Datasheet Z86E6320PSC, Z86E6320VSC, Z86E6116PSC, Z86E6116VSC, Z86E6120PSC Datasheet (ZILOG)
...
1
Z86E61/E63 Z8® MCU
WITH 16K/32K EPROM
PRELIMINARY
P
RELIMINAR Y PRODUCT SPECIFICA TION
FEATURES
■ 8-Bit CMOS Microcontroller
■ 40-Pin DIP, 44-Pin PLCC Style Packages
■ 4.5V to 5.5V Operating Range
■ Clock Speeds: 16 and 20 MHz
■ Low Power Consumption: 275 mW (max)
■ Fast Instruction Pointer: 1.0 ms @ 12 MHz
■ Two Standby Modes: STOP and HALT
■ 32 Input/Output Lines
■ Full-Duplex UART
■ All Digital Inputs are TTL Levels
■ Auto Latches
Z86E61/E63
CMOS Z8® 16K/32K EPROM
MICROCONTROLLER
■ High Voltage Protection on High Voltage Inputs
■ RAM and EPROM Protect
■ EPROM: 16 Kbytes Z86E61
32 Kbytes Z86E63
■ 256 Bytes Register File
- 236 Bytes of General-Purpose RAM
- 16 Bytes of Control and Status Registers
- 4 Bytes for Ports
■ Two Programmable 8-Bit Counter/Timers Each
with 6-Bit Programmable Prescaler
■ Six Vectored, Priority Interrupts from Eight
Different Sources
■ On-Chip Oscillator that Accepts a Crystal, Ceramic
Resonator, LC, or External Clock Drive
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The Z86E61/E63 microcontrollers are members of the Z8
®
single-chip microcontroller family with 16K/32 Kbytes of
EPROM and 236 bytes of general-purpose RAM. Offered
in 40-pin DIP or 44-pin PLCC package styles, these devices are pin-compatible EPROM versions of the Z86C61/
63. The ROMless pin option is available on the 44-pin
versions only.
With 4 Kbytes of ROM and 236 bytes of general-purpose
RAM, the Z86E61/E63 offers fast execution, efficient use of
memory, sophisticated interrupts, input/output bit manipulation capabilities, and easy hardware/software system
expansion.
For applications demanding powerful I/O capabilities, the
Z86E61/E63 offers 32 pins dedicated to input and output.
These lines are grouped into four ports. Each port consists
of eight lines, and is configurable under software control to
provide timing, status signals, serial or parallel
I/O with or without handshake, and an address/data bus
for interfacing external memory.
The Z86E61/E63 can address both external memory and
preprogrammed ROM, making it well suited for highvolume applications or where code flexibility is required.
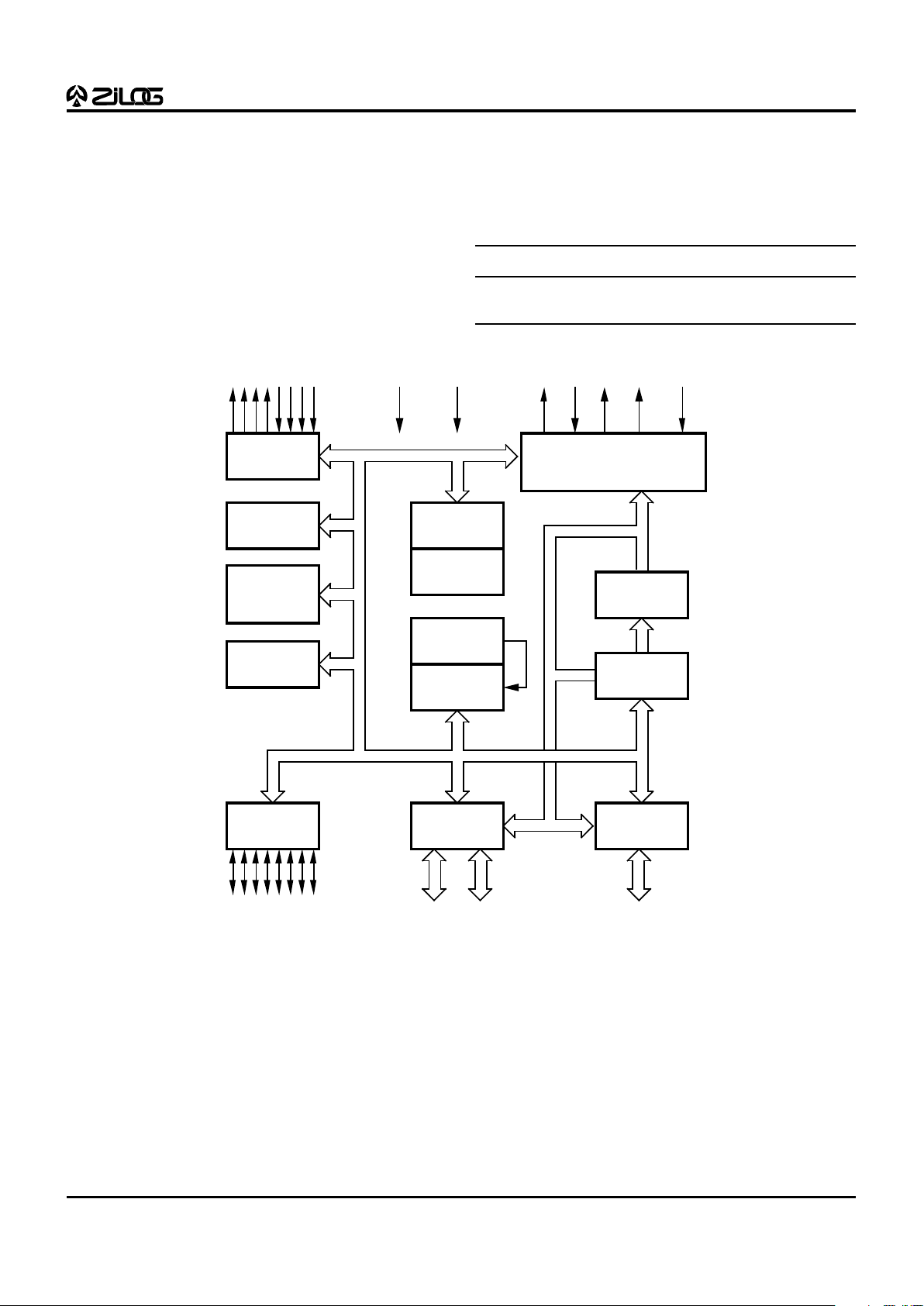
2
Z86E61/E63 Z8® MCU
WITH 16K/32K EPROM
PRELIMINARY
GENERAL DESCRIPTION (Continued)
There are three basic address spaces available to support
this configuration: Program Memory, Data Memory, and
236 general-purpose registers.
To unburden the system from coping with real-time tasks
such as counting/timing and serial data communication,
the Z86E61/E63 offers two on-chip counter/timers with a
large number of user selectable modes (Figure 1).
Notes:
All Signals with a preceding front slash, "/", are active Low, e.g.,
B//W (WORD is active Low); /B/W (BYTE is active Low, only).
Power connections follow conventional descriptions below:
Connection Circuit Device
Power V
CC
V
DD
Ground GND V
SS
Port 3
UART
Counter/
Timers
(2)
Interrupt
Control
Port 2
I/O
(Bit Programmable)
ALU
FLAGS
Register
Pointer
Register File
256 x 8-Bit
Machine Timing and
Instruction Control
Prg. Memory
16K/32K
Program
Counter
Vcc GND XTAL
44
Port 0
Output Input
Address or I/O
(Nibble Programmable)
8
Port 1
Address/Data or I/O
(Byte Programmable)
/AS /DS R//W /RESET
Figure 1. Z86E61/E63 Functional Block Diagram
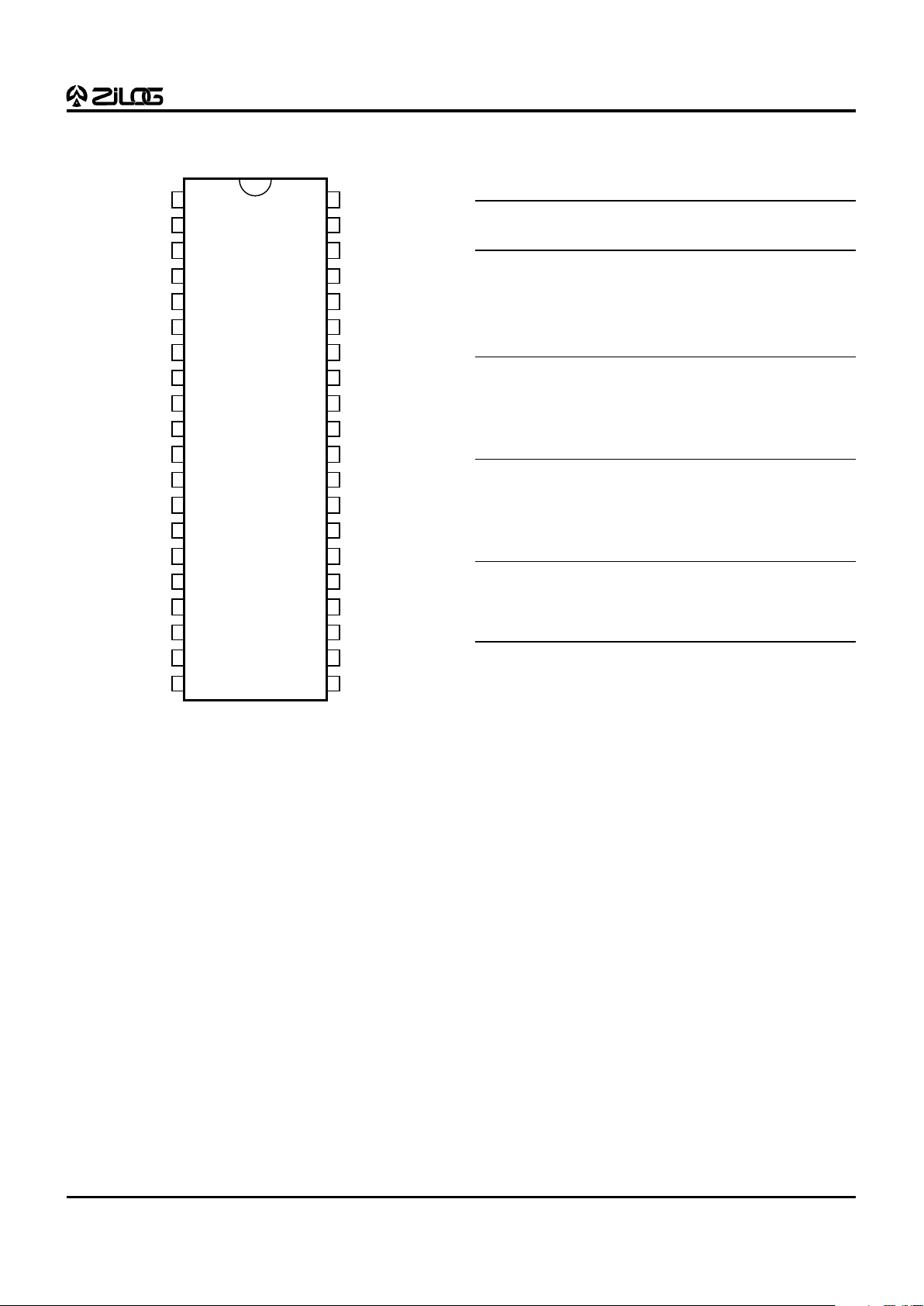
3
Z86E61/E63 Z8® MCU
WITH 16K/32K EPROM
PRELIMINARY
PIN DESCRIPTION
Standard Mode
Table 1. 40-Pin DIP Pin Identification
Standard Mode
Pin # Symbol Function Direction
1VCCPower Supply Input
2 XTAL2 Crystal, Oscillator Clock Output
3 XTAL1 Crystal, Oscillator Clock Input
4 P37 Port 3, Pin 7 Output
5 P30 Port 3, Pin 0 Input
6 /RESET Reset Input
7 R//W Read/Write Output
8 /DS Data Strobe Output
9 /AS Address Strobe Output
10 P35 Port 3, Pin 5 Output
11 GND Ground Input
12 P32 Port 3, Pin 2 Input
13-20 P07-P00 Port 0, Pins 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7 In/Output
21-28 P17-P10 Port 1, Pins 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7 In/Output
29 P34 Port 3, Pin 4 Output
30 P33 Port 3, Pin 3 Input
31-38 P27-P20 Port 2, Pins 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7 In/Output
39 P31 Port 3, Pin 1 Input
40 P36 Port 3, Pin 6 Output
1
2
9
3
4
5
6
7
8
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
P36
P31
P21
P27
P26
P25
P24
P23
P22
VCC
XTAL2
P37
P30
/RESET
R//W
/DS
31
30
29
28
2714
10
11
12
13
XTAL1
GND
P32
P00
P01
P20
P33
P34
P17
P16
Z86E61
/E63
DIP
15
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
16
17
18
19
/AS
P35
P02
P03
P06
P07
P05
P04 P13
P15
P14
P12
P11
P10
Figure 2. 40-Pin DIP Pin Configuration
4
Z86E61/E63 Z8® MCU
WITH 16K/32K EPROM
PRELIMINARY
PIN DESCRIPTION (Continued)
Standard Mode
Figure 3. 44-Pin PLCC Pin Configuration
N/C
P30
P37
XTAL1
XTAL2
VCC
P36
P31
P27
P26
P25
P03
P04
P05
P06
P07
P10
P11
P12
P13
P14
N/C
NC
P24
P23
P22
P21
P20
P33
P34
P17
P16
P15
/RESET
R//W
/DS
/AS
P35
GND
P32
P00
P01
P02
R//RL
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
39
Z86E61/E63
PLCC
6543214443424140
18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28
Standard Mode
Pin # Symbol Function Direction
1VCCPower Supply Input
2 XTAL2 Crystal, Osc. Clock Output
3 XTAL1 Crystal, Osc. Clock Input
4 P37 Port 3, Pin 7 Output
5 P30 Port 3, Pin 0 Input
6 N/C Not Connected Input
7 /RESET Reset Input
8 R//W Read/Write Output
9 /DS Data Strobe Output
10 /AS Address Strobe Output
11 P35 Port 3, Pin 5 Output
12 GND Ground Input
13 P32 Port 3, Pin 2 Input
Standard Mode
Pin # Symbol Function Direction
14-16 P02-P00 Port 0, Pins 0,1,2 In/Output
17 R//RL ROM/ROMless control Input
18-22 P07-P03 Port 0, Pins 3,4,5,6,7 In/Output
23-27 P10-P14 Port 1, Pins 0,1,2,3,4 In/Output
28 N/C Not Connected Input
29-31 P17-P15 Port 1, Pins 5,6,7 In/Output
32 P34 Port 3, Pin 4 Output
33 P33 Port 3, Pin 3 Input
34-38 P24-P20 Port 2, Pins 0,1,2,3,4 In/Output
39 N/C Not Connected Input
40-42 P27-P25 Port 2, Pins 5,6,7 In/Output
43 P31 Port 3, Pin 1 Input
44 P36 Port 3, Pin 6 Output
Table 2. 44-Pin PLCC Pin Identification
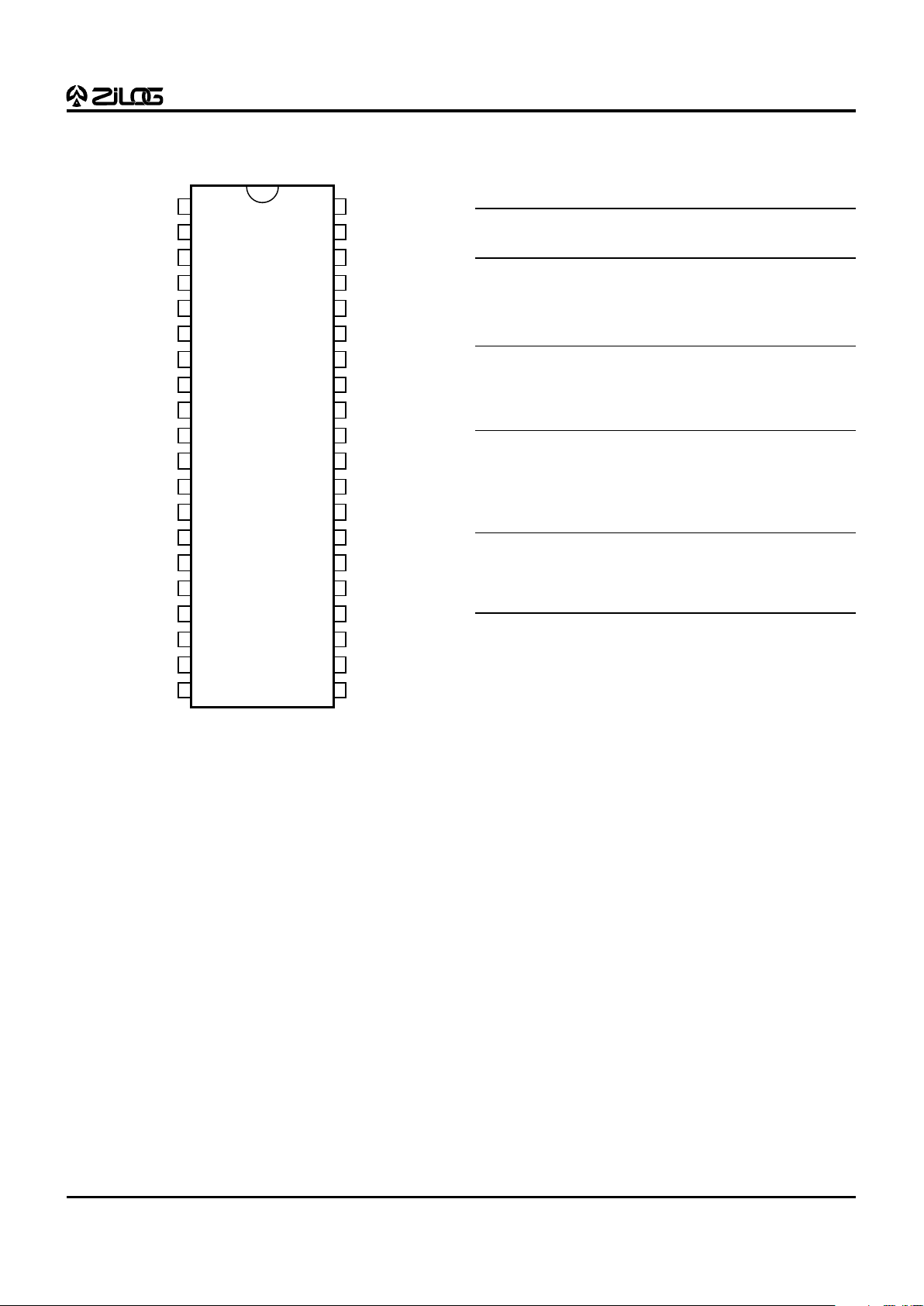
5
Z86E61/E63 Z8® MCU
WITH 16K/32K EPROM
PRELIMINARY
PIN DESCRIPTION
EPROM Mode
1
2
9
3
4
5
6
7
8
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
N/C
/OE
A9
/PGM
A14
A13
A12
A11
A10
VCC
XTAL2
N/C
/CE
/RESET
N/C
N/C
31
30
29
28
2714
10
11
12
13
XTAL1
GND
EPM
A0
A1
A8
VPP
N/C
D7
D6
Z86E61
/E63
DIP
15
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
16
17
18
19
N/C
N/C
A2
A3
A6
A7
A5
A4
D3
D5
D4
D2
D1
D0
Figure 4. 40-Pin DIP Pin Configuration
Table 3. 40-Pin DIP Pin Identification
EPROM Mode
Pin # Symbol Function Direction
1VCCPower Supply Input
2 XTAL2 Crystal, Osc. Clock Output
3 XTAL1 Crystal, Osc. Clock Input
4 N/C Not Connected Input
5 /CE Chip Enable Input
6 /RESET Reset Input
7-10 N/C Not Connected Input
11 GND Ground Input
12 EPM EPROM Prog Mode Input
13-20 A7-A0 Address 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7 Input
21-28 D7-D0 Data 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7 In/Output
29 N/C Not Connected Input
30 V
PP
Prog Voltage Input
31-37 A14-A8 Address 8,9,10,11,12,13,14 Input
38 /PGM Prog Mode Input
39 /OE Output Enable Input
40 N/C Not Connected Input
6
Z86E61/E63 Z8® MCU
WITH 16K/32K EPROM
PRELIMINARY
N/C
/CE
N/C
XTAL1
XTAL2
VCC
N/C
/OE
/PGM
A14
A13
A3A4A5A6A7D0D1D2D3
D4
N/C
N/C
A12
A11
A10
A9
A8
VPP
N/C
D7
D6
D5
/RESET
N/C
N/C
N/C
N/C
GND
EPM
A0
A1
A2
N/C
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
39
Z86E61/E63
PLCC
6 5 4 3 2 1 44 43 42 41 40
18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28
PIN DESCRIPTION (Continued)
EPROM Mode
EPROM Mode
Pin # Symbol Function Direction
1VCCPower Supply Input
2 XTAL2 Crystal, Osc. Clock Input
3 XTAL1 Crystal, Osc. Clock Input
4 N/C Not Connected Input
5 /CE Chip Enable Input
6 N/C Not Connected Input
7 /RESET Reset Input
8-11 N/C Not Connected Input
12 GND Ground Input
13 EPM EPROM Prog Mode Input
14-16 A0-A2 Address 0,1,2 Input
17 N/C Not Connected Input
EPROM Mode
Pin # Symbol Function Direction
18-22 A7-A3 Address 3,4,5,6,7 Input
23-27 D4-D0 Data 0,1,2,3,4 In/Output
28 N/C Not Connected Input
29-31 D7-D5 Data 5,6,7 In/Output
32 N/C Not Connected Input
33 V
PP
Prog Voltage Input
34-38 A12-A8 Address 8,9,10,11,12 Input
39 N/C Not Connected Input
40-41 A13-A14 Address 13, 14 Input
42 /PGM Prog Mode Input
43 /OE Output Enable Input
44 N/C Not Connected Input
Table 4. 44-Pin PLCC Pin Identification
Figure 5. 44-Pin PLCC Pin Configuration

