Zhone zNID-GPON-2402, zNID-GPON-2424, zNID-GPON-2403, zNID-GPON-2426, zNID-GPON-2427 Configuration Manual
...
zNID 24xx Series Configuration Guide
For software version 2.5.x
August 2012
Document Part Number: 830-03782-01

Zhone Technologies
@Zhone Way
7195 Oakport Street
Oakland, CA 94621
USA
510.777.7000
www.zhone.com
info@zhone.com
COPYRIGHT C2000-2012 Zhone Technologies, Inc. and its licensors. All rights reserved.
This publication is protected by copyright law. No part of this publication may be copied or
distributed, transmitted, transcribed, stored in a retrieval system, or translated into any human
or computer language in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, magnetic, manual
or otherwise, or disclosed to third parties without the express written permission from Zhone
Te chnologies, Inc.
Bitstorm, EtherXtend, EZ Touch, IMACS, MALC, MXK, Raptor, SLMS, Z-Edge, Zhone,
ZMS, zNID and the Zhone logo are trademarks of Zhone Technologies, Inc.
Zhone Technologies makes no representation or warranties with respect to the contents hereof
and specifically disclaims any implied warranties of merchantability, non infringement, or
fitness for a particular purpose.
Further, Zhone Technologies reserves the right to revise this publication and to make changes
from time to time in the contents hereof without obligation of Zhone T echnologies to notify any
person of such revision or changes.
2 zNID 24xx Series Configuration Guide

TABLE OF CONTENTS
About This Guide...............................................................................................................................7
Style and notation conventions..............................................................................7
Typographical conventions.......................................................................................8
Related documentation.............................................................................................8
Acronyms......................................................................................................................9
Technical support.....................................................................................................11
Important safety instructions................................................................................11
Chapter 1 zNID 24xx Series.................................................................................................... 1 3
Overview ....................................................................................................................13
Web user interface...................................................................................................15
zNID 24xx series components...............................................................................16
zNID 24xx models and interfaces.........................................................................17
GPON models.........................................................................................................17
Gigabit Ethernet models .........................................................................................17
Chapter 2 Management ............................................................................................................19
Management interfaces...........................................................................................19
CLI..........................................................................................................................19
Web.........................................................................................................................1 9
SNMP......................................................................................................................20
OMCI......................................................................................................................20
OMCI vs. Residential Gateway management....................................................21
Comparing RG, OMCI and VEIP by service, traffic forwarding...........................22
RG ....................................................................................................................22
OMCI................................................................................................................22
Dual Managed ..................................................................................................22
RG configured flows...............................................................................................22
OMCI configured ONU flows................................................................................24
OMCI unique features......................................................................................25
OMCI configured video ...................................................................................25
OMCI configured voice....................................................................................25
Statistics in UNI mode .................................................... .................................26
zNID 24xx Series Configuration Guide 3

Table of Contents
Reserved GEM ports........................................................................................26
Dual Managed mode using the VEIP......................................................................27
Logging in to the 24xx series zNIDs....................................................................29
Logging in on the Ethernet ports ............................................................................29
Logging in with CLI ...............................................................................................29
System features........................................................................................................30
Management access control....................................................................................31
User names and passwords...............................................................................31
Registration ID.................................................................................................32
Default interface......................................................................................................33
DNS.........................................................................................................................34
DNS client........................................................................................................34
DNS Proxy Server............................................................................................36
Internet time............................................................................................................37
System log...............................................................................................................39
Power shedding........................................... ........................................................... .42
Backup/Restore.......................................................................................................43
Backup..............................................................................................................43
Restore..............................................................................................................45
Restore default..................................................................................................46
SNMP agent............................................................................................................47
TR-069 Client .........................................................................................................49
Certificates..............................................................................................................51
Local certificates ..............................................................................................52
Trusted CA.......................................................................................................53
Software..................................................................................................................54
Restore software...............................................................................................54
Update software............................................................................ ..... .... ...........55
Reboot.....................................................................................................................56
Status and statistics................................................................................................57
Device info..............................................................................................................58
Statistics..................................................................................................................61
LAN interface status...............................................................................................65
GPON interface status.............................................................................................66
PPPoE status ...........................................................................................................68
Route....................................................................................................................... 6 9
ARP table................................................................................................................70
Bridge table.............................................................................................................71
DHCP status............................................................................................................72
IGMP.......................................................................................................................73
OMCI......................................................................................................................74
Wireless...................................................................................................................7 8
Voice....................................................................................................................... 7 9
4 zNID 24xx Series Configuration Guide

Chapter 3 Configuration ..........................................................................................................85
Interfaces....................................................................................................................86
Interface naming conventions.................................................................................86
Ethernet port............................................................................................................86
Factory default VLAN definition...........................................................................87
Configuration pages................................................................................................89
System info .............................................................................................................90
Static route..............................................................................................................91
Access control.........................................................................................................92
Lists..................................................................................................................92
Rules.................................................................................................................93
Firewall...................................................................................................................94
Global...............................................................................................................94
Management access..........................................................................................95
Port forwarding.................................................................................................96
Interfaces...............................................................................................................100
Bridged...........................................................................................................100
Routed ............................................................................................................101
Brouted...........................................................................................................102
PPPoE.............................................................................................................103
Ethernet ..........................................................................................................104
GPON.............................................................................................................106
Rate Limits............................................... ......................................................107
Wireless.................................................................................................................108
Basic...............................................................................................................108
Security...........................................................................................................110
MAC filter......................................................................................................126
Wireless bridge................... ............................................................................127
Advanced ........................................................................................................130
Voice.....................................................................................................................134
SIP..................................................................................................................135
SIP-PLAR.......................................................................................................136
MGCP.............................................................................................................139
Lines...............................................................................................................140
VLAN ...................................................................................................................143
Settings...........................................................................................................143
Modes.............................................................................................................151
WAN backup ........................................................................................................153
Deployment scenarios ..........................................................................................156
IP configuration options........................................................................................157
Creating data connections............................................................... .... ..................162
Creating bridge connections ...................................................... ...........................163
Creating routed connections ...................................................... ...........................166
Creating brouted connections ...............................................................................172
Creating PPPoE tunnels........................................................................................179
Creating wireless connections...............................................................................188
Creating video connections...................................................................................190
Creating voice connections................................................................. ..... .... .........191
zNID 24xx Series Configuration Guide 5

Table of Contents
Creating Dual Managed connections....................................................................194
Advanced features.................................................................................................197
VLANS.................................................................................................................197
All ports untagged..........................................................................................197
Tagged uplink port untagged LAN ports .......................................................198
Tagged uplink port and tagged LAN ports.....................................................200
S-Tagged ........................................................................................................200
TLS mode.......................................................................................................202
NAT and DHCP....................................................................................................205
DHCP server.........................................................................................................209
Data services....................................................................................... ..... .... .........210
Rate limiting...................................................................................................210
Priority............................................................................................................211
Chapter 4 Special scenarios................................................................................................213
Microsoft Media Room support..........................................................................213
Any port, any service.............................................................................................217
Chapter 5 Troubleshooting tests.......................................................................................219
Diagnostics ..............................................................................................................219
Ping ............................................................................................................................221
Trace route...............................................................................................................222
Voice ..........................................................................................................................223
Hardware reset........................................................................................................224
Index....................................................................................................................................................225
6 zNID 24xx Series Configuration Guide

