Page 1

XGS-4526/4528F/4728F
Intelligent Layer 3+ Switch
Default Login Details
IP Address http://192.168.0.1
(Out-of-band
MGMT port)
http://192.168.1.1
(In-band ports)
User Name admin
Password 1234
Firmware Version 4.00
Edition 1, 03/2011
www.zyxel.com
www.zyxel.com
Copyright © 2011
ZyXEL Communications Corporation
Page 2

Page 3

About This User's Guide
About This User's Guide
Intended Audience
This manual is intended for people who want to configure the Switch using the
web configurator.
Related Documentation
• Web Configurator Online Help
The embedded Web Help contains descriptions of individual screens and
supplementary information.
• Command Reference Guide
The Command Reference Guide explains how to use the Command-Line
Interface (CLI) and CLI commands to configure the Switch.
Note: It is recommended you use the web configurator to configure the Switch.
• Support Disc
Refer to the included CD for support documents.
Documentation Feedback
Send your comments, questions or suggestions to: techwriters@zyxel.com.tw
Thank you!
The Technical Writing Team , ZyXEL Communications Corp.,
6 Innovation Road II, Science-Based Industrial Park, Hsinchu, 30099, Taiwan.
Need More Help?
More help is available at www.zyx el.com.
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
3
Page 4

About This User's Guide
• Download Library
Search for the latest product updates and documentation from this link. Read
the Tech Doc Overview to find out how to efficiently use the User Guide, Quick
Start Guide and Command Line Interface Reference Guide in order to better
understand how to use your product.
• Knowledge Base
If you have a specific question about your product, the answer may be here.
This is a collection of answers to previously asked questions about ZyXEL
products.
•Forum
This contains discussions on ZyXEL prod ucts. Learn from others who use ZyXEL
products and share your experiences as well.
Customer Support
Should problems arise that cannot be solved by the methods listed above, you
should conta ct your vendor. If you cannot cont act your vendor, then contact a
ZyXEL office for the region in which you bought the device.
See http://www.zyxel.com/web/contact_us.php for contact information. Please
have the following informatio n ready when you contact an office.
• Product model and serial number.
•Warranty Information.
• Date that you received your device.
• Brief description of the problem and the steps you took to solve it.
4
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
Page 5

Document Conventions
Document Conventions
Warnings and Notes
These are how warnings and notes are shown in this User’s Guide.
Warnings tell you about things that could harm you or your device.
Note: Notes tell you other important information (for example, other things you may
need to configure or helpful tips) or recommendations.
Syntax Conventions
• The XGS-4526/4528F/4728F may be referred to as the “Switch”, the “device”,
the “system” or the “product” in this User’s Guide.
• Product labels, screen names, field labels and field choices are all in bold font.
• A key stroke is denoted by square brackets and uppercase text, for example,
[ENTER] means the “enter” or “ret urn” key on your keyboard.
• “Enter” means for you to type one or more characters and then press the
[ENTER] key. “Select” or “choose” means for you to use one of the predefined
choices.
• A right angle bracket ( > ) within a screen name denotes a mouse click. For
example, Maintenance > Log > Log Setting means you first click
Maintenance in the navigation panel, then the Log sub menu and finally the
Log Setting tab to get to that screen.
• Units of measurement may denote the “metric” value or the “scientific” value.
For example, “k” for kilo may denote “1000” or “1024”, “M” for mega may
denote “1000000” or “1048576” and so on.
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
5
Page 6

Document Conventions
Icons Used in Figures
Figures in this User’s Guide may use the following generic icons. The S witch icon is
not an exact representation of your device.
The Switch Computer Notebook computer
Server DSLAM Firewall
Telephone Switch Router
6
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
Page 7
Safety Warnings
Safety Warnings
• Do NOT use this product near water, for example, in a wet basement or near a swimming
pool.
• Do NOT expose your device to dampness, dust or corrosive liquids.
• Do NOT store things on the device.
• Do NOT install, use, or service this device during a thunderstorm. There is a remote risk
of electric shock from lightning.
• Connect ONLY suitable accessories to the device.
• Do NOT open the device or unit. Opening or removing covers can expose you to
dangerous high voltage points or other risks. ONLY qualified service personnel should
service or disassemble this device. Please contact your vendor for further information.
• For continued protection against risk of fire replace only with same type and rating of
fuse.
• Make sure to connect the cables to the correct ports.
• Place connecting cables carefully so that no one will step on them or stumble over them.
• Always disconnect all cables from this device before servicing or disassembling.
• Use ONLY an appropriate power adaptor or cord for your device. Connect it to the right
supply voltage (for example, 110V AC in North America or 230V AC in Europe).
• Do NOT allow anything to rest on the power adaptor or cord and do NOT place the
product where anyone can walk on the power adaptor or cord.
• Do NOT use the device if the power adaptor or cord is damaged as it might cause
electrocution.
• If the power adaptor or cord is damaged, remove it from the device and the power
source.
• Do NOT attempt to repair the power adaptor or cord. Contact your local vendor to order a
new one.
• Do not use the device outside, and make sure all the connections are indoors. There is a
remote risk of electric shock from lightning.
• Do NOT obstruct the device ventilation slots, as insufficient airflow may harm your
device.
Your product is m arked with this symbol, which is known as the WEEE mark. WEEE
stands for Waste Electronics and Electrical Equipment. It means that used electrical
and electronic products should not be mixed with general waste. Used electrical
and electronic equipment should be treated separately.
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
7
Page 8

Safety Warnings
8
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
Page 9

Contents Overview
Contents Overview
User’s Guide ........................................................................................................ ...................25
Getting to Know Your Switch ..................................................................................................... 27
Hardware Installation and Connection ................................... ................................. ................... 33
Hardware Overview ................................................................................................................... 37
The Web Configurator ............................................................................................................... 47
Initial Setup Example ................................................................................................................. 57
Tutorials ..................................................................................................................................... 63
Technical Reference ..............................................................................................................93
System Status and Port Statistics ....................................... .......................................................95
Basic Setting ........................................................................................................................... 101
VLAN ........................................................................................................................................117
Static MAC Forward Setup ...................................................................................................... 137
Static Multicast Forward Setup ................................................................................................ 141
Filtering ..................................... .................................................... ........................................... 145
Spanning Tree Protocol ...................... ... ... ... .... ... ..................................................................... 147
Bandwidth Control .... ... ... .... ... ... ... ............................................................................................ 169
Broadcast Storm Control ......................................................................................................... 173
Mirroring .................................................................................................................................. 175
Link Aggregation ................. .....................................................................................................177
Port Authentication ...... ... .... ... ..................................................................................................187
Port Security .................................... ... ... ... ............................................. .... ... ... ... .... ... ..............197
Classifier ................................... .................................................... ........................................... 201
Policy Rule .............................................................................................................................. 207
Queuing Method ...................................................................................................................... 215
VLAN Stacking ......................................................................................................................... 219
Multicast ..................................................................................................................................227
AAA ......................................................................................................................................... 243
IP Source Guard ...................................................................................................................... 259
Loop Guard ..................... .... ... ... ............................................. .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... .................283
VLAN Mapping ........................................................................................................................ 287
Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling .............. ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .................................................. 291
sFlow .......................................................................................................................................295
PPPoE ..................................................................................................................................... 299
Error Disable ............................................................................................................................ 309
Private VLAN ............................ ... .... ... ... ... ............................................. .... ... ... ... ..................... 315
Static Route ............................................................................................................................. 319
Policy Routing .......................................................................................................................... 323
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
9
Page 10

Contents Overview
RIP ............................... .................... ................... ................... .................... ..............................327
OSPF .............................. .................................................... ..................................................... 331
IGMP .......................................................................................................................................345
DVMRP ..................................... ....................... ...................... ....................... ........................... 349
Differentiated Services ........................................ ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ........................................... 353
DHCP ...................................................................................................................................... 361
VRRP .............................. .................... ................... .................... ................... ........................... 371
ARP Learning ........... ... ........................................................................................... ... ... ........... 381
Load Sharing ............ ... ........................................................................................... ... ... ........... 387
Maintenance ............................................................................................................................ 389
Access Control ........................................................................................................................ 397
Diagnostic .................................... ....................................................... ..................................... 423
Syslog ....................................... .................................................... ........................................... 425
Cluster Management .......... ... ................................................ .... ... ... ........................................ 435
MAC Table ............................................................................................................................... 443
IP Table .................................. ... ... .... ... ... ... ............................................. .... ... ... ... .... .................447
ARP Table .............................. ... ... .... ... ... ... ............................................. .... ... ... ... .... ... ..............451
Routing Table ........................................................................................................................... 453
Configure Clone ....................................................................................................................... 455
Troubleshooting ..................................................... .................................................................. 457
Product Specifications ............................................................................................................. 463
10
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
Page 11

Table of Contents
Table of Contents
About This User's Guide..........................................................................................................3
Document Conventions............................................................................................................5
Safety Warnings ........................................................................................................................7
Contents Overview ...................................................................................................................9
Table of Contents....................................................................................................................11
Part I: User’s Guide................................................................................ 25
Chapter 1
Getting to Know Your Switch.................................................................................................27
1.1 Introduction ......................... ... .... ... ... ... ............................................. .... ... ... ... .... ... ... .............27
1.1.1 Bridging Example ......... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ................................................ ... ... .... ... 27
1.1.2 High Performance Switching Example .......................................................................28
1.1.3 Gigabit Ethernet to the Desktop ................................................................................. 29
1.1.4 IEEE 802.1Q VLAN Application Example .................................................................. 29
1.1.5 IPv6 Support ....................................................... ... .... ... ... .......................................... 30
1.2 Ways to Manage the Switch ............................ ... .............................................. ... ... ... ... .... ... 30
1.3 Good Habits for Managing the Switch ................................................................................. 31
Chapter 2
Hardware Installation and Connection .................................................................................33
2.1 Freestanding Installation ..................................................................................................... 33
2.2 Mounting the Switch on a Rack .......................................................................................... 34
2.2.1 Rack-mounted Installation Requirements .................................................................. 34
2.2.2 Attaching the Mounting Brackets to the Switch ................................ .......................... 34
2.2.3 Mounting the Switch on a Rack .................................................................................. 35
Chapter 3
Hardware Overview.................................................................................................................37
3.1 Front Panel Connections ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ................................................ .... ... ................ 37
3.1.1 Dual Personality Interfaces ........................................................................................ 38
3.1.2 1000Base-T Ports ...................................................................................................... 38
3.1.3 Mini-GBIC Slots .........................................................................................................39
3.2 Rear Panel .................... ... ............................................. ... .... ... ... ... ... .................................... 41
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
11
Page 12

Table of Contents
3.2.1 XGS-4526 ..................................................... ... ... ... ............................................. .... ... 41
3.2.2 XGS-4528F or XGS-4728F ........................................................................................41
3.2.3 Uplink Module ..................................................... ... .... ... .............................................42
3.2.4 Rear Panel Connections ............................................................................................42
3.2.5 Power Connector ................................................... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ... .......................... 43
3.2.6 External Backup Power Supply Connector ................................................................ 44
3.2.7 Console Port ......................................................... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ... .......................... 44
3.3 LEDs ................................................................................................................................ 45
Chapter 4
The Web Configurator............................................................................................................47
4.1 Introduction ......................... ... .... ... ... ... ............................................. .... ... ... ... .... ... ... .............47
4.2 System Login ....................................................................................................................47
4.3 The Web Configurator Layout ............................................................................................ 48
4.3.1 Change Your Password .......................................................................................... 53
4.4 Saving Your Configuration ...................................................................................................54
4.5 Switch Lockout .............................................. ... .... ... ... ............................................. .......... 54
4.6 Resetting the Switch ............................... ... ... ... .............................................. ... ... ... ... ....... 54
4.6.1 Reload the Configuration File .................................................................................... 55
4.7 Logging Out of the Web Configurator ................................................................................. 56
4.8 Help ................................................... ... .... ... ... ............................................. .... ... ................56
Chapter 5
Initial Setup Example..............................................................................................................57
5.1 Overview ............. ............................................. ... .... ... ... ... .... ................................................ 57
5.1.1 Configuring an IP Interface ........................................................................................57
5.1.2 Configuring DHCP Server Settings .. ... ....................................................................... 59
5.1.3 Creating a VLAN ........................................................................................................ 59
5.1.4 Setting Port VID .................................................. ... .... ... ... ..........................................61
5.1.5 Enabling RIP ................ .... ... ... ............................................. ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .......62
Chapter 6
Tutorials...................................................................................................................................63
6.1 How to Use DHCP Snooping on the Switch ........................................................................ 63
6.2 How to Use DHCP Relay on the Switch .............................................................................. 67
6.2.1 DHCP Relay Tutorial Introduction .............................................................................. 67
6.2.2 Creating a VLAN ........................................................................................................ 68
6.2.3 Configuring DHCP Relay .............................................. ... ... ....................................... 71
6.2.4 Troubleshooting ............................................... ... ... .... ... ... ... ....................................... 71
6.3 How to Use PPPoE IA on the Switch .................................................................................. 72
6.3.1 Configuring Switch A ..................................... ... .......................................................... 73
6.3.2 Configuring Switch B ..................................... ... .......................................................... 75
6.4 How to Use Error Disable and Recovery on the Switch ......................................................77
12
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
Page 13

