
Wireless 125Mbps AP Router
User’s Manual
Contents
1.Introduction....................................................................................2
2.SafetyNotification...........................................................................3
3.Hardware Installation.....................................................................4
4.Web Management Settings............................................................6
4.1.PrimarySetup……………………………………..…………………7
( how to set up 125Mbps mode )………………………………12
4.2.Security…………………………………………………………….13
4.3.System……………………………………………………………..19
4.4.DHCPServer…….…………………………………………………23
4.5.SNMPInfo………………………………………………………….25
4.6.Status………………………………………………………………27
4.7.AdvancedWireless………. .. …………………………………….29
4.8.AccessFilters………………………………………………………33
4.9.VirtualServer…………..…………………………………………..36
4.10.RoutingTable……………………………………………………..39
4.11.DynamicDNS……………….……………………………………42
5. Troubleshooting.....................................................................….44
1

1. Introduction
Thank you for purchasing this Wireless 125Mbps AP Router.
This user guide will assist you with the installation proc edure.
The package you have received should contain the following items:
---AP Router Wireless 125Mbps AP Router
---Installation CD(with manual inside)
---Quick Installation Guide
---Power Supply / Cord
---Ethernet Cabl e
Note: if anything is missing, please contact your vendor
2

2. Safety Notification
Your Wireless AP Router should be placed in a safe and secure location. To
ensure proper operation, please keep the unit away from water and other
damaging elements. Please read the user manual thoroughly before you install
the device. The device should only be repaired by authorized and qualified
personnel.
---Please do not try to open or repair the device yourself.
---Do not place the device in a damp or humid location, i.e . a bathroom.
---The device should be placed in a sheltered and non-slip location within a
temperature range of +5 to +40 Celsius degree.
---Please do not expose the device to direct sunlight or other he at sources. The
housing and electronic components may be damaged by direct sunlight or heat
sources.
3
3. Hardware Installation
Front Panel
The front panel provides LED’s for device status. Refer to the following table for
the meaning of each feature.
LED STATUS Description
PWR/STAT
Off No power
Red On
1. Power on 2. Reset to default 3.
Firmware upgrade (first 1 minute)
Red On
Red Blink
1. System up 2. Power on 3.
Firmware upgrade
Red Blink
LAN
Off no Ethernet link detected
Green ON
10/100Mbps Fast Ethernet link
detected. No activity.
Green On
Green Blink
WAN Orange Blink
G Yellow Blink
Indicates data traffic on the 10/100
Mbps LAN
Indicates data traffic on the 10/100
Mbps LAN
Indicates the device is linking or
active data through wireless links
4
Rear Panel
The rear panel features 4 LAN ports, 1 WAN port and Reset button. Refer to the
following table for the meaning of each feature.
Used to connect to the power outlet. Only
use the power adapter provided with the
Power (DC 5v)
device. Use of an unauthorized power
adapter may cause damage to your device
and violate your warranty.
Press the Reset Button for approximately
Reset
ten seconds, all configurations will set to
factory default settings.
LAN
The RJ-45 Ethernet ports used to connect
your PC, hub, switch or Ethernet network.
The RJ-45 Ethernet port labeled WAN is
WAN
used to connect your AP Router to your
xDSL or Cable modem.
AP Router Default Settings
The default settings are shown following.
User
Password admin
AP Router IP Address 192.168.1.1
AP Router Subnet Mask 255.255.255.0
RF ESSID wlan-g
11g RF Channel 6
Disabled
Mode
11b+g
11g only
AfterBurner
Encryption Disabled
DHCP client Enabled
5
4 Web Management Settings
START UP & LOGIN
In order to configure the Wireless 11g AP Router, you must use your web
browser and manually input http://192.168.1.1 into the Address box and press
Enter. The Main Page will appear.
In order to configure the Wireless 125Mbps AP Router, you must input the
password into the Password box and leave blank on the User Name box. The
default password is “admin”.
Once you have logged-in as administrator, it is a good idea to change the
administrator password to ensure a secure protection to the Wireless 125Mbps
AP Router. The Security Settings section described later in this manual describes
how to change the password.
Once you have input the correct password and logge d-in, the screen will change
to the Setup page screen.
WARNING : TURN ON POWER SUPPLY
Quick power cycle can caused system corruption. When power on, be careful
not to shut down in about 5 seconds, because data is writing to the flash.
6

4.1. Primary Setup
Primary Setup
This screen contains all of the Router's basic setup functions.
.
7

Most users will be able to configure the AP Router and get it working properly
using the settings on this screen. Some Internet Service Providers (ISPs) will
require that you enter AP Router Wireless 802.11g AP Router specific
information, such as User Name, Password, IP Address, Default Gateway
Address, or DNS IP Address. This information can be obtained from your ISP, if
required.
MAKE CORRECT NETWORK SETTINGS OF YOUR COMPUTER
To change the configuration, use Internet Explorer (IE) or Netscape
Communicator to connect the WEB management 192.168.1.1.
WAN:
Host Name:
This entry is necessary for some ISPs and can be provided by them.
Domain Name:
This entry is necessary for some ISPs and can be provided by them.
Configuration Type:
The Router supports four connection types:
Dynamic IP Setting:
Static IP Address
PPPoE (Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet)
PPTP (Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol)
Dynamic
8

Static IP Address
PPPoE
9

PPTP
These types can be selected from the drop-down menu next to Internet
Connection. The information required and available features will differ depending
on what kind of connection type you select.
Some descriptions of this information are included here:
Internet IP Address and Subnet Mask
This is the Router's IP Address and Subnet Mask as seen by external users on
the Internet (including your ISP). If your Internet connection requires a static IP
address, then your ISP will provide you with a Static IP Address and Subnet
Mask.
Default Gateway
Your ISP will provide you with the Gateway IP Address.
DNS (Domain Name Server) IP Address
Your ISP will provide you with at least one DNS IP Address.
User Name and Password
Enter the User Name and Password you use when logging onto your ISP
through a PPPoE or PPTP connection.
10