7
Z86E61/E63 Z8® MCU
WITH 16K/32K EPROM
PRELIMINARY
PIN FUNCTIONS
ROMless (input, active Low). Connecting this pin to GND
disables the internal ROM and forces the device to function as a Z86C91 ROMless Z8 (see the Z86C91 product
specification for more information). When left unconnected
or pulled High to VCC, the device functions as a normal
Z86E61/E63 EPROM version. Note: This pin is only available on the 44-pin versions of the Z86E61/E63.
/DS (output, active Low). Data Strobe is activated once for
each external memory transfer. For a READ operation,
data must be available prior to the trailing edge of /DS. For
WRITE operations, the falling edge of /DS indicates that
output data is valid.
/AS (output, active Low). Address Strobe is pulsed once at
the beginning of each machine cycle. Address output is
through Port 1 for all external programs. Memory address
transfers are valid at the trailing edge of /AS. Under
program control, /AS can be placed in the highimpedance state along with Ports 0 and 1, Data Strobe,
and Read/Write.
XTAL2, XTAL1
Crystal 2, Crystal 1
(time-based input and
output, respectively). These pins connect a parallelresonant crystal, ceramic resonator, LC, or any external
single-phase clock to the on-chip oscillator and buffer.
R//W (output, write Low). The Read/Write signal is Low
when the MCU is writing to the external program or data
memory.
/RESET (input, active Low). To avoid asynchronous and
noisy reset problems, the Z86E61/E63 is equipped with a
reset filter of four external clocks (4TpC). If the external
/RESET signal is less than 4TpC in duration, no reset
occurs.
On the fifth clock after the /RESET is detected, an internal
RST signal is latched and held for an internal register count
of 18 external clocks, or for the duration of the external
/RESET, whichever is longer. During the reset cycle, /DS is
held active Low while /AS cycles at a rate of TpC/2. When
/RESET is deactivated, program execution begins at location 000C (HEX). Power-up reset time must be held low for
50 ms, or until VCC is stable, whichever is longer.
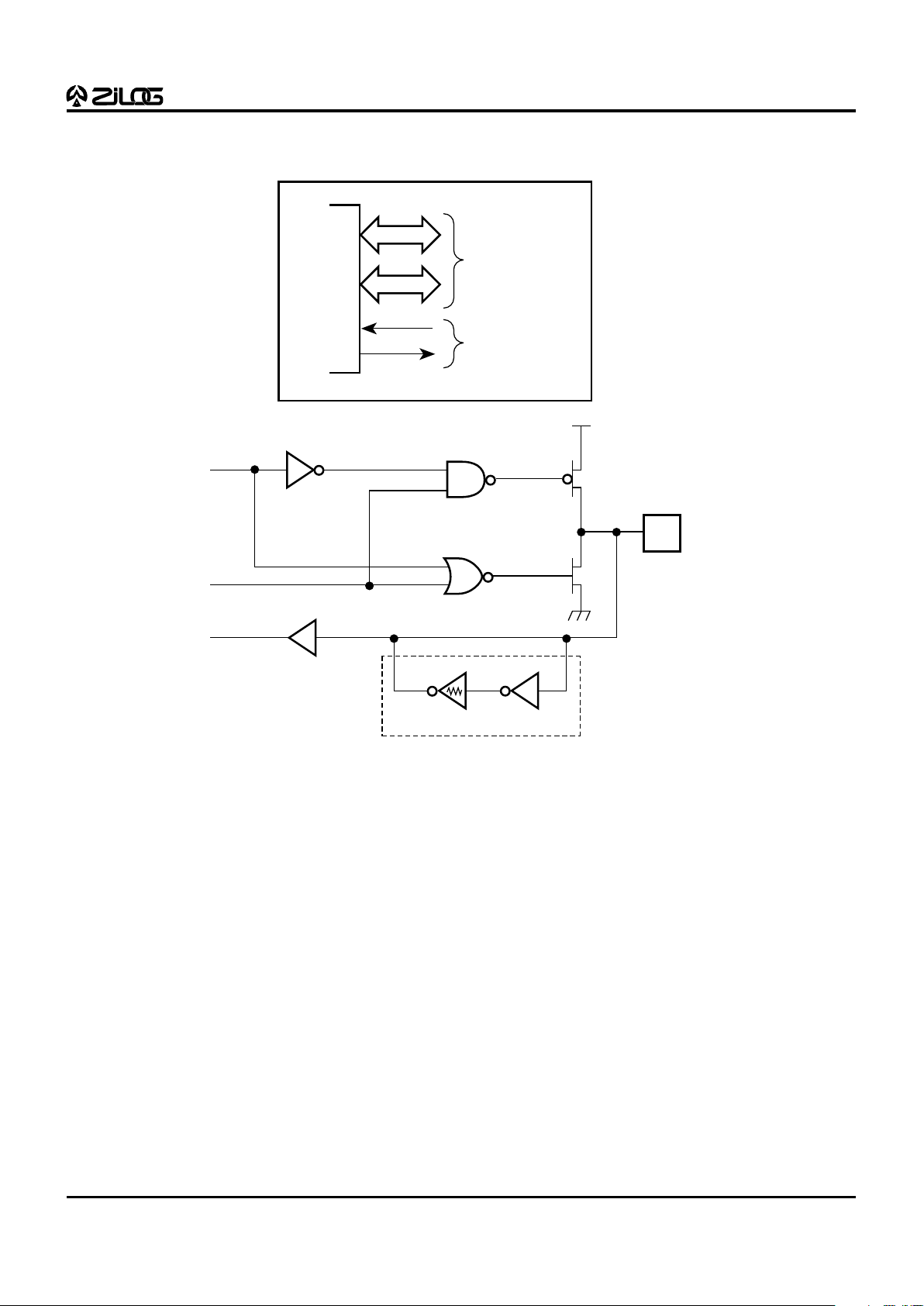
Port 0 (P07-P00). Port 0 is an 8-bit, nibble programmable,
bidirectional, TTL compatible port. These eight I/O lines
can be configured under software control as a nibble I/O
port, or as an address port for interfacing external memory.
When used as an I/O port, Port 0 may be placed under
handshake control. In this configuration, Port 3, lines P32
and P35 are used as the handshake control /DAV0 and
RDY0 (Data Available and Ready). Handshake signal
assignment is dictated by the I/O direction of the upper
nibble P07-P04. The lower nibble must have the same
direction as the upper nibble to be under handshake
control.
For external memory references, Port 0 can provide address bits A11-A8 (lower nibble) or A15-A8 (lower and
upper nibbles) depending on the required address space.
If the address range requires 12 bits or less, the upper
nibble of Port 0 can be programmed independently as I/O
while the lower nibble is used for addressing. If one or both
nibbles are needed for I/O operation, they must be configured by writing to the Port 0 Mode register.
In ROMless mode, after a hardware reset, Port 0 lines are
defined as address lines A15-A8, and extended timing is
set to accommodate slow memory access. The initialization routine can include reconfiguration to eliminate this
extended timing mode (Figure 8).
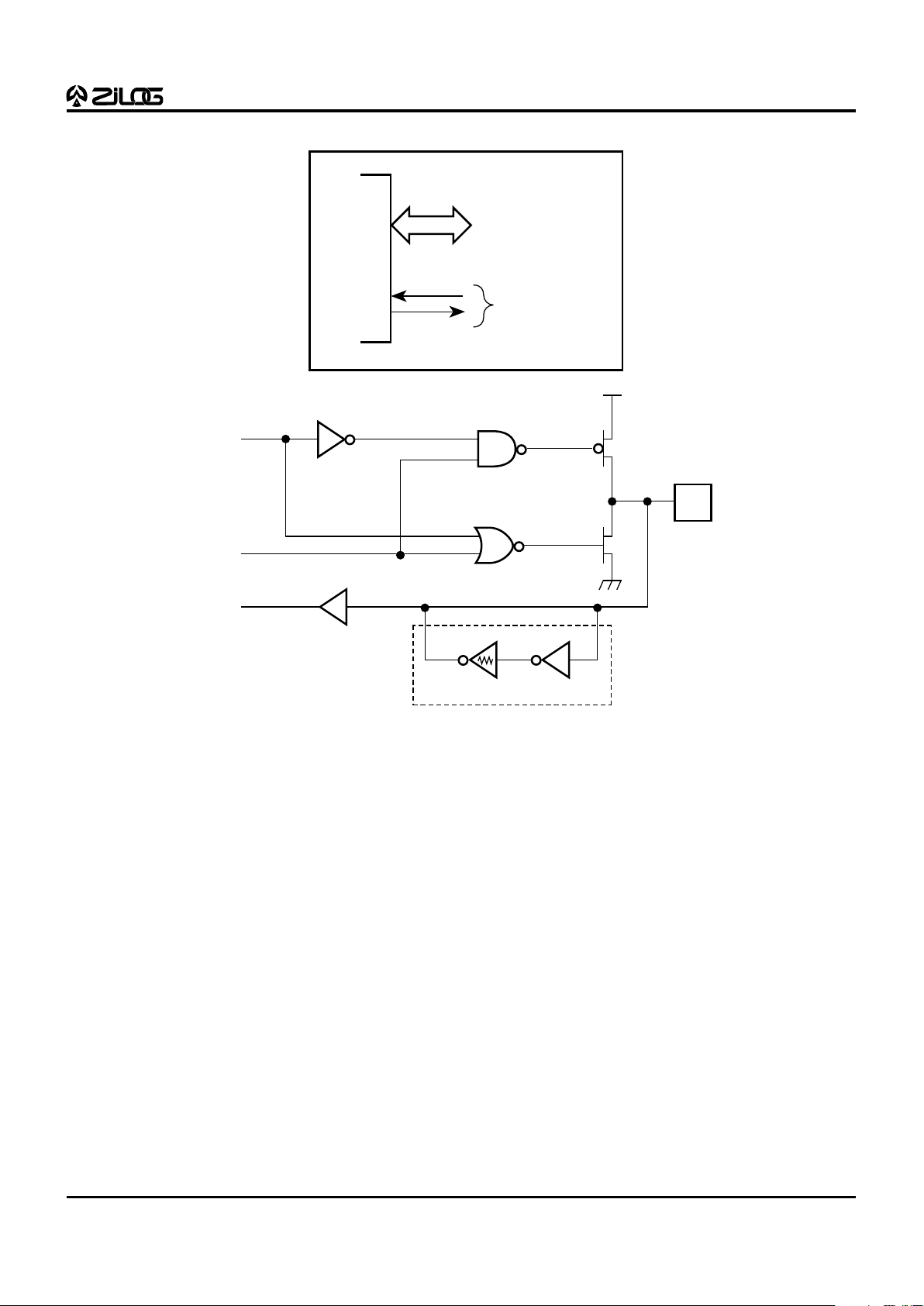
Port 1 (P17-P10). Port 1 is an 8-bit, byte programmable,
bidirectional, TTL compatible port. It has multiplexed Address (A7-A0) and Data (D7-D0) ports. For Z86E61/E63,
these eight I/O lines can be programmed as input or output
lines or are configured under software control as an
address/data port for interfacing external memory. When
used as an I/O port, Port 1 can be placed under handshake
control. In this configuration, Port 3 lines, P33 and P34, are
used as the handshake controls RDY1 and /DAV1.
Memory locations greater than 16384 (E61) or 32768 (E63)
are referenced through Port 1. To interface external memory,
Port 1 must be programmed for the multiplexed Address/
Data mode. If more than 256 external locations are required, Port 0 must output the additional lines.
Port 1 can be placed in high-impedance state along with
Port 0, /AS, /DS, and R//W, allowing the MCU to share
common resources in multiprocessor and DMA applications. Data transfers are controlled by assigning P33 as a
Bus Acknowledge input, and P34 as a Bus Request output
(Figure 9).
8
Z86E61/E63 Z8® MCU
WITH 16K/32K EPROM
PRELIMINARY
PIN FUNCTIONS (Continued)
Figure 6. Port 0 Configuration
OEN
Out
In
PAD
Port 0 (I/O)
Handshake Controls
/DAV0 and RDY0
(P32 and P35)
Z86E61
/E63
MCU
4
TTL Level Shifter
Auto Latch
R ≈ 500 kΩ
4
9
Z86E61/E63 Z8® MCU
WITH 16K/32K EPROM
PRELIMINARY
OEN
Out
In
PAD
Port 1
(AD7-AD0)
Z86E61
/E63
MCU
TTL Level Shifter
Auto Latch
R ≈ 500 kΩ
8
Handshake Controls
/DAV1 and RDY1
(P33 and P34)
Figure 7. Port 1 Configuration
10
Z86E61/E63 Z8® MCU
WITH 16K/32K EPROM
PRELIMINARY
PIN FUNCTIONS (Continued)
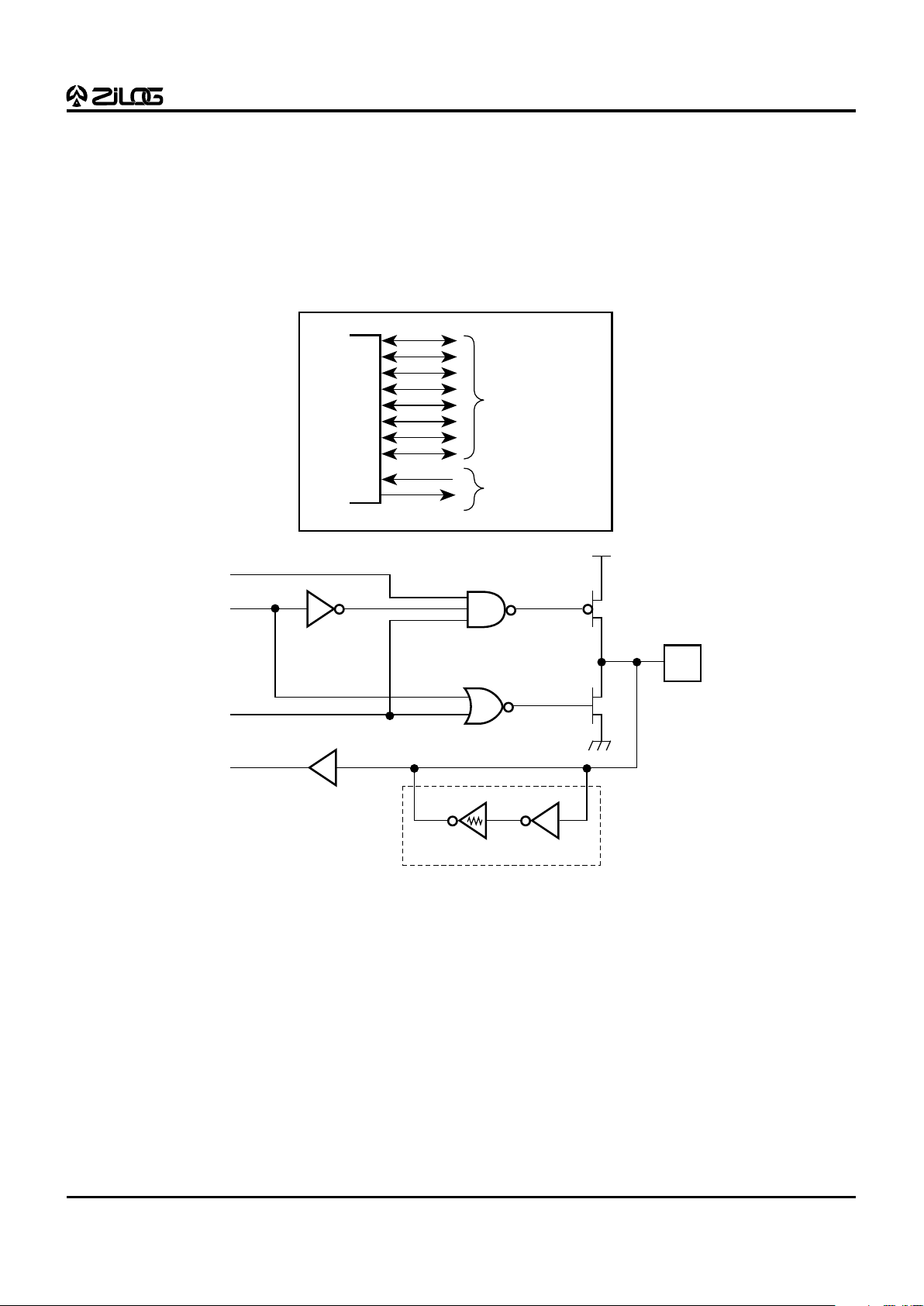
Port 2 (P27-P20). Port 2 is an 8-bit, bit programmable, bi-
directional, CMOS compatible port. Each of these eight
I/O lines can be independently programmed as an input or
output, or globally as an open-drain output. Port 2 is always
available for I/O operation. When used as an I/O port,
Port 2 can be placed under handshake control. In this
configuration, Port 3 lines P31 and P36 are used as the
handshake control lines /DAV2 and RDY2. The handshake
signal assignment for Port 3 lines, P31 and P36, is dictated
by the direction (input or output) assigned to P27
(Figure 8 and Table 5).
OEN
Out
In
PAD
Port 2 (I/O)
Handshake Controls
/DAV2 and RDY2
(P31 and P36)
Z86E61
/E63
MCU
TTL Level Shifter
Auto Latch
R ≈ 500 kΩ
Open-Drain
Figure 8. Port 2 Configuration

