Page 1

Motherboard
AMD Socket AM2
User’s Manual
Introduction
Hardware Setup
BIOS Setup Driver & Utility CD Appendix
For more information:
www.abit.com.tw
AMD Socket AM2
ATX Motherboard
NB: NVIDIA C51XE
SB: NVIDIA MCP55PXE
2GHz HT
Dual DDR2 800 DIMM Slots
NVIDIA SLI Technology
Dual PCI-E X16 Slots
Dual GbE LAN
IEEE 1394a
6x SATA 3Gb/s with
RAID 0/1/0+1/5/JBOD
Fatal1ty Guru™
ABIT OTES GT™ Technology
7.1 Channel HD Audio
Technology
Page 2

User’s Manual
English, 2
July, 2006
nd
Edition
Copyright and Warranty Notice
The information in this document is subject to change without notice and does not represent a
commitment on part of the vendor, who assumes no liability or responsibility for any errors that may
appear in this manual.
No warranty or representation, either expressed or implied, is made with respect to the quality,
accuracy or fitness for any particular part of this document. In no event shall the manufacturer be
liable for direct, indirect, special, incidental or consequential damages arising from any defect or
error in this manual or product.
Product names appearing in this manual are for identification purpose only and trademarks and
product names or brand names appearing in this document are the property of their respective
owners.
This document contains materials protected under International Copyright Laws. All rights reserved.
No part of this manual may be reproduced, transmitted or transcribed without the expressed written
permission of the manufacturer and authors of this manual.
If you do not properly set the motherboard settings, causing the motherboard to malfunction or fail,
we cannot guarantee any responsibility.
The Fatal1ty name, Fatal1ty logos and the Fatal1ty likeness are trademarks of Fatal1ty,
Inc. All rights reserved. Built to Kill is a trademark of PWX, LLC.
© 2006 Universal ABIT Co.,
All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
ii
Ltd.
Page 3

Contents
Introduction
1. Introduction..................................................................... 1-1
1.1 Fatal1ty ......................................................................................1-1
1.2 Features & Specifications .............................................................1-3
1.3 Motherboard Layout.....................................................................1-5
2. Hardware Setup ............................................................... 2-1
2.1 Choosing a Computer Chassis.......................................................2-1
2.2 Installing Motherboard .................................................................2-1
2.3 Checking Jumper Settings ............................................................2-2
2.3.1 CMOS Memory Clearing Header and Backup Battery ..............2-3
2.3.2 Wake-up Headers................................................................2-5
2.4 Connecting Chassis Components...................................................2-6
2.4.1 ATX Power Connectors ........................................................2-6
2.4.2 Front Panel Switches & Indicators Headers............................2-7
2.4.3 FAN Power Connectors ........................................................2-8
2.5 Installing Hardware......................................................................2-9
2.5.1 CPU Socket AM2 .................................................................2-9
2.5.2 DDR2 Memory Slots ..........................................................2-11
2.5.3 PCI Express X16 Add-on Slots (Install Graphics Card) ..........2-13
2.5.4 AudioMAX Connection Slot .................................................2-16
2.6 Connecting Peripheral Devices .................................................... 2-19
2.6.1 Floppy and IDE Disk Drive Connectors ................................2-19
2.6.2 Serial ATA Connectors ....................................................... 2-20
2.6.3 Additional USB 2.0 Port Headers......................................... 2-21
2.6.4 Additional IEEE1394 Port Headers ......................................2-21
2.6.5 PCI Express X1 Add-on Slots .............................................. 2-22
2.6.6 PCI Add-on Slots ............................................................... 2-22
2.6.7 GURU Panel Connection Header ......................................... 2-23
2.7 Onboard Status Display.............................................................. 2-24
2.7.1 POST Code Displayer.........................................................2-24
2.7.2 Power Source Indicators .................................................... 2-25
2.8 Connecting I/O Devices.............................................................. 2-26
Hardware Setup
BIOS Setup Driver & Utility CD Appendix
3. BIOS Setup....................................................................... 3-1
3.1 µGuru™ Utility..............................................................................3-2
3.1.1 OC Guru .............................................................................3-2
3.1.2 ABIT EQ .............................................................................3-4
iii
Page 4

3.2 Standard CMOS Features............................................................ 3-11
3.3 Advanced BIOS Features ............................................................ 3-14
3.4 Advanced Chipset Features......................................................... 3-16
3.5 Integrated Peripherals................................................................ 3-18
3.6 Power Management Setup.......................................................... 3-22
3.7 PnP/PCI Configurations ..............................................................3-24
3.8 Load Fail-Safe Defaults ..............................................................3-26
3.9 Load Optimized Defaults ............................................................3-26
3.10 Set Password........................................................................... 3-26
3.11 Save & Exit Setup ....................................................................3-26
3.12 Exit Without Saving.................................................................. 3-26
4. Driver & Utility CD............................................................ 4-1
4.1 nVidia nForce Chipset Driver......................................................... 4-2
4.2 Realtek HD Audio Driver...............................................................4-3
4.3 Silicon Image 3132 RAID Driver....................................................4-4
4.4 Cool’n’Quiet Driver.......................................................................4-5
4.5 USB 2.0 Driver.............................................................................4-7
4.6 ABIT µGuru Utility........................................................................4-7
4.7 NVRaid Floppy Disk......................................................................4-8
5. Appendix .......................................................................... 5-1
5.1 POST Code Definitions .................................................................5-1
5.1.1 AWARD POST Code Definitions.............................................5-1
5.1.2 AC2005 POST Code Definitions.............................................5-4
5.2 Troubleshooting (How to Get Technical Support?)..........................5-5
5.2.1 Q & A.................................................................................5-5
5.2.2 Technical Support Form ......................................................5-8
5.2.3 Universal ABIT Contact Information......................................5-9
iv
Page 5

1. Introduction
Introduction
1.1 Fatal1ty
FATAL1TY STORY
Who knew that at age 19, I would be
a World Champion PC gamer. When
I was 13, I actually played
competitive billiards in professional
tournaments and won four or five
games off guys who played at the
highest level. I actually thought of
making a career of it, but at that
young age situations change rapidly.
Because I’ve been blessed with great
hand-eye coordination and a grasp of
mathematics (an important element
in video gaming) I gravitated to that
activity.
GOING PRO
I started professional gaming in 1999 when I entered the CPL (Cyberathlete Professional
League) tournament in Dallas and won $4,000 for coming in third place. Emerging as one of
the top players in the United States, a company interested in sponsoring me flew me to Sweden
to compete against the top 12 players in the world. I won 18 straight games, lost none, and
took first place, becoming the number one ranked Quake III player in the world in the process.
Two months later I followed that success by traveling to Dallas and defending my title as the
world’s best Quake III player, winning the $40,000 grand prize. My earned frags allowed at
this tournament were 2.5. From there I entered competitions all over the world, including
Singapore, Korea, Germany, Australia, Holland and Brazil in addition to Los Angeles, New York
and St. Louis.
WINNING STREAK
I was excited to showcase my true gaming skills when defending my title as CPL Champion of
the year at the CPL Winter 2001 because I would be competing in a totally different first person
shooter (fps) game, Alien vs. Predator II. I won that competition and walked away with a new
car. The next year I won the same title playing Unreal Tournament 2003, becoming the only
three-time CPL champion. And I did it playing a different game each year, something no one
else has ever done and a feat of which I am extremely proud.
At QuakeCon 2002, I faced off against my rival ZeRo4 in one of the most highly anticipated
matches of the year, winning in a 14 to (-1) killer victory. Competing at Quakecon 2004, I
became the World’s 1
matches and earning $25,000 for the victory.
st
Doom3 Champion by defeating Daler in a series of very challenging
1-1
Page 6

LIVIN’ LARGE
Since my first big tournament wins, I have been a “Professional Cyberathlete”, traveling the
world and livin’ large with lots of International media coverage on outlets such as MTV, ESPN
and G4TV to name only a few. It's unreal - it's crazy. I’m living a dream by playing video
games for a living. I’ve always been athletic and took sports like hockey and football very
seriously, working out and training hard. This discipline helps me become a better gamer and
my drive to be the best has opened the doors necessary to become a professional.
A DREAM
Now, another dream is being realized – building the ultimate gaming computer, made up of the
best parts under my own brand. Quality hardware makes a huge difference in competitions…a
couple more frames per second and everything gets really nice. It's all about getting the
computer processing faster and allowing more fluid movement around the maps.
My vision for Fatal1ty hardware is to allow gamers to focus on the game without worrying
about their equipment, something I’ve preached since I began competing. I don’t want to
worry about my equipment. I want it to be there – over and done with - so I can focus on the
game. I want it to be the fastest and most stable computer equipment on the face of the
planet, so quality is what Fatal1ty brand products will represent.
FATAL1TY BRAIN TRUST
This is just the beginning. We’re already in development for several new products, and I’m
really grateful to all my Fatal1ty Brain Trust partners for helping make my dreams a reality.
I know there is a business side to all of this, but for me the true reward is making products that
are so good I can win with them – and making them available to fellow gamers. Gaming is my
life, and many fellow gamers around the world are also some of my best friends, so giving back
to the gaming community is really important to me.
Johnathan “Fatal1ty” Wendel
1-2
Page 7

1.2 Features & Specifications
CPU
• Supports Socket 940 AM2 Processor with 2GHz system bus using Hyper-Transport™
Technology
• Supports AMD CPU Cool ‘n’ Quiet Technology
Chipset
• Northbridge: NVIDIA®C51XE Chipset
• Southbridge: NVIDIA
Memory
• Four 240-pin DIMM slots
• Supports Dual Channel DDR2 800 Un-buffered ECC/Non-ECC memory
• Supports maximum memory capacity up to 8GB
ABIT Engineered
• ABIT Fatal1ty Guru™ Technology
• ABIT OTES GT
NVIDIA SLI Technology
• Two PCI-Express X16 slots support NVIDIA Scalable Link Interface
SATA 3Gb/s RAID
• Supports 6 ports NV SATA 3Gb/s RAID 0/1/0+1/5/JBOD
Dual GbE LAN
• Dual NVIDIA® Gigabit Ethernet
IEEE 1394
• Supports 2 Ports IEEE 1394a at 400Mb/s transfer rate
Audio
• ABIT AudioMAX HD 7.1 CH
• Supports auto jack sensing and optical S/PDIF In/Out
Expansion Slots
• 2x PCI Express x16 slots
• 2x PCI Express x1 slots
• 1x PCI slot
• 1x AudioMAX slot
Internal I/O Connectors
• 1x Floppy port
• 1x UDMA 133/100/66/33 connector
• 6x SATA connectors
• 3x USB 2.0 headers
®
MCP55PXE Chipset
™
Technology
Introduction
1-3
Page 8

• 2x IEEE1394a headers
Rear Panel I/O
• OTES GT™
• 1x PS/2 Keyboard connector
• 1x PS/2 Mouse connector
• 2x RJ-45 Gigabit LAN ports
• 4x USB 2.0 ports
RoHS Compliancy
• 100% Lead-free process and RoHS compliancy
Miscellaneous
• ATX form factor (305mm x 245mm)
Specifications and information contained herein are subject to change without notice.
For more information:
www.abit.com.tw
1-4
Page 9
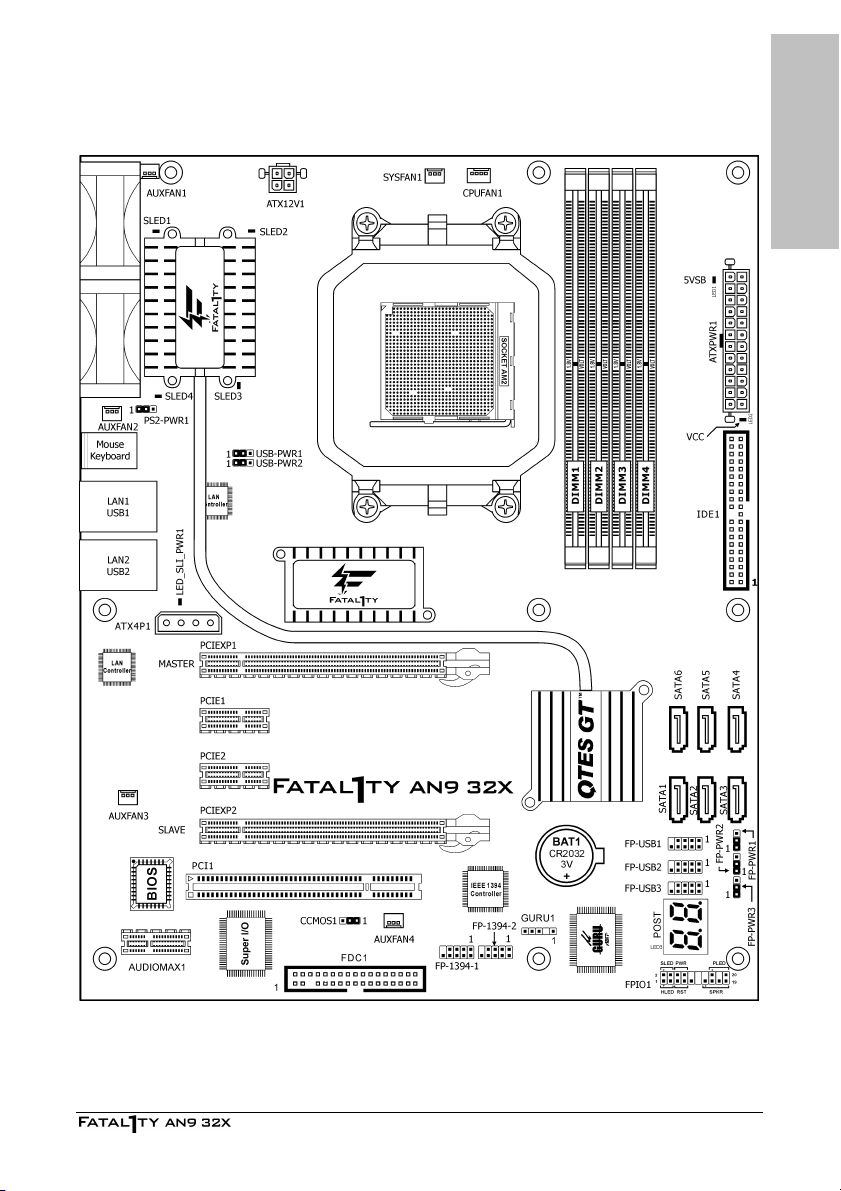
1.3 Motherboard Layout
Introduction
1-5
Page 10

