Page 1

Overview
CHAPTER
2
Provisioning
The Provisioning Management chapter of the Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager
(Cisco VoIP: Infrastructure Manager) Solution is the second chapter in a four chapter Cisco VoIP:
Infrastructure Manager Solution document. Provisioning management, in the context of this Solution,
deals with the provisioning of network elements and the management of those configuration files. This
guide details the network architecture, provisioning management applications, configuration file
management applications, and the deployment strategies surrounding Cisco's Configuration
Management Solution.
Cisco employs adistributed model for its service provider, Voice overIP (VoIP) product suite. Although,
at a certain level, each deployed device requires a unique instance of an Element Management System
(EMS) to provide upstream information pertaining to fault, performance, and provisioning, it is
incumbent upon the Network Management System (NMS) to appear as a virtual entity that hides the
individual element complexity.
A complete NMS Solution adheres to the Fault, Configuration, Accounting, Performance and Security
(FCAPS) model. The solution covered in this document finds its place in the Configuration portion of
the FCAPS model. It is a component chapter in the Cisco VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Solution and
deals specifically with configuration and provisioning management. It is intended to be referenced in
conjunction with the companion chapters dealing with performance and fault management.
Description
OL-2706-01
This chapter is a collection of published material, all available on Cisco Connection Online (CCO). All
the specifics of importance in this document can be found in one or more of the documents listed in the
“Related Documents” section. Each URL listed in the “Related Documents” section points to
documentation for a particularapplication orpair ofapplications and is complete in its own right for that
application. This guide pulls together the information available for all of the provisioning applications
of importance to the Cisco VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Solution.
For all of the applications or functionality detailed in this guide, there is a comprehensive set of
documents available on CCO. The “Related Documents” section is a to guide to finding them.
Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Implementation Guide
2-1
Page 2

Overview
Target Market
The applications and devices described in this document are positioned for service providerscale, VoIP
networks. Although many ofthe applications can be deployedin enterprises andsmaller scale networks,
the solution suite referred to in this Solution guide is aimed at the large carriers and providers of VoIP
network bandwidth and services. It also concentrates on the devices deployed in a VoIP network,
although non-VoIP devices integral to the VoIP network must also be taken into account.
Scope of the Solution
The provisioning component of the Cisco VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Solution provides the
applications and network level visibility required to manage the distributed telephony architectures
detailed in the next sections.
The Cisco Packet Telephony Center application operates at the Network Management Layer (NML) of
the Telecommunications Management Network (TMN) hierarchy. Its most important function is the
realization of a virtual entity view, hiding much of the internal complexity of the OPT network detailed
in the“Solution Architecture”section. The Cisco Voice RoutingCenter (CiscoVRC) application is used
to help service providers manage dial plans for H.323 based VoIP networks. Cisco VRC can be applied
to existing networks with working dial plans and can also be used to design new dial plans for the set of
gateways, gatekeepers, and directory gatekeepers.
The Cisco CNS Intelligence Engine 2100 Series (Cisco CNS IE2100 Series) is a network management
device that acts as a configuration service for automating the deployment and management of network
devices and services.
The Cisco MGC Node Manager (CMNM) provides an element management system for the PSTN
Gateway (PGW 2200). CMNM provides alarm processing and performance data collection that can be
displayed in a self contained Graphical User Interface (GUI) or forwarded to upstream processing
applications.
The provisioning component of the CMNM comprises two applications:
• Voice Services Provisioning Tool (VSPT)
• CiscoView.
VSPT is used as a provisioning service for the PGW 2200. VSPT communicates in Man Machine
Language (MML) to the PGW 2200, to configure point codes, link sets and SS7 paths and routes
CiscoView displays and monitors, and provides a GUI for chassis configuration for the Cisco SLT
(c2600 series) and LAN switch (Cisco Catalyst 2900, 5500 and 6509) devices.
Chapter 2 Provisioning
Document Purpose
A large collection of documentation, referenced in the “Related Documents” section, covering the
descriptions, installation,and preliminary setup of theapplications and components of thisProvisioning
Management Solution.The purposeof this chapter is todescribe a basic network containing the network
elements that are covered by these applications, install the management applications that comprise the
provisioning application set of the Internet OSS (IOSS) for packet voice networks, complete initial
configuration of those applications, and then use them to provision a sample network.
For detailed, in-depth information on installation and configuration of the individual applications, refer
to the documentation listed in the “Related Documents” section, that is available on Cisco Connection
Online. This chapter attempts to serve as a quick start guide to help you understand the entire
Provisioning Solution and how it fits into the overall Cisco VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Solution.
Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Implementation Guide
2-2
OL-2706-01
Page 3

Chapter 2 Provisioning
Solution Architecture
Open Packet Telephony Overview
As an introduction to the Cisco VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Solution’s provisioning component
applications and devices, the following overview of the emerging technology of distributed packet
telephony is presented.
Telephony is no longer solely the domain of Public Switched Telephone Networks (PSTNs). Software
and protocols that allow telephone calls over packet networks, such as the Internet, have entered the
market place. They are based on:
• the Media Gateway Control Protocol (MGCP) and related protocols such as the Simple Gateway
Control Protocol (SGCP) and Megaco/H.248
• the Session Initiation Protocol (SIP)
• H.323.
This discussion focuses on MGCP and H.323, which are both supported by the Cisco Packet Telephony
Center and the entire provisioning suite of applications in the Internet OSS for packet based voice
networks.
Solution Architecture
Examples of Open Packet Telephony Networks
Figure 2-1 depicts an example of an MGCP-based OPT network. (In this discussion, there is no need to
distinguish further between the different MGCP derivatives, Megaco, H.248, and SGCP.) The bearer
plane is responsible for the transport of the actual payload. Network elements within the bearer plane
need not be concerned with the specifics of telephony applications. Switches or routers between media
gateways at the edge of the OPT network provide for the actual bearer fabric (the data cloud), shuffling
data packets back and forth. The control plane is responsible for signaling processing and call control;
it is here that the actual call-processing intelligence resides. The components in the control plane are
commonly referred to as Media Gateway Controllers (MGCs). MGCs control media gateways by
instructing them when to set up or tear down connections, requesting notification of specific events for
further processing, and so on. They contain all the logic required for telephony applications, including
Signaling System 7 (SS7) signaling termination, collection of accounting information, and, very
importantly, directory functions and call-level routing based on dial plans. In terms of numbers of
devices, there tend tobe much fewer MGCs than media gateways, meaningthat call intelligence is fairly
centralized.
OL-2706-01
Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Implementation Guide
2-3
Page 4

Solution Architecture
Figure 2-1 MGCP Packet Voice Network
Media Gateway Controller (MGC)
MGC
VoP network
Circuit
Core/TDM
Class 4
Signaling and control
IP
network
SS7
STP STP
network
Chapter 2 Provisioning
Call control
MGCP, H. 248,
Megaco, SCTP,
signaling
backhaul,....
V
Media
PBX
Gateway
Figure 2-2 depicts an H.323-based network for Voice Infrastructure and Applications (VIA) Solution.
Similar to the MGCP network, gateways are at the edge of the network, with routers between them
providing for the bearer fabric that shuffles the payload back and forth. In H.323, unlike in MGCP, call
intelligence and the ability to process signaling does reside in the H.323 gateways. Intelligence is,
therefore, much more distributed, compared with MGCP-based networks. However, call processing is
still distributed between gateways and gatekeepers. Gatekeepers are able to make call-level routing
decisions based on dial plans.
In addition, gatekeeper hierarchies can be deployed, reflecting dial-plan hierarchies, with directory
gatekeepers on top of gatekeepers. Likewise, gatekeepers can be supported by route servers in their
decisions. If required, SS7 capabilities are provided through signaling converters that mediate and back
haul the signaling information between the gateway and the SS7 Signal Transfer Point.
Figure 2-2 H.323 Based Packet Voice Network
IP, PNNI, ...
Media
Gateway
Bearer
V
V
PBX
84405
CPE
Ingress
ITSP
STP
Ingress/Egress
SS7 TDM
carrier
Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Implementation Guide
2-4
GK
Ingress DGK
Ingress DGK
V
V
V
Prompts RADIUS
VV
GK GK
GK
GK
V
GK
Egress DGK
Egress DGK
Egress
TDM
carrier
Egress
ITSP
Egress
ASP
84408
OL-2706-01
Page 5
Chapter 2 Provisioning
Virtual Entities in the Network
The requirements for coordinated element management are extensive. For instance, the media gateway
and MGC must be synchronized regarding the voice endpoints. Although the MGC has a concept of a
trunk, this concept is unknown to the media gateway that has the actual resources (TDM endpoints,
ports) that constitute the trunk.Therefore, theknowledge that boththe mediagateway and theMGC have
of the trunk must be managed in a coordinated way. Registration and synchronization of capabilities
must be assured. Beyond element management, failuresin voice service, observed at the MGC, must be
correlated with failures in the bearer network. Resources used at the media gateway and controlled by
the MGC must be associated with voice service, which the media gateway has no concept of.
Users require support for such management coordination. Components in the bearer and control planes
operate in conjunction to perform the function of a switch, as far as voice service is concerned.
Usually an MGC and a set of media gatewaysare clearlyassociated withone anotherand jointlyperform
the same function as a TDM switch, thus forming a virtual switch. This raises the expectation that this
virtual switch can, in fact, be managed as a switch, with a management system shielding many of the
aspects of the distribution of this virtual entity from users. This way, users do not have to be concerned
with the peculiarities of setting up control communications between the devices (interfaces that used to
be closed); for example, MGCP and signaling back haul, with the coordination of the configuration of
endpoints on the media gateway and of trunks that refer to those end points on the MGC and that now
collectively simply form virtual trunks of the virtual switch, and so on. Figure 2-3 depicts the concept
of a virtual switch.
Solution Architecture
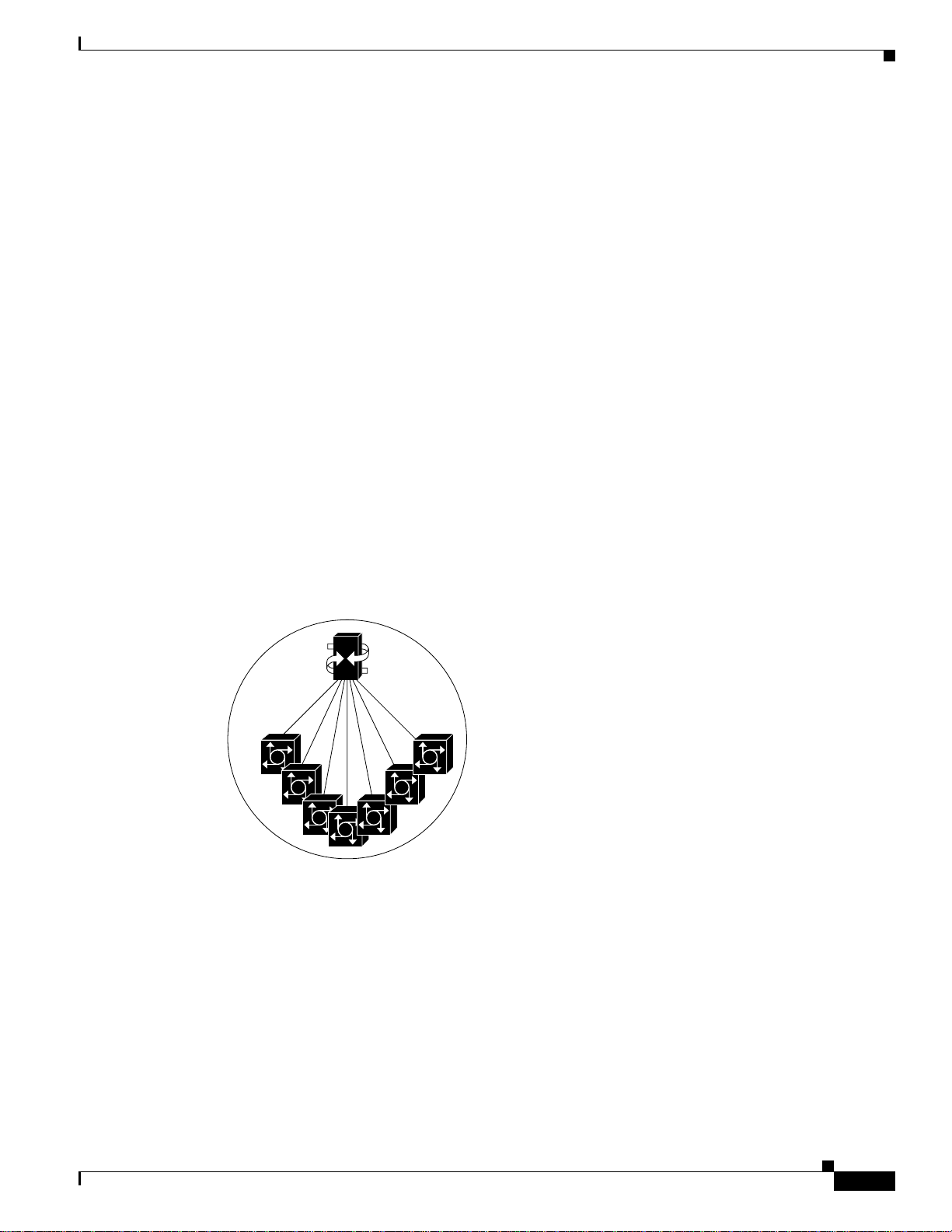
Figure 2-3 Virtual Switch
Virtual switch
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
84409
Similarly, H.323 gateways and gatekeepers in a zone should be managed as just that, a virtual zone, as
if they were one entity. A virtual zone is in essence the H.323 flavor of a virtual switch. Also, gateways
and the signaling controller jointly provide the functionality of a virtual gateway that has SS7
capabilities.
A potent Management Solution should allow for a holistic management of those entities. Figure 2-4
depicts the concept of a virtual zone (which deals with dependencies between gateways within a zone,
as well as between gateways and gatekeepers), a virtual SS7 gateway (which deals with dependencies
between an H.323 gateway and a signaling controller that converts SS7 to Q.931 signaling for the
gateway), and a zone connection (which deals with dependencies between gatekeepers, or between
gatekeepers and directory gatekeepers).
OL-2706-01
Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Implementation Guide
2-5
Page 6
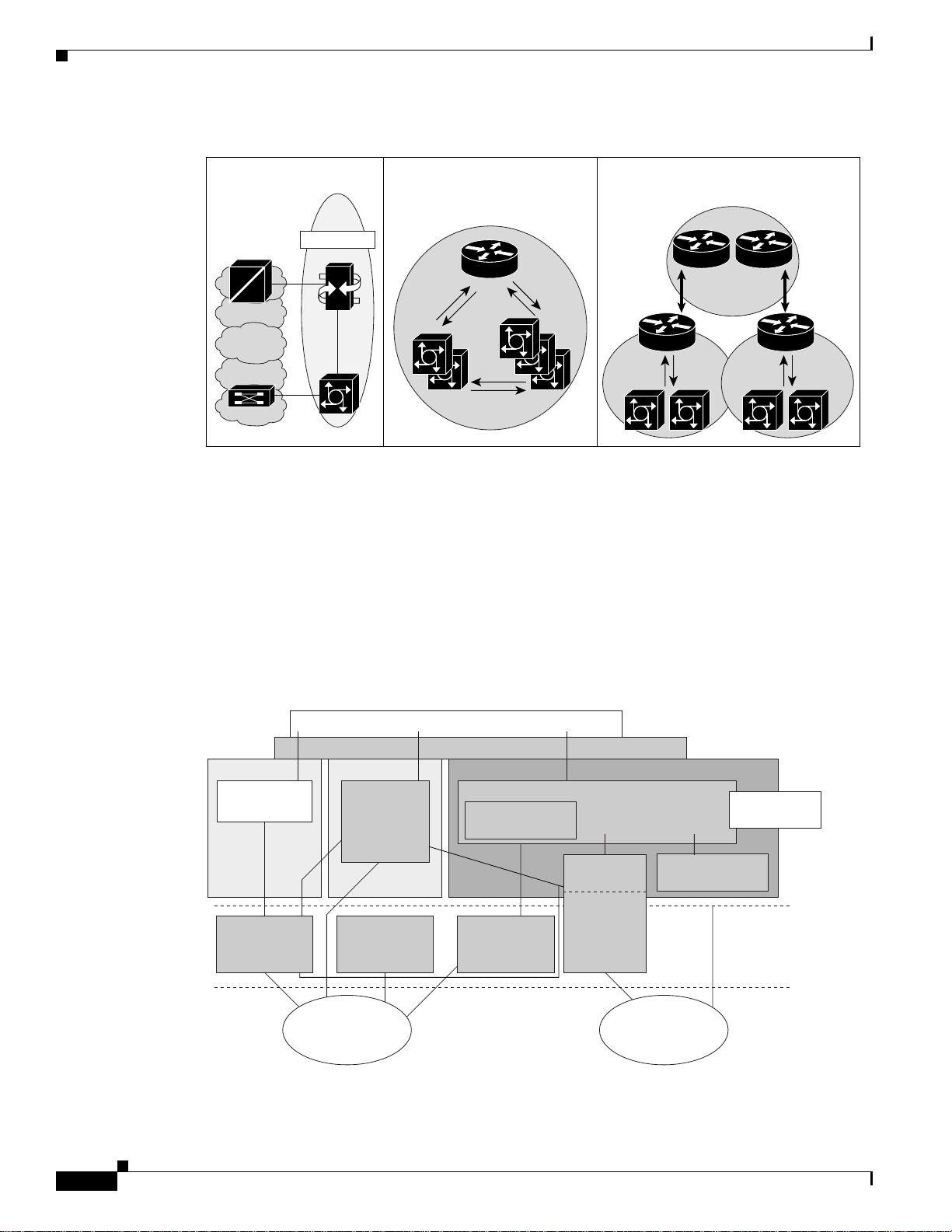
Solution Architecture
Chapter 2 Provisioning
Figure 2-4 Other Virtual Network Entities
Ingress
The concept of virtual network entities is key to the management of packet voice networks. Cisco PTC
and it's companion provisioning management applications readily support this concept.
NMS Architecture
Figure 2-5 depicts theentire CiscoInternet OSS forVoIP: InfrastructureManager Solution architecture.
The three functional areas are provisioning/configuration, fault, and performance. This architecture is
shown here to help you better understand the complete Packet Voice Management Solution.
Virtual SS7
Gateway
SS7
STP
ITSP
Trunk
PGW 2200
V
AS5xxx
Virtual zone
V
V
GK
Virtual region
DGK DGK
V
V
V
GK
V V
GK
V V
84410
Figure 2-5 Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Solution Architecture
Customer provided OSS components
Launcpad/portal (PTC)
Performance
Perform
(3rd party)
CNS
Perf ormance
Engine
Fault
Cisco
Info
Center
CNS
Notification
Engine
Gateways/
Gatekeepers
Pack et Telephony Center
Voice
Routing Center
CNS
Intelligence
Engine
Configuration/Provisioning
V oice
CORBA GW
Cisco
MGC
Node
Manager
Voice Services
Provisioning Tool
PGW 2200
Management
entry point
Network
elements
80941
2-6
Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Implementation Guide
OL-2706-01
Page 7

