Zhone Z-Edge 64 Configuration Manual

Z-Edge 64 Config urati on Gui de
For software version 1.6.1
October 2002
Document Part Number: 830-00519-04, Rev B

Zhone Technologies
@Zhone Way
7001 Oakpor t Street
Oakland, CA 94621
USA
510.777.7000
www.zhone.com
info@zhone.com
COPYRIGHT ©2000-2002 Zhone Technologies, Inc. and its licensors. All rights reser ved.
This publication is prot ected by copyright law . No part of this publication may be copied or
distributed, transmitted, tran scribed, stored in a retrie val system, or translated into any human
or computer language in any form or by any means , electronic, mechanical, ma gnetic, manual
or otherwise, or disclosed to third parties without the express written permission from Zhone
Technologi es, Inc.
AccessNod e, A rca- DACS, BAN, MA LC, NetHo ri zhon, Sec htor, SkyZhone 45, SLM S, Z-E dge,
Z-Plex, ZMS, and Universal Edge are trademarks of Zhone Technologies, Inc.
Zhone and the Zhone logo are trademarks of Zhone Technologies, Inc.
All other trademarks and registe red trademarks are the property of thei r respectiv e holders.
Zhone Technologies makes no representation or warranties with respect to the contents here of
and specifically discl aims any implied w arranties of merchantabili ty, noninfringement, or
fitness for a particular purpose. Further, Zhone T echnologie s reserves the right to revise this
publication and to ma ke changes from time to ti me in the contents hereof without obligation of
Zhone Technologies to notify any person of such r evision or changes.
2 Z-Edge 64 Configuration Guide

CONTENTS
About This Guide...............................................................................................................................7
Document organization.............................................................................................7
Style and notation conventions ..............................................................................8
Typographical conventions.......................................................................................8
Acronyms......................................................................................................................9
Related documents..................................................................................................10
Contacting Global Service and Support.............................................................10
Technical support ....................................................................................................11
Service requi rements...... .. .. ......... ... .. ......... .. .. ......... ... .. ......... .. .. ......... ... .. ......... .. ......11
Chapter 1 Features and capabilities...................................................................................13
Product description.................................................................................................13
Features ......................................................................................................................14
Protocols and technologies...................................................................................14
ATM........................................................................................................................14
DSL.........................................................................................................................15
NAT ........................................................................................................................15
DHCP......................................................................................................................16
RIP ..........................................................................................................................16
SNMP......................................................................................................................17
Automatic rate adaption..........................................................................................17
Physi cal interfaces...................................................................................................18
Managing the Z-Edge 64.........................................................................................18
SNMP......................................................................................................................19
CLI ..........................................................................................................................19
ZMS ........................................................................................................................19
Chapter 2 WAN configu rat ion................................................................................................21
Configuring the local management channel.....................................................21
Logging in and out of the system............................................................................21
Syst em securit y........................................................................................................22
Changing the default user password .......................................................................22
Z-Edge 64 Configuration Guide 3

Contents
Configuring a DSL connection..............................................................................22
SDSL interface........................................................................................................24
G.SHD S L int e r f ace.......... .. ... ......... .. .. ......... .. ... ......... .. .. ......... .. ... ......... .. .. ......... .. ... .2 5
Verifying connection with showlinestatus command.............................................28
Chapter 3 System config uratio n..........................................................................................29
System defaults ........................................................................................................29
Configuring a connection to the ZMS.................................................................30
Chapter 4 Basic configu rat ion..............................................................................................33
Configuration overview...........................................................................................33
Interface type s (ift y p e )..... .. ......... ... .. ......... .. .. ......... ... .. ......... .. .. ......... ... .. ......... .. .. ....33
Profiles....................................................................................................................34
Interface inde x es ....... ... ......... .. .. ......... .. ... ......... .. .. ......... .. ... ......... .. .. ......... .. ......... ... .34
Configuring an Ethernet interface........................................................................35
Configuring static routes........................................................................................37
Adding a de f au l t ro u t e . ......... .. .. ......... .. ... ......... .. .. ......... .. ... ......... .. .. ......... .. ... ......... .37
Delet in g r o u t es............. .. .. ......... .. ... ......... .. .. ......... .. ......... ... .. ......... .. .. ......... ... .. ........38
Verifying routes ......................................................................................................38
Displaying the routing table .............................................................................39
traceroute command .........................................................................................39
Configuring RIP on the WAN interface...............................................................39
Displaying RIP information....................................................................................40
Chapter 5 Configuring Data and Voice..............................................................................41
Overview.....................................................................................................................41
Configuring data communications......................................................................41
Updating the ATM traffic descriptor for data.........................................................42
Calculating PCR for an interface......................................................................42
Updating the ATM Virtual Channel Link...............................................................43
Updating the IP interface record .............................................................................44
Configuring voice communications....................................................................45
Creat i n g a n ew AT M traffic des c ri p t o r..... .. .. ......... ... .. ......... .. ......... .. ... ......... .. .. ......45
Creat i n g a n ew AT M V irtual Circ u i t Lin k (VCL)...... ......... .. .. ......... ... .. ......... .. .. .... 4 6
AAL2 VCL profiles ................................................................................................47
POTS ................................................................................................................49
ISDN.................................................................................................................49
AAL2 au d io p ro fi l e s ................ .. ... ......... .. .. ......... .. ... ......... .. .. ......... .. ... ......... .. .. ......50
AAL2 CID profiles .................................................................................................51
POTS ................................................................................................................51
ISDN.................................................................................................................53
Subscriber profiles ..................................................................................................54
POTS ................................................................................................................55
4 Z-Edge 64 Configuration Guide

ISDN.................................................................................................................55
Subscriber voice profiles.........................................................................................56
POTS ................................................................................................................57
ISDN.................................................................................................................57
Subscriber-voice endpoint profiles .........................................................................59
POTS ................................................................................................................59
ISDN.................................................................................................................60
Activating voice conne ctions................................... .......................... ............ .........62
Chapter 6 Advanced IP configura tio n................................................................................63
Configuring NAT on the WAN interface..............................................................63
Configuring the Z-Edge 64 as a DHCP server...................................................64
DHCP ser v e r profiles an d scope........ ......... .. ... ......... .. .. ......... .. ... ......... .. .. ......... .. ... .65
Setting DHCP server options..................................................................................66
Creat i n g DH CP server s ubn e t o pti o n s . ... .. ......... .. .. ......... ... .. ......... .. ......... .. ... ......... .67
Creating dhcp-server-group profile.........................................................................69
Creat i n g dh c p -s er v e r -h o s t pro fi l e ............... .. ... ......... .. .. ......... .. ... ......... .. .. ......... .. ... .70
Enabl in g D H CP server... .. .. ......... ... .. ......... .. .. ......... ... .. ......... .. .. ......... ... .. ......... .. .. ....71
Creating DHCP client identifiers...........................................................................72
Transpa r en t b r i d gin g...............................................................................................73
Configuring DNS resolver......................................................................................76
PPP over A T M............................................................................................................79
Chapter 7 Advanced voic e config urat ion.........................................................................85
ADPCM voice compression...................................................................................85
POTS voice options.................................................................................................86
ISDN B-channel data................................................................................................89
Silence suppression and comfort noise generation.......................................92
Chapter 8 Administration........................................................................................................97
LED indicators...........................................................................................................97
Power LED..............................................................................................................98
Diagnostic LED......................................................................................................98
Operational LED.....................................................................................................98
WAN L ED ............ .. .. ......... ... .. ......... .. .. ......... ... .. ......... .. .. ......... ... .. ......... .. .. ......... ... .98
Line LEDs...............................................................................................................99
Z-Edge 64 BH2A (ISDN BRI)........................................................................99
Z-Edge 64 H2A (POTS)..................................................................................99
CLI diagnostic methods..........................................................................................99
showli n e s t at u s co mmand ........ .. .. ......... ... .. ......... .. .. ......... ... .. ......... .. ......... .. ... ......... .99
interface show command ......................................................................................101
traceroute command..............................................................................................101
Z-Edge 64 Configuration Guide 5