Connect on Demand
You can configure the Router to disconnect your Internet connection after a
specified period of inactivity (Max Idle Time). If your Internet connection has been
terminated due to inactivity, Connect on Demand enables the Router to
automatically re-establish your connection as soon as you attempt to access the
Internet again.
If you wish to activate Connect on Demand, click the radio button. If you want
your Internet connection to remain active at all times, enter 0 in the 125Mbps AP
Router max Idle Time field. Otherwise, enter the number of minutes you want to
have elapsed before your Internet connection terminates.
Keep Alive Option
This option keeps you connected to the Internet indefinitely, even when your
connection sits idle. To use this option, click the radio button next to Keep Alive.
The default Redial
Period is 30 seconds (in other words, the Router will check the Internet
connection every 30 seconds).
LAN IP Address and Subnet Mask:
This is the Router's IP Address and Subnet Mask as seen on the internal LAN.
The default value is 192.168.1.1 for IP Address and 255.255.255.0 for Subnet
Mask.
11

Wireless:
This section provide the Wireless Network settings for your WLAN
Mode:
This unit supports 3 wireless mode – 11b+g , 11g Only and AfterBurner (turbo
mode).
Caution : In case to reach the 125 Mbps turbo mode speed , user have to
use the device which supported 125 Mbps technology
SSID:
The service set identifier ( SSID ) or network name. It is case sensitive and must
not exceed 32 characters, which may be any keyboard character. You shall have
selected the same SSID for a ll the APs that will be communicating with mobile
wireless stations.
Domain:
The displaying information is related with each domain regulation.
Channel:
Select the appropriate channel from the list provided to correspond with your
network settings. You shall assign a different channel for each AP to avoid signal
interference.
12

4.2 Security:
There are 3 types of security to be selected. To secure your Wireless Networks,
it’s strongly recommended to enable this feature.
WEP / WPA Preshared Key / WPA Radius
select the “enable” to enter “configure security” screen
then you can see WEP / Preshared Key / WPA Radius mode
13
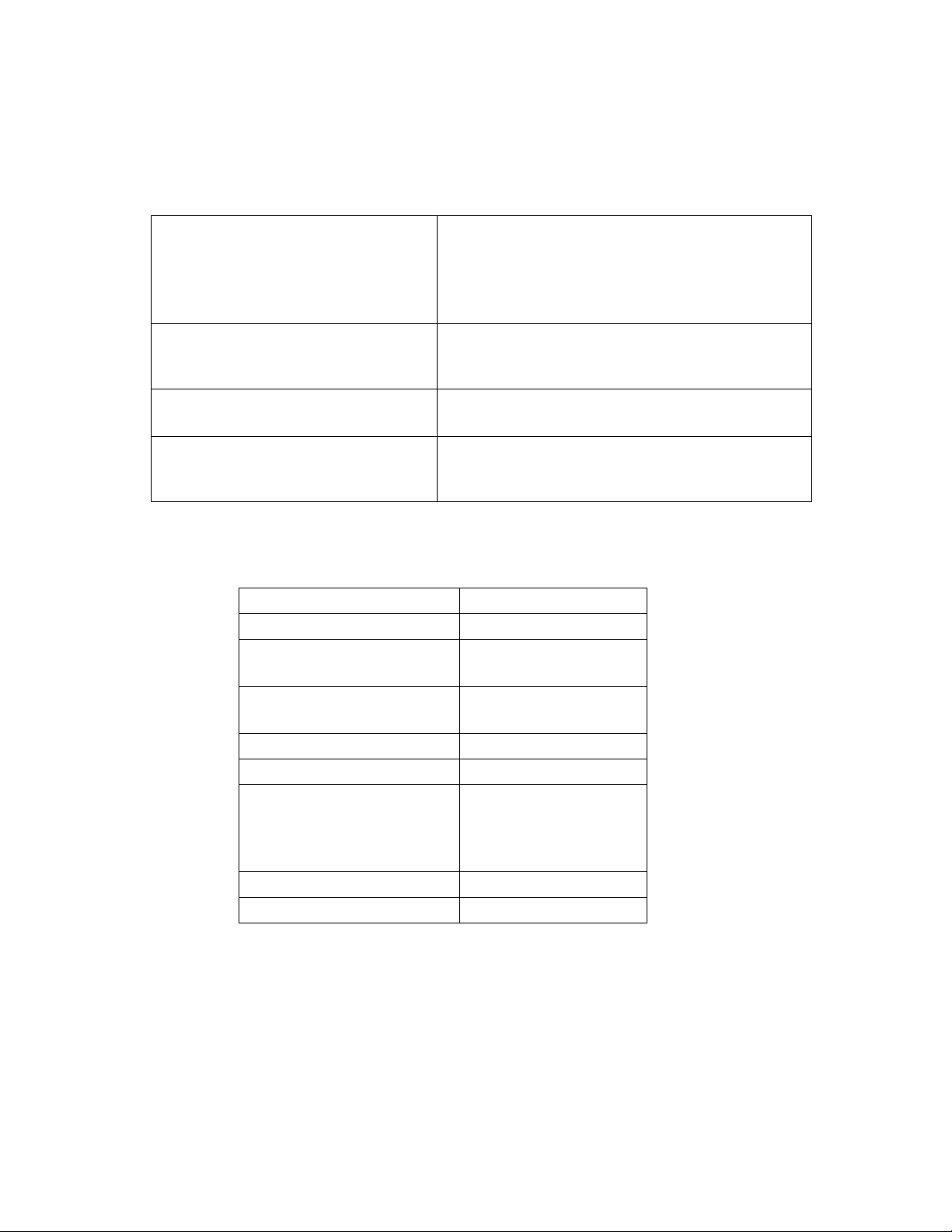
WEP:
Make sure that all wireless devices on your network are using the same
encryption level and key. WEP keys must consist of the letters "A" through "F"
and the numbers "0" through "9."
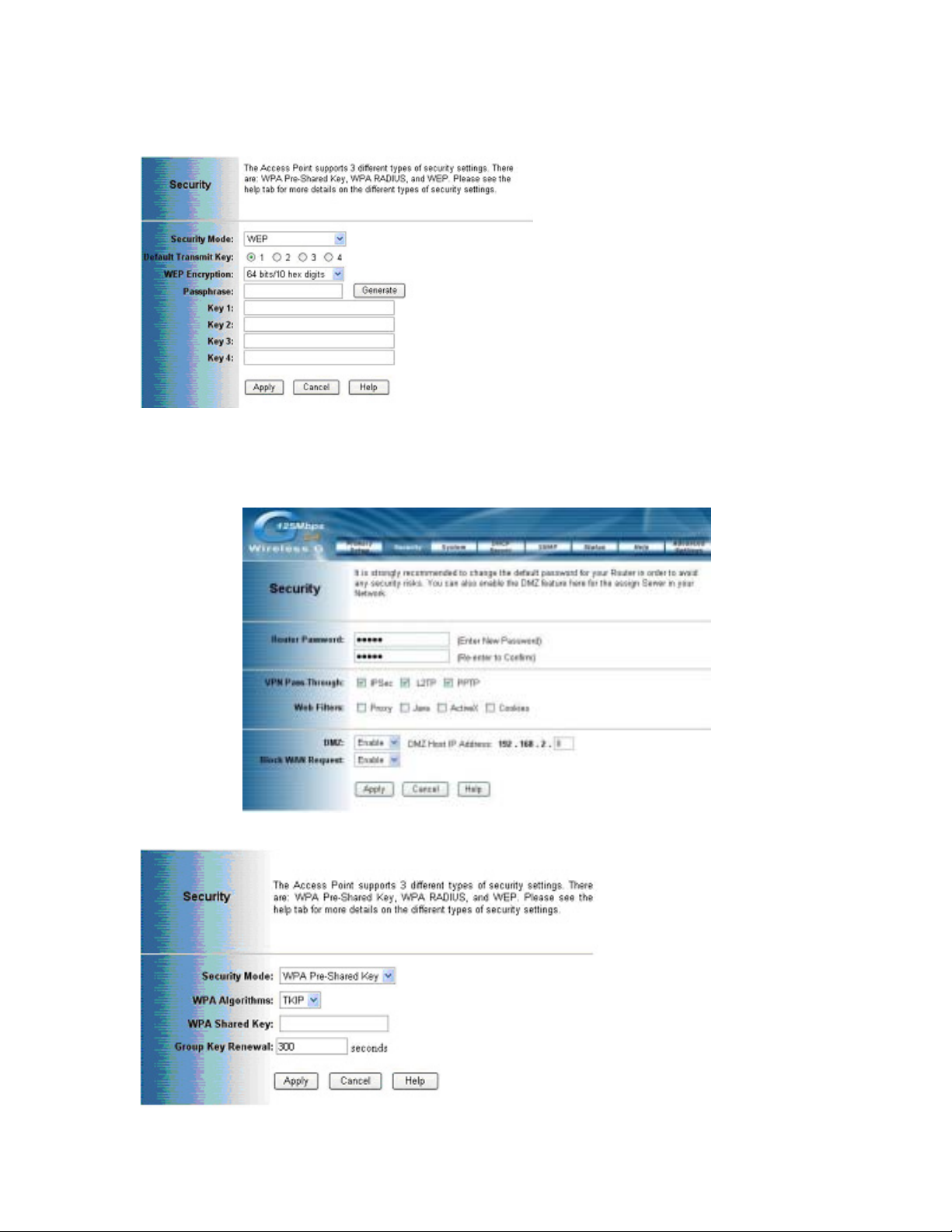
WPA-Preshared key
14