11
Z86E61/E63 Z8® MCU
WITH 16K/32K EPROM
PRELIMINARY
Port 3 (P37-P30). Port 3 is an 8-bit, CMOS compatible four-
fixed input and four-fixed output port. These eight I/O lines
have four-fixed (P33-P30) input and four-fixed (P37-P34)
output ports. Port 3, when used as serial I/O, is programmed as serial in and serial out, respectively
(Figure 9).
Z86E61
/E63
MCU
Port 3
(I/O or Control)
Figure 9. Port 3 Configuration
Port 3 is configured under software control to provide the
following control functions: handshake for Ports 0 and 2
(/DAV and RDY); four external interrupt request signals
(IRQ3-IRQ0); timer input and output signals (TIN and T
OUT
),
Data Memory Select (/DM) and EPROM control signals
(P30 = /CE, P31 = /OE, P32 = EPM and P33 = VPP).
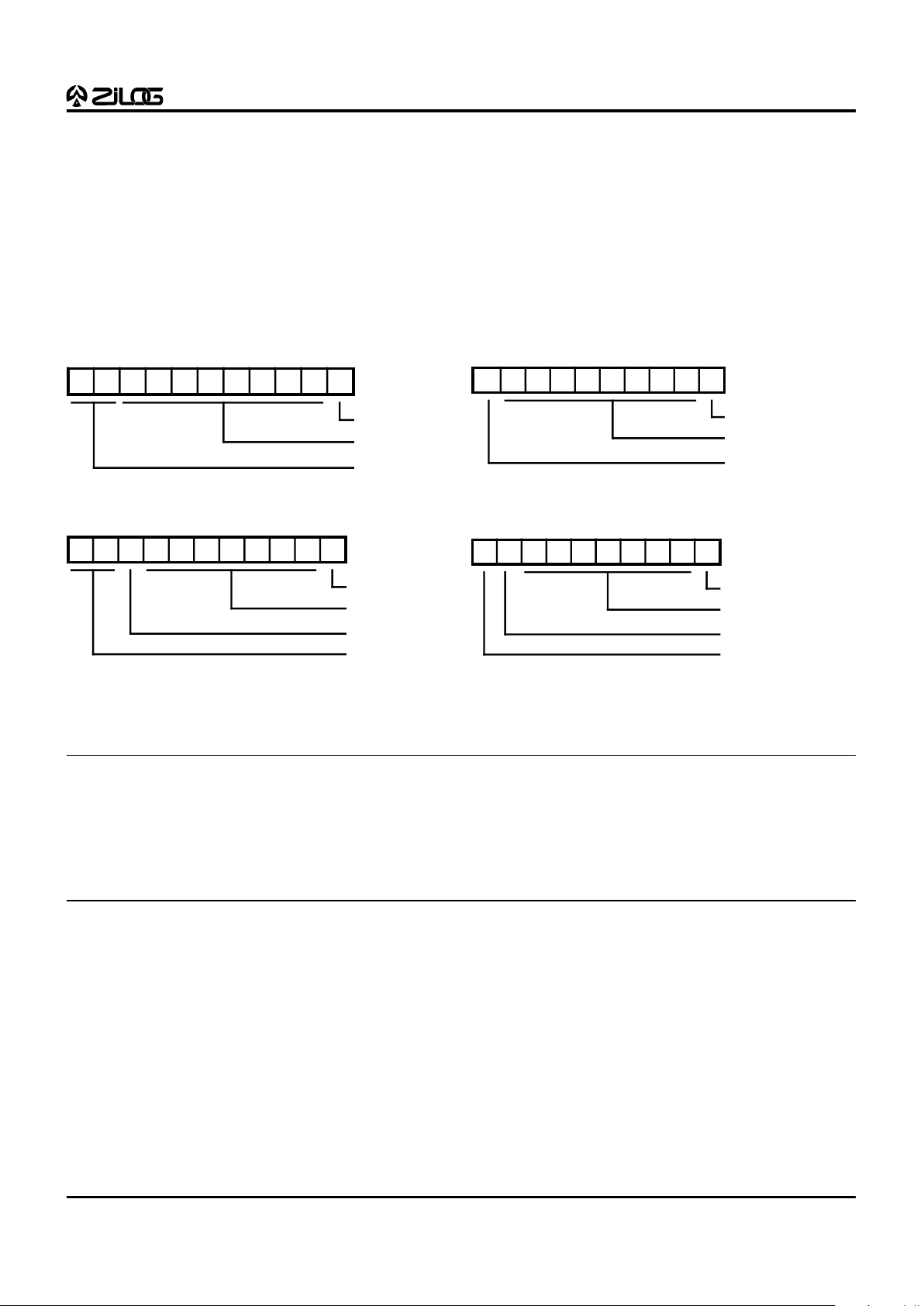
Table 5. Port 3 Pin Assignments
Pin I/O CTC1 Int. P0 HS P1 HS P2 HS UART Ext EPROM
P30 IN IRQ3 Serial In /CE
P31 IN T
IN
IRQ2 D/R /OE
P32 IN IRQ0 D/R EPM
P33 IN IRQ1 D/R V
PP
P34 OUT R/D DM
P35 OUT R/D
P36 OUT T
OUT
R/D
P37 OUT Serial Out
T0 IRQ4
T1 IRQ5
Notes:
HS = Handshake Signals
D = Data Available
R = Ready
12
Z86E61/E63 Z8® MCU
WITH 16K/32K EPROM
PRELIMINARY
UART OPERATION
Port 3 lines, P37 and P30, are programmed as serial I/O
lines for full-duplex serial asynchronous receiver/transmitter operation. The bit rate is controlled by Counter/
Timer0.
The Z86E61/E63 automatically adds a start bit and two
stop bits to transmitted data (Figure 10). Odd parity is also
available as an option. Eight data bits are always transmit-
ted, regardless of parity selection. If parity is enabled, the
eighth bit is the odd parity bit. An interrupt request (IRQ4)
is generated on all transmitted characters.
Received data must have a start bit, eight data bits, and at
least one stop bit. If parity is on, bit 7 of the received data
is replaced by a parity error flag. Received characters
generate the IRQ3 interrupt request.
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
Start Bit
Eight Data Bits
Transmitted Data (No Parity)
Two Stop Bits
SP SP ST
P D6D5D4D3D2D1D0
Start Bit
Seven Data Bits
Transmitted Data (With Parity)
Odd Parity
Two Stop Bits
SP SP ST
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
Start Bit
Eight Data Bits
Received Data (No Parity)
One Stop Bit
SP ST
PD6D5D4D3D2D1D0
Start Bit
Seven Data Bits
Received Data (With Parity)
Parity Error Flag
One Stop Bit
STSP
Figure 10. Serial Data Formats
Auto Latch. The Auto Latch puts valid CMOS levels on all
CMOS inputs that are not externally driven. This reduces
excessive supply current flow in the input buffer when it is
not driven by any source.
Note: P33-P30 inputs differ from the Z86C61/C63 in that
there is no clamping diode to VCC because of the EPROM
high voltage detection circuits. Exceeding the VIH maximum specification during standard operating mode may
cause the device to enter EPROM mode
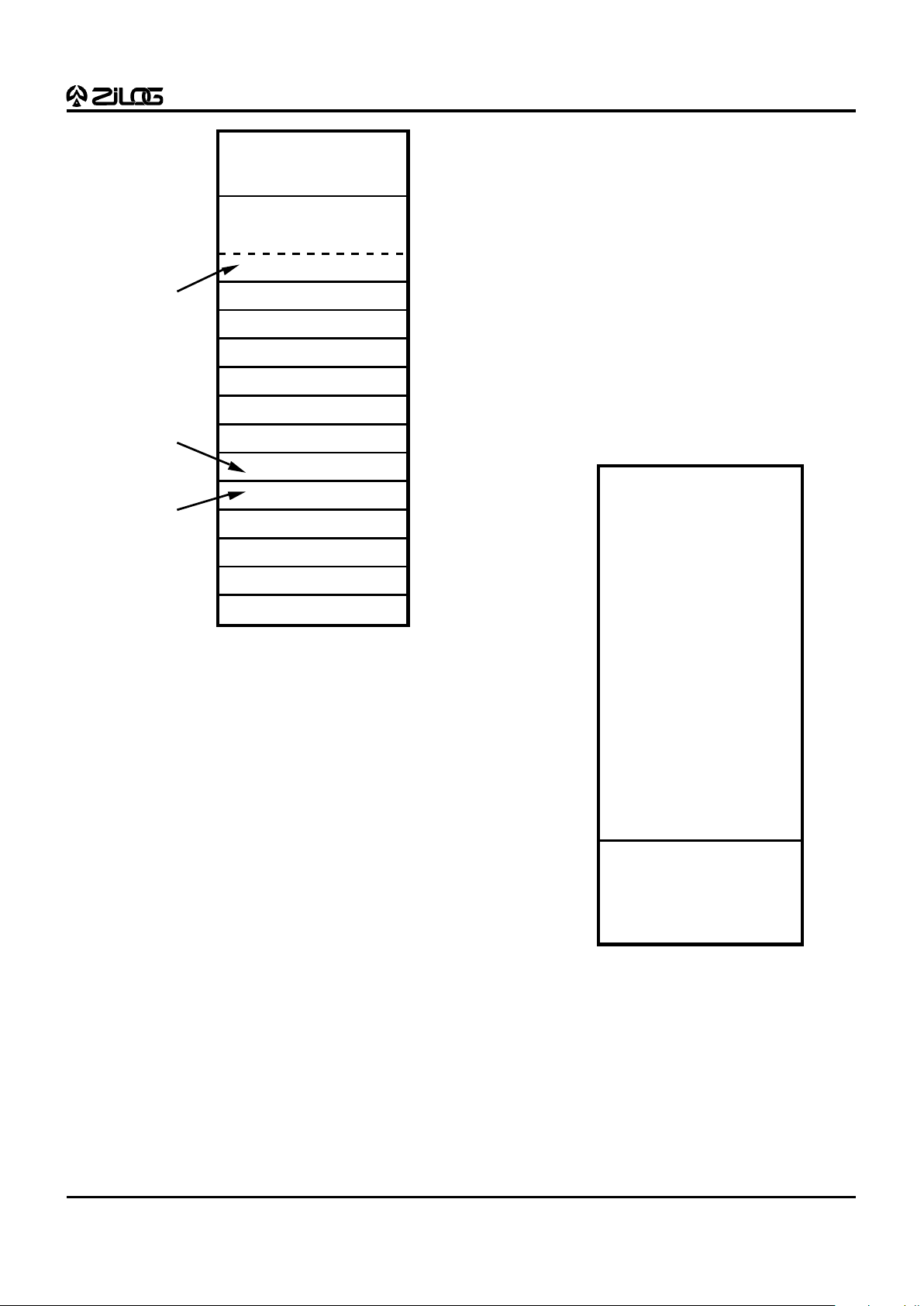
ADDRESS SPACE
Program Memory. The Z86E61/E63 can address 48
Kbytes (E61) or 32 Kbytes (E63) of external program
memory (Figure 11). The first 12 bytes of program memory
are reserved for the interrupt vectors. These locations
contain six 16-bit vectors that correspond to the six
available interrupts. For EPROM mode, byte 13 to byte
16383 (E61) or 32767 (E63) consists of on-chip EPROM. At
addresses 16384 (E61) or 32768 (E63) and above, the
Z86E61/E63 executes external program memory fetches.
In ROMless mode, the Z86E61/E63 can address up to 64
Kbytes of program memory. Program execution begins at
external location 000C (HEX) after a reset.
13
Z86E61/E63 Z8® MCU
WITH 16K/32K EPROM
PRELIMINARY
access registers directly or indirectly through an 8-bit
address field. The Z86E61/E63 also allows short 4-bit
register addressing using the Register Pointer (Figure 14).
In the 4-bit mode, the Register File is divided into 16
working register groups, each occupying 16 continuous
locations. The Register Pointer addresses the starting
location of the active working register group.
Stack. The Z86E61/E63 has a 16-bit Stack Pointer (R255-
R254) used for external stacks that reside anywhere in the
data memory for the ROMless mode, but only from 16384
(E61) or 32768 (E63) to 65535 in the EPROM mode. An
8-bit Stack Pointer (R255) is used for the internal stack that
resides within the 236 general-purpose registers (R239R4). The high byte of the Stack Pointer (SPH Bits 15-8) can
be use as a general purpose register when using internal
stack only.
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
External
ROM and RAM
Location of
First Byte of
Instruction
Executed
After RESET
Interrupt
Vector
(Lower Byte)
Interrupt
Vector
(Upper Byte)
IRQ5
IRQ4
IRQ4
IRQ3
IRQ3
IRQ2
IRQ2
IRQ1
IRQ1
IRQ0
IRQ0
IRQ5
65535
On-Chip PROM
16384 (E61)
32768 (E63)
16383 (E61)
32767 (E63)
Figure 11. Program Memory Configuration
Data Memory (/DM). The EPROM version can address up
to 48 Kbytes (E61) or 32 Kbytes (E63) of external data
memory space beginning at location 16384 (E61) or 32768
(E63). The ROMless version can address up to 64 Kbytes
of external data memory. External data memory may be
included with, or separated from, the external program
memory space. /DM, an optional I/O function that can be
programmed to appear on pin P34, is used to distinguish
between data and program memory space (Figure 12).
The state of the /DM signal is controlled by the type
instruction being executed. An LDC opcode references
PROGRAM (/DM inactive) memory, and an LDE instruction
references DATA (/DM active Low) memory.
Register File. The register file consists of four I/O port
registers, 236 general-purpose registers, and 16 control
and status registers (Figure 13). The instructions can
65535
16383 (E61)
32767 (E63)
0
External
Data
Memory
Not Addressable
32768 (E63)
16384 (E61)
Figure 12. Data Memory Configuration
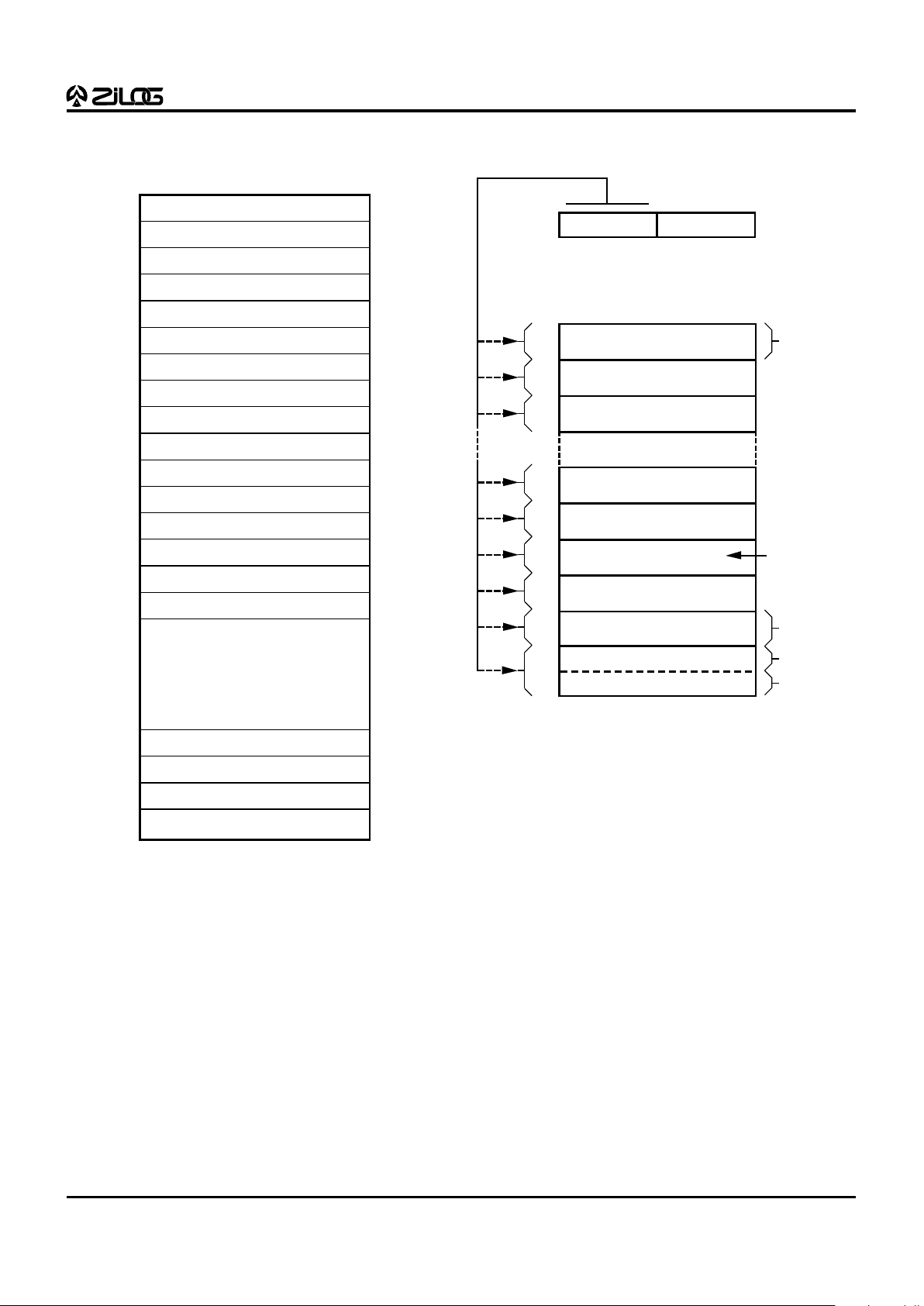
14
Z86E61/E63 Z8® MCU
WITH 16K/32K EPROM
PRELIMINARY
ADDRESS SPACE (Continued)
Stack Pointer (Bits 7-0)
R255
Stack Pointer (Bits 15-8)
Register Pointer
Program Control Flags
Interrupt Mask Register
Interrupt Request Register
Interrupt Priority Register
Ports 0-1 Mode
Port 3 Mode
Port 2 Mode
T0 Prescaler
Timer/Counter0
T1 Prescaler
Timer/Counter1
Timer Mode
Serial I/O
General-Purpose
Registers
Port 3
Port 2
Port 1
Port 0
R254
R253
R252
R251
R250
R249
R248
R247
R246
R245
R244
R243
R242
R241
R240
R239
R3
R2
R1
R0
SPL
SPH
RP
FLAGS
IMR
IRQ
IPR
P01M
P3M
P2M
PRE0
T0
PRE1
T1
TMR
SIO
P3
P2
P1
P0
R4
LOCATION IDENTIFIERS
The upper nibble of the register file address
provided by the register pointer specifies
the active working-register group.
r7 r6 r5 r4 R253
(Register Pointer)
I/O Ports
Specified Working
Register Group
The lower nibble
of the register
file address
provided by the
instruction points
to the specified
register.
r3 r2 r1 r0
Register Group 1
Register Group 0
R15 to R0
Register Group F
R15 to R4
R3 to R0
R15 to R0
•
•
•
•
•
FF
F0
0F
00
1F
10
2F
20
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Figure 14. Register Pointer
Figure 13. Register File