For more information:
www.abit.com.tw
1-6
Page 11
2. Hardware Setup
In this chapter we will elaborate all the information you need upon installing this motherboard
to your computer system.
※ Always power off the computer and unplug the AC power cord before adding or
removing any peripheral or component. Failing to so may cause severe damage
to your motherboard and/or peripherals. Plug in the AC power cord only after
you have carefully checked everything.
2.1 Choosing a Computer Chassis
• This motherboard carries an ATX form factor of 305 x 245 mm. Choose a chassis big
enough to install this motherboard.
• As some features for this motherboard are implemented by cabling connectors on the
motherboard to indicators and switches or buttons on the chassis, make sure your chassis
supports all the features required.
• If there is possibility of adopting some more hard drives, make sure your chassis has
sufficient power and space for them.
• Most chassis have alternatives for I/O shield located at the rear panel. Make sure the I/O
shield of the chassis matches the I/O port configuration of this motherboard. You can find
an I/O shield specifically designed for this motherboard in its package.
2.2 Installing Motherboard
Hardware Setup
Most computer chassis have a base with
many mounting holes to allow the
motherboard to be securely attached, and at
the same time, prevent the system from
short circuits. There are two ways to attach
the motherboard to the chassis base:
1. with studs,
2. or with spacers
In principle, the best way to attach the board
is with studs. Only if you are unable to do
this should you attach the board with spacers.
Line up the holes on the board with the mounting holes on the chassis. If the holes line up and
there are screw holes, you can attach the board with studs. If the holes line up and there are
only slots, you can only attach with spacers. Take the tip of the spacers and insert them into
the slots. After doing this to all the slots, you can slide the board into position aligned with slots.
After the board has been positioned, check to make sure everything is OK before putting the
chassis back on.
2-1
Page 12
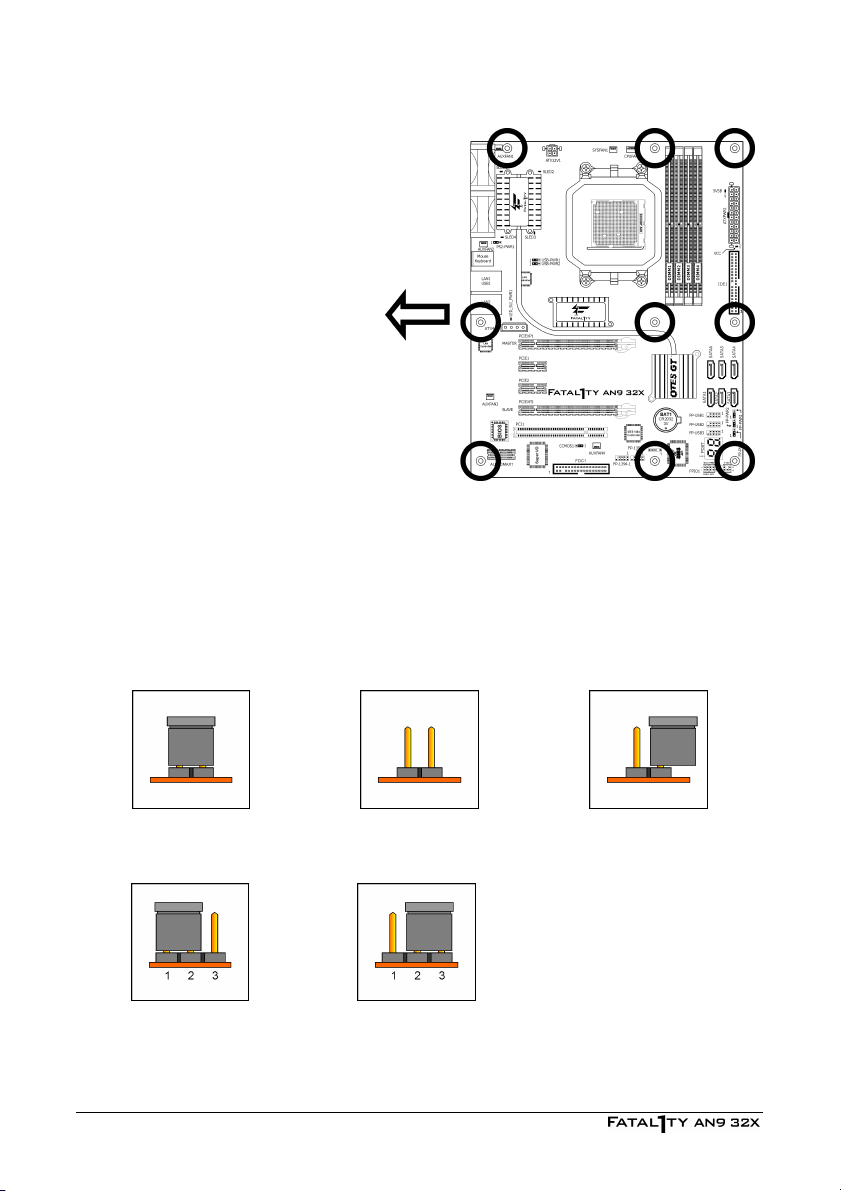
r
To install this motherboard:
1. Locate all the screw holes on
the motherboard and the
chassis base.
2. Place all the studs or spacers
needed on the chassis base
and have them tightened.
3. Face the motherboard’s I/O
ports toward the chassis’s rear
panel.
4. Line up all the motherboard’s
screw holes with those studs o
spacers on the chassis.
5. Install the motherboard with
screws and have them
tightened.
※ To prevent shorting the PCB circuit, please REMOVE the metal studs or spacers if
they are already fastened on the chassis base and are without mounting-holes
on the motherboard to align with.
Face the chassis’s rear panel.
2.3 Checking Jumper Settings
For a 2-pin jumper, plug the jumper cap on both pins will make it CLOSE (SHORT). Remove the
jumper cap, or plug it on either pin (reserved for future use) will leave it at OPEN position.
SHORT OPEN OPEN
For 3-pin jumper, pin 1~2 or pin 2~3 can be shorted by plugging the jumper cap in.
Pin 1~2 SHORT Pin 2~3 SHORT
2-2
Page 13
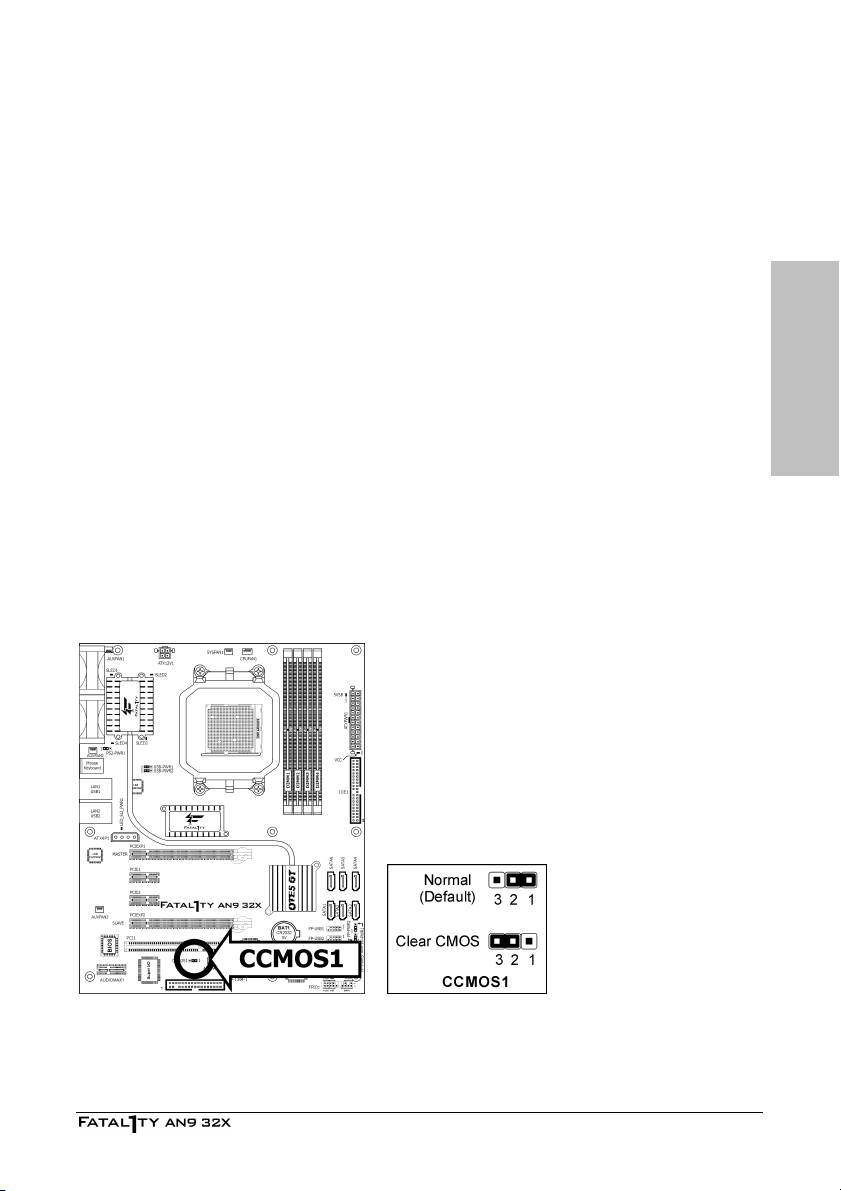
2.3.1 CMOS Memory Clearing Header and Backup Battery
The time to clear the CMOS memory occurs when (a) the CMOS data becomes corrupted, (b)
you forgot the supervisor or user password preset in the BIOS menu, (c) you are unable to
boot-up the system because the CPU ratio/clock was incorrectly set in the BIOS menu, or (d)
whenever there is modification on the CPU or memory modules.
This header uses a jumper cap to clear the CMOS memory and have it reconfigured to the
default values stored in BIOS.
• Pins 1 and 2 shorted (default): Normal operation.
• Pins 2 and 3 shorted: Clear CMOS memory.
To clear the CMOS memory and load in the default values:
1. Power off the system and disconnect with AC power source.
2. Set pin 2 and pin 3 shorted by the jumper cap. Wait for a few seconds. Set the jumper cap
back to its default settings --- pin 1 and pin 2 shorted.
3. Power on the system.
4. For incorrect CPU ratio/clock settings in the BIOS, press <Del> key to enter the BIOS setup
menu right after powering on system.
5. Set the CPU operating speed back to its default or an appropriate value.
6. Save and exit the BIOS setup menu.
Hardware Setup
2-3
Page 14
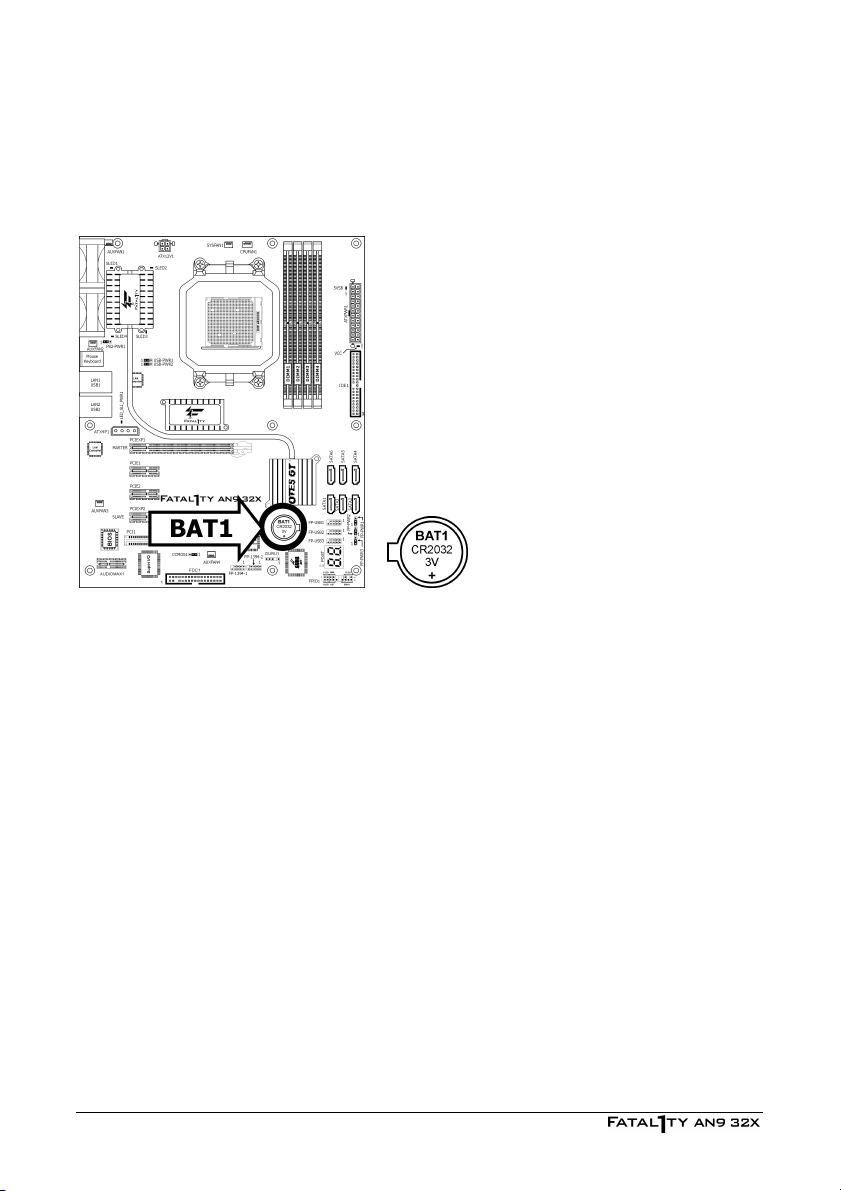
CMOS Backup Battery:
An onboard battery saves the CMOS memory to keep the BIOS information stays on even after
disconnected your system with power source. Nevertheless, this backup battery exhausts after
some five years. Once the error message like “CMOS BATTERY HAS FAILED” or “CMOS
checksum error” displays on monitor, this backup battery is no longer functional and has to
be renewed.
To renew the backup battery:
1. Power off the system and disconnect with AC power source.
2. Remove the exhausted battery.
3. Insert a new CR2032 or equivalent battery. Pay attention to its polarity. The “+” side is its
positive polarity.
4. Connect AC power source and power on the system.
5. Enter the BIOS setup menu. Reconfigure the setup parameters if necessary.
CAUTION:
※ Danger of explosion may arise if the battery is incorrectly renewed.
※ Renew only with the same or equivalent type recommended by the battery
manufacturer.
※ Dispose of used batteries according to the battery manufacturer’s instructions.
2-4
Page 15
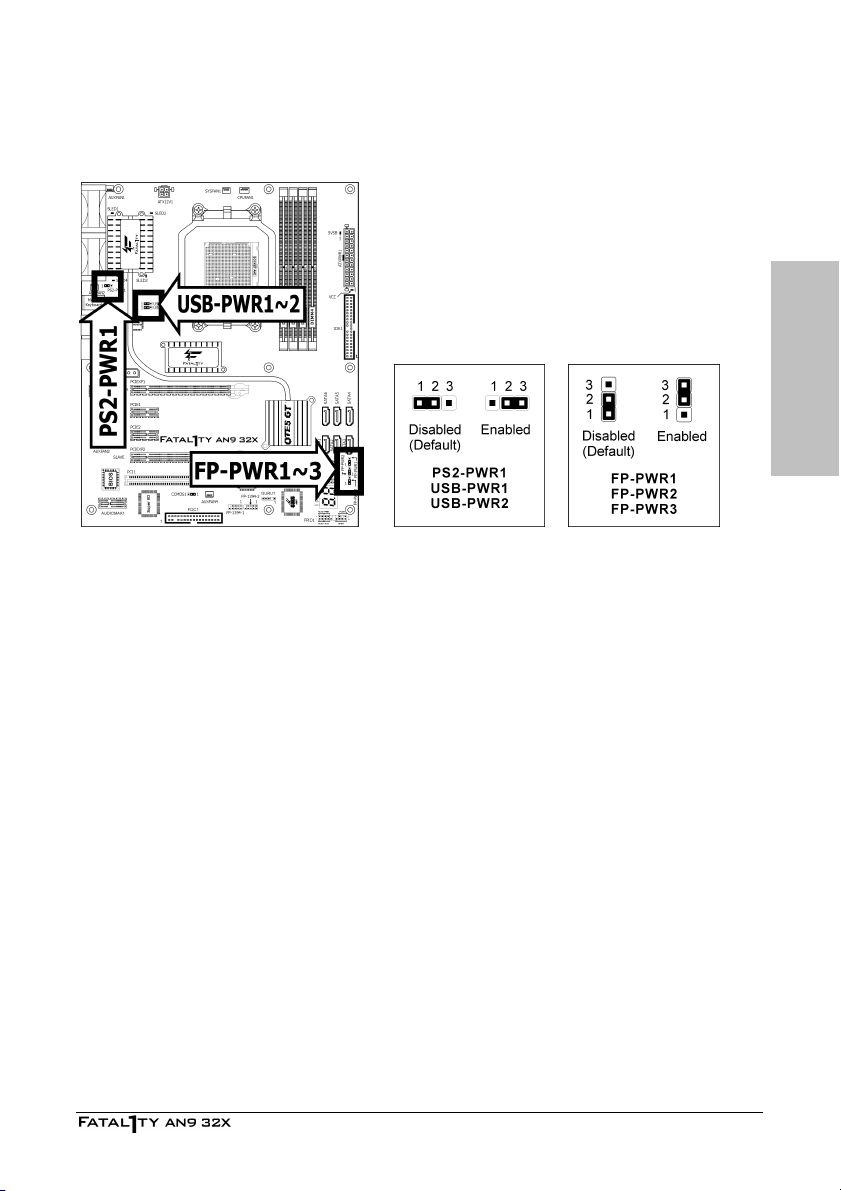
2.3.2 Wake-up Headers
These headers use a jumper cap to enable/disable the wake-up function.
Hardware Setup
• PS2-PWR1:
Pin 1-2 shorted (Default): Disable wake-up function support at Keyboard/Mouse port.
Pin 2-3 shorted: Enable wake-up function support at Keyboard/Mouse port.
• USB-PWR1:
Pin 1-2 shorted (Default): Disable wake-up function support at USB1 port.
Pin 2-3 shorted: Enable wake-up function support at USB1 port.
• USB-PWR2:
Pin 1-2 shorted (Default): Disable wake-up function support at USB2 port.
Pin 2-3 shorted: Enable wake-up function support at USB2 port
• FP-PWR1:
Pin 1-2 shorted (Default): Disable wake-up function support at FP-USB1 port.
Pin 2-3 shorted: Enable wake-up function support at FP-USB1 port.
• FP-PWR2:
Pin 1-2 shorted (Default): Disable wake-up function support at FP-USB2 port.
Pin 2-3 shorted: Enable wake-up function support at FP-USB2 port
• FP-PWR3:
Pin 1-2 shorted (Default): Disable wake-up function support at FP-USB3 port.
Pin 2-3 shorted: Enable wake-up function support at FP-USB3 port
2-5
Page 16
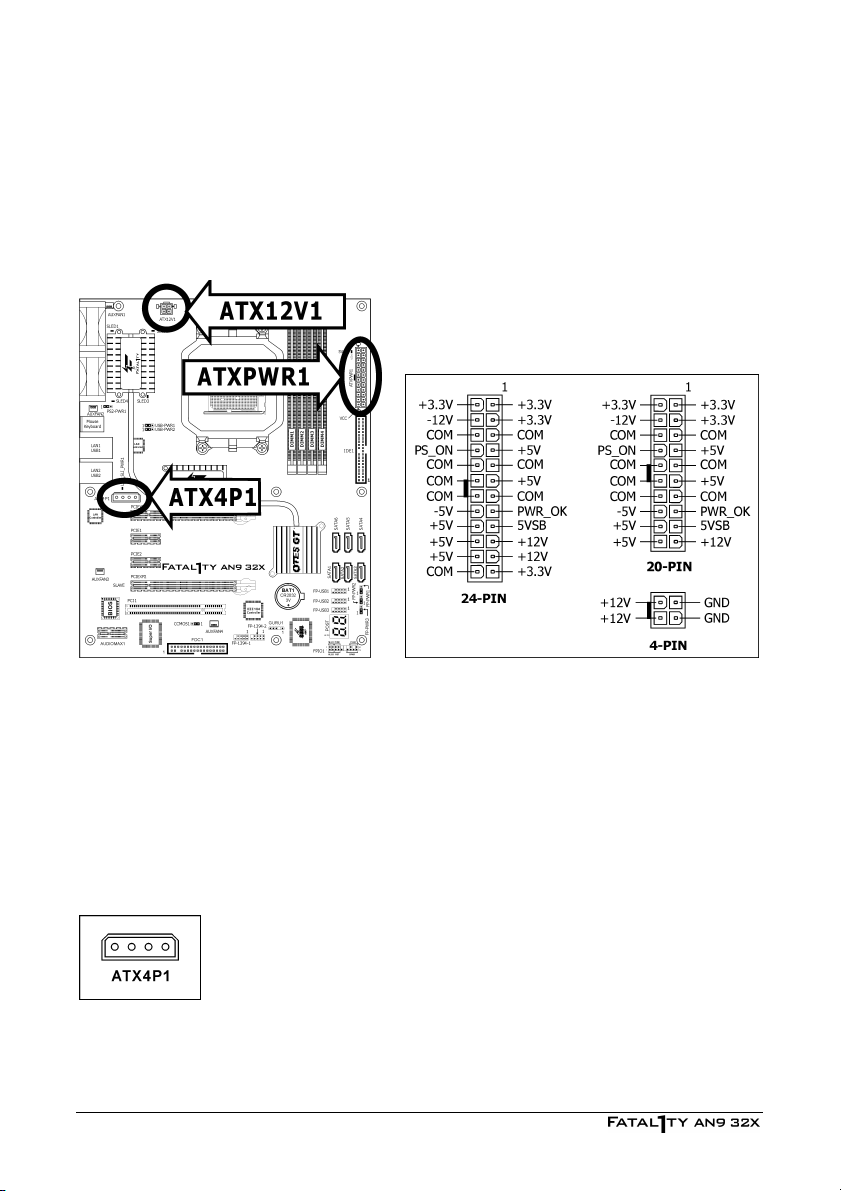
2.4 Connecting Chassis Components
2.4.1 ATX Power Connectors
These connectors provide the connection from an ATX power supply. As the plugs from the
power supply fit in only one orientation, find the correct one and push firmly down into these
connectors.
ATX 24-Pin Power Connector:
The power supply with 20-pin or 24-pin cables can both be connected to this 24-pin connector.
Connect from pin-1 for either type. However, a 20-pin power supply may cause the system
unstable or even unbootable for the sake of insufficient electricity. A minimum power of 300W
or higher is recommended.
ATX 12V 4-Pin Power Connector:
This connector supplies power to CPU. The system will not start without connecting power to
this one.
Auxiliary 12V Power Connector:
This connector provides an auxiliary power source for devices added on PCI
Express slots.
2-6
Page 17
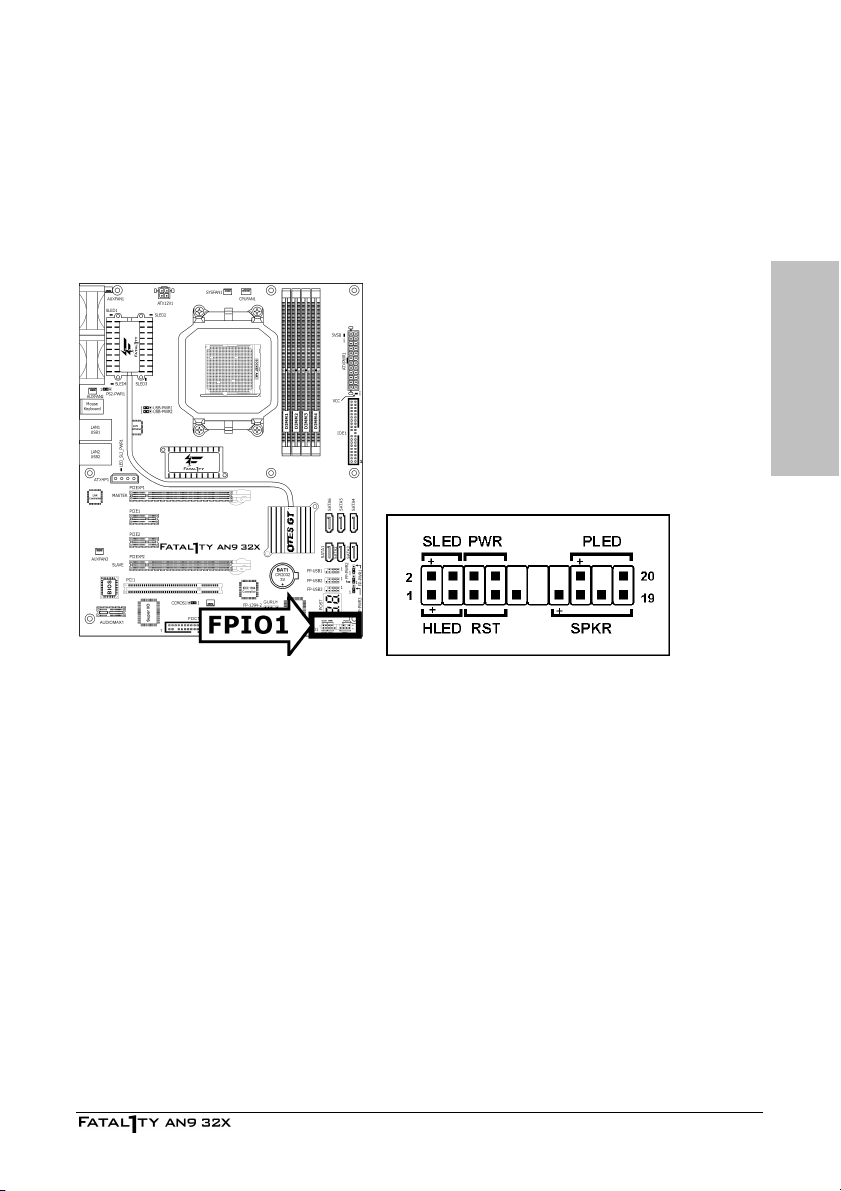
2.4.2 Front Panel Switches & Indicators Headers
This header is used for connecting switches and LED indicators on the chassis front panel.
Watch the power LED pin position and orientation. The mark “+” align to the pin in the figure
below stands for positive polarity for the LED connection. Please pay attention to connect these
headers. A wrong orientation will only cause the LED not lighting, but a wrong connection of
the switches could cause system malfunction.
Hardware Setup
• HLED (Pin 1, 3):
Connects to the HDD LED cable of chassis front panel.
• RST (Pin 5, 7):
Connects to the Reset Switch cable of chassis front panel.
• SPKR (Pin 13, 15, 17, 19):
Connects to the System Speaker cable of chassis.
• SLED (Pin 2, 4):
Connects to the Suspend LED cable (if there is one) of chassis front panel.
• PWR (Pin 6, 8):
Connects to the Power Switch cable of chassis front panel.
• PLED (Pin 16, 18, 20):
Connects to the Power LED cable of chassis front panel.
2-7
Page 18
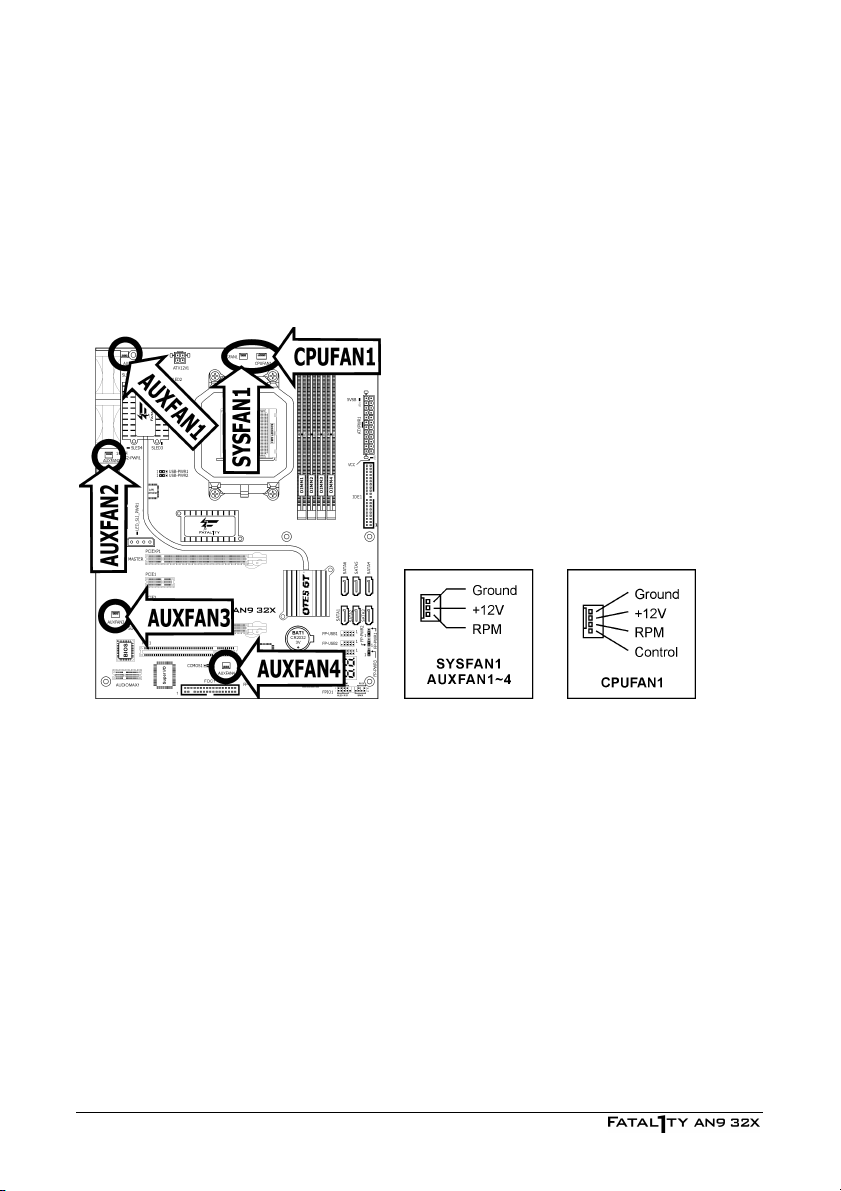
2.4.3 FAN Power Connectors
These connectors each provide power to the cooling fans installed in your system.
• CPUFAN1: CPU Fan Power Connector
• SYSFAN1: System Fan Power Connector
• AUXFAN1~4: Auxiliary Fan Power Connector
※ These fan connectors are not jumpers. DO NOT place jumper caps on these
connectors.
2-8
Page 19