Chapter 2 Provisioning
IOSS Provisioning Component Architecture
Figure 2-6 depicts the proposed Provisioning Management Solution for OPT networks, as applied to an
H.323-based global long-distance network. The key component is the Cisco Packet Telephony Center
(Cisco PTC),which provides for overall configuration managementof the OPT network and realizes the
virtual entities as discussed. A module within Cisco PTC, called Cisco VRC, provides for H.323
dial-plan management. Cisco PTC enables context sensitive launching of other management tools, that
is, where itmakes sensefrom a navigationstandpoint, foran integrated userexperience. A pre-integrated
application is the Voice Services Provisioning Tool (VSPT), which can be used to bulk configure the
Cisco PSTN Gateway (PGW) 2200. VSPT is used for initial configuration of the PGW 2200 with SS7
components suchas pointcodes, link sets, SS7 paths and routes,SS7 subsystems,and ethernet cards and
interfaces, which are prerequisites to Cisco PTC configuringRLMs and nailed trunks in the PGW2200.
To communicate with underlying network devices, Cisco PTC makes use of underlying EMSs, such as
the Cisco MGC Node Manager (CMNM) for the Cisco PGW 2200. EMSs can also be launched as
auxiliary tools by the user to drill downinto the device or obtaina graphical device view. In cases where
an EMS is not readily available, Cisco PTC can also interface to devices directly or, as in the case of
Cisco IOS devices, utilize the Cisco CNS Intelligence Engine (Cisco CNS IE2100). It should be noted
that theapplicability ofthe Cisco PTC and itsfundamental concepts goes beyond any particular solution
and is not limited to support only certain device types; it is expected that essentially any Open Packet
Telephony (OPT) Solution can be added.
The network elements that can be provisioned with the pictured applications include:
1. Virtual zones of IOS based H.323 voice gateways and gatekeepers including:
a. AS5000 series.
b. c2600, c3600, c7200 series.
2. Virtual gateway node elements including:
a. Signaling Link Terminals.
b. PGW 2200 Signaling Controller.
c. Catalyst switches.
d. AS5000 series voice gateways.
Solution Architecture
OL-2706-01
Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Implementation Guide
2-7
Page 8
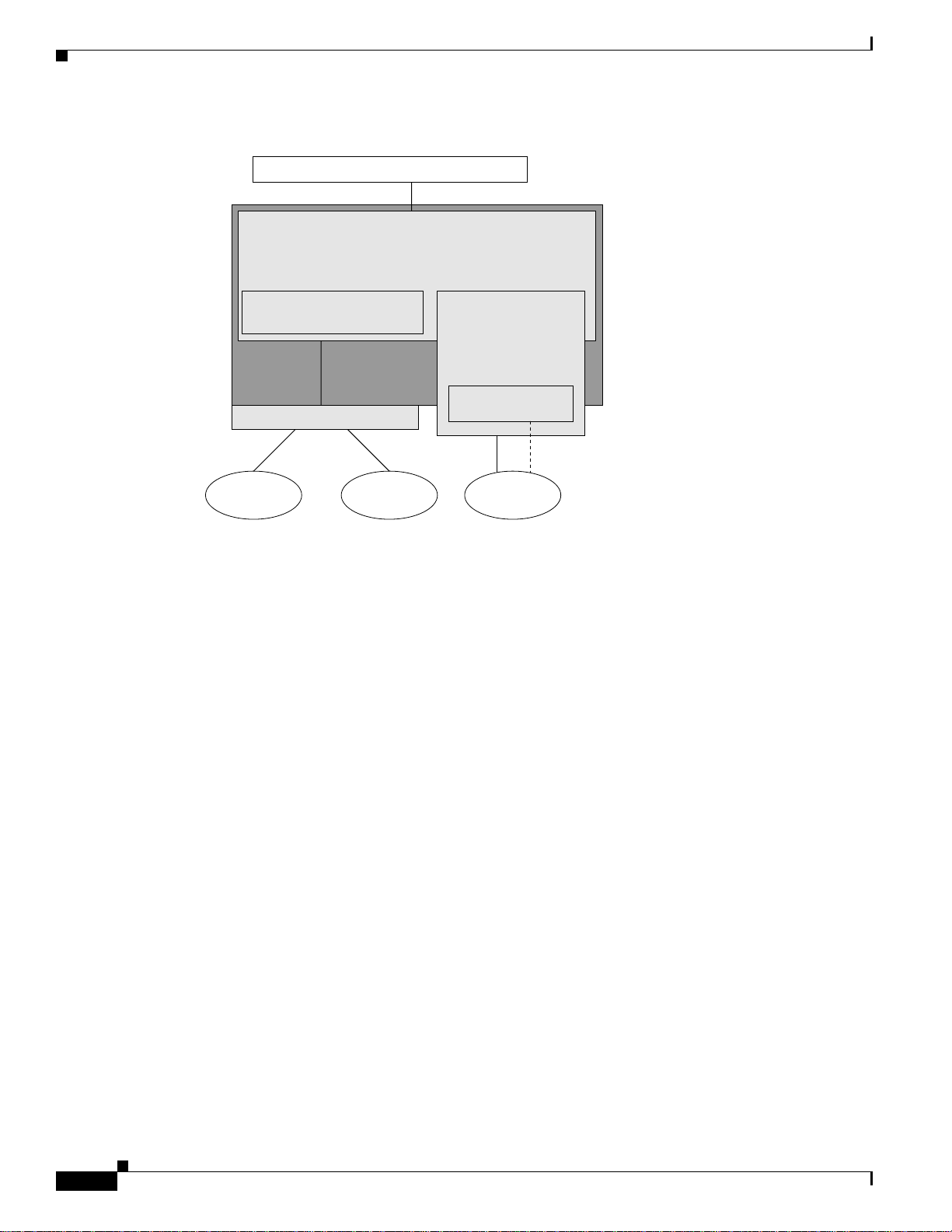
Solution Architecture
Chapter 2 Provisioning
Figure 2-6 Provisioning Management Component Devices
Customer provided OSS components
Pack et Telephony Center
Voice Services
Cisco Voice Routing Center
CNS Intelligence Engine
Functional Description
Cisco PTC oversees the entire network. It is a network management tool that provides a GUI for the
initial andongoing support for configuringCisco Voice over IP(VoIP) networks, comprising PGW 2200
elements, H.323 gateways, and gatekeeper devices.
Cisco PTC is fully integrated with the Cisco VRC application. Cisco VRC provisions the dial plan
related functionality of the H.323 VoIP network elements (gateways and gatekeepers).
The Cisco MGC Node Manager (CMNM), built upon the Cisco Element Management Framework
(CEMF), integrates the management interfaces and management functionality of the PGW 2200
components into onecomprehensive human interfaceand datarepository.CMNM provides anintegrated
management application for fault, configuration, performance, and security of the PGW 2200 node
elements. CiscoView is integrated into theCMNM application asa monitoring andprovisioning tool for
PGW 2200 network elements.
The VSPT provides a GUI for bulk provisioning the PGW 2200.
The Cisco CNS Intelligence Engine is a networkmanagement device that acts as a configurationservice
for automating the deployment and management of network devices and services. The Cisco CNS
IE2100 Series is the hardware platform for the Cisco CNS Configuration Registrar application.
Cisco MGC
Node Manager
Voice Services
Provisioning Tool
PGW 2200Gateways Gatekeepers
84412
Interconnection/Interoperability
This chapter of the Cisco VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Solution specifically details the configuration
and provisioning management components of the Solution. These applications are intended to operate
in conjunction with applications that deal with fault and performance processing. There are several
points of interconnection between the function-specific applications.
Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Implementation Guide
2-8
OL-2706-01
Page 9

Chapter 2 Provisioning
Configuration and Provisioning Solution Components
The gateways and gatekeepers that comprise the H.323 voice network send fault and performance data
directly to the fault and performance processing applications (Cisco CNS Notification Engine,
Cisco Info Center, and Cisco CNS Performance Engine). Protocols for transporting this data include
SNMP, Syslog, and RADIUS.
CMNM is a self-contained fault,configuration,performance, andsecurity (FCPS)Element Management
System (EMS) for the PGW 2200. It can stand on its own or operate in conjunction with the fault and
performance components of the Cisco VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Solution. CMNM can send
performance datato the CiscoCNS Performance Engine through periodic FTP uploads and can transmit
fault data directly to theCisco InfoCenter usingthe CEMFprobe describedin detailin Chapter 4,“Fault
Management.” Cisco PTC sends provisioning commands to the PGW 2200 elements through the Voice
CORBA interface in CMNM provided by CEMF.
Configuration and Provisioning Solution Components
Component List
The components that comprise the Cisco VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Solution’s configuration and
provisioning solution suite provision the network elements and manage the configuration files for those
elements. Version 1.1 of the Cisco VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Solution includes:
1. Cisco Packet Telephony Center integrated with:
a. Cisco Voice Routing Center (Cisco VRC).
2. Cisco MGC Node Manager built upon the Cisco Element Management Framework including:
a. Voice Services Provisioning Tool (VSPT).
b. CiscoView (native component in CiscoWorks2000).
c. Cisco CNS Configuration Registrar (Cisco CNS IE2100 Series).
The following sections detail the specifics of each of these applications.
Cisco Packet Telephony Center
The Cisco Packet Telephony Center provides a Management Solution for large-scale H.323 networks.
Cisco PTC providesnetwork managementlayer functionalityand managesthe network through Element
Management Systems (EMSs), or through the network element's management interface (for example,
SNMP or Command Line Interface (CLI)). Cisco PTC maintains a repository of the data, consisting of
customer and services information, for the managed network. This repository is used to configure the
network, provision new services, and to detect network layer configuration inconsistencies.
Refer to the Cisco Packet Telephony Center User Guide for an overview of the Cisco PTC domain
manager as well as other useful information about the product.
For a Cisco H.323 VoIP network composed of VoIP gateways and gatekeepers, Cisco PTC is integrated
with Cisco VRC.
OL-2706-01
Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Implementation Guide
2-9
Page 10
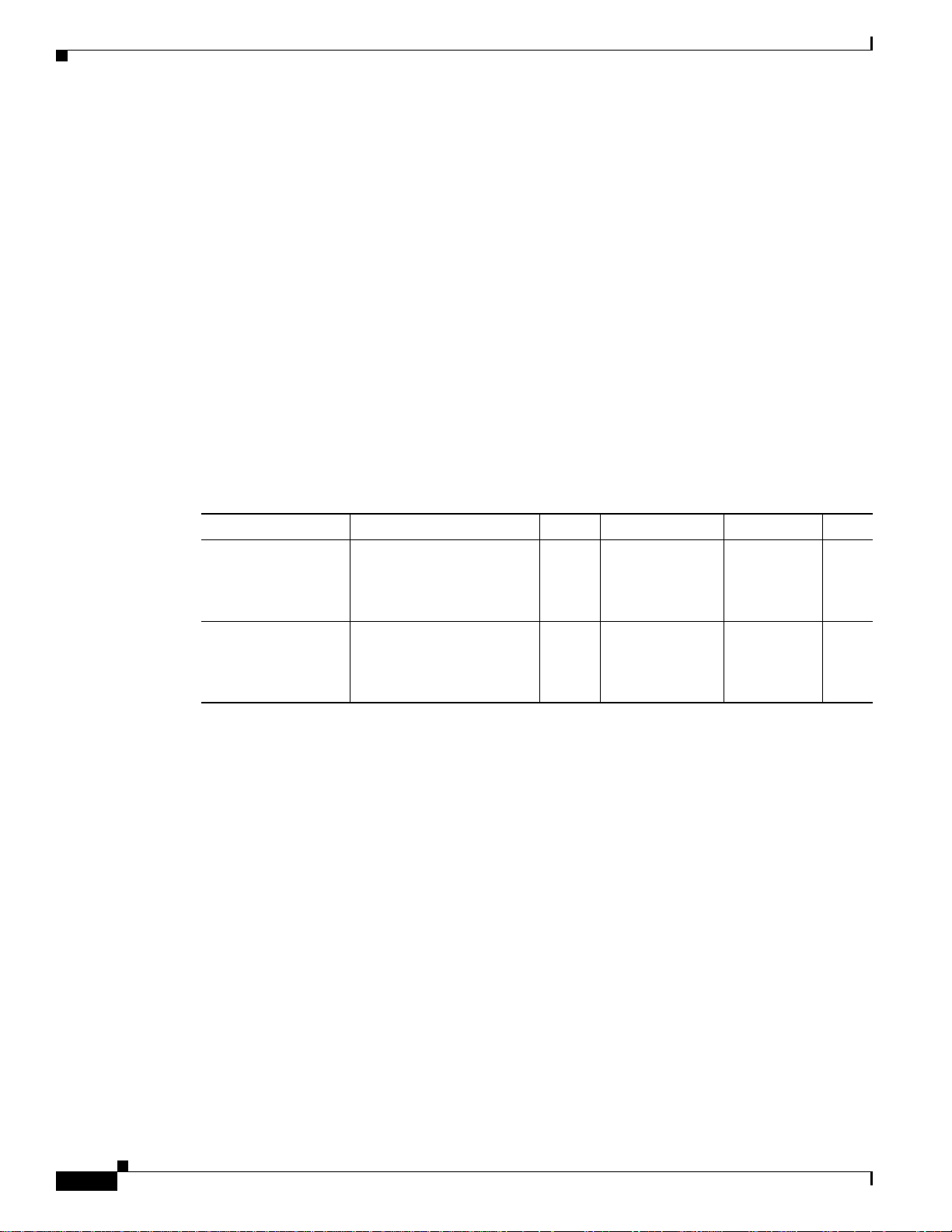
Configuration and Provisioning Solution Components
Cisco Voice Routing Center
Cisco VRC is a GUI-based networkmanagement tool specifically designed for managing dial plans in a
Voice over IP (VoIP) network.
Cisco VRC, version 1.1, is targeted for H.323-based networks. H.323 VoIP dial plans are statically
configured and managed on gateway and gatekeeper platforms. The infrastructure of a typical H.323
VoIP network includes gateways and gatekeepers.
You can deploy Cisco VRCto discoverthe dial plan of an existing network. Youcan alsouse it to design
new dial plans incorporating Cisco routers running as gateways, gatekeepers, and directory gatekeepers.
For a complete description, installation instructions, and Release Notes for the Cisco VRC application,
refer to the “Related Documents” section.
Recommended Hardware Configuration for Cisco PTC and Cisco VRC
The minimum platform recommendations for the Cisco PTC and Cisco VRC applications are provided
in Table 2-1.
Table 2-1 Cisco PTC and Cisco VRC Hardware Requirements
Chapter 2 Provisioning
Number of Gateways Sun Workstation Model RAM Hard Disk Space Swap Space CPUs
Less than 1000 Entry level UltraSparcIII
(for example, a
Sun Fire 280R)
1000 to 3000 Entry level UltraSparcIII
(for example, a
Sun Fire 280R)
Cisco Media Gateway Control Node Manager
CMNM integrates the management interfaces and management functionality of the PGW 2200
components into one comprehensive human interface and data repository. The PGW 2200 consists of the
Cisco MGC host, one or more Cisco Signaling Link Terminals (Cisco SLTs) and the Cisco Catalyst
5500, Catalyst 2900 XL, or Catalyst 6509 LAN switch. CMNM provides fault, configuration, and
performance management for all components of the Cisco MGC node.
CMNM provides the element-specific management features for the Cisco MGC node. It blends the
management framework features of the Cisco Element Management Framework (Cisco EMF) with the
individual interfaces and object structures of each managed element to produce an integrated
management application. Figure 2-7 illustrates the element details of the MGC node and the CMNM
applications server(s).
Figure 2-7 provides the details of the network elements that comprise the PGW 2200 and CMNM.
1GB 9GB with at least
6GB available
under the /opt
directory
2GB 18GB with at
least 12GB
available under
the /opt directory
2GB 2
4GB 2
2-10
Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Implementation Guide
OL-2706-01
Page 11
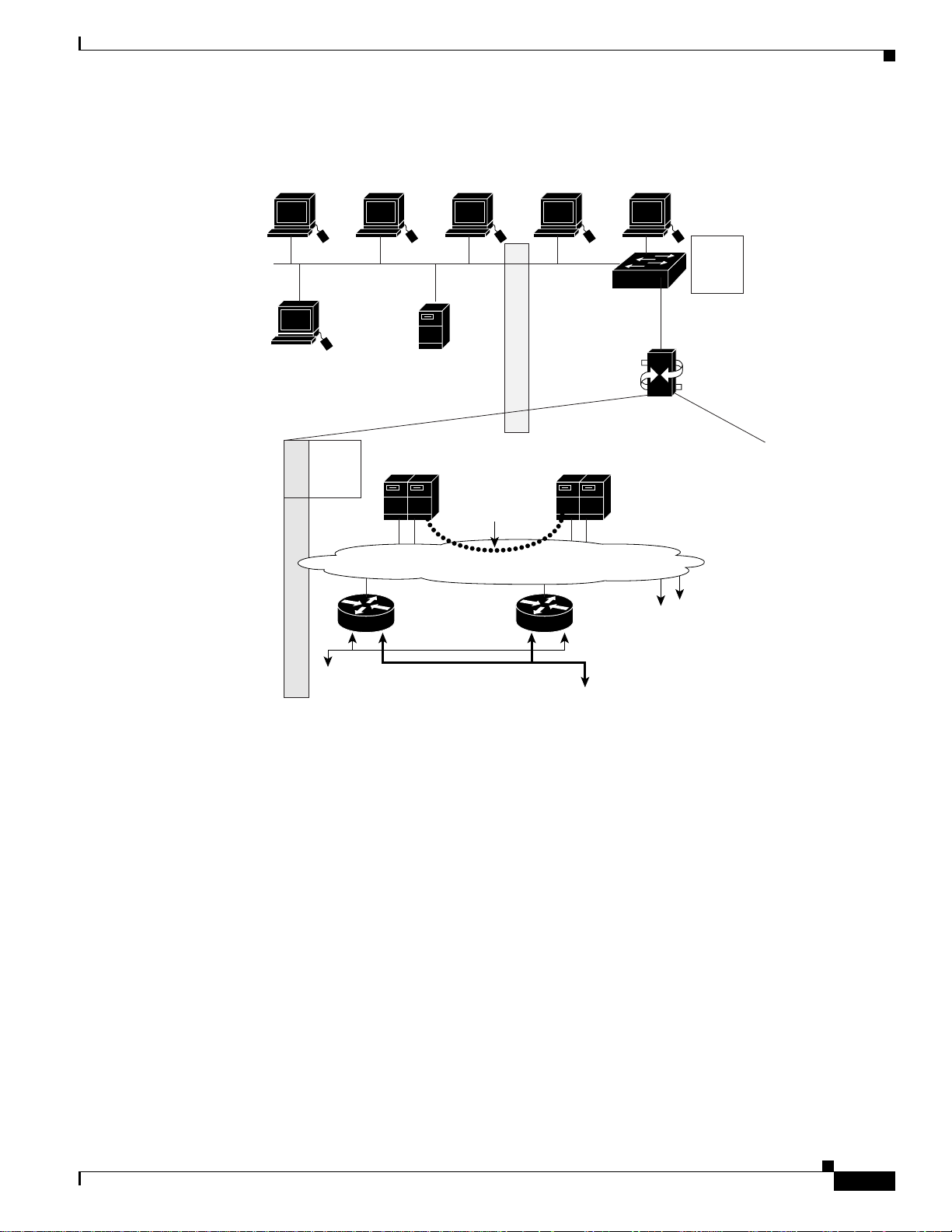
Chapter 2 Provisioning
Configuration and Provisioning Solution Components
Figure 2-7 PGW 2200 and MGC Node Manager Details
End user Xterminal
Cisco
PGW
2200
Catalyst
CMNM Features
MGC Node Manager
Presentation Server
Host/
SLT
detail
SLT SLT
Link
set A
MGC Node Manager
Management Server
Active Host Standby Host
Checkpointing
Signaling Control network
To Gateways and other
SS7 A or F links
set B
Cisco PGW 2200 nodes
Link
84413
The mostcommon Cisco EMF installation includesplug-in modules referred to asElement Managers or
Element Management Systems (EMSs). In the Cisco MGC node architecture, CMNM is a Cisco
EMF-based EMS responsible for managing the Cisco MGC node (PGW 2200). CMNM adds specific
GUI windows and modeling behavior to the standard Cisco EMF system to allow the management of
specific network elements.
CMNM uses Cisco EMF to manage the following components of the Cisco MGC node:
• Cisco MGC
• Cisco SLT
• LAN switch (Cisco Catalyst 2900, 5500 and 6509).
OL-2706-01
Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Implementation Guide
2-11
Page 12
Configuration and Provisioning Solution Components
CMNM Configuration
You can open the following configuration tools from CMNM:
• Voice Services Provisioning Tool (VSPT)
• CiscoView, which allows you to configure and monitor the Cisco SLT and the LAN switch (Cisco
Catalyst 2900, 5500 and 6509) devices.
CMNM Troubleshooting
CMNM providesa fullrange of diagnostic and troubleshootingtools, such as IP and SNMP Ping, Alarm
and System Log, Host Status Check, Cross-Device Audit, and the Cisco MGC Toolbar that includes
CDR Viewer, Log Viewer, Trace Viewer, and Translation Verification Viewer.
Recommended Hardware Configuration for CMNM
The CMNM has substantial hardware requirements. The main consumer of resources in the CMNM
application is the CEMF application. The requirements below have been designed in order to create an
environment optimized for speed of response. These are general “rule of thumb” requirements and can
be adjusted to suit specific network deployments. Consultation with an experienced network design
specialist is recommended.
Chapter 2 Provisioning
Table 2-2 CMNM Hardware Requirements
Small Network:
1-3Operators
1-5 Nodes
Network Element
Number of machines One machine Two machines Three machines
Configuration Standalone Distributed
RAM (GB) 2 2 2 2 4
Swap (GB) 2 1 2 1 2
Hard drives @ 9GB
each (minimum)
Number of CPUs
and Speed
1 trap/second
41418
2 at 440Mhz 2 at 440Mhz 2 at 440Mhz 4 at 440Mhz 2 at 440Mhz
The Sun Fire 280R entrylevel server satisfies the above requirements.Refer to the CMNM User'sGuide,
at the following URL, for in depth details about CEMF and the Cisco MGC Node Manager:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/access/sc/rel9/cmnm21/index.htm.
Medium Network:
4-6 Operators
6-10 Nodes
2 traps/second
Presentation Server Management Server
Large Network:
7-10 Operators
11-20 Nodes
4 traps/second
Distributed
Presentation Server Management Server
2-12
Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Implementation Guide
OL-2706-01
Page 13