There are two encryption options for WPA Pre-Shared Key, TKIP and AES. TKIP
stands for Temporal Key Integrity Protocol. TKIP utilizes a stronger encryption
method and incorporates Message Integrity Code (MIC) to provide protection
against hackers. AES stands for Advanced Encryption System, which utilizes a
symmetric 128-Bit block data encryption.
To use WPA Pre-Shared Key, enter a password in the WPA Shared Key field
between 8 and 63 characters long. You may also enter a Group Key Renewal
Interval time between 0 and 99,999 seconds.
WPA Algorithms Please choose your algorithms method. You can select
between TKIP or AES.
WPA Shared Key Please input the Pre-Shared Key. The key should be 8
characters or 63 characters in alphanumeric.
Group Key Renewal Please input the period of renewal time. The default selection
is 300 seconds.
Important Notice
In order to make right use of WPA, please ensure that your current Wireless
Adapter’s driver, and Wireless Utility can support it, WPA needs 802.1x
authentication (when RADIUS mode is chosen), though the Operating System
must also support 802.1x protocol. For Microsoft’s OS family, only Windows XP
has incorporated this by default. The rest of the OS must installed 3er party’s
client software such as Funk Odyssey.
WPA RADIUS
15

WPA RADIUS uses an external RADIUS server to perform user
authentication. To use WPA RADIUS, enter the IP address of the
RADIUS server, the RADIUS Port (default is 1812) and the shared secret
from the RADIUS server.
WPA Algorithms Please choose your algorithms
method. You can select between
TKIP or AES.
Radius Server Address Please input your RADIUS Server IP
address.
RADIUS Server Port Please input the Authentication port
of your RADIUS server. The default
port being used is 1812
RADIUS Shared Key The RADIUS server will accept the
authentication if both Shared Key
matched.
Group Key Renewal Please input the period of renewal
time. The default selection is 300
seconds.
16

