Page 1

BBPCHOME
MOTHER BOARD
USER’S MANUAL
Ver 2.
February 28, 2004
Page 2

Page 3

Copyright Notice
©Copyright 2000
The information contained in this user’s manual and all
accompanying documentation is copyrighted and all rights are
reserved. This publication may not, in whole or in part, be
reproduced, transcribed, stored in a retrieval system, translated into
any language or computer language, or transmitted in any form
whatsoever without the prior written consent from the manufacturer,
except for copies retained by the purchasers for their personal
archival purposes.
The manufacturer reserves the right to revise this user’s manual and
all accompanying documentation and to make changes in the
content without obligation to notify any person or organization of the
revision or change.
IN NO EVENT WILL THE VENDOR BE LIABLE FOR DIRECT,
INDIRECT, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL
DAMAGES ARISING OUT OF THE USE OR INABILITY TO USE
THIS PRODUCT OR DOCUMENTATION, EVEN IF ADVISED OF
THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES. IN PARTICULAR, THE
VENDOR SHALL NOT HAVE LIABILITY FOR ANY HARDWARE,
SOFTWARE, OR DATA STORED OR USED WITH THE
PRODUCT, INCLUDING THE COSTS OF REPAIRING,
REPLACING, OR RECOVERING SUCH HARDWARE,
SOFTWARE, OR DATA.
All trademarks mentioned in this document are acknowledged.
The specifications in this manual are subject to change without
notice.
i
Page 4

Using This Manual
This manual is designed to help you build a reliable Personal
Computer based on the BBPCHOME platform.
Chapter 1—Quick Reference
This chapter is for advanced users who want to quickly assemble a system.
The motherboard layout along with jumper and switch settings, and memory
configuration are provided.
Chapter 2—Introduction
This chapter includes an introduction, a checklist of the items that ship with
this motherboard, and a summary of the principal features and components.
Chapter 3—Hardware Installation
This chapter explains how to prepare your motherboard for use and how to
make the various connections to other computer components and peripheral
items.
Perface
Chapter 4—BIOS Configuration
This chapter explains how to use the system setup utility that is stored in the
motherboard’s firmware.
Chapter 5—Driver and Utility
This chapter briefly describes the drivers and utility programs that are
packaged with the motherboard.
ii
Page 5

Perface
.
.
.
.
.
Table of Contents
1. BBPCHOME
1.1. Motherboard Layout.................................................
1.2. Back I/O Ports..........................................................
1.3. Back I/O Ports (Optional).........................................
1.4. Front I/O Ports..........................................................
1.5. Jumpers ...................................................................
1.6. Extended Connector Board......................................
1.7. PCI Frequency Settings...........................................
1.8. Memory Installation..................................................
1.9. Connectors...............................................................
QUICK REFERENCE
...........................
2. INTRODUCTION............................................................
2.1. Overview..................................................................
2.2. Motherboard Specifications and Features ...............
2.2.1. Hardware..................................................................
2.2.2. Software...................................................................
2.3. Motherboard Layout.................................................
2.4. Microprocessor.........................................................
2.5. CPU Packaging........................................................
2.6. AC97 Codec.............................................................
2.7. Chipset.....................................................................
3. HARDWARE INSTALLATION....................................
3.1. Unpacking................................................................
3.2. Installation................................................................
3.3. Safety Measures......................................................
3.4. Connector/Jumper Location.....................................
1
1
2
2
2
2
3
3
3
4
5
5
6
6
8
9
11
11
11
12
13
13
14
14
15
iii
Page 6

Perface
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
3.5. Attaching Connectors...............................................
3.5.1. Audio CD-In Connector (CD1)................................
3.5.2. Audio AUX-IN Connector (AUX1).........................
3.5.3. Infrared (IR) Connector (IR)....................................
3.5.4. LAN/Modem Wake up connectors (WOL1)............
3.5.5. IDE Connectors........................................................
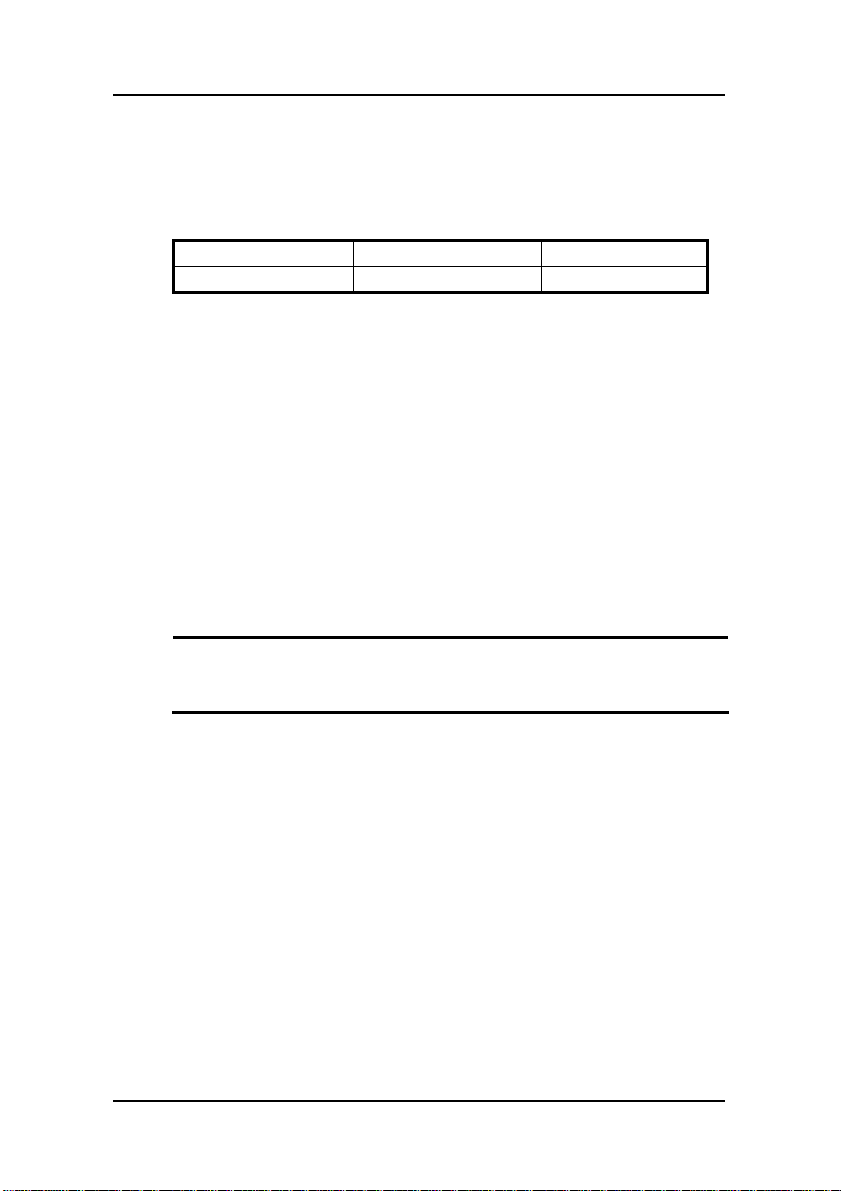
3.5.6. PCI Connector (PCI)................................................
3.5.7. Serial COM2 Connector (COM2)............................
3.5.8 CON1 Connector (CON1) .......................................
3.5.9. HDD & CD-ROM Power Connector.......................
3.5.10. CPU/Chipset/System FAN Power Supplies.............
3.5.11. Back I/O Port...........................................................
3.5.12. Front I/O Port...........................................................
3.5.13. Back I/O Port (Optional)..........................................
3.5.14. 5.1 Channel Sound Connectors................................
3.6. Installing the CPU ....................................................
3.6.1. Before You Begin....................................................
3.6.2. Installation Procedure..............................................
3.6.3. Removing the Processor ..........................................
3.7. Installing System Memory................................................
3.8. Setting Jumpers...................................................................
3.8.1. Clear CMOS Jumper (JP4).......................................
4. BIOS CONFIGURATION ..............................................
4.1. Entering Setup .........................................................
4.2. Standard CMOS Features........................................
4.3. Advanced BIOS Features ........................................
4.4. Advanced Chipset Features.....................................
4.5. Integrated Peripherals..............................................
4.6. Power Management Setup.......................................
16
16
16
17
17
18
19
19
20
20
21
22
26
27
28
29
29
29
30
31
32
32
34
35
37
40
44
47
52
iv
Page 7

Perface
.
.
.
.
.
4.7. PnP/PCI Configurations...........................................
4.8. PC Health Status Option..........................................
4.9. Frequency/Voltage Control ......................................
4.10. Load Fail-Safe Defaults Option................................
4.11. Load Optimized Defaults Option..............................
4.12. Set Supervisor/User Password................................
4.13. Save & Exit Setup....................................................
4.14. Exit Without Saving..................................................
5. DRIVER AND UTILITY.................................................
5.1. Flash Utility...............................................................
5.2. CD Driver Overview .................................................
5.2.1. Intel Chipset 845GV software installation utility ....
5.2.2. Intel Chipset 845GV Bus master IDE Driver ..........
5.2.3. ALC650 Audio Driver.............................................
5.2.4. LAN Driver..............................................................
57
59
61
63
63
63
64
64
65
65
66
67
67
68
68
v
Page 8