ABOUT THIS GUIDE
This guide is intended for use by installation technicians, system
administrators, or network administrators. It explains the Web user interface
for the zNID 24xx series and how to configure the zNID 24xx series of
products.
Style and not ation conventions
This document uses the following conventions to alert users to information
that is instructional, warns of potential damage to system equipment or data,
and warns of potential injury or death. Carefully read and follow the
instructions included in this document.
Caution: A caution alerts users to conditions or actions that could
damage equipment or data.
Note: A note provides important supplemental or amplified
information.
Tip: A tip provides additional information that enables users to more
readily complete their tasks.
WARNING! A warning alerts users to conditions or actions that
could lead to injury or death.
WARNING! A warning with this icon alerts users to conditions or
actions that could lead to injury caused by a laser.
WARNING! This icon warns the user that metal surfaces can
become hot to touch. Avoid contact or use caution when touching
these surfaces.
zNID 24xx Series Configuration Guide 7
About This Guide
Typographical conventions
The following typographical styles are used in this guide to represent specific
types of information.
Bold Used for names of buttons, dialog boxes, icons, menus,
profiles when placed in body text, and property pages (or
sheets). Also used for commands, options, parameters in
body text, and user input in body text.
Fixed Used in code examples for computer output, file names, path
names, and the contents of online files or directories.
Fixed Bold Used in code examples for text typed by users.
Fixed Bold
Italic
Italic Used for book titles, chapter titles, file path names, notes in
PLAIN UPPER
CASE
Related documentation
Refer to the following publication for additional information:
• zNID 24xx Hardware Installation Guide — explains how to install the
zNID, describes the variations of the zNID models in 24xx family, their
LEDs and interfaces.
• zNID Quick Installation Instructions — There is a set of Quick
Installation Instructions for GPON and GE models which describe in
shorter procedures the steps for installing the zNID. These instructions
are shipped with the zNID, but are also available on the Zhone website.
Refer to the release notes for software installation information and for
changes in features and functionality of the product (if any).
Used in code examples for variable text typed by users.
body text requiring special attention, section titles,
emphasized terms, and variables.
Used for environment variables.
8 zNID 24xx Series Configuration Guide

Acronyms
Acronyms
The following acronyms are related to Zhone products and may appear
throughout this manual:
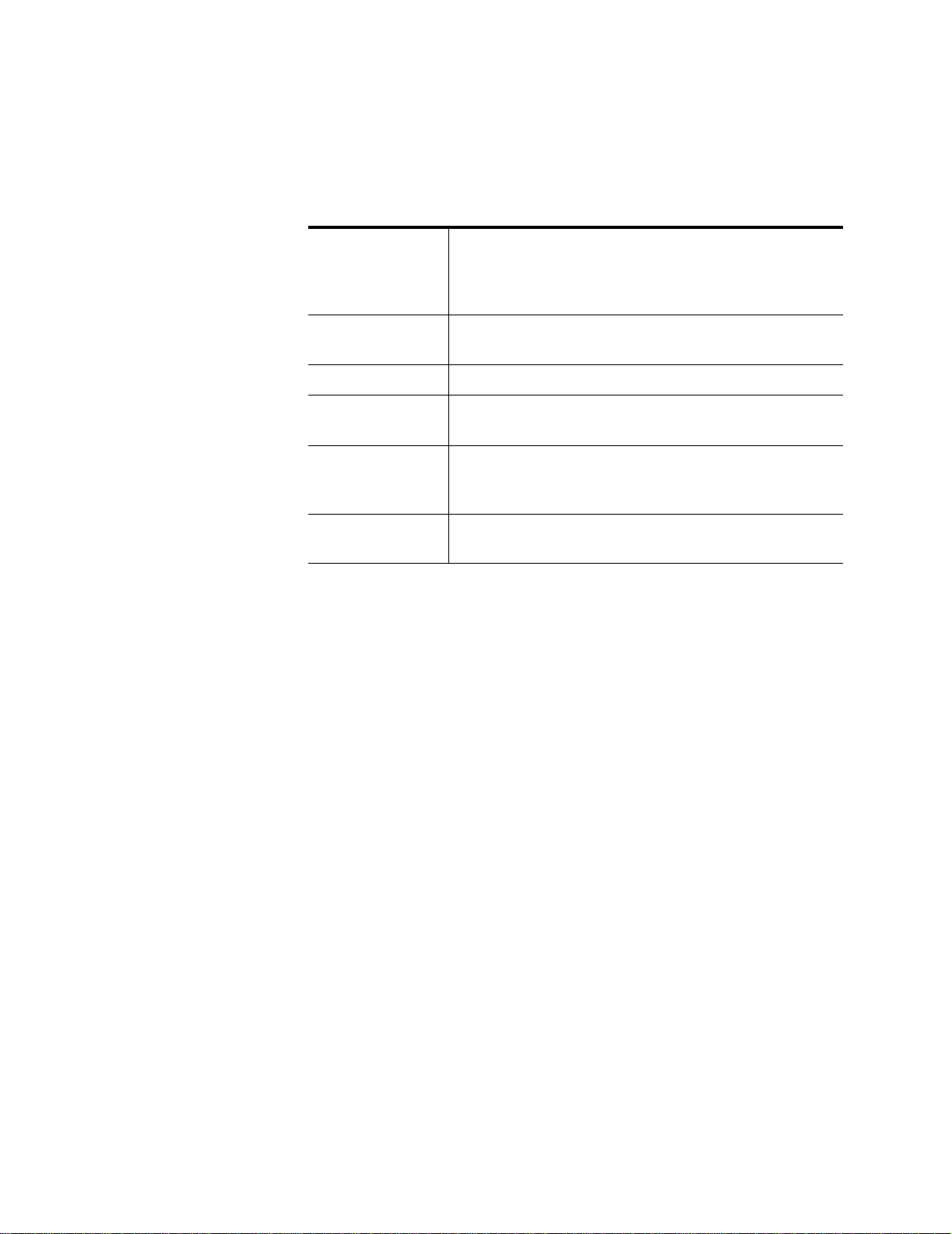
T able 1: Acronyms and their descriptions
Acronym Description
Active E Active Ethernet, also known as Gigabit Ethernet
APC Angled physical contact (for fiber connector)
Coax Coaxial cable
CPE Consumer Premises Equipment
DHCP server Dynamic host configuration protocol server
EZ touch Zhone’s implementation for managing CPEs and zNIDs
GigE Gigabit Ethernet
GPON Gigabit passive optical network
HPNA Home phone line networking alliance
IPTV Internet protocol TV
LED Light-emitting diode
MALC Multi-access line concentrator
MDU Multiple Dwelling Unit
MIB Management information bases
MoCA
OLT Optical Line Terminator
OMCI ONU Management and Control Interface
ONT Optical Network Terminator
ONU Optical Network Unit
PoE Power over Ethernet
PPPoE Point-to-point protocol over Ethernet
QoS Q ualit y of service
RF Rad io Frequ ency
Multimedia over Coax Alliance
RFoG Radio Frequency over Glass
SC adaptor Subscriber connector adaptor
SIP Session initiation protocol
SNMP Simple network management protocol
zNID 24xx Series Configuration Guide
9