Table of Contents
6.5 How to Set Up a Guest VLAN ............................................................................................. 80
6.5.1 Creating a Guest VLAN .............................................................................................. 81
6.5.2 Enabling IEEE 802.1x Port Authentication ................................................................. 83
6.5.3 Enabling Guest VLAN ................................................................................................84
6.6 How to Do Port Isolation in a VLAN ..................................................................................... 85
6.6.1 Creating a VLAN ........................................................................................................ 86
6.6.2 Creating a Private VLAN Rule .................................................................................... 89
6.7 How to Configure Routing Policy ..................... ....................................................... .............90
6.7.1 Create a Layer-3 Classifier ........................................................................................ 90
6.7.2 Create a Policy Routing Rule .... ... .... ... ... ... ................................................................. 91
Part II: Technical Reference.................................................................. 93
Chapter 7
System Status and Port Statistics.........................................................................................95
7.1 Overview ............. ............................................. ... .... ... ... ... .... ................................................ 95
7.2 Port Status Summary ............................................................................................ ... ....... 95
7.2.1 Status: Port Details ................................................................................................97
Chapter 8
Basic Setting ........................................................................................................................101
8.1 Overview ............. ............................................. ... .... ... ... ... .... .............................................. 101
8.2 System Information ......................................................................................................... 102
8.3 General Setup ................................................................................................. ... ... ........ 104
8.4 Introduction to VLANs ........... .... ... ..................................................................................... 106
8.4.1 Smart Isolation ................. ... ... ............................................. ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .....107
8.5 Switch Setup Screen ... ... ... ... .... ........................................................................................ 108
8.6 IP Setup ...........................................................................................................................110
8.6.1 IP Interfaces .......... ... ... .... ... ... ............................................. ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ...............110
8.7 Port Setup ................ .... ... ... ............................................. .... ... ... ... ... .... ...............................113
Chapter 9
VLAN......................................................................................................................................117
9.1 Introduction to IEEE 802.1Q Tagged VLANs .................................................................117
9.1.1 Forwarding Tagged and Untagged Frames ...............................................................117
9.2 Automatic VLAN Registration ................................ ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... ...................................118
9.2.1 GARP . .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ............................................. .... ... ... .........................................118
9.2.2 GVRP . .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ............................................. .... ... ... .........................................118
9.3 Port VLAN Trunking ........... ............................................. .... ... ... ... ... ...................................119
9.4 Select the VLAN Type .... ... ... .... ... ............................................. ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ........120
9.5 Static VLAN . .... ... ... ... .............................................. ... ... ... .... .............................................. 120
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
13
Page 14

Table of Contents
9.5.1 VLAN Status ............................................................................................................121
9.5.2 VLAN Details ................................ .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ............................................. ... .... . 122
9.5.3 Configure a Static VLAN ...................................................................................... 122
9.5.4 Configure VLAN Port Settings .............................................................................. 124
9.6 Subnet Based VLANs .......................................................................................................126
9.7 Configuring Subnet Based VLAN ..... ................................................. ... ... ........................ 127
9.8 Protocol Based VLANs ...................................... .... ... ........................................................128
9.9 Configuring Protocol Based VLAN ............................................. ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ........129
9.10 Create an IP-based VLAN Example ................................................................................ 131
9.11 Port-based VLAN Setup ............................................................................................... 132
9.11.1 Configure a Port-based VLAN ............................................................................... 132
Chapter 10
Static MAC Forward Setup...................................................................................................137
10.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................... 137
10.2 Configuring Static MAC Forwarding ........................................................................... 137
Chapter 11
Static Multicast Forward Setup............................................................................................141
11.1 Static Multicast Forwarding Overview ..............................................................................141
11.2 Configuring Static Multicast Forwarding ........................................................................... 142
Chapter 12
Filtering..................................................................................................................................145
12.1 Configure a Filtering Rule ..............................................................................................145
Chapter 13
Spanning Tree Protocol........................................................................................................147
13.1 STP/RSTP Overview ..................................................................................................... 147
13.1.1 STP Terminology ................................................................................................... 147
13.1.2 How STP Works .................................................................................................... 148
13.1.3 STP Port States .....................................................................................................149
13.1.4 Multiple RSTP ......................................................................................................149
13.1.5 Multiple STP ........................................................................................................... 150
13.2 Spanning Tree Protocol Status Screen ............................................................................ 153
13.3 Spanning Tree Configuration ..........................................................................................153
13.4 Configure Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol ..................................................................... 154
13.5 Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol Status ........................................................................... 156
13.6 Configure Multiple Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol ........................................................ 158
13.7 Multiple Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol Status .......................................................... 160
13.8 Configure Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol .................................................................. 162
13.8.1 Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol Port Configuration ............................................. 165
13.9 Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol Status ..................................................................... 166
14
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
Page 15

Table of Contents
Chapter 14
Bandwidth Control................................................................................................................169
14.1 Bandwidth Control Overview ......................................................................................... 169
14.1.1 CIR and PIR ........................................................................................................... 169
14.2 Bandwidth Control Setup ................................................................................................. 170
Chapter 15
Broadcast Storm Control.....................................................................................................173
15.1 Broadcast Storm Control Setup ...................................................................................... 173
Chapter 16
Mirroring................................................................................................................................175
16.1 Port Mirroring Setup ....................................................................................................... 175
Chapter 17
Link Aggregation ..................................................................................................................177
17.1 Link Aggregation Overview ........................ ....................... ...................... ....................... . 177
17.2 Dynamic Link Aggregation ..............................................................................................177
17.2.1 Link Aggregation ID ............................................................................................... 178
17.3 Link Aggregation Status ....................................................... .......................... .................179
17.4 Link Aggregation Setting ................................................................................................ 181
17.5 Link Aggregation Control Protocol ................................................................................ 183
17.6 Static Trunking Example .................................................................................................. 184
Chapter 18
Port Authentication...............................................................................................................187
18.1 Port Authentication Overview ......................................................................................... 187
18.1.1 IEEE 802.1x Authentication ................................................................................... 187
18.1.2 MAC Authentication ............................................................................................... 188
18.2 Port Authentication Configuration ............................ ....................................................... .189
18.2.1 Activate IEEE 802.1x Security ........................................................................... 190
18.2.2 Guest VLAN ..........................................................................................................191
18.2.3 Activate MAC Authentication ................................................................................. 194
Chapter 19
Port Security..........................................................................................................................197
19.1 About Port Security ..........................................................................................................197
19.2 Port Security Setup .............................. ....................... ....................... ................... ........... 198
19.3 VLAN MAC Address Limit .............................................................................................. 199
Chapter 20
Classifier................................................................................................................................201
20.1 About the Classifier and QoS .......................................................................................... 201
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
15
Page 16

Table of Contents
20.2 Configuring the Classifier ...............................................................................................201
20.3 Viewing and Editing Classifier Configuration ................................. .................................. 204
20.4 Classifier Example ...........................................................................................................206
Chapter 21
Policy Rule............................................................................................................................207
21.1 Policy Rules Overview ....................................................................................................207
21.1.1 DiffServ .................................................................................................................. 207
21.1.2 DSCP and Per-Hop Behavior ................................................................................. 207
21.2 Configuring Policy Rules ................................................................................................. 208
21.3 Viewing and Editing Policy Configuration .........................................................................211
21.4 Policy Example ................................................................................................................ 213
Chapter 22
Queuing Method....................................................................................................................215
22.1 Queuing Method Overview ............................................................................................. 215
22.1.1 Strictly Priority ........................................................................................................215
22.1.2 Weighted Fair Queuing .......................................................................................... 215
22.1.3 Weighted Round Robin Scheduling (WRR) ........................................................... 216
22.2 Configuring Queuing ........................................................................................................ 217
Chapter 23
VLAN Stacking......................................................................................................................219
23.1 VLAN Stacking Overview ................................................................................................ 219
23.1.1 VLAN Stacking Example ........................................................................................ 219
23.2 VLAN Stacking Port Roles ................ ... .... ........................................................................ 220
23.3 VLAN Tag Format .......... ..................................................................................................221
23.3.1 Frame Format ........................................................................................................221
23.4 Configuring VLAN Stacking ............................................................................................. 222
23.4.1 Port-based Q-in-Q .................................................................................................. 223
23.4.2 Selective Q-in-Q .................................................................................................... 224
Chapter 24
Multicast ................................................................................................................................227
24.1 Multicast Overview ......................................................................................................... 227
24.1.1 IP Multicast Addresses ........................................................................................... 227
24.1.2 IGMP Filtering ........................................................................................................ 227
24.1.3 IGMP Snooping ..................................................................................................... 228
24.1.4 IGMP Snooping and VLANs ................................................................................... 228
24.2 Multicast Status .............................................................................................................. 228
24.3 Multicast Setting .............. ... .... ... ................................................ ... .... .............................. 229
24.4 IGMP Snooping VLAN .................................................................................................... 232
24.5 IGMP Filtering Profile ..................................................................................................... 233
16
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
Page 17

Table of Contents
24.6 MVR Overview ................................................................................................................ 235
24.6.1 Types of MVR Ports ............................................................................................... 235
24.6.2 MVR Modes ........................................................................................................... 236
24.6.3 How MVR Works .................................................................................................... 236
24.7 General MVR Configuration ............................................................................................ 237
24.8 MVR Group Configuration ..............................................................................................239
24.8.1 MVR Configuration Example ... ... .... ... ..................................................................... 240
Chapter 25
AAA........................................................................................................................................243
25.1 Authentication, Authorization and Accounting (AAA) ...................................................... 243
25.1.1 Local User Accounts .................. .... ... ... ... .... ... ................................................ ... .... . 244
25.1.2 RADIUS and TACACS+ ........................................................................................ 244
25.2 AAA Screens ................................................................................................................... 244
25.2.1 RADIUS Server Setup .......................................................................................... 245
25.2.2 TACACS+ Server Setup ..................................................................................... 247
25.2.3 AAA Setup .............................................................................................................. 249
25.2.4 Vendor Specific Attribute ........................................................................................ 252
25.2.5 Tunnel Protocol Attribute ........................................................................................ 253
25.3 Supported RADIUS Attributes ......................................................................................... 254
25.3.1 Attributes Used for Authentication ............................ ............ .......... .......... ......... ..... 254
25.3.2 Attributes Used for Accounting ............................................................................... 255
Chapter 26
IP Source Guard ....................................................................................................................259
26.1 IP Source Guard Overview .............................................................................................. 259
26.1.1 DHCP Snooping Overview ..................................................................................... 260
26.1.2 ARP Inspection Overview ...................................................................................... 262
26.2 IP Source Guard .............................................................................................................. 263
26.3 IP Source Guard Static Binding ....................................................................................... 264
26.4 DHCP Snooping .............................................................................................................. 266
26.5 DHCP Snooping Configure ...................... ........................................................................ 269
26.5.1 DHCP Snooping Port Configure ............................................................................. 271
26.5.2 DHCP Snooping VLAN Configure .......................................................................... 272
26.6 ARP Inspection Status .....................................................................................................274
26.6.1 ARP Inspection VLAN Status .................................................................................275
26.6.2 ARP Inspection Log Status .................................................................................... 276
26.7 ARP Inspection Configure ............................................................................................... 277
26.7.1 ARP Inspection Port Configure .............................................................................. 279
26.7.2 ARP Inspection VLAN Configure ........................................................................... 280
Chapter 27
Loop Guard............................................................................................................................283
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
17
Page 18

Table of Contents
27.1 Loop Guard Overview .....................................................................................................283
27.2 Loop Guard Setup ...........................................................................................................285
Chapter 28
VLAN Mapping ......................................................................................................................287
28.1 VLAN Mapping Overview ............................................................................................... 287
28.1.1 VLAN Mapping Example ........................................................................................ 287
28.2 Enabling VLAN Mapping ................................................................................................. 288
28.3 Configuring VLAN Mapping ............................................................................................. 289
Chapter 29
Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling..................................................................................................291
29.1 Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling Overview ............................................................................. 291
29.1.1 Layer-2 Protocol Tunneling Mode .......................................................................... 292
29.2 Configuring Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling .................................................................. ... .... . 293
Chapter 30
sFlow......................................................................................................................................295
30.1 sFlow Overview ............................................................................................................... 295
30.2 sFlow Port Configuration ................................................................................................. 296
30.2.1 sFlow Collector Configuration ................................................................................ 297
Chapter 31
PPPoE....................................................................................................................................299
31.1 PPPoE Intermediate Agent Overview ............................................................................. 299
31.1.1 PPPoE Intermediate Agent Tag Format .................................................................299
31.1.2 Sub-Option Format ......................... ......... .......... .......... ......... ....... .......... ......... ........ 300
31.1.3 Port State ...............................................................................................................301
31.2 The PPPoE Screen ......................................................................................................... 302
31.3 PPPoE Intermediate Agent ............................................................................................. 302
31.3.1 PPPoE IA Per-Port ................................................................................................ 303
31.3.2 PPPoE IA Per-Port Per-VLAN ............................................................................... 305
31.3.3 PPPoE IA for VLAN ............................................................................................... 307
Chapter 32
Error Disable ........................................................................ .................................................309
32.1 CPU Protection Overview ................................................................................................309
32.2 Error-Disable Recovery Overview ................................................................................... 309
32.3 The Error Disable Screen ................................................................................................ 310
32.4 CPU Protection Configuration ........................................................................................ 310
32.5 Error-Disable Detect Configuration ..................................................................................311
32.6 Error-Disable Recovery Configuration ............................................................................ 313
18
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
Page 19