Page 9

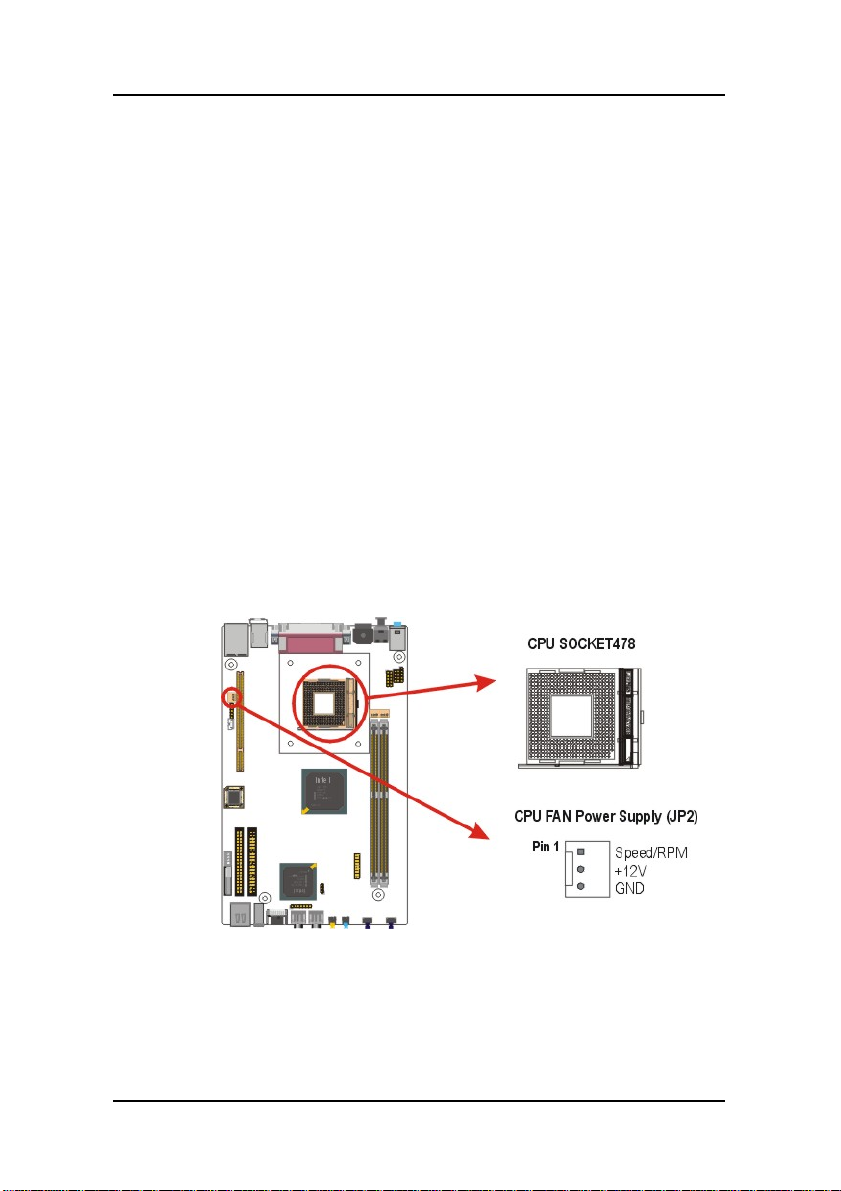
1. BBPCHOME Quick Reference
This section is for users to get started using the motherboard straight away.
1.1. Motherboard Layout
1.
mPGA478B CPU socket (PGA478)
2.
184-pin DIMM DDR module sockets (DIMM1~2)
3.
IDE connector (IDE1)
4.
IDE connector (IDE2)
5.
PCI expansion connector (PCI)
6.
LAN/Modem Wake up connector (WOL1)
7.
IR connector (IR)
8.
CPU FAN (JP2)
9.
HDD & CD-ROM Power connector
10.
COM2 connector (COM2)
11.
AUDIO connector (AUX1)
12.
AUDIO connector (CD1)
13
TV-Out & DVI connector (CON1)
14.
Chipset FAN(JP11)
15.
System FAN(JP7)
16.
CMOS Jumper (JP4)
17.
RTC Battery
18.
Flash BIOS
1
Page 10

Mainboard User’s Manual
1.2. Back I/O Ports
1.3. Back I/O Ports (Optional)
1.4. Front I/O Ports
1.5. Jumpers
1-2 Normal Mode JP4
(CMOS Clear)
2
2-3 Clear CMOS
Back I/O Port
Page 11

Mainboard User’s Manual
1.6. Extended Connector Board
1.7. PCI Frequency Setting
The PCI frequency settings are automatically set by the system
1.8. Memory Installation
Note: This motherboard supports up to two double-sided or two
single-sided DIMMs when the DDR DRAM interface is
operating at 133 MHz. Installing DDR DIMM modules that
exceed these specifications requires that the BIOS down-shifts
the DRAM clocks to 100 MHz through a two-wire interface of
the system clock generator.
184-Pin DIMM DDR SDRAM Memory Configuration.
Each 184-pin DIMM bank can install from 64MB up to 1GB of
PC1600/PC2100/PC2700 compliant 2.5V single or double side
buffered with or without ECC DDR SDRAM modules.
Extended Connector Board
3
Page 12

Mainboard User’s Manual
Bank 0 (DIMM1) 64MB, 128MB, 256MB, 512MB, 1GB
Bank 1 (DIMM2) 64MB, 128MB, 256MB, 512MB, 1GB
Total 2 GB
1.9. Connectors
JP2
CPU FAN : This 3-pin header is used for connecting
a CPU fan.
JP7 System fan
JP11 Chipset fan
AUX1
CD1
Auxiliary-IN connector : This 4-pin header is an
auxiliary input connector.
CD-IN connector : This 4-pin header is used for
connecting the CD ROM audio input to the sound
card.
COM2 COM2 connector
CON1 TV-Out & DVI connector
IR
WOL1
S-ATA
( optional )
S/PDIF
Infrared (IR) connector : This 5-pin header is used
connect an IR port for use of IR devices.
Wake On LAN Connector : This 3-pin header is
used for remote wake up of the computer through a
network card.
S-ATA Connector : S-ATA stands for serial ATA.
Serial ATA is newest ATA transmission interface.
Serial ATA is able to reach 150MB/sec.
S/PDIF Connector : S/PDIF stands for Sony/Philips
digital interface. It’s a standard audio transfer file
format. It allows the transfer of audio from one file to
another without the conversion to and from an
analog format.
4
Connectors
Page 13

2. Introduction
2.1. Overview
The high quality
function motherboard that supports mPGA478 Intel® Pentium® 4
processors that support a 400/533 MHz front side bus (FSB). This
motherboard is designed around the latest and fastest Intel 845GV
chipset in a special ATX form factor.
The motherboard delivers workstation-level performance with bus
mastering EIDE (Enhanced IDE) controller, S_ATA(serial ATA)
( optional ) controller, and concurrent PCI bus. The motherboard
accommodates DDR SDRAM (Synchronous DRAM) memory and
supports ATA33/66/100.
In addition to superior hardware capabilities, provided with this
platform are these features:
Supports Intel®Pentium® 4 processors in a 478-pin package
Supports a 100/133 memory bus
Supports up to 2 GB of PC1600/PC2100 DDR SDRAM
845GV new version will support PC2700(DDR333) DDR after
May, 2003.
Supports serial ATA, serial ATA speed up to 150MB/s ( optional )
Bus mastering EIDE driver
Supports four USB ports, Plug and Play devices
Soft-off APM (Advanced Power Management)
ACPI (Advanced Configuration and Power Interface)
Keyboard power on
External modem ring on
LAN wake up
BIOS upgrade
BBPCHOME
is a high-performance, enhanced
5
Page 14

Mainboard User’s Manual
2.2. Motherboard Specifications and Features
2.2.1. Hardware
CPU Intel
®
Pentium
package, compatible Auto-detection CPU
compatible with HT(Hyper Threading)
technology
VRM Onboard Voltage Regulator Module
Provides 1.1V to 1.85V operating voltage
Coprocessor
Speed
CPU has built-in floating point unit
400/533 MHz PSB(100/133 MHz bus clock)
PCI bus clock 33 MHz
Chipset Intel 845GV supports
PC1600/PC2100/PC2700(after May, 2003)
DDR SDRAM and
peripheral controller supports Ultra
ATA100
DRAM Two 184-pin DDR sockets, up to 2GB
Supports 64 MB to 2GB DDR SDRAM
memory types
EIDE
Controller
Supports for IDE devices in two channels
Supports one 3.5” HDD
Supports one 2.5”HDD
Supports one slim CD-ROM
Supports Iomega ZIP or LS-120 removable
drives
Supports serial ATA device
Sound Chip Chip integrated direct Sound AC97 2.2
interface.
Realtek ALC650
®
4 processors in a 478-pin
super-I/O integrated
6
Mainboard Specification and Feature
Page 15

Introduction
On-Board TV out
& LAN ( optional )
Realtek 8100 LAN chipset, supports 10/100
Mb/s
TV-out with 1024×768 input video resolution.
Enhanced I/O One floppy disk controller
One Standard/EPP/ECP parallel port
connector
One 16550 compatible serial port connector
One serial connector by cable
Four USB (Universal Serial Bus) ports
One audio port connector, include line-out,
line-in, mic-in ports
I/O Options One connector for front panel USB ports 3/4
One IrDA compatible infrared (IR) connector
Mouse PS/2 mouse connector
Keyboard PS/2 keyboard connector
Expansion Slots One 32-bit PCI slot
Power
Management
System
Management
Compliant with EPA, APM 1.2 and ACPI
ATX soft-off power control
Power on by keyboard and mouse
Power on by external modem ring
Power on by alarm
Power on by LAN wake up
Fan off in sleep mode
CPU and system voltage detection
CPU and secondary fan RPM detection
Voltage Regulator Switching regulator
CPU voltage auto-detection
Form Factor Special A TX
Board Size 155 × 250 mm
Mainboard Specification and Feature
7
Page 16

Mainboard User’s Manual
2.2.2. Software
BIOS AWARD AGP/PCI BIOS
Driver and
Utility
Operating
System
2M-bit Flash BIOS with ESCD (Extended
System Configuration Data) block
Supports APM, Plug and Play, Multi-Boot, DMI
and EIDE devices
Supports ACPI
Supports high-capacity LS-120 and ZIP
removable media drive
IDE Bus mastering Ultra DMA driver
AC97 codec audio driver
Flash utility for BIOS upgrade
Operates with MS_DOS, Windows
3.x/9x/ME/XP/2000/NT, OS/2, Novell
NetWare/UnixWare 1.1, and SCO Unix 4.2
8
Mainboard Specification and Feature
Page 17

2.3. Motherboard Layout
Introduction
Note: Because of optional items and design changes, your
motherboard may not be identical to the one shown in
the illustration.
Mainboard Layout
9
Page 18

Mainboard User’s Manual
Key to Motherboard Components
NO. Name Function
1 PGA478 CPU socket
2 DIMM1~2 DDR SDRAM Memory module slots
3 IDE1 IDE 1 connector
4 IDE2 IDE 2 connector
5 PCI 32-bit PCI Slot
6 WOL1 LAN/Modem Wake up Connector
7 IR IrDA compliant Infrared (IR) connector
8 JP2 CPU FAN Connector
9 Power HDD & CD-ROM Power Connector
10 COM2 COM2 Connector
11 AUX1 Audio AUX-In header
12 CD1 Audio CD-In header
13 CON1 TV-Out & DVI Connector
14 JP6 System FAN
15 JP7 System FAN
16 JP4 Clear CMOS
17 BAT RTC battery
18 U20 Flash BIOS
10
Mainboard Layout
Page 19
2.4. Microprocessor
The motherboard is designed to operate with the following
processor:
Processor Type Speed FSB
Intel Pentium 4 1.7GHz~3.06GMHz+ 400, 533 MHz
An onboard switching voltage regulator provides the required 1.1 to
1.85 volts for the processor. The processor sends five VID (Voltage
identification) signals to the switching voltage regulator. The
switching regulator generates the correct voltage for the processor.
2.5. CPU Packaging
The motherboard’s CPU socket is a surface mount, mPGA478B type
ZIF (Zero Insertion Force) socket. The socket has 478 pins with 50
mil pin pitch.
Note:
ZIF sockets are sockets designed for easy insertion of pin
grid array (PGA) chips. The chip is dropped into the
socket, and a lever is used to secure the chip in place.
Introduction
2.6. AC 97 Codec
This motherboard features the AC 97 (ALC650) codec. The AC 97
(ALC650) Audio codec is compliant with the AC 97 2..2
specification, and supports 18-bit ADC (Analog Digital Converter)
and DAC (Digital Analog Converter) resolution as well as 18-bit
stereo full-duplex codec with independent and variable sampling
rates. Further features include support for four analog line-level
stereo inputs.
Microprocessor
11
Page 20

