Page 1
SERVICE MANUAL
Model Series:
Product Type: Projection TV
Chassis:ZP94/ZP95
Manual Series:PV152
Manual Part #:923-03439
Model Line:C
Product Year:2000
General Information.......................................1
Servicing/Troubleshooting..............................2
Circuit Description......................................... 3
Model Parts Lists..........................................4
Exploded Views.............................................5
PCB Layouts
Schematics
................................................
..................................................67
IQC60H94W
IQC50H94W
IQC60H95W
IQC50H95W
CONTENTS
Printed in U.S.A.
ZP DG 4.3k
Published by Technical Publications
Zenith Electronics Corporation
201 James Record Road - Huntsville, Alabama 35824-1513
ÓCopyright July 2000 by Zenith Electronics Corporation
Page 2

PRODUCT SAFETY SERVICING GUIDELINES FOR AUDIO-VIDEO PRODUCTS
A.C. Voltmeter
10 WATT
Place this probe
on each exposed
IMPORTANT SAFETY NOTICE
This manual was prepared for use only by properly trained audio-visual service
technicians.
When servicing this product, under no circumstances should the original
design be modified or altered without permission from Zenith Electronics
Corporation. All components should be replaced only with types identical to
those in the original circuit and their physical location, wiring and lead dress
must conform to original layout upon completion of repairs.
Special components are also used to prevent x-radiation, shock and fire hazard.
These components are indicated by the letter “x” included in their component
designators and are required to maintain safe performance. No deviations are
allowed without prior approval by Zenith Electronics Corporation.
Circuit diagrams may occasionally differ from the actual circuit used. This way,
implementation of the latest safety and performance improvement changes into
the set is not delayed until the new service literature is printed.
CAUTION: Do not attempt to modify this product in any way. Never perform
customized installations without manufacturer’s approval. Unauthorized
modifications will not only void the warranty, but may lead to property damage
or user injury.
Service work should be performed only after you are thoroughly familiar with
these safety checks and servicing guidelines.
GRAPHIC SYMBOLS
The exclamation point within an equilateral triangle is intended
to alert the service personnel to important safety information in
the service literature.
The lightning flash with arrowhead symbol within an equilateral
triangle is intended to alert the service personnel to the presence
of noninsulated “dangerous voltage” that may be of sufficient
magnitude to constitute a risk of electric shock.
The pictorial representation of a fuse and its rating within an
equilateral triangle is intended to convey to the service personnel
the following fuse replacement caution notice:
CAUTION: FOR CONTINUED PROTECTION AGAINST RISK OF FIRE,
REPLACE ALL FUSES WITH THE SAME TYPE AND RATING AS MARKED
NEAR EAch FUSE.
SERVICE INFORMATION
While servicing, use an isolation transformer for protection from AC line shock.
After the original service problem has been corrected, make a check of the
following:
FIRE AND SHOCK HAZARD
1. Be sure that all components are positioned to avoid a possibility of
adjacent component shorts. This is especially important on items transported to and from the repair shop.
2. Verify that all protective devices such as insulators, barriers, covers,
shields, strain reliefs, power supply cords, and other hardware have been
reinstalled per the original design. Be sure that the safety purpose of the
polarized line plug has not been defeated.
3. Soldering must be inspected to discover possible cold solder joints, solder
splashes, or sharp solder points. Be certain to remove all loose foreign
particles.
4. Check for physical evidence of damage or deterioration to parts and components, for frayed leads or damaged insulation (including the AC cord), and
replace if necessary.
5. No lead or component should touch a receiving tube or a resistor rated at
1 watt or more. Lead tension around protruding metal surfaces must be
avoided.
6. After reassembly of the set, always perform an AC leakage test on all exposed
metallic parts of the cabinet (the channel selector knobs, antenna terminals,
handle and screws) to be sure that set is safe to operate without danger of
electrical shock. DO NOT USE A LINE ISOLATION TRANSFORMER DURING THIS
TEST. Use an AC voltmeter having 5000 ohms per volt or more sensitivity in
the following manner: Connect a 1500 ohm, 10 watt resistor, paralleled by
a .15 mfd 150V AC type capacitor between a known good earth ground
water pipe, conduit, etc.) and the exposed metallic parts, one at a time.
Measure the AC voltage across the combination of 1500 ohm resistor and
.15 mfd capacitor. Reverse the AC plug by using a non-polarized adaptor
and repeat AC voltage measurements for each exposed metallic part. Voltage
measured must not exceed 0.75 volts RMS. This corresponds to 0.5 milliamp
AC. Any value exceeding this limit constitutes a potential shock hazard and
must be corrected immediately.
Good Earth Ground
such as the Water
Pipe, Conduit, etc.
X-RADIATION
1. Be sure procedures and instructions to all service personnel cover the
subject of x-radiation. The only potential source of x-rays in current TV
receivers is the picture tube. However, this tube does not emit x-rays when
the HV is at the factory-specified level. The proper value is given in the
applicable schematic. Operation at higher voltages may cause a failure of
the picture tube or high-voltage supply and, under certain circumstances
may produce radiation in excess of desirable levels.
2. Only factory-specified CRT anode connectors must be used.
3. It is essential that the service personnel have available an accurate and
reliable high-voltage meter.
4. When the high-voltage circuitry is operating properly, there is no possibility
of an x-radiation problem. Every time a color Chassis is serviced, the
brightness should be run up and down while monitoring the high voltage
with a meter, to be certain that the high voltage does not exceed the
specified value and that it is regulating correctly.
5. When troubleshooting and making test measurements in a product with a
problem of excessively high voltage, avoid being unnecessarily close to
the picture tube and the high voltage power supply. Do not operate the
product longer than necessary to locate the cause of excessive voltage.
6. Refer to HV, B+, and shutdown adjustment procedures described in the
appropriate schematics and diagrams (where used).
IMPLOSION
1. All direct view picture tubes are equipped with an integral implosion
protection system; take care to avoid damage during installation.
2. Use only the recommended factory replacement tubes.
TIPS ON PROPER INSTALLATION
1. Never install any receiver in a closed-in recess, cubbyhole, or closely
fitting shelf space over, or close to, a heat duct, or in the path of heated
air flow.
2. Avoid conditions of high humidity such as: outdoor patio installations
where dew is a factor, near steam radiators where steam leakage is a factor,
etc.
3. Avoid placement where draperies may obstruct venting. The customer
should also avoid the use of decorative scarves or other coverings that
might obstruct ventilation.
4. Wall- and shelf-mounted installations using a commercial mounting kit
must follow the factory-approved mounting instructions. A product mounted
to a shelf or platform must retain its original feet (or the equivalent
thickness in spacers) to provide adequate air flow across the bottom. Bolts
or screws used for fasteners must not touch any parts or wiring. Perform
leakage tests on customized installations.
5. Caution customers against mounting a product on a sloping shelf or in a
tilted position, unless the receiver is properly secured.
6. A product on a roll-about cart should be stable in its mounting to the cart.
Caution the customer on the hazards of trying to roll a cart with small
casters across thresholds or deep pile carpets.
7. Caution customers against using a cart or stand that has not been listed
by Underwriters Laboratories, Inc. for use with its specific model of
television receiver or generically approved for use with TVs of the same or
larger screen size.
8. Caution customers against using extension cords. Explain that a forest of
extensions, sprouting from a single outlet, can lead to disastrous
consequences to home and family.
0.15uF
1500 OHM
metal part.
PV152 PRO1200 - SAFETY
i
Page 3
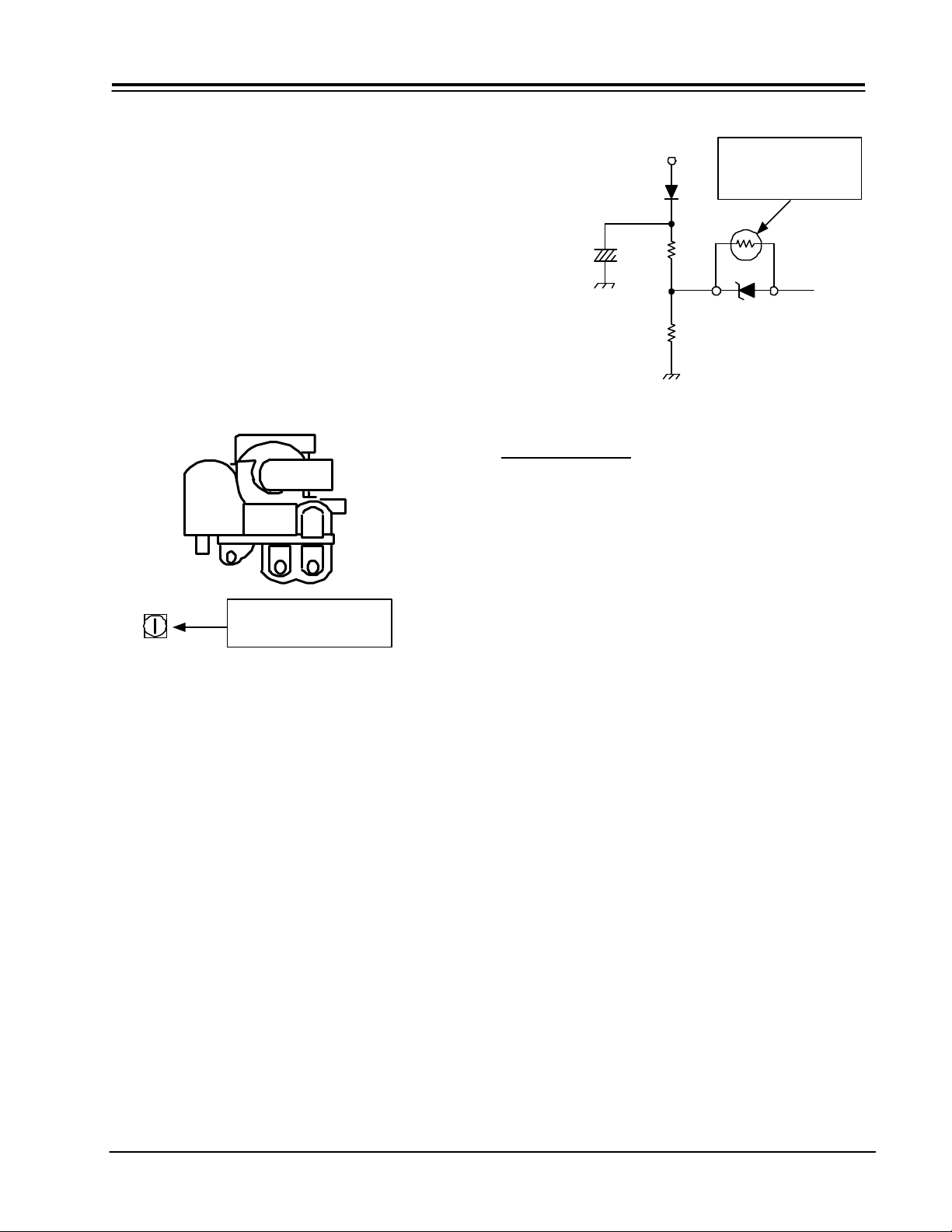
PRODUCT SAFETY SERVICING GUIDELINES FOR AUDIO-VIDEO PRODUCTS
CHASSIS HIGH VOLTAGE ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURE
1. Connect High Voltage meter to FBT High Voltage output. Connect Ground of High Voltage meter to CRT
Ground or FBT Ground.
2. Check that the High Voltage adjustment VR (RH44) is
set to it’s mechanical center on the Deflection PWB.
This VR is located just behind the Flyback transformer
as viewed from the Front of the set. (See diagram below)
3. Receive an NTSC generator signal. (Picture should be
stationary for this adjustment.
4. Video Controls should be set to Factor Settings.
5. Adjust the High Voltage to the following specifications by turning RH44 slowly.
6. Lock Paint the control. If available.
TH01
FBT
RH44
High Voltage ADJ.
+50V Pulse
Add JIG to check Hi
Volt Limit Circuit
JIG = 1k ohm 1/8W
CH30
DH24
RH54
DH31
RH55
Checking Procedure :
1. Check that the picture is turned off and the horizontal deflection circuit stops operation.
After Checking:
1. Unplug set and Remove Jig. Allow set to remain in the
off condition for at least 15 seconds.
2. Apply AC and confirm the set returns to normal operation.
CHASSIS HIGH VOLTAGE LIMITER CHECK
Check Preparation:
1. The set can face any direction.
2. Receive the Cross-Hatch Signal
3. VIDEO CONTROLS: Brightness to Maximum.
4. SCREEN FORMAT: Should be PROGRESSIVE mode.
5. Attach the JIG (1k ohm 1/8W resistor) to both ends
of DH31 as shown in the diagram below. (See Diagram
Below)
CHASSIS FLYBACK PROTECTION CIRCUIT CHECK
Check Preparation:
1. The set can face any direction.
2. Receive the Cross-Hatch Signal
3. VIDEO CONTROLS: Factory Preset.
4. SCREEN FORMAT: Should be PROGRESSIVE mode.
5. Attach a 100 K ohm 1/16W ~ 1/8W resistor between
QP02 base and Gnd. (SD4 connector Pin 4) and check
operation.
After Checking:
1. Unplug set and Remove Jig. Allow set to remain in the
off condition for at least 15 seconds.
2. Apply AC and confirm the set returns to normal operation.
PV151 PROJO
ii
Page 4
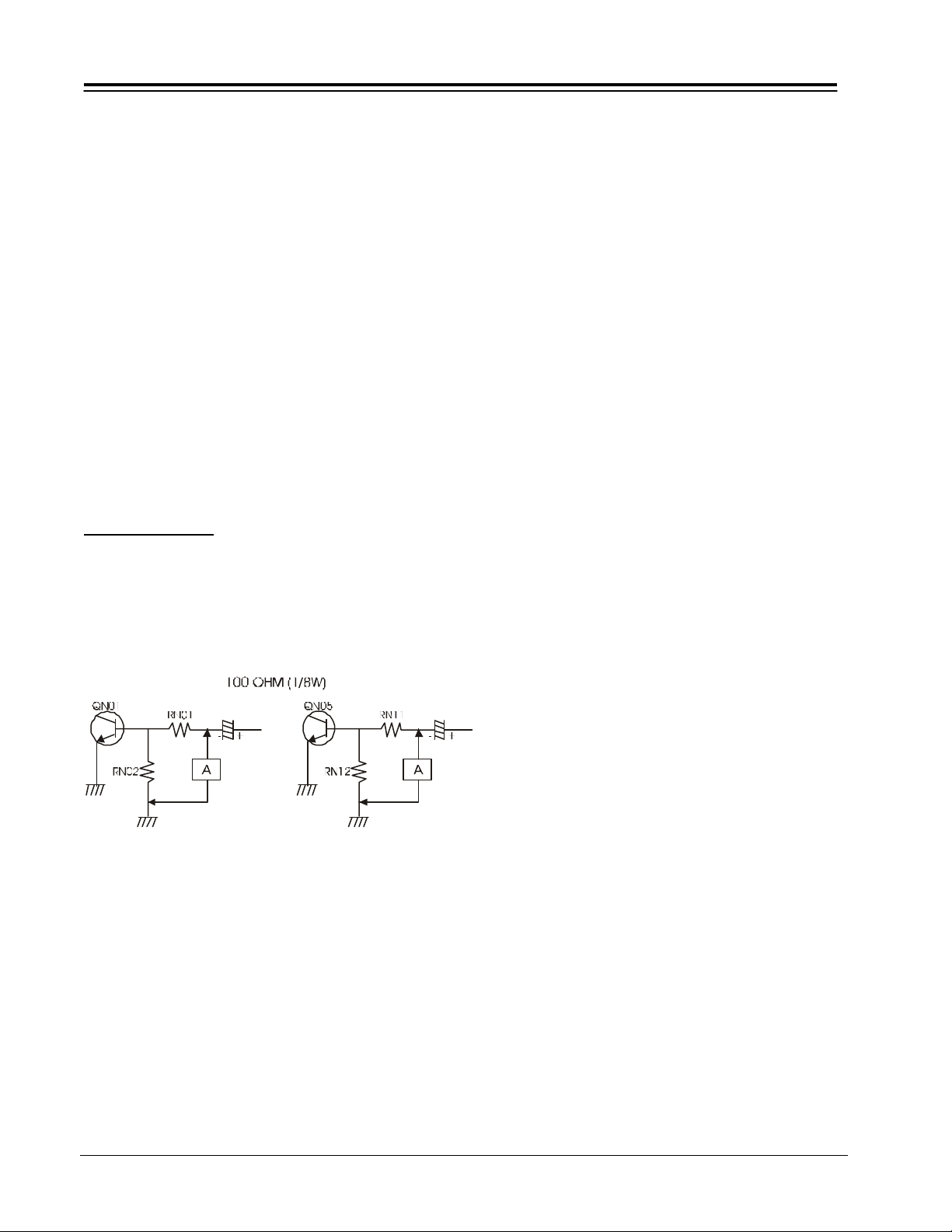
PRODUCT SAFETY SERVICING GUIDELINES FOR AUDIO-VIDEO PRODUCTS
CN04
CHASSIS SWEEP LOSS DETECTION CIRCUIT CHECK
Check Preparation:
Check Number (1):
1. The set can face any direction.
2 Receive the Cross-Hatch Signal
3. VIDEO CONTROLS: Factory Preset.
4. SCREEN FORMAT: Should be PROGRESSIVE mode.
5. Attach the JIG (A) (100 ohm 1/8W resistor) to right
hand side of RN01 and to Ground as shown in the
diagram below.
Check Number (2):
1. The set can face any direction.
2. Receive the Cross-Hatch Signal
3. VIDEO CONTROLS: Factory Preset.
4. SCREEN FORMAT: Should be PROGRESSIVE mode.
5. Attach the JIG (B) (100 ohm 1/8W resistor) to right
hand side of RN11 and to Ground as shown in the
diagram below.
Checking Procedure :
1. Check that the picture is turned off in either check.
After Checking:
1. Remove Jig after each check.
2. Confirm the set returns to normal operation.
CN01
PV151 PROJO
iii
Page 5