15
Z86E61/E63 Z8® MCU
WITH 16K/32K EPROM
PRELIMINARY
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
Counter/Timers. There are two 8-bit programmable
counter/timers (T0-T1), each driven by its own 6-bit programmable prescaler. The T1 prescaler is driven by internal or external clock sources; however, the T0 prescaler is
driven by the internal clock only (Figure 15).
The 6-bit prescalers can divide the input frequency of the
clock source by any integer number from 1 to 64. Each
prescaler drives its counter, which decrements the value
(1 to 256) that has been loaded into the counter. When both
the counters and prescalers reach the end of the count,
a timer interrupt request, IRQ4 (T0) or IRQ5 (T1), is
generated.
The counter is programmed to start, stop, restart to continue, or restart from the initial value. The counters can also
be programmed to stop upon reaching zero (single pass
mode) or to automatically reload the initial value and
continue counting (modulo-n continuous mode).
The counter, but not the prescalers, are read at any time
without disturbing their value or count mode. The clock
source for T1 is user-definable and is either the internal
microprocessor clock divided-by-four, or an external signal input through Port 3. The Timer Mode register configures the external timer input (P31) as an external clock, a
trigger input that can be retriggerable or non-retriggerable,
or as a gate input for the internal clock. Port 3 line P36 also
serves as a timer output (T
OUT
) through which T0, T1, or the
internal clock can be output. The counter/timers are cascaded by connecting the T0 output to the input of T1.
Figure 15. Counter/Timers Block Diagram
OSC PRE0
Initial Value
Register
T0
Initial Value
Register
T0
Current Value
Register
6-Bit
Down
Counter
8-bit
Down
Counter
÷4
6-Bit
Down
Counter
8-Bit
Down
Counter
PRE1
Initial Value
Register
T1
Initial Value
Register
T1
Current Value
Register
÷ 2
Clock
Logic
IRQ4
IRQ5
Internal Data Bus
Write Write Read
Internal Clock
Gated Clock
Triggered Clock
Tin P31
Write Write Read
Internal Data Bus
External Clock
Internal
Clock
÷4
÷ 2
Serial I/O
Clock
TOUT
P36