About This Guide
Table 1: Acronyms and their descriptions (Continued)
Acronym Description
T1/E1 T1 is Trunk line 1 (or DS 1, digital signal level 1). E1 is the
European equivalent, though there are a number of differences
between the North American T1 and the European E1.
UPC Ultra physical contact (for fiber connector)
Wi-Fi Wireless local area network (trademark of Wi-Fi alliance)
VoIP Voice over IP
zNID Zhone Network Interface Device
ZMS Zhone Management System
10 zNID 24xx Series Configuration Guide

T echnical support
Technical Support for this product is provided by your Internet Service
Provider.
Important safety instructions
Read and follow all warning notices and instructions marked on the product
and included in the Hardware Installation Guide, available at Zhone.com.
Technical support
zNID 24xx Series Configuration Guide
11

About This Guide
12 zNID 24xx Series Configuration Guide

ZNID 24XX SERIES
Overview
This chapter describes the zNID 24xx. It includes the following sections:
• Overview, page 13
• zNID 24xx series components, page 16
• zNID 24xx models and interfaces, page 17
The zNID 24xx Series (Zhone Network Interface Device) is a family of
indoor, full-featured gateways for residential installations. These next
generation zNIDs support GPON or Active Ethernet termination to meet the
demands of multi-service network deployments to the user.
With either GPON or Active Ethernet uplinks, the 24xx Series zNIDs deliver
data, voice, or video (IPTV) over fiber.
The 24xx series of zNIDs share a common software architecture with the
42xx and 9xxx series of zNIDs, including the same intuitive Web interface
and command line interface. The zNID can also be managed by the Zhone
Network Management System (ZMS) which uses SNMP. Software upgrades
and configuration backups can be handled automatically by the ZMS using
the EZ To uch management feature.
The zNID is a full-featured gateway supporting services such as DHCP
server, rate limiting, filtering, comprehensive logging, and more. The zNID
product line implements a very flexible QoS allowing the service provider to
guarantee that services are being prioritized correctly and the end-user
receives the Quality of Experience that is expected.
All 24xx series Single Family Unit (SFU) ONTs provide the sa me voice
features found on the 42xx series of outdoor residential SFU ONTs and the
9xxx series of Multiple Dwelling Unit (MDU) ONTs. SIP-PLAR signaling is
supported for connection via Zhone's Voice Gateway to traditional Class 5
TDM switches, while both MGCP and SIP are supported for direct connection
to a VoIP Softswitch. This flexibility allows Zhone's 9xxx, 42xx and 24xx
Series ONTs to work in nearly all Telco networks, with interoperability
support for a broad array of Softswitches.
Zhone’s GPON ONTs are commonly are used in the 20km range with other
GPON ONTs in the distribution network, though can reach up to 6 0km
depending on the configuration of the optical distribution network (ODN).
zNID 24xx Series Configuration Guide 13