Table of Contents
Chapter 33
Private VLAN.........................................................................................................................315
33.1 Private VLAN Overview .................................................................................................. 315
33.2 Configuring Private VLAN ................................................................................................ 316
Chapter 34
Static Route...........................................................................................................................319
34.1 Static Routing Overview ................................................................................................ 319
34.2 Configuring Static Routing .............................................................................................. 320
Chapter 35
Policy Routing .......................................................................................................................323
35.1 Policy Route Overview ................................................................................................... 323
35.1.1 Benefits ..................................................................................................................323
35.2 Configuring Policy Routing Profile ................................................................................... 324
35.2.1 Policy Routing Rule Configuration ........................................................................ 325
Chapter 36
RIP..........................................................................................................................................327
36.1 RIP Overview ................................................................................................................... 327
36.1.1 Administrative Distance .......................................................................................... 327
36.2 Configuring RIP ............................................................................................................... 328
Chapter 37
OSPF......................................................................................................................................331
37.1 OSPF Overview .............................................................................................................. 331
37.1.1 OSPF Autonomous Systems and Areas . .... ... ... ... .... .............................................. 331
37.1.2 How OSPF Works ... ............................................. .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ........................... 332
37.1.3 Interfaces and Virtual Links .................................................................................... 332
37.1.4 OSPF and Router Elections ...................................................................................333
37.1.5 Configuring OSPF .................................................................................................333
37.2 OSPF Status ................................................................................................................. 334
37.3 OSPF Configuration .......................................................................................................336
37.4 Configure OSPF Areas ................................................................................................... 337
37.4.1 View OSPF Area Information Table ....................................................................... 339
37.5 Configuring OSPF Redistribution ................................................................................... 339
37.6 Configuring OSPF Interfaces .......................................................................................... 341
37.7 OSPF Virtual-Links ....................................................................................................... 343
Chapter 38
IGMP.......................................................................................................................................345
38.1 IGMP Overview ............................................................................................................... 345
38.1.1 How IGMP Works ................. ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ............................................. ... ... .... . 346
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
19
Page 20

Table of Contents
38.2 Port-based IGMP ............................................................................................................. 347
38.3 Configuring IGMP ............................................................................................................ 348
Chapter 39
DVMRP...................................................................................................................................349
39.1 DVMRP Overview ............................................................................................................349
39.2 How DVMRP Works ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ................................................ ... ... .....349
39.2.1 DVMRP Terminology ............................................................................................. 350
39.3 Configuring DVMRP ....................................................................................................... 350
39.3.1 DVMRP Configuration Error Messages ........................................... .... ... ... ... ........351
39.4 Default DVMRP Timer Values ........................................................................................ 352
Chapter 40
Differentiated Services.........................................................................................................353
40.1 DiffServ Overview ...........................................................................................................353
40.1.1 DSCP and Per-Hop Behavior ................................................................................. 353
40.1.2 DiffServ Network Example .................................................................................... 354
40.2 Two Rate Three Color Marker Traffic Policing ................................................................. 354
40.2.1 TRTCM - Color-blind Mode .................................................................................... 355
40.2.2 TRTCM - Color-aware Mode .......................................... ........................................ 355
40.3 Activating DiffServ .......................................................................................................... 356
40.3.1 Configuring 2-Rate 3 Color Marker Settings ......................................................... 357
40.4 DSCP-to-IEEE 802.1p Priority Settings ....... .............................................. ... ... ... ... .....359
40.4.1 Configuring DSCP Settings ............................ .......................................... .............. 360
Chapter 41
DHCP......................................................................................................................................361
41.1 DHCP Overview ............................................................................................................. 361
41.1.1 DHCP Modes ........................................................................................................361
41.1.2 DHCP Configuration Options ................................................................................. 361
41.2 DHCP Status ................................................................................................................... 362
41.3 DHCP Server Status Detail ............................................................................................. 362
41.4 DHCP Relay ....... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... ............................................................................ 364
41.4.1 DHCP Relay Agent Information ............................................................................. 364
41.4.2 Configuring DHCP Global Relay ............................................................................ 365
41.4.3 Global DHCP Relay Configuration Example .......................................................... 366
41.5 Configuring DHCP VLAN Settings ................................................................................ 367
41.5.1 Example: DHCP Relay for Two VLANs .................................................................. 369
Chapter 42
VRRP......................................................................................................................................371
42.1 VRRP Overview .............................................................................................................. 371
42.2 VRRP Status .................................................................................................................... 372
20
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
Page 21

Table of Contents
42.3 VRRP Configuration .......................................................................................................373
42.3.1 IP Interface Setup ................................................................................................. 373
42.3.2 VRRP Parameters ................................................................................................. 375
42.3.3 Configuring VRRP Parameters .............................................................................. 376
42.3.4 Configuring VRRP Parameters .............................................................................. 377
42.4 VRRP Configuration Examples ...................................................................................... 377
42.4.1 One Subnet Network Example ..............................................................................378
42.4.2 Two Subnets Example ........................................................................................... 379
Chapter 43
ARP Learning........................................................................................................................381
43.1 ARP Overview ................................................................................................................ 381
43.1.1 How ARP Works ......................................................... ... ... ... .... ... ... ........................ 381
43.1.2 ARP Learning Mode ............................................................................................... 381
43.2 Configuring ARP Learning ............................................................................................... 384
Chapter 44
Load Sharing.........................................................................................................................387
44.1 Load Sharing Overview .................................................................................................. 387
44.2 Configuring Load Sharing ................................................................................................ 387
Chapter 45
Maintenance..........................................................................................................................389
45.1 The Maintenance Screen ................................. .... ... ... ... .... ............................................. . 389
45.2 Load Factory Default ...................................................................................................... 390
45.3 Save Configuration .......................................................................................................... 390
45.4 Reboot System ................................................................................................................ 391
45.5 Firmware Upgrade ........................................................................................................... 391
45.6 Restore a Configuration File ....................... ....................................................... ..............392
45.7 Backup a Configuration File ............................................................................................ 393
45.8 FTP Command Line ........................................................................................................ 393
45.8.1 Filename Conventions .......................................................................................... 393
45.8.2 FTP Command Line Procedure ............................................................................ 394
45.8.3 GUI-based FTP Clients .......................................................................................... 395
45.8.4 FTP Restrictions .................................................................................................... 395
Chapter 46
Access Control......................................................................................................................397
46.1 Access Control Overview ............................................................................................ 397
46.2 The Access Control Main Screen .................................................................................... 397
46.3 About SNMP .................................................................................................................. 398
46.3.1 SNMP v3 and Security ........................................................................................... 399
46.3.2 Supported MIBs ................................................................................................... 399
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
21
Page 22

Table of Contents
46.3.3 SNMP Traps .......................................................................................................... 400
46.3.4 Configuring SNMP .............................................................................................. 407
46.3.5 Configuring SNMP Trap Group ...........................................................................409
46.3.6 Configuring SNMP User ...................................................................................... 410
46.4 Setting Up Login Accounts ............................................................................................ 412
46.5 SSH Overview ................................................................................................................. 413
46.6 How SSH works ................ ... ............................................................................................ 414
46.7 SSH Implementation on the Switch ................................................................................. 415
46.7.1 Requirements for Using SSH .................................................................................415
46.8 Introduction to HTTPS .....................................................................................................415
46.9 HTTPS Example .............................................................................................................. 416
46.9.1 Internet Explorer Warning Messages ..................................................................... 416
46.9.2 Netscape Navigator Warning Messages ................................................................ 417
46.9.3 The Main Screen .................................................................................................... 419
46.10 Service Port Access Control ....................................................................................... 419
46.11 Remote Management ............................................................................................... 420
Chapter 47
Diagnostic..............................................................................................................................423
47.1 Diagnostic ....................................................................................................................... 423
Chapter 48
Syslog....................................................................................................................................425
48.1 Syslog Overview .............................................................................................................. 425
48.2 Syslog Setup .................................................................................................................. 426
48.3 Syslog Server Setup ....................................................................................................... 427
48.4 Syslog Messages ............................................................................................................ 428
Chapter 49
Cluster Management.............................................................................................................435
49.1 Clustering Management Status Overview ...................................................................... 435
49.2 Cluster Management Status ........................................................................................... 436
49.2.1 Cluster Member Switch Management ................................................................... 437
49.3 Clustering Management Configuration .......................................................................... 440
Chapter 50
MAC Table..............................................................................................................................443
50.1 MAC Table Overview ...................................................................................................... 443
50.2 Viewing the MAC Table ....................................................................................................444
Chapter 51
IP Table ..................................................................................................................................447
51.1 IP Table Overview ...........................................................................................................447
22
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
Page 23

Table of Contents
51.2 Viewing the IP Table ........................................................................................................448
Chapter 52
ARP Table..............................................................................................................................451
52.1 ARP Table Overview .......................................................................................................451
52.1.1 How ARP Works ......................................................... ... ... ... .... ... ... ........................ 451
52.2 The ARP Table Screen ................................................................................................... 452
Chapter 53
Routing Table........................................................................................................................453
53.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................... 453
53.2 Viewing the Routing Table Status ................................................................................... 453
Chapter 54
Configure Clone....................................................................................................................455
54.1 Configure Clone ..............................................................................................................455
Chapter 55
Troubleshooting....................................................................................................................457
55.1 Power, Hardware Connections, and LEDs .............................. ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ........457
55.2 Switch Access and Login .................................................................................................458
55.3 Switch Configuration ........................................................................................................461
Chapter 56
Product Specifications.........................................................................................................463
Appendix A Common Services.............................................................................................473
Appendix B Legal Information..............................................................................................477
Index.......................................................................................................................................481
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
23
Page 24

Table of Contents
24
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
Page 25