16
Z86E61/E63 Z8® MCU
WITH 16K/32K EPROM
PRELIMINARY
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION (Continued)
Interrupts. The Z86E61/E63 has six different interrupts
from eight different sources. The interrupts are maskable
and prioritized. The eight sources are divided as follows:
four sources are claimed by Port 3 lines P33-P30, one in
Serial Out, one in Serial In, and two in the counter/timers
(Figure 16). The Interrupt Mask Register globally or individually enables or disables the six interrupt requests.
When more than one interrupt is pending, priorities are
resolved by a programmable priority encoder that is controlled by the Interrupt Priority register (refer to Table 5).
All Z86E61/E63 interrupts are vectored through locations
in the program memory. When an interrupt machine cycle
is activated, an interrupt request is granted. Thus, this
disables all of the subsequent interrupts, saves the Program Counter and Status Flags, and then branches to the
program memory vector location reserved for that interrupt. This memory location and the next byte contain the
16-bit address of the interrupt service routine for that
particular interrupt request.
To accommodate polled interrupt systems, interrupt inputs are masked and the Interrupt Request register is
polled to determine which of the interrupt requests need
service. Software initialized interrupts are supported by
setting the appropriate bit in the Interrupt Request Register (IRQ).
Internal interrupt requests are sampled on the falling edge
of the last cycle of every instruction, and the interrupt
request must be valid 5TpC before the falling edge of the
last clock cycle of the currently executing instruction.
For the ROMless mode, when the device samples a valid
interrupt request, the next 48 (external) clock cycles are
used to prioritize the interrupt, and push the two PC bytes
and the FLAG register on the stack. The following nine
cycles are used to fetch the interrupt vector from external
memory. The first byte of the interrupt service routine is
fetched beginning on the 58th TpC cycle following the
internal sample point, which corresponds to the 63rd TpC
cycle following the external interrupt sample point.
IRQ
IMR
IPR
PRIORITY
LOGIC
6
Global
Interrupt
Enable
Vector Select
Interrupt
Request
IRQ0 - IRQ5
Figure 16. Interrupt Block Diagram

17
Z86E61/E63 Z8® MCU
WITH 16K/32K EPROM
PRELIMINARY
Clock. The Z86E61/E63 on-chip oscillator has a high
gain, parallel resonant amplifier for connection to a crystal,
LC, ceramic resonator, or any suitable external clock
source (XTAL1 = Input, XTAL2 = Output). The crystal
should be AT cut, 1 MHz to 16 MHz max; series resistance
(RS) is less than or equal to 100 Ohms. The crystal should
be connected across XTAL1 and XTAL2 using the recommended capacitors (10 pF < CL < 100 pF) from each pin
to ground (Figure 17). Note: Actual capacitor value specified by crystal manufacturer.
XTAL1
XTAL2
C1
C2
C1
C2
XTAL1
XTAL2
XTAL1
XTAL2
Ceramic Resonator
or Crystal
LC Clock
External Clock
L
Pin 11
Pin 11
Pin 11
Pin 11
Figure 17. Oscillator Configuration
Z86E61/E63 User Modes
The Z86E61/E63 uses separate AC timing cycles for the
different User Modes available. Table 6 shows the Z86E61/
E63 User Modes. Table 7 shows the timing of the programming waveforms.
User MODE 1 EPROM Read
The Z86E61/E63 EPROM read cycle is provided so that the
user may read the Z86E61/E63 as a standard 27128 (E61)
or 27256 (E63) EPROM. This is accomplished by driving
the /EPM pin (P32) to VH and activating /CE and /OE. /PGM
remains inactive. This mode is not valid after execution of
an EPROM protect cycle. Timing for the EPROM read cycle
is shown in Figure 18.
PROGRAMMING
HALT. Turns off the internal CPU clock but not the XTAL
oscillation. The counter/timers and external interrupts IRQ0,
IRQ1, IRQ2, and IRQ3 remain active. The devices are
recovered by interrupts, either externally or internally generated. An interrupt request must be executed (enabled)
to exit HALT mode. After the interrupt service routine, the
program continues from the instruction after the HALT.
STOP. This instruction turns off the internal clock and
external crystal oscillation, and reduces the standby current to 5 µA (typical) or less. The STOP mode is terminated
by a reset, which causes the processor to restart the
application program at address 000C (HEX).
In order to enter STOP (or HALT) mode, it is necessary to
first flush the instruction pipeline to avoid suspending
execution in mid-instruction. To do this, the user must
execute a NOP (opcode = OFFH) immediately before the
appropriate SLEEP instruction. i.e.,
FF NOP ; clear the pipeline
6F STOP ; enter STOP mode
or
FF NOP ; clear the pipeline
7F HALT ; enter HALT mode
User MODE 2 EPROM Program
The Z86E61/E63 Program function conforms to the Intelligent programming algorithm. The device is programmed
with VCC at 6.0V and VPP = 12.5V. Programming pulses are
applied in 1 ms increments to a maximum of 25 pulses
before proper verification. After verification, a programming pulse of three times the duration of the cycles
necessary to program the device is issued to ensure
proper programming. After all addresses are programmed,
a final data comparison is executed and the programming
cycle is complete. Timing for the Z86E61/E63 programming cycle is shown in Figure 18.

