Page 1

Page 2

the reader should use caution to understand
completely the warnings. Ignoring the warnings may result in serious hazards or
Before You Use This Product
The use of surveillance devices may be prohibited by law in your country. The
Network Camera is not only a high-performance web-ready camera but also can be
part of a flexible surveillance system. It is the user’s responsibility to ensure that the
operation of such devices is legal before installing this unit for its intended use.
It is important to first verify that all contents received are complete according to the
list in the "Package Contents" chapter. Take notice of the warnings in “Quick
installation guide” before the Network Camera is installed, then carefully read and
follow the instructions in the “Installation” chapter to avoid damages due to faulty
assembly and installation. This also ensures the product is used properly as
intended.
The Network Camera is a network device and its use should be straightforward for
those who have basic network knowledge. The “Troubleshooting” chapter in the
Appendix provides remedies to the most common errors in set up and configuration.
You should consult this chapter first if you run into a system error.
The Network Camera is designed for various applications including video sharing,
general security/surveillance, etc. The “How to Use” chapter suggests ways to best
utilize the Network Camera and ensure proper operations. For the creative and
professional developers, the "URL Commands of The Network Camera" chapter
serves to be a helpful reference to customize existing homepages or integrating with
the current web server.
For paragraphs preceded by
injuries.
- 1 -
Page 3

Table of Contents
Before You Use This Product 1
Package Contents 4
Installation 6
Hardware Installation 6
Software Installation 8
Initial Access to the Network Camera 11
Check Network Settings 11
Add Password to Prevent Unauthorized Access 11
How to Use 12
Authentication 12
Installing Plug-in 13
Primary User’s Capabilities 14
Main Screen with Camera View 14
Client Settings 16
Administrator’s Capabilities 18
Fine-Tuning for Best Performance 18
Opening Accounts for New Users 20
Building a Multimedia Web Attraction Site 21
Building a Security Application 24
Software Revision Upgrade 27
Definitions in Configuration 28
System Parameters 29
User Group Administration 30
Network Settings 31
HTTP 31
Streaming 32
WLAN Configuration 32
Mail & FTP 34
SMTP 34
FTP 34
Video Codec Parameters 36
Motion Detection 38
Application Setup 39
- 2 -
Page 4

Weekly Schedule 39
Event Operation 39
Sequential Operation 40
Camera Control 41
UPnP and DDNS Settings 43
Remote Controller 44
Viewing System Parameters 45
Factory Default 45
Appendix 46
A. Troubleshooting 46
B. Frequently Asked Questions 46
C. URL Commands of the Network Camera 49
Capture Update Snapshot of JPEG Image 49
Query Status of the Digital Input 49
Drive the Digital Output 49
Restore Factory Default Settings 49
Restart System 50
Page URL 51
System Resource URL 51
General Format of Command URL 52
System Configuration URL 52
Security Configuration URL 53
Network Configuration URL 53
DDNS & UPnP Configuration URL 54
Mail&FTP Configuration URL 55
Audio/Video Configuration URL 56
Camera Control URL 57
Image Quality Configuration URL 58
Application Configuration URL 58
D. Technical Specifications 60
- 3 -
Page 5

Package Contents
Network Camera IPCAMWLPT
Power adapter
Software CD
A/V Cable
Remote Controller
Antennas
Camera stand
- 4 -
Page 6

Connect the power adapter jack to the
Network Camera before plugging in to the
. This will reduce the risk of
Installation
Hardware Installation
Please verify that your product package contains
all the accessories listed in the foregoing Package
Contents. Depending on the user’s application,
an Ethernet cable may be needed. The Ethernet
cable should meet the specs of UTP Category 5
and not exceed 100 meters in length.
Upon powering up, the device runs through a self-test procedure and the front LEDs
will blink between green and red a few times. If self-test passes, the LEDs will shut off
and the Network Camera will be on stand-by and ready for software installation. If
self-test fails the red LED will blink several times. Refer to Appendix A for
troubleshooting.
The Network Camera will first detect Ethernet. If it does not connect to Ethernet, the
Network Camera will try WLAN. During the searching and connecting process to the
wireless access point or station, the red LED of the Network Camera will flash every
second. Until the Network Camera connects to the other wireless device, the red LED
will become lighted. Operating in either network mode, the green LED will flash every
power socket
accidental electric shock.
second as heartbeat to indicate alive.
To install in Ethernet
Make sure the Ethernet is firmly connected to a switch hub. After attaching the
Ethernet cable plug in the power adapter. If the LED turns out to be steady green after
- 6 -
Page 7

self-test, go to next paragraph “Software installation”. If the Ethernet is not available,
Network Camera will switch to wireless LAN mode.
To install in wireless LAN
If the Ethernet is not available while power on, the Network Camera will search for any
access point with the SSID “default”. Once any access point is found, the LED will turn
green to wait for installation. If the network environment cannot meet the default
settings, install Network Camera in Ethernet to proceed with wireless LAN
configuration.
The Network Camera provides a general I/O terminal block with one digital input and
one relay switch for device control. Pin 1 and Pin 2 can be connected to an external
sensor device and the state of voltage can be monitored from the initial state 'LOW'.
The relay switches Pin 3 and Pin 4 can be used to turn on or off an external device.
1 DI+ INPUT (Max. 50mA, 12VDC)
2 DI- INPUT (Initial state of DI is Low)
3 SW_COMMON OUTPUT (open from SW_OPEN at initial state)
(close with SW_OPEN when DO is set to ON)
4 SW_NOPEN OUTPUT (Max. 1A, 24VDC or 0.5A, 125VAC)
- 7 -
Page 8