PART I
User’s Guide
25
Page 26

26
Page 27

CHAPTER 1
Getting to Know Your Switch
This chapter introduces the main features and applications of the Switch.
1.1 Introduction
Your Switch is a stand-alone, layer-3, Gigabit Ethernet (GbE) switch with support
for an optional 2-port 10 Gigabit uplink module. The XGS-4528F or XGS-4728F
also provides two 12 Gigabit stacking ports. By integrating router functions, the
Switch performs wire-speed layer-3 routing in addition to layer-2 switching.
The XGS-4526 comes with 20 100/1000 Mbps Ethernet ports and 4 GbE dual
personality interfaces. The XGS-4528F or XGS-4728F comes with 24 GbE dual
personality interfaces. A dual personality interface includes one Gigabit port and
one slot for a mini-GBIC transceiver (SFP module) with one port active at a time.
The XGS-4526 requires 100 VAC to 240 VAC, 0.8 A power.
There are two XGS-4528F or XGS-4728F models. The XGS-4528F or XGS-4728F
DC model requires DC power supply input of -36 VDC to -72 VDC, 1.5 A Max no
tolerance. The XGS-4528F or XGS-4728F AC model requires 100 VAC to 240 VAC,
0.8 A power.
With its built-in web configurat or, managing and configuring the Switch is easy. In
addition, the Switch can also be managed via Telnet, any terminal emulator
program on the console port, or third-party SNMP management.
See Chapter 56 on page 463 for a full list of software features available on the
Switch.
1.1.1 Bridging Example
In this example the Switch connects different company departments (RD and
Sales) to the corporate backbone. It can alleviate bandwidth contention and
eliminate server and network bottlenecks. All users that need high bandwidth can
connect to high-speed department servers via the Switch. You can provide a
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
27
Page 28
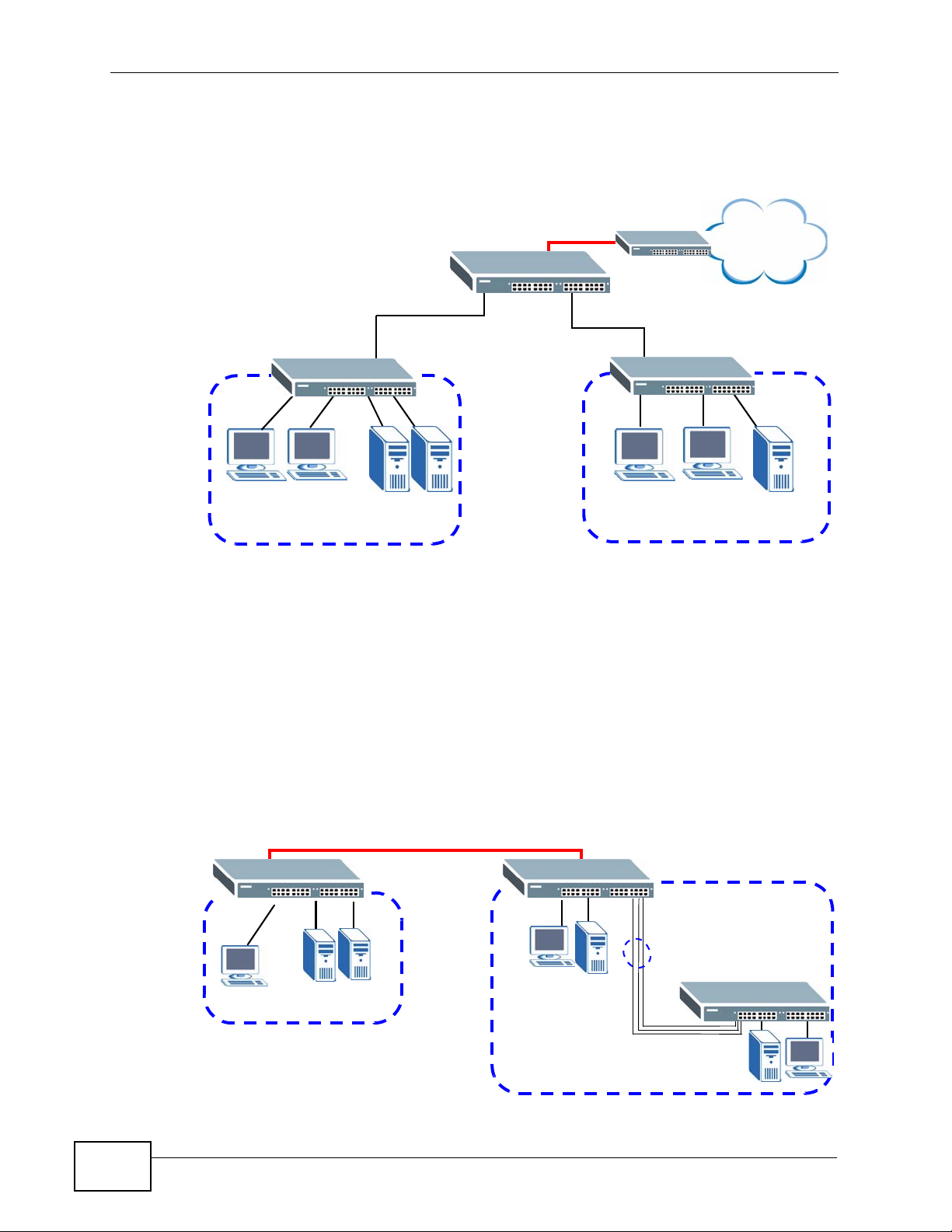
Chapter 1 Getting to Know Your Switch
super-fast uplink connection by using the optional 10 Gigabit uplink module on the
Switch.
Figure 1 Bridging Application
Backbone
RD
Sales
1.1.2 High Performance Switching Example
The Switch is ideal for connecting two geographically dispersed networks that
need high bandwidth. In the following example, a company uses the optional 10
Gigabit uplink modules to connect the headquarters to a branch office network.
Within the headquarters network, a company can use trunking to group several
physical ports into one logical hig h er-capacity link. Trunking can be used if for
example, it is cheaper to use multiple lower-speed links than to under-utilize a
high-speed, but more costly, single-port link.
Figure 2 High Performance Switching
10 Gbps
Trunk
28
Branch
HQ
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
Page 29
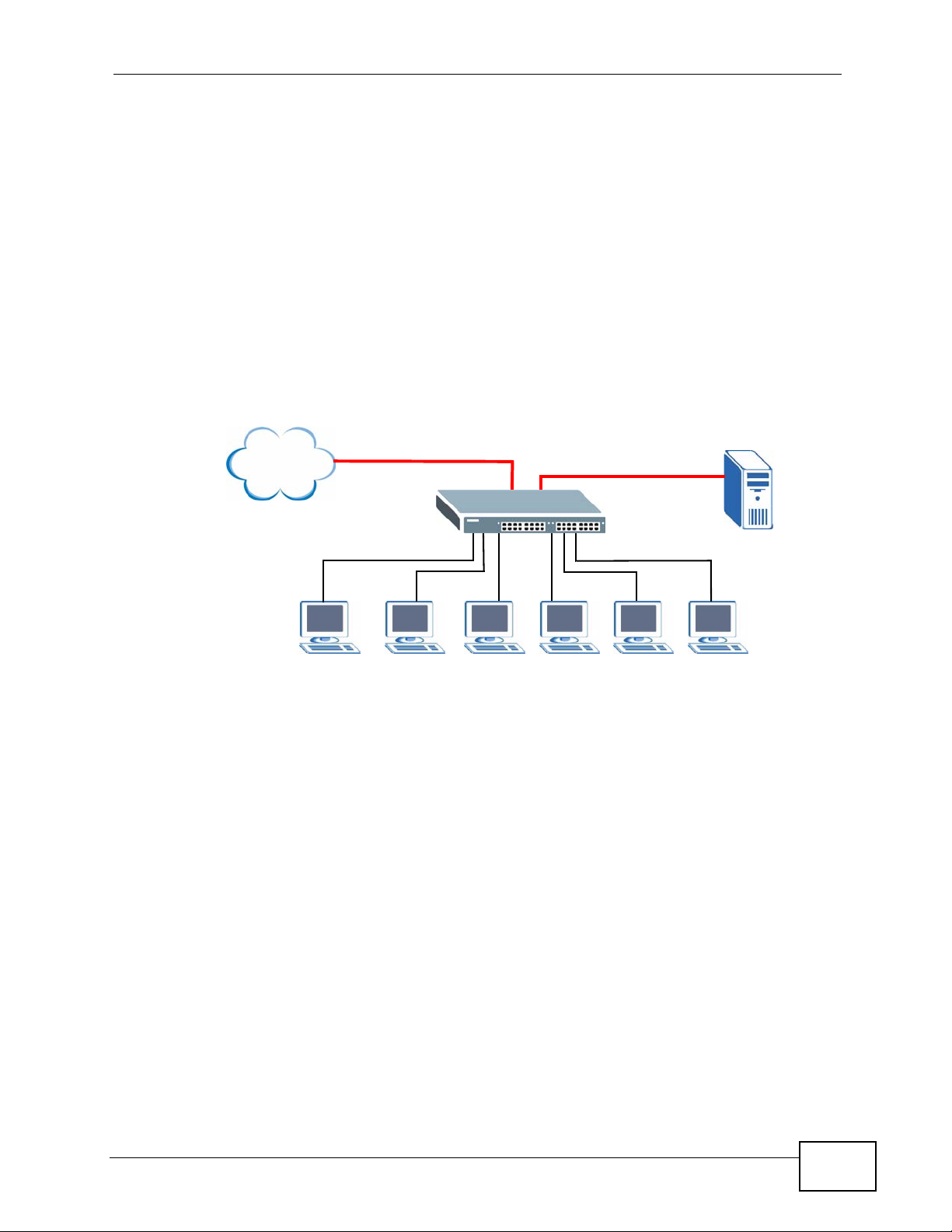
1.1.3 Gigabit Ethernet to the Desktop
The Switch is an ideal solution for small networks which demand high bandwidth
for a group of heavy traffic users. Y ou can conn ect computers an d servers directly
to the Switch’s port or connect other switches to the Switch. Use the optional 10
Gigabit uplink module to provide high speed access to a data server and the
Internet. The uplink module supports a fiber-optic connection which alleviates the
distance limitations of copper cabling.
In this example, all computers can share high-speed applications on the server
and access the Internet. To expand the network, simply add more networking
devices such as switches, routers, computers, print servers and so on.
Figure 3 Gigabit to the Desktop
Internet
Chapter 1 Getting to Know Your Switch
1.1.4 IEEE 802.1Q VLAN Application Example
A VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) allows a physical network to be partitioned
into multiple logical networks. Stations on a logical network belong to one or more
groups. With VLAN, a station cannot directly talk to or hear from stations that are
not in the same group(s) unless such traffic first goes through a router.
For more information on VLANs, refer to Chapter 9 on page 117.
1.1.4.1 Tag-based VLAN Example
Ports in the same VLAN group share the same frame broadcast domain, thus
increasing network performance by reducing broadcast traffic. VLAN groups can
be modified at any time by adding, moving or changing ports without any recabling.
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
29
Page 30
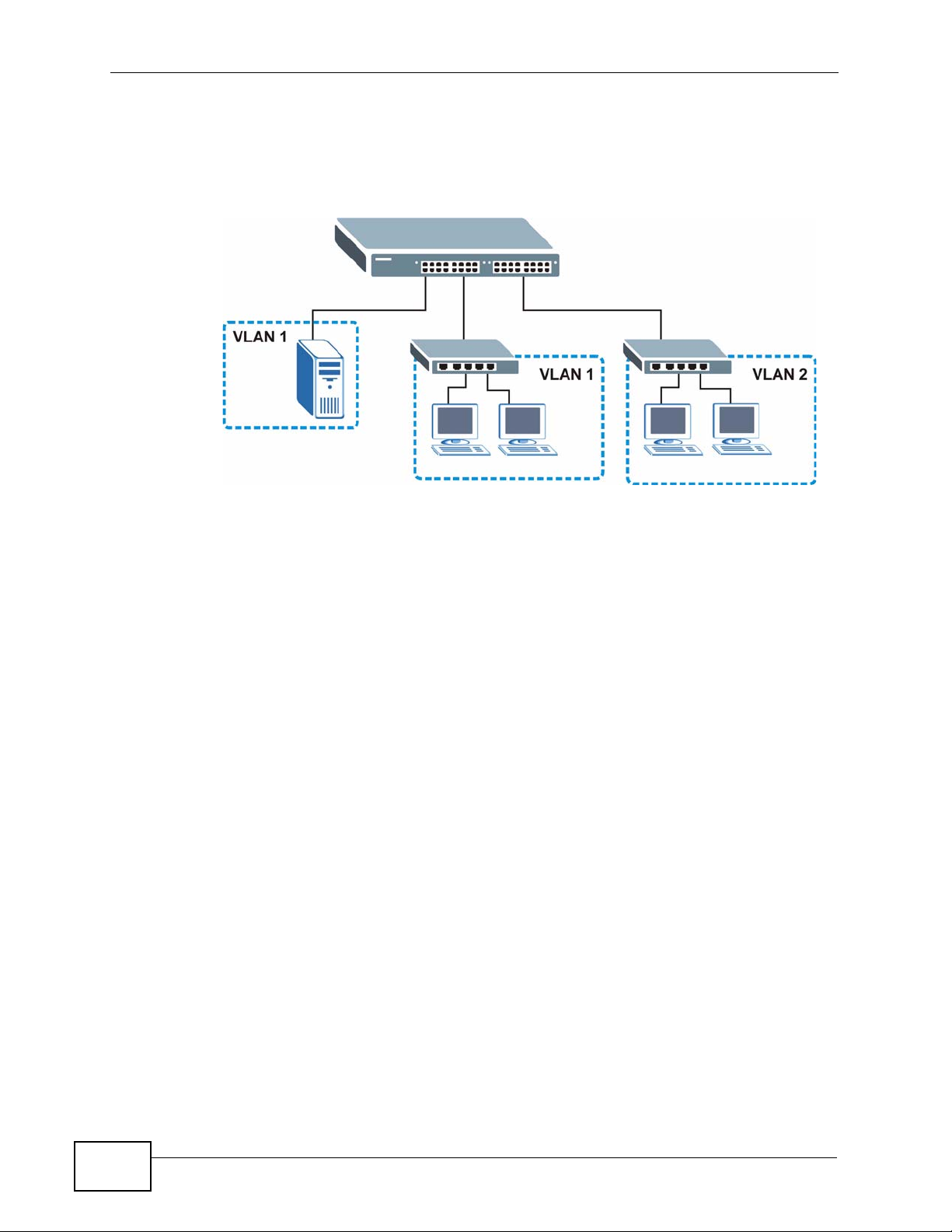
Chapter 1 Getting to Know Your Switch
Shared resources such as a server can be used by all ports in the same VLAN as
the server. In the following figure only ports that need access to the server need
to be part of VLAN 1. Ports can belong to other VLAN groups too.
Figure 4 Shared Server Using VLAN Example
1.1.5 IPv6 Support
IPv6 (Internet Protocol version 6), is designed to enhance IP address size and
features. The increase in IPv6 address size to 128 bits (from the 32-bit IPv4
address) allows up to 3.4 x 10
supports the following features.
• Static address assignment and stateless auto-configuration
• Neighbor Discovery Protocol (a protocol used to discover other IPv6 d evices in a
network)
• Remote Management using ping SNMP, telnet, HTTP and FTP services
• ICMPv6 to report errors encountered in packet processing and perform
diagnostic functions, such as "ping”
• IPv4/IPv6 dual stack; the Switch can run IPv4 and IPv6 at the same time
• DHCPv6 client and relay
• Multicast Listener Discovery (MLD) snooping and proxy
For more information on IPv6, refer to the CLI Reference Guide.
38
IP addresses. At the time of writing, the Switch
1.2 Ways to Manage the Switch
Use any of the following methods to manage the Switch.
30
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
Page 31

Chapter 1 Getting to Know Your Switch
• Web Co nfigurator. This is recommended for ev eryday management of the S witch
using a (supported) web browser. See Chapter 4 on page 47.
• Command Line Interface. Line commands offer an alternative to the Web
Configurator and may be necessary to configure advanced features. See the CLI
Reference Guide.
• FTP. Use File Transfer Protocol for firmware upgrades and configuration backup/
restore. See Section 45.8 on page 393.
• SNMP. The device can be monitored and/or managed by an SNMP manager. See
Section 46.3 on page 398.
1.3 Good Habits for Managing the Switch
Do the following things regularly to make the Switch more secure and to manage
the Switch more effectively.
• Change the password. Use a password that’s not easy to guess and that consists
of different types of characters, such as numbers and letters.
• Write down the password and put it in a safe place.
• Back up the configuration (and make sure you know how to restore it).
Restoring an earlier working configuration may be useful if the device becomes
unstable or even crashes. If you forget y our password, you will hav e to reset the
Switch to its factory default settings. If you backed up an earlier configuration
file, you would not have to totally re-configure the Switch. You could simply
restore your last configuration.
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
31
Page 32

Chapter 1 Getting to Know Your Switch
32
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
Page 33

CHAPTER 2
Hardware Installation and
Connection
This chapter shows you how to install and connect the Switch.
2.1 Freestanding Installation
1 Make sure the Switch is clean and dry.
2 Set the Switch on a smooth, level surface strong enough to support the weight of
the Switch and the connected cables. Make sure there is a power outlet nearby.
3 Make sure there is enough clearance around the Switch to allow air circulation and
the attachment of cables and the power cord.
4 Remove the adhesive backing from the rubber feet.
5 Attach the rubber feet to each corner on the bottom of the Switch. These rubber
feet help protect the Switch from shock or vibration and ensure space between
devices when stacking.
Figure 5 Attaching Rubber Feet
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
33
Page 34

