in Bank C.
Multi settings). This function is also available in the TORE menu for easy access.
ingle Bank D All 128 programs in Bank D.
Controller Dump A ingle program, but in the form of a succession of individual parameter changes.
Arrangement All 16 sounds in the current Multi buffer or equencer mode buffer plus the additional
Multi Bank All Multi programs.
These can take the form of MIDI CCs, Polypressure or ysex, depending on the value of
two other parameters. The Controller Dump setting is mainly used for updating the data
in parameter-based editors (e.g. a Logic environment) and can be relatively slow.
“multi” settings.
MIDI Control: Governs how Page A and Page B parameters are handled during MIDI communication with
e.g. a computer or MIDI controller unit. Note that system exclusive data is always recognized, irrespective of
the settings here.
Page 90

PARAMETER REFERENCE MANUAL90
Page A
Value Meaning
ysEx Page A parameters are transmitted/received as system exclusive packets. Controller
Controller Data Page A parameters are transmitted/received in the form of MIDI CC (see glossary)
data reception is disabled.
data.
Page B
Value Meaning
ysEx Page B parameters are transmitted and received in the form of system exclusive
Poly Pressure Page B parameters are transmitted and received in the form of Poly-pressure data.
packets. Controller data reception is disabled.
Inputs
Boost
0 to 127: Boosts the input - use this only for very low level signals.
Input Thru
0 to 127: The level of external signal sent directly to output 1.
Sensitivity
+16 dBV .. -16 dBV: Select sensitivity to suit different external audio sources.
Page 91

Characteristic
Charateristics Meaning
Linear For all applications besides a phono input
CONFIG MENU PARAMETER
Phono Vinyl discs have a special frequency response which generally needs adjusting for. et this
parameter to Phono when either connecting a turntable directly or using audio material
recorded directly from vinyl (i.e. without deemphasis).
Audio Clock
Source
Species the source of audio clock used for synchronization.
ource Meaning
Auto The default setting. Audio clock via UB or /PDIF is automatically recognized, otherwise the
Internal Only use the internally generated audio clock.
Frequency
Frequency Meaning
internal one is used.
44.1 kHz, 48.0 kHz Basic audio clocking frequency.
Page 92

PARAMETER REFERENCE MANUAL92
Frequency Meaning
ynced to Host Virus is slave clocked by host.
Global Soft Knob settings
Destination
Off, Analog Boost Int ... Velo>Volume: Global destination. Used whenever the Soft Knob is left undened in a
program or the Global parameter is set to On here...
Response
Determines when and how parameters react to knob movements. Required because the position of knobs
seldom reects the stored values after changing to another program. The Snap and Rel modes are useful for
preventing sudden changes in the sound, especially during live performance.
Mode Meaning
Off Knobs have no effect whatsoever.
Jump The value jumps immediately to reect the new knob position.
nap The value is not affected until the original is reached by turning the knob.
Rel The value immediately changes in the direction of knob movement (without jumping), but limits may
not be reachable directly – knob positions only reect values after the original (stored) value has
been reached.
Knob Display Time
Mode Meaning
Off Knob values not be displayed.
1 to 127 Knob values will be displayed for up to 7 seconds.
Knob Target
Page 93

CONFIG MENU PARAMETER
Target Meaning
Internal Knobs control internal functions directly and do not send MIDI.
Internal+MIDI Knob data is also sent to MIDI Out.
MIDI Knobs do not directly control internal functions, the data is sent to MIDI Out only. This
setting is similar to the “Local Off” mode found in several other synthesizers.
Global Tuning
Master Tuning
-64 to +63: Fine control over the pitch of the entire Virus, from 50 cents lower to 50 cents higher. A “cent” is
one hundredth of a semitone.
Pure Tuning
Tempered, 1 to 63, Natural, 65 to 126, Pure: Variable degree of “Pure” tuning (see glossary) – slight pitch adjustment of each note within a chord to minimize dissonance between them. The default value is Tempered
i.e. standard (Western) keyboard tuning.
Random Patch Generator (PG)
The Random Program Generator global settings. Use the RANDOM function to randomly modify an existing
program.
Strength
0 to 127: How drastically the Random function will affect program parameters.
Scope
0 to 127: How many program parameters will be affected. Note that if this value is set very high, successive
use of the Random PG will tend to create sounds will little or no tonality.
Page 94

PARAMETER REFERENCE MANUAL94
Page 95

YTEM ETTING
System Settings
This menu is opened by pressing the CONFIG button to the left of the display. It contains global parameters
that determine how the entire Virus works. Conguration data does not have to be explicitly stored.
Switches
All Delays
Disabled, Enabled: Global switch to disable / enable any Delay effects.
All Reverbs
Disabled, Enabled: Global switch to disable / enable any Reverb effects.
All Arpeggiators
Disabled, Enabled: Global switch to disable / enable any Arpeggios.
All EQs
Disabled, Enabled: Global switch to disable / enable any EQ settings.
User Interface
LED Lux
0 to 127: Brightness of all LEDs.
BPM LED Brightness
0% to 100%: Relative brightness of the BPM LED.
LED Mode
Species what the multi purpose BPM/LFO LED will indicate.
Page 96

PARAMETER REFERENCE MANUAL96
Mode Meaning
LFO The default value. LED intensity follows LFO oscillation.
Ext Inputs LED intensity shows the level of external input.
Auto Either of the above, depending on whether there is a signal at the inputs.
Output LED intensity shows output levels.
Voice teal Indicates note-stealing (see glossary). LED intensity follows the immediate levels of notes
being stolen.
LCD Contrast
0 to 127: Optimize the display for different viewing angles.
Mem Protect
Mode Meaning
Disabled Data can be stored.
Enabled Full memory protect – no data can be overwritten.
Page 97

Page 98

PARAMETER REFERENCE MANUAL98
Page 99

Page 100

 Loading...
Loading...