
Zilog
FEATURES
PRELIMINARY
P
RELIMINARY PRODUCT SPECIFICATION
Z80189/Z8L189
GENERAL-PURPOSE
EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
Part CPU UART I/O Speed (MHz)
Z80189 S180* 16550 24 33
Z8L189 S180* 16550 24 20
■ Fully Static Z180™ MPU Core*
– On-Chip 1 MByte MMU
– Two Enhanced UART Channels (up to 512 Kbps)†
– Two Chain-Linked DMA Channels†
– x 2 Clock Multiplier
– Low-Power Consumption Modes
– Two 16-Bit Timer/Counters
– Clocked Serial I/O
– On-Chip Wait State Generator (WSG)
– On-Chip Interrupt Controller
On-Chip Clock Oscillator/Generator
–
■ 16550 Compatible MIMIC Interface
– 16 mA MIMIC Output Drive Capability
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The Z80189/Z8L189 are cost-effective modem controllers
that address a new generation of data pumps having the
HDLC formatting feature. Data pumps of these types do
not require an HDLC interface; therefore, the Z80189 does
not need the ESCC™. The addition of the PC DMA Mailbox
Registers allow DMA data transfer between the PC memory
and the modem speaker/microphone CODEC. The Z80189
is a smart peripheral controller chip for modem (in particular V.34 applications), fax, voice messaging, and other
communications applications.
The Z80189/Z8L189 consists of an enhanced Z8S180
microprocessor, a 16550 MIMIC with increased MIMIC
drive capability for direct connection to the IBM PC, XT, AT
bus, and 24 bits of parallel I/O. Current PC modem software compatibility can be maintained with the Z80189's
ability to mimic the 16550 UART chip. The Z80180 core is
the intelligent controller between the data pump and
16550 MIMIC interface when used in internal applications.
This intelligent controller performs the data compression
and error correction on outgoing and incoming data.
■ Com Port Decode
■ PC DMA Mailbox Registers
■ Host I/O Mailbox
■ Programmable Fixed /ROMCS and
/RAMCS Boundaries
■ 100-Pin QFP and VQFP Packages
■ 3.3 and 5.0-Volt Operating Ranges
■ 0°C to +70°C Temperature Range
Notes:
† Enhancements from the Discrete S180 device.
The integration of COM Port Decode circuitry to the Z80189
allows the MIMIC to be selected for a specific COM Port
Address (PC COM Port Address 1-4). COM Port Decode
circuitry is simplified by allowing the user to select the
MIMIC COM Port addresses through software, in addition
to eliminating the need for external circuitry required for
COM Port Decode logic.
The PC DMA and I/O Mailbox Interface can be used to
provide communication paths between the PC Host and
the Z80189. These new communication paths can be used
for voice, DTAD, or jumperless COM Port selection.
Notes:
All Signals with a preceding front slash, "/", are active Low, e.g.:
B//W (WORD is active Low); /B/W (BYTE is active Low, only).
Power connections follow conventional descriptions below:
Connection Circuit Device
Power V
Ground GND V
CC
V
DD
SS
DS971890301
1
Zilog
PRELIMINARY
GENERAL DESCRIPTION (Continued)
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
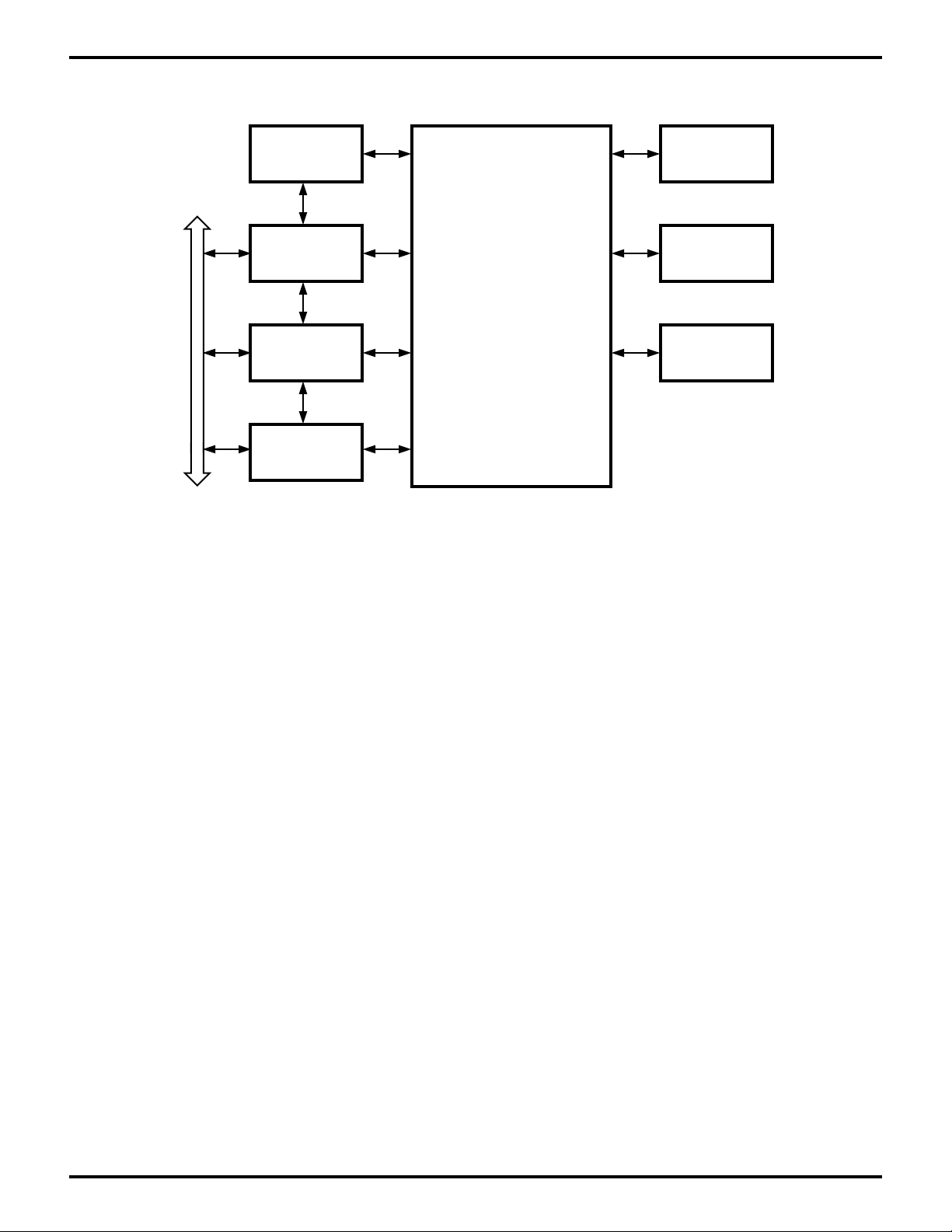
PC ISA BUS
Baud Rate
Generator
16550 MIMIC
Interface
COM Decoder
PC DMA
DMA & I/O
Interface
8-Bit Parallel
Port A
8-Bit Parallel
Port B
Enhanced
S180 MPU
8-Bit Parallel
Port C
Figure 1. Z80189 Block Diagram
2
DS971890301
Zilog
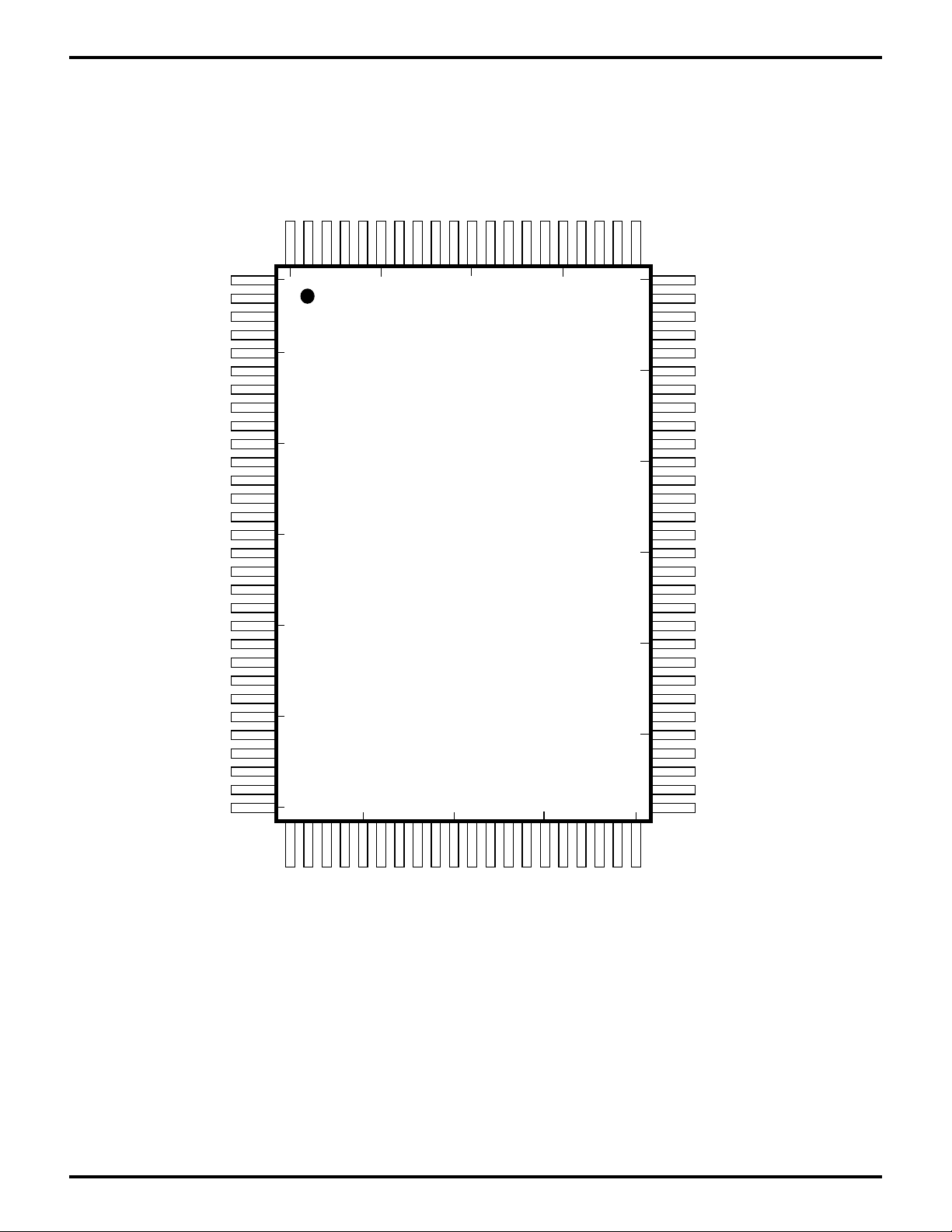
PIN DESCRIPTION
/NMI
/RESET
/HDACK1//BUSREQ
PRELIMINARY
PHI
VSS
/RD
/WR
/M1
/IOCS2/E
EXTAL
HA4//WAIT
XTAL
HDRQ1//BUSACK
/MRD//MREQ
/IORQ
HA3//RFSH
/HALT
/HCS/HC1
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
HA2
HA1/RXA0
/INT0
/INT1/PC6
/INT2/PC7
ST
A0
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
A8
A9
A10
A11
A12
VSS
A13
A14
A15
A16
A17
A18
VDD
A19
D0
D1
D2
D3
100
1
95
90
85
80
HA0
/HDDIS/TXA0
/HWR//CTS0
/HRD//DCD0
5
75
HINTR2
HAEN
HA6
VDD
HA7/IEI
10
70
/IOCS1/IEO
VSS
HA8
PC4
15
100-Pin QFP
65
Z80189/Z8L189
PC0
PC1
/MWR/PC2
PC3
PC5
HD7/PA7
20
60
HD6/PA6
HD5/PA5
HD4/PA4
HD3/PA3
HD2/PA2
25
55
HD1/PA1
HD0/PA0
EV2
EV1
30
50454035
/ROMCS
/RAMCS
DS971890301
D4
PB0/TXS
PB1//CTS0
PB4/RXA0
PB3/TXA0
PB2//DCD0
PB5/TXA1
PB6/RXA1
VSS
PB7/RXS//CTS1
/HDACK0/CKA0//DREQ0
HINTR1/TOUT
HA9/CKA1//TEND0
HC2/CKS
HA5//DREQ1
VDD
HDRQ0//RTS0
D7
D5
D6
Figure 2. Z80189/Z8L189 100-Lead QFP Pin Identification
3
Zilog
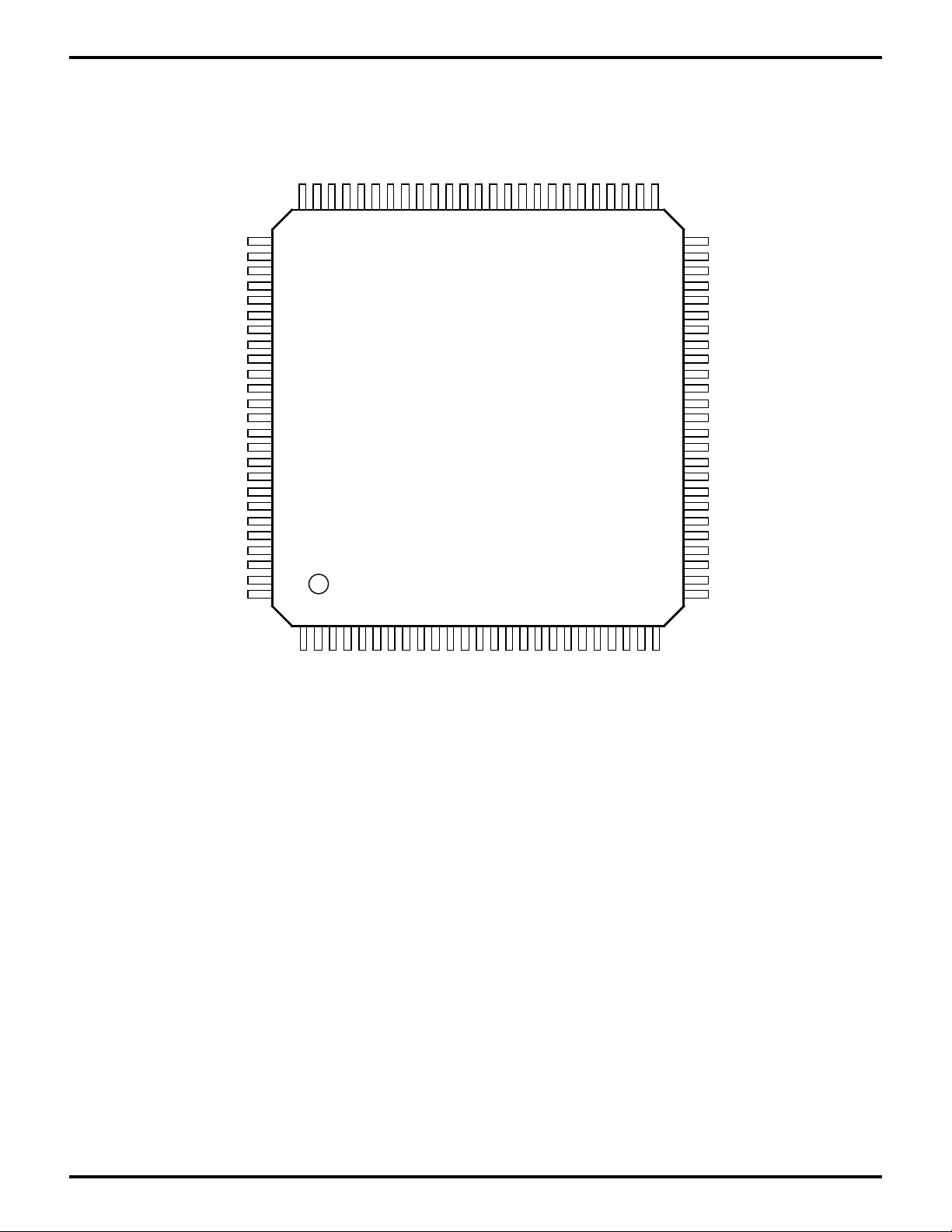
PIN DESCRIPTION (Continued)
PRELIMINARY
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
/HDDIS/TXA0
HA0
HA1/RXA0
HA2
/HCS/HC1
/HALT
HA3//RFSH
/IORQ
/MRD//MREQ
/IOCS2/E
/M1
/WR
/RD
PHI
VSS
XTAL
EXTAL
HA4//WAIT
HDRQ1//BUSACK
/HDACK1//BUSREQ
/RESET
/NMI
/INT0
/INT1/PC6
/INT2/PC7
/HRD//DCD0
/HWR//CTS0
75 51
76
80
85
90
95
100
125
HINTR2
HAEN
HA6
5
VDD
HA7/IEI
/IOCS/IEO
VSS
HA8
PC0
PC1
PC4
Z80189/Z8L189
100-Pin VQFP
10 15 20
/MWR/PC2
PC3
PC5
6070 5565
HD7/PA7
HD6/PA6
HD5/PA5
HD4/PA4
HD3/PA3
HD2/PA2
HD1/PA1
HD0/PA0
EV2
50
45
40
35
30
26
EV1
/ROMCS
/RAMCS
HDRQ0/RTS0
VDD
HA5//DREQ1
HC2/CKS
HINTR1/TOUT
HA9/CKA1//TEND0
VSS
/HDACK0/CKA0//DREQ0
PB7/RXS//CTS1
PB6/RXA1
PB5/TXA1
PB4/RXA0
PB3/TXA0
PB2//DCD0
PB1//CTS0
PB0/TXS
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
ST
A0A1A2
A3A4A5
A6A7A8
A9
A11
A10
A12
A14
A15
A16
A17
VSS
A13
A18
VDD
A19
D1
D0
Figure 3. Z80189/Z8L189 100-Lead VQFP Pin Identification
4
DS971890301
Zilog
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
PRELIMINARY
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
Symbol Description Min Max Units
V
CC
V
IN
T
OPR
T
STG
Notes:
(*) Voltage on all pins with respect to GND.
Supply Voltage (*) –0.3 +7.0 V
Input Voltage –0.3 VCC+0.3 V
Operating Temp. 0 70 °C
Storage Temp. –55 +150 °C
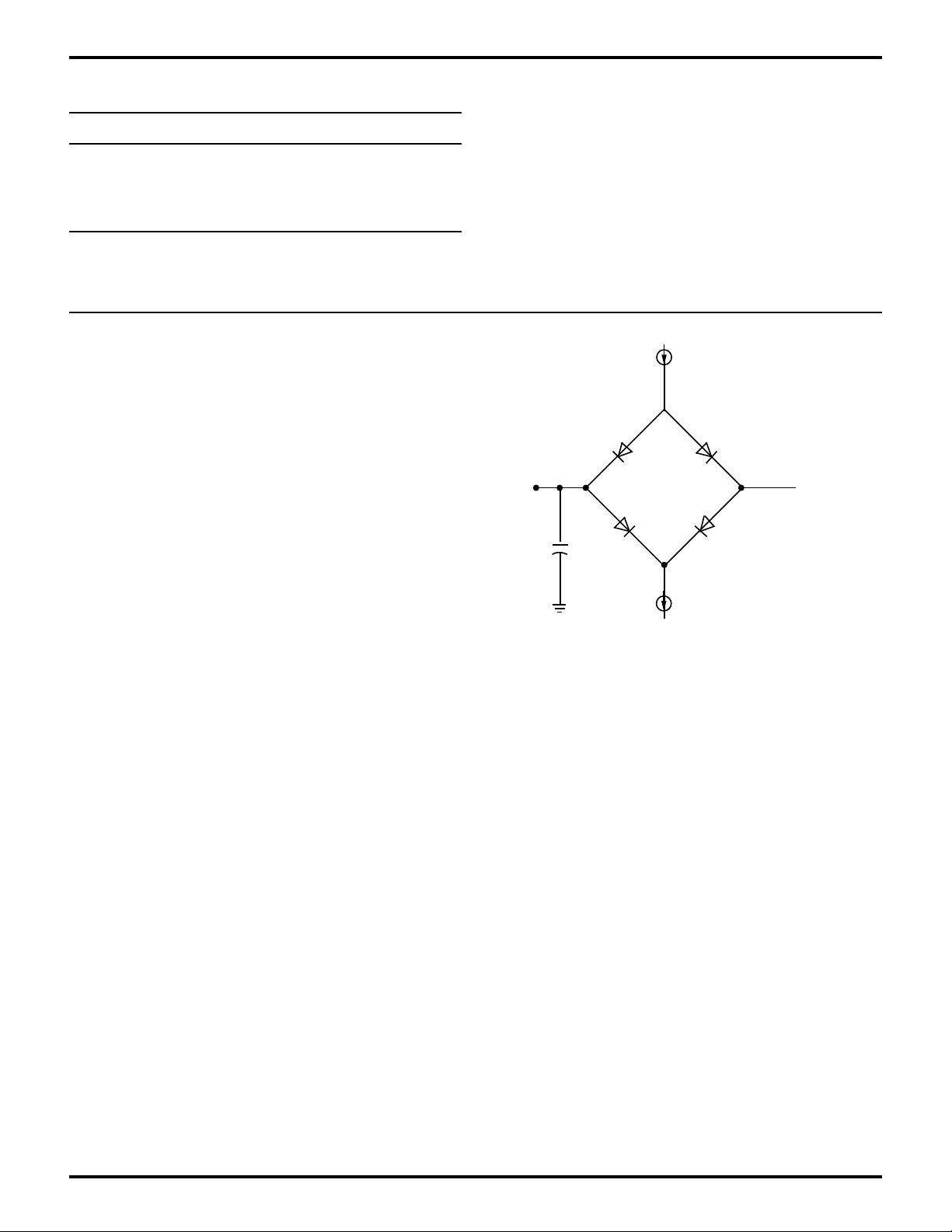
STANDARD TEST CONDITIONS
The DC Characteristics and capacitance sections below
apply for the following standard test conditions, unless
otherwise noted. All voltages are referenced to GND (0V).
Positive current flows into the referenced pin (Test Load).
Available operating temperature range is:
S=0°C to 70°C
Voltage Supply Range:
+4.5V ≤ VCC ≤ +5.5V
+3.0V ≤ VCC ≤ +3.6V
Stresses greater than those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress rating only; operation of the device at
any condition above those indicated in the operational
sections of these specifications is not implied. Exposure to
absolute maximum rating conditions for extended periods
may affect device reliability.
= 2 mA
I
OL
1.4 V
100 pF
All AC parameters assume a load capacitance of 50 pF.
Add 10 ns delay for each 50 pF increase in load up to a
maximum of 150 pF for the data bus and 100 pF for
address and control lines. AC timing measurements are
referenced to 1.5 volts (except for clock, which is referenced to the 10% and 90% points). Maximum capacitive
load for PHI is 125 pF.
= 250 µA
I
OH
Figure 4. Test Load Diagram
DS971890301
5