2.5 Installing Hardware
※ DO NOT scratch the motherboard when installing hardware. An accidentally
scratch of a tiny surface-mount component may seriously damage the
motherboard.
2.5.1 CPU Socket AM2
※ DO NOT touch or bend the delicate pins on the CPU whenever you are holding it.
The installation procedures vary with different types of CPU fan-and-heatsink assembly. The
one shown here is served for DEMO only. For detailed information on how to install the one
you bought, refer to its installation guidelines.
1. Pull out the socket lever away from the
socket and fully lift it up over 90-degree
angle.
Locate and align the triangle mark with
both the CPU and the socket body.
Vertically place the CPU with its pin-side
down into the socket.
Be careful to insert the CPU into the
socket. The CPU only fits in one
orientation with the socket. DO NOT
force the CPU into the socket.
2. After placing the CPU into position, push
the socket lever down into its locked
position to secure the CPU. The lever
clicks when it’s locked into position.
3. The heatsink for CPU may have thermal
interface material attached to its
bottom. If not, applying a few squeeze
of thermal paste to the CPU die will help
to increase the contact.
Hardware Setup
2-9
Page 20
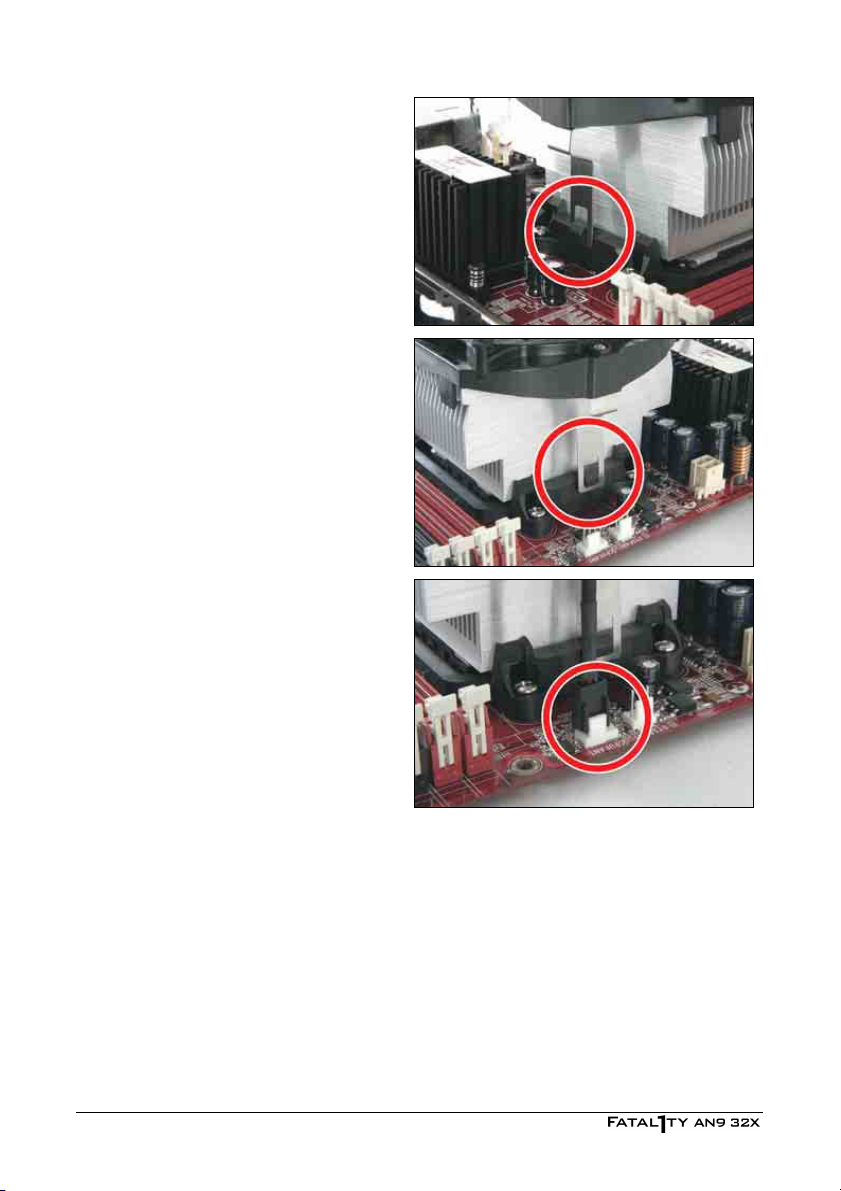
A
4. Place the heatsink and fan assembly
onto the retention frame. Match the
heatsink clip with the socket
mounting-lug. Hook the spring clip to
the mounting-lug.
5. On the other side, push the retention
clip straight down to lock into the plastic
lug on the retention frame.
6. Connect the CPU cooling fan power
cable to the CPUFAN1 connector on this
motherboard.
※ The “CPUFAN1” connector can be
connected either with a 3-Pin or
4-Pin CPU cooling fan. For a 3-Pin
connection, there will be no speed
control available in the BIOS setup
menu; the CPU fan will run at full
speed.
lso, please watch out for the
orientation when inserting 3-Pin
plug into this 4-Pin fan connector.
※ A higher fan speed will be helpful for better airflow and heat-dissipation.
Nevertheless, stay alert to touch any heatsink since the high temperature
generated by the working system is still possible.
2-10
Page 21
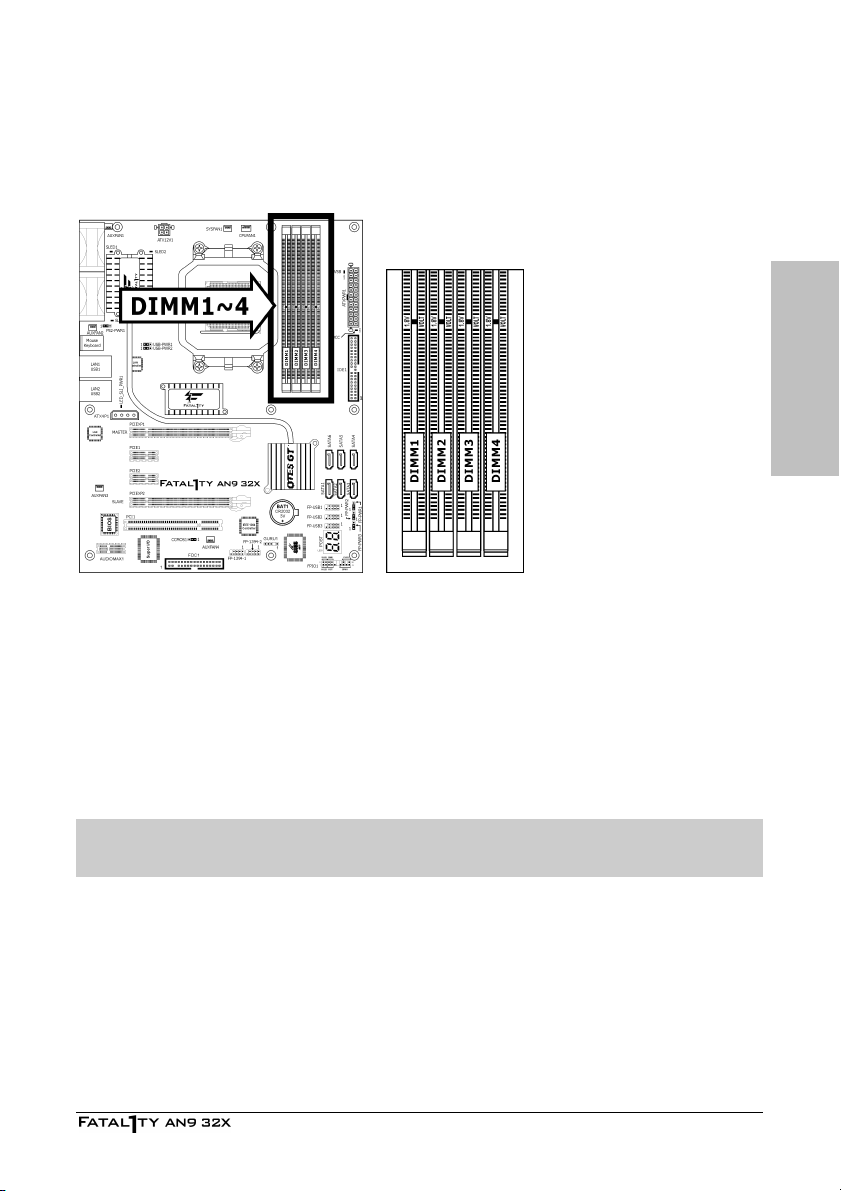
2.5.2 DDR2 Memory Slots
This motherboard provides four 240-pin DIMM slots for Dual Channel DDR2 800 memory
modules with memory expansion size up to 8GB.
To reach the performance of Dual Channel DDR2, the following rules must be obeyed:
• For a 2-DIMM dual-channel installation:
Populate DIMM modules of the same type and size on slots [DIMM1]+[DIMM2], or slots
[DIMM3]+[DIMM4].
• For a 4-DIMM dual-channel installation:
Populate 2 DIMM modules of the same type and size on slots [DIMM1]+[DIMM2], and
another 2 DIMM modules of the same type and size on slots [DIMM3]+[DIMM4].
※ [DIMM1] and [DIMM2] slots are made of the same color.
[DIMM3] and [DIMM4] are made of another same color.
Usually there is no hardware or BIOS setup requires after adding or removing memory modules,
but you will have to clear the CMOS memory first if any memory module related problem
occurs.
Hardware Setup
2-11
Page 22
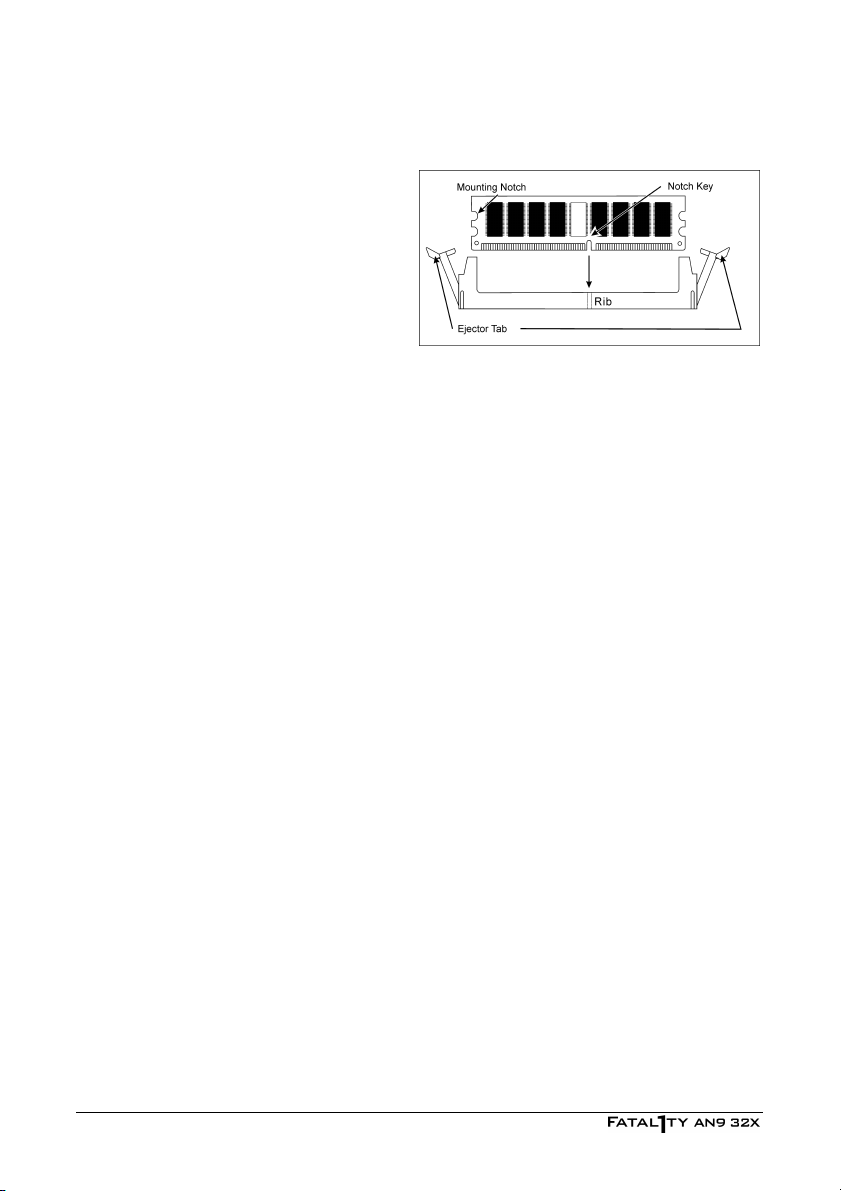
To install system memory:
1. Power off the computer and unplug the AC power cord before installing or removing
memory modules.
2. Locate the DIMM slot on the board.
3. Hold two edges of the DIMM module
carefully, keep away of touching its
connectors.
4. Align the notch key on the module with
the rib on the slot.
5. Firmly press the module into the slots
until the ejector tabs at both sides of the slot automatically snaps into the mounting notch.
Do not force the DIMM module in with extra force as the DIMM module only fit in one
direction.
6. To remove the DIMM modules, push the two ejector tabs on the slot outward
simultaneously, and then pull out the DIMM module.
※ Static electricity can damage the electronic components of the computer or
optional boards. Before starting these procedures, ensure that you are
discharged of static electricity by touching a grounded metal object briefly.
2-12
Page 23
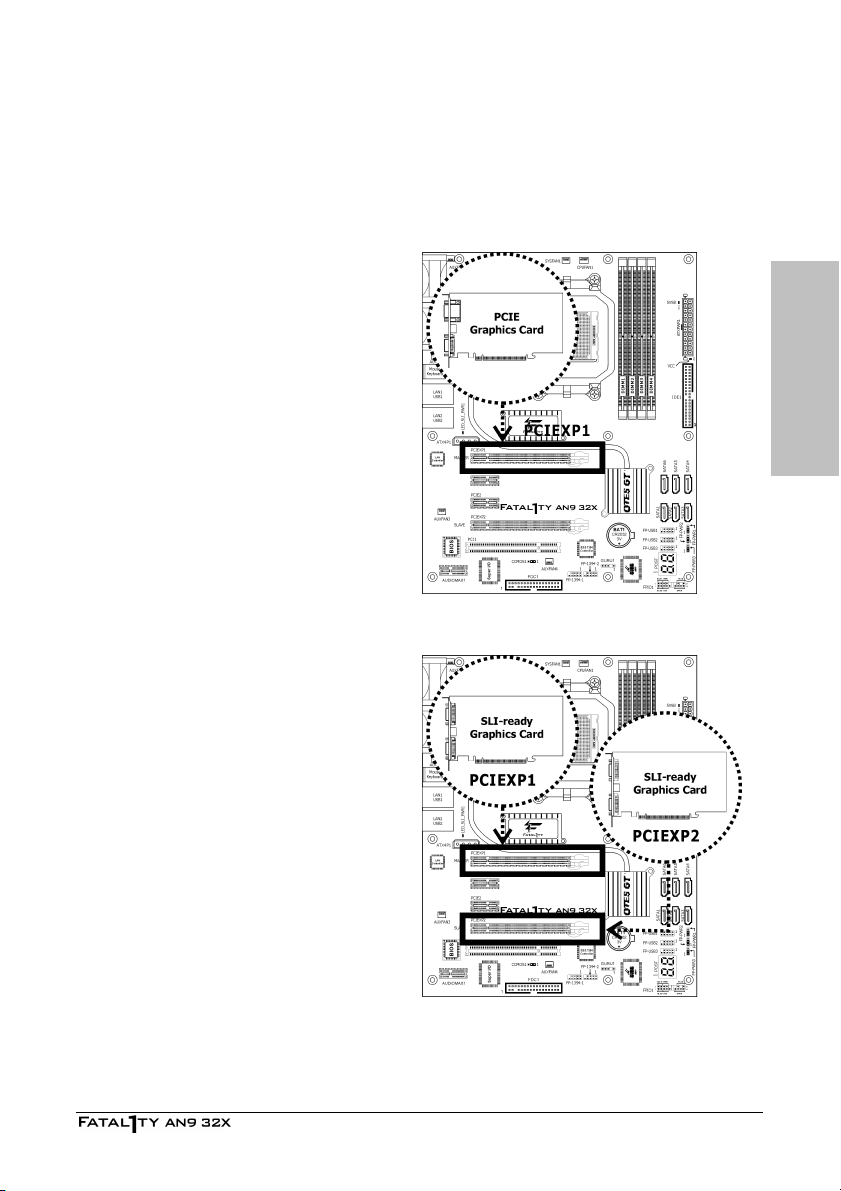
2.5.3 PCI Express X16 Add-on Slots (Install Graphics Card)
These slots support the connections of graphics cards that comply with PCI Express
specifications. This motherboard provides dual PCI-Express X16 slots for one or two graphics
cards installation:
One PCIE graphics card installation (Normal Mode):
Insert your PCIE graphics card into [PCIEXP1]
slot.
Hardware Setup
Two PCIE graphics cards installation (SLI Mode):
Insert two identical SLI-ready graphics cards
into both PCIEXP1 and PCIEXP2 slots.
※ The NVIDIA SLI technology currently
supports the Windows XP operating
system only.
2-13
Page 24

To install two SLI-ready graphics cards under SLI Mode, you will need to:
• Prepare two identical NVIDIA certified, SLI-ready PCI Express x16 graphics cards (the same
model from the same manufacturer).
• Make sure the graphics card driver supports the NVIDIA SLI technology. Download the
latest driver form NVIDIA website (www.nvidia.com
).
• Make sure your power supply unit is sufficient to provide the minimum power required.
※ The following illustration is served for DEMO only. All the devices, including the
motherboard, the graphics cards, the SLI Bridge Connector, or the SLI bracket,
may not be exactly the same type, shape, or model as the one you bought.
1. Unscrew and remove five of the I/O
brackets at the chassis’s rear panel
starting from the first one for PCIEXP1
slot.
Carefully insert two graphics cards into
both the PCI Express X16 slots on this
motherboard. Secure the graphics cards
with the two screws removed from the
I/O bracket to the first and last screw
holes. Leave the three screw holes in
between unscrewed.
2. Place Abit’s exclusive SLI FAN assembly
“SLIpstream” atop the two graphics
cards. For not installing the SLI
supporting bracket, you may secure the
fan assembly now with the three screws
removed from the I/O bracket.
Keep any components on the graphics
cards away from been touched by the
metal frame of the SLI FAN assembly.
3. Bridge connect two graphics cards with
the “SLI Connector Card” (fit in both
direction).
Keep any components on the “SLI
Connector Card” away from been
touched by the metal frame of the SLI
FAN assembly.
Now complete the installation of two
graphics cards, SLI FAN assembly, and
the “SLI Connector Card”.
2-14
Page 25

4. To install together with the SLI
supporting bracket, unscrew the central
hole of the I/O panel, insert the SLI
supporting bracket, and then have it
secured.
The default airflow direction blows the
motherboard. To reverse the airflow,
pull out the fan body from the frame,
overturn and push it in.
5. To install without the SLI FAN assembly,
connect the “SLI Connector Card” right
after having installed two graphics
cards, and then insert and secure the
SLI supporting bracket.
6. Connect the power plug from the SLI
FAN assembly either to the three-leaded
fan-power connector on your
motherboard, or directly to the ATX12V
power supply.
Hardware Setup
For more information:
www.abit.com.tw
2-15
Page 26

2.5.4 AudioMAX Connection Slot
This slot provides the audio input/output connection over the rear I/O part through an add-on
daughter-card. Find your “AudioMAX” daughter-card and its driver in the motherboard
package.
• S/PDIF Out: This connector provides an S/PDIF-Out connection through optical fiber to
digital multimedia devices.
• S/PDIF In: This connector provides an S/PDIF-In connection through optical fiber to
digital multimedia devices.
Line-In: Connects to the line out from external audio sources.
• Mic-In: Connects to the plug from external microphone.
• Line-Out: Connects to the front left and front right channel in the 7.1-channel or regular
2-channel audio system.
• Cen/Sub: Connects to the center and subwoofer channel in the 7.1-channel audio system.
• R.L./R.R. (Rear Left / Rear Right): Connects to the rear left and rear right channel in
the 7.1-channel audio system.
• S.L./S.R. (Surround Left / Surround Right): Connects to the surround left and
surround right channel in the 7.1-channel audio system.
• CD1: This connector connects to the audio output of internal CD-ROM
drive or add-on card.
2-16
Page 27

• FP-AUDIO1: This header provides the connection to audio connector
at front panel.
This header provides the front panel connection for HD (High Definition)
Audio, yet for AC’97 Audio CODEC connection, you must carefully check the
pin assignment before connecting from the front panel module. An incorrect
connection may cause malfunction or even damage the motherboard.
※ Please do not connect the
“Ground” cable or “USB VCC”
cable from the front panel
module to the Pin 4 “AVCC”
of this header.
Driver Configuration for AC’97
audio connection:
The audio driver is originally
configured to support HD Audio. For
AC’97 audio connection, you may:
1. Right-click the “Realtek HD Audio Manager”
in system tray.
icon
Pin Assignment
Pin
(HD AUDIO)
1 MIC2 L 1 MIC In
2 AGND 2 GND
3 MIC2 R 3 MIC Power
4 AVCC 4 NC
5 FRO-R 5 Line Out (R)
6 MIC2_JD 6 NC
7 F_IO_SEN 7 NC
9 FRO-L 9 Line Out (L)
10 LINE2_JD 10 NC
Pin
Pin Assignment
(AC’97 AUDIO)
Hardware Setup
2. Click “Audio I/O” tab, and then click
“Connector Settings”.
2-17
Page 28