Chapter 2 Provisioning
Voice Services Provisioning Tool
Provisioning with the VSPT is the process of preparing a Cisco Media PGW 2200 to communicate with
an SS7 network, with Cisco media gateways, and with the other components of an OPT Solution. The
VSPT application provides an easy to use GUI to provision the Cisco PGW 2200.
VSPT can be deployed as an integrated component of the CMNM or as a standalone application. In the
Cisco VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Solution configuration, it runs on the CMNM server. It allows you
to import an existing configuration, modify the configuration, and export it to the same or different
devices; or wizards guide you through high-level configuration steps to create the initial network
provisioning informationfor a newlyinstalled node, creating iterative entries from a single operation.It
can alsofacilitate provisioningof individualcall parameters, simplifying the provisioningof a large live
network.
During a provisioning session, VSPT automatically generates the Man Machine Language (MML) or
command line interface (CLI) scripts used to configure network elements, assembles these commands
into a batch file, and deploys the file to the appropriate network device. VSPT is used to augment the
Cisco PTC provisioning application, providing bulk provisioning support and an alternative for
provisioning the PGW 2000.
Configuration and Provisioning Solution Components
Recommended Hardware Configuration for VSPT
VSPT runs on the CMNM server in this Cisco VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Solution.
CiscoView
CiscoView is a device monitoring application that is built into the CiscoWorks 2000 network
management package. Installing CiscoWorks 2000 is the method of adding CiscoView to your network
management applications. This Solution installs CiscoView (through the installation of
CiscoWorks 2000) on a separate Solaris 8 host. A prerequisite to the installation of CiscoWorks2K on
Solaris 8 is the installation of Solaris 8 patch 108827-19 or later. This Solution assumes you will install
the entire recommended patch cluster for Solaris 8 as outlined in the “Installing the Solaris 8 Patch
Cluster” section.
CiscoView is launched by the CMNM application to provide a device level view of Cisco network
devices.CiscoViewprovidessupport fora widerange ofdevicesand hasthe capabilityof adding support
for futuredevices throughdownload ofdevice specific description files. CiscoView aids in zeroing in on
trouble spots in the network or in providing device specific hardware and interface usage data.
Recommended Hardware Configuration for CiscoView
CiscoView is installed on the CMNM host machine and is already considered in the hardware
recommendations for CMNM.
OL-2706-01
Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Implementation Guide
2-13
Page 14

Configuration and Provisioning Solution Components
Cisco CNS Intelligence Engine
Cisco CNS Intelligence Engine and Cisco CNS Bus Technology
The Cisco CNS IntelligenceEngine (CiscoCNS IE2100Series) isa networkmanagement appliancethat
acts as a configuration service for automating the deployment and management of network devices and
services. The Cisco CNS IE2100 appliance sits between Cisco PTC/Cisco VRC and the network
elements, utilizing the Cisco CNS Integration Bus for data transport between the provisioning
applications and the network elements.
The Cisco CNS Configuration Registrar applicationis aweb-based systemfor automaticallydistributing
configurationfiles to Cisco IOS network devices running Cisco IOSversion 12.2(2) T, or later. Once the
Cisco CNS IE2100 appliance is initially configured and the network elements are configured to use the
Cisco CNS IE2100appliance withtwo command linearguments, the systemthen operatesautomatically.
Note If youare running devices that useand earlier version of CiscoIOS or a different operating system, such
as Catalyst, you should invoke the Intelligent Modular Gateway (IMG) for communicating with the
device.
Chapter 2 Provisioning
The Cisco CNS Configuration Registrar application utilizes the following industry standards and
technologies:
• eXtensible Markup Language (XML)
• Java Naming Directory Interface (JNDI)
• Hypertext Transport Protocol (HTTP)
• Java servlets
• Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP).
The Cisco CNS IE2100 Series can be used as the runtime component for deployment of
customer-developed applications. These applications can be developed using the Cisco CNS SDK 1.5.
Complete descriptions and installation and configuration information can be found at the URL listed in
the “Related Documents” section.
Hardware Requirements
The Cisco CNS Configuration Registrar is an application that runs on its own piece of hardware which
is typically a 1 RU IBM rack mount server running the Linux Operating System.
2-14
Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Implementation Guide
OL-2706-01
Page 15

Chapter 2 Provisioning
Step by Step Installation and Initial Configuration
Step by Step Installation and Initial Configuration
Overview of Installation
The order of installation follows the plan below:
1. Install and configure the Cisco CNS IE2100 appliance with a subnet IP address.
2. On the CMNM host, install the Cisco MGC Node Manager application, including:
a. Voice Services Provisioning Tool.
b. CEMF 3.2.
c. CiscoView upgrade if necessary.
d. Cisco MGC Node Manager (server).
3. On the Cisco PTC/Cisco VRC host, install Cisco PTC, version 2.1.1, integrated with Cisco VRC,
version 1.1.
Once the applications are installed, they are started, and then checked for running processes on each
machine.
Dependencies
It is highly recommended that you obtain all of the Installation and User Guides referenced in the
“Related Documents” section, for Cisco CNS IE2100 Series, CMNM, and Cisco PTC/Cisco VRC.
Although lengthy, these guides provide a clear, organized way to approach preparing for, obtaining, and
installing thevarious applicationsoftware. There are many interdependenciesthat make the deployment
of this management software non-trivial. This chapter makes many references to the User and
Installation Guides, as well as the other collateral referenced in the “Related Documents” section.
You may wonder why the installation information is repeated in this chapter when it is available in the
other guides as well. In fact, the installation information in this chapter is mostly copied from the
individual User and Installation guides of the different applications adding little that is new or specific
to this chapter. The answer is that this chapter is detailing a solution that incorporates at least five
different applications and devices. So, instead of pointing you to the many guides, requiring that you
either read the guide electronically and activate the various links or much typing of URLs into web
browsers, we wish to create a guide that can be accessed either in soft or hard copy that is somewhat
complete in itself.
Somewhat complete means that the “official” User and Installation guides cover every situation that the
developers could envision, whereas this guide is specifically pointed at a certain solution and
deployment and can be less detailed than the guides that accompany the application.
Installing the Cisco CNS IE2100 Configuration Engine
The Cisco CNS Configuration Registrarrefers to the application, while the Cisco CNS IE2100 appliance
is a specific device that makes use of the application software. The Cisco CNS Configuration Registrar
is a self contained, Linux based application, which runs on a one RU, rack mount, IBM host. In
preparation for installation, the Cisco CNS IE2100 appliance should be rack mounted and connected to
the management network through its Ethernet port.
OL-2706-01
Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Implementation Guide
2-15
Page 16

Step by Step Installation and Initial Configuration
Installation Overview
The installation procedure for the Cisco CNS Configuration Registrar is straightforward. The software
is installed and configured through a console connection to the serial port. The console connection
parameters are the same as for other Cisco IOS devices, that is:
• 9600 baud
• Parity: 8/None
• Stop bits: 1.
Step 1 After the Cisco CNS IE2100 appliance is optionally racked, plugged in, and turned on, insert the
CDROM installation disk and press the Reset button.
You can not monitor the installation procedure as the console logic does not begin until the Operating
System isstarted. After the automatic installation procedure completes, theCD ejects automatically and
the system restarts, at which point the login prompt appears in the Console window.
Step 2 Log in as user setup.
The Setup program starts.
Step 3 Enter responses to the prompts that appear.
After you enter a response, you cannot edit it again. To change an entered response, you must exit the
Setup program and enter your responses again. You can exit the Setup program in two ways:
• Press Ctrl-c. The login prompt appears. Use the login setup to run the Setup program.
• Enter n at the final prompt. The Setup program exits, then restarts.
Refer to the sample setup session below for an example of the prompts and their responses:
Step 4 Press ESC to log in:
USER ID:
LILO
boot:
boot:
Loading linux......................
Linux version 2.4.2-2 (root@porky.devel.redhat.com) (gcc version 2.96
20000731 (Red Hat Linux 7.1 2.96-79)) #1 Sun Apr 8 20:41:30 EDT 2001
BIOS-provided physical RAM map:
BIOS-e820: 000000000009dc00 @ 0000000000000000 (usable)
BIOS-e820: 0000000000002400 @ 000000000009dc00 (reserved)
BIOS-e820: 0000000000020000 @ 00000000000e0000 (reserved)
BIOS-e820: 000000003feec340 @ 0000000000100000 (usable)
BIOS-e820: 0000000000010000 @ 000000003fff0000 (reserved)
BIOS-e820: 0000000000003cc0 @ 000000003ffec340 (ACPI data)
BIOS-e820: 0000000001400000 @ 00000000fec00000 (reserved)
127MB HIGHMEM available.
On node 0 totalpages: 262124
zone(0): 4096 pages.
zone DMA has max 32 cached pages.
zone(1): 225280 pages.
zone Normal has max 1024 cached pages.
Chapter 2 Provisioning
2-16
Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Implementation Guide
OL-2706-01
Page 17

Chapter 2 Provisioning
Step by Step Installation and Initial Configuration
zone(2): 32748 pages.
zone HighMem has max 255 cached pages.
hm, page 01000000 reserved twice.
Kernel command line: auto BOOT_IMAGE=linux ro root=806
BOOT_FILE=/boot/vmlinuz-2.4.2-2 console=ttyS0,9600n8
Initializing CPU#0
Detected 1130.197 MHz processor.
Console: color VGA+ 80x25
Calibrating delay loop... 2254.43 BogoMIPS
Memory: 1028188k/1048496k available (1365k kernel code, 19912k reserved,
92k data, 236k init, 130992k highmem)
Dentry-cache hash table entries: 131072 (order: 8, 1048576 bytes)
Buffer-cache hash table entries: 65536 (order: 6, 262144 bytes)
Page-cache hash table entries: 262144 (order: 9, 2097152 bytes)
Inode-cache hash table entries: 65536 (order: 7, 524288 bytes)
VFS: Diskquotas version dquot_6.5.0 initialized
CPU: Before vendor init, caps: 0383fbff 00000000 00000000, vendor = 0
CPU: L1 I cache: 16K, L1 D cache: 16K
CPU: L2 cache: 512K
Intel machine check architecture supported.
Intel machine check reporting enabled on CPU#0.
CPU: After vendor init, caps: 0383fbff 00000000 00000000 00000000
CPU: After generic, caps: 0383fbff 00000000 00000000 00000000
CPU: Common caps: 0383fbff 00000000 00000000 00000000
CPU: Intel(R) Pentium(R) III CPU family 1133MHz stepping 01
Enabling fast FPU save and restore... done.
Enabling unmasked SIMD FPU exception support... done.
Checking 'hlt' instruction... OK.
POSIX conformance testing by UNIFIX
mtrr: v1.37 (20001109) Richard Gooch (rgooch@atnf.csiro.au)
mtrr: detected mtrr type: Intel
PCI: PCI BIOS revision 2.10 entry at 0xfd61c, last bus=1
PCI: Using configuration type 1
PCI: Probing PCI hardware
PCI: Discovered peer bus 01
isapnp: Scanning for PnP cards...
isapnp: No Plug & Play device found
Linux NET4.0 for Linux 2.4
Based upon Swansea University Computer Society NET3.039
Initializing RT netlink socket
apm: BIOS not found.
Starting kswapd v1.8
Detected PS/2 Mouse Port.
pty: 256 Unix98 ptys configured
block: queued sectors max/low 682808kB/551736kB, 2048 slots per queue
RAMDISK driver initialized: 16 RAM disks of 4096K size 1024 blocksize
OL-2706-01
Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Implementation Guide
2-17
Page 18

Step by Step Installation and Initial Configuration
Uniform Multi-Platform E-IDE driver Revision: 6.31
ide: Assuming 33MHz system bus speed for PIO modes; override with idebus=xx
ServerWorks OSB4: IDE controller on PCI bus 00 dev 79
ServerWorks OSB4: chipset revision 0
ServerWorks OSB4: not 100% native mode: will probe irqs later
ide0: BM-DMA at 0x0700-0x0707, BIOS settings: hda:DMA, hdb:DMA
ide1: BM-DMA at 0x0708-0x070f, BIOS settings: hdc:DMA, hdd:DMA
hda: LG CD-ROM CRN-8245B, ATAPI CD/DVD-ROM drive
ide0 at 0x1f0-0x1f7,0x3f6 on irq 14
Floppy drive(s): fd0 is 1.44M
FDC 0 is a National Semiconductor PC87306
RAMDISK: Compressed image found at block 0
Freeing initrd memory: 359k freed
Serial driver version 5.02 (2000-08-09) with MANY_PORTS MULTIPORT
SHARE_IRQ SERIAL_PCI ISAPNP enabled
ttyS00 at 0x03f8 (irq = 4) is a 16550A
Real Time Clock Driver v1.10d
md driver 0.90.0 MAX_MD_DEVS=256, MD_SB_DISKS=27
md.c: sizeof(mdp_super_t) = 4096
autodetecting RAID arrays
autorun ...
... autorun DONE.
NET4: Linux TCP/IP 1.0 for NET4.0
IP Protocols: ICMP, UDP, TCP, IGMP
IP: routing cache hash table of 8192 buckets, 64Kbytes
TCP: Hash tables configured (established 262144 bind 65536)
Linux IP multicast router 0.06 plus PIM-SM
NET4: Unix domain sockets 1.0/SMP for Linux NET4.0.
VFS: Mounted root (ext2 filesystem).
Red Hat nash verSCSI subsystem driver Revision: 1.00
version 3.0.10 starting
Loading sc(scsi0) <Adaptec AIC-7892 Ultra 160/m SCSI host adapter> found at si_mod module
LPCI 1/3/0
Loading sd_mod mo(scsi0) Wide module
Loading aiChannel, SCSI ID=7, c7xxx module
32/255 SCBs
(scsi0) Downloading sequencer code... 396 instructions downloaded
scsi0 : Adaptec AHA274x/284x/294x (EISA/VLB/PCI-Fast SCSI) 5.2.4/5.2.0
<Adaptec AIC-7892 Ultra 160/m SCSI host adapter>
(scsi0:0:0:0) Synchronous at 80.0 Mbyte/sec, offset 63.
Vendor: IBM-ESXS Model: ST318305LC !# Rev: B245
Type: Direct-Access ANSI SCSI revision: 03
Vendor: IBM Model: FTlV1 S2 Rev: 0
Type: Processor ANSI SCSI revision: 02
Attached scsi disk sda at scsi0, channel 0, id 0, lun 0
SCSI device sda: 35548320 512-byte hdwr sectors (18201 MB)
Chapter 2 Provisioning
2-18
Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Implementation Guide
OL-2706-01
Page 19

Chapter 2 Provisioning
Step by Step Installation and Initial Configuration
Partition check:
sda: sda1 sda2 < sda5 sda6 sda7 sda8 sda9 sda10 sda11 sda12 sda13 >
VFS: Mounted root (ext2 filesystem) readonly.
change_root: old root has d_count=3
Trying to unmount old root ... okay
Freeing unused kernel memory: 236k freed
INIT: version 2.78 booting
Welcome to Red Hat Linux
Press 'I' to enter interactive startup.
Mounting proc filesystem: [OK]
Configuring kernel parameters: [OK]
Setting clock (localtime): Fri Oct 4 10:02:43 PDT 2002 [OK]
Activating swap partitions: [OK]
Setting hostname localhost.localdomain: [OK]
Mounting USB filesystem: [OK]
Initializing USB controller (usb-ohci): [OK]
Checking root filesystem
/: clean, 16950/263296 files, 22733/526120 blocks
[/sbin/fsck.ext2 -- /] fsck.ext2 -a /dev/sda6 [OK]
Remounting root filesystem in read-write mode: [OK]
Finding module dependencies: [OK]
Checking filesystems
/boot: clean, 28/14056 files, 5656/56196 blocks
/extra: clean, 12/131616 files, 4147/263056 blocks
/home: clean, 27/244320 files, 7697/487966 blocks
/opt: clean, 3290/263296 files, 68085/526120 blocks
/tmp: clean, 16/131616 files, 4153/263056 blocks
/usr: clean, 33248/525888 files, 142855/1050241 blocks
/var: clean, 338/131616 files, 7654/263056 blocks
Checking all file systems.
[/sbin/fsck.ext2 -- /boot] fsck.ext2 -a /dev/sda1
[/sbin/fsck.ext2 -- /extra] fsck.ext2 -a /dev/sda13
[/sbin/fsck.ext2 -- /home] fsck.ext2 -a /dev/sda10
[/sbin/fsck.ext2 -- /opt] fsck.ext2 -a /dev/sda7
[/sbin/fsck.ext2 -- /tmp] fsck.ext2 -a /dev/sda12
[/sbin/fsck.ext2 -- /usr] fsck.ext2 -a /dev/sda5
[/sbin/fsck.ext2 -- /var] fsck.ext2 -a /dev/sda11 [OK]
Mounting local filesystems: [OK]
Turning on user and group quotas for local filesystems: [OK]
Enabling swap space: [OK]
INIT: Entering runlevel: 3
Entering non-interactive startup
Updating /etc/fstab [OK]
Checking for new hardware [OK]
Setting network parameters: [OK]
Bringing up interface lo: [OK]
OL-2706-01
Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Implementation Guide
2-19
Page 20

Step by Step Installation and Initial Configuration
Starting system logger: [OK]
Starting kernel logger: [OK]
Starting portmapper: [OK]
Starting NFS file locking services:
Starting NFS statd: [OK]
Starting keytable: [OK]
Initializing random number generator: [OK]
Mounting other filesystems: [OK]
Starting automount:[OK]
Starting atd: [OK]
Starting sshd: [OK]
Starting xinetd: [OK]
Starting lpd: No Printers Defined[OK]
Starting sendmail: [OK]
Starting console mouse services: [OK]
Starting crond: [OK]
Starting xfs: [OK]
Starting anacron: [OK]
This Appliance is not configured.
Please login as setup to configure the appliance.
Chapter 2 Provisioning
localhost.localdomain login: setup
Cisco Intelligence Engine 2110
Cisco Configuration Registrar (tm) Software, Version 1.2(1a) [ming_cao-ie2100_1_2_fcs.p1
100]
Copyright (c) 2001, 2002 by cisco Systems, Inc.
Compiled Tue 05-Mar-2002 20:37 by ming_cao
Entering Network Appliance Setup
Type ctrl-c to exit
Where is the setup file? 0=local, 1=remote. [0]
Choose operational mode for the appliance. 0=internal directory mode,
1=external directory mode. [0]
Enter the root user password: ******
Re-Enter the root user password: ******
Enter the host name: ie-tme
Enter the domain name: cisco.com
Enter the administrative username: admin
Enter the admin password: ******
Re-Enter the admin password: ******
Enter the eth0 ip address: 172.19.49.20
Enter the eth0 network mask: 255.255.255.224
Enter the eth0 default gateway ip address: 172.19.49.1
Enter the eth1 ip address:
Enter the Primary DNS Server IP address: 171.70.168.183
2-20
Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Implementation Guide
OL-2706-01
Page 21

Chapter 2 Provisioning
Step by Step Installation and Initial Configuration
Enter the Secondary DNS Server IP address: 171.68.226.120
Enter the Country Code: us
Enter the Company Code: cisco
Enter the ConfigService AdminID: csadmin
Enter the ConfigService password: ******
Re-Enter the ConfigService password: ******
Enter the NSM Directives:
This field requires an input.
Enter the NSM Directives: default://
Enter the Event Gateway Debug Log (y/n): n
Enter the # of Event Gateways N for serving 500 x N devices: 1
Enter the CNS Event Bus Network Parameter: [ie-tme]
Enter the CNS Event Bus Service Parameter: [7500]
Current settings of IMGW:
------------------------Gateway ID: ie-tme
Run as daemon (true/false): true
Script Operation Timeout (sec): 180
Device Prompt Timeout (sec): 60
Concurrent Telnet Session Limit: 20
Remove Temp File (true/false): true
Location of Temp Files: /tmp
Hoptest Success Retry Interval (sec): 7200
Hoptest Failure Retry Interval (sec): 3600
Logging Level (error,verbose,silent): error
Logging File Prefix: IMGW-LOG
Log File Size (byte): 50331648
Log File Rotation Timer (minute): 60
Logging Mode (append,overwrite): append
OL-2706-01
Re-configure IMGW (y/n): n
Please review the following parameters:
root user password: ******
host name: ie-tme
domain name: cisco.com
administrative username: admin
admin password: ******
eth0 ip address: 172.19.49.20
eth0 network mask: 255.255.255.224
eth0 default gateway ip address: 172.19.49.1
eth1 ip address:
Primary DNS Server IP address: 171.70.168.183
Secondary DNS Server IP address: 171.68.226.120
Country Code: us
Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Implementation Guide
2-21
Page 22