Zilog
PRELIMINARY
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
DC CHARACTERISTICS
Z80189
(V
= 5.0V ±10% or VCC = 3.3v ±10%, over specified temperature range unless otherwise noted.)
CC
Symbol Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Condition
Z80189/Z8L189
V
IH1
Input H Voltage VCC –0.6 VCC +0.3 V
RESET, EXTAL, NMI, INT0, INT1, INT2
V
IH2
Input H Voltage 2.0 VCC +0.3 V
Except RESET, EXTAL, NMI, INT0, INT1, INT2
V
IL1
Input L Voltage –0.3 0.6 V
RESET, EXTAL, NMI, INT0, INT1, INT2
V
IL2
Input L Voltage –0.3 0.8 V
Except RESET, EXTAL, NMI, INT0, INT1, INT2
V
OH1
Output H Voltage V
All outputs 2.4 V IOH = –200 µA
V
OH2
V
OL1
Output H PHI VCC –0.6 V I
= –200 µA
OH
Output L Voltage 0.40 V IOL = 2.2 mA
All outputs
V
OL2
V
OH
V
OL
V
OH
V
OL
I
IL
Output L PHI 0.40 V IOL= 2.2 mA
All MIMIC Outputs 2.4 V IOH = 16 mA,**
All MIMIC Outputs 0.4 V I
= 16 mA,**
OL
All MIMIC Outputs 2.4 V IOH =8 mA,VCC= 3.3 V**
All MIMIC Outputs 0.4 V I
=8 mA,VCC= 3.3 V**
OL
Input Leakage 10 µAVIN = 0 to VCC 5
Current All Inputs
Except XTAL, EXTAL
I
TL
Tri-State Leakage Current 10 µAVIN = 0 to VCC 5
ICC* Power Dissipation* 18 30 mA f = 20 MHz, 3.3v
Normal Operation 80 120 mA f = 33 MHz, 5v
ICC* Power Dissipation* 1.8 3.6 mA f = 20 MHz, 3.3v
(System STOP Mode) 6 9 mA f = 33 MHz, 5v
Power Dissipation 15 50 µA
(Standby Mode)
Notes:
* VIH Min = VCC -1.0 V, V
** Total loading current in or out of the Z189 cannot exceed 150 mA from
pins 41 to 70.
Max = 0.8 V (all output terminals are at no load).
IL
6
DS971890301
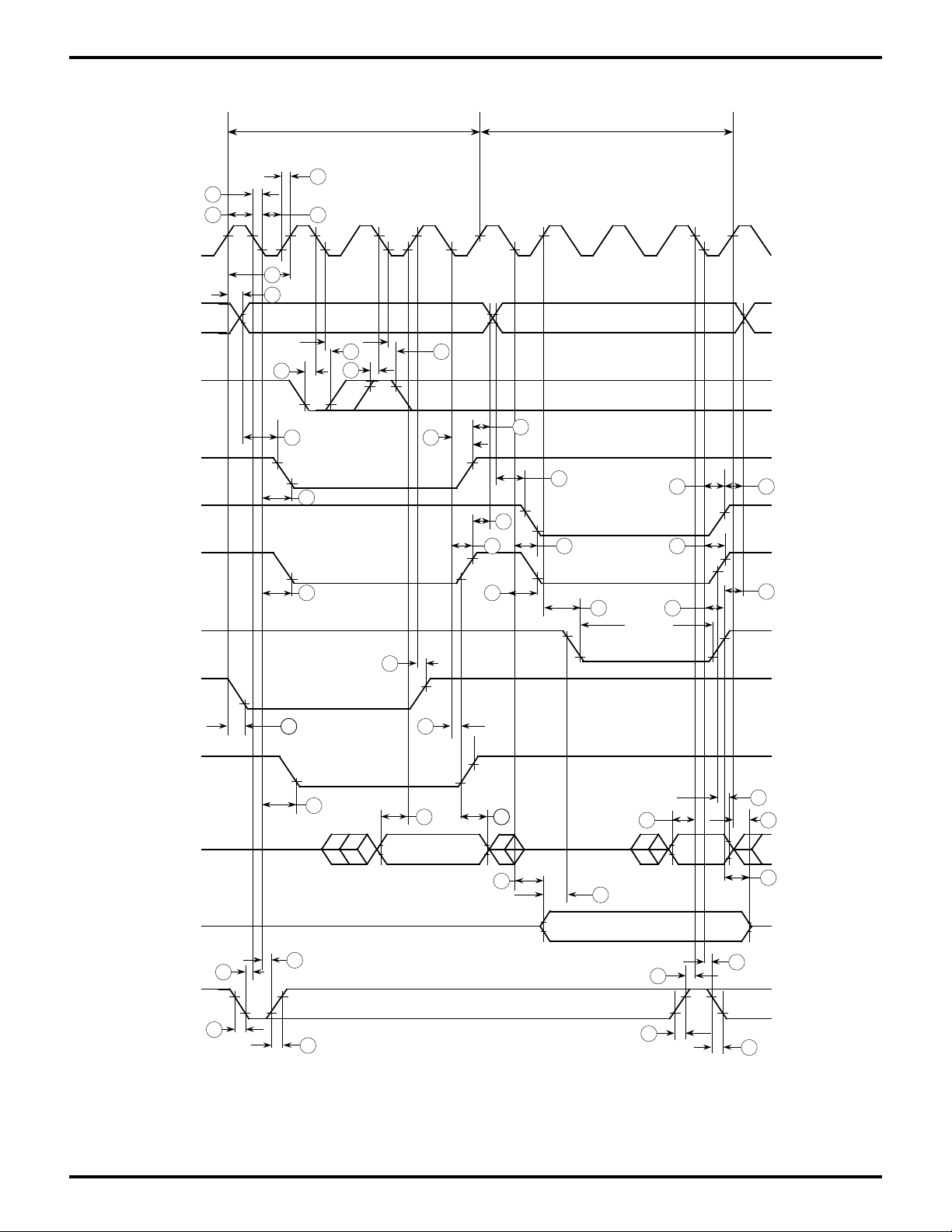
Zilog
TIMING DIAGRAMS
PRELIMINARY
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
ø
Address
/WAIT
/MREQ
/IORQ
/RD
/WR
Opcode Fetch Cycle
I/O Write Cycle †
I/O Read Cycle †
T1 T2 TW T3 T1 T2 TW T3 T1
5
4
32
1
6
19
20
19
7
8
9
14
12
20
11
7
11
13 28
9
22
13
25
26 and 26a
1129
11
/M1
ST
Data
IN
Data
OUT
/RESET
68
62
10
17
63
67
15
18
23
16
15
24
62
67
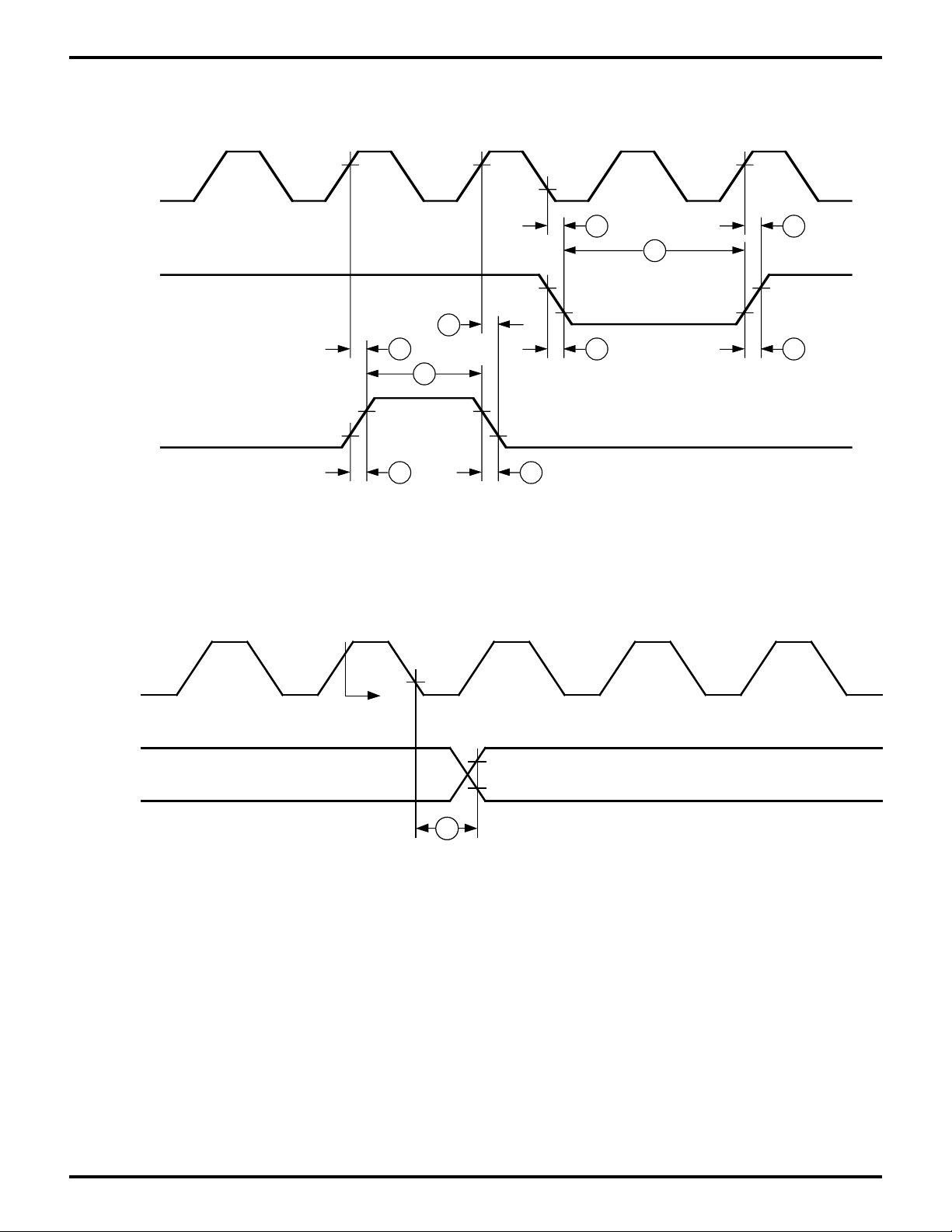
Figure 5. CPU Timing
(Opcode Fetch Cycle, Memory Read/Write Cycle I/O Read/Write Cycle)
16
21
27
63
68
DS971890301
7
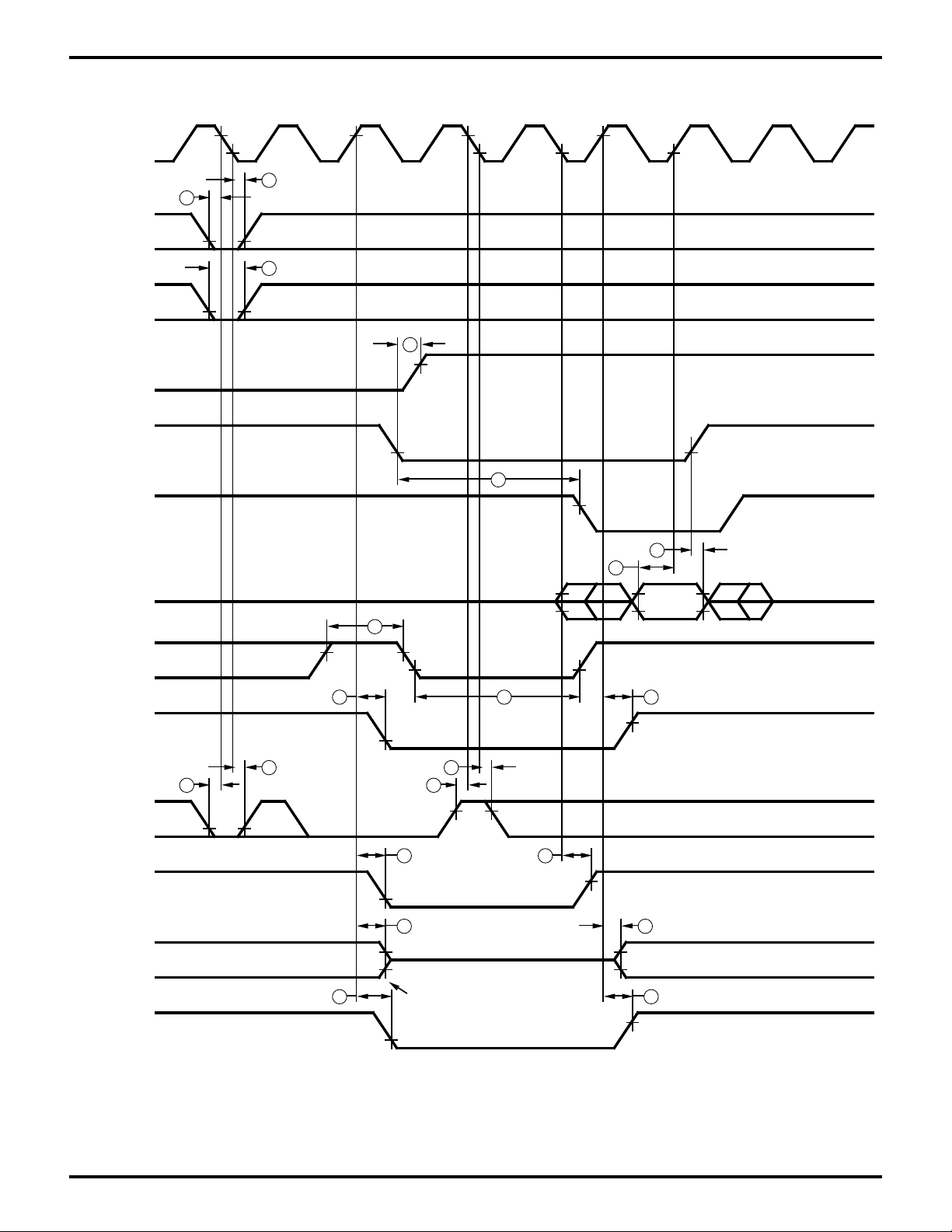
Zilog
TIMING DIAGRAMS (Continued)
Ø
32
31
/INTI
33
/NMI
/INTSCC
/M1 [1]
PRELIMINARY
C7
30
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
/IORQ [1]
/Data IN [1]
/MREQ [2]
/RFSH [2]
/BUSREQ
/BUSACK
Address
Data /MREQ,
/RD, /WR,
/IORQ
16
15
39
4041 42
35 35
34
43
[3]
34
3736
3838
44
/HALT
Notes:
[1] During /INT0 acknowledge cycle
[2] During refresh cycle
[3] Output buffer is off at this point
Figure 6. CPU Timing
(/INT0 Acknowledge Cycle, Refresh Cycle, BUS RELEASE Mode
HALT Mode, SLEEP Mode, SYSTEM STOP Mode)
8
DS971890301
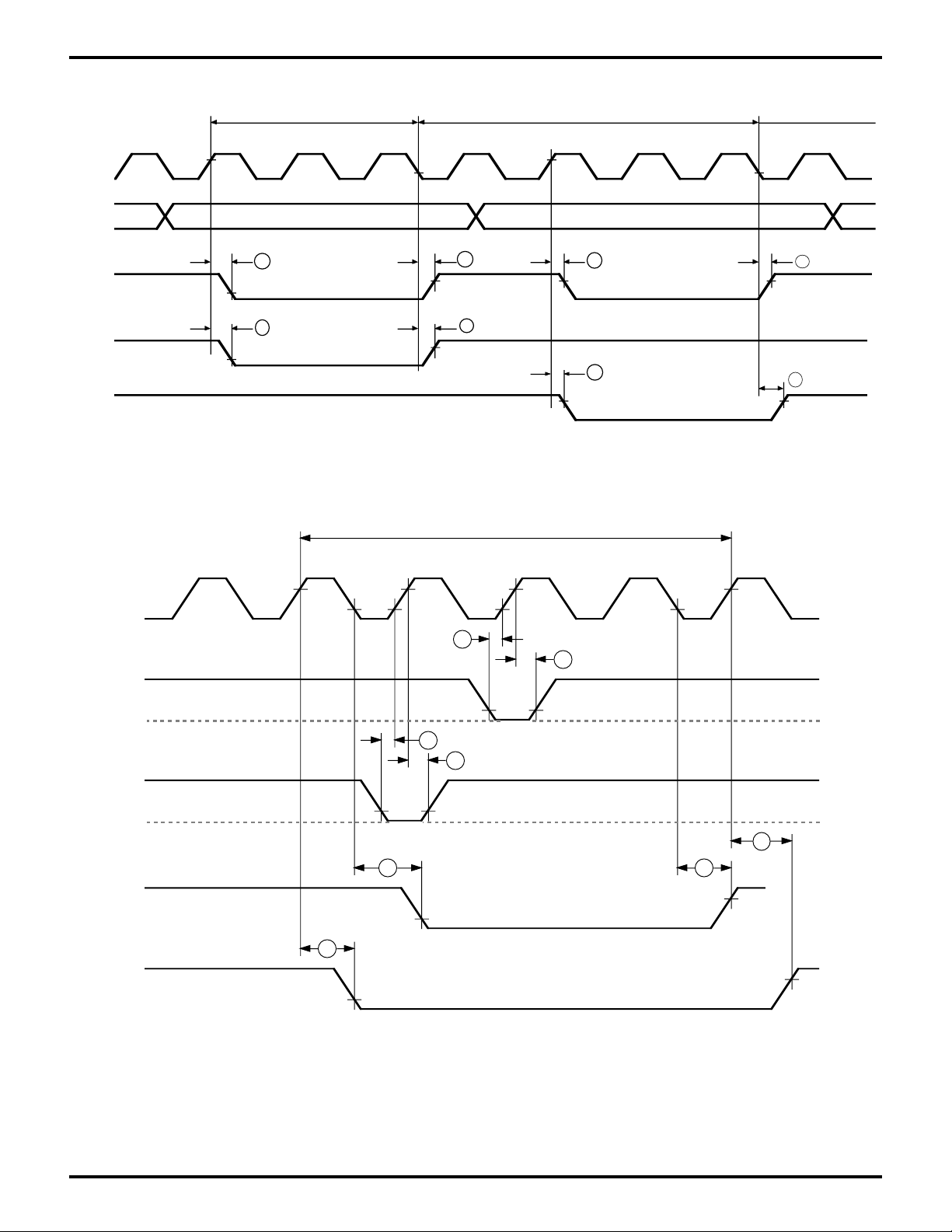
Zilog
TIMING DIAGRAMS (Continued)
PRELIMINARY
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
Address
/IROQ
/RD
/WR
I/O Read Cycle
T1 T2 TW T3 T1
0
28
9
CPU or DMA Read/Write Cycle (Only DMA Write Cycle for /TENDi)
T1 T2 Tw T3 T1
29
13
Figure 7. CPU Timing
I/O Write Cycle
T2 TW T3
28
22
29
25
/DREQi
(At level
sense)
/DREQi
(At edge
sence)
/TENDi
ST
Ø
45
[1]
46
45
[2]
45
18
47
48
[4]
[3]
17
DMA Control Signals
[
1] tDRQS and tDRQH are specified for the rising edge of clock followed by T3.
[2] tDRQS and tDRQH are specified for the rising edge of clock.
[3] DMA cycle starts.
[4] CPU cycle starts.
DS971890301
Figure 8. DMA Control Signals
9
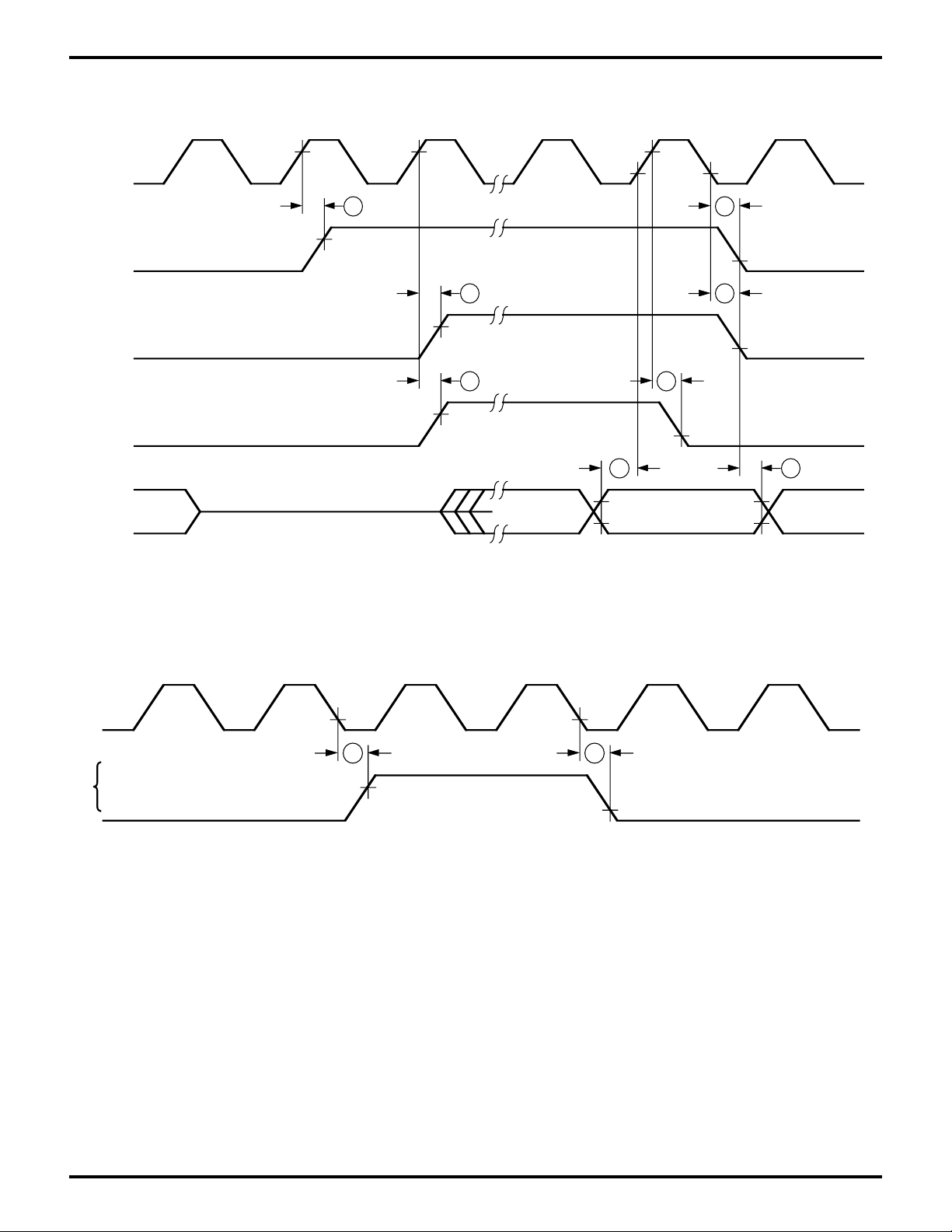
Zilog
TIMING DIAGRAMS (Continued)
T1 T2 Tw Tw T3
Ø
PRELIMINARY
49 50
49 50
49 50
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
1615
D7-D0
Ø
BUS RELEASE Mode
E
SLEEP Mode
SYSTEM STOP Mode
Figure 9. E Clock Timing
(Memory Read/Write Cycle
I/O Read/Write Cycle)
5049
Figure 10. E Clock Timing
10
DS971890301
Zilog
TIMING DIAGRAMS (Continued)
T2 Tw T3 T1 T2
Ø
PRELIMINARY
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
(Example:
I/O Read -
Opcode
Fetch)
(I/O Write)
Ø
50
52
49
E
50
49
51
54
53
E
53
54
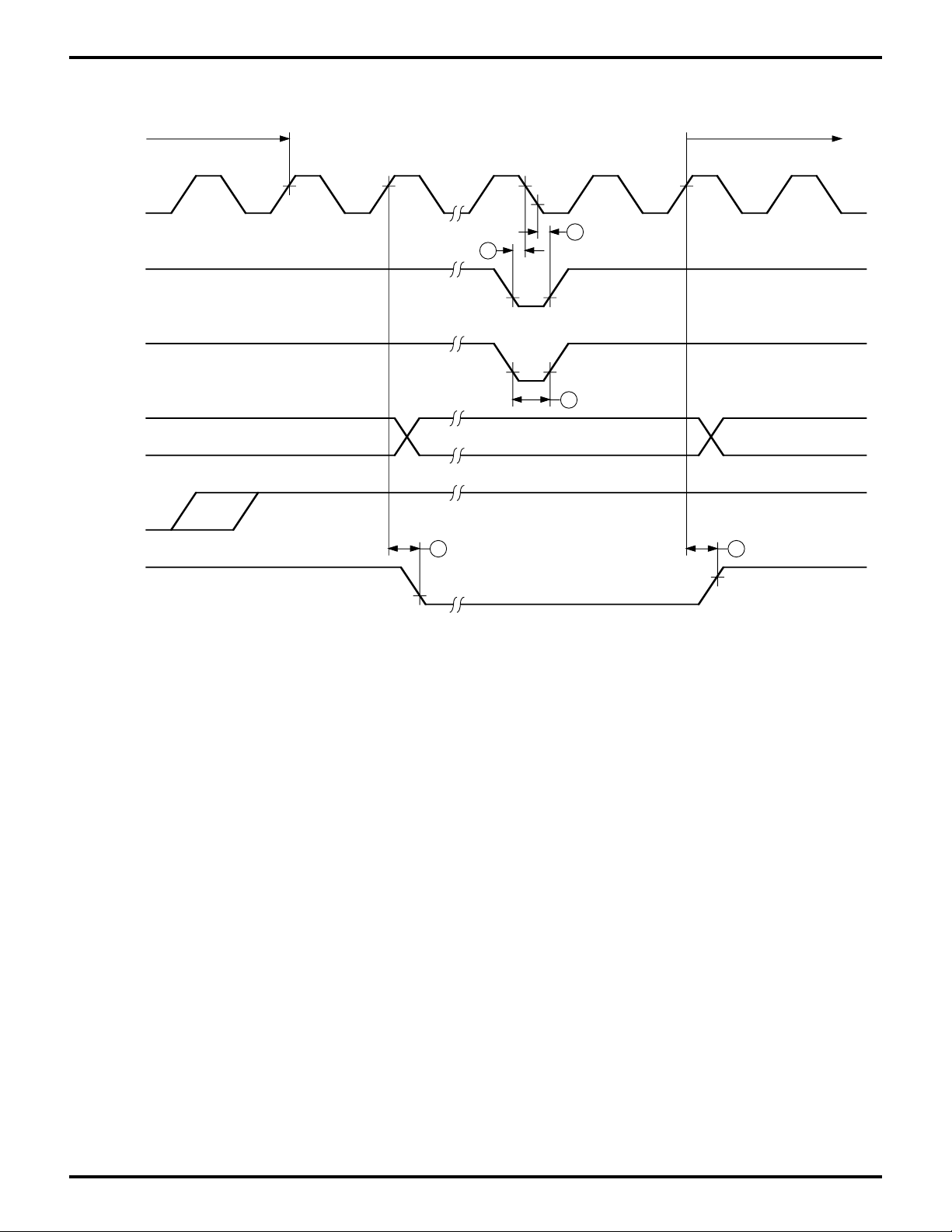
Figure 11. E Clock Timing
(Minimum timing example
of PWEL and PWEH)
TOUT
Timer Data
Reg = 0000H
55
Figure 12. Timer Output Timing
DS971890301
11
Zilog
TIMING DIAGRAMS (Continued)
SLP Instruction Fetch Next Opcode Fetch
T3 T1 T2 TS TS T1 T2
Ø
/INTi
/NMI
A18-A0
PRELIMINARY
32
31
33
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
/MREQ, /M1
/RD
/HALT
43 44
Figure 13. SLEEP Execution Cycle
12
DS971890301
Zilog
TIMING DIAGRAMS (Continued)
CSI/O Clock
Transmit Data
(Internal Clock)
Transmit Data
(External Clock)
Receive Data
(Internal Clock)
PRELIMINARY
56 56
5757
11 tcyc 11 tcyc
5958 5958
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
Receive Data
(External Clock)
/MREQ
/RAMCS
11.5 tcyc
16.5 tcyc 16.5 tcyc
6160 60 61
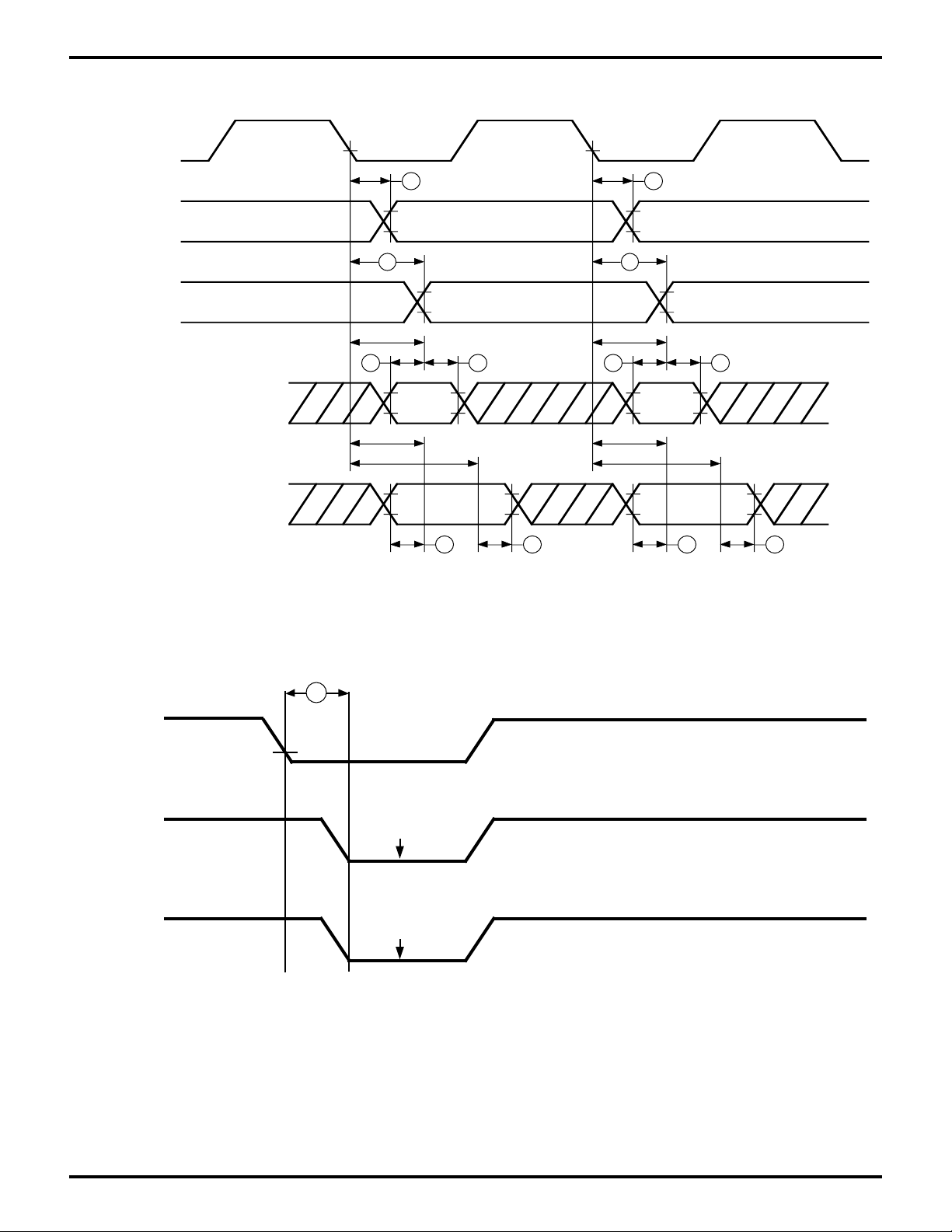
Figure 14. CSI/O Receive/Transmit Timing
71
11.5 tcyc
/ROMCS
DS971890301
Figure 15. /ROMCS and /RAMCS Timing
13
Zilog
TIMING DIAGRAMS (Continued)
T1 T2 TW T3 T1
0
PRELIMINARY
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
Address
/MREQ
/RD
/WR
Address Valid
7
8
9
22
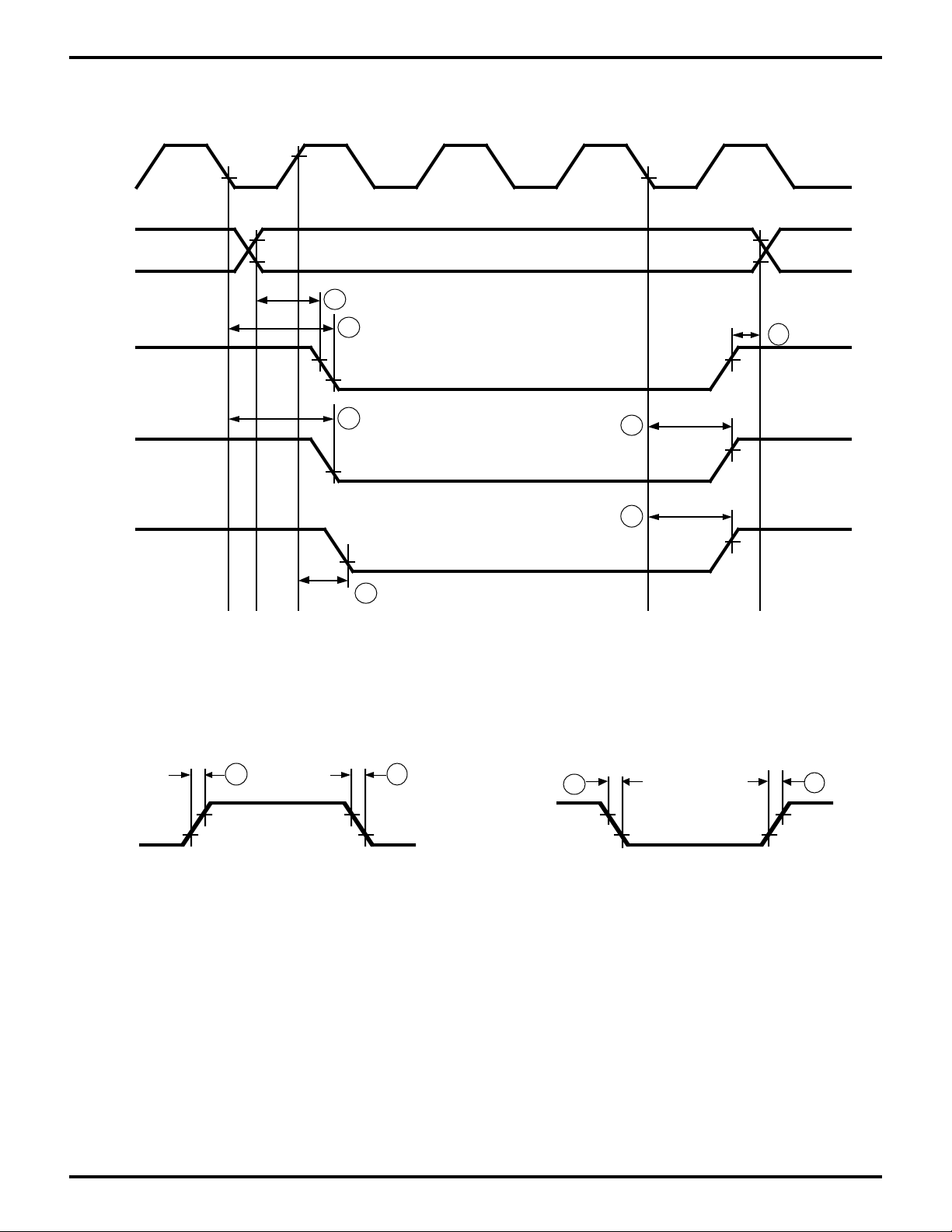
Figure 16. /MWR and /MRD Timing
11
13
24
65 66
EXTAL
VIL1
Figure 17. External Clock Rise Time and Fall Time
14
VIH1
VIH1
VIL1
70
Figure 18. Input Rise and Fall Time
(Except EXTAL, /RESET)
DS971890301
69

Zilog
PRELIMINARY
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
AC CHARACTERISTICS
(V
= 5V ±10% or VCC = 3.3V ±10%, over specified temperature range unless otherwise noted
CC
33 MHz Characteristics Apply Only to 5V Operation.)
Z8L189-20 MHz Z80189-33 MHz
No Sym Parameter Min Max Min Max Unit Notes
1 tcyc Clock Cycle Time 50 2000 33 2000 ns [1]
2 tCHW Clock H Pulse Width 15 10 ns [1]
3 tCLW Clock L Pulse Width 15 10 ns [1]
4 tcf Clock Fall Time 10 5 ns [1]
5 tcr Clock Rise Time 10 5 ns [1]
6 tAD /PHI to Address Valid 15 15 ns
7 tAS Address Valid to /MREQ, /IRQ 5 5 ns
8 tMED1 /PHI to /MREQ Delay 3 3 ns [3]
9 tRDD1 /PHI to /RD Delay (IOC=1) 25 15 ns
/ PHI to /RD Delay (IOC=0) 25 15 ns
10 tM1D1 /PHI to /M1 Delay 35 15 ns
11 tAH Address Hold Time from (MREQ, IOREQ, RD, WR) 5 5 ns
12 tMED2 /PHI to /MREQ Delay 25 15 ns
13 tRDD2 /PHI to /RD Delay 25 15 ns
14 tM1D2 /PHI to /M1 Delay 40 15 ns
15 tDRS Data Read Setup Time 10 10 ns [3]
16 tDRH Data Read Hold Time 0 0 ns
17 tSTD1 /PHI to /ST Delay 30 15 ns
18 tSTD2 /PHI to /ST Delay 30 15 ns
19 tWS WAIT Setup Time to /PHI 15 10 ns [2]
20 tWH WAIT Hold Time from /PHI 10 5 ns
21 tWDZ /PHI to Data Float Display 35 20 ns
22 tWRD1 /PHI to /WR Delay 25 15 ns
23 tWDD /PHI to Write Data Delay Time 25 15 ns
24 tWDS Write Data Setup Time to /WR 10 10 ns
25 tWRD2 /PHI to /WR Delay 25 15 ns
26 tWRP Write Pulse Width (Memory Write Cycle) 75 45 ns
26a tWRP Write Pulse Width (I/O Write Cycle) 130 70 ns
27 tWDH Write Data Hold Time from /WR 10 5 ns
28 tIOD /PHI to /IORQ Delay (IOC=1) 25 15 ns
/PHI to /IORQ Delay (IOC=0) 25 15 ns
29 tIOD2 /PHI to /IORQ Delay 25 15 ns
30 tIOD3 /M1 to /IORQ Delay 100 80 ns
31 tINTS /INT Setup Time to /PHI 20 15 ns
32 tINTH /INT Hold Time from /PHI 10 10 ns
33 tNMIW NMI Pulse Width 35 25 ns
34 tBRS BUSREQ Setup Time to /PHI 10 10 ns
35 tBRH BUSREQ Hold Time from /PHI 10 10 ns
36 tBAD1 /PHI to /BUSACK Delay 25 15 ns
37 tBAD2 /PHI to /BUSACK Delay 25 15 ns
38 tBZD /PHI to Bus Floating Delay Time 40 30 ns
39 tMEWH MREQ Pulse Width (High) 35 25 ns
40 tMEWL MREQ Pulse Width (Low) 35 25 ns
DS971890301
15

Zilog
PRELIMINARY
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
AC CHARACTERISTICS (Continued)
Z80189/Z8L189
(V
= 5V ±10% or VCC = 3.3V ±10%, over specified temperature range unless otherwise noted
CC
33 MHz Characteristics Apply Only to 5V Operation.)
Z8L189-20 MHz Z80189-33 MHz
No Sym Parameter Min Max Min Max Unit Notes
41 tRFD1 /PHI to /RFSH Delay 20 15 ns
42 tRFD2 /PHI to /RFSH Delay 20 15 ns
43 tHAD1 /PHI to /HALT Delay 15 15 ns
44 tHAD2 /PHI to /HALT Delay 15 15 ns
45 tDRQS DREQ Setup Time to /PHI 20 15 ns
46 tDRQH DREQ Hold Time from /PHI 20 15 ns
47 tTED1 /PHI to /TEND Delay 25 15 ns
48 tTED2 /PHI to /TEND Delay 25 15 ns
49 tED1 /PHI to /E Delay 30 15 ns
50 tED2 /PHI /or to /E Delay 30 15 ns
51 PWEH E Pulse Width (High) 25 20 ns
52 PWEL E Pulse Width (Low) 50 40 ns
53 tEr Enable Rise Time 10 10 ns
54 tEf Enable Fall Time 10 10 ns
55 tTOD /PHI to Timer Output Delay 75 50 ns
56 tSTDI CSI/O Transmit Data Delay (Internal Clock Operation) 75 60 ns
57 tSTDE CSI/O Transmit Data Delay (External Clock Operation) 7.5 tcyc+75 7.5 tcyc+60 ns
58 tSRSI CSI/O Receive Data Setup Time (Internal Clock Operation) 1 1 phi cycles
59 tSRHI CSI/O Receive Data Hold Time (Internal Clock Operation) 1 1 phi cycles
60 tSRSE CSI/O Receive Data Setup Time (External Clock Operation) 1 1 phi cycles
61 tSRHE CSI/O Receive Data Hold Time (External Clock Operation) 1 1 phi cycles
62 tRES RESET Setup Time to /PHI 40 25 ns
63 tREH RESET Hold Time from /PHI 25 15 ns
64 tOSC Oscillator Stabilization Time 20 20 ns
65 tEXr External Clock Rise Time (EXTAL) 10 5 ns
66 tEXf External Clock Fall Time (EXTAL) 10 5 ns
67 tRr Reset Rise Time 50 50 ms [2]
68 tRf Reset Fall Time 50 50 ms [2]
69 tIr Input Rise Time (Except EXTAL, RESET) 50 50 ns [2]
70 tIf Input Fall Time (Except EXTAL, RESET) 50 50 ns [2]
71 tdCS MREQ Valid to RAMCS and ROMCS Valid Delay 5 5 ns [3]
Notes:
[1] tcyc = tCHW + tCLW + tcf + tcr.
[2] If the rise and fall times are greater than the specified maximums,
other specifications will not be met.
[3] SL1832 is test screened such that specifications 8, 15, and 71 are
tested to 18 ns (Tmeol + Tors + Trlcs = 18 ns).
16
DS971890301
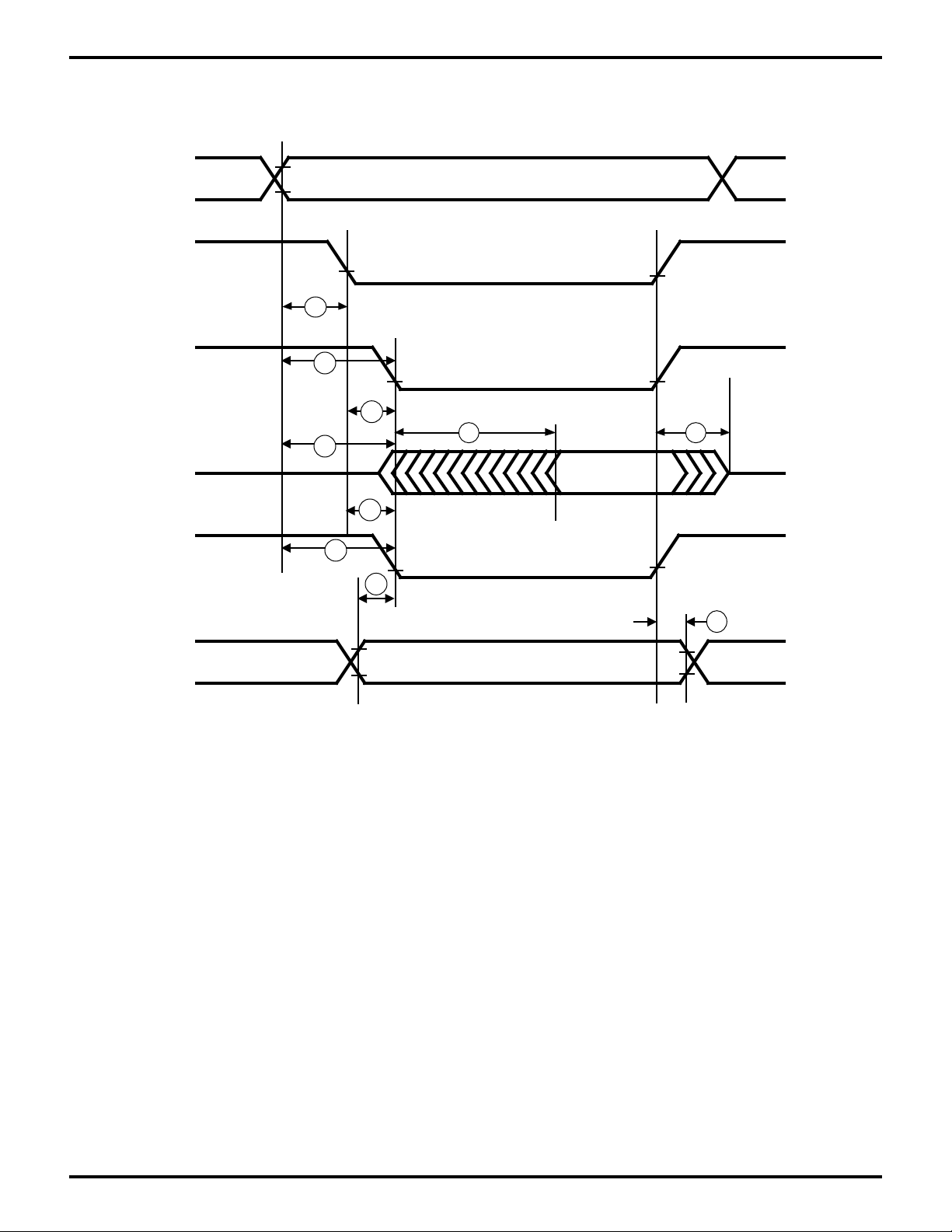
Zilog
PRELIMINARY
AC CHARACTERISTICS (Continued)
Read/Write External Bus Master Timing
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
Address
/IORQ
/RD
Data
/WR
A7-A0
7
8
2
1
4
5
Data Out
2
9
6
3
Data
Data In
Figure 19. Read/Write External Bus Master Timing
DS971890301
17