3. Click “Disabled front panel jack
detection”, and then click “OK” to confirm.
S/PDIF Connection:
In the motherboard package you can find one audio daughter-card and one optical-fiber cable.
• S/PDIF Input Connection:
1. Remove the rubber protection-cap. Attach one end of the optical cable with the 3.5mm
Optical-to-Stereo adapter, and have it plugged into the [Line-In] jack on this
daughter-card. (This jack is served for either optical or line input.)
2. Connect the other end of the optical cable to the [Digital-Out] (SPDIF-Out) jack on your
digital multimedia device.
• S/PDIF Output Connection:
1. Remove the rubber protection-cap. Plug one end of the optical cable into the
[SPDIF-Out] jack on this daughter-card.
2. Connect the other end of the optical cable to the [Digital-In] (SPDIF-In) jack on your
digital multimedia device.
2-18
Page 29

2.6 Connecting Peripheral Devices
2.6.1 Floppy and IDE Disk Drive Connectors
The FDC1 connector connects up to two floppy drives with a 34-wire, 2-connector floppy cable.
Connect the single end at the longer length of ribbon cable to the FDC1 on the board, the two
connectors on the other end to the floppy disk drives connector. Generally you need only one
floppy disk drive in your system.
※ The red line on the ribbon cable must be aligned with pin-1 on both the FDC1
port and the floppy connector.
Each of the IDE port connects up to two IDE drives
at Ultra ATA/100 mode by one 40-pin, 80-conductor,
and 3-connector Ultra ATA/66 ribbon cables.
Connect the single end (blue connector) at the
longer length of ribbon cable to the IDE port of this
board, the other two ends (gray and black connector)
at the shorter length of the ribbon cable to the
connectors of your hard drives.
Hardware Setup
※ Make sure to configure the “Master” and “Slave” relation before connecting two
drives by one single ribbon cable. The red line on the ribbon cable must be
aligned with pin-1 on both the IDE port and the hard-drive connector.
2-19
Page 30

A
A
2.6.2 Serial ATA Connectors
Each SATA connector serves as one single channel to connect one SATA device by a thin SATA
cable.
The RAID 0/1/0+1/5/JBOD configuration is also possible through the combination of disk arrays
through these SATA connectors:
To connect SATA device:
1.
ttach either end of the signal cable to
the SATA connector on motherboard.
Attach the other end to SATA device.
ttach the SATA power cable to the
2.
SATA device and connect the other end
from the power supply.
The motherboard in this illustration is served for demonstration only, may not be the same type
or model as the one described in this user’s manual.
2-20
Page 31

2.6.3 Additional USB 2.0 Port Headers
Besides the 4x USB 2.0 ports located at rear I/O part, this motherboard also features 3x more
USB 2.0 headers onboard. Each header supports 2x additional USB 2.0 ports by connecting
bracket or cable to the rear I/O panel or the front-mounted USB ports of your chassis.
Pin Pin Assignment Pin Pin Assignment
1 VCC 2 VCC
3 Data0 - 4 Data1 5 Data0 + 6 Data1 +
7 Ground 8 Ground
10 NC
※ Make sure the connecting cable bears the same pin assignment.
2.6.4 Additional IEEE1394 Port Headers
Each header supports 1x additional IEEE1394 port by connecting bracket or cable to the rear
I/O panel or the front-mounted IEEE1394 port of your chassis.
Hardware Setup
Pin Pin Assignment Pin Pin Assignment
1 TPA0 + 2 TPA0 3 Ground 4 Ground
5 TPB0 + 6 TPB0 7 +12V 8 +12V
10 Ground
※ Make sure the connecting cable bears the same pin assignment.
2-21
Page 32
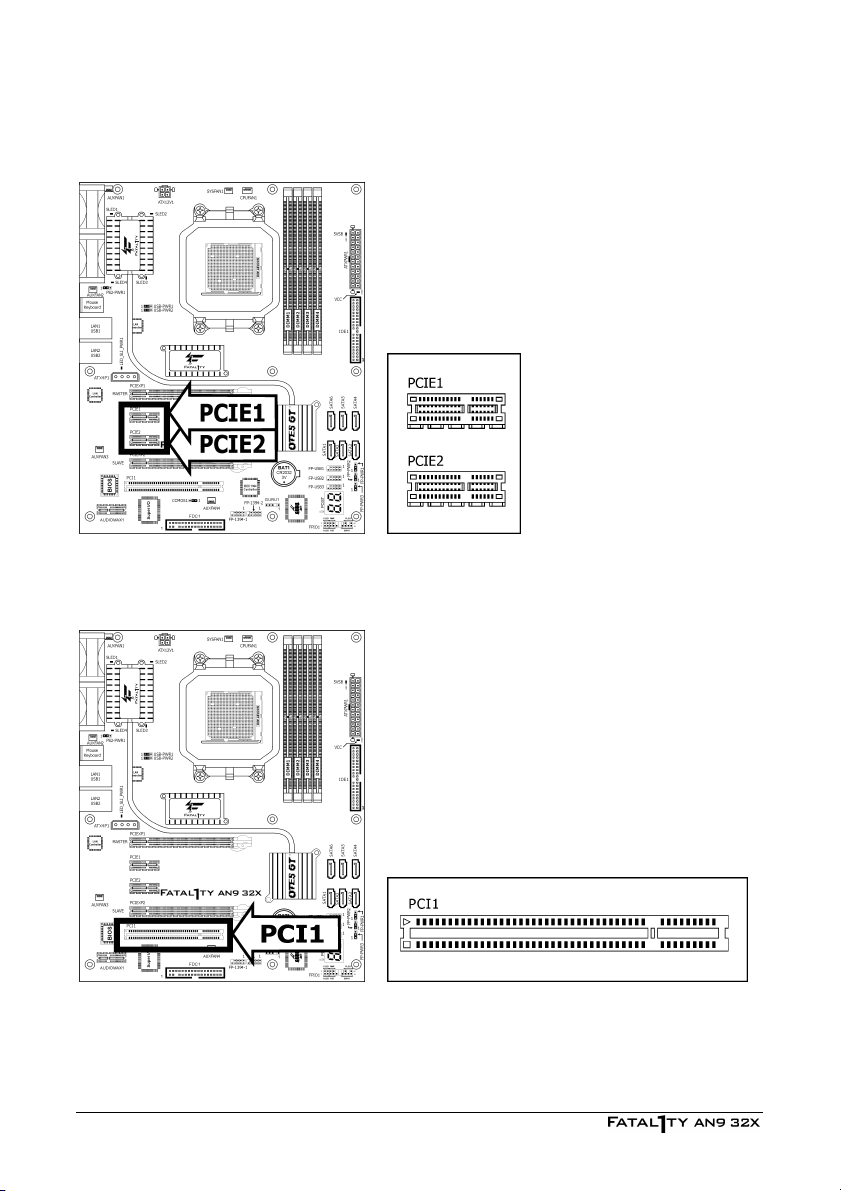
2.6.5 PCI Express X1 Add-on Slots
These slots provide the connection of add-on cards that comply with PCI Express specifications.
2.6.6 PCI Add-on Slots
This slot provides the connection of add-on cards that comply with PCI specifications.
2-22
Page 33
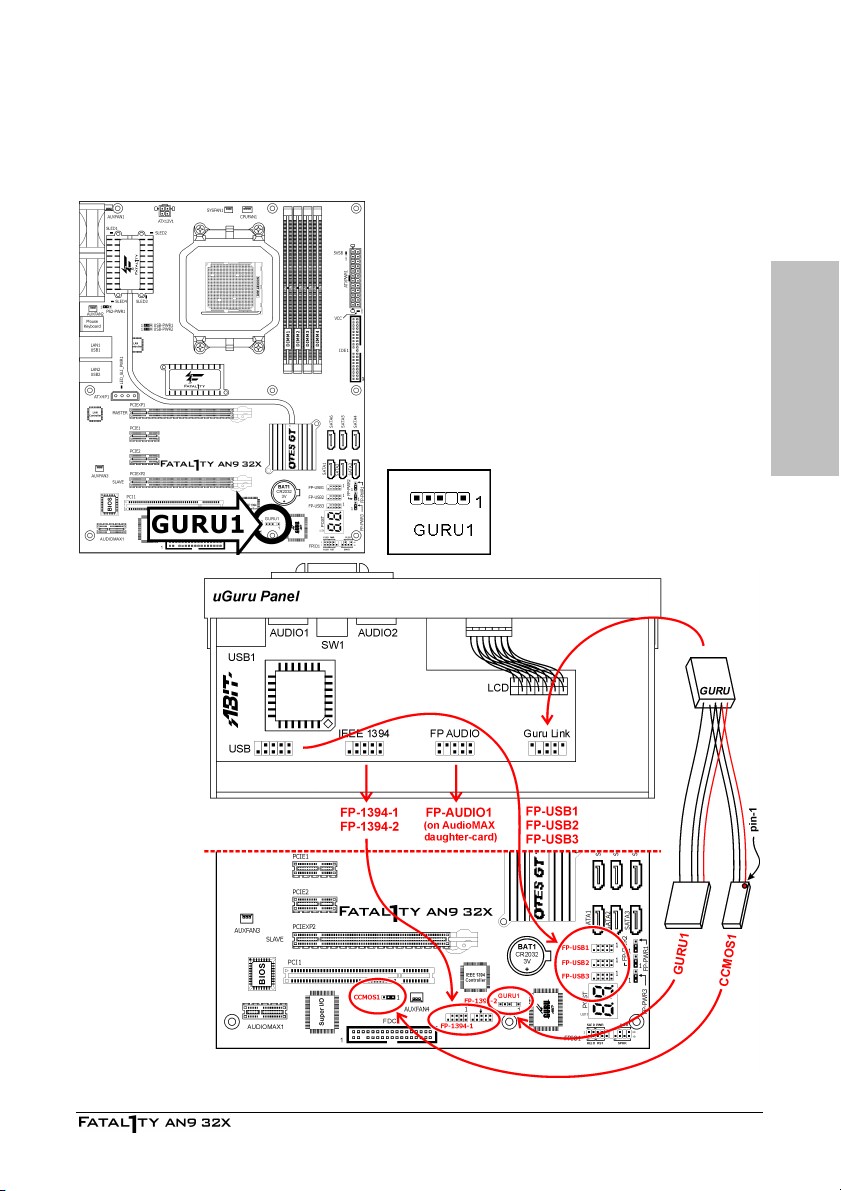
2.6.7 GURU Panel Connection Header
This header is reserved for connecting ABIT’s exclusive GURU Panel. For more information,
please refer to the included GURU Panel Installation Guide.
Hardware Setup
2-23
Page 34
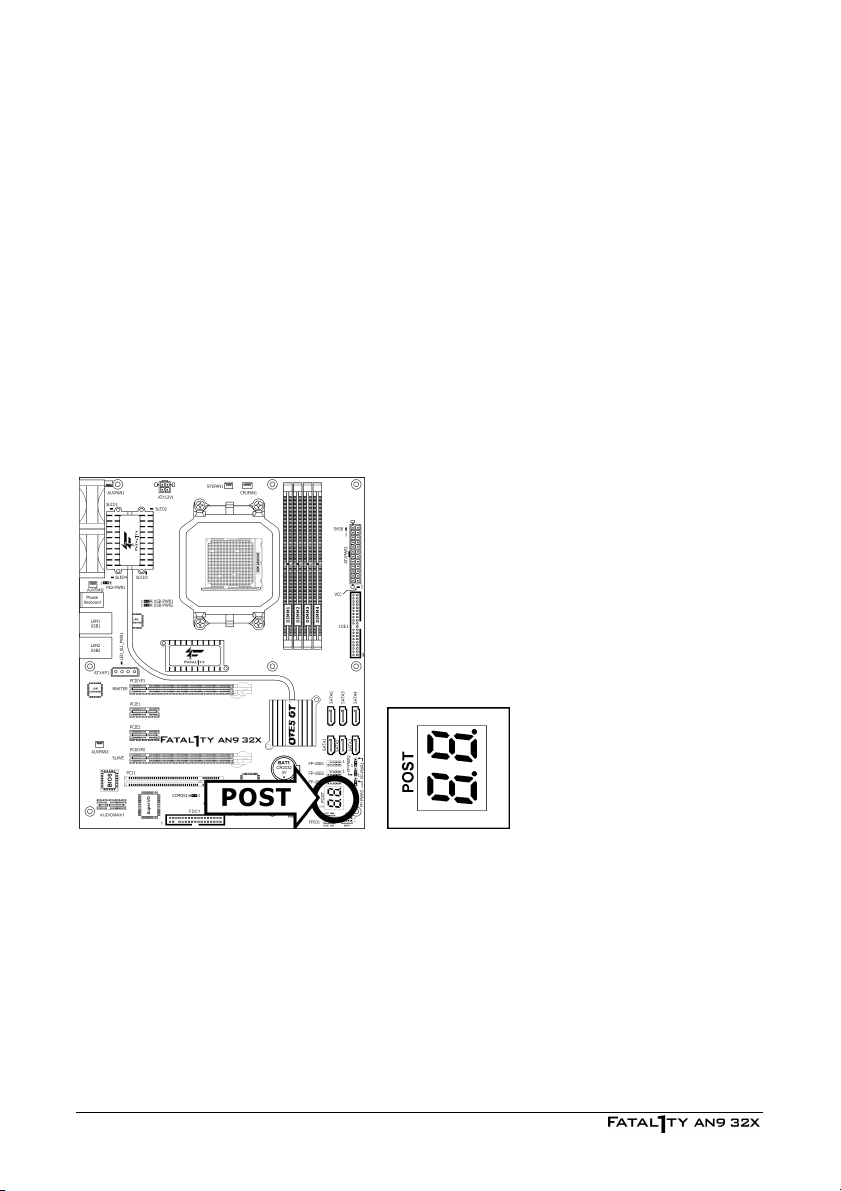
2.7 Onboard Status Display
2.7.1 POST Code Displayer
This is an LED device to display the “POST” Code, the acronym of Power On Self Test. The
computer will execute the POST action whenever you power on the computer. The POST
process is controlled by the BIOS. It is used to detect the status of the computer’s main
components and peripherals. Each POST Code corresponds to different checkpoints that are
also defined by the BIOS in advance. For example, “memory presence test” is an important
checkpoint and its POST Code is “C1”. When the BIOS execute any POST item, it will write the
corresponding POST Code into the address 80h. If the POST passes, the BIOS will process the
next POST item and write the next POST Code into the address 80h. If the POST fails, we can
check the POST Code in address 80h to find out where the problem lies.
This LED device also displays the “POST” Code of AC2005, an “uGuru” chipset developed
exclusively by Universal ABIT.
※ The decimal point lights up during the AC2005 POST action.
See Appendix for both AWARD and AC2005 POST Code definitions.
2-24
Page 35
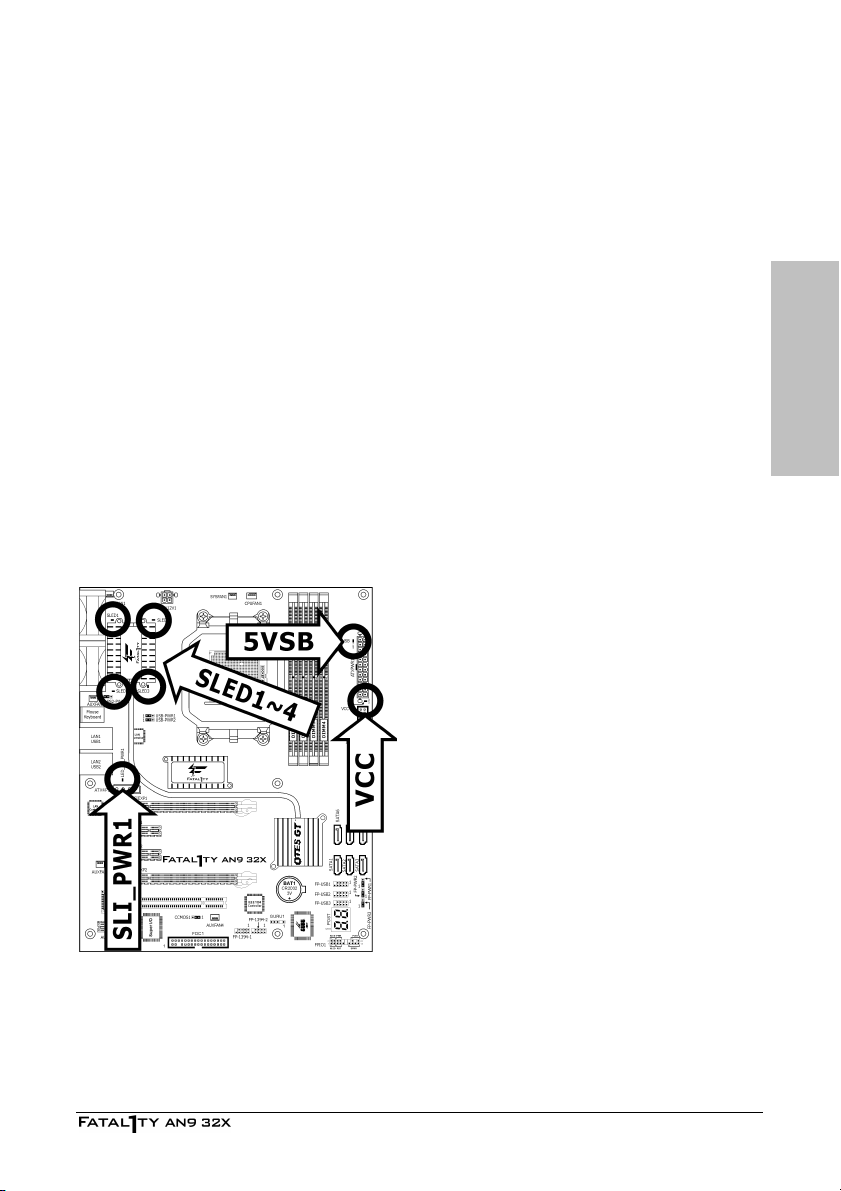
2.7.2 Power Source Indicators
These indicators work as a reminding device to display the power status of this motherboard
with power source connected.
• 5VSB:
Lights On: Your ATX power supplier is connected with power source, and its power switch
is on.
Lights Off: Your ATX power supplier is not connected with power source, or connected with
power source but its power switch is off.
• VCC:
Lights On: The system power is on.
Lights Off: The system power is off.
• SLED1~4:
Lights On: The system power is on.
Lights Off: The system power is off.
• SLI_PWR1:
Lights On: The system power is on.
Lights Off: The “ATX4P1” connector is connected with power source from your ATX power
supplier.
Hardware Setup
2-25
Page 36
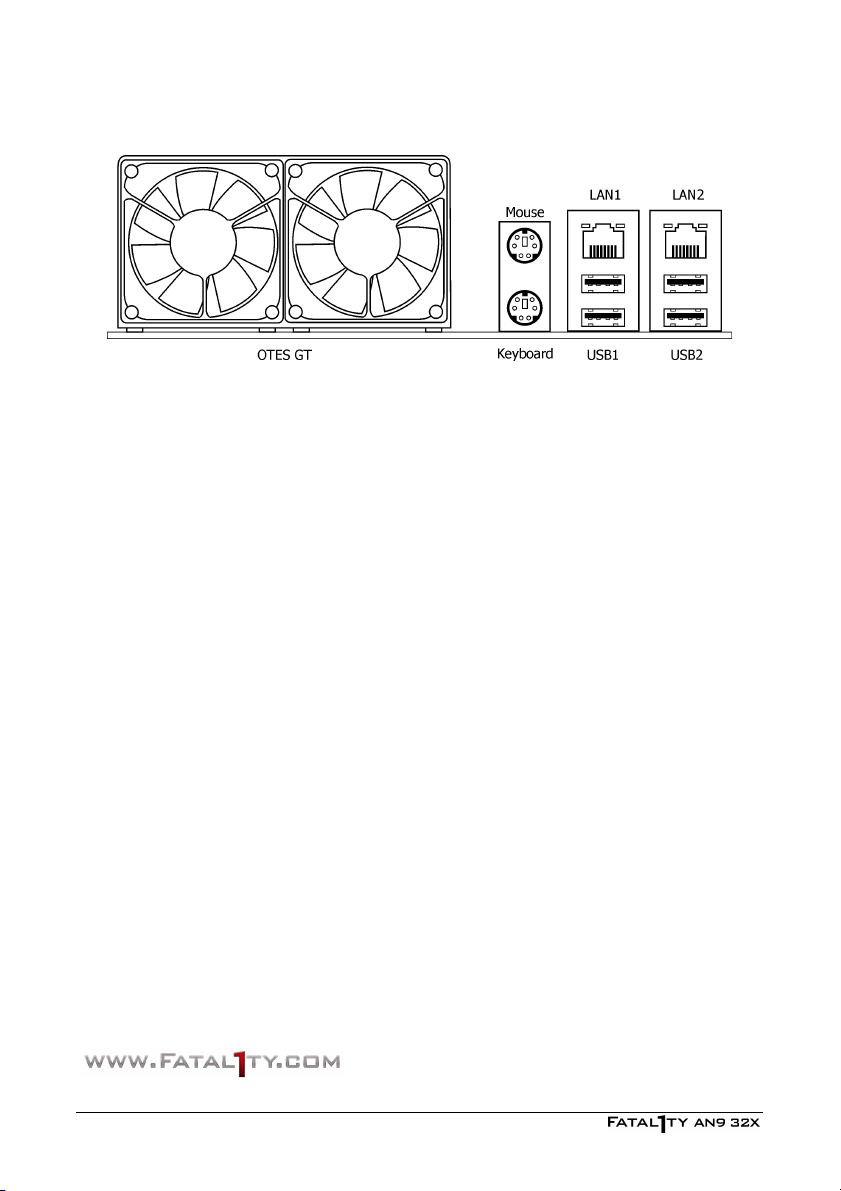
2.8 Connecting I/O Devices
• OTES GT™: This exclusive technology is served to cool the motherboard's heat-source by
the cool-assembly consisted of fin-heatsink, heat pipe, and fans. (Keep the area for
outgoing heat wave open.)
• Mouse: Connects to PS/2 mouse.
• Keyboard: Connects to PS/2 keyboard.
• LAN1/LAN2: Connects to Local Area Network.
• USB1/USB2: Connects to USB devices such as scanner, digital speakers, monitor, mouse,
keyboard, hub, digital camera, joystick etc.
For more information:
www.abit.com.tw
2-26
Page 37
3. BIOS Setup
This motherboard provides a programmable EEPROM so that you can update the BIOS utility.
The BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) is a program that deals with the basic level of
communication between processor and peripherals. Use the BIOS Setup program only when
installing motherboard, reconfiguring system, or prompted to “Run Setup”. This chapter
explains the Setup Utility of BIOS utility.
After powering up the system, the BIOS message appears on the screen, the memory count
begins, and then the following message appears on the screen:
PRESS DEL TO ENTER SETUP
If this message disappears before you respond, restart the system by pressing <Ctrl> + <Alt>
+ <Del> keys, or by pressing the Reset button on computer chassis. Only when these two
methods fair should you restart the system by powering it off and then back on.
After pressing <Del> key, the main menu screen appears.
Phoenix – Award BIOS CMOS Setup Utility
► uGuru Utility ► PnP/PCI Configurations
► Standard CMOS Features Load Fail-Safe Defaults
► Advanced BIOS Features Load Optimized Defaults
► Advanced Chipset Features Set Password
► Integrated Peripherals Save & Exit Setup
► Power Management Setup Exit Without Saving
Esc: Quit
F10: Save & Exit Setup
F6 : Save PROFILE To BIOS
Change CPU’s Clock & Voltage
※ In order to increase system stability and performance, our engineering staff is
constantly improving the BIOS menu. The BIOS setup screens and descriptions
illustrated in this manual are for your reference only, and may not completely
match with what you see on your screen.
↓↑→← : Select Item
(C51XE/MCP55-6A61JA1BC-00)
F7 : Load PROFILE From BIOS
BIOS Setup
3-1
Page 38
3.1 µGuru™ Utility
There are two setup menus in this µGuru utility. You may switch between these two by clicking
the left or right arrow key on keyboard:
3.1.1 OC Guru
OC Guru AMD Athlon(tm) 64 X2 Dual Core Processor 3800+ Item Help ►
Frequency : 2000MHz
SLI-Ready Memory Disabled
CPU Operating Speed 2000(200)
X - Multiplier Factor x10.0
X - External Clock Auto
Voltages Control Auto Detect
X - CPU Core Voltage 1.3500V
X - DDR2 Voltage 1.85 V
X - NB 1.2V Voltage 1.20 V
X - NB PCIE 1.2V Voltage 1.20 V
X - SB 1.5V Voltage 1.50 V
X - HyperTransport Voltage 1.20 V
X - DDR2 Reference Voltage -20 mv
Power Cycle Statistics Press Enter
↓↑→←:Move Enter:Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit
Brand Name
This item displays the CPU model name installed on this motherboard.
µGuru Utility V1.00C
Frequency
This item displays the processor speed of the CPU installed on this motherboard.
SLI-Ready Memory
This item allows you to select the SPD profile for SLI-Ready memory modules of EPP standard.
The default setting is [Disabled]. You may determine the percentage of how much you would
like to raise up according to the type of memory module you installed.
CPU Operating Speed
This item displays the CPU operating speed according to the type and speed of your CPU. You
can also select the [User Define] option to enter the manual option.
3-2
Page 39

