Page 1

WI-1P
Intel Pentium 4 Workstation Board
Socket 478
User’s Manual
4200-0391-01
Rev. 1.00
Page 2

Copyright and Warranty Notice
The information in this document is subject to change without notice and does not
represent a commitment on part of the vendor, who assumes no liability or
responsibility for any errors that may appear in this manual.
No warranty or representation, either expressed or implied, is made with respect to the
quality, accuracy or fitness for any particular part of this document. In no event shall
the manufacturer be liable for direct, indirect, special, incidental or consequential
damages arising from any defect or error in this manual or product.
Product names appearing in this manual are for identification purpose only and
trademarks and product names or brand names appearing in this document are
property of their respective owners.
This document contains materials protected under International Copyright Laws. All
rights reserved. No part of this manual may be reproduced, transmitted or transcribed
without the expressed written permission of the manufacturer and authors of this
manual.
WI-1P
Page 3

Table Of Contents
Chapter 1. Introduction .................................................... 1-1
1.1. Specifications .........................................................................1-1
1.2. Layout..................................................................................... 1-3
1.3. Jumpers & Connectors Description........................................ 1-4
Chapter 2. Hardware Setup.............................................. 2-1
2.1. Install Pentium® 4 CPU and Heatsink Supporting-Base........ 2-1
2.2. System Memory .....................................................................2-3
2.2.1. Memory Configuration Table................................... 2-3
2.2.2. Installing and Removing Memory Modules............. 2-3
2.3. Connectors, Headers, and Switches .......................................2-5
2.3.1. ATX Power Connectors............................................ 2-5
2.3.2. FAN Power Connectors............................................ 2-6
2.3.3. CMOS Memory Clearing Header.............................2-7
2.3.4. PS/2 & USB Device Wake-up Connection Header.. 2-8
2.3.5. Front Panel Switches & Indicators Connection
Headers .....................................................................2-9
2.3.6. Front Panel Audio Connection Header................... 2-10
2.3.7. Internal Audio Sources Connectors........................ 2-11
2.3.8. PCI Slots .................................................................2-12
2.3.9. Additional IEEE1394 Port Connection Header...... 2-13
2.3.10. Additional USB Port Connection Header............... 2-14
2.3.11. System Management Bus Connection Header ....... 2-15
2.3.12. Infrared Device Connection Header .......................2-16
2.3.13. Chassis Intrusion Device Header............................ 2-17
2.3.14. AGP Pro Display Card Slot ....................................2-18
2.3.15. Additional COM2 Port Connection Header ........... 2-19
2.3.16. Floppy and IDE Disk Drive Connectors................. 2-20
2.3.17. Serial ATA Connectors........................................... 2-21
2.3.18. Status Indicators......................................................2-23
2.3.19. External I/O Panel Connectors ...............................2-24
User’s Manual
Page 4

Chapter 3. BIOS Setup...................................................... 3-1
3.1. SoftMenu Setup...................................................................... 3-2
3.2. Standard CMOS Features....................................................... 3-5
3.3. Advanced BIOS Features ....................................................... 3-9
3.4. Advanced Chipset Features.................................................. 3-12
3.5. Integrated Peripherals........................................................... 3-15
3.6. Power Management Setup.................................................... 3-23
3.7. PnP/PCI Configurations .......................................................3-27
3.8. PC Health Status................................................................... 3-30
3.9. Load Fail-Safe Defaults........................................................ 3-32
3.10. Load Optimized Defaults .....................................................3-32
3.11. Set Password......................................................................... 3-32
3.12. Save & Exit Setup ................................................................3-32
3.13. Exit Without Saving ............................................................. 3-32
Chapter 4. Driver Installation .......................................... 4-1
Appendix A. How to Get Technical Support ..................... A-1
WI-1P
Page 5

Introduction 1-1
Chapter 1. Introduction
1.1. Specifications
CPU
• Supports Intel Pentium 4 Northwood/ Prescott Socket 478 processors
with 800/533MHz FSB
• Up to 3.06GHz and higher (Prescott supports 3.4GHz and higher)
• Supports Intel Hyper-Threading Technology
Chipset
• Intel 875P/ ICH-Hance Rapid
• Supports Dual Channel DDR 400/333 with ECC function and Turbo
mode
• Supports Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI)
Memory
• Four 184-pin DIMM sockets
• Supports 144-bit wide Dual Channel DDR 400/333 memory
• Up to 4GB, un-buffered with ECC/ Non-ECC memory capacity
Graphics
• Accelerated Graphics Port slot supports AGP 8X/4X (0.8V/1.5V)
Serial ATA
• 2 channel Serial ATA 150MB/s data transfer rate via Intel Hance
Rapid
• 4 channel Serial ATA 150MB/s data transfer rate via Silicon Image
3114 (Option)
Audio
• 6-Channel AC97 CODEC on board
System BIOS
• Supports ABIT SoftMenu
• Supports Plug-and-Play (PNP)
• Supports Advanced Configuration Power Interface (ACPI)
• Write-Protect Anti-Virus function by AWARD BIOS
• 4MB Flash ROM
User’s Manual
Page 6

1-2 Chapter 1
LAN
• Intel 82547GI single port Gigabit Ethernet Controller
• Front panel LAN Active/Link LED
Extension Slot
• 1x AGP
• 1x PCI 32bit/33MHz (5V)
• 3x PCI-X 64bit/66MHz (3.3V)
Internal I/O Connectors
• 1x Floppy Port supports up to 2.88MB
• 2x Ultra ATA 100/66/33 connectors
• 1x COM port header (COM2)
• 6x Serial ATA 150 connectors
• 1x USB 2.0 header (Each header supports two USB 2.0 devices)
• 1x SM Bus header (For SM Bus and I
• 1x CD-IN, 1x AUX-IN connector
• 1x IEEE1394 header
• 1x IrDA header
2
C)
External I/O Connectors
• 1x PS/2 keyboard, 1x PS/2 mouse port
• 1x printer port
• 1x COM port
• 1x S/PDIF in
• 1x S/PDIF out
• 1x audio connector (Lin-out, Line-in, Mic)
• 1x audio connector (Surround-out, Center/Subwoofer)
• 2x USB 2.0, 1x RJ-45 w/Transformer LAN Connector
• 1x IEEE 1394 connector
Miscellaneous
• ATX form factor (305mm x 243mm)
• Hardware monitoring – Including Fan speeds, Voltages, System
environment temperature
• Chassis intrusion detector header
Specifications and information contained herein are subject to change
without notice.
WI-1P
Page 7
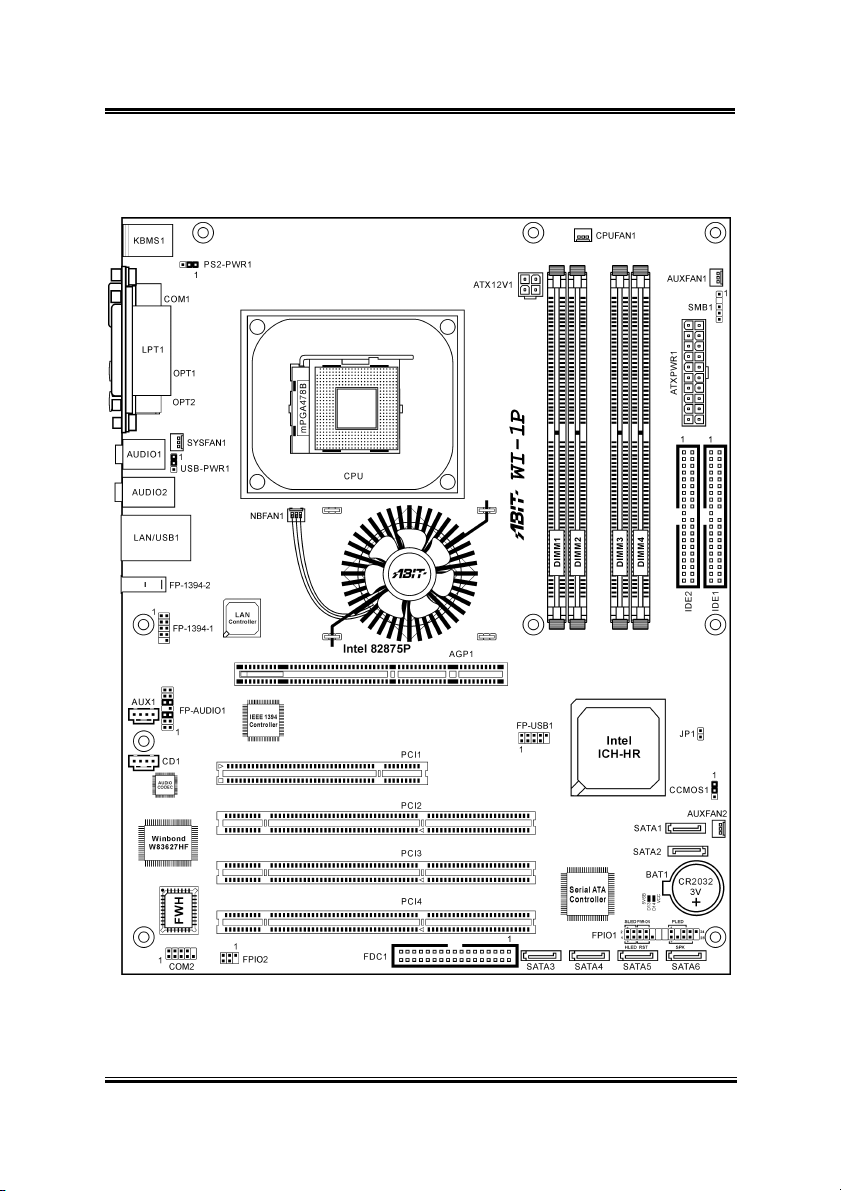
Introduction 1-3
1.2. Layout
User’s Manual
Page 8