Step by Step Installation and Initial Configuration
Company Code: cisco
ConfigService AdminID: csadmin
ConfigService password: ******
NSM Directives: default://
Event Gateway Debug Log (y/n): n
# of Event Gateways N for serving 500 x N devices: 1
CNS Event Bus Network Parameter: ie-tme
CNS Event Bus Service Parameter: 7500
Re-configure IMGW (y/n): n
Commit changes (y/n): y
Update administrator info ...
Shutdown servers ...
Configure network ...
eepro100.c:v1.09j-t 9/29/99 Donald Becker
http://cesdis.gsfc.nasa.gov/linux/drivers/eepro100.html
eepro100.c: $Revision: 1.36 $ 2000/11/17 Modified by Andrey V. Savochkin
<saw@saw.sw.com.sg> and others
Configure IMGW ...
Configure DCL ...
Run configurator ...
Configure EvtGateway start/stop file ...
Register tibco rvrd start/stop script for system shutdown/restart ...
Run NSM configurator ...
Start servers ...
/etc/rc.d/init.d/NetAppDCL start
Start tibco
Chapter 2 Provisioning
2-22
/etc/rc.d/init.d/tibco start >> /var/log/appliance-setup.log 2>&1
/etc/rc.d/init.d/httpd start
/etc/rc.d/init.d/Imgw start >> /var/log/appliance-setup.log 2>&1
/etc/rc.d/init.d/EvtGateway start >> /var/log/appliance-setup.log 2>&1
Initialize DCL for Internal Mode ...
Configure DAT ...
Install IBM Director takes approximately 4 minutes ...
IBM Advanced System Management Device Driver loaded.
cd /opt/IBMDirectorInstall; nohup sh /opt/IBMDirectorInstall/dirinstall
>> /var/log/appliance-setup.log 2>&1
Setup completed!
Press <Enter> to login!
Red Hat Linux release 7.1 (Seawolf)
Kernel 2.4.2-2 on an i686
ie-tme.cisco.com login: root
Password:
Last login: Fri Oct 4 10:12:27 on ttyS0
Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Implementation Guide
OL-2706-01
Page 23
Chapter 2 Provisioning
Step by Step Installation and Initial Configuration
Cisco Intelligence Engine 2110
Cisco Configuration Registrar (tm) Software, Version 1.2(1a) [ming_cao-ie2100_1_2_fcs.p1
100]
Copyright (c) 2001, 2002 by cisco Systems, Inc.
Compiled Tue 05-Mar-2002 20:37 by ming_cao
[root@ie-tme /root]#
Refer to the Cisco CNS Configuration Registrar Installation Guide for more details. The “Related
Documents” section provides a URL to the Cisco CNS Configuration Registrar documentation.Once the
Cisco CNS IE2100 appliance has been setup, you should be able to access it through a web browser at
the URL:
http://<hostname or IP address of IE2100>/config/login.html.
The Cisco CNS Configuration Registrar Login window, shown in Figure 2-8, appears.
Figure 2-8 Cisco CNS IE2100 Cisco CNS Configuration Registrar Login Window
When you see this screen, you are ready to configure the Cisco CNS IE2100 appliance.
Configuring IOS Devices to Communicate with a Cisco CNS IE2100 Appliance
In order to support communication with the Cisco CNS IE2100 appliance, IOS network elements must
be operating with IOS version 12.2(8)T or later. Two IOS commands must be entered into the IOS
device:
• us-gw-1(config)# cns config partial 172.19.49.20 80
• us-gw-1(config)# cns event 172.19.49.20 keepalive 100 30
Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Implementation Guide
OL-2706-01
2-23
Page 24

Chapter 2 Provisioning
Step by Step Installation and Initial Configuration
The variable parameters are the IP address of the Cisco CNS IE2100 appliance (172.19.49.20), the
communication port (80), the keep alive time (100 seconds), and the retry count (30).
There are several ways for this to happen. The method of choice in this chapter is to do it through the
Cisco PTCTopologyManager.If the elements are includedin the Cisco PTC NetworkInformation Seed
File for discovery or added through the Cisco PTC Topology Manager, the commands are entered into
the devices by Cisco PTC.
Installing Cisco MGC Node Manager (including VSPT, CiscoView, and CEMF)
Successful network management using Cisco MGC Node Manager (CMNM) begins witha well-planned
and carefully executed installation. Network element management involves many interdependent
factors, including:
• the correct hardware for your environment
• the correct software release and patch levels on the managed devices
• the correct installation of Cisco Element Manager Framework, the foundation software for CMNM.
To organize the installation process, use the Planning and Installation Checklist below to plan and carry
out your installation. Begin by reading it over to understand the major tasks in a successful installation
and check off each task as completed.
Planning and Installation Checklist
Procedures for completing each task are described in the sections that follow.
Before you begin, be familiar with each product’s Release Notes document. The Release Notes
supplement and, when different, take precedence over the information provided in this document.
1. Gather installation software and required information.
2. Determine hardware requirements for your environment.
3. Ensure the network devices have the correct software.
4. Ensure the Sun Solaris operating system is installed on your server.
5. Partition the hard drives when you install the OS.
6. Install the recommended patch cluster for Solaris 8.
7. Obtain a Cisco EMF license.
8. Check system prerequisites. (DNS)
9. Install the Cisco MGC Host Voice Services Provisioning Tool.
10. Install Cisco EMF 3.2 and any necessary patches.
11. If you plan to use raw file systems, configure raw file systems in ObjectStore.
12. Install and verify CMNM 2.1 and any necessary patches.
Gathering Installation Software
2-24
Your order of CMNM includes three product CDs:
1. Cisco Element Management Framework3.2 on the first CD. The software includes ObjectStore 5.1
Service Pack 2, which provides databasemanagement. Go to the Release Notes and the latest Cisco
EMF 3.2 software patch.
Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Implementation Guide
OL-2706-01
Page 25

Chapter 2 Provisioning
2. CMNM 2.3.1 on the second CD, including:
a. the CMNM Element Managers that work with Cisco EMF.
b. Cisco MGC Node Manager for provisioning the Cisco Media Gateway Controller.
c. CiscoView 5.1, installedautomatically when CMNM is installed (management interface for the
Cisco SLT).
3. CiscoWorks on the third CD.
You will also need VSPT version 2.3.1 with patch P01 and Release Notes available from:
http://www.cisco.com/cgi-bin/tablebuild.pl/vspt
as well as patches for CMNM and CEMF, if available, at:
http://www.cisco.com/cgi-bin/tablebuild.pl/cemf (CEMF latest patches)
http://www.cisco.com/cgi-bin/tablebuild.pl/mgc-nm (CMNM latest patches).
Determining the Hardware Requirements for Your Environment
See the“Recommended HardwareConfigurationfor CMNM” section or theCMNM User’s Guideat the
following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/access/sc/rel9/cmnm21/index.htm.
Step by Step Installation and Initial Configuration
Ensuring the Network Devices have the Correct Software
Refer to the CMNM User’s Guide for various pairings of software images on different network devices.
For the purpose of this chapter, the following is used:
• PGW 2200 version 9.x
• Cisco SLT on c2651 IOS version 12.2(8)T or later
• Cisco LAN switch (Catalyst 2924) version.
Ensuring the Sun Solaris 8 Operating System is Installed on Your Workstation
Our management hostmachines have been configured with Solarisversion 8and the recommendedpatch
cluster available from http://sunsolve.sun.com as of October 1, 2002. If you are unsure of the version
and patch info on your host machines, consult with your Solaris system administrator. The Sun host
setup is detailed in the next sections of this chapter.
Partitioning the Hard Drives
Refer to the User Guides for various partitioning suggestions for different sized networks. Our test lab
setup uses the suggestions for a Standalone system.
Installing the Solaris 8 Patch Cluster
OL-2706-01
Assuming sufficient hard drive space, it is recommended that the Solaris 8 recommended Patch Cluster
should be installed. Down load the recommended Patch Cluster from the following URL:
http://sunsolve.Sun.COM/pub-cgi/show.pl?target=patches/patch-access.
Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Implementation Guide
2-25
Page 26

Step by Step Installation and Initial Configuration
The following stepsinstall the recommendedPatch Cluster thathas beendownloadedto the /opt/patches
directory (create this directory first) on the Cisco PTC machine.
Step 1 Go to the /opt directory:
ptc-tme# cd /opt
Step 2 Create the patches directory:
ptc-tme# mkdir patches
Step 3 Go to the /patches directory:
ptc-tme# cd patches
Step 4 List the contents of the patches directory:
ptc-tme# ls
8_Recommended.zip
Step 5 Unzip the contents of the Patch Cluster:
ptc-tme# unzip 8_Recommended.zip (this can take fifteen minutes or more)
Archive: 8_Recommended.zip
creating: 8_Recommended/
inflating: 8_Recommended/CLUSTER_README
inflating: 8_Recommended/copyright
inflating: 8_Recommended/install_cluster
?----------------output suppressed--------------?
inflating: 8_Recommended/10900707/SUNWesu/install/patch_checkinstall
inflating: 8_Recommended/109007-07/SUNWesu/install/patch_postinstall
inflating: 8_Recommended/109007-07/SUNWesu/install/postinstall
inflating: 8_Recommended/109007-07/SUNWesu/install/preinstall
creating: 8_Recommended/109007-07/SUNWesu/reloc/
creating: 8_Recommended/109007-07/SUNWesu/reloc/usr/
creating: 8_Recommended/109007-07/SUNWesu/reloc/usr/bin/
inflating: 8_Recommended/109007-07/SUNWesu/reloc/usr/bin/batch
inflating: 8_Recommended/109007-07/README.109007-07
Chapter 2 Provisioning
2-26
Step 6 List the contents of the patches directory again:
cnote-tme# ls
8_Recommended 8_Recommended.zip
Step 7 Go to the 8_Recommended directory:
cnote-tme# cd 8_Recommended
Step 8 Install the contents of the Patch Cluster:
cnote-tme# ./install_cluster
Patch cluster install script for Solaris 8 Recommended
Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Implementation Guide
OL-2706-01
Page 27

Chapter 2 Provisioning
Step 9 Note some of the installation of patches fail.This is normal behavior and is not fatal. Just make sure the
Step by Step Installation and Initial Configuration
*WARNING* SYSTEMS WITH LIMITED DISK SPACE SHOULD *NOT* INSTALL PATCHES:
With or without using the save option, the patch installation process
will still require some amount of disk space for installation and
administrative tasks in the /, /usr, /var, or /opt partitions where
patches are typically installed. The exact amount of space will
depend on the machine's architecture, software packages already
installed, and the difference in the patched objects size. To be
safe, it is not recommended that a patch cluster be installed on a
system with less than 4 MBytes of available space in each of these
partitions. Running out of disk space during installation may result
in only partially loaded patches. Check and be sure adequate disk space
is available before continuing.
Are you ready to continue with install? [y/n]: y
Determining if sufficient save space exists...
Sufficient save space exists, continuing...
Installing patches located in /opt/8_Recommended
Using patch_order file for patch installation sequence
Installing 110380-04...
Installation of 110380-04 failed. Return code 2.
Installing 110934-08...
Installing 111111-03...
Installing 110662-09...
Installing 112396-02...
Installing 108987-09...
Installing 111293-04...
Installation of 111293-04 failed. Return code 2.
?---------------------output suppressed----------------------------?
the three required patches listed in the various product Release Notes did not fail to install. You can
check which patches are installed on a Solaris host or for the presence of a particular patch and its
dependencies with the following commands:
host# showrev –p
host# showrev –p | grep 108987-09
Patch: 108528-16 Obsoletes: 108874-01, 108966-06, 108979-10, 109153-01,
109236-01, 109291-06, 109296-05, 109309-02, 109313-02, 10934
5-02, 109348-05, 109350-06, 109571-02, 109656-01, 109663-01, 109801-02,
109880-01, 110096-05, 110118-02, 110121-01, 110132-02, 11013
3-03, 110134-02, 110141-02, 110201-01, 110225-01, 110231-01, 110372-02,
110517-04, 110599-02, 109041-04, 111050-03, 111205-02, 11010
1-01, 110562-01, 110384-05, 110783-01, 110850-01, 111372-04, 111456-01,
108947-01, 109048-06, 110180-01, 110552-01, 111541-02, 10905
2-01, 110556-01, 109054-02, 110558-01, 111207-01, 109056-01, 110196-01,
OL-2706-01
Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Implementation Guide
2-27
Page 28

Step by Step Installation and Initial Configuration
110554-01, 109472-07, 109740-04, 109742-04, 109060-02, 11018
2-01, 111537-01, 109062-01, 110186-01, 110186-02, 110595-01, 110932-01,
111054-02, 109181-04, 109279-19, 109904-05, 109906-06, 10995
4-01, 110098-01, 110383-02, 111035-01, 111884-02, 111919-04, 112334-02
Requires: 108987-09, 111111-03, 111293-01, 111310-01, , I
incompatibles: 109079-01 Packages: SUNWkvmx, SUNWkvm, SUNWcarx, SUNWcar,
SUNWcsu, SUNWcsr, SUNWcslx, SUNWcsl, FJSVhea, SUNWscpu, SUNW
csxu, SUNWpmu, SUNWpmr, SUNWcpr, SUNWcprx, SUNWefcx, SUNWdrr, SUNWdrrx,
SUNWidn, SUNWidnx, SUNWpmux, SUNWmdb, SUNWmdbx, SUNWsrh, SUN
Wtnfc, SUNWtnfcx, SUNWhea, SUNWarc, SUNWarcx, SUNWcstl, SUNWcstlx,
SUNWcpc, SUNWcpcx
Patch: 108987-09 Obsoletes: Requires: 112396-02 Incompatibles:
Packages: SUNWadmr, SUNWswmt
Obtaining a Cisco EMF License
Chapter 2 Provisioning
You need a valid license key file available on the system to start Cisco EMF. In a distributed
configuration, the license key is required on the Management server.
The following steps describe how to obtain a Cisco EMF license.
Step 1 If you are a registered Cisco Connection Online (CCO) user, go to the Cisco Software Registration site,
and look for Cisco Element Management Framework under Network Management Products:
http://cco.cisco.com/cgi-bin/Software/FormManager/formgenerator.pl.
If you are not a registered CCO user, go to the Cisco Software Registration site:
http://cco.cisco.com/public/sw-center/sw-registration.shtml.
Step 2 In the Contact Information section, fill all required fields (denoted by an asterisk).
Step 3 In the Version number field, select version 3.2.
Step 4 If it was not automatically filled in for you when you completed the Contact Information, enter the
Product Authorization Key (PAK) number which is on your product CD.
Step 5 Enter the host name of the server where Cisco EMF is to be installed.
Step 6 Enter the host ID of the server where Cisco EMF is to be installed.
Step 7 If you do not know the hostname or hostid of your machine, perform the following commands on the
host machine:
cmnm-pri# hostname
cmnm-pri
cmnm-pri# hostid
80b8cb59
2-28
Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Implementation Guide
OL-2706-01
Page 29

Chapter 2 Provisioning
Step 8 Provide answers to the questions at the end of the form, then click Enter Form.
To update a Cisco EMF licensecurrently in use (for example,if you wish to extendan evaluation license
or convert an evaluation system to aproper installationwith a permanent license) refer to theCisco EMF
Installation and Administration Guide at:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/rtrmgmt/cemf/3_2/install/license.htm#xtocid183871.
Checking System Prerequisites
If you do not know the procedure for networking your host machine and activating DNS, consult with a
system administrator or the CMNM User’s Guide at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/access/sc/rel9/cmnm21/index.htm.
Verify that your machine host(s) can be reached through DNS by invoking the following command:
cmnm-pri# nslookup cmnm-pri
Server: dns-sj.cisco.com
Address: 171.x.x.x
Step by Step Installation and Initial Configuration
Name: cmnm-pri.cisco.com
Address: 172.19.49.2
You are now ready to begin the installation procedures for VSPT, CEMF, and CMNM.
Order of Installation
1. The first application to be installed is VSPT and any associated patches. VSPT must be installed
prior to CMNM.
2. The next procedure is to install CEMF with its patches.
3. The next procedure is to install CMNM with its patches.
Installing VSPTand Available Patches
Installation Prerequisites
The Voice Services Provisioning Tool can be installed locally or remotely. If your host machine is
equipped witha Frame buffer, keyboard, mouse, and monitor, the installation isstraight forward. If your
host machine is not equipped with the setup for a local monitor and you wish to install VSPT from a
remote machine, you can install it through the GUI remotely. If your terminal emulation program is not
X-based, then you can install using the nodisplay option. This example uses the nodisplay option.
OL-2706-01
Step 1 Untar the image file in a temporary directory:
cmnm-pri# cd /opt/images
cmnm-pri# pwd
/opt/images
Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Implementation Guide
2-29
Page 30

Step by Step Installation and Initial Configuration
cmnm-pri# mkdir tmp
cmnm-pri# cd tmp
cmnm-pri# ls
CSCOvspt-2.3.1.tar
Step 2 Untar the contents of the CSCOvspt-2.3.1.tar file:
cmnm-pri# tar -xvof CSCOvspt-2.3.1.tar
x ., 0 bytes, 0 tape blocks
x ./version, 343 bytes, 1 tape blocks
x ./README_FIRST.txt, 5545 bytes, 11 tape blocks
x ./README_NOTES.txt, 20779 bytes, 41 tape blocks
x ./jre, 0 bytes, 0 tape blocks
x ./jre/lib, 0 bytes, 0 tape blocks
?----------------------output suppressed-------------------?
x ./classes/GetFileList.class, 3385 bytes, 7 tape blocks
x ./classes/ModifyFiles.class, 2614 bytes, 6 tape blocks
x ./classes/QueryBackupUserPanel.class, 9314 bytes, 19 tape blocks
x ./classes/QueryMGCTypePanel.class, 3435 bytes, 7 tape blocks
x ./classes/QueryWebBrowserPanel.class, 11258 bytes, 22 tape blocks
Chapter 2 Provisioning
Step 3 List the contents of the directory:
cmnm-pri# ls -l
total 91328
-rw-r--r-- 1 root other 26754560 Sep 24 17:14 CSCOvspt-
2.3.1.tar
-r--r--r-- 1 root other 5545 Aug 21 10:25 README_FIRST.txt
-r--r--r-- 1 root other 20779 Aug 21 10:25 README_NOTES.txt
drwxrwxrwx 2 root other 512 Aug 21 10:27 classes
drwxr-xr-x 4 root other 512 Aug 21 10:25 jre
drwxrwxrwx 2 root other 512 Aug 21 10:27 modules
drwxr-xr-x 3 root other 512 Aug 21 10:25 pkg
-r-xr-xr-x 1 root other 7664 Aug 21 10:27 setup
-r--r--r-- 1 root other 19908895 Aug 21 10:27 setup.class
-r--r--r-- 1 root other 343 Aug 21 10:25 version
Step 4 Run the setup program with the nodisplay option (don't forget the dash before the option argument):
cmnm-pri# ./setup -nodisplay
WARNING: This program is protected by copyright law and international treaties.
Unauthorized reproduction or distribution of this program, or any portion of it, may
result in severe civil and criminal penalties, and will be prosecuted to the maximum
extent possible under law.
2-30
Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Implementation Guide
OL-2706-01
Page 31

Chapter 2 Provisioning
Step 5 You are asked to read a description of the application and then the license agreement whose output is
Step 6 Enter “I accept the terms of the license agreement.” to approve, or “I do not accept the terms of the
Step 7 Click Next to install to this folder or click Change to install to a different folder. [/opt/CSCOvsp23]
Step by Step Installation and Initial Configuration
omitted here. At the end of the license agreement, you must accept the agreement in order to continue.
Then follow the on screen prompts. The default answers are in block parentheses. If you want to accept
the default response, just click Enter:
license agreement.” to disapprove [I accept the terms of the license agreement.]: hit Enter to accept).
The directory "/opt/CSCOvsp23" does not exist. Do you want to create it now [y]? y
Enter the Backup User ID:
1. Yes
2. No
Select a Backup User ID [2] 2 (a backup user is not required)
Ready to Install
The following items will be installed:
Cisco Voice Services Provisioning Tool
Destination: /opt/CSCOvsp23
Product (900KB)
Selected Features:
Program Files (26.9MB)
Data Files (162KB)
1. Install Now
2. Exit
What would you like to do [1]? 1
Installing Cisco Voice Services Provisioning Tool
|-----------|-----------|-----------|------------|
0% 25% 50% 75% 100%
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
OL-2706-01
Installation Summary
The following items were installed:
Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Implementation Guide
2-31
Page 32