Refer to the
Software Installation
In this manual, "User" refers to whoever has access to the Network Camera, and
"Administrator" refers to the person who can configure the Network Camera and grant
user access to the camera.
At the end of the hardware installation, the Administrator must place the product
software CD into the CD-ROM drive of the PC running in MS Windows. An auto-run
program will pop up (If the program is not on auto-run, go to the root directory of the
software CD and click on “autorun.exe”).
Click on the IP installer to execute the installation program.
network setting chapter to setup wireless network parameters.
Install the Network Camera on Ethernet before install it on WLAN.
- 8 -
Page 9
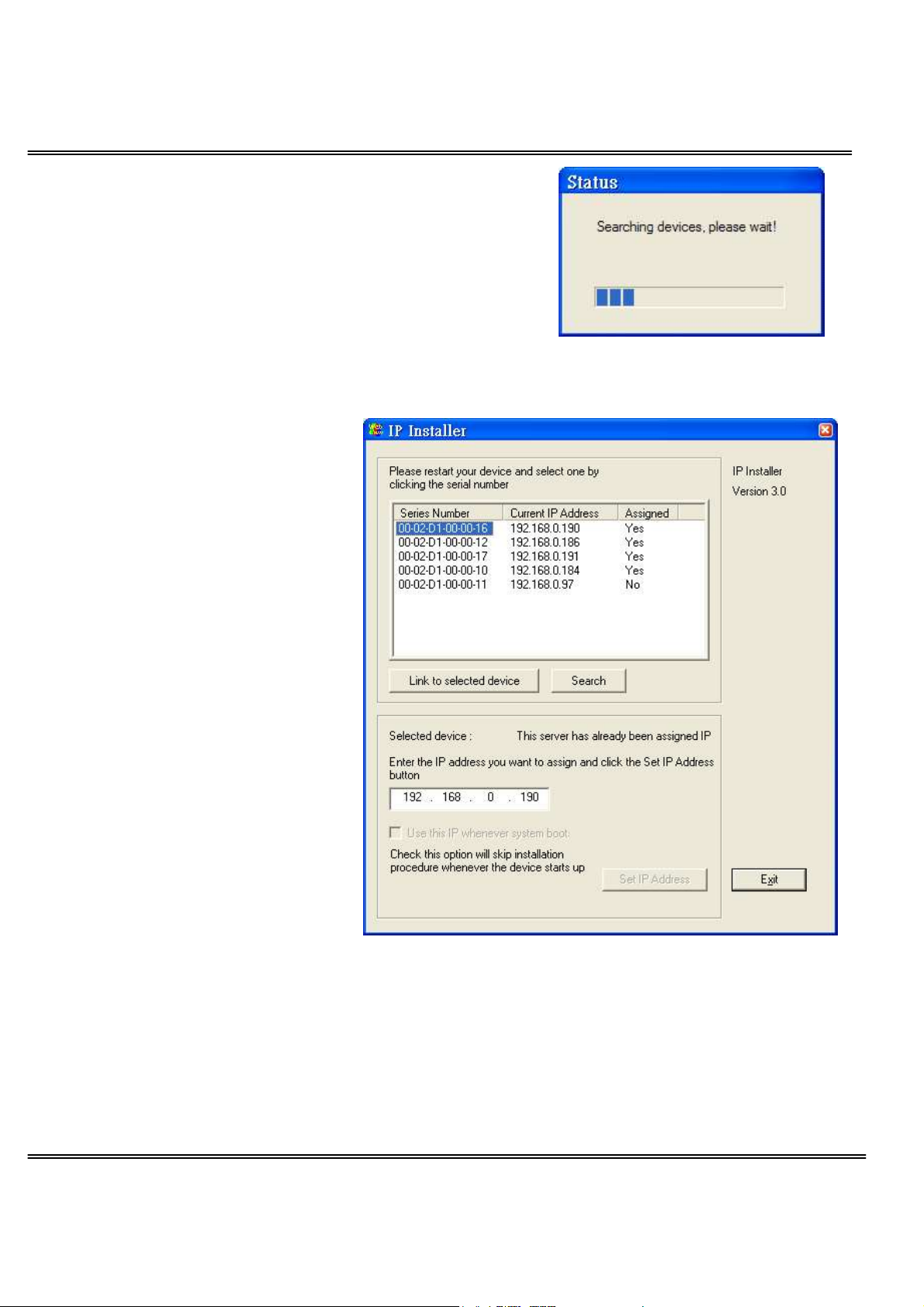
Upon IP installer’s start up, a searching box will pop
up. This program searches for the Network
Cameras on the same LAN:
After searching the LAN, the main window of IP installer will pop up.
The IP addresses shown in
the "Current IP Address"
field reflect those on the
local network. They may
be from the DHCP server.
If there is no DHCP server,
the camera will try to find a
free IP address (this takes
from 15 second to 3
minutes, depending on the
LAN status). The method of
finding IP address is
seeking from 192.168.0.99,
to 192.168.0.254. If any of
the address inside this
range is free, the Network
Camera will be assigned to
this IP, and its subnet mask
would be 255.255.255.0. If
none of the addresses is free, the Network Camera will try the range from 192.168.0.2
to 192.168.0.98. After an IP address is assigned to the camera, the “Activity” status
LED blinks.
- 9 -
Page 10
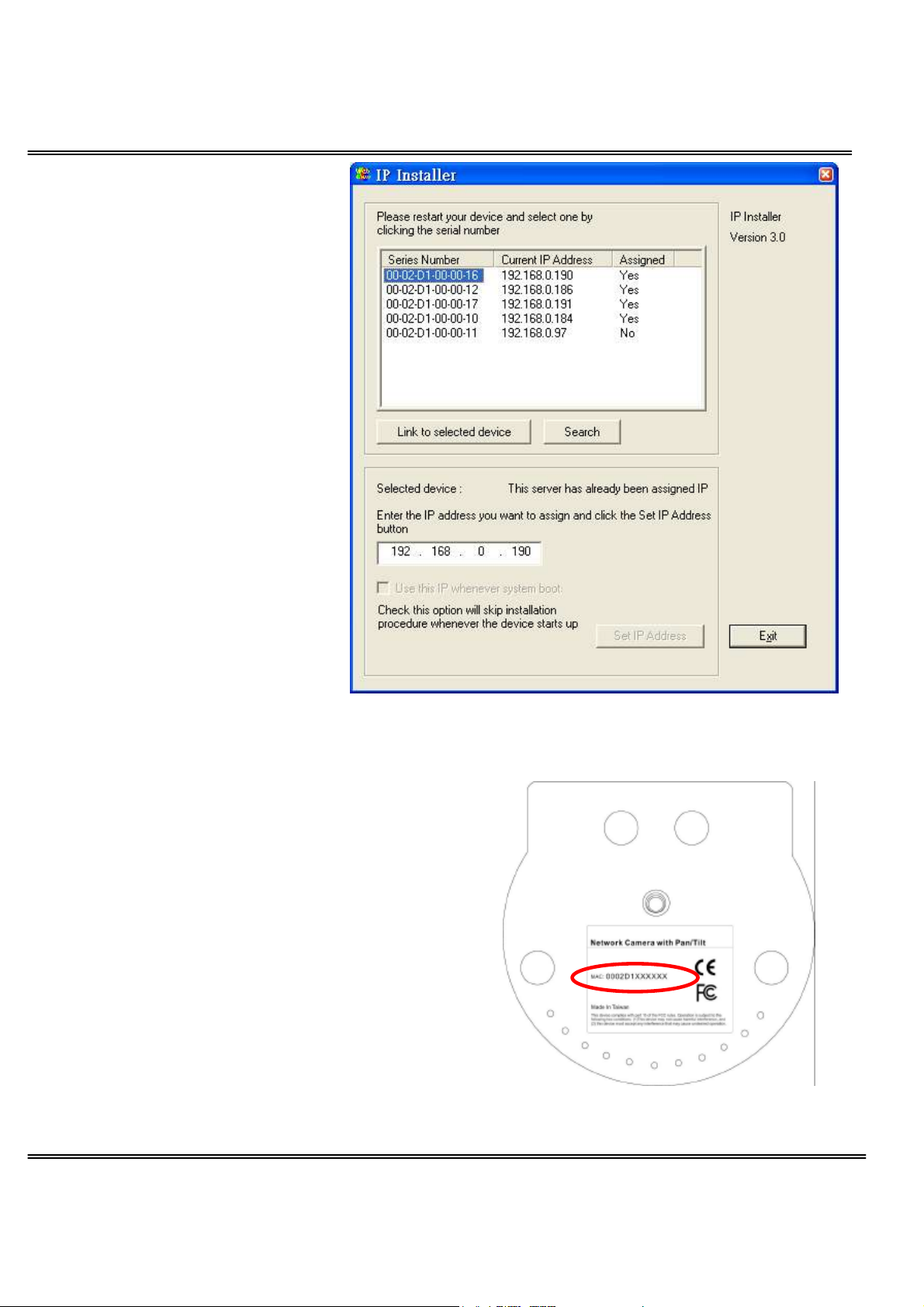
The UPnP function will
always assign an IP
address for the Network
Camera.
The Administrator can
click on button “Link to
selected device” to
connect the I.E. to the
camera.
If the camera is not on
the IP installer list, click
on the “Search” button to
search for the camera on
the LAN.
For the series number in the “Serial
Number” field, please check the label on the
bottom of the camera.
- 10 -
Page 11

Initial Access to the Network Camera
Check Network Settings
The Network Camera can be connected either before or immediately after software
installation onto the Local Area Network. The Administrator should complete the
network settings on the configuration page, including the correct subnet mask and IP
address of gateway and DNS. Ask your network administrator or Internet service
provider for the detail information. By default the Network Camera requires the
Administrator to run installation every time it reboots. If the network settings are to
remain unchanged, disable the Install option. Refer to “Network settings” on the
System Configuration page for details. If any setting is entered incorrectly and cannot
proceed to setting up the Network Camera, restore the factory settings following the
steps in the “Troubleshooting” chapter of the Appendix.
Add Password to Prevent Unauthorized Access
The default Administrator’s password is blank and the Network Camera initially will not
ask for any password. The Administrator should immediately implement a new
password as a matter of prudent security practice. Once the Administrator’s password
is saved, the Network Camera will ask for the user’s name and password before each
access. The Administrator can set up a maximum of twenty (20) user accounts. Each
user can access the Network Camera except to perform system configuration. Some
critical functions are exclusive for the Administrator, such as system configuration,
user administration, and software upgrades. The user name for the Administrator is
permanently assigned as “root”. Once the password is changed, the browser will
display an authentication window to ask for the new password. Once set, there is
no provision to recover the Administrator’s password. The only option is to
restore to the original factory default settings.
- 11 -
Page 12

How to Use
Authentication
After opening the Web browser and typing in the URL of the Network Camera, a
dialogue window pops up to request a username and password. Upon successful
authentication, the following figure is displayed.
The foreground is the login window and the background shows the message if
authentication fails. The user may check the option box to save the password for future
convenience. This option is not available to the Administrator for obvious reason.
- 12 -
Page 13