zNID 24xx Series
Zhone's 24xx Active Ethernet ONTs can operate at distances up to 20km.
The zNID enclosure is designed to provide outstanding reliability and simple
installation.
The zNID 24xx series may be managed by
• EZ Touch (Zhone’s CPE and zNID management application)
• Zhone Management System (ZMS)
• Web (HTTP)
• Command Line Interface (CLI/Telnet/SSH)
• ONT Management Control Interface (OMCI) for GPON only
More information about management capabilities see Management on
page 19 and Logging in to the 24xx series zNIDs on page 29.
For information about special configurations such as Microsoft Media Room
and Any Port, Any Service, see Chapter 4, Special scenarios, on page 213 for
Microsoft Media Room support and Any port, any service.
14 zNID 24xx Series Configuration Guide
Web user interface
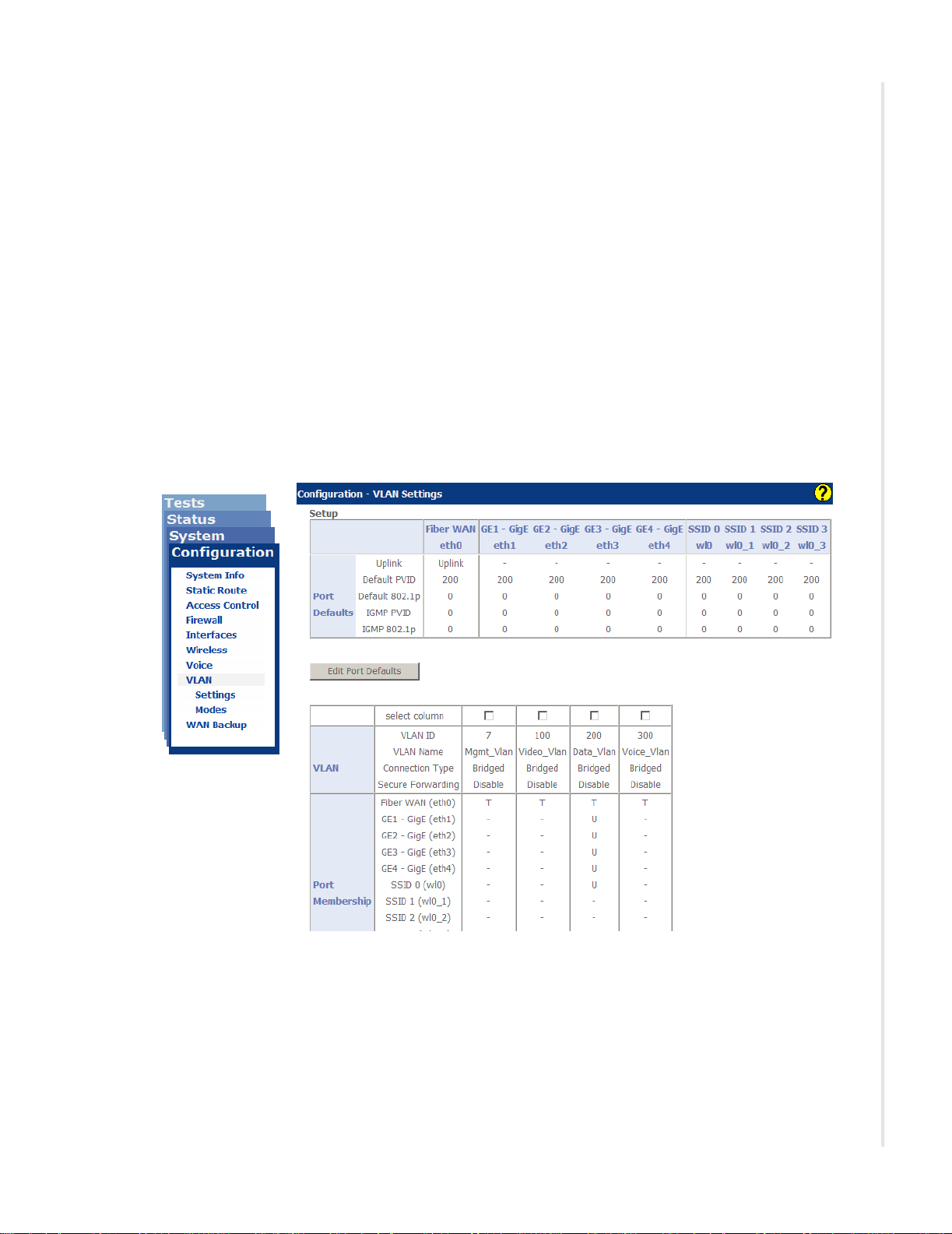
The zNID 24xx data path architecture is VLAN centric. In other words to pass
traffic VLANs must be defined. The main page for seeing how the zNID is
configured is the Configuration | VLAN | Settings page which shows in the
lower table the VLANs which have been created and the ports which are
members of each VLAN. The type of connection is also displayed in the
lower table. The upper table shows the port defaults. Figure 1 shows the
default state of the zNID 24xx.
To read the Configuration | VLAN | Settings page, see Factory default
VLAN definition on page 87 and Edit Port Defaults on page 145. To
understand more about VLAN options, see VLANS on page 197.
To create bridged, routed, or PPPoE connections as well as configure Voice
interfaces see Deployment scenarios on page 156.
Figure 1: The VLAN settings p age shows the V LANs and the port s which b elong to each VLAN
Web user interface
zNID 24xx Series Configuration Guide
15
zNID 24xx Series
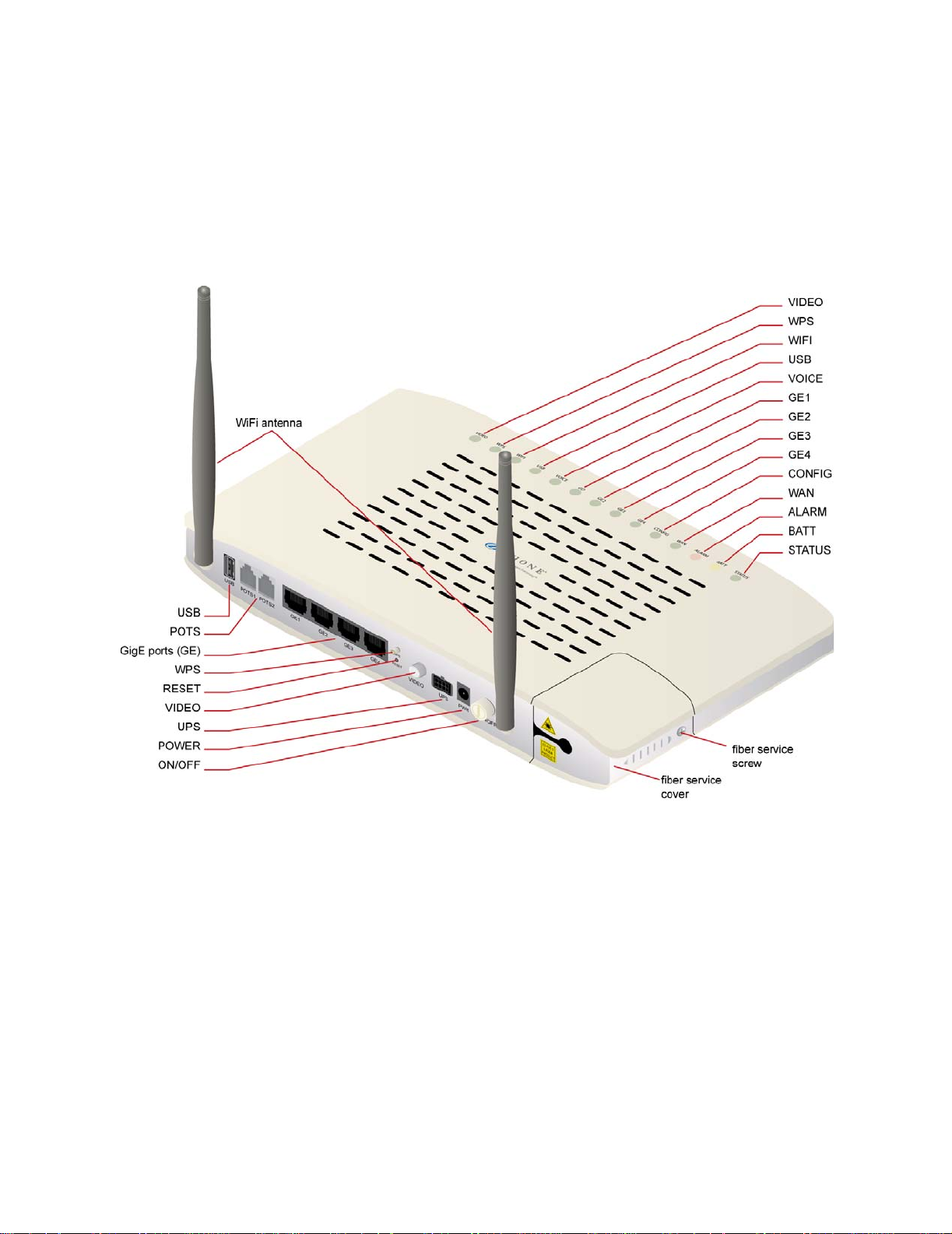
zNID 24xx series components
The zNID 24xx series has models which have either GPON or Gigabit
Ethernet interfaces on the WAN side and Gigabit Ethernet ports, POTS, Coax
and USB. See the list of zNID 24xx models and interfaces on page 17 for
information on which models support which interfaces.
Figure 2: The interfaces, displays and buttons for the zNID 24xx
Depending upon the zNID model selected, the interfaces on the zNID can
include:
• One, two, or four Gigabit Ethernet RJ45 ports
• Two Phone Ports (POTS)
• One Coax Port with RF Video
• USB port
To reset the zNID 24xx
1 Press a pin into the reset button and hold it down until all LEDs are on
2 Release the reset button.
16 zNID 24xx Series Configuration Guide
together.