Mainboard User’s Manual
2.7. Chipset
BBPCHOME
The
use in a desktop system based on an Intel® Pentium® 4 processor in
a 478-pin package. The Intel 845GV chipset supports the Pentium 4
processor with 256-KB L2 cache and the Pentium 4 processor with
512-KB L2 cache on 0.13 micron process. The processor interface
supports the Pentium 4 processor subset of the Extended Mode of
the Scalable Bus Protocol. In an Intel 845GV chipset-based platform,
I/O functions are integrated onto the ICH4.
The GMCH provides the processor interface, system memory
interface, hub interface, and additional interface in an Intel 845GV
chipset desktop platform. Each GMCH contains an integrated
graphics controller (IGD). Intel 845GV chipset use the 82801DB
ICH4 for the I/O Controller Hub.
z Advanced packaging technology and industry leading
electrical design innovations ensure long-term system
reliability over wide operating conditions.
z The AGP4X interface providing the most advanced graphics
support available, enabling graphics ba n dwidth of over 1GB/s.
z Two USB controllers provi de high-performance peripherals
with 480 Mbps of bandwidth, while enabling support for up to
four USB ports.
z AC97 (ALC650) six channels of audio.
z Dual Ultra ATA/100 controllers support faster IDE transfers to
storage devices.
z Sil3112 (serial ATA controllers) supports speed up to 150MB/s
supports the Intel 845GV chipset is designed for
12
This concludes Chapter 2. Chapter 3. covers hardware installation.
Chipset
Page 21

3. Hardware Installation
This chapter explains how to use your motherboard to build a powerful
computer system. At a minimum, you will need the following components
in order to build a fully functioning system.
z Computer case with P4 special ATX power supply
z mPGA478B Processor
z One DDR SDRAM memory module
z One UDMA-66/100 IDE hard disk drive
z One CD-ROM drive
z One display monitor
z One mouse
z One PS/2 keyboard
z One S/PDIF
z One S-Video ( optional )
z One TV-out & DVI ( optional )
z One 1394
z One S_ATA ( optional )
z One LAN / Modem
z One set of loudspeakers
z Four USB
Introduction
3.1. Unpacking
BBPCHOME
The
items:
z One motherboard
z One ATA100 5.5cm IDE cable (3.5’ HDD)
z One ATA33 10cm IDE cable (slim CD-ROM)
z One 15cm power cable
z One 1x8, 5cm LAN cable ( optional )
z One 2x9, 28cm DVI & TV-out cable ( optional )
z Driver and utility CD with User’s manual inside
After removing the motherboard from its anti-static bag, place it on
a grounded or antistatic surface (component side up). Inspect the
motherboard and contact your vendor immediately if it is damaged.
motherboard package contains the following
13
Page 22

Mainboard User’s Manual
3.2. Installation
BBPCHOME
The
chassis. The chassis comes with various mounting fasteners, which
are made of metal or plastic. It is highly recommended to use as
many metal fasteners as possible to mount the motherboard in the
chassis for better grounding.
To install the motherboard you need to install the CPU and DDR
memory modules, attach the connectors.
is designed to fit into a special ATX form factor
3.3. Safety Measures
Computer components and electronic circuit boards can be damaged
by discharges of static electricity. Working on computers that are
still connected to a power supply can be extremely dangerous.
Follow the simple guidelines below to avoid damaging you
computer:
z Always disconnect the motherboard from the ATX power
supply, and disconnect the computer from the power outlet
whenever you are working inside the computer case.
z If possible, wear a grounded wrist strap when you are
installing the motherboard or working inside the computer
case. Alternatively, discharge any static electricity by touching
the bare metal chassis of the computer case, or the bare metal
body of ay other grounded appliance.
z Hold electronic circuit boards by the edges only. Do not touch
the components on the board unless it is necessary to do so.
Do not flex or stress the circuit board.
z Leave each component inside the static-proof packaging that it
ships with until you are ready to use the component for the
installation.
14
Installation
Page 23

Hardware Installation
3.4. Connector/Jumper Location
Connector/Jumper Location
15
Page 24

Mainboard User’s Manual
3.5. Attaching Connectors
3.5.1. Audio CD-In Connector (CD1)
This connector enables you to connect a CD-ROM to the
motherboard and receive stereo audio input.
3.5.2. Audio AUX-IN Connectors (AUX1)
16
This connector enables you to connect a stereo audio input from
CD-ROM, TV-tuner, or MPEG card.
Attaching Connector
Page 25

Hardware Installation
3.5.3. Infrared (IR) Connector (IR)
This 5-pinheader connects to an optional wireless transmitting and
receiving infrared module via a cable and a bracket. Configure BIOS
to enable the IrDA port if you attach an infrared module to this
connector. Refer to Integrated Peripherals in Chapter 4 for details.
3.5.4. LAN/Modem Wake up connectors (WOL1)
This 3-pin header is used for remote wake up of the computer
through a network or modem signal.
Attaching Connector
17
Page 26

Mainboard User’s Manual
3.5.5. IDE Connectors
Connect “Extended Connector Board” to motherboard firstly.
The length of 5.5cm ATA100 IDE cable, one side to connect to 3.5”
HDD connect over the “Extended Connector Board”, another side to
connector to 3.5” HDD.
The length of 10cm ATA33 IDE cable, one side to connect to the
slim CD-ROM over the “Extended Connector Board”, another side
to connect to slim CD-ROM.
Connect the slim HDD to slim HDD connector over the “Extended
Connector Board”. Since slim HDD and slim CD-ROM use the
same channel. You should separate the master and slave.
S_ATA(serial ATA) ( optional ) and parallel(IDE) HDD can be used
simultaneously. Also, they can copy each other.
18
Attaching Connector
Page 27
Hardware Installation
3.5.6. PCI Connector (PCI)
PCI connector is one of equipment interfaces that connects
peripheral equipment and motherboard. Its transfer speed is faster
than traditional ISA. PCI is the mainstream transfer interface for
extra adopter.
3.5.7. Serial COM2 Connector (COM2) ( optional )
The motherboard provides one onboard serial COM2 connector. The
COM2 connector has the same signal with COM1 on the back panel.
Attaching Connector
19
Page 28

Mainboard User’s Manual
3.5.8. CON1 Connector (CON1) ( optional )
CON1 is DVI & TV-OUT connector. Connect “Extended Connector
Board” and “Back I/O optional ports” to motherboard firstly.
The length of 28cm DVI & TV-Out cable, one side to connect to the
DVI & TV-Out over the “Extended Connector Board”, another side
to connect to DVI & TV-Out over the Back I/O optional ports.
3.5.9. HDD & CD-ROM Power Connector
Connect 15cm power cable attached from this connector to HDD or
CD-ROM.
20
Attaching Connector
Page 29

Hardware Installation
3.5.10. CPU/Chipset/System Fan Power Supplies
(JP2/JP7/JP11)
There are three fan co nnectors on the motherboard for the cooling
fans. The connectors support fans of 12VDC/500mAMP (six watt)
or less. When the system goes into sleep state, fans should be shut
down to eliminate audible noise and reduce power consumption.
Attaching Connector
21
Page 30

Mainboard User’s Manual
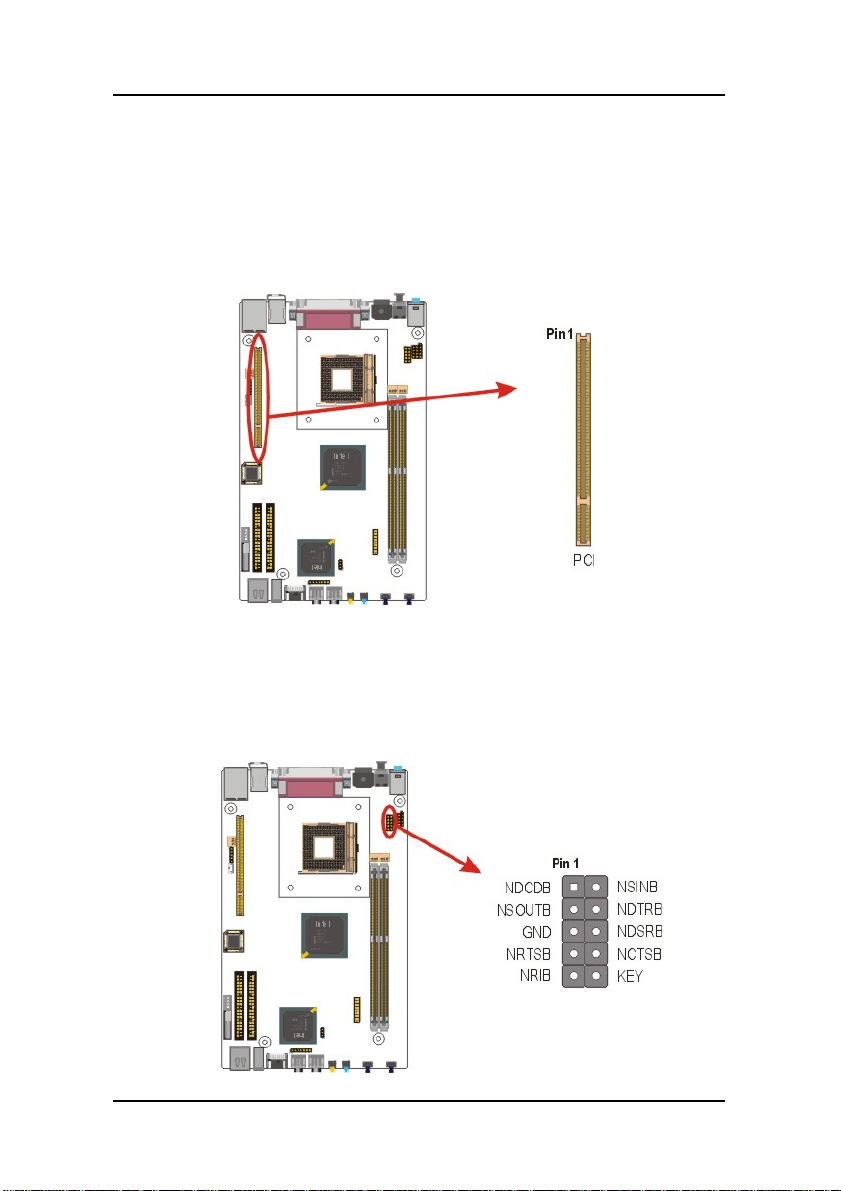
3.5.11. Back I/O Port
The back panel provides external access to PS/2 style keyboard and
mouse connectors, one serial ports, one parallel port, one S /PDIF
port, VIN_19V port, one VGA port, one LAN port, dual USB ports,
and audio Line-out, Line-in, Mic-in, ports which are integrated on
the motherboard. The figures below show the location of the back
panel I/O connectors.
Audio Line-In Port
You can connect a tape player or another audio source to the light
blue Line-in connector to record audio on your computer or to play
audio through your computer’s sound chip and speakers.
22
Audio Line-Out Port
You can connect various audio devices to this audio jacks. Connect
headphones or powered speakers to the lime-colored lineout
connector.
Attaching Connector
Page 31
Hardware Installation
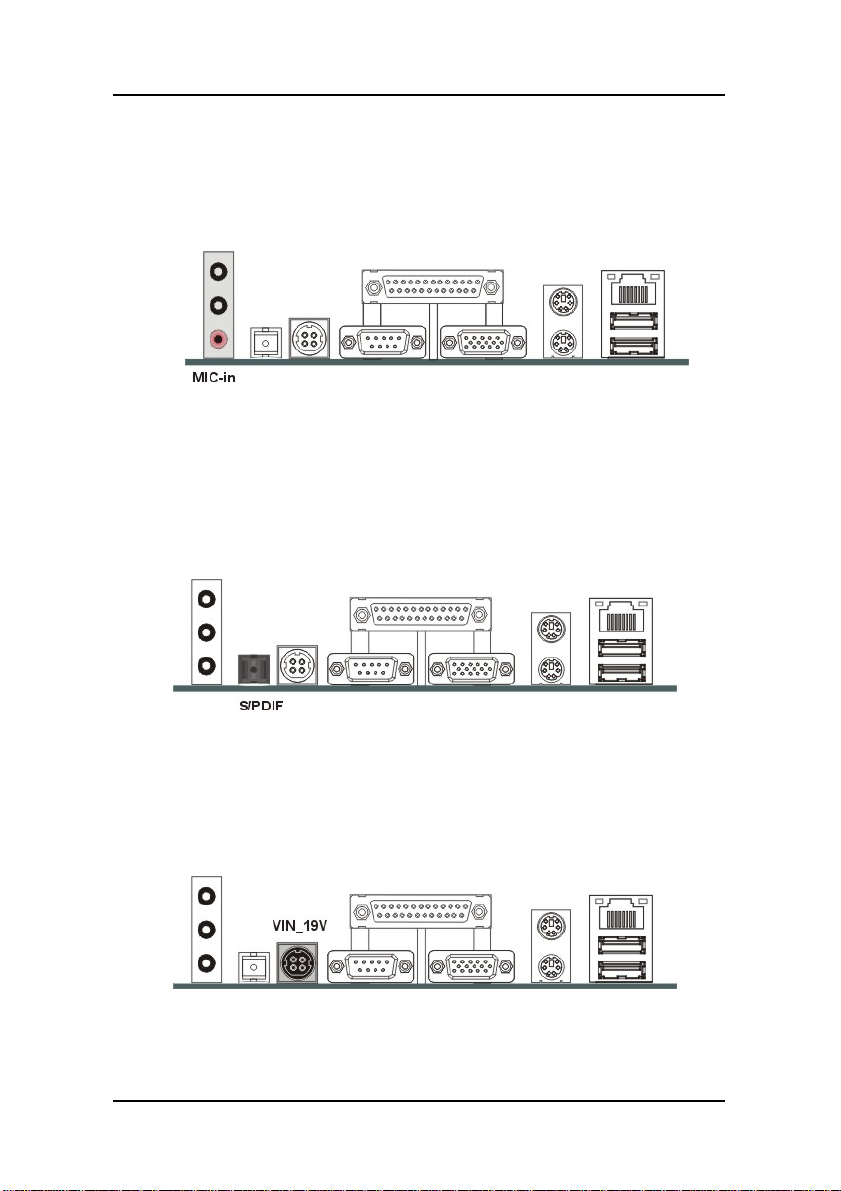
Audio Mic-In Port
You can connect a microphone to the pink microphone connector to
record audio to your computer.
S/PDIF Port
You can connect S/PDIF device to the black connector to your
computer. S/PDIF (Sony / Philips Digital Interface) is a standard
audio transfer file format.
VIN_19V Port
You can connect a VIN_19V adapter to the black connector to your
computer.
Attaching Connector
23
Page 32