Zilog
PRELIMINARY
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
AC CHARACTERISTICS (Continued)
Read/Write External Bus Master Timing
Table 1. External Bus Master Timing
Z8L189-20 MHz Z80189-33 MHz
No Sym Parameter Min Max Min Max Unit Notes
1 TsA(wf)(rf) Address to WR or RD Fall Time 20 20 ns
2 TsIO(wf)(rf) IORQ Fall to WR or RD Fall Time 20 20 ns
3 Th Data Hold Time (from WR Rise) 0 0 ns
4 TdRD(DO) RD Fall to Data Out Delay 35 35 ns
5 TdRIr(DOz) RD, IORQ Rise to Data Float Time 0 0 ns
6 TsDI(WRf) Data In to WR Fall Setup Time 20 20 ns
7 TsA(IORQf) Address to IORQ Fall Setup Time 35 35 ns
8 TsA(RDf) Address to RD Fall Setup Time 35 35 ns
9 TsA(WRf) Address to WR Fall Setup Time 35 35 ns
Table 2. 16550 MIMIC Timing
Z8L189-20 MHz Z80189-33 MHz
No Sym Parameter Min Max Min Max Unit Notes
1 TsAR Address Setup to HRD Fall Time 30 30 ns
2 TsCSR Address Setup to CS Fall Time 30 30 ns
3 TsAW Address Setup to HWR Fall Time 30 30 ns
4 TsCSW HCS Setup to HWR Fall Time 30 30 ns
5 tAh Address Hold Time 20 20 ns
6 tCSh HCS Hold Time 20 20 ns
7 tDs Data Setup Time 30 30 ns
8 tDh Data Hold Time 30 30 ns
9 tWc Write Cycle Delay 2.5 2.5 phi cycles
10 tRvD Delay from HRD Fall to Data Valid 125 125 ns
11 tHz HRD Rise to Data Float Delay 100 100 ns
12 tRc Read Cycle Delay 125 125 ns
13 tRDD HRD Toggle to Driver Enable/Disable 60 60 ns
14 tSINT Delay fromwr RBR Reg. to Assert HINTR 2.0 2.0 phi cycles
15 tRINT Delay from /HRD of RBR to Deassert HINTR 2.0 2.0 phi cycles
16 tHR Delay from /WR THR to Reset HINTR 2.5 2.5 phi cycles
17 TSTI Delay from MPU /RD of THR to Assert HINTR 2.0 2.0 phi cycles
18 TIR Delay from /RD to Reset Interrupt 75 75 ns
18
DS971890301
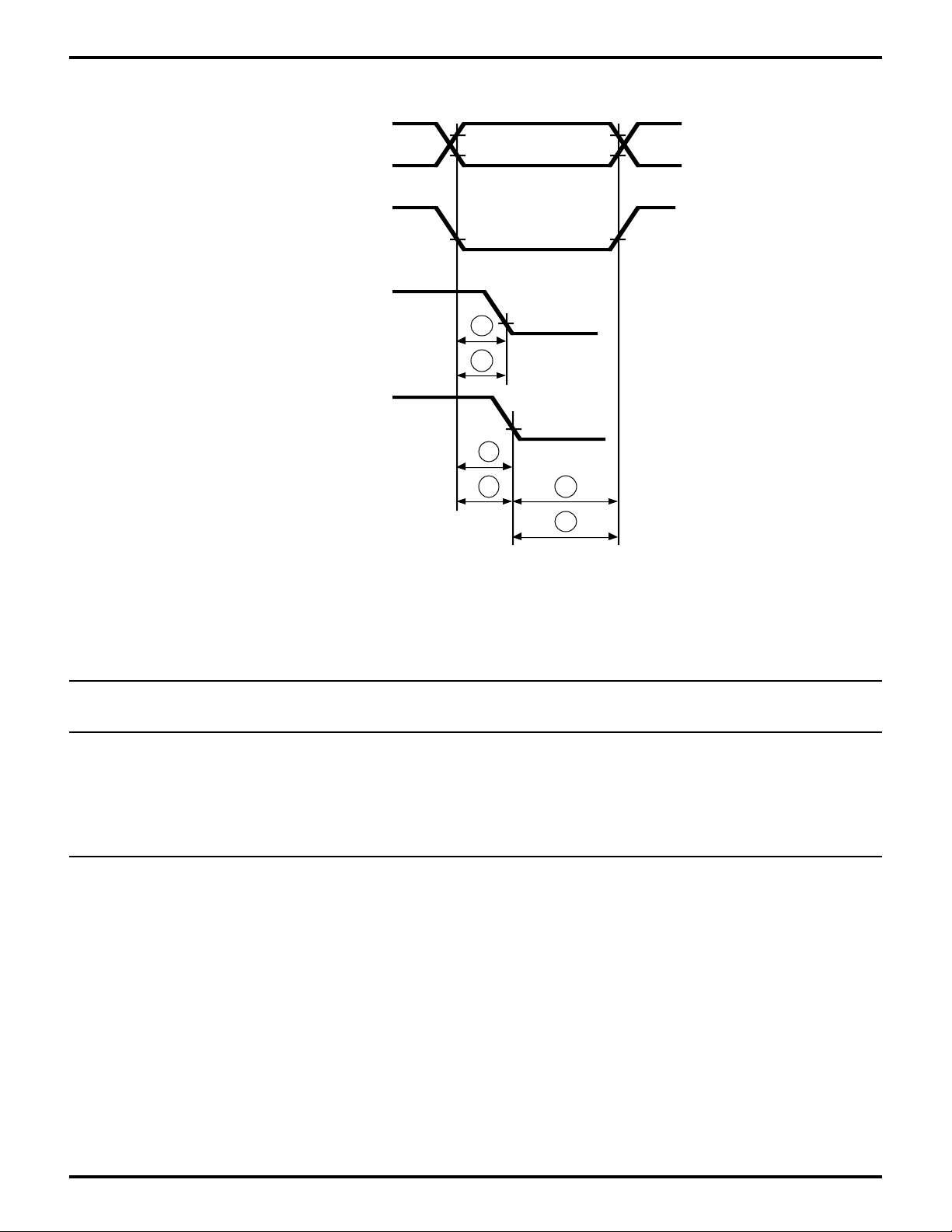
Zilog
16550 MIMIC TIMING
/HCS
PRELIMINARY
ValidHA2, HA1, HA0
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
/HRD
/HWR
Figure 20. PC Host /RD /WR Timing
Table 3. PC Host /RD /WR Timing Table
No Symbol Parameter Min Max Min Max Units
1 TsAR H Address to/HRD Fall Setup 30 30 ns
2 tsCSR /HCS to /HRD Fall Setup 30 30 ns
3 tsAW H Address to /HWR Fall Setup 30 30 ns
4 tsCSW /HCS to /HRD Fall Setup 30 30 ns
5 tAh H Address from /HRD /HWR Hold 20 20 ns
6 tCSh /HCS from /HRD /HWR Hold 20 20 ns
1
2
3
4 5
6
Z80L189-20 MHz Z80189-33 MHz
DS971890301
19
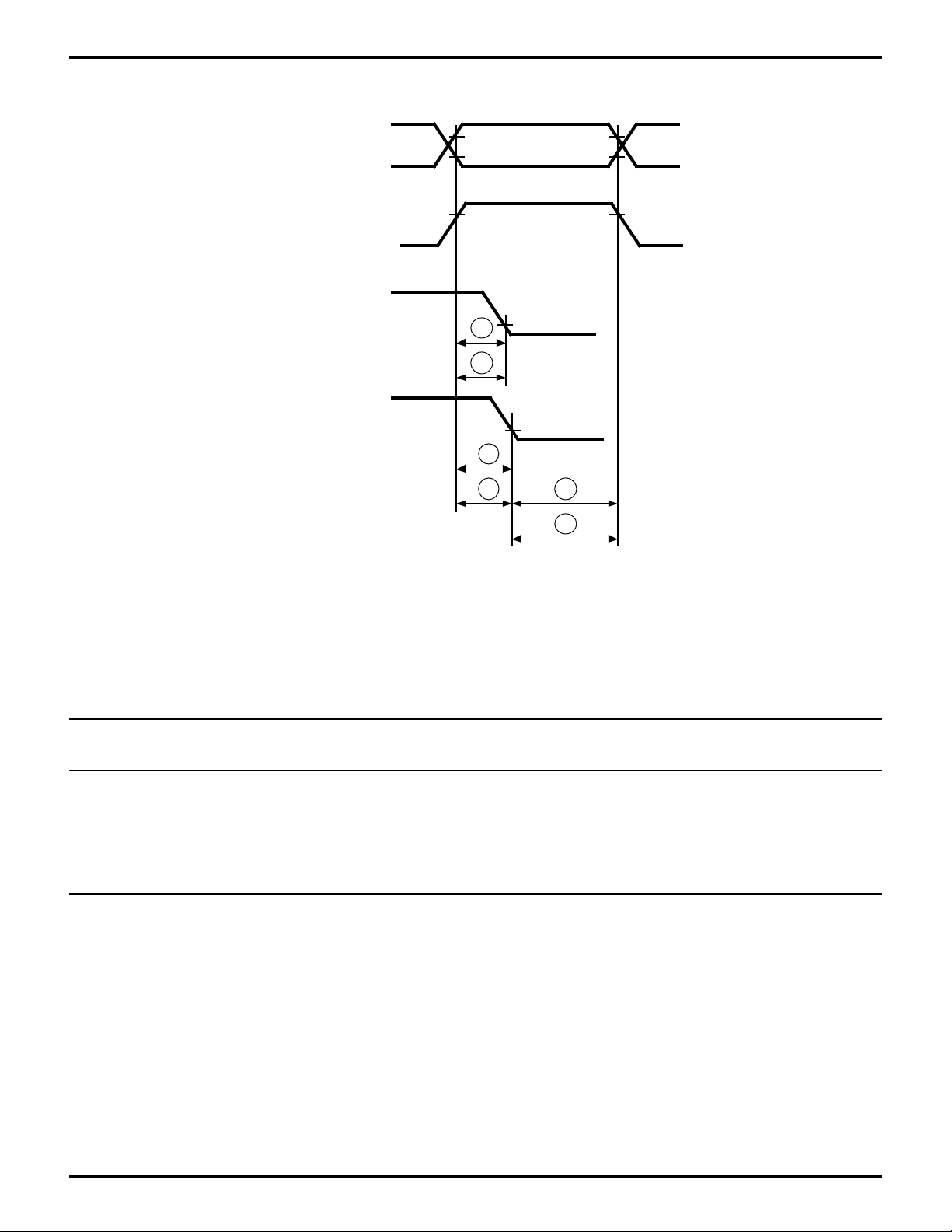
Zilog
16550 MIMIC TIMING (Continued)
HAEN
PRELIMINARY
Valid/HA3 - /HA9
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
/HRD
/HWR
Figure 21. Com Port Decode Mode
PC Host /RD /WR Timing
Table 4. Com Port Decode Mode
PC Host /RD /WR Timing Table
No Symbol Parameter Min Max Min Max Units
1
2
3
4 5
6
Z8L189-20 MHz Z80189-33 MHz
1 tsAR H Address to/HRD Fall Setup 30 30 ns
2 tsCSR /HCS to /HRD Fall Setup 30 30 ns
3 tsAW H Address to /HWR Fall Setup 30 30 ns
4 tsCSW /HCS to /HRD Fall Setup 30 30 ns
5 tAh H Address from /HRD /HWR Hold 20 20 ns
6 tCSh /HCS from /HRD /HWR Hold 20 20 ns
20
DS971890301
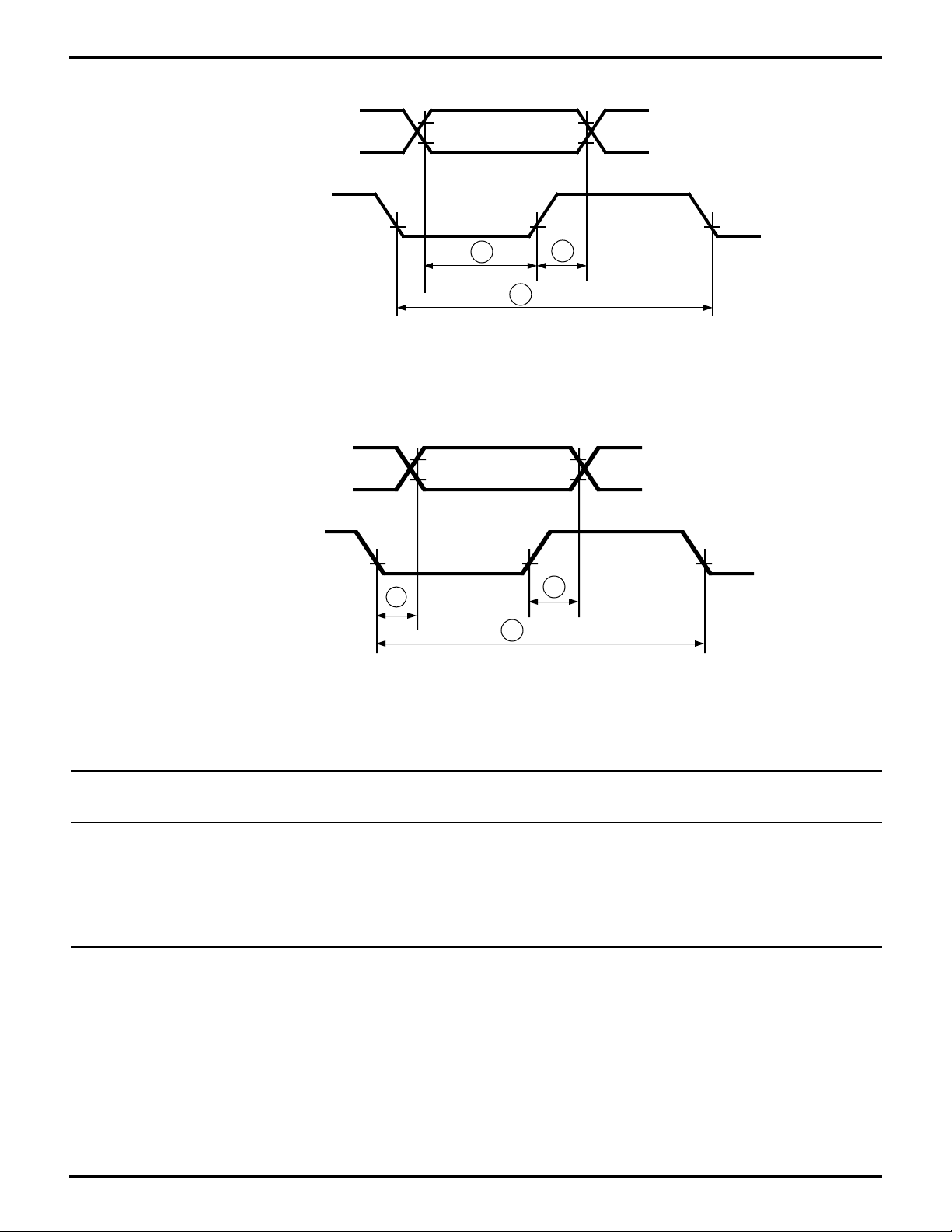
Zilog
16550 MIMIC TIMING (Continued)
/HWR
PRELIMINARY
ValidHD7-HD0
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
7
Figure 22. Data Setup and Hold, Output Delay, Write Cycle
ValidHD7-HD0
/HRD
10
12
Figure 23. Data Setup and Hold, Output Delay, Read Cycle
8
9
11
Table 5. Data Setup and Hold, Output Delay, Read Cycle Table
Z8L189-20 MHz Z80189-33 MHz
No Sym Parameter Min Max Min Max Units
7 tDs Data In to /HWR Rise Setup 30 30 ns
8 tDh Data In from /HWR Rise Hold 30 30 ns
9 tWc Write Cycle Delay 2.5 2.5 phi cycles
10 tRvd /HRD Fall to Data Out Valid Delay 125 125 ns
11 THz /HRD Rise to Data Out Float Delay 100 100 ns
12 tRc Read Cycle Delay 2.5 2.5 phi cycles
DS971890301
21
Zilog
PRELIMINARY
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
16550 MIMIC TIMING (Continued)
/HRD
/HDDIS
13
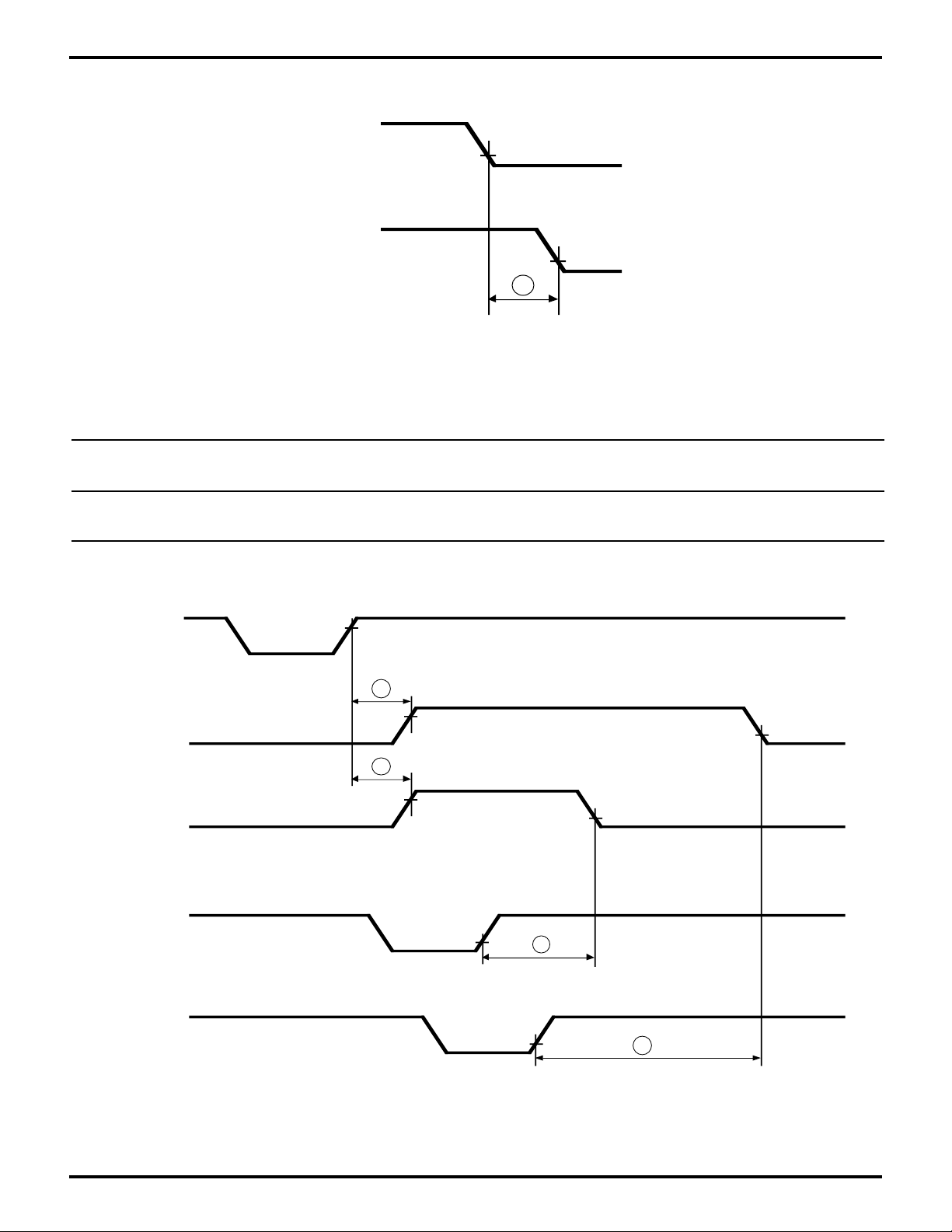
Figure 24. Driver Enable Timing
Table 6. Driver Enable Timing Table
Z8L189-20 MHz Z80189-33 MHz
No Sym Parameter Min Max Min Max Units
Z80189/Z8L189
13 tRDD /HRD to Driver
Enable/Disable 60 60 ns
/WR (MPU)
RBR
HINTR
(Trigger
Level)
HINTR
(Line
Status
RDR
/HRD LSR
14
14
15
22
/HRD RBR
15
Figure 25. Interrupt Timing RCVR FIFO
DS971890301
Zilog
PRELIMINARY
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
16550 MIMIC TIMING (Continued)
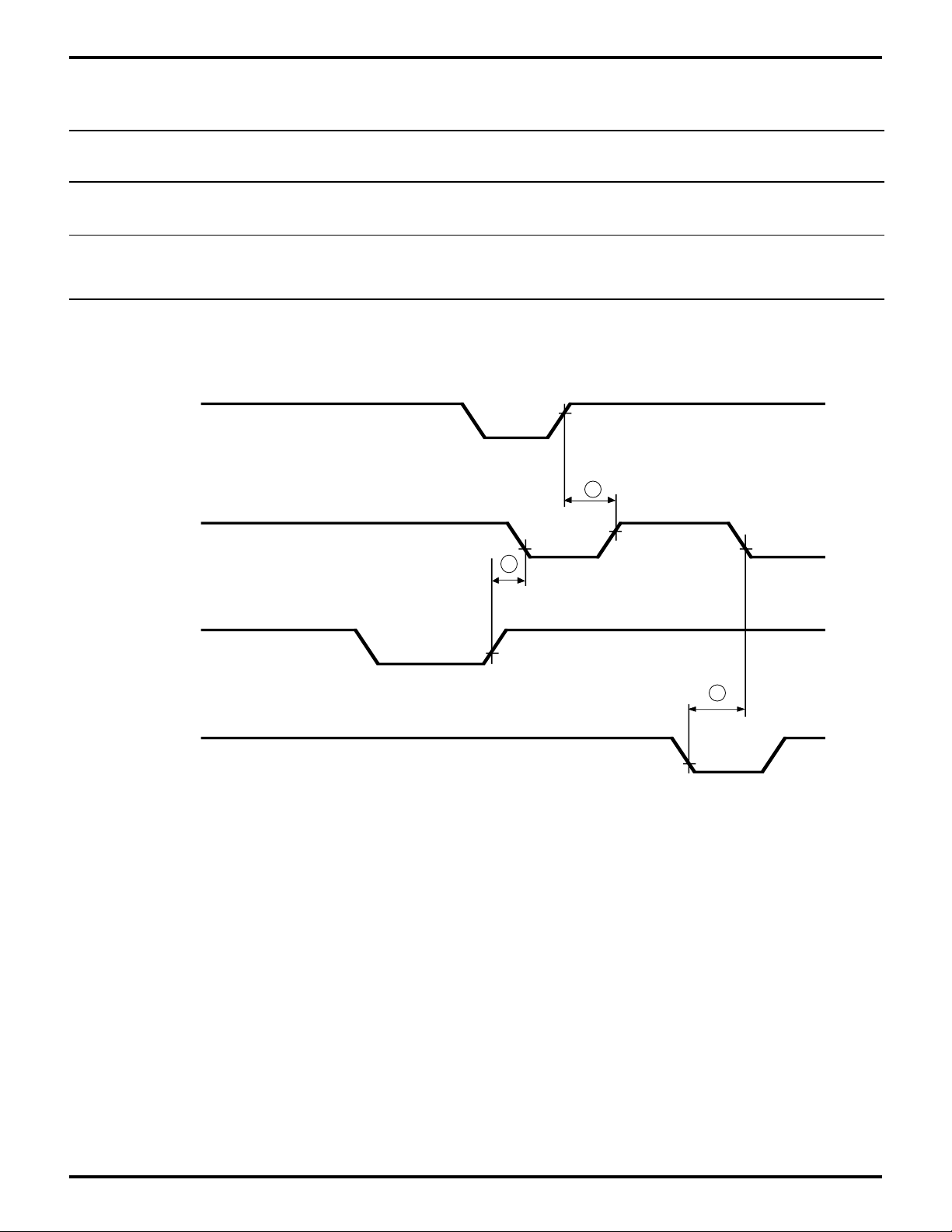
Table 7. Interrupt Timing RCVR FIFO Table
Z8L189-20 MHz Z80189-33 MHz Units
No Sym Parameter Min Max Min Max
14 tSINT Delay from Stop to Set 2 2 phi cycles
Interrupt
15 tRINT Delay from /HRD
(RD RBR or RD LSR) 2 2 phi cycles
to Reset Interrupt
/RD (MPU)
TxFIFO
Z80189/Z8L189
HINTR
THRE
/WR (Host)
THR
/RD (Host)
11R
17
16
18
Figure 26. Interrupt Timing Transmitter FIFO
DS971890301
23
Zilog
PRELIMINARY
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
16550 MIMIC TIMING (Continued)
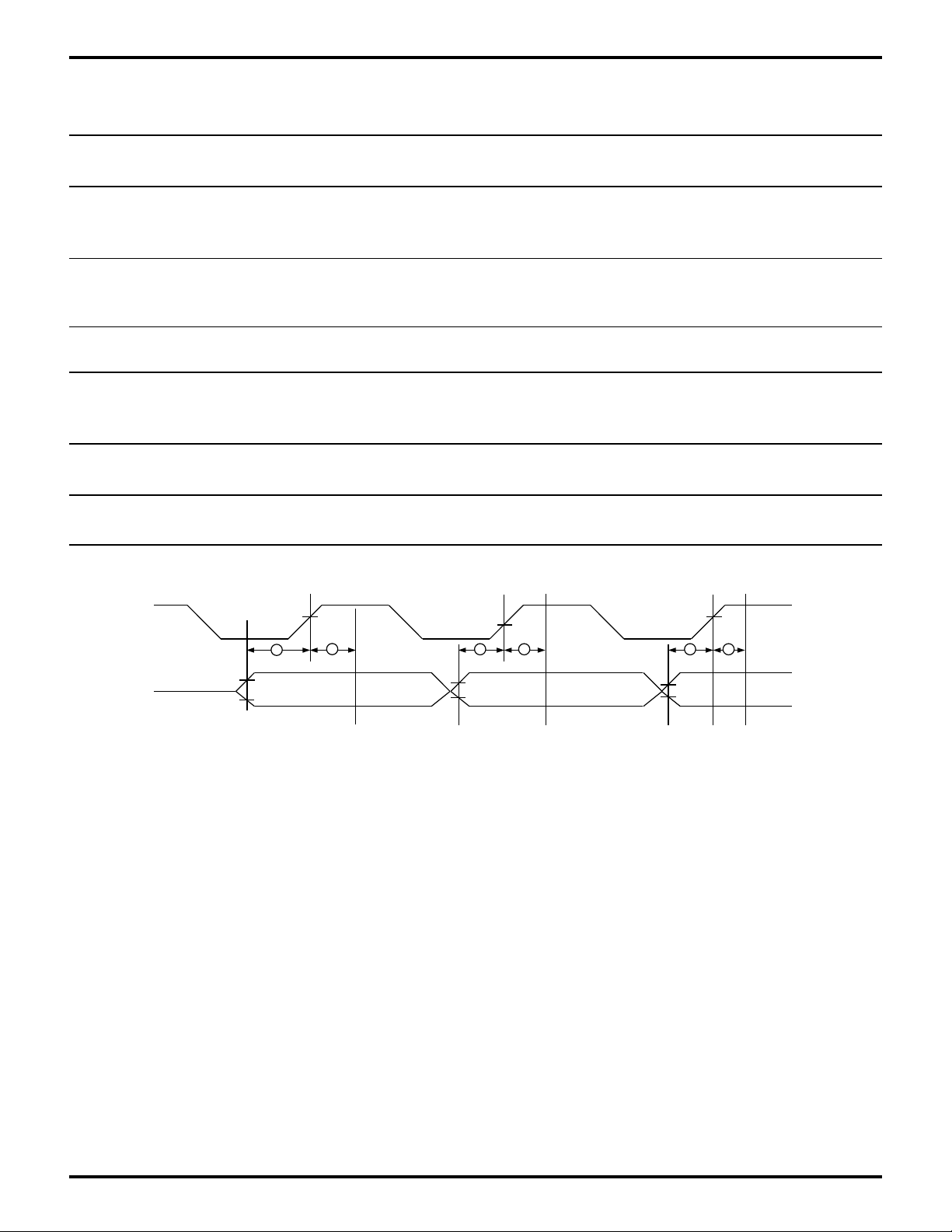
Table 8. Interrupt Timing Transmitter FIFO Table
Z8L189-20 MHz Z80189-33 MHz
No Sym Parameter Min Max Min Max Units
16 tHR Delay from /WR 2.5 2.5 phi cycles
(WR THR) to Reset
Interrupt
17 TSTI Delay from Stop to 2 2 phi cycles
Interrupt (THRE)
18 TIR Delay from /RD to 2.5 2.5 phi cycles
Reset Interrupt
Table 9. I/O Port Timing Table
Z8L189-20 MHz Z80189-33 MHz
No Sym Parameter Min Max Min Max Units
Z80189/Z8L189
1 TsPIA(WR) Data Setup Time to (Port) WR Fall 20 20 ns
2 TdWR(PIA) Data Valid Delay from WR Rise 60 60 ns
/WR
Port
1
2
Port (Output)
1 2 1 2
Port Output Data 1 (Out) Port Output Data 2 (Out)
Figure 27. I/O Port Timing Diagram
24
DS971890301

Zilog
PRELIMINARY
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
PC DMA TIMING
Table 10. PC DMA Mailbox Timing
PD DMA Write: Memory-Read, I/O Write DMA Bus Cycle
Z8L189-20 MHz Z80189-33 MHz
No Sym Parameter Min Max Min Max Units
1 tACKWh /HDACK Active Hold 144 144 ns
/HWR Inactive
2 tWRs /HDACK Active to 301 301 ns
/HWR Active
3 tWR /HWR Active to 454 454 ns
Inactive
4 tvWR Data Valid to /HWR 133 133 ns
Inactive
5 tDWRh Write Data Valid Hold 25 25 ns
from /HWR Inactive
Table 11. PC DMA Mailbox Timing
PD DMA Read: I/O-Read, Memory-Write DMA Bus Cycle
Z8L189-20 MHz Z80189-33 MHz
No Sym Parameter Min Max Min Max Units
1 tACKRh /HDACK Active Hold 89 89 ns
/HRD Inactive
2 tRDs /HDACK Active to 62 62 ns
/HRD Active
3 tRD /HRD Active to 749 749 ns
Inactive
4 tvRD Data Valid from /HRD 215 215 ns
Active
5 tDRDh Read Data Valid Hold 0 0 ns
from /HRD Inactive
6 tDZ Data Float from /HRD 50 50 ns
Inactive
DS971890301
25
Zilog
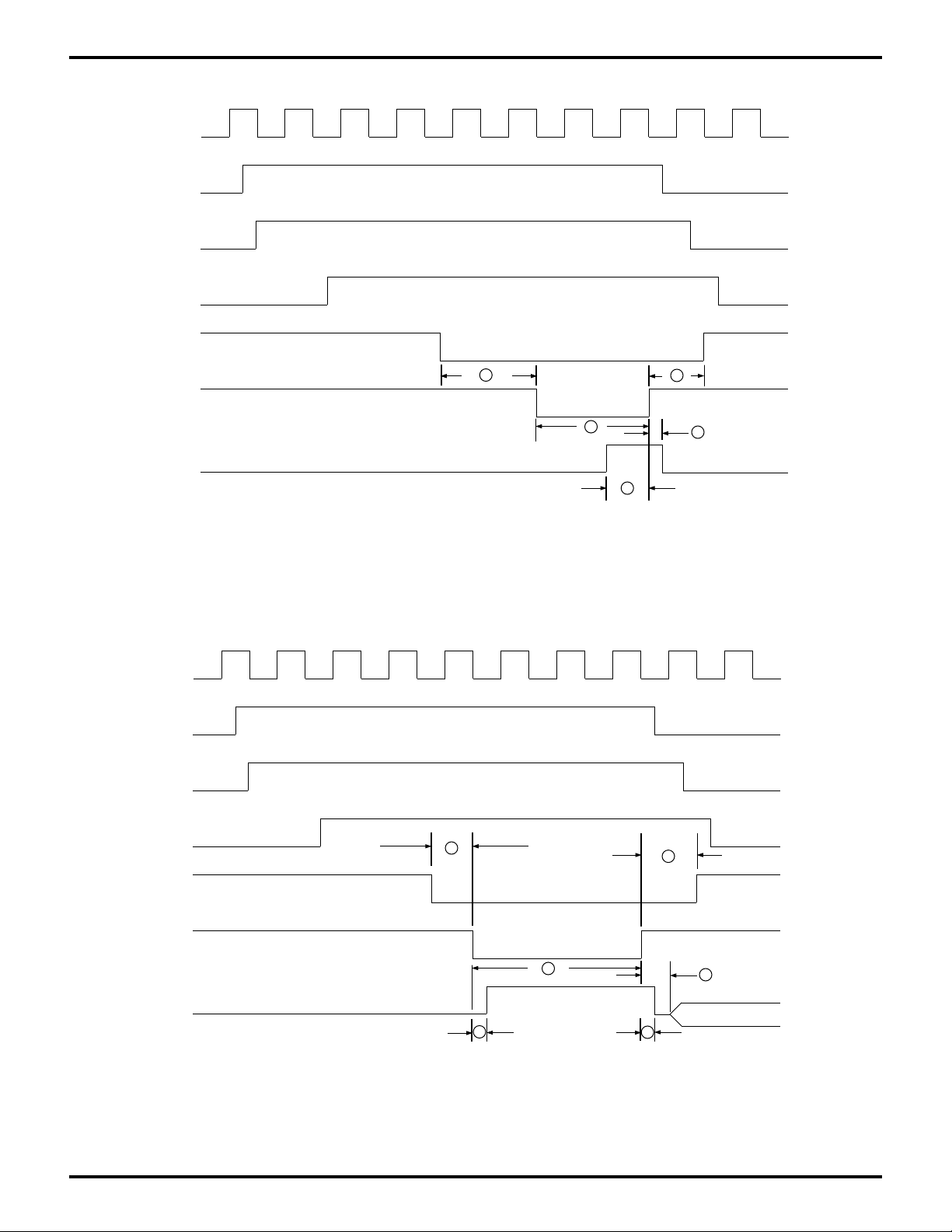
PC DMA TIMING DIAGRAMS
PC Clock
Internal
HDRQR
HDRQ
/AEN
/HDACK
PRELIMINARY
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
(1)
/HWR
HD [0:7]
Valid
PC Clock
Internal
HDRQR
HDRQ
(1) The HDRQ will not fall inactive until it ses the
falling edge of /HWR during the /HDACK cycle.
Figure 28. PC DMA Write: Memory-Read, I/O Write
DMA Bus Cycle on PC AT Bus
2
3
5
1
4
(1)
26
/AEN
/HDACK
/HRD
HD [0:7]
Valid
(1) The HDRQ will not fall inactive until it sees the
falling edge of /HRD during the /HDACK cycle.
2
3
4
5
Figure 29. PC DMA Read: I/O-Read, Memory-Write
DMA Bus Cycle on PC AT Bus
1
6
DS971890301