Step by Step Installation and Initial Configuration
Cisco Voice Services Provisioning Tool
Destination: /opt/CSCOvsp23
Installed Features:
Program Files (26.9MB)
Data Files (162KB)
1. Exit
What would you like to do [1]? 1
Cisco Voice Services Provisioning Tool installation is complete.
__________________________________________________________________
Step 8 After the main image is installed, do the same with the patch file for VSPT:
cmnm-pri# ls
CSCOvspt-2.3.1.tar CSCOvspt-2.3.1-patch-01.tar
Step 9 Untar the contents of the CSCOvspt-2.3.1-patch-01.tar file:
cmnm-pri# tar -xvof CSCOvspt-2.3.1-patch-01.tar
x ., 0 bytes, 0 tape blocks
x ./patchCSCOvspt, 5508 bytes, 11 tape blocks
x ./modules, 0 bytes, 0 tape blocks
Chapter 2 Provisioning
?---------------output suppressed---------------------------?
x ./pkgs/CSCOvsp23/reloc/uninstall/patchCSCOvspt, 5508 bytes, 11 tape blocks
x ./pkgs/CSCOvsp23/reloc/version, 415 bytes, 1 tape blocks
cmnm-pri#
Step 10 Run the patch file patchCSCOvspt executable program:
cmnm-pri# ./patchCSCOvspt
--------------------------------------------------------------------- Welcome to the Cisco Voice Services Provisioning Tool
Patch Program
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Enter the logfile directory location [/var/tmp] [?] <Enter>
Enter the logfile name [patchCSCOvspt-01.log] [?] <Enter>
Do you wish to install CSCOvsp23 Patch 01 [y,n,?,q] y
2-32
Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Implementation Guide
OL-2706-01
Page 33

Chapter 2 Provisioning
Step by Step Installation and Initial Configuration
----------------------------------Installing Patch 01 to CSCOvsp23
-----------------------------------
----------------------------------Backing up file to be patched
---------------------------------- /var/sadm/pkg/CSCOvsp23/pkginfo to
?---------------output suppressed---------------------?
Processing package instance <CSCOvsp23> from </opt/images/tmp/pkgs>
Cisco Voice Services Provisioning Tool
(sparc) 2.3(1)
Cisco Systems, Inc.
Using </opt/CSCOvsp23> as the package base directory.
## Processing package information.
## Processing system information.
## Verifying disk space requirements.
Installing Cisco Voice Services Provisioning Tool as <CSCOvsp23>
## Installing part 1 of 1.
/opt/CSCOvsp23/classes/com/cisco/transpath/dart/editor/configEditor.properties
/opt/CSCOvsp23/classes/dart.jar
/opt/CSCOvsp23/docs/README_FIRST.txt
/opt/CSCOvsp23/docs/README_NOTES.txt
/opt/CSCOvsp23/uninstall/modules/vsptPatchUtilities
/opt/CSCOvsp23/uninstall/patchCSCOvspt
/opt/CSCOvsp23/version
[verifying class <none>]
Installation of <CSCOvsp23> was successful.
Done
Please see logfile:
/var/tmp/patchCSCOvspt-01.log
OL-2706-01
Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Implementation Guide
2-33
Page 34

Step by Step Installation and Initial Configuration
Checking for Package Install
Step 11 Check to ensure the entire package was installed:
cmnm-pri# pkginfo -l CSCOvsp23
PKGINST: CSCOvsp23
NAME: Cisco Voice Services Provisioning Tool
CATEGORY: application
ARCH: sparc
VERSION: 2.3(1)
BASEDIR: /opt/CSCOvsp23
VENDOR: Cisco Systems, Inc.
PSTAMP: Mon Sep 23 09:55:18 EDT 2002
INSTDATE: Sep 25 2002 14:05
STATUS: completely installed
FILES: 7 installed pathnames
1 executables
7295 blocks used (approx)
Step 12 If you see any message other than “completely installed”, you must solve the problem and retry.
Chapter 2 Provisioning
Installing CEMF 3.2 and Available Patches
Step 13 Load the first of the three CMNM CDs into your host CD drive and install CEMF:
cmnm-pri# cd cdrom/cdrom0
cmnm-pri# ./cemfinstall
INSTALL PACKAGE
===============
1) Cisco Element Manager Framework - Server
2) Cisco Element Manager Framework - Client
q) Quit
Which package do you wish to install? (Def:1) [?,q] 1
Option "Cisco Element Manager Framework - Server" chosen.
Installing the Server option installs both the Server and Client applications. If you wish to have a
distributed installation, you can install the Client on a separate machine. This guide installs the Server
option and runs both the presentation and management servers on the same host.
Installing package(s) "CSCOcemfm".
2-34
Processing package instance <CSCOcemfm> from
</opt/images/tmp/CEMF3.2/.cemf/packages>
Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Implementation Guide
OL-2706-01
Page 35

Chapter 2 Provisioning
Step by Step Installation and Initial Configuration
CEMF Manager
(sparc) 3.2
Cisco Systems, Inc.
CEMF Manager Installation
CEMF Manager will be installed into directory: /opt/cemf
Is this directory correct [y] [y,n,?]
CEMF Manager Installation
CEMF Manager backup directory is: /opt/Backup
Is this directory correct [y] [y,n,?]
CEMF Manager Installation
CEMF Manager logs directory is: /opt/cemf/logs
Is this directory correct [y] [y,n,?]
CEMF Manager Installation
This machine is configured with multiple network interfaces.
Please choose the number that corresponds to the interface
you wish to use. Or hit return to enter the name by hand.
1 cmnm-pri/172.19.49.2
Please choose a number (default: Other) [?,??]: 1
The hostname specified was "cmnm-pri".
Is this correct? [y] [y,n,?]
The IP Address of cmnm-pri is "172.19.49.2".
Is this correct? [y] [y,n,?]
CEMF Manager Installation
OL-2706-01
Local Hostname : cmnm-pri
Server Hostname : cmnm-pri
Server IP Address : 172.19.49.2
Is this setup correct? [y] [y,n,?]
CEMF Manager Installation
Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Implementation Guide
2-35
Page 36

Step by Step Installation and Initial Configuration
ObjectStore has not been found on the system.
ObjectStore needs to be installed.
Is this correct [y] [y,n,?]
CEMF Manager Installation
To gain extra performance ObjectStore can be configured to use
a raw partition to store its databases. Choosing this option
will require ObjectStore to be correctly configured before any
attempt to start CEMF Manager can be made.
Do you wish to store the databases in a raw partition [n] [y,n,?] n
CEMF Manager Installation
Utilizing ObjectStore with raw file partitions can improve the performance of CEMF and its EMS
applications. It requires some expertise and follows certain rules. If you wish to enable this option, you
must refer to the CMNM User Guide, at the following URL, for more details:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/access/sc/rel9/cmnm21/index.htm.
Step 14 Confirm the directory for the ObjectStore database files. This should preferably be a separate partition
from where the CEMF Manager is installed.
Chapter 2 Provisioning
CEMF Manager Installation
Databases will be placed in "/opt/cemf/db"
Is this correct [y] [y,n,?] y
CEMF Manager Installation
Please confirm the directory for the ObjectStore transaction log file.
This should preferably be a separate partition from where CEMF Manager
is installed and separate from where the ObjectStore databases will be
created.
WARNING This file can reach a size of 1GB.
Transaction log will be placed in "/opt"
Is this correct [y] [y,n,?] y
CEMF Manager Installation
CEMF Manager requires a FlexLM license manager daemon to be running
before CEMF Manager will start. You have two options:
2-36
* The default option is to Run the FlexLM daemon
which is provided with CEMF Manager (recommended).
Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Implementation Guide
OL-2706-01
Page 37

Chapter 2 Provisioning
Note If you answer no to the following question, you should be able to provide a valid path for your licence
Step by Step Installation and Initial Configuration
* Alternatively you can use an existing FlexLM daemon
if one is already running on your system.
file. It is then copied to the /opt/cemf/config/licenses directory.
Do you want to run CEMF Manager's FlexLM daemon [y] [y,n,?] y
Do you have a valid license file to use [y] [y,n,?] y
CEMF Manager Installation
CEMF Manager requires that a valid license is available to the installation program.
Please enter the full name (including path) of the license file [?]
/opt/cemf/config/licenses/cmnm-pri80b8cb59.lic
Note You can store the license file anywhere you wish on the host, however, understand that the host will
subsequently copy it to the directory listed in the previous step. If you upgrade or update your license
file, you must replace the file that is in the above directory. Only one license file can be accommodated
at any one time.
CEMF will store its uploaded IOS config files into directory:
/opt/cemf/cemfIos/archive/configArchive
Is this directory correct [y] [y,n,?] y
Using </opt/cemf> as the package base directory.
## Processing package information.
## Processing system information.
8 package pathnames are already properly installed.
## Verifying disk space requirements.
OL-2706-01
Installing CEMF Manager as <CSCOcemfm>
## Installing part 1 of 1.
/opt/cemf/Orbix2000/bin/bi2tcl <symbolic link>
/opt/cemf/Orbix2000/bin/it_generic_server <symbolic link>
/opt/cemf/Orbix2000/bin/itactivator <symbolic link>
/opt/cemf/Orbix2000/bin/itadmin <symbolic link>
Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Implementation Guide
2-37
Page 38

Step by Step Installation and Initial Configuration
/opt/cemf/Orbix2000/bin/itconfig_rep <symbolic link>
/opt/cemf/Orbix2000/bin/itevent <symbolic link>
/opt/cemf/Orbix2000/bin/itifr <symbolic link>
/opt/cemf/Orbix2000/bin/itkdm <symbolic link>
/opt/cemf/Orbix2000/bin/itlocator <symbolic link>
?-----------output suppressed------------------------?
/opt/cemf/db/pollerServer.adb
/opt/cemf/db/serviceMgrServer.adb
/opt/cemf/db/statusPropagationRecalculator.adb
/opt/cemf/db/statusPropagationServer.adb
/opt/cemf/db/trServer.adb
/opt/cemf/db/vectorServer.adb
/opt/cemf/db/virtualAttributeServer.adb
[verifying class <schema>]
## Executing postinstall script.
020925 163258 ObjectStore Release 5.1 Service Pack 4 Database Server
020925 163258 LOG 0001 There are no partitions specified in the parameters file.
Only file databases will be accessible through this server.
CEMF Manager License Installer...
Installing /opt/cemf/config/licenses/cmnm-pri80b8cb59.lic
Starting ATL license manager daemon
Chapter 2 Provisioning
Creating /opt/cemf/lochness/config/IOSDrep.locService
Installation of <CSCOcemfm> was successful.
The option install "Cisco Element Manager Framework - Server" was completed successfully.
Step 15 After a successful installation of CEMF, eject the CD. Next step is to install any CEMF patches.
CEMF Patch Installation
CEMF patches are found on the Cisco Connection Online site (with a registered login) at the following
location:
http://www.cisco.com/cgi-bin/tablebuild.pl/cemf.
Note The latest patch for this product at the time this chapter was written is Patch 3, with a smaller patch
(P3.2) which is dependent upon the installation of Patch 3.
2-38
Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Implementation Guide
OL-2706-01
Page 39

Chapter 2 Provisioning
Step 1 List the contents of the Patch directory:
Step 2 Uncompress the Patch files:
Step 3 Untar Patch P3:
Step by Step Installation and Initial Configuration
cmnm-pri# ls
-rw-r--r-- 1 root other 1280455 Sep 26 09:31 CEMF3.2P3.2.tar.Z
-rw-r--r-- 1 root other 145691565 Sep 26 09:31 CEMF3.2P3.tar.Z
cmnm-pri# uncompress *
cmnm-pri# tar -xvof CEMF3.2P3.tar
x ., 0 bytes, 0 tape blocks
x ./CEMF_3.2_PATCH_3, 0 bytes, 0 tape blocks
x ./CEMF_3.2_PATCH_3/packages, 0 bytes, 0 tape blocks
x ./CEMF_3.2_PATCH_3/packages/CSCOcemfm, 0 bytes, 0 tape blocks
x ./CEMF_3.2_PATCH_3/packages/CSCOcemfm/pkgmap, 82207 bytes, 161 tape blocks
x ./CEMF_3.2_PATCH_3/packages/CSCOcemfm/pkginfo, 414 bytes, 1 tape blocks
x ./CEMF_3.2_PATCH_3/packages/CSCOcemfm/reloc, 0 bytes, 0 tape blocks
x ./CEMF_3.2_PATCH_3/packages/CSCOcemfm/reloc/ODI, 0 bytes, 0 tape blocks
?------------output suppressed---------------------?
x ./CEMF_3.2_PATCH_3/packages/CSCOcemfc/install/patch_postinstall, 822 bytes, 2 tape
blocks
x ./CEMF_3.2_PATCH_3/packages/CSCOcemfc/install/postinstall, 7356 bytes, 15 tape blocks
x ./CEMF_3.2_PATCH_3/packages/CSCOcemfc/install/preinstall, 5512 bytes, 11 tape blocks
x ./CEMF_3.2_PATCH_3/packages/170103-10, 0 bytes, 0 tape blocks
x ./CEMF_3.2_PATCH_3/packages/170103-10/CSCOcemfc symbolic link to ../CSCOcemfc
x ./CEMF_3.2_PATCH_3/packages/170103-10/.diPatch, 0 bytes, 0 tape blocks
x ./CEMF_3.2_PATCH_3/packages/.CSCOcemfc-patch.pkginfo, 26255 bytes, 52 tape blocks
x ./CEMF_3.2_PATCH_3/cemfinstall, 40982 bytes, 81 tape blocks
Step 4 List the contents of the current directory:
cmnm-pri# ls
CEMF3.2P3.2.tar CEMF3.2P3.tar CEMF_3.2_PATCH_3
Step 5 Change to the CEMF_3.2_PATCH_3 directory:
cmnm-pri# cd CEMF_3.2_PATCH_3
Step 6 List the contents of the CEMF_3.2_PATCH_3 directory:
cmnm-pri# ls
cemfinstall packages
OL-2706-01
Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Implementation Guide
2-39
Page 40

Step by Step Installation and Initial Configuration
Step 7 Invoke the CEMF installation script:
cmnm-pri# ./cemfinstall
INSTALL PACKAGE
===============
1) CEMF Server 3.2 Patch 170003-10
2) CEMF Client 3.2 Patch 170103-10 - Not Installed
q) Quit
Which package do you wish to install? (Def:1) [?,q] 1
Option "CEMF Server 3.2 Patch 170003-10" chosen.
Installing package(s) "CSCOcemfm".
CEMF Manager system not running.
There are no previous patches to remove.
Chapter 2 Provisioning
Checking installed patches...
Verifying sufficient filesystem capacity (dry run method)...
Installing patch packages...
Patch number 170003-10 has been successfully installed.
See /var/sadm/patch/170003-10/log for details
Patch packages installed:
CSCOcemfm
Uncompressing patch...
Transferring <CSCOcemfm> package instance
Uncompressing completed
The option install "CEMF Server 3.2 Patch 170003-10" was completed successfully.
Step 8 Now do the same with Patch 3.2:
cmnm-pri# tar -xvof CEMF3.2P3.2.tar
cmnm-pri# ls
CEMF3.2P3.2.tar CEMF3.2P3.tar CEMF_3.2_PATCH_3
CEMF_3.2_PATCH_190302-01
Step 9 Change to the CEMF_3.2_PATCH_190302-01 directory:
cmnm-pri# cd CEMF_3.2_PATCH_190302-01
Step 10 List the contents of the CEMF_3.2_PATCH_190302-01 directory:
cmnm-pri# ls
cemfinstall packages
2-40
Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Implementation Guide
OL-2706-01
Page 41

Chapter 2 Provisioning
Step 11 Invoke the CEMF installation script:
Step by Step Installation and Initial Configuration
cmnm-pri# ./cemfinstall
INSTALL PACKAGE
===============
1) CEMF Server 3.2 Patch 190302-01
2) CEMF Client 3.2 Patch 200302-01 - Not Installed
q) Quit
Which package do you wish to install? (Def:1) [?,q] 1
Option "CEMF Server 3.2 Patch 190302-01" chosen.
Installing package(s) "CSCOcemfm".
CEMF Manager system not running.
Checking installed patches...
Verifying sufficient filesystem capacity (dry run method)...
Installing patch packages...
Starting CEMF
Step 12 Start the CEMF application:
Patch number 190302-01 has been successfully installed.
See /var/sadm/patch/190302-01/log for details
Patch packages installed:
CSCOcemfm
Uncompressing patch...
Transferring <CSCOcemfm> package instance
Uncompressing completed
The option install "CEMF Server 3.2 Patch 190302-01" was completed successfully.
cmnm-pri# cd /opt/cemf
cmnm-pri# bin/cemf start
This process takes ten to fifteen minutes. It requires a current, valid license file in order to start.
OL-2706-01
Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Implementation Guide
2-41
Page 42

Step by Step Installation and Initial Configuration
Installing the Cisco MGC Node Manager
Step 1 Before installing CMNM, ensure CEMF is running:
cmnm-pri# cd /opt/cemf
cmnm-pri# bin/cemf query
CEMF Manager 3.2 initialized
8957 /opt/cemf/bin/sysmgr
8974 serverLockCoordinator
8972 coordinator
8973 eventChannelHost EventChannelHost
8975 configServer
8976 objectServer
8977 appsServer
8983 queryServer
8985 ogServer
8984 mgrTransRouter
8986 localDBServer
8999 alarmDirServer
9000 notificationServer
9001 trServer
9002 vectorServer
9003 clearCorrelationServer
9004 abstractionServer
9005 statusPropagationServer
9006 agServer
9007 /opt/cemf/tools/bin/perl - I /opt/cemf/tools/lib/perl5/5.00502/sun4-solaris:/opt
9012 attributeHistoryCollector
9013 attributeHistoryServer
9014 pollerServer
9015 attributePollerServer
9016 virtualAttributeServer
9017 eventScheduler
9018 icmpServer
9019 asyncSnmpDataRepository
9021 asyncSnmpDataRepository -id 1
9022 asyncSnmpDataRepository -id 2
9023 asyncSnmpDataRepository -id 3
9024 asyncSnmpDataRepository -id 4
9025 trapManager
9026 trapAlarmMapper
9027 perfRepository
9028 asyncIosDataRepository
9138 /bin/sh /opt/cemf/bin/cgw_wrap_itloc
Chapter 2 Provisioning
2-42
Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Implementation Guide
OL-2706-01
Page 43

Chapter 2 Provisioning
Step by Step Installation and Initial Configuration
9151 /opt/cemf/Orbix2000/orbix_art/1.2/bin/sc42/itlocator -ORBname locator run
9139 nbinterface
9153 /opt/cemf/Orbix2000/orbix_art/2.0/bin/itlocator run -ORBdomain_name CEMF_2.0 -O
9152 /bin/sh /opt/cemf/bin/cgw_wrap_itact
9182 /opt/cemf/Orbix2000/orbix_art/1.2/bin/sc42/itactivator - ORBname activator run
9185 /opt/cemf/Orbix2000/orbix_art/1.2/bin/sc42/itnaming
9154 /opt/cemf/Orbix2000/orbix_art/2.0/bin/itnode_daemon run - ORBdomain_name CEMF_2.
9160 /opt/cemf/Orbix2000/orbix_art/2.0/bin/itnotify run - ORBdomain_name CEMF_2.0 -OR
9161 /opt/cemf/bin/corbaGatewayManager
9170 /opt/cemf/bin/corbaMetadata
9186 /opt/cemf/bin/corbaDataAbstractor
9190 /opt/cemf/bin/corbaActionLauncher
9194 /opt/cemf/bin/corbaParticipation
9198 /opt/cemf/bin/corbaObjectGroups
9202 /opt/cemf/bin/corbaEventChannelManager
9206 genericController
9207 mapServer
14566 hostController
15062 serviceMgrServer
15100 mgcController
15102 mgcTrapProcessor
15210 sessionMgrServer
15211 dialogMgrServer
15212 discoveryServer
15213 discoveryScheduler
15695 /opt/cemf/VCG/bin/ObjectAccess
15697 /opt/cemf/VCG/bin/McgNotifyServer
OL-2706-01
Step 2 Verify the Volume Management daemon is running:
cmnm-pri# ps -ef | grep vold
root 253 1 0 Sep 24 ? 0:00 /usr/sbin/vold
root 9354 8572 0 10:34:04 pts/2 0:00 grep vold
Step 3 If you do not see the vold process, try starting it:
cmnm-pri# /etc/init.d/volmgt start
Step 4 Check for the process again to see if you were successful starting it. If you were not, consult with your
system administrator to rectify the situation before continuing. Assuming success,insert the second CD
into the CDROM driveand run the CMNM install program. You must be root to install CMNM. It takes
up to ten minutes depending on the platform.
cmnm-pri# cd /cdrom/cscocmnm
cmnm-pri# ./installCSCOcmnm
--------------------------------------------------------------------- Cisco MGC-Node Manager Installation
Thu Sep 26 10:38:49 AM
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Implementation Guide
2-43
Page 44