User Define:
※ The wrong settings of the multiplier and external clock in certain circumstances
may cause CPU damage. Setting the working frequency higher than the PCI
chipset or processor specs, may cause abnormal memory module functioning,
system hangs, hard disk drive data lose, abnormal functioning of the VGA card,
or abnormal functioning with other add-on cards. Using non-specification
settings for your CPU is not the intention of this explanation. These should be
used for engineering testing, not for normal applications.
※ There will be no guaranty for the settings beyond specification. Any damage of
any component on this motherboard or peripherals resulting therein is not our
responsibility.
- Multiplier Factor
This item displays the multiplier factor for the CPU installed.
- External Clock
This item selects the external clock frequency. Due to the specification limit of the CPU you
installed, the speed you set over its standard bus speed is supported, but not guaranteed.
Voltages Control
This option allows you to switch between the default and user-defined voltages. Leave this
setting at default unless the current voltage setting cannot be detected or is not correct. The
option “User Define” enables you to select the following voltages manually.
- CPU Core Voltage
- DDR2 Voltage
- NB 1.2V Voltage
- NB PCIE 1.2V Voltage
- SB 1.5V Voltage
- HyperTransport Voltage
- DDR2 Reference Voltage
BIOS Setup
3-3
Page 40
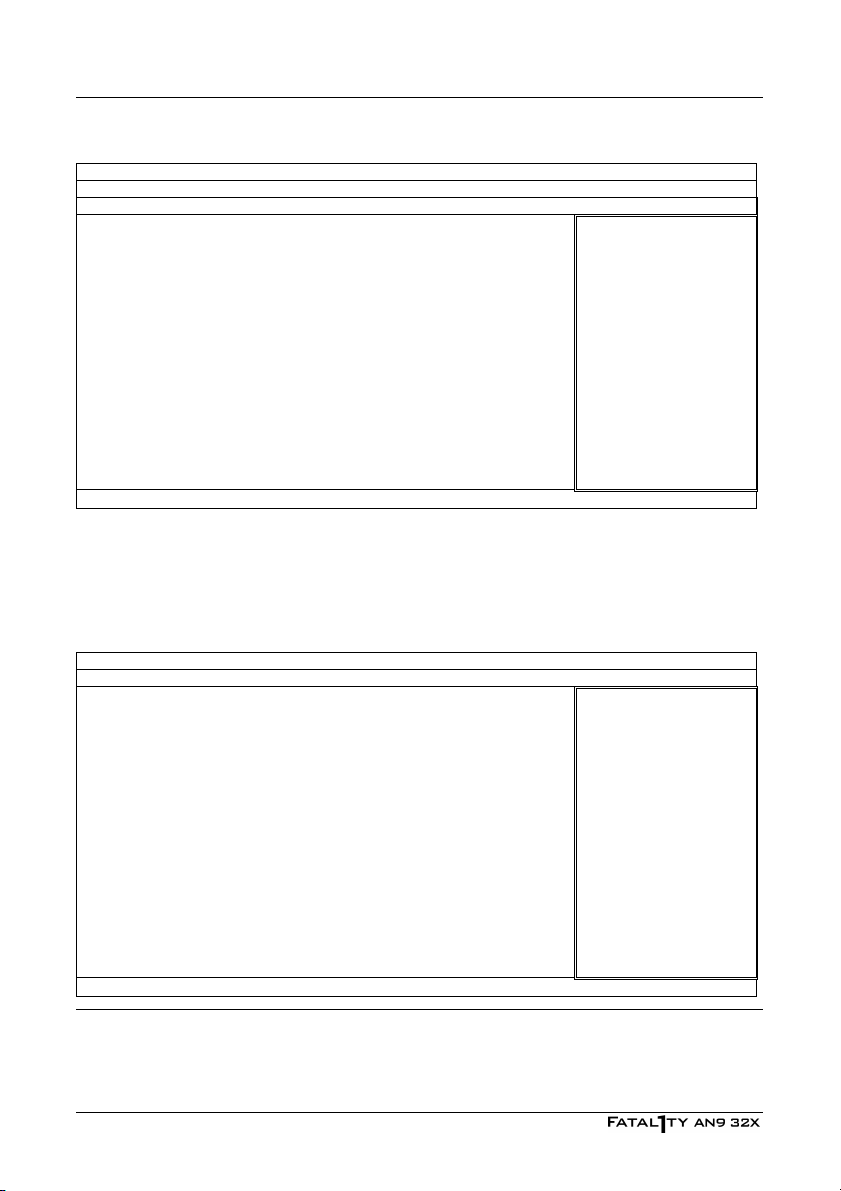
Power Cycle Statistics
Click <Enter> key to enter its submenu:
OC Guru
Power Cycle Statistics
PC Up Time 0 Hours Item Help ►►
PC Up Time Total 119 Hours
PC Reset Button Cycles 123 Cycles
PC Power Cycles 538 Cycles
AC Power On Total Time 288 Hours
AC Power Cycles 228 Cycles
↓↑→←:Move Enter:Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit
µGuru Utility V1.00C
These items display the power cycle statistics for each element.
3.1.2 ABIT EQ
Click right-arrow <→> key to switch from OC Guru setup menu to ABIT EQ setup menu:
ABIT EQ
ABIT EQ Beep Control Enabled Item Help ►
► Temperature Monitoring Press Enter
► Voltage Monitoring Press Enter
► Fan Speed Monitoring Press Enter
► FanEQ Control Press Enter
↓↑→←:Move Enter:Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit
µGuru Utility V1.00C
ABIT EQ Beep Control
This item allows you to enable or disable ABIT EQ Beep Control function.
3-4
Page 41

Temperature Monitoring
Click <Enter> key to enter its submenu:
ABIT EQ
Temperature Monitoring
(*)CPU Temperature 34°C/93°F (*) 85°/185°F (*) 75°C/167°F
(*)System Temperature 29°C/84°F ( ) 65°°C/149°F (*) 55°C/131°F
(*)PWM Temperature 36°C/96°F ( ) 90°°C/194°F (*) 88°C/176°F
↓↑→←:Move Enter:Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit
CPU Temperature/System Temperature/PWM Temperature
These items display the temperature of CPU, System, and Power Module.
- Shutdown Enable
Use <Space> key to enable system shutdown function. If the CPU/System/PWM’s temperature
exceeds the shutdown temperature limit, the system will shutdown automatically.
- Shutdown Temp.
This items sets the temperature that will shutdown the system automatically in order to prevent
system overheating.
- Beep Enable
Use <Space> key to enable warning beeps function. Once the system has detected that the
CPU/System/PWM’s temperature exceeded the beep temperature limit, warning beeps will
sound.
- Beep Temp.
This item selects the warning temperature limit.
※ The shutdown temperature must be set above the warning temperature.
µGuru Utility V1.00C
Reading Shutdown
Enable
Shutdown
Temp.
Beep
Enable
Beep
Temp.
BIOS Setup
3-5
Page 42

Voltage Monitoring
Click <Enter> key to enter its submenu:
ABIT EQ
Voltage Monitoring
(*)CPU Core Voltage 1.40 V (*) (*) 1.60 V 0 V
(*)DDR2 Voltage 1.80 V ( ) (*) 2.20 V 1.50 V
(*)DDR2 VTT Voltage 0.90 V ( ) (*) 1.10 V 0.75 V
(*)HyperTransport Voltage 1.20 V ( ) (*) 1.45 V 0.95 V
(*)NB Voltage 1.20 V ( ) (*) 1.45 V 0.95 V
(*)CPU VDDA 2.5V Voltage 2.50 V ( ) (*) 3.00 V 2.00 V
(*)SB Voltage 1.50 V ( ) (*) 1.00 V 1.20 V
(*)ATX +12V (24-Pin Connector) 12.00 V ( ) (*) 14.40 V 9.60 V
(*)ATX +12V (4-Pin Connector) 12.00 V ( ) (*) 14.40 V 9.60 V
(*)ATX +5V 5.00 V ( ) (*) 6.00 V 4.00 V
(*)ATX +3.3V 3.30 V ( ) (*) 3.95 V 2.65 V
(*)ATX 5VSB 5.00 V ( ) (*) 6.00 V 4.00 V
↓↑→←:Move Enter:Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit
All Voltages
These items display the voltage of each element.
- Shutdown Enable
Use <Space> key to enable system shutdown function. If the voltage of corresponding element
is higher/lower than the high/low limit, the system will automatically shutdown.
- Beep Enable
Use <Space> key to enable warning beeps function. If the voltage of corresponding element is
higher/lower than the high/low limit, warning beeps will sound.
- High/Low Limit
These items set the high and low voltage limit.
※ The value of high limit must be set above the one of low limit.
µGuru Utility V1.00C
Reading Shutdown
Enable
Beep
Enable
High
Limit
Low
Limit
3-6
Page 43

Fan Speed Monitoring
Click <Enter> key to enter its submenu:
ABIT EQ
Fan Speed Monitoring
(*)CPU FAN Speed 7440 RPM (*) (*) 300 RPM
( )SYS FAN Speed N/A ( ) ( ) 300 RPM
( )AUX1 FAN Speed N/A ( ) ( ) 300 RPM
( )AUX2 FAN Speed N/A ( ) ( ) 300 RPM
( )AUX3 FAN Speed N/A ( ) ( ) 300 RPM
( )AUX4 FAN Speed N/A ( ) ( ) 300 RPM
↓↑→←:Move Enter:Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit
CPU/SYS/AUX1~4 FAN Speed
These items display the speed of the fans connected to CPU, SYS, and AUX1~4 FAN headers.
- Shutdown Enable
Use <Space> key to enable system shutdown function. Once the system has detected that the
fan speed is lower than the low limit value, system will shutdown automatically.
- Beep Enable
Use <Space> key to enable warning beeps function. If the fan speed is lower than the low limit
value, warning beeps will sound.
- Low Limit
These items set the low limit of fan speed.
µGuru Utility V1.00C
Reading Shutdown
Enable
Beep
Enable
Low
Limit
BIOS Setup
3-7
Page 44

FanEQ Control
ABIT EQ
FanEQ Control
► CPU FanEQ Control Press Enter Item Help ►►
► SYS FanEQ Control Press Enter
► AUX1 FanEQ Control Press Enter
► AUX2 FanEQ Control Press Enter
► AUX3 FanEQ Control Press Enter
► AUX4 FanEQ Control Press Enter
↓↑→←:Move Enter:Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit
Click <Enter> key to enter its submenu (CPU FanEQ Control):
ABIT EQ
CPU FanEQ Control
CPU FanEQ Control Enabled Item Help ►►►
-Reference Temperature CPU Temperature
-Control Temperature High 65°C/149°F
-Control Temperature Low 35°C/95°F
-DC Fan Voltage High 12.0 V
-DC Fan Voltage Low 8.0 V
↓↑→←:Move Enter:Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit
µGuru Utility V1.00C
µGuru Utility V1.00C
CPU FanEQ Control
When set to [Enabled], these items control the CPU fan speed by the following setting
combinations.
- Reference Temperature
This item selects the reference point for taking temperature among the available options of CPU,
SYS, and PWM Temperature, but there is only one “CPU Temperature” item to choose for the
“CPU FanEQ Control”.
3-8
Page 45

- Control Temperature High/Low
These items set the high and low temperature limit that you want to do the fan speed control.
- DC Fan Voltage High/Low
These items set the high and low voltage limit that you want to provide the fan with.
※ The value of high limit must be set above the one of low limit.
Click <ESC> key to exit this menu and move back to the main menu of “ABIT EQ”. Move the
down-arrow key to the next item (SYS FanEQ Control), and then click <Enter> key to enter its
submenu:
ABIT EQ
SYS FanEQ Control
SYS FanEQ Control Enabled Item Help ►►►
-Reference Temperature System Temperature
-Control Temperature High 40°C/104°F
-Control Temperature Low 30°C/86°F
-DC Fan Voltage High 12.0 V
-DC Fan Voltage Low 8.0 V
↓↑→←:Move Enter:Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit
µGuru Utility V1.00C
BIOS Setup
SYS FanEQ Control
When set to [Enabled], these items control the SYS fan speed by the following setting
combinations.
- Reference Temperature
This item selects the reference point for taking temperature among the available options of CPU,
SYS, and PWM Temperature.
- Control Temperature High/Low
These items set the high and low temperature limit that you want to do the fan speed control.
- DC Fan Voltage High/Low
These items set the high and low voltage limit that you want to provide the fan with.
※ The value of high limit must be set above the one of low limit.
3-9
Page 46

Click <ESC> key to exit this menu and move back to the main menu of “ABIT EQ”. Move the
down-arrow key to the next item (AUX1 FanEQ Control ~ AUX4 FanEQ Control), and then click
<Enter> key to enter its submenu:
ABIT EQ
AUX1 FanEQ Control
AUX1 FanEQ Control Enabled Item Help ►►►
-Reference Temperature System Temperature
-Control Temperature High 40°C/104°F
-Control Temperature Low 30°C/86°F
-DC Fan Voltage High 12.0 V
-DC Fan Voltage Low 8.0 V
↓↑→←:Move Enter:Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit
µGuru Utility V1.00C
AUX1 FanEQ Control ~ AUX4 FanEQ Control
When set to [Enabled], these items control the AUX1~4 fan speed by the following setting
combinations.
- Reference Temperature
This item selects the reference point for taking temperature among the available options of CPU,
SYS, and PWM Temperature.
- Control Temperature High/Low
These items set the high and low temperature limit that you want to do the fan speed control.
- DC Fan Voltage High/Low
These items set the high and low voltage limit that you want to provide the fan with.
※ The value of high limit must be set above the one of low limit.
3-10
Page 47

3.2 Standard CMOS Features
Phoenix – Award BIOS CMOS Setup Utility
Date (mm:dd:yy) Mon. Jul 03 2006 Item Help
Time (hh:mm:ss) 12 : 34 : 56
► IDE Channel 1 Master None
► IDE Channel 1 Slave None
► IDE Channel 3 Master None
► IDE Channel 4 Master None
► IDE Channel 5 Master None
► IDE Channel 6 Master None
► IDE Channel 7 Master None
► IDE Channel 8 Master None
Drive A 1.44M, 3.5 in.
Drive B None
Floppy 3 Mode Support Disabled
Halt On All, But keyboard
Base Memory 640K
Extended Memory 1046520K
Total Memory 1047552K
↓↑→←:Move Enter:Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1:General Help
F5: Previous Values F6: Fail-Safe Defaults F7: Optimized Defaults
Date (mm:dd:yy)
This item sets the date you specify (usually the current date) in the format of [Month], [Date],
and [Year].
Standard CMOS Features
BIOS Setup
Time (hh:mm:ss)
This item sets the time you specify (usually the current time) in the format of [Hour], [Minute],
and [Second].
3-11
Page 48
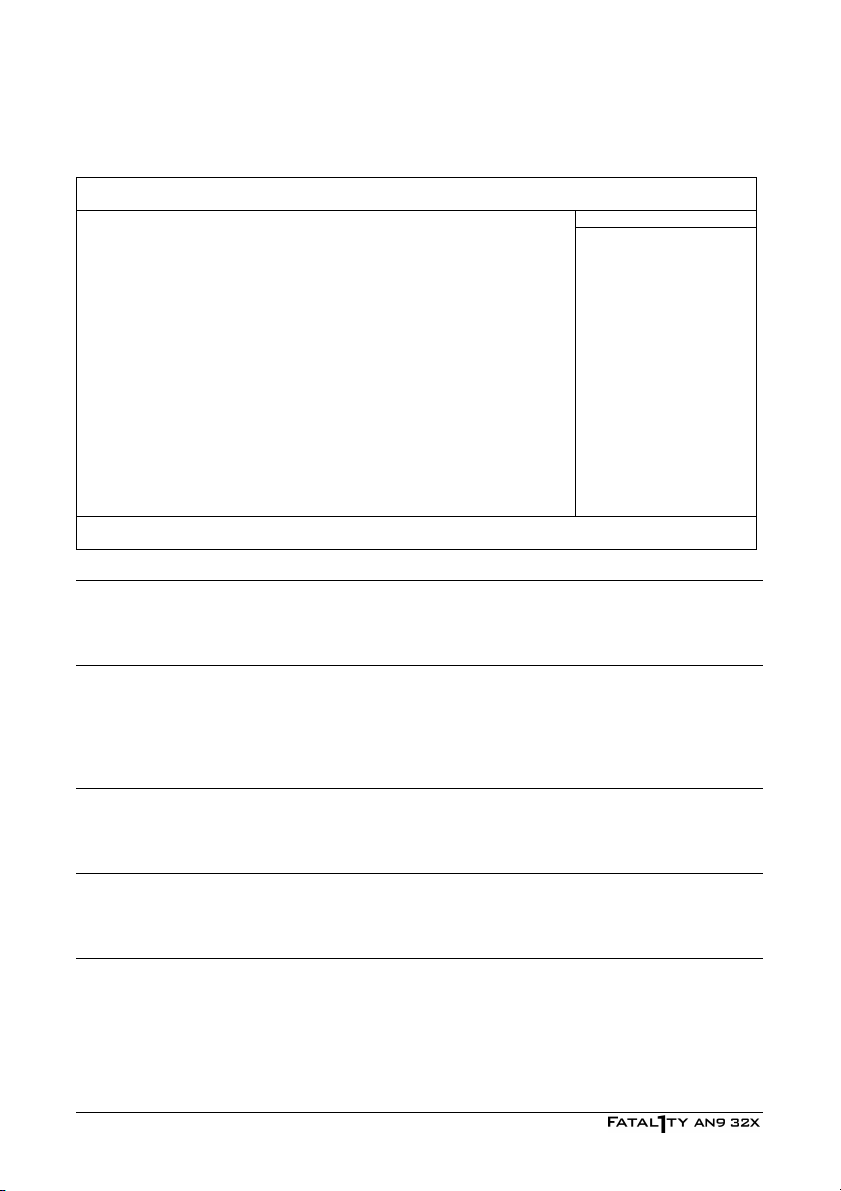
IDE Channel 1 Master/Slave, IDE Channel 3~8 Master:
Click <Enter> key to enter its submenu:
Phoenix – Award BIOS CMOS Setup Utility
IDE HDD Auto-Detection Press Enter Item Help
IDE Channel 1 Master Auto
Access Mode Auto
Capacity 0 MB
Cylinder 0
Head 0
Precomp 0
Landing Zone 0
Sector 0
↓↑→←:Move Enter:Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1:General Help
F5: Previous Values F6: Fail-Safe Defaults F7: Optimized Defaults
IDE HDD Auto-Detection
This item allows you to detect the parameters of IDE drives by pressing <Enter> key. The
parameters will be shown on the screen automatically.
IDE Channel 1 Master
IDE Channel 1 Master/Slave, IDE Channel 3~8 Master
When set to [Auto], the BIOS will automatically check what kind of IDE drive you are using. If
you want to define your own drive by yourself, set it to [Manual] and make sure you fully
understand the meaning of the parameters. Please refer to the instruction manual provided by
the device’s manufacturer to get the setting right.
Access Mode
This item selects the mode to access your IDE devices. Leave this item at its default [Auto]
setting to detect the access mode of your HDD automatically.
Capacity
This item displays the approximate capacity of the disk drive. Usually the size is slightly greater
than the size of a formatted disk given by a disk-checking program.
Cylinder
This item configures the number of cylinders.
3-12
Page 49