Zilog
PIN DESCRIPTION
CPU Signals
PRELIMINARY
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
A19-A0. Address Bus (Input/Output, active High, tri-state).
A0-A19 form a 20-bit address bus. The Address Bus
provides the address for memory data bus exchanges, up
to 1 Mbyte, and I/O data bus exchanges, up to 64K. The
address bus enters a high impedance state during reset
and external bus acknowledge cycles, as well as during
SLEEP and HALT states. This bus is an input when the
external bus master is accessing the on-chip peripherals.
D7-D0. Data Bus (Bidirectional, active High, tri-state). D0D7 constitute an 8-bit bidirectional data bus, used for the
transfer of information to and from I/O and memory devices. The data bus enters the high impedance state
during reset and external bus acknowledge cycles, as well
as during SLEEP and HALT states.
/RD. Read (Input/Output, active Low, tri-state). /RD indicates that the CPU wants to read data from memory or an
I/O device. The addressed I/O or memory device should
use this signal to gate data onto the CPU data bus.
/WR. Write (Output, active Low, tri-state). /WR indicates
that the CPU data bus holds valid data to be stored at the
addressed I/O or memory location.
/IORQ. I/O Request (Input/Output, active Low, tri-state).
/IORQ indicates that the address bus contains a valid I/O
address for an I/O read or I/O write operation. /IORQ is also
generated, along with /M1, during the acknowledgment of
the /INT0 input signal to indicate that an interrupt response
vector can be placed onto the data bus.
/M1. Machine Cycle 1 (Input/Output, active Low). Together
with /MREQ, /M1 indicates that the current cycle is the
opcode fetch cycle of an instruction execution. Together
with /IORQ, /M1 indicates that the current cycle is for an
interrupt acknowledge. It is also used with the /HALT and
ST signal to decode status of the CPU machine cycle.
/MREQ. Memory Request (Input/Output, active Low, tristate). /MREQ indicates that the address bus holds a valid
address for a memory read or memory write operation.
/WAIT. (Input, active Low). /WAIT indicates to the MPU that
the addressed memory or I/O devices are not ready for a
data transfer. This input is used to induce additional clock
cycles into the current machine cycle. The /WAIT input is
sampled on the falling edge of t2 (and subsequent wait
states). If the input is sampled low, then additional wait
states are inserted until the /WAIT input is sampled high, at
which time execution will continue.
/HALT. Halt/Sleep Status (Output, active Low). This output
is asserted after the CPU has executed either the HALT or
SLP instruction, and is waiting for either non-maskable or
maskable interrupt before operation can resume. It is also
used with the /M1 and ST signals to decode status of the
CPU machine cycle. On exit of Halt/Sleep, the first instruction fetch is delayed 16 clock cycles after the /HALT pin
goes high.
/BUSACK. Bus Acknowledge (Output, active Low
tri-state). /BUSACK indicates to the requesting device, the
MPU address and data bus, and some control signals,
have entered their high-impedance state.
/BUSREQ. Bus Request (Input, active Low). This input is
used by external devices (such as DMA controllers) to
request access to the system bus. This request has a
higher priority than /NMI and is always recognized at the
end of the current machine cycle. This signal will stop the
CPU from executing further instructions and places the
address and data buses, and other control signals, into the
high impedance state.
/NMI. Non-maskable interrupt (Input, negative edge triggered). /NMI has a higher priority than /INT and is always
recognized at the end of an instruction, regardless of the
state of the interrupt enable flip-flops. This signal forces
CPU execution to continue at location 0066H.
/INT0. Maskable Interrupt Request 0 (Input, active Low).
This signal is generated by external I/O devices. The CPU
will honor this request at the end of the current instruction
cycle as long as the /NMI and /BUSREQ signals are
inactive. The CPU acknowledges this interrupt request
with an interrupt acknowledge cycle. During this cycle,
both the /M1 and /IORQ signals will become active.
/INT1, /INT2. Maskable Interrupt Requests 1 and 2 (inputs,
active Low). This signal is generated by external I/O
devices. The CPU will honor these requests at the end of
the current instruction cycle as long as the /NMI, /BUSREQ,
and /INT0 signals are inactive. The CPU will acknowledge
these interrupt requests with an interrupt acknowledge
cycle. Unlike the acknowledgment for /INT0, during this
cycle neither the /M1 or /IORQ signals will become active.
These pins may be programmed to provide active low
level, rising or falling edge interrupts. The level of the
external /INT1 and /INT2 pins may be read through bits
PC6 and PC7 of parallel port C.
DS971890301
27

Zilog
PIN DESCRIPTION (Continued)
PRELIMINARY
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
/RFSH. Refresh (Output, active Low, tri-state). Together
with /MREQ,/RFSH indicates that the current CPU machine
cycle and the contents of the address bus should be used
for refresh of dynamic memories. The low order 8 bits of the
address bus (A7-A0) contain the refresh address.
/MRD. Memory Read (Output, active Low, tri-state). /MRD
is active when both the internal /MREQ and /RD signals are
active.
/MWR. Memory write (output, active Low, tri-state). /MWR
is active when both the internal /MREQ and /WR signals are
active.
Z180™ MPU UART and SIO Signals
CKA0, CKA1. Asynchronous Clock 0 and 1 (Bidirectional,
active High). When in output mode, these pins are
the transmit and receive clock outputs from the ASCI
baud rate generators. When in input mode, these pins
serve as the external clock inputs for the ASCI baud rate
generators.
CKS. Serial Clock (Bidirectional, active High). This line is
the clock for the CSIO channel.
/DCD0. Data Carrier Detect 0 (Input, active Low). This is a
programmable modem control signal for ASCI channel 0.
/RTS0. Request to Send 0 (Output, active Low, tri-state).
This is a programmable modem control signal for ASCI
channel 0.
/CTS0/CTS1. Clear to Send 0 (Input, active Low). This line
is a modem control signal for the ASCI channel 0 and 1.
Z180™ MPU DMA Signals
/TEND0. Transfer End 0 (outputs, active Low). This output
is asserted active during the last write cycle of a DMA
operation. It is used to indicate the end of the block
transfer.
/DREQ0, /DREQ1. DMA request 0 and 1 (Input, active
Low). /DREQ is used to request a DMA transfer from one
of the on-chip DMA channels. The DMA channels monitor
these inputs to determine when an external device is ready
for a read or write operation. These inputs can be programmed to be either level or edge sensed.
Z180™ MPU Timer Signals
T
. Timer Out (Output, active High). T
OUT
output from PRT channel 1. This line is multiplexed with
HINTR1 of the 16550 MIMIC.
is the pulse
OUT
16550 MIMIC Interface Signals
HD7-HD0. Host Data Bus (Input/Output, tri-state). In
Z80189, the host data bus is used to communicate between the 16550 MIMIC interface and the PC/XT/AT. It is
multiplexed with the PA7-PA0 of parallel port A.
/HDDIS. Host Driver Disable (Output, active Low). In
Z80189, this signal goes low whenever the PC/XT/AT is
reading data from the 16550 MIMIC interface. The /HDDIS
pin should also go active low on each PC DMA read cycle.
HA2-HA0. Host Address (Input). In Z80189, these pins are
the address inputs to the 16550 MIMIC interface. This
address determines which register the PC/XT/AT accesses.
TXA0. Transmit Data 0 (Output, active High). This signal is
the transmitted data from the ASCI channel 0.
TXS. Clocked Serial Transmit Data (Output, active High).
This line is the transmitted data from the CSIO channel.
RXA0. Receive Data 0 (Input, active High). This signal is
the receive data to ASCI channel 0.
RXS. Clocked Serial Receive Data (Input, active High).
This line is the receiver data for the CSIO channel.
RXA1. Received Data ASCI Channel 1.
TXA1. Transmitted Data ASCI Channel 1.
28
HA9-HA3, HAEN. Host COM Port Decode Address (Input). In Z80189, these pins are multiplexed when COM
Port Decode is enabled (default). These pins are used to
provide internal MIMIC Enable when HA9-HA3 match the
programmed MIMIC address field. HAEN is also used to
access the PC DMA Mailbox registers.
/HCS. Host Chip Select (Input, active Low). In Z80189, this
input is used by the PC/XT/AT to select the 16550 MIMIC
interface for an access. The /HCS input is disabled when
using the internal COM Port Decoder. When setting the
/HCS Force bit in the CDR register, the /HCS output is
asserted when HA3-HA9 is within the boundaries programmed by bits 3-4 of the CDR register and /HRD or
/HWR is asserted. /HCS is NOT asserted for PC DMA
Mailbox accesses.
DS971890301

Zilog
PRELIMINARY
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
/HWR. Host Write (Input, active Low). In Z80189, this input
is used by the PC/XT/AT to signal the 16550 MIMIC
interface that a write operation is taking place.
/HRD. Host Read (Input, active Low). In Z80189, this input
is used by the PC/XT/AT to signal the 16550 MIMIC
interface that a read operation is taking place.
HINTR1, HINTR2. Host Interrupt (Output, active High tristate). In Z80189, this output is used by the 16550 MIMIC
interface to signal the PC/XT/AT that an interrupt is pending. In Z80189 COM Port Decode mode, the MIMIC interrupt request can be routed to either HINTR1 or 2 depending on the COM Port Decode selected. The deselected
HINTR line will be forced to tri-state, while the selected
HINTR will follow what is programmed in the MIMIC Master
Control Register.
HC1, HC2. Host COM Select Pin 1&2 (Input). HC1 and HC2
are general-purpose inputs that can be used for COM Port
selection. The status of these pins are read by use of the
CDR register. The status of these pins can be used by
firmware to select the appropriate COM Port address
decode range.
PC7-PC0. Parallel Port C (Input/Output). These lines can
be configured as inputs or outputs on a bit by bit basis for
bits PC5-PC0. Bits PC7 and PC6 are input only and read
the level of the external /INT2 and /INT1 pins. When /INT2
and/or /INT1 are in edge capture mode writing a ‘1’ to the
respective PC7, PC6 bit clears the interrupt capture latch.
Writing a ‘0’ has no effect.
Emulation Signals
EV1, EV2. Emulation Select (Input). These two pins
determine the emulation mode the Z180 MPU is in. They
are as follows:
EV2 EV1
Mode 0 0 0 Normal mode, on-chip Z180 bus
master.
Mode 1 0 1 Emulation Adapter Mode
Mode 2 1 0 Emulator Probe Mode
Mode 3 1 1 Reserved
System Control Signals
PC DMA Mailbox Signals
/HDACK0, /HDACK1. Host DMA Acknowledge (Input,
active Low). This input signal indicates to the Z80189 that
the PC DMA controller has acknowledged the request and
will begin data transfer. /HDACK0 is multiplexed with
/CKA0 and /DREQ0. /HDACK1 is multiplexed with
/BUSREQ.
HDRQ0, HDRQ1. Host DMA Request (output, active high,
tri-state). This output requests to the PC DMA controller
that the Z80189 is ready for a DMA data transfer. HDRQ is
multiplexed with /RTS0. HDRQ1 is multiplexed with
/BUSACK.
Parallel Ports
PA7-PA0. Parallel Port A (Input/Output). These lines can
be configured as inputs or outputs on a bit-by-bit basis
when the Z80189 is operated in mode 0.
PB7-PB0. Parallel Port B (Input/Output). These lines can
be configured as inputs or outputs on a bit-by-bit basis
when the port function is selected in the System
Configuration register.
ST. Status (Output, active High). This signal is used with
the M1 and /HALT output to decode the status of the CPU
machine cycle.
/RESET. Reset Signal (Input, Active Low). /RESET signal
is used for initializing the MPU and other devices in the
system. It must be kept in the active state for a period of at
least 6 system clock cycles.
IEI. Interrupt Enable Signal (Input, active High). IEI is used
with the IEO to form a priority daisy chain when there is
more than one interrupt driven peripheral.
IE0. Interrupt Enable Output Signal (Output, active High).
In the daisy-chain interrupt control, IEO controls the interrupt
of external peripherals. IEO is active when IEI is “1” and the
CPU is not servicing an interrupt from the on-chip
peripherals. This pin is multiplexed with /IOCS1.
/IOCS1. I/O Chip Select 1 (output, active Low) is an
auxiliary chip select that decodes A7, A6, /IORQ, /M1 and
effectively decodes the address space XX80 to XXBF for
I/O transactions. A15 through A8 are not decoded so that
the chip select is active in all pages of I/O address space.
The /IOCS1 function is the default on power on or reset
condition and is changed by programming bit 2 in the
Interrupt Edge/Pin Mux Register.
DS971890301
29

Zilog
System Control Signals (Continued)
PRELIMINARY
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
/IOCS2. I/O Chip Select 2 (output, active Low) This pin is
a secondary peripheral I/O chip select. This pin is active for
I/O accesses between XXC0H to XXC7H or XXC8H to
XXCFH (programmable by bit 1 of the IOBRG register).
/RAMCS. RAM Chip Select (Output, active Low). Signal
used to access RAM based upon the address and the
RAMLBR and RAMUBR registers.
/ROMCS. ROM Chip Select (Output, active Low). Signal
used to access ROM based upon the address and the
ROMBR register.
XTAL. Crystal (Output, active High). Crystal oscillator
connection. This pin should be left open if an external clock
PIN MULTIPLEXING
To allow for COM Port decode and omission of ESCC core,
Pin Multiplexing is changed with respect to the Z182.
ESCC CH.A pins will be replaced by COM Decode and
ASCI CH.A pins as follows:
RxDA → HA6
/TRxCA → HAEN
TxDA → HINTR2
DCDB → /HRD//DCD0
/CTSB → /HWR//CTS0
is used instead of a crystal. The oscillator input is not a TTL
level (reference DC characteristics).
EXTAL. External Clock/Crystal (Input, active High). Crystal
oscillator connections. An external clock can be input to
the Z80189 on this pin when a crystal is not used. This input
is Schmitt-triggered.
PHI. System Clock (Output, active High). The output is
used as a reference clock of the MPU and the external
system.
VCC. Power Supply. +5 Volts
VSS. Power Supply. 0 Volts
When COM decode bit is set (enabled during reset) the
following pins become multiplexed as follows.
/RFSH → HA3
/WAIT → HA4
/DREQ1 → HA5
/HA6 → HA6
IEI → HA7
/HA8 → HA8
CKA1/TEND0 → HA9
/HAEN → HAEN
Note that ASCI channel 0 functions can be found in two
places. These pins are ORed with ASCI channel 0 functions that are multiplexed with Port B (pins 35-39 QFP).
/DCD0, /CTS0, RXA0 inputs will come from 78, 79, 81
(respectively) when Port B (0-4) is enabled. When MIMIC
is disabled, /HDDIS pin doubles as TXA0 output. Note that
/RTS0 has also been changed to pin 50.
These pins are selected such that they are all high-z inputs
at power up to prevent any problems with connecting
address lines directly to PC bus. Although, the COM
decode multiplexing is enabled on power-up, the COM
address decoding is disabled.
30
DS971890301

Zilog
PRELIMINARY
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Table 12. Z80189 Pin-Out
Multiplexed Pin Descriptions Primary, Secondary Pin Functions
PIN # PIN # DEFAULT SECONDARY
VQFP QFP FUNCTION FUNCTION CONTROL
14 ST
25 A0
36 A1
47 A2
58 A3
69 A4
710 A5
811 A6
912 A7
10 13 A8
11 14 A9
12 15 A10
13 16 A11
14 17 A12
15 18 V
SS
16 19 A13
17 20 A14
18 21 A15
19 22 A16
20 23 A17
21 24 A18
22 25 V
DD
23 26 A19
24 27 D0
25 28 D1
26 29 D2
27 30 D3
28 31 D4
29 32 D5
30 33 D6
Z80189/Z8L189
DS971890301
31

Zilog
PRELIMINARY
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
PIN MULTIPLEXING (Continued)
Table 12. Z80189 Pin-Out (Continued)
Multiplexed Pin Descriptions Primary, Secondary Pin Functions
PIN # PIN # DEFAULT SECONDARY
VQFP QFP FUNCTION FUNCTION CONTROL
31 34 D7
32 35 PB0 TXS System Config Reg bit 5
33 36 PB1 /CTS0 System Config Reg bit 5
34 37 PB2 /DCD0 System Config Reg bit 5
35 38 PB3 TXA0 System Config Reg bit 5
36 39 PB4 RXA0 System Config Reg bit 5
37 40 PB5 TXA1 System Config Reg bit 6
38 41 PB6 RXA1 System Config Reg bit 6
39 42 PB7 RXS//CTS1 System Config Reg bit 6
40 43 /HDACK0 CKA0//DREQ0 Host DMA Enable Reg bit 3
Z80189/Z8L189
41 44 V
42 45 HA9 CKA1//TENDO COM Decode Reg bit 0
43 46 HINTR1 T
44 47 HC2 CKS COM Decode Reg bit 0
45 48 HA5 /DREQ1 (4)
46 49 V
47 50 HDRQ0 /RTSO (6) Host DMA Enable Reg bit 3
48 51 /RAMCS
49 52 /ROMCS
50 53 EV1
51 54 EV2
52 55 HD0 PA0 Sys Config Reg bit 1
53 56 HD1 PA1 Sys Config Reg bit 1
54 57 HD2 PA2 Sys Config Reg bit 1
55 58 HD3 PA3 Sys Config Reg bit 1
56 59 HD4 PA4 Sys Config Reg bit 1
57 60 HD5 PA5 Sys Config Reg bit 1
58 61 HD6 PA6 Sys Config Reg bit 1
59 62 HD7 PA7 Sys Config Reg bit 1
DD
SS
OUT
System Config Reg bit 2
32
DS971890301

Zilog
PRELIMINARY
Z80189 MPU FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
The Z80189 includes a Zilog Z8S180 MPU (Static Z80180
MPU). This allows software code compatibility with existing Z80/Z180 software code. The following is an overview
of the major functional units of the Z80189.
Architecture
The Z80189 combines a high performance CPU core with
a variety of system and I/O resources useful in a broad
range of applications. The CPU core consists of four
functional blocks:
■ Clock Generator
■ Bus State Controller (Dynamic Memory Refresh)
■ Memory Management Unit (MMU)
■ Central Processing Unit (CPU).
The integrated I/O resources make up the remaining
functional blocks:
■ Direct Memory Access (DMA control—two channels)
■ Asynchronous Serial Communications Controller
(ASCI, two channels)
■ Programmable Reload Timers (PRT, two channels)
■ Clocked Serial I/O
■ 16550 Compatible MIMIC Interface
■ COM Port Decoder
■ PC DMA Mailbox Registers
■ Host I/O Mailbox Registers
Clock Generator. This logic generates the system clock
from either an external crystal or clock input. The external
clock is divided by two, or one if programmed, and is
provided to both internal and external devices.
In addition, there is also a clock multiplier feature which
doubles the internal clock frequency from that of the
external clock input.
Bus State Controller. This logic performs all of the status
and bus control activity associated with both the CPU and
some on-chip peripherals. This includes wait state timing,
reset cycles, DRAM refresh, and DMA bus exchanges.
Interrupt Controller. This logic monitors and prioritizes
the variety of internal and external interrupts and traps to
provide the correct responses from the CPU. To maintain
compatibility with the Z80 CPU, three different interrupt
modes are supported.
Memory Management Unit. The MMU allows the user to
“map” the memory used by the CPU (logically only 64
Kbytes) into the 1 Mbyte addressing range supported by
the Z80189. The organization of the MMU object code
maintains compatibility with the Z80 CPU while offering
access to an extended memory space. This is accomplished by using an effective “common area-banked area”
scheme.
Central Processing Unit. The CPU is microcoded to
provide a core that is object-code compatible with the Z80
CPU. It also provides a superset of the Z80 instruction set,
including 8-bit multiply. This core has been modified to
allow many of the instructions to execute in fewer clock
cycles.
DS971890301
33

Zilog
PRELIMINARY
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Table 12. Z80189 Pin-Out (Continued)
Multiplexed Pin Descriptions Primary, Secondary Pin Functions
PIN # PIN # DEFAULT SECONDARY
VQFP QFP FUNCTION FUNCTION CONTROL
60 63 PC5
61 64 PC3
62 65 PC2 /MWR Int Edge/Pin Reg bit 3
63 66 PC1
64 67 PC0
65 68 PC4
66 69 HA8
Z80189/Z8L189
67 70 V
SS
68 71 /IOCS1 IEO Int Edge/Pin reg bit 2
69 72 HA7 IEI (1) COM Decode reg bit 0
70 73 V
DD
71 74 HA6
72 75 HAEN
73 76 HINTR2
74 77 /HRD /DCD0 (2)
75 78 /HWR /CTS0 (2)
76 79 /HDDIS TXA0 Sys Conf reg bit 1
77 80 HA0
78 81 HA1 RXA0 (2)
79 82 HA2
80 83 /HCS HC1 (3)
81 84 /HALT
82 85 HA3 /RFSH COM Decode reg bit 0
83 86 /IORQ
84 87 /MREQ /MRD Int Edge/Pin Reg bit 3
85 88 /IOCS2 E I/O brg reg bit 2
86 89 /M1
87 90 /WR
88 91 /RD
89 92 PHI
90 93 V
SS
91 94 XTAL
92 95 EXTAL
93 96 HA4 /WAIT (5) COM Decode reg bit 0
94 97 HDRQ1 /BUSACK (6) Host DMA Enable Reg bit 2
95 98 /HDACK1 /BUSREQ (5) Host DMA Enable Reg bit 2
96 99 /RESET
97 100 /NMI
98 1 /INT0
99 2 /INT1 PC6
100 3 /INT2 PC7
All inputs feature an auto latch that assures that an unconnected input is seen as a logic high or logic low by both the
Notes:
1. IEI pulled high internally when default function is active
2. Pins also act as ASCI inputs only when Port B is enabled
3. MIMIC access is disabled until the system configuration register is
written. /HCS can be forced to output the result of COM Port Decoder.
34
Z189 or any measurement device connected to the inputs.
The auto latch will latch onto the previous state of input pin.
4. Pin simultaneously acts as input for both default and secondary
functions.
5. /WAIT is pulled high internally when default function is active.
6. Upon power-up or reset, this pin is tri-state.
DS971890301

Zilog
PRELIMINARY
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
TOUT
TxS
RxS
CKS
/WR
XTAL
Timing &
Ø
Clock
Generator
16-Bit
Programmable
Reload T imers
Clocked
Serial I/O
EXTAL
(2)
Port
/RD
/RESET
/IORQ
/MREQ
/M1
Bus State Control Interrupt
/WAIT
/HALT
CPU
DMACs
(2)
Asynchronous
SCI
(Channel 0)
ST
/RFSH
/BUSACK
/BUSREQ
/NMI
E
/DREQ1
/TEND0
TxA0
CKA0/ /DREQ0
RxA0
/RTS0
/CTS0
/INT0
/INT1
/INT2
Address Bus (16-Bit)
MMU
A19-A0 D7-D0
Figure 30. Z189 MPU Block Diagram
Data Bus (8-Bit)
Asynchronous
SCI
(Channel 1)
/DCD0
TxA1
RxA1
/CTS1
/CKA1
DS971890301
35

Zilog
PRELIMINARY
Z80189 MPU FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION (Continued)
DMA Controller
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
DMA Controller. The DMA controller provides high-speed
transfers between memory and I/O devices. Transfer operations supported are memory-to-memory, memory to or
from I/O, and I/O-to-I/O. Transfer modes supported are
Table 13. SAR18-16 and DAR18-16 I/O Device Encoding
SM1-0 SAR18-16 Source
11 000 ext (CKA0/DREQ)
11 001 ASCI0 Rx
11 010 ASCI1 Rx
11 011 ext (/DREQ1)
11 100 *
11 101 *
11 110 *
11 111 *
Asynchronous Serial Communications
Interface (ASCI)
request, burst, and cycle steal. DMA transfers can access
the full 1 Mbyte addressing range with a block length up to
64 Kbytes, and can cross over the 64 Kbytes boundaries.
DM1-0 DAR18-16 Destination
11 000 ext (CKA0//DREQ0)
11 001 ASCI0 Tx
11 010 ASCI1 Tx
11 011 ext (/DREQ1)
11 100 *
11 101 *
11 110 *
11 111 *
* Reserved do not use.
Reset DCD (ASCI0 with Auto Enables) and
I/O Stop Mode Conditions
The ASCI logic provides two individual full-duplex UARTs.
Each channel includes a programmable baud rate generator. The ASCI channels can also support a multiprocessor communications format. For ASCI0, up to three modem
control signals and one clock signal can be pinned out,
while ASCI1 has a data-only interface and 1 clock signal.
The receiver includes a 4-byte FIFO, plus a shift register as
shown in Figure 31.
Error
Latches
4x4 Bit
Overrun
Error
Error
FIFO
P F O B
E E R K
Error Shift Register
MP
Bit
During Reset and in I/O Stop state, and for ASCI0 if /DCD0
is auto-enabled and is High, an ASCI is forced to the
following conditions:
■ FIFO Empty
■ All Error Bits Cleared (including those in the FIFO)
■ Receive Enable Cleared (cntla bit 6 = 0)
■ Transmit Enable Cleared (cntla bit 5 = 0).
If DCD is not auto-enabled, the /DCD pin has no effect on
the FIFOs or enable bits.
Notes:
PE = Parity Error
FE = Framing Error
OR = Overrun
BK = Break
MP = Multiprocessor Bit
4-Byte
Data FIFO
RXA
36
Figure 31. ASCI Receiver
DS971890301

Zilog
PRELIMINARY
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
FIFO and Receiver Operation
The 4-byte Receive FIFO is used to buffer incoming data
to reduce the incidence of overrun errors. When the RE bit
is set in the CNTLA register, the RXA pin is monitored for
a Low transition. One-half bit time after the Low transition
of the RXA pin, the ASCI samples RXA again. If it has gone
back to High, the ASCI ignores the previous Low transition
and resumes looking for a new one, but if RXA is still Low,
it considers this a start bit and proceeds to clock in the data
based upon the internal baud rate generator or the external CKA pin. The number of data bits, parity, multiprocessor and stop bits are selected by the MOD2, MOD1, MOD0
and MP bits in the CNTLA and CNTLB registers. After the
data has been received, the appropriate MP, parity and
one stop bit are checked. Data and any errors are clocked
into the FIFOs during the stop bit. Interrupts, Receive Data
Register Full Flag, and DMA requests will also go active
during this time.
Error Condition Handling
When the receiver places a data character in the Receive
FIFO, it also places any associated error conditions in the
error FIFO. The outputs of the error FIFO go to the set inputs
of the software-accessible error latches. Writing a 0 to
CNTLA EFR is the only way to clear these latches. In other
words, when an error bit reaches the top of the FIFO, it sets
an error latch. If the FIFO has more data and the software
reads the next byte out of the FIFO, the error latch remains
set, until the software writes a 0 to the EFR bit. The error bits
are cumulative, so if additional errors are in the FIFO, they
will set any upset error latches as they reach the top.
Overrun Error
An overrun occurs if the receive FIFO is full when the
receiver has just assembled a byte in the shift register and
is ready to transfer it to the FIFO. If this occurs, the overrun
error bit associated with the previous byte in the FIFO is
set. The latest data byte is not transferred from the shift
register to the FIFO in this case, and is lost. Once an
overrun occurs, the receiver does not place any further
data in the FIFO, until the “last good byte received” has
come to the top of the FIFO so that the Overrun latch is set,
and software then clears the Overrun latch. Assembly of
bytes continues in the shift register, but this data is ignored
until the byte with the overrun error reaches the top of the
FIFO and is cleared with a write of 0 to the EFR bit.
Break Detect
A Break is defined as a framing error with the data equal to
all zeros. When a break occurs, the all-zero byte with its
associated error bits are transferred to the FIFO, if it is not
full. If the FIFO is full, an overrun is generated, but the
break, framing error and data, are not transferred to the
FIFO. Any time a break is detected, the receiver will not
receive any more data until the RXA pin returns to a High
state. If the channel is set in multiprocessor mode and the
MPE bit of the CNTLA register is set to 1, then breaks,
errors and data will be ignored unless the MP bit in the
transmission is a 1. Note: The two conditions listed above
could cause a break condition to be missed if the FIFO is
full and the break occurs, or if the MP bit in the transmission
is not a 1 with the conditions specified above.
Parity and Framing Errors
Parity and Framing Errors do not affect subsequent receiver operation.
DS971890301
37

Zilog
PRELIMINARY
Z80189 MPU FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION (Continued)
Baud Rate Generator
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
The Baud Rate Generator (BRG) has two modes. The first
is the same as in the Z80180. The second is a 16-bit down
counter that divides the processor clock by the value in a
16-bit time constant register, and is identical to the ESCC
BRG. This allows a common baud rate of up to 512 Kbps
to be selected. The BRG can also be disabled in favor of
an external clock on the CKA pin.
The Receiver and Transmitter will subsequently divide the
output of the BRG (or the signal from the CKA pin) by 1, 16
or 64, under the control of the DR bit in the CNTLB register,
and the X1 bit in the ASCI Extension Control Register. To
compute baud rate, use the following formulas.
If ss2,1,0 = 111, baud rate = f
else if BRG mode baud rate = f
/ Clock mode
CKA
/ (2 * (TC+2) * Clock
PHI
mode)
else baud rate = f
/ ((10 + 20*PS) * 2^ss * Clock mode)
PHI
Where:
BRG mode is bit 3 of the ASEXT register
PS is bit 5 of the CNTLB register
TC is the 16-bit value in the ASCI Time Constant registers
The TC value for a given baud rate is:
TC = (f
/ (2 * baud rate * Clock mode)) - 2
PHI
The requirement of having very close to the 50% duty cycle
when the CKA pin is used as an input, has been removed
on the 189. Minimum High and Low times on CKA0 are
typical of most CMOS devices.
RDRF is set, and if enabled an Rx Interrupt or DMA
Request is generated, when the receiver transfers a character from the Rx Shift Register to the Rx FIFO. The FIFO
merely provides margin against overruns. When there’s
more than one character in the FIFO, and software or a
DMA channel reads a character, RDRF either remains set
or is cleared and then immediately set again. Similarly, if a
receive interrupt service routine doesn’t read all the characters in the RxFIFO, RDRF and the interrupt request
remain asserted.
The Rx DMA request is disabled when any of the error flags
PE or FE or OVRN are set, so that software can identify with
which character the problem is associated.
Programmable Reload Timer (PRT)
This logic consists of two separate channels, each containing a 16-bit counter (timer) and count reload register.
The time base for the counters is derived from the system
clock (divided by 20) before reaching the counter. PRT
channel 1 provides an optional output to allow for waveform generation.
Clock mode depends on bit 4 in ASEXT and bit 3 in CNTLB:
X1 DR Clock Mode
00=16
01=64
10=1
1 1 = Reserved, do not use.
2^ss depends on the three LS bits of the CNTLB register:
ss2 ss1 ss0 2^ss
000=1
001=2
010=4
011=8
100=16
101=32
110=64
1 1 1 = External Clock from CKA0
(see above).
The T
output of PRT1 is available on a multiplexed pin.
OUT
Clocked Serial I/O (CSIO)
The CSI0 channel provides a half-duplex serial transmitter
and receiver. This channel can be used for simple highspeed data connection to another microprocessor or
microcomputer.
38
DS971890301

Zilog
/M1
PRELIMINARY
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
If the M1E bit of the operation Mode Control Register is set
to 1, the RETI cycle occurs only once. The /M1 output is
asserted LOW during the opcode fetch cycle, the /INT0
acknowledge cycle, and the first machine cycle of the /NMI
acknowledge. When M1E bit is rest to 0, the /M1 output is
normally inactive an asserted LOW only during the refetch
of the RETI instruction sequence and during /INTO
acknowledge cycle.
Z8S180 POWER-DOWN MODES
The following is a detailed description of the enhancements to the Z8S180 from the standard Z80180 in the areas
of STANDBY, IDLE, and STANDBY-QUICK RECOVERY
modes.
Add-On Features
There are five different power-down modes. SLEEP and
SYSTEM STOP are inherited from the Z80180. In SLEEP
Table 14. Power Down Modes
Power-Down CPU On-Chip Recovery Recovery Time
Modes Core I/O OSC. CLKOUT Source (Minimum)
mode, the CPU is in a stopped state while the on-chip
I/Os are still operating. In I/O STOP mode, the on-chip I/Os
are in a stopped state while leaving the CPU running. In
SYSTEM STOP mode, both the CPU and the on-chip I/Os
are in the stopped state to reduce current consumption.
The Z8S180 has added two additional power-down modes,
STANDBY and IDLE, to reduce current consumption even
further. The differences in these power-down modes are
summarized in Table 14.
SLEEP Stop Running Running Running RESET, Interrupts 1.5 Clock
I/O STOP Running Stop Running Running By Programming SYSTEM STOP Stop Stop Running Running RESET, Interrupts 1.5 Clock
†
IDLE
STANDBY
†
Stop Stop Running Stop RESET, Interrupts, BUSREQ 8 +1.5 Clock
Stop Stop Stop Stop RESET, Interrupts, BUSREQ 217 +1.5 Clock (Normal Recovery)
26 +1.5 Clock (Quick Recovery)
Notes:
†
IDLE and STANDBY modes are only offered in the Z8S180. Note that the
minimum recovery time can be achieved if INTERRUPT is used as the
Recovery Source.
DS971890301
39