Installing Plug-in
For the initial access to the Network Camera in Windows, the web browser may prompt
for permission to install a new plug-in that is the Network Camera. Permission request
depends on the Internet security settings of the user’s PC or notebook. If the highest
security level is set, the computer may prohibit any installation and execution attempt.
This plug-in has been registered for certificate and is used to display the video in the
browser. Users may click on to proceed. If the web browser does not allow the
user to continue to install, check the Internet security option and lower the security
levels or contact your IT or networking supervisor for help.
- 13 -
Page 14
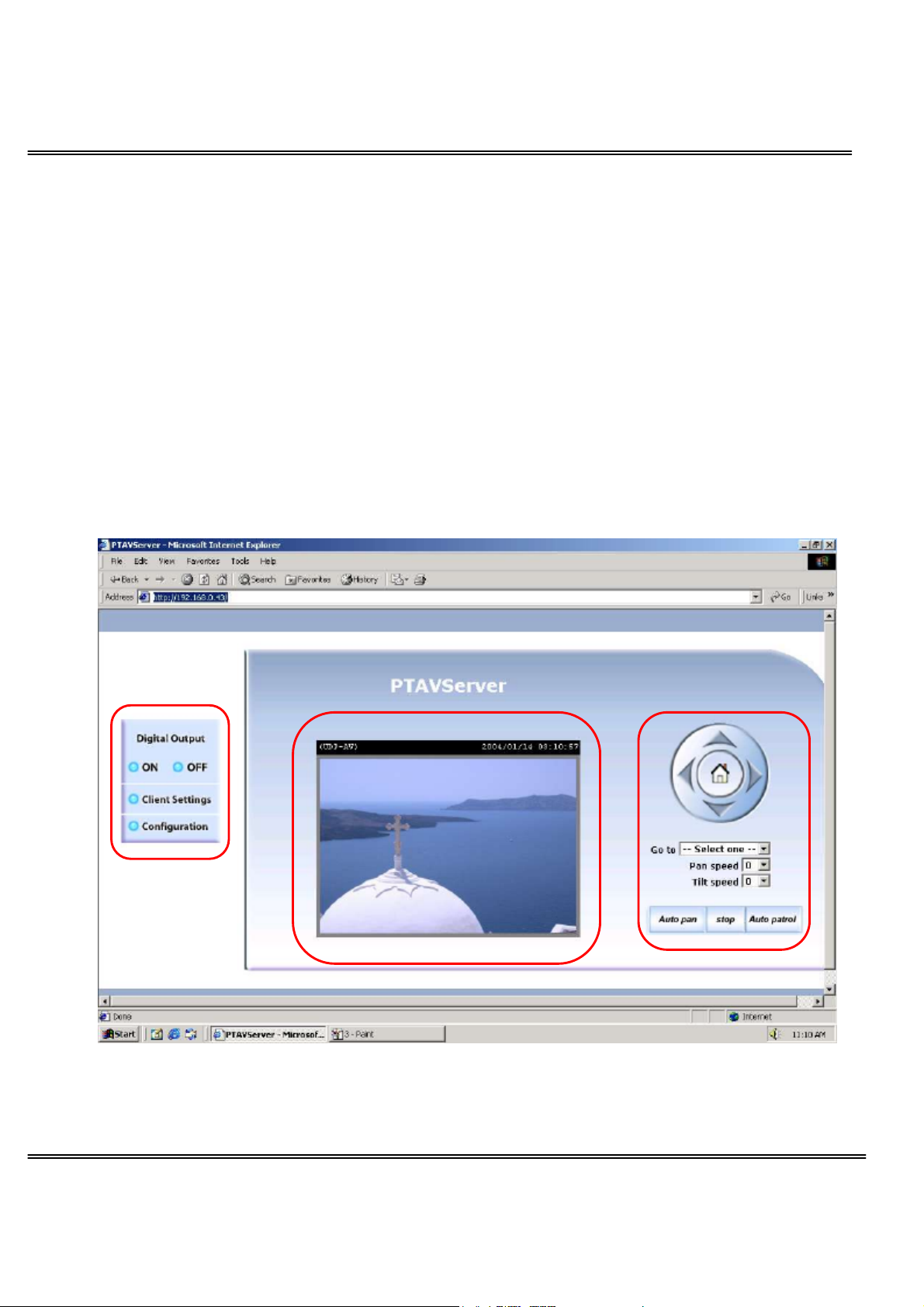
Primary User’s Capabilities
Main Screen with Camera View
The main page layout has three parts:
Configuration functions: The camera can be configured using these user interfaces.
Camera View: What the camera sees.
Pan/Tilt control buttons: These buttons provide a command interface to control the
aim of the camera.
Click on the configuration link to the left of the image window to enter the configuration
page.
The Configuration:
“Digital Output”
Clicking on the “On” or “Off” button turns the digital output to either on or off status.
- 14 -
Page 15

“Client Settings”
Clicking on this button links you to the client setting pages, please check the following
session for more details.
“Configuration” Only the Administrator can access camera configurations.
The Camera View:
The information bar at the top of the camera view shows the connection type to the
Network Camera and the current date/time.
The camera view provides not only the live video, but also a way to aim the Network
Camera to different target. Using mouse to click on the target inside the video will
command the Network Camera to aim at the target.
The Pan/Tilt Control Buttons:
The direction buttons are for Left, Right, Up, Down, and Home functions. The Home
button centers the camera.
“Go to” Once the Administrator has determined the preset positions; the User can aim
the camera using this control.
“Pan speed”
This button sets the moving range of the “Left” and “Right” commands.
“Tilt speed”
This button sets the moving range of the “Up” and “Down” commands.
“Auto pan”
This button commands the camera to pan from the current position to the left-most
and then to the right-most position. After panning, the camera returns to the original
position.
“Auto patrol”
This button commands the camera to patrol between the preset positions on the Patrol
List, which can be modified on the “Camera control page”. After one patrol cycle, the
camera returns to the original position.
“Stop” This stops the “Auto Pan” command or “Auto Patrol” command.
- 15 -
Page 16

Client Settings
At the initial access to the “Connection type” page in Windows, the web browser will
ask for a new plug-in installation, the plug-in being the Network Camera. This plug-in
has been registered for certification and can be used to change the parameters at the
client’s site. The user may click on to install the plug-in. If the web browser
does not allow the user to complete the installation, check the Internet security to
lower the security level or contact your IT or networking supervisor.
There are two settings for the Client site. One is “Media Option” for the User to
determine if audio should be muted. The other is “Protocol Option” which allows
choices on connection protocol between client and server. There are three protocol
choices to optimize your usage - UDP, TCP and HTTP.
The UDP protocol allows for more real-time audio and video streams. However, some
packets may be lost due to network burst traffic and images may be obscured.
- 16 -
Page 17

The TCP protocol allows for less packet loss and produce a more accurate video display.
The downside with this protocol is that the real-time effect is worse than that with the
UDP protocol.
The HTTP protocol must be selected if the network is protected by a firewall and it only
allows HTTP Port (80) to be opened. In this mode, audio will not be sent and only video
is operational. If no special need is required, UDP protocol is recommended.
Generally speaking, the client’s choice will be in the order of UDP → TCP → HTTP.
After the Network Camera is connected successfully, “Protocol Option” will indicate the
selected protocol. The selected protocol will be recorded in the user's PC and will be
used for the next connection. If the network environment is changed, or the user wants
to let the web browser to detect again, manually select the UDP protocol, save, and
return HOME to re-connect.
<url> http://<Network Camera>/protocol.html
<Network Camera> is the domain name or the original IP address of the Network
Camera.
- 17 -
Page 18

Administrator’s Capabilities
Fine-Tuning for Best Performance
There are a few choices the Administrator is allowed to maximize the capabilities of the
Network Camera. Best performance generally equates to the fastest image refresh
rate with the best video quality, and at the lowest network bandwidth as possible. The
three factors, “Maximum frame rate”, “Fix bit rate”, and “Fix quality” on the Video
Configuration page, are correlative to allow for achieving the best performance
possible.
For Best Real-time Video Images
To achieve good real-time visual effect, the network bandwidth should be large enough
to allow a transmission rate of greater than 20 image frames per second. If the
broadband network is over 1 Mbps, set the “Fix bit rate” to 1000Kbps or 1200Kbps, and
set “Fix quality” at the highest quality. The maximum frame rate is 25 fps in a 50Hz
system and 30 fps in a 60Hz system. If your network bandwidth is more than 384Kbps,
you can fix the bit rate according to your bandwidth and set the maximum frame rate
- 18 -
Page 19

to 25 fps or 30 fps. If you are shooting fast-moving images, you may want to slow the
maximum frame rate down to 20 fps in order to lower the rate of data transmission.
This allows for better video quality and the human eyes cannot readily detect the
differences between those of 20, 25, or 30 frames per second. If your network
bandwidth is below 384 Kbps, set the “Fix bit rate” according to your bandwidth and try
to get the best performance by fine-tuning with the “Maximum frame rate”. In a slow
network, greater frame rate results in blur images. Another work-around is to choose
“Half” in the “Size” option for better images, or “Halfx2” for a larger image view. Video
quality performance will vary somewhat due to the number of users viewing on the
network; even when the parameters have initially been finely tuned. Performance will
also suffer due to poor connectivity because of the network’s burst constraint.
Only Quality Images Will Do
To have the best video quality, you should set “Fix quality” at “Detailed” or “Excellent”
and adjust the “Maximum frame rate” to match your network’s bandwidth. If your
network is slow and you receive “broken” pictures, go to the TCP protocol in
“Connection type” and choose a more appropriate mode of transmission. The images
may suffer a time delay due to a slower connection. The delay will also increase with
added number of users.
Somewhere Between Real-time and Clear Images
If you have a broadband network, set “Fix quality” at ”Normal” or better, rather than
setting “Fix bit rate”. You can also fix the bandwidth according to your actual network
speed and adjust the frame rate. Start from 30 fps down for best results but not
below 15 fps. If the image qualities are not improved, select a lower bandwidth
setting.
- 19 -
Page 20