Head
This item configures the number of read/write heads.
Precomp
This item displays the number of cylinders at which to change the write timing.
Landing Zone
This item displays the number of cylinders specified as the landing zone for the read/write
heads.
Sector
This item configures the number of sectors per track.
Back to Standard CMOS Features Setup Menu:
Drive A & Drive B
This item sets the type of floppy drives (usually only Drive A) installed.
Floppy 3 Mode Support
This item allows you to use “3 Mode Floppy Drive” in Japanese computer system by selecting
drive A, B, or both. Leave this item at its default [Disabled] setting if you are not using this
Japanese standard floppy drive.
Halt On
This item determines whether the system stops if an error is detected during system boot-up.
[All Errors]: The system-boot will stop whenever the BIOS detect a non-fatal error.
[No Errors]: The system-boot will not stop for any error detected.
[All, But Keyboard]: The system-boot will stop for all errors except a keyboard error.
[All, But Diskette]: The system-boot will stop for all errors except a diskette error.
[All, But Disk/Key]: The system-boot will stop for all errors except a diskette or keyboard
error.
BIOS Setup
Base Memory
This item displays the amount of base memory installed in the system. The value of the base
memory is typically 640K for system with 640K or more memory size installed on the
motherboard.
Extended Memory
This item displays the amount of extended memory detected during system boot-up.
Total Memory
This item displays the total memory available in the system.
3-13
Page 50
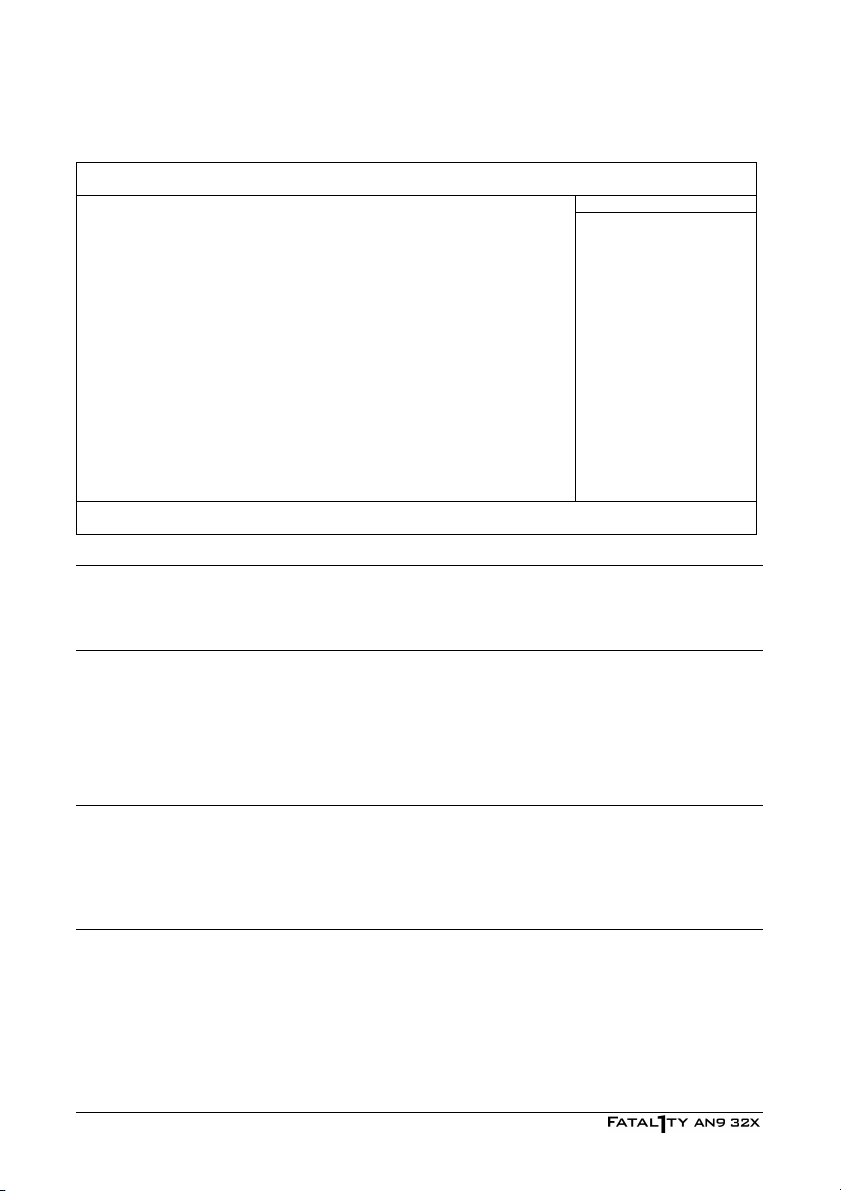
3.3 Advanced BIOS Features
Phoenix – Award BIOS CMOS Setup Utility
Quick Power on Self Test Enabled Item Help
► Hard Disk Boot Priority Press Enter
First Boot Device Floppy
Second Boot Device Hard Disk
Third Boot Device CDROM
Boot Other Device Enabled
Boot Up Floppy Seek Disabled
Boot Up NumLock Status On
Security Option Setup
MPS Version Ctrl For OS 1.4
Full Screen Logo Show Enabled
↓↑→←:Move Enter:Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1:General Help
F5: Previous Values F6: Fail-Safe Defaults F7: Optimized Defaults
Advanced BIOS Features
Quick Power On Self Test
When set to [Enabled], this item speeds up the Power On Self Test (POST) after powering on
the system. The BIOS shorten or skip some check during the POST.
Hard Disk Boot Priority
This item selects the hard disks booting priority. By pressing <Enter> key, you can enter its
submenu where the hard disks detected can be selected for the booting sequence to boot up
system.
This item functions only when there is the option of [Hard Disk] in any one of the
First/Second/Third Boot Device items.
First Boot Device / Second Boot Device / Third Boot Device / Boot Other Device
Select the drive to boot first, second and third in the [First Boot Device], [Second Boot Device],
and [Third Boot Device] items respectively. The BIOS will boot the operating system according
to the sequence of the drive selected. Set [Boot Other Device] to [Enabled] if you wish to boot
from another device other than these three items.
Boot Up Floppy Seek
When the computer boots up, the BIOS detects if the system has a FDD or not. When this item
is set to Enabled, if the BIOS detects no floppy drive, it will display a floppy disk drive error
message. If this item is disabled, the BIOS will skip this test. The default setting is Disabled.
3-14
Page 51

Boot Up NumLock Status
This item determines the default state of the numeric keypad at system booting up.
[On]: The numeric keypad functions as number keys.
[Off]: The numeric keypad functions as arrow keys.
Security Option
This item determines when the system will prompt for password - every time the system boots
or only when it enters the BIOS setup.
[Setup]: The password is required only when accessing the BIOS Setup.
[System]: The password is required each time the computer boots up.
To disable security, select Set Password at main menu and then you will be asked to enter the
password. Do not type anything and just press the <Enter> key and it will disable security.
Once security is disabled, the system will boot and you can enter the BIOS setup menu freely.
※ Don’t forget your password. If you forget the password, you will have to open
the computer case and clear all information in the CMOS before you can start up
the system. But by doing this, you will have to reset all previously set options.
MPS Version Ctrl For OS
This item specifies which version of MPS (Multi-Processor Specification) this motherboard will
use. Leave this item at its default setting.
Full Screen LOGO Show
This item determines if the full screen logo is shown when booting.
BIOS Setup
3-15
Page 52
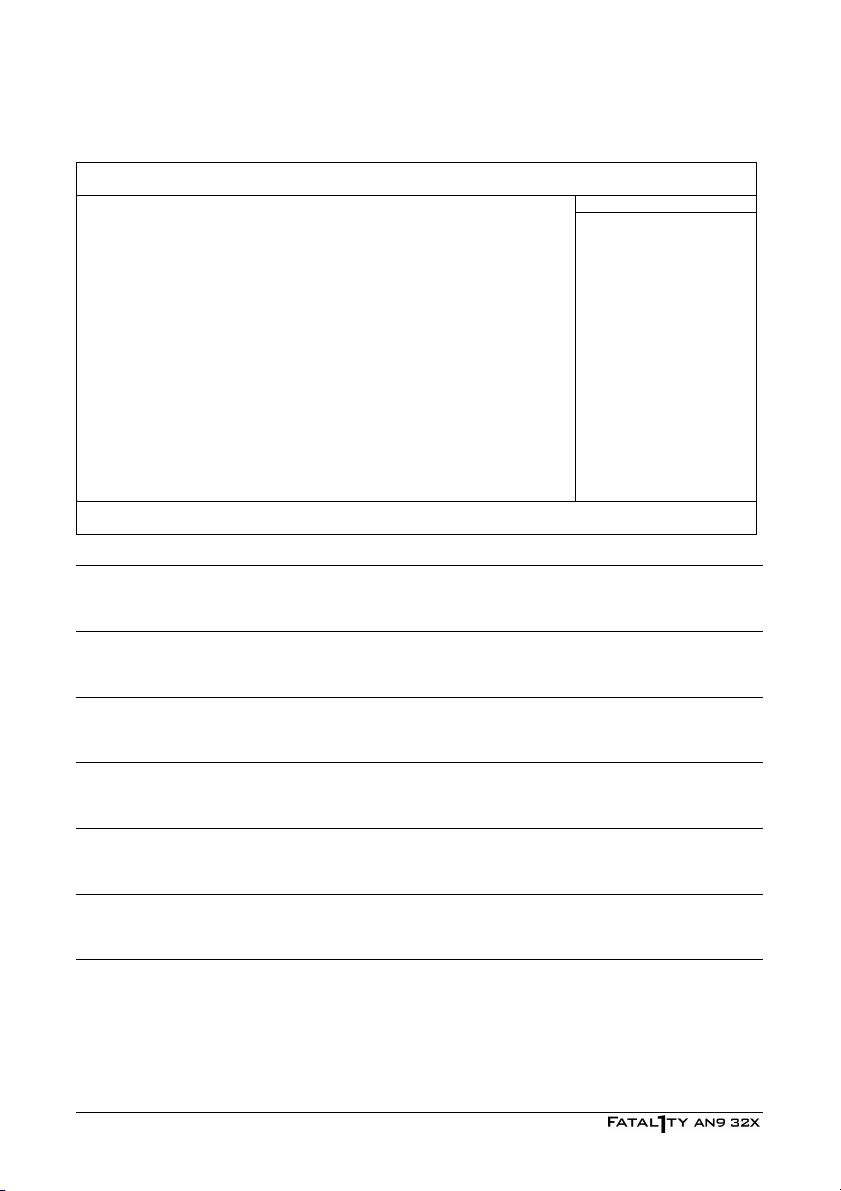
3.4 Advanced Chipset Features
Phoenix – Award BIOS CMOS Setup Utility
K8<->NB HT Speed Auto Item Help
K8<->NB HT Width Auto
NB-->SB HT Speed Auto
NB<->SB HT Width Auto
PCI Express bus(SB) Hyperclk GPU
NB<->SB Reference clock Auto
PCI Express bus(NB) Hyperclk GPU
► DRAM Configuration Press Enter
SSE/SSE2 Instructions Enable
System BIOS Cacheable Enable
NVIDIA GPU Ex Disabled
↓↑→←:Move Enter:Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1:General Help
F5: Previous Values F6: Fail-Safe Defaults F7: Optimized Defaults
Advanced Chipset Features
K8<->NB HT Speed:
This item selects the LDT Bus Frequency between CPU and NB.
K8<->NB HT Width:
This item selects the LDT Bus Width between CPU and NB.
NB-->SB HT Speed:
This item selects NB to SB LDT Bus Frequency.
NB<->SB HT Width:
This item selects the LDT Bus Width between NB and SB.
PCI Express bus(SB)
This item adjusts the bus clock for “PCIEXP2” slot.
NB<->SB Reference clock
This item adjusts the bus clock between NB and SB.
PCI Express bus(NB)
This item adjusts the bus clock for “PCIEXP1” slot.
3-16
Page 53

DRAM Configuration:
Click <Enter> key to enter its submenu.
You may manually set the DRAM timing parameters through the following sub-items, or leave
them at their default settings according to the SPD (Serial Presence Detect) data stored in the
DRAM.
Phoenix – Award BIOS CMOS Setup Utility
DRAM Timing Selectable Auto Item Help
X - DRAM Clock DDR2 533
- DQS Timing Training Skip DQS
- CKE Base Power Down Mode Enabled
- CKE Base Power Down by Channel
- Memclock Tri-Stating Disabled
X - TwTr Command Delay 2 Clocks
X - Trfc0 for DIMM1 105 ns
X - Trfc1 for DIMM2 75 ns
X - Trfc2 for DIMM3 75 ns
X - Trfc3 for DIMM4 75 ns
X - Write Recovery Time(Twr) 4 Clocks
X - Precharge Time(Trtp) 2 Clocks
X - Row Cycle Time(Trc) 17 Clocks
X - RAS2CAS R/W Delay(Trcd) 4 Clocks
X - RAS to RAS Delay(Trrd) 2 Clocks
X - Row Precharge Time(Trp) 4 Clocks
X - Min. RAS Act-Time(Tras) 12 Clocks
Memory Hole Remapping Enabled
DRAM ECC Enable Disabled
X - DRAM MCE Enable Disabled
X - Chip-Kill Mode Enable Disabled
X - DRAM ECC Redirection Disabled
X - DRAM Scrub Rate Disabled
X - L2 Cache Scrub Rate Disabled
X - DCache Scrub Rate Disabled
Auto Optimize Bottom IO Enabled
X - [31:24] IO Space F0
↓↑→←:Move Enter:Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1:General Help
F5: Previous Values F6: Fail-Safe Defaults F7: Optimized Defaults
DRAM Configuration
BIOS Setup
Back to Advanced Chipset Features Setup Menu:
SSE/SSE2 Instructions
This item allows you to Enable or Disable the SSE/SSE2 (Streaming SIMD Extensions)
instruction set.
System BIOS Cacheable
This item enables or disables caching the system BIOS for faster execution.
NVIDIA GPU Ex
Stands for “GPU Extra Performance”. Enable this item to work for certain NVIDIA SLI graphics
cards with certain driver version, but only minor performance will be expected. Leave this item
at its default setting (Disabled).
3-17
Page 54
3.5 Integrated Peripherals
Phoenix – Award BIOS CMOS Setup Utility
► OnChip IDE/RAID Function Press Enter Item Help
Init Display First PCIEXP1
OnChip USB V1.1+V2.0
- USB Keyboard Support OS
- USB Mouse Support OS
OnChip Audio Controller Auto
OnChip LAN1 Controller Auto
OnChip LAN2 Controller Auto
Onboard LAN Boot ROM Disabled
Onboard FDD Controller Enabled
Onboard 1394 Controler Enabled
↓↑→←:Move Enter:Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1:General Help
F5: Previous Values F6: Fail-Safe Defaults F7: Optimized Defaults
Integrated Peripherals
OnChip IDE/RAID Function
Click <Enter> key to enter its submenu:
Phoenix – Award BIOS CMOS Setup Utility
► IDE Function Setup Press Enter Item Help
► RAID Configuration Press Enter
↓↑→←:Move Enter:Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1:General Help
F5: Previous Values F6: Fail-Safe Defaults F7: Optimized Defaults
OnChip IDE/RAID Function
3-18
Page 55

IDE Function Setup:
Click <Enter> key to enter its submenu:
Phoenix – Award BIOS CMOS Setup Utility
IDE 1 Controller Enabled Item Help
IDE DMA transfer access Enabled
IDE HDD Block Mode Enabled
Serial-ATA Controller All Enabled
↓↑→←:Move Enter:Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1:General Help
F5: Previous Values F6: Fail-Safe Defaults F7: Optimized Defaults
IDE 1 Controller
This item allows you to enable or disable the IDE1 controller.
IDE Function Setup
BIOS Setup
IDE DMA transfer access:
This item selects the DMA mode for devices connected through IDE channels.
IDE HDD Block Mode
This item enables or disables the IDE HDD Block Mode.
Serial-ATA Controller
This item enables or disables the on-chip SATA controller.
3-19
Page 56

RAID Configuration:
Click <Enter> key to enter its submenu:
Phoenix – Award BIOS CMOS Setup Utility
RAID Function Disabled Item Help
X - Serial-ATA 1 RAID Disabled
X - Serial-ATA 2 RAID Disabled
X - Serial-ATA 3 RAID Disabled
X - Serial-ATA 4 RAID Disabled
X - Serial-ATA 5 RAID Disabled
X - Serial-ATA 6 RAID Disabled
X - OnChip SATA Boot ROM Enabled
↓↑→←:Move Enter:Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1:General Help
F5: Previous Values F6: Fail-Safe Defaults F7: Optimized Defaults
RAID Function
This item allows you to enable or disable the RAID function for Serial-ATA 1~6 ports.
- Serial-ATA 1 RAID ~ Serial-ATA 6 RAID
This item allows you to enable or disable the RAID function for each of the Serial-ATA 1~6 port
individually.
- OnChip SATA Boot ROM
This item allows you to use the boot ROM of OnChip SATA to boot up system.
RAID Configuration
Back to Integrated Peripherals Setup Menu:
Init Display First
This item selects which display slot to initialize first when the system boots.
OnChip USB
Select the type of USB controller. Three options are available: Disabled V1.1+V2.0 V1.1.
The default setting is V1.1+V2.0. If you choose to disable this item, the “USB Keyboard
Support” and “USB Mouse Support” items will not be available to select in Integrated
Peripherals menu.
3-20
Page 57

- USB Keyboard Support
Select [BIOS] for the legacy operating system (such as DOS) that does not support USB
keyboard.
- USB Mouse Support
Select [BIOS] for the legacy operating system (such as DOS) that does not support USB
mouse.
OnChip Audio Controller
This option enables or disables the audio controller.
OnChip LAN1 Controller
This option enables or disables the LAN1 controller.
OnChip LAN2 Controller
This option enables or disables the LAN2 controller.
Onboard LAN Boot ROM
This item allows you to use the boot ROM (instead of a disk drive) to boot-up the system and
access the local area network directly.
Onboard FDD Controller
Two options are available: Enabled and Disabled. The default setting is Enabled. You can
enable or disable the onboard FDD controller.
Onboard 1394 Controller:
This option enables or disables the IEEE 1394 controller.
BIOS Setup
3-21
Page 58

3.6 Power Management Setup
Phoenix – Award BIOS CMOS Setup Utility
ACPI Suspend Type S3(Suspend-To-RAM) Item Help
- USB Resume from S3 Disabled
Power Button Function Instant-Off
Wakeup by PME# of PCI Enabled
Wakeup by OnChip LAN Enabled
Wakeup by Alarm Disabled
X - Day (of Month) Alarm 0
X - Time (hh:mm:ss) Alarm 0: 0 : 0
Cool’n’Quiet Technology Auto
Power On Function Button Only
X - KB Power On Password Enter
X - Hot Key Power On Ctrl-F1
Restore on AC Power Loss Power Off
↓↑→←:Move Enter:Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1:General Help
F5: Previous Values F6: Fail-Safe Defaults F7: Optimized Defaults
Power Management Setup
ACPI Suspend Type
This item selects the type of Suspend mode.
[S1(PowerOn-Suspend)]: Enables the Power On Suspend function.
[S3(Suspend-To-RAM)]: Enables the Suspend to RAM function.
- USB Resume from S3
When set to [Enabled], this item allows you to use a USB device to wake up a system that is in
the S3 (STR - Suspend To RAM) state. This item can be configured only if the item “ACPI
Suspend Type” is set to [S3(STR)].
Power Button Function
This item selects the method of powering off your system:
[Delay 4 Sec.]: Pushing the power button for more than 4 seconds will power off the system.
This will prevent the system from powering off in case you accidentally hit or pushed the power
button.
[Instant-Off]: Pressing and then releasing the power button at once will immediately power
off the system.
Wakeup by PME# of PCI
When set to [Enabled], access through the add-on PCI card can remotely wake up the system
that was in Soft-Off condition. The PCI card must support the wake up function.
3-22
Page 59

Wakeup by OnChip LAN
When set to [Enabled], you can remotely wake up a PC in Soft-Off condition via a LAN card that
support the wake up function.
Wakeup by Alarm
When set to [Enabled], you can set the date and time you would like the Soft-Off PC to
power-on in the “Date (of Month) Alarm” and “Time (hh:mm:ss) Alarm” items. However,
if the system is being accessed by incoming calls or the network (Resume On Ring/LAN) prior to
the date and time set in these items, the system will give priority to the incoming calls or
network instead.
- Date (of Month) Alarm
[0]: This option power-on the system everyday according to the time set in the “Time
(hh:mm:ss) Alarm” item.
[1-31]: This option selects a date you would like the system to power-on. The system will
power-on on the date set, and the time set in the “Time (hh:mm:ss) Alarm” item.
- Time (hh:mm:ss) Alarm
This item sets the time you would like the system to power-on.
Cool ’n’ Quiet Technology:
This option enables or disables the AMD K8 cool and quiet function.
Power On Function
This item selects the way you want your system to power on.
[Password]: Use a password to power on the system, select this option then press <Enter>.
Enter your password. You can enter up to 5 characters. Type in exactly the same password to
confirm, and then press <Enter>.
[Hot KEY]: Use any of the function keys between <F1> to <F12> to power on the system.
[Mouse Left]: Double click the mouse left button to power on the system.
[Mouse Right]: Double click the mouse right button to power on the system.
[Any KEY]: Use any keyboard keys to power on the system.
[Button Only]: Use only the power button to power on the system.
[Keyboard 98]: Use the power-on button on the “Keyboard 98” compatible keyboard to power
on the system.
※ The mouse wake up function can only be used with the PS/2 mouse, not with
the COM port or USB type. Some PS/2 mice cannot wake up the system because
of compatible problems. If the specs of your keyboard are too old, it may fail to
power on.
- KB Power ON Password
This item sets the password required in order to power on your computer.
BIOS Setup
3-23
Page 60