Zilog
STANDBY Mode
PRELIMINARY
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
The Z8S180 has been designed to save power. Two lowpower programmable power-down modes have been
added; STANDBY mode and IDLE mode. The
STANDBY/IDLE mode is selected by multiplexing D6 and
D3 of the CPU Control Register (CCR, I/O Address = 1FH).
To enter STANDBY mode:
1. Set D6 and D3 to 1 and 0, respectively.
2. Set the I/O STOP bit (D5 of ICR,
I/O Address = 3FH) to 1.
3. Execute the SLEEP instruction.
When the part is in STANDBY mode, it behaves similar to
the SYSTEM STOP mode which currently exists on the
Z80180, except that the STANDBY mode stops the clock
oscillator, internal clocks and reduces the power consumption to a minimum.
Since the clock oscillator has been stopped, a restart of the
oscillator requires a period of time for stabilization. An 18bit counter has been added in the Z8S180 to allow for
oscillator stabilization. When the part receives an external
IRQ or BUSREQ during STANDBY mode, the oscillator is
restarted and the timer counts down 217 counts before
acknowledgment is sent to the interrupt source.
The clocking is resumed within the Z8S180 and at the
system clock output after /RESET is asserted when the
crystal oscillator is restarted, but not yet stabilized.
STANDBY Mode Exit with BUS REQUEST
Optionally, if the BREXT bit (D5 of CPU Control Register) is
set to 1, the Z8S180 exits STANDBY mode when the
/BUSREQ input is asserted; the crystal oscillator is then
restarted. An internal counter automatically provides time
for the oscillator to stabilize, before the internal clocking
and the system clock output of the Z8S180 are resumed.
The Z8S180 relinquishes the system bus after the clocking
is resumed by:
- Tri-State the address outputs A19 through A0.
- Tri-State the bus control outputs /MREQ, /IORQ,
/RD and /WR.
- Asserting /BUSACK.
The Z8S180 regains the system bus when /BUSREQ is
deactivated. The address outputs and the bus control
outputs are then driven High; the STANDBY mode is
exited.
The recovery source needs to remain asserted for duration
of the 217 count, otherwise standby will be resumed.
The following is a description of how the part exits STANDBY
for different interrupts and modes of operation.
STANDBY Mode Exit with /RESET
The /RESET input needs to be asserted for a duration long
enough for the crystal oscillator to stabilize and then exit
from the STANDBY mode. When /RESET is de-asserted, it
goes through the normal reset timing to start instruction
execution at address (logical and physical) 0000H.
If the BREXT bit of the CPU Control Register (CCR) is
cleared, asserting the /BUSREQ would not cause the
Z8S180 to exit STANDBY mode.
If STANDBY mode is exited due to a reset or an external
interrupt, the Z8S180 remains relinquished from the system bus as long as /BUSREQ is active.
40
DS971890301

Zilog
PRELIMINARY
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
STANDBY Mode Exit with External Interrupts
STANDBY mode can be exited by asserting input /NMI.
The STANDBY mode may also exit by asserting /INT0,
/INT1 or /INT2, depending on the conditions specified in
the following paragraphs.
/INT0 wake-up requires assertion throughout duration of
clock stabilization time (2
If exit conditions are met, the internal counter provides time
for the crystal oscillator to stabilize, before the internal
clocking and the system clock output within the Z8S180
are resumed.
1. Exit with Non-Maskable Interrupts
If /NMI is asserted, the CPU begins a normal NMI interrupt
acknowledge sequence after clocking resumes.
2. Exit with External Maskable Interrupts
If an External Maskable Interrupt input is asserted, the CPU
responds according to the status of the Global Interrupt
Enable Flag IEF1 (determined by the ITE1 bit) and the
settings of the corresponding interrupt enable bit in the
Interrupt/Trap Control Register (ITC: I/O Address = 34H):
a. If an interrupt source is disabled in the ITC, asserting
the corresponding interrupt input would not cause the
Z8S180 to exit STANDBY mode. This is true regardless
of the state of the Global Interrupt Enable Flag IEF1.
b. If the Global Interrupt Flag IEF1 is set to 1, and if an
interrupt source is enabled in the ITC, asserting the
corresponding interrupt input causes the Z8S180 to
exit STANDBY mode. The CPU performs an interrupt
acknowledge sequence appropriate to the input being asserted when clocking is resumed if:
- The interrupt input follows the normal interrupt
daisy chain protocol.
- The interrupt source is active until the acknowledge
cycle is completed.
17
clocks).
If the External Maskable Interrupt input is not active when
clocking resumes, the Z8S180 will not exit STANDBY
mode. If the Non-Maskable Interrupt (/NMI) is not active
when clocking resumes, the Z8S180 still exits the STANDBY
mode even if the interrupt sources go away before the
timer times out, because /NMI is edge-triggered. The
condition is latched internally once /NMI is asserted Low.
IDLE Mode
IDLE mode is another power-down mode offered by the
Z8S180. To enter IDLE mode:
1. Set D6 and D3 to 0 and 1, respectively.
2. Set the I/O STOP bit (D5 of ICR,
I/O Address = 3FH) to 1.
3. Execute the SLEEP instruction.
When the part is in IDLE mode, the clock oscillator is kept
oscillating, but the clock to the rest of the internal circuit,
including the CLKOUT, is stopped completely. IDLE mode
is exited in a similar way as STANDBY mode, i.e., RESET,
BUS REQUEST or EXTERNAL INTERRUPTS, except that
17
the 2
bit wake-up timer is bypassed; all control signals are
asserted eight clock cycles after the exit conditions are
gathered.
STANDBY-QUICK RECOVERY Mode
STANDBY-QUICK RECOVERY mode is an option offered
in STANDBY mode to reduce the clock recovery time in
STANDBY mode from 217 clock cycles (6.5 ms at 20 MHz)
to 26 clock cycles (3.2 µs at 20 MHz). This feature can only
be used when providing an oscillator as clock source.
To enter STANDBY-QUICK RECOVERY mode:
1. Set D6 and D3 to 1 and 1, respectively.
2. Set the I/O STOP bit (D5 of ICR,
I/O Address = 3FH) to 1.
3. Execute the SLEEP instruction.
c. If the Global Interrupt Flag IEF1 is disabled, i.e., reset
to 0, and if an interrupt source is enabled in the ITC,
asserting the corresponding interrupt input will still
cause the Z8S180 to exit STANDBY mode. The CPU
will proceed to fetch and execute instructions that
follow the SLEEP instruction when clocking is resumed.
DS971890301
When the part is in STANDBY-QUICK RECOVERY mode,
the operation is identical to STANDBY mode except when
exit conditions are gathered, i.e., RESET, BUS REQUEST
or EXTERNAL INTERRUPTS; the clock and other control
signals are recovered sooner than the STANDBY mode.
Note: If STANDBY-QUICK RECOVERY is enabled, the
user must make sure stable oscillation is obtained within
64 clock cycles.
41

Zilog
PRELIMINARY
Z8S180 MPU REGISTER MAP
Notes:
Registers listed in boldface type represent new registers
added to the Z8S180.
All register addresses not listed are Reserved.
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
Register Name I/O Addr/Access
ASCI Control Register A Ch 0 %0000/40/80 R/W
ASCI Control Register A Ch 1 %0001/41/81 R/W
ASCI Control Register B Ch 0 %0002/42/82 R/W
ASCI Control Register B Ch 1 %0003/43/83 R/W
ASCI Status Register Ch 0 %0004/44/84 R/W
ASCI Status Register Ch 1 %0005/45/85 R/W
ASCI TX Data Register Ch 0 %0006/46/86 R/W
ASCI TX Data Register Ch 1 %0007/47/87 R/W
ASCI RX Data Register Ch 0 %0008/48/88 R/W
ASCI RX Data Register Ch 1 %0009/49/89 R/W
CSIO Control Register %000A/4A/8A R/W
CSIO Transmit/Receive Data Reg. %000B/4B/8B R/W
Timer Data Register Ch OL %000C/4C/8C R/W
Timer Data Register Ch OH %000D/4D/8D R/W
Reload Register Ch OL %000E/4E/8E R/W
Reload Register Ch OH %000F/4F/8F R/W
Timer Control Register %0010/50/90
ASCI0 Extension Control Reg. %0012/52/92 R/W
ASCI1 Extension Control Reg. %0013/53/93 R/W
Timer Data Register Ch 1L %0014/54/94 R/W
Timer Data Register Ch 1H %0015/55/95 R/W
Timer Reload Register Ch 1L %0016/56/96 R/W
Timer Reload Register Ch 1H %0017/57/97 R/W
Free Running Counter %0018/58/98 R/W
ASCI0 Time Constant Low %001A/5A/9A R/W
ASCI0 Time Constant High %001B/5B/9B R/W
ASCI1 Time Constant Low %001C/5C/9C R/W
ASCI1 Time Constant High %001D/5D/9D RW
Clock Multiplier Register %001E/5E/9E RW
Register Name I/O Addr/Access
CPU Control Register %001F/5F/9F R/W
DMA Source Addr Register Ch OL %0020/60/A0 R/W
DMA Source Addr Register Ch OH %0021/61/A1 R/W
DMA Source Addr Register Ch OB %0022/62/A2 R/W
DMA Dest Addr Register Ch OL %0023/63/A3 R/W
DMA Dest Addr Register Ch OH %0024/64/A4 R/W
DMA Dest Addr Register Ch OB %0025/65/A5 R/W
DMA Byte Count Register Ch OL %0026/66/A6 R/W
DMA Byte Count Register Ch OH %0027/67/A7 R/W
DMA Memory Addr Register Ch 1L %0028/68/A8 R/W
DMA Memory Addr Register Ch 1H %0029/69/A9 R/W
DMA Memory Addr Register Ch 1B %002A/6A/AA R/W
DMA I/O Addr Register Ch 1L %002B/6B/AB R/W
DMA I/O Addr Register Ch 1H %002C/6C/AC R/W
DMA I/O Addr Register Ch 1B %002D/6D/AD R/W
DMA Byte Count Register Ch 1L %002E/6E/AE R/W
DMA Byte Count Register Ch 1H %002F/6F/AF R/W
DMA Status Register %0030/70/B0 R/W
DMA Mode Register %0031/71/B1 R/W
DMA/WAIT Control Register %0032/72/B2 R/W
IL Register %0033/73/B3 R/W
INT/TRAP Control Register %0034/74/B4 R/W
Refresh Control Register %0036/76/B6 R/W
MMU Common Base Register %0038/78/B8 R/W
MMU Bank Base Register %0039/79/B9 R/W
MMU Common/Bank Area Register %003A/7A/BA R/W
Operation Mode Control Register %003E/7E/BE R/W
I/O Control Register %003F/7F/BF R/W
42
DS971890301

Zilog
PRELIMINARY
Z8S180 MPU REGISTERS
ASCI CHANNELS CONTROL REGISTERS
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
Bit
Upon RESET
R/W
CNTLA0
MPE
R/W0R/W0R/W1R/WxR/W0R/W0R/W0R/W
RE TE /RTS0
0
MPBR/
MOD2 MOD1 MOD0
EFR
0 0 0 Start + 7-Bit Data + 1 Stop
0 0 1 Start + 7-Bit Data + 2 Stop
0 1 0 Start + 7-Bit Data + Parity + 1 Stop
0 1 1 Start + 7-Bit Data + Parity + 2 Stop
1 0 0 Start + 8-Bit Data + 1 Stop
1 0 1 Start + 8-Bit Data + 2 Stop
1 1 0 Start + 8-Bit Data + Parity + 1 Stop
1 1 1 Start + 8-Bit Data + Parity + 2 Stop
Addr 00H
MODE Selection
Read - Multiprocessor Bit Receive
Write - Error Flag Reset
Request To Send
Transmit Enable
Receive Enable
Multiprocessor Enable
Bit
Upon RESET
R/W
Figure 32. ASCI Control Register A (Ch. 0)
CNTLA1
MPE RE TE
0
R/W0R/W0R/W1R/WxR/W0R/W0R/W0R/W
CKA1D
MPBR/
EFR
MOD2 MOD1 MOD0
0 0 0 Start + 7-Bit Data + 1 Stop
0 0 1 Start + 7-Bit Data + 2 Stop
0 1 0 Start + 7-Bit Data + Parity + 1 Stop
0 1 1 Start + 7-Bit Data + Parity + 2 Stop
1 0 0 Start + 8-Bit Data + 1 Stop
1 0 1 Start + 8-Bit Data + 2 Stop
1 1 0 Start + 8-Bit Data + Parity + 1 Stop
1 1 1 Start + 8-Bit Data + Parity + 2 Stop
Addr 01H
MODE Selection
Read - Multiprocessor Bit Receive
Write - Error Flag Reset
CKA1 Disable
Transmit Enable
Receive Enable
DS971890301
Multiprocessor Enable
Figure 33. ASCI Control Register A (Ch. 1)
43

Zilog
PRELIMINARY
Z8S180 MPU REGISTERS (Continued)
ASCI CHANNELS CONTROL REGISTERS
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
Addr 02H
Clock Source and Speed Select
Divide Ratio
Parity Even or Odd
Clear To Send/Prescale
Multiprocessor
Multiprocessor Bit Transmit
Bit
Upon Reset
R/W
CNTLB0
MPBT MP
Invalid
R/W0R/W†R/W0R/W0R/W1R/W1R/W1R/W
† /CTS - Depending on the condition of /CTS pin.
PS - Cleared to 0.
/CTS/
PS
DRPE0
SS2 SS1 SS0
General PS = 0 PS = 1
Divide Ratio (Divide Ratio = 10) (Divide Ratio = 30)
SS, 2, 1, 0 DR = 0 (x16) DR = 1 (x64) DR = 0 (x16) DR = 1 (x64)
000 Ø ÷ 160 Ø ÷ 640 Ø ÷ 480 Ø ÷ 1920
001 Ø ÷ 320 Ø ÷ 1280 Ø ÷ 960 Ø ÷ 3840
010 Ø ÷ 640 Ø ÷ 2560 Ø ÷ 1920 Ø ÷ 7680
011 Ø ÷ 1280 Ø ÷ 5120 Ø ÷ 3840 Ø ÷ 15360
100 Ø ÷ 2560 Ø ÷ 10240 Ø ÷ 7680 Ø ÷ 30720
101 Ø ÷ 5120 Ø ÷ 20480 Ø ÷ 15360 Ø ÷ 61440
110 Ø ÷ 10240 Ø ÷ 40960 Ø ÷ 30720 Ø ÷ 122880
111 External Clock (Frequency < Ø)
Figure 34. ASCI Control Register B (Ch. 0)
44
DS971890301

Zilog
PRELIMINARY
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
Addr 03H
Clock Source and Speed Select
Divide Ratio
Parity Even or Odd
Read - Status of /CTS pin
Write - Select PS
Multiprocessor
Multiprocessor Bit Transmit
Bit
Upon Reset
R/W
CNTLB1
MPBT MP
Invalid
R/W0R/W†R/W0R/W0R/W1R/W1R/W1R/W
† /CTS - Depending on the condition of /CTS pin.
PS - Cleared to 0.
/CTS/
PS
DRPE0
SS2 SS1 SS0
General PS = 0 PS = 1
Divide Ratio (Divide Ratio = 10) (Divide Ratio = 30)
SS, 2, 1, 0 DR = 0 (x16) DR = 1 (x64) DR = 0 (x16) DR = 1 (x64)
000 Ø ÷ 160 Ø ÷ 640 Ø ÷ 480 Ø ÷ 1920
001 Ø ÷ 320 Ø ÷ 1280 Ø ÷ 960 Ø ÷ 3840
010 Ø ÷ 640 Ø ÷ 2560 Ø ÷ 1920 Ø ÷ 7680
011 Ø ÷ 1280 Ø ÷ 5120 Ø ÷ 3840 Ø ÷ 15360
100 Ø ÷ 2560 Ø ÷ 10240 Ø ÷ 7680 Ø ÷ 30720
101 Ø ÷ 5120 Ø ÷ 20480 Ø ÷ 15360 Ø ÷ 61440
110 Ø ÷ 10240 Ø ÷ 40960 Ø ÷ 30720 Ø ÷ 122880
111 External Clock (Frequency < Ø)
Figure 35. ASCI Control Register B (Ch. 1)
DS971890301
45

Zilog
PRELIMINARY
ASCI CHANNELS CONTROL REGISTERS (Continued)
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
Bit
Upon Reset
R/W
STAT0
RDRF OVRN /DCD0 TDRE TIE
PE
0R0
RIEFE
†
Addr 04H
R0R0R0R/W R††R0R/W
† /DCD0 - Depending on the condition of /DCD0 Pin.
††
TDRE is reset to 0, when /CTSO input is high.
/CTS0 Pin = L: TDRE = 1
/CTS0 Pin = H: TDRE = 0
Figure 36. ASCI Status Register
Transmit Interrupt Enable
Transmit Data Register
Empty
Data Carrier Detect
Receive Interrupt Enable
Framing Error
Parity Error
Over Run Error
Receive Data Register Full
Bit
Upon Reset
R/W
STAT1
RDRF OVRN CTS1E TDRE TIE
0
R0R
PE
0
R
RIEFE
0R0
R/W R/W1R0R/W
0
Addr 05H
Figure 37. ASCI Status Register (Ch. 1)
Transmit Interrupt Enable
Transmit Data Register
Empty
/CTS1 Enable
Receive Interrupt Enable
Framing Error
Parity Error
Over Run Error
Receive Data Register Full
46
DS971890301

Zilog
PRELIMINARY
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
TDR0
Write Only Addr 06H
76543210
Transmit Data
Figure 38. ASCI Transmit Data Register (Ch. 0)
TDR1
Write Only
76543210
Addr 07H
Transmit Data
Figure 39. ASCI Transmit Data Register (Ch. 1)
TSR0
Read Only
xxxxxxxx
Addr 08H
Received Data
765 43210
00000000
New Z8S180 Register
Send Break
0 = Normal Xmit
1 = Drive TXA Low
Break Detect (RO)
Break Feature Enable
BRG0 Mode
0 = as S180
1 = Enable 16-bit BRG Counter
X1 Bit CLK ASCIO
0 = CKA0 /16 or /64
1 = CKA0 is bit clock
CTS0 Disable
0 = CTS0 Auto-enables Tx
1 = CTS0 Advisory to SW
DCD0 Disable
0 = DCD0 Auto-enables Rx
1 = DCD0 Advisory to SW
Reserved (Program as 0.)
Figure 42. ASCI0 Extension Control Register
(I/O Address 12)
Figure 40. ASCI Receive Data Register (Ch. 0)
TSR1
Read Only Addr 09H
xxxxxxxx
Received Data
Figure 41. ASCI Receive Data Register (Ch. 1)
765 43210
00000000
New Z8S180 Register
Send Break
0 = Normal Xmit
1 = Drive TXA Low
Break Detect (RO)
Break Feature Enable
BRG1 Mode
0 = As S180
1 = Enable 16-bit BRG Counter
X1 Bit CLK ASCI1
0 = CKA1 /16 or /64
1 = CKA1 is bit Clock
Reserved (Program as 0.)
Figure 43. ASCI1 Extension Control Register
(I/O Address 13)
DS971890301
47

Zilog
PRELIMINARY
ACSI TIME CONSTANT REGISTERS
New Z8S180 Registers
76543210 76543210
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
Register: ASCI0 Time Constant Low
Address: 1Ah
76543210
Register: ASCI0 Time Constant High
Address: 1Bh
Register: ASCI1 Time Constant Low
Address: 1Ch
76543210
Register: ASCI1 Time Constant High
Address: 1Dh
CLOCK MULTIPLIER REGISTER (Z180 MPU ADDRESS 1EH)
Bit 7.
X2 Clock Multiplier Mode.
allows the programmer to double the internal clock from
that of the external clock. This feature will only operate
effectively with frequencies of 10-16 MHz (20-33 MHz
internal).
When this bit is set to 1, this
When this bit is set to 0, the Z189 device will operate in
normal mode. Upon powerup, this feature is disabled.
Bit 0-6.
Reserved.
New Z8S180 Register
765 43210
Maintains a logic 1 value when read.
01111111
Figure 44. Clock Multiplier Register
(Z180 MPU Address 1EH)
Reserved
X2 Clock Multiplier Mode
0 = Disable
1 = Enable
48
DS971890301

Zilog
PRELIMINARY
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
CNTR
Bit
EF EIE SS2 SS1 SS0
Upon Reset
R/W
0
R0R/W0R/W0R/W
SS2, 1, 0 Baud Rate
000 Ø ÷ 20
001 Ø ÷ 40
010 Ø ÷ 80
011 Ø ÷ 100
RE
Addr 0AH
-TE
11
R/W1R/W1R/W
Speed Select
Transmit Enable
Receive Enable
End Interrupt Enable
End Flag
SS2, 1, 0 Baud Rate
100 Ø ÷ 320
101 Ø ÷ 640
110 Ø ÷ 1280
111 External Clock
(Frequency < Ø ÷ 20)
Figure 45. CSI/O Control Register
TRDR
Read/Write Addr 0BH
76543210
Read - Received Data
Write - Transmit Data
Figure 46. CSI/O Transmit/Receive Data Register
DS971890301
49

Zilog
TIMER DATA REGISTERS
PRELIMINARY
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
TMDR0L
Read/Write Addr 0CH
76543210
Figure 47. Timer 0 Data Register L
TMDR1L
Read/Write
76543210
Figure 48. Timer 1 Data Register L
Addr 14H
TIMER RELOAD REGISTERS
TMDR0H
Read/Write Addr 0DH
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8
When Read, read Data Register L
before reading Data Register H.
Figure 49. Timer 0 Data Register H
TMDR1H
Read/Write Addr 15H
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8
When Read, read Data Register L
before reading Data Register H.
Figure 50. Timer 1 Data Register H
RLDR0L
Read/Write
76543210
Figure 51. Timer 0 Reload Register L
RLDR1L
Read/Write
76543210
Figure 52. Timer 1 Reload Register L
Addr 0EH
Addr 16H
RLDR0H
Read/Write
Addr 0FH
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8
Figure 53. Timer 0 Reload Register H
RLDR1H
Read/Write
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8
Figure 54. Timer 1 Reload Register H
Addr 17H
50
DS971890301

Zilog
TIMER CONTROL REGISTER
PRELIMINARY
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
Bit
Upon Reset
R/W
TCR
TIF1 TIF0 TOC0 TDE1 TDE0
0
R
TOC1,0 A15/TOUT
00 Inhibited
01 Toggle
10 0
11 1
TIE1
0
R0R/W0R/W0R/W R/W0R/W0R/W
TOC1TIE0
Addr 10H
0
Figure 55. Timer Control Register
Timer Down Count Enable 1,0
Timer Output Control 1,0
Timer Interrupt Enable 1,0
Timer Interrupt Flag 1,0
DS971890301
51

Zilog
FREE RUNNING COUNTER
CPU CONTROL REGISTER
PRELIMINARY
FRC
Read Only Addr 18H
76543210
Figure 56. Free Running Counter
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
The Z8S180 has an additional register which allows the
programmer to select options that directly affect the CPU
performance as well as controlling the STANDBY operating mode of the chip. The CPU Control Register (CCR)
allows the programmer to change the divide-by-two internal clock to divide-by-one. In addition, applications where
CPU Control Register (CCR)Addr 1FH
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
00000000
Clock Divide
0 = XTAL/2
1 = XTAL/1
Standby/Idle Enable
00 = No Standby
01 = IdleAfter Sleep
10 = Standby After Sleep
11 = StandbyAfter Sleep
64 Cycle Exit
(Quick Recovery)
BREXT
0 = Ignore BUSREQ
In Standby/Idle
1 = Standby/Idle Exit
on BUSREQ
EMI noise is a problem, the Z8S180 can reduce the output
drivers on selected groups of pins to 33% of normal pad
driver capability which minimizes the EMI noise generated
by the part.
LNAD/DATA
0 = Standard Drive
1 = 33% Drive On
A19-A0, D7-D0
LNCPUCTL
0 = Standard Drive
1 = 33% Drive On CPU
Control Signals
LNIO
0 = Standard Drive
1 = 33% Drive or
ASCI Signals
LNPHI
0 = Standard Drive
1 = 33% Drive On
EXT.PHI Clock
52
Figure 57. CPU Control Register
DS971890301

Zilog
PRELIMINARY
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
Bit 7.
programmer to set the internal clock to divide the external
clock by 2 if the bit is 0 and divide-by-one if the bit is 1.
Upon reset, this bit is set to 0 and the part is in
divide-by-two mode. Since the on-board oscillator is not
guaranteed to operate above 20 MHz, an external source
must be used to achieve the maximum 33 MHz operation
of the part, i.e., an external clock at 66 MHz with 50% duty
cycle.
If an external oscillator is used in divide-by-one mode, the
minimum pulse width requirement must be satisfied.
Bits 6 and 3.
used for enabling/disabling the IDLE and STANDBY mode.
Setting D6, D3 to 0 and 1, respectively, enables the IDLE
mode. In the IDLE mode, the clock oscillator is kept
oscillating but the clock to the rest of the internal circuit,
including the CLKOUT, is stopped. The Z8S180 enters
IDLE mode after fetching the second opcode of a SLEEP
instruction, if the I/O STOP bit is set.
Setting D6, D3 to 1 and 0, respectively, enables the
STANDBY mode. In the STANDBY mode, the clock oscillator is stopped completely. The Z8S180 enters STANDBY
after fetching the second opcode of a SLEEP instruction,
if the I/O STOP bit is set.
Setting D6, D3 to 1 and 1, respectively, enables the
STANDBY-QUICK RECOVERY mode. In this mode, its
operations are identical to STANDBY except that the clock
recovery is reduced to 64 clock cycles after the exit
conditions are gathered. Similarly, in STANDBY mode, the
Z8S180 enters STANDBY after fetching the second opcode
of a SLEEP instruction, if the I/O STOP bit is set.
Clock Divide Select.
STANDBY/IDLE Enable.
Bit 7 of the CCR allows the
These two bits are
Bit 5.
BREXT.
honor a bus request during STANDBY mode. If this bit is
set to 1 and the part is in STANDBY mode, a BUSREQ is
honored after the clock stabilization timer is timed out.
Bit 4.
LNPHI.
PHI Clock output. If this bit is set to 1, the PHI Clock output
is reduced to 33% of its drive capability.
Bit 2.
LNIO.
external I/O pins of the Z80189/Z80L189. When this bit is
set to 1, the output drive capability of the following pins is
reduced to 33% of the original drive capability:
Bit 1.
LNCPUCTL.
the CPU Control pins. When this bit is set to 1, the output
drive capability of the following pins is reduced to 33% of
the original drive capability:
Bit 0.
LNAD/DATA.
the Address/Data bus output drivers. If this bit is set to 1,
the output drive capability of the Address and Data bus
output is reduced to 33% of its original drive capability.
This bit controls the ability of the Z8S180 to
This bit controls the drive capability on the
This bit controls the drive capability of the
- CKS - TxAI
- RxS/CTS1 - CKA0/DREQ0
- TxS - TxA0
- CKAI/TEND0 - /RTS0
This bit controls the drive capability of
- /BUSACK - /MREQ - TEST
- /RD - /IORQ - STATUS
- /WR - /RFSH
- /M1 - /HALT
- E - /TEND1
This bit controls the drive capability of
DS971890301
53

Zilog
DMA REGISTERS
PRELIMINARY
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
SAR0L
Read/Write Addr 20H
SA7 SA0
SAR0H
Read/Write Addr 21H
SA15 SA8
SAR0B
Read/Write Addr 22H
SA16SA19
----
Bits 0-2 (3) are used for SAR0B
A19,
A18,
A17,
A16
x
x
0
x
x
x
x
0
x
1
x
1
DMATransfer Request
0
ext (CKA0//DREQ0
1
ASCI0 Rx
0
ASCI1 Rx
1
ext (/DREQ1)
Figure 58. DMA 0 Source Address Registers
BCR0L
Read/Write
Addr 26H
BC7 BC0
BCR0H
Read/Write
Addr 27H
BC15 BC8
Figure 60. DMA 0 Byte Counter Registers
MAR1L
Read/Write
MA7 MA0
MAR1H
Read/Write
MA15 MA8
Addr 28H
Addr 29H
DAR0L
Read/Write Addr 23H
DA7 DA0
DAR0H
Read/Write Addr 24H
DA15 DA8
DAR0B
Read/Write Addr 25H
----
Bits 0-2 (3) are used for DAR0B
A19,
A18,
A17,
x
x
x
x
x
0
x
0
x
1
x
1
A16
0
1
0
1
DA16DA19
DMATransfer Request
ext (CKA0//DREQ0)
ASCI0 Tx
ASCI1 Tx
ext (/DREQ1)
MAR1B
Read/Write
----
Addr 2AH
MA16MA19
Figure 61. DMA 1 Memory Address Registers
Figure 59. DMA 0 Destination Address Registers
54
DS971890301

Zilog
PRELIMINARY
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
IAR1L
Read/Write
IA7 IA0
IAR1H
Read/Write
IA15 IA8
Addr 2BH
Addr 2CH
IAR1B Addr 2D
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
BCR1L
Read/Write
BC7 BC0
BCR1H
Read/Write
BC15 BC8
Addr 2EH
Addr 2FH
Figure 63. DMA 1 Byte Count RegistersFigure 62. DMA I/O Address Registers
New Z8S180 Register
000 = DMA1 ext TOUT/DREQ
001 = DMA1 ASCI0
010 = DMA1 ASCI1
011 = DMA1 ext CKA0//DREQ0
111 = Reserved, do not program
Reserved, program as 0.
Currently selected DMA
Channel when Bit 7 = 1
Alternating Channels
0 = DMA Channels
are independent
1 = Toggle between DMA
channels for same device
Figure 64. DMA I/O Address Register Ch. 1
DS971890301
55

Zilog
DMA REGISTER DESCRIPTION
PRELIMINARY
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
Bit 7. This bit should be set to 1 only when both DMA
channels are set to take their requests from the same
device. If this bit is 1 (it resets to 0), the TEND output of DMA
channel 0 sets a flip-flop, so that thereafter the device’s
request is visible to channel 1, but is not visible to channel
0. The internal TEND signal of channel 1 clears the FF, so
that thereafter, the device’s request is visible to channel 0,
but not visible to channel 1.
If DMA requests are from differing sources, DMA channel
0 request will be forced onto DMA channel 1 once TEND
output of DMA channel 0 sets the flop-flop to alternate.
Bit 6. When both DMA channels are programmed to take
their requests from the same device, this bit (FF mentioned
in the previous paragraph) controls which channel the
device’s request is presented to: 0 = DMA 0, 1 = channel
1. When bit 7 is 1, this bit is automatically toggled by the
channel end output of the channels, as described above.
Bits 5-3. Reserved and should be programmed as 0.
Bits 2-0. With “DIM1”, bit 1 of DCNTL, these bits control
which request is presented to DMA channel 1, as follows:
DIM1 IAR18-16 Request Routed to DMA Channel 1
0 000 /DREQ1
0 001 ASCI0 Tx
0 010 ASCI1 Tx
0 011 ext CKA0//DREQ0
0 10X Reserved, do not program.
0 1X0 Reserved, do not program.
0 111 Reserved, do not program
1 000 ext /DREQ1
1 001 ASCI0 Rx
1 010 ASCI1 Rx
1 011 ext CKA0//DREQ0
1 10X Reserved, do not program.
1 1X0 Reserved, do not program.
1 111 Reserved, do not program
56
DS971890301

Zilog
PRELIMINARY
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
Bit
Upon Reset
Upon Reset
D S TAT
DE1 DE0 DIE0
/DWE1
DIE1/DWE0
0
R/W0R/W1W1W
R/W
Figure 65. DMA Status Register
DMODE
Bit
R/W
- -
110
DM1
R/W0R/W
00
R/W
SM0 MMOD
SM1DM0
00
R/W R/W
R/W
Addr 30H
-
DIME
10
RR/W
Addr 31H
01
DMA Master Enable
DMA Interrupt Enable 1, 0
DMA Enable Bit Write Enable 1, 0
DMA Enable Ch 1, 0
-
Memory MODE Select
DM1, 0
00
01
10
11
MMOD
0
1
Destination
M
M
M
I/O
Mode
Cycle Steal Mode
Burst Mode
Address
DAR0+1
DAR0-1
DAR0 Fixed
DAR0 Fixed
SM1, 0
00
01
10
11
Figure 66. DMA Mode Registers
Source
M
M
M
I/O
Ch 0 Source Mode 1, 0
Ch 0 Destination Mode 1, 0
Address
SAR0+1
SAR0-1
SAR0 Fixed
SAR0 Fixed
DS971890301
57

Zilog
DMA REGISTERS (Continued)
PRELIMINARY
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
Bit
Upon Reset
R/W
DCNTL
MWI1 MWI0 DMS0 DIM1 DIM0
111
*
MWI1, 0
00
01
10
11
DMSi
1
0
IWI1
R/W1R/W
No. of Wait States
0
1
2
3
Sense
Edge Sense
Level Sense
DMS1IWI0
00
R/W R/WR/WR/W R/W
R/W
IWI1, 0
00
01
10
11
00
No. of Wait States
Addr 32H
DMA Ch 1 I/O Memory
Mode Select
/DREQi Select, i = 1, 0
I/0 Wait Insertion
Memory Wait Insertion
1
2
3
4
DM1, 0
00
01
10
11
Note:
* If using ROM/RAM Chip Select wait state generators,
the Z180 wait state generator should be set to 0.
Transfer Mode
M - I/O
M - I/O
I/O - M
I/O - M
Address Increment/Decrement
MAR1+1
MAR1-1
IAR1 Fixed
IAR1 Fixed
Figure 67. DMA/WAIT Control Register
IAR1 Fixed
IAR1 Fixed
MAR1+1
MAR1-1
58
DS971890301