zNID 24xx models and interfaces
GPON models
The zNID 24xx series GPON models have the following interfaces:
Model Description
zNID-GPON-2402 GPON Uplink, 2 GigE
zNID-GPON-2403 GPON Uplink, 2 GigE, RFV
zNID-GPON-2424 GPON Uplink, 2 POTS, 4 GigE
zNID-GPON-2425 GPON Uplink, 2 POTS, 4 GigE, RFV
zNID-GPON-2426 GPON Uplink, 2 POTS, 4 GigE, WiFi, USB
zNID-GPON-2427 GPON Uplink, 2 POTS, 4 GigE, WiFi, RFV, USB
zNID 24xx models and interfaces
Gigabit Ethernet models
The zNID 24xx series Gigabit Ethernet models have the following interfaces:
Model Description
zNID-GE-2402 GE Uplink, 2 GigE
zNID-GE-2424 GE Uplink,
zNID-GE-2426 GE Uplink, 2 POTS, 4 GigE, WiFi, USB
2 POTS, 4 GigE
zNID 24xx Series Configuration Guide
17

zNID 24xx Series
18 zNID 24xx Series Configuration Guide

MANAGEMENT
This chapter describes the zNID 24xx. It includes the following sections:
• Management interfaces, page 19
• Management access control, page 31
• System features, page 30
• Status and statistics, page 57
Management interfaces
The zNID 24xx products can be fully managed through any of several
methods (CLI, Web, SNMP and OMCI).
The device uses VLAN 7 as the default management VLAN, with DHCP
Client enabled. This allows the ONU to automatically obtain an IP address
when connected to an MXK.
CLI
The zNID 24xx products can be managed using a command line interface.
Web
The zNID 24xx products can also be fully managed through the web (HTTP)
interface. The web pages are very intuitive and they include a context
sensitive help button for additional information. The web interface will be
used for the configuration examples used in this document.
Note: The web pages will vary slightly depending on model.
zNID 24xx Series Configuration Guide 19

Management
SNMP
OMCI
The zNID 24xx products can also be managed through SNMP. The zNID
24xx family is compatible with any industry standard SNMP agent. However ,
Zhone provides a CPE manager feature that makes managing the ONUs even
easier.
ONU Management Control Interface (OMCI) provides policy based
configuration and management capabilities for GPON. OMCI management is
intergrated into the OLT command set, so configuration of the ONU with
OMCI is done from the OLT, not directly as with the Web UI or CLI
interfaces. Not all modules in the zNID, such as the wireless interface, can be
configured directly from OMCI, however they may be used with OMCI via
the Virtual Ethernet Interface Point. See OMCI vs. Residential Gateway
management, page 21 for more information.
20 zNID 24xx Series Configuration Guide

OMCI vs. Residential Gateway management
OMCI vs. Residential Gateway management
For GPON zNIDs, the zNID 24xx may be configured and managed from both
OMCI and from a residential gateway interface (CLI or Web UI). When using
both methods of management it is important to understand how each method
configures traffic flows. OMCI configured data flows are very different from
residential gateway data flows.
The zNID-GPON-24xx models support multiple management interfaces,
however for the purposes of this discussion, the management interfaces fall
into two groups, the OMCI management interface and the RG management
interfaces which includes the Web GUI, CLI and SNMP.
OMCI and RG combine for three types of management modes:
• RG only
The RG architecture utilizes and Etherswitch, supporting MAC address
learning and forwarding (ISO layer 2 bridging) as well as routing. This
combination of bridging and routing supported by the zNID provides a
broad base of routing options. See IP configuration options, page 157 for
more information.
The RG interface supports wireless and VoIP options for SIP, SIP-PLAR
and MGCP See Voice, page 134 and Creating voice connections,
page 191 for more information about Voice. Most of this document
explains the RG Web UI interface.
RG only mode is also called RG or RG mode.
• OMCI only
Data flows are handled differently for OMCI configured flows than for
the RG flows. For OMCI data flows there is a one to one mapping
between the WAN side GEM port and the LAN side UNI port. All packets
are ‘cut-through’ the zNID with no MAC address learning or forwarding.
The wireless interface is not supported by OMCI. However to map WiFi
to OMCI there is another type of management which combines RG and
OMCI.
OMCI only mode is also called ONU mode.
• Dual mode: OMCI and RG
With dual mode management, the downstream LAN interfaces are
configured via the RG interface, and mapped to the Virtual Ethernet
Interface Point (VEIP). The VEIP is the common interface point between
RG features and OMCI-configured filter rules.
OMCI and RG combined mode always uses the VEIP.
zNID 24xx Series Configuration Guide
21