Contents
SNMP administration.............................................................................................101
Creating SNMP community names and access lists.............................................101
Creat i n g a co mmunity p ro fi le...... .. ... ......... .. .. ......... .. ... ......... .. .. ......... .. ... ........102
Creat i n g co m m u n it y a c c es s li s ts ...... ......... .. .. ......... .. ... ......... .. .. ......... .. ... ........102
Configuring traps ..................................................................................................103
User accounts ........................................................................................................104
Adding a use r . .. ......... ... .. ......... .. .. ......... ... .. ......... .. ......... .. ... ......... .. .. ......... .. ... ........104
Manually binding interfaces................................................................................105
System logging .......................................................................................................106
Real time statistics.................................................................................................107
Saving and restoring configurations ................................................................107
Setting system date and time ..............................................................................109
Rebooting the system...........................................................................................109
Appendix A Specifications........................................................................................................111
Appendix B Cable pinouts........................................................................................................113
Index....................................................................................................................................................117
Z-Edge 64 specifications......................................................................................111
RJ11 pinouts for WAN line...................................................................................113
RJ45 pinouts for LAN line....................................................................................114
ISO 8877 pinouts for ISDN BRI voice lines......................................................115
RJ11 pinouts for POTS voice lines....................................................................116
6 Z-Edge 64 Configuration Guide

ABOUT THIS GUIDE
This guide is intended for use by Z-Edge 64 users and admi nistrators. Z-Edge
64 users should have a fundamental knowl edge of telephony, derived voice
concepts, ATM networking, DSL protocols, and IP bridging and routing.
Refer to the Z - E dge 64 Q uick Star t Guide fo r hard w ar e inst al latio n and
connection information.
Document organization
This guide contains the following information:
T o Learn About Read
Z-Edge 64 functionality and features. Chapter 1, Featu res and
capabilities, on page 13
Configuring a local management channel;
system security; as well as configuring and
activati ng a DSL conn ection.
System on the Z-Edge 64; and configuring a
connection to the ZMS.
Configuring an Ethernet interfa ce; confi guring
static r outes; confi guring RIP; and conf iguring
DNS.
Configuring data communications; and
configuring voice communications.
Configuring NAT; configuring the Z-Edge 64
as a DHCP ser v er ; and creating DHCP clien t
identifiers.
Configuring ADPCM voic e c ompression;
POTS voice options; and ISDN B-channel
data
Chapter 2, WAN configuration,
on pag e 21
Chapter 3, Sys tem configuration,
on pag e 29
Chapter 4, Basic configuration,
on pag e 33
Chapter 5, C onfi guring Dat a and
Voice, on page 41
Chapter 6, Advanced IP
configuration, on page 63
Chapter 7, Advanced voice
configuration, on page 85
Z-Edge 64 Configuration Guide 7

About This Guide
T o Learn About Read
LEDs; CLI diagnostics; SNMP
administrat ion; user accounts; manually
binding interfa ces; saving and restoring
configurations; and rebooting the system.
Z-Edge 64 product spe cifications. Appendix A, Spec ifications, on
Pinouts for cables that attach to the Z-Edge
64.
Style and not ation conventions
The following conventions are used in this document to alert users to
information that is instr uctional, warns of potential damage to syst em
equipment or data, and warns of potential injury or death. Carefully read and
follow the instruct ions included in this document.
Caution: A caution aler ts users to conditions or actions that could
damage equipment or data.
Note: A note provides important supplemental or amplified
information.
Chapter 8, Administration, on
page 97
page 111
Appendix B, Cable pinouts, on
page 113
Tip: A tip provides additional information tha t enables users to more
readily com plete their ta sks.
WARNING! A warning alerts users to conditions or actions that
could lead to injury or death.
WARNING! A warning with this i con alert s users to c ondition s or
actions that could lead to injury caused by a laser.
Typographical conventions
The following ty pographical styles are use d in this guide to represe nt specific
types of information.
Bold Used for names of buttons, dialog boxes, icons, menus,
Fixed Used in code e xamples for c omput er output, f ile n ames, pa th
profiles when pl ac ed in body text, and property pages (or
sheets). Also used for co mmands, options, parameters i n
body text, and user input in body text.
names, and the contents of online files or directories.
8 Z-Edge 64 Configuration Guide

Fixed Bold Used in code examples for te xt typed by users.
Acronyms
Acronyms
Fixed Bold
Italic
Italic Used for book titles, chapter titles, file path names, notes in
PLAIN UPPER
CASE
The following acronyms are related to the Z-Edge 64 and will appear
throughout this manual:
Acronym Description
AAL2 ATM Adaption Layer 2
AAL5 ATM Adaption Layer 5
ATM Asynchronous Transfer Mode
BAN Zho ne Broa dband Access Node
Used in code examples for variable text typed by users.
body text requiring special attention, section titles,
emphasized terms, and variables.
Used for environment variables.
CAS Channel Associated Signaling
CID AAL2 Channel Identifier
CLI Command Line Interface
CO Central O f fice
CPE Customer Premises Equipment
dB Decibel
DHCP Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
DSL Digital Subscriber Lin e
DSLAM Digital Subscriber Line Access Multiplexer
DSS1 Digital Subscriber Signaling System number 1
ELCP Emulated Loop Control Protocol
FXO Foreign eXchange Office
FXS Forei g n eXchange Station
G.SHDSL Global Symmetrical High-bit-rate Digital Subscriber Line
HDSL2 High-bit-rate Digital Subscriber Line , second generation
IANA Internet Assigned Numbers Authority
Z-Edge 64 Configuration Guide 9

About This Guide
Acronym Description
ISDN BRI Integrated Services Digital Network Basic Rate Interface
Kbps kilobits per second
LAN Local Area Network
MALC Zhone Multi-Access Loop Concentrator
MIB Management Information Base
NAT Network Address Translation
PBX Private Bra n ch Ex ch a ng e
POTS Plain Old Telephone Service
PSTN Public Switched Telephone Network
RIP Routing Information Protocol
SDSL Symmetric Digital Subscriber Line
SNMP Simple Network Management Protocol
TDM Time Division Multiplexing
TFTP Trivial File Transfer Protocol
VCI Virtual Channel Identifier
VCL Virtual Cha nnel Link
VPI Virtual Path Identifier
WAN Wide Area Network
Related documents
Refer to the following public ations for additional information:
• Z-Edge 64 Quick Start Guide
• Z-Edge 64 Release Notes
Contacting Global Service and Support
Contact Global Service and Support (GSS) if you have any questions about
this or other Zhone products. Before contacting GSS, make sure you have the
following information:
10 Z-Edge 64 Configuration Guide
• Zhone product you are using
• System configuration
• Software version running on the system