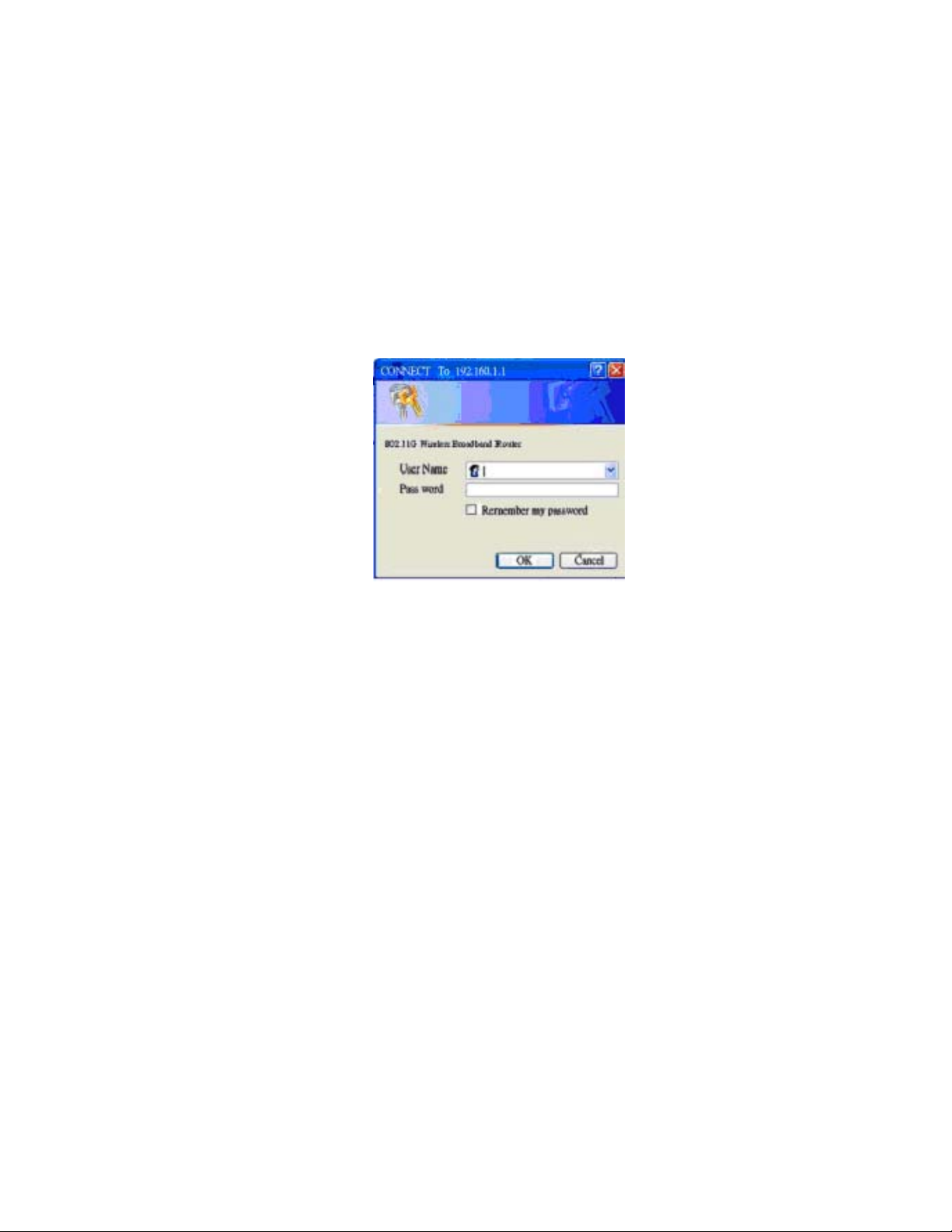
Router Password:
Changing the password for the AP Router is as easy as typing the password into
the Enter New Password field. Then, type it again into the Re-enter to confirm.
* Click the Apply button to save the setting.
Use the default password when you first open the configuration pages, after you
have configured these settings, you should set a new password for the Router
(using the Security screen). This will increase security, protecting the Router from
unauthorized changes.
VPN Pass-Through:
Virtual Private Networking (VPN) is typically used for work-related networking.
For VPN tunnels, the Router supports IPSec Pass-Through, L2TP Pass-Through,
and PPTP Pass-Through.
• IPSec - Internet Protocol Security (IPSec) is a suite of protocols used to
implement secure exchange of packets at the IP layer. To allow IPSec tunnels to
pass through the Router, IPSec Pass-Through is enabled by default. To disable
IPSec Pass-Through, uncheck the box next to IPSec.
• L2TP - Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol is a protocol used to tunnel Point-to-Point
Protocol (PPP) over the Internet. To allow L2TP tunnels to pass through the
Router, L2TP Pass-Through is enabled by default. To disable L2TP
Pass-Through, uncheck the box next to L2TP.
• PPTP - Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol is the method used to enable VPN
sessions to a Windows NT 4.0 or 2000 server. To allow PPTP tunnels to pass
17

through the Router, PPTP
Pass-Through is enabled by default. To disable PPTP Pass-Through, uncheck
the box next to PPTP.
Web Filter s: Using the Web Filters feature, you may enable up to four different
filters.
• Proxy - Use of WAN proxy servers may compromise network security.
Denying Proxy will disable access to any WAN proxy servers. To enable proxy
filtering, click the box next to Proxy.
• Java - Java is a programming language for websites. If you deny Java, you run
the risk of not having access to Internet sites created using this programming
language. To enable Java filtering, click the box next to Java.
• ActiveX - ActiveX is a programming language for websites. If you deny
ActiveX, you run the risk of not having access to Internet sites created using this
programming language. To enable ActiveX filtering, click the box next to ActiveX.
• Cookies - A cookie is data stored on your PC and used by Internet sites when
you interact with them. To enable cookie filtering, click the box next to Cookies.
DMZ:
The DMZ hosting feature allows one local user to be exposed to the Internet for
use of a special-purpose service such as Internet gaming or videoconferencing.
DMZ hosting forwards all the ports at the same time to one PC. The Port
Forwarding feature is more secure because it only opens the ports you want to
have opened, while DMZ hosting opens all the ports of one computer, exposing
the computer so the Internet can see it.
Any PC whose port is being forwarded must have its DHCP client function
disabled and should have a new static IP address assigned to it because its IP
address may change when using the DHCP function.
1. To expose one PC, select Enable.
2. Enter the computer's IP address in the DMZ Host IP Address field.
3. Click the Apply button.
Block WAN ICMP Request: By enabling the Block WAN Request feature, you
can prevent your network from being "pinged," or detected, by other Internet
users. The Block WAN Request feature also reinforces your network security by
hiding your network ports. Both functions of the Block WAN Request feature
make it more difficult for outside users to work their way into your network. This
feature is enabled by default. Select Disable to disable this feature.
* Check all the settings and click Apply to save them.
18