Chapter 2 Hardware Installation and Connection
Note: Do NOT block the ventilation holes. Leave space between devices when
stacking.
Note: For proper ventilation, allow at least 4 inches (10 cm) of clearance at the front
and 3.4 inches (8 cm) at the back of the Switch. This is especially important for
enclosed rack installations.
2.2 Mounting the Switch on a Rack
This section lists the rack mounting requirements and precautions and describes
the installation steps.
2.2.1 Rack-mounted Installation Requirements
• Two mounting brackets.
• Eight M3 flat head screws and a #2 Philips screwdriver.
• Four M5 flat head screws and a #2 Philips screwdriver.
Failure to use the proper screws may damage the unit.
2.2.1.1 Precautions
• Make sure the rack will safely sup port the combined weight of all the equipment
it contains.
• Make sure the position of the Switch does not make the rack unstable or topheavy. Tak e all necessary precautions to anchor the rack securely before
installing the unit.
2.2.2 Attaching the Mounting Brackets to the Switch
1 Position a mounting bracket on one side of the Switch, lining up the four screw
holes on the bracket with the screw holes on the side of the Switch.
Figure 6 Attaching the Mounting Brackets
34
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
Page 35

Chapter 2 Hardware Installation and Conn ec t ion
2 Using a #2 Philips screwdriver, install the M3 flat head screws through the
mounting bracket holes into the Switch.
3 Repeat steps 1 and 2 to install the second mounting bracket on the other side of
the Switch.
4 You may now mount the Switch on a rack. Proceed to the next section.
2.2.3 Mounting the Switch on a Rack
1 Position a mounting br acket (that is already attached to the Switch) on one s ide of
the rack, lining up the two screw holes on the br ack et with the screw holes on the
side of the rack.
Figure 7 Mounting the Switch on a Rack
2 Using a #2 Philips screwdriver, install the M5 flat head screws through the
mounting bracket holes into the rack.
3 Repeat steps 1 and 2 to attach the second mounting bracket on the other side of
the rack.
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
35
Page 36

Chapter 2 Hardware Installation and Connection
36
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
Page 37

CHAPTER 3
Hardware Overview
This chapter describes the front panel and rear panel of the Switch and shows y ou
how to make the hardware connections.
3.1 Front Panel Connections
The figure below shows the front panel of the Switch.
Figure 8 Front Panel: XGS-4526
100/1000 Mbps RJ-45
Ethernet Ports
Figure 9 Front Panel: XGS-4528F
Figure 10 Front Panel: XGS-4728F
RJ-45 Gigabit / MiniGBIC Dual Personality
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
37
Page 38

Chapter 3 Hardware Overview
The following table describes the ports.
Table 1 Panel Connections
CONNECTO
R
20 100/1000
Mbps RJ-45
Ethernet
Ports (XGS4526 only)
4 or 24 Dual
Personality
Interfaces
DESCRIPTION
Connect these ports to a computer, a hub, an Ethernet switch or router.
Each interface has one 1000Base-T copper RJ-45 port and one mini-GBIC
(Gigabit Interface Converter) fiber port, with one port active at a time.
• 4 or 24 1000Base-T Ports:
Connect these ports to high-bandwidth backbone network Ethernet
switches using Category 5/5e/6 1000Base-T Ethernet cables.
Use an 8-wire Ethernet cable for Gigabit connections. Using a 4-wire
Ethernet cable limits your connection to 100 Mbps. Note that the
connection speed also depends on what the Ethernet device at the
other end can support.
•4 or 24 Mini-GBIC Ports:
Use Small Form-Factor Pluggable (SFP) transceivers in these ports for
1000Base-X fiber-optic connections to backbone Ethernet switches.
3.1.1 Dual Personality Interfaces
There are 4 or 24 Dual Personality interfaces, comprising 4 or 24 1000Base-T/
mini-GBIC combo ports. For each interface you can connect either to the
1000Base-T port or the mini-GBIC port. The mini-GBIC ports have priority over
the 1000Base-T ports. This means that if a mini-GBIC port and the corresponding
1000Base-T port are connected at the same time, the 1000Base-T port will be
disabled.
3.1.2 1000Base-T Ports
The Switch has 24 1000Base-T auto-negotiating, auto-crossover Ethernet ports.
In 100/1000 Mbps Gigabit Ethernet, the speed can be 100 Mbps or 1000 Mbps.
The duplex mode can be both half or full duplex at 100 Mbps and full duplex only
at 1000 Mbps.
An auto-negotiating port can detect and adjust to the optimum Ethernet speed
(100/1000 Mbps) and duplex mode (full duplex or half duplex) of the connected
device.
An auto-crossover (auto-MDI/MDI-X) port automatically works with a straightthrough or crossover Ethernet cable.
38
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
Page 39

3.1.2.1 Default Ethernet Settings
The factory default negotiation settings for the Ethernet ports on the Switch are:
• Speed: Auto
•Duplex: Auto
• Flow control: Off
3.1.3 Mini-GBIC Slots
These are 4 or 24 slots for Small Form-Factor Pluggable (SFP) transceivers. A
transceiver is a single unit that houses a transmitter and a receiver. Use a
transceiver to connect a fiber-optic cable to the Switch. The Switch does not come
with transceivers. You must use transceivers that comply with the Small FormFactor Pluggable (SFP) Transceiver MultiSource Agreement (MSA). See the SFF
committee’s INF-8074i specification Rev 1.0 for details.
You can change transceivers while the Switch is operating. You can use different
transceivers to connect to Ethernet switches with different types of fiber-optic
connectors.
Chapter 3 Hardware Overview
• Type: SFP connection interface
• Connection speed: 1 Gigabit per second (Gbps)
To avoid possible eye injury, do not look into an operating fiberoptic module’s connectors.
3.1.3.1 Transceiver Installation
Use the following steps to install a mini GBIC transceiver (SFP or XFP module).
1 Insert the transceiver into the slot with the exposed section of PCB board facing
down.
Figure 11 Transceiver Installation Example
2 Press the transceiver firmly until it clicks into place.
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
39
Page 40

Chapter 3 Hardware Overview
3 The Switch automatically detects the installed transceiver. Check the LEDs to
verify that it is functioning properly.
Figure 12 Installed Transceiver
3.1.3.2 Transceiver Removal
Use the following steps to remove a mini GBIC transceiver (SFP module).
1 Open the transceiver’s latch (latch styles vary).
Figure 13 Opening the Transceiver’s Latch Example
2 Pull the transceiver out of the slot.
Figure 14 Transceiver Removal Example
40
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
Page 41

3.2 Rear Panel
3.2.1 XGS-4526
The following figure shows the rear panel of the Switch.
Figure 15 Rear Panel
Chapter 3 Hardware Overview
A
The rear panel contains:
• A connector for the backup power supply (A)
• An optional slot (B) for installing an EM-422 or EM-412 uplink module
• An RJ-45 out-of-band management port (C)
• An RS-232 management console port (D)
• A connector for the power receptacle (E)
B
3.2.2 XGS-4528F or XGS-4728F
The following figures show the rear panels of the AC and DC power input model
switches. The rear panels contain:
• A connector for the backup power supply (A)
• An optional slot (B) for installing an EM-422 or EM-412 uplink module
• Two stacking ports (C)
• An RJ-45 out-of-band management port (D)
C
D
E
• An RS-232 management console port (E)
• A connector for the power receptacle (F)
•A power switch (G) (DC power input model only).
Figure 16 Rear Panel - AC Model
BDEFA
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
C
41
Page 42

Chapter 3 Hardware Overview
Figure 17 Rear Panel - DC Model
3.2.3 Uplink Module
The following figure shows the front panel of the EM-422 and EM-412 modules.
Figure 18 The Front Panel of the EM-422 and EM-412 Modules
EM-422
3.2.4 Rear Panel Connections
The following table describes the ports on the rear panel.
Table 2 Panel Connections
CONNECTO
R
Optional two
XFP or CX4
Ports
DESCRIPTION
These ports are available when you install an EM-422 or ES-412 in the
optional uplink module (B in the figure above). Both the EM-422 and ES412 are used to connect your switch to other high-speed Ethernet
switches for stacking in you network.
EM-412
G
F
42
• For EM-422 connection: Use 10 Gigabit Small Form Factor Pluggable
(XFP) transceivers to connect 1000Base-X fiber-optic cables to these
ports. See Section 3.1.3.1 on page 39 and Section 3.1.3.2 on page 40
for information on installing and removing transceivers.
• For EM-412 connection: Use 10GBase-CX4 cables to connect to these
ports.
See the EM-422 and EM-412 User’s Guides for more information.
Two stacking
ports
(XGS-4528F
or XGS4728F)
Management
Port
Console Port Only connect this port to your computer (using an RS-232 cable) if you
Connect these ports to other XGS-4528F or XGS-4728F switches for
stacking using stacking cables.
Connect to a computer using an RJ-45 Ethernet cable for local
configuration of the Switch.
want to configure the Switch using the command line interface (CLI) via
the console port.
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
Page 43

3.2.5 Power Connector
Make sure you are using the correct power source as shown on the panel and that
no objects obstruct the airflow of the fans.
Use the following procedures to connect the Switch to a power source after you
have installed it.
Note: Check the power supply requirements in Chapter 56 on page 463, and make
sure you are using an appropriate power source.
Keep the power supply switch and the Switch’s power switch in
the OFF position until you come to the procedure for turning on
the power.
Use only power wires of the required diameter for connecting the Switch to a
power supply.
3.2.5.1 AC Power Connection
Chapter 3 Hardware Overview
Note: This is only for the AC model of the Switch.
Connect the female end of the power cord to the power socket of your Switch.
Connect the other end of the cord to a power outlet.
3.2.5.2 DC Power Connection
Note: This is only for the DC model of the Switch.
The Switch uses a single ETB series terminal block plug with four pins which al lows
you to connect up to two separate power supplies. If one power supply fails the
system can operate on the remaining power supply. Use two wires to connect to a
single terminal pair, one wire for the positive terminal and one wire for the
negative terminal.
Note: The current rating of the power wires must be greater than 20 Amp s. The power
supply to which the Switch connects must have a built-in circuit breaker or
switch to toggle the power.
Note: When installing the power wire, push it wire firmly into the terminal as deep as
possible and make sure that no exposed (bare) wire can be seen or touched.
Exposed power wire is dangerous. Use extreme care when
connecting a DC power source to the device.
To connect a power supply:
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
43
Page 44

Chapter 3 Hardware Overview
1 Use a screwdriver to loosen the terminal block captive screws.
2 Connect one end of a power wire to the Switch’s RTN (return) pin and tighten the
captive screw.
3 Connect the other end of the power wire to the positive terminal on the power
supply.
4 Connect one end of a power wire to the Switch’s -48V (input ) pin and tighten the
captive screw.
5 Connect the other end of the power wire to the negative terminal on the power
supply.
6 Insert the terminal block plug in the Switch’s terminal block header.
3.2.6 External Backup Power Supply Connector
The Switch supports external backup power supply (BPS).
The Switch constantly monitors the sta tus of the internal power supply. The
backup power supply automatically provides power to the S witch in the event of a
power failure. Once the Switch receives power from the backup power supply, it
will not automatically switch back to using the internal power supply even when
the power is resumed.
3.2.7 Console Port
For local management, you can use a computer with terminal emulation software
configured to the following parameters:
• VT100 terminal emulation
• 9600 bps
• No parity, 8 data bits, 1 stop bit
• No flow control
Connect the male 9-pin end of the RS-232 console cable to the console port of the
Switch. Connect the female end to a serial port (COM1, COM2 or other COM port)
of your computer.
44
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
Page 45

3.3 LEDs
The following table describes the LEDs.
Table 3 LEDs
LED
BPS Green Blinking The system is receiving power from the backup power
PWR Green On The system is turned on.
SYS Green Blinking The system is rebooting and performing self-diagnostic
ALM Red On There is a hardware failure.
S1
(XGS-
4528F or
XGS4728F)
S2
(XGS-
4528F or
XGS4728F)
System Status Displays
1000Base-T Gigabit Ports ( )
1-24 Green Blinking The system is transmitting/receiving to/from a 10/1000
1000Base-X Mini-GBIC Slots ( )
Chapter 3 Hardware Overview
COLO
R
Green On The Switch is connected to other switches in the stack on
Green On The Switch is connected to other switches in the stack on
Amber Blinking The system is transmitting/receiving to/from a 100 Mbps
STATUS DESCRIPTION
supply.
On The backup power supply is connected and active.
Off The backup power supply is not ready or not active.
Off The system is off.
tests.
On The system is on and functioning properly.
Off The power is off or the system is not ready/
malfunctioning.
Off The system is functioning normally.
Stacking Port 1.
Off The Switch is not connected to other switches in the
stack on Stacking Port 1.
Stacking Port 2.
Off The Switch is not connected to other switches in the
stack on Stacking Port 2.
The Switch is starting up.
hourglas
s icon
Displays
Stack ID
number
On The link to a 10/1000 Mbps Ethernet network is up.
On The link to a 100 Mbps Ethernet network is up.
Off The link to an Ethernet network is down.
The LED is showing the Stack ID number of the Switch.
Mbps Ethernet network.
Ethernet network.
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
45
Page 46

Chapter 3 Hardware Overview
Table 3 LEDs (continued)
LED
1-24 or
21-24
COLO
R
Green On The port has a successful connection.
STATUS DESCRIPTION
Blinking The port is receiving or transmitting data.
Off This link is disconnected.
46
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
Page 47

CHAPTER 4
The Web Configurator
This section introduces the configuration and functions of the web configurator.
4.1 Introduction
The web configurator is an HTML-based managem ent interface that allows easy
Switch setup and management via Inter n et br ows e r. Use Internet Explorer 6.0
and later or Firefox 2.0 and later versions. The recommended screen resolution i s
1024 by 768 pixels.
In order to use the web configurator you need to allow:
• Web brows er pop-up windows from your device. W eb pop-up blocking i s enabled
by default in Windows XP SP (Service Pack) 2.
• JavaScript (enabled by default).
• Java permissions (enabled by default).
4.2 System Login
1 Start your web browser.
2 Type “http://” and the IP address of the Switch (for example, the default
management IP address is 192.168.1.1 through an in-band (non-MGMT) port and
192.168.0.1 through the MGMT port) in the Location or Address field. Press
[ENTER].
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
47
Page 48