Zilog
SYSTEM CONTROL REGISTERS
PRELIMINARY
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
Upon Reset
Bit
Upon Reset
R/W
IL
Bit
R/W
IL7 IL6 - - -
000
R/WR/W
Figure 68. Interrupt Vector Low Register
ITC
TRAP UFO ITE2 ITE1 ITE0
001
R/W
00000
110
--IL5
---
R/W
Addr 33H
Interrupt Vector Low
Addr 34H
01
R/WRR/W R/W
/INT Enable 2, 1, 0
Undefined Fetch Object
TRAP
Bit
Upon Reset
R/W
Figure 69. INT/TRAP Control Register
RCR
REFE REFW
111
CYC1, 0
00
01
10
11
Interval of Refresh Cycle
11100
10 states
20 states
40 states
80 states
--
-
CYC1 CYC0
R/WR/WR/W R/W
Addr 36H
Cycle Select
Refresh Wait State
Refresh Enable
DS971890301
Figure 70. Refresh Control Register
59

Zilog
MMU REGISTERS
PRELIMINARY
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
Bit
Upon Reset
R/W
Bit
Upon Reset
R/W
CBR
CB7 CB6 CB2 CB1 CB0
000
R/W0R/W
CB3CB4CB5
00
R/W R/WR/WR/W R/W
R/W
Addr 38H
00
Figure 71. MMU Common Base Register
BBR
BB7
BB6 BB2 BB1 BB0
000
R/W0R/W
BB3BB4BB5
00
R/W R/WR/WR/W R/W
R/W
Addr 39H
00
Figure 72. MMU Bank Base Register
MMU Common Base
Register
MMU Bank Base Register
Bit
Upon Reset
R/W
CBAR
CA3 CA2 BA2 BA1 BA0
111
R/W1R/W
BA3CA0CA1
00
R/W R/WR/WR/W R/W
R/W
Addr 3AH
00
Figure 73. MMU Common/Bank Area Register
MMU Bank Area Register
MMU Common Area Register
60
DS971890301

Zilog
SYSTEM CONTROL REGISTERS
PRELIMINARY
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
Upon Reset
R/W
Bit
Upon Reset
R/W
OMCR
M1E /M1TE
Bit
111
Notes:
1. This register should be programmed to 0x0xxxxxb
(x = don't care) as a part of Initialization.
2. If the M1E bit is set to 1, the processor does not
fetch a RETI instruction.
ICR
IOA7 IOA6
000
Addr 3EH
--
/IOC
---
11111
WR/W R/W
Figure 74. Operation Mode Control Register
Addr 3FH
--
IOSTP
11111
R/WR/W R/W
---
I/O Compatibility
/M1 Temporary Enable
/M1 Enable
Figure 75. I/O Control Register
I/O Stop
I/O Address
Combination of 11
is reserved
DS971890301
61

Zilog
PRELIMINARY
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189 MIMIC REGISTER MAP
Register Name MPU Addr/Access PCAddr/Access
MMC MIMIC Master Control Reg. XXFF R/W None
IUS/IP Interrupt Pending XXFE R/Wb7 None
IE Interrupt Enable XXFD R/W None
IVEC Interrupt Vector XXFC R/W None
RTCR Receive Time Constant XXFB R/W None
TTCR Transmit Time Constant XXFA R/W None
DLM Divisor Latch (MSByte) XXF9 R only 01,DLAB=1,R/W
DLL Divisor Latch (LSByte) XXF8R only 00,DLAB=1,R/W
SCR Scratch Register XXF7 R only 07 R/W
MSR Modem Status Register XXF6 R/Wb7-4 06 R only
LSR Line Status Register XXF5 R/Wb6432 05 R only
MCR Modem Control Register XXF4 R only 04 R/W
LCR Line Control Register XXF3 R only 03 R/W
IER Interrupt Enable Register XXF1 R only 01,DLAB=0 R/W
RBR Receiver Buffer Register XXF0 W only 00,DLAB=0 R only
THR Transmitter Holding Reg. XXF0 R only 00,DLAB=0 W only
FSCR FIFO Status and Control XXEC R/W7-4 None
TTTC Tran. Timeout Time Const. XXEB R/W None
RTTC Rec. Timeout Time Const. XXEA R/W None
IIR Interrupt Identification None 02 R only
FCR FIFO Control Register XXE9 R only 02 W only
Z80189/Z8L189
Z80189 PC DMA MAILBOX BRG,COM_PORT, PIA AND MISC REGISTERS
Register Name MPU Addr/Access PCAddr/Access
PA Data Direction Register XXEDH R/W None
PA Data Register XXEEH R/W None
MIMIC Modification Register XXE9 W only None
ROM Address Boundary Reg. XXE8 R/W None
RAMLBR RAM Lower Boundary Reg. XXE7 R/W None
RAMUBR RAM Upper Boundary Reg. XXE6 R/W None
PB Data Register XXE5 R/W None
PB Data Direction Register XXE4 R/W None
BRG High Constant XXE1 R/W None
BRG Low Constant XXE0 R/W None
Interrupt Edge/Pin Mux Control XXDF R/W None
PC Data Register XXDE R/W None
PC Data Direction Register XXDD R/W None
Z80189 Enhancements Register XXD9 R/W None
WSG Chip Select Register XXD8 R/W None
IOBRG Register XXD6 R/W None
COM Decode Register XXD7 R/W None
System Configuration Register XXEF R/W None
62
DS971890301

Zilog
PRELIMINARY
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
Z80189 MAILBOX REGISTER MAP
Register Name MPU Addr/Access PC Addr/Access
Host I/O Status Register %XXD5 W bit 1/R Prog + 10b R (2)
Host Output Register 1 %XXD4 R Prog + 01b W (2)
Host Input Register 1 %XXD4 W Prog + 01b R (2)
Host Output Register 0 %XXD3 R Prog + 00b W (2)
Host DMA Mailbox Cntrl Reg %XXD2 R/W None
Host DMA Transmit Register 1 %XXD1 R DMA1 W (3)
Host DMA Receive Register 1 %XXD1 W DMA1 R
Host DMA Transmit Register 0 %XXD0 R (1) DMA0 W
Host DMA Receive Register 0 %XXD0 W DMA0 R
1. This register is defaulted to 91h to indicate revision code.
(Z189 revision #1 - Z80189AA)
2. The PC Host Addresses are HA9:2 are programmable by writing to PADATA.
3. The HDMAT1 can be used as an extra host output mailbox register. If the Host DMA Mailbox 1 function is disabled
(bit 1 of HMC register is zero), a Host write in the programmed Mailbox range with HA1, 0=1,1 will cause the host data
to be latched into the HDMAT1 register.
Note: All register addresses not listed are Reserved.
DS971890301
63

Zilog
s
16550 MIMIC INTERFACE
PRELIMINARY
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
The Z80189 has a 16550 MIMIC interface that allows it to
mimic the 16550 device. It has all the interface pins
necessary to connect up to the PC/XT/AT bus without any
extra circuitry. It contains the complete register set of the
16550 part with the same interrupt structure. The data path
allows parallel transfer of data to and from the register set
by the internal Z80180 of the Z80189. There is no shift
register associated with the MIMIC of the 16550 UART.
This interface saves the application from doing a serial
transfer before performing data compression or error
correction on the data.
Control of the register set is maintained by six priority
encoded interrupts to the Z80189. When the PC/XT/AT
writes to THR, MCR, LCR, DLL, DLM, FCR or reads the
RBR, an interrupt to the Z80189 is generated. Each interrupt can be individually masked off or all interrupts can be
disabled by writing a single bit. Both mode 0, mode 1 and
mode 2 interrupts are supported by the 16550 MIMIC
interface.
Two 8-bit timers are also available to control the data
transfer rate of the 16550 MIMIC interface. Their input is
tied to the BRG clock so a down count of 24 bits is possible.
An additional two 8-bit timers are available for programming the FIFO time-out feature (4 Character Time Emulation) for both Receiver and Transmitter FIFO’s.
The 16550 MIMIC interface supports the PC/XT/AT interrupt structure as well as an additional mode that allows for
a wired AND interrupt structure.
All registers of the 16550 MIMIC interface are accessible
in any page of I/O space since only the lowest 8 address
lines are decoded.
COM Port Decode functionality is integrated into the Z189.
This allows the MIMIC to be selected for a specific COM
Port Address (PC COM Port Address 1-4). Previously for
the Z80182, the COM Port Address selected for the MIMIC
was implemented through external COM Port Decode
circuitry. The COM Port Decode circuitry in the Z80189
simplifies this process by allowing the user to select the
MIMIC Com Port addresses through software, as well as
reducing the system board level costs by saving board
space and external circuitry.
See Figure 76 for a block diagram of the 16550 MIMIC
interface.
PC Side
Host Addr Decode
Host Data Bus
PC IRQ
PC DMA Control
Selectable
10
4
8
1
4
COM Port Decode
16550 MIMIC
Register Set
PC Host IRQ
PC DMA Mailbox
and I/O Mailbox
Rx Timer
Tx Timer
6
D
A
T
A
B
U
S
Z80180
Control
Figure 76. 16550 MIMIC Block Description
IRQ &
Control
Config
Register
Z80180 Data Bu
180 Side
Z80180
Address
8
64
DS971890301

Zilog
16550 MIMIC FIFO DESCRIPTION
PRELIMINARY
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
The receiver FIFO consists of a 16-word FIFO capable of
storing eight data bits and three error bits for each character stored (Figure 77). Parity error, Framing error and Break
detect bits are stored, along with the data bits, by copying
their value from three shadow bits, which are write only bits
for the Z80180 MPU LSR address. The three shadow bits
are cleared after they are copied to the FIFO memory. In
FIFO mode, to write error bits into the receiver FIFO, the
MPU must first write the Parity, Framing and Break detect
status to the Line Status Register (shadow bits) and then
write the character associated into the receiver buffer. The
data and error bits will then move into the same address in
the FIFO. The error bits become available to the PC side of
the interface when that particular location becomes the
next address to read (top of FIFO). At that time they may
either be read by the PC by accessing them in the LSR, or
they may cause an interrupt to the PC interface if so
enabled. The error bits are set by the error status of the byte
at the top of the FIFO but may only be cleared by reading
the LSR. If successive reads of the receiver FIFO are
performed without reading the LSR, the status bits will be
set if any of the bytes read have the respective error bit set.
The PC interface may be interrupted when 1, 4, 8 or 14
bytes are available in the receiver FIFO by setting bits 6
and 7 in the FCR (FIFO Control Register, PC address 02h
to the appropriate value. If the FIFO is not empty, but below
the above trigger value, a time-out interrupt is available if
the receiver FIFO is not written by the MPU or read by the
PC by an interval determined by the Character Time-out
Timer. This is an additional Timer with MPU access only
which is used to emulate the 16550 4 character time-out
delay. The timer receives the BRG as its input clock.
Software must determine the correct values to program
into the Receiver Time-out register and the BRG to achieve
the correct delay interval for time-out. These interrupts are
cleared by the FIFO reaching the trigger point or by
resetting the Time-out interval timer by FIFO MPU write or
PC read access.
With FIFO mode enabled, the MPU is interrupted when the
receiver FIFO is empty, corresponding to bit 5 being set in
the IUS/IP register (MPU access only). This bit corresponds to a PC read of the receiver buffer in non-FIFO
(16450) mode. The interrupt source is cleared when the
FIFO becomes non-empty or the MPU reads the IUS/IP
register.
The transmitter FIFO is a 16 byte FIFO with PC write and
MPU read access (Figure 78). In FIFO mode, the PC will
receive an interrupt when the transmitter becomes empty
corresponding to bit 5 being set in the LSR. This bit and the
interrupt source are cleared when the transmitter FIFO
becomes non-empty or the IIR register is read by the PC.
On the MPU interface, the transmitted data available can
be programmed to interrupt the MPU on 1, 4, 8 or 14 bytes
of available data by seeing the appropriate value in the
MPU FSCR control register (MPU write only XXECH) bits 6
and 7. A time-out feature exists, Transmitter Time-out
Timer, which is an additional 8 bit timer with BRG as the
input source. If the transmitter FIFO is non-empty and no
PC write or MPU read of the FIFO has taken place within the
timer interval, a time-out will occur causing a corresponding interrupt to the MPU.
DS971890301
65

Zilog
PRELIMINARY
16550 MIMIC FIFO DESCRIPTION (Continued)
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
MPU Write
LSR Shadow
B2-B4
MPU_RD
MPU
Databus
(MPU Side Write)
phi
MPU
IRQ
phi
Sync
16x3
Error
Bits
Read
Pointer
error
3
R
E
A
D
B
U
F
F
E
R
3
W
R
I
T
E
B
U
8
F
F
E
R
Write
Pointer
16x8
Data Bits
ALU
8
5
phi
Sync
PC Read
LSR
B2-B4
PC_RD
PC Side
Databus
(PC Side Read)
FIFO Control
Register
PC
IRQ
MPU Side
Interface
16550
MIMIC or
PC Side
Interface
Figure 77. Receiver FIFO Block Diagram
66
DS971890301

Zilog
d
.
r
e
PRELIMINARY
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
PC_WR
Write
IRQ
PC
phi
PC
phi
Sync
phi
W
R
I
T
E
B
U
8
F
F
E
R
Write
Pointer
16x8
Data Bits
ALU
Read
Pointer
R
E
A
D
B
U
F
F
E
R
Sync
8
5
MPU_RD
MPU Rea
(Data)
FCR Reg
MPU
IRQ
16550
MIMIC or
PC side
interface
16550
MIMIC o
PC Side
Interfac
Figure 78. Transmitter FIFO Block Diagram
DS971890301
67

Zilog
PRELIMINARY
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
16550 MIMIC FIFO DESCRIPTION (Continued)
Table 15. 16550 Line Status Register
Error Description How to Set How to Clear
Error in At least one data byte available At least one error in receiver When there are no more
RCVR in FIFO with one error FIFO errors
FIFO
*TEMT Transmitter empty MPU writes a 1 MPU writes a 0
† *THRE Transmitter holding When MPU has When holding register
register is empty read or emptied is not empty
the holding register
Break Break occurs when MPU writes 1 There is a
Detect received data input PC-side read
is held in logic-0 of the LSR
for longer than a
full word transmission
Framing Received character MPU writes 1 There is a
Error did not have a valid PC-side read
stop bit of the LSR
Z80189/Z8L189
Parity Received character MPU writes 1 There is a
Error did not have correct PC-side read
even or odd parity of the LSR
Overrun Overlapping received MPU makes There is a
Error characters, thereby two writes PC-side read
destroying the to receiver of the LSR
previous character buffer register
†Data Indicates complete MPU writes to Empty Receiver
Ready incoming data has RCVR FIFO or or Receiver FIFO
been received receiver buffer
register
Notes:
* The TEMT and THRE bits take on different functions when
TEMT/Double Buffer mode is enabled.
† These signals are delayed to HOST when using character
emulation delay.
68
DS971890301

Zilog
PRELIMINARY
Z80189 MIMIC SYNCHRONIZATION CONSIDERATIONS
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
Because of the asynchronous nature of the FIFO’s on the
MIMIC, some scheme of synchronization must be provided to prevent conflict from the dual port accesses of the
MPU and the PC.
To solve this problem, I/O to the FIFO is buffered, the
buffers allowing both PC and MPU to access the FIFO
asynchronously. Read and Write requests are then synchronized by means of the MPU clock. Incoming signals
are buffered in such a way that meta-stable input levels will
be stabilized to valid 1 or 0 levels. Actual transfers to and
from the buffers from and to the FIFO memory are timed by
the MPU clock. ALU evaluation is performed on a different
phase than the transfer to ensure stable pointer values.
Another potential problem is that of simultaneous access
of the MPU and PC to any of the various ‘mailbox’ type
registers. This is solved by dual buffering of the various
read/write registers. During a read access by either MPU
or PC to a mailbox register, the data in the buffered slave
register is not permitted to change. Any write that might
take place during this time will be stored in the input of the
master register. The corresponding status/interrupt will be
reset as appropriate based on the write having followed
the read to the register. For example, the IUS/IP bit for the
LCR write will not be cleared by the MPU read of the LCR
if a simultaneous write to the LCR by the PC takes place.
Instead the LSR data will change after the read access and
IUS/IP bit 3 will remain at logic 1.
DOUBLE BUFFERING FOR THE TRANSMITTER IN 16450 MODE
The Z80189 implements double buffering for the transmitter in 16450 mode and sets the TEMT bit in the LSR
Register automatically.
If character delay emulation is being used (see Figure 79):
1. The PC THRE bit in the LSR Register is set when the
THR Register is empty;
2. PC Host writes to the 16450 THR Register;
3. Whenever the Z80189 TSR buffer is empty and one
character delay timer is in a time out state, the byte
from the THR Register is transferred to the TSR buffer;
4. Restart character delay timer (timer reloads and counts
down) with byte transfer from THR Register to the TSR
buffer;
7. TEMT bit in LSR Register for MPU is set with no delay
whenever the TSR buffer is empty;
8. When the TSR buffer is read by MPU and THR Register
is empty and one character delay timer reaches zero
the TEMT bit in the LSR Register for Host is set from 0
to 1.
The PC THRE bit in the LSR Register is reset whenever the
THR Register is full and set whenever THR Register is
empty. MPU IREQ and DMA Request for the transmit data
is triggered whenever the TSR buffer is full and cleared
whenever TSR buffer is empty.
If character delay emulation is not used the TEMT bit in the
LSR Register is set whenever both the THR Register and
the TSR buffer are both empty. The Host TEMT bit is clear
if there is data in either the TSR buffer or THR Register.
5. Whenever the TSR buffer is full, the TEMT bit in LSR
Register for MPU is reset with no delay;
6. MPU reads TSR buffer;
DS971890301
Disable this feature when 16550 FIFO mode is enabled.
69

Zilog
PRELIMINARY
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
DOUBLE BUFFERING FOR THE TRANSMITTER IN 16450 MODE (Continued)
Host Write
Z80189/Z8L189
Empty/Full
Host & MPU THRE =
(MPU TEMT) TSRE =
Host TEMT = 1 if -THRE = 1 and
-TSRE = 1 and
- Emulation delay timer is timed out
Note: MPU seesTSR bit in the LSR Register as TEMT bit
1 0
Empty/Full
1 0
16450
THR
Register
THR to TSR
delay
transfer
TSR
Transmit
Shift Reg.
Emulation
Byte Transfer if:
- THRE=0; and
- TSRE = 1; and
- Character delay timer is timed out.
Note: Timer reloads and counts down
whenever data is transferred fromTHR to TSR.
Added TSR Buffer for the
transmit data
Figure 79. TEMT Emulation Logic Implementation
Z80189 MIMIC DMA Consideration
Since the /HRXRDY and /HTXRDY is removed in the Z189,
the MIMIC DMA feature found on the Z182 is not available
on the Z189.
Z80189 MIMIC Design Hint
The MIMIC output drive capability has been increased to
16 mA on the Z189. This may eliminate the need for
buffering to the PC Bus.
70
DS971890301

Zilog
PRELIMINARY
16550 MIMIC INTERFACE REGISTERS
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
The 16550 MIMIC interface is controlled by the MMC
register. Setting it allows for different modes of operation
such as using the eight bit counters and which IRQ
structure is used with the PC/XT/AT.
765 43210
00000000
VIS Vector Include Status
0 = Mode 0 Interrupts
1 = Mode 2 Interrupts
HINTR1
00 = Normal
01 = Wire And
10 = Out 2 Control
11 = Reserved
Reserved as 0
Reserved as 0
Reserved as 0
Rx Timer Enable
Tx Timer Enable
Figure 80. MIMIC Master Control Register
(Z180 MPU Address XXFFH)
Bit 7 Transmit Timer Delay Counter
Enable (Read/Write)
If bit 7 is set to a one, it enables the transmit delay timer.
When the Z180 reads the Transmit Register, the transmit
delay timer is automatically loaded with the Transmit Time
Constant Register and the timer is enabled to countdown
to zero. This timer delays setting the Transmitter Holding
Register Empty (THRE) bit until the timer times out. If this
bit is zero, then THRE is set immediately on a Z180 read of
the Transmit Register.
Both counters are single pass and stop on a count of zero.
Their purpose is to delay data transfer just as if the 16550
UART had to shift the data in and out. This is provided to
alleviate any software problems a high speed continuous
data transfer might cause to existing software. If this is not
a problem, then data can be read and written as fast as the
two machines can access the devices. In FIFO mode of
operation, the timers are used to delay the status to the PC
interface by the time that would be required to actually shift
the characters out or in if an actual UART were present.
Bit 5 Reserved as 0
Bit 4 Reserved as 0
Bit 3 Reserved as 0
Bit 2,1 Interrupt Select (Read/Write)
Bits 2, 1
00 If both bits 2 and 1 are set to zero, then the active
HINTR1 pin is set to normal 16550 MIMIC mode.
01 If bit 2 is zero and bit 1 is one, then the 16550
MIMIC will enable a wire AND condition on the
active HINTR1 pin to the PC/XT/AT.
10 If bit 2 is one and bit 1 is zero, then the active
HINTR1 pin will be driven only if out 2 of the
Modem Control register is a one. If out 2 is a zero,
then the active HINTR1 pin will be tri-stated.
11 Both bits should never be set to one. This is a
reserved condition and should not be used.
Bit 0 Vector Include Status (Read/Write)
This bit is used to select the interrupt response mode of the
Z180. A 0 in this bit enables mode 0 interrupts; a 1 enables
mode 2 response.
Bit 6 Receive Timer Delay Counter
Enable (Read/Write)
If bit 6 is set to a one, it enables the receive delay timer.
When the Z180 writes to the Receive Buffer, it loads the
receive delay timer from the Receive Time Constant Register and enables the timer to countdown to zero. This timer
delays setting the Data Ready (DR) bit in the LSR until the
timer times out. If this bit is a zero, then DR is set immediately on a Z180 write to the Receive Buffer.
DS971890301
71

Zilog
PRELIMINARY
16550 MIMIC INTERRUPT REGISTERS
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
IUS/IP Register
The IUS/IP Register is used by the Z180 MPU to determine
what has caused the Interrupt. This register will have the
appropriate bit set when an interrupt occurs.
765 43210
00010000
Interrupt Pending
6 THR Write
5 TTO Transmitter Timeout
4 RBR Read
3 MCR Write
2 LCR Write
1 DLL Write
1 DLM Write
0 FCR Write or Tx Overrun
Interrupt Under Service (RD)
Reset Highest IUS (WR)
Figure 81. IUS/IP Register
(Z180 MPU Address XXFEH)
Bit 7 Interrupt Under Service (Read/Write)
This bit represents a logical OR of each individual IUS bit
for the internal MIMIC interrupt daisy chain. An IUS bit is set
when an interrupt is registered (IP set) and enabled (IE
set), the incoming IEI daisy chain is active (chain enabled)
and an interrupt acknowledge cycle is entered. By writing
a ‘1’ to this bit the highest priority IUS bit that is set will be
reset. Writing a ‘0' to this bit has no effect.
Bit 6 Transmitter Holding Register Written
(Read Only)
This bit is set when the PC/XT/AT writes to the Transmitter
Holding Register. It is reset when the Z180 MPU reads the
Transmitter Holding Register. In FIFO mode, this bit is set
when the trigger level is reached (4, 8, 14 bytes available).
Bit 5 Transmitter Time-out with Data in FIFO
(Read Only)
This bit is set when the transmitter FIFO has been idle (no
read or write and timer decrements to zero) with data bytes
below the trigger level. It is cleared when the FIFO is read
or written.
Bit 4 Receive Buffer Read (Read Only)
This bit is set when the PC/XT/AT reads the Receive Buffer
Register. It is reset when the Z180 MPU writes to the
Receive Buffer Register. In FIFO mode, this bit is set upon
the PC reading all the data in the receiver FIFO. Note: RBR
is set and interrupts when the receiver FIFO has been
emptied by the PC. This bit and interrupt are cleared when
one or more bytes are written into the receiver FIFO by the
MPU.
Bit 3 Modem Control Register Write (Read Only)
This bit is set when the PC/XT/AT writes to the Modem
Control Register. It is reset when the Z180 MPU reads the
Modem Control Register.
Bit 2 Line Control Register Write (Read Only)
This bit is set when the PC/XT/AT writes to the Line Control
Register. It is reset when the Z180 MPU reads the Line
Control Register.
Bit 1 Divisor Latch LS/MS Write (Read Only)
This bit is set when the PC/XT/AT writes to the Divisor Latch
Least Significant or Most Significant bytes. It is reset when
the PC reads the LS/MS register(s). To determine which
byte(s) have been written, the Z180 must read either LS or
MS locations and then repoll this bit. If only one location is
interrupting, the interrupt will be cleared when that location
is read by the Z180.
Bit 0 FIFO Control Register Write (Read Only)
This bit is set when the PC/XT/AT writes to the FCR. It is
reset when the Z180 MPU reads this register.
If THR timer is enabled, this interrupt is delayed by the
number of character times programmed as the trigger
level.
Note: The THR bit is set (interrupts) when the transmitter
FIFO reaches the data available trigger level set in the MPU
FSCR control register. The bit and interrupt source is
cleared when the number of data bytes falls below the set
trigger level.
72
DS971890301

Zilog
Interrupt Enable Register
PRELIMINARY
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
The IE Register allows each of the 16550/8250 interrupts to
the Z180 MPU to be masked off individually or globally.
765 43210
00000000
Interrupt Enable
6 Enable THR IRQ
5 Enable TTO IRQ
4 Enable RBR IRQ
3 Enable MCR IRQ
2 Enable LCR IRQ
1 Enable DLL/DLM IRQ
0 Enable FCR IRQ
MIE
Figure 82. IE Register
(Z180 MPU Address XXFDH)
Bit 7 Master Interrupt Enable (Read/Write)
If bit 7 is a zero, all interrupts from the 16550 MIMIC are
masked off. If this bit is a one, then Interrupts are enabled
individually by setting the appropriate bit.
Priority of interrupts are in this order:
Highest 6. THR IRQ
5. TTO IRQ
4. RBR IRQ
3. MCR IRQ
2. LCR IRQ
1. DLL IRQ
1. DLM IRQ
Lowest 0. FCR IRQ
Interrupt Vector Register
The Interrupt Vector Register contains either the opcode or
the Lower Address for a Z180 interrupt, depending upon
the VIS bit in the MMC Register. If the VIS bit is a zero, then
Z180 Mode 0 interrupt is selected, if the VIS bit is a one then
Z180 Mode 2 is selected.
765 43210
00000000
0/Opcode
Bit 6 Enable THR Interrupt (Read/Write)
If this bit is a one, it enables the Transmitter Holding
Register Interrupt.
Bit 5 Enable TTO Interrupt (Read/Write)
If this bit is a one, it enables the Transmitter Time-out
Interrupt. This will interrupt the CPU when characters
remain in the FIFO below the trigger level and the FIFO is
not read or written for the length of time in the transmitter
time-out register.
Bit 4 Enable RBR Interrupt (Read/Write)
If this bit is a one, it enables the Receiver Buffer Register
Interrupt.
Bit 3 Enable MCR Interrupt (Read/Write)
If this bit is 1, it enables the Modem Control Register
Interrupt
Bit 2 Enable LCR Interrupt (Read/Write)
If this bit is a one, it enables the Line Control Register
interrupt.
Bit 1 Enable DLL/DLM Interrupt (Read/Write)
If this bit is 1, it enables the Divisor Latch least and Most
Significant Byte Interrupts
Bit 0 Enable FCR Interrupt (Read/Write)
If this bit is a one, then interrupts are enabled for a PC write
to the FIFO control register (FCR).
Status/Opcode
Upper Nibble IVEC
Figure 83. IVEC Register
(Z180 MPU Address XXFCH)
Bit 7-4 Upper Nibble IVEC (Read/Write)
These four bits are to generate either an opcode or the
upper four bits of the eight bit address to support the Z180
interrupt modes. These bits are read/write and always read
back what was last written to them.
Bits 3-1 Status/Opcode (Read/Write)
These three bits are the Interrupt Status bits when VIS in the
MMC register is a one. If the VIS bit is a zero, then these bits
contain what was last written to them.
Bits 321
000 NO IRQ
001 FCR IRQ
010 DLL/DLM IRQ
011 LCR IRQ
100 MCR IRQ
101 RBR IRQ
110 TTO IRQ
111 THR IRQ
DS971890301
73

Zilog
PRELIMINARY
Interrupt Vector Register (Continued)
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
Bit 0 Opcode (Read/Write)
This bit is always a zero when the VIS bit is a one. If the VIS
bit is a zero, then this bit reads back what was last written
to it.
This register serves both interrupt modes. When the VIS bit
is a zero, the last value written to the register can be read
back. If the VIS bit is a one and an interrupt is pending, the
value read will be the last value written to the upper nibble
plus the status for the interrupt that is pending. If no
interrupt is pending, then the last value written to the upper
nibble plus the lower nibble will be read from the register.
If the vector includes the status, then the lower four bits of
the vector will change asynchronously depending on the
interrupting source. Since this vector changes asynchronously, then the interrupt service routine to read the IVEC
register might read the source of the most recent IRQ/
INTACK cycle if that IRQ does not have its IUS set.
765 43210
00000000
FORCE_450
Receive Timeout to PC Host Enable
TEMT_DBLBUFF
Reserved (Always 0)
XMITTimeout Enable
RCVR Timeout Enable
XMITTrigger (LSB)
XMITTrigger (MSB)
Bit 5 Receiver Time-out Enable
This bit enables the Z80189 Receiver Time-out Timer that
is used to emulate the four character time-out delay that is
specified by the 16550. An RTO interrupt will occur under
the following conditions: no read or write to the RCVR FIFO,
data bytes are available, but below the PC trigger level, or
the receiver timeout timer reaches zero.
Bit 4 Transmitter Time-out Enable
This bit enables the Z80189 timer that is used to interrupt
the Z180 MPU if characters are available, but are below the
trigger level. The timer is enabled to count down if this bit
is one and the number of bytes is below the set transmitter
trigger level. The timer will time-out and interrupt the MPU
if no read or write to the XMIT FIFO takes place within the
timer interval.
Bit 3 Reserved for Future Use
Always write and read as ‘0’ by users. Writing ‘1’ enables
a test mode for emulation timers.
Bit 2 Double Buffer Mode (Write/Read)
(Reset value=0) Setting this bit will enable (only in 16450
mode) the TEMT hardware emulation and transmitter double
buffering.
Double Buffer
This enables a transmit shift register (TSR) to act as a slave
register, while the PC writes to a transmit holding register.
The Z180 reads from the transmit shift register. This allows
the PC to write two consecutive bytes into the MIMIC.
Figure 84. FIFO Status and Control Register
(Z180 MPU Read/Write Add XXECH)
Bit 7 and Bit 6 XMIT Trigger MSB, LSB
This field determines the number of bytes available to read
in the transmitter FIFO before an interrupt will occur to the
MPU:
b7 b6 Level (#bytes)
001
014
108
1114
TEMT Emulation
If character delay emulation is being used, the TEMT is set
as follows:
The TSR is emptied and the associated delay logic has set
the (delayed) THRE bit in the LSR.
At this time a one character delay timer begins. After this
timer reaches zero count, the TEMT bit will be set if the THR
and TSR output buffer are empty. TEMT is clear whenever
there is data in either THR or the TSR output buffer.
Bit 1 Receive Timeout to the PC Host (Write/Read)
(Reset Value=0) setting this bit will enable the RTO timeout
to emulate the 16550 device. If enabled, the RTO timer will
not start timeout until all delayed characters have been
clocked through the receiver character delay emulation
logic. This will prevent an RTO from occurring before a
(delayed) receiver trigger level interrupt. When cleared,
the RTO will begin timeout from the last read or write to the
receiver FIFO.
74
DS971890301

Zilog
PRELIMINARY
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
Bit 0 Force 16450 mode (Write/Read)
(Reset value=0) This bit=1 will force the MIMIC into 16450
mode. Bit 0 in the FCR reg is forced to zero as well as the
MIMIC internal FIFO enable. Bits 7 and 6 in the IIR will
remain at their last value when this bit is set.
765 43210
1
1111111
Rec Timeout Constant
Figure 85. Receiver Time-out Timer Constant
(Z180 MPU Add XXEAH)
This register contains an 8-bit constant for emulation of the
16550 4 character time-out feature. Software must determine the value to load into this register based on the bit rate
and word length specified by the MIMIC interface with the
PC. This timer receives its input from the BRG Clock. This
timer is enabled to down count when the enable bit in the
FSCR register is set and the trigger level has not been
reached on the RCVR FIFO. The counter will reload each
time there is a read or write to the RCVR FIFO.
765 43210
11111111
Transmitter Timeout
Constant
Figure 86. Transmitter Time-out Timer Constant
(Z180 MPU Add XXEBH)
This register contains an 8-bit constant for determining the
interval for the transmitter time-out timer. If allowed to
decrement to zero, this timer will interrupt the MPU by
setting the THR bit in the IUS/IP register. This timer receives its input from the BRG Clock. The timer is enabled
to down count when the enable bit in the FSCR register is
set and the trigger level has not been reached on the XMIT
FIFO. The counter will reload each time there is a read or
write to the XMIT FIFO.
TRANSMIT AND RECEIVE TIMERS
Because of the speed at which data transfers can take
place between the Z180 MPU and the PC/XT/AT, two
timers have been added to alleviate any software problems that a high-speed data transfer might cause. These
timers allow the programmer to slow down the data transfer just as if the 16550 MIMIC interface had to shift the data
in and out. The Timers receive their input from the BRG
Clock. This allows the programmer access to a 24-bit timer
to slow down the data transfer.
765 43210
11111111
Transmitter Time
Constant
Figure 87. Transmitter Time Constant Register
(Z180 MPU Address XXFAH)
When a write from the PC/XT/AT is made to the Transmitter
Holding register, an interrupt to the Z180 MPU is generated. The Z180 MPU then reads the data in the Transmitter
Holding Register. Upon this read if the Transmitter timer is
enabled, the time constant from the Transmitter Time
Constant Register is loaded into the Transmitter timer and
enables the count. After the timer reaches a count of zero,
the Transmitter Holding Register Empty bit is set. However,
the above is only true when the PC/XT/AT is reading the
Transmitter Holding Register Empty bit. To allow the Z180
MPU to know that it has already read the byte of data, a
mirrored Transmitter Holding Register Empty bit is set
immediately following a read from the Transmitter Holding
Register. This mirrored bit is always read back to the Z180
MPU when it reads the Line Status Register. If the transmitter timer is not enabled when the Z180 MPU reads the
transmitter holding register, then both Transmitter Holding
Register Empty bits are set immediately. In FIFO mode of
operation, the effect is similar in that the status to PC is
always delayed such that a PC interrupt for empty FIFO will
not occur before the time required for each character read
from the FIFO by the Z180 has elapsed. The effect is that
the PC will not see data requests from an empty FIFO any
faster than would occur with a true UART when the delay
feature is enabled. This timer is also used to delay data
transfer from THR Register to Z80189 TSR buffer in double
buffer mode.
DS971890301
75