2 3 4
Opening Accounts for New Users
Protect Network Camera by passwords
1
Network Camera is shipped without any password by default. That means everyone
can access Network Camera including the configuration as long as the IP address is
known. It is necessary to assign a password if Network Camera is intended to be
accessed by others. Type a new word twice in ○
1
to enable protection. This password
is used to identify the administrator. Then add an account with user name and
password for your friends in ○
2
. Network Camera can provide twenty accounts for your
valuable customers or friends. Each account identifies the access right rather than the
real visitor. That allows multiple visitors share the same account of different level. An
option to access DI/DO is provided for each account. Some users may need to prohibit
- 20 -
Page 21

from controlling your attached devices. Another option allows different control to
pan/tilt functions of the Network Camera. You may delete some users from ○
3
.
More flexible options for viewers ○
The first option allows anyone uses “demo” as the user name to view without password.
The Administrator can also decide if more viewers are allowed to watch the video if the
viewers exceed the limit. The overloaded viewers will have snapshot mode instead.
4
Building a Multimedia Web Attraction Site
Demo on multiple sites – mid-scale service
The Network Camera can allow ten visitors to view on-line simultaneously. After
Installation, focus the Network Camera on any object you wish to share, and tell the
visitors to type in the web browser address. Caution: You may want to maintain your
visitor’s list in the security configuration page to block out unexpected visitors.
Product demo for e-business – Large-scale Service
If the number of visitors has exceeded the limit, the Network Camera can allow the
"overload" viewers to see the snapshots in JPEG mode, on the homepage. These are
still images and will be refreshed periodically and automatically. It needs a script
function supported by the web browser.
1. Click on “Configuration” on the homepage,
2. Click on “Security” in the left column,
3. Go to the bottom of the page and check off on “Allow more viewers with snapshot
mode”,
4. Set the snapshot interval to refresh the still image automatically. The longer the
snapshot interval, the better the snapshot mode works for multiple viewers.
- 21 -
Page 22

If you want to expand to allow in more viewers, the host server should be able to
handle large network traffic, which must handle the picture refreshing from the
Network Camera.
If the web server space has FTP service
Set the Network Camera up as an FTP client to upload the pictures. The access to the
Network Camera will be independent of the number of viewers and the picture quality
will remain constant.
1. Click on “Configuration” on the homepage,
2. Click on “Network” in the left column,
3. Fill in the FTP related settings including server, user name and password, as well as
the upload path if it is specified by the web space,
4. Click on ”Save” and wait for the system to restart,
5. Click on “Application” in the left column,
6. Select the day or days of the week in “Weekly schedule” you want to upload the
pictures,
7. Select “Sequential operation” and set the interval,
- 22 -
Page 23

8. Unselect "FTP put snapshots with date and time suffix" as the upload method and
click on "Save",
9. The image file uploaded to the web space is named “video.jpg”. Check if the file is
successfully uploaded to the correct folder,
10. Prepare a homepage with the embedded image reference to the image file
uploaded via FTP in advance.
If the web space has no FTP service
An auto-refresh homepage can be used to periodically poll the newest image from the
Network Camera. It is most efficient if using a free web space provider as the FTP
service may be limiting.
1. Prepare an auto-refresh homepage as the following example. The URL of image is
http://“IP address of the Network Camera”/cgi-bin/video.jpg. Modify the IP address
according to your Network Camera. Define the refresh interval according to your
network bandwidth for best result. If the refresh rate is too fast and there is a large
number of visitors, this may overload the Network Camera and slows the response.
- 23 -
Page 24

Building a Security Application
The Administrator can
combine options on the
application page to perform
many useful security
applications. There are two
trigger sources coming from
attached devices, such as for
motion detection. There are
also two kinds of actions
responding to such events,
including uploading
snapshots over the Internet
and driving other attached
devices. To upload the
snapshots, the User can
choose either email or FTP
according to user’s needs. Both e-mail and FTP use the network settings on the
network page. Refer to the definition section for detail configuration.
1. Click on “Configuration” on
homepage,
2. Click on “Application” in the left
column,
3. Check the weekdays as you
need and give the period of
"Snapshots begin" time and
"Snapshots end" time to monitor
the triggering conditions every
day,
4. Check the “Event operation”. The triggering condition can be set to detected motion
or status of the attached device,
- 24 -
Page 25

5. Set the delay before detecting next event to avoid continuous false alarms following
the original event,
6. Set the delay to take snapshots after event to capture the direction of the moving
objects,
Send snapshots when motion is detected
If no external sensor is available, the Administrator can use the built-in motion
detection to monitor any movement and sends snapshots via email for security check.
Enable
7. Click on “Motion detection” in the left column,
8. Check “Enable motion detection”,
9. Click on “New” to have a new window to monitor video,
10. Type in a name to identify the new window,
11. Use the mouse to click, hold, and drag the window corner to resize or the title bar
to move,
12. Fine-tune using the “Sensitivity” and “Percentage” fields to best suit the camera’s
environment. Higher ”Sensitivity” detects the slighter motion. Higher “Percentage”
discriminates smaller objects,
- 25 -
Page 26

13. Clicking on “Save” enables the activity display. Green means the motion in the
window is under the watermark set by the Administrator and red means it is over the
watermark,
14. Click on “Application” in the left column,
15. Check on the window name set in Step 10,
16. Check “Upload snapshots while motion detected”, if e-mailing the snapshots is
preferred,
17. Check “Send snapshots by email”,
18. Click on “Save” to validate.
- 26 -
Page 27

the
the Network
Software Revision Upgrade
Customers can obtain the up-to-date software from the distributor. An easy-to-use
Upgrade Wizard is provided to upgrade the Network Camera with just a few clicks. The
upgrade function is opened to the Administrator only. To upgrade the system, follow
the procedures below.
1. Download the firmware file named “FLASH.BIN” from the appropriate product folder.
2. Run the Upgrade Wizard and proceed following the prompts. Refer to the
instructions of the Upgrade Wizard for details.
3. The whole process will finish in a few minutes and it will automatically restart the
system.
If power fails during the writing process of Flash memory, the program in
memory of the Network Camera may be destroyed permanently. If
Camera cannot restart properly, ask your dealer for technical service.
- 27 -
Page 28

Definitions in Configuration
Only the Administrator can access system configuration. Each category in the left
column will be explained in the following pages. The bold texts are the specific phrases
on the Option pages. The Administrator may type the URL below the figure to directly
enter the frame page of configuration. If the Administrator also wants to set certain
options through the URL, read the reference appendix for details.
<url> http://<Network Camera>/setup/config.html
<Network Camera> is the domain name or original IP address of the Network Camera.
- 28 -
Page 29

System Parameters
"Host name" The text displays the title at the top of the main page.
“Turn off the LED indicator” Check this option to shut off the LED beside the lens.
It can prevent the camera’s operation being noticed.
"Keep current date and time" Click on this to reserve the current date and time of
the Network Camera. An internal real-time clock maintains the date and time even
when the power of the system is turned off.
"Sync with computer time" Synchronizes the date and time of the Network Camera
with the local computer. The read-only date and time of the PC is displayed as updated.
“Manual” Adjust the date and time according to what is entered by the Administrator.
Notice the format in the related fields while doing the entry.
“Automatic” Synchronize with the NTP server over the Internet whenever the
Network Camera starts up. It will fail if the assigned time-server cannot be reached.
“NTP server” Assign the IP address or domain name of the time-server. Leaving the
text box blank connects the Network Camera to the default time-servers.
“Time zone” Adjust the time with that of the time-servers for local settings.
“Update interval” Select hourly, daily, weekly, or monthly update with the time on the
NTP server.
Remember to click on to immediately validate the changes. Otherwise, the
correct time will not be synchronized.
- 29 -
Page 30

User Group Administration
“Root password” Change the Administrator’s password by typing in the new
password identically in both text boxes. The typed entries will be displayed as asterisks
for security purposes. After pressing , the web browser will ask the Administrator
for the new password for access.
“Add user” Type the new user's name and password and press to insert the new
entry. The new user will be displayed in the user name list. There is a maximum of
twenty user accounts. Each user can have the privilege to "Permit for I/O control"
and "Permit for PT control". “Delete user” Pull down the user list to find the user’s
name and press to complete.
"Permit for I/O control" Allows user to control the DO and get status of the DI.
"Permit for PT control" Allows user to aim the Network Camera to different targets.
“Allow ‘demo’ account to view” Check this to permit anyone who types in “demo” as
user name. No password is needed for demo account. Note that a demo account is
restricted to view only.
“Allow more viewers with snapshot mode” There can only be a maximum of 10
users to simultaneously view the video. This option allows for the 11th viewer on, the
overloaded viewers, to see only still images. These still images are automatically
refreshed by the interval defined below. This feature must be supported by the java
script capability of the web browsers.
“Snapshot interval” defines the refresh rate of the still image in the homepage seen
by the overloaded viewers.
- 30 -
Page 31