Step by Step Installation and Initial Configuration
Setup has detected that the CEMF Manager software is installed.
Do you wish to install the CSCOcmnm Manager software. [y/n]: y
It is recommended that your databases are backed up before running this command.
Have your databases been backed up [y/n]: [n] y
Note If your install is brand new, there are no databases to backup, so you can answer y to the above query
and the install continues. Otherwise, if you answer n, the install script displays instructions on how to
back up your databases.
Please enter the CiscoView Server IP address [def: 0.0.0.0] [?,q] 172.19.49.2 (this
machine)
Enter the logfile directory location [/var/tmp] [?]
Chapter 2 Provisioning
Enter the logfile name [installCSCOcmnm.log] [?]
Disk Space OK.
Continue with CSCOcmnm install [y,n,?] y
Cisco MGC-Node Manager (CMNM) 2.3
(sparc) 2.3(1)
Cisco Systems, Inc.
Using </opt/cemf> as the package base directory.
## Processing package information.
## Processing system information.
## Verifying disk space requirements.
Installing Cisco MGC-Node Manager (CMNM) 2.3 as <CSCOcmnm>
## Installing part 1 of 1.
/opt/cemf/bin/cmnmstatus <symbolic link>
/opt/cemf/bin/cmnmstatus.pl
/opt/cemf/bin/cmnmtrapforward
/opt/cemf/bin/cmnmversion
/opt/cemf/bin/cmnmversion.pl
/opt/cemf/bin/modules/avUtilities
/opt/cemf/bin/modules/avUtilitiesAC.pm
2-44
?-----------------output suppressed-----------------------?
Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Implementation Guide
OL-2706-01
Page 45

Chapter 2 Provisioning
Step by Step Installation and Initial Configuration
[verifying class <none>]
Installation of <CSCOcmnm> was successful.
The following packages are available:
1 CSCOcmnm Cisco MGC-Node Manager (CMNM) 2.3
(sparc) 2.3(1)
Select package(s) you wish to process (or 'all' to process
all packages). (default: all) [?,??,q]:
Processing package instance <CSCOcmnm> from
</opt/images/tmp/pkgs/manager/CSCOcmnm.pkg>
Skipping CiscoView uninstallation
Processing package instance <CSCOcmhp> from </opt/images/tmp/pkgs>
CMNM 2.3 Online Help
(sparc) 2.3
Cisco Systems, Inc.
Using </opt/cemf/help> as the package base directory.
## Processing package information.
## Processing system information.
?-----------------output suppressed-----------------------?
/opt/cemf/help/CSCOcmnm/userguide/toc.gif
[verifying class <none>]
Installation of <CSCOcmhp> was successful.
Processing package instance <CSCOcmcd> from </opt/images/tmp/pkgs>
CMNM 2.3 Online CD-ROM Help
(sparc) 2.3
Cisco Systems, Inc.
Using </opt/cemf/help> as the package base directory.
## Processing package information.
## Processing system information.
1 package pathname is already properly installed.
## Verifying package dependencies.
## Verifying disk space requirements.
OL-2706-01
?-----------------output suppressed-----------------------?
Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Implementation Guide
2-45
Page 46

Step by Step Installation and Initial Configuration
/opt/cemf/help/CSCOcmnm/cdapp/launched
/opt/cemf/help/CSCOcmnm/cdapp/search.ini
[verifying class <none>]
Installation of <CSCOcmcd> was successful.
Processing package instance <CSCOcmcv> from </opt/images/tmp/pkgs>
CMNM 2.3 CiscoView Client Package Stub
(sparc) 2.3
Cisco Systems, Inc.
Please enter the CiscoView Server IP address [def: 0.0.0.0] [?,q]
Using </opt/cemf> as the package base directory.
## Processing package information.
## Processing system information.
## Verifying disk space requirements.
Chapter 2 Provisioning
Installing CMNM 2.3 CiscoView Client Package Stub as <CSCOcmcv>
## Installing part 1 of 1.
/opt/cemf/bin/cmnmSecurityClient
/opt/cemf/bin/cmnmupdateCVip
/opt/cemf/bin/cmnmupdateCVip.pl
/opt/cemf/bin/modules/cvUtilities.pm
[verifying class <none>]
Installation of <CSCOcmcv> was successful.
Installing CSCOcmnm ...
## Finding cemf root dir
cemf basedir = "/opt/cemf"
cemf logs dir = "/opt/cemf/logs"
** Warning **
** It is strongly advised that you backup your databases
** before running this command.
** This can be achieved using the command "cemf backup"
** Warning **
** This command will stop all sessions connected to this
** machine.
2-46
## Script executed
Start of "mgcEMm" Installation
Time stamp Thu Sep 26 10:49:36 PDT 2002
Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Implementation Guide
OL-2706-01
Page 47

Chapter 2 Provisioning
Step by Step Installation and Initial Configuration
## Checking package suitability
Package Ok.
## Installing package
Processing package instance <mgcEMm> from
</opt/images/tmp/elementmanagers/mgcEM/packages>
Cisco Media Gateway Node Manager
(sparc) 2.3
Cisco Systems, Inc.
## Executing checkinstall script.
Using </opt/cemf> as the package base directory.
## Processing package information.
## Processing system information.
24 package pathnames are already properly installed.
## Verifying disk space requirements.
Installing Cisco Media Gateway Node Manager as <mgcEMm>
## Executing preinstall script.
## Installing part 1 of 1.
/opt/cemf/config/C/help/objectFiles/S00generic.types
/opt/cemf/config/C/help/objectFiles/S01alarms.types
/opt/cemf/config/C/help/objectFiles/S01containers.types
/opt/cemf/config/C/help/objectFiles/S01ip.types
/opt/cemf/config/C/help/objectFiles/S01trees.types
/opt/cemf/config/C/help/objectFiles/S02partitioning.types
?-----------------output suppressed-----------------------?
/opt/cemf/config/dataload/historyCriteria/switch5500PortHistoryCriteria
/opt/cemf/config/dataload/historyCriteria/switchCatChassisHistoryCriteri
a
/opt/cemf/config/dataload/historyCriteria/switchIOSChassisHistoryCriteri
a
[verifying class <histcriteria>]
[verifying class <replace>]
## Executing postinstall script.
OL-2706-01
Installation of <mgcEMm> was successful.
Installation Ok.
## Registering package with CEMF Manager
Registration successful.
## Reading environment
Done.
Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Implementation Guide
2-47
Page 48

Step by Step Installation and Initial Configuration
## Reading Package Files
Done.
## Changing the current run level
Saving old run level as "100000"
Setting new run level as "19999"
## Executing actions
configospec - Running "/opt/cemf/config/selfManagement/actions/l.configospec"
events - Running "/opt/cemf/config/selfManagement/actions/l.events configospec"
mibcontrol - Running "/opt/cemf/config/selfManagement/actions/l.mibcontrol"
events - Running "/opt/cemf/config/selfManagement/actions/l.events mibcontrol"
objecttype - Running "/opt/cemf/config/selfManagement/actions/l.objecttype"
events - Running "/opt/cemf/config/selfManagement/actions/l.events objecttype"
clearcor - Running "/opt/cemf/config/selfManagement/actions/l.clearcor"
events - Running "/opt/cemf/config/selfManagement/actions/l.events clearcor"
partitioning - Running "/opt/cemf/config/selfManagement/actions/l.partitioning"
events - Running "/opt/cemf/config/selfManagement/actions/l.events
partitioning"
viewspec - Running "/opt/cemf/config/selfManagement/actions/l.viewspec"
events - Running "/opt/cemf/config/selfManagement/actions/l.events viewspec"
processes - Running "/opt/cemf/config/selfManagement/actions/l.processes"
events - Running "/opt/cemf/config/selfManagement/actions/l.events processes"
objectspec - Running "/opt/cemf/config/selfManagement/actions/l.objectspec"
events - Running "/opt/cemf/config/selfManagement/actions/l.events objectspec"
histcriteria - Running "/opt/cemf/config/selfManagement/actions/l.histcriteria"
events - Running "/opt/cemf/config/selfManagement/actions/l.events
histcriteria"
binary - No Action Defined.
events - Running "/opt/cemf/config/selfManagement/actions/l.events binary"
em_config - No Action Defined.
events - Running "/opt/cemf/config/selfManagement/actions/l.events em_config"
none - No Action Defined.
events - Running "/opt/cemf/config/selfManagement/actions/l.events none"
noreplace - No Action Defined.
events - Running "/opt/cemf/config/selfManagement/actions/l.events noreplace"
replace - No Action Defined.
events - Running "/opt/cemf/config/selfManagement/actions/l.events replace"
schema - No Action Defined.
events - Running "/opt/cemf/config/selfManagement/actions/l.events schema"
## Resetting run level
Setting run level to "100000"
## Program Finished
Completed successfully.
Chapter 2 Provisioning
2-48
## Finding cemf root dir
cemf basedir = "/opt/cemf"
Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Implementation Guide
OL-2706-01
Page 49

Chapter 2 Provisioning
Step by Step Installation and Initial Configuration
cemf logs dir = "/opt/cemf/logs"
** Warning **
** It is strongly advised that you backup your databases
** before running this command.
** This can be achieved using the command "cemf backup"
** Warning **
** This command will stop all sessions connected to this
** machine.
## Script executed
Start of "hostEMm" Installation
Time stamp Thu Sep 26 10:59:16 PDT 2002
## Checking package suitability
Package Ok.
## Installing package
Processing package instance <hostEMm> from
</opt/images/tmp/elementmanagers/hostEM/packages>
Cisco Media Gateway Node Manager
(sparc) 2.3
Cisco Systems, Inc.
## Executing checkinstall script.
Using </opt/cemf> as the package base directory.
## Processing package information.
## Processing system information.
100 package pathnames are already properly installed.
## Verifying disk space requirements.
Installing Cisco Media Gateway Node Manager as <hostEMm>
## Executing preinstall script.
## Installing part 1 of 1.
/opt/cemf/config/C/help/objectFiles/x_hostEM.types
/opt/cemf/config/images/24x24/mnm-adigtree.gif
OL-2706-01
?-----------------output suppressed-----------------------?
/opt/cemf/config/dataload/historyCriteria/hostSIPPathHistoryCriteria
/opt/cemf/config/dataload/historyCriteria/hostSS7PathHistoryCriteria
/opt/cemf/config/dataload/historyCriteria/hostSS7SGIPLinkHistoryCriteria
/opt/cemf/config/dataload/historyCriteria/hostTrunkGroupHistoryCriteria
Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Implementation Guide
2-49
Page 50

Step by Step Installation and Initial Configuration
[verifying class <histcriteria>]
[verifying class <replace>]
## Executing postinstall script.
Installation of <hostEMm> was successful.
Installation Ok.
## Registering package with CEMF Manager
Registration successful.
## Reading environment
Done.
## Reading Package Files
Warning "/opt/cemf/config/objectTypes/avmt.types" is already referenced
by the package(s) "mgcEMm hostEMm".
Done.
## Changing the current run level
Saving old run level as "100000"
Setting new run level as "19999"
## Executing actions
Chapter 2 Provisioning
?-----------------output suppressed-----------------------?
"/opt/cemf/config/selfManagement/actions/l.events schema"
## Resetting run level
Setting run level to "100000"
## Program Finished
Completed successfully.
CEMF shell parameters set
(Note: LD_LIBRARY_PATH and PATH may be reset by your shell startup files)
Running /bin/csh
CEMF shell parameters set
(Note: LD_LIBRARY_PATH and PATH may be reset by your shell startup files)
Running /bin/csh
--------------------------------------- Verifying CSCOcmnm Installation
Everything appears to be installed correctly.
Please see installation logfile:
2-50
/var/tmp/installCSCOcmnm.log
Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Implementation Guide
OL-2706-01
Page 51

Chapter 2 Provisioning
Verifying Correct Installation Before Continuing
Step 5 Before continuing, you should check to ensure everything was installed correctly.
cmnm-pri# pkginfo -l CSCOcmnm
PKGINST: CSCOcmnm
NAME: Cisco MGC-Node Manager (CMNM) 2.3
CATEGORY: application
ARCH: sparc
VERSION: 2.3(1)
BASEDIR: /opt/cemf
VENDOR: Cisco Systems, Inc.
INSTDATE: Oct 03 2002 17:24
STATUS: completely installed
FILES: 34 installed pathnames
5 shared pathnames
8 directories
4 executables
1 setuid/setgid executables
528 blocks used (approx)
Step by Step Installation and Initial Configuration
Step 6 Obtain CMNM version information:
cmnm-pri# bin/cmnmversion -verbose
CSCOcmnm Tool Versions
Patch Build Build
Name Version Level Num Type
----------------------------------- CSCOcmnm 2.3(1) 02 091802 REL
CSCOcmcv 2.3
CSCOcmhp 2.3 00
CSCOcemfm 3.2 Patch: 170003-10
Patch: 190302-01
----------------------------------- CSCOcmnm Element Manager Versions
Patch Build Build
Name Version Level Num Type
----------------------------------- hostEMm 2.3 02 091802 REL
mgcEMm 2.3 02 091802 REL
------------------------------------
OL-2706-01
Note Specific information displayed from running the above script above varies according to the release and
patch you installed.
Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Implementation Guide
2-51
Page 52

Step by Step Installation and Initial Configuration
Verifying the Installation of CiscoView 5.1
Step 7 Verify the CiscoView 5.1 installation:
cmnm-pri# pkginfo -l CSCOcmcv
PKGINST: CSCOcmcv
NAME: CMNM 2.3 CiscoView Client Package Stub
CATEGORY: application
ARCH: sparc
VERSION: 2.3
BASEDIR: /opt/cemf
VENDOR: Cisco Systems, Inc.
INSTDATE: Oct 03 2002 17:25
STATUS: completely installed
FILES: 6 installed pathnames
2 shared pathnames
2 directories
2 executables
116 blocks used (approx)
Step 8 Run the following script to determine the packages installed with CiscoView.
Chapter 2 Provisioning
Installing CMNM Patches
Installing Patch 01 for CMNM is very much like installing the entire package. The output is not shown
here, just the feedback from a successful install. The Patch01 file is untarred into a temporary directory,
just like you did with the original distribution file. The install script is called patchCSCOcmnm.
Step 9 Untar the CSCOcmnm-2.3.1-P01.tar file:
cmnm-pri# tar -xvof CSCOcmnm-2.3.1-P01.tar
Step 10 Get the contents of the CMNM Patch01 file:
cmnm-pri# ./patchCSCOcmnm
--------------------------------------------------------------------- Cisco MGC-Node Manager Patch Program
Thu Sep 26 11:46:41 AM
Setup has detected that both the CEMF Manager and CSCOcmnm Manager
software is installed on this workstation.
Do you wish to patch the CSCOcmnm Manager software. [y/n]: [y]
?-----------------------output suppressed--------------------------?
2-52
## Resetting run level
Setting run level to "100000"
## Program Finished
Completed successfully.
Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Implementation Guide
OL-2706-01
Page 53

Chapter 2 Provisioning
Please see patch logfile:
/var/tmp/patchCSCOcmnm.log
The final output above reports a successful installation of the first patch.
Step 11 Install any more recent patches in the same manner as the first patch.
Verifying Patch Installation Success
Step 12 Get a listing of the installed patches:
cmnm-pri# bin/cmnmversion -verbose
CSCOcmnm Tool Versions
Patch Build Build
Name Version Level Num Type
----------------------------------- CSCOcmnm 2.3(1) 02 091802 REL
CSCOcmcv 2.3
CSCOcmhp 2.3 00
CSCOcemfm 3.2 Patch: 170003-10
Patch: 190302-01
Step by Step Installation and Initial Configuration
Starting CMNM
Step 13 Set the DISPLAY environment variable to the host you are accessing CMNM from:
Step 14 Change to the CEMF directory and start CMNM:
------------------------------------
CSCOcmnm Element Manager Versions
Patch Build Build
Name Version Level Num Type
----------------------------------- hostEMm 2.3 02 091802 REL
mgcEMm 2.3 02 091802 REL
------------------------------------
You must be logged into CMNM with an X windows connection in order to start CMNM.
cmnm-pri# setenv DISPLAY 171.71.73.38:0.0
cmnm-pri# cd /opt/cemf
cmnm-pri# bin/cemf session
OL-2706-01
Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Implementation Guide
2-53
Page 54

Step by Step Installation and Initial Configuration
Starting CEMF Manager Applications.
ILOG Views 3.0.2, Copyright (C) 1990-1998 by ILOG.
ILOG TGO 1.0.3, Copyright (C) 1997-1998 by ILOG.
You initially see the CEMF Logo and Login windows, as shown in Figure 2-9 and Figure 2-10.
Figure 2-9 CEMF Logo Window
Chapter 2 Provisioning
Figure 2-10 CMNM Login Window
Note The default user name and password values are both admin.
Step 15 When you see the above windows, the installation and start up were successful. you should now check
to see if any upgrades exist for the CiscoView application.
2-54
Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Implementation Guide
OL-2706-01
Page 55

Chapter 2 Provisioning
Upgrading CiscoView
CiscoView 5.1 is installed with CMNM. You should check for upgrades and, if any exist, install them.
If no CiscoView upgrades exist, you are now ready to install Cisco PTC and its integrated component
application, Cisco VRC. Go to the “Installing Cisco PTC 2.1.1 Integrated with Cisco VRC 1.1” section.
Step 1 Check the CiscoView web site for the latest supported version of the package:
http://www.cisco.com/kobayashi/library/netmanage/cview/.
Step 2 If anupgrade exists,install it as shown inthe followingsteps. Otherwise, go to the “Installing Cisco PTC
2.1.1 Integrated with Cisco VRC 1.1” section.
Step 3 Download the latest CiscoView packages and place them in a temporary directory (for example,
/scratch/cvUpgrade).
Step 4 Make sure the package files are readable by the root user. If not, the packages do not appear in the
CiscoView upgrade tool.
Step 5 Become user root:
% su root
Step 6 Change to the /scratch/cvUpgrade directory.
# cd /scratch/cvUpgrade
Step 7 To run the CiscoView upgrade tool, type:
# <Cisco EMF Directory>/ciscoview5.1/bin/xdsu
Step 8 Click Install. Ignore the following exception:
“ERROR: exception occurred while examining Integration Utility configuration:
com.cisco.nm.nmim.nmic.IntgUtilCheckConfig”.
Step 9 Type in the exact location of the CiscoView packages in the Directory box, then press Enter or click
Browse, navigate to your CiscoView packages' temporary directory, and then click Select.
Step 10 Select the CiscoView packages you want to upgrade, click Install, and then click the appropriate
confirmation button.
Step 11 You are now ready to install Cisco PTC and its integrated component application, Cisco VRC.
Step by Step Installation and Initial Configuration
Installing Cisco PTC 2.1.1 Integrated with Cisco VRC 1.1
This section provides the Cisco PTC Client machine requirements, the devices that are supported by
Cisco PTC in the 2.1.1 release and their corresponding platforms and IOS releases, the integrated and
optional product components, as well as the Cisco PTC installation instructions.
Cisco PTC Client Requirements
The Java 1.3.1 runtime environment/plugin for web browsers should be installed on the Cisco PTC
Client machine. Table 2-3 details the minimum system requirements of the Cisco PTC Client machine.
Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Implementation Guide
OL-2706-01
2-55
Page 56