• Description of the issue
Technical support
If you require assistance with the installation or operation of your product, or
if you want to return a product for repair under warranty , c ontact GSS. The
contact information is a s follows:
E-mail support@zhone.com
Telephone (North America) 877-ZHONE20
Telephone (International) 510-777-7133
Internet www.zhone.com/support
If you purchased the product from an authorized dealer, distributor, Value
Added Reseller (VAR), or third party, contact that supplier for technical
assistance and warranty support.
Service requirements
Contacting Global Service and Support
If the product malfunctions, all repairs must be performed by the
manufacturer or a Zhone-authorized agent. It is the responsibility of users
requiring service to report the need for service to GSS.
Z-Edge 64 Configuration Guide 11

About This Guide
12 Z-Edge 64 Configuration Guide
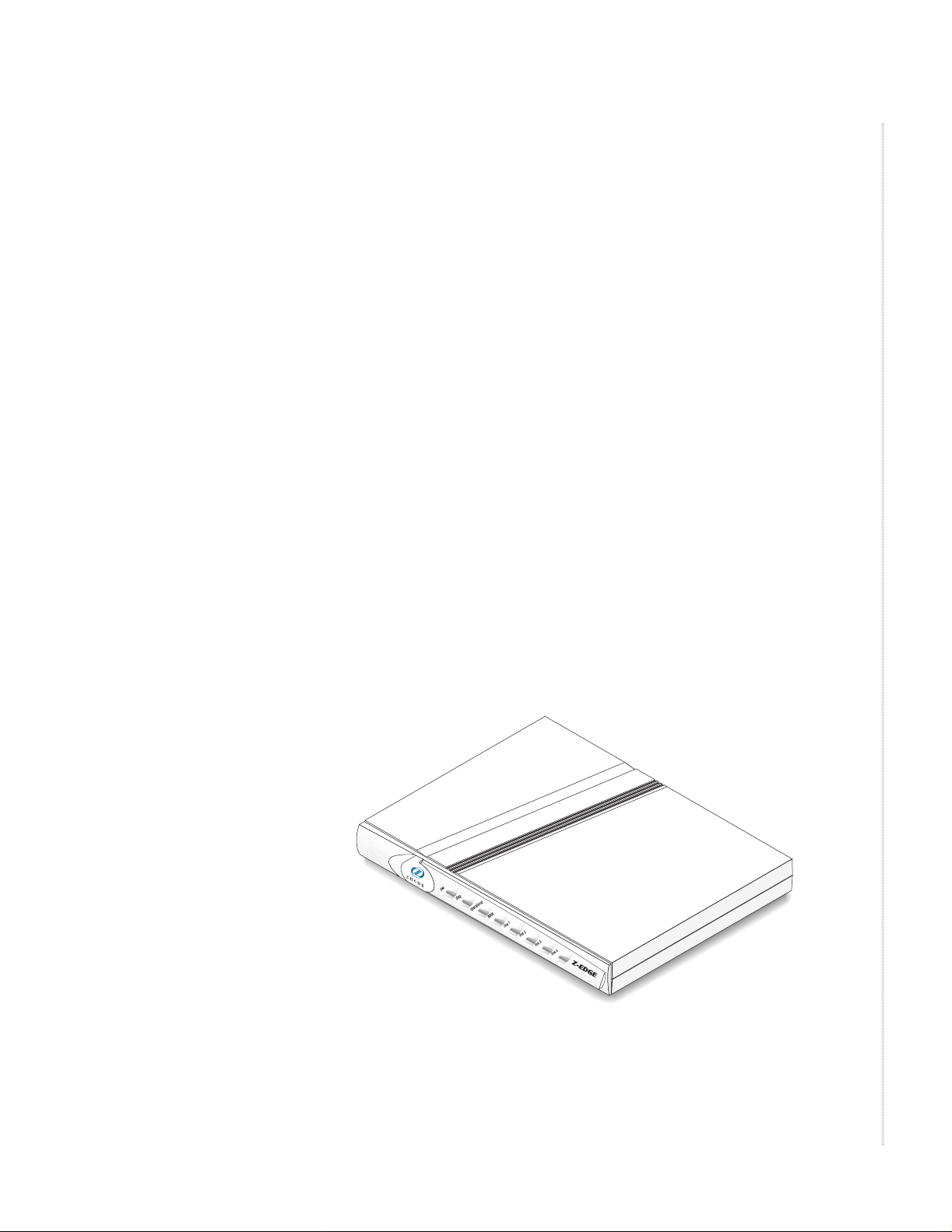
FEATURES AN D CAPABILITIES
1
Product description
This chapter includes the following topics:
• Product description, page 13
• Protocols and technolo gies, page 14
• Physical interfac es, page 18
• Managing the Z-Edge 64, page 18
The Z-Edge 64 is a compact integrated access device (IAD) that provides
Internet Protocol (IP) routing features as well as traditional voice services
over a single Di gital Subsc ribe r Line (DSL) WAN connection. The Z-Edge 64
BH2A offers Integrated Services Digital Network Basic Rate Interface (ISDN
BRI) voice transport. The Z-Edge 64 H2A supports Plain Old Te lephone
Service (POT S ).
Figure 1: The Z-Edge 64
In a traditional Voice over DSL (VoDSL) architecture, the Z-Edge 64 can
operate with a Digital Loop Carrier (DLC), like the Zhone Multi-Access Loop
Concentrator (MALC), or a voice gateway, such as a Zhone Sechtor 100A.
Figure 2 shows an example application for the Z-Edge 64.
Z-Edge 64 Configuration Guide 13
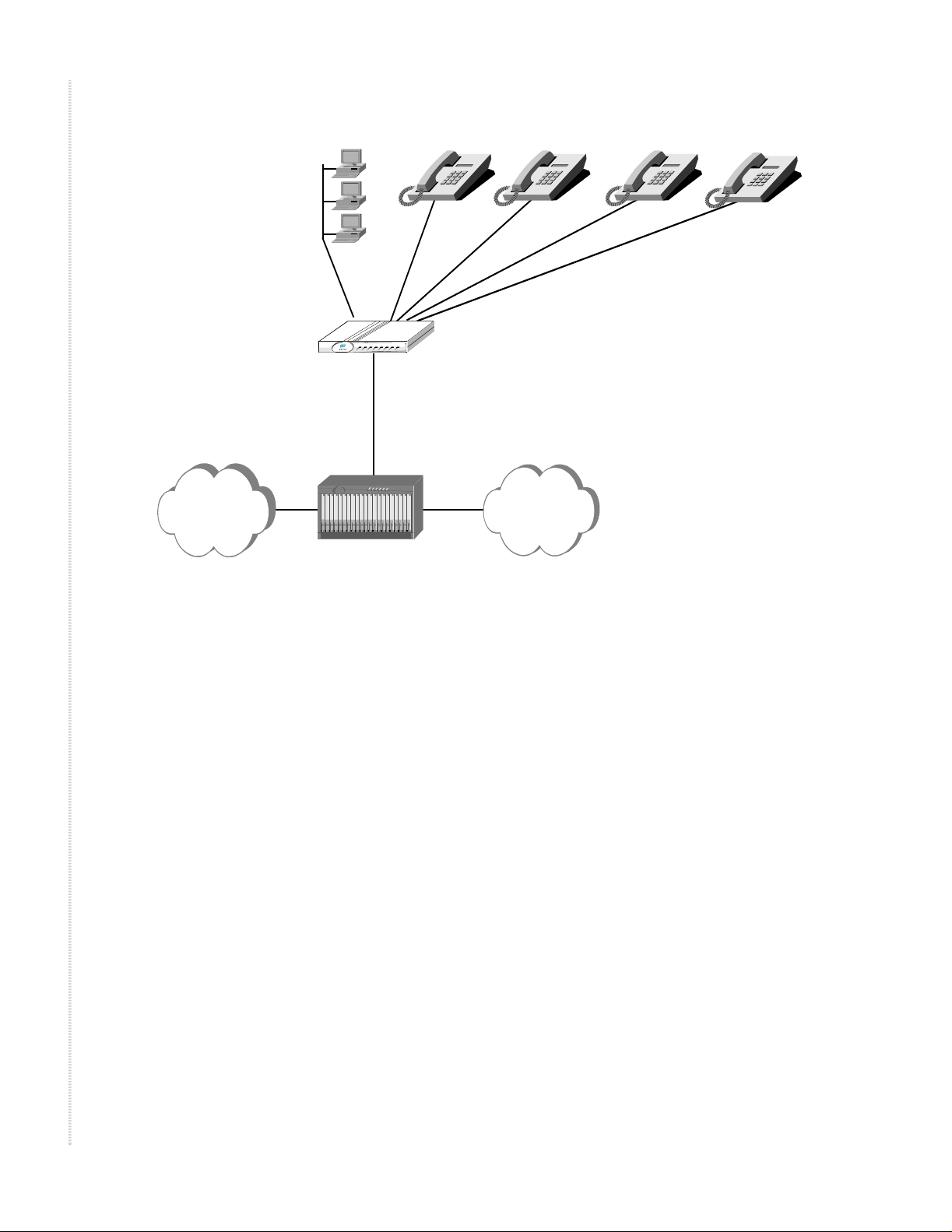
Features and capabilities
Figure 2: Typical Z-Edge 64 network application
Internet
Features
LAN
connection
voice lines
Z-Edge 64
WAN connection
PSTN
MALC
The Z-Edge 64 has the following featur es:
• T oll-quality voice support with c ustom calling features
• Internet Protocol (IP) routing
• Network Address T ranslation (NAT) capabilities
• Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server/client functionality
• Simple Network Management Protoco l (SNMP) manageability
Protocols and technologies
The Z-Edge 64 supports the followi ng networking protocols a nd technologies.
You should have an understanding of these concepts before operating the
Z-Edge 64:
ATM
Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM ) is a cell-based, high-speed networking
technology. The ATM cell has a fixed length of 53 bytes. The cell is broken
into two parts, the header and the payloa d. The header (5 bytes) contains the
14 Z-Edge 64 Configuration Guide