Mainboard User’s Manual
Parallel Port
Connect a printer or other parallel device to the burgundy-colored
25-pin parallel port. You can set the parallel port IRQ and parallel
port mode in BIOS. Refer to Integrated Peripherals in Chapter 4 for
details.
Serial Port
Connect a serial device such as a mouse or modem to the 9-pin
serial port. You can set the serial port IRQs in BIOS. Refer to
integrated Peripherals in Chapter 4 for details.
24
VGA Port
Connect an external monitor to the blue 15-pin VGA port.
Attaching Connector
Page 33

Hardware Installation
PS/2 Mouse and PS/2 Key board Ports
Connect a PS/2 mouse to the green 6-pin mini DIN connector. The
system will automatically assign IRQ 12 to the PS/2 mouse if one is
connected.
Connect a PS/2 keyboard to the purple 6-pin mini DIN connector.
If you want to connect a standard AT size (large DIN) connector, you
must use an adapter.
Universal Serial Bus Ports
You can connect two USB devices or USB hubs to the USB ports.
The USB ports provide a hardware interface for low-speed
peripherals such as the keyboard, mouse, joystick, scanner, printer
and telephony devices, and also support MPEG-1 and MPEG-2
digital video. The USB ports have a m axi mum bandwidth of 480
Mbits/sec (equivalent to 60 Mbytes/sec), and up to 127devices can
be attached. Fast devices can use the full bandwidth, while
lower-speed ones can transfer data using a 60 Mbytes/sec
sub-channel.
Attaching Connector
25
Page 34

Mainboard User’s Manual
3.5.12. Front I/O Port
The Front panel provides two USB ports, one 1394 port, one S_ATA
port ( optional ) , one earphone port, one MIC port. The figure below
show the location of the front panel connectors.
Universal Serial Bus Ports
You can connect two USB devices or USB hubs to the USB ports.
The USB ports provide a hardware interface for low-speed
peripherals such as the keyboard, mouse, joystick, scanner, printer
and telephony devices, and also support MPEG-1 and MPEG-2
digital video. The USB ports have a m axi mum bandwidth of 480
Mbits/sec (equivalent to 60 Mbytes/sec), and up to 127devices can
be attached. Fast devices can use the full bandwidth, while
lower-speed ones can transfer data using a 60 Mbytes/sec
sub-channel.
1394 Port
Connect a device to the 1394 port on the front panel.
Earphone Port
Connector JP8 and JP10 with attached 1x5, 31cm sound cable when
you want to hear from this connector.
26
Attaching Connector
Page 35
Hardware Installation
S_ATA Port ( optional )
Connect a device to the S_ATA port on the back panel. Serial ATA is the
latest ATA transmission interface, developed for multi-purposes, including
fast data transmission, user-friendly interface, self-adjusting capability, and
above all, it must be compatible with the Parallel ATA software.
Internal storage devices are serial ATA target in the market. Its projected
speed is 150MB/s in generation 1 and 300MB/s in generation 2. When
system boots up from S_ATA HDD, The S_ATA is recognized as SCSI
device in BIOS setup. It supports hot plug function.
Mic-In Port
You can connect a microphone to the microphone connector to
record audio to your computer.
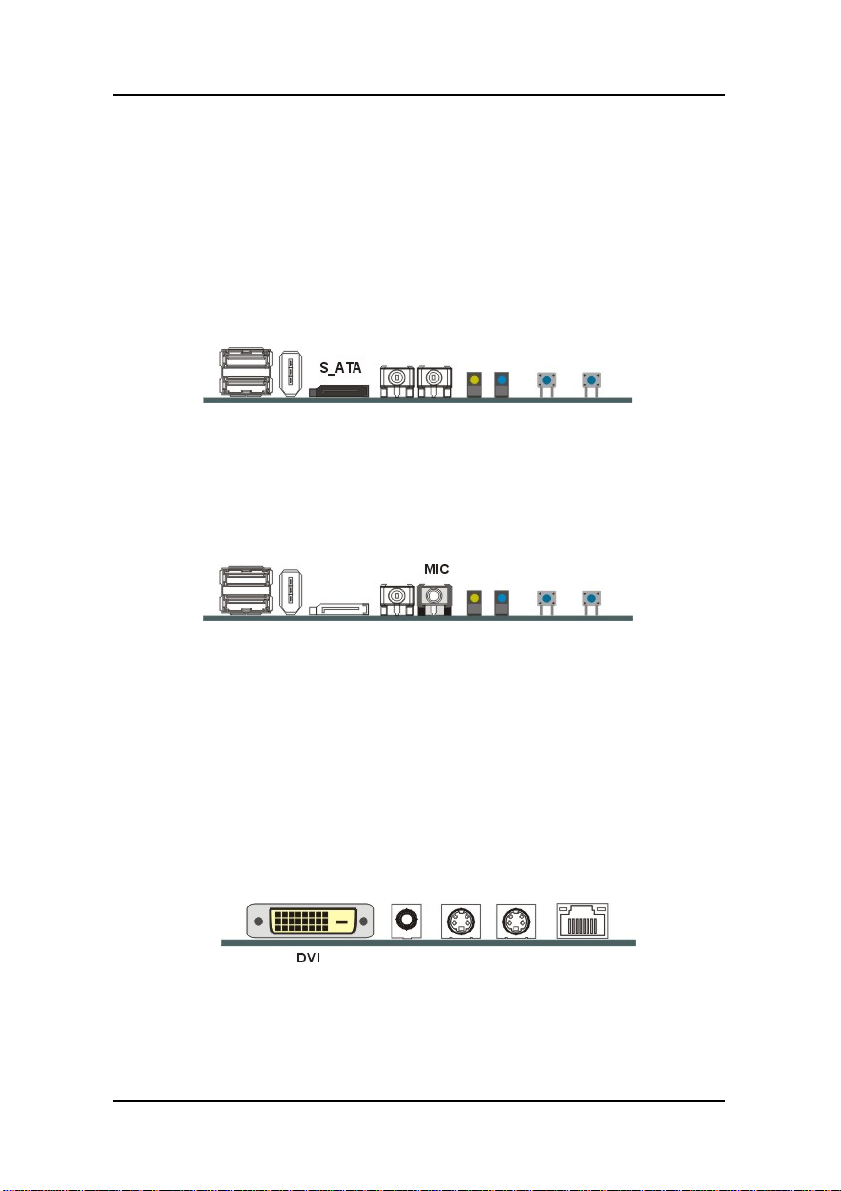
3.5.13. Back I/O Ports (Optional)
The back I/O panel ports support one DVI port, one AV port, one
S-Vedio port, one Capture port and one LAN port. The figure below
show the location of the back I/O panel connectors.
DVI Port
You can connect DVI devices to DVI port on the back panel.
Attaching Connector
27
Page 36