TABLE OF CONTENTS
SECTION 1 GENERAL INFO / REMOTE CONTROL
CAUTIONS FOR HV CONNECTOR ................................. 1-1
SPECIFICATIONS .................................................... 1-2
GENERAL INFORMATION ........................................... 1-3
REMOTE ..............................................................1-4
REMOTE CODES ..................................................... 1-5
CUSTOMER AUDIO/VIDEO ADJUSTMENT ........................ 1-7
CUSTOMER CONVERGENCE ADJUSTMENT ....................... 1-9
SECTION 2 SERVICING
SERVICE MENUES .............................................. 2-1
SERVICE ADJUSTMENT ORDER .................................. 2-6
MEMORY INITIALIZATION ........................................ 2-7
PRE HEAT .............................................. 2-7
CUT OFF ADJUSTMENT ............................................ 2-7
PRE FOCUS ADJUSTMENT ........................................ 2-7
DCU PHASE ADJUSTMENT (COARSE) ........................... 2-9
HORIZONTAL PHASE ADJUSTMENT .............................. 2-9
RASTER INCLINATION ............................................. 2-9
BEAM ALIGNMENT .............................................. 2-10
VERT/HORIZ POSITION ADJUSTMENT ........................... 2-10
HORIZONTAL SIZE ADJUSTMENT ................................ 2-11
VERTICAL SIZE ADJUSTMENT .................................... 2-11
BEAM FORM ADJUSTMENT ....................................... 2-11
LENS FOCUS ADJUSTMENT ....................................... 2-12
STATIC FOCUS ADJUSTMENT ..................................... 2-12
BLUE DEFOCUS ADJUSTMENT ................................... 2-12
WHITE BALANCE ADJUSTMENT .................................. 2-13
SUB BRIGHT ADJUSTMENT ....................................... 2-14
HORIZONTAL POSITION ADJUSTMENT (FINE).................. 2-14
DIGITAL CONVERGENCE ADJUSTMENT .......................... 2-14
DIGITAL CONVERGENCE REMOTE ................................ 2-15
CONVERGENCE POINT ADJUSTMENT ............................ 2-16
CONVERGENCE 3X3 ADJUSTMENT ............................... 2-17
CONVERGENCE 7X5 ADJUSTMENT ............................... 2-17
CONVERGENCE 13X9 ADJUSTMENT ............................. 2-17
TROUBLE SHOOTING .............................................. 2-19
ZP 94/95 SIGNAL TOP PCB LAYOUT ............................ 6-3
ZP 94/95 SIGNAL BOTTOM PCB LAYOUT ....................... 6-4
ZP 94/95 SWITCH MODE POWER TOP PCB LAYOUT ........... 6-5
ZP 94/95 SWITCH MODE POWER BOTTOM PCB LAYOUT ..... 6-6
ZP 94/95 CPT TOP PCB LAYOUT ................................. 6-7
ZP 94/95 CPT BOTTOM PCB LAYOUT ........................... 6-8
ZP 94/95 SRS AUDIO TOP PCB LAYOUT ....................... 6-9
ZP 94/95 SRS AUDIO BOTTOM PCB LAYOUT .................. 6-10
ZP 94/95 JACKPACK TOP PCB LAYOUT ......................... 6-11
ZP 94/95 JACKPACK BOTTOM PCB LAYOUT .................... 6-12
ZP 94/95 CONTROL PANEL TOP PCB LAYOUT .................. 6-13
ZP 94/95 CONTROL PANEL BOTTOM PCB LAYOUT ........... 6-14
ZP 94/95 VELOCITY MODULATOR AND SUB TOP
PCB LAYOUT ............................... 6-15
ZP 94/95 VELOCITY MODULATOR AND SUB BOTTOM
PCB LAYOUT ............................... 6-16
ZP 94/95 YC & COMB FILTER TOP PCB LAYOUT ............... 6-17
ZP 94/95 YC & COMB FILTER BOTTOM PCB LAYOUT ......... 6-18
SECTION 7 SCHEMATICS
ZP 94/95 MICRO PWB CIRCUIT .................................. 6-1
ZP 94/95 SIGNAL INTERCONNECT CIRCUIT .................... 6-2
ZP 94/95 TUNER IF CIRCUIT ..................................... 6-3
ZP 94/95 POWER SUPPLY PWB CIRCUIT ....................... 6-4
ZP 94/95 DEFLECTION CIRCUIT ................................. 6-5
ZP 94/95 CONVERGENCE POWER SUPPLY ...................... 6-6
ZP 94/95 REGISTRATION / CONVERGENCE CORRECT PWB ... 6-7
ZP 94/95 JACKPACK / TERMINAL DIAGRAM ................... 6-8
ZP 94/95 2 LINE COMB FILTER CIRCUIT ....................... 6-9
ZP 94/95 CHROMA / LUMMA CIRCUIT ......................... 6-10
ZP 94/95 VELOCITY MODULATOR PWB CIRCUIT ............... 6-11
ZP 94/95 CRT PWB CIRCUIT ..................................... 6-12
ZP 94/95 AUDIO MATRIX / CONTROL PANEL PWB ............ 6-13
SECTION 3 CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
POWER SUPPLY OPERATION ...................................... 3-1
TURNING ON THE DEFLECTION POWER SUPPLY ............... 3-2
POWER SUPPLY SHUTDOWN EXPLANATION .................... 3-3
ABL CIRCUIT .............................................. 3-4
MICRO PROCESSOR DATA COMMUNICATION ................... 3-5
SECTION 4 PARTS LIST
MODEL PARTS .............................................. 4-1
SECTION 5 DIAGRAMS
ZP 94/95 EXPLODED VIEW....................................... 5-1
ZP 94/95 EXPLODED VIEW FRONT .............................. 5-2
ZP 94/95 EXPLODED BACK ...................................... 5-3
ZP 94/95 INTERCONNECT ........................................ 5-4
ZP 94/95 WIRING DIAGRAM ..................................... 5-5
SECTION 6 PCB LAYOUTS
ZP 94/95 DEFLECTION TOP PCB LAYOUT ...................... 6-1
ZP 94/95 DEFLECTION BOTTOM PCB LAYOUT ................. 6-2
PV152 TOC PROJO
Page 6
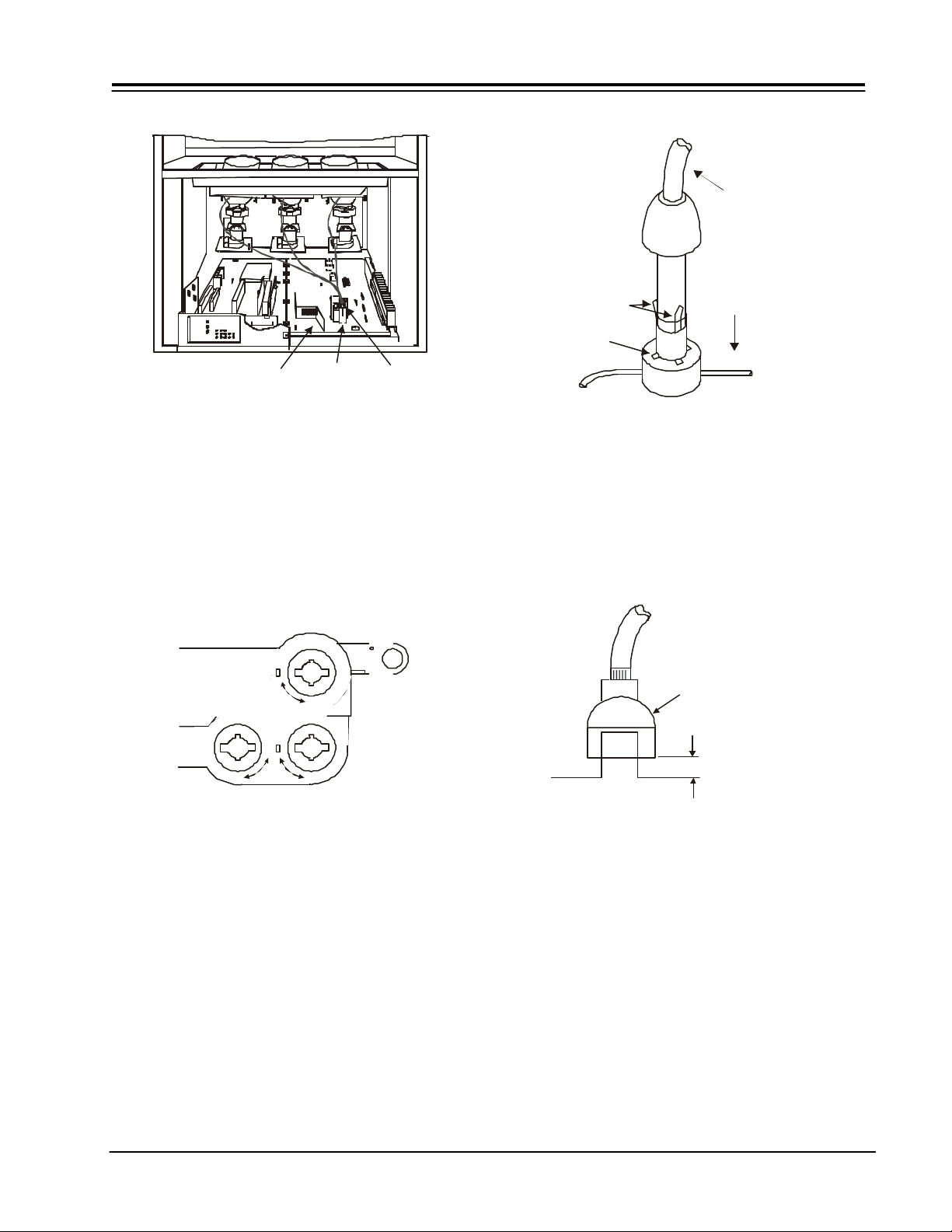
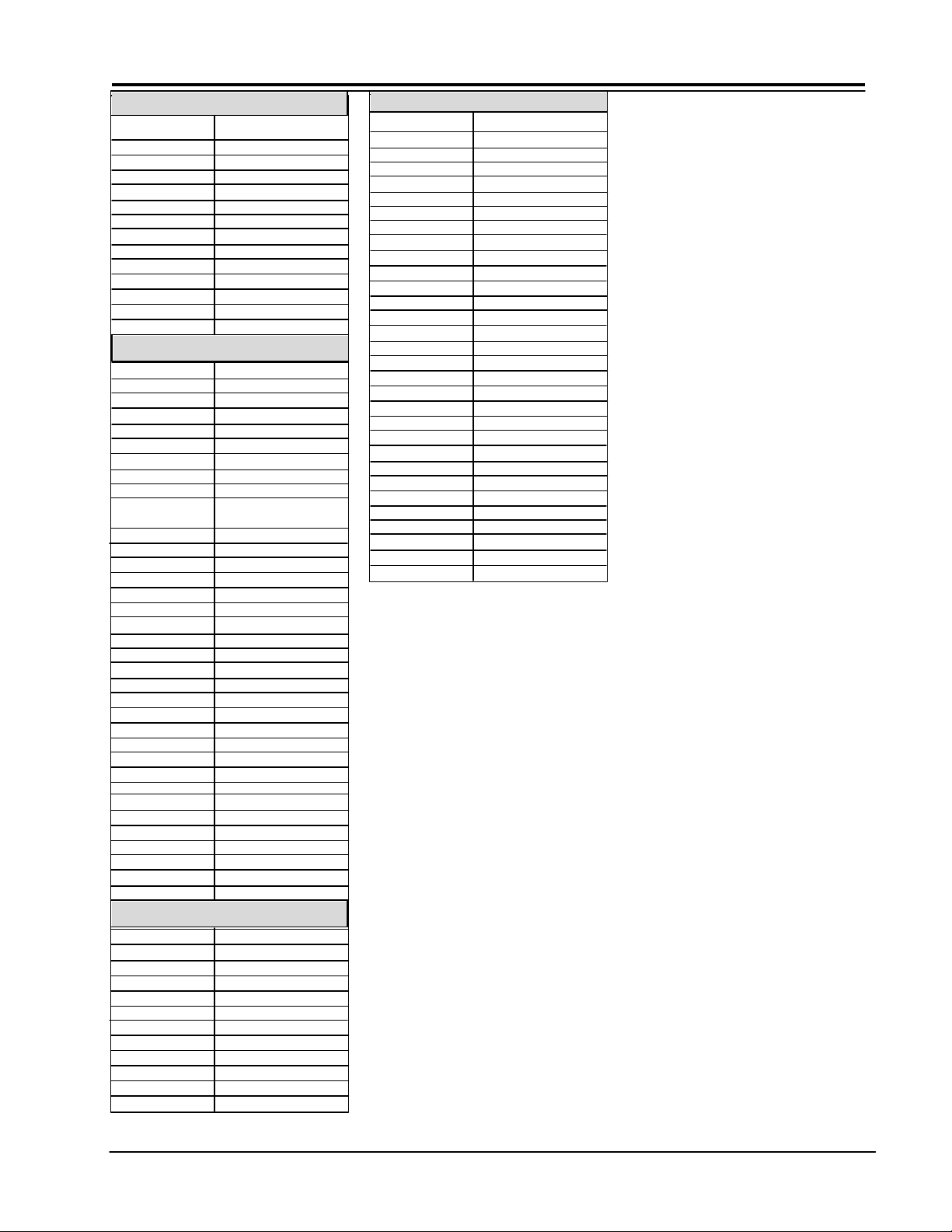
CAUTIONS WHEN CONNECTING / DISCONNECTING THE HV CONNECTOR
FIG. A
HV Cable
POSITION
FIG. B
Boot Assembly
LESS THAN 1mm
DEFLECTION
FBT
ANODE
CONNECTOR
FlybackTAB
P.W.B
Perform the following when the HV connector (anode
connector) is removed or inserted for CPT replacement,
etc.
PUSH
PUSH
During Removal
1. Roll out silicon cover from FBT’s contact area slowly.
2. While turning the connector about 90 degrees following the arrow
(0 position). Push the connector slightly toward the case. (Fig. A)
3. Remove the connector slowly by pulling it away from the case.
HV Cable &
Flyback
During Insertion
1. Please refer to direction for insertion as shown in Fig. B (L position).
Insert connector until “CLICK” sound is heard.
2. Make sure the connector is pressed right in, so that it has a good
contact with the spring.
3. Confirm the contact by pulling the connector slightly. (Don’t pull
hard because it may damage the connector).
4. Cover the high voltage output by carefully pushing silicon boot
onto it. (Don’t turn the connector).
Note: Make sure the silicon boot is covering the high
voltage output.
PV151 1-1 PROJO
Page 7
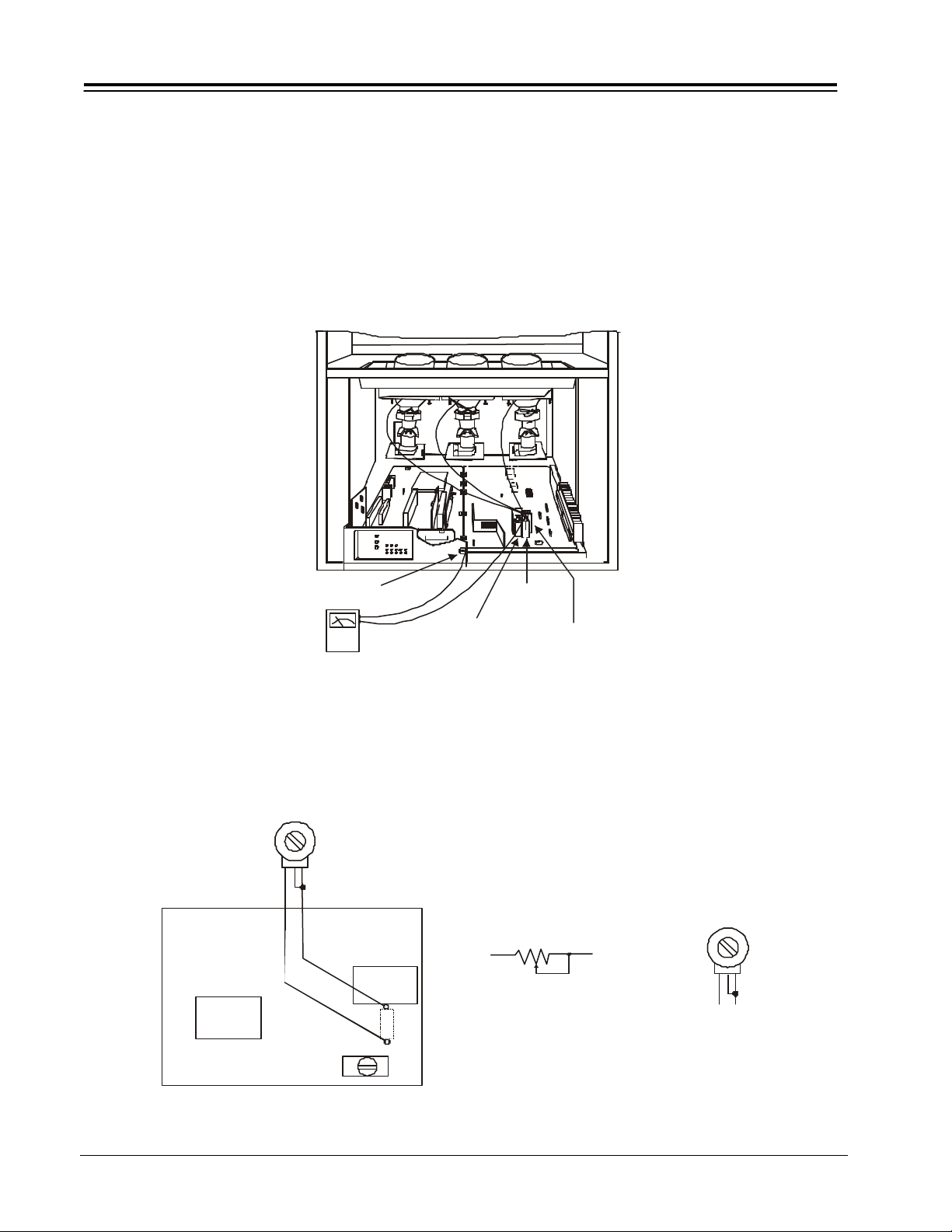
TECHNICAL CAUTIONS
SECTION 1
High Voltage
FBT)(TH01
Defelection
H.V. Meter
Remove 80 and connect 50K Ohm jig as shown
High Voltage limiter circuit check
1. Turn off TV and connect jig as shown in Figure 2.
Adjust jig fully counter clockwise for minimun
resistance.
2. Set the AC input to 120V AC and turn on TV.
3. Confirm test pattern on CRT is a usable picture, then
slowly adjust jig until the picture disappears and TV
shuts down.
4. When the limiter circuit is operating properly, Voltage
will be less than 36.5kV at 0.6mA when TV shuts down.
5. Turn off set immediately after checking circuit operations.
6. Unplug set for one minute to reset shutdown circuit.
Remove jig and voltmeter.
TP91
Chassis Ground
High Impedance
Figure 2. Deflection/Power PCB
FBT
RH80
P.W.B.
RH
Connector
50K Ohm VR
JIG
POWER/DEFLECTION PWB
PV151 1-2 PROJO
RH44
Page 8
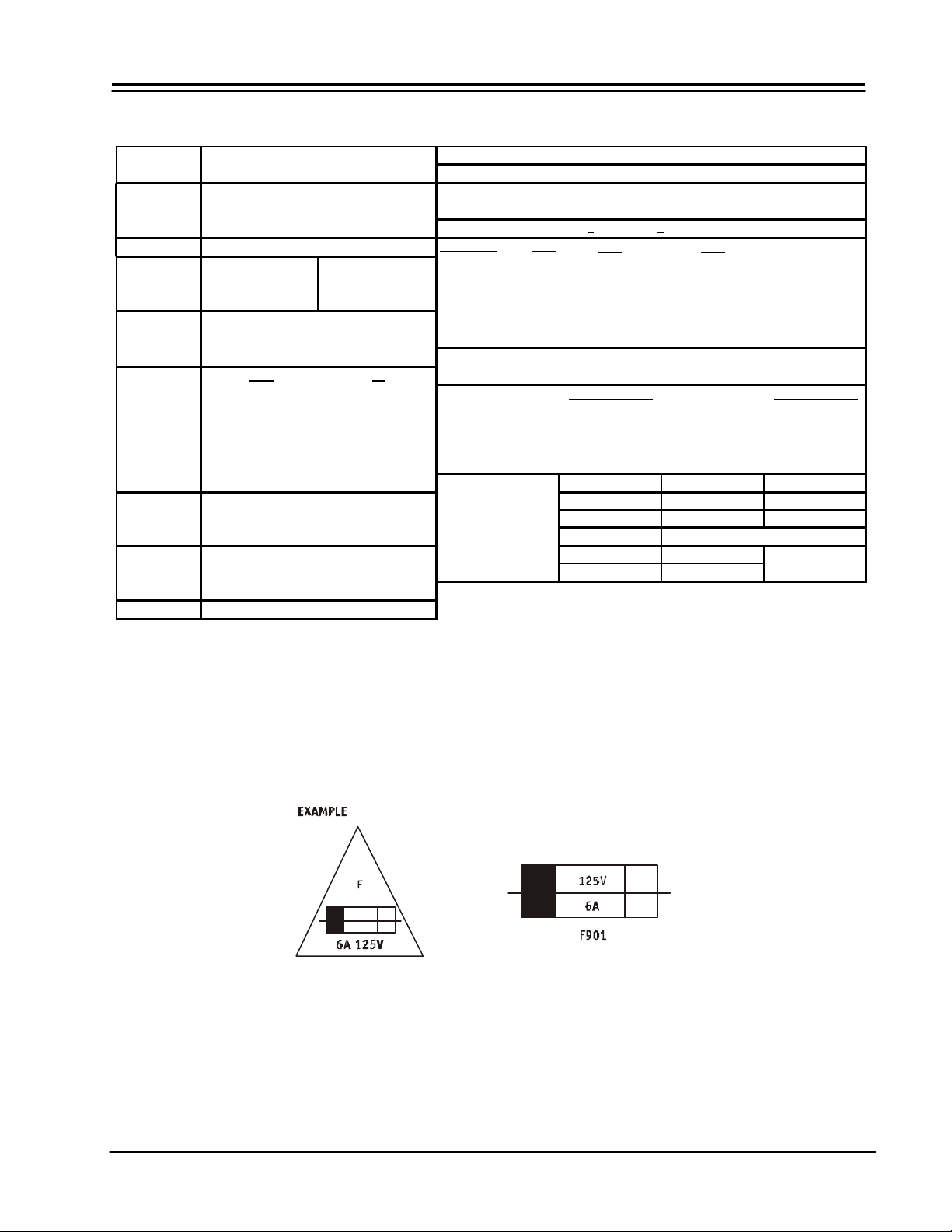
SPECIFICATIONS FOR 94 & 95 SERIES MODELS
ZP94
ZP95
Model:
Cathode-Ray
Tube:
Power Input 120 Volt AC, 6OHz
Power
Consumption:
Antenna
Impedence:
Receiving
Channel:
Intermediate
Frequency:
Video Input:
Video Output: 1 Volt p-p, 75 Ohm
IQC60H95W IQC50H95W Audio Input: 470 mVrms, 47 k Ohm
IQC60H94W IQC50H94W Stereo Audio Output: 470 mVrms, 1 k Ohm
R=P16LFM00RFA(LU) Front- 12 Watt at 10% distortion, 8 Ohm Imp.
G=P16LFM00HHA(LU) Max Output - 15 Watt
B=P16LFM00BMB(EU) Anode Voltage:
224 Watts - Maximum
192 Watts - Operating 206 Watts - Operating
75ohm Unbalanced
VHF / UHF / CATV 2 woofers - 5 Inch
BAND CH (12 cm) Round
VHF 2-13 Dimension: 50" Series Models 60" Series Models
UHF 14-69 Height 52 60 1/2
EXT. Mid (A-5)~(A-1), 4+ Width 43 1/5 51 1/2
CATV Mid A~I Depth 23 1/2 26 1/2
CATV Super J~W Weight
CATV Hyper (W+1) (W+28) Power Supply P.W.B. C.P.T. (B) P.W.B Control P.W.B
Picture I-F Carrier 45.75 MHz VM P.W.B. C.P.T. (G) P.W.B. Sensor Dist. P.W.B.
Sound I-F Carrier 41.25 MHz Surround P.W.B. C.P.T. (R) P.W.B. Sub Deflect. P.W.B
Color Sub Carrier 42.17 MHz Signal P.W.B. Power/Deflection P.W.B.
1 Volt p-p, 75 Ohm Audio Out P.W.B. Control P.W.B.
1 Volt p-p, 75 Ohm (Y) 2H P.W.B. Terminal P.W.B.
07. Volt p-p, 75 Ohm, (Cb, Cr)
Audio Output Power:
30.0 + 1.5kv (1.27 + 0.2ma)
Brightness Size
232 Watts - Maximum Full White 50" 130 130
Brightness Max 60"
Speakers:
Circuit Board
Assemblies:
ZP94 ZP95
100 100
CIRCUIT PROTECTION
CAUTION: Below is an EXAMPLE only. See Replacement Parts List for details. The following symbol near the fuse
indicates fast operation fuse (to be replaces). Fuse ratings appear within the symbol.
The rating of fuse F901 is 6.0A - 125V.
“RISK OF FIRE - REPLACE FUSE AS MARKED”
PV151 1-3 PROJO
Replace with the same type fuse for continued
protection against fire.
Page 9
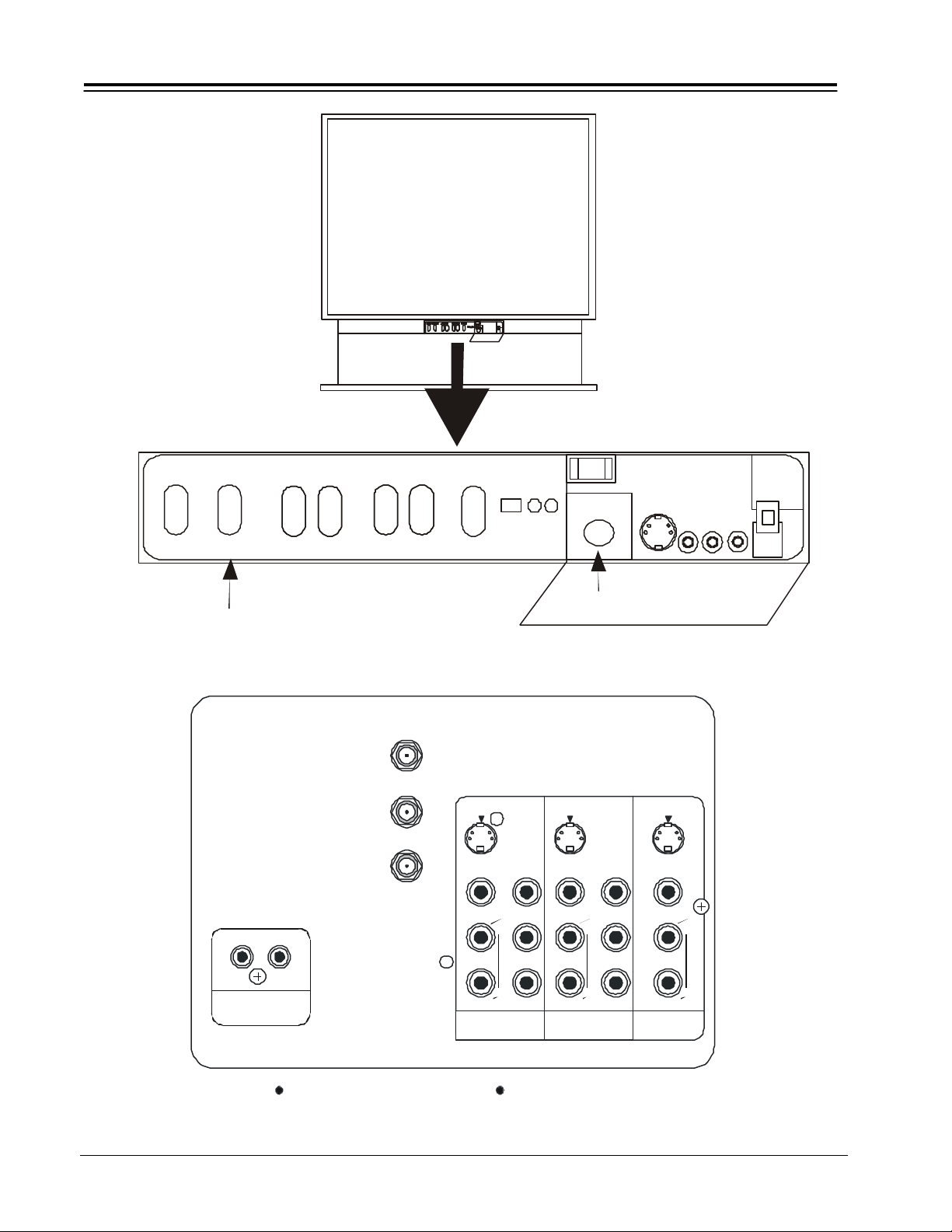
GENERAL INFORMATION
-CHANNEL+
DIGITAL
Source Selector
DIGITAL CONVERGENCE
S-VIDEO
VIDEO
(MONO
)
AUDIOINPUT1INPUT2LRS-VIDEOMONITOROUTY
PBP
R
ANT
B
VIDEO
(MONO
)
AUDIORS-VIDEOVIDE
O
(MONO
)
AUDIOLRS-VIDEOY
PBP
R
MENU
SOURCE
SOURCE
EXIT
TV / VIDEO
-VOLUME+
65
POWER
65
Figure 3. Control Panel
ANT A
To
Converter
SETUP
SETS ONLY
VIDEO
LEFT
AUDIO
RIGHT
AUDIO
PV151 1-4 PROJO
R
A UDIO
TO HI-FI
L
Figure 4. Rear Connection Panel
Page 10
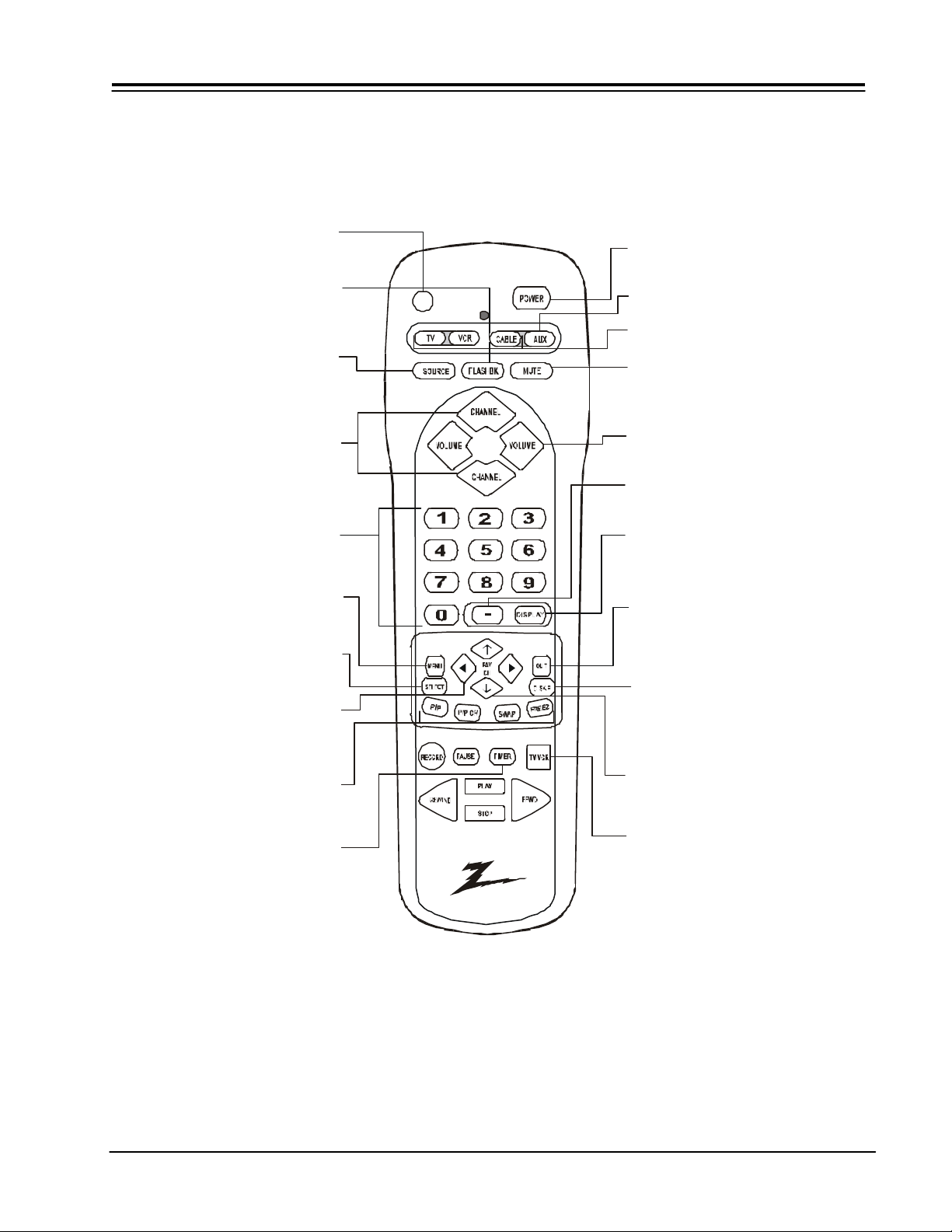
REMOTE CONTROL MODEL MBR3475Z
Selects the remote's mode of operation
Increases / Decreases TV’s sound
level.
QUIT
MBR3475Z
924-10092
C. SKIP
AUX
Auxilliary equipment control
Channel Skip. Tunes Entertainment
Machine to last channel viewed. Tunes
back to original channel after 30, 60,
HELP
PIP MODE
Activates the on-screen help feature.
FLASHBK (Flashback)
Returns to previous Channel.
SOURCE
Signal Source
CHANNEL (Up/Down)
Selects next channel in
TV’s memory. Press
and hold to repeat.
NUMBER PAD
Selects channels directly.
MENU
Displays menus for TV
and other options.
SELECT
POWER
Turns TV On or Off.
MODE
MUTE
Turns sound Off and On
while picture remains.
VOLUME (Left/Right)
Changes PIP Mode
DISPLAY
Shows Channel/Time, enters
channel, or removes any
on-screen menus.
Leaves programming menus
and clear screen of display.
LEFT/RIGHT ARROWS
Chooses and shows the
desired menu option.
PIP KEYS
Special features of some TV’s
TIMER
Press repeatedly to set desired
TV shut-off time.
90, 120, 150, or 180 seconds.
.
UP and DOWN ARROWS
Moves highlighted bar within
menu to select an option.
TV/VCR SOURCE
Steps through source options.
Remote Control Part Number.
PV151 1-5 PROJO
Page 11