DSL
Protocols and technologies
addressing information, and the payload (48 bytes) carries the voice or data
message. Since each ATM cell has its own addressing mechanism, the cells
can be sent asynchronously, or in any order.
ATM uses virtual channels (VCs) and virtual paths (VPs) to route cells in an
ATM network. A VC, identified by a virtual channel identifier (VCI) is a
connection between two communic ating ATM entities. A VC consists of a
concatenation of one or more ATM links. A VC provides a certain quality of
service, which is defined in t he ATM Traffic Descri ptor. A VP, identified by a
virtual path identi fier (VPI), is a group of VCs between two ATM endpoints.
A physical link can support many VPs. Similarly, a VP can contain many
VCs.
Digital Subscr iber Line (DSL) t echnol ogies pr ovide access to high- bandwidt h
networks over a unshielded twisted pair (UTP) of copper wires. By using
frequencies above the te lephone bandwidth (300Hz to 3,200Hz), DSL can
encode more data to achieve higher data rates than would otherwise be
possible in the restric ted frequency range of a POTS network. The DSL
family includes several variations.
NAT
Symmetric Digital Subscr iber Line (SDSL) provides data-only symmetric
transfer rate s of up t o 2.32Mbps over a si ngle pa ir of cop per wire s. SDSL uses
the same 2B + 1Q si gnaling as I SDN. SDSL servi ce requir es t hat the customer
is no further than 10,000 feet from the central office. SDSL is defined in ITU
G.991.1.
Global Symmetric High-bit-rate Digital Subscriber Line (G.SHDSL) is
designed to operate with both HDSL and SDSL networks. G.SHDSL extends
the reach and transfe r rates of DSL servic es. G.SHDSL supports adaptive data
transfer rates of 192Kbps to 2.3Mbps with a reach of over 20,000 f eet. The
G.SHDSL specification (ITU standard G.991.2) allows for transmission over
single-pair and two- pair copper wires.
Network Address T ranslation (NAT) is an Internet standard that enables a
local area n etwork (LAN) to use one set of IP a ddress es for internal tra ffic and
a second set of addresses for external traffic. Hosts in a private network c an
transparently access an external network and enable access to selective local
hosts from the outside.
A NAT device connecting the public Internet and the network it serves
rewrites IP addresses and port numbers in IP headers. The packets appear to
be coming from a single public IP address of the NAT device, instead of the
actual source or destin at ion.
NAT serves two main purposes: It provides a type of firewall by hiding
internal IP addresses, and it enables a company to define more internal IP
Z-Edge 64 Configuration Guide 15
Features and capabilities
DHCP
addresses. Since the addresses are used internally only, there is no possibility
of conflict with IP addresses used by other companies and organizations.
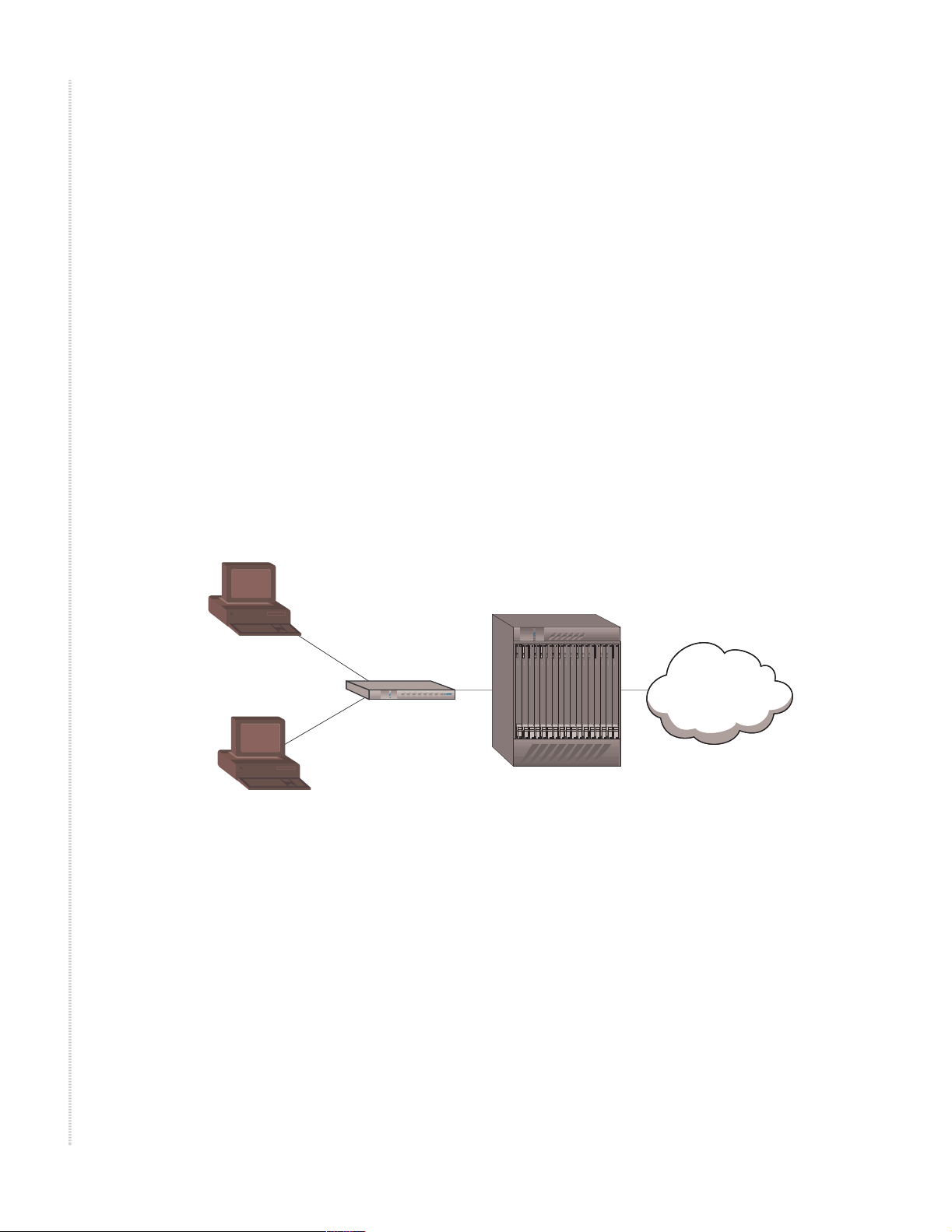
The Dynamic Host Control Protocol (DHCP) provides a mechanism through
which client computers using TCP/I P can obtain configuration parameters
(such as the default router and the Domain Name System [DNS] ser ver,
subnet mask, gate way addre ss, a nd lease time) fr om a ce ntrally lo cated DHCP
server. DHCP dynamic rec onfiguration requires a DHCP server , a forwarding
agent in each router, and DHCP capability in each client TCP/IP stack. The
most important configuration parameter carried by DHCP is the IP address.
Dynamic addressin g allows a device to have a different IP address every time
it connects to the network, and in some systems, the device IP address can
change while it i s still c onnec ted to the ne twork. DHCP also suppo rts a mix of
static and dynamic IP addresses.
Figure 3: Z-Edge 64 as DHCP client
10.0.0.1
10.0.0.2
DHCP server
DHCP client
Internet
Z-Edge 64
BAN
A DHCP client is an Internet host using DHCP to obtain confi guration
parameters such as a network address. A DHCP server is an Internet host that
returns configur ation parameters to DHCP clients. As a DHCP client, the
Z-Edge 64 receives its IP address and configurati on parameters fr om a DHCP
server, such as the BAN.
RIP
16 Z-Edge 64 Configuration Guide
Routing Information Protocol (RIP) is widely used for routing traffic on the
Internet and is an interi or gate way protocol (IGP), which means that it
performs routing withi n a single autonomous system. RIP is based on