1-4 Chapter 1
1.3. Jumpers & Connectors Description
Jumpers Description Default Setting
CCMOS1 CMOS Memory Clearing Header Pins 1-2 Closed (Normal)
JP1 Chassis Intrusion Device Header Opened
Connectors Description
AGP1 AGP Pro Display Card Slot
ATXPWR1/ATX12V1 ATX Power Connectors
CPUFAN1
NBFAN1
SYSFAN1
AUXFAN1/AUXFAN2
CD1/AUX1 Internal Audio Sources Connectors
COM2 Additional COM2 Port Connection Header
DIMM 1~4 DDR DIMM Slots
FDC1 Floppy Disk Drive Connector
FP-1394-1 Additional IEEE1394 Port Connection Header
FP-AUDIO1 Front Panel Audio Connection Header
FPIO1 Front Panel Switches & Indicators Connection Headers
FPIO2 Infrared Device Connection Header
FP-USB1 Additional USB Port Connection Header
IDE1/IDE2 Hard Disk Drive Connectors
PCI1 32bit/33MHz PCI Slot
PCI2/PCI3/PCI4 64bit/66MHz PCI-X Slots
PS2-PWR1
USB-PWR1
SATA1~SATA6 Serial ATA Connectors
SMB1 System Management Bus Connection Header
CPU Fan Power Connector
Chipset Fan Power Connector
System Fan Power Connector
Auxiliary Fan Power Connectors
PS/2 & USB Device Wake-up Connection Header
WI-1P
Page 9
Hardware Setup 2-1
Chapter 2. Hardware Setup
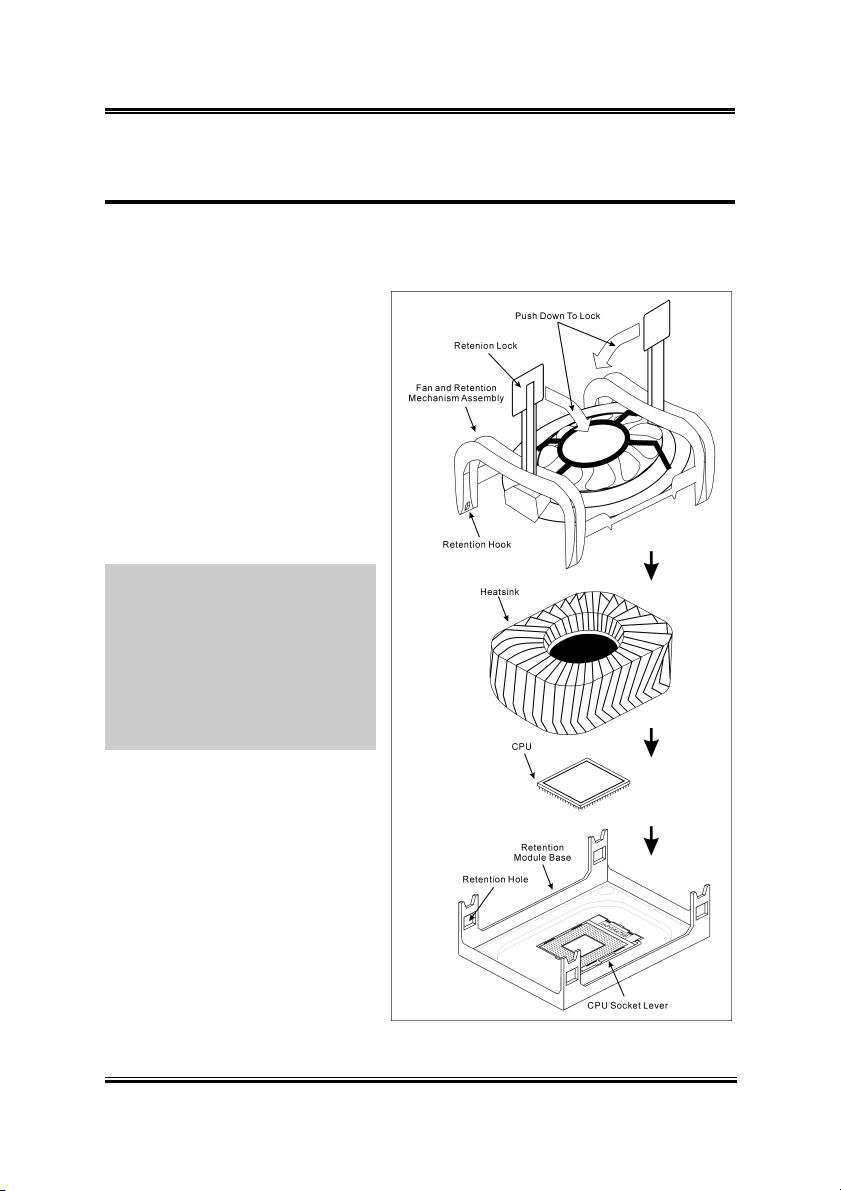
2.1. Install Pentium® 4 CPU and Heatsink Supporting-Base
This motherboard provides a ZIF
(Zero Insertion Force) Socket 478
to install Intel
The CPU you bought should have a
kit of heatsink and cooling fan along
with. If that’s not the case, buy one
specially designed for Pentium
Socket 478.
1. Locate the 478-pin ZIF socket
on the motherboard. Fasten the
Retention Module Base onto the
motherboard.
ATTENTION: If you are using
chassis specially designed for
Pentium® 4, please pay attention to
the location of metal studs or
spacers if they are already installed
on the chassis. Be careful not let the
metal studs or spacers contact the
printed circuit wire or parts on the
PCB.
®
Pentium® 4 CPU.
®
4
2. Pull the CPU socket lever
sideways away from the socket
and then upwards to 90 degree.
Insert the CPU with the correct
orientation. Do not use extra
force to insert CPU; it only fits
in one orientation. Close down
the socket lever while holding
down the CPU.
3. Put the heatsink faces down
onto the CPU until it completely
covers the CPU.
User’s Manual
Page 10