Step by Step Installation and Initial Configuration
Table 2-3 Cisco PTC Client Machine Requirements
Machine Type Operating System CPU Speed RAM Browser
PC Windows2000 or NT 400MHz 256MB Netscape 6.0 (or later) or
Sun Ultra60 Solaris 7 or 8 360MHz 256MB Netscape 6.0 (or later)
Cisco PTC Dependencies on Platform Versions
Table 2-4 describes the devices that are supported by Cisco PTC in the 2.1.1 release, as well as their
corresponding platforms and IOS releases.
Table 2-4 Cisco PTC Supported Devices
Category Platform IOS Release
Signaling Controller SC2200 7.4(12), 9.2(2)
Signal Link Terminations 2600 SLT, C2611 SLT 12.2(1c)
Gateways AS5300, AS5400 12.2(2)XU3, 12.2.7c, 12.2(11)T
Gateway AS5350 12.2(2)XU3, 12.2(11)T
Gateway AS5800 12.2.7c, 12.2(11)T
Gateway AS5850 12.2(2)XU3, 12.2(11)T
Gateway c7200 12.2(2)XU3, 12.2(11)T
Gateway c3600 12.2(11)T
Gatekeepers c7200, 3640, 3660 12.2(2)T, 12.2(11)T, 12.2(2)XU3
Chapter 2 Provisioning
Microsoft Internet Explorer 5.5
(or later)
Note Cisco PTC must be installed by user root.
Product Prerequisite
The Cisco CNS IE2100 appliance, version 1.2.2, is used by Cisco PTC to download and upload IOS
configurationfilesto and from Cisco IOS devices. The Cisco CNS IE2100appliance is a separate device
and is not installed as part of the Cisco PTC installation process. You must ensure it is configured and
operating properly; preferably prior to installing Cisco PTC.
To obtain access to Cisco CNS IE2100 documentation, go to the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/rtrmgmt/ie2100/cnfg_reg/rel_1_2/index.htm.
Integrated Product Component
The Cisco Voice RoutingCenter (CiscoVRC) application,version 1.1, can be used by Cisco PTC to help
manage dial plans for H.323 based VoIP networks. Cisco PTC and Cisco VRC are fully integrated and
can be installed and configured to run on the same machine while simultaneously using some common
servers and processes.
Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Implementation Guide
2-56
OL-2706-01
Page 57

Chapter 2 Provisioning
To obtain access to Cisco VRC documentation, go to the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/rtrmgmt/vrc/vrc1_1/index.htm.
Optional Product Components
The following applications can be launched from the Cisco PTC Topology Manager, however, they are
not installed as part of the Cisco PTC installation process. If you plan on Cisco PTC using or working
with any of the following applications, you must ensure they are installed, configured, and operating
properly; preferably prior to installing Cisco PTC:
• Cisco MGCNode Manager (CMNM), version 2.3.1(plusPatch 1 and 2)—the Element Management
System (EMS) for managing signaling controllers.
• Voice Services Provisioning Tool (VSPT), versions 2.3—used to configure and provision the
PGW2200
• CiscoView—is a web based device management application that provides dynamic status,
monitoring, and configuration information for the broad range of Cisco internetworking products.
To obtain access to CiscoView documentation, go to the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/rtrmgmt/cw2000/cw2000_d/4steditn/use_view/i
ndex.htm.
• Cisco Info Center (CIC)—is a Service-Level Management system that collects event streams or
messages from many different data sources and then providesa consolidated viewof the events and
status information. To obtain access to Cisco Info Center documentation, go to the following URL:
Step by Step Installation and Initial Configuration
• Carrier Sensitive Router (CSR) Server—provides the capability to affect the routing of calls from
Installing Cisco PTC
This section describes how to install the Cisco PTC product software from the product CDROM.
Cisco PTC installation is a component based installation process. Each component is installed through
the Cisco PTC installation process in either Standalone or Integrated mode.
Note The Cisco PTC andCisco VRCapplications arefully integratedand areable to simultaneously use some
common servers and processes. As such, Cisco PTC is installed in Standalone mode when the
Cisco VRC application is not currently installed on themachine where Cisco PTC is being installed and
allows you to install all of the Cisco PTC subcomponents.
Cisco PTC is installed in Integrated mode when the Cisco PTC installation process detects that the
Cisco VRC application is already installed on the machine. As such, the Cisco PTC subcomponents are
not reinstalled. Instead, Cisco PTC is configured to use the common subcomponents that were installed
with the Cisco VRC application.
This chapter installs Cisco PTC in Standalone mode, integrated with Cisco VRC, because it is a new
install and Cisco VRC has not been installed previously.
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/rtrmgmt/info_ctr/index.htm.
the gatekeeper based upon the INGRES carrier and the dialed number.
OL-2706-01
Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Implementation Guide
2-57
Page 58

Step by Step Installation and Initial Configuration
Pre Installation Checks
This section lists a set of tasks you must perform prior to beginning the Cisco PTC installation process.
1. Make sure the Cisco PTC CNSC CORE and CNS INTEGRATION BUS packages were not
previously installed on the Cisco PTC server machine:
#pkginfo -l CNSC
#pkginfo - l TIBRV
The above checks should return error messages when the packages are not found.
2. If CiscoPTC isinstalled inStandalone mode, make sure adirectory namedvnm doesnot exist under
the /opt directory or under the directory where you plan on installing the Cisco PTC product
software. Also make sure that the vnm user and a vnm group accounts do not exist.
3. If Cisco PTC is installed in Standalone mode, make sure a soft link of type /opt/cisco/vnmdoes not
exist.
4. If Cisco PTC is installed in Standalone mode, make sure the Cisco CNS Security Services
Administration server is not installed on the system (that is, the /opt/vnm/common/spe and
/opt/vnm/common/dcdsrvr directories should not exist on the system).
5. Make sure noCisco VRC, MYSQL, Cisco CNS IntegrationBus, and CiscoCNS Security processes
are running before installation.
6. Make sure the Cisco PTC server machine has a static IP address assigned and is reachable using
telnet.
7. Make sure the Perl package is installed on this machine when the Cisco VRC application is to be
installed.
8. Make sure the default Java package exists in the system in order for Cisco CNS Security
configuration to be successful.
9. Make sure a previously created vnm user account is removed prior to installing Cisco PTC.
Chapter 2 Provisioning
Tip Ifnon-English characters are displayed onyour screen while using CiscoPTC, ensure that the C-POSIX
character set is being used and that the display resolution is set to 1280 * 1024 or higher.
Cisco PTC Server Installation
The Cisco PTC installation script allows you to install the following components:
• CNSC Core servers—Cisco PTC must be installed in the /opt/vnm directory
• Sybase Database
• Cisco CNS Integration Bus
• Cisco CNS Security
• Cisco Voice Routing Center
• Java
• Tomcat
Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Implementation Guide
2-58
OL-2706-01
Page 59

Chapter 2 Provisioning
Copying Cisco PTC Files From the Product CD
Step 1 Insert the Cisco PTC product CD into the CDROM drive.
Step 2 Open a X-terminal window and log in as user root.
Step 3 Set the terminal mode to C shell:
ptc-tme# csh
Step 4 Set the DISPLAY environment variable:
ptc-tme# setenv DISPLAY 171.71.73.38:0.0
Step 5 Go to the CDROM directory:
ptc-tme# cd /cdrom/cdrom0
Step 6 Copy the compressed Cisco PTC tar file to the /opt directory and navigate to that directory:
ptc-tme# cp cisco-ptc2.1.1.tar.Z /opt
ptc-tme# cd /opt
Step 7 Uncompress the cisco-ptc2.1.1.tar.Z file:
ptc-tme# uncompress cisco-ptc2.1.1.tar.Z
The tar file is uncompressed creating a cisco-ptc2.1.1.tar file in the /opt directory.
Step 8 Untar the cisco-ptc2.1.1.tar file:
ptc-tme# tar -xvf cisco-ptc2.1.1.tar
A /opt/PTC-2.1.1 directory is created and the Cisco PTC files are placed there.
Step 9 After the tar process completes, delete the cisco-ptc2.1.1.tar file:
ptc-tme# rm cisco-ptc2.1.1.tar
Step 10 Eject the Cisco PTC product CD:
ptc-tme# eject cd
Step by Step Installation and Initial Configuration
Installing the CNSC CORE Package
This section describes how to install the Cisco PTC CNSC - CORE package. These directions are for a
host on which there is no previous installation of Cisco VRC. If this is not the case for your installation,
and if you already have Cisco VRC installed on the Cisco PTC host, you must refer to the Cisco Packet
Telephony Center Installation and Configuration Guide for instructions on how to properly shut down
the Cisco VRC, Cisco CNS, and DCD server processes:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/rtrmgmt/ptc/2_1_1/install/install.htm#xtocid14.
Step 11 AssumingCisco VRC isnot presenton this host,begin theinstallation process. Goto thedirectory where
you installed the Cisco PTC product files:
ptc-tme% cd /opt/PTC-2.1.1
Step 12 Make sure the DISPLAY environment variable is set:
ptc-tme% setenv DISPLAY 171.71.150.111:0.0
Step 13 Invoke the Cisco PTC installation script:
ptc-tme% ./cnscInstall
Launching the installation GUI ...
OL-2706-01
Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Implementation Guide
2-59
Page 60

Step by Step Installation and Initial Configuration
The Cisco PTC Installation window appears, as shown in Figure 2-11, allowing you to install the
following packages:
• CNSC - CORE
• CNS INTEGRATION BUS
• CNS SECURITY
• JAV A
• TOMCAT
• VRC
Figure 2-11 Cisco PTC Installation Window
Chapter 2 Provisioning
2-60
Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Implementation Guide
OL-2706-01
Page 61

Chapter 2 Provisioning
Step 14 Click the CNSC - CORE check box.
Step 15 Enter the following information in the Input Parameters fields:
Step 16 Click the Start button to invoke the CNSC - CORE package installation process.
Step 17 Upon successful completion of the installation process, click the Exit button.
Step 18 Verify the CNSC - CORE package installation was successful by invoking the following command:
Step by Step Installation and Initial Configuration
Only the CNSC - CORE check box should be selected at this time.
Note If youcannot see thebottom of theCisco PTC Installationwindow (the Start and Exit buttons),
it is likely that your screen resolution is too low. A minimum of 1280x1024 is required.
Product Source Directory: /opt/PTC-2.1.1 (location of the Cisco PTC install scripts)
Product Install Directory: /opt/vnm (base directory where Cisco PTC must be installed)
Product Admin Password:(Cisco PTC systemadministrator password-remember this passwordbecause
you must use the same password for each module that you install. If you get distracted in between
module installations, you may forget what password you used.
System Host Name: ptc-tme
VSPT Package Name: CSCOvsp23
The Output log displays the progress of the installation.
The Cisco PTC Installation window is closed.
ptc-tme% pkginfo -l CNSC
PKGINST: CNSC
NAME: PTC-2.1.1
CATEGORY: Application
ARCH: sparc
VERSION: 02_01_18_00
BASEDIR: /opt/cisco/vnm
VENDOR: Cisco Systems
PSTAMP: 13thSep2002
INSTDATE: Sep 24 2002 15:37
EMAIL: zbigniew@cisco.com
STATUS: completely installed
FILES: 4419 installed pathnames
258 directories
1001 executables
1 setuid/setgid executables
810447 blocks used (approx)
OL-2706-01
The command output should be “Completely Installed”. If however, the output states “Partially
Installed” or an error is returned, you must uninstall the CNSC – CORE package (refer to the
“Uninstalling Cisco PTC Software” section in the Cisco Packet Telephony Center Installation and
Configuration Guide) and then attempt to reinstall the CNSC - CORE package again.
Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Implementation Guide
2-61
Page 62

Step by Step Installation and Initial Configuration
Before proceeding, you must refer to the “Caveats” section in the Release Notes for Cisco Packet
Telephony Center, Release 2.1 to see whether you must modify anyof the parameters in the /etc/system
file. After the following the instructions in the “Caveats” section:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/rtrmgmt/ptc/2_1/relnotes/relnote.htm#65500.
Assuming compliance, proceed.
Step 19 Reboot the Cisco PTC machine.
You must reboot the Cisco PTC Server machine at this time, no matter if this is an initial installation
or reinstallation of Cisco PTC, or the parameters in the /etc/system file were modified.
Step 20 Upon rebooting the Cisco PTC machine, proceed to the next section (“Installing the Cisco CNS
Integration Bus and Cisco CNS Security Packages”).
Installing the Cisco CNS Integration Bus and Cisco CNS Security Packages
This section describes how to install the CNS INTEGRATION BUS and CNS SECURITY packages
once you have successfully installed the Cisco PTC CNSC -CORE package.
Chapter 2 Provisioning
Step 1 Open an Xwindow session and log in as user root:
Step 2 Set the DISPLAY environment variable to the IP address of the machine you are using (assuming C
shell):
ptc-tme# setenv DISPLAY 171.71.150.111:0.0
Step 3 Invoke the Cisco PTC installation script from the product directory:
ptc-tme# ./cnscInstall
Step 4 Observe the Cisco PTC Installation window again, as shown in Figure 2-11.
Step 5 Click the CNS INTEGRATION BUS check box. Only the CNS INTEGRATION BUS check box
should be selected at this time.
Step 6 Enter the same information as you did for the CORE installation.
Step 7 Upon successful completion of the installation process, deselect the CNS INTEGRATION BUS
package and then select the CNS SECURITYpackage byclicking ontheir respective check boxes.Only
the CNS SECURITY check box should be selected at this time.
Step 8 Enter Input parameters again for the CNS SECURITY package.
Step 9 Upon successful completion of the CNS SECURITY package's installation process, click the Exit
button.
The Cisco PTC Installation window is closed.
Step 10 Verify the CNS INTEGRATION BUS package installation was successful by invoking the following
command:
ptc-tme# pkginfo -l TIBRV
PKGINST: TIBRV
NAME: TIB(r)/Rendezvous(tm) Software V6
CATEGORY: application
ARCH: sparc
VERSION: 6_4
BASEDIR: /opt/cisco/vnm/common/tibrv
2-62
Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Implementation Guide
OL-2706-01
Page 63

Chapter 2 Provisioning
Step 11 Once again, make sure the package was “completely installed”.
Step 12 Verify the CNS SECURITY packageinstallation was successfulby checking whetherthe default Cisco
Step by Step Installation and Initial Configuration
VENDOR: TIBCO Software INC.
PSTAMP: 99/12/10
INSTDATE: Sep 24 2002 15:54
EMAIL: support@tibco.com
STATUS: completely installed
FILES: 133 installed pathnames
15 directories
30 executables
2 setuid/setgid executables
23870 blocks used (approx)
CNS Security installation directories (spe and dcdsrvr) exist:
ptc-tme# cd /opt/vnm/common
ptc-tme# ls
dcdsrvr installer spe
uninstallCnsIB.sh uninstallJava.sh
installEnvVar.csh sybase uninstallCnsSec.sh
uninstallSybase.sh
installEnvVar.sh tibrv uninstallGdpm.sh
uninstallTomCat.sh
Step 13 If these directories do not exist, you must attempt to reinstall the CNS SECURITY package.
Installing the JAVA and TOMCAT Packages
This section describes how to install the Cisco PTC JAVA and TOMCAT packages once you have
successfully installed the Cisco PTC CNSC - CORE, CNS INTEGRATION BUS, and CNS
SECURITY packages.
Step 1 Follow the initial steps for starting the CNSC - CORE install process as in the previous sections.
Step 2 Click the JAVA check box. Only the JAVA check box should be selected at this time. Enter the same
parameters in the Input Parameters fields, using the same password.
Step 3 Click the Start button to invoke the JAVA package's installation process.
The Output log in the Cisco PTC Installation window displays the progress of the installation.
Step 4 Upon successful completion of the installation process, deselect the JAVA package and select the
TOMCAT package by clicking their respective check boxes. Only the TOMCAT check box should be
selected at this time.
Step 5 Enter the Input Parameters again and click start.
Step 6 Upon successful completion of the TOMCAT package's installation process, click the Exit button.
The Cisco PTC Installation window is closed.
OL-2706-01
Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Implementation Guide
2-63
Page 64

Step by Step Installation and Initial Configuration
Step 7 Verify the JAVA package installation was successful by checking whether the /opt/vnm/common/jre
directory exists.
ptc-tme# cd /opt/vnm/common
ptc-tme# ls
dcdsrvr installer spe
uninstallCnsIB.sh uninstallJava.sh
installEnvVar.csh jakarta-tomcat-3.3.1 sybase
uninstallCnsSec.sh uninstallSybase.sh
installEnvVar.sh jre tibrv
uninstallGdpm.sh uninstallTomCat.sh
Step 8 Verify the TOMCAT package installation was successful by checking whether the
/opt/vnm/common/jakarta-tomcat-3.3.1 directory exists.
Installing the Cisco Voice Routing Center Application
Chapter 2 Provisioning
Following is a list of important items you should be awareof prior to installing the Cisco VRC package:
1. Make sure no mysql or Cisco VRC processes are running before installing the Cisco VRC package
in Integrated mode. You should get a null return or just a return of the grep process:
ptc-tme# ps -ef | grep mysql
ptc-tme# ps -ef | grep Gdpm
2. Perl must already be installed on the machine you plan on using to install the Cisco VRC package.
Note Even if theCisco VRCapplication waspreviouslyinstalled onthe machineyou justinstalled Cisco PTC,
you must perform the following steps so that Cisco PTC is configured to use the common components
that were installed with the Cisco VRC application.
Step 1 Follow initial setup steps as detailed in the previous sections and invoke the cnscInstall executable:
ptc-tme# pwd /opt/PTC-2.1.1
ptc-tme# ./cnscInstall
Step 2 In the Cisco PTC Installation window, click the VRC check box. Only the VRC check box should be
selected at this time. The same as all the other installations, enter the Input Parameter fields, this time
pointing to the directory where the Cisco VRC distribution file is located. Click the Start button.
Note You must set the Product Source Directoryvalue to the directory where the Cisco VRC install
scripts are located. Look for the directory with the scripts install.sh and install.pl.
2-64
Step 3 Upon successful completion of the installation process, click the Exit button.
The Cisco PTC Installation window is closed.
Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Implementation Guide
OL-2706-01
Page 65

Chapter 2 Provisioning
Step 4 Verify the VRCpackage installation wassuccessful by verifying that thefollowing linksand directories
Step by Step Installation and Initial Configuration
exist under the /opt/vnm directory:
a. a gdpm soft link.
b. a mysql soft link.
c. the mysql-3.23.42-sun-solaris2.8-sparc (for Solaris 8) directory exists.
ptc-tme# pwd
/opt/vnm
ptc-tme# ls -l
total 3670
-rw-rw-r-- 1 vnm vnm 0 Sep 27 14:58 -i
-rw-rw-r-- 1 vnm vnm 0 Sep 27 12:04 02_01_18_00
-rw-rw-r-- 1 vnm vnm 0 Sep 27 12:04 02_01_18_01.tar
drwxr-xr-x 2 vnm vnm 512 Sep 27 14:59 Database
drwxr-xr-x 2 vnm vnm 512 Sep 24 15:37 IORS
-rwxr-xr-x 1 vnm vnm 347 Sep 24 16:43 InstalledProduct
drwxr-xr-x 5 vnm vnm 512 Sep 24 15:37 NAgent
-rwxr-xr-x 1 vnm vnm 5112 Aug 7 07:20 README.TXT
drwxr-xr-x 2 vnm vnm 512 Sep 24 15:37 behmgr
drwxr-xr-x 2 vnm vnm 3072 Sep 24 15:38 bin
drwxr-xr-x 4 vnm vnm 512 Sep 27 15:03 cm
-rwxr-xr-x 1 vnm vnm 1566 Sep 13 14:01 cnscUninstall
-rw-rw-r-- 1 vnm vnm 5 Sep 27 14:58 coldstart.started
drwxr-xr-x 9 vnm vnm 512 Sep 24 16:04 common
-rw-r--r-- 1 vnm vnm 912 Sep 24 16:43 common.csh
-rw-r--r-- 1 vnm vnm 912 Sep 24 16:43 common.ksh
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root other 25 Sep 24 15:41 commonenv.csh ->
/opt/cisco/vnm/common.csh
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root other 25 Sep 24 15:41 commonenv.ksh ->
/opt/cisco/vnm/common.ksh
drwxr-xr-x 5 vnm vnm 1536 Sep 27 14:58 config
-rw-r--r-- 1 vnm vnm 2091 Sep 24 16:43 cshenv.gdpm
-rwxr-xr-x 1 vnm vnm 90 Sep 27 14:58 csm.properties
drwxr-xr-x 2 vnm vnm 512 Sep 24 15:41 db
drwxr-xr-x 3 vnm vnm 512 Feb 22 2002 emsdata
-rwxr-xr-x 1 vnm vnm 1616 Sep 24 15:41 env.csh
-rwxr-xr-x 1 vnm vnm 1603 Sep 24 15:41 env.ksh
drwxr-xr-x 2 vnm vnm 512 Sep 24 15:38 eventmgmt
lrwxrwxrwx 1 vnm vnm 8 Sep 24 16:42 gdpm -> gdpm_1.1
drwxrwxr-x 9 vnm vnm 512 Sep 24 16:43 gdpm_1.1
drwxr-xr-x 2 vnm vnm 512 Sep 24 16:42 gdpm_install
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root other 85 Sep 24 16:04 installedPackage
-rwxr-xr-x 1 vnm vnm 59 Sep 13 13:59 java.policy
drwxr-xr-x 7 vnm vnm 3072 Sep 27 14:58 lib
drwxr-xr-x 2 vnm vnm 1536 Sep 30 10:11 log
drwxrwxr-x 2 vnm vnm 512 Sep 27 15:39 logs
OL-2706-01
Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Implementation Guide
2-65
Page 66