PROGRAMMING CODES
Adventura 00
Aiko 08
Aiwa 00
Akai 01, 48, 49
American High 22
Asha 45
Audiovox 23
Beaumark 45
Bell & Howell 32
Brandt 43
Broksonic 33, 34, 42, 42, 52
Calix 23
Canon 22
Capehart 06
Carver 31
CCE 08, 30
Citizen 08, 23
Colt 30
Craig 18, 23, 30, 45
Curtis Mathis 01, 22, 47
Cybernex 45
Daewoo 06, 08, 16, 38, 50
Daytron 06
Dynatech 00
Electrohome 23
Electrophonic 23
Emerx 07
Emerson 00, 08, 12, 15, 23, 27,
28, 33, 34, 37, 42, 48,
51, 52
Fisher 18, 20, 32, 46
Fuji 09, 22
Funai 00
Garrad 00
General Electric 03, 22, 41, 47
Goldstar 23, 24, 44
Gradiente 00
Harley Davidson 00
Harman / Kardon 24
Harwood 30
Headquarter 17
Hi-Q 18
Hitachi 01, 02, 03, 04
Jensen 01
JVC 01, 13, 26
KEC 08, 23
Kenwood 01, 24, 26
KLH 30
Kodak 22, 23
Lloyd 00
Lloyd’s 27
Logik 30
LXI 23
Magnavox 14, 2, 29, 31, 35
Magin 45
Marantz 22, 3
Marta 23
Matsushita 22
MEI 22
Memorex 00, 14, 17, 18, 19, 22,
23, 32, 45
MGA 15, 48
MGN Tech 45
Minolta 02, 04
Mitsubishi 15, 26, 40, 48, 49
Motorola 19, 22
MTC 00, 45
Multitech 00, 30
VCRS (continued)VCRS
NEC 01, 05, 24, 26, 32
Nikko 23
Noblex 45
Olympus 11, 22
Optimus 19, 23, 32
Orion 51
Panasonic 10, 11, 22, 39, 53
Penny 02, 05, 22, 23, 24, 45,
46
Pentax 02, 03, 04
Philco 22
Philips 20, 29, 31
Pilot 23
Pioneer 26
Portland 06
Protec 30
Pulsar 14
Quarter 17
Quartz 17
Quasar 22
Radio Shack 00, 23
Radix 23
Randex 23
RCA 02, 03, 04, 35, 41, 47
Realistic 00, 17, 18, 19, 20, 22,
23, 32, 45
Ricoh 21
Runco 14
Samsung 16, 45
Sanky 14, 19
Sansui 01, 26
Sanyo 17, 18, 32, 45
Scott 15, 16, 33, 34, 37, 42
Sears 02, 04, 17, 18, 20, 22,
23, 32, 46
Sharp 19
Shintom 30
Shogun 45
Shinger 30
Sony 07, 09, 21, 22
STS 02
Sylvania 00, 15, 22, 29, 31
Symphonic 00
Tatung 01
Teac 00, 01
Technics 22, 39
Teknika 00, 22, 23
Telefunken 43
THK 27, 45
Toshiba 15, 16, 20, 37
Totevision 23, 45
Unitech 45
Vector 16
Vector Research 05, 24
Video Concepts 05, 16, 48
Videosonic 45
Wards 00, 02, 18, 19, 22, 30,
35, 37, 45, 47
XR 1000 00, 22, 30
Yamaha 24
Zenith 09, 14, 21, 55
Cable Satelites
ABC 00, 07, 08, 18, 19, 21,
37, 38, 53
Antronixs 40
Archer 12, 25, 40
Belcor 33
Cable Star 33
Cable Satelites (continued)
Century 12
Citizen 12
Colour Voice 31, 45
Contronics 26, 29
Contec 22
Dae Ryung 21
Eastern 15
Electricord 32
Everquest 56
Focus 57
Garrard 12
GC Electronics 33, 40
Gemini 04, 39, 44, 56
Goldstar 11, 26
General Insturments 00, 13
Hamlin 03, 09, 14, 23, 24
Hitachi 00
Hytex 37
Jasco 12
Jerrold 00, 08, 13, 38, 53, 55,
56
Macom 36
Magnavox 16
Memorex 02
Movie Time 30, 32, 34
NSC 30, 34, 39
Oak 22, 37, 50
Panasonic 02, 10, 49
Paragon 02
Philips 12, 16, 17, 27, 31, 43,
44, 45, 47
Pioneer 06, 11, 20
Popular Mechanics 57
Pulsar 02
RCA 49
Realistic 40
Recoton 57
Regal 03, 09, 23, 35
Regency 15
Rembrandt 00, 39
Runco 02
Samsung 11, 26
Scientific Atlanta 18, 21, 42, 48
Signal 26, 56
Signature 00
SL Marx 26
Sprucer 01, 49
Starcom 38, 53, 56
Stargate 26, 56
Starquest 56
Starsight 58, 59
Sylvania 19
Teleview 26
Texscan 19
Tocom 07, 28, 55
Toshiba 02
Tusa 56
TV 86 30
Unika 12, 40
United Artist 37
United Cable 53
Universal 12, 25, 32, 33, 35, 40
Videoway 51
Viewstar 16, 29, 30, 41
Zenith 16, 29, 30, 41, 64
Zentek 57
Hitachi (SAT) 61
RCA (SAT) 62
Sony (SAT) 63
PV151 1-6 PROJO
Page 12
PROGRAMMING CODES
DVD Players
Denon 03
Hitachi 06
JVC 00
Kenwood 03
Magnavox 04
Mitsubishi 09
Panasonic 03
Pioneer 02
Philips 05
RCA (ProScan) 08
Sony 01
Toshiba 04
Yamaha 07
Zenith 04, 10
CD Players
Adcom 11
Aiwa 12
California Audio 13
Carver 12
Denon 14
DKK 15
Emerson 11
Fisher 16
Genexxa 17
Hitachi 11, 17, 18, 19, 20,
21, 22
JVC 23
Kenwood 16, 24, 25
Krell 12
Magnavox 12
Marantz 12, 13
MCS 13
Mission 13
NSM 12
Onkyo 26
Optimus 15, 17, 27
Panasonic 13
Philips 12
Pioneer 17, 27
Proton 12
QED 12
Quasar 13
RCA 11, 31
Realistic 11
Rotel 12
SAE 12
Sansui 12
Scott 11
Sony 15, 28
Technics 13, 29, 30
Victor 23
Tape Players
Awia 42, 43
Hitachi 32, 33, 34, 35
Jerrold 44, 45
JVC 36
Kenwood 37
Optimus 38
Panasonic 39
Pioneer 38
Scientific Atlanta 46
Sony 40, 52, 42, 43
Starcom 44
Wards 38
Audio Amplifiers
Aiwa 51, 52
Carver 47, 52, 53, 54
Casio 55
Clarinette 55
Denon 56
Fisher 54, 57
Hitachi 58
JVC 59
Kenwood 60, 61, 63, 64
Lloyd’s 55
Magnavox 57, 63, 55
Marantz 47, 52, 62
MCS 62
Modulaire 55
Onkyo 55
Optimus 49, 50, 57, 61, 66
Panasonic 62
Penney 55
Philips 47, 52
Pioneer 49, 50, 66, 67, 68
Quasar 62
Realistic 55
Sansui 52
Sanyo 57
Sharp 61
Sony 51
Technics 48, 62, 69, 70, 71
Victor 59
Ward 49, 51, 52, 54, 66, 67
Yamaha 61, 72
York 55
PV151 1-7 PROJO
Page 13