Mainboard User’s Manual
AV Port
You can connect AV device to AV port (TV-Out) on the back-panel.
S-Video Port
You can connect S-Video devices to S-Video port on the back panel.
Capture Port
You can connect Capture devices to Capture port on the back panel.
LAN Port
Connect a device to the LAN port on the back panel.
3.5.14. 5.1 Channel Sound Connectors
28
5.1 channel sound is piped through six. separate channels : front left,
front right, center, rear right, rear left and a subwoofer for deep bass.
Attaching Connector
Page 37
3.6. Installing the CPU
3.6.1. Before You Begin
1. Be sure that your processor kit includes the following items:
z One processor with the fan or heat sink attached
z One power cable (for CPU with cooling fan attached)
2. Place the motherboard on a workbench (not in a chassis). Be
sure that the motherboard is empty (that is, no DIMMs, cables,
or cards are installed) and that the holes for the fan or heat sink
support pegs are empty.
3.6.2. Installation Procedure
1. On the motherboard, identify the CPU Socket 478 and the
cooling fan power supply connector CPU FAN.
Hardware Installation
2. Push the CPU socket level slightly to the side and then raise it
as far as it can go.
Installing the CPU
29
Page 38
Mainboard User’s Manual
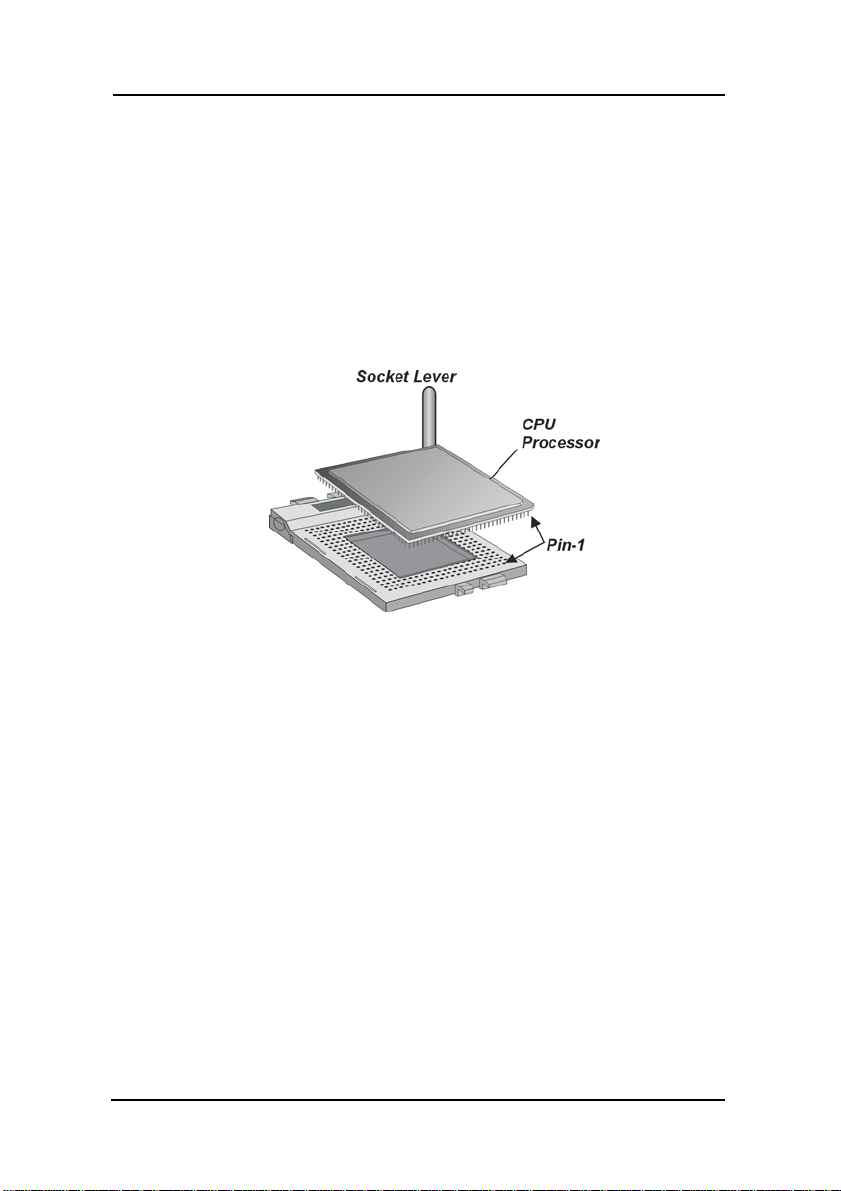
3. Identify the pin-1 corner of the mPGA478. The pin-1 corner is
on the same side as the locking lever, as shown in the
illustration below.
4. Identify the pin-1 corner of the processor (the pin-1 corner on
the processor has a beveled edge).
5. Align the pin-1 corners and drop the processor into the
mPGA478. The processor should drop into place without any
force. I f it doesn’t seat proper ly, check that you have the pin-1
corner in the correct position.
6. Swing the locking lever down to lock the processor in place and
latch the lever under the catch on the side of the socket.
7. Plug the cable from the heat sink/cooling fan assembly into the
processor cooling fan power supply CPU FAN.
8. Configuration of the processor is carried out using the system
setup utility as described in Chapter 4. Configure the processor
the first time you turn on the assembled computer.
30
3.6.3. Removing the Processor
First, remove the motherboard from the chassis. To remove the
processor from the motherboard, follow these steps:
1. Disconnect the fan power cable from the motherboard.
2. Push the CPU socket lever slightly to the side and then raise
it as far as it can go. You will feel a resistance as the
processor is freed from the socket.
3. Remove the processor.
Installing the CPU
Page 39

Hardware Installation
3.7. Installing System Memory
Maximum system memory supported by the motherboard is 2GB.
The motherboard has two DIMM Sockets. Memory can be installed
using 184-pin DDR SDRAM DIMM memory modules. These are no
jumper settings required for the memory size or type, which is
automatically detected by the BIOS.
You must use 2.5V DIMMs in the motherboard. To determine the
DIMM type, check the notches on the DIMMs.
Install the 184-pin DDR SDRAM modules in any combination as
follows:
Bank 0 (DIMM1) 64MB/128MB/512MB/1GB
Bank 1 (DIMM2) 64MB/128MB/512MB/1GB
Total System Memory 64MB ~ 2GB
Installing System Memory
31
Page 40

Mainboard User’s Manual
3.8. Setting Jumpers
Refer to the following illustration and instructions to set the jumpers
on your motherboard.
3.8.1. Clear CMOS Jumper (JP4)
You may need to clear the CMOS if your system cannot boot up
because you forgot your password, the CPU clock setup is incorrect,
or the CMOS setting need to reset to default values after the system
BIOS has been updated.
Refer to the following solutions to reset your CMOS setting:
32
Solution A
1. Power off the system and disconnect the power cable.
2. Place a shunt to short pin 2 and pin 3 of JP4 for five
seconds.
3. Place the shunt back to pin 1 and pin 2 of JP4.
4. Power on the system.
Setting Jumpers
Page 41

Hardware Installation
Solution B
If the CPU clock setup is incorrect, you may not be able to boot up .
In this case, follow these instructions:
1. Turn the system off, then on again. The CPU will
automatically boot up using standard parameters.
2. As the system boots, enter BIOS and set up the CPU clock.
Note:
If you are unable to enter BIOS setup, turn the system on
and off a few times.
Setting Jumpers
33
Page 42

4. BIOS Configuration
After the hardware configuration of the motherboard is finished, and the
system hardware has been assembled, the system may be powered up. At
this point, CMOS setup should be run to ensure that system information is
correct.
The motherboard employs the latest Award BIOS CMOS chip with support
for Windows Plug and Play. This CMOS chip contains the ROM Setup
instructions for configuring the motherboard’s BIOS. The BIOS (Basic
Input and Output System) Setup program is a menu driven utility that
enables you to make changes to the system configuration and tailor your
system to suit your individual work needs. It is a ROM-based configuration
utility that displays the system’s configuration status and provides you with
a tool to set system parameters. These parameters are stored in non-volatile
battery-backed-up CMOS RAM that saves this information even when the
power is turned off. When the system is turned back on, the system is
configured with the values found in CMOS.
Using easy-to-use pull down menus, you can configure such items as:
Hard drives, diskette drives, and peripherals
Video display type and display options
Password protection fr om una ut horized use
Power management features
The settings made in the Setup program intimately affect how the computer
performs. It is important, therefore, first to try to understand all the Setup’s
options, and second, to make settings appropriate for the way you use the
computer. This chapter provides clear explanations for all Setup options.
34
Page 43

BIOS Configuration
This program should be executed under the following conditions:
When changing the system configuration
When a configuration error is detected by the system and you
are prompted to make changes to the Setup program
When resetting the system clock
When setting the CPU clock speed so that it automatically
runs either fast or slow
When redefining the communication ports to prevent any con
flicts
When making changes to the Power Management
configuration
When changing the password or making other changes to the
security setup
Normally, CMOS setup is needed when the system hardware is not
consistent with the information contained in the CMOS RAM,
whenever the CMOS RAM has lost power, or the system features
need to be changed.
4.1. Entering Setup
When the system is powered on, the BIOS will enter the Power-On
Self Test (POST) routines. These routines perform various
diagnostic checks; if an error is encountered, the error will be
reported in one of two different wa ys:
1. If the error occurs before the display device is initialized, a
series of beeps will be transmitted.
2. If the error occurs after the display device is initialized, the
screen will display the error message.
After the POST routines are completed, the following message
appears:
Entering Setup
35
Page 44
Mainboard User’s Manual
“Press DEL to enter SETUP”
To access the AWARD BIOS SETUP program, press the <DEL> key
to display the “CMOS SETUP UTILITY” screen:
These screens provide access to the utility’s various functions.
Listed below are explanations of the keys displayed at the bottom of the
screen:
Key
Esc Escape key: Exits the current menu
+/-/PU/PD
F10 F10 key: Saves the current configuration and exits setup
F1 F1 key: Displays a screen that explains all key functions
F5 F5 key: Loads previously saved values to CMOS
F6 F6 key: Loads a minimum configuration for troubleshooting
F7 F7 key: Loads optimum set of values for peak performance
Function
Cursor keys: Scroll through the items on a menu
Plus, minus, Page Up and Page Down keys: Modify the
selected field’s values
36
Entering Setup
Page 45

BIOS Configuration
4.2. Standard CMOS Features
Standard CMOS Features is the same for all three chipsets. Selecting
“Standard CMOS Features” on the main program screen displays
the following menu:
The Standard CMOS Setup utility is similar for all three chipsets and
is used to configure the following features:
Date : Month, Day, Year
Time : Hour, Minute, and Second. Use 24 Hour clock format (for
PM numbers, add 12 to the hour, you would enter 4:30 p.m. As
16:30).
IDE Devices : Your computer has two IDE channels (Primary and
Secondary) and each channel can be installed with one or two
devices (Master and Slave). Use these items to configure each device
on the IDE channel. Press Enter to display the IDE sub-menu:
Standard CMOS Features
37
Page 46

Mainboard User’s Manual
IDE HDD Auto-Detection : Press <Enter> while this item is
highlighted if you want the Setup Utility to automatically detect and
configure a hard disk drive on the IDE channel.
If your system has an IDE hard drive, you can use this utility to
detect its parameters and enter them into the Standard CMOS Setup
automatically
If the auto-detected parameters displayed do not match the ones
that should be used for your hard drive, do not accept them. Press
the <N> key to reject the values and enter the correct ones manually
in the Standard CMOS Setup screen.
Note:
If you are setting up a new hard disk drive that supports LBA
mode, more than one line will appear in the parameter box.
Choose the line that lists LBA for an LBA drive.
Do not choose “Large” or “Normal” if the hard disk drive is already
fully formatted when you installed it. Select the mode that was used
to format it.
IDE Primary/Secondary Master/Slave : If you leave this item
at “Auto,” the system will automatically detect and configure any
IDE devices it finds. If it fails to find a hard disk, change the value to
“Manual” and then manually configure the drive by entering the
characteristics of the drive in the items below (Capacity, Cylinder,
Head, Precomp, etc.). Refer to your drive’s documentation or look
on the drive if you need to obtain this information. If no device is
installed, change the value to “None.”
Access Mode : This item defines some special ways that can be
used to access IDE hard disks such as LBA (Large Block
Addressing). Leave this value at “Auto” and the system will
automatically decide the fastest way to access the hard disk drive.
38
Standard CMOS Features
Page 47