4.3. System
Restore Factory Defaults: Click the Yes button to reset all configuration
settings to factory default values. Note: Any settings you have saved will be lost
when the default settings are restored. Click the No button to disable the Restore
Factory Defaults feature.
Click the Apply button to save the setting.
Firmware Upgrade: Click the Upgrade button to load new firmware onto the
Router. If the Router is not experiencing difficulties, then there is no need to
download a more recent firmware version, unless that version has a new feature
that you want to use.
Note: When you upgrade the Router’s firmware, you may lose its
configuration settings, so make sure you write down the Router’s settings
before you upgrade its firmware.
To upgrade the Router’s firmware:
1. Download the firmware upgrade file from the internet.
2. Extract the firmware upgrade file.
3. Click the Upgrade button.
19

4. On the Firmware Upgrade screen, click the Browse button to find the firmware
upgrade file.
5. Double-click the firmware upgrade file.
6. Click the Upgrade button, and follow the on-screen instructions.
Note: Do not power off the Router or press the Reset button while the
firmware is being upgraded.
Multicast Pass-Through: IP Multicasting occurs when a signal data
transmission is sent to multiple recipients at the same time. Using the Multicast
Pass-Through feature, the Router allows IP multicast packets to be forwarded to
the appropriate computers. Keep the default setting, Enable, to support the
feature, or select Disable to disable it.
MAC Cloning: The Router’s MAC address is a 12-digit code assigned to a
unique piece of hardware for identification. Some ISPs require that you register
the MAC address of your network card/adapter, which was connected to your
cable or DSL modem during installation. If your ISP requires MAC address
registration, find your adapter’s MAC address by following the instructions for
your PC’s operating system.
For Windows 98 and Millennium:
1. Click the Start button, and select Run.
2. Type winipcfg in the field provided, and press the OK key.
3. Select the Ethernet adapter you are using.
4. Click More Info.
5. Write down your adapter’s MAC address.
20

For Windows 2000 and XP:
1. Click the Star button, and select Run.
2. Type cmd in the field provided, and press the OK key.
3. At the command prompt, run ipconfig /all, and look at your adapter’s physical
address.
4. Write down your adapter’s MAC address.
To clone your network adapter’s MAC address onto the Router and avoid calling
your ISP to change the registered MAC address, follow these instructions.
1. Select Enable.
2. Enter your adapter's MAC address in the MAC Address field.
3. Click the Apply button
To disable MAC address cloning, keep the default setting, Disable.
Remote Management:
This feature allows you to manage your Router from a remote location, via the
Internet. To disable this feature, keep the default setting, Disable. To enable this
feature, select
Enable, and use the specified port ( default is 8080) on your PC to remotely
manage the Router. You Must also change the Router’s default password to one
of your own, if you haven’t already. A unique password will increase security.
To remotely manage the Router, enter http://xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx:8080
(the x’s
represent the Router’s Internet IP address, and 8080 represents the specified
port) in your web browser’s address field. You will be asked for the Router’s
password. After successfully ente ring the password, you will be able to access
the Router’s web-based utility.
Note: If the Remote Management feature is enabled, anyone who knows the
Router’s Internet IP address and password will be able to alter the Router’s
settings.
MTU: MTU is the Maximum Transmission Unit. It specifies the largest packet size
permitted for Internet transmission. Keep the default setting, Auto, to have the
Router select the best MTU for your Internet connection, To specify a MTU size,
select Manual, and enter the value desired (default is 1400). You should leave
this value in the 1200 to 1500 range.
Traffic Log: The Router can keep logs of all incoming or outgoing traffic for your
Internet connection. This feature is disabled by default. To keep activity logs,
select Enable.
To keep a permanent record of activity logs as a file on your PC’s hard drive, Log
21

viewer software must be used. In the Send Log to field, enter the fixed IP
address of the PC running the Log viewer software. The Router will send
updated logs to that PC.
To see a temporary log of the Router’s most recent incoming traffic, click the
Incoming Access Log button. To see a temporary log of the Router’s most
recent outgoing traffic, click the Outgoing Access Log button.
Click the Apply button to save the setting.
22

4.4. DHCP Server
The DHCP Server screen allows you to configure the settings for the Router's
Dynamic Host Configuratio n Protoco l (DHCP) server fun ction. The Route r can be
used as a DHCP server for your network. A DHCP se rver automatically assigns
an IP address to each computer on your network. If you choose to enable the
Router's DHCP server option, you must configure your entire network PCs to
connect to a DHCP server, the Router.
If you disable the Router's DHCP server function, you must configure the IP
Address, Subnet Mask, and DNS for each network computer (note that each IP
Address must be unique).
DHCP Server: Select the Enable option to enable the Router's DHCP server
option. If you alre ady ha ve a DHCP se rver on you r ne twork o r you d o n ot want a
DHCP server, then select Disable from the options.
Starting IP Address: Enter a numerical value for the DHCP server to start with
when issuing IP addresses. Because the Router's default IP address is
192.168.1.1, the Starting IP Address must be 192.168.1.2 or greater, but smaller
23

than192.168.5.253. The default Starting IP Address is 192.168.1.100.
Maximum Number of DHCP Users: Enter the maximum number of PCs that
you want the DHCP server to assign IP addresses to. The absolute maximum is
253 - possible if 192.168.1.1 is your starting IP address. The default is 50.
Client Lease Time: The Client Lease Time is the amount of time a network user
will be allowed connection to the Router with their current dynamic IP address.
Enter the amount of time, in minutes, that the user will be "leased" this dynamic
IP address. The default is 0 minutes, which means one day.
Static DNS 1-3: The Domain Name System (DNS) is how the Internet translates
domain or website names into Interne t addresses or URLs. Your ISP will pro vide
you with at least one DNS Server IP Address. If you wish to utilize another, enter
that IP Address in one of these fields. You can enter up to three DNS Server IP
Addresses here. The Router will utilize these for quicker access to functioning
DNS servers.
WINS: The Windows Internet Naming Service (WINS) manages each PC’s
interaction with the Internet. If you use a WINS server, enter that server’s IP
Address here. Otherwise, leave this blank.
Currently Assigned: Click the DHCP Clients Table button to see a list of PCs
assigned IP addresses by the Router. For each PC, the list shows the client
hostname, MAC address, IP address, and the amount of DHCP client lease time
left. Click the Refresh button to display the most current information.
* Click Apply to save your settings.
24