2-2 Chapter 2
4. Put the Fan and Retention Mechanism Assembly onto the heatsink. Make sure all
the four Retention Locks at each side of the Fan and Retention Mechanism
Assembly snap into the Retention Holes.
5. Push down the Retention Lock at both sides of the Fan and Retention Mechanism
Assembly to lock up together with the Retention Module Base.
6. The Fan and Retention Mechanism Assembly and Retention Module Base should
now firmly lock up with each other with the heatsink inside.
ATTENTION: Do not forget to set the correct bus frequency and multiple for your
processor.
WI-1P
Page 11
Hardware Setup 2-3
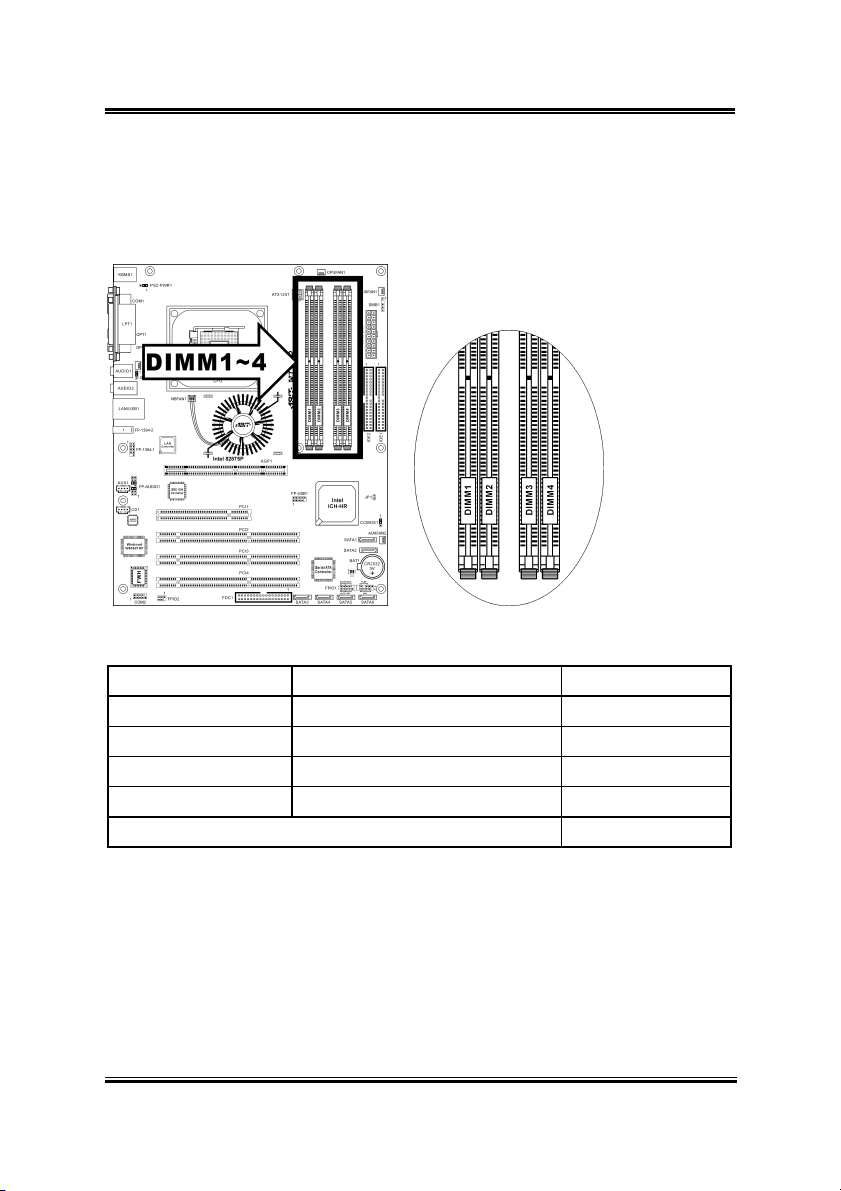
2.2. System Memory
This workstation board provides four 184-pin DDR DIMM slots for Single/Dual
Channel DDR 400/333/266 memory modules with memory expansion size up to 4GB.
2.2.1. Memory Configuration Table
Bank Memory Module Total Memory
Bank 0, 1 (DIMM1) 128, 256, 512MB, 1GB 128MB ~ 1GB
Bank 2, 3 (DIMM2) 128, 256, 512MB, 1GB 128MB ~ 1GB
Bank 4, 5 (DIMM3) 128, 256, 512MB, 1GB 128MB ~ 1GB
Bank 6, 7 (DIMM4) 128, 256, 512MB, 1GB 128MB ~ 1GB
Total System Memory 128MB ~ 4GB
2.2.2. Installing and Removing Memory Modules
To reach the performance of Dual Channel DDR, the following rules must be obeyed:
• When installing TWO DIMM modules: Install DIMM modules of the same
type and size for slots [DIMM1]+[DIMM3] or slots [DIMM2]+[DIMM4].
• When installing FOUR DIMM modules: Install DIMM modules of the
same type and size for slots [DIMM1]+[DIMM3], and slots
[DIMM2]+[DIMM4].
User’s Manual
Page 12
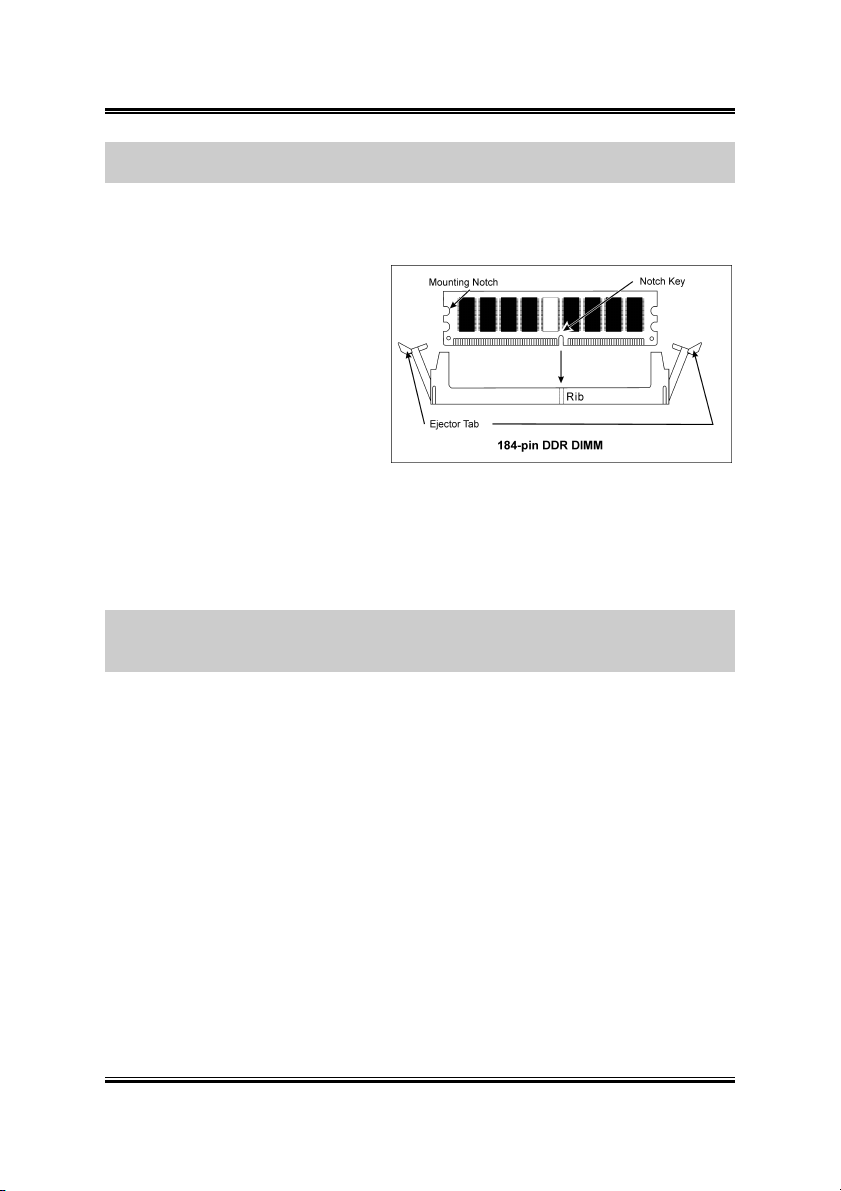
2-4 Chapter 2
NOTE: No hardware or BIOS setup required after adding or removing memory
modules.
Power off the computer and unplug the AC power cord before installing or removing
memory modules.
1. Locate the DIMM slot on the
board.
2. Hold two edges of the DIMM
module carefully, keep away of
touching its connectors.
3. Align the notch key on the
module with the rib on the slot.
4. Firmly press the module into the
slots until the ejector tabs at
both sides of the slot automatically snaps into the mounting notch. Do not force
the DIMM module in with extra force as the DIMM module only fit in one
direction.
5. To remove the DIMM modules, push the two ejector tabs on the slot outward
simultaneously, and then pull out the DIMM module.
ATTENTION: Static electricity can damage the electronic components of the
computer or optional boards. Before starting these procedures, ensure that you are
discharged of static electricity by touching a grounded metal object briefly.
WI-1P
Page 13
Hardware Setup 2-5
2.3. Connectors, Headers, and Switches
All the connectors, headers and switches mentioned here are depending on your
system configuration. Some features you may (or may not) have to connect or to
configure depending on the peripherals you have connected.
WARNING: Always power off the computer and unplug the AC power cord before
adding or removing any peripheral or component. Failing to do so may cause severe
damage to your workstation board and/or peripherals. Plug in the AC power cord only
after you have carefully checked everything.
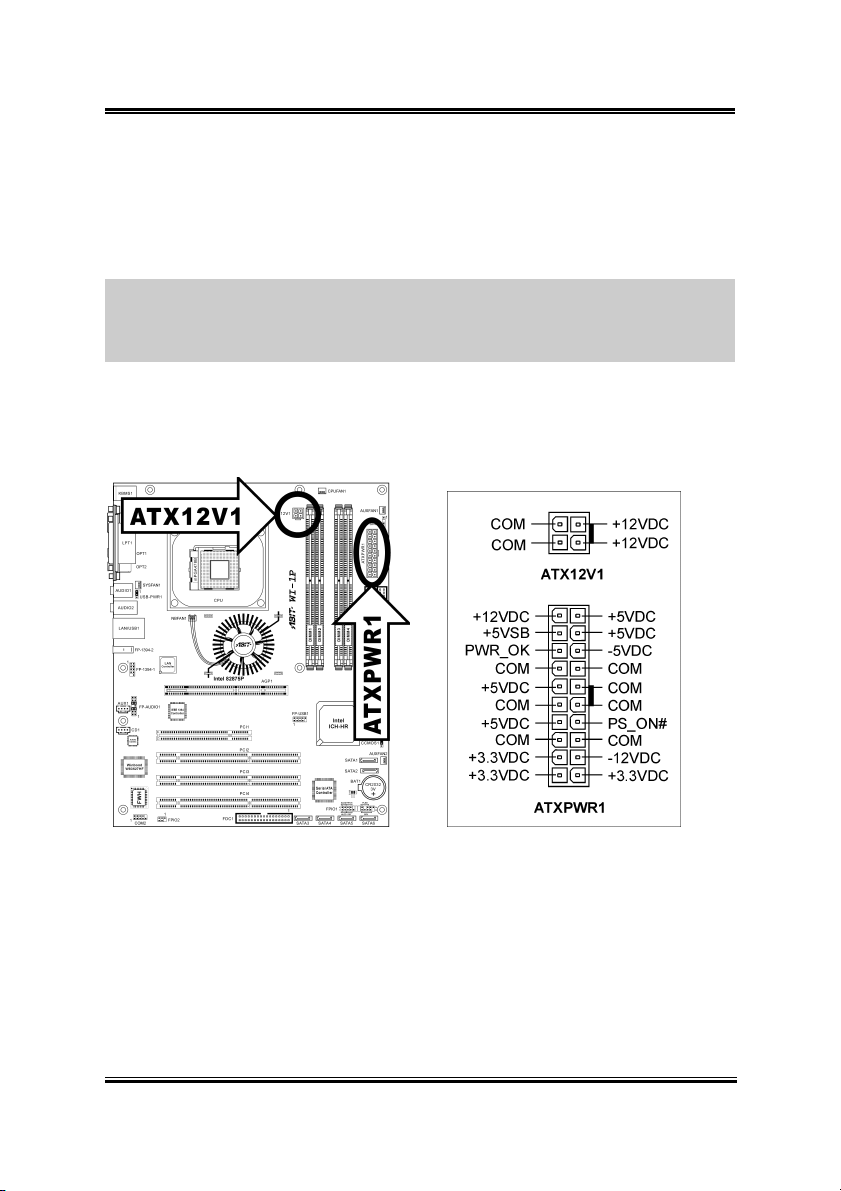
2.3.1. ATX Power Connectors
These two connectors connect to ATX12V power supply.
User’s Manual
Page 14
2-6 Chapter 2
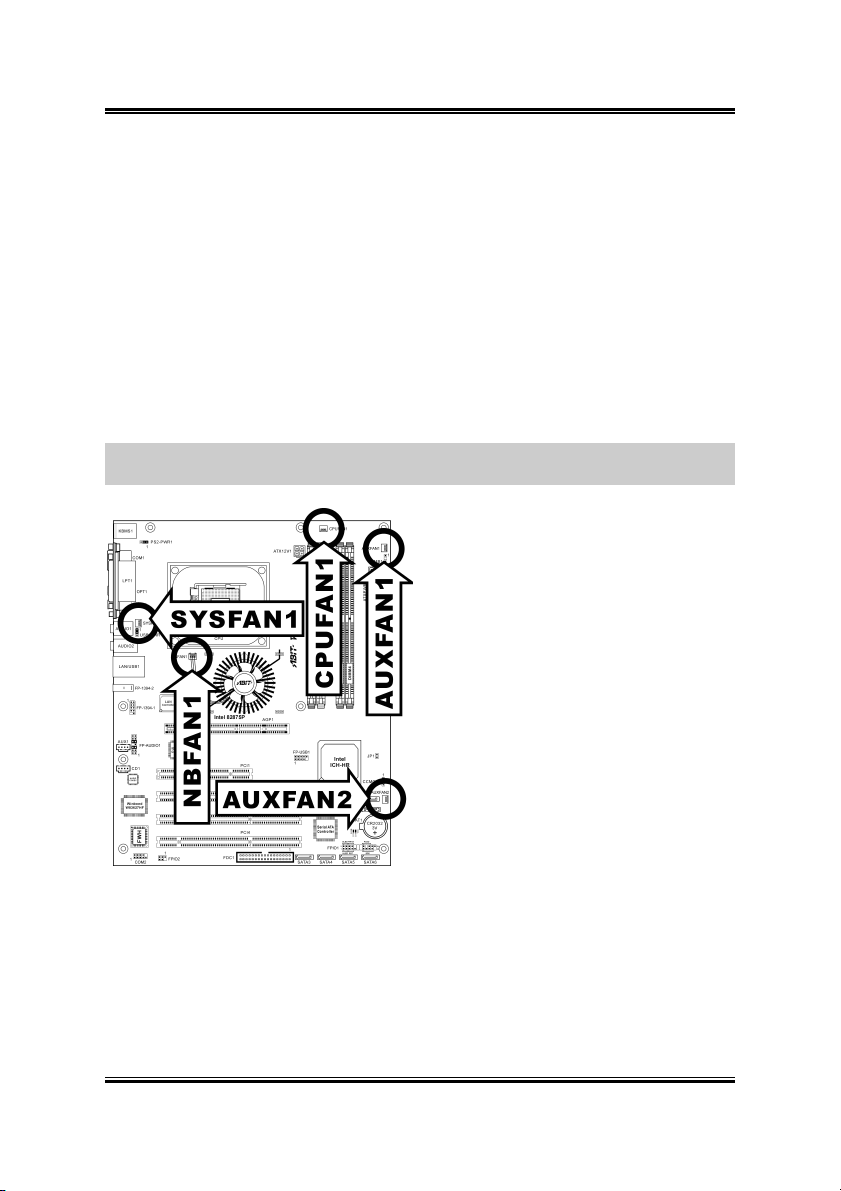
2.3.2. FAN Power Connectors
These 3-pin connectors each provide power to the cooling fans installed in your
system.
The CPU must be kept cool by using a powerful fan with heatsink. The system is
capable of monitoring the speed of the CPU fan.
• CPUFAN1: CPU Fan Power Connector
• NBFAN1: Chipset Fan Power Connector
• SYSFAN1: System Fan Power Connector
• AUXFAN1, AUXFAN2: Auxiliary Fan Power Connectors