CUSTOMIZED VIDEO AND AUDIO ADJUSTMENTS
THEATER
THEATER
Select VIDEO to adjust picture settings and improve picture quality.
SPECIAL
SETUP
CONTRAST 75 %
BRIGHTNESS 50%
COLOR
TINT
SHARPNESS 50%
RESET
ADVANCED
MENU TO MENU BAR
SETTINGS
VIDEO
AUDIO
TO EXIT
50%
QUIT
Note: If contrast is selected, you are adjusting
CONTRAST. The additional menu items,
BRIGHTNESS, COLOR, TINT, and SHARPNESS
can be adjusted in the same manner.
Contrast and Brightness adjustmens will
effect only the main picture. These
adjustments will not affect the subpicture.
SETUP SPECIAL VIDEO AUDIO
Advanced Settings
View Rite
Auto Flesh
Video
Color Temperature
Cool Warm
Aspect Ratio
4.3 16.9
V. Position +10
MENU TO MENU BAR
TO EXIT
QUIT
Use Cursor Up or Down to highlight the
function to be adjusted.
Press Cursor Left or Right to adjust function.
Press QUIT to exit menu.
CONTRAST
Use this function to change the contrast
between black and white levels in the
picture. This adjustment will only affect the
picture when LIGHT SENTRY is OFF.
BRIGHTNESS
Use this function to adjust overall picture
brightness.
COLOR
Use this function to adjust the color level in
the picture.
TINT
Use this function to adjust flesh tones so they
appear natural. (It may be necessary to adjust
TINT to abtain optimum picture quality when
using the COMPONENT:Y-CbCr Input 2 jacks).
SHARPNESS
Use this function to adjust the amount of
detail in the picture.
RESET
When RESET is selected, press CURSOR RIGHT
to reset video settings to factory preset
conditions.
PV151 1-8 PROJO
Page 14