※ Do not forget your password, or you will have to clear the CMOS and reset all
parameters in order to utilize this function again.
- Hot Key Power ON
This item powers on the system by pressing <Ctrl> key plus one of each function key (<F1> ~
<F12>) simultaneously.
Restore on AC Power Loss
This item selects the system action after an AC power failure.
[Power Off]: When power returns after an AC power failure, the system’s power remains off.
You must press the Power button to power-on the system.
[Power On]: When power returns after an AC power failure, the system’s power will be
powered on automatically.
[Last State]: When power returns after an AC power failure, the system will return to the
state where you left off before power failure occurs. If the system’s power is off when AC
power failure occurs, it will remain off when power returns. If the system’s power is on when
AC power failure occurs, the system will power-on when power returns.
3.7 PnP/PCI Configurations
Phoenix – Award BIOS CMOS Setup Utility
Resources Controlled By Auto(ESCD) Item Help
X - IRQ Resources Press Enter
PCI/VGA Pallete Snoop Disbaled
** PCI Express relative items **
Maximum Payload Size 4096
↓↑→←:Move Enter:Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1:General Help
F5: Previous Values F6: Fail-Safe Defaults F7: Optimized Defaults
PnP/PCI Configurations
Resources Controlled By
This item configures all of the boot and Plug-and-Play compatible devices.
[Auto(ESCD)]: The system will automatically detect the settings.
[Manual]: Choose the specific IRQ resources in the “IRQ Resources” menu.
3-24
Page 61

- IRQ Resources
Click <Enter> key to enter its submenu:
This item sets each system interrupt to either [PCI Device] or [Reserved].
Phoenix – Award BIOS CMOS Setup Utility
IRQ-4 assigned to Reserved Item Help
IRQ-5 assigned to PCI Device
IRQ-7 assigned to PCI Device
IRQ-10 assigned to PCI Device
IRQ-11 assigned to PCI Device
↓↑→←:Move Enter:Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1:General Help
F5: Previous Values F6: Fail-Safe Defaults F7: Optimized Defaults
- IRQ Resources
Back to PnP/PCI Configurations Setup Menu:
PCI/VGA Palette Snoop
This item determines whether the MPEG ISA/VESA VGA cards can work with PCI/VGA or not.
[Disabled]: MPEG ISA/VESA VGA cards do not work with PCI/VGA.
[Enabled]: MPEG ISA/VESA VGA cards work with PCI/VGA.
BIOS Setup
Maximum Payload Size
This item sets the maximum TLP payload size for the PCI Express devices.
3-25
Page 62

3.8 Load Fail-Safe Defaults
This option loads the BIOS default values for the most stable, minimal-performance system
operations.
3.9 Load Optimized Defaults
This option loads the BIOS default values that are factory settings for optimal-performance
system operations.
3.10 Set Password
This option protects the BIOS configuration or restricts access to the computer itself.
3.11 Save & Exit Setup
This option saves your selections and exits the BIOS setup menu.
3.12 Exit Without Saving
This option exits the BIOS setup menu without saving any changes.
For more information:
www.abit.com.tw
3-26
Page 63

4. Driver & Utility CD
The “Driver & Utility CD” that came packed with this motherboard contains drivers, utilities and
software applications required for its basic and advanced features.
Place the “Driver & Utility CD” into the CD-ROM drive in your system. The following installation
auto-run screen appears. If not, browse the root directory of the CD-ROM via the File Manager,
and double click the “AUTORUN” file.
• [Drivers]: Click to enter the driver installation menu.
• [Manual]: Click to enter the user’s manual menu.
• [Utility]: Click to enter the utilities installation menu.
• [ABIT Utility]: Click on this tab to enter the menu for installing utilities exclusively
developed by ABIT.
•
[
•
[
Browse CD]: Click to browse the contents of this “Driver & Utility CD”.
Close]: Click to exit this installation menu.
4-1
Driver & Utility CD
Page 64
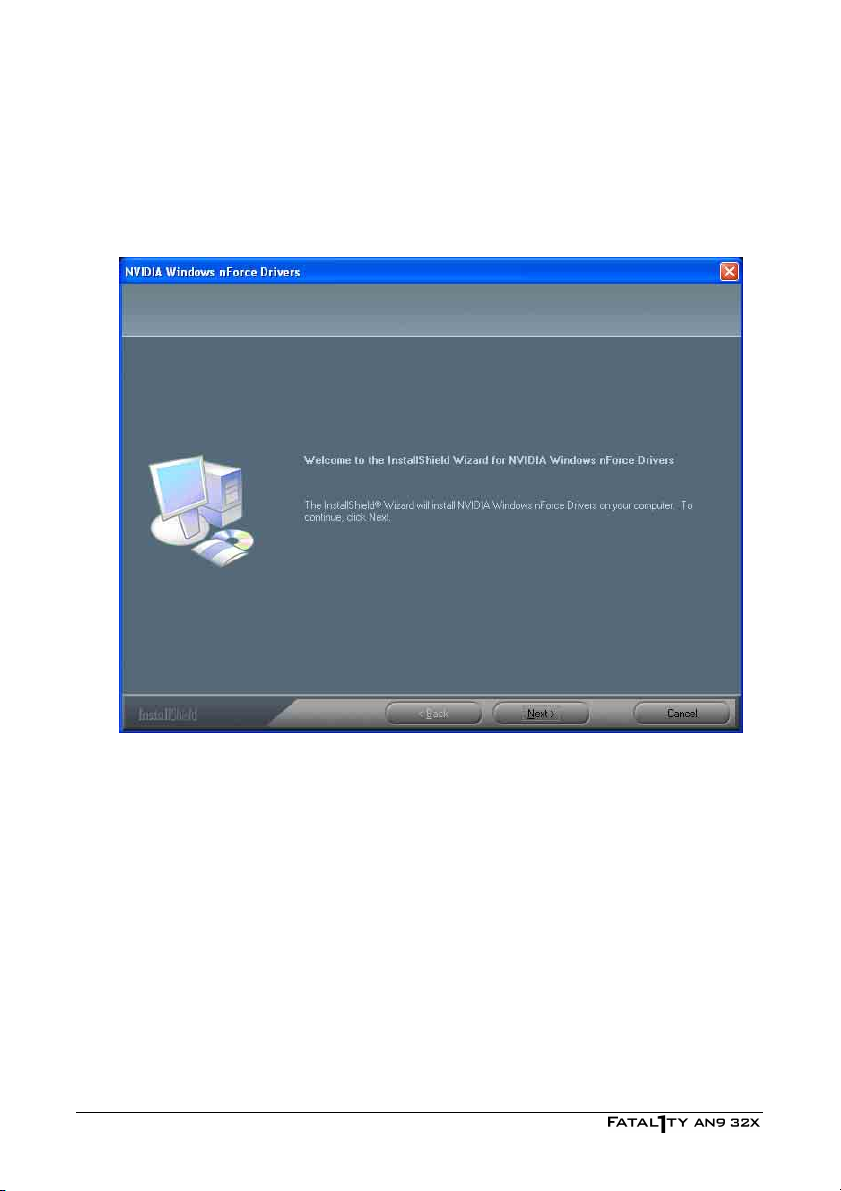
4.1 nVidia nForce Chipset Driver
To install this driver:
1. Click on the [Drivers] tab in the installation menu screen.
2. Click the [nVidia nForce Chipset Driver]. The following screen appears:
3. Follow the prompts on the screen to complete installation.
4. Restart the system for the driver to take effect.
※ Please install this nVidia nForce Chipset Driver first after having installed the
Windows operating system.
4-2
Page 65
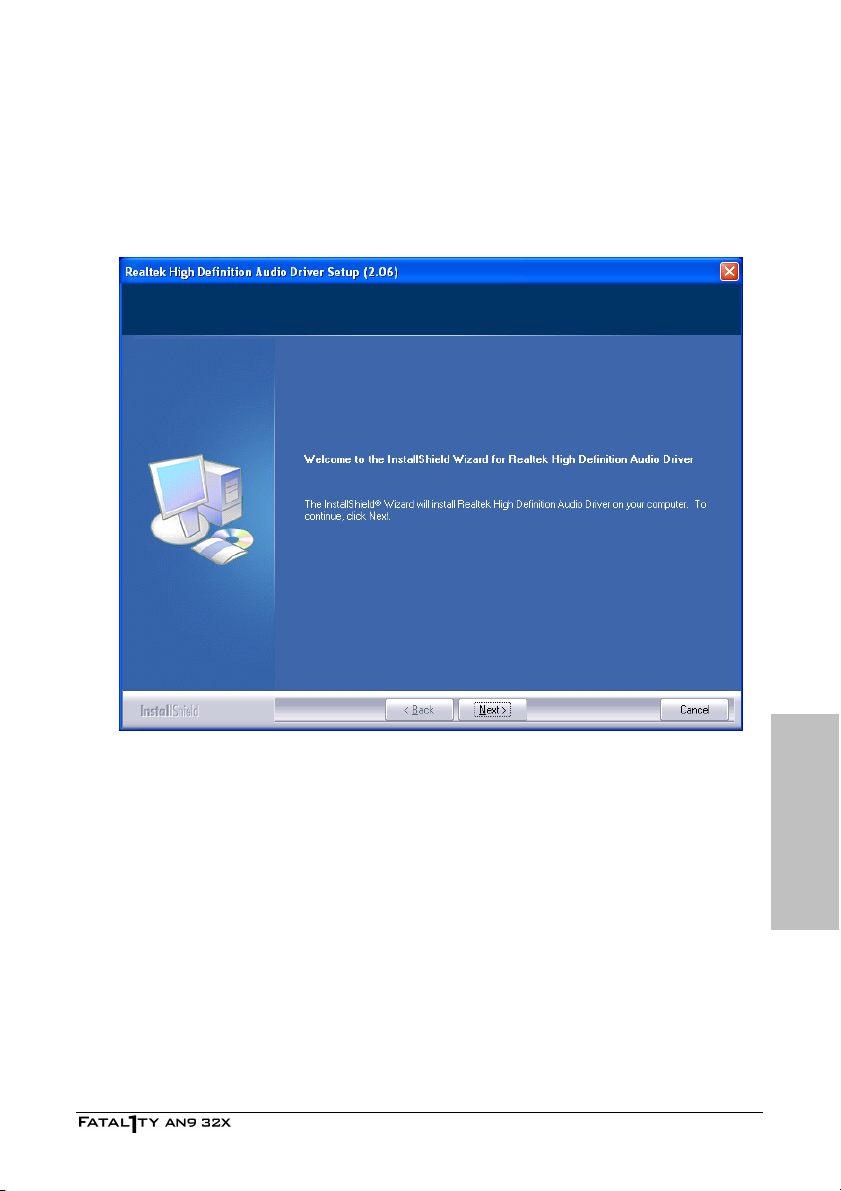
4.2 Realtek HD Audio Driver
To install this driver:
1. Click on the [Drivers] tab in the installation menu screen.
2. Click the [Realtek HD Audio Driver] item. The following screen appears:
3. Follow the prompts on the screen to complete installation.
4. Restart the system for the driver to take effect.
※ Install this Driver after having installed the “AudioMAX” daughter-card.
4-3
Driver & Utility CD
Page 66
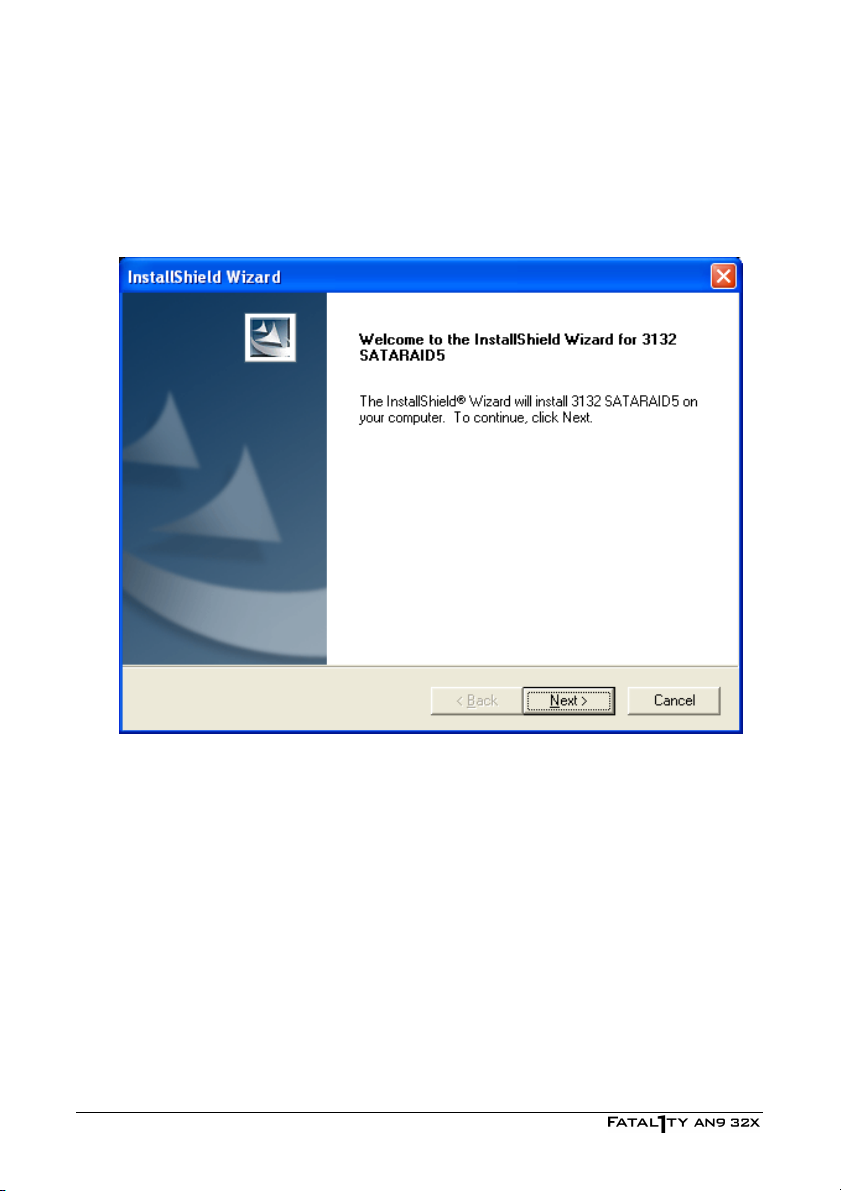
4.3 Silicon Image 3132 RAID Driver
To install this driver:
1. Click on the [Drivers] tab in the installation menu screen.
2. Click the [Silicon Image 3132 RAID Driver] item. The following screen appears:
3. Follow the prompts on the screen to complete installation.
4. Restart the system for the driver to take effect.
4-4
Page 67
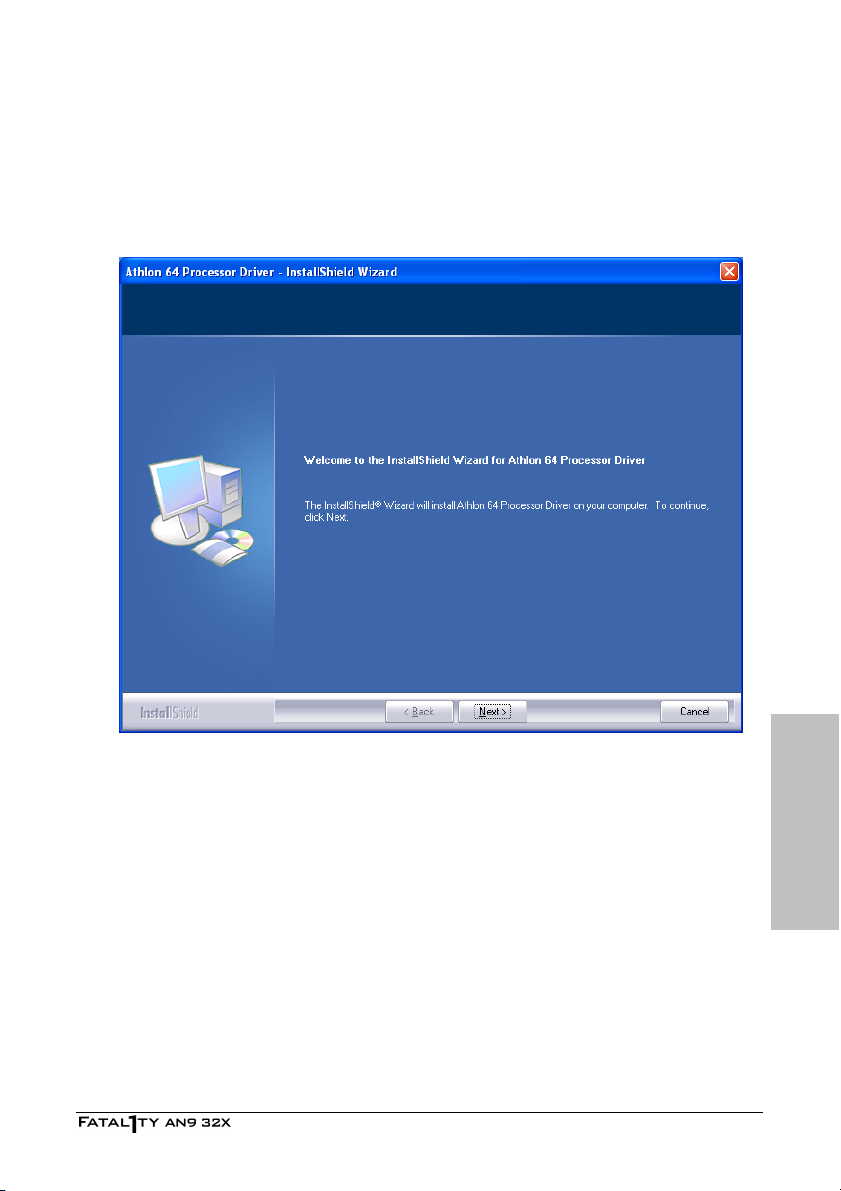
4.4 Cool’n’Quiet Driver
To install this driver:
1. Click on the [Drivers] tab in the installation menu screen.
2. Click the [Cool’n’Quiet Driver] item. The following screen appears:
3. Follow the prompts on the screen to complete installation.
4. Restart the system for the driver to take effect.
4-5
Driver & Utility CD
Page 68
5. After the system restarted, open the “Power Options” from the control panel and choose
the power scheme “Minimal Power Management” to enable Cool ‘n’ Quiet.
※ For Windows 2000 or ME system, an AMD Cool ‘n’ Quiet tab will appear under
“Power Options” when the Cool ‘n’ Quiet software for Windows 2000 and ME is
installed. This must be set to “Automatic Mode” for Cool ‘n’ Quiet to be enabled.
4-6
Page 69
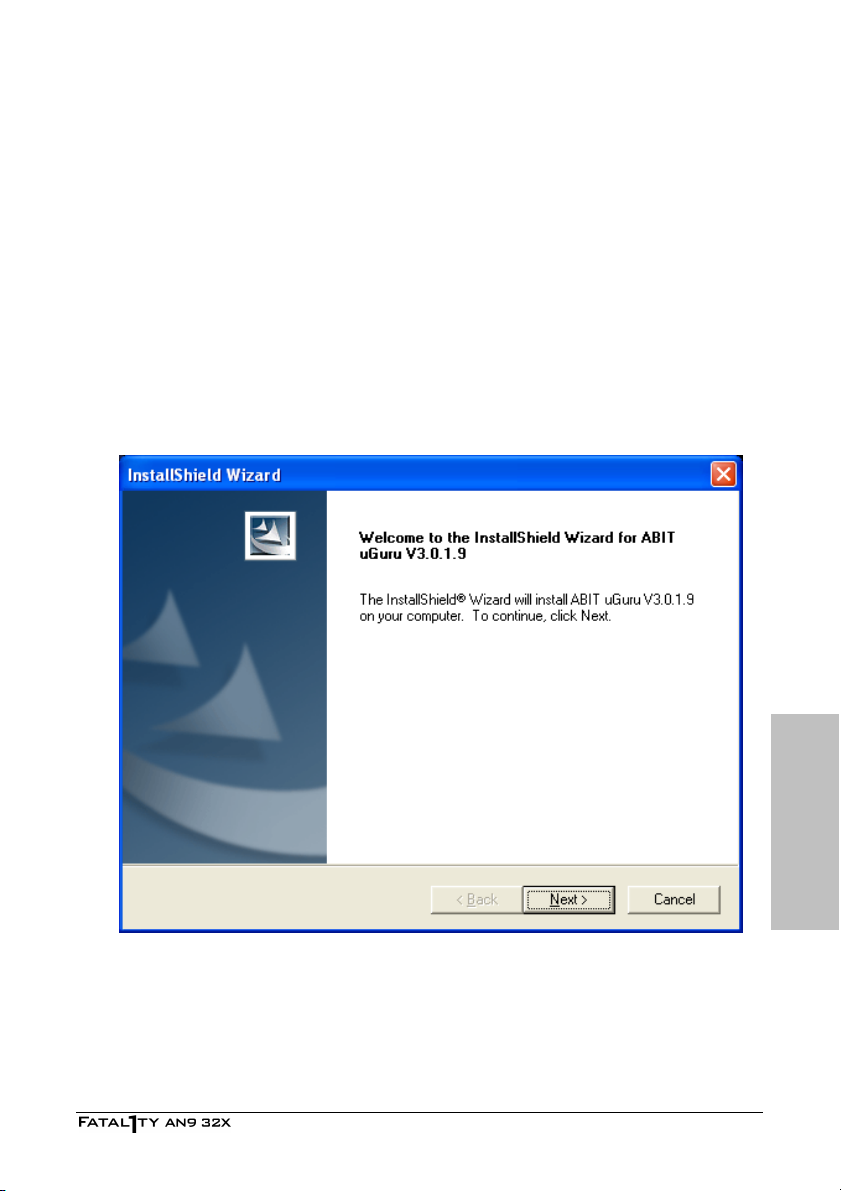
4.5 USB 2.0 Driver
※ There is no need to install this driver for Windows 2000 with Service Pack 4,
Windows XP with Service Pack 1, or their later version.
4.6 ABIT µGuru Utility
The µGuru Utility combined with the optional Guru Clock allows you to access and select system
performance of your system while playing games, listening music, browsing Internet or office
applications in full screen with no need to stop or close the running application.
To install this utility:
1. Click on the [ABIT Utility] tab in the installation menu screen.
2. Click the [ABIT Guru] item. The following screen appears:
3. Follow the prompts on the screen to complete installation.
4. Restart the system for the driver to take effect.
4-7
Driver & Utility CD
Page 70
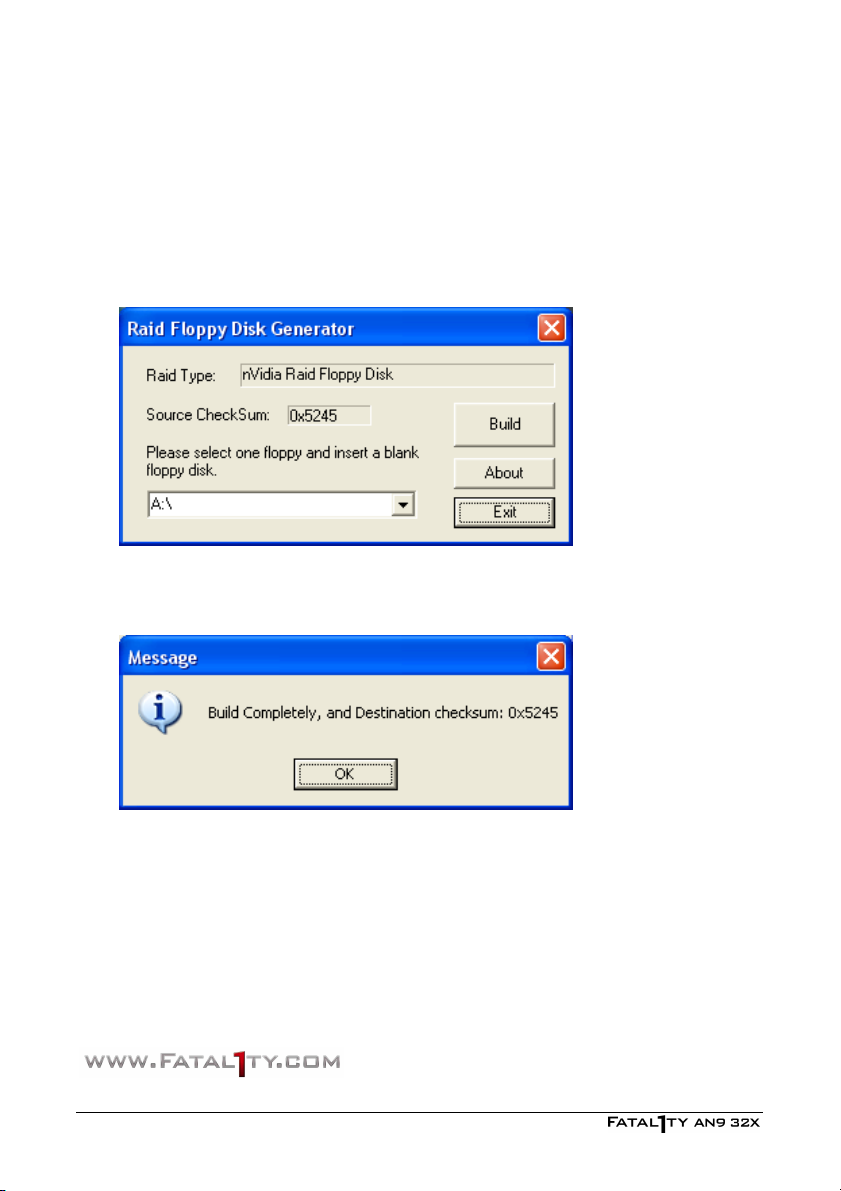
4.7 NVRaid Floppy Disk
If you lost or damaged the SATA Driver Disk that came with the package, use the NVRaid
Floppy Disk to create another one.
To install this utility:
1. Click on the [ABIT Utility] tab in the installation menu screen.
2. Click the [Generate NVRaid Floppy Disk[32bit]]. The following screen appears:
Insert one blank floppy disk to the selected floppy drive and click [Build].
3. Click [OK] to finish building the SATA Driver Disk.
※ If you are using a windows 2000 operating system, please update your system
to Service Pack 4 before starting to setup the NVIDIA RAID.
For more information:
www.abit.com.tw
4-8
Page 71
5. Appendix
5.1 POST Code Definitions
5.1.1 AWARD POST Code Definitions
POST
(hex)
1D Initial EARLY_PM_INIT switch
Description
CF Test CMOS R/W functionality
Early chipset initialization:
C0
C1
C3 Expand compressed BIOS code to DRAM
C5 Call chipset hook to copy BIOS back to E000 & F000 shadow RAM
01 Expand the Xgroup codes locating in physical address 1000:0
03 Initial Superio_Early_Init switch
05
07
08
0A
0E
10
12
14
16
18 Detect CPU information including brand, SMI type (Cyrix or Intel) and CPU level (586 or 686)
1B
1F Load keyboard matrix (notebook platform)
21 HPM initialization (notebook platform)
23
24
-Disable shadow RAM
-Disable L2 cache (socket 7 or below)
-Program basic chipset registers
Detect memory
-Auto-detection of DRAM size, type and ECC
-Auto-detection of L2 cache (socket 7 or below)
1. Blank out screen
2. Clear CMOS error flag
1. Clear 8042 interface
2. Initialize 8042 self-test
1. Test special keyboard controller for Winbond 977 series Super I/O chips
2. Enable keyboard interface
1. Disable PS/2 mouse interface (optional)
2. Auto detect ports for keyboard & mouse followed by a port & interface swap (optional)
3. Reset keyboard for Winbond 977 series Super I/O chips
Test F000h segment shadow to see whether it is R/W-able or not. If test fails, keep beeping
the speaker
Auto detect flash type to load appropriate flash R/W codes into the run time area in F000 for
ESCD & DMI support
Use walking 1’s algorithm to check out interface in CMOS circuitry. Also set real-time clock
power status, and then check for override
Program chipset default values into chipset. Chipset default values are MODBINable by
OEM customers
Initial onboard clock generator if Early_Init_Onboard_Generator is defined. See also POST
26.
Initial interrupts vector table. If no special specified, all H/W interrupts are directed to
SPURIOUS_INT_HDLR & S/W interrupts to SPURIOUS_soft_HDLR.
1. Check validity of RTC value: e.g. a value of 5Ah is an invalid value for RTC minute.
2. Load CMOS settings into BIOS stack. If CMOS checksum fails, use default value instead.
Prepare BIOS resource map for PCI & PnP use. If ESCD is valid, take into consideration of
the ESCD’s legacy information.
Appendix
5-1
Page 72
Early PCI Initialization:
25
26
27 Initialize INT 09 buffer
29
2B Invoke Video BIOS
2D
33
35 Test DMA Channel 0
37 Test DMA Channel 1.
39 Test DMA page registers.
3C Test 8254
3E Test 8259 interrupt mask bits for channel 1
40 Test 8259 interrupt mask bits for channel 2
43 Test 8259 functionality
47 Initialize EISA slot
49
4E
50 Initialize USB
52 Test all memory (clear all extended memory to 0)
53 Clear password according to H/W jumper (Optional)
55 Display number of processors (multi-processor platform)
57
59 Initialize the combined Trend Anti-Virus code
5B (Optional Feature) Show message for entering AWDFLASH.EXE from FDD (optional)
5D
60
63 Reset keyboard if Early_Reset_KB is not defined
65 Initialize PS/2 Mouse
67 Prepare memory size information for function call: INT 15h ax=E820h
69 Turn on L2 cache
-Enumerate PCI bus number.
-Assign memory & I/O resource
-Search for a valid VGA device & VGA BIOS, and put it into C000:0
1. If Early_Init_Onboard_Generator is not defined Onboard clock generator initialization.
Disable respective clock resource to empty PCI & DIMM slots.
2. Init onboard PWM
3. Init onboard H/W monitor devices
1. Program CPU internal MTRR (P6 & PII) for 0-640K memory address.
2. Initialize the APIC for Pentium class CPU.
3. Program early chipset according to CMOS setup. Example: onboard IDE controller.
4. Measure CPU speed.
1. Initialize double-byte language font (Optional)
2. Put information on screen display, including Award title, CPU type, CPU speed, full screen
logo.
Reset keyboard if Early_Reset_KB is defined e.g. Winbond 977 series Super I/O chips. See
also POST 63.
1. Calculate total memory by testing the last double word of each 64K page
2. Program writes allocation for AMD K5 CPU
1. Program MTRR of M1 CPU
2. Initialize L2 cache for P6 class CPU & program CPU with proper cacheable range
3. Initialize the APIC for P6 class CPU
4. On MP platform, adjust the cacheable range to smaller one in case the cacheable ranges
between each CPU are not identical
Display PnP logo
Early ISA PnP initialization
-Assign CSN to every ISA PnP device
1. Initialize Init_Onboard_Super_IO
2. Initialize Init_Onbaord_AUDIO
Okay to enter Setup utility; i.e. not until this POST stage can users enter the CMOS setup
utility
5-2
Page 73
6B Program chipset registers according to items described in Setup & Auto-configuration table
6D
8D
1. Assign resources to all ISA PnP devices
2. Auto assign ports to onboard COM ports if the corresponding item in Setup is set to
“AUTO”
1. Initialize floppy controller
6F
2. Set up floppy related fields in 40:hardware
75 Detect & install all IDE devices: HDD, LS120, ZIP, CDROM …
(Optional Feature)
Enter AWDFLASH.EXE if:
76
77 Detect serial ports & parallel ports.
7A Detect & install co-processor
7C Init HDD write protect
7F
82
83 Save all data in stack back to CMOS
84 Initialize ISA PnP boot devices
85
87 NET PC: Build SYSID Structure
89
8B
8F Clear noise of IRQs
93 Read HDD boot sector information for Trend Anti-Virus code
94
95 Update keyboard LED & typematic rate
96
FF Boot attempt (INT 19h)
-AWDFLASH is found in floppy drive
-ALT+F2 is pressed
Switch back to text mode if full screen logo is supported
-If errors occur, report errors & wait for keys
-If no errors occur or F1 key is pressed to continue: Clear EPA or customization logo
E8POST.ASM starts
1. Call chipset power management hook
2. Recover the text font used by EPA logo (not for full screen logo)
3. If password is set, ask for password
1. USB final Initialization
2. Switch screen back to text mode
1. Assign IRQs to PCI devices
2. Set up ACPI table at top of the memory.
1. Invoke all ISA adapter ROMs
2. Invoke all PCI ROMs (except VGA)
1. Enable/Disable Parity Check according to CMOS setup
2. APM Initialization
1. Enable L2 cache
2. Program Daylight Saving
3. Program boot up speed
4. Chipset final initialization.
5. Power management final initialization
6. Clear screen & display summary table
7. Program K6 write allocation
8. Program P6 class write combining
1. Build MP table
2. Build & update ESCD
3. Set CMOS century to 20h or 19h
4. Load CMOS time into DOS timer tick
5. Build MSIRQ routing table
Appendix
5-3
Page 74