18
Z86E61/E63 Z8® MCU
WITH 16K/32K EPROM
PRELIMINARY
PROGRAMMING (Continued)
User Mode 3: PROM Verify
The Program Verify cycle is used as part of the intelligent
programming algorithm to insure data integrity under
worst-case conditions. It differs from the EPROM Read
cycle in that VPP is active and VCC must be driven to 6.0V.
Timing is shown in Figure 18.
User Modes 4 and 5: EPROM and RAM Protect
To extend program security, EPROM and RAM protect
cycles are provided for the Z86E61/E63. Execution of the
EPROM protect cycle prohibits proper execution of the
EPROM Read, EPROM Verify, and EPROM programming
cycles. Execution of the RAM protect cycle disables accesses to the upper 128 bytes of register memory (excluding mode and configuration registers), but first the user’s
program must set bit 6 of the IMR (R251). Timing is shown
in Figures 20 and 21.
User Modes. Table 6 shows the programming voltage of
each mode of the Z86E61/E63.
Table 6. OTP Programming Table
User/Test Mode Device Pins Port 1
Device Pin No. P33 P32 P30 P31 P20 CNFG
User Modes V
PP
EPM /CE /OE /PGM ADDR V
CC
Data
EPROM Read V
IH
V
H
V
IL
V
IL
V
IH
Addr 5.0V Out
Program V
PP
XVILV
IH
V
IL
Addr 6.0V In
Program Verify V
PP
XVILV
IL
V
IH
Addr 6.0V Out
EPROM Protect V
PP
V
H
V
H
V
IH
V
IL
XX 6.0V XX
RAM Protect V
PP
XV
H
VIHV
IL
XX 6.0V XX
Notes:
VPP= 12.0V ±0.5V
VH= 12.0V ±0.5V
VIH=5V
VIL=0V
XX = Irrelevant
IPP during programming = 40 mA maximum.
ICC during programming, verify, or read = 40 mA maximum.
Z86E63 Signal Description for EPROM
Program/Read
The following signals are required to correctly program or
read the Z86E63 device.
ADDR. The address must remain stable throughout the
program read cycle.
DATA. The I/O data bus must be stable during programming (/OE High, /PGM Low, VPP High). During read the data
bus outputs data.
XCLK. A clock is required to clock the /RESET signal into
the registers before programming.
A constant clock can be applied, or the XCLK input can be
toggled a minimum of 12 cycles before any programming
or verify function begins. The maximum clock frequency to
be applied when in the EPROM mode is 12 MHz.
/RESET. The reset input can be held to a constant Low or
High value throughout normal programming. It must be
held High to program the EPROM protect option bit. Also,
any time the /RESET input changes state the XCLK must be
clocked a minimum of 12 times to clock the /RESET
through the reset filter.
/OE. When the device is placed in EPROM mode, the /OE
input also serves as the precharge for the sense amp. The
precharge signal should be Low for the first half of the
stable address and High for the second half. The PRECHG
signal is inverted from the /OE signal so the /OE should be
High on the first half and Low on the second half, or stable
address. The EPROM output data should be sampled
during the second half of stable address.
The access time of the EPROM is defined in later sections.
This two part calculation of access time is required because this is a precharged sense amp with a precharge
clock.

19
Z86E61/E63 Z8® MCU
WITH 16K/32K EPROM
PRELIMINARY
Table 7. Timing of Programming Waveforms
Parameters Name Min Max Units
1 Address Setup Time 2 µs
2 Data Setup Time 2 µs
3V
PP
Setup 2 µs
4V
CC
Setup Time 2 µs
5 Chip Enable Setup Time 2 µs
6 Program Pulse Width 0.95 ms
7 Data Hold Time 2 µs
8 /OE Setup Time 2 µs
9 Data Access Time 200 ns
10 Data Output Float Time 100 ns
11 Overprogram Pulse Width 2.85 ms
12 EPM Setup Time 2 µs
13 /PGM Setup Time 2 µs
14 Address to /OE Setup Time 2 µs
15 Option Program Pulse Width 78 ms
Figure 18. EPROM Read
Data
VIH
VIL
Invalid Valid Invalid Valid
VIH
VIL
Address Stable
Address
Address Stable
0 Min
9
12
0 Min
EPM
VH
VIL
VCC
4.5V
/CE
VIH
VIL
/OE
VIH
VIL
VPP
VH
VIL
5.5V
/PGM
VIH
VIL
3
16
16

20
Z86E61/E63 Z8® MCU
WITH 16K/32K EPROM
PRELIMINARY
PROGRAMMING (Continued)
Figure 19. EPROM Program and Verify
Address
V
IH
VIL
Address Stable
Data
V
IH
VIL
Data Stable Data Out Valid
1
2 109
3
VPP
VH
VIH
EPM
VIL
4
5
7
/CE
VIL
6 8
11
/PGM
V
IH
VIL
VIH
VH
VCC
4.5V
6V
/OE
V
IH
VIL
Program Cycle Verify Cycle
16

21
Z86E61/E63 Z8® MCU
WITH 16K/32K EPROM
PRELIMINARY
Address
V
IH
V
IL
Data
V
IH
V
IL
V
PP
V
IH
V
CC
6V
/OE
/PGM
V
IH
V
IL
3
4
5
12
1515
12
EPM
V
H
V
IL
/CE
ROM Protect
Programming
RAM Protect
Programming
V
H
V
IH
Address 003
4.5V
V
H
V
IH
14
V
H
V
IH
V
IH
Figure 20. Programming EPROM, RAM Protect and 4K Size Selection

22
Z86E61/E63 Z8® MCU
WITH 16K/32K EPROM
PRELIMINARY
PROGRAMMING (Continued)
Address
V
IH
V
IL
Data
V
IH
V
IL
V
PP
V
IH
V
CC
6V
/OE
/PGM
V
IH
V
IL
3
4
5
12
1515
12
EPM
V
H
V
IL
/CE
ROM Protect
Programming
RAM Protect
Programming
V
H
V
IH
Address 008
4.5V
V
H
V
IH
14
V
H
V
IH
V
IH
Figure 21. Programming EPROM, RAM Protect and 16K Size Selection

23
Z86E61/E63 Z8® MCU
WITH 16K/32K EPROM
PRELIMINARY
Start
Vcc = 6.0V
Vpp = 12.5V
N = 0
Program
1 ms Pulse
Increment N
N = 25 ?
Yes
No
Verify
One Byte
Pass
Fail
Prog. One Pulse
3xN ms Duration
Verify Byte
Fail
Pass
Increment
Address
Last Addr ?
Yes
No
Vcc = Vpp = 4.5V
Verify All
Bytes
Device Failed
Addr =
First Location
Fail
Pass
Vcc = Vpp = 5.5V
Verify All
Bytes
Device Passed
Pass
Fail
Figure 22. Intelligent Programming Flowchart

24
Z86E61/E63 Z8® MCU
WITH 16K/32K EPROM
PRELIMINARY
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Symbol Description Min Max Units
V
CC
Supply Voltage* –0.3 + 7.0° V
T
STG
Storage Temp –65° +150° C
T
A
Oper Ambient Temp † C
Stresses greater than those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress rating only; operation of the device at
any condition above those indicated in the operational
sections of these specifications is not implied. Exposure to
absolute maximum rating conditions for an extended period may affect device reliability.
Notes:
* Voltages on all pins with respect to GND.
† See Ordering Information
STANDARD TEST CONDITIONS
The characteristics listed below apply for standard test
conditions as noted. All voltages are referenced to GND.
Positive current flows into the referenced pin (Figure 23).
From Output
Under Test
I
150 pF
Figure 23. Test Load Diagram

25
Z86E61/E63 Z8® MCU
WITH 16K/32K EPROM
PRELIMINARY
DC CHARACTERISTICS
TA = 0°C to +70°C Typical
Sym Parameter Min Max @ 25°C Units Conditions
Max Input Voltage 7 V IIN 250 µA
Max Input Voltage 13 V P33-P30 Only
V
CH
Clock Input High Voltage 3.8 VCC+ 0.3 V Driven by External Clock Generator
V
CL
Clock Input Low Voltage –0.3 0.8 V Driven by External Clock Generator
V
IH
Input High Voltage 2.0 VCC+ 0.3 V
V
IL
Input Low Voltage –0.3 0.8 V
V
OH
Output High Voltage 2.4 V IOH = –2.0 mA
V
OL
Output Low Voltage 0.4 V IOL = +2.0 mA
V
RH
Reset Input High Voltage 3.8 VCC+ 0.3 V
V
Rl
Reset Input Low Voltage –0.3 0.8 V
I
IL
Input Leakage –10 10 µA 0V VIN + 5.25V
I
OL
Output Leakage –10 10 µA 0V VIN + 5.25V
I
IR
Reset Input Current –50 µAVCC= + 5.25V, VRL = 0V
I
CC
Supply Current 50 25 mA @ 16 MHz
60 35 mA @ 20 MHz
I
CC1
Standby Current 15 5 mA HALT Mode VIN = 0V, V
CC
@ 16 MHz
20 10 mA HALT Mode VIN = 0V, V
CC
@ 20 MHz
I
CC2
Standby Current 20 5 µA STOP Mode VIN = 0V, V
CC
@ 16 MHz
20 5 µA STOP Mode VIN = 0V, V
CC
@ 20 MHz
Notes:
I
CC2
requires loading TMR (%F1H) with any value prior to STOP execution.
Use this sequence:
LD TMR,#00
NOP
STOP

26
Z86E61/E63 Z8® MCU
WITH 16K/32K EPROM
PRELIMINARY
AC CHARACTERISTICS
External I/O or Memory Read or Write Timing Diagram
R//W
9
12
18
3
16
13
4
5
8 11
6
17
10
15
7
14
Port 0, /DM
Port 1
/AS
/DS
(Read)
Port 1
/DS
(Write)
A7 - A0 D7 - D0 IN
D7 - D0 OUTA7 - A0
17
1
2
Figure 24. External I/O or Memory Read/Write Timing

27
Z86E61/E63 Z8® MCU
WITH 16K/32K EPROM
PRELIMINARY
AC CHARACTERISTICS
External I/O or Memory Read and Write Timing Table
T
A
= 0°C to +70°C
16 MHz 20 MHz
No Symbol Parameter Min Max Min Max Units Notes
1 TdA(AS) Address Valid to /AS Rise Delay 20 26 ns [2,3]
2 TdAS(A) /AS Rise to Address Float Delay 30 28 ns [2,3]
3 TdAS(DR) /AS Rise to Read Data Req’d Valid 180 160 ns [1,2,3]
4 TwAS /AS Low Width 35 36 ns [2,3]
5 TdAZ(DS) Address Float to /DS Fall 0 0 ns
6 TwDSR /DS (Read) Low Width 135 130 ns [1,2,3]
7 TwDSW /DS (Write) Low Width 80 75 ns [1,2,3]
8 TdDSR(DR) /DS Fall to Read Data Req’d Valid 75 100 ns [1,2,3]
9 ThDR(DS) Read Data to /DS Rise Hold Time 0 0 ns [2,3]
10 TdDS(A) /DS Rise to Address Active Delay 35 48 ns [2,3]
11 TdDS(AS) /DS Rise to /AS Fall Delay 30 36 ns [2,3]
12 TdR/W(AS) R//W Valid to /AS Rise Delay 20 32 ns [2,3]
13 TdDS(R/W) /DS Rise to R//W Not Valid 30 36 ns [2,3]
14 TdDW(DSW) Write Data Valid to /DS Fall (Write) Delay 25 40 ns [2,3]
15 TdDS(DW) /DS Rise to Write Data Not Valid Delay 30 40 ns [2,3]
16 TdA(DR) Address Valid to Read Data Req’d Valid 200 200 ns [1,2,3]
17 TdAS(DS) /AS Rise to /DS Fall Delay 40 48 ns [2,3]
18 TdDM(AS) /DM Valid to /AS Fall Delay 30 36 ns [2,3]
Notes:
[1] When using extended memory timing add 2 TpC.
[2] Timing numbers given are for minimum TpC.
[3] See clock cycle dependent characteristics table.
Standard Test Load
All timing references use 2.0 V for a logic 1 and 0.8 V for a logic 0.
Clock Dependent Formulas
Number Symbol Equation
1 TdA(AS) 0.40 TpC + 0.32
2 TdAS(A) 0.59 TpC – 3.25
3 TdAS(DR) 2.83 TpC + 6.14
4 TwAS 0.66 TpC – 1.65
6 TwDSR 2.33 TpC – 10.56
7 TwDSW 1.27 TpC + 1.67
8 TdDSR(DR) 1.97 TpC – 42.5
10 TdDS(A) 0.8 TpC
11 TdDS(AS) 0.59 TpC – 3.14
12 TdR/W(AS) 0.4 TpC
13 TdDS(R/W) 0.8 TpC – 15
14 TdDW(DSW) 0.4 sTpC
15 TdDS(DW) 0.88 TpC – 19
16 TdA(DR) 4 TpC – 20
17 TdAS(DS) 0.91 TpC – 10.7
18 TdDM(AS) 0.9 TpC – 26.3