Management
Comparing RG, OMCI and VEIP by service, traffic forwarding
Another way to understand the three GPON interface types is by service and
traffic forwarding.
RG
With RG interfaces you can configure all service modules on the zNID 24xx.
RG VLANs pass through an integrated Etherswitch and are forwarded based
on Destination MAC to any interface, including the integrated Router. Packets
are classified on ingress and handled by the integrated Ethernet Switch and
CPU routing, voice or WiFi.
RG VLANs use the 5xx GEM exclusively (unless mapped to the VEIP, in
Dual Managed mode, in which case any GEM can be used).
See RG configured flows on page 22 for more information.
OMCI
OMCI configured ONU flows require a 1:1 UNI:GEM mapping.
OMCI configured ONU flows are cut-through flows with no bridging, no
switching, no routing.
WiFi is not supported in OMCI only mode.
Voice can operate as an OMCI-configured function or an RG-configured
function.
RG configured flows and OMCI configured flows can co-exist, but Voice
must be OMCI-configured. Remember the following rule: OMCI always
wins.
See OMCI configured ONU flows on page 24 for more information.
Dual Managed
Dual Managed connections mapped to the VEIP connections may use any
GEM. In this mode, RG VLANs operate as described above, but instead of
using the default 5xx GEM, OMCI is used to configure the GEM and VLAN
filter rule.
See Dual Managed mode using the VEIP on page 27 for more information.
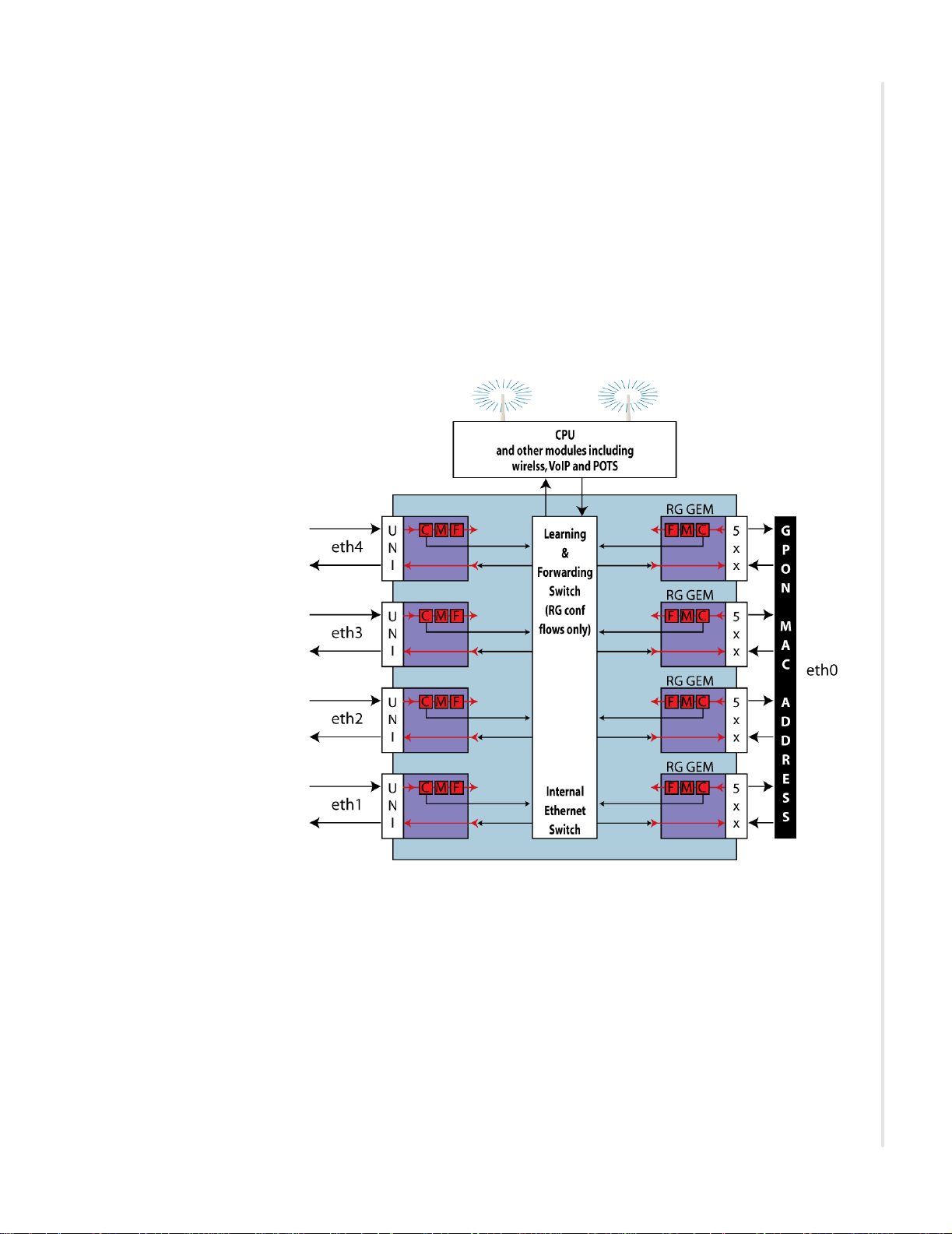
RG configured flows
RG configured flows are flows configured via an RG management interface:
TR-069, Web GUI, Telnet/CLI, or SNMP. This document mainly describes
the Web GUI, so we will not go into much detail about the various
configurations in this section.
For a discussion of the configurations available and example procedures see
Deployment scenarios, page 156 and IP configuration options, page 157.
22 zNID 24xx Series Configuration Guide
OMCI vs. Residential Gateway management
All services are configured on a per VLAN basis. The RG interfaces can
configure data, video, and voice.
for all RG VLANs, an integrated Etherswitch is included in the data
forwarding path. This enables RG VLANs to support local Bridging and
peer-to-peer communications for LAN client devices such as PCs.
Additionally , a Bridge Table is maintained for all Bridged RG VLANs to
show learned source MACs per VLAN and per Port.
Packets are classified on ingress, then the learning and forwarding switch
determines where to send. See VLANS on page 197 for a discussion of layer 2
forwarding behaviors.
Figure 3: Remote Gateway configured flows
GEM ports in the 5xx - 6xx range are reserved for Residential Gateway traffic
flows.
By default, all RG VLANs map to the 5xx RG GEM. This mapping is not
configurable, and does not require any OMCI provisioning action to create the
5xx GEM on the 24xx unit.
The OLT must not send any OMCI provisioning commands for the 5xx GEM
to the 24xx ONT. The reason is that “OMCI always wins.” Whatever
provisioning actions that are specified by OMCI commands will occur. If
OMCI attempts to provision the 5xx GEM, the 24xx ONT will create the
specified ONU traffic flows on the 5xx GEM and disruption to RG traffic
flows may occur.
zNID 24xx Series Configuration Guide
23
Management
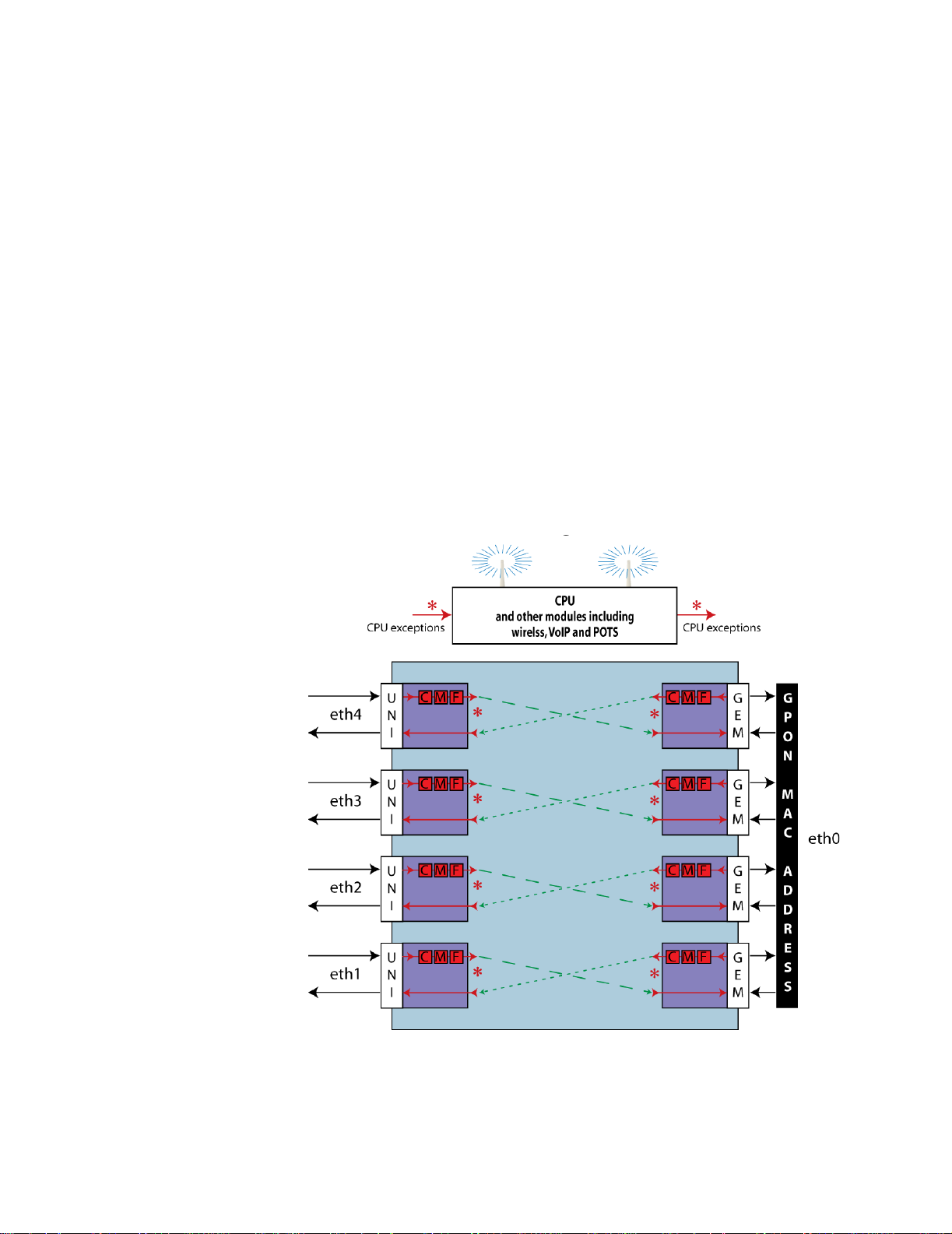
OMCI configured ONU flows
OMCI configured ONU flows have a one to one mapping between the WAN
side GEM port (GPON Encryption Method port) and the LAN side UNI (User
Network Interface). Other than exception packets which require analysis, such
as IGMP joins and leaves or ARPs, the traffic is generally a cut-through
between the GEM and the UNI.
OMCI configured ONU flows are handled entirely by Classification,
Modification, and Forwarding (CMF) hardware functions. The GPON
interface and each Ethernet LAN port of the 24xx have dedicated CMFs.
Downstream packets that arrive on each GEM are classified based on the
classification rules that have been created by OMCI provisioning actions.
Packets that match a Classification Rule are Modified as specified by that rule
and Forwarded to the egress port specified by that rule. Packets that are not
classified are dropped/blocked. Exception packets that require CPU analysis
(like the IGMP joins and leaves or ARPs) are classified on ingress and
forwarded to the CPU for action. This ONU forwarding architecture is
illustrated in the diagram below.
Figure 4: OMCI configured flows
You cannot map two UNIs to the same GEM when configuring ONU flows. If
three Ethernet Ports must be configured as members of the same VLAN for
High Speed Internet Access Service, three GEMs are required. The same
24 zNID 24xx Series Configuration Guide