5.1.2 AC2005 POST Code Definitions
POST
(hex)
8.1. Start power on sequence
8.2. Enable ATX power supply
8.3. ATX power supply ready
8.4. DDR voltage ready
8.5. Setup PWM for CPU core voltage
8.6. Assert PWM for CPU core voltage
8.7. Check CPU core voltage
8.8. CPU core voltage ready
8.9. Initial clock generator IC
8.A. North Bridge chipset voltage ready
8.B. AGP voltage ready
8.C. 3VDUAL voltage ready
8.D. VDDA 2.5V voltage ready
8.D. GMCHVTT voltage ready
8.E. Check CPU fan speed
8.F. Assert all power ready
9.0.
9.1. Start power off sequence
9.2. De-Assert all power
9.3. De-Assert power on
9.4. De-Assert LDT Bus power
9.5. De-Assert PWM for CPU core voltage
9.6. De-Assert CPU core voltage
9.7. Check CPU core voltage
9.8. De-Assert ATX power supply
9.9. Complete power off sequence
F.0. Button reset
F.1. SoftMenu reset
F.2. Power on sequence timeout
F.3. Power off sequence timeout
Description
Power On Sequence
Complete µGuru initial process
AWARD BIOS take over booting job
Power Off Sequence
Others
5-4
Page 75

5.2 Troubleshooting (How to Get Technical Support?)
5.2.1 Q & A
Q: Do I need to clear the CMOS before I use a new motherboard to assemble my
new computer system?
A: Yes, we highly recommend that you clear the CMOS before installing a new motherboard.
Please move the CMOS jumper from its default 1-2 position to 2-3 for a few seconds, and
then back. When you boot up your system for the first time, follow the instructions in the
user's manual to load the optimized defaults.
Q: If my system hangs when I update the BIOS or set the wrong CPU parameters,
what should I do?
A: Whenever you update the BIOS or if the system hangs due to wrong CPU parameters
setting, always clear CMOS jumper before booting up again.
Q: Why does the system fail to boot up again right after a mechanical power-off?
A: Please keep a 30-second interval between each mechanical power On/Off.
Q: Why does the system fail to boot up and nothing displays on the screen after I
did some over-clocking or non-standard settings inside the BIOS?
A: It should not cause hardware or permanent damage to motherboard when BIOS settings
were changed from default to over-clocking or non-standard status.
We suggest the following three troubleshooting methods to discharge CMOS data, recover
the hardware default status, and then making the motherboard work again. There is no
need to bother returning the motherboard to where you bought it from or go through an
RMA process.
Step 1. Switch off the power supply unit and then switch it on again after one minute. If
there is no power-switch on the power supply unit, disconnect its power cord for
one minute and then reconnect.
Press and hold the <Insert> key on the keyboard, and press the power-on button
to boot up system. If it works, release the <Insert> key and hit <Del> key to enter
the BIOS setup page to apply the correct settings.
If the situation remains the same, repeat the procedures in Step 1 for three times,
or try Step 2.
Step 2. Switch off the power supply unit or disconnect the power cord. Open the chassis
cover. Locate the CCMOS jumper near the button battery. Change the jumper
position from default 1-2 to 2-3 for one minute to discharge the CMOS data, and
then put it back to default 1-2 position.
Close the chassis and switch on the power supply unit or plug in the power cord.
Press the power-on button to boot up system. If it works, hit <Del> key to enter
the BIOS setup page to do the correct settings.
If the situation remains the same, try Step 3.
Step 3. The same procedure as Step 2, but while discharging the CMOS data, pull out the
ATX power connectors from motherboard and remove the button battery during
CMOS discharge.
Appendix
5-5
Page 76

Q: How to get a quick response for my request on technical support?
A: Please carry out a simple troubleshooting before sending “Technical Support Form”:
System boot-up fails after the system had been assembled:
Check the motherboard’s supporting specifications first to see if all the key components
attached in your system can meet.
To do so, you may:
Remove all the unnecessary add-on devices (except the CPU, VGA card, DRAM, and
Power Supply), and then reboot.
If the trouble still exists, try another VGA card of different brand/model to see if the
system will start.
If the trouble still exists, try another memory module of different brand/model.
If the trouble still exists, try another CPU and Power Supply.
If the system runs successfully, shut it down and start re-installing the interface cards and
devices that were previously installed in the system. Re-install and start the system one at a
time until the system won’t start.
Malfunction in the OS:
If the system hangs after resuming from S3 or some testing program, if the CPU cannot be
recognized properly, if the display resolution mixed, or if a certain program cannot be
executed, etc, you may:
Upgrade the motherboard’s latest BIOS version.
Upgrade the add-on device’s latest driver version.
Check if there is any conflict in the “Control Panel/System Properties”.
Q: How to fill in the “Technical Support Form”?
A: To fill in this “Technical Support Form”, please refer to the following instructions:
• Region: Type in your country name.
• E-mail: Type in your contact E-mail information.
• First name: Type in your first name.
• Last name: Type in your last name.
• Subject: Type in the model name and the problem of your motherboard.
Example 1: AA8XE and SCSI 29160 malfunction
Example 2: AA8XE boot fails, POST code AF
Example 3: AA8XE (system hang when S3 resume)
• Motherboard: Type in the model name and revision number of your motherboard.
Example: AA8XE REV: 1.00
• BIOS Version: Type in the BIOS version of your motherboard. (You can find it on the
screen during the POST sequence.)
• CPU: Type in the brand name and the speed (MHz) of your CPU. (Illustrate the
over-clocking status if you had done so.)
Example: Intel 650 3.4GHz (OC FSB=220MHz)
• Memory brand: Type in the brand and model name of your memory module.
Example: Memory brand: Kingston (KVR533D2N4/1G)
5-6
Page 77

• Memory size: Type in the size of your memory module.
Example: 512M* 4PCS
• Memory configuration: Type in the memory configuration in BIOS setting.
Example: Memory Timing: 2.5-3-3-7 @533MHz
• Graphics information: Note Graphics card’s brand, model and driver version
• Graphics card: Type in the brand and model name of your graphics card.
Example: ATI RADEON X850 XT PE
• Graphics driver version: Type in the driver version of your graphics card
Example: Catalyst 5.12V
• Power supply maker: Type in the brand and model name of your power supply unit.
• Power supply wattage: Type in the power wattage of your power supply unit.
• Storage devices: Type in the brand and specifications of your HDD drive and quantity.
Specify if it was inserted on IDE (Master or Slave) or SATA ports, including the RAID
allocation status.
Example 1: WD Caviar WD600 60GB (on IDE2 master), Maxtor DiamondMax 10 SATA
300GB (on SATA 3)
Example 2: Maxtor DiamondMax 10 SATA 300GB *2 (on SATA 3, SATA 4 RAID 1)
• Optical devices: Type in the brand and specifications of your optical drives and
quantity. Specify if it was inserted on IDE (Master or Slave) or SATA ports.
• Other devices: Indicate which add-on cards or USB devices that you absolutely sure
are related to the problem. If you cannot identify the problem’s origin, indicate all the
add-on cards or USB devices inserted on your system.
Example: AHA 29160 (on PCI 2), Sandisk Cruzer mini 256MB USB Flash-disk.
• Operating system: Indicate which OS and language version
Example: Microsoft Windows XP SP2, English version
Example: Microsoft Media Center Edition 2005, Korean version
• Problem description: Describe the problem of your system configuration. Indicate
the steps to duplicate problem if possible.
See the next page for a blank Technical Support Form, or visit our website to fill in the
form on line (http://www.abit.com.tw/page/en/contact/technical.php
).
Q. Is the motherboard dead? Do I need to return it to where I bought from or go
through an RMA process?
A: After you had gone through the troubleshooting procedures, yet the problem still exists, or
you find an evident damage on the motherboard. Please contact our RMA center.
(http://www2.abit.com.tw/page/en/contact/index.php?pFUN_KEY=18000&pTITLE_IMG
5-7
)
Appendix
Page 78

5.2.2 Technical Support Form
Region:
E-mail:
First name:
Last Name:
Subject:
Motherboard:
BIOS Version:
CPU:
Memory brand:
Memory size:
Memory configuration:
Graphics card:
Graphics driver version:
Power supply maker:
Power supply wattage:
Storage devices:
Optical devices:
Other devices:
Operating system:
Problem description:
5-8
Page 79

5.2.3 Universal ABIT Contact Information
Taiwan Head Office
Universal ABIT Co., Ltd.
No. 323, Yang Guang St., Neihu,
Taipei, 114, Taiwan
Tel: 886-2-8751-3380
Fax: 886-2-8751-3381
Sales: sales@abit.com.tw
Marketing: market@abit.com.tw
North America, South America
Universal ABIT (USA) Corporation
2901 Bayview Drive,
Fremont, CA 94538, U.S.A.
Tel: 1-510-623-0500
Fax: 1-510-623-1092
Website: http://www.abit-usa.com
Latin America: ventas@abit-usa.com
RMA Center: http://rma.abit-usa.com
UK, Ireland
Universal ABIT UK Corporation
Unit 3, 24-26 Boulton Road, Stevenage,
Herts SG1 4QX, UK
Tel: 44-1438-228888
Fax: 44-1438-226333
Germany and Benelux (Belgium,
Netherlands, Luxembourg), France,
Italy, Spain, Portugal, Greece,
Denmark, Norway, Sweden, Finland,
Switzerland
Universal ABIT NL B.V.
Jan van Riebeeckweg 15, 5928LG,
Venlo, The Netherlands
Tel: 31-77-3204428
Fax: 31-77-3204420
Austria, Czech, Romania, Bulgaria,
Slovakia, Croatia, Bosnia, Serbia,
Macedonia, Slovenia
Universal ABIT Austria Computer
GmbH
Schmalbachstrasse 5, A-2201 Gerasdorf /
Wien, Austria
Tel: 43-1-7346709
Fax: 43-1-7346713
Contact: office@abit-austria.at
Website: http://www.abit-austria.at
Shanghai
Universal ABIT (Shanghai) Co. Ltd.
FL 19 Xuhui Yuan BLOG NO.1089
ZhongShan s 2 RD, ShangHai 200030
The People's Republic of China
Tel: (86-21) 54102211
Fax: (86-21) 54104791
Website: http://www.abit.com.cn
Poland
Universal ABIT Poland (Rep. office)
Strzegomska 310/2, 54-432 Wroclaw
Tel: +48-71-718-12-39
Contact: Grzegorz Morgiel
Russia
Universal ABIT Russia (Rep. office)
Contact: info@abit.ru
Website: www.abit.ru
Turkey
Universal ABIT Turkey (Rep. office)
Tel: 90 532 211 6860
Appendix
5-9
Page 80

www.abit.com.tw
Johnathan “Fatal1ty” Wendel
P/N: 4310-0000-25
Rev. 2.00
 Loading...
Loading...