4.5. SNMP
SNMP: The SNMP INFO screen allows you to customize the Simple Network
Management Protocol (SNMP) settings. SNMP is a popular network monitoring
and management protocol.
SNMPv2c
To enable the
SNMP support
feature, select
Enable.
Otherwise, select
Disable.
Identification
Contact In the contact
field, enter
contact
information for
the Router.
Unit Name
and
Description
In the Unit Name
and Description
field, enter the
name of the
Router.
Physical
Location
In the Physical
Location field,
specify the area
or location where
the Router
resides.
25

SNMP Community
public You may change
the SNMP
Community’s
name from its
default, public.
Then configure
the community’s
access as either
Read-Only or
Read-Write.
private You may change
the SNMP
Community’s
name from its
default, public.
Then configure
the community’s
access as either
Read-Only or
Read-Write.
Click Apply to save your settings.
26

4.6. Status
27

This screen displays the Wireless Router's current status and settings. This
information is read-only.
This page will auto re-flash every 5 seconds to keep most update information.
Host Name: The Host Name is the name of the Router. This entry is necessary
for some ISPs.
Domain Name: The Domain Name is the name of the Router's domain. This
entry is necessary for some ISPs.
WAN IP Release: Click the WAN IP Release button to delete the Router's
current Internet IP address.
WAN IP Renew: Click the WAN IP Renew button to get a new Internet IP
address for the Router.
*Click the Refresh button to refresh the Router's status and settings.
28

4.7. Advanced Wireless
Wireless MAC Filters:
This function allow administrator to have access control by enter MAC address of
client stations. When Enable this function, two new options will show up.
Depend on the filtering propose, it can be selected to Prevent or Permit.
Click on Edit MAC Filter List to add the client stations MAC list.
The table could store up to 40 different MAC addresses. Please follow the format
that it required when an address is input.
Authentication Type:
29

Auto:
Auto is the default authentication algorithm. It will change its authentication type
30

automatically to fulfill client’s requiremen t.
Open System:
Open System authentication is not required to be successful while a client may
decline to authenticate with any particular other client.
Shared Key:
Shared Key is only available if the WEP option is implemented. Shared Key
authentication supports authentication of clients as either a member of those who
know a shared secret key or a member of those who do not. IEEE 802.11 Shared
Key authentication accomplishes this without the need to transmit the secret key
in clear. Requiring the use of the WEP privacy mechanism.
Transmission Rate:
The rate of data transmission should be set depending on the speed of your
wireless network. You can select from a range of transmission speeds, or you
can select AUTO to have the Router automatically use the fastest possible data
rate and enable the Auto-Fallback feature. Auto-Fallback will negotiate the best
possible connection speed between the Router and a wireless client. The default
setting is AUTO.
Xpress:
This is another wireless turbo mode. If wireless network card can support such
turbo mode, then suggest to enable this function for enhance your WLAN
performance.
DTIM Interval:
This value indicates the interval of the Delivery Traffic Indication Message (DTIM).
A DTIM field is a countdown field informing clients of the next window for
listening to broadcast and multicast messages. When the Access Point has
buffered broadcast or multicast messages for associated clients, it sends the
next DTIM with a DTIM Interval value.
Access Point Clients hear the beacons and awaken to receive the broadcast and
multicast messages.
Beacon Interval:
The Beacon Interval value indicates the frequency interval of the beacon. Enter a
value between 20 and 1000. A beacon is a packet broadcast by the Router to
synchronize the wireless network. The default value is 100.
User’s Guide 22
RTS Threshold:
This value should remain at its default setting of 2346. Should you encounter
inconsistent data flow, only minor modifications are recommended. If a network
packet is smaller than the preset RTS threshold size, the RTS/CTS mechanism
will not be enabled. The Router sends Request to Send (RTS) frames to a
particular receiving station and negotiates the sending of a data frame. After
31

receiving an RTS, the wireless station responds with a Clear to Send (CTS)
frame to acknowledge the right to begin transmission.
Fragmentation Threshold:
This value specifies the maximum size for a packet before data is fragmented
into multiple packets. It should remain at its default setting of 2346. If you
experience a high packet error rate, you may slightly increase the Fragmentation
Threshold. Setting the Fragmentation Threshold too low may result in poor
network performance. Only minor modifications of this value are recommended.
AP Mode or Wireless Bridge Mode:
802.11g AP Router can operate in two modes. When the AP Mode is selected,
the device operates as a normal Access Point. Proving every wireless client
station a join network point.
The Wireless Bridge Mode will be able to join different AP Router wirelessly by
input the destination MAC Address.
* Click Apply to save your settings.
32

4.8. Access Filters
User’s Guide 24
The Access Filter screen allows you to block or allow specific kinds of Internet
usage. You can set up Internet access policies for specific PCs and set up filters
by using network port numbers.
33