Step by Step Installation and Initial Configuration
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root other 37 Sep 24 16:42 mysql -> mysqlcom-
3.23.51-sun-solaris2.8-sparc
drwxr-xr-x 13 root vnm 512 Jun 13 09:04 mysqlcom-3.23.51-sun-solaris2.8-sparc
drwxr-xr-x 4 vnm vnm 512 Sep 24 15:39 packages
drwxr-xr-x 2 vnm vnm 512 Sep 27 13:51 rel
-rwxr-xr-x 1 vnm vnm 40 Sep 30 17:36 status.txt
-rwxr-xr-x 1 vnm vnm 1727 Sep 24 15:41 system.ini
drwxr-xr-x 10 vnm vnm 512 Sep 24 15:40 tools
drwxr-xr-x 5 vnm vnm 512 May 28 14:36 topodisc
drwxr-xr-x 5 vnm vnm 512 Sep 24 15:41 topology
-rw-rw-r-- 1 vnm vnm 1175529 Sep 30 17:33 trace.swapper
-rwxr-xr-x 1 vnm vnm 21187 Aug 7 07:14 vcginstall
-rwxr-xr-x 1 vnm vnm 21356 Sep 13 13:59 vcginstallPTC
-rwxr-xr-x 1 vnm vnm 577680 Sep 13 14:00 vnm.xml
drwxr-xr-x 2 vnm vnm 512 Sep 24 15:41 webserver
Chapter 2 Provisioning
Installing the Voice CORBA Gateway on the CMNM Host
When aCisco MGC NodeManager exists in the network,you must install the latest version of theVoice
CORBA Gateway (VCG) software that is provided on the Cisco PTC product CD, onto the remote
CMNM machine(s), upon successful installation of the Cisco PTC CNSC - CORE package.
VCG supports FTP (File Transfer Protocol) and SFTP (Secure File Transfer Protocol) for transferring
information from the VCG to Cisco PTC. When you use the SFTP mode, make sure the SFTP package
is installed and the sshd process is up and running on both the Cisco PTC and VCG machines.
Step 1 Login in as root with an Xwindows client to the Cisco PTC machine.
Last login: Fri Sep 27 14:54:16 from dhcp-171-71-150
Sun Microsystems Inc. SunOS 5.8 Generic Patch October 2001
ptc-tme#
Step 2 Set the DISPLAY environment variable to the machine you are working from:
ptc-tme# setenv DISPLAY 171.71.150.111:0.0
Step 3 Ensure the /usr/sbin/share directory is in the PATH environment variable of the user root on the
Cisco PTC machine. If it is not, add it:
ptc-tme# more /.cshrc
# @(#)cshrc 1.11 89/11/29 SMI
umask 022
set path=(/bin /usr/bin /usr/local/bin /usr/sbin/share /usr/openwin/bin /usr/ucb /etc .)
if ($?prompt) then
set history=32
endif
setenv TERM vt100
2-66
Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Implementation Guide
OL-2706-01
Page 67

Chapter 2 Provisioning
Step 4 To confirm the /usr/sbin/share directory is in your PATH variable, execute:
Step 5 Go to the Cisco PTC scripts directory:
Step 6 Run the configureVNM script:
Step 7 Choose Option number 2 (Install MCG):
Step by Step Installation and Initial Configuration
ptc-tme# which share
/usr/sbin/share
ptc-tme# cd /opt/cisco/vnm/tools/scripts
ptc-tme# ./configureVNM
The Configure VNM window appears.
---------------- VNM Configuration
-----------------
Main Menu
---------
1. Configure EMSs
2. Install MCG
3. Add EMS (CMGM)
4. Add EMS (CMNM)
5. Remove EMS
6. List existing EMSs
7. Quit
Enter (1 to 7): 2
Installing MCG...
Step 8 When prompted, enter 1 as the number of EMSs.
Configuring EMS...
Number of EMSs: 1
Now please enter data for the 1 EMSs.
EMS 0 hostname: cmnm-pri
Note cmnm-pri is the host being used in this example. You should substitute your own CMNM
hostname. When VCG is installed on a non-DNS machine, use theremote CMNM machine's IP
address instead of its hostname.
OL-2706-01
Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Implementation Guide
2-67
Page 68

Step by Step Installation and Initial Configuration
Step 9 Enter the File Transfer Protocol (SFTP or FTP) method to be used:
Enter the Transfer Mode (SFTP/FTP): FTP
Installing on host cmnm-pri
TransferMethod FTP
Sharing volume /opt/cisco/vnm via NFS
found share -F nfs -o ro -d "VNM CDROM" /opt/cisco/vnm
MOUNTPOINT-----/opt
Restarting NFS...
Done.
Logging on to cmnm-pri as root
Please enter the root password on the host cmnm-pri: Password: ******
This is the password to login to the CMNM host machine.
Installing on host cmnm-pri
TransferMethod FTP
Sharing volume /opt/cisco/vnm via NFS
found share -F nfs -o ro -d "VNM CDROM" /opt/cisco/vnm
MOUNTPOINT-----/opt
Restarting NFS...
Done.
Logging on to cmnm-pri as root
Please enter the root password on the host cmnm-pri: Password:
mount 172.19.49.18:/opt/cisco/vnm /tmp/mcg
Chapter 2 Provisioning
cd /tmp/mcg
Spawning /usr/openwin/bin/xterm -display 171.71.150.111:0.0 -e ./vcginstallPTC FTP
ptc-tme on the remote host.
The VCG Installation process is launched in an Xterm window. This is a window from the CMNM host
machine.
Step 10 In this window choose Option 1 to install VCG Client and Server:
******************************************************************
* This script installs/Uninstalls Voice Corba Gateway *
******************************************************************
1> Install VCG Server and Client
2> Install VCG Client
3> Uninstall VCG Server and Client
2-68
Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Implementation Guide
OL-2706-01
Page 69

Chapter 2 Provisioning
Step 11 Press Enter to choose the default installation location.
Step 12 If you entered SFTP in Step 9, you are prompted with the following message:
Step 13 Enter yes.
Step 14 When prompted, enter the root password of the VCG host machine.
Step 15 When prompted with the sftp> prompt, type quit.
Step 16 Choose q to quit the xterm process.
Step 17 Enter the root password for the remote CMNM machine.
Step 18 Press Enter to continue.
Step 19 Choose Option number 7 to quit the VCG installation.
Step 20 To verify the installation of VCG was successful, verify that the ObjectAccess and McgNotifyServer
Step by Step Installation and Initial Configuration
4> Uninstall VCG Client
q> Quit
Choose an option: 1
The MCG Server and Client installation process starts.
“The authenticity of host <ipaddress of the host machine> cannot be established. Client machine is
<mac address of the client>. Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)?”
The following message appears:
Warning: Permanently added <172.19.49.2> (RSA) to the list of known hosts.
The installation of VCG is now complete.
processes are running on the CMNM machine:
cmnm-tme# ps -ef | grep ObjectAccess
root 7376 6392 0 Jul 16? 0:11 /opt/cemf/VCG/bin/ObjectAccess
cmnm-tme# ps -ef | grep McgNotifyServer
root 7378 6392 0 Jul 16? 0:46 /opt/cemf/VCG/bin/McgNotifyServer
OL-2706-01
If these processes arerunning, theinstallation ofVCG wassuccessful. You mustnow install the required
Cisco PTC patches.
Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Implementation Guide
2-69
Page 70

Step by Step Installation and Initial Configuration
Cisco PTC Patch Information
This section identifies and describes how to install the Cisco PTC 2.1.1 patches you must install after
the Cisco PTC product and component software have been installed.
Table 2-5 Cisco PTC 2.1.1 Patches
Patch Number Patch File Name
1 02_01_18_01.tar
2 02_01_18_02.tar
4 02_01_18_04.tar
You can access the Cisco PTC 2.1.1 patches at the following location:
http://www.cisco.com/cgi-bin/tablebuild.pl/cptc.
Read the README.txt file fordetailed instructions on how to install the Cisco PTC 2.1.1 patches. You
must install all of the Cisco PTC patches listed in Table 2-5. Upon completion, you must ensure that the
CMNM application is synchronized with the SC2200. Go to the “Synchronizing CMNM with the
SC2200” section.
Chapter 2 Provisioning
Synchronizing CMNM with the SC2200
This section describes the steps you are required to perform to ensure the CMNM application is
synchronized with the SC2200 prior to performing a Cisco PTC Cold Start.
Step 1 Start the CEMF Launchpad on the CMNM host as you did in section 4.6.8 and log in (user admin,
password admin).
cmnm-pri# setenv DISPLAY 171.71.150.111:0.0
cmnm-pri# cd /opt/cemf
cmnm-pri# bin/cemf session &
[1] 19680
Starting CEMF Manager Applications.
ILOG Views 3.0.2, Copyright (C) 1990-1998 by ILOG.
ILOG TGO 1.0.3, Copyright (C) 1997-1998 by ILOG.
Step 2 Click the Viewer icon in the CEMF Launchpad window.
Step 3 Click the MGC-Node-View node object in the Tree View pane in the Map Viewer window.
Step 4 Right-click on the MGC Node menu, then choose the MGC Node States option.
Step 5 Click on the Rediscover button in the States pane in the MGC Node States window.
Step 6 Click yes to confirm.
Synchronization between the CMNM and the SC2200 is complete. You should now start the Cisco PTC
servers.
2-70
Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Implementation Guide
OL-2706-01
Page 71

Chapter 2 Provisioning
System Startup
Step 1 Log into the Cisco PTC host, as user vnm, with an Xwindow terminal and start the Cisco CNS Security
Step by Step Installation and Initial Configuration
This section describes how to start the Cisco CNS Security and Cisco CNS Integration Bus processes
and then perform a Cisco PTC Cold Start. A Cisco PTC Cold Start does the following:
• creates and initializes the Cisco PTC database
• loads the data types and meta information
• starts the orbixd daemon, the Event Distributor, and the ACT Server
• starts the Cisco PTCProvisioning, Topology,Northbound API,Synchronization Manager, and Auto
discovery Servers
• uploads the runningconfigurationsof thedevicesfound inthe Cisco PTCNetwork InformationSeed
File (NISF), parses them, and then populates the Cisco PTC database. The NCSF provides to
Cisco PTC, a list of the network elements and theirproperties that are tobe managed by Cisco PTC.
• starts the Cisco VRC application if it is installed and the vnm --coldstart --INTEGRATED
command is executed.
Server process:
ptc-tme# su - vnm
Sun Microsystems Inc. SunOS 5.8 Generic Patch October 2001
Path and environment for DC Directory set up
ptc-tme% dcdstart
Starting DC Directory Server...
DC Directory Server initializing ...
DC Directory Server initialized
OL-2706-01
Note Upon starting the Cisco CNS Security Server process, error messages containing
“seminfo_semmin is not defined in the semsys” and “seminfo_semune is not defined in the
semsys” may be output. These error messages are not serious and can be ignored.
Step 2 Verify the Cisco CNS Security process is running:
ptc-tme% ps -ef | grep dcx500
root 2165 1 2 15:52:53 pts/3 0:09
/opt/cisco/vnm/common/dcdsrvr/bin/dcx500
Step 3 If it isn't running (the dcx500 daemon was not found), go back and restart the DCD server.
Step 4 Start the Cisco CNS Integration Bus process:
ptc-tme% startCnsBus
Starting CNS INTEGRATION BUS
TIB/Rendezvous daemon
Copyright 1994-2000 by TIBCO Software Inc.
All rights reserved.
Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Implementation Guide
2-71
Page 72

Step by Step Installation and Initial Configuration
Version 6.4.8
CNS INTEGRATION BUS is up
Note If the Cisco CNS IE2100 appliance and the Cisco PTC Server machine are in different subnets,
you must configure the Cisco CNS Integration Bus and Cisco CNS IE2100 appliance as
described in the “Post Installation Configuration” section, prior to performing the following
steps.
Step 5 Verify the Cisco CNS Integration Bus is running:
ptc-tme% ps -ef | grep rvrd
vnm 2186 1 0 15:55:27 ? 0:00
/opt/cisco/vnm/common/tibrv/bin/rvrd -store
/opt/cisco/vnm/common/tibrv/bin/rvr
Step 6 If it isn't running (the rvrd daemon was not found), go back to the last step and start it again.
Starting the Cisco PTC Server Processes
Chapter 2 Provisioning
Step 7 Go to the /opt/cisco/vnm/topodisc directory:
ptc-tme% cd /opt/cisco/vnm/topodisc
Step 8 Add the network devices to the Cisco PTC Network Information Seed File (NISF) through the
Cisco PTC Seed File Editor.
Refer to the “Cisco PTCNetwork InformationSeed File”appendix in the Cisco Packet Telephony Center
User Guide for a detailed description of how to add the network devices to the NISF through the
Cisco PTC Seed File Editor.
Step 9 Go to the /opt/cisco/vnm/topology directory and edit the LocalStrings.properties file as follows:
a. If you plan on connecting from the Cisco PTC Server machine to the machine where the Carrier
SensitiveRouter (CSR) applicationis running, youmust ensure the props.naboo_prompt variableis
set to the default prompt that is used by the machine where CSR is running (the prompt you receive
when you log in to the CSR machine).
b. If you plan on connecting from the Cisco PTC Server machine to the machine where the Cisco Info
Center (CIC) application is running, you must ensure the props.cic_prompt variable is set to the
default prompt that is used by the machine where CIC is running (the prompt you receive when you
log in to the CIC machine):
ptc-tme% pwd
/opt/cisco/vnm/topology
ptc-tme% ls
LocalStrings.properties images topology.dtd
topology.xml
WEB-INF resources topology.jar
topoview.html
2-72
Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Implementation Guide
OL-2706-01
Page 73

Chapter 2 Provisioning
Step 10 Edit the LocalStrings.properties file:
Step by Step Installation and Initial Configuration
ptc-tme% vi LocalStrings.properties
props.baseurl=http://172.19.49.18:8080/topology/servlet/
props.rmiserverhostname=172.19.49.18
props.codebaseurl=http://172.19.49.18:8080/lib
props.provsvrhost=172.19.49.18
props.actualinstallationdir=/opt/vnm
props.uploadedfilesdir=/opt/cisco/vnm/topodisc/uploadedfiles
props.seedfilelocation=/opt/cisco/vnm/topodisc/seedfile.txt
props.majserver=http://majewski-u10:8080/layout/servlet/LayoutServer
props.seedfilename=seedfile.txt
props.imagebase=http://172.19.49.18:8080/topology/images/vnm/Topology
props.discoverydir=/opt/vnm/topodisc
props.apppath=/opt/vnm/topology/resources
props.gdpmurl=http://172.19.49.18:8080/VRC/
props.discoverbts=false
props.vspt_user=vnm
props.cmnm_user=vnm
props.cisview_user=vnm
props.cic_user=root
props.cic_prompt=trapman#
props.naboo_user=ciscocsr
props.naboo_prompt=csr-tme%
props.sysadmin_user=vnm
props.sysadmin_prompt=%
props.smservername=:SMTest
props.httpport=8080
props.pinginterval=3000
props.sessiontimeout=-1
props.warnbefore=60
props.dointervalbasedresync=false
props.resyncstarttime=23:30
props.resyncinterval=24
props.rdbms=sybase
props.dbhost=localhost
props.dbsharedcon=1
props.dbpooledcon=0
props.dbname=PTC
props.dbuser=dba
props.dbpassword=sql
props.dbinformixserver=
props.dbport=49152
props.metaxmlfile=/opt/cisco/vnm/lib/vnm.xml
props.softwareVersion=Cisco Packet Telephony Center 2.1.1
OL-2706-01
Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Implementation Guide
2-73
Page 74

Step by Step Installation and Initial Configuration
Step 11 Go to the /opt/cisco/vnm directory:
ptc-tme% cd /opt/cisco/vnm
Perform a Cisco PTC Cold Start:
Note Cisco PTC can be started in either Standalone (the default) or Integrated mode. In Standalone
mode, only Cisco PTC Server processes are started. In Integrated mode, Cisco PTC Server and
Cisco VRC processes are started.
Step 12 Wait until the “Start Operation is Complete” and “Cisco PTC is Up” messages appear.
Step 13 Upon seeing the above messages, the Cisco PTC server processes are started. Proceed to the “Post
Installation Configuration” section for details about the configuration steps you must now perform.
Post Installation Configuration
This section describes the Cisco CNS Integration Bus and Cisco CNS IE2100 appliance configuration
procedures you must follow upon successful installation of the Cisco PTC product.
Chapter 2 Provisioning
Note In order for the Cisco PTC Provisioning Manager to function properly, you must set the Enter the NSM
Directives parameter value to default://, as opposed to its default value (http://), on all Cisco CNS
IE2100 appliances that are part of the Cisco PTC network. You set this parameter by running the setup
command when you add a new Cisco CNS IE2100 appliance to the network.
Note When the Cisco CNS IE2100 appliance and the machine you installed Cisco PTC on are located in the
same subnet, you need not configure the Cisco CNS Integration Bus or Cisco CNS IE2100 appliance.
Go to the “Configuring the Cisco PTC Client” section for detailed information.
If, however, they are in different subnets, you must perform the steps described in the “Configuring the
Cisco CNS Integration Bus” and “Configuring the Cisco IE2100 Appliance” sections in the Cisco Packet
Telephony Center Installation and Configuration Guide.
Configuring the Cisco PTC Client
This section describes how to configure the Cisco PTC Windows based Client machine after having
successfully installed, configured, and started the Cisco PTC Server processes. This section also
describes the changes you must make to the Java security policy file prior to launching the Cisco PTC
Client on a Windows-based PC.
Step 1 Go to the Java security directory:
C:\Program Files\JavaSoft\JRE\1.3.1_0\lib\security
Step 2 Create a backup copy (java.policy.bak) of the java.policy file.
2-74
Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Implementation Guide
OL-2706-01
Page 75

Chapter 2 Provisioning
Step 3 Open the java.policy file and replace the contents of the java.policy file with the following lines:
Step 4 Save the modified java.policy file, then exit the text editor.
Step 5 Open a web browser of your choice.
Step 6 Go tothe “Starting the Cisco PTC Client GUI”section inthe Cisco PacketTelephony Center UserGuide
Implementation and Testing
// Standard extensions get all permissions by default
grant {
permission java.security.AllPermission;
};
for detailed information about how to start and use the Cisco PTC Client.
Implementation and Testing
Once all of the applications are started, you must deploy the network devices in your network. This can
be done manually or through the use of a seed file, which contains the access and SNMP passwords of
the devices, as well as their place in the network and other values. Once the devices are deployed, you
can make changes, additions, and deletions to the network.
Refer to the various User Guides for information on how to access and configure the Cisco PTC,
Cisco VRC, VSPT, and CMNM.
Related Documents
This section provides links to the various product documentation referenced through this chapter.
• Cisco Packet Telephony Center White Paper:
http://www.cisco.com/warp/public/cc/pd/nemnsw/pctlcrsw/prodlit/ptccr_wp.htm
• Cisco Packet Telephony Center documentation, version 2.1.1:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/rtrmgmt/ptc/2_1_1/index.htm
• Cisco Packet Telephony Center product literature:
http://www.cisco.com/warp/public/cc/pd/nemnsw/pctlcrsw/prodlit/index.shtml
• Cisco Voice Routing Center, version 1.1:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/rtrmgmt/vrc/vrc1_1/index.htm
• Voice Services Provisioning Tool, version 2.1 User Guide:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/access/sc/rel9/dart21/index.htm
• Cisco MGC Node Manager User's Guide:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/access/sc/rel9/cmnm21/index.htm
• Cisco CNS Intelligence Engine IE2100 Series, version 1.2
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/rtrmgmt/ie2100/cnfg_reg/rel_1_2/index.htm.
OL-2706-01
Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Implementation Guide
2-75
Page 76

Related Documents
Chapter 2 Provisioning
2-76
Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Implementation Guide
OL-2706-01
 Loading...
Loading...