SNMP
Protocols and technologies
distance-vector algorithms that measure the shortest path between two points
on a network, based on the addresses of the originating and destination
devices. The shortest path is determine d by the number of hops between those
points. RIP routers maintain only the best route (the route with the lowest
metric value) to a destinat ion. After updating its routing table, the router
immediately begins transmitting routing updates to inform other network
routers of the shortest r oute.
Routing Information Protocol version 2 (RIPv2) is the latest enhancement to
RIP. RIPv2 allows more information to be included in RIP packets and
provides an authentication mechanism.
Z-Edge 64 users ca n manage their system with Simpl e Network Management
Protocol (SNMP) software. SNMP is based on network management stations
(managers) and network managed elements ( agents). SNMP allows network
managers and network agents to communic ate.
There are three types of SNMP transactions—a Get, a Set, or a Trap. The Get
and Set commands are sent from the manager to the agent to determine (Get)
or configure (Se t) network variables and st atus. A Trap is an e xception to this
SNMP transaction patter n, in tha t the Trap is an unsolicited event report sent
from the agent to the ma na ger. When the SNM P m an ag er re cei ves the Trap
message, it can be stored in the Management Information Base (MIB) and
displayed on a terminal screen.
A MIB is a virtual database that identi fi es each manageable object by name,
syntax, accessibility, status, a text description, and a unique
manageable-Object I dentification number (OID). MIBs come in three
varieties: Public , Expe rimental, and Private Enterprise .
Automatic rate adaption
Automatic baud rate de tection (also known as rate adaption) allows receiving
devices to communicate with transmitting devices operating at different
speeds without the need to est ablish data rates in advance . By determini ng the
baud rate from the tra nsmitti ng device, the receiv ing Z-Edge 64 automatica lly
trains to match the line rate of the incoming da ta.
Usually the re is one centr al office (CO) device transmi tting to many customer
premises equipment (CPE) units. When a CO device trains with a CPE unit,
the devices will settle on the lower of the two devices’ line rates. It is optimal
to set the CPE line rate to 2320 kbps because it allows a wide range of rates
for CO and CPE devices to agree upon.
The training of line rates is faster on G.SHDSL than on SDSL. The G.SHDSL
rate adaption process occurs during the CO and CPE modems’ handshake,
where the devices probe the G.SHDSL line to find the best possible line rate.
The SDSL autobaud process is slower because the CO and CPE modems use
an algorithm to step through a sequenc e of line rates, where the devices
Z-Edge 64 Configuration Guide 17