OMCI vs. Residential Gateway management
VLAN is configured on all three GEMs. When configured this way a PC
connected on eth 1 will NOT be able to communicate directly with a PC
connected to eth 2 or eth 3. All packets are forwarded upstream in a secure
manner, and no locally switched port-to-port communication is supported.
All communication between a PC on eth1 and a PC on eth 2 will go upstream
to the OLT and back down again.
OMCI unique features
There are some features which OMCI provides which are not provided
through the RG:
• VLAN Translation (changing the VLAN tag)
• VLAN Promotion (adding an outer tag)
• VLAN Translation & Promotion (changing the inner tag and adding an
outer tag)
• Open Trunk (provisioning a cut-through path from an Ethernet Port to a
GEM Port that will pass all traffic through, unmodified, regardless of
VLAN ID). This open trunk is a useful feature for business applications
where a large number of VLANs must be supported.
OMCI configured video
The IP TV application is fully supported in pure ONU mode. The 4095 GEM
is used for all downstream multicast traffic, and the same 1:1 mapping of
UNIs to GEMs is required for handling of uni-cast traffic.
VLAN Translation is supported for the IP TV application, as long as all
Ethernet Ports are members of the same original VLAN. It is not possible to
translate a single downstream multicast video packet to VLAN A for sending
out eth 1, while simultaneously translating the same packet to VLAN B for
sending out eth 2
OMCI configured voice
The SIP Voice application is fully supported in pure ONU mode.
OMCI-configured SIP voice must be mapped to a dedicated GEM. SIP-PLAR
and MGCP voice are not supported in ONU mode.
Voice is unique because it is an ISO layer 3 application that can be fully
provisioned via OMCI and handled as an ONU function, or it can be fully
provisioned via Telnet/CLI, Web GUI, SNMP or TR-069 and handled as an
RG function. In either case, Voice actually operates as an RG function. OMCI
is used to configure the exact same database parameters for voice that are
provisioned via any of the RG configuration interfaces (e.g. Web GUI).
The only difference between ONU Voice and RG Voice is the Bound Interface
that is assigned. When Voice is OMCI-configured, the Bound Interface is a
“brg” interface created via OMCI. When Voice is RG-configured, the Bound
Interface is an IP Interface created via the Web GUI or TR-069.
zNID 24xx Series Configuration Guide
25