28
Z86E61/E63 Z8® MCU
WITH 16K/32K EPROM
PRELIMINARY
Clock
1
3
4
8
2
2 3
TIN
IRQN
6
5
7
7
9
AC CHARACTERISTICS
Additional Timing Diagram
AC CHARACTERISTICS
Additional Timing Table
T
A
= 0°C to +70°C
16 MHz 20 MHz
No Symbol Parameter Min Max Min Max Units Notes
1 TpC Input Clock Period 62.5 1000 50 1000 ns [1]
2 TrC,TfC Clock Input Rise & Fall Times 10 15 ns [1]
3 TwC Input Clock Width 21 37 ns [1]
4 TwTinL Timer Input Low Width 50 75 ns [2]
5 TwTinH Timer Input High Width 5TpC 5TpC [2]
6 TpTin Timer Input Period 8TpC 8TpC [2]
7 TrTin,TfTin Timer Input Rise & Fall Times 100 100 ns [2]
8A TwIL Interrupt Request Input Low Times 70 50 ns [2,4]
8B TwIL Interrupt Request Input Low Times 5TpC 5TpC [2,5]
9 TwIH Interrupt Request Input High Times 5TpC 5TpC [2,3]
Notes:
[1] Clock timing references use 3.8V for a logic 1 and 0.8V for a logic 0.
[2] Timing references use 2.0V for a logic 1 and 0.8V for a logic 0.
[3] Interrupt references request through Port 3.
[4] Interrupt request through Port 3 (P33-P31).
[5] Interrupt request through Port 30.
Figure 25. Additional Timing

29
Z86E61/E63 Z8® MCU
WITH 16K/32K EPROM
PRELIMINARY
Data In
1 2
3
4 5 6
/DAV
(Input)
RDY
(Output)
Next Data In Valid
Delayed RDY
Delayed DAV
Data In Valid
Data Out
/DAV
(Output)
RDY
(Input)
Next Data Out Valid
Delayed RDY
Delayed DAV
Data Out Valid
7
8 9
10
11
AC CHARACTERISTICS
Handshake Timing Diagrams
Figure 26. Input Handshake Timing
Figure 27. Output Handshake Timing

30
Z86E61/E63 Z8® MCU
WITH 16K/32K EPROM
PRELIMINARY
AC CHARACTERISTICS
Handshake Timing Table
TA = 0°C to +70°C
16 MHz 20 MHz Data
No Symbol Parameter Min Max Min Max Direction
1 TsDI(DAV) Data In Setup Time 0 0 IN
2 ThDI(DAV) Data In Hold Time 145 145 IN
3 TwDAV Data Available Width 110 110 IN
4 TdDAVI(RDY) DAV Fall to RDY Fall Delay 115 115 IN
5 TdDAVId(RDY) DAV Rise to RDY Rise Delay 115 115 IN
6 TdRDY0(DAV) RDY Rise to DAV Fall Delay 0 0 IN
7 TdD0(DAV) Data Out to DAV Fall Delay TpC TpC OUT
8 TdDAV0(RDY) DAV Fall to RDY Fall Delay 0 0 OUT
9 TdRDY0(DAV) RDY Fall to DAV Rise Delay 115 115 OUT
10 TwRDY RDY Width 110 110 OUT
11 TdRDY0d(DAV) RDY Rise to DAV Fall Delay 115 115 OUT

31
Z86E61/E63 Z8® MCU
WITH 16K/32K EPROM
PRELIMINARY
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
Serial Data (D0 = LSB)
R240 SIO
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
Count Mode
0 T1 Single Pass
1 T1 Modulo N
Clock Source
1 T1 Internal
0 T1 External Timing Input
(T
IN
) Mode
Prescaler Modulo
(Range: 1-64 Decimal
01-00 HEX)
R243 PRE1
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
T0 Initial Value
(When Written)
(Range: 1-256 Decimal
01-00 HEX)
T0 Current Value
(When Read)
R244 T0
0 T0 Single Pass
1 T0 Modulo N
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
Count Mode
Reserved (Must be 0)
Prescaler Modulo
(Range: 1-64 Decimal
01-00 HEX)
R245 PRE0
Z8 CONTROL REGISTER DIAGRAMS
Figure 33. Prescaler 0 Register
(F5H: Write Only)
Figure 28. Serial I/O Register
(F0H: Read/Write)
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
0 Disable T0 Count
1 Enable T0 Count
0 No Function
1 Load T0
0 No Function
1 Load T1
0 Disable T1 Count
1 Enable T1 Count
TIN Modes
00 External Clock Input
01 Gate Input
10 Trigger Input
(Non-retriggerable)
11 Trigger Input
(Retriggerable)
T
OUT
Modes
00 Not Used
01 T0 Out
10 T1 Out
11 Internal Clock Out
R241 TMR
Figure 29. Timer Mode Register
(F1H: Read/Write)
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
T1 Initial Value
(When Written)
(Range: 1-256 Decimal
01-00 HEX)
T1 Current Value
(When Read)
R242 T1
Figure 30. Counter/Timer 1 Register
(F2H: Read/Write)
Figure 31. Prescaler 1 Register
(F3H: Write Only)
Figure 32. Counter/Timer 0 Register
(F4H: Read/Write)

32
Z86E61/E63 Z8® MCU
WITH 16K/32K EPROM
PRELIMINARY
Z8 CONTROL REGISTER DIAGRAMS (Continued)
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
P20 - P27 I/O Definition
0 Defines Bit as Output
1 Defines Bit as Input
R246 P2M
Figure 34. Port 2 Mode Register
(F6H: Write Only)
Figure 36. Port 0 and 1 Mode Register
(F8H: Write Only)
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
R247 P3M
0 Port 2 Pull-Ups Open Drain
1 Port 2 Pull-Ups Active
0 Parity Off
1 Parity On
0 P32 = Input
P35 = Output
1 P32 = /DAV0/RDY0
P35 = RDY0//DAV0
0 P31 = Input (TIN)
P36 = Output (TOUT)
1 P31 = /DAV2/RDY2
P36 = RDY2//DAV2
0 P30 = Input
P37 = Output
1 P30 = Serial In
P37 = Serial Out
Reserved (Must be 0)
00 P33 = Input
P34 = Output
01 P33 = Input
10 P34 = /DM
11 P33 = /DAV1/RDY1
P34 = RDY1//DAV1
Figure 35. Port 3 Mode Register
(F7H: Write Only)
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
Interrupt Group Priority
Reserved = 000
C > A > B = 001
A > B > C = 010
A > C > B = 011
B > C > A = 100
C > B > A = 101
B > A > C = 110
Reserved = 111
IRQ3, IRQ5 Priority (Group A)
0 IRQ5 > IRQ3
1 IRQ3 > IRQ5
IRQ0, IRQ2 Priority (Group B)
0 IRQ2 > IRQ0
1 IRQ0 > IRQ2
IRQ1, IRQ4 Priority (Group C)
0 IRQ1 > IRQ4
1 IRQ4 > IRQ1
Reserved (Must be 0)
R249 IPR
Figure 37. Interrupt Priority Register
(F9H: Write Only)
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
R248 P01M
P00 - P00 Mode
00 Output
01 Input
1X A
11
- A
8
Stack Selection
0 External
1 Internal
P17 - P10 Mode
00 Byte Output
01 Byte Input
10 AD
7
- AD
0
11 High-Impedance AD7 - DA0,
/AS, /DS, /R//W, A
11
- A8,
A
15
- A12, If Selected
P0
7
- P04 Mode
00 Output
01 Input
1X A
15
- A
12
Reserved (Must be 0)

33
Z86E61/E63 Z8® MCU
WITH 16K/32K EPROM
PRELIMINARY
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
R253 RP
0 Reserved (Must be 0)
Register Pointer
r4
r5
r6
r7
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
R250 IRQ
Reserved (Must be 0)
IRQ0 = P32 Input (D0 = IRQ0)
IRQ1 = P33 Input
IRQ2 = P31 Input
IRQ3 = P30 Input, Serial Input
IRQ4 = T0 Serial Output
IRQ5 = T1
Figure 38. Interrupt Request Register
(FAH: Read/Write)
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
1 Enables RAM Protect
1 Enables IRQ5-IRQ0
(D
0
= IRQ0)
1 Enables Interrupts
R251 IMR
Figure 39. Interrupt Mask Register
(FBH: Read/Write)
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
R252 FLAGS
User Flag F1
User Flag F2
Half Carry Flag
Decimal Adjust Flag
Overflow Flag
Sign Flag
Zero Flag
Carry Flag
Figure 40. Flag Register
(FCH: Read/Write)
Figure 41. Register Pointer Register
(FDH: Read/Write)
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
Stack Pointer Upper
Byte (SP
15
- SP8)
R254 SPH
Figure 42. Stack Pointer Register
(FEH: Read/Write)
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
Stack Pointer Lower
Byte (SP
7
- SP0)
R255 SPL
Figure 43. Stack Pointer Register
(FFH: Read/Write)

34
Z86E61/E63 Z8® MCU
WITH 16K/32K EPROM
PRELIMINARY
DC CHARACTERISTICS
Supply Current
10
20
30
40
84 201612
I (mA)
B
Frequency (MHz)
0
Legend:
A - Vcc = 5.6V
B - Vcc = 5.0V
C - Vcc = 4.4V
A
26 181410
C
CC
Figure 44. Typical ICC vs Frequency

35
Z86E61/E63 Z8® MCU
WITH 16K/32K EPROM
PRELIMINARY
DC CHARACTERISTICS
Standby Current
2
4
6
8
84 201612
B
Frequency (MHz)
0
Legend:
A - Vcc = 5.6V
B - Vcc = 5.0V
C - Vcc = 4.4V
A
26 181410
C
10
12
I (mA)
CC1
Figure 45. Typical I
CC1
vs Frequency

36
Z86E61/E63 Z8® MCU
WITH 16K/32K EPROM
PRELIMINARY
INSTRUCTION SET NOTATION
Addressing Modes. The following notation is used to
describe the addressing modes and instruction operations as shown in the instruction summary.
Symbol Meaning
IRR Indirect register pair or indirect working
register pair address
Irr Indirect working register pair only
X Indexed address
DA Direct address
RA Relative address
IM Immediate
R Register or working register address
r Working register address only
IR Indirect register or indirect
working register address
Ir Indirect working register address only
RR Register pair or working register pair
address
Symbols. The following symbols are used in describing
the instruction set.
Symbol Meaning
dst Destination location or contents
src Source location or contents
cc Condition Code
@ Indirect address prefix
SP Stack Pointer
PC Program Counter
FLAGS Flag Register (Control Register 252)
RP Register Pointer (R253)
IMR Interrupt Mask Register (R251)
Flags. Control register (R252) contains the following six
flags:
Symbol Meaning
C Carry flag
Z Zero flag
S Sign flag
V Overflow flag
D Decimal-adjust flag
H Half-carry flag
Affected flags are indicated by:
0 Clear to zero
1 Set to one
* Set to clear according to operation
- Unaffected
x Undefined

37
Z86E61/E63 Z8® MCU
WITH 16K/32K EPROM
PRELIMINARY
CONDITION CODES
Value Mnemonic Meaning Flags Set
1000 Always True
0111 C Carry C = 1
1111 NC No Carry C = 0
0110 Z Zero Z = 1
1110 NZ Not Zero Z = 0
1101 PL Plus S = 0
0101 MI Minus S = 1
0100 OV Overflow V = 1
1100 NOV No Overflow V = 0
0110 EQ Equal Z = 1
1110 NE Not Equal Z = 0
1001 GE Greater Than or Equal (S XOR V) = 0
0001 LT Less than (S XOR V) = 1
1010 GT Greater Than [Z OR (S XOR V)] = 0
0010 LE Less Than or Equal [Z OR (S XOR V)] = 1
1111 UGE Unsigned Greater Than or Equal C = 0
0111 ULT Unsigned Less Than C = 1
1011 UGT Unsigned Greater Than (C = 0 AND Z = 0) = 1
0011 ULE Unsigned Less Than or Equal (C OR Z) = 1
0000 F Never True (Always False)