BIOS Configuration
Press <Esc> to close the IDE device sub-menu and return to the
Standard CMOS Features page.
Drive A and Drive B :
BBPCHOME
doesn’t support FDD
Video : Set this field to the type of graphics card installed in your system.
If you are using a VGA or higher resolution card, choose the
“EGA/VGA” option. The options are:
MONO
CGA 40
CGA 80
EGA/VGA
Halt On : This setting determines which type of errors will cause the
system to halt during boot up. The options are:
All Errors
No Errors
All, But Keyboard
All, But Diskette
All, But Disk / Key”.
Base/Extended/Total Memory : These items are automatically
detected by the system at start up time. These are display-only fields.
You cannot make changes to these fields.
After you have made your selections in the Standard CMOS Setup
screen, press <ESC> to go back to the main screen.
Standard CMOS Features
39
Page 48

Mainboard User’s Manual
4.3. Advanced BIOS Features
Selecting “Advanced BIOS Features” on the main program screen
displays this menu, which allows you to define advanced information
about your system. You can make modifications to most of these
items without introducing fatal errors to your system. Note that the
page has a scroll-bar to scroll down to more items.
The following explains the options for each feature:
Virus Warning : When enabled, any attempt to write to the boot
sector or partition table will halt the system and cause a warning
message to appear. If this happens, you can use an anti-virus utility
on a virus free, bootable floppy diskette to reboot and clean your
system. The default setting is “Disabled”.
CPU L1 & L2 Cache : These settings enable the CPU internal (L1)
and external (L2) cache. Enabling these items provides better
performance. The default setting is “Enabled”.
Hyper-Threading Technology : Hyper Threading Technology
helps your PC work more efficiently by maximizing processor
resources and enabling a single processor to run two separate threads
of software simultaneously.
40
Advanced BIOS Features
Page 49

BIOS Configuration
Quick Power On Self Test : This will skip some diagnostic checks
during the Power On Self Test (POST) to speed up the booting
process. The default setting is “Enabled”.
First/Second/Third Boot Device : Use these three items to select
the priority and order of the devices that your system searches for an
operating system at start-up time. The default settings are “Floppy”,
“HDD-0”, or “LS120” respectively. If you want to boot up the
system from S_ATA then you should choose the “SCSI” option.
Boot Other Device : If you enable this item, the system will search
all other possible locations for an operating system if it fails to find
one in the devices specified under the First, Second, and Third boot
devices. The default setting is “Enabled”.
Swap Floppy Drive : If you have two floppy diskette drives in your
system, this item allows you to swap the assigned drive letters so that
drive A becomes drive B, and drive B becomes drive A. The default
setting is “Disabled”.
Boot Up Floppy Seek : If this item is enabled, it checks the
geometry of the floppy disk drives at start-up time. You don’t need
to enable this item unless you have an old diskette drive with 360K
capacity. The default setting is “Enabled”.
Boot Up Numlock Status : If set to “Off,” the cursor controls will
function on the numeric keypad. The default setting is “On”.
Gate A20 Option : This option accesses memory above 1 MB using
the fast gate A20 line when set to “Fast” (default). The other option
is “Normal.”
Advanced BIOS Features
41
Page 50

Mainboard User’s Manual
Typematic Rate Setting : If set to “Enabled,” enables you to set the
Typematic Rate and Typematic Delay. The default setting is
“Disabled”.
Typematic Rate (Chars/Sec) : This setting controls the
speed at which the system registers repeated keystrokes. The
choices range from 6 to 30 Chars/Sec. The default setting is
“6” Chars/Sec.
Typematic Delay (Msec) : This setting controls the time
between the display of the first and second characters. There
are four delay choices: 250ms, 500ms, 750ms and 1000ms.
The default setting is “250” ms.
Security Option : This setting controls the password feature. The
options are “Setup” and “System.” Selecting “Setup” will protect the
configuration settings from being tampered with. Select “System” if
you want to use the password feature every time the system boots up.
The default setting is “Setup.” You can create your password by
using the “SUPERVISOR/USER PASSWORD” utility in the main
program screen.
APIC Mode : Enables or disables APIC (Advanced Progra mmable
Interrupt Controller) mode. APIC provides symmetric
multiprocessing (SMP) for systems, allowing support for up to 60
processors.
MPS Version Control For OS : Selects the operating system
multiprocessor support version. The default setting is “1.4”.
OS Select For DRAM > 64MB : Set to “OS2” if the system
memory size is greater than 64 MB and the operating system is OS/2.
The default setting is “Non-OS2”.
42
Advanced BIOS Features
Page 51

BIOS Configuration
Report No FDD For WIN 95 : If you are running a system with no
floppy drive and using the Windows 95 OS, select Yes for this it em
to ensure compatibility with the Windows 95 logo certification.
The default setting is “Yes.”
Small Logo (EPA) Show : Enables and disables the EPA logo when
booting up. The default setting is “Enabled”.
After you have made your selections in the BIOS Features Setup
screen, press <ESC> to go back to the main screen.
Advanced BIOS Features
43
Page 52

Mainboard User’s Manual
4.4. Advanced Chipset Features
Selecting “Advanced Chipset Features” on the main program
screen displays this menu:
This option displays a table of items that define critical timing
parameters of the motherboard. You should leave the items on this
page at their default values unless you are very familiar with the
technical specification of your system hardware. If you change the
values incorrectly, you may introduce fatal errors or recurring
instability into your system.
DRAM Timing Selectable : Enables you to set the DRAM timing
manually, or automatically using SPD (Serial Presence Detect). SPD
is an EEPROM chip on the memory module that stores information
about the memory chips it contains, including size, speed, voltage,
row and column addresses, and manufacturer. We recommend setting
this field to By SPD.
CAS Latency Time : This item enables you to optimize the speed at
which data is accessed in a column by defining CAS latency time.
The CAS latency defines the time delay (in CLKs) before SDRAM
starts a read command after receiving it. Because reading data in a
row is twice as fast, reducing this number can increase performance
at the expense of stability. We recommend that you leave this item at
the default value. The default setting is “1.5”.
44
Advanced Chipset Features
Page 53

BIOS Configuration
Active to Precharge Delay : This item enables you to set the
number of DRAM clocks for TRAS. TRAS indicates the time
required for the memory to restore data and come to a full charge.
The default setting is “7”.
DRAM RAS# to CAS# Delay : Enables you to select the RAS to
CAS delay time in HCLKs of 2/2 or 3/3. The value is set at the
factory depending on the DRAM installed. Do not change the values
in this field unless you have changed the specifications of the
installed DRAM or the installed CPU. The default setting is “3”.
DRAM RAS# Precharge : DRAM must continually be refreshed or
it will lose its data. Normally, DRAM is refreshed entirely as the
result of a single request. This option allows you to determine the
number of CPU clocks allocated for the Row Address Strobe (RAS)
to accumulate its charge before the DRAM is refreshed. If
insufficient time is allowed, refresh may be incomplete and data lost.
The default setting is “3”.
Turbo Mode : Enable you to set the system to enter “ Turbo” mode.
The default is “Disabled”.
Memory Frequency For : Enables you to set the memory frequency
for the installed memory. Select “Auto” (default) to enable the
system to set the memory frequency automatically according to the
installed DRAM. The other options are “PC100”, or “PC133”.
System/ Video BIOS Cacheable : When set to “Enabled”, the
System and Video BIOS will be cached for faster execution. The
default setting is “Enabled”.
Advanced Chipset Features
45
Page 54

Mainboard User’s Manual
Memory Hole At 15M-16M : If Set to “Enabled”, when the system
memory size is equal to or greater than 16M bytes, the physical
memory address from 15M to 16M will be passed to PCI or ISA and
there will be a 1 MB hole in your system memory. This option is
designed for some OS with special add-in cards which need 15-16
MB memory space. The default setting is “Disabled”.
Delayed T ransacti on : The chipset has an embedded 32-bit posted
write buffer to support delayed transactions cycles. Select Enabled to
support compliance with PCI specification version 2.1. The default
setting is “ Enabled”.
Delay Prior to Thermal : This item allows you to select the delay
time to enable the Pentium 4 CPU Thermal feature. Enable this
feature when using Windows NT 4.0 to prevent the syst em from
hanging. The default setting is “ 16Min”, and other options are
“4Min”, “8Min”, or “32Min”.
AGP Aperture Size <MB> : This option determines the effective
size of the AGP Graphic Aperture, where memory-mapped graphic
data structures are located. The default setting is “ 64”, and other
options are “4”, “8”, “16”, “32”, “128”, or “256”.
** On-Chip VGA Setting **
On-Chip VGA : The item allows you to Enable/Disable the VGA
onboard.
On-Chip VGA Frame Buffer Size : This item allows you to control
the VGA Frame Buffer size. The default setting is “8M”.
After you have made your selections in the Standard CMOS Setup
screen, press <ESC> to go back to the main screen.
46
Advanced Chipset Features
Page 55

BIOS Configuration
4.5. Integrated Peripherals
Selecting “Integrated Peripherals” on the main program screen
displays field.
On-Chip Primary/ Secondary PCI IDE :
disable the primary and secondary onboard IDE controllers. The
default setting is “Enabled.”
IDE Primary/Secondary Master/Slave PIO : Each IDE channel
supports a master device and a salve device. These four items let you
assign which kind of PIO (Programmed Input/Output) is used by
IDE devices. Choose select a PIO mode from 0-4.
IDE Primary/Secondary Master/Slave UDMA : Each IDE channel
supports a master device and a salve device. This motherboard
supports Ultra DMA technology, which provides faster access to
IDE devices.
If you install a device that support Ultra DMA, change the
appropriate item on this list to “Auto”. You may have to install the
Ultra DMA driver supplied with this motherboard in order to use an
Ultra DMA device.
These options enable or
Integrated Peripherals
47
Page 56

Mainboard User’s Manual
USB Controller : Enables the USB controller. Leave this at the
default “Enabled” if you want to connect USB devices to your
computer.
USB2.0 Controller : Enables this item if you want to use the
USB2.0 faction.
USB Keyboard Support : Enables USB keyboard support for leg acy
operating systems. The default setting is “Disabled”.
USB Mouse Support : Enabled this function when a USB mouse is
used. Set to “Disabled” (default) when a PS/2 mouse is being used.
AC97 Audio : Set these items to “Auto” when you are using the
on-board AC’97 audio chip. If you are using an audio add-in card,
you should disable this item.
Init Display First : Use this item to specify whether your graphics
adapter is installed in one of the PCI slots or is integrated on the
motherboard.
IDE HDD Block Mode : Enable this field if your IDE hard drive
supports block mode. Block mode enables BIOS to automatically
detect the optimal number of block reads and writes per sector that
the drive can support and improve the speed of access to IDE
devices.
POWER ON Function : Enables you to set keyboard or mouse
events, or a password to power on the computer. When set to
“Password,” you must key in your password before pressing any
keyboard key to start the computer. The password is set in the “KB
Power ON Password” field.
48
Integrated Peripherals
Page 57