Chapter 4 The Web Configurator
3 The login screen appears. The default username is admin and associated default
password is 1234. The date and time display as shown if you hav e not configured
a time server nor manually entered a time and date in the General Setup screen.
Figure 19 Web Configurator: Login
4 Click OK to view the first web configurator screen.
4.3 The Web Configurator Layout
The Status screen is the first screen that displays when you access the web
configurator. This guide uses the XGS-4728F screens as an example. The screens
may vary slightly for different models.
48
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
Page 49

Chapter 4 The Web Configurator
The following figure shows the navigating components of a web configurator
screen.
Figure 20 The Web Configurator Layout
BDC
E
A
A - Click the menu items to open submenu links, and then click on a submenu link
to open the screen in the main window.
B, C, D, E - These are quick links which allow you to perform certain tasks no
matter which screen you are currently working in.
B - Click this link to save your configuration into the Switch’s nonvolatile memory.
Nonvolatile memory is saved in the configuration file from which the Switch
booted from and it stays the same even if the Switch’s power is turned off. See
Section 45.3 on page 390 for information on saving your settings to a specific
configuration file.
C - Click this link to go to the status page of the Switch.
D - Click this link to log out of the web config urator.
E - Click this link to display web help pages. The help pages provide descriptions
for all of the configuration screens.
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
49
Page 50

Chapter 4 The Web Configurator
In the navigation panel, click a main link to reveal a list of submenu links.
Table 4 Navigation Panel Sub-links Overview
BASIC SETTING
ADVANCED
APPLICATION
IP APPLICATION MANAGEMENT
50
The following table describes the links in the navigation panel.
Table 5 Navigation Panel Links
LINK DESCRIPTION
Basic Settings
System Info This link takes you to a screen that displays general system and
hardware monitoring information.
General Setup This link takes you to a screen where you can configure general
identification information and time settings for the Switch.
Switch Setup This link takes you to a screen where you can set up global Switch
parameters such as VLAN type, MAC address learning, GARP and priority
queues.
IP Setup This link takes you to a screen where you can configure the IP address,
subnet mask (necessary for Switch management) and DNS (domain
name server) and set up to 64 IP routing domains.
Port Setup This link takes you to screens where you can configure speed, flow
control and priority settings for individual Switch ports.
Advanced Application
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
Page 51

Chapter 4 The Web Configurator
Table 5 Navigation Panel Links (continued)
LINK DESCRIPTION
VLAN This link takes you to screens where you can configure port-based or
802.1Q VLAN (depending on what you configured in the Switch Setup
menu). You can also configure a protocol based VLAN or a subnet based
VLAN in these screens.
Static MAC
Forwarding
Static
Multicast
Forwarding
Filtering This link takes you to a screen to set up filtering rules.
Spanning Tree
Protocol
Bandwidth
Control
Broadcast
Storm Control
Mirroring This link takes you to screens where you can copy traffic from one port
Link
Aggregation
Port
Authentication
Port Security This link takes you to a screen where you can activate MAC address
Classifier This link takes you to a screen where you can configure the Switch to
Policy Rule This link takes you to a screen where you can configure the Switch to
Queuing
Method
VLAN Stacking This link takes you to screens where you can activate and configure
Multicast This link takes you to screen where you can configure various multicast
AAA This link takes you to a screen where you can configure authentication,
IP Source
Guard
Loop Guard This link takes you to a screen where you can configure protection
This link takes you to screens where you can configure static MAC
addresses for a port. These static MAC addresses do not age out.
This link takes you to a screen where you can configure static multicast
MAC addresses for port(s). These static multicast MAC addresses do not
age out.
This link takes you to screens where you can configure the RSTP/MRSTP/
MSTP to prevent network loops.
This link takes you to screens where you can cap the maximum
bandwidth allowed on a port.
This link takes you to a screen to set up broadcast filters.
or ports to another port in order that you can examine the traffic from
the first port without interference.
This link takes you to screen where you can logically aggregate physical
links to form one logical, higher-bandwidth link.
This link takes you to a screen where you can configure IEEE 802.1x port
authentication as well as MAC authentication for clients communicating
via the Switch.
learning and set the maximum number of MAC addresses to learn on a
port.
group packets based on the specified criteria.
perform special treatment on the grouped packets.
This link takes you to a screen where you can configure queuing with
associated queue weights for each port.
VLAN stacking.
features, IGMP snooping and create multicast VLANs.
authorization and accounting services via external servers. The external
servers can be either RADIUS (Remote Au thentication Dial-In User
Service) or TACACS+ (Terminal Access Controller Access-Control System
Plus).
This link takes you to screens where you can configure filtering of
unauthorized DHCP and ARP packets in your network.
against network loops that occur on the edge of your network.
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
51
Page 52

Chapter 4 The Web Configurator
Table 5 Navigation Panel Links (continued)
LINK DESCRIPTION
VLAN Mapping This link takes you to screens where you can configure VLAN mapping
settings on the Switch.
Layer 2
Protocol
Tunneling
sFlow This link takes you to screens where you can configure sFlow settings on
PPPoE This link takes you to screens where you can configure how the Switch
Errdisable This link takes you to a screen where you can configure CPU protection
Private VLAN This link takes you to a screen where you can block traffic between ports
IP Application
Static Route This link takes you to a screen where you can configure static routes. A
Policy Routing This link takes you to screens where you can configure policy routing
RIP This link takes you to a screen where you can configure the RIP (Routing
OSPF This link takes you to screens where you can view the OSPF status and
IGMP This link takes you to a screen where you can configure the IGMP
DVMRP This link takes you to a screen where you can configure the DVMRP
DiffServ This link takes you to screens where you can enable DiffServ, configure
DHCP This link takes you to screens where you can configure the DHCP
VRRP This link takes you to screens where you can configure redundant virtual
ARP Learning This link takes you to a screen where you can configure ARP learning
Load Sharing This link takes you to a screen where you can enable Equal-Cost
Management
Maintenance This link takes you to screens where you can perform firmware and
Access Control This link takes you to screens where you can change the system login
Diagnostic This link takes you to screens where you can view system logs and can
This link takes you to a screen where you can configure L2PT (Layer 2
Protocol Tunneling) settings on the Switch.
the Switch.
gives a PPPoE termination server additional subscriber information that
the server can use to identify and authenticate a PPPoE client.
and error disable recovery.
in a VLAN on the Switch.
static route defines how the Switch should forward traffic by configuring
the TCP/IP parameters manually.
rules.
Information Protocol) direction and versions.
configure OSPF settings.
settings.
(Distance Vector Multicast Routing Protocol) settings.
marking rules and set DSCP-to-IEEE802.1p mappings.
settings.
router for your network.
mode on a per-port basis.
MultiPath (ECMP) routing and set the criteria the Switch uses to
determine the routing path for a packet.
configuration file maintenance as well as reboot the system.
password and configure SNMP and remote management.
test port(s).
52
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
Page 53

Chapter 4 The Web Configurator
Table 5 Navigation Panel Links (continued)
LINK DESCRIPTION
Syslog This link takes you to screens where you can setup system logs and a
system log server.
Cluster
Management
MAC T able This link takes you to a screen where you can view the MAC address and
IP Table This link takes you to a screen where you can view the IP addresses and
ARP T able This link takes you to a screen where you can view the MAC address – IP
Routing Table This link takes you to a screen where you can view the routing table.
Configure
Clone
This link takes you to a screen where you can configure clustering
management and view its status.
VLAN ID of a device attach to a port. You can also view what kind of MAC
address it is.
VLAN ID of a device attached to a port.You can also view what kind of
device it is.
address resolution table.
This link takes you to a screen where you can copy attributes of one port
to (an)other port(s).
4.3.1 Change Your Password
After you log in for the first time, it is recommended you change the default
administrator password. Click Management > Access Control > Logins to
display the next screen.
Figure 21 Change Administrator Login Password
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
53
Page 54

Chapter 4 The Web Configurator
4.4 Saving Your Configuration
When you are done modifying the settings in a screen, click Apply to save your
changes back to the run-time memory. Settings in the run-time memory are lost
when the Switch’s power is turned off.
Click the Save link in the upper right hand corner of the web configur ator to save
your configuration to nonvolatile memory. Nonvolatile memory refers to the
Switch’s storage that remains even if the Switch’s power is turned off.
Note: Use the Save link when you are done with a configuration session.
4.5 Switch Lockout
You could block yourself (and all others) from using in-band-management
(managing through the data ports) if you do one of the following:
1 Delete the management VLAN (default is VLAN 1).
2 Delete all port-based VLANs with the CPU port as a member. The “CPU port” is the
management port of the Switch.
3 Filter all traffic to the CPU port.
4 Disable all ports.
5 Misconfigure the text configuration file.
6 Forget the password and/or IP address.
7 Prevent all services from accessing the Switch.
8 Change a service port number but forget it.
Note: Be careful not to lock yourself and others out of the Switch. If you do lock
yourself out, try using out-of-band management (via the management port) to
configure the Switch.
4.6 Resetting the Switch
If you lock yourself (and others) from the Switch or forget the administrator
password, you will need to reload the factory-default configur ation file or reset the
Switch back to the factory defaults.
54
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
Page 55

4.6.1 Reload the Configuration File
Uploading the factory-default configuration file replaces the current configuration
file with the factory-default configuration file. This means that you will lose all
previous configurations and the speed of the console port will be reset to the
default of 9600bps with 8 data bit, no parity, one stop bit and flow control set to
none. The password will also be reset to “1234” and the IP address to
192.168.1.1.
To upload the configuration file, do the following:
1 Connect to the console port using a computer with terminal emulation software.
See Section 3.2 on page 41 for details.
2 Disconnect and reconnect the Switch’s power to begin a session. When you
reconnect the Switch’s power, you will see the initial screen.
3 When you see the message “Press any key to enter Debug Mode within 3
seconds ...” press any key to enter debug mode.
Chapter 4 The Web Configurator
4 Type atlc after the “Enter Debug Mode” message.
5 Wait for the “Starting XMODEM upload” message before activating XMODEM
upload on your terminal.
6 After a configuration file upload, type atgo to restart the Switch.
Figure 22 Resetting the Switch: Via the Console Port
Bootbase Version: V1.00 | 10/22/2007 12:48:50
RAM:Size = 128 Mbytes
DRAM POST: Testing:131072K OK
DRAM Test SUCCESS !
FLASH: Intel 64M
ZyNOS Version: V4.00(BBC.0)b1 | 10/14/2010 17:32:18
Press any key to enter debug mode within 3 seconds.
.....................................
Enter Debug Mode
ras> atlc
Starting XMODEM upload (CRC mode)....
CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC
Total 393216 bytes received.
Erasing..
................................................................
OK
ras> atgo
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
55
Page 56

Chapter 4 The Web Configurator
The Switch is now reinitialized with a default configuration file including the default
password of “1234”.
4.7 Logging Out of the Web Configurator
Click Logout in a screen to exit the web configurator. Y ou hav e to log in with your
password again after you log out. This is recommended after you finish a
management session for security reasons.
Figure 23 Web Configurator: Logout Screen
4.8 Help
The web configurator’s online help has descriptions of individual screens and some
supplementary information.
Click the Help link from a web configurator screen to view an online help
description of that screen.
56
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
Page 57

CHAPTER 5
Initial Setup Example
This chapter shows how to set up the Switch for an example network.
5.1 Overview
The following lists the configuration steps for the example network:
• Configure an IP interface
• Configure DHCP server settings
• Create a VLAN
• Set port VLAN ID
•Enable RIP
5.1.1 Configuring an IP Interface
On a layer-3 switch, an IP interface (also known as an IP routing domain) is not
bound to a physical port. The default IP address of the S witch is 192.168. 1.1 wi th
a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0.
In the example network, since the RD network is already in the same IP interface
as the Switch, you don’t need to create an IP interface for it. However , if you want
to have the Sales network on a different routing domain, you need to create a
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
57
Page 58

Chapter 5 Initial Setup Example
new IP interface. This allows the Switch to route traffic between the RD and Sales
networks.
Figure 24 Initial Setup Network Example: IP Interface
1 Connect your computer to the MGMT port that is used only for management.
Make sure your computer is in the same subnet as the MGMT port.
2 Open your web browser and enter 192.168.0.1 (the default MGMT port IP
address) in the address bar to access the web configurator. See Section 4.2 on
page 47 for more information.
3 Click Basic Setting and IP Setup
in the navigation panel.
4 Configure the related fields in the
IP Setup screen.
EXAMPLE
58
For the Sales network, enter 192.168.2.1 as the IP address and 255.255.255.0 as
the subnet mask.
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
Page 59

5 In the VID field, enter the ID of the VLAN group to which you want this IP
interface to belong. This is the same as the VLAN ID you configure in the Static
VLAN screen.
6 Click Add to save the settings to the run-time memory. Settings in the run-time
memory are lost when the Switch’s power is turned off.
5.1.2 Configuring DHCP Server Settings
You can set the Switch to assign network information (such as the IP address,
DNS server, etc.) to DHCP clients on the network.
For the example network, configure two DHCP client pools on the Switch for the
DHCP clients in the RD and Sales networks.
1 In the web configurator, click IP
Application and DHCP in the
navigation panel and click the
VLAN link.
Chapter 5 Initial Setup Example
2 In the VLAN Setting screen,
specify the ID of the VLAN to
which the DHCP clients belong,
the starting IP address pool,
subnet mask, default gateway
address and the DNS server
address(es).
3 Click Add to save the settings to
the run-time memory. Settings in
the run-time memory are lost when the Switch’s power is turned off.
5.1.3 Creating a VLAN
VLANs confine broadcast frames to the VLAN group in which the port(s) belongs.
You can do this with port-based VLAN or tagged static VLAN with fixed port
members.
EXAMPLE
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
59
Page 60