WARNING: These fan connectors are not jumpers. DO NOT place jumper caps on
these connectors.
WI-1P
Page 15
Hardware Setup 2-7
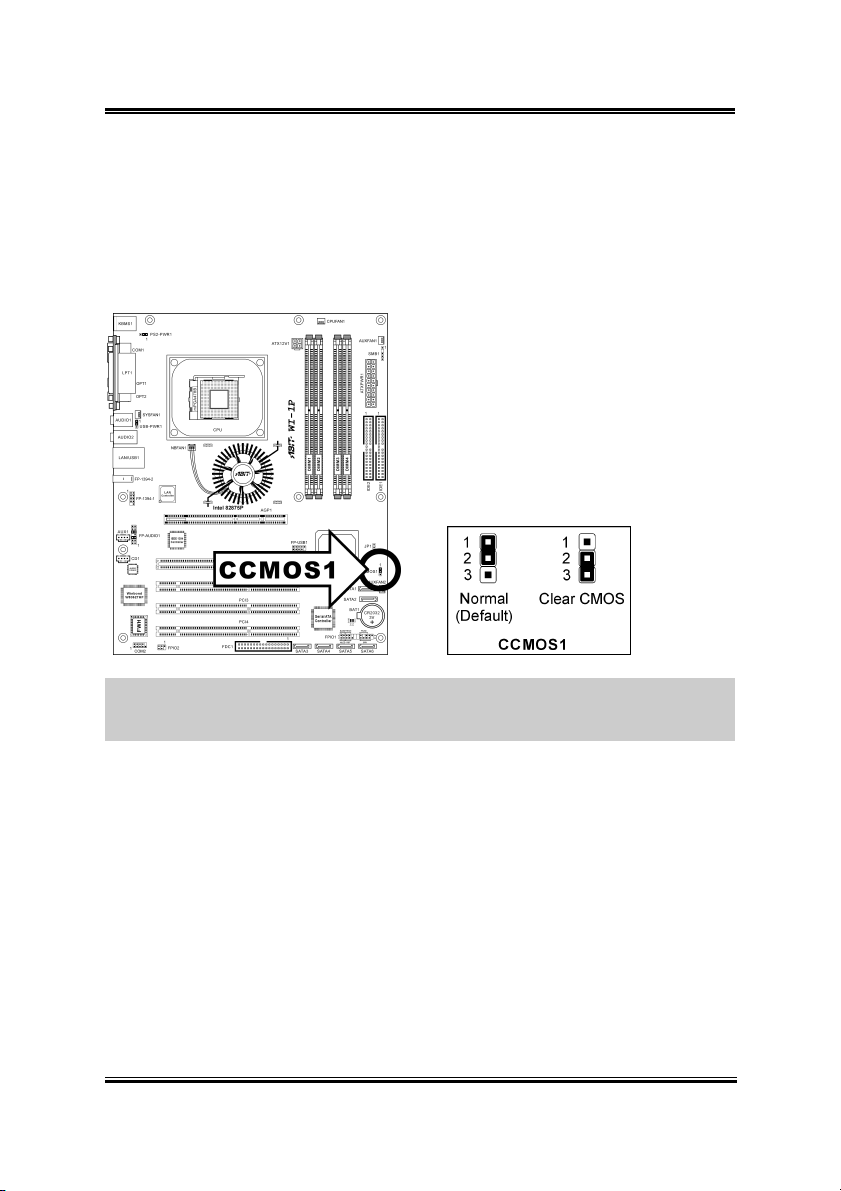
2.3.3. CMOS Memory Clearing Header
This header uses a jumper cap to clear the CMOS memory.
• Pin 1-2 shorted (default): Normal operation.
• Pin 2-3 shorted: Clear CMOS memory.
WARNING: Turn the power off first (including the +5V standby power) before
clearing the CMOS memory. Failing to do so may cause your system to work
abnormally or malfunction.
User’s Manual
Page 16
2-8 Chapter 2
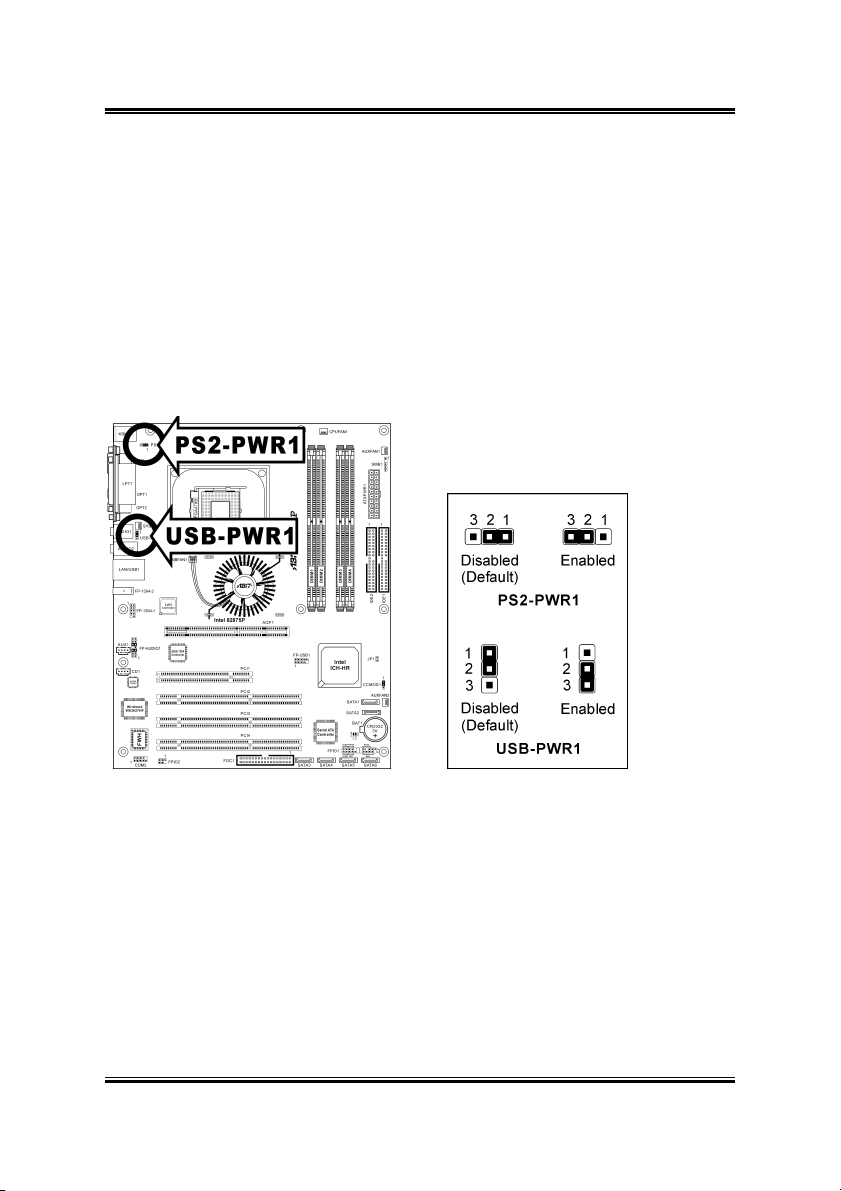
2.3.4. PS/2 & USB Device Wake-up Connection Header
These headers use a jumper cap to enable/disable the wake-up function.
• PS2-PWR1:
Pin 1-2 shorted (default): Disable wake-up function support at
Keyboard/Mouse port.
Pin 2-3 shorted: Enable wake-up function support at Keyboard/Mouse port
• USB-PWR1:
Pin 1-2 shorted (default): Disable wake-up function support at USB1 port.
Pin 2-3 shorted: Enable wake-up function support at USB1 port.
WI-1P
Page 17
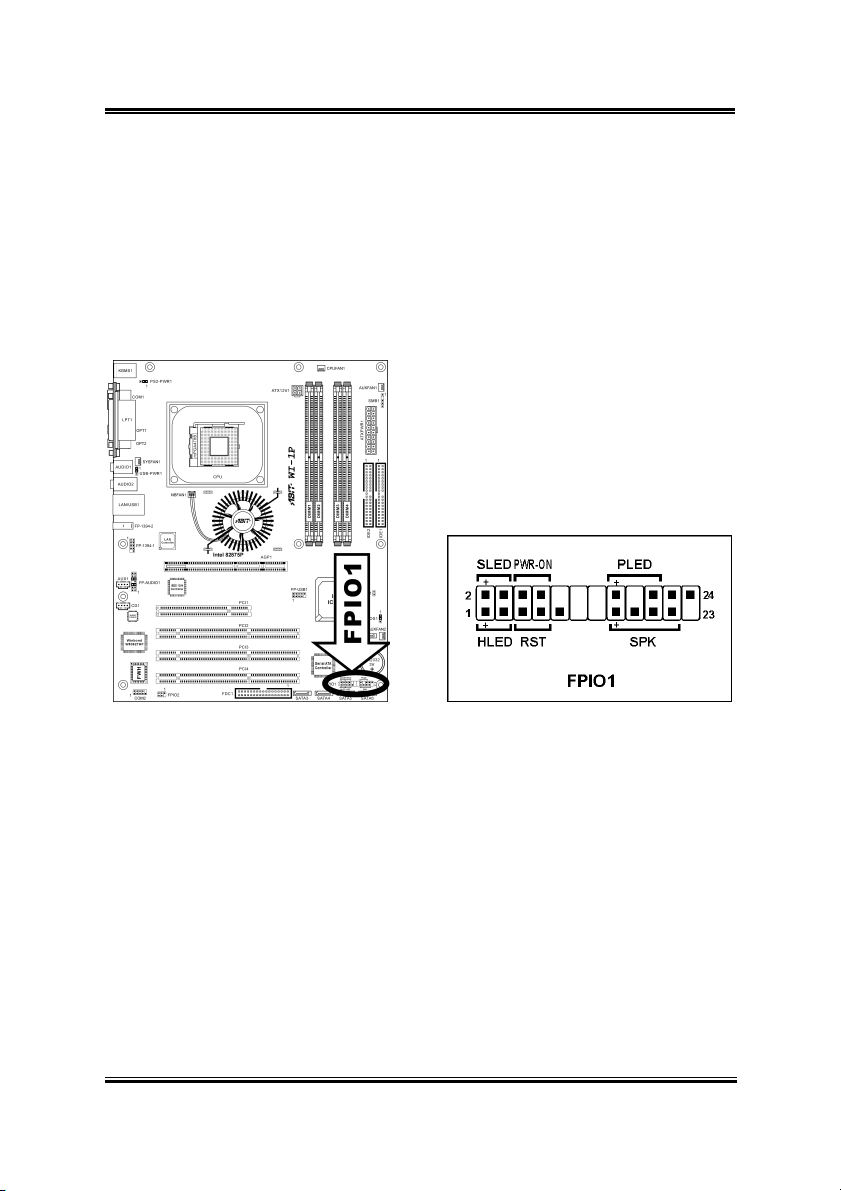
Hardware Setup 2-9
2.3.5. Front Panel Switches & Indicators Connection Headers
This header is used for connecting switches and LED indicators on the chassis front
panel.
Watch the power LED pin position and orientation. The mark “+” align to the pin in
the figure below stands for positive polarity for the LED connection. Please pay
attention to connect these headers. A wrong orientation will only cause the LED not
lighting, but a wrong connection of the switches could cause system malfunction.
• HLED (Pin 1, 3):
Connects to the HDD LED cable of chassis front panel.
• RST (Pin 5, 7):
Connects to the Reset Switch cable of chassis front panel.
• SPK (Pin 15, 17, 19, 21):
Connects to the System Speaker cable of chassis.
• SLED (Pin 2, 4):
Connects to the Suspend LED cable (if there is one) of chassis front panel.
• PWR-ON (Pin 6, 8):
Connects to the Power Switch cable of chassis front panel.
• PLED (Pin 16, 18, 20):
Connects to the Power LED cable of chassis front panel.
User’s Manual
Page 18
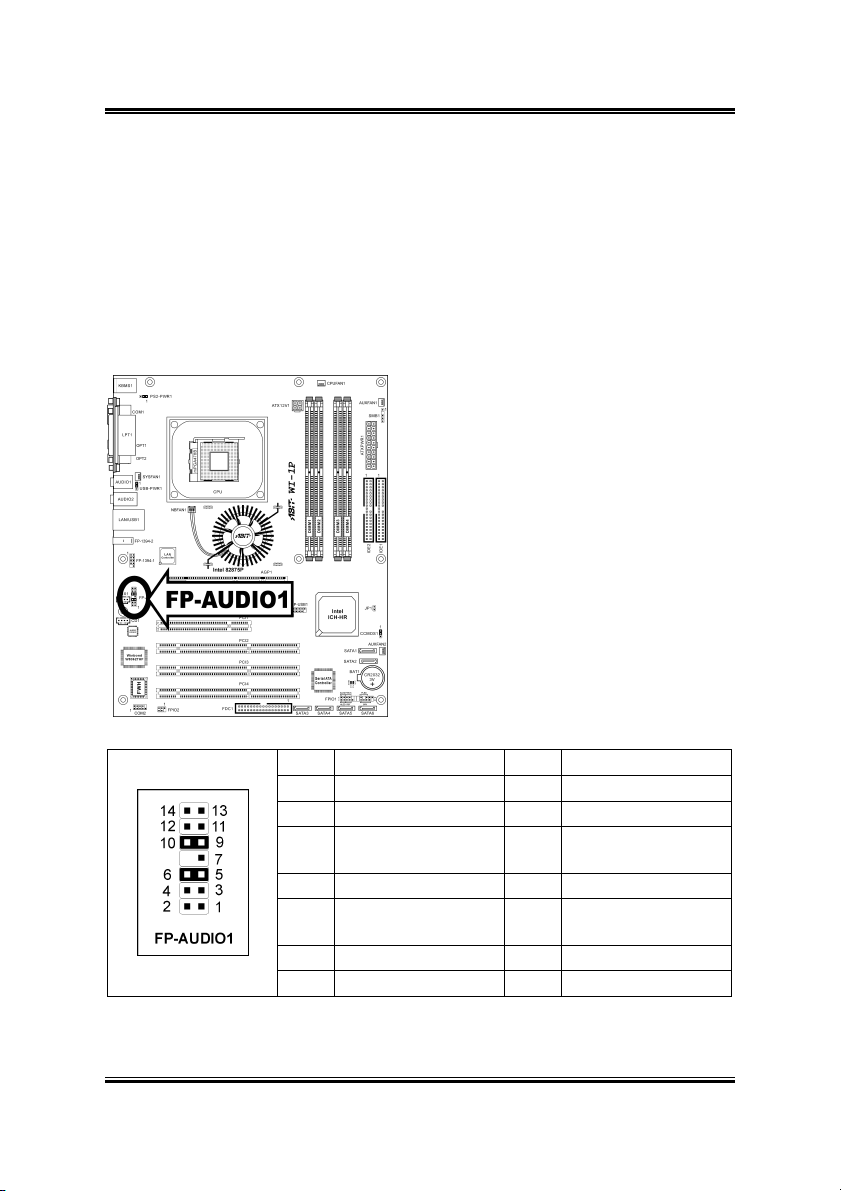
2-10 Chapter 2
2.3.6. Front Panel Audio Connection Header
This header provides the connection to audio connector at front panel.
• To use the audio connector at front panel, remove all the jumpers on this
header, and then connect to front panel by the extension cable provided with
the chassis.
• To use the audio connector at rear panel, disconnect the extension cable,
attach the jumpers back at pin 5-6, and pin 9-10 (default setting).
WI-1P
Pin Pin Assignment Pin Pin Assignment
1 Audio Mic. 2 Ground
3 Audio Mic. Bias 4 VCC
Speaker Out Right
5
Channel
7 X 8 NC
Speaker Out Left
9
Channel
11 Ground 12 S/PDIF In
13 VCC 14 S/PDIF Out
Speaker Out Right
6
Channel Return
Speaker Out Left
10
Channel Return
Page 19
Hardware Setup 2-11
2.3.7. Internal Audio Sources Connectors
These connectors connect to the audio output of internal CD-ROM drive or add-on
audio card.
User’s Manual
Page 20
2-12 Chapter 2
2.3.8. PCI Slots
PCI1: 32bit/33MHz PCI Slot
PCI2/PCI3/PCI4: 64bit/66MHz PCI-X Slots
WI-1P
Page 21
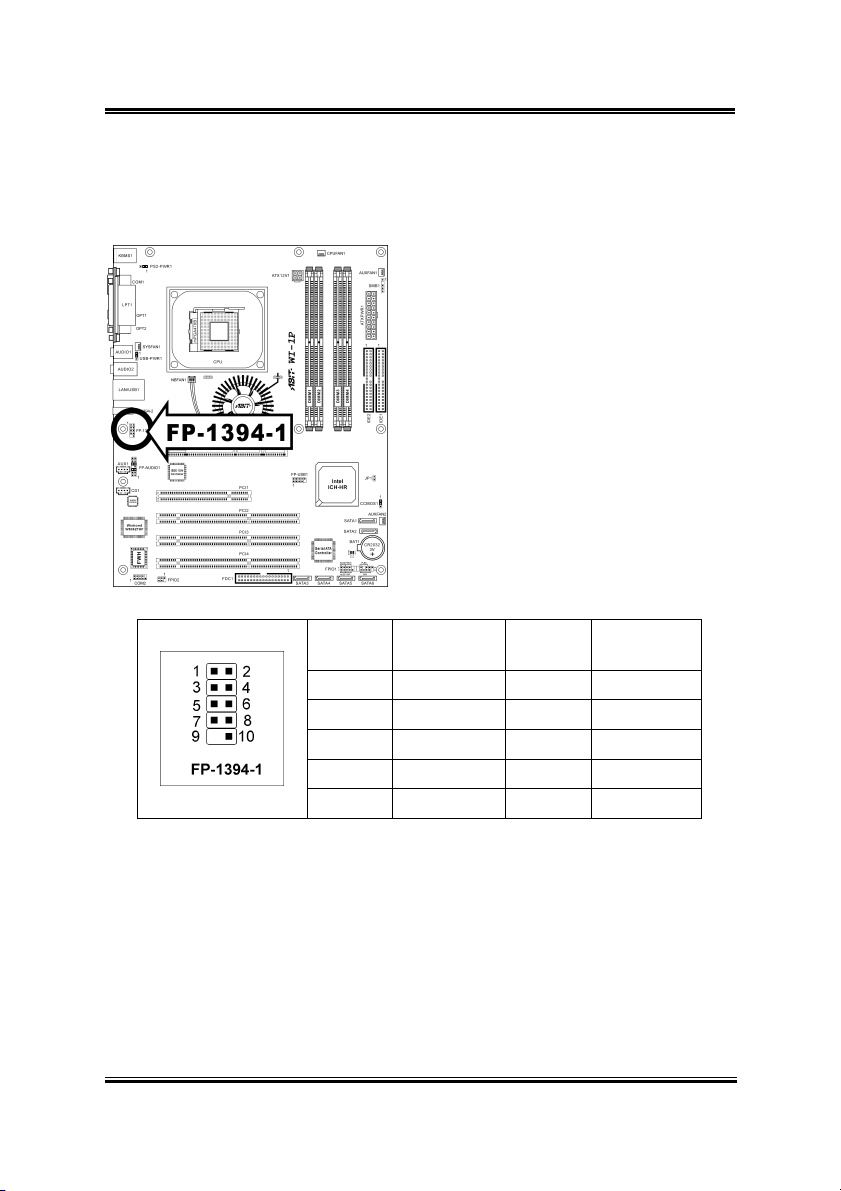
Hardware Setup 2-13
2.3.9. Additional IEEE1394 Port Connection Header
This header provides one external IEEE1394 port connection.
Pin Pin
Assignment
1 TPA1 + 2 TPA1 -
3 Ground 4 Ground
5 TPB1 + 6 TPB1 -
7 +12V 8 +12V
9 NC 10 Ground
Pin Pin
Assignment
User’s Manual
Page 22
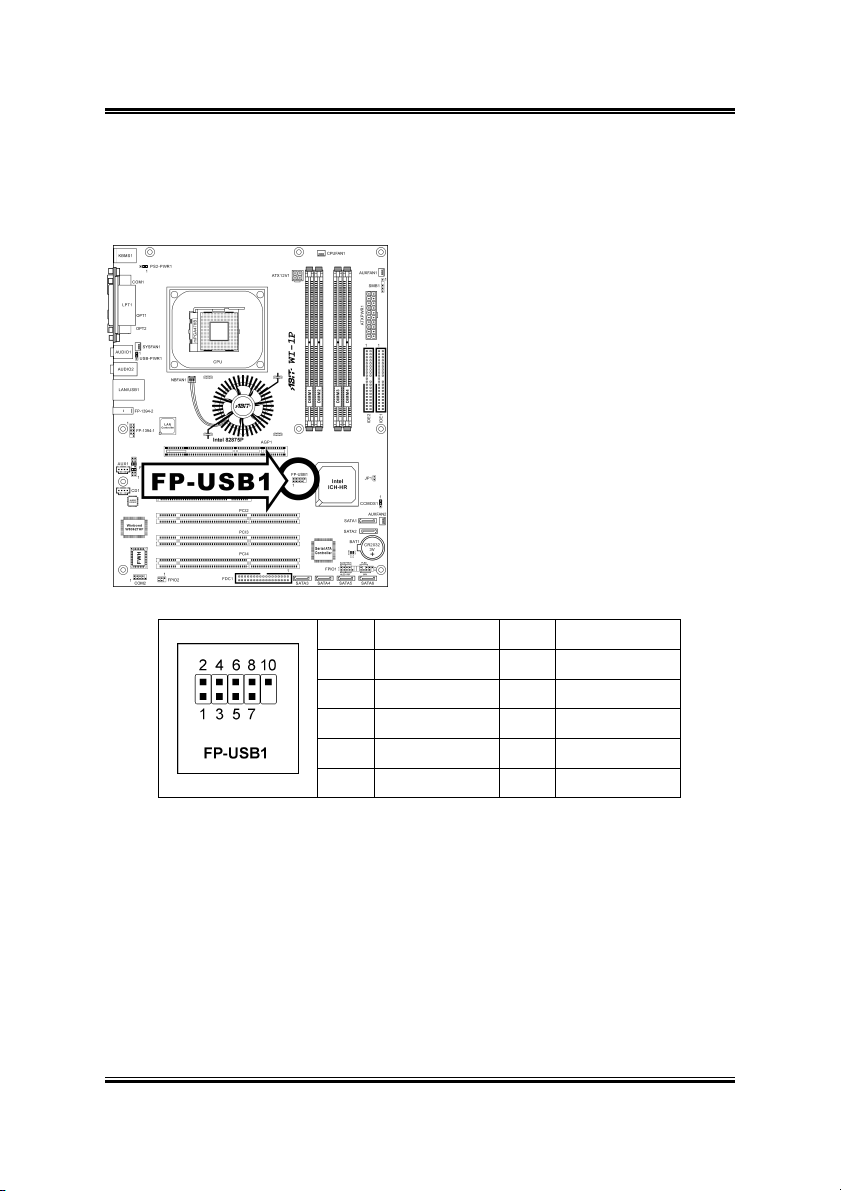
2-14 Chapter 2
2.3.10. Additional USB Port Connection Header
This header provides two additional USB port connections.
Pin Pin Assignment Pin Pin Assignment
1 VCC 2 VCC
3 Data2 - 4 Data3 -
5 Data2 + 6 Data3 +
7 Ground 8 Ground
9 NC 10 NC
WI-1P
Page 23