BIOS Configuration
If you set this field to “Hot KEY,” you can press a hot key
combination to power on the computer. The hot key is set in the “Hot
Key Power ON” field. Options are:
BUTTON ONLY (default)
Keyboard 98
Password
Hot KEY
Mouse Left
Mouse Right
Any KEY
KB Power ON Password : This field becomes available when you
select “Password” in the POWER ON Function field. Select this field
and press ENTER. You are prompted to input a password. Type in
your password and press ENTER. You are prompted to confirm your
password. Retype your password and press ENTER. Your pa ssword
is saved. The next time you power on your computer, you must type
in your password before you can power the computer on. After you
type your password, press any key or the power button.
Hot Key Power ON : This field becomes available when you select
“Hot Key” in the POWER ON Function field. Options for this field
are “Ctrl-F1” ~ ”Ctrl-F12.”
Onboard Serial Port 1 : This option is used to assign the I/O
address and address and interrupt request (IRQ) for onboard serial
port 1 (COM1).
Onboard Serial Port 2 ( optional ) : This option is used to assign
the I/O address and address and interrupt request (IRQ) for onboar d
serial port 2 (COM2).
UART Mode Select : This field is available if the Onboard Serial
Port 2 field is set to any option but Disabled. UART Mode Select
enables you to select the infrared communication protocol-Normal
Integrated Peripherals
49
Page 58

Mainboard User’s Manual
(default), IrDA, or ASKIR. IrDA is an infrared communication
protocol with a maximum baud rate up to 115.2K bps. ASKIR is
Sharp’s infrared communication protocol with a maximum baud rate
up to 57.6K bps.
RxD , TxD Active : Define the voltage level for Infrared module
RxD(receive) mode and TxD(transmit) mode. This setting has to
match the requirements of the infrared module used in the system.
The options are:
Hi, Lo (default)
Lo, Hi
Lo, Lo
Hi, Hi
IR Transmission Delay : When set to “Enabled”(default), utilizes
the capability of the motherboard to allow faster infrared
transmission rates. The options are “Enabled” and “Disabled”
UR2 Duplex Mode : This field is available when UART 2 Mode
Selects is set to either ASKIR or IrDA. This item enables you to
determine the infrared (IR) function of the onboard infrared chip.
The option are “Full” and “Halt” (default).Full-duplex means that
you can transmit and send information simultaneously. Half-duplex
is the transmission of data in both directions , but onl y one direction
at a time.
Use IR Pins : Use this item to set the IR pins. The options are
“IR-Rx2Tx2”(default) and “RxD2, TxD2”.
Onboard Parallel Port : This option is used to assign the I/O
address for the onboard parallel port. The options are:
378 / IRQ7 (default)
278 / IRQ5
3BC / IRQ7
Disabled (disables the onboard parallel port).
Parallel Port Mode : There are four options: “SPP” (Standard
Parallel Port), “EPP” (Enhanced Parallel Port), “ECP” (Extended
Capabilities Port) and “ECP+EPP” and “Normal”. Change the mode
50
Integrated Peripherals
Page 59

BIOS Configuration
from “SPP”(default) to the enhanced mode only if your peripheral
device can support it.
EPP Mode Select : Sets the EPP specification. There are two option
“EPP1.7”(default) and “EPP1.9”.
ECP Mode Use DMA : When the onboard parallel port is set to
ECP mode, the parallel port can use DMA “3” or DMA “1”.
Game Port Address : Enables you to specify the I/O address of the
game port. Options are “Disabled”,”201”(default), and “209”.
Midi Port Address : Enables you to specify the I/O address of the
MIDI port. Options are “Disabled”,”330”(default), and “300” and
“290”.
Midi Port IRQ : Enables you to specify the IRQ address of the
MIDI port if installed. Option are “5” and “10”(default).
After you have mode your selections in the BIOS Features Setup
screen, press <ESC> to go back to the main screen.
Integrated Peripherals
51
Page 60

Mainboard User’s Manual
ff by
4.6. Power Management Setup
This option lets you control system power management. The system
has various power-saving modes including p owe ri n g d ow n the har d
disk, turning off the video, suspending to RAM, and software power
down that allows the system to be automatically resumed by certain
events.
ACPI Function : When set to “Enabled”, turns on the ACPI
Function . The default setting is “Disabled”.
Note:
ACPI (Advanced Configuration and Power Interface)
is a power management specification that makes
hardware status information available to the
operating system. ACPI enables a PC to turn its
peripherals on and off for improved power
management. It also allows the PC to be turned on
and o
activity wakes up the computer.
external devices, so that mouse or keyboard
52
Power Management Setup
Page 61

BIOS Configuration
ACPI Suspend Type : Use this item to define how your system
suspends. If set to S1(POS) (default), the suspend mode is equivalent
to a software power down. If set to S3(STR), the suspend mode is a
suspend to RAM the system shuts down with the exception of a
refresh current to the system memory.
Run VGABIOS if S3 Resume : The options are “Auto”,
“Yes”, “No”. This item sets to run VGA BIOS when S3
Resume.
Power Management : This item acts like a master switch for the
power-saving modes and hard disk timeouts. If this item is set to Max
Saving, power-saving modes occur after a short timeout. If this item
is set to Min Saving, power-saving modes occur after a longer
time-out. If the item is set to User Define, you can insert your own
timeouts for the power-saving modes. There are four options:
User Define: allows you to customize all power saving timer
features
Max Saving: recommended setting for general use
Min Saving: sets power saving at minimum values
Video Off Method : This setting controls the video off method in
power saving mode. The setting “V/H SYNC+Blank” disables V/H
SYNC signals and blanks the screen. Other options are “DPMS” and
“Blank Screen.” The “DPMS” option allows the BIOS to control the
video card if it has the DPMS (Display Power Management System)
feature. The “Blank Screen” option is used when you do not have a
“Green” monitor.
Video Off In Suspend : Set this to “Yes ” (default) if you want the
Video display to turn off during suspend mode.
Suspend Type : Enables you to select the Suspend type. Options are
“Stop Grant” (default) and “PwrOn Suspend.”
Power Management Setup
53
Page 62

Mainboard User’s Manual
MODEM Use IRQ : If you want an incoming call on a modem to
automatically resume the system from a power-saving mode, use this
item to specify the interrupt request line (IRQ) that is used by the
modem. You might have to connect the fax/modem to the
motherboard Wake On Modem connector for this feature to work
Suspend Mode : The CPU clock will be stopped and the video
signal will be suspended if no Power Management events occur for a
specified length of time. Full power function will return when a
Power Management event is detected. Options are from “1 Min” to
“1 Hour” and “Disable.” The default is “Disable.”
HDD Power Down : The IDE hard drive will spin down if it is not
accessed within a specified length of time. Options are from 1 Min to
15 Min and Disable.
Soft-Off by PWR-BTTN : When set to “Instant-Off” (default),
pressing the power button will turn off the system power. When set
to “Delay 4 Sec.” you have to press the power button and hold it for
more than 4 seconds to turn off the system power. Otherwise, the
system just goes into suspend mode. The options are “Instant-Off”
and “Delay 4 Sec”.
CPU THRM-Throttling : This item sets the percentage of time that
the CPU is idled if CPU throttling is initiated by excess heat. The
options are:
z 50.0% (default)
z 37.5%
z 25.0%
z 12.5%
z 87.5%
z 75.0%
z 62.5%
54
Power Management Setup
Page 63

BIOS Configuration
Wake-Up by PCI card : This setting enables/disables PCI card
wakeup for PCI spec2.2. The default is “Enabled.”
Power On by Ring : When set to “Enabled,” any activity on the
Modem port will wake up the system from a power saving mode. The
options are “Disabled” and “Enabled” (default).
Wake Up On LAN : When set to “Enabled”, the system power will
be turned on if the LAN port receives an incoming signal. Default
setting is “Enabled.”
USB KB Wake-Up F rom S3 : Use this item to enable USB
activity to wakeup the system from a power saving mode.
The default setting is “Disabled.”
Resume By Alarm : When set to “Enabled,” you may set the date
(day of the month), hour, minute and second to turn on your system.
When set to set “0” (zero) for the day of the month, the alarm will
power on your system every day at the specified time. The default
setting is “Disabled.”
Date <of Month> Alarm :
Time <hh:mm:ss> Alarm :
**Reload Global Timer Events**
Global Timer (power management) events are I/O events whose
occurrence can prevent the system from entering a power saving
mode or can awaken the system from such a mode. In effect, the
system remains alert for anything that occurs to a device that is
configured as Enabled, even when the system is in a power down
mode.
Power Management Setup
55
Page 64

Mainboard User’s Manual
Primary/Secondary IDE 0/1: When enabled, any activity on the
primary or secondary IDE channels will wake up the system from a
power saving mode.
FDD, COM, LPT Port: When enabled, any activity on the floppy
disk drive (FDD), serial ports (COM), or parallel ports (LPT) will
wake up the system from a power saving mode.
PCI PIRQ[A-D]#: When enabled, any activity on the PCI card
channels will wake up the system from a power saving mode.
Press <ESC> to return to the main menu.
.
56
Power Management Setup
Page 65

4.7. PnP/PCI Configuration
This option displays a table of items that configures how PnP (Plug
and Play) and PCI expansion cards operate in your in your system.
Both the ISA and PCI buses on the Motherboard use system IRQs
(Interrupt Requests) and DMAs (Direct Memory Access). You must
set up the IRQ and DMA assignments correctly through the PnP/PCI
Configurations Setup utility; otherwise, the motherboard will not
properly.
Selecting PnP/PCI Configurations on the main program screen
displays this menu:
BIOS Configuration
Reset Configuration Data : The system BIOS supports the Plug
and Play feature so the resources assigned to each peripheral have to
be recorded to prevent them from conflicting. The location to store
the assigned resources is called ESCD (Extended System
Configuration Data) which is located in the system flash EEPROM.
If this option is set to “Disabled,” the ESCD will update
automatically when the new configuration varies from the last one.
If set to “Enable,” the ESCD will be cleared and updated and then
this option will automatically be set to “Disabled.”
PnP/PCI Configuration
57
Page 66