Features and capabilities
Physical interfaces
establish a connecti on at each line rate and then move to the next higher rate
until they r each the f inal rate, which is the lowe r of the l ine r ates. Note t hat the
Z-Edge 64 does not currently support SDSL autobaud.
The Z-Edge 64 has following physical inte rfaces:
• WAN: One RJ11 port.
A standard RJ1 1 port connects un shielde d twis ted pair (UTP ) copper wir e
to DSL networks.
• LAN: One 10/100BaseT RJ45 port.
A RJ45 port carries both management and data traffic, and interconnects
with most Tr ansfer Control Protocol/I nternet Protocol (TCP/IP) hubs and
networks.
• Phone lines:
Z-Edge 64 BH2A: Four ISO 8877 ports support ISDN BRI.
or
Z-Edge 64 H2A: Four RJ11 ports support POTS.
• Serial: One DB9 port.
A single DB9 asynchronous serial port provides direct PC or virtual
terminal (such as VT100) acces s to the Z-Edge 64. The serial port allows
access to the CLI.
Figure 4: The back panel of the Z-Edge 64
WAN Phone
lines
Serial port LAN Power
Managing the Z-Edge 64
18 Z-Edge 64 Configuration Guide
The Z-Edge 64 provides the following physic al interfaces to configu re the
unit:
• Serial (craft)—An out-of-band RS232 serial interface
• Ethernet—A 10/100Base-T RJ45 port

SNMP
Managing the Z-Edge 64
You can configure the Z-Edge 64 using any of the following methods:
• Simple Network Management Protoco l (SNMP)
• Command Line Interface (CLI)
• Zhone Management System (ZMS)
The Z-Edge 64 supports SNMP version 1 and version 2 for system
management. Network object variables are MIB-II compliant.
SNMP can be accessed over IP interfaces or the Ethernet interface. The
SNMP agent on the Z-Edge 64 u ses port 1 61 of us er data gra m protocol (UDP)
for management traff ic and UDP port 162 for error events and SNMP traps.
The MIBs for the Z-Edge 64 control the following:
• Data port configuration, status, and diagnostics
• General system management, field upgrades, and alarms
CLI
ZMS
• Traps
The CLI is functionally simila r to SNMP . The CLI commands are equivalent
to SNMP get and set commands and allow you to configure the unit. The
interface is accessible both using telnet and through a local serial port. You
can configu re the sam e elements with the CLI as you can w ith SN M P.
ZMS allows Z-Edge 64 users to navigate, monitor, and manage their Zhone
networks with a graphical use r interface.
Z-Edge 64 Configuration Guide 19

