Zonet ZEW2501 user manual
IEEE 802.11b/g
Wireless LAN USB
Adapter
USER’S GUIDE
Tested To Comply
With FCC Standards
FOR HOME OR OFFICE USE
VERSION 1.1
2004/10/06

© All rights reserved.
All trade names are registered trademarks of respective manufacturers listed.
This manual may not be copied in any media or form without the written consent of original maker.

TABLE OF CONTENTS
Information To User .................................................... i
1. Introduction ........................................................... 1
2. Wireless LAN Basics .................................................. 3
3. IP ADDRESS ............................................................ 4
4. Install Driver/Utility ................................................. 5
5. Wireless Network Configuration .................................. 7
5.1 General Connection Setting .................................. 8
5.2 WEP Encryption Key Setting ................................. 9
5.3 WPA Encryption Setting ....................................... 10
5.4 Profile............................................................11
5.5 Advanced Setting ..............................................12
5.6 System Information ...........................................13
6. Technical Specifications ............................................. 14
7. Troubleshooting ...................................................... 15
8. Glossary ................................................................ 16

INFORMATION TO USER
Federal Communication Commission Interference Statement
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits
for a Class B digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These
limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful
interference in a residential installation.
This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency
energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions,
may cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there
is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular
installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or
television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment
off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by
one of the following measures:
Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from
that to which the receiver is connected.
Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is
subject to the following two conditions: (1) This device may not cause
harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference
received, including interference that may cause undesired operation.
FCC Caution: Any changes or modifications not expressly approved
by the party responsible for compliance could void the user's authority to
operate this equipment.
IMPORTANT NOTE:
FCC Radiation Exposure Statement:
This equipment complies with FCC radiation exposure limits set
forth for an uncontrolled environment. This equipment should be
installed and operated with minimum distance 20cm between the
radiator & your body.
This transmitter must not be co-located or operating in conjunction
with any other antenna or transmitter.
i
REGULATORY INFORMATION
ˇˇˇ
ˇˇˇ
ˇˇˇ
ˇ
ˇˇˇ
ˇ
ˇˇˇ
ˇ
ˇˇˇ
ˇ
ˇˇˇ
ˇ
ˇˇˇ
ˇ
ˇˇˇ
ˇ
ˇˇˇˇˇ
ˇˇˇˇˇ
ˇˇˇ
ˇˇˇ
ˇ
WLAN Mini USB Adapter must be installed and used in strict
accordance with the instructions. This device complies with the
following radio frequency and safety standards.
USA - Federal Communications Commission (FCC)
This device complies with Part 15 of FCC Rules. Operation is
subject to the following two conditions:
1. This device may not cause harmful interference.
2. This device must accept any interference that may cause undesired operation.
Europe - R&TTE Directive
This device complies with the specifications listed below
• ETS 300-826 General EMC requirements for Radio equipment.
• ETS 300-328 Technical requirements for Radio equipment.
• EN60950 Safety Requirements for Radio equipment
The channel identifiers, channel center frequencies, and
regulatory domains of each 22-MHz-wide channel are shown in
following Table.
Channel Center
Identifier Frequency
12412
22417
32422
42427
52432
62437
72442
82447
92452
10 2457
11 2462
12 2467
13 2472
14 2484
Regulatory Domains
(MHZ) North
Japan ETSI Israel France Mexico
America
ii

INTRODUCTION
Thank you for your purchase of the WLAN Mini USB Adapter.
Featuring wireless technology, this wireless networking solution has
been designed for both large and small businesses, and it is scalable
so that you can easily add more users and new network features
depending on your business scale.
FEATURES
Support Microsoft Windows 98SE, Me, 2000 and XP.
Operating distance of up to 300 meters in free space.
54/48/36/24/18/12/11/9/6/5.5/2/1 Mbps selectable Data Rate.
Support USB 2.0 interface.
64-bit or 128-bit WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy).
2.400GHz ~ 2.4835GHz unlicensed ISM Frequency Band.
Modulation Method :
IEEE 802.11b : DSSS (Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum).
IEEE 802.11g : OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing).
Easy operation and setting up.
SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS
Windows System : Windows 98SE, Me, 2000 or XP.
PCs must have a device driver installed. It allows you to commu-
nicate with WLAN Mini USB Adapter.
1