Internet
Access
Policy
This feature allows you to customize up to 10 different Internet
Access Policies for particular PCs, which are identified by their IP
or MAC addresses. For each policy's designated PCs, the Router
can do one or more of the following:
• block or allow Internet access or inbound traffic during the days
and time periods
specified
• block designated services
• block websites with specific URL addresses
• block websites that use specific keywords in their URL
addresses.
To create or edit a policy, follow these instructions:
1. Select the policy's number (1-10) in the drop-down menu.
2. Enter a name in the Enter Policy Name field.
3. Select Internet Access or Inbound Traffic from the Policy Type
drop-down
box, depending on the kind of access you want to control.
Select Internet
Access to control your network PCs' access to the Internet.
Select Inbound
Traffic to control Internet PCs' access to your local area
network.
Note: The screen's settings will vary depending on which Policy
Type you select.
4. Select Deny or Allow, depending on how you want to control
access for specific PCs.
5. Click the Edit List button next to PCs or Internet PCs.
a. On the List of PCs or List of Internet PCs screen, specify PCs by
IP address or MAC address. Enter the appropriate IP addresses
into the IP fields. If you have a range of IP addresses to filter,
complete the appropriate IP Range fields. Enter the appropriate
MAC addresses into the MAC fields.
b. Click the Apply button to save your changes. Click the Cancel
button to cancel your unsaved changes. Click the Close button to
return to the Internet Filter screen.
6. Set the days when access will be filtered. Keep the default
setting, Everyday, or select the appropriate days of the week.
7. Set the time when access will be filtered. Keep the default
setting, 24 Hours, or check the box next to From and use the
34
drop-down boxes to designate a specific time period.
Note: Access for the listed PCs will be controlled during the

Internet
Access
Policy
Delete
8. In the Blocking Services drop-down boxes, select the services
you want to block (the default setting is None). In the Blocking
Services fields, the range of ports for this service will appear. If
you want to change the range of ports, enter the new numbers in
the Blocking Services fields, or edit the service’s settings (see
below).
To add a service or edit a service's settings, follow these
instructions:
a. Click the Add Service button.
b. To create a new service, enter the name of the service in the
Service Name field. To edit a service's settings, select the
service from the box on the right of the screen.
c. From the Protocol drop-down menu, select the protocol type
for this service: ICMP, UDP, TCP, or UDP & TCP.
d. In the Port Range fields, enter the r ange of ports for this
service.
e. To add a service, click the Add button. To edit the settings for
a service, click the Modify button.
f. To delete a service, select the service from the box on the
right of the screen. Click the Delete button.
g. Click the Apply button to save your changes. Click the
Cancel button to undo your changes. Click the Close button to
close the Add Service window.
9. If you want to block websites with specific URL addresses,
enter each URL address in a Website Blocking by URL Address
field. You can enter up to four URL addresses. (This feature is
not available if you chose Inbound Traffic for the Policy Type.)
10. If you want to block websites that use specific keywords as
part of their URL addresses, enter each keyword in a Website
Blocking by Keyword field. You can enter up to six keywords.
(This feature is not available if you chose Inbound Traffic for
the Policy Type.)
11. Click the Apply button to save your settings for an Internet
Access Policy. Click the Cancel button to cancel your unsaved
changes.
12. To create or edit additional policies,
To delete an Internet Access Policy, select the policy's number,
and click the Delete button.
Summary
To see a summary of all the policies, click the Summary button.
The Internet Policy Summary screen will show each policy's
number, Name, Type, Days, and Time of Day. To delete a
policy, click its box, and then click the Delete button. Click the
Close button to return to the Internet Filter screen.
35

4.9. Virtual Server
The Virtual Server screen sets up public services on your network, such as web
servers, ftp servers, e-mail servers, or other specialized Internet applications.
(Specialized Internet applications are any applications that use Internet access to
36

perform functions such as videoconferencing or online gaming. Some Internet
pp
applications may not require any forwarding.)
When users send this type of request to your network via the Internet, the Router
will forward those requests to the appropriate PC. Any PC whose port is being
forwarded must have its DHCP client function disabled and must have a new
static IP address assigned to it because its IP address may change when using
the DHCP function.
Enter the name of the public
Customized Applications
service or other Internet
application in the field
provided.
Enter the numbers of the
External Port
External Ports (the port
numbers seen by users on the
Internet).
TCP Protocol
UDP Protocol
IP Address
Click this checkbox if the
application requires TCP.
Click this checkbox if the
application requires UDP.
Enter the IP Address of the PC
running the application.
Click the Enable checkbox to
Enable
enable port forwarding for the
application.
Port Triggering is used for
special Internet applications
whose outgoing ports differ
from the incoming ports. For
this feature, the Router will
watch outgoing data for
specific port numbers. The
Router will remember the IP
address of the computer that
Port Triggering
sends a transmission
requesting data, so that when
the requested data returns
through the Router, the data is
pulled back to the proper
computer by way of IP address
and port mapping rules. Click
the Port Triggering button to
set up triggered ports, and
follow these instructions:
1. Enter the A
lication Name
37

of the trigger.
2. Enter the Outgoing Port
Range used by the application.
Check with the Internet
application for the port
number(s) needed.
3. Enter the Incoming Port
Range used by the application.
Check with the Internet
application for the port
number(s) needed.
4. Click the Apply button to
save your changes. Click the
Cancel button to cancel your
unsaved changes. Click the
Close button to return to the
Port Forwarding screen.
Check all the settings and click Apply to save them.
38

4.10. Routing Table
On the Routing Table screen, you can set the routing mode and settings of the
Router. Gateway mode is recommended for most users.
The default setting is Gateway.
Choose the correct working mode. Keep the default
Operating Mode
Dynamic Routing (RIP)
setting, Gateway, if the Router is hosting your
network's connection to the Internet (Gateway mode
is recommended for most users). Select Router if
the Router exists on a network with other routers.
Note: This feature is not available in Gateway
mode.
The default setting is Disable.
Dynamic Routing enables the Router to
automatically adjust to physical changes in the
network's layout and exchange routing tables with
other routers. The Router determines the network
packets' route based on the fewest number of hops
between the source and destination.
To enable the Dynamic Routing feature, select
Enable. To disable the Dynamic Routing feature for
all data transmissions, keep the default setting,
Disable.
39