Network Settings
Any changes made on this page will restart the system in order to validate the changes.
Make sure every field is entered correctly before clicking on .
"Reset IP address at next boot", the default status is checked to avoid erroneous
entries during installation. This can be tedious having to perform software installation
whenever the Network Camera starts. Therefore, once the network settings, especially
the IP address, have been entered correctly, uncheck this option. If this option is
disabled, the Network Camera will skip installation at the next boot. The Network
Camera can automatically restart and operate normally after a power outage. Users
can run IP installer to check the IP address assigned to the Network Camera if the IP
address is forgotten or using the UPnP function provided by the Network Camera (MS
Windows XP provides UPnP function at Network Neighbors).
General
“IP address” This is necessary for network identification.
“Subnet mask” This is used to determine if the destination is in the same subnet. The
default value is “255.255.255.0”.
“Default router” This is the gateway used to forward frames to destinations in a
different subnet. Invalid router setting will fail the transmission to destinations in
different subnet.
“Primary DNS” The primary domain name server that translates hostnames into IP
addresses.
“Secondary DNS” Secondary domain name server that backups the Primary DNS.
HTTP
“Http port” This can be other than the default Port 80. Once the port is changed, the
User must be notified the change for the connection to be successful. For instance,
when the Administrator changes the HTTP port of the Network Camera whose IP
address is 192.168.0.100 from 80 to 8080, the User must type in the web browser
“http://192.168.0.100:8080” instead of “http://192.168.0.100”.
- 31 -
Page 32

Streaming
“Control channel port” This can be something other than the default port 5001 in
order to work with the port opened by the firewall.
“Audio channel port” This can be something other than the default port 5002 in order
to work with the port opened by the firewall.
“Video channel port” This can be something other than the default port 5003 in order
to work with the port opened by the firewall.
“Improve audio quality in low bandwidth environment” If the Network Camera
seems to work in a low bandwidth network environment, the User can use this option
to see if audio quality can be improved by sacrificing some real-time synchronization.
WLAN Configuration
“SSID” (Service Set Identifier), it is a name that identifies a wireless network. Access
Points and wireless clients attempting to connect to a specific WLAN (Wireless Local
Area Network) must use the same SSID. The default setting is default. Note: The
maximum length of SSID is 32 single-byte characters and SSID can’t be any of “, <, >
and space character.
“Wireless mode” Clicking on the pull-down menu to select from the following
options:
“Infrastructure” Make the Network Camera connect to the WLAN via an Access Point.
(The default setting)
“Ad-Hoc” Make the Network Camera connect directly to a host equipped with a
wireless adapter in a peer-to-peer environment.
“Channel” While in infrastructure mode, the channel is selected automatically to
match the channel setting for the selected Access Point. In Ad-Hoc mode, the channel
must be manually set to the same channel for each wireless adapter. The default
channel setting depends on the installed region.
“TX rate” This field is for selecting the maximum transmission rate on the network.
The default setting is “auto”, that is the Network Camera will try to connect to the other
wireless device with highest transmitting rate.
- 32 -
Page 33

“Preamble”, either “Long preamble” or “Short preamble” defines the length of
the CRC block (Cyclic Redundancy Check is a common technique for detecting data
transmission errors) for communication between the Access Point and the roaming
wireless device. Long Preamble is the default setting. Note: High network traffic areas
should use the shorter preamble type.
“Data encryption” Checking the box to enable the data encryption. By default it is
disabled.
“Auth. Mode” Choosing one of the following modes, (Auto is the default setting)
l “Auto” – Will automatically decide the authentication mode of the wireless client.
l “Shared” – allows communication only with other devices with identical WEP
settings.
l “Open” – communicates the key across the network.
“Key length” The administrator can select the key length among 64, 128 or 256 bits.
64bits is the default setting.
“Key format” Hexadecimal or ASCII. “HEX” is the default setting.
l “HEX” digits consist of the numbers 0~9 and the letters A-F.
l “ASCII” is a code for representing English letters as numbers from 0-127 except
“, <, > and space characters that are reserved.
“Network Key” Entering a key in either hexadecimal or ASCII format. When selecting
different key length, acceptable input length is listed as following:
64 bits key length: 10 Hex digits or 5 characters.
128 bites key length: 26 Hex digits or 13 characters.
256 bits key length: 58 Hex digits or 29 characters.
Note: When 22(“), 3C(<) or 3E(>) are input in network key, the key format can’t be
changed to ASCII format.
- 33 -
Page 34

Mail & FTP
SMTP
“SMTP (mail) server 1” The domain name or IP address of the external email server.
“Recipient email address 1” The email address of the recipients for snapshots or log
file. Multiple recipients must be separated by semicolons, ‘;’.
“SMTP (mail) server 2” The domain name or IP address o f another email server once
the previous server is unreachable.
“Recipient email address 2” The email addresses of the recipients for the backup
server.
“Return email address” The return email address used in the event the mails fail to
be sent out.
FTP
“Local FTP server port” This can be other than the default Port 21. The user can
change this value from 1 to 65535. After the change, the external FTP client program
must change the server port of connection accordingly.
“1st FTP server” The domain name or the IP address of the external FTP server. The
following user settings must be correctly configured for remote access.
“1st FTP user name” Granted user name on the external FTP server.
“1st FTP password” Granted password on the external FTP server.
“1st FTP remote folder” Granted folder on the external FTP server. The string must
conform to that of the external FTP server. Some FTP servers cannot accept preceding
slash symbol before the path without virtual path mapping. Refer to the instructions for
the external FTP server for details. The folder privilege must be open for upload.
“Primary FTP passive mode” The Network Camera is located inside the network
protected by a firewall, data connection for FTP may be prohibited. By selecting
passive mode, the FTP can bypass the rule and allow snapshot upload to proceed. If
the passive mode is selected, the Network Camera can automatically attempt for
active mode, if the external FTP server does not support passive mode.
- 34 -
Page 35

to respond. Change the
network supervisor or experienced
lost contact, refer to Appendix A for reset
“2nd FTP server” The domain name or IP address of the backup external FTP server.
“2nd FTP user name” Granted user name on the backup FTP server.
“2nd FTP password” Granted password on the backup FTP server.
“2nd FTP remote folder” Granted folder on the backup FTP server.
“Secondary FTP passive mode” Passive mode setting for the backup FTP server.
address is 192.168.0.100 from 80 to 8080, the User must type in the web browser
“http://192.168.0.100:8080” instead of “http://192.168.0.100”.
Some invalid settings may cause the system failing
configuration only if necessary and consult with your
users for correct settings. Once the system has
and restore procedures.
- 35 -
Page 36

Video Codec Parameters
“Text on video” The text will be displayed in the black bar above the video window
with a timestamp. The timestamp is captured from the date and time of the Network
Camera that is maintained by a built-in real-time clock.
“Color” Select either for color or monochrome video display.
"Size" There are three options for two video sizes. “Half” is the quarter size of “Normal”.
“Half x 2” has the same video size as “Normal” but of a lesser quality, while consuming
less network bandwidth.
"Maximum frame rate" This limits the maximal refresh frame rate, which can be
combined with the "Video quality control" to optimize bandwidth utilization and
video quality. If the User wants to fix the bandwidth utilization regardless of the video
quality, choose "Fix bit rate" and select the desired bandwidth. The video quality may
be poor due to the sending of maximal frame rate within the limited bandwidth when
images are moving rapidly. Consequently, to ensure detailed video quality
(quantization rate) regardless of the network, it will utilize more bandwidth to send the
maximal frames when images change drastically.
"Flip" Vertically rotate the video.
"Mirror" Horizontally rotate the video. Check options both if the Network Camera is
installed upside down.
“White balance” Adjust the value for best color temperature.
Click on this button to pop up another window to tune "Brightness",
“Contrast”, “Hue” and "Saturation" for video compensation. Each field has eleven
levels ranging from -5 to +5. The User may press to fine-tune the image. When
the image is O.K., press to set the image settings. Click on this to recall
the original settings without incorporating the changes.
- 36 -
Page 37