Hardware Setup 2-15
2.3.11. System Management Bus Connection Header
This header provides one external System Management Bus connection.
User’s Manual
Page 24

2-16 Chapter 2
2.3.12. Infrared Device Connection Header
This header provides one external IR device port connection.
WI-1P
Page 25

Hardware Setup 2-17
2.3.13. Chassis Intrusion Device Header
This header provides a cable connection to an intrusion device attached to chassis.
User’s Manual
Page 26

2-18 Chapter 2
2.3.14. AGP Pro Display Card Slot
This slot supports an optional AGP graphics card up to AGP 4X/8X mode.
ATTENTION: This motherboard does not support 3.3V AGP cards. Use only 1.5V
or 0.8V AGP cards.
WI-1P
Page 27

Hardware Setup 2-19
2.3.15. Additional COM2 Port Connection Header
This header provides an additional COM2 port connection.
Pin Definition Pin Definition
1 DCDA 2 SINA
3 SOUTA 4 DTRA
5 Ground 6 DSRA
7 RTSA 8 CTSA
9 RIA
User’s Manual
Page 28

2-20 Chapter 2
2.3.16. Floppy and IDE Disk Drive Connectors
The FDC1 connector connects up to two floppy drives with a 34-wire, 2-connector
floppy cable. Connect the single end at the longer length of ribbon cable to the FDC1
on the board, the two connectors on the other end to the floppy disk drives connector.
Generally you need only one floppy disk drive in your system.
NOTE: The red line on the ribbon cable must be aligned with pin-1 on both the FDC1
port and the floppy connector.
Each of the IDE port connects up to two
IDE drives at Ultra ATA/100 mode by one
40-pin, 80-conductor, and 3-connector Ultra
ATA/66 ribbon cables.
Connect the single end (blue connector) at
the longer length of ribbon cable to the IDE
port of this board, the other two ends (gray
and black connector) at the shorter length of
the ribbon cable to the connectors of your
hard drives.
NOTE: Make sure to configure the “Master” and “Slave” relation before connecting
two drives by one single ribbon cable. The red line on the ribbon cable must be
aligned with pin-1 on both the IDE port and the hard-drive connector.
WI-1P
Page 29

Hardware Setup 2-21
2.3.17. Serial ATA Connectors
These connectors each provide one Serial ATA channel connection.
SATA1 and SATA2 are controlled by South Bridge. To enable the SATA1 and
SATA2 controller, you have to enable the item “OnChip Serial ATA” first in the
BIOS menu of “OnChip IDE Device”.
User’s Manual
Page 30

2-22 Chapter 2
The following table displays the quantity of devices at IDE1, IDE2, SATA1 and
SATA2 channel under different “OnChip Serial ATA” configuration:
WinXP / Windows .NET Server:
OnChip Serial ATA /
OnChip Serial ATA
Mode
Enhanced Mode / IDE 2 2 1 1
DOS / Win2K / Win98 / WinME:
OnChip Serial ATA /
OnChip Serial ATA
Mode
Combined Mode / IDE
SATA Only / IDE 0 0 1 1
Disabled 2 2 0 0
SATA3~6 are controlled by Silicon Image PCI Chip. To enable the SATA3~6
controller, you have to enable the item “Serial ATA Controller” first in the BIOS
menu of “Onboard PCI Device”.
For more information on how to configure the function mode for SATA1 and SATA2,
please refer to the item “Serial ATA 1 Mode” and “Serial ATA 2 Mode” in the BIOS
menu of “OnChip IDE Device”.
IDE1 IDE2 SATA1 SATA2
IDE1 IDE2 SATA1 SATA2
0 2 1 1
2 0 1 1
WI-1P
Page 31

Hardware Setup 2-23
2.3.18. Status Indicators
• D13 (5VSB): 5VSB LED Indicator
This LED lights up when the power supply is connected with power source.
• D14 (VCC): Power on Indicator
This LED lights up when the system power is on.
User’s Manual
Page 32

2-24 Chapter 2
2.3.19. External I/O Panel Connectors
• Mouse: PS/2 mouse connector.
• Keyboard: PS/2 keyboard connector.
• LPT1: Parallel port connector.
• COM1: Serial port connector.
• OPT1: S/PDIF-In connector.
• OPT2: S/PDIF-Out connector.
• AUDIO1:
R.L./R.R. (Rear Left / Rear Right): Connects to the rear left and rear right
channel in the 5.1 channel audio system.
Cen./Sub. (Center / Subwoofer): Connects to the center and subwoofer
channel in the 5.1 channel audio system.
• AUDIO2:
Mic In: Connects to the plug from external microphone.
Line In: Connects to the line out from external audio sources.
F.L./F.R. (Front Left / Front Right): Connects to the front left and front
right channel in the 5.1-channel or regular 2-channel audio system.
• LAN: Local Area Network connector.
• USB1: Universal Serial Bus connector.
• FP-1394-2: IEEE1394 connector.
WI-1P
Page 33

BIOS Setup 3-1
Chapter 3. BIOS Setup
This motherboard provides a programmable EEPROM that you can update the BIOS
utility. The BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) is a program that deals with the basic
level of communication between processor and peripherals. Use the BIOS Setup
program only when installing motherboard, reconfiguring system, or prompted to
“Run Setup”. This chapter explains the Setup Utility of BIOS utility.
After powering up the system, the BIOS message appears on the screen, the memory
count begins, and then the following message appears on the screen:
PRESS DEL TO ENTER SETUP
If this message disappears before you respond, restart the system by pressing <Ctrl> +
<Alt> + <Del> keys, or by pressing the Reset button on computer chassis. Only when
it failed by these two methods can you restart the system by powering it off and then
back on.
After pressing <Del> key, the main menu screen appears.
NOTE: In order to increase system stability and performance, our engineering staffs
are constantly improving the BIOS menu. The BIOS setup screens and descriptions
illustrated in this manual are for your reference only, may not completely match what
you see on your screen.
User’s Manual
Page 34