38
Z86E61/E63 Z8® MCU
WITH 16K/32K EPROM
PRELIMINARY
MODE
dst/src
OPC
dst
OPC
MODEOPC
srcdst
OPC
VALUE
OPC
OPCMODE
src/dstdst/src
OPC
src/dst
dst/src
OPC
VALUE
dst
OPC
RA
dst/CC
7FH
FFH
6FH
OPCdst
dst/src1 1 1 0
dst1 1 1 0
src1 1 1 0
MODE
src
OPC
dst
MODE
dst
OPC
VALUE
OPC
src
MODE
dst
OPCMODE
ADDRESS
xdst/src
OPC
DAU
cc
DAL
DAU
DAL
OPC
src1 1 1 0
dst1 1 1 0
dst1 1 1 0
src1 1 1 0
dst1 1 1 0
CLR, CPL, DA, DEC,
DECW, INC, INCW,
POP, PUSH, RL, RLC,
RR, RRC, SRA, SWAP
JP, CALL (Indirect)
OR
OR
OR
OR
OR
OR
OR
SRP
ADC, ADD, AND, CP,
OR, SBC, SUB, TCM,
TM, XOR
LD, LDE, LDEI,
LDC, LDCI
LD
LD
DJNZ, JR
STOP/HALT
LD
LD
JP
CALL
ADC, ADD, AND, CP,
LD, OR, SBC, SUB,
TCM, TM, XOR
ADC, ADD, AND, CP,
LD, OR, SBC, SUB,
TCM, TM, XOR
One-Byte Instructions
Two-Byte Instructions Three-Byte Instructions
CCF, DI, EI, IRET, NOP,
RCF, RET, SCF
OR
INSTRUCTION FORMATS
INSTRUCTION SUMMARY
Note: Assignment of a value is indicated by the symbol
“ ← ”. For example:
dst ← dst + src
indicates that the source data is added to the destination
data and the result is stored in the destination location. The
notation “addr (n)” is used to refer to bit (n) of a given
operand location. For example:
dst (7)
refers to bit 7 of the destination operand.

39
Z86E61/E63 Z8® MCU
WITH 16K/32K EPROM
PRELIMINARY
INSTRUCTION SUMMARY
Address Opcode
Instruction Mode Byte Flags Affected
and Operation dst src (Hex) C Z S V D H
ADC dst, src † 1[ ] ✻✻✻✻0✻
dst←dst + src +C
ADD dst, src † 0[ ] ✻✻✻✻0✻
dst←dst + src
AND dst, src † 5[ ] - ✻✻0--
dst←dst AND src
CALL dst DA D6 -----SP←SP – 2 IRR D4
@SP←PC,
PC←dst
CCF EF ✻ ----C←NOT C
CLR dst R B0 -----dst←0IRB1
COM dst R 60 - ✻✻0--
dst←NOT dst IR 61
CP dst, src † A[ ] ✻✻✻✻-dst – src
DA dst R 40 ✻✻✻X--
dst←DA dst IR 41
DEC dst R 00 - ✻✻✻-dst←dst – 1 IR 01
DECW dst RR 80 - ✻✻✻-dst←dst – 1 IR 81
DI 8F -----IMR(7)←0
DJNZr, dst RA rA -----r←r – 1 r = 0 - F
if r ≠ 0
PC←PC + dst
Range: +127,
–128
EI 9F -----IMR(7)←1
HALT 7F ------
Address Opcode
Instruction Mode Byte Flags Affected
and Operation dst src (Hex) C Z S V D H
INC dst r rE - ✻✻✻--
dst←dst + 1 r = 0 – F
R20
IR 21
INCW dst RR A0 - ✻✻✻--
dst←dst + 1 IR A1
IRET BF ✻✻✻✻✻✻
FLAGS←@SP;
SP←SP + 1
PC←@SP;
SP←SP + 2;
IMR(7)←1
JP cc, dst DA cD ------
if cc is true, c = 0 – F
PC←dst IRR 30
JR cc, dst RA cB ------
if cc is true, c = 0 – F
PC←PC + dst
Range: +127,
–128
LD dst, src r Im rC ------
dst←src r R r8
Rr r9
r = 0 – F
rX C7
Xr D7
rIr E3
Ir r F3
RR E4
RIR E5
RIM E6
IR IM E7
IR R F5
LDC dst, src r Irr C2 ------
dst←src
LDCI dst, src Ir Irr C3 ------
dst←src
r←r + 1;
rr←rr + 1

40
Z86E61/E63 Z8® MCU
WITH 16K/32K EPROM
PRELIMINARY
INSTRUCTION SUMMARY (Continued)
Address Opcode
Instruction Mode Byte Flags Affected
and Operation dst src (Hex) C Z S V D H
NOP FF ------
OR dst, src † 4[ ] - ✻✻0 --
dst←dst OR src
POP dst R 50 ------
dst←@SP; IR 51
SP←SP + 1
PUSH src R 70 ------
SP←SP – 1; IR 71
@SP←src
RCF CF 0-----
C←0
RET AF -----PC←@SP;
SP←SP + 2
RL dst R 90 ✻✻✻✻--
IR 91
RLC dst R 10 ✻✻✻✻--
IR 11
RR dst R E0 ✻✻✻✻--
IR E1
RRC dst R C0 ✻✻✻✻--
IR C1
SBC dst, src † 3[ ] ✻✻✻✻1✻
dst←dst←src←C
SCF DF 1-----
C←1
SRA dst R D0 ✻✻✻0--
IR D1
SRP dst Im 31 -----RP←src
Address Opcode
Instruction Mode Byte Flags Affected
and Operation dst src (Hex) C Z S V D H
STOP 6F 1-----
SUB dst, src † 2[ ] [[[[1[
dst←dst←src
SWAP dst R F0 X ✻✻X--
IR F1
TCM dst, src † 6[ ] - ✻✻0--
(NOT dst)
AND src
TM dst, src † 7[ ] - ✻✻0--
dst AND src
XOR dst, src † B[ ] - ✻✻0--
dst←dst
XOR src
† These instructions have an identical set of addressing modes, which
are encoded for brevity. The first opcode nibble is found in the instruction
set table above. The second nibble is expressed symbolically by a ‘[ ]’
in this table, and its value is found in the following table to the left of the
applicable addressing mode pair.
For example, the opcode of an ADC instruction using the addressing
modes r (destination) and Ir (source) is 13.
Address Mode Lower
dst src Opcode Nibble
r r [2]
r Ir [3]
R R [4]
R IR [5]
R IM [6]
IR IM [7]
C 70
C70
C70
C70
C70
7430

41
Z86E61/E63 Z8® MCU
WITH 16K/32K EPROM
PRELIMINARY
6.5
DEC
R1
6.5
DEC
IR1
6.5
ADD
r1, r2
6.5
ADD
r1, Ir2
10.5
ADD
R2, R1
10.5
ADD
IR2, R1
10.5
ADD
R1, IM
10.5
ADD
IR1, IM
0123456789ABCDE F
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
A
B
C
D
E
F
Lower Nibble (Hex)
Upper Nibble (Hex)
Bytes per Instruction
23 231
6.5
RLC
R1
6.5
RLC
IR1
6.5
ADC
r1, r2
6.5
ADC
r1, Ir2
10.5
ADC
R2, R1
10.5
ADC
IR2, R1
10.5
ADC
R1, IM
10.5
ADC
IR1, IM
6.5
INC
R1
6.5
INC
IR1
6.5
SUB
r1, r2
6.5
SUB
r1, Ir2
10.5
SUB
R2, R1
10.5
SUB
IR2, R1
10.5
SUB
R1, IM
10.5
SUB
IR1, IM
10.5
DECW
RR1
10.5
DECW
IR1
6.5
RL
R1
6.5
RL
IR1
10.5
INCW
RR1
10.5
INCW
IR1
6.5
CP
r1, r2
6.5
CP
r1, Ir2
10.5
CP
R2, R1
10.5
CP
IR2, R1
10.5
CP
R1, IM
10.5
CP
IR1, IM
6.5
CLR
R1
6.5
CLR
IR1
6.5
XOR
r1, r2
6.5
XOR
r1, Ir2
10.5
XOR
R2, R1
10.5
XOR
IR2, R1
10.5
XOR
R1, IM
10.5
XOR
IR1, IM
6.5
RRC
R1
6.5
RRC
IR1
12.0
LDC
r1, Irr2
18.0
LDCI
Ir1, Irr2
10.5
LD
r1,x,R2
6.5
SRA
R1
6.5
SRA
IR1
20.0
CALL*
IRR1
20.0
CALL
DA
10.5
LD
r2,x,R1
6.5
RR
R1
6.5
RR
IR1
6.5
LD
r1, IR2
10.5
LD
R2, R1
10.5
LD
IR2, R1
10.5
LD
R1, IM
10.5
LD
IR1, IM
8.5
SWAP
R1
8.5
SWAP
IR1
6.5
LD
Ir1, r2
10.5
LD
R2, IR1
6.5
LD
r1, R2
6.5
LD
r2, R1
12/10.5
DJNZ
r1, RA
12/10.0
JR
cc, RA
6.5
LD
r1, IM
12.10.0
JP
cc, DA
6.5
INC
r1
6.0
STOP
7.0
HALT
6.1
DI
6.1
EI
14.0
RET
16.0
IRET
6.5
RCF
6.5
SCF
6.5
CCF
6.0
NOP
10.5
CP
R1, R2
4
A
Lower
Opcode
Nibble
Pipeline
Cycles
Mnemonic
Second
Operand
Execution
Cycles
Upper
Opcode
Nibble
First
Operand
Legend:
R = 8-bit Address
r = 4-bit Address
R1 or r1 = Dst Address
R2 or r2 = Src Address
Sequence:
Opcode, First Operand,
Second Operand
Note: Blank areas not defined.
*2-byte instruction appears as
a 3-byte instruction
8.0
JP
IRR1
6.1
SRP
IM
6.5
SBC
r1, r2
6.5
SBC
r1, Ir2
10.5
SBC
R2, R1
10.5
SBC
IR2, R1
10.5
SBC
R1, IM
10.5
SBC
IR1, IM
8.5
DA
R1
8.5
DA
IR1
6.5
OR
r1, r2
6.5
OR
r1, Ir2
10.5
OR
R2, R1
10.5
OR
IR2, R1
10.5
OR
R1, IM
10.5
OR
IR1, IM
10.5
POP
R1
10.5
POP
IR1
6.5
AND
r1, r2
6.5
AND
r1, Ir2
10.5
AND
R2, R1
10.5
AND
IR2, R1
10.5
AND
R1, IM
10.5
AND
IR1, IM
6.5
COM
R1
6.5
COM
IR1
6.5
TCM
r1, r2
6.5
TCM
r1, Ir2
10.5
TCM
R2, R1
10.5
TCM
IR2, R1
10.5
TCM
R1, IM
10.5
TCM
IR1, IM
10/12.1
PUSH
R2
12/14.1
PUSH
IR2
6.5
TM
r1, r2
6.5
TM
r1, Ir2
10.5
TM
R2, R1
10.5
TM
IR2, R1
10.5
TM
R1, IM
10.5
TM
IR1, IM
12.0
LDC
r1, Irr2
18.0
LDCI
Ir1, Irr2
12.0
LDE
r1, Irr2
18.0
LDEI
Ir1, Irr2
12.0
LDE
r2, Irr1
18.0
LDEI
Ir2, Irr1
OPCODE MAP

42
Z86E61/E63 Z8® MCU
WITH 16K/32K EPROM
PRELIMINARY
PACKAGE INFORMATION
40-Pin DIP Package Diagram
44-Pin PLCC Package Diagram

43
Z86E61/E63 Z8® MCU
WITH 16K/32K EPROM
PRELIMINARY
44-Pin QFP Package Diagram

44
Z86E61/E63 Z8® MCU
WITH 16K/32K EPROM
PRELIMINARY
ORDERING INFORMATION
Z86E61
16 MHz 20 MHz
40-Pin DIP 44-Pin PLCC 40-Pin DIP 44-Pin PLCC
Z86E6116PSC Z86E6116VSC Z86E6120PSC Z86E6120VSC
44-Pin QFP
Z86E6116FEC
Z86E63
16 MHz 20 MHz
40-Pin DIP 44-Pin PLCC 40-Pin DIP 44-Pin PLCC
Z86E6316PSC Z86E6316VSC Z86E6320PSC Z86E6320VSC
For fast results, contact your local Zilog sales office for assistance in ordering the part desired.
CODES
Preferred Package
P = Plastic DIP
V = Plastic Chip Carrier
Temperature
S = 0°C to +70°C
Speeds
12 = 16 MHz
16 = 20 MHz
Environmental
C = Plastic Standard
Example:
Z 86E61 16 P S C is an Z86E61, 16 MHz, DIP, 0°C to +70°C, Plastic Standard Flow
Environmental Flow
Temperature
Package
Speed
Product Number
Zilog Prefix
 Loading...
Loading...