Zilog
PRELIMINARY
TRANSMIT AND RECEIVE TIMERS (Continued)
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
765 43210
11111111
Receiver Time Constant
Figure 88. Receiver Time Constant Register
(Z180 MPU Address XXFB)
When the Z180 MPU writes to the Receive Buffer register
and the Receive Timer is enabled, the Receive Timer is
loaded with the Receiver Time Constant, the timer is
16550 MIMIC REGISTERS
The Z80189 contains a register set for interfacing with the
PC/XT/AT. The registers are:
Receiver Buffer Register
Transmit Holding Register
Interrupt Enable Register
Interrupt Identification Register
Line Control Register
Modem Control Register
Line Status Register
Modem Status Register
Scratch Register
Divisor Latch Least Significant/Most Significant Bytes
FIFO Control Register
MIMIC Modification Register
enabled and counts down to zero. When the timer reaches
zero, the Data Ready bit in the Line Status Register is set.
As with the Transmit Timer the Data Ready bit is also
mirrored. Immediately upon a write to the Receive Buffer,
the mirrored bit is set to let the Z180 MPU know that the byte
has already been written. If the timer is not enabled, then
both Data Ready bits are set immediately upon a write to
the Receive Buffer. The FIFO mode of operation is similar
in that the status to the PC is always delayed by the time
required for each character written to the FIFO by the Z180.
The effect is that the PC will not see a FIFO trigger level or
DMA request faster than would occur with a true UART
when the delay feature is enabled.
Receive Buffer Register
When the Z180 has assembled a byte of data to pass to the
PC/XT/AT, it places it in the Receiver Buffer Register. If the
Received Data Available interrupt is enabled, then an
interrupt is generated for the PC/XT/AT and the Data
Ready bit is set (if the Receiver Timer is enabled, the
interrupt and setting of the Data Ready bit is delayed until
after the timer times out). Also, the shadow bits of the Line
Status Register are transferred to their respective bits
when the Z180 MPU writes to the Receiver Buffer Register
(see Line Status Register Bits 1, 2, 3 and 4). This allows a
simultaneous setting of error bits when the data is written
to the Receiver Buffer Register. In FIFO mode, this address
is used to read (PC) and write (Z180) the Receiver FIFO.
These registers are used to emulate the 16550 UART. The
PC/XT/AT can access these registers just as if it was
interfacing with the 16550 UART. This allows the Z80189 to
be software compatible with existing Z80189 modem
software.
76
765 43210
XXXXXXXX
Receiver Buffer
Register
PC Read Only,
(Address 00h, DLAB=0, R/W=Read)
(Z180 MPU Write Only, Address xxF0H)
Figure 89. Receiver Buffer Register
DS971890301

Zilog
PRELIMINARY
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
Transmit Holding Register
When the PC/XT/AT writes to the Transmitter Holding
Register, the Z80189 responds by setting the appropriate
bit in the IP register and by generating an interrupt to the
Z180 MPU if it is enabled. When the Z180 MPU reads this
register, the Transmitter Holding register empty flag is set
(if the transmitter timer is enabled, this bit is set after the
timer times out). In FIFO mode of operation, this address is
used to read (Z180) and write (PC) the Transmitter FIFO.
765 43210
XXXXXXXX
Transmitter Holding
Register
(PC Write Only, Address 00H, DLAB=0, R/W=Write)
(Z180 MPU Read Only, Address XXF0H)
Figure 90. Transmitter Holding Register
FIFO Control Register
765 43210
Bit 6 and Bit 7 RCVR trigger LSB and MSB bits
This 2-bit field determines the number of required bytes in
the receiver FIFO before an interrupt to the PC occurs.
b7 b6 Trigger Level, Number of Bytes
00 01
01 04
10 08
11 14
Bit 4 and Bit 5 Reserved
Note: From the MPU side, bit 4 and bit 5 flag two sources
of interrupts. Bit 5 is a FIFO interrupt, indicating that the
FCR had changed; bit 4 is a Tx overrun interrupt, indicating
transmit overrun. A read of the FCR from the MPU side will
clear a previously set bit 4 or bit 5.
Bit 3 Reserved
Reserved for future use.
Bit 2 XMIT FIFO Reset
Setting this bit to a 1 will cause the transmitter FIFO pointer
logic to be reset; any data in the FIFO will be lost. This bit
is self clearing; however, a shadow bit exists that is cleared
only when read by the Z180 MPU, allowing the MPU to
monitor a FIFO reset by the PC.
00000000
FIFO Enable
RCVR FIFO Reset
XMIT FIFO Reset
Reserved (Must be 0)
Reserved
(Tx Overrun, MPU Only)
Reserved
(FCR Write, MPU Only)
RCVR Trigger (LSB)
RCVR Trigger (MSB)
PC/XT/AT Write Only, PC Address 02h
Z180 MPU Read Only, MPU Address XXE9H
Figure 91. FIFO Control Register
Bit 1 RCVR FIFO Reset
Setting this bit to a 1 will cause the receiver FIFO pointer
logic to be reset; any data in the FIFO will be lost. This bit
is self clearing; however, a shadow bit exists that is cleared
only when read by the Z180 MPU, allowing the MPU to
monitor a FIFO reset by the PC.
Bit 0 FIFO Enable
The PC writes this bit to logic 1 to put the 16550 MIMIC into
FIFO mode. This bit must be a 1 when writing to the other
bits in this register or they will not be programmed. When
this bit changes state, any data in the FIFO’s or transmitter
holding and receiver buffer registers is lost and any pending interrupts are cleared.
DS971890301
77

Zilog
PRELIMINARY
Interrupt Identification RegisterMIMIC Modification Register
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
D7
D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
00000000
Reserved - Program to Zero
16550/450 RCVR Overrun
Figure 92. MIMIC Modification Register
(Z189 MPU Write only, Address XXE9H)
Bit 7-2 Reserved. Program to zero.
Bit 1 RCVR Overrun Modification
The actual 16450/16550 device allows the last position in
FIFO to be overwritten by MPU during receiver overrun
condition. When this bit is enabled (programmed to 1) the
last position in FIFO can be overwritten by Z180 during
receiver overrun. This feature is disabled by default. When
this modification is not enabled, the MIMIC will ignore any
write to RBR during an overrun condition.
Bit 0 Reserved
Program to zero.
765 43210
00000000
0 if Interrupt Pending
Interrupt ID Bit (0)
Interrupt ID Bit (1)
Interrupt ID Bit (2)
Always 0
FIFO Enabled Flag
PC/XT/AT Read Only, PC Address 02H
Z180 MPU No Access
Figure 93. Interrupt Identification Register
Bit 7 and Bit 6 FIFO’s enabled
These bits will read 1 if FIFO mode is enabled on the
MIMIC.
Bit 5 and Bit 4 Always read 0
Reserved bits.
Bits 3-1 Interrupt ID bits
This 3 bit field is used to determine the highest priority
interrupt pending. See Table 16 for the 3-bit field
descriptions.
Table 16. Interrupt Identification Field
b3 b2 b1 Priority Interrupt Source Inter. Reset Control
0 1 1 Highest Overrun, Parity, Read Line Stat. Reg.
Framing error or
Break detect bits
set by MPU.
0 1 0 2nd Received Data RCVR FIFO drops below
trigger level trigger level.
1 1 0 2nd Receiver Time-out Read RCVR FIFO.
with data in
RCVR FIFO.
0 0 1 3rd Transmitter Writing to the
Holding Register IIR or transmitter
Empty. Holding Register.
0 0 0 4th MODEM status: Reading the MODEM
CTS,DSR,RI or
DCD.
78
DS971890301

Zilog
PRELIMINARY
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
Bit 0 Interrupt Pending
This bit is logic 0 and interrupt is pending. When the PC
accesses the IIR, the contents of the register and all
pending interrupts are frozen. Any new interrupts will be
recorded, but not acknowledged during the IIR access.
Line Status Register
765 43210
00010000
Data Ready
Overrun Error
Parity Error
Framing Error
Break Interrupt (BI)
THRE
TEMT
Error in RCVR FIFO
PC/XT/AT Read Only, PC Address 05H
Z180 MPU Read/Write Bits 6,4,3,2 MPU Address XXF5H
Figure 94. Line Status Register
Bit 2, 3, 4 Parity Error, Framing Error, Break Detect
These bits are written, indirectly, by the MPU as follows:
The bits are first written to shadow bit locations when the
MPU write accesses the LSR. When the next character is
written to the Receiver Buffer or RCVR FIFO, the data in the
shadow bits is then copied to the LSR (16450 mode) or
FIFO RAM (16550 mode). In FIFO mode, the bits become
available to the PC when the data byte associated with the
bits is next to be read (top of FIFO). In FIFO mode, with
successive reads of the receiver, the status bits will be set
if an error occurs on any byte. Once the MPU writes to the
Receiver Buffer or RCVR FIFO, the shadow bits are auto
cleared. The register bits are cleared upon the PC reading
the LSR. In FIFO mode, these bits will be set if any byte has
the respective error bit set while the PC reads multiple
characters from the FIFO.
Bit 1 Overrun Error
This bit is set if the Z180 MPU makes two writes to the
Receiver Buffer before the PC reads the data in the Buffer
(16450 mode) or with a full RCVR FIFO (16550) mode. No
data will be transferred to the RCVR FIFO under these
circumstances. This bit is reset when the PC reads the Line
Status Register.
Bit 7 Error in RCVR FIFO
In 16450 mode, this bit will read logic 0. In 16550 mode, this
bit is set if at least one data byte is available in the FIFO with
one of its associated error bits set. This bit will clear when
there are no more errors (or break detects) in the FIFO.
Bit 6 Transmitter Empty
This bit must be set or reset by the MPU by a write to this
register bit. If Double Buffer Mode is enabled this bit is set
automatically by hardware whenever both THR buffer and
TSR is empty.
Bit 5 Transmitter Holding Register Empty, THRE
This bit is set to one when either the THR has been read
(emptied) by the MPU (16450 mode) or the XMIT FIFO is
empty (16550 mode). This bit is set to 0 when either the
THR or XMIT FIFO become non-empty. A shadow bit exists
so that the register bit setting to 1 is delayed by the
Transmitter Timer if enabled. The MPU when reading this
bit will not see the delay. Both shadow and register bits are
cleared when the PC writes to the THR of XMIT FIFO.
Note: The THRE bit is forced to 0 in the PC side to prevent
THR overruns when /HALT is asserted (Powerdown Mode)
and bit 3 (/INTO assertion on MIMIC access feature) is set.
When the MIMIC comes out of powerdown (/HALT
deasserted), the THRE bit resumes normal functionality.
Bit 0 Data Ready
This bit is set to 1 when received data is available, either in
the RCVR FIFO (16550 mode) or Receiver Buffer Register
(16450 mode). This bit is set immediately upon the MPU
writing data to the Receiver Buffer or FIFO if the Receiver
Timer is not enabled but is delayed by the timer interval if
the Receiver Timer is enabled. For MPU read access, a
shadow bit exists, so that the MPU does not see the delay
the PC does. Both bits are cleared to logic zero immediately upon reading all the data in either the Receiver Buffer
or FIFO.
Interrupt Enable Register
765 43210
00000000
Bit 0 Received Data Available Int.
Bit 1 THRE Interrupt
Bit 2 Receiver Line Status Int.
Bit 3 Modem Status Interrupt
Bit 7,6,5,4 always 0
PC/XT/AT Read/Write, PC Address 01H
Z180 MPU Read Only, Z180 MPU Address XXF1H
Figure 95. Interrupt Enable Register
DS971890301
79

Zilog
PRELIMINARY
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
Interrupt Enable Register (Continued)
Bits 7,6,5,4 Reserved
These bits will always read 0 (PC and MPU)
Bit 3 Modem Status IRQ
If bits 0,1,2 or 3 of the Modem Status Register are set and
this enable bit is a logic 1, then an interrupt to the PC is
generated.
Bit 2 Receiver Line Status IRQ
If bits 1,2,3 or 4 of the LSR are set and this enable bit is a
logic 1, then an interrupt to the PC is generated.
Bit 1 Transmitter Holding Register Empty IRQ
If bit 5 of the LSR is set and this enable bit is a logic 1, then
an interrupt to the PC is generated.
Bit 0 Received Data Available IRQ
If bit 0 of the LSR is set or a Receiver Timeout occurs and
this enable bit is a logic 1, then an interrupt to the PC is
generated.
Line Control Register
Bit 6-Bit 0
These bits do not affect the Z80189 directly; however, they
can be read by the Z180 MPU and the 16550 MIMIC
modes can be emulated by the Z180 MPU.
Modem Control Register
765 43210
00000000
DTS
RTS
Out 1
Out 2
Loop
Reserved
PC/XT/AT Read/Write, PC/XT/AT Address 4H
Z180 MPU Read Only, Z180 MU Address XXF4H
Figure 97. Modem Control Register
765 43210
00000000
Word Length Sel.
Number of Stop Bits
Parity Enable
Even Parity Sel.
Stick Parity
Set Break
DALB
PC/XT/AT Read/Write, PC/XT/AT Address 3H
Z180 MPU Read Only, Z180 MU Address XXF3H
Figure 96. Line Control Register
Bit 7 Divisor Latch Access Bit (DALB)
This bit allows access to the divisor latch by the PC/XT/AT.
If this bit is set to a one, access to the Transmitter, Receiver
and Interrupt Enable Registers is disabled, and when an
access is made to address 0, the Divisor Latch Least
Significant byte is accessed and if an access is made to
address 1, the Divisor Latch Most Significant byte is
accessed.
Bit 7-5 Reserved
Reserved for future use, always 0.
Bit 4 Loop
When this bit is set to a one then:
RI = Out 1
DCD = Out 2
DSR = DTR
CTS = RTS
Emulation of the loop back feature of the 16550 UART must
be done by the Z180 MPU except for the above conditions.
Bit 3 Out 2
This bit controls the state on the active HINTR pin if bits 2
and 1 of the MIMIC Master Control Register are a 10. Or
else it can be read by the Z180 MPU.
Bit 2-Bit 0
These bits have no direct control of the 16550 MIMIC
interface and the Z180 MPU must emulate the function if it
is to be implemented.
80
DS971890301

Zilog
PRELIMINARY
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
Modem Status Register
765 43210
00000000
DCTS
DDSR
TERI
DDCD
CTS
DSR
RI
DCD
PC/XT/AT Read Only, PC/XT/AT Address 6H
Z180 MPU Read/Write Bits 7-4, Z180 MPU Address XXF6H
Figure 98. Modem Status Register
Bit 7 Data Carrier Detect
This bit must be written by the Z180 MPU.
Bit 6 Ring Indicator
This bit must be written by the Z180 MPU.
Scratch Register
765 43210
XXXXXXXX
Scratch Register
PC/XT/AT Read/Write, PC/XT/AT Address 07H
Z180 MPU Read Only, Z180 MPU Address XXF7H
Figure 99. Scratch Register
Bits 7-0 Scratch Register
This register is used by the PC/XT/AT programmer for
temporary data storage. The Z180 MPU is able to read this
register. If the PC/XT/AT writes to this register, no interrupt
to the Z180 MPU is generated.
Divisor Latch (LS)
765 43210
XXXXXXXX
Divisor Latch (LS)
PC/XT/AT Read/Write, PC/XT/AT Address 00H and DLAB = 1
Z180 MPU Read Only, Z180 MPU Address XXF8H
Bit 5 Data Set Ready
This bit must be written by the Z180 MPU.
Bit 4 Clear to Send
This bit must be written by the Z180 MPU.
Bit 3 Delta Data Carrier Detect
This bit is set to a one whenever the Data Carrier Detect bit
changes state. This bit is reset when the PC/XT/AT reads
the Modem Status Register.
Bit 2 Trailing Edge Ring Indicator
This bit is set to a one on the falling edge of the Ring
Indicator bit. This bit is reset when the PC/XT/AT reads the
Modem Status Register.
Bit 1 Delta Data Set Ready
This bit is set to a one whenever the Data Set Ready bit
changes state. This bit is reset when the PC/XT/AT reads
the Modem Status Register.
Bit 0 Delta Clear To Send
This bit is set to a one whenever the Clear To Send bit
changes state. This bit is reset when the PC/XT/AT reads
the Modem Status Register.
Figure 100. Divisor Latch (LS)
Bit 7-0 Divisor Latch Most Significant (MS)
This register contains the low order byte of the Baud rate
divisor. Writing to this register with the PC/XT/AT will
generate an interrupt to the Z180 MPU. It can then read the
Baud rate divisor and set up the application.
Divisor Latch (MS)
765 43210
XXXXXXXX
Divisor Latch (MS)
PC/XT/AT Read/Write, PC/XT/AT Address 01H and DLAB = 1
Z180 MPU Read Only, Z180 MPU Address XXF9H
Figure 101. Divisor Latch (MS)
Bit 7-0 Divisor Latch Most Significant (MS)
This register contains the high order byte of the Baud rate
divisor. Writing to this register with the PC/XT/AT will
generate an interrupt to the Z180 MPU. It can then read the
Baud rate divisor and set up application.
DS971890301
81

Zilog
PC DMA Mailbox
PRELIMINARY
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
General Description
The concept behind the PC DMA Mailbox Registers is to
provide a path for the PC DMA data transfer separate from
the MIMIC COM Port. Commands and data flow over the
COM Port, while the DMA path is reserved for other
purposes. The PC DMA Mailbox Register functionality will
require control registers which will allow PC DMA data
transfer between the PC memory and for example, a
modem speaker/microphone codec. Note that the transfer
will be driven by the PC Host DMAs. This feature only
allows for the handshaking and data path for the PC Host
DMAs.
The host (PC) DMA channels will use the following four
Z189 pins for the PC DMA Mailbox feature. Each pair of
pins are individually selectable:
PC DMA MAILBOX BIT FUNCTIONS
HDRQ0 Host DMA request 0, Z189 output,
active high, high-Z control
/HDACK0 Host DMA acknowledge 0, Z189 input,
active low
HDRQ1 Host DMA request 1, Z189 output,
active high, high-z control
/HDACK1 Host DMA acknowledge 1, Z189 input,
active low
The pins labeled as HDRQ0 and HDRQ1 are asserted by
the Z180 to signal the PC HOST of a DMA request. The pins
labelled /HDACK0 and /HDACK1 are asserted by the PC
to signal a PC DMA access. Dual request/acknowledge
pairs are provided to interface with two PC DMA channels.
The PC Mailbox channels are independent and can be
used simultaneously or individually for jumperless DMA
channel selection.
HDREQ. Host DMA request bit, default value = 0
Two bits will serve to request a PC HOST DMA access.
When this bit is set and the Host DMA channel is enabled
(HDMAE=1), the corresponding HDRQ pin will be asserted high. Z180 software sets this bit (OUT0 instruction)
to request a DMA transfer, and Z189 hardware clears the
bit when the byte transfer is complete. Z180 software can
also clear the bit. The Z180 will be able to read the bit (IN0
instruction) to indicate that the transfer has occurred.
I/O address of XXD2h (HMC register) contains a request
bit for each DMA channel (bit 4 and bit 5 of the HMC
register). Write enable bits are provided to simplify code
(read-modify-write cycles not required).
HDMAE Host DMA enable default=0, HDRQ is tri-stated
Two bits will serve to enable the dual DMA channels
request/acknowledge pairs. When the HDMAE1 bit is set,
the output will become fully driven, otherwise (HDMAE1 bit
is reset) the HDRQ1 will be tri-stated. When the HDMAE0
bit is set the HDRQ0 output will become fully driven,
otherwise, the HDRQ0 output will be tri-stated.
I/O address XXD2h is assigned the HMC register. Bits 0
and 1 of the HMC register are respectively assigned
HDMAE0 and HDMAE1.
82
DS971890301

Zilog
PC MAILBOX DATA REGISTERS
PRELIMINARY
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
HDMAT0 Host DMA Transmit Register 0,
Z180 Read Only, PC Write Only
HDMAT1 Host DMA Transmit Register 1,
Z180 Read Only, PC Write Only
HDMAR0 Host DMA Receive Register 0,
Z180 Write Only, PC Read Only
HDMAR1 Host DMA Receive Register 1,
Z180 Write Only, PC Read Only
There are four separate 8-bit mailbox registers available
for DMA data. The I/O address for the mailbox registers will
be XXDOH for Mailbox 0 and XXD1H for Mailbox 1. Note
that there are separate registers for read and write access.
The mailbox register can latch data from the host data bus
HD[0:7] and is readable by the Z180 using IN0 a, (DOH) or
IN0 a, (D1H). Data can be written into the mailbox registers
using the OUT0 (DOH), a or OUT0 (D1H), a and can output
its contents onto HD [0:7} during a PC HOST DMA access.
Note: The following is a description of other Z189 signals
relevant in a PC DMA Mailbox access.
– The /HDDIS signal will go low during a PC DMA Read
access (selected /HDACK and /HRD going low).
– The /HCS pin will not asserted low during a PC DMA
Mailbox access (/HDACK active) if the HDRQ/HDACK
channel is enabled.
3. Z189 hardware forces HDRQ inactive low on the
leading (falling) edge of /HWR during the /HDACK
cycle. Note that the HDREQ register bit is not to be
cleared yet, since the DMA cycle has not yet completed.
4. The PC places valid data on the ISA bus (HD[0:7] and
asserts /HWR low.
5. Z189 hardware latches data into the HDMAT register
on the trailing (rising) edge of /HWR while /HDACK is
still active low. On this same edge, hardware clears the
HDREQ register bit.
6. Z180 software polls the HDREQ bit until it's 0, and then
can input the data byte from HDMAT. The polling of the
HDREQ bit is used to indicate when the PC DMA Write
has been completed. The PC software program should
program its DMA controller to stop DMA at the end of
valid data or when commanded by the application.
When the Z180 software sets HDREQ, but doesn't see
the HDREQ bit automatically cleared within a reasonable time (because /HDACK remains inactive high),
then software can stop the PC DMA write by resetting
the HDREQ bit.
7. Messages on the COM Port confirm that the PC DMA
write operation is complete. Z180 software clears
HDREQ, then clears HDMAE to disable host DMA.
PC DMA Read
PC DMA Write
Through commands exchanged over the MIMIC COM
Port, PC software and the Z180 agree to configure DMA for
a PC DMA write, in which data flows from PC memory to,
for example, a modem's speaker codec. The PC sets up its
8237 DMA controller in auto-initialize mode to assure that
data is always available whenever the modem makes a
DMA request. The Z180 clears HDREQ and sets HDMAE,
forcing HDRQ low.
The PC DMA Write proceeds as follows:
1. Z180 software writes a 1 to the HDREQ bit, causing the
HDRQ pin to go active High.
2. The rising edge of HDRQ causes the 8237 DMA
controller to begin a memory-read, I/O-write DMA bus
cycle on the ISA bus at the end of the current PC bus
cycle. The PC asserts /HDACK low to acknowledge
the DMA request.
PC DMA Read is almost the same as a PC DMA Write, but
the data flows the other direction through the HDMAR
register.
Through commands exchanged over the MIMIC COM
Port, PC software and the Z180 agree to configure DMA for
a PC DMA Read, in which data flows from, for example, a
modem's microphone codec to PC memory. The PC sets
up its 8237 DMA controller in auto-initialize mode to assure
that there is always buffer space available whenever the
modem makes a DMA request. The Z180 clears HDREQ
and sets HDMAE, forcing HDRQ low.
The PC DMA Read proceeds as follows:
1. Z180 software outputs the data byte to HDMAR, where
it is latched.
2. Z180 software writes a 1 to the HDREQ bit, causing the
HDRQ pin to go active high.
DS971890301
83

Zilog
PRELIMINARY
PC MAILBOX DATA REGISTERS (Continued)
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
3. The rising edge of HDRQ causes the 8237 DMA
controller to begin an I/O-read, memory-write DMA
bus cycle on the ISA bus at the end of the current PC
bus cycle. The PC asserts /HDACK low to acknowledge the DMA request.
4. Z189 hardware forces HDRQ inactive low on the
leading (falling) edge of /HRD during the /HDACK
cycle. Note that the HDREQ register is not to be
cleared yet, since the DMA cycle has not completed.
5. The PC asserts /HRD low while /HDACK is still active
low, causing Z189 hardware to enable the latched
HDMAR byte onto HD[0:7].
6. While Z189 hardware holds valid data on the ISA bus,
the PC does its memory-write half of the DMA cycle.
On the trailing (rising) edge of /HRD, Z189 hardware
disables the output of the HDMAR register, putting
HD[0:7] in high impedance state. On this same edge,
hardware clears the HDREQ register bit. Note: /HDDIS
will go low while the HDMAR register is accessed on
the ISA bus.
7. Z180 software polls the HDREQ bit until it's 0, then
continues with step 0 for the next byte.
PC DMA Read will not be stopped as with the case for PC
DMA Write if the HDREQ handshake is not met. If software
fails to see HDREQ reset soon after making the DMA
request (because /HDACK remains inactive high), Z180
software should clear HDREQ and HDMAE and configure
the data pump to stop the PC DMA Read.
Clear HDREQ bit:
Reset
OR I/O write 0 to HDREQ bit in HMC register
OR (Rising edge of (/HRD and /HWR) while /HDACK=0)
Drive HDRQ pin active high:
HDREQ bit = 1 while HDMAE=1
Drive HDRQ pin inactive low:
Reset
OR /HDACK=0
OR HDREQ bit = 0
Latch PC DMA Write data to HDMAT register:
HDMAE=1
AND /HDACK=0
AND /HWR=0
Drive PC DMA Read data from HDMAR register:
HDMAE=1
AND /HDACK=0
AND /HRD=0
Selectable DMA Channels
The Z189 features jumperless selection of PC DMA channels. On the 8-bit PC/XT bus, DMA channels 0 and 3 are
generally available, therefore reference designs may connect to those. 2 HDREQ bits and 2 HDMAE Enable bits are
used to enable which PC DMA Channel is to be implemented. In addition, there are two additional bits which
allow for the multiplexing of PC DMA Mailbox functions with
Bus Mastering and Z180 peripheral functions.
Logic Equations for PC DMA Read/Write
This section summarizes the significant events for PC DMA
Read/Write that was explained in the previous sections.
This section can be used as a quick check of the circuit
implementation.
Set HDREQ bit:
I/O write 1 to HDREQ bit in HMC register.
84
PC DMA Mailbox Pin Designations
The four request/acknowledge pins will be designated as
follows, and are assigned the following QFP pins as shown
below:
HDRQ, pin 50, output (mux with RTS0)
/HDACK0, pin 43, input (mux with CKA0 and /DREQ0)
HDRQ1, pin 97, output (mux with /BUSACK)
/HDACK1, pin 98, input (mux with /BUSREQ)
DS971890301

Zilog
PRELIMINARY
PC MAILBOX DATA REGISTERS (Continued)
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
765 43210
11000000
Figure 102. Host DMA Mailbox
Control Register, HMC
(Z180 MPU Read/Write Address XXD2H)
0 = HDRQ0 Tri-State
1 = HDMA Enable
0 = HDRQ1 Tri-State
1 = HDMA Enable
HDRQ /HDACK0,
CKA0//DREQ0, /RTS0
0 = HDRQ0, /HDACK0 Select
1 = /RTS0, CKA0//DREQ0 Select
HDRQ1, /HDACK1,
/BUSACK, /BUSREQ
0 = HDRQ1, /HDACK1 Select
1 = /BUSACK, /BUSREQ Select
HDREQ0 (DMA request 0)
HDREQ1 (DMA request 1)
Revision Data Avail
Write Enable HDREQ0
Revision Data Avail
Write Enable HDREQ1
Bit 5 HDREQ1 Bit
When Mailbox 1 is multiplexed and enabled (HDMAE1=1),
setting this bit will cause the HDRQ1 pin to go active high,
which puts out a request to the PC for a DMA transfer. Z189
hardware clears this bit when byte transfer is complete.
This bit is disabled upon reset. This bit can also be reset to
force the HDRQ1 pin to inactive low. Note that Bit 7 must
be set to modify HDREQ1.
Bit 4 HDREQ0 Bit
When Mailbox 0 is multiplexed and enabled (HDMAE0=1),
setting this bit will cause the HDRQ0 pin to go active high,
which puts out a request to the PC for a DMA transfer. Z189
hardware clears this bit when byte transfer is complete.
This bit is disabled upon reset. This bit can also be reset to
force the HDRQ0 pin to inactive low. Note that Bit 6 must
be set to modify HDREQ0.
Bit 3 HDRQ1/HDACK1, /BUSACK /BUSREQ
This bit selects the multiplexing that will occur between the
HDRQ1//BUSACK and the /HDACK1/BUSREQ pins. If this
bit is set to 0, the HDRQ1 and /HDACK1 functions are
enabled for this pin. Otherwise, if this bit is set to 1, the
/BUSACK and /BUSREQ functions are enabled for this pin.
This bit is reset to 0.
Bits 7 Write Enable HDREQ1 (Write only)
Revision Data Available (Read only)
Set this bit whenever setting/resetting the HDREQ1 bit.
When this bit is written with 1, bit 5 will be written into the
HDREQ bit and bits 0-3 are ignored. When this bit is written
with zero, bits 0-3 can be written and bit 5 is ignored. Note
that this bit does not change the write access to bits 4 and
6. The Write Enable is not latched and must be set for each
HDREQ1 write.
When bit 7 is read it is set upon powerup and becomes
reset during the 1st read of the HDMAT1 register.
Bits 6 Write Enable HDREQ0 (Write only)
Set this bit whenever setting/resetting the HDREQ0 bit.
When this bit is written with 1, bit 4 will be written into the
HDREQ0 bit and bits 0-3 are ignored. When this bit is
written with zero, bits 0-3 can be written and bit 4 is
ignored. Note that this bit does not change the write
access to bits 5 and 7. The Write enable is not latched and
must be set for each HDREQ0 write.
When bit 6 is read, it indicates the availability of the revision
data in the Host DMA transmit register (HDMAT0). When
the revision data is read by the Z180 CPU, this bit will
become reset and the revision data will no longer be
available in the HDMAT0 register.
Bit 2 HDRQ/HDACK0, /RTS0 CKA0//DREQ0
This bit selects the multiplexing that will occur between the
HDRQ0//RTS0 and the /HDACK/CKA0//DREQ0 pins. If this
bit is set to 0, the HDRQ and /HDACK0 functions are
enabled for this pin. Otherwise, if this bit is set to 1, the
CKA0//DREQ0 and /RTS0 functions are enabled for this
pin. This bit is reset to 0.
Bit 1 HDMAE1 bit
When this bit is set to 1, it allows Mailbox 1 to request a PC
DMA cycle given that the Mailbox 1 pins are multiplexed
(bit 4=1). When this bit is cleared to 0, the HDREQ1 is tristated if Mailbox 1 pins are multiplexed. When this bit is
cleared, the HDMAT1 can be used to store HOST OUTPUT
MAILBOX DATA.
Bit 0 HDMAE0 bit
When this bit is set to 1, it allows Mailbox 0 to request a PC
DMA cycle given that the Mailbox 0 pins are multiplexed
(bit 4=1). When this bit is cleared to 0, the HDREQ0 is tristated if Mailbox 0 pins are multiplexed.
DS971890301
85

Zilog
PRELIMINARY
PC DMA MAILBOX DATA REGISTERS
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
765 43210
10010001
Figure 103. Host DMA Transmit Register, HDMAT0
(Z180 MPU Read Only Address XXD0H)
(PC Write Only)
Note: 91hex is defaulted into this register to indicate
revision (9 for Z189 and 1 for 1st revision). Once the
revision data is read by the Z180 CPU, bit 6 of the HMC
register (Revision Data Avail bit) will be read as zero.
765 43210
00000000
Figure 104. Host DMA Receive Register, HDMAR0
(Z180 MPU Write Only Address XXD0H)
(PC Read Only)
765 43210
00000000
Figure 105. Host DMA Transmit Register, HDMAT1
(Z180 MPU Read Only Address XXD1H)
(PC Write Only)
HDMAT1 can also be used as a HOST OUTPUT MAILBOX
DATA REGISTER. Refer to Host Output Mailbox function
for details.
765 43210
00000000
Figure 106. Host DMA Receive Register, HDMAR1
(Z180 MPU Write Only Address XXD1H)
(PC Read Only)
HOST INPUT/OUTPUT MAILBOX ENHANCEMENTS
The purpose of Host I/O Mailbox is to provide an additional
data path between PC HOST and Z80189 in a Modem
Control Application. This is required in order to accommodate transfer of data other than data (flows through COM
Port) or audio (flows through PC DMA MAILBOX). An
example implementation of this feature is described
below:
– PC HOST controlled COM Port selection. In a Psuedo
"Plug & Play" environment, the PC BIOS will assign a
modem to a COM Port address upon powerup. Therefore, the Modem will need to "listen" to the PC bus for
BIOS calls that query the existence of a modem card.
In order to facilitate the feature listed above, a communication path needs to be available between a PC BIOS and
Modem PRIOR to the selection of COM Port, DMA, or IRQ
selection.
The modem will then need to reply and output information on its capabilities and requirements. The PC BIOS
will then assign the Modem to a COM Port and interrupt
such that there are no resource conflicts.
86
DS971890301