3-2 Chapter 3
3.1. SoftMenu Setup
The SoftMenu utility is ABIT’s exclusive and ultimate solution in programming the
CPU operating speed. All the parameters regarding CPU FSB speed, multiplier factor,
the AGP & PCI clock, and even the CPU core voltage are all available at your
fingertips.
Brand Name:
This item displays the CPU model name, for example: Intel Pentium (R) 4.
Frequency:
This item displays the processor speed.
Cache Size:
This item displays the L2 cache size of your CPU.
CPU Operating Speed:
This item displays the CPU operating speed according to the type and speed of your
CPU. You can also select the [User Defined] option to enter the manual option.
WI-1P
Page 35

BIOS Setup 3-3
User Defined:
WARNING: The wrong settings of the multiplier and external clock in certain
circumstances may cause CPU damage. Setting the working frequency higher than the
PCI chipset or processor specs, may cause abnormal memory module functioning,
system hangs, hard disk drive data lose, abnormal functioning of the VGA card, or
abnormal functioning with other add-on cards. Using non-specification settings for
your CPU is not the intention of this explanation. These should be used for
engineering testing, not for normal applications.
There will be no guaranty for the settings beyond specification, any damage of any
component on this motherboard or peripherals result therein is not our responsibility.
Ext. Clock (CPU/AGP/PCI):
This item selects the external clock frequency.
Multiplier Factor:
This item selects the multiplier factors for your CPU if it is not locked.
Estimated new CPU clock:
This item displays the frequency sum up from the previous item [Ext. Clock] and
[Multiplier Factor].
N/B Strap CPU As:
This item sets the external hardware reset strap assigned to MCH (Memory Controller
Hub). The options are: [PSB400], [PSB533], [PSB800], and [By CPU]. The default
setting is By CPU.
To set this option manually:
• Select [PSB400] for CPU of 100MHz FSB frequency.
• Select [PSB533] for CPU of 133MHz FSB frequency.
• Select [PSB800] for CPU of 200MHz FSB frequency.
DRAM Ratio (CPU:DRAM):
This item determines the frequency ratio between CPU and DRAM.
AGP Ratio (CPU:AGP:PCI):
This item determines the ratio among CPU, AGP, and PCI.
Fixed AGP/PCI Frequency:
This item determines the AGP/PCI bus frequency. This option allows you to keep
your AGP/PCI clock at some fixed frequency to improve system stability.
User’s Manual
Page 36

3-4 Chapter 3
CPU Power Supply:
This option allows you to switch between CPU default and user-defined voltages.
Leave this setting to default unless the current CPU type and voltage setting cannot be
detected or is not correct. The option “User Defined” enables you to select the Core
Voltage manually.
CPU Core Voltage:
This item selects the CPU core voltage.
ATTENTION: A wrong voltage setting may cause the system unstable or even
damage the CPU. Please leave it to default settings unless you are fully aware of its
consequences.
DDR SDRAM Voltage:
This item selects the voltage for DRAM slot.
AGP Voltage:
This item selects the voltage for AGP slot.
WI-1P
Page 37

BIOS Setup 3-5
3.2. Standard CMOS Features
This section contains the basic configuration parameters of the BIOS. These
parameters include date, hour, VGA card, FDD and HDD settings.
Date (mm:dd:yy):
This item sets the date you specify (usually the current date) in the format of [Month],
[Date], and [Year].
Time (hh:mm:ss):
This item sets the time you specify (usually the current time) in the format of [Hour],
[Minute], and [Second].
User’s Manual
Page 38

3-6 Chapter 3
IDE Channel 1 Master/Slave, IDE Channel 2 Master/Slave, IDE
Channel 3 Master, IDE Channel 4 Master:
Click <Enter> key to enter its submenu:
NOTE: Item “IDE Channel 3 Master” and “IDE Channel 4 Master” appears only
when the item “OnChip Serial ATA” in the “OnChip IDE Device” menu is set as
[Enhanced Mode], and the item “OnChip Serial ATA Mode” in the “OnChip IDE
Device” menu is set as [IDE].
IDE HDD Auto-Detection:
This item allows you to detect the parameters of IDE drives by pressing <Enter> key.
The parameters will be shown on the screen automatically.
IDE Channel 1 Master/Slave, IDE Channel 2 Master/Slave, Extended IDE Drive:
When set to [Auto], the BIOS will automatically check what kind of IDE drive you
are using. If you want to define your own drive by yourself, set it to [Manual] and
make sure you fully understand the meaning of the parameters. Please refer to the
instruction manual provided by the device’s manufacturer to get the setting right.
Access Mode:
This item selects the mode to access your IDE devices. Leave this item to its default
[Auto] setting to detect the access mode of your HDD automatically.
WI-1P
Page 39

BIOS Setup 3-7
Capacity:
This item displays the approximate capacity of the disk drive. Usually the size is
slightly greater than the size of a formatted disk given by a disk-checking program.
Cylinder:
This item configures the numbers of cylinders.
Head:
This item configures the numbers of read/write heads.
Precomp:
This item displays the number of cylinders at which to change the write timing.
Landing Zone:
This item displays the number of cylinders specified as the landing zone for the
read/write heads.
Sector:
This item configures the numbers of sectors per track.
Back to Standard CMOS Features Setup Menu:
Drive A & Drive B:
This item sets the type of floppy drives (usually only Drive A) installed.
Floppy 3 Mode Support:
This item allows you to use “3 Mode Floppy Drive” in Japanese computer system by
selecting drive A, B, or both. Leave this item to its default [Disabled] setting if you
are not using this Japanese standard floppy drive.
Halt On:
This item determines whether the system stops if an error is detected during system
boot-up.
[All Errors]: The system-boot will stop whenever the BIOS detect a non-fatal error.
[No Errors]: The system-boot will not stop for any error detected.
[All, But Keyboard]: The system-boot will stop for all errors except a keyboard
error.
[All, But Diskette]: The system-boot will stop for all errors except a diskette error.
User’s Manual
Page 40

3-8 Chapter 3
[All, But Disk/Key]: The system-boot will stop for all errors except a diskette or
keyboard error.
Base Memory:
This item displays the amount of base memory installed in the system. The value of
the base memory is typically 640K for system with 640K or more memory size
installed on the motherboard.
Extended Memory:
This item displays the amount of extended memory detected during system boot-up.
Total Memory:
This item displays the total memory available in the system.
WI-1P
Page 41

BIOS Setup 3-9
3.3. Advanced BIOS Features
CPU L3 Cache:
This item is used to enable the L3 cache (default setting), and appears only for certain
CPU (Intel Pentium 4 processor with HT Technology Extreme Edition) that possesses
L3 cache.
Hyper-Threading Technology:
This item is used to enable the functionality of the processor with Hyper-Threading
Technology and will appear only when using such processor.
The Hyper-Threading Technology helps your PC work more efficiently by
maximizing processor resources and enabling a single processor to run two separate
threads of software simultaneously, bringing forth greater performance and system
responsiveness when running multiple applications at once.
Quick Power On Self Test:
When set to [Enabled], this item speeds up the Power On Self Test (POST) after
powering on the system. The BIOS shorten or skip some check during the POST.
Hard Disk Boot Priority:
This item selects the hard disks booting priority. By pressing <Enter> key, you can
enter its submenu where the hard disks detected can be selected for the booting
sequence to boot up system.
User’s Manual
Page 42

3-10 Chapter 3
This item functions only when there is the option of [Hard Disk] in any one of the
First/Second/Third Boot Device items.
Bootable Add-in Device:
This item allows you to select the add-in device among the [PCI Slot Device],
[OnChip SATA RAID], and [Onboard SATA] channel to serve as the bootable device
listed in the item “Hard Disk Boot Priority”.
HDD Change Message:
When set to [Enabled], a pop-up message will be displayed on the screen during the
POST process if the hard drives installed in your system had been changed.
First Boot Device / Second Boot Device / Third Boot Device / Boot Other Device:
Select the drive to boot first, second and third in the [First Boot Device], [Second
Boot Device], and [Third Boot Device] items respectively. The BIOS will boot the
operating system according to the sequence of the drive selected. Set [Boot Other
Device] to [Enabled] if you wish to boot from another device other than these three
items.
Boot Up Floppy Seek:
When set to [Enabled], the BIOS will check whether the floppy disk drive is installed
or not.
Boot Up NumLock Status:
This item determines the default state of the numeric keypad at system booting up.
[On]: The numeric keypad functions as number keys.
[Off]: The numeric keypad functions as arrow keys.
Security Option:
This item determines when the system will prompt for password - every time the
system boots or only when enters the BIOS setup.
[Setup]: The password is required only when accessing the BIOS Setup.
[System]: The password is required each time the computer boots up.
NOTE: Don’t forget your password. If you forget the password, you will have to
open the computer case and clear all information in the CMOS before you can start up
the system. But by doing this, you will have to reset all previously set options.
WI-1P
Page 43

BIOS Setup 3-11
MPS Version Ctrl For OS:
This item specifies which version of MPS (Multi-Processor Specification) this
motherboard will use. Leave this item to its default setting.
Report No FDD For OS:
When set to [Yes], this item allows you to run some older operating system without
floppy disk drive. Leave this item to its default setting.
Delay IDE Initial (Secs):
This item allows the BIOS to support some old or special IDE devices by prolonging
this delay time. A larger value will give more delay time to the device for which to
initialize and to prepare for activation.
Intel OnScreen Branding:
This item determines whether to display the “Intel Inside” logo or not at system boots
up.
Disable Unused PCI Clock:
This option disables the clock of PCI slot that is not in use.
[Yes]: The system automatically detect the unused DIMM and PCI slots, and stop
sending clock signal to these unused PCI slots.
[No]: The system always send clock signal to all PCI slots.
NOTE: Set this option to [No] setting if there are adapters that cannot be
automatically detected by the system and will cause malfunction.
User’s Manual
Page 44

3-12 Chapter 3
3.4. Advanced Chipset Features
DRAM Timing Selectable:
This item sets the optimal timings for the following four items, depending on the
memory module you are using. The default setting “By SPD” configures these four
items by reading the contents in the SPD (Serial Presence Detect) device. The
EEPROM on the memory module stores critical parameter information about the
module, such as memory type, size, speed, voltage interface, and module banks.
CAS Latency Time:
This item controls the latency between the DRAM read command and the time that
the data becomes actually available.
Act to Precharge Delay:
This item controls the number of DRAM clocks used for the DRAM parameters.
DRAM RAS# to CAS# Delay
This item controls the latency between the DRAM active command and the read/write
command.
DRAM RAS# Precharge:
This item controls the idle clocks after issuing a precharge command to the DRAM.
WI-1P
Page 45

BIOS Setup 3-13
Video BIOS Cacheable:
As with caching the system BIOS, enabling the Video BIOS cache will allow access
to video BIOS addressed at C0000H to C7FFFH to be cached, if the cache controller
is also enabled. The larger the range of the Cache RAM, the faster the video
performance will be.
Memory Hole At 15M-16M:
When set to [Enabled], the memory address space at 15M-16M will be reserved for
ISA expansion cards that specifically requires this setting. This makes the memory
from 15MB and up unavailable to the system. Leave this item to its default setting.
Delay Prior to Thermal:
This item selects the delay time before thermal activation.
AGP Aperture Size:
This option specifies the amount of system memory that can be used by the AGP
device. The aperture is a portion of the PCI memory address range dedicated for
graphics memory address space.
Init Display First:
This item selects to initialize AGP or PCI Slot first when the system boots.
[AGP]: When the system boots, it will first initialize AGP.
[PCI Slot]: When the system boots, it will first initialize PCI.
DRAM Data Integrity Mode:
This item selects the type of DRAM in your system. ECC is “Error Checking and
Correction”. Choose the ECC option only when your memory is ECC type.
AGP Data Rate Capability:
This item selects the data transfer rate of AGP device. A higher rate delivers faster
and better graphics to your system. Make sure your graphics card supports the mode
you select.
Game Accelerator:
This item selects the mode for Game Accelerator among the options of [Auto],
[Turbo], [Street Racer], and [F1].
NOTE: The option [Street Racer] and [F1] mode will stress the DDR memory
critically; not every kind of DDR memories could be stable with these two options.
[Turbo] mode is okay for most of DDR memories.
User’s Manual
Page 46

3-14 Chapter 3
Refresh Cycle Time:
This item determines the DRAM Refresh Cycle among [Auto], [Normal], [Enhanced],
[Strengthened], and [Aggressive].
Read Delay (tRD):
This item determines the timing of DRAM Read Delay.
Read delay Adjust(tRDA):
This item determines to adjust the timing of DRAM Read Delay.
Command Per Clock(CPC):
This item determines the address command timing according to the DRAM strobe
clock.
WI-1P
Page 47