CUSTOMIZED VIDEO AND AUDIO ADJUSTMENTS
THEATER
MENU
TO EXIT
THEATER
MENU
Select AUDIO SETTINGS to adjust the AUDIO to your preference and improve the sound quality.
VIDEO
SETUP SPECIAL
AUDIO
VIDEOSETUP SPECIAL AUDIO
BASS 72 %
TREBLE
BALANCE
RESET
ADVANCED
SETTINGS
TO MENU BAR
50%
QUIT
Note: If BASS is selected you are adjusting BASS.
The additional menu items, TREBLE and
BALANCE can be selected and adjusted in
the same manner
BASS
This function controls the Low Frequency
audio to all speakers.
TREBLE
This function controls the High Frequency
audio to all speakers.
Advanced Settings
Stereo
Mono
Second Audio Programming
Internal Speakers
Auto Noise Control
Loudness
SoundRite
TO MENU BAR TO EXIT QUIT
Use Cursor Up or Down to highlight the
function to be adjusted.
Press Cursor Left or Right to adjust function.
Press QUIT to exit menu.
BALANCE
This function will control the left to right
balance of the TV internal speakers and the
VARIBLE AUDIO OUT output.
RESET
When RESET is selected, press CURSOR RIGHT
to return audio adjustments to factory preset
conditions.
PV151 1-9 PROJO
Page 15
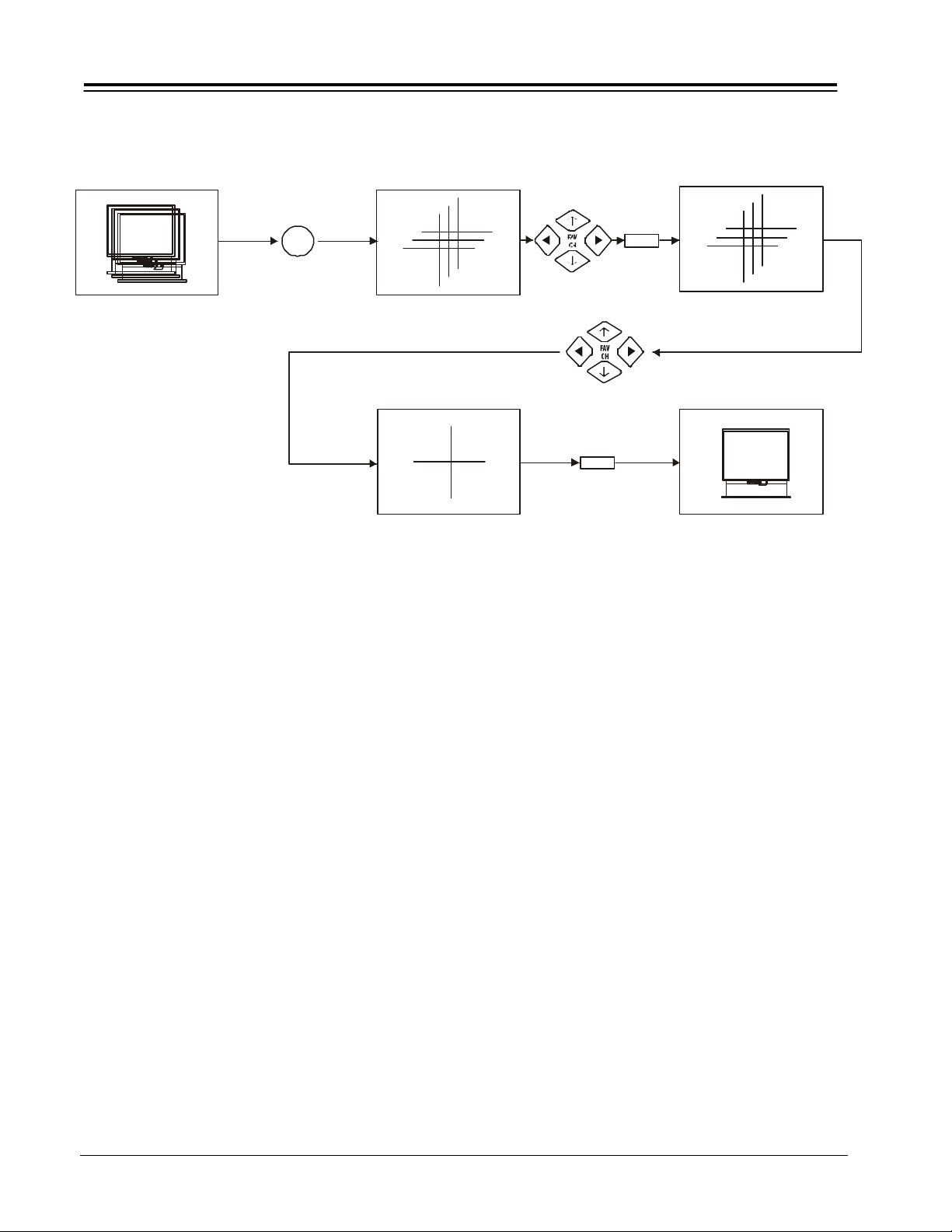
ZP94/95 CUSTOMER CONVERGENCE ADJUSTMENT
Flashes Blue
MENU
Flashes Red
Digital
Setup
MENU
CONVERGENCE ADJUSTMENT (DIGITAL SETUP)
To enter this adjustnment mode, press the front panel
DIGITAL SETUP button.
Press the ARROW buttons on the remote control to move
the displayed color up, down, left, or right. (Press the
QUIT button to toggle between red and blue)
Press MENU on the remote control to change the color
you want to adjust.
Press the front panel DIGITAL SETUP button or the
remote comtrol MENU button when adjustment is done.
This will save your adjustment into memory.
Note:
Only a momentary press of the DGITAL SETUP button is
necessary to enter DIGITAL SETUP convergence adjustment mode.
Do not press the DIGITAL SETUP button for more than
three seconds.
To save your adjustment data into memory, press the
front panel DIGITAL SETUP button or the remote
control MENU button. If you do NOT wish to save your
adjustment data into memory, turn the TV off. When
the TV is ON again, your old convergence data will be
restored.
To exit this function, press DIGITAL SETUP on the front
panel of your Entertainment machine.
PV151 1-10 PROJO
Page 16
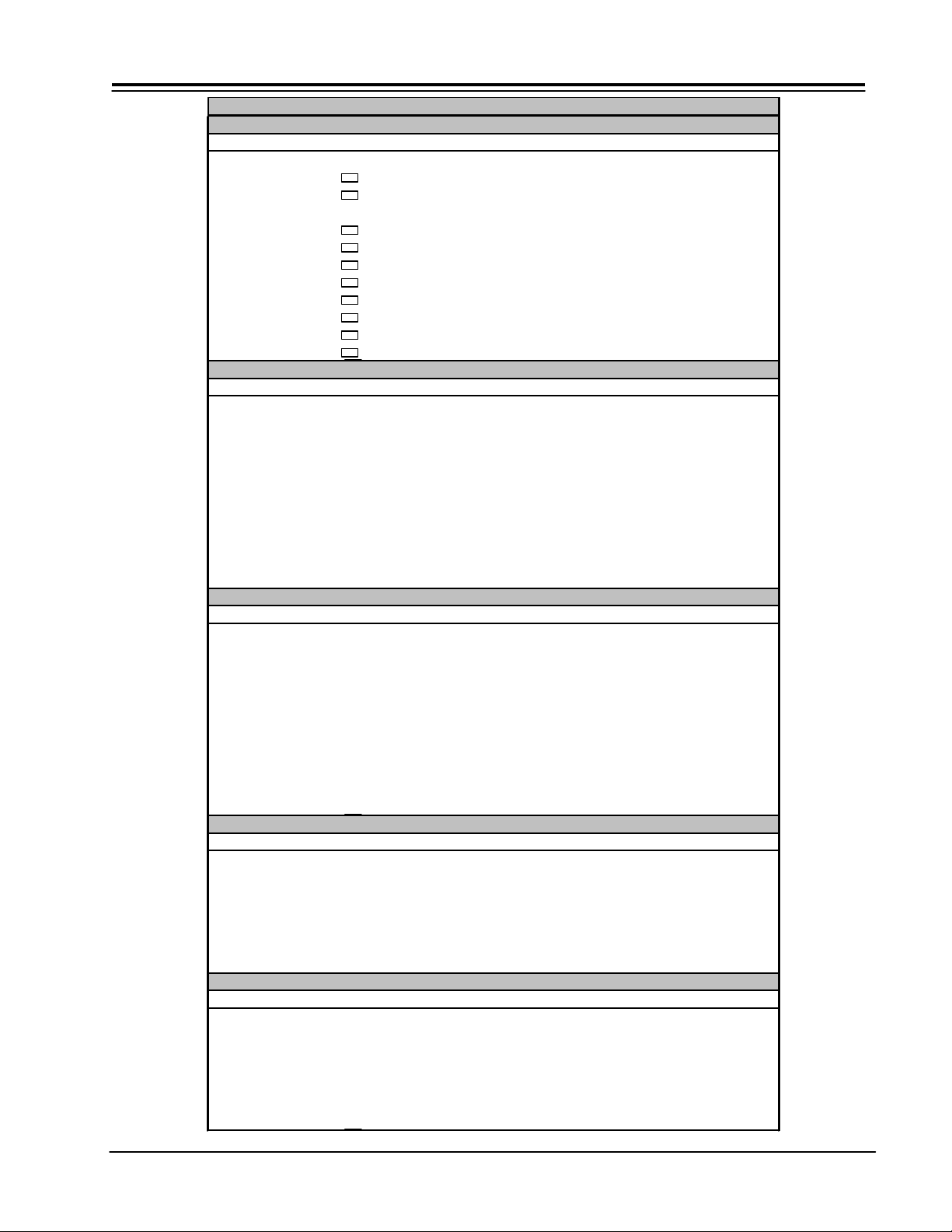
SERVICE MENUES
TA1300 31.5khz Mode
TA1300 33.75khz Mode
ITEM SETTING RANGE DESCRIPTION
P01 ZP94/95 *Non-Adjustable Data
ADJUST MODE Version 704
SUB BRT 3C-C3 Sub Brightness
SERVICE 0 SERVICE
DEF RESET 0
V/P RESET 0
3DYC RESET 0
FLEX RESET 0
DSP RESET 0
CCD RESET 0
FACT RESET 0 Resets Memory
MEMORY INITIAL 0 Resets Memory
P02 ZP94/95
ADJUST MODE
315
H POSI 40 00-7F Horizontal Position
FLEX CONT
VD POS 3F 00-7F Vertical Position
UPD64081
DYGA 09 00-0F Y Motion Detection Gain
DCGA 06 00-0F Chroma Motion Detection Gain
VAPGA 00 00-07 Vertical Aperture Controle Gain
VAPIN 00 00-1F Vertical Aperture Controle Invert
YHCOR 00 00-01 Y Output High Frequency Coring
P02 ZP94/95
ADJUST MODE
3375
H POSI 40 00-7F Horizontal Position
FLEX CONT
VD POS 3F 00-7F Vertical Position
UPD64081
DYGA 09 00-0F Y Motion Detection Gain
DCGA 06 00-0F Chroma Motion Detection Gain
VAPGA 00 00-07 Vertical Aperture Controle Gain
VAPIN 00 00-1F Vertical Aperture Controle Invert
YHCOR 00 00-01 Y Output High Frequency Coring
P03 ZP94/95
ADJUST MODE
TA1270-M
TINT (TV) 3C 00-7F Main NTSC Tint
TOFFO (TV) 00 00-07 Main NTSC TOF fO Peak Frequency Switch
TOFQ (TV) 00 00-07 Main NTSC TOFQ Switch
SUB CNT 0F 00-1F Main NTSC Contrast
SUB CL 1B 00-1F Main NTSC Color
P03 ZP94/95
ADJUST MODE
TA1270-S
TINT (TV) 3C 00-7F Main NTSC Tint
TOFFO (TV) 00 00-07 Main NTSC TOF fO Peak Frequency Switch
TOFQ (TV) 00 00-07 Main NTSC TOFQ Switch
SUB CNT 0F 00-1F Main NTSC Contrast
SUB CLR 1B 00-1F Main NTSC Color
PV152 2-1 PROJO
Page 17

SERVICE MENUES CONT.
ITEM SETTING RANGE DESCRIPTION
P04 ZP94/95 *Non-Adjustable Data
FLEX CONT NTSC
39 HHPF1 00 00-01 Characteristic Switch 0 = Low Frequency, 1 = High Frequency
41 V-CRG 00 00-03 Vertical Enhance Coring
42 H-CRG 00 00-03 Horizontal Enhance Coring
43 V-ENH 00 00-03 Vertical Enhance
44 H-ENH 00 00-03 Horizontal Enhance
96 YVHENH 0B 00-1F Y Vertical & Horizontal Enhance Gain
100 CVHENH 12 00-1F Color Vertical & Horizontal Enhance Gain
P04 ZP94/95
FLEX CONT ATSC (480i, 480p, 1080i, 720p)
39 HHPF1 00 00-01 Characteristic Switch 0 = Low Frequency, 1 = High Frequency
41 V-CRG 00 00-03 Vertical Enhance Coring
42 H-CRG 00 00-03 Horizontal Enhance Coring
43 V-ENH 00 00-03 Vertical Enhance
44 H-ENH 00 00-03 Horizontal Enhance
96 YVHENH (720p) 00 (10) 00-1F Y Vertical & Horizontal Enhance Gain
100 CVHENH 12 00-1F Color Vertical & Horizontal Enhance Gain
P05 ZP94/95
FLEX CONT NTSC
71 YV-ENH 00 00-0F Y Vertical Enhance Gain
79 CV-ENH 00 00-0F Color Vertical Enhance Gain
87 YH-ENH 07 00-0F Y Horizontal Enhance Gain
94 CH-ENH 0F 00-0F Color Horizontal Enhance Gain
66 YV-DSB 00 00-03 Y Vertical Dynamic Shoot Balance Gain
75 CV-DSB 00 00-03 Color Vertical Dynamic Shoot Balance Gain
82 YH-DSB 00 00-03 Y Horizontal Dynamic Shoot Balance Gain
90 CH-DSB 00 00-03 Color Horizontal Dynamic Shoot Balance Gain
69 YV-CLP 00 00-0F Y Vertical Enhance Clip Offset
84 YH-CLP 00 00-0F Y Horizontal Enhance Clip Offset
P05 ZP94/95
FLEX CONT ATSC (480i, 480p, 1080i, 720p)
71 YV-ENH 00 00-0F Y Vertical Enhance Gain
79 CV-ENH 00 00-0F Color Vertical Enhance Gain
87 YH-ENH (1080i) 07 (00) 00-0F Y Horizontal Enhance Gain
94 CH-ENH 0F 00-0F Color Horizontal Enhance Gain
66 YV-DSB 00 00-03 Y Vertical Dynamic Shoot Balance Gain
75 CV-DSB 00 00-03 Color Vertical Dynamic Shoot Balance Gain
82 YH-DSB 00 00-03 Y Horizontal Dynamic Shoot Balance Gain
90 CH-DSB 00 00-03 Color Horizontal Dynamic Shoot Balance Gain
69 YV-CLP 00 00-0F Y Vertical Enhance Clip Offset
84 YH-CLP 00 00-0F Y Horizontal Enhance Clip Offset
P06 ZP94/95
FLEX CONT NTSC
97 YV-NLP 00 00-3F Y Vertical Nonlinear Peaking
98 YH-NLP 0A 00-3F Y Horizontal Nonlinear Peaking
101 Y-LMT FF 00-FF Y Amplitude Limit
83 YH-FRQ 00 00-03 Y Horizontal HPF Peak Frequency Switch
91 CH-FRQ 02 00-03 Color Horizontal HPF Peak Frequency Switch
70 YV-LTI 00 00-01 Y Vertical Enhance Clip 0 = Enhance, 1 = LTI
78 CV-CTI 00 00-01 Color Vertical Enhance Clip 0 = CTI, 1 = Enhance
86 YH-LTI 01 00-01 Y Horizontal Enhance Clip 0 = Enhance, 1 = LTI
93 CH-CTI 01 00-01 Color Horizontal Enhance Clip 0 = CTI, 1 = Enhance
PV152 2-2 PROJO
Page 18

SERVICE MENUES CONT.
ITEM SETTING RANGE DESCRIPTION
P06 ZP94/95 *Non-Adjustable Data
FLEX CONT ATSC (480i, 480p, 1080i, 720p)
97 YV-NLP 00 00-3F Y Vertical Nonlinear Peaking
98 YH-NLP 0A 00-3F Y Horizontal Nonlinear Peaking
101 Y-LMT FF 00-FF Y Amplitude Limit
83 YH-FRQ 00 00-03 Y Horizontal HPF Peak Frequency Switch
91 CH-FRQ 02 00-03 Color Horizontal HPF Peak Frequency Switch
70 YV-LTI 00 00-01 Y Vertical Enhance Clip 0 = Enhance, 1 = LTI
78 CV-CTI 00 00-01 Color Vertical Enhance Clip 0 = CTI, 1 = Enhance
86 YH-LTI 01 00-01 Y Horizontal Enhance Clip 0 = Enhance, 1 = LTI
93 CH-CTI 01 00-01 Color Horizontal Enhance Clip 0 = CTI, 1 = Enhance
P07 ZP94/95
FLEX CONT NTSC
69 YVDSBC 00 00-07 Y Vertical Dynamic Shoot Balance Coring Amplitude
77 CVDSBC 00 00-07 Color Vertical Dynamic Shoot Balance Coring Amplitude
85 YHDSBC 00 00-07 Y Horizontal Dynamic Shoot Balance Coring Amplitude
92 CHDSBC 00 00-07 Color Horizontal Dynamic Shoot Balance Coring Amplitude
95 Y-CRG 00 00-07 Y Coring Amplitude
99 C-CRG 00 00-07 Color Coring Amplitude
64 YNR-IN 04 00-07 YNR Input Level Gain
73 CNR-IN 04 00-07 CNR Input Level Gain
80 YNRPAS 00 00-07 YNR Passage Level Limit
88 CNRPAS 02 00-07 CNR Passage Level Limit
P07 ZP94/95
FLEX CONT ATSC (480i, 480p, 1080i, 720p)
69 YVDSBC 00 00-07 Y Vertical Dynamic Shoot Balance Coring Amplitude
77 CVDSBC 00 00-07 Color Vertical Dynamic Shoot Balance Coring Amplitude
85 YHDSBC 00 00-07 Y Horizontal Dynamic Shoot Balance Coring Amplitude
92 CHDSBC 00 00-07 Color Horizontal Dynamic Shoot Balance Coring Amplitude
95 Y-CRG 00 00-07 Y Coring Amplitude
99 C-CRG 00 00-07 Color Coring Amplitude
64 YNR-IN 04 00-07 YNR Input Level Gain
73 CNR-IN 04 00-07 CNR Input Level Gain
80 YNRPAS 00 00-07 YNR Passage Level Limit
88 CNRPAS 02 00-07 CNR Passage Level Limit
P08 ZP94/95
FLEX CONT NTSC/ATSC (480i, 480p, 1080i, 720p)
65 YNRRDC 00 00-07 YNR Reducing Gain
74 CNRRDC 00 00-07 CNR Reducing Gain
67 YNR-DC 00 00-03 YNR DC Shift
76 CNR-DC 00 00-03 Color DC Shift
81 YNR-O 00 00-07 YNR 0 Point
89 CNR-O 00 00-0F CNR 0 Point
45 CB-BLK 07 00-0F CB Blanking Level Offset
46 CR-BLK 07 00-0F CR Blanking Level Offset
27 FRMBRT* 60 00-7F Y Frame Bright
102 CLPOUT 7F 00-FF Clamp Output Offset
P09 ZP94/95
FLEX CONT NTSC/ATSC
10 MPLL-S 0F 00-1F Main PLL Vertical Mask Pulse Start Position Offset
17 SPLL-S 0F 00-1F Sub PLL Vertical Mask Pulse Start Position Offset
12 MPLL-E 0F 00-1F Main PLL Vertical Mask Pulse End Position Offset
19 SPLL-E 0F 00-1F Sub PLL Vertical Mask Pulse End Position Offset
11 MVW-PH 05 00-07 Main Vertical Write Input Horizontal Phase Adjustment
18 SVW-PH 05 00-07 Sub Vertical Write Input Horizontal Phase Adjustment
14 MHS-HP 0F 00-1F Main Horizontal Sync Horizontal Phase Offset
21 SHS-HP 0F 00-1F Sub Horizonyal Sync Horizontal Phase Offset
13 MY-CLP 03 00-07 Main Y Clamp Refrence Offset
20 SY-CLP 03 00-07 Sub Y Clamp Refrence Offset
PV152 2-3 PROJO
Page 19