- 37 -
Page 38

Motion Detection
“Enable motion detection” Check this option to turn on motion detection.
Click on this button to add a new window. At most three windows can exist
simultaneously. Use the mouse to click, hold, and drag the window frame to resize or
the title bar to move. Clicking on the ‘x’ at the upper right-hand corner of the window
to delete the window. Remember to save in order to validate the changes.
Click on this button to save the related window settings. A graphic bar will rise or
fall depending on the image variations. A green bar means the image variation is under
monitoring level and a red bar means the image variation is over monitoring level.
When the bar goes red, the detected window will also be outlined in red. Going back to
the homepage, the monitored window is hidden but the red frame shows when motion
is detected.
"Window Name" The text will show at the top of the window.
“Sensitivity” This sets the endurable difference between two sequential images.
“Percentage” This sets the space ratio of moving objects in the monitoring window.
Higher sensitivity and small percentage will allow easier motion detection.
The following figure shows the screen when is clicked.
- 38 -
Page 39

Application Setup
Weekly Schedule
“Sun” ~ “Sat” Select the days of the week to perform the following operations.
“Snapshots begin at” Set the time to start operations. “Snapshots stop at” Set the
time to stop operations.
Setting identical begin time and stop time means 24-hour operation.
Event Operation
“Delay second(s) before detecting next event” Set the time delay before
restarting to check on the triggering condition when the current condition is triggered.
“Take snapshots at second(s) after event” After the camera has taken a snapshot
when a condition is triggered, another snapshot will be taken after this configured
interval, in seconds.
“Trigger condition” There are four conditions relative to the digital input and the
three windows for motion detection. More than one condition can be selected at once.
Select the appropriate digital input condition that suits the characteristics of the
external device. “high”, “low” selects level-triggering via external voltage input.
“rising”, “falling” is for edge-triggering. There are three windows for motion detection
each can be assigned a name. If motion detection has not been set up, “undefined”
will be shown instead of the window title. If this happens, clicking on “Motion
detection” and a note will show to direct the User to the configuration page for motion
detection.
“Trigger action” There are four options for two types of action. More than one
condition can be selected at once. While choosing to trigger an output alarm, the digital
output will short both pins and complete the external device’s circuit. The normal
state is open. Either email or FTP can be used to command uploading snapshots. The
snapshot names will be “vpre.jpg”, “vtrg.jpg”, and “vpos.jpg”, respectively. They
stand for the snapshots, before event, right upon event, and after event. The date and
- 39 -
Page 40

time suffix may also be added as an option. Confirm the external mail or FTP server
settings in the network configuration.
“Reset output” Select and save this option to reset the external device at the digital
output to return to the original state.
Sequential Operation
“Snapshot every second(s)” The Network Camera will send snapshots at the
specified intervals to the external server using the method selected below. Remember:
This operation is still subject to the conditions set in the weekly schedule.
“Send snapshots by email” This selects the uploading method following the intervals
set above. The snapshot named “video.jpg” will be attached in the email with the
subject title “Periodic snapshots”.
“Send snapshots by FTP” The snapshots will be uploaded to the external FTP server
with the file name defined in the next option. This can also be used to refresh the
captured images stored in the external web server to build creative homepages.
“FTP put snapshots with date and time suffix” This option sets up the snapshot
capture date and time, which can be used to easily differentiate the snapshot file
names in either the sequential or event operation. For instance,
“video@20030102030405.jpg” means the JPEG image was captured in the year 2003,
January the 2nd, at 3 o’clock, 4 minute, and 5 second. If this suffix is omitted, the file
named “video.jpg” on the external FTP server will be refreshed at the specified
interval.
- 40 -
Page 41

Preset function
Camera Control
Camera
control
area
On the Camera Control page, there are two main function control areas:
Camera Control Area
The pan and tilt functions can be controlled with these buttons. The “Left” button aims
the camera to the left; the “Right”, “Up”, and “Down” buttons aim the camera
accordingly. The “Home” button aims the camera to the center.
“Pan speed” This controls the range of the horizontal movement of the camera. The
greater the value, the greater angular movement when performing the “Left” or
“Right” functions.
“Tilt speed” This controls the range of the vertical movement of the camera. The
greater the value, the greater angular movement when performing the “Up” or “Down”
functions would be.
“Auto pan/patrol speed” This defines the speed of panning and patrol, the greater
the value, the faster the speed.
- 41 -
Page 42

Preset Function Area
”Enable IR control” Checking this box allows the Administrator to enable the IR
controller to move the aim of the camera. To allow controls only through URL
commands or web pages, leave this box unchecked.
”Current position”, If the User wants to save the current view as a preset location,
enter a name for each of the current video view at “current position” and click on the
“Add” button. The camera allows for 20 preset locations.
”Preset position” This keeps a list for preset positions. Clicking on the “Delete”
button will remove the current selected position from the preset list.
”Dwelling time” The value set here specifies:
1. The stop time of each preset location during auto patrol of the Network Camera.
2. The stay time at the most left and the most right positions when the Network
Camera is doing auto panning.
”Patrol selection”, After the User has saved a list of preset positions, the “Preset
locations” box will also keep a list of the preset positions. And once the “Select>”
button is clicked, the “Selected location” box will keep a list of the patrol stops. The
“Remove” button removes the preset position from the patrol stops. The “UP”, “DOWN”
buttons adjust the order of the patrol stops. Several preset positions can be added to
the patrol stops. The camera can accept up to 40 patrol stops.
“Save” button
The button is valid for “Pan speed”, “Tilt speed”, “Auto pan/patrol speed”, “Enable IR
control”, “Dwelling time” and “Patrol selections”. In other words, after changing these
settings, and the “Save” button is not clicked, the new setting of the camera will not
take effect.
- 42 -
Page 43

UPnP and DDNS Settings
“Enable DDNS” This option turns on the DDNS function.
“Provider” The provider list contains four hosts that provide DDNS services. Please
connect to the service provider’s website to make sure the service charges.
“Host name” If the User wants to use DDNS service, this field must be filled. Please
input the hostname that is registered in the DDNS server.
“Username/E-mail” The Username or E-mail field is necessary for logging in the
DDNS server or notify the User of the new IP address. Note: when this field is input as
“Username” the following field must be input as “Password”.
“Password/Key” Please input the password or key to get the DDNS service.
“Enable UPnP” This turns on or off the UPnP function. When UPnP is turned off, the
camera cannot be found through network neighbors in MS Windows XP. If the UPnP
network component is installed in Windows XP, the hostname of the Network Camera
will be shown with bracketed IP address in the Network neighbors. Ex: Network
Camera with Pan/Tilt (96). That is: The hostname of the Network Camera is “Network
Camera with Pan/Tilt”, and the IP address of the Network Camera is xxx.xxx.xxx.96,
depends on the last value of the IP address assigned to the Network Camera.
“Save” Click on this button to save current settings for the DDNS service and UPnP
function.
- 43 -
Page 44

Direction control
Auto movement
Remote Controller
The Network Camera with Pan/Tilt provides a remote controller to command the
camera’s pan/tilt and other functions. The direction control part provides the function
as on the main web page.
The Pan/Patrol/Stop functions are also the same as on the main web page.
area
control area
“Auto Patrol” This button commands the camera to patrol between the preset
positions on the patrol list that was set on the “Camera control page”. After each patrol
cycle, the camera stops at the original staring position. “Auto Pan” This button
commands the camera to pan from the current position to the left most or right most
and back. After panning both horizontal end positions, the camera would stop at the
original starting position.
“Center” This calibrates the camera’s position to aim at the center as the camera boots
up.
“Stop” This stops the auto movements (auto pan & auto patrol) of the camera.
- 44 -
Page 45

Viewing System Log
Click on the link on the configuration page to view the system log file. The content of
this file provides useful information about configuration and connections after system
boot-up.
Viewing System Parameters
Click on this link on the configuration page to view the entire system’s parameter set.
The content is the same as those in CONFIG.INI.
Factory Default
“Factory default”
Click on this link on the configuration page to restore factory default settings. Any
changes made so far will be lost and the system will be reset to the initial factory
settings. After clicking on the “Restore” button and make confirmation, the system
will restart and require the installer program to set up the network again.
“Calibrate”
Recalibrate the home position to the default center to recover the tolerance cased by
some external forces. This function is the same as the “Center” button on the Remote
Controller. Please note that there is no confirming message box after clicking on the
“Calibrate” button, the Network Camera will calibrate immediately.
- 45 -
Page 46

Restoring the factory defaults
will erase any previous settings.
Reset or restore the system after
Appendix
A. Troubleshooting
Status LED
After powering up, the Network Camera performs a self-diagnostic to detect any
hardware defects. The following table lists the LED patterns in general. In case of any
fatal error, the LED will blink in a pattern other than those below.
Condition LED color
During self-diagnostic after power on Blink in interchanged green and red
Ethernet signal is lost Red LED is blinking till Ethernet is detected
Before network is setup Steady green till IP address is confirmed
After network is setup Blink green every second
Any hardware failure Other patterns
Reset and Restore
At the left side of the camera there is a button
hidden in the pinhole as shown in the picture. It is
used to reset the system or restore the factory
default settings. Sometimes resetting the system
sets the system back to normal state. If the system
problems remain after reset, restore the factory
settings and install again.
RESET: Poke the wrench to click on the button.
RESTORE:
power on.
1. Poke the wrench to press on the button
continuously.
2. Wait for self-diagnostic to run twice.
3. Withdraw the wrench as soon as the second
self-diagnostic starts.
- 46 -
Page 47