Management
This display is useful for troubleshooting purposes, because you c an easily
see how voice is configured using the Web GUI, TR-069, or Telnet/CLI
interface, even when OMCI actually configured it.
Statistics in UNI mode
There are not as many packet-level statistics available for ONU flows since
they are ISO layer 2 “cut-through” flows as illustrated in OMCI configured
flows, page 24. However there are several useful debug tools.
• There is an IGMP Table for OMCI-configured flows, accessible via
Telnet/CLI or Web GUI
• Voice Packet Log, Audit Log, and Line Status. Accessible via Telnet/CLI
or Web GUI
• Ethernet Port Statistics are provided. Accessible via OMCI, T elnet/CLI or
Web GUI
• GPON physical layer statics are provided. Accessible via OMCI, Telnet/
CLI or Web GUI
There is no Bridge Table to show learned MACs for any OMCI configured
flows.
Reserved GEM ports
When using any configuration mode:
• GEM ports in the 0xx, 1xx and 2xx range are not supported
The first usable GEM ports for the 24xx ONTs are in the 3xx - 4xx range.
• GEM ports in the 5xx - 6xx range are reserved for Residential Gateway
traffic flows
The “501 - 628 GEM range” is reserved for Residential Gateway VLANs
configured via the TR-069 or Web GUI interface. The 2426 uses (501 +
ONU ID) as its RG GEM for ONU IDs from 0 to 127.
26 zNID 24xx Series Configuration Guide
Dual Managed mode using the VEIP
OMCI vs. Residential Gateway management
In Dual Managed mode a “virtual UNI” is the glue between the RG interfaces
and OMCI. The virtual UNI is a Virtual Ethernet Interface Point (VEIP) as
described in G.984.4 Amendment 2 and G.Impl.984.4).
The VEIP allows the features such as Voice and WiFi which cannot be
implemented directly by OMCI, to be configured via RG interfaces. The
uplink is then set to “O” to designate an OMCI interface. This mechanism ties
the uplink to the virtual UNI.
Figure 5: RG and OMCI in Dual Managed mode, features via VEIP are matched by VLAN Identifier
When the eth0 interface of an RG VLAN is configured as an OMCI member,
it will be automatically mapped to the VEIP. Conversely, when eth0 is
configured as a tagged or untagged member of the VLAN, it is automatically
mapped to the default 5xx RG GEM.
Up to 24 RG VLANs are supported, and all 24 of them could be mapped to
the VEIP. Each RG VLAN must have a unique V L AN ID. However, VLAN
translation rules may be configured via OMCI to map multiple different RG
VLANs into the same Network-side VLAN (Not configured on the zNID, but
on the OLT).
VEIP Mapping is supported by the following VLAN types: Bridged-CPU,
BRouted, Routed, PPPoE-Bridged, PPPoE-Routed.
All IP attributes of an RG VLAN remain under RG configuration control.
OMCI is NOT used for provisioning of IP Addresses, DNS Addresses, Subnet
Masks, or other IP attributes
zNID 24xx Series Configuration Guide
27
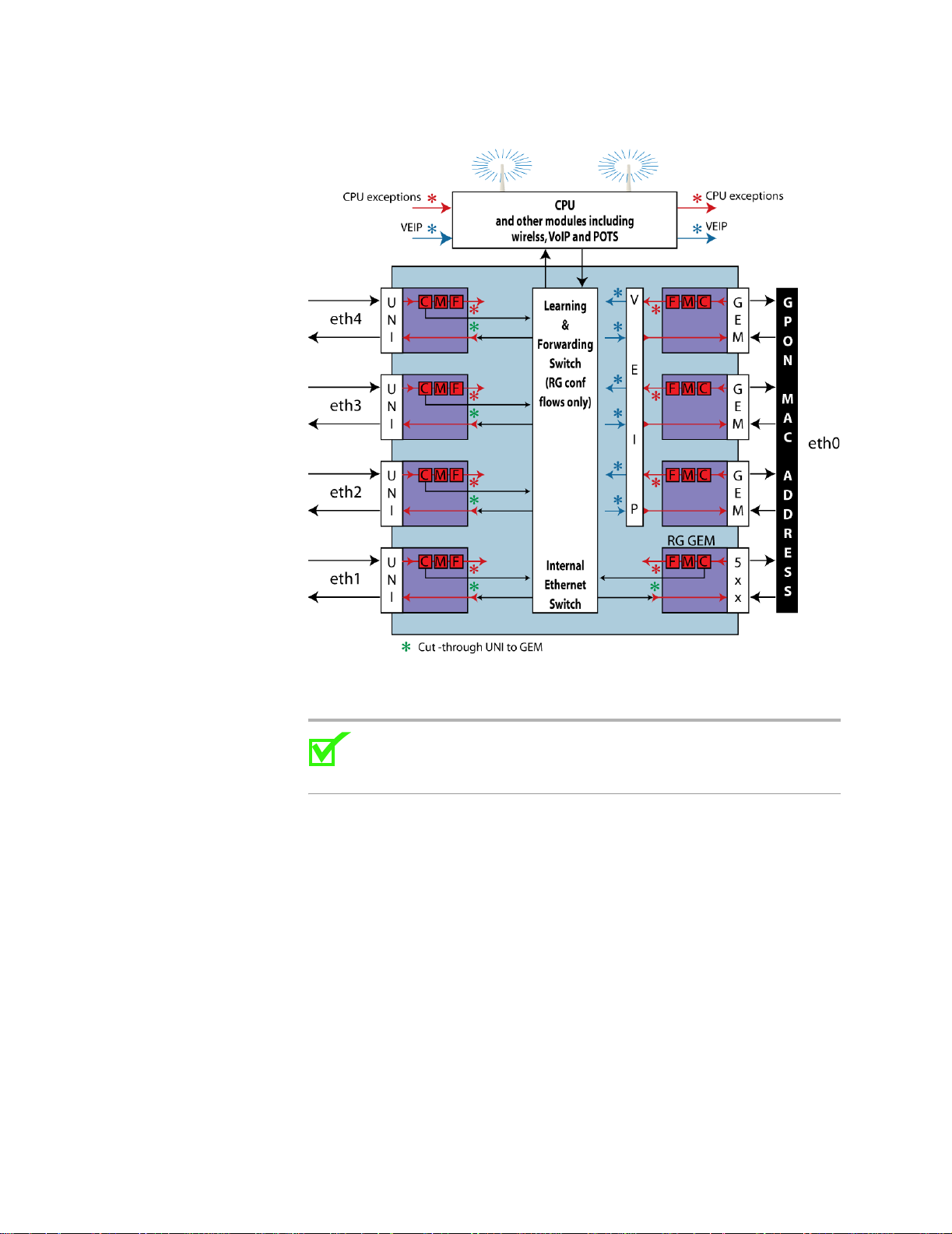
Management
Figure 6: In Dual Managed mode, the VEIP provides access to the oth er
modules including the wireless interface
VLAN ID is used to automatically bind the RG VLAN and the OMCI Filter
together.
Note: If there are no OMCI Filter Rules provisioned on the VEIP
with a matching Original VLAN ID, then the RG VLAN will not
have a connection into the network.
The VEIP provides mapping of RG VLANs to one or more additional GEMs,
beyond the default 5xx RG GEM. This mapping enables upstream tra ffic
prioritization via GPON Traffic Profile (GTP) parameters on a per-VLAN
basis. It also provides VLAN translation and promotion features that are not
available for RG VLANs mapped to the default 5xx GEM.
28 zNID 24xx Series Configuration Guide
Logging in to the 24xx series zNIDs
There are a few ways to log directly into the 24xx series zNIDs, both out of
Logging in on the Ethernet ports
band and in band.
• Logging in on the Ethernet ports
• Logging in with CLI
The zNID 24xx can be managed from the Ethernet ports.
• The ONU has a default IP address of 192.168.1.1 on the Ethernet port.
The user can connect a standard PC to the Ethernet port (eth1) and
configure the ONU using a standard web browser or telnet session. The
PC will need to have an IP address on the same subnet. Typically,
192.168.1.100 is used. Of course, if you change the IP address of the
ONU, you will lose connectivity. You would then need to reconfigure
your PC to be on the same subnet.
Logging in to the 24xx series zNIDs
Logging in with CLI
• The default login is “admin” and the default password is “zhone”
Note: For security reasons the password should be changed from the
default password. To change the password see User names and
passwords on page 31.
The complete list of CLI commands can be found in the CLI guide located at:
www.zhone.com/support/manuals.
Login:admin
Password:zhone
ZNID24xx-Router>
To log out of the system, enter the logout command:
ZNID24xx-Router> logout
Note: For security reasons the password should be changed from the
default password. To change the password in the CLI, see the zNID
Command Line Interface Reference Guide at zhone.com.
zNID 24xx Series Configuration Guide
29

Management
System features
The System pages define and configure access and applications used directly
by the zNID, such as DNS and Internet Time. The System pages also provide
options for updating and restoring software versions, as well as rebooting the
zNID.
For ONUs equipped with POTS there is a power saving feature, power
shedding, which cuts power to non-voice services during power outages, so
essential voice services may be provided for as long as possible on battery
power.
Figure 7: The System menu
This section describes the following System pages:
• Management access control on page 31
• Default interface on page 33
• DNS client on page 34
• Internet time on page 37
• System log on page 39
• Power shedding on page 42
• Backup/Restore on page 43
• SNMP agent on page 47
• TR-069 Client on page 49
• Certificates on page 51
• Restore software on page 54
• Update software on page 55
• Reboot on page 56
30 zNID 24xx Series Configuration Guide
 Loading...
Loading...