SERVICE MENUES CONT.
ITEM SETTING RANGE DESCRIPTION
P10 ZP94/95 *Non-Adjustable Data
FLEX CONT NTSC/ATSC (480i, 480p, 1080i, 720p)
23 V-POS 3F 00-3F Wide Vertical Position
24 V-SIZ 7F 00-FF Wide Vertical Size
50 HD-POS 3F 00-7F HD Position Offset
48 VBLK-T 7F 00-FF Vertical Blanking Top Position Offset
49 VBLK-B 7F 00-FF Vertical Blanking Bottom Position Offset
51 HBLK-R 7F 00-FF Horizontal Blanking Right Position Offset
52 HBLK-L 7F 00-FF Horizontal Blanking Left Position Offset
40 READ F 10 00-3F A/D Converter Clock Sampling Phase
P11 ZP94/95
FLEX CONT NTSC/ATSC (480i, 480p, 1080i, 720p)
35 FRMTOP-2 07 00-0F Frame Top Position Offset (2Pix)
FRMTOP-L* 07 00-0F Frame Top Position Offset (Letter)
36 FRMBTM-2 07 00-0F Frame Bottom Position Offset (2Pix)
FRMBTM-L* 07 00-0F Frame Bottom Position Offset (Letter)
37 FRMRGT 07 00-0F Frame Right Position Offset
38 FRMLFT 07 00-0F Frame Left Position Offset
59 BS-TOP 07 00-0F Black Strech Stop Pulse Top Position Offset
60 BS-BTM 07 00-0F Black Strech Stop Pulse Bottom Position Offset
61 BS-RGT 07 00-0F Black Strech Stop Pulse Right Position Offset
62 BS-LFT 07 00-0F Black Strech Stop Pulse Left Position Offset
P12 ZP94/95
FLEX CONT
120 TV/CINE 01 00-01 TV Cinema Detection
121 T/C DET 07 00-0F TV Cinema Detection Vertical Gate Area Start Position
122 T/C UNL 01 00-07 TV Cinema Detection Unlock Protection Count
123 T/C LCK 03 00-0F TV Cinema Detection Lock Protection Count
126 T/C ARE 05 00-FF TV Cinema Detection Motion Area Border Volume Offset
127 T/C CBR 07 00-0F TV Cinema Detection Color 2 Bit Border Volume Offset
128 T/C YBR 07 00-0F TV Cinema Detection Y 2 Bit Border Volume
P13 ZP94/95
TA1298 NTSC
SHARP 0C 00-1F Sharpness (Center Adjustment)
APACON 06 00-07 APACON Peak fO
YNR 00 00-03 YNR
P13 ZP94/95
TA1298 480I
SHARP 0A 00-1F Sharpness (Center Adjustment)
APACON 06 00-07 APACON Peak fO
YNR 00 00-03 YNR
P13 ZP94/95
TA1298 480P
SHARP 0A 00-1F Sharpness (Center Adjustment)
APACON 06 00-07 APACON Peak fO
YNR 00 00-03 YNR
P13 ZP94/95
TA1298 1080I
SHARP 07 00-1F Sharpness (Center Adjustment)
APACON 05 00-07 APACON Peak fO
YNR 00 00-03 YNR
P13 ZP94/95
TA1298 720P
SHARP 0A 00-1F Sharpness (Center Adjustment)
APACON 06 00-07 APACON Peak fO
YNR 00 00-03 YNR
PV152 2-4 PROJO
Page 20

SERVICE MENUES CONT.
ITEM SETTING RANGE DESCRIPTION
P14 ZP94/95 *Non-Adjustable Data
TA1298 NTSC
COLOR 40 00-7F Color (Center Adjustment)
TINT 45 00-7F Tint (Center Adjustment)
R-Y PH 02 00-03 R-Y Phase
R/B GA 01 00-03 R/B Gain
G-Y PH 00 00-03 G-Y Phase
G/B GA 00 00-03 G/B Gain
COLOR SYSTEM 00 00-07 COLOR SYSTEM
P14 ZP94/95
TA1298 SDTV
COLOR 4F 00-7F Color (Center Adjustment)
TINT 3B 00-7F Tint (Center Adjustment)
R-Y PH 02 00-03 R-Y Phase
R/B GA 02 00-03 R/B Gain
G-Y PH 01 00-03 G-Y Phase
G/B GA 00 00-03 G/B Gain
COLOR SYSTEM 01 00-07 COLOR SYSTEM
P14 ZP94/95
TA1298 HDTV
COLOR 40 00-7F Color (Center Adjustment)
TINT 43 00-7F Tint (Center Adjustment)
R-Y PH 00 00-03 R-Y Phase
R/B GA 02 00-03 R/B Gain
G-Y PH 02 00-03 G-Y Phase
G/B GA 00 00-03 G/B Gain
COLOR SYSTEM 01 00-07 COLOR SYSTEM
P15 ZP94/95
TA1298
RGB BRT 50 00-7F RGB Brightness
RGB CNT 50 00-7F RGB Contrast
G DRV (W) 39 00-7F Green Drive (WARM)
B DRV (W) 2D 00-7F Blue Drive (WARM)
SUB CLR 10 00-1F Sub Color (Demodulator)
SUB CNT 1F 00-1F Main NTSC Contrast
VSM PH 05 00-07 VM Phase
VSM GA 00 00-03 VM Gain
OS ACL 01 00-01 OSD Auto Contrast Limiter Switch
RGB ACL 00 00-01 RGB Auto Contrast Limiter Switch
P16 ZP94/95
TA1298
CLR G 00 00-03 Color G Corection Piont
CLT 00 00-01 Color Limiter Level
YOUT G 00 00-01 Y G (After Contrast) Switch
YG PNT 00 00-01 Y G Point
S TRK 00 00-03 Sharpness Tracking
RGBG 00 00-01 RGB Switch
DC PNT 00 00-07 DC Restoration Point
DC RAT 00 00-07 DC Restoration Rate
DC LMT 00 00-03 DC Restoration Limit Point
PV152 2-5 PROJO
Page 21
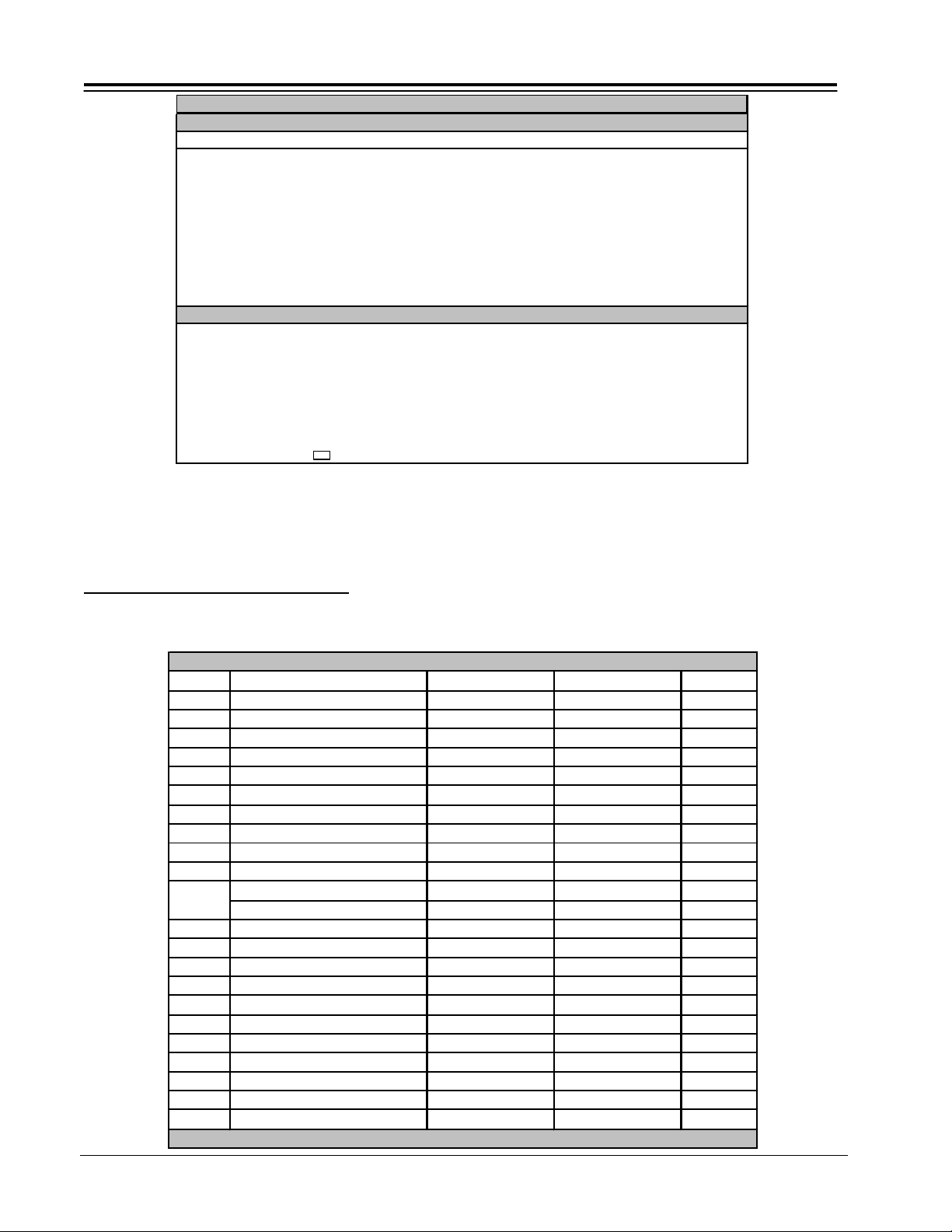
SERVICE MENUES CONT.
ITEM SETTING RANGE DESCRIPTION
P17 ZP94/95 *Non-Adjustable Data
TA1298
BSP 03 00-07 Black Strech Point
APL/BS 00 00-03 APL / Black Strech Point
B COR 01 00-01 Black Level Correction
B GA 00 00-01 Black Strech Gain
B DET 00 00-01 Black Detect Level
DABL PN 00 00-07 Dynamic ABL Detection Point
DABL GA 07 00-07 Dynamic ABL Gain
ABL PN 07 00-07 ABL Detection Point
ABL GA 05 00-07 ABL Gain
P18 ZP94/95
V CHIP RATING
POLLING 0F 00-0F 0
TIMEOUT 05 00-0F 0
STATUS 02 00-0F 0
AFC/CLOCK TEST
SERVICE ADJUSTMENTS ORDER
SERVICE ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURE ORDER
The following is the suggested order for adjustment
procedures.
ZP 94/95 SERVICE ADJUSTMENT ORDER “PREHEAT BEFORE BEGINNING”
Order Adjustment Item Screen Format Signal DCU Data
Pre HEAT N/A NTSC N/A
1 Cut Off Progressive NTSC
2 Pre Focus Lens and Static Progressive NTSC
3 DCU Phase Data Setting Progressive NTSC
4 DCU Phase Data Setting HD 2.14H
5 Horz. Position Adj. (Coarse) Progressive NTSC
6 Horz. Position Adj. (Coarse) HD 2.14H
7 Raster Tilt Progressive NTSC CLEAR
8 Beam Alignment Progressive NTSC
9 Raster Position Progressive NTSC CLEAR
Horz. Size Adjust Progressive NTSC CLEAR
10
Horz. Size Adjust HD 2.14 CLEAR
11 Vertical Size Adjust Progressive NTSC CLEAR
12 Beam Form Progressive NTSC
13 Lens Focus Adjust Progressive NTSC
14 Static Focus Adjust Progressive NTSC
15 Blue Defocus Progressive NTSC
16 White Balance Adjustment Progressive NTSC
17 Sub Brightness Adjustment Progressive NTSC Color Bar
18 Horz. Position Adjustment Progressive NTSC
19 Horz. Position Adjustment HD 2.14H
20 Convergence Alignment Progressive NTSC
21 Convergence Alignment HD 2.14H
It is necessary to follow the order when performing an alignment on the ZP 94/95 chassis.
CLEAR to start
PV152 2-6 PROJO
Page 22

12~2DRIVEVR
NVR
CUSVR
CONVERGENCE ADJUSTMENT
MEMORY INITIALIZATION PROCEDURE
WARNING: This should only be done in extreme cases. I2C
Data will be reset as well. Be sure and write down
all data values before continuing.
1. Disconnect Power to Television.
2. Remove the Back Cover.
3. Remove the two screws holding the Main chassis to
the Cabinet if necessary.
4. Disconnect wiring harness clips to free up the chassis
if necessary.
5. Reconnect Power to the Television and turn the set
ON.
6. Locate PP1 and add a jumper between pins 1 and 2 of
the PP1 connector.
7. Hold jumper in place for 5 seconds. (A beep will NOT
be heard).
8. Remove the jumper.
9. Confirm EEPROM reset, Input source is now set to Air
and not to Cable 1 or 2. No Child Lock, and only
channels 2 through 13 are in memory.
10.Reassemble Chassis and reinstall PTV back. Set is now
ready to operate.
NOTE: All customers' Auto Programming and Set-Ups are
returned to factory settings.
CUT OFF
ADJUSTMENT PREPARATION:
A) Pre Heat Run should be finished.
ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURE:
1. Go to I2C ADJ Mode. Press and hold the “Source” key
on the front panel and then POWER ON to access I2C
adjustment mode.
2. Choose SERVICE item [2] of I2C ADJ. Mode. (Select
CURSOR RIGHT (right arrow key).
3. Screen VR should be turned clockwise gradually and
set so that retrace lines begin to appear.
4. Return to “normal” mode by using the “left arrow” key.
5. Adjust focus VR’s so that focus is even all around the
screen.
PRE-FOCUS ADJUSTMENT
Adjustment preparation
1. The set can face in any direction: west, east, north or
south.
2. Receive the cross-hatch pattern signal.
CONTRAST : 60-70%
Pre HEAT
PRESET EACH ADJUSTMENT VR TO CONDITION AS SHOWN:
A) Before Pre Heat Run.
1. Red and Green Drive VR on the CRT PWB. (Not on Blue
CRT).
Pre set between the 12 o’clock and 2 o’clock position.
2. SCREEN VR ON FOCUS PACK.
SCREE
Pre Set fully counter clockwise.
3. Focus VR on focus pack
BRIGHTNESS : 50%
3. The electrical focus adjustment should have been
completed.
4. The centering DY inclination should have been
adjusted.
Adjustment procedure
1. Loosen the fixing screw on the lens cylinder so that
the lens cylinder can be turned. (Be careful not to
loosen too much. If the screw is loosened too
much, rattling when tightening becomes greater and
the focus may drift). After completing steps (5), (6),
and (7) below, tighten the fixing screws for each lens
with a torque of 12~17 Kgf cm.
2. Apply covers to 2 of R, G, and B lenses, and project a
single color on the screen and adjust in sequence.(The
adjustment order of R, G, and B is only an example.)
3. For each of the R, G, and B lenses, observe the color
aberration generated on the outer circumference of
the cross-hatch bright line at the center section (3
pitches vertically and horizontally from the center.)
4. If the lens adjustment knob is turned clockwise,
viewed from the front, the color aberration changes as
follows.
FO
Pre Set fully clockwise.
PV152 2-7 PROJO
Page 23

RED
CHROMATIC
ABERRATION
OR NO COLOR
RED
CHROMATIC
ABERRATION
CHROMATIC ABERRATION
CHROMATIC ABERRATION
LENS
FIXING SCREW
CROSS-HATCH
CONVERGENCE ADJUSTMENT
Lens Change of color aberration
R Lens Red Crimson
G Lens Blue Red
B Lens Purple Green
5. In case of G lens, set to the point where the chromatic aberration switches from blue to red. If the
chromatic aberration appearing all over the screen is
not the same, observe the vertical bright line at the
center of the screen and set to the position where red
chromatic aberration slightly appears inside and blue
outside (reference value: 1~3mm) within the crosshatch pitches specified in next table. When the red
chromatic aberration appearing at both sides of the
bright line is not equal, observe the side with larger
chromatic aberration when adjusting.
L1
L2
Set Size Pitch between L
50" 3.0 cross-hatch pitches
60" 3.0 cross-hatch pitches
7. In case of B lens, set to the position where the
chromatic aberration changes from purple to green.
As shown below, observe the vertical bright line at the
center and set to the position where green chromatic
aberration slightly appears inside and purple outside
(reference value: 1~3mm) within the cross-hatch
pitches specified in next table.
L
SLIGHTY BLUE CHROMATIC ABERRATION
Set Size Pitch between L1 & L2
50" 3.0 cross-hatch pitches
60" 3.0 cross-hatch pitches
6. In case of R lens, set to the position where the
chromatic aberration changes from red to crimson. As
shown below, observe the vertical bright line at the
center and set to the position where the crimson
chromatic aberration slightly appears inside and red
outside (reference value: 1~3mm) within the crosshatch pitches specified in next
L
PURPLE CHROMATIC
ABERRATION
SLIGHTY GREEN
Set Size Pitch between L
50" 3.0 cross-hatch pitches
60" 3.0 cross-hatch pitches
NOTES:
1. Fixing screw 2. Color aberration
COLOR
ABERRATION
table.
PV152 2-8 PROJO
SLIGHTY CRIMSON
3. Since the G light is very important for picture quality
and performance, pay special attention in its
adjustment.
NOTE: Be careful not to touch the lens with your fingers
when adjusting.
Page 24