Zilog
Enhancement Detail
PRELIMINARY
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
PC HOST Address Selection. There are a total of 4 registers addresses that are accessible by the PC HOST. They
are as follows:
Address
HA9-HA2 programmable
Function HA1 HA0
Host Output Register 0 0 0
Host Output/Input Register 1 0 1
Host I/O Status Register 1 0
*Host Output to HDMAT1 Register 1 1
The HA9-HA2 is programmable by writing the contents into
Port A Data Register. The PC HOST access will occur
during a PC HOST input/output cycle at the programmed
address range (/HRD or /HWR=0, HAEN=0,
PA[9:2]=PADATA[7:0]). NOTE: PADATA SHOULD BE
WRITTEN WITH THE ADDRESS RANGE PRIOR TO
ENABLING THIS FEATURE.
* If the Host DMA Mailbox 1 function is disabled (bit 1 of
HMC register is zero), a Host write in the programmed
Mailbox range with HA1,0=1,1, will cause the host data to
be latched into the HDMAT1 register. This can be used as
an auxiliary host output register. Note that a host read from
this address is invalid.
765 43210
00000000
Figure 107. Host Output Register 0 (HOR0)
(180 MPU Read Only Address XXD3H)
(PC Host Read/Write HA9-2 (PADATA) + 00b)
765 43210
00000000
765 43210
00000000
Unlock Bit
Host Output Register 0
Data Available
Host Output Register 1
Data Available
Host Input Register 1
Data Available
Auxilliary Bits
Host I/O Mailbox Enable
Figure 110. Host I/O Status Register (HIOS)
(180 MPU Read/Write Address xxD5H)
(PC Host Read Only HA9-HA2 (PADATA) + 10b)
Bit 7.
Host I/O Mailbox Enable.
The Z180 must write a logic
one to this bit to enable the Host I/O Mailbox. When this bit
is at zero (default), Host accesses are disabled. This bit is
only writable by the Z180, but is readable by both Z180 and
PC Host. When this bit is zero, registers D3, D4 and D5
cannot be read or written except for a write to the enable
bit in register D5 bit 7. Also, when this bit is zero the Host
side is not accessible. Once this bit is set, all registers
become visible to the Z180 and the Host.
Note: The PADATA should be programmed with HA9:HA2
address range prior to setting this bit. This bit should be
programmed as zero when the COM Decode Mux (CDR bit
0) is disabled.
Bits 6-4.
Auxiliary bits.
these bits can be written by the
Z180 and can be read by both the PC HOST and the Z180.
Note that the PC HOST cannot write to these bits. The
Auxillary Bits are zero by default and have no function other
than to serve as scratch bits for the HOST I/O Mailbox.
Figure 108. Host Output Register 1 (HOR1)
(180 MPU Read Only Address XXD4H)
(PC Host Write Only HA9-2 (PADATA) +01b)
765 43210
00000000
Figure 109. Host Input Register 1 (HIR1)
(180 MPU Write Only Address XXD4H)
(PC Host Read Only HA9-2 (PADATA) + 01b)
DS971890301
Bit 3.
Host Input Register 1 Data Available.
This bit be-
comes set when the Z180 writes to the Host Input Register
1. A PC Host read of the Host Input Register 1 will cause
this bit to clear. This bit cannot be set unless the Host I/O
Mailbox enable bit is set.
Bit 1.
Host Output Register 0 Data Available.
This bit
becomes set when the PC Host writes to the Host Output
Register 0. A Z180 read of the Host Output Register 0 will
cause this bit to clear. This bit cannot be set unless the Host
I/O Mailbox enable bit is set.
87

Zilog
PRELIMINARY
HOST INPUT/OUTPUT MAILBOX ENHANCEMENTS (Continued)
Bit 0.
Unlock Bit.
PC Host Write to Address 0FBHex will cause this bit to set.
A PC host write to address 0F9hex will cause this bit to
reset. The data written to these registers will NOT be
stored. A read access or access with HAEN=1 will NOT
cause this bit to toggle. Note that this bit has no function
other than a status bit (there is no locking or unlocking
caused by the state of this bit). The state of the unlock bit
is not controlled by the Host I/O Mailbox bit. Any I/O write
to FB will set the bit and a write to F9 will clear it regardless
of the state of the Host I/O Mailbox enable bit. Note that the
data written to 0FBhex or 0F9hex will not be stored by the
Z189.
When the Host I/O Mailbox is enabled, a
If COM Port decode is disabled and COM Port decode
mux is enabled (default), COM Decode Pins HA9-HA3,
HAEN are ignored inputs. If HC1 is forced low the MIMIC
Data latch will be forced open. Therefore, care should be
taken that the HC1//HCS pin is NEVER connected directly
to logic high or low, when COM Port Decode is disabled.
/HCS pin can also be programmed as an output for debug
purposes. When the /HCS Force bit (Bit 7 in the COM Port
Decode Register) is enabled, the /HCS pin will be asserted
low whenever the MIMIC is being accessed by the PC host.
This feature is only available when the COM Port Decode
is enabled.
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
I/O Chip Select w/Prog. Range
The Z80187 has two I/O Chip Selects labelled
/IOCS1 and /IOCS2. The /IOCS1 will have same functionality as the Z80182’s /IOCS pin (multiplexed with IEO and
active during I/O accesses between ranges XX80H to
XXBFH). The IOCS pins will be asserted if /IORQ is active,
/M1 is inactive, and address compare is within range.
The Z80189 also has a secondary IOCS labeled
/IOCS2. This pin will be active for I/O accesses in the range
of XXC0H - XXC7H or XXC8H-XXCFH. The /IOCS2 pin will
be multiplexed over the E pin when enabled.
COM Port Decode
COM Port decode allows MIMIC to be selected when PC
address HA9-HA3 specifies a selected COM port address
range by HC pins 1 and 2 (selects COM Port address 1-4).
HC1 and HC2 can be read in software and program an
appropriate comport range for the decode circuitry. HC1
and HC2 can also be used for general input purposes. The
status of these pins can also be read when the COM
Decode Mux is disabled.
A dual HINTR option will provide two MIMIC Interrupt
requests to the HOST. HINTR1 will be asserted during a
MIMIC interrupt request when COM Decode is configured
for COM 1 & 3. HINTR2 will be asserted during a MIMIC
interrupt request when COM Decode is configured for
COM 2 & 4. The unasserted HINTR line will be tri-stated.
Note that during initialization, the COM Decode Register must be written to before the System Configuration
Register.
Single Baud Rate Generator
A Baud Rate Generator is included to provide emulation
timing for the MIMIC device. This BRG is very similar to
ESCC BRG in functionality. There are 2x8 bit registers to
program the clock divider. The input to the BRG is the PHI
clock output of the S180 core.
The time constant required for a specific bit rate is as
follows:
Time constant (decimal) = (PHI freq. / (2*baud rate))-2
This formula is exactly the same as used in the ESCC.
88
The output of the BRG is directly connected to MIMIC
emulation counter input.
DS971890301

Zilog
Baud Rate Generator Register
PRELIMINARY
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
The following registers are used to store BRG constant.
The timer is enabled after setting bit 0 of IOBRG register.
Design is such that on-the-fly modification of registers do
not cause irregular BRG output.
765 43210
11111111
Lower Byte of
Time Constant
Figure 111. BRGL Baud Rate Generator Low
(Address XXE0H) Default 00 Hex
IOBRG Register
The following register handles the IOCS feature and MIMIC
BRG. IOBRG-IOCS & BRG enable (Address XXD6H)
Default 04 hex.
765 43210
00000100
BRG Enable
/IOCS2 Range
1 = I/O Access between
xxC0h-xxC7
0 = I/O Access between
xxC8h-xxCF
/IOCS2 Enable
/INTO Assertion of
MIMIC Access
Reserved as 0
Figure 113. IOBRG-IOCS and BRG Enable
(Address XXD6H)
Bits 4-7 Reserved
Bit 3 /INT0 assertion on MIMIC access. When this bit
R/W is enabled, and the /HALT is active (power-down)
any HOST access to the MIMIC will cause a low
edge. Since this interrupt source has no vector,
/INT0 MODE 1 must be used when enabling this
mode. This is disabled on power-up. /INT0 assertion is released when /HALT is deasserted.
765 43210
11111111
Upper Byte of
Time Constant
Figure 112. BRGH Baud Rate Generator High
(Address XXE9H) Default 00 Hex
Note: The THRE bit is forced to 0 on the PC side to prevent
THR overrun during powerdown modes when this feature
is enabled. When the MIMIC comes out of power-down,
THRE resumes normal functionality.
Bit 2 /IOCS2 enable
When set, IOCS2 is muxed over E pin. This is
enabled on reset.
Bit 1 /IOCS2 range.
R/W When set, IOCS2 is active during I/O accesses
between XXC0H-XXC7H.
When reset, IOCS2 is active during I/O accesses
between XXC8H-XXCFH. This is disabled on
power-up.
Bit 0 BRG enable. When set,
R/W the MIMIC BRG begins counting down to gener-
ate a programmed square wave to the MIMIC
emulation timers. This is disabled on power-up.
Note: When waking from Standby Mode using a PC-THR
write, the THRE bit will not reset until clock is stabilized.
This may cause a THR overrun. Therefore, data integrity
cannot be guaranteed. Care should be taken so that
standby mode is only used when data integrity is not
essential.
DS971890301
89

Zilog
PRELIMINARY
HOST INPUT/OUTPUT MAILBOX ENHANCEMENTS (Continued)
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
The register that handles and enables COM port decode
and multiplexing is as follows:
76543210
00000001
COM Port Decode MUX
State of HC1 (Read Only)
State of HC2
COM Port Decode Selection
Bit 4 3
0 0 COM 1 (3F8-3FF) Default
0 1 COM 2 (2F8-2FF)
1 0 COM 3 (3E8-3EF)
1 1 COM 4 (2E8-2EF)
COM Port Decode Enable
Dual HINTR
Reserved as 0
Figure 114. CDR - COM Decode Register
(Address XXD7H)
CDR - COM Decode Register (Address XXD7H) default
01hex
Bit 0 COM Port Decode Mux. When set, COM Port
R/W Decode pins (HA9-HA3, HAEN HC1-2) are
enabled. This is set on default. Refer to multiplexing section for further detail.
Bit <1-2> Read only registers that specify the state of
HC1 and HC2 input pins when COM Port
select feature is enabled in bit 0.
Bit 1 represents HC1 input. Bit 2 represents
HC2 input. Since HC1 is multiplexed with
/HCS, care should be taken that if COM Port
Decode is disabled, /HCS is not forced low.
Bit <3-4> COM Port decode selection. These two bits
are used to select COM Port decode 1-4 as
R/W follows:
decoder during a PC-DMA cycle. This circuitry is
not used when COM Port Decode (bit 5) is disabled.
HA2-HA0 are used to select between internal
MIMIC registers.
Bit 5 COM Port Decode enable. When this bit
R/W is set, HA3-HA9 inputs are used for COM Port
Decoder. The MIMIC will be accessible given
that the address inputs HA3-HA9 are within the
range programmed by bits 3 & 4 when HAEN
is active low.
Please refer to MULTIPLEXING section for details on pin HA3-HA9 muxing. This is disabled
on reset. When disabled, the COM Port Decode inputs are still treated as inputs, but have
no affect on MIMIC operation.
Bit 6 Dual HINTR. When this bit is set, the
R/W HINTR2 output will be asserted for MIMIC
interrupt requests when configured for COM 2
& 4. HINTR1 output will be asserted for MIMIC
interrupt requests when configured for COM 1
& 3. When disabled, HINTR2 is always inactive
(tri-stated) while HINTR1 is active for all MIMIC
interrupt requests. This is disabled on reset
(HINTR2 is tri-state on power-up).
Note that the unselected HINTR line will be tristated while the active HINTR line will be driven
as per the MIMIC Master Control Register
Bit 7 /HCS Force Bit. When Bit 0 and Bit 5 of this
register is set to 1 (COM Decode Mux and
Logic Enabled), it forces the /HCS signal to be
exported out of the /HCS/HC1 pin. /HCS output
is asserted when HA3-HA9 is within the boundaries programmed by bits 3-4 of CDR (regardless of /HRD and /HWR). /HCS is NOT asserted
for PC DMA Mailbox accesses. If this bit is zero
(default), the /HCS/HC1 pin becomes an input.
Bit 4 Bit 3
0 0 COM 1 (3F8-3FF) default
0 1 COM 2 (2F8-2FF)
1 0 COM 3 (3E8-3EF)
1 1 COM 4 (2E8-2EF)
MIMIC access will only be allowed if inputs HA9HA3 reflect the above address ranges and HAEN
is deasserted. HAEN is used to disable the COM
90
Note: The /HCS/HC1 pin is tied to both /HCS function and
HC1 functions simultaneously when bit 7 is reset to zero.
Therefore, MIMIC access is disabled until the first System
Configuration Register Write on COM Decode (bit 5) is
enabled. This mechanism prevents accidental bus contention if /HCS/HC1 pin is pulled low.
Note: The COM Decode Register must be written first,
prior to the System Configuration Register during initialization.
DS971890301

Zilog
PRELIMINARY
Z189 MISCELLANEOUS CONTROL AND INTERFACE REGISTERS
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
The Z80189 has the same capability of the Z180 MPU.
Some extra I/O registers have been added to the Z180
MPU to interface with the Parallel ports, COM Port Decode
and the 16550 MIMIC interface. A System Configuration
765 43210
11100111
Register is located at the Z180 MPU I/O Address %EF
which determines the current operating mode. This register must be WRITTEN before the MIMIC is enabled.
Reserved as 1
MIMIC/Port A
0 = Port A
1 = MIMIC Data
Borrow
0 = Z80180
1 = 16550 MIMIC
Disable ROMs
0 = /ROMCS Enabled
1 = /ROMCS Disabled
DOUT
0 = No Data Out
1 = Data Out
Port PB4-PB0 Select
0 = ASCI Channel 0 Function
1 = PB4-PB0 Selected
Port PB7-PB5 Select
0 = ASCI Channel 1 Function
1 = PB7-PB5 Selected
Port C Read Select
0 = From Output Pad
1 = From Input Pins
Figure 115. System Configuration Register
(Z80180 MPU Address XXEFH)
Note: The COM Decode Register should be written prior to writing to this register.
Bit 7 Port C read
When this bit is set, a read from Port C will return value of
logic state on Port C. When this bit is reset, a read from Port
C will return the contents of Port C output pads (last value
Bit 5 PB4-PB0 Select
When this bit is set Port B bits 4-0 are multiplexed over
ASCI 0 functions. When this bit is reset ASCI functions are
active.
output on port C). This bit is not relevant when Port C is
programmed for output.
Bit 4 D
ROM Emulator Mode Enable
DOUT
When this bit is set to a 1, the Z182 is in “ROM emulator
Bit 6 PB7-PB5 Select
When this bit is set Port B bits 7-5 are multiplexed over
ASCI 1 functions. When this bit is reset ASCI 1 functions are
active.
mode”. In this mode, bus direction for certain transaction
periods are set to the opposite direction to export internal
bus transactions outside the Z80189. This allows the use
of ROM emulators/logic analyzers for application development. See Figures 115 and 116.
DS971890301
91

Zilog
PRELIMINARY
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z189 MISCELLANEOUS CONTROL AND INTERFACE REGISTERS (Continued)
I/O and Memory Transactions
Z80189/Z8L189
Z80189
Data Bus
(DDOUT=0)
Z80189
Data Bus
(DDOUT=1)
I/O Write
to On-Chip
Peripherals
Out
Out
I/O Read
from On-Chip
Peripherals
Z
Out
Interrupt Acknowledge Transaction
Z80189
Data Bus
(DDOUT=0)
Z80189
Data Bus
(DDOUT=1)
Intack for
On-Chip
Peripheral
Z
Out
Intack for
Off-Chip
Peripheral
In
In
I/O Write
to Off-Chip
Peripherals
Out
Out
I/O Read
from Off-Chip
Peripherals
In
In
Write to
Memory
Out
Out
Write from
Memory Refresh
In
In
Z
Z
Z80189
Idle Mode
Z
Z
Figure 116. Data Bus Direction (Z180 Bus Master)
The word “Out” means that the Z189 data bus direction is
in output mode, “In” means input mode, and “Z” means
High impedance. D
stands for Data Direction out and
DOUT
is the status of the D4 bit in the System Configuration
Register.
Bit 3 Disable ROMs
If this bit is a one it disables the /ROMCS pin. If it is a zero
addresses below the ROM boundary set by the ROMBR
register will cause the /ROMCS pin to go low.
Bit 2 Borrow
For Bit 2 of the System Configuration Register when the bit
is set to 0, the HINTR1/T
bit is set to 1, the HINTR1/T
is multiplexed to T
OUT
bit is multiplexed to HINTR1.
OUT
OUT
. When this
This bit is set to 1 upon reset.
Bit 1 MIMIC/Port A
When this bit is set, MIMIC is multiplexed over Port A. This
is enabled on power-up.
Bit 0 Reserved
Note: MIMIC access is disabled until the first system
configuration register write after Power-up or reset. This
mechanism prevents accidental bus counter from if
/HDCS/HC1 pin is pulled Low. To avoid accidental contention when /HCS/HC1 is pulled low, it is advisable that the
COM Decode Register is written first prior to when the
system configuration register is initialized.
92
DS971890301

Zilog
PRELIMINARY
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z189 MISCELLANEOUS CONTROL AND INTERFACE REGISTERS (Continued)
I/O and Memory Transactions
Z80189/Z8L189
Z80189
Data Bus
(DDOUT=0)
Z80189
Data Bus
(DDOUT=1)
I/O Write
to On-Chip
Peripherals
In
In
I/O Read
from On-Chip
Peripherals
Out
Out
Interrupt Acknowledge Transaction
Z80189
Data Bus
(DDOUT=0)
Z80189
Data Bus
(DDOUT=1)
Intack for
On-Chip
Peripheral
Out
Out
Figure 117. Data Bus Direction (Z80180 is Not Bus Master)
Intack for
Off-Chip
Peripheral
In
In
I/O Write
to Off-Chip
Peripherals
Z
Z
I/O Read
from Off-Chip
Peripherals
Z
Z
Write to
Memory
Z
Z
Write from
Memory Refresh
In
In
Z
Z
Z80189
Idle Mode
Z
Z
DS971890301
93

Zilog
RAMCS/ROMCS
PRELIMINARY
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
To assist with decoding of ROM and RAM blocks of
memory, three more registers and two pins have been
added to the Z80189. The two pins are /ROMCS and
/RAMCS. The three registers are the ROMBR, RAMLBR
and RAMUBR.
RAMUBR, RAMLBR RAM Upper Boundary, RAM Lower
Range Boundary Range
These two registers specify the address range for the
/RAMCS signal. When accessed memory addresses are
less than or equal to the value programmed in the RAMUBR
and greater than or equal to the value programmed in the
RAMLBR, /RAMCS is asserted. In the case that these
registers are programmed to overlap, /ROMCS takes priority over /RAMCS (/ROMCS is asserted and /RAMCS is
inactive).
765 43210
11111111
A19-A12 RAMLBR
Figure 118. RAMUBR
(Z180 MPU Address XXE6H)
765 43210
11111111
A19-A12 RAMUBR
Chip Select signals are going active for the address range:
ROMCS: (ROMBR) >= A19-A12 >= 0
/RAMCS: (RAMUBR) >= A19-A12 >= (RAMLBR)
These registers are set to “FFH” at power-on reset, and the
boundary addresses of ROM and RAM are as follows:
ROM lower boundary address
(fixed) = 00000H
ROM upper boundary address
(ROMBR register) = 0FFFFFH
RAM lower boundary address
(RAMLBR register) = 0FFFFFH
RAM upper boundary address
(RAMUBR register) = 0FFFFFH
Since /ROMCS takes priority over /RAMCS, the latter will
never be asserted until the value in the ROMBR and
RAMLBR registers are re-initialized to lower values.
ROMBR ROM Address Boundary Register
This register specifies the address range for the /ROMCS
signal. When accessed memory addresses are less than
or equal to the value programmed in this register, the
/ROMCS signal is asserted.
This signal can be forced to a "1" (inactive state) by setting
Bit 3 in the System Configuration Register, to allow the user
to overlay the RAM area over the ROM area.
94
Figure 119. RAMLBR
(Z180 Address XXE7H)
765 43210
11111111
A19-A12 ROMBR
Figure 120. ROMBR
(Z180 Address xxE8H)
DS971890301

Zilog
PRELIMINARY
Z80189 ROM/RAM WAIT STATE GENERATOR
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
A separate Wait State Generator is provided for access
memory using /ROMCS and /RAMCS. A single eight bit
register is added to enable/disable this feature as well as
provide two 3-bit fields that provides a 1-8 waits for each
chip select.
Bit 7 /RAMCS Wait State Generator Enable.
Disable on power-up or reset.
Bit 6-4 /RAMCS Wait States 1-8.
8 wait states on power-up or reset.
Bit 3 /ROMCS Wait State Generator Enable.
Disable on power-up or reset.
Bit 2-0 /ROMCS Wait States 1-8.
8 wait states on power-up or reset.
If Wait State is disabled or RAMCS and ROMCS is not
asserted, the memory access is default to Wait State
programmed in the DCNTL register of Z180 DMAs. Note
that the wait states inserted by this register and DCNTL do
not add. The actual number of wait states inserted is the
greater of the two.
765 43210
00
/ROMCS
Wait States
1 - 8
/ROMCS Wait State
Generator Enable
/RAMCS
Wait States
1 - 8
/RAMCS Wait State
Generator Enable
Figure 121. WSG Chip Select Register
(Z180 MPU Read/Write, Address XXD8H)
Note: That the wait states inserted by this register and
DCNTL do not add. The actual number of wait states
inserted is the greater of the two.
DS971890301
95

Zilog
PRELIMINARY
INTERRUPT EDGE/PIN MUX REGISTERS
765 43210
00001100
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
Halt Recovery Select
1 = 16 Cycle Delay on Halt Recovery
0 = No Wait Delay on Halt Recovery
Low Noise Select
1 = Select Low Noise for Z189 (not Z180)
0 = Select Normal Drive for Z189 Pins
IEO, /IOCS1 Select
1 = Select /IOCS1 Function
0 = Select IEO Function
/MREQ, /HRD,PC2, /MWR Select
1 Select /MRD, /MWR
0 Select /MREQ, PC2
/INT1 Mode Select
0X = Normal Level Detect
10 = Falling (Neg) Edge Det
11 = Rising (Pos) Edge Det
Figure 122. Interrupt Edge/Pin Mux Register
(Z180 MPU Address XXDFH)
Bits 7-6 control the interrupt capture logic for the external
/INT2 PIN. When programmed as ‘0X’, the /INT2 pin performs as the normal level detecting interrupt pin. When
programmed as ‘10’, the negative edge detection is enabled. Any falling edge will latch an active low on the
internal /INT2 of the Z180. This interrupt must be cleared by
writing a ‘1’ to bit 7 of the Port C Data Register. Programming these control bits to ‘11’ will enable rising edge
interrupts to be latched. The latch is cleared in the same
fashion as the falling edge. Interrupt Capture logic is not
available in EV mode 1 (emulation adapter mode).
Bits 5-4 control the interrupt capture logic for the external
/INT1 PIN. When programmed as ‘0X’, the /INT1 pin performs as the normal level detecting interrupt pin. When
programmed as ‘10’, the negative edge detection is enabled. Any falling edge will latch an active low on the
internal /INT1 of the Z180. This interrupt must be cleared by
writing a ‘1’ to bit 6 of the Port C Data Register. Programming these control bits to ‘11’ will enable rising edge
interrupts to be latched. The latch is cleared in the same
fashion as the falling edge. Interrupt Capture Logic is not
available in EV mode 1 (emulator adaption mode).
/INT2 Mode Select
0X = Normal Level Detect
10 = Falling (Neg) Edge Det
11 = Rising (Pos) Edge Det
Bit 3 Programming this bit to 1 selects the /MRD and the
/MWR outputs. When this bit is set, /MREQ will be removed
for the qualification of both /RAMCS and /ROMCS. By
programming this bit to 0, the /MREQ Z180 and PC2
outputs are enabled. This bit is 0 upon reset.
Bit 2 selects the /IOCS1 function which is the default for
power up and /RESET conditions. By programming this bit
to ‘0’, the IEO function is enabled for this multiplexed pin.
Bit 1 selects the low noise or normal drive feature for the
Z189 pins. The default at power up is normal drive for Z189
pins. By programming this bit to ‘1’, low noise for the Z189
pins is chosen (not the Z180 pins). Programming this bit to
‘0’ selects normal drive for the Z189 pins. Z189 pins
include: all MIMIC output pins, ROM/RAM chip selects, bit
I/O, IOCS1, IOCS2, and PC DMA Mailbox outputs.
96
DS971890301

Zilog
PRELIMINARY
INTERRUPT EDGE/PIN MUX REGISTERS (Continued)
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
Bit 0 A ‘1’ selects 16 cycle wait delay on recovery from Halt
if bit 5 of the Z80189 Enhancements Register Z180 MPU
Address D9H is set to zero. A ‘0’ selects no wait delay on
Halt recovery. The definition of Halt recovery is as follows.
If this mode is selected the following pins assume the
following states during halt and during the recovery, whether
it is in Halt, SLP, IDLE or STBY Modes:
Address = Z
Data Bus = Z
/RD = Z
/WR = Z
/MREQ = Z
/M1 = 1
ST = 1
/IORQ = 1
/BUSACK = 1 (1)
/RFSH = 1 (2)
/IOCS1 = Z (3)
/IOCS2 = Z
HDRQ0 = Z (3)
HDRQ1 = Z (3)
Note 1. This assumes that BUSREQ is not activated during
the halt.
Note 2. This assumes that the refresh is not enabled. This
would not be a logical case since the address bus
is tri-stated during the Halt mode.
Note 3. This is only true if the function is enabled.
The Halt recovery mode is implemented by applying wait
states to the next cpu operation following the exit from halt.
All signals listed above are forced to their specified state
(unless otherwise noted) during halt and also during the
recovery state. Sixteen cycles after the halt pin goes high
the signals are released to their normal state. Then eight
wait states are inserted to allow proper access to accommodate slow memories.
Z80189 ENHANCEMENTS REGISTER (Z180 MPU ADDRESS D9H)
Bit 7 Forced /ROMCS Memory Boundary. When this bit is
set to 1, it will force the /ROMCS boundary. A19 will be
connected directly to /ROMCS. /ROMCS will then be
asserted from 00000H-7FFFFH. When this bit is cleared,
/ROMCS will be accessed under the programmed address decoder range. This bit is 0 upon rest.
Note: In this mode, chip select assertion is NOT dependent on /MREQ assertion. During Sleep, /ROMCS will be
forced inactive high.
Bit 6 Forced /RAMCS Memory Boundary. When this bit is
set to 1, it will force the /RAMCS boundary. /A19 will be
connected to /RAMCS. /RAMCS will then be asserted from
8000H-FFFFFH. When this bit is cleared,
/RAMCS will be accessed under the programmed address
decoder range. This bit is 0 upon reset.
Note: In this mode, chip select assertion is NOT dependent on /MREQ assertion. During sleep, /RAMCS is forced
inactive.
When using the forced memory boundaries, the memory
access time requirement is improved. The improved
Memory access time equation is shown below:
Note: When using forced ROM boundary without forced
RAM boundary, or forced RAM boundary without forced
ROM boundary, contention is possible (both /ROMCS &
/RAMCS active). Care should be taken when programming memory boundaries such that there is no overlap.
Bit 5 Force Z180 Halt Mode (Write/Read). MPU Signals
are the same as Z180 during HALT modes. This allows
bus acknowledge cycles during Z189 HALT modes.
Bit 1:4 Reserved
Bit 0 PHI Output Disable. When this bit is set, the PHI
output is not driven by the system clock. The PHI output will
be forced high in this mode. On production boards that do
not use the PHI output, this feature can be used to reduce
EMI. When this bit is reset, the system clock is output to PHI
pin. This bit is reset by default. This feature is not usable in
EV mode 1 (emulation adapter) or EV mode 2 (emulation
probe).
ACC Time < (2 + WS) *clkperiod-Tad-Tdrs
DS971890301
97

Zilog
PRELIMINARY
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189 ENHANCEMENTS REGISTER I(Z180 MPU ADDRESS D9H) (Continued)
765 43210
000XXXX0
PHI Output Disable
Reserved
Force Z180 Halt Mode
Forced /RAMCS
Memory Boundary
Forced /ROMCS
Memory Boundary
Figure 123. Z80189 Enhancements Register
(Z180 MPU Address 09H)
Z80189/Z8L189
PARALLEL PORTS REGISTERS
The Z80189 has three eight bit bidirectional ports. Each bit
is individually programmable for input or output. The ports
consist of two registers: the Port Direction Control Register
and the Port Data Register. The port and direction register
can be accessed in any page of I/O space since only the
lowest eight address lines are decoded. Bits PC7 and PC6
are input only bits and have the special function of reading
the external value of the /INT2 AND /INT1 pins. Writing ‘1’
to these bits will clear the edge detect interrupt logic when
operating /INT2 and/or /INT1 in edge detect mode.
When Port B and Port C bits 5-0 are deselected in the
System Configuration Register, the Data and Data Direction Registers are still available as read/write scratch
registers. If a port is deselected and if the DDR bit is a ‘0’,
then the written value to that bit will be latched; and this
value can be read back. If a port is deselected and if the
DDR bit is a ‘1’, then you could read only the external pin
value; any write to that bit is latched but can be read back
only with DDR=0.
765 43210
11111111
PA Data Direction Register
0 = Output
1 = Input
Figure 124. PA Data Direction Register
(Z180 MPU Address XXEDH)
The data direction register determines which are inputs
and outputs in the PA Data Register. When a bit is set to a
one, the corresponding bit in the PA Data Register is an
input. If the bit is zero, then the corresponding bit is an
output.
98
DS971890301

Zilog
PRELIMINARY
PARALLEL PORTS REGISTERS (Continued)
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
765 43210
XXXXXXXX
PA Data Register
Figure 125. PA Data Register
(Z180 MPU Address XXEEH)
When the Z180 MPU writes to the PA Data Register, the
data is stored in the internal buffer. Any bits that are output
are then sent on to the output buffers.
When the Z180 MPU reads the PA Data Register, the data
on the external pins is returned.
765 43210
11111111
PB Data Direction Register
0 = Output
1 = Input
Figure 126. PB Data Direction Register
(Z180 MPU Address XXE4H)
765 43210
XX111111
PB Data Direction Register
0 = Output
1 = Input
Reserved
Figure 128. PC Data Direction Register
(Z180 MPU Address XXDDH)
The data direction register determines which are inputs
and outputs in the PB Data Register. When a bit is set to a
one, the corresponding bit in the PB Data Register is an
input. If the bit is zero, then the corresponding bit is an
output.
765 43210
XXXXXXXX
/INT2, /INT1 Read Ext Data
Write B7=1 Clears /INT2 Edge
Write B6=1 Clears /INT1 Edge
PC Data Register
The data direction register determines which are inputs
and outputs in the PB Data Register. When a bit is set to a
one, the corresponding bit in the PB Data Register is an
input. If the bit is zero, then the corresponding bit is an
output.
765 43210
XXXXXXXX
PB Data Register
Figure 127. PB Data Register
(Z180 MPU Address XXE5H)
When the Z180 MPU writes to the PB Data Register, the
data is stored in the internal buffer. Any bits that are output
are then sent on to the output buffers.
When the Z180 MPU reads the PB Data Register, the data
on the external pins is returned.
Figure 129. PC, Port C, Data Register
(Z180 MPU Address XXDEH)
When the Z180 MPU writes to the PC Data Register, the
data is stored in the internal buffer. Any bits that are output
are then sent on to the output buffers.
When the Z180 MPU reads the PC Data Register, the data
on the external pins is returned.
Bits 7 and 6 serve the special function of reading the value
of the external /INT2 and /INT1 lines. When operating either
/INT2 or /INT1 in edge detection mode, the edge detect
latch is reset by writing a '1' to bit 7 or 6 respectively.
Writing a '0' has no effect. These latches should be reset
at the end of an /INT1 or /INT2 interrupts service routine
when using edge-triggered interrupt routine.
DS971890301
99

Zilog
EMULATION MODES
PRELIMINARY
GENERAL-PURPOSE EMBEDDED CONTROLLERS
Z80189/Z8L189
Z80189 provides four modes of operation. The modes are
selected by the EV1 and EV2 pins. These four modes allow
for system development while the MIMIC is disabled, and
T
is active.
OUT
EV2 EV1
Mode 0 0 0 Normal Mode, on-chip Z180
bus master
Mode 1 0 1 Emulation Adapter Mode
Mode 2 1 0 Emulator Probe Mode
Mode 3 1 1 Reserved Mode 0 Description
Mode 0 Normal Mode
This is the normal operating mode for the Z80189.
Mode 1 Description
The Emulation Adapter Mode enables system development for the Z189 with a readily available Z180 emulator.
The Emulator provides the Z180 MPU and Z180 peripheral
functions to the target system, with their signals passing
through the emulation adapter. In Emulation Adapter Mode,
the Z189’s, Z180 MPU and Z180 peripheral signals are tristated or physically disconnected. The Z189 continues to
provide its BRG, COM Port Decoder, MIMIC and Port
functions and signals to the target system. The Mode 1
effects on the Z189 are:
Mode 0 Mode 1
Signal Normal Emulation Adapter
PHI Output Input
/M1 Output Input
/MREQ,/MRD Output Input
/MWR Output Input
/IORQ Output Input
/RD Output Input
/WR Output Input
/RFSH Output Input
/HALT Output Input
ST Output Input
/BUSACK Output Input
/WAIT Input Output
A19,A18 Output Input
A17-A0 Output Input
D7-D0 Input/Output Input/Output
TXA0 Output Tri-state
/RTS0 Output Tri-state
TXA1 Output Tri-state
/INT0 Input Output, Open-Drain
Mode 2 Description
In the Emulator Probe Mode, all the Z189 output signals are
tri-stated. This scheme allows a Z189 emulator probe to
grab onto the Z189 package leads on the target system.
Mode 3 Description
Reserved for Test Mode.
Note also that in Mode 1 and 3, the emulator must provide
/MREQ on the (/MREQ) Z80189 pin.
100
DS971890301
 Loading...
Loading...