BEFORE YOU START
1. Confirm Box Contents
Wireless LAN Adapter
Driver CD
Quick Start Guide
CONNECTING YOUR WLAN USB ADAPTER TO PC
Connect your WLAN USB dongle to your
PC.
Install driver.
GETTING TO KNOW WIRELESS LAN USB ADAPTER
LED
LED turns on when POWER is applied to the WLAN Mini USB Adapter.
LED is blinking when PC is sending data through WLAN Mini USB
Adapter.
2
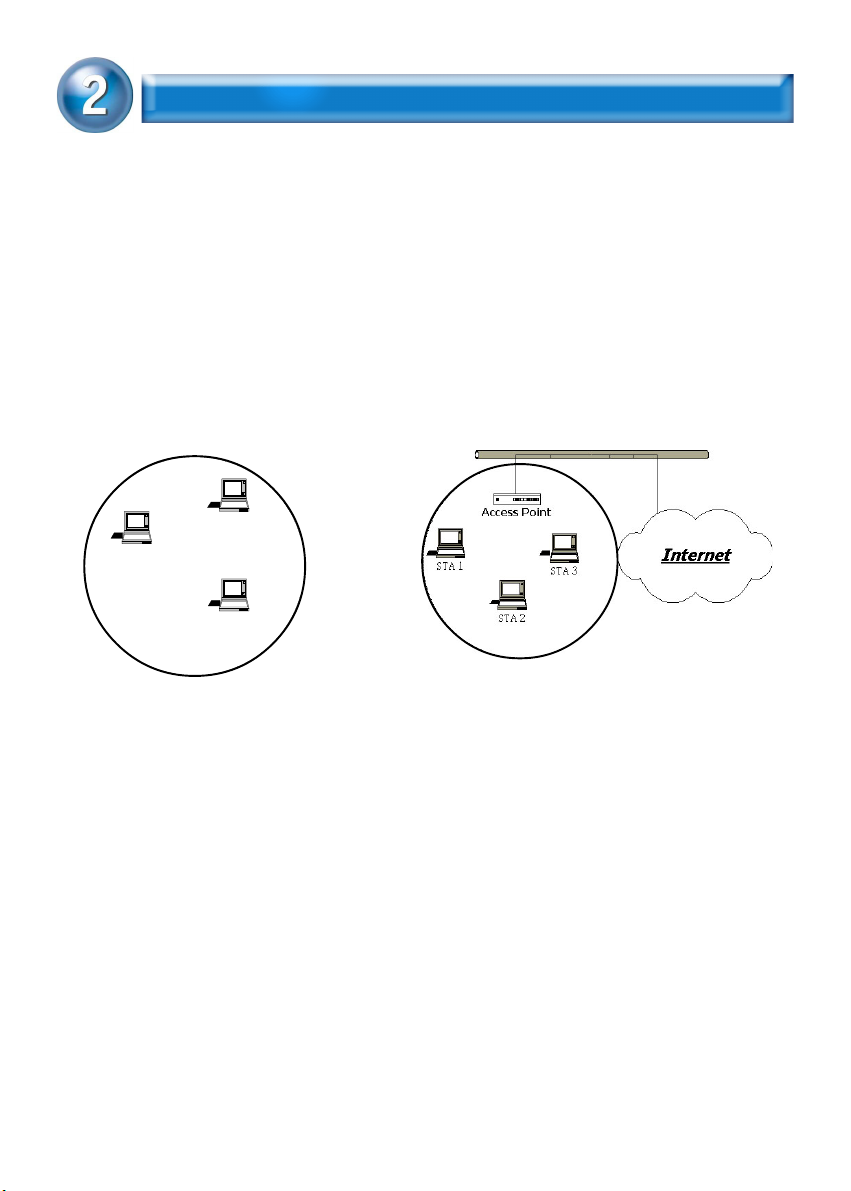
WIRELESS LAN BASICS
Wireless LAN network defined by IEEE 802.11b/g standard committee
could be configured as :
Ad Hoc wireless LAN, or
Infrastructure wireless LAN.
Ad Hoc network is a group of PCs installed with wireless LAN cards, this
group of PCs is called a BSS (Basic Service Set). PCs in this group can use
their wireless LAN cards to communicate with each other, but can not
connect to the Internet.
STA 2
STA 1
STA 3
Ad Hoc Wireless Network
Infrastructure Wireless Network
The most obvious difference between Infrastructure wireless network
and Ad Hoc wireless network is that the PCs in Infrastructure wireless
network can access the resource in the Internet through Access Point.
Depending on your requirement, you can easily set up your PC’s
network to be a “Ad Hoc” or “Infrastructure” wireless network. Generally speaking, if in your network, there is an Access Point in it, we recommend you to set your network as an “Infrastructure”, so it can connect to
the Internet.
3
 Loading...
Loading...