HD MODE
PROGRESSIVE MODE
BEFORE
USE CURSOR
KEYS TO MOVE
DOTTED LINES
BETWEEN BENT
CONVERGENCE ADJUSTMENT
4. For red, setting to the center between red and crimson
is optimum.
5. For blue, setting to the center between purple and
green is optimum.
DCU PHASE DATA SETTINGS
Adjustment Preparation
1. Cut off adjustment should be finished
2. VIDEO CONTROL: Factory Preset Condition
Adjustment procedure
PROGRESSIVE MODE
1. Receive any NTSC signal (Set is in Progressive mode)
2. Push “SERVICE ONLY” SW on Deflection PWB (Enter to
DCU ADJ. Mode)
3. Push (?) key on R/C. (Green cross hatch is displayed).
Then push (QUIT) key on R/C. (Character pattern is
displayed. This is the PHASE setting mode)
4. Set PH-H phase data as shown below using (4) and
(6) key.
5. Set PH-V phase data as shown below using (2) and (5)
key.
6. Set CR-H phase data as shown below using (<) and (>)
key.
7. Set CR-V phase data as shown below using (up) and
(down) arrow keys.
8. Push (?) key on R/C to exit from the PHASE mode.
9. Push (-)* key on R/C 2 time to write the phase data
to the E2PROM.
10.When Green dots are displayed, push (MUTE) key to
return to DCU ADJ. mode.
11. Push “SERIVCE ONLY” SW to return to RF or VIDEO
mode.
HD MODE
12. Receive any HD signla (Set is in HD Mode)
13. Repeat (2)~(11) procedure again.
PROGRESSIVE MODE
1) Receive any NTSC crosshair signal.
2) Screen Format is PROGRESSIVE.
3) Press the SERVICE ONLY switch on the deflection PWB
and display the Digital Convergence Crosshatch pattern.
4) Mark the center of the Digital Convergence Crosshatch
Pattern with finger and press the SERVICE ONLY switch
to return to normal mode.
5) Enter the I2C Bus alignment menu and select Item [12]
H POSI and adjust the data so that the center of Video
matches the location of the Digital Crosshatch pattern noted in step {4}.
6) Exit from the I2C Menu.
HD Mode Adjustment
1) Receive any 2.14H signal.
2) Screen Format is HD.
3) Press the SERVICE ONLY switch on the deflection PWB
and display the Digital Convergence Crosshatch pattern.
4) Mark the center of the Digital Convergence Crosshatch
Pattern with finger and press the SERVICE ONLY switch
to return to normal mode.
5) Enter the I2C Bus alignment menu and select Item [12]
H POSI and adjust the data so that the center of Video
matches the location of the Digital Crosshatch pattern noted in step {4}.
6) Exit from the I2C Menu.
ACTIVE
VIDEO
CENTER
FROM
STEP (5)
LINES FIRST
CHASSIS HORIZ PHASE (COARSE) ADJUSTMENT
Adjustment Preparation:
1) Cut Off, DCU Phase adjustments should be finished.
2) Video Control: Brightness 90%, Contrast Max.
Adjustment Procedure
PV152 2-9 PROJO
PHASE MODE: PHASE MODE:
PH-H: BB
PH-V: OC
CR-H: 4C
CR-V: 00
PH-H: BB
PH-V: O7
CR-H: 4C
CR-V: 0C
THEN USE NUMBER KEYS TO MATCH INTERNAL
CROSSHATCH CENTER TO ACTIVE VIDEO CENTER
AFTER
RASTER INCLINATION ADJUSTMENT (DEFLECTION YOKE)
Adjustment preparation
1. The set can face any direction.
2. Input the single cross test signal.
Page 25

E 1
E 1
Crosshatch (Green)
E1 2mm
<+
CONVERGENCE ADJUSTMENT
3. Set video conditions to factory reset.
4. The lens focus adjustment should have been completed, screen format should be progressive.
5. The electric focus should have been coarse adjusted.
6. The digital convergence RAM should be cleared
(uncorrected state). With the TV set off, press and
hold the service switch located on the Power/
Deflection PWB and then press the power button.
7. Start adjustment 20 minutes or more after TV is
turned on.
Adjustment procedure
1. Apply covers to the R and B lenses and project only
green light or short 2P plug on R & B.
2. Turn the G deflection yoke and adjust the vertical
raster inclination.
3. Then, remove the cover of R or B lens and project red
or blue light together on the screen.
4. Turn the deflection yoke of R or B and set so that the
inclination of R or B with respect to the green light is
as shown below on the top and bottom sides.
5. After raster inclination adjustment, fixing screw of DY
should be screwed with 12+2kg-cm torque.
3. Set video conditions, Brightness to 90% and Contrast
MAX.
4. Receive cross-hatch signals. (Use of internal crosshatch signals allowed.) Raster Tilt should be finished.
5. Screen format should be Progressive.
Adjustment procedure
1. Green (G) tube beam alignment adjustment. Shortcircuit 2P subminiature connector plug pins of Red
(R) and Blue (B) on the CPT boards and project only
Green (G) tube.
2. Put Green (G) tube beam alignment magnet to the
cancel state as shown below.
3. Turn the Green (G) static focus (Focus Pack) counterclockwise all the way and make sure of position of
cross-hatch center on screen. (Halo state.)
4. Turn the Green (G) static focus (Focus Pack) clockwise
all the way. (Blooming state.)
Green Red or
Blue
E 2
Notes:
1. If internal cross-hatch does not appear after clearing
RAM data, press service switch again, on POWER/
DEFLECTION PWB.
2. To restore old RAM data, turn TV off and on.
BEAM ALIGNMENT
Adjustment preparation
1. Adjust at least 30 minutes after turning on power
switch.
5. Turn two magnets forming alignment magnet in any
desired direction and move cross-hatch center to
position found in (3).
6. If image position does not shift when Green (G) static
focus (Focus Pack) is turned. Green (G) beam alignment has been completed.
7. If image position shifts when Green (G) static focus
(Focus Pack) is turned, repeat (2)-(6).
8. Conduct beam alignment for Red (R) focus: Focus
Pack UFPK, Blue (B) focus: Focus Pack UFPK.
9. Upon completion of adjustment, fix beam alignment
magnets with white paint.
VERT & HORIZ PICTURE POSITION ADJUSTMENT
Adjustment preparation
1. Select signal on main picture.
2. Video settings have to be at normal condition.
Adjustment procedure
1. Press the SOURCE and POWER button on Control Panel
at same time to access VIDEO CHROMA ADJUST mode.
2. Raster inclination, centering, horizontal and vertical
PV152 2-10 PROJO
amplitudes, and optical focus adjustment should be
completed.
2. Select H POSI and V POSI using 56 buttons.
3. Adjust the H POSI (HORIZONTAL) and VPOSI (VERTICAL) position using 34 buttons.
Page 26

CONVERGENCE ADJUSTMENT
4. Press MENU button to exit VIDEO CHROMA ADJUST
mode.
5. Select single PINP mode and move the sub picture,
using the MOVE button. Distance between PINP and
edge of screen should be equal when moved. If it is
not, repeat (1) ~ (5).
NOTE: For ZP94/95 Models check the position of MULTI
PINP mode. Check the right edge of the sub pictures
for MV-4 to make sure there is no separation between
the MULTI PINP and the edge of the screen.
HORIZONTAL SIZE
· Digital Convergence RAM should be cleared. With Power
Off, press and hold the Service Only Switch on the Deflection PWB, then press Power.
Adjustment Prerparation
1. The set can face east or west
2. Set video conditions to factory preset.
3. The electric focus should have been coarse adjusted.
4. Start adjustment 20 minutes or more after TV is turned
on.
Adjustment Procedure
PROGRESSIVE MODE
1. Receive any NTSC signal.
2. Press the SERVICE ONLY SW on DEFLECTION PWB.
3. Locate the horizontal size VR (R683). Adjustable the
horizotal size to the table below.
HD MODE
1. Input 1080i (fH=33.75kHz) component signal to VIDEO
1 or 2.
2. Press the SERVICE ONLY SW on DEFLECTION PWB.
3. Locate the horizontal size VR (R686). Adjustable the
horizotal size to the following table.
l
VERTICAL SIZE
· Digital Convergence RAM should be cleared. With Power
Off, press and hold the Service Only Switch on the
Deflection PWB, then press Power.
Adjustment Prerparation
1. The set can face east or west
2. Set video conditions to factory preset.
3. The electric focus should have been coarse adjusted.
4. Start adjustment 20 minutes or more after TV is turned
on.
Adjustment Procedure
PROGRESSIVE MODE
1. Receive any NTSC signal.
2. Press the SERVICE ONLY SW on DEFLECTION PWB.
3. Locate the vertical size VR (R630). Adjustable the vertical size according to the table below.
Size l
50" 670mm
60" 775mm
Adjust Vertical Size until the size matches the chart below.
Size Progressive Mode HD Mode
50" 1050mm 1050mm
60" 1200mm 1200mm
Adjust Horizontal Size until the size matches the chart below.
BEAM FORM
Adjustment preparation
1. The beam alignment should have been completed.
2. The raster inclination, centering, horizontal/vertical
amplitude and optical focus adjustments should have
been completed.
PV152 2-11 PROJO
l
Page 27

PRT Surface Side
True Circle Degree: a/b
LENS
FIXING SCREW
CONVERGENCE ADJUSTMENT
3. Set video conditions to Brightness to 90 %
andContrast to MAX.
4. Input the dot signal.
Adjustment procedure
1. Green CRT beam shape adjustment. Short-circuit 2P
sub-mini connectors on Red and Blue CRT P.W.B.’s to
project only the Green beam.
2. Turn the green static focus fully clockwise. (Blooming.)
3. Make the dot at the screen center a true circle using
the 4-pole magnet as shown below.
4. Also adjust the Red and Blue CRT beam shapes
according to the steps (1) to (3).
5. After the adjustment has been completed, return R,G
and B static VRs to the just focus point.
4-Pole Beam
Alignment
Zero Field
Spacer (No
Adjustment)
Magnet
2-Pole Beam
Alignment
Magnet
8. Rotate the cylinder back and forth to obtain the best
focus point, while observing the Cross-Hatch. (Observe
the center of the screen).
Hint: Located just below the screen are the two wooden
panels. Remove the panels to allow access to the focus
rings on the Lenses.
9. After completing optical focus, tighten the fixing
screws for each lens.
10. When adjusting the Green Optical focus, be very careful. Green is the most dominant of the color guns and
any error will be easily seen.
11. Repeat Electrical Focus if necessary.
b
Specification: .09-1.1
a
LENS FOCUS ADJUSTMENT
Preparation for adjustment
1. Receive the Cross-hatch pattern signal.
2. The electrical focus adjustment should have been completed.
3. Deflection Yoke tilt should have been adjusted.
4. Brightness = 50%
5. Contrast = 60% to 70%
Adjustment procedure
6. Short the 2 pin sub-miniature connector on the CRT
P.W.B. TS, to produce only the color being adjusted
and adjust one at a time. (The adjustment order of R,
G and B is just an example.)
7. (See Figure below) Loosen the fixing screw on the lens
assembly so that the lens cylinder can be turned. (Be
careful not to loosen the screw too much, as this may
cause movement of the lens cylinder when tightening.)
STATIC FOCUS ADJUSTMENT
Adjustment preparation
1. The lens focus should be finished.
2. Set video conditions to Contrast to MAX and
birightness to 50%.
3. Receive the cross-hatch pattern signal.
4. Apply covers to the lenses of colors other than the
color to be adjusted and project a single color.
Adjustment procedure
1. Red (R), Green (G) and Blue (B) static focus adjustment. Vary the static focus VR(focus pack UFPK) and
make the center of the cross-hatch pattern clearest.
2. Observe the corners of the picture and check that the
focus does not get conspicuously worse.
PV152 2-12 PROJO
Page 28

OBSERVING POINTS
OBSERVING POINTS OF THE
RGBRGBScreenVRFocusVR
USPAC
K
CONVERGENCE ADJUSTMENT
CORNER OF THE PICTURE
BLUE DEFOCUS ADJUSTMENT
Adjustment preparation
1. Optical and electrical focus adjustment should have
been completed.
2. The convergence adjustment should have been
completed.
3. Set Video conditions to factory reset.
Adjustment procedure
1. Input a Crosshatch Signal to VIDEO input.
2. Short-circuit 2P sub-mini connectors on the red and
green CPT P.W.B.s to display only the blue beam.
3. Turn the B Focus VR(Focus Pack) fully clockwise.
4. Adjust BLUE defocus according to the following
specifications. 1mm on each side equaling 2mm total
See figure Below.
Blue Defocus “Sticking Out”
Center of Blue crosshatch line
FOC
WHITE BALANCE ADJUSTMENT
1. Screen adjustment
2. High brightness white balance
3. Low brightness balance
Screen Adjustment VRs Drive Adjustment VRs
Red: on Focus Pack Red: R829R on CRT P.W.B.
Green: on Focus Pack Green: R879G on CRT P.W.B.
Blue: on Focus Pack N/A
Adjustment VRs:
Screen adjustment VRs on Focus Block
Drive adjustment VRs on CRT P.W.B.
Red Drive = R829R
Green Drive = R879G
Preparation for adjustment
1. Start adjustment 20 minutes or more after the power
is turned on.
2. Turn the brightness and black level OSD to minimum
by remote control.
3. Receive a tuner signal, (any channel, B/W would be
best).
4. Set the drive adjustment VRs (Red R829R and Green
R879G) to their mechanical centers.
Adjustment procedure
1. Go to I2C ADJ. Mode. (With power ON, press DTV/SAT
and Cursor Down buttons at the same time. Service
Menu is displayed.)
2. Choose SERVICE item Number [2] of I2C ADJ. Mode.
(Select ON by Cursor Right and the Vertical will
collapses).
3. Gradually turn the screen adjustment VRs (red, green,
blue) clockwise and set them where the red, green
and blue lines are equal and just barely visible.
4. Return Service item on I2C ADJ to Off by Cursor Right.
Number [2].
Adjust the Sub Brightness Number [1] SUBBRT using
I2C Bus alignment procedure so only the slightest
white portions of the raster can be seen.
5. Input a gray scale signal into any Video input and
select that input using the INPUT button on the
remote or front control panel.
6. Turn the Brightness and Contrast OSD all the way up.
7. Make the whites as white as possible using the drive
adjustment VRs (Red R829 and Green R879).
8. Set the Brightness and Contrast to minimum. (10800
Kelvin)
9. Adjust the low brightness areas to black and white,
using screen adjustment VRs (red, green, blue).
10. Check the high brightness whites again. If not OK,
repeat steps 6 through 9.
11. Press the MENU key on remote to Exit Service Menu.
PV152 2-13 PROJO
Page 29

CONVERGENCE ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURE
ADJUSTMENT POINT
SUB BRIGHTNESS ADJUSTMENT
Adjustment preparation
1. Start adjustment 20 minutes or more after the power
is turned ON. Receive the color bar signal.
2. Set the contrast and color controls to minimum.
Adjustment procedure
1. Go to “Sub Brightness” adjustement in VIDEO CHROMA
ADJUST mode (press Source and Power button on
Control panel at the same time), using 56 buttons
and then 4 button.
2. Then adjust “Sub Brightness” using 34 buttons to
increase or decrease the value, according to figure.
(Visually adjust).
3. After adjustment, press MENU button to exit VIDEO
CHROMA ADJUST mode. (Data is stored in memory).
NOTE: When selecting SUB-BRIGHTNESS mode, the
microprocessor sets the CONTRAST and COLOR to MIN.
automatically, but make sure that the other conditions
are center. Directly observe the screen by eye without
using a mirror.
HD Mode Adjustment:
1. Receive any 2.14H 33.75kHZ signal.
2. Display Format is HD mode.
3. Enter the I2C Bus alignment menu and select Item [12]
HPOSI
4. Adjust the data using the left and right cursor keys
and balance the Left and Right hand side.
5. Press the “MENU” button to exit from the Service
Menu.
DIGITAL CONVERGENCE ADJUSTMENT
Adjustment preparation
1. Receive an RF or video signal.
2. Set controls to factory preset.
3. Install jig screen on the set.
4. Note the center of the video pattern displayed. This
is necessary to match dotted lines (adjustment point
viewed) and actual point that is adjusted and
displayed by the video signal.
5. Press the service only switch (on POWER/DEFLECTION
PWB). The pattern displayed is now the digital
convergence mode.
Fade to black
18 HORIZONTAL POSITION (FINE)
Adjustment Preparation:
1. Video Control: Brightness 90%, Contrast Max.
Adjustment Procedure
PROGRESSIVE MODE:
1. Receive any NTSC crosshatch signal.
2. Screen Format is PROGRESSIVE
3. Enter the I2C Bus alignment menu and select Item [12]
HPOSI
4. Adjust the data so that the Left and Right hand side
are equal.
5. Press the “MENU” button to exit from the Service
Menu.
6. When performing a complete digital convergence
adjustment CLEAR DATA in RAM. See 2.6 (1)-(7).
7. To clear data turn TV set off. Press and hold the
service switch and then press POWER on.
NOTE: If only minor adjustments to convergence are
needed, the jig screen is not necessary. Use digital
data stored in memory and one color as a
reference(red,green or blue). DO NOT CLEAR DATA
and WRITE to ROM memory.
PV152 2-14 PROJO
Page 30