Mainboard User’s Manual
Resources Controlled By : The setting “Manual” allows you to
control IRQs and DMAs individually. The other option is “Auto”
which will detect the system resources and automatically assign the
relative IRQs and DMAs for each peripheral.
IRQ Resources : The submenu allows you to individually
assign an interrupt type for interrupts IRQ3 to IRQ15.
PCI/VGA Palette Sn oo p : This item is designed to overcome
problems that can be caused by some non-standard VGA cards.
This board includes a built-in VGA system that does not require
palette snooping so you must leave this item disabled.
After you have made your selections in the PC Health Status Setup,
press <Esc> to go back to the main program screen.
58
PnP/PCI Configuration
Page 67
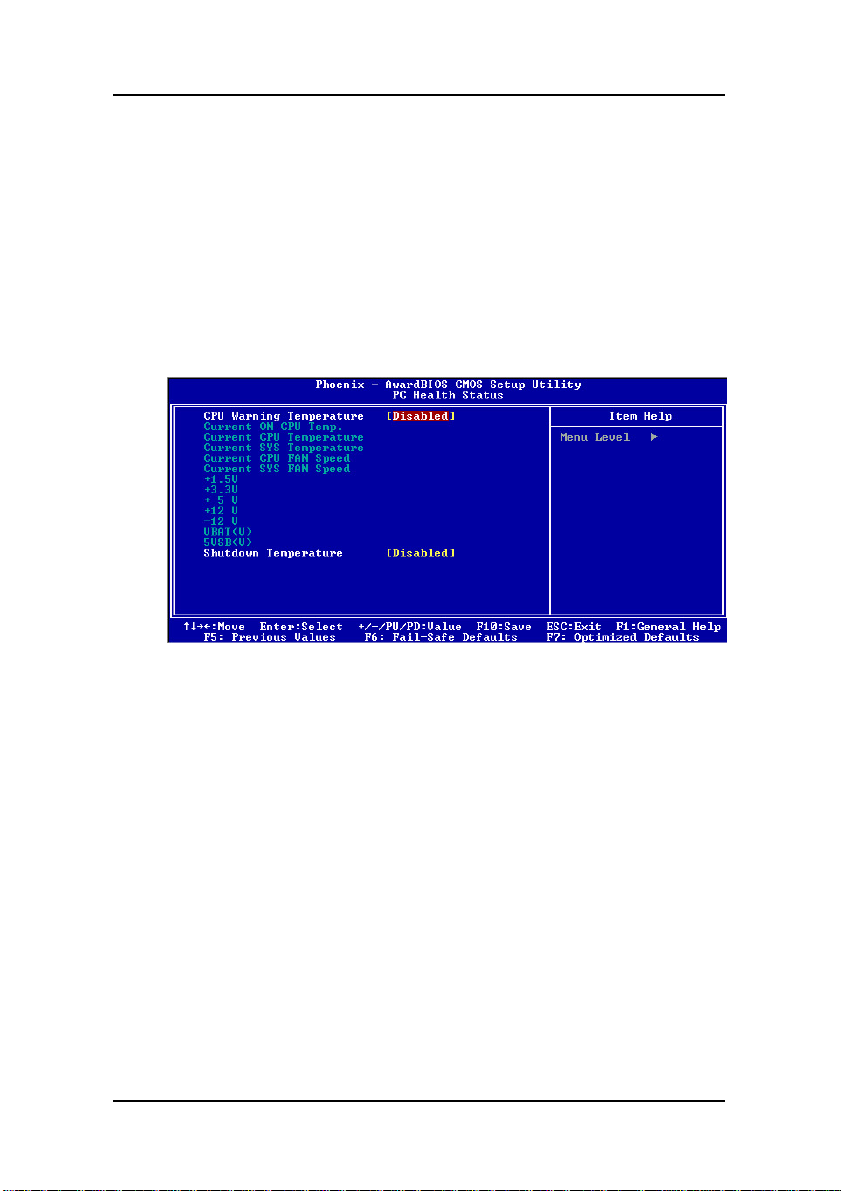
4.8. PC Health Status
On motherboards the support hardware monitoring, this item lets
you monitor the parameters for critical voltages, critical
temperatures and fan speeds:
Selecting “PC Health Status” on the main program screen displays
this menu:
BIOS Configuration
CPU Warning Temperature : This feature enables you to set the
warning temperature for CPU overheating. When the CPU
temperature exceeds the set temperature, the PC speaker will beep.
The beep sound will not turn off unless you power down the
computer and allow your CPU to cool down.
System Component Characteristics: These fields provide you with
information about the systems current operating status. You cannot
make changes to these fields. The following information is
displayed:
• Current ON CPU T e mp.
• Current CPU Temperature
• Current SYS T em perature
• Current CPU FAN Speed
PC Health Status
59
Page 68

Mainboard User’s Manual
• Current SYS FAN Speed
• 1.5V
• + 3.3V
• + 5V
• +12V
• -12V
• VBAT(V)
• 5VSB(V)
Shutdown Temperature : Enables you to set the maximum
temperature the system can reach before powering down.
After you have made your selections in the PC Health Status Setup,
press <Esc> to go back to the main program screen.
60
PC Health Status
Page 69

BIOS Configuration
4.9. Frequency/Voltage Control
This item enables you to set the clock speed ad system bus for your
system. The clock speed ad system bus is determined by the kind of
processor you have installed in your system.
CPU Clock Ratio : Use this item to select a multiplier for the
system front side bus (FSB) frequency. Th e value of the multiplier
must be set so that: Multiplier x Front side Bus Frequency = CPU
Clock Speed.
For example, if you have a processor that is rated to run at 450 MHz
and the system in running a front side bus frequency of 100 M Hz,
you should select a multiplier of 4.5 so that:
4.5 (Multiplier) x 100 MHz (front side bus) = 450 MHz (CPU clock)
Auto Detect PCI Clk : When this item is enabled, BIOS will
disable the clock signal of free DIMM and PCI slots.
Spread Spectrum : If you enable spread spectrum, it can
significantly reduce the EMI (Electro-Magnetic Interference)
generated by the system.
Frequency/Voltage Control
61
Page 70

Mainboard User’s Manual
CPU Clock : This item can be used to set the system bus frequency
for installed processor. The value for this field range for 100MHz to
165MHz
After you have made your selections in the Frequency / Voltage
Control Setup, press the <Esc> to return to the previous screen.
62
Frequency/Voltage Control
Page 71

BIOS Configuration
4.10. Load Fail-Safe Defaults Option
This option opens a dialog box that lets you install fail-safe
defaults for all appropriate items in the Setup Utility:
Press <Y> and then <Enter> to install the defaults. Press <N> and
then <Enter> to not install the defaults. The fail-safe defaults
place no great demands on the system and are generally stable. If
your system is not functioning correctly, try installing the fail-safe
defaults as a first step in getting your system working properly
again. If you only want to install fail-safe defaults for a specific
option, select and display that option, and then press <F6>.
4.11. Load Optimized Defaults
This option opens a dialog box that lets you install optimized
defaults for all appropriate items in the Setup Utility. Press <Y>
and then <Enter> to install the defaults. Press <N> and then
<Enter> to not install the defaults. The optimized defaults place
demands on the system that may be greater than the performance
level of the components, such as the CPU and the memory. You
can cause fatal errors or instability if you install the optimized
defaults when your hardware does not support them. If you only
want to install setup defaults for a specific option, select and
display that option, and then press <F7>.
4.12. Set Supervisor/User Passwords
The “Supervisor/User Password” utility sets the password.
The motherboard is shipped with the password disabled. If you
want to change the password, you must first enter the current
password, then at the prompt enter your new password. The
password is case sensitive. You can use up to eight alphanumeric
characters.
Load Fail-Safe Defaults Option
63
Page 72

Mainboard User’s Manual
p
p
Press <Enter> after entering the password. At the next prompt,
confirm the new password by retyping it and pressing <Enter>
again.
To disable the password, press <Enter> instead of entering a new
password when the “Enter Password” dialog box appears. A
message appears confirming that the password has been disabled.
If you have set supervisor and user passwords, only the supervisor
password allows you to enter the BIOS Setup Program.
Note:
If you forget your password, the only way to solve this
roblem is to discharge the CMOS memory by turning
power off and placing a shunt on jumper JP12 to
short
shunt back to pin 1 and pin 2 of JP12.
in 2 and pin 3 for five seconds, then putting the
4.13. Save & Exit Setup Option
Selecting this option and pressing <Enter> will save the new
setting information in the CMOS memory and continue with the
booting process.
4.14. Exit Without Saving
Selecting this option and pressing <Enter> will exit the Setup
Utility without recording any new values or changing old ones.
Thi s c o n c l u d e s C h a p t e r 4 . C h a p t e r 5 describes the drivers and utility
programs that are packaged with the motherboard.
64
Load Fail-Safe Defaults Optionl
Page 73

5. Driver and Utility
5.1 Flash Utility
The BIOS of the
using a Flash utility. A new version of the BIOS can be downloaded
from the factory’s BBS and Web site. The system BIOS is stored in a
4 M-bit Flash EEPROM that can be erased and reprogrammed by the
Flash utility.
The Flash utility will not work with any memory manager software
running in the system. In order to make sure no memory manager
software is running, boot your system from a bootable floppy diskette
which does not contain CONFIG.SYS and AUTOEXE.BAT files. If
you are using MS-DOS 6.x, you can press the <F5> function key
when the “Starting MS-DOS.” Message appears on the screen to by
pass the CONFIG.SYS and AUTOEXEC.BAT.
BBPCHOME
motherboard can be upgraded by
65
Page 74

Mainboard User’s Manual
5.2. CD Driver Overview
The motherboard has drivers and utilities designed for the Intel
845GV chipset. You can install AGP, IRQ, ACPI and IDE drivers
together from the manufacturer support CD.
BBPCHOME CD
The
1. Install Motherboard Software ( Intel Chip set software
installation utility )
2. Install Motherboard Software ( Intel Graphic )
3. Install IDE Busmaster driver ( IAA )
4. Install Audio Device Software ( Sound )
5. Install LAN Device ( LAN , RTL8139 family )
6. Install Intel USB2.0 driver ( Intel USB2.0 )
Introduction to products feature
Click the links to install the listed software.
You can also browse the CD and install the software manually
from Windows Explorer We recommend that you install all of
the supplied software and drivers item for maximum
performance.
include :
66
5.2.1. Intel chipset software installation utility
This folder has chipset 845 chip set INF drivers for WIN 95 / 98 /
ME / NT / 2000 / XP.
The Installation Steps:
1. Insert the manufacturer CD-ROM into your CD-ROM drive.
2. Click to the folder for Driver Install.
3. Follow the instructions on the screen to complete the
installation. After setup is completed, you need to restart the
computer.
CD Driver Overview
Page 75

5.2.2 . Intel chipset 845 Busmater IDE driver
The IAA folder has chipset 845 Busmater IDE drivers for WIN
95 / 98 / ME / NT / 2000 / XP.
The Installation Steps:
1. Insert the manufacturer CD-ROM into your PC CD-ROM
drive.
2. Click this folder for IDE bus master Driver Install.
3. Follow the instructions on the screen to complete the
installation. After setup is completed, you need to restart the
computer.
CD Driver Overview
67
Page 76

Mainboard User’s Manual
5.2.3. ALC650 Audio Driver
Software and drivers are provided for the AC97 codec ALC650
sound system that is integrated on this motherboard. The
ALC650 codec allows the system to generate optimal sound
effects. Drivers are provided for Windows 95 / 98 / ME / NT /
2000 / XP.
The manual Installation Steps:
1. Insert the manufacturer CD-ROM into your PC CD-ROM
drive.
2. Click to the folder sound for the Driver Installation.
3. Follow the instructions on the screen to complete the
installation. After setup is completed, you need to restart the
computer.
5.2.4. LAN Driver
Software and drivers are provided for the Realtek RTL8100
controller that is integrated on this motherboard. The Realtek
RTL8100 controller allows the system to transmit effects.
Drivers are provided for Windows WIN 95 / 98 / ME / NT / 2000
/ XP.
The installation Steps:
1. Insert the manufacturer CD-ROM into your PC CD-ROM
drive.
2. Click to the folder LAN for Driver Installation.
3. Select the folder LAN\RTL8139 Family for WIN95 / 98 /
ME / NT / 2000 / XP to start the installation.
68
CD Driver Overview
Page 77

 Loading...
Loading...