B. Frequently Asked Questions
Q What if I forget my password?
A After the Administrator's password has been assigned, every access to the Network
Camera needs authentication. If you are one of the managed users, you have to ask
the Administrator for the password. If you are the Administrator, there is no way to
recover the root password except by restoring the factory default settings. Refer to
Appendix A for the procedures.
Q Why can I not watch video from the Network Camera after it is authenticated?
A There are many possible scenarios regarding this problem,
1. If you have just installed the Network Camera and are unable to watch the video,
check if the heartbeat LED is blinking or the lens cap is off. If the heartbeat LED is dim,
perform the software installation again.
2. If the Network Camera is well installed and you are accessing the Network Camera
for the first time using Internet Explorer, adjust the security level of Internet Explorer
to allow installation of plug-ins.
3. If the problem still exists after adjusting, and the message over the image window
is showing "connecting", the network traffic may be too crowded.
Q What is the plug-in for?
A The plug-in provided by the Network Camera is used to display motion pictures and
audio in Internet Explorer. If your system does not allow installation of any plug-in
software, the security level of the web browser may need to be lowered. It is
recommended that you consult your network supervisors in your office regarding
adjustment of the security level. Software installation may be regulated in some
offices.
Q Why is the timestamp different from the system time of my PC or notebook?
A The timestamp is based on the system time of the Network Camera. It is maintained
by a real-time clock inside and can be automatically synchronized with the time-server
if the Network Camera is connected to the Internet and the function is enabled.
Differences of several hours may result from the time zone setting.
- 46 -
Page 48

Q Can I install it on ceiling?
A Yes. There are flip and mirror options in the video configuration page to correct the
images for upside down installation.
Q The image is not clear enough.
A Rotate the lens to adjust the focus after the Network Camera has been installed in
the proper position. The image settings and white balance can be fine tuned to achieve
the best visual effect. Also notice the power line frequency must match the local utility
to synchronize and minimize the effect of flickering florescent lights.
Q Why does the image not refresh regularly?
A Some anti-virus programs filter the received web content. It takes time to perform
data examination and affect the streaming application such as that of the Network
Camera. However, it only affects the HTTP mode of the Network Camera. If the
network allows only HTTP mode, disable the web filtering function of the anti-virus
program temporarily. During this period, the User should be aware of the risk of
malicious network activity.
Q I have opened motion detection windows but it cannot work.
A If the motion detection windows are set up and names are given, check to see if the
function is checked on the first line. While it is enabled, adjust the sensitivity and
percentage to monitor the level indicator for best results.
Q I cannot hear any sound while watching.
A If there is "V_ONLY" shown above the image, click on connection type to uncheck
"Disable audio". If there is "V" shown instead of "AV", the sound card in your PC may
not have been properly installed. If "AV" is shown, check the audio source of the
Network Camera, make sure you are using internal or external microphone.
Q How many users are allowed to watch the Network Camera at the same time?
A Too many users requesting the real-time multimedia content will jam the network.
For best results, the Network Camera is designed to accommodate a maximum of ten
(10) users to watch and listen at the same time. For a larger number of users, it is
recommended to build another web server to host the retrieved contents from the
Network Camera.
- 47 -
Page 49

Q How fast is the video rate of the Network Camera?
A The MPEG4 codec engine can process up to 30 frames per second internally. However,
the total performance is subject to many coefficients such as:
1. Network throughput,
2. Bandwidth share,
3. Number of users,
4. The complicated/detailed objects and movement in view,
5. The power of your PC or notebook computer that is responsible for displaying
images.
In general, the transfer rate in a general local network environment can achieve over
200 kilobytes per second and approximately 10 to 20 pictures per second from a
regular environment.
Q How can I keep the Network Camera as private as possible?
A The Network Camera is designed for surveillance purposes and has many flexible
interfaces. The user authentication and special confirmation in installation can keep
the Network Camera from unauthorized access. You may also change the HTTP port to
a non-public number. The demo account is good to separate guests from normal users
and thus you can easily block the guests anytime. You can check the system log to
examine any abnormal activities and trace the origins.
Q Why can I not access the Network Camera when I set up some options in the
application?
A Since the Network Camera is a "network camera", any incorrect network settings will
make it inaccessible. If this happens, restore the factory default settings following the
procedures in Appendix A.
- 48 -
Page 50

C. URL Commands of the Network Camera
For some customers who already have their own web site or web control application,
the Network Camera can be easily integrated through convenient URLs. This section
lists the commands in URL format corresponding to the basic functions of the Network
Camera.
Capture Update Snapshot of JPEG Image
/cgi-bin/video.jpg
The Network Camera will return the most up-to-date snapshot in JPEG format.
Query Status of the Digital Input
/cgi-bin/getdi.cgi
The Network Camera will return the status of digital input.
Drive the Digital Output
/cgi-bin/setdo.cgi?do=<state>
The state is either “h” or “l”. “h” means high, that is NC is connected with COMMON and
“l” means “low” that is NO is connected with COMMON.
For instance, typing http://192.168.0.201/cgi-bin/setdo.cgi?do=h in the address bar
of the web browser will command the Network Camera, with IP address of
192.168.0.201, to set digital output to connect to NC with COMMON.
Restore Factory Default Settings
/setup/restore.cgi
The Network Camera will automatically restart after restoring factory default
configurations.
- 49 -
Page 51

Restart System
/setup/reset.cgi
Restart the Network Camera without warning.
- 50 -
Page 52

Page URL
The configuration page has a frame layout including an option list frame and an option
page frame. Referenced URLs, except for the configuration page, direct users to the
option page frame only. Some pages, such as image quality setting and preset setting,
are opened in new windows for preview.
Only the Administrator can access these URLs.
Homepage name Referenced URL
Client settings page /client.html
configuration page /setup/config.html
system option /setup/system.html
security option /setup/security.html
network option /setup/network.html
DDNS & UPnP option /setup/ddns.html
audio/video option /setup/video.html
camera control option /setup/ptframe.html
motion detection /setup/motion.html
image quality option /setup/image.html
application option /setup/app.html
system log /setup/logfile.html
system parameters /setup/parafile.html
set factory default /setup/factory.html
System Resource URL
There are some images used on the homepage when the homepage layout is in image
mode. The Administrator may use the following links to show the images saved in the
Network Camera on another page.
Resource name Referenced URL
system logo image /pic/logo.gif
background image /pic/wallppr.jpg
- 51 -
Page 53

<text string shorter than 15
year, month and date separated by
hour, minute and second separated
General Format of Command URL
Every configuration can be set through URL with the POST method by the
Administrator only.
<general format>
URL[?[name=value][&name=value]……]
<method>
POST
<authorized user>
root
System Configuration URL
URL: /setup/system.cgi
NAME VALUE DESCRIPTION
host
characters>
yes turn off front LED ledoff
no turn off front LED
method
keep keep date and time unchanged
auto use NTP server to synchronize
manu directly adjust date and time
date <yyyy/mm/dd>
time <hh:mm:ss>
ntp <domain name or IP address> NTP server
system name
slash
by colon
zone -12 ~ 12 time zone, 8 means GMT +8:00
updateInterval
one hour Synchronize with NTP hourly
one day Synchronize with NTP daily
one week Synchronize with NTP weekly
One month Synchronize with NTP monthly
- 52 -
Page 54

horter than 15
<text string shorter than 15
<text string shorter than 15
<text string shorter than 15
<text string shorter than 40
Security Configuration URL
URL: /setup/security.cgi
NAME VALUE DESCRIPTION
rootpass <text string s
characters>
username
characters>
userpass
characters>
deluser
characters>
action <blank> validate demo users with “open”
yes grant for demo account open
no prohibit for demo account
yes permission for DIDO access dido
no prohibit for DIDO access
change root password
add new user
new user's password
existing user name
Network Configuration URL
URL: /setup/network.cgi
NAME VALUE DESCRIPTION
yes enable installation at next boot reset
no disable installation at next boot
ip <IP address> The Network Camera's IP address
subnet <IP address> subnet mask
router <IP address> default gateway
domain
characters>
dns1 <IP address> primary DNS server
- 53 -
domain name of the Network Camera
Page 55