Features and capabilities
20 Z-Edge 64 Configuration Guide

W AN CONF IGURATION
2
Configuring the local management channel
This chapter details how to configure the Z-Edge 64 physical connection to
the WAN. The W AN c onnection is ne cessary f or a ll automat ic pr ovisioning of
the Z-Edge 64. This chapter includes the following topics:
• Configuring the local management channel, page 21
• System security, page 22
• Configuring a DSL connection, page 22
The Z-Edge 64 unit pr ovides an out- of-band serial (local o r cra ft) i nterfac e for
managing the uni t. To access the seria l port, configure your terminal interface
software with the following settings:
• 9600bps
• 8 data bits
• No parity
• 1 stop bit
• No hardware flow control
Logging in and out of the system
Perform the initial configuration of the system using the serial interface. After
you have completed the initia l configuration, you can manage the Z-Edge 64
unit over the network using a telnet session.
Log into the system (the default user name is admin, the default password is
zhone):
login:admin
password: *****
zSH>
To log out of the system, enter the logout command:
zSH> logout
Z-Edge 64 Configuration Guide 21
WAN configuration
Note: W hen you turn the Z-Edge 64 on, you may receive error
messages about automat ic DHCP client configu ration because the re is
no WAN connection se t up. This is normal. Proceed to configure the
WAN connection.
System security
There are several methods to guard against unauthorized access to your
Z-Edge 64, such as changing the default user password. You can also set up
SNMP access lists to re stric t acc ess to your syst em. See SNMP adminis tration
in Chapter 7 for mo re in fo rm at ion ab out se t ting SN MP acce ss lis ts.
Changing the default user password
When adding us ers, t he syst em a utomatic ally assigns a tempor ary pas sword t o
each user. Most users will want to change their password. The changepass
command changes the passwor d for the current logged in user. The following
is an example of chang ing a pa s sword:
jsmith> changepass
Current Password: the password is case- se nsitive and will not appear as you type it
New Password : the password is case-sensitive and will not appear as you ty pe it
Confirm New Password : the password is case-sensitive and will not appear as you type it
User record updated.
Password change successful.
Configuring a DSL connection
The first step in configuring your Z-Edge 64 is connecting to the WAN by
setting up a DSL connection over the Z-Edge 64 WAN interface.
The dsl-config profile is automaticall y created by the system when the
Z-Edge 64 is turned on. Update the dsl-config profile to match your line-type
and unit-mode.
22 Z-Edge 64 Configuration Guide
Configuring a DSL connec ti on
The dsl-config profile supports the following parameters:
Parameter Description
line-type The DSL type supported on this
interface.
Values:
shdsl GlobespanVirata firmware for
G.SHDSL (not compatible with
shdsllatest firmware)
sdsl GlobespanVirata firmware for
SDSL (not compatible with sdsllatest
firmware).
shdsllatest Compatible with most
GlobespanVirata G.SHDSL firmware.
This value is required for automatic
rate adapti on on G.SHDSL.
sdsllatest Compatible with most
transparent mode ATM SDSL
impleme n tations. This v alue is
required for automa tic rate a dapti on on
SDSL.
Default: shdsllatest
unit-mode S p ec if i es w h et he r th e un i t is
configured as a CO or CPE device. If
you are connecting Z-Edge 64 units
back-t o -b a ck , set the unit-mode to co
(central office) on one Z-Edge 64, and
set the downstream Z-Edge 64 to cpe
(customer premises equipment).
Values:
co
cpe
Default: cpe
Below is an example showing the default settings for a dsl-config profile:
zSH> get dsl-config 1-1-1-0/hdsl2 hdsl2 type includes HDSL2, SDSL, and G.SHDSL
line-type: -> {shdsllatest} shdsl | sdsl | shdsllatest | sdsllatest
unit-mode: -> {cpe}
Depending on the line-type, configuration profiles are automatically created
for the DSL variations. To change the DSL variation, modify the line-type in
the dsl-config profile and then update the specific DSL confi guration profiles.
Z-Edge 64 Configuration Guide 23
WAN configuration
SDSL interface
Parameter Description
config-line-rate The line rate.
The sdsl-config profile supports the foll owing parameters (all others should
be left at their default values):
Values:
line-rate-144kbps, line-rate-160kbps, line-rate-192kbps, line-rate-208kbps,
line-rate-224kbps, line-rate-256kbps, line-rate-272kbps, line-rate-320kbps,
line-rate-368kbps, line-rate-384kbps, line-rate-400kbps, line-rate-416kbps,
line-rate-528kbps, line-rate-768kbps, line-rate-784kbps, line-rate-1040kbps,
line-rate-1 152kbps, line-rate-1 168kbps , li ne-r ate-1536kbps, line-rate-1552kbps,
line-rate-1568kbps, line-rate-2320kbps, line-rate-176kbps, line-rate-240kbps,
line-rate-288kbps, line-rate-304kbps, line-rate-336kbps, line-rate-352kbps,
line-rate-432kbps, line-rate-464kbps, line-rate-496kbps, line-rate-560kbps,
line-rate-592kbps, line-rate-624kbps, line-rate-656kbps, line-rate-688kbps,
line-rate-720kbps, line-rate-752kbps, line-rate-816kbps, line-rate-848kbps,
line-rate-880kbps, line-rate-912kbps, line-rate-944kbps, line-rate-976kbps,
line-rate-1008kbps, line-rate-1072kbps, line-rate-1104kbps, line-rate-1136kbps,
line-rate-1200kbps, line-rate-1232kbps, line-rate-1264kbps, line-rate-1296kbps,
line-rate-1328kbps, line-rate-1360kbps, line-rate-1392kbps, line-rate-1424kbps,
line-rate-1456kbps, line-rate-1488kbps, line-rate-1520kbps, line-rate-1584kbps,
line-rate-1616kbps, line-rate-1648kbps, line-rate-1680kbps, line-rate-1712kbps,
line-rate-1744kbps, line-rate-1776kbps, line-rate-1808kbps, line-rate-1840kbps,
line-rate-1872kbps, line-rate-1904kbps, line-rate-1936kbps, line-rate-1968kbps,
line-rate-2000kbps, line-rate-2032kbps, line-rate-2064kbps, line-rate-2096kbps,
line-rate-2128kbps, line-rate-2160kbps, line-rate-2192kbps, line-rate-2224kbps,
line-rate-2256kbps, line-rate-2288kbps
Default: line-rate-1552kbps
fix-bit-rate Enables or disables automatic baud rate dete ction.
Values:
fix-bit-disable This value enable s automatic bau d rate detection. I f the CO and CPE
devices have different line rates at startup, the lower of the two rates will be selected.
fix-bit-enable This value is used for static (set) ba ud rates. This option is avail able if the
device’s unit-mode is set to co in the dsl-config profile. This val ue is ignor ed if the device ’s
unit-mode is set to cpe.
Default: fix-bit-disable
ntr Network timing recove ry (NTR ) specifies that the system synchronizes with an external
(network) clocking so urce .
Values:
ntr-enable the system synchroni ze s with the network.
ntr-disable the system reli es on its own clocking source.
Default: ntr-disable
24 Z-Edge 64 Configuration Guide
Note: In order to achieve optimum results when provisioning
automatic baud rate adapt ion tha n 9000 feet, set the fix-bit-rate
parameter to fix-bit- enable in the sdsl-config profile on both ends of
the connection. Also, ensure that the config-line-rate is the same on
both ends of the connection.
Belo w i s a n ex am p le of the sdsl-config recor d crea ted by settin g the line-type
parameter to sdsllatest in the d sl-config profile. Update this profile if you
want to change the line rate or to override autobaud.
zSH> update sdsl-config 1-1-1-0/hdsl2
Please provide the following: [q]uit.
config-line-rate: -> {line-rate-1552kbps}: line-rate-2320kbps
fix-bit-rate: -----> {fix-bit-disable}:
connect-mode: -----> {flowpoint-mode}:
ntr: --------------> {ntr-disable}:
framer-type: ------> {atm-clear-channel}:
power-scale: ------> {17664}:
....................
Save changes? [s]ave, [c]hange or [q]uit: s
Record updated.
Configuring a DSL connec ti on
G.SHDSL interface
Updating the dsl-config profile, with the line-t ype set to shdsl, automatically
creates an associated shdsl-config profile. To configure a G.SHDSL interface:
zSH> update dsl-config 1-1-1-0/hdsl2
line-type: -> {sdsl}: shdsl
unit-mode: -> {cpe}:
....................
Save changes? [s]ave, [c]hange or [q]uit: s
Record updated
Z-Edge 64 Configuration Guide 25
WAN configuration
Parameter Description
shdsl-config-line-rate The line rate.
The shdsl-config profile support s the following parameters (all othe rs should
be left at their default values):
Values:
line-rate-72kbps, line-rate-80kbps, line-rate-136kbps, line-rate-144kbps,
line-rate-200kbps, line-rate-208kbps, line-rate -264kbps ,
line-rate-272kbps, line-rate-328kbps, line-rate -336kbps ,
line-rate-392kbps, line-rate-400kbps, line-rate -456kbps ,
line-rate-464kbps, line-rate-520kbps, line-rate -528kbps ,
line-rate-584kbps, line-rate-592kbps, line-rate -648kbps ,
line-rate-656kbps, line-rate-712kbps, line-rate -720kbps ,
line-rate-776kbps, line-rate-784kbps, line-rate -840kbps ,
line-rate-848kbps, line-rate-904kbps, line-rate -912kbps ,
line-rate-968kbps, line-rate-976kbps, line-rate -1032kbps ,
line-rate-1040kbps, line-rate-1 096kb ps, line-rat e-1104kbps,
line-rate-1 160kbps, line-rate-1168kbps, line-r ate-1224kbps,
line-rate-1232kbps, line-rate-1288kbps, line-rate-1296kbps,
line-rate-1352kbps, line-rate-1360kbps, line-rate-1416kbps,
line-rate-1424kbps, line-rate-1480kbps, line-rate-1488kbps,
line-rate-1544kbps, line-rate-1552kbps, line-rate-1608kbps,
line-rate-1616kbps, line-rate-1672kbps, line-rate-1680kbps,
line-rate-1736kbps, line-rate-1744kbps, line-rate-1800kbps,
line-rate-1808kbps, line-rate-1864kbps, line-rate-1872kbps,
line-rate-1928kbps, line-rate-1936kbps, line-rate-1992kbps,
line-rate-2000kbps, line-rate-2056kbps, line-rate-2064kbps,
line-rate-2120kbps, line-rate-2128kbps, line-rate-2184kbps,
line-rate-2192kbps, line-rate-2248kbps, line-rate-2256kbps,
line-rate-2312kbps, line-rate-2320kbps, line-rate-2368kbps
Default: line-rate-2320kbps
shdsl-transmit-power-back-off
-mode
shdsl-fix-bit-rate Enables or disables automa tic baud rate detection.
26 Z-Edge 64 Configuration Guide
Determines if the transmit power backoff, defined in the SHDSL standard, is
used:
Values:
backoffdisable
backoffenable
Default: backoffenable
Values:
fix-bit-disable This value enables automati c baud rate detec tion. If the CO
and CPE devices have different line rates at startup, the lower of the two rates
will be sele cted.
fix-bit-enable This value is used for static (set) baud rates. This option is
availab l e if th e d ev ic e’s unit-mode is set to co in the dsl-config profile. Th is
value is ignored if the device’s unit-mode is se t to cpe.
Default: fix-bit-disable