Chapter 5 Initial Setup Example
In this example, you want to configure port 1 as a member of VLAN 2.
Figure 25 Initial Setup Network Example: VLAN
1 Click Advanced Application > VLAN in the navigation panel and click the Static
VLAN link.
60
2 In the Static VLAN screen, select
ACTIVE, enter a descriptive name
in the Name field and enter 2 in
the VLAN Group ID field for the
VLAN2 network.
EXAMPLE
Note: The VLAN Group ID field in this screen and the VID field in the IP Setup
screen refer to the same VLAN ID.
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
Page 61

3 Since the VLAN2 network is connected to port 1 on the Switch, select Fixed to
configure port 1 to be a permanent member of the VLAN only.
4 To ensure that VLAN-unaware devices (such as computers and hubs) can receive
frames properly, clear the TX Tagging check box to set the Switch to remove
VLAN tags before sending.
5 Click Add to save the settings to the run-time memory. Settings in the run-time
memory are lost when the Switch’s power is turned off.
5.1.4 Setting Port VID
Use PVID to add a tag to incoming untagged frames received on that port so that
the frames are forwarded to the VLAN group that the tag defines.
In the example network, configure 2 as the port VID on port 1 so that any
untagged frames received on that port get sent to VLAN 2.
Figure 26 Initial Setup Network Example: Port VID
Chapter 5 Initial Setup Example
1 Click Advanced Applications
and VLAN in the navigation
panel. Then click the VLAN Port
Setting link.
2 Enter 2 in the PVID field for port
1 and click Apply to save your
changes back to the run-time
memory . Settings in the run-time
memory are lost when the
Switch’s power is turned off.
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
EXAMPLE
61
Page 62

Chapter 5 Initial Setup Example
5.1.5 Enabling RIP
To exchange routing information with other routing devices across different
routing domains, enable RIP (Routing Information Protocol) in the RIP screen.
1 Click IP Application and RIP in the navigation panel.
2 Select Both in the Direction
field to set the Switch to
broadcast and receive routing
information.
3 In the Version field, select
RIP-1 for the RIP packet
format that is universa lly
supported.
4 Click Apply to save your changes back to the run-time memory. Settings in the
run-time memory are lost when the Switch’s power is turned off.
EXAMPLE
62
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
Page 63

CHAPTER 6
Tutorials
This chapter provides some examples of using the web configurator to set up and
use the Switch. The tutorials include:
• How to Use DHCP Snooping on the Switch
• How to Use DHCP Relay on the Switch
• How to Use PPPoE IA on the Switch
• How to Use Error Disable and Recovery on the Switch
• How to Set Up a Guest VLAN
• How to Do Port Isolation in a VLAN
• How to Configure Routing Policy
6.1 How to Use DHCP Snooping on the Switch
You only wan t DHCP server A connected to port 5 to assign IP addresses to all
devices in VLAN network (V). Create a VLAN containing ports 5, 6 and 7. Con nect
a computer M to the Switch’s MGMT port.
Figure 27 Tutorial: DHCP Snooping Tutorial Overview
M
V
C
Note: For related information about DHCP snooping, see Section 26.1 on page 259.
B
A
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
63
Page 64

Chapter 6 Tutorials
The settings in this tutorial are as the following.
Table 6 Settings in this Tutorial
HOST
DHCP Server (A) 5 1 and 100 100 Yes
DHCP Client (B) 6 1 and 100 100 No
DHCP Client (C) 7 1 and 100 100 No
1 Access the Switch from the MGMT port through http://192.168.0.1 by default.
Log into the Switch by entering the username (default: admin) and password
(default: 1234).
2 Go to Advanced Application > VLAN > Static VLAN, and create a VLAN with ID
of 100. Add ports 5, 6 and 7 in the VLAN by selecting Fixed in the Control field as
shown.
Deselect Tx Tagging because you don’t want outgoing traffic to contain this VLAN
tag.
PORT
CONNECTED
VLAN PVID
DHCP SNOOPING
PORT TRUSTED
Click Add.
64
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
Page 65

Chapter 6 Tutorials
3 Go to Advanced Application > VLAN > VLAN Port Setting, and set the PVID
of the ports 5, 6 and 7 to 100. This tags untagged incoming frames on ports 5, 6
and 7 with the tag 100.
4 Go to Advanced Application > IP Source Guard > DHCP snooping >
Configure, activate and specify VLAN 100 as the DHCP VLAN as shown. Click
Apply.
5 Click the Port link at the top right corner.
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
65
Page 66

Chapter 6 Tutorials
6 The DHCP Snooping Port Configure screen appears. Select Trusted in the
Server Trusted state field for port 5 because the DHCP server is connected to
port 5. Keep ports 6 and 7 Untrusted because they are connected to DHCP
clients. Click Apply.
7 Go to Advanced Application > IP Source Guard > DHCP snooping >
Configure > VLAN, show VLAN 100 by entering 100 in the Start VID and End
VID fields and click Apply. Then select Yes in the Enabled field of the VLAN 100
entry shown at the bottom section of the screen.
If you want to add more information in the DHCP request packets such as source
VLAN ID or system name, you can also select the Option82 and Information
fields in the entry. See Section 26.1.1.3 on page 261.
8 Click Save at the top right corner of the web
configurator to save the configuration permanently.
66
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
Page 67

Chapter 6 Tutorials
9 Connect your DHCP server to port 5 and a computer (as DHCP client) to either
port 6 or 7. The computer should be able to get an IP address from the DHCP
server. If you put the DHCP server on port 6 or 7, the computer will not able to get
an IP address.
10 To check if DHCP snooping works, go to Advanced Application > IP Source
Guard, you should see an IP assignment with the type dhcp-snooping as shown.
You can also telnet or log into the Switch’s console. Use the command “ show dhcp
snooping binding” to see the DHCP snooping binding table as shown next.
sysname# show dhcp snooping binding
MacAddress IpAddress Lease Type VLAN Port
----------------- --------------- ------------ ------------- ---- ---- 00:02:00:00:00:1c 10.10.1.16 6d23h59m20s dhcp-snooping 100 7
Total number of bindings: 1
6.2 How to Use DHCP Relay on the Switch
This tutorial describes how to configure your Switch to forward DHCP client
requests to a specific DHCP server. The DHCP server can then assign a specific IP
address based on the information in the DHCP requests.
6.2.1 DHCP Relay Tutorial Introduction
In this example, you have configured your DHCP server (192.168.2.3) and want to
have it assign a specific IP address (say 172.16.1.18) and gatew ay i nformation to
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
67
Page 68

Chapter 6 Tutorials
DHCP client A based on the system name, VLAN ID and port number in the DHCP
request. Client A connects to the Switch’s port 2 in VLAN 102.
Figure 28 Tutorial: DHCP Relay Scenario
DHCP Server
192.168.2.3
6.2.2 Creating a VLAN
Port 2
PVID=102
A
172.16.1.18
VLAN 102
Follow the steps below to configure port 2 as a member of VLAN 102.
1 Access the web configurator through the Switch’s management port.
2 Go to Basic Setting > Switch Setup and set the VLAN type to 802.1Q. Click
Apply to save the settings to the run-time memory.
68
3 Click Advanced Application > VLAN > Static VLAN.
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
Page 69

Chapter 6 Tutorials
4 In the Static VLAN screen, select ACTIVE, enter a descriptive name (VALN 102
for example) in the Name field and enter 102 in the VLAN Group ID field.
5 Select Fixed to configure port 2 to be a permanent member of this VLAN.
6 Clear the TX Tagging check box to set the Switch to remove VLAN tags before
sending.
7 Click Add to save the settings to the run-time memory. Settings in the run-time
memory are lost when the Switch’s power is turned off.
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
69
Page 70

Chapter 6 Tutorials
8 Click the VLAN Status link in the Static VLAN screen and then the VLAN Port
Setting link in the VLAN Status screen.
9 Enter 102 in the PVID field for port 2 to add a tag to incoming untagged frames
received on that port so that the frames are forwarded to the VLAN group that the
tag defines.
10 Click Apply to save your changes back to the run-time memory.
11 Click the Save link in the upper right corner of the web configurator to save your
configuration permanently.
70
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
Page 71

6.2.3 Configuring DHCP Relay
Follow the steps below to enable DHCP relay on the Switch and allow the Switch to
add relay agent information (such as the VLAN ID) to DHCP requests.
1 Click IP Application > DHCP and then the Global link to open the DHCP Relay
screen.
2 Select the Active check box.
3 Enter the DHCP server’s IP address (192.168.2.3 in this example) in the Remote
DHCP Server 1 field.
4 Select the Option 82 and the Information check boxes.
5 Click Apply to save your changes back to the run-time memory.
Chapter 6 Tutorials
6 Click the Save link in the upper right corner of the web configurator to save your
configuration permanently.
7 The DHCP server can then assign a specific IP address based on the DHCP
request.
6.2.4 Troubleshooting
Check the client A’s IP address. If it did not receive the IP address 172.16.1.18,
make sure:
1 Client A is connected to the Switch’s port 2 in VLAN 102.
2 You configured the correct VLAN ID, port number and system name for DHCP relay
on both the DHCP server and the Switch.
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
71
Page 72

Chapter 6 Tutorials
3 You clicked the Save link on the Switch to have your settings take effect.
6.3 How to Use PPPoE IA on the Switch
You want to configure PPPoE Intermediate Agent on the Switch (A) to pass a
subscriber’s information to a PPPoE server (S). There is another switch (B)
between switch A and server S. Switch B is connected to switch A. In this way,
PPPoE server S can identify subscriber C and may apply different settings to it.
Figure 29 Tutorial: PPPoE Intermediate Agentt Tutorial Overview
A
B
Port 12 - Trusted
S
Port 11 - Trusted
Port 12 - Trusted
C
Port 5 - Untrusted
Note: For related information about PPPoE IA, see Section 31.3 on page 302.
The settings in this tutorial are as follows:
Table 7 Settings in this Tutorial
SWITCH
A Port 5 (to C)
B Port 11 (to A)
PORT
CONNECTED
Port 12 (to B)11
Port 12 (to S)11
VLAN CIRCUIT-ID REMOTE-ID
userC
N/A
N/A
N/A
00134900000A
N/A
N/A
N/A
PPPOE IA PORT
TRUSTED
Untrusted
Trusted
Trusted
Trusted
72
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
Page 73

6.3.1 Configuring Switch A
1 Click Advanced Application > PPPoE > Intermediate Agent. Select Active
then click Apply.
Chapter 6 Tutorials
Click Port on the top of the screen.
2 Select Untrusted for port 5 and enter userC as Circuit-id and 00134900000A
as Remote-id.
Select Trusted for port 12 and then leave the other fields empty. Click Apply.
Then Click Intermediate Agent on the top of the screen.
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
73
Page 74

Chapter 6 Tutorials
3 The Intermediate Agent screen appears. Click VLAN on the top of the screen.
4 Enter 1 for both Start VID and End VID since both the Switch and PPPoE server
are in VLAN 1 in this example. Click Apply.
74
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
Page 75

5 Then select Yes to enable PPPoE IA in VLAN 1 and also select Circuit-id and
Remote-id to allow the Switch to add these two strings to frames tagged with
VLAN 1 and pass to the PPPoE server. Click Apply.
6.3.2 Configuring Switch B
Chapter 6 Tutorials
The example uses another XGS-4728F as switch B.
1 Click Advanced Application > PPPoE > Intermediate Agent. Select Active
then click Apply.
Click Port on the top of the screen.
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
75
Page 76

Chapter 6 Tutorials
2 Select Trusted for ports 11 and 12 and then click Apply.
Then Click Intermediate Agent on the top of the screen.
3 The Intermediate Agent screen appears. Click VLAN on the top of the screen.
76
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
Page 77

Chapter 6 Tutorials
4 Enter 1 for both Start VID and End VID. Click Apply.
5 Then select Yes to enable PPPoE IA in VLAN 1 and also select Circuit-id and
Remote-id to allow the Switch to add these two strings to frames tagged with
VLAN 1 and pass to the PPPoE server. Click Apply.
The settings are completed now. If you miss some settings above, subscriber C
could not successfully receive an IP address assigned by the PPPoE Server. If this
happens, make sure you follow the steps exactly in this tutorial.
6.4 How to Use Error Disable and Recovery on the Switch
This tutorial shows you how to shut down a port when:
• there is a loop occurred
or
• too many ARP requests (over 100 packets per second) received on a port
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
77
Page 78

Chapter 6 Tutorials
You also want the S witch to wait for a period of time (10 minutes) before resuming
the port automatically, after the problem(s) are gone. Loop guard and Errdiable
features are helpful for this demand.
Note: Refer to Section 27.2 on page 285 and Section 32.3 on page 310 for more
To configure the settings:
1 First, click Advanced Application > Loop Guard. Select the Active option in
the first section to enable loop guard on the Switch. Then select the Active option
of the first entry (port *) to enable loop guard for all ports. Click Apply.
information about Loop Guard and Errdiable.
78
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
Page 79

Chapter 6 Tutorials
2 Click Advanced Application > Errdisable > CPU Protection, sele ct ARP as the
reason, enter 100 as the rate limit (packets per second) for t he first entry (port *)
to apply the setting to all ports. Th en cl ic k Apply.
3 Click Advanced Application > Errdisable > Errdisable Detect, select Active
for cause ARP and inactive-port as the mode. Then click Apply.
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
79
Page 80