<string shorter than 80
<text string shorter than 80
<text string shorter than 80
<text string shorter than 15
<text string shorter than 15
<text string shorter than 40
<text string shorter than 15
<text string shorter than 15
ring shorter than 40
upload folder in secondary FTP
dns2 <IP address> secondary DNS server
smtp1 <domain name or IP address> primary SMTP server
mailto1
mail recipient address
characters>
smtp2 <domain name or IP address> secondary SMTP server
mailto2
mail recipient address
characters>
returnemail
return email address
characters>
ftpp <number less than 65535> FTP port
ftp1 <domain name or IP address> primary FTP server
ftpuser1
user name for primary FTP server
characters>
ftppass1
password for primary FTP server
characters>
ftpfolder1
upload folder in primary FTP server
characters>
ftp2 <domain name or IP address> secondary FTP server
ftpuser2
user name for secondary FTP server
characters>
ftppass2
password for secondary FTP server
characters>
ftpfolder2 <text st
characters>
server
http <number less than 65535> HTTP port
controlport <number less than 65535> control Channel port
videoport <number less than 65535> video Channel port
audioport <number less than 65535> audio Channel port
yes optimal for the low bandwidth lowband
no keep the original way
DDNS & UPnP Configuration URL
URL: /setup/ddns.cgi
- 54 -
Page 56

able DDNS function. This option must be resent
s called, if DDNS function is to
The login username of DDNS server or the email
The login password of DDNS server or the key
able UPnP function. This option must be resent
whenever the URL is called, if UPnP function is to
<string shorter than 80
<text string shorter than 80
<text string shorter than 80
ext string shorter than 15
<text string shorter than 15
NAME VALUE DESCRIPTION
enddns anything En
whenever the URL i
be enabled.
provider
1 DynDDNS.org(Dynamic)
2 DynDDNS.org(Custom)
3 TZO.com
4 dhs.org
host <the hostname> The hostname of the Network Camera
usermail username or mail
address registered in DDNS server.
passkey password or key
given by the DDNS server.
enupnp anything En
be enabled.
Mail&FTP Configuration URL
URL: /setup/mailftp.cgi
NAME VALUE DESCRIPTION
smtp1 <domain name or IP address> primary SMTP server
mailto1
mail recipient address
characters>
smtp2 <domain name or IP address> secondary SMTP server
mailto2
mail recipient address
characters>
returnemail
return email address
characters>
ftpp <number less than 65535> FTP port
ftp1 <domain name or IP address> primary FTP server
ftpuser1 <t
user name for primary FTP server
characters>
ftppass1
- 55 -
password for primary FTP server
Page 57

<text string shorter than 40
<text string shorter than 15
<text string shorter than 15
<text string shorter than 40
upload folder in secondary FTP
<text string shorter than 15
characters>
ftpfolder1
upload folder in primary FTP server
characters>
ftp2 <domain name or IP address> secondary FTP server
ftpuser2
user name for secondary FTP server
characters>
ftppass2
password for secondary FTP server
characters>
ftpfolder2
characters>
server
Audio/Video Configuration URL
URL: /setup/video.cgi
NAME VALUE DESCRIPTION
text
enclosed caption
characters>
size
1 half
2 half x 2
3 normal
B/W monochrome color
<other than B/W> color
fixb fix bit rate quality
<other than fixb> fix quantization
quan
1 lowest quality of video
2 lower quality of video
3 normal quality of video
4 higher quality of video
5 highest quality of video
64000 set bit rate to 64K bps bitrate
128000 set bit rate to 128K bps
- 56 -
Page 58

mprove audio quality in low
his option
nt whenever the URL is
in
in
256000 set bit rate to 256K bps
384000 set bit rate to 384K bps
512000 set bit rate to 512K bps
768000 set bit rate to 768K bps
1000000 set bit rate to 1000K bps
1200000 set bit rate to 1200K bps
frame
1 set maximum frame rate to 1 fps
2 set maximum frame rate to 2 fps
3 set maximum frame rate to 3 fps
5 set maximum frame rate to 5 fps
10 set maximum frame rate to 10 fps
15 set maximum frame rate to 15 fps
20 set maximum frame rate to 20 fps
25 set maximum frame rate to 25 fps
30 set maximum frame rate to 30 fps
yes flip image flip
no normal image
yes mirror image mirror
no normal image
improve anthing to i
bandwidth environment, t
must be rese
mphone
internal set the audio source from built-
external set the audio source from line-
Camera Control URL
URL: /setup/ptcamera.cgi
called, if it is to be enabled.
microphone.
microphone.
- 57 -
Page 59

the pan/tilt control using
able the pan/tilt control using
change the speed of auto pan or auto
NAME VALUE DESCRIPTION
addpos <the position name> add preset location with its name
delpos <the position name> delete preset location with its name
selloc <index value, 0~19> add preset location into patrol list
irenable
yes enable
remote controller
no dis
remote controller
speedpan -5~5 change the horizontal aim-range
speedtilt -5~5 change the vertical aim-range
speedapp 1~5
patrol.
Image Quality Configuration URL
URL: /setup/image.cgi
NAME VALUE DESCRIPTION
brightness <-5 ~ 5> adjust brightness of image
contrast <-5 ~ 5> adjust contrast of image
hue <-5 ~ 5> adjust hue of image
saturation <-5 ~ 5> adjust saturation of image
preview <not required> not save the parameters
restore <not required> recall the original settings
save <not required> save the parameters
Application Configuration URL
URL: /setup/app.cgi
NAME VALUE DESCRIPTION
emode <not required> event mode application
smode <not required> sequential mode application
- 58 -
Page 60

w1 as trigger
set motion window2 as trigger
set motion window3 as trigger
trigger DO when DI condition
upload snapshot when DI condition
upload snapshot when motion
mail upload snapshots by email smethod
ftp upload snapshots by FTP
suffix <not required> FTP file with date and time suffix
delay <integer> seconds delay to detect next event
inter <integer> seconds delay to capture post-event
dihigh < not required > set DI high as trigger condition
dilow < not required > set DI low as trigger condition
dirise < not required > set DI rising as trigger condition
difall < not required > set DI falling as trigger condition
motion1 < not required > set motion windo
condition
motion2 < not required >
condition
motion3 < not required >
condition
ioalarm < not required >
matched
mdalarm < not required > trigger DO when motion detected
ioupload < not required >
matched
mdupload < not required >
detected
sinter <integer> seconds interval for sequential mode
sbegin <hh:mm:ss> time to start sequential mode
send <hh:mm:ss> time to stop sequential mode
- 59 -
Page 61

D. Technical Specifications
- System
CPU: Trimedia PNX1300
RAM: 16MB SDRAM
ROM: 2MB FLASH ROM
- Networking
Protocol
TCP/IP, HTTP, SMTP, FTP, Telnet, NTP, DNS and
DHCP
Physical
10BaseT Ethernet or 100BaseT Fast Ethernet
WLAN
2.4GHz 802.11b+ DSSS CSMA/CA
22/11/5.5/2/1Mbps
Coverage: 100M/22Mbps, 150M/11Mbps,
250M/5.5Mbps, 300M/2Mbps, 350M/1Mbps
- Video Codec
Algorithm Supported
MPEG4(short header mode)
Features
Adjustable image size, quality and bit rate
Timestamp and text overlay
3 motion detection windows
Resolution
Up to 30/25 frames at 176x120 or 176x144
Up to 30/25 frames at 352x240 or 352x288
- Camera Specification
1/4 inch color CCD sensor
704x480 or 704x576
1 Lux / F2.0
AGC, AWB
Electronic shutter: Up to 1/100,000 sec
- Lens
Board lens with 4.3mm focal length, F1.8
- Audio Codec
24Kbps, 8Kbps(optional)
- Microphone
Omni-directional
Frequency: 20 – 20,000Hz
S/N ratio: more than 58dB
- General I/O
1 sensor input(max. 12VDC 50mA)
1 relay output(max. 24VDC 1A, 125VAC 0.5A)
- LED Indicator
Dual color status indicator
- Dimension
104.5mm(L) * 104.5mm(W) * 113.6mm(H)
- Weight
NET. 336.6g
- Power
Consumption: near 8.5 W
Universal switching power-supply included
Adapter input: 100-240VAC, 50/60Hz, 0.4A
Adapter output: 12VDC, 1.5A
- Operating Environment
Temperature: 0-40°C/32-104°F
Humidity: 95%RH
- EMI & Safety
CE, FCC
- Viewing System Requirement
Operating System
Microsoft Windows 98SE/ME/2000/XP
Browser
Internet Explorer 5.x or above
- 60 -
Page 62

Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC)
This device compiles with FCC Rules Part 15. Operation is subject to the following two conditions.
l This device may not cause harmful interference, and
l This device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause
undesired operation.
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant
to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful
interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio
frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful
interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in
a partial installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television reception,
which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct
the interference by one or more of the following measures:
-- Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
-- Increase the seperation between the equipment and receiver.
-- Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is connected.
-- Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
Shielded interface cables must be used in order to comply with emission limits.
Europe - This digital equipment fulfills the requirement for radiated emission according to Limit
B of EN55022/EN55024, and the requirement for immunity according to EN50082-1/1992.
 Loading...
Loading...