BIOS Setup 3-15
3.5. Integrated Peripherals
OnChip IDE Device:
Click <Enter> key to enter its submenu:
User’s Manual
Page 48

3-16 Chapter 3
IDE Bus Master:
This option enables or disables the IDE bus mastering capability under the DOS
environment.
OnChip IDE-1 Controller:
This item allows you to enable or disable the primary and secondary IDE controller.
Select [Disabled] if you want to add a different hard drive controller.
OnChip IDE-2 Controller:
The description is same as the OnChip IDE-1 Controller.
OnChip Serial ATA:
This item determines the function for on-chip Serial ATA.
[Disabled]: Disable the Serial ATA controller.
[Auto]: Allows the Serial ATA controller to be arranged by BIOS automatically.
[Combined Mode]: Parallel ATA and Serial ATA are combined together. Supports
up to 4 IDE drives.
[Enhanced Mode]: Enable both Parallel ATA and Serial ATA. Supports up to 6 IDE
drives.
[SATA Only]: The SATA is operating in legacy mode.
WI-1P
Page 49

BIOS Setup 3-17
Serial ATA 1 Mode / Serial ATA 2 Mode:
This item determines the function mode for Serial ATA Port 1 (i.e. The SATA1
connector in this model) and Serial ATA Port 2 (i.e. The SATA2 connector in this
model). Both SATA1 and SATA2 will be served each as one single IDE connector
after selected as the following modes:
Mode
Serial ATA Port
1 (SATA1)
Serial ATA Port
2 (SATA2)
Description
• SATA1 serves as IDE-3 Master
IDE-3 Master IDE-4 Master
Enhanced
IDE-4 Master IDE-3 Master
• SATA2 serves as IDE-4 Master
• OnChip IDE-1 and IDE-2 controller
enabled
• SATA1 serves as IDE-4 Master
• SATA2 serves as IDE-3 Master
• OnChip IDE-1 and IDE-2 controller
enabled
• SATA1 serves as IDE-1 Master
IDE-1 Master
IDE-1 Slave
• SATA2 serves as IDE-1 Slave
• OnChip IDE-1 controller disabled
• SATA1 serves as IDE-1 Slave
Combined
IDE-1 Slave IDE-1 Master
IDE-2 Master
IDE-2 Slave
• SATA2 serves as IDE-1 Master
• OnChip IDE-1 controller disabled
• SATA1 serves as IDE-2 Master
• SATA2 serves as IDE-2 Slave
• OnChip IDE-2 controller disabled
• SATA1 serves as IDE-2 Slave
IDE-2 Slave IDE-2 Master
• SATA2 serves as IDE-2 Master
• OnChip IDE-2 controller disabled
• SATA1 serves as IDE-1 Master
IDE-1 Master IDE-2 Master
• SATA2 serves as IDE-2 Master
• OnChip IDE-1 and IDE-2 controller
disabled SATA
Only
IDE-2 Master IDE-1 Master
• SATA1 serves as IDE-2 Master
• SATA2 serves as IDE-1 Master
• OnChip IDE-1 and IDE-2 controller
disabled
User’s Manual
Page 50

3-18 Chapter 3
OnChip PCI Device:
Click <Enter> key to enter its submenu:
OnChip USB Controller:
This option enables or disables the USB controller.
USB 2.0 Controller:
This option enables or disables the USB 2.0 controller.
USB Keyboard Support Via:
This item allows you to select [BIOS] for using USB keyboard in DOS environment,
or [OS] in OS environment.
USB Mouse Support Via:
This item allows you to select [BIOS] for using USB mouse in DOS environment, or
[OS] in OS environment.
OnChip Audio Controller:
This option enables or disables the audio controller.
OnChip LAN Controller:
This option enables or disables the LAN controller.
WI-1P
Page 51

BIOS Setup 3-19
LAN Boot ROM:
This item allows you to use the boot ROM (instead of a disk drive) to boot-up the
system and access the local area network directly.
SuperIO Device:
Click <Enter> key to enter its submenu:
Onboard FDC Controller:
This option enables or disables the onboard FDC controller.
Onboard Serial Port 1:
This item determines which I/O addresses the onboard Serial Port 1 controller will
access.
[Auto]: The system automatically select an I/O address for the onboard Serial Port 1.
[3F8/IRQ4, 2F8/IRQ3, 3E8/IRQ4, 2E8/IRQ3]: Allows you to manually select an
I/O address for the onboard Serial Port 1.
[Disabled]: Disables the onboard Serial Port 1.
Onboard Serial Port 2:
This item determines which I/O addresses the onboard Serial Port 2 controller will
access.
User’s Manual
Page 52

3-20 Chapter 3
[Auto]: The system automatically select an I/O address for the onboard Serial Port 2.
[3F8/IRQ4, 2F8/IRQ3, 3E8/IRQ4, 2E8/IRQ3]: Allows you to manually select an
I/O address for the onboard Serial Port 2.
[Disabled]: Disables the onboard Serial Port 2.
UART Mode Select:
This item selects the Infrared (IR) function mode.
RxD, TxD Active:
This item sets the IR transmission/reception polarity.
IR Transmission Delay:
This option enables or disables the IR transmission delay. When set to [Enabled], the
transmission will be slower. This is recommended when transmission problem arise.
UR2 Duplex Mode:
This item selects the duplex mode required by the IR device connected to the IR port.
Full-duplex mode permits simultaneous two-direction transmission. Half-duplex
mode permits transmission in one direction only at a time. Refer to your IR KIT user's
guide to find out which setting is correct.
Use IR Pins:
Two options are available: RxD2, TxD2 and IR-Rx2Tx2. The default setting is
IR-Rx2Tx2.
If you choose RxD2, TxD2, your motherboard must support a COM port IR KIT
connection. Otherwise, you can only choose the IR-Rx2Tx2 to use the IR header on
your motherboard to connect your IR KIT.
Please use the default setting.
Onboard Parallel Port:
This item specifies the I/O address used by the parallel port.
[Disabled]: This option prevents the parallel port from accessing any system
resources. When the value of this option is set to [Disabled], the printer port becomes
unavailable.
[378/IRQ7]: This option allows the parallel port to use [378/IRQ7] as its I/O port
address. The majority of parallel ports on computer systems use IRQ7 and I/O Port
378H as the standard setting.
WI-1P
Page 53

BIOS Setup 3-21
[278/IRQ5]: This option allows the parallel port to use [278/IRQ5] as its I/O port
address.
[3BC/IRQ7]: This option allows the parallel port to use [3BC/IRQ7] as its I/O port
address.
Parallel Port Mode:
This item specifies the parallel port mode.
[Normal]: Allows the standard parallel port mode to be used.
[SPP]: (Standard Parallel Port) Allows bi-directional parallel port operation at normal
speed.
[EPP]: (Enhanced Parallel Port) Allows bi-directional parallel port operation at
maximum speed.
[ECP]: (Extended Capabilities Port) Allows bi-directional parallel port operation at a
speed faster than the normal mode’s data transfer rate.
[ECP+EPP]: Allows parallel port operation at ECP and EPP mode.
EPP Mode Select:
This item selects the EPP mode.
ECP Mode Use DMA:
This item selects the DMA channel of the parallel port.
User’s Manual
Page 54

3-22 Chapter 3
Onboard PCI Device:
Click <Enter> key to enter its submenu:
IEEE 1394 Controller:
This option enables or disables the IEEE 1394 controller.
Serial ATA Controller:
This option enables or disables the Serial ATA controller of Silicon Image PCI Chip
SATA RAID ROM:
This item allows you to use the boot ROM of on-chip Serial ATA RAID to boot-up
system.
WI-1P
Page 55

BIOS Setup 3-23
3.6. Power Management Setup
ACPI Suspend Type:
This item selects the type of Suspend mode.
[S1(PowerOn Suspend)]: Enables the Power On Suspend function.
[S3(Suspend To RAM)]: Enables the Suspend to RAM function.
Resume by USB From S3:
When set to [Enabled], this item allows you to use a USB device to wake up a system
that is in the S3 (STR - Suspend To RAM) state. This item can be configured only if
the item “ACPI Suspend Type” is set to [S3(STR)].
Power Button Function:
This item selects the method of powering off your system:
[Delay 4 Sec.]: Pushing the power button for more than 4 seconds will power off the
system. This will prevent the system from powering off in case you accidentally hit or
pushed the power button.
[Instant-Off]: Pressing and then releasing the power button at once will immediately
power off the system.
User’s Manual
Page 56

3-24 Chapter 3
CPU THRM-Throttling
This item controls the CPU speed by cutting down its regular power to a percentage
during the STR (Suspend To RAM) state.
WakeUp by PME# of PCI:
When set to [Enabled], access to the onboard LAN or a PCI card such as a modem or
LAN card will cause the system to wake up. The PCI card must support the wake up
function.
WakeUp by Ring:
When set to [Enabled], telephone calls coming through an external or internal modem
will power-on your system.
WakeUp by OnChip LAN:
When set to [Enabled], you can remotely wake up a PC in Soft-Off condition via a
LAN card that support the wake up function.
WakeUp by Alarm:
When set to [Enabled], you can set the date and time you would like the Soft-Off PC
to power-on in the “Date (of Month) Alarm” and “Time (hh:mm:ss) Alarm” items.
However, if the system is being accessed by incoming calls or the network (Resume
On Ring/LAN) prior to the date and time set in these items, the system will give
priority to the incoming calls or network instead.
Date (of Month) Alarm
[0]: This option power-on the system everyday according to the time set in the “Time
(hh:mm:ss) Alarm” item.
[1-31]: This option selects a date you would like the system to power-on. The system
will power-on on the date set, and the time set in the “Time (hh:mm:ss) Alarm” item.
Time (hh:mm:ss) Alarm
This item sets the time you would like the system to power-on.
POWER ON Function:
This item selects the way you want your system to power on.
[Password]: Use a password to power on the system, select this option then press
<Enter>. Enter your password. You can enter up to 5 characters. Type in exactly the
same password to confirm, and then press <Enter>.
WI-1P
Page 57

BIOS Setup 3-25
[Hot KEY]: Use any of the function keys between <F1> to <F12> to power on the
system.
[Mouse Left]: Double click the mouse left button to power on the system.
[Mouse Right]: Double click the mouse right button to power on the system.
[Any KEY]: Use any keyboard keys to power on the system.
[BUTTON ONLY]: Use only the power button to power on the system.
[Keyboard 98]: Use the power-on button on the “Keyboard 98” compatible keyboard
to power on the system.
NOTE: To enable this “Power On” function, the wake-up header of [PS2-PWR1] and
[USB-PWR1] must be set to [Enabled] position. Please refer to the configuration of
“Wake-up Header” [PS2-PWR1] and [USB-PWR1] in section 2-4, chapter 2.
The mouse wake up function can only be used with the PS/2 mouse, not with the
COM port or USB type. Some PS/2 mice cannot wake up the system because of
compatible problems. If the specs of your keyboard are too old, it may fail to power
on.
KB Power ON Password:
This item sets the password required in order to power on your computer.
NOTE: Do not forget your password, or you will have to clear the CMOS and reset
all parameters in order to utilize this function again.
Hot Key Power ON:
This item powers on the system by pressing <Ctrl> key plus one of each function key
(<F1> ~ <F12>) simultaneously.
Restore On AC Power Loss:
This item selects the system action after an AC power failure.
[Power Off]: When power returns after an AC power failure, the system’s power
remains off. You must press the Power button to power-on the system.
[Power On]: When power returns after an AC power failure, the system’s power will
be powered on automatically.
User’s Manual
Page 58

3-26 Chapter 3
[Last State]: When power returns after an AC power failure, the system will return to
the state where you left off before power failure occurs. If the system’s power is off
when AC power failure occurs, it will remain off when power returns. If the system’s
power is on when AC power failure occurs, the system will power-on when power
returns.
WI-1P
Page 59

BIOS Setup 3-27
3.7. PnP/PCI Configurations
Resources Controlled By:
This item configures all of the boot and Plug-and-Play compatible devices.
[Auto]: The system will automatically detect the settings.
[Manual]: Choose the specific IRQ resources in the “IRQ Resources” menu.
User’s Manual
Page 60