Chapter 6 Tutorials
4 Click Advanced Application > Errdisable > Errdisable Recovery, select
Active and Timer Status for loopguard and ARP entries. Also enter 180 (180
seconds = 3 minutes) in the Interval field for both entries. Then click Apply.
6.5 How to Set Up a Guest VLAN
All ports on the Switch are in VLAN 1 by default. Say you enable IEEE 802.1x
authentication on ports 1 to 8. Clients that connect to these ports should provide
the correct user name and password in order to access the ports. You want to
assign clients that connect to ports 1, 2 or 3 to a guest VLAN (200 for example)
before they can authenticate with the authentication server. In this guest VLAN,
clients can surf the Internet through the default gateway attached to port 10, but
are not allowed to access other network resources, such as the mail server or local
data base.
VLAN 1
80
Guest VLAN 200
Ports 1, 2, 3 and 10
Internet
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
Page 81

6.5.1 Creating a Guest VLAN
Follow the steps below to configure port 1, 2, 3 and 10 as a member of V LAN 200.
1 Access the web configurator through the Switch’s management port.
2 Go to Basic Setting > Switch Setup and set the VLAN typ e to 802.1Q. Click
Apply to save the settings to the run-time memory.
Chapter 6 Tutorials
3 Click Advanced Application > VLAN > Static VLAN.
4 In the Static VLAN screen, select ACTIVE, enter a descriptive name (VLAN 200
for example) in the Name field and enter 200 in the VLAN Group ID field.
5 Select Fixed to configure ports 1, 2, 3 and 10 to be permanent members of this
VLAN.
6 Clear the TX Tagging check box to set the Switch to remove VLAN tags before
sending frames out of these ports.
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
81
Page 82

Chapter 6 Tutorials
7 Click Add to save the settings to the run-time memory. Settings in the run-time
memory are lost when the Switch’s power is turned off.
8 Click the VLAN Status link in the Static VLAN screen and then the VLAN Port
Setting link in the VLAN Status screen.
9 Enter 200 in the PVID field for ports 1, 2, 3 and 10 to add a tag to incoming
untagged frames received on these ports so that the frames are forwarded to the
VLAN group that the tag defines.
82
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
Page 83

10 Click Apply to save your changes back to the run-time memory.
Chapter 6 Tutorials
11 Click the Save link in the upper right corner of the web configurator to save your
configuration permanently.
6.5.2 Enabling IEEE 802.1x Port Authentication
Follow the steps below to enable port authentication to validate access to ports
1~8 to clients based on a RADIUS server.
1 Click Advanced Application > Port Authentication and then the Click Here
link for 802.1x.
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
83
Page 84

Chapter 6 Tutorials
2 Select the first Active checkbox to enable 802.1x authentication on the Switch.
Select the Active checkboxes for ports 1 to 8 to turn on 802.1x authentication on
the selected ports.
Click Apply.
6.5.3 Enabling Guest VLAN
1 Click the Guest Vlan link in the 802.1x screen.
84
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
Page 85

Chapter 6 Tutorials
2 Select Active and enter the guest VLAN ID (200 in this example) on ports 1, 2
and 3. The Switch puts unauthenticated clients in the specified guest VLAN.
Set Host-mode to Multi-Secure to have the Switch authenticate each client that
connects to one of these ports, and specify the maximum number of clients that
the Switch will authenticate on each of these port (5 in this example).
Click Apply.
3 Click the Save link in the upper right corner of the web configurator to save your
configuration permanently.
Clients that attach to port 1, 2 or 3 and fail to authenticate with the RADIUS
server now should be in VLAN 200 and can access the Internet, but cannot
communicate with devices in VLAN 1.
6.6 How to Do Port Isolation in a VLAN
You want to prevent communications between specific ports in a VLAN but still
allow them to access the Internet or network resources in the same VLAN. Y ou use
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
85
Page 86

Chapter 6 Tutorials
Private VLAN to do port isolation in a VLAN instead of assigning each port to a
separate VLAN and creating a different IP routing domain for each individual port.
In this example, you put ports 2 to 5 in VLAN 123 and create a private VLAN rule
for VLAN 123 to block traffic between ports 2, 3 and 4.
6.6.1 Creating a VLAN
Internet
Follow the steps below to configure port 2, 3, 4 and 5 as a member of VLAN 123.
1 Access the web configurator through the Switch’s management port.
2 Go to Basic Setting > Switch Setup and set the VLAN typ e to 802.1Q. Click
Apply to save the settings to the run-time memory.
86
3 Click Advanced Application > VLAN > Static VLAN.
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
Page 87

Chapter 6 Tutorials
4 In the Static VLAN screen, select ACTIVE, enter a descriptive name (VLAN 123
for example) in the Name field and enter 123 in the VLAN Group ID field.
5 Select Fixed to configure ports 2, 3, 4 and 5 to be permanent members of this
VLAN.
6 Clear the TX Tagging check box to set the Switch to remove VLAN tags before
sending frames out of these ports.
7 Click Add to save the settings to the run-time memory. Settings in the run-time
memory are lost when the Switch’s power is turned off.
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
87
Page 88

Chapter 6 Tutorials
8 Click the VLAN Status link in the Static VLAN screen and then the VLAN Port
Setting link in the VLAN Status screen.
9 Enter 123 in the PVID field for ports 2, 3, 4 and 5 to add a tag to incoming
untagged frames received on these ports so that the frames are forwarded to the
VLAN group that the tag defines.
10 Click Apply to save your changes back to the run-time memory.
88
11 Click the Save link in the upper right corner of the web configurator to save your
configuration permanently.
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
Page 89

6.6.2 Creating a Private VLAN Rule
Follow the steps below to configure private VLAN for VLAN 123.
1 Click Advanced Application > Private VLAN.
2 In the Private VLAN screen, select Active.
Enter a descriptive name (PrivateVLAN123 for example) in the Name field and
enter 123 in the VLAN ID field.
List the port(s) that can communicate with any port in VLAN 123 (5 in this
example). Then other ports in this VLAN (2, 3 and 4 for example) will be added to
the isolated port list and cannot send traffic to each other.
Click Add.
Chapter 6 Tutorials
3 Click the Save link in the upper right corner of the web configurator to save your
configuration permanently.
From port 2, 3, or 4, you should be able to access the device that attachs to port
5, such as a server or default gateway.
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
89
Page 90

Chapter 6 Tutorials
6.7 How to Configure Routing Policy
The Switch checks the routing table and then forwards traffic through the default
gateway (R1) based on the destination address. This example shows you how to
configure policy route to send traffic that matches a layer-3 classifier to a different
gateway (R2) for special treatment. The layer-3 classifier groups packets mark ed
with DSCP value 58 into a flow. Packets marked with different DSCP values, such
as 13 are forwarded to the default gateway. The Switch applies policy-based
routing rules to incoming packets prior to the normal routing.
DSCP 58
DSCP 13
6.7.1 Create a Layer-3 Classifier
Follow the steps below to configure a classifier that sorts traffic with DSCP value
58 into a data flow.
1 Access the web configurator through the Switch’s management port.
2 Go to Advanced Application > Classifier and select Active.
Enter a descriptive name (“DSCP58” in this example).
Select the second option of DSCP and enter 58 in the field provided.
R1
R2
90
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
Page 91

3 Click Add to save the settings to the run-time memory.
Chapter 6 Tutorials
6.7.2 Create a Policy Routing Rule
Follow the steps below to set up a policy routing profile first and then a rule to
forward traffic of classifier DSCP58 to gateway R2.
1 Click IP Application > Policy Routing.
2 Select Active and enter a descriptive name for t his profile (“To_R2” for example).
Click Add to save the settings to the run-time memory.
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
91
Page 92

Chapter 6 Tutorials
3 Click the Rule Configuration link in the Policy Route screen to create a rule in
this profile.
4 Select the name of the profile with which the rule associates.
Set the rule’s index number to 1 in the Sequence field.
Select Permit to have the Switch send matched traffic to the specified gateway.
Select the name of the layer-3 classifier to which the rule applies.
Enter the IP address of gateway R2 in the Next Hop field (“10.1.2.3” in this
example).
Click Add to save the settings to the run-time memory.
92
5 Click the Save link in the upper right corner of the web configurator to save your
configuration permanently.
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
Page 93

PART II
Technical Reference
93
Page 94

94
Page 95

CHAPTER 7
System Status and Port
Statistics
This chapter describes the system status (web configurator home page) and port
details screens.
7.1 Overview
The home screen of the web configurator displays a port stati stical summary with
links to each port showing statistical details.
7.2 Port Status Summary
To view the port statistics, click Status in all web configurator screens to display
the Status screen as shown next.
Figure 30 Status
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
95
Page 96

Chapter 7 System Status and Port Statistics
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 8 Status
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Port This identifies the Ethernet port. Click a port number to display the Port
Details screen (refer to Figure 31 on page 97).
Name This is the name you assigned to this port in the Basic Setting > Port
Setup screen.
Link This field displays the speed (either 10M for 10 Mbps, 100M for 100
Mbps, 1000M for 1000 Mbps, and 10G for 10 Gbps) and the duplex (F
for full duplex or H for half). It also shows the cable type (Copper or
Fiber) for the combo ports. This field displays Down if the port is not
connected to any device.
State If STP (Spanning Tree Protocol) is enabled, this field displays the STP
state of the port. (See Section 13.1.3 on page 149 for more information).
If STP is disabled, this field displays FORWARDING if the link is up,
otherwise, it displays STOP.
LACP This fields displays whether LACP (Link Aggregation Control Protocol) has
been enabled on the port.
TxPkts This field shows the number of transmitted frames on this port.
RxPkts This field shows the number of received frames on this port.
Errors This field shows the number of received errors on this port.
Tx KB/s This field shows the transmission speed of data sent on this port in
kilobytes per second.
Rx KB/s This field shows the transmission speed of data received on this port in
kilobytes per second.
Up Time This field shows the total amount of time in hours, minutes and seconds
the port has been up.
Clear Counter Type a port number, select Port and then click Clear Counter to erase
the recorded statistical information for that port, or select Any to clear
statistics for all ports.
96
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
Page 97

7.2.1 Status: Port Details
Click a number in the Port column in the Status screen to display individual port
statistics. Use this screen to check status and detailed perf ormance data about an
individual port on the Switch.
Figure 31 Status: Port Details
Chapter 7 System Status and Port Statistics
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 9 Status > Port Details
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Port Info
Port NO. This field displays the port number you are viewing.
Name This field displays the name of the port.
Link This field displays the speed (either 10M for 10Mbps, 100M for
100Mbpsl, 1000M for 1000 Mbps, and 10G for 10 Gbps) and the duplex
(F for full duplex or H for half duplex). It also shows the cable type
(Copper or Fiber).
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
97
Page 98

Chapter 7 System Status and Port Statistics
Table 9 Status > Port Details (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Status If STP (Spanning Tree Protocol) is enabled, this field displays the STP
state of the port (see Section 13.1.3 on page 149 for more information).
If STP is disabled, this field displays FORWARDING if the link is up,
otherwise, it displays STOP.
LACP This field shows if LACP is enabled on this port or not.
TxPkts This field shows the number of transmitted frames on this port
RxPkts This field shows the number of received frames on this port
Errors This field shows the number of received errors on this port.
Tx KB/s This field shows the transmission speed of data sent on this port in
kilobytes per second.
Rx KB/s This field shows the transmission speed of data received on this port in
kilobytes per second.
Up Time This field shows the total amount of time the connection has been up.
Tx Packet
The following fields display detailed information about packets transmitted.
Unicast This field shows the number of good unicast packets transmitted.
Multicast This fie ld shows the number of good multicast packets transmitted.
Broadcast This field shows the number of good broadcast packets transmitted.
Pause This field shows the number of 802.3x Pause packets transmitted.
Tagged This field shows the number of packets with VLAN tags transmitted.
Rx Packet
The following fields display detailed information about packets received.
Unicast This field shows the number of good unicast packets received.
Multicast This fie ld shows the number of good multicast packets received.
Broadcast This field shows the number of good broadcast packets received.
Pause This field shows the number of 802.3x Pause packets received.
Control This field shows the number of control packets received (including those
with CRC error) but it does not include the 802.3x Pause packets.
TX Collision
The following fields display information on collisions while transmitting.
Single This is a count of successfully transmitted packets for which transmission
is inhibited by exactly one collision.
Multiple This is a count of successfully transmitted packets for which transmission
was inhibited by more than one collision.
Excessive This is a count of packets for which transmission failed due to excessive
collisions. Excessive collision is defined as the number of maximum
collisions before the retransmission count is reset.
Late This is the number of times a late collision is detected, that is, after 512
bits of the packets have already been transmitted.
Error Packet The following fields display detailed information about packets received
that were in error.
98
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
Page 99

Chapter 7 System Status and Port Statistics
Table 9 Status > Port Details (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
RX CRC This field shows the number of packets received with CRC (Cyclic
Redundant Check) error(s).
Length This field shows the number of packets received with a length that was
out of range.
Runt This field shows the number of packets received that were too short
(shorter than 64 octets), including the ones with CRC errors.
Distribution
64 This field shows the number of packets (including bad packets) received
that were 64 octets in length.
65-127 This field shows the number of packets (including bad packets) received
that were between 65 and 127 octets in length.
128-255 This field shows the number of packets (including bad packets) received
that were between 128 and 255 octets in length.
256-511 This field shows the number of packets (including bad packets) received
that were between 256 and 511 octets in length.
512-1023 This field shows the number of packets (including bad packets) received
that were between 512 and 1023 octets in length.
1024-
1518
Giant This field shows the number of packets (including bad packets) received
This field shows the number of packets (including bad packets) received
that were between 1024 and 1518 octets in length.
that were between 1519 octets and the maximum frame size.
The maximum frame size varies depending on your switch model. See
Chapter 56 on page 463.
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
99
Page 100

Chapter 7 System Status and Port Statistics
100
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
 Loading...
Loading...