Static Routing,
Destination IP
Address, Subnet
Mask, Gateway,
and Interface
Delete This Entry
1. To set up a static route between the Router and
another network, select a number from the Static
Routing drop-down list. (A static route is a
pre-determined pathway that network information must
travel to reach a specific host or network.)
2. Enter the following data:
• Destination IP Address - The Desti nation IP Address
is the address of the network or host to which you want
to assign a static route.
• Subnet Mask - The Subnet Mask determines which
portion of an IP address is the network portion, and
which portion is the host portion.
• Gateway - This is the IP address of the gateway
device that allows for contact between the Router and
the network or host.
3. Depending on where the Destination IP Address is
located, select LAN & Wireless or Internet (WAN) from
the Interface drop-down menu.
4. To save your changes, click the Apply button. To
cancel your unsaved changes, click the Cancel button.
For additional static routes, repeat steps 1-4.
To delete a static route entry:
1. From the Static Routing drop-down list, select the
entry number of the static route.
2. Click the Delete This Entry button.
3. To save a deletion, click the Apply button. To cancel
a deletion, click the Cancel button.
Show Routing
Table
Click the Show Routing Table button to view all of the
valid route entries in use. The Destination IP address,
Subnet Mask, Gateway, and Interface will be displayed
for each entry. Click the Refresh button to refresh the
data displayed.
• Destination LAN IP - The Destination IP Address is
the address of the network or host to which the static
route is assigned.
• Subnet Mask - The Subnet Mask determines which
portion of an IP address is the network portion, and
which portion is the host portion.
• Gateway - This is the IP address of the gateway
device that allows for contact between the Router and
the network or host.
• Interface - This interface tells you whether the
40

Destination IP Address is on the LAN & Wireless
(internal wired and wireless networks), the WAN
(Internet), or Loop back (a dummy network in which
one PC acts like a network—necessary for certain
software programs).
* Click Apply to save your settings.
41

4.11. Dynamic DNS
The Router offers a Dynamic Domain Name System (DDNS) feature. DDNS lets
you assign a fixed host and domain name to a dynamic Internet IP address. It is
useful when you are hosting your own website, FTP server, or other server
behind the Router. Before using this feature, you need to sign up for DDNS
service with one of two DDNS service providers, DynDNS.org or TZO.
DynDNS.org
To disable DDNS Service, keep the default setting,
Disable. To enable DDNS Service using DynDNS.org,
follow these instructions:
1. On the DDNS screen, select DynDNS.org from the
DDNS Service Provider drop-down menu.
DDNS Service
2. Sign up for DynDNS service at www.dyndns.org
(you can click the link on the DDNS screen). Write
down your account information.
3. Complete the User Name, Password, and Host
Name fields.
4. Click the Apply button to save your changes. Click
the Cancel button to cancel unsaved changes.
Internet IP Address
Status
The Router's current Internet IP Address is displayed
here.
The status of the DDNS service connection is
displayed here.
42

TZO.com
To disable DDNS Service, keep the default setting, Disable. To
enable DDNS Service using TZO.com, follow these instructions:
1. On the DDNS screen, select TZO.com from the DDNS Service
Provider drop-down menu.
2. Sign up for a free, 30-day trial of TZO service at
DDNS Service
www.tzo.com/order.html (you can click the appropriate link on the
DDNS screen). Write down your account information.
3. Complete the Email Address, TZO Password Key, and Domain
Name fields.
4. Click the Apply button to save your changes. Click the Cancel
button to cancel unsaved changes.
Internet IP Address
The Router’s current Internet IP Address is displayed here.
Status The status of the DDNS service connection is displayed here.
* Click Apply to save your settings.
43

5. Troubleshooting
Basic Functions
Note: If you are using a cable or DSL modem and are experiencing problems
connecting
to the Internet, follow these steps:
1. Power off your cable or DSL modem, PC, and the Router.
2. Power on your modem and wait a few minutes until the modem has
established a connection with your ISP.
3. Power on the Router.
4. Power on your PC and attempt to connect to the Internet. For most users, the
Router's default values should be satisfactory. Some users may need to enter
additional information in order to connect to the Internet through their ISP or
broadband (cable or DSL) carrier. For example, some cable providers require a
specific MAC address for connection to the Internet. To learn more about this,
click the Advanced tab and then the MAC Address Clone tab.
My Wireless AP Router will not turn on. No LED’s light up.
Cause:
The power is not connected.
Resolution:
Connect the power adapter to your AP and plug it into the power outlet.
Note: Only use the power adapter provided with your AP. Using any other
adapter may damage your AP Router.
LAN Connection Problems I can’t access my AP Router.
Cause:
The unit is not powered on.
There is not a network connection.
The computer you are using does not have a compatible IP Address.
Resolution:
Make sure your AP is powered on.
Make sure that your computer has a compatible IP Address. Be sure that the IP
Address used on your computer is set to the same subnet as the AP. For
example, if the AP is set to 192.168.1.1, change the IP address of your computer
to 192.168.1.15 or another unique IP Address that corresponds to the
192.168.1.X subnet.
Use the Reset button located on the rear of the AP Router to revert to the default
settings.
I can’t connect to other computers on my LAN.
Cause:
The IP Addresses of the computers are not set correctly.
Network cables are not connected properly.
Windows network settings are not set correctly.
User’s Guide 32
44

User’s Guide 33Resolution: Make sure that each computer has a unique IP
Address. If using DHCP through the A P Router, makes sure that each co mputer
is enable DHCP function and restart the computer. Make sure that the Link
LED is on. If it is not, try a different network cable. Check each computer for
correct network settings. Wireless Troubleshooting I can’t access the
Wireless AP Router from a wireless network card Cause: Out of range. IP
Address is not set correctly. Resolution: Make sure that the Mode; SSID,
Channel and encryption settings are set the same on each wireless adapter.
Make sure that your computer is within range and free from any strong electrical
devices that may cause interference. Check your IP Address to make sure that
it is compatible with the Wireless AP Router.
45
 Loading...
Loading...