Configuring a DSL connec ti on
Parameter Description
shdsl-standard Determines the SHDSL standards .
Values:
annex-a
annex-b
Default: annex-b
shdsl-startup-margin Used to negotiate the bit rate duri ng startup. The amount of margin is
specified in dec ibels (dB) and its value ranges from 0 to 15.
Values:
0 to 15
Default: 6
shdsl-frame-sync Enables the user to s elect a 14-bit frame sync word identifier (FSW).
Values:
shdsl-power-scale Adjusts transmit power in small inc r ements to compensate for minor
From 0 to 65535
Default: 45
differe nces in power between units.
Values:
17664 For loop lengths from 0 to 10 feet (0 to 3.05 meters). Corresponds to
-3.39dB.
20992 For loop lengths less than 4000 feet (1219 meters). Corresponds to
-1.9dB.
29952 For loop lengths greater than 4000 fee t (1219 meters). Correspon ds to
-1.19dB.
Default: 29298
Note: S et both ends (CO and CPE devices) of the G.SHDSL
connection to fix-bit-disable in the shdsl-config profile to ensure
automatic baud rate adapt ion.
Below is an exam ple o f the shdsl-config record created by setting the
line-type parameter to shdsllatest in the dsl-config profile. Update this
profile if you want to change the line rate or to override autobaud.
zSH> update shdsl-config 1-1-1-0/hdsl2
Please provide the following: [q]uit.
shdsl-config-line-rate: -------------> {line-rate-2320kbps}:
shdsl-transmit-power-back-off-mode: -> {backoffenable}:
shdsl-fix-bit-rate: -----------------> {fix-bit-disable}:
shdsl-ntr: --------------------------> {ntr-local-osc}:
shdsl-clock-offset: -----------------> {0}:
shdsl-repeater-id: ------------------> {repeaterdisable}:
shdsl-standard: ---------------------> {annex-b}:
shdsl-startup-margin: ---------------> {6}:
shdsl-wire-mode: --------------------> {four-wire-disable}:
shdsl-frame-sync: -------------------> {45}:
Z-Edge 64 Configuration Guide 27

WAN configuration
shdsl-decoder-coeffA: ---------------> {366}:
shdsl-decoder-coeffB: ---------------> {817}:
shdsl-power-scale: ------------------> {29298}:
....................
Save changes? [s]ave, [c]hange or [q]uit: s
Record updated.
Note: If sdsl-config or shdsl-config profiles exist before setting the
line-type parameter to shdsllatest or sdsllatest in the dsl-config
profile, the parameter settings will not be changed in the sdsl-config
or shdsl-config profiles. You may need to update these profiles to
change the line rate or enable autobaud.
Table 1: Automatic baud rate detection configuration settings
DSL line type setting Fixed bit rate setting Suggested line rates
sdsllatest fix-bit-disable for
both CO and CPE
devices
shdsllatest shdsl-fix-bit-disable
for both CO and CPE
devices
Verifying connection with showlinestatus command
Verify that the DSL connection is operational by enter ing a showlinestatus
command fo r the WAN port. The showlinestatus command uses this syntax:
showlinestatus shelf slot port subport
The following example displays the status of the co nnection on shelf 1, slot 1,
port 1 (the WAN interfa ce):
zSH> showlinestatus 1 1 1
Search in progress .........
.................
GroupId --------> 6
Status ---------> ACTIVE (1)
TxClk ----------> NONE (1)
RefClkSrc ------> NO
If_index -------> 3
Peer If_Index --> 0
Shelf ----------> 1
Slot -----------> 1
Port -----------> 1
SubPort --------> 0
CPE - 2320 kbps
CO - any supported rate
CPE - 2320 kbps
CO - any supported rate
28 Z-Edge 64 Configuration Guide
Now that the WAN connection is active, you can proceed to configure rest of
the system.

SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
3
This chapter details how to configure system-wide settings of the Z-Edge 64.
It includes the following topics:
• System defaults, page 29
• Configuring a connection to the ZMS, page 30
System defaults
When the Z-Edge 64 is turned on, several profiles are automatically
configured. Here are some of the Z-Edge 64 defau lt configurations:
• The Z-Edge 64 is set up as a DHCP client in the ip-interface-record for
the WAN port of the system.
• The Ethernet (LAN) interfa ce is 10/100 Mbps autosensing,
autonegotiating.
• The DSL (WAN) interface is set to SDSL, customer premises equipment,
with a line speed of 1552kbps.
• The Virtual Path Indicator (VPI) and Virtual Channel Identifier (VCI)
values for the W AN interface: VPI/VCI = 0/35.
The Z-Edge 64 automatically creates ip-interface-record, atm-traf-descr
record and atm-vcl profiles for the WAN interface when the Z-Edge 64 is
turned on. Thes e thre e pr o file s enabl e ATM traffic over IP on the WA N por t.
Enter get commands to view these default profiles:
zSH> get ip-interface-record 1-1-1-0/ip
vpi: ---------------> {0}
vci: ---------------> {35}
rdindex: -----------> {1}
dhcp: --------------> {client}
addr: --------------> {0.0.0.0}
netmask: -----------> {0.0.0.0}
bcastaddr: ---------> {0.0.0.0}
destaddr: ----------> {0.0.0.0}
farendaddr: --------> {0.0.0.0}
mru: ---------------> {1500}
reasmmaxsize: ------> {0}
ingressfiltername: -> {}
egressfiltername: --> {}
Z-Edge 64 Configuration Guide 29

System configur ation
pointtopoint: ------> {no}
mcastenabled: ------> {yes}
ipfwdenabled: ------> {yes}
mcastfwdenabled: ---> {yes}
natenabled: --------> {no}
bcastenabled: ------> {yes}
ingressfilterid: ---> {0}
egressfilterid: ----> {0}
ipaddrdynamic: -----> {dhcpclient}
dhcpserverenable: --> {false}
zSH> get atm-traf-descr 1
td_type: -------------> {atmNoClpNoScr}
td_param1: -----------> {3659} this is the peak cell rate (PCR)
td_param2: -----------> {0}
td_param3: -----------> {0}
td_param4: -----------> {0}
td_param5: -----------> {0}
td_service_category: -> {ubr}
trnk-vcl-rate: -------> {unused}
zSH> get atm-vcl 1-1-1-0-hdsl2/atm/0/35
vpi: -----------------------------> {0}
vci: -----------------------------> {35}
admin_status: --------------------> {up}
receive_traffic_descr_index: -----> {1}
transmit_traffic_descr_index: ----> {1}
vcc_aal_type: --------------------> {aal5}
vcc_aal5_cpcs_transmit_sdu_size: -> {9188}
vcc_aal5_cpcs_receive_sdu_size: --> {9188}
vcc_aal5_encaps_type: ------------> {llcencapsulation}
vcl_cast_type: -------------------> {p2p}
vcl_conn_kind: -------------------> {pvc}
fault-detection-type: ------------> {disabled}
The Z-Edge 64 uses DHCP to obtain configuration pa rameters, such as an IP
address, from a DHCP server. To act a s a DHCP c lient, the Z-Edge 64 must be
connected to the DHCP server over an active WAN connection. Set up the
WAN connection and the DHCP client configuration will occur as set up on
the DHCP server.
Configuring a connection to the ZMS
Note: Most of the parameters in the system profile should be left at
their default values. ZMS uses them to update status of the
configuration process.
The system profile is automatically created. The following parameter in the
system profile determines whether authentication failure traps are sent to
ZMS:
30 Z-Edge 64 Configuration Guide
 Loading...
Loading...