3-28 Chapter 3
IRQ Resources:
Click <Enter> key to enter its submenu:
This item sets each system interrupt to either [PCI Device] or [Reserved].
PCI/VGA Palette Snoop:
This item determines whether the MPEG ISA/VESA VGA cards can work with
PCI/VGA or not.
[Enabled]: MPEG ISA/VESA VGA cards work with PCI/VGA.
[Disabled]: MPEG ISA/VESA VGA cards do not work with PCI/VGA.
PCI Latency Timer(CLK):
This item controls how long each PCI device can hold the bus before another takes
over. When set to higher values, every PCI device can conduct transactions for a
longer time and thus improve the effective PCI bandwidth. For better PCI
performance, you should set the item to higher values.
PIRQ_0 Use IRQ No. ~ PIRQ_7 Use IRQ No.:
This item specifies the IRQ number manually or automatically for the devices
installed on PCI slots.
WI-1P
Page 61

BIOS Setup 3-29
For the relations between the hardware layout of PIRQ (the signals from the ICH
chipset), INT# (means PCI slot IRQ signals) and devices, please refer to the table
below:
Signals AGP
PIRQ_0
Assignment
PIRQ_1
Assignment
PIRQ_2
Assignment
PIRQ_3
Assignment
PIRQ_4
Assignment
PIRQ_5
Assignment
PIRQ_6
Assignment
PIRQ_7
Assignment
LAN PCI-1 PCI-2 PCI-3 PCI-4
INT A
INT B
INT D
INT A
INT A INT B INT A
INT C INT A INT A INT A INT A
IEEE-
1394
SATA
User’s Manual
Page 62

3-30 Chapter 3
3.8. PC Health Status
FAN Fail Alarm Selectable:
This item selects the fan that will be monitored for malfunction.
Shutdown When CPU Fan Fail:
When set to [Enabled], the system will be shut down if the CPU fan is not running.
CPU FanEQ Speed Control:
This item allows you to control the CPU fan speed down to a specific percentage.
When set to a specific percentage, the CPU fan speed will run at the percentage you
set in this item if the temperature limit set in the item “Active Temperature” is not
exceeded.
The CPU fan speed will run at 100% regardless of what the percentage you set in this
item if the temperature limit set in the item “Active Temperature” is exceeded.
Active Temperature:
This item sets the temperature limit that would activate the function of “CPU FanEQ
Speed Control” option.
WI-1P
Page 63

BIOS Setup 3-31
Case Open Warning
This option controls the action to take when the chassis intrusion device connected to
header JP1 is activated.
[Disabled]: Disable the case-open warning.
[Message]: Display a warning message in the monitor.
[Shutdown]: Shutdown the system.
CPU Shutdown Temperature:
This item sets the temperature that would shutdown the system automatically in order
to prevent system overheats.
CPU Warning Temperature:
This item selects the CPU’s warning temperature limit. Once the system has detected
that the CPU’s temperature exceeded the limit, warning beeps will sound.
NOTE: The onboard hardware monitor function is capable of detecting these system
health conditions. If you want a warning message to pop-up or a warning alarm to
sound when an abnormal condition occurs, you must install the “Hardware Doctor”
utility. This utility is included in the “Driver & Utility CD” that came packed with this
motherboard.
All Voltages, Fans Speed and Thermal Monitoring:
These unchangeable items list the current status of the CPU and environment
temperatures, fan speeds, and system power voltage.
NOTE: The hardware monitoring features for temperatures, fans and voltages will
occupy the I/O address from 294H to 297H. If you have a network adapter, sound
card or other add-on cards that might use those I/O addresses, please adjust your
add-on card I/O address to avoid using these addresses.
User’s Manual
Page 64

3-32 Chapter 3
3.9. Load Fail-Safe Defaults
This option loads the BIOS default values for the most stable, minimal-performance
system operations.
3.10. Load Optimized Defaults
This option loads the BIOS default values that are factory settings for
optimal-performance system operations.
3.11. Set Password
This option protects the BIOS configuration or restricts access to the computer itself.
3.12. Save & Exit Setup
This option saves your selections and exits the BIOS setup menu.
3.13. Exit Without Saving
This option exits the BIOS setup menu without saving any change.
WI-1P
Page 65

Driver Installation 4-1
Chapter 4. Driver Installation
After all the hardware has been installed, you must first install the operating system
and then the software drivers. The necessary drivers are all included within the
Drivers & Utilities CD that came packaged with your workstation board.
The display shown in the following figure should appear after inserting this CD into
your CD-ROM drive, if not, enter [My Computer] CD-ROM drive double
click [Launch].
User’s Manual
Page 66

4-2 Chapter 4
Setup Items
• Intel Chipset Software Utility
Install Intel chipset driver for Windows Operating System.
• Audio Driver
Install AC 97 CODEC driver for Windows Operating System.
• Intel LAN Driver
Install the drivers needed to run Fast Ethernet controller.
• Silicon Serial ATA RAID
Install Serial ATA RAID driver for Windows Operating System.
• USB 2.0 Driver
Update USB 2.0 driver for Windows Operating System.
• Manual
View the user’s manual in PDF.
• Utility
Click to enter the sub-screen for installing software like Award Flash,
Microsoft DirectX, and Acrobat Reader.
• Browse CD
Browse the contents of this CD-ROM.
• Close
Exit the CD setup items.
WI-1P
Page 67

How to Get Technical Support A-1
Appendix A. How to Get Technical Support
(From our website) http://www.abit.com.tw
(In North America) http://www.abit-usa.com
(In Europe) http://www.abit.nl
Thank you for choosing ABIT products. ABIT sells all our products through
distributors, resellers and system integrators; we have no direct sales to end-users.
Before sending email for tech support please check with your resellers or integrators if
you need any services, they are the ones who sold you your system and they should
know best as to what can be done, how they serve you is a good reference for future
purchases.
We appreciate every customer and would like to provide the best service to you.
Providing fast service to our customers is our top priority. However we receive many
phone calls and a huge amount of email from all over the world. At the present time it
is impossible for us to respond to every single inquiry. Therefore it is quite possible
that if you send an email to us that you may not receive a response.
We have done many compatibility tests and reliability tests to make sure our products
have the best quality and compatibility. In case you need service or technical support,
please understand the constraint we have and always check with the reseller who
sold the product to you first.
To expedite service, we recommend that you follow the procedures outlined below
before contacting us. With your help, we can meet our commitment to provide the
best service to the greatest number of ABIT customers:
1. Check the Manual. It sounds simple but we have taken a lot of care in making a
well-written and thorough manual. It is full of information that doesn't only
pertain to motherboards. The CD-ROM included with your board will have the
manual as well as drivers. If you don't have either one, go to our Program
Download Area of the Website or FTP workstation.
2. Download latest BIOS, software or drivers. Please go to our Program
Download area on our Website to check to see if you have the latest BIOS. They
are developed over periods of time to fixes bugs or incompatibilities. Also please
make sure you have the latest drivers from your peripheral cards makers!
3. Check the ABIT Technical Terms Guide and FAQ on our Website. We are
trying to expand and make the FAQs more helpful and information rich. Let us
know if you have any suggestions. For hot topics check out our HOT FAQ!
User’s Manual
Page 68

A-2 Appendix A
4. Internet Newsgroups. They are a great source of information and many people
there can offer help. ABIT's Internet News group,
alt.comp.periphs.mainboard.abit
information and discuss experiences they have had with ABIT products. Many
times you will see that your question has already been asked before. This is a
public Internet news group and it is reserved for free discussions. Here is a list of
some of the more popular ones:
alt.comp.periphs.mainboard.abit
comp.sys.ibm.pc.hardware.chips
alt.comp.hardware.overclocking
alt.comp.hardware.homebuilt
alt.comp.hardware.pc-homebuilt
5. Ask your reseller. Your ABIT authorized distributor should be able to provide
the fastest solution to your technical problem. We sell our products through
distributors who sell to resellers and stores. Your reseller should be very familiar
with your system configuration and should be able to solve your problem much
more efficiently than we could. After all, your reseller regards you as an important
customer who may purchase more products and who can urge your friends to buy
from him or her as well. They integrated and sold the system to you. They should
know best what your system configuration is and your problem. They should have
reasonable return or refund policies. How they serve you is also a good reference
for your next purchase.
6. Contacting ABIT. If you feel that you need to contact ABIT directly you can
send email to the ABIT technical support department. First, please contact the
support team for the branch office closest to you. They will be more familiar with
local conditions and problems and will have better insight as to which resellers
offer what products and services. Due to the huge number of emails coming in
every day and other reasons, such as the time required for problem reproduction,
we will not be able to reply to every email. Please understand that we are selling
through distribution channels and don't have the resources to serve every end-user.
However, we will try to do our best to help every customer. Please also remember
that for many of our technical support team English is a second language, you will
have a better chance of getting a helpful answer if your question can be
understood in the first place. Be sure to use very, simple, concise language that
clearly states the problem, avoid rambling or flowery language and always list
your system components. Here is the contact information for our branch offices:
, is an ideal forum for the public to exchange
WI-1P
Page 69

How to Get Technical Support A-3
North America and South America:
ABIT Computer (U.S.A.) Corporation
45531 Northport Loop West,
Fremont, California 94538, U.S.A.
Tel: 1-510-623-0500
Fax: 1-510-623-1092
sales@abit-usa.com
technical@abit-usa.com
http://www.abit-usa.com
U.K. and Ireland:
ABIT Computer (U.K.) Corporation Ltd.
Unit 3, 24-26 Boulton Road,
Stevenage, Herts SG1 4QX, U.K.
Tel: 44-1438-228888
Fax: 44-1438-226333
sales@abitcomputer.co.uk
technical@abitcomputer.co.uk
Germany, Benelux (Belgium, Netherlands, Luxembourg),
Denmark, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Switzerland:
AMOR Computer B.V. (ABIT’s European Office)
Van Coehoornstraat 7,
5916 PH Venlo, The Netherlands
Tel: 31-77-3204428
Fax: 31-77-3204420
sales@abit.nl
technical@abit.nl
http://www.abit.nl
Austria, Czech, Romania, Bulgaria, Yugoslavia, Slovakia,
Slovenia, Croatia, Bosnia, Serbia, and Macedonia:
Asguard Computer Ges.m.b.H
Schmalbachstrasse 5,
A-2201 Gerasdorf/Wien, Austria
Tel: 43-1-7346709
Fax: 43-1-7346713
asguard@asguard.at
User’s Manual
Page 70

A-4 Appendix A
Japan:
ABIT Computer (Japan) Co. Ltd.
Fax: 81-3-5396-5110
http://www.abit4u.jp
Shanghai:
ABIT Computer (Shanghai) Co. Ltd.
Tel: 86-21-6235-1829
Fax: 86-21-6235-1832
http://www.abit.com.cn
Russia:
ABIT Computer (Russia) Co. Ltd.
Fax: 7-095-937-2837
techrussia@abit.com.tw
http://www.abit.ru
France, Italy, Spain, Portugal, and Greece:
ABIT Computer France SARL
Tel: 33-1-5858-0043
Fax: 33-1-5858-0047
http://www.abit.fr
All other territories not covered above please contact Taiwan
Head Office:
When contacting our headquarters please Note we are located in Taiwan and we are
8+ GMT time. In addition, we have holidays that may be different from those in your
country.
ABIT Computer Corporation
No.323, Yang Guang St., Neihu, Taipei, 114, Taiwan
Tel: 886-2-8751-8888
Fax: 886-2-8751-3382
sales@abit.com.tw
market@abit.com.tw
technical@abit.com.tw
http://www.abit.com.tw
WI-1P
Page 71

How to Get Technical Support A-5
7. RMA Service. If your system has been working but it just stopped, but you have
not installed any new software or hardware recently, it is likely that you have a
defective component. Please contact the reseller from whom you bought the
product. You should be able to get RMA service there.
8. Reporting Compatibility Problems to ABIT. Because of tremendous number of
email messages we receive every day, we are forced to give greater weight to
certain types of messages than to others. For this reason, any compatibility
problem that is reported to us, giving detailed system configuration information
and error symptoms will receive the highest priority. For the other questions, we
regret that we may not be able to reply directly. But your questions may be posted
to the Internet news group in order that a larger number of users can have the
benefit of the information. Please check the news group from time to time.
Thank You
ABIT Computer Corporation
http://www.abit.com.tw
User’s Manual
Page 72

A-6 Appendix A
Technical Support Form
Company Name: Phone Number:
Contact Person: Fax Number:
E-mail Address:
Model * BIOS ID # *
Motherboard Model No. DRIVER REV
OS/Application *
Hardware Name Brand Specifications
CPU *
IDE1
HDD
CD-ROM-Drive
System Memory
ADD-ON CARD
IDE2
IDE1
IDE2
Problem Description:
WI-1P
 Loading...
Loading...