DIGITAL CONVERGENCE REMOTE
MBR3475Z
924-10092
AUXILLIARY
CURSOR RIGHT
(3X3 ADJUSTMENT)
RASTER
ROM WRITE
DIGITAL CONVERGENCE REMOTE CONTROL
PHASE
(13X9 ADJUSTMENT)
BLUE
CURSOR LEFT
CURSOR DOWN
RED
(7X5 ADJUSTMENT)
REMOVE COLOR
INITIALIZE
CURSOR UP
GREEN
ADJUSTMENT
CROSSHATCH /
VIDEO MODE
POSITION
ROM READ
PV152 2-15 PROJO
Page 31

CONVERGENCE ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURE
CONVERGENCE POINT ADJUSTMENT
Adjustment preparation
1. Select color to adjust.
“DISPLAY”-Green
“O”-Red
“SOURCE”-Blue
2. Use 4,6,2, and 5 to move the cursor position(dotted
lines).
3. Use cursor buttons to move the convergence point.
4. Three adjustment modes are available:
1. (3x3) Press “DISPLAY” 5 times
(only works when DCU is in uncorrected state).
2. (7x5) Press “O” 5 times
3. (13x9) Press “SOURCE” 5 times
For touch-up, only the (13x9) mode is necessary.
This will adjust every cross-hatch intersection point
on the screen.
For complete adjustment, start with (3x3) mode. This
will adjust center point and eight edge points only,
but will greatly reduce adjustment time. Then use
(7x5) mode, and finally (13x9) mode to finish
convergence.
If “S” distortion appears between cross-hatch lines
repeat (7x5) mode to change calculation process
while adjusting to remove distortion, then return
to(13x9) mode to finish touch-up convergence.
9. Press ”-” (ROM write) mode.
HD MODE
Receive any HD signal and repeat progressize mode
procedure.
NOTES:
1. Display only green for easier adjustment and match to
jig screen. Press “MENU”, THEN PRESS “DISPLAY”.
2. Write Data to ROM after green adjustment. Once green
has been confirmed to match jig screen, the jig screen
can be removed. Do not readjust the green color after
jig screen has been removed. This is now your reference
color.
3. Display green and red only and match red to green.
4. Display all colors and match blue to green and red.
Touch-up red color if necessary.
5. Existing DATA in ROM can be read by pressing the SWAP
button 2 times. This data can be used after replacing
a component(CRT,DY,etc.) Where complete convergence
adjustment is not necessary be careful not to overwrite
this data. DO NOT write cleared RAM data into ROM or
a completec convergence adjustment will be necessary.
WARNING: Advanced Convergence Adjustment
Procedure is to be performed only when
replacement of the Small Signal Main Module
or one or more the the CRT’s is replaced.
RASTER CENTERING
1. Press the FREEZE button to enter the Raster Phase
Adjustment Mode. Two additional lines appear, one near
the top, and one near the bottom of the screen.
Adjustment procedure
1. Recelive any NTSC signal.
2. Start adjustment at the center of the screen.
3. Continue adjustment at next closest position.
4. Adjust center area first, ending with edge sections.
5. When convergence is acceptable, press “-” to write
data to ROM memory. ROM WRITE? is displayed to
alarm system that ROM will be overwritten with new
data. Press the “-” button again to write displayed
data to ROM.
6. DATA WRITE TO ROM will take approximately 4 seconds
and no picture will be displayed.
7. Green dots will be displayed when operation is
completed.
8. Press MUTE to return to convergence pattern, then
confirm again convergence is acceptable.
PV152 2-16 PROJO
Press the MENU button to see all colors if the center cross is
other than White.
2. Press the Cursor Keys to match the selected color to
the green at the geometric center of the screen.
3. Press the RECALL, 0, or SOURCE buttons to select the
next color to be adjusted.
0= Red / Green (Yellow)
SOURCE= Green / Blue (Cyan)
RECALL= Green Only
4. Press Freeze button to exit the Raster Phase Mode. (The
two lines disappear)
Page 32

Starting Adjustment Point
Location (Intersection of
5
7
6
Lines symmetrically aligned at the
G-Only Screen
Red Alignment
Yellow Cross-hatch
Magenta Cross-hatch
CONVERGENCE ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURE
CONVERGENCE 3X3
Green 3x3 Mode Alignment
1. Start with power off, press the service button SKO1 and
hold, then press the front panel POWER button at the
same time. Set should come on with distored
convergence.
Note: Un-adjusted convergence will appear, DO NOT PRESS
ROM WRITE (“MOVE” button twice). If you do so, you
will save this un-adjusted convergence data.
2. Press DISPLAY button 5 times to access 3x3 Mode.
3. Press 2,3,4, and 6 keys to select the center adjustment
point (if not already selected).
1
G-Only Screen
3
2
4
Blinking Cursor)
8
4. Press the CURSOR KEYS at the selected adjustment point
to match the Green horizontal and vertical lines to the
Screen Jig lines.
Adjustment Points
PRT.
CONVERGENCE 7X5
Green 7X5 Mode Alignment
1. Press the 0 button 5 times to enter the 7X5 Adjustment
Mode.
2. Press the MENU button and then the RECALL button
again to project the Green color only.
3. Repeat the same 3X3 steps 3 to 5 for the GREEN 7X5
Mode Adjustment.
Red 7X5 Mode Alignment
1. Press the 0 key to select the RED + GREEN internal cross-
hatch signal.
2. Repeat the 7X5 steps 2 to 3 for the Red 7X5 adjustment.
Blue 7X5 Mode Alignment
3. Press the AVX ket to select the BLUE + GREEN colors.
4. Repeat the 7x5 steps 2 to 3 for the Blue 7X5 mode
adjustments.
Red and Blue 3x3 Mode Alignment
1. Press the 0 key to project the RED + GREEN internal
cross-hatch colors.
Cursor blinks
selected color
Internal cross-hatch is Yellow when the Red and Green lines
match, and Cyan when the Blue and Green Match
2. Press the CURSOR Keys at the selected adjustment point
to match the RED or BLUE horizontal/vertical lines tp
the Green cross-hatch lines.
3. Press the SOURCE key to select the BLUE and GREEN
cross-hatch colors. Perform step 2 and 3 for the BLUE
PV152 2-17 PROJO
Blue Alignment
CONVERGENCE 13X9
Green 13X9 Mode Alignment
1. Press the SOURCE button 5 times to enter the 13X9
Mode.
2. Press the MENU button and then the RECALL button
again to project the GREEN PRT only.
Page 33

Yellow Cross-hatch
Magenta Cross-hatch
CONVERGENCE ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURE
3. Repeat the same 3X3 steps 3 to 5, for the Green 13X9
Mode Adjustment.
Red 13X9 Mode Alignment
1. Press the 0 key to select the RED + GREEN internal cross-
hatch signals.
2. Repeat the 7x5 steps 2 to 3 for the Red 13X9 mode
adjustments.
Blue 13X9 Mode Alignment
3. Press the SOURCE key to select the BLUE + GREEN colors.
4. Repeat the 7x5 steps 2 to 3 for the Blue 13X9 mode
adjustment.
Red Alignment
Blue Alignment
ROM WRITE
Storing the New Data
Press the “-” button twice to store the convergence data
in the EPROM. (Screen goes blank for 4 seconds)
1. 1st press of “-”
2. 2nd press of “-”
3. Operation complete (Green Dots appear after completion
of operation).
PV152 2-18 PROJO
Page 34

TROUBLESHOOTING
No Raster
Is Power LED on Control Panel on?
No
Yes No
Turn off power wait (3) seconds, turn ON carefully
inspect all Green LED's on SMPS.
Did all 5 LED's turn off at the same time?
Find which LED fails to light or dims first on SMPS.
D949
-SMPS STBY +11v
Check D918,I906,I007,I009
D931
Yes
Yes
-SMPS SW +5v
Check D918,I907,I011,I012
D927
-SMPS STBY +7v
Check D918,I905,I008,I010
D912
-SMPS SW +29v (Audio)
Check E992,D910,IC01
Is Red LED Blinking on SMPS?
Yes
No
Yes
Is voltage at pin(4) of I901 14v-18v?
Check D904,R905,R906,C907,F901,R902
Has protector E991 blown?
Check I901,D961,R918,R919,Q901
Replace E991
Replace I901
Check R918,R919
No
No
Does raster appear with G and K of
Q905 shorted?
Yes
Replace Q905
No
Check Q905,D921,D908,I902,Q902,D923
Is Click of Relay heard
No
Is the voltage at pin(51) and (33) of I0013.3v?
Yes
No
Is Voltage at pin(53) of I001 low? Is the voltage at PQS2 pin(1) 7volts?
Yes
Check Q003,Q004,D922,S901,Q002
Yes
No
Is voltage at pin(23) of I001"AC Clock" in?
Yes
Check Q008,Q009,I904,D909
No
Yes
Check Q029,D035,L004
No
D927-SMPS STBY +7v
Check D918,I905,I008,I010
Check I001 pin(54)
Yes
Does reset occur?
Check I001 pin(62)
Yes
Yes
is 4mhz present?
Check I002
Replace I001
Check I001 pin(63)
Is 1.6v present?
Replace I001
No
No
No
Replace X001
Replace I006
PV152 2-19 PROJO
Page 35

Turn off power wait (3) seconds, turn ON ,carefully
inspect Green LED.
Does the Green LED tun off at the same time?
Yes
Check EP98,DP11,Q777,QH01,TH01,DH11, on
deflection module.
Does raster appear with G and K of
Yes
QP01 shorted?
Check QP01/ Replace QP01
Is the base of Q751 normal?
Yes
Check I701 pin(15) H-out,pin(8) Hvcc,
QP04,DP35,DP36
Are voltages of both ends of T751(primary side)
normal?
Yes
Check Q777,QH01,T751,T752
Check T751,R754,R755
TROUBLESHOOTING
Inspect Red LED (DP37) on Deflection, Blinking?
Yes
No
No
No Yes
No
Yes
Yes
No
Is voltage at pin(4) of IP01 14v-18v?
Has protector EP01 blown?
Check IP01,
RP10,RP11,RP12
Check IP01,DP04&5
RP10,RP11,RP12
Replace EP91
Check PQD1 for 120vac
Check DP04&5, Rp02&3,CP05
RP10,RP11,RP12
CheckVR923 on SMPS
No
No
No
Poor Video Sync
Yes
Is voltage on I601 pin (10) +28VDC?
Are Voltages on connector PZC pins (1,3,5,) normal?
Yes
Is waveform on I601 pin (3) as shown?
Refer to diag (1) below.
Yes
Yes
Is waveform on PSD3 pin (8) as shown?
Refer to diag (2) below.
Replace Deflection PWB
No
No
No
Replace Small Signal PWB
Poor White Ballance
Replace CRT PCB assy.
Replace Small Signal PWB.
No Color
No
Is input signal RF or Composite?
Diag 1
4.00Vpp
Yes
Yes
Is waveform on I201 pins (7,9) normal?
Replace Small Signal PWB.
Replace 3 Line PWB.
No
No
Diag 2
3.20Vpp
PV152 2-20 PROJO
Page 36

POWER / DEFLECTION P.W.B. DIAGRAM
CONVERGENCE
HEAT SINK
SK01:
SERVICE
SWITCH
R630
V.Size
Adj.
Convergence Unit
IK01
QK01
YOKE PLUGS
PMR
PMG
PMB
R686
H.Size
Adj. HD
Digital
PSD1
D656
D657
Q657
QH01
IK04 IK05
PCGPCR
TH01
PCB
FBT
High Voltage ADJ.
RH44
PDF
QF06
REAR
VIEW
RH44
R683
H.Size Adj.
Progressive
Mode
PV152 2-21 PROJO
D752 Q777
Q701
I601
PSD1 PSD2 PSD3
+B 120V Green LED
PQD2
DP29
PDC1
DP01
IP01
TP91
DP37
Red LED
PQD1
Page 37

SMALL SIGNAL P.W.B. DIAGRAM
MICROPROCESSOR
PFS
IC01
PR
PL
DIGITAL BOARD
HC4051
SURROUND PWB
I007
PP1
LINE COMB
PWB
I010
I011
I001
2H
VIDEO
PWB
I012
U201
Main
Tuner
U202
PinP
Tuner
REAR
VIEW
U205
FLEX
Conv.
and
PinP
Unit
TERMINAL PWB
U204
3D/
YC
QS4
PV152 2-22 PROJO
Page 38

CRT AND CONTROL P.W.B. DIAGRAM
DAG
GND
E831
PRV
DAG
GND
PGV
P851
P801
W801
R879
P852
Cathode
GREEN
R829
PTSG
PTSR
SHORT TO
KILL THE
COLOR
SHORT TO
KILL THE
COLOR
E801
PVB
DAG
GND
E8A1
P8A1
W801
P802
Cathode
RED
P8A2
CATHODE
BLUE
PTSB
SHORT TO
KILL THE
COLOR
PV152 2-23 PROJO
Page 39

CHASSIS POWER SUPPLY P.W.B.
1 9
1 11
I905
I907
1 10
PQS2 PQU2
D912
Audio F SW +29V
GREEN
D927
STBY +7V
GREEN
D931
SW +5V
GREEN
7 1
1 8
PQD2PQS1PQU1
D903
IC POWER
MONITOR RED
PQD1
2 1
S901
F901
6 Amp
D901
PA
2
1
3
PQS4
1
REAR
VIEW
I906
D949
STBY +11V
GREEN
SWITCHING
S904
S903
= RED or GREEN LED USED FOR VISUAL TROUBLESHOOTING
TRANSFORMER
I901
T901
S902
PV152 2-24 PROJO
Page 40

MENU
SM09
CONTROL P.W.B.
SOURCE
VOL -
VOL +
CH -
CH +
POWER
J
F
P
V
F
P
PV152 2-25 PROJO
Page 41

CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
POWER SUPPLY OPERATION EXPLANATION
POWER ON AND OFF
The power supply in the ZP94 & 95 chassis works very similar to the previous models, with only a few exceptions.
This power supply runs all the time when the AC is applied.
The use of the power supply creating Standby Voltage supplies eliminates the need for a Standby transformer. The
following explanation will describe the Turning ON and OFF
of the projection television. The Microprocessor I001 generates the ON-OFF control signal from pin (53). The logic
states of this pin are High = On and Low = Off. When the
set is turned On, the high from pin (53) is routed to the
Relay Driver Q002 base. This turns on Q002 and it’s collector goes low. This On/Off from the Relay Driver Q002 will
perform the following :
· Turns on the SW5+V I907 and SW+12V I908 regulators.
Which do not operate in Standby.
· Turns on the Shut Down “Power Shorted” detection circuit, Q908 and Q909.
· Turns on the Horizontal Vcc supply to the Horizontal and
Vertical drive IC, I701.
· Turns on the Relay providing AC to the Deflection Power
Supply on the Power/Deflection PWB.
B+ GENERATION FOR THE SUB POWER SUPPLY DRIVER IC:
Vcc for the Driver IC is first generated by the AC input.
This voltage is called Start Up Voltage. I901 requires 21V
DC to operate normal. However, it will begin operation at
14.5V DC on pin (4) of I901.When AC is applied, AC is
routed through the main fuse F901 (a 5 Amp fuse), then
through the Line filters L901, 902, 903 and 904 to prevent any internal high frequency radiation from radiating
back into the AC power line. After passing the filters it
arrives at the main full wave bridge rectifier D901 where it
is converted to DC voltage. One leg of the AC is routed to
a half wave rectifier D902 where it is rectified, routed
through R905 and R906 (both a 5.6K ohm resistor), filtered by C907, clamped by a 30V Zener D904 and made
available to pin (4) of I901 as start up voltage. The Red
LED D903 is illuminated by this power supply. When this
voltage reaches 14.4Vdc, the internal Regulator of I901 is
turned On and begins the operation of I901. The primary
control element of the power supply is I901 (the Switching Regulator IC), in conjunction with transformer T901.
These two components, along with the supporting circuitry,
comprise a closed loop regulation system. Unlike previous
Pulse Width Modulated (PWM) Switch Mode power supplies, the regulation system in the this chassis utilizes Frequency Control Modulation with an operational frequency
of 85KHZ to 100KHZ, corresponding to full load and no
load conditions, respectively. Primary regulation is provided by Q902, I902 and Q910, regulating the switching
frequency at pin (3) of I901 via pin 1, the regulation in-
put to the IC. Three primary voltages are developed that
are needed to sustain run, maintain regulation, and support shutdown circuitry; Run Voltage generated from pin
(8 and 9) of T901, +28V used for regulation, and STBY
+11V, respectively. The “STBY” represents “always on, designating a supply that is active whenrver the unit is connected to AC power. The Power Supply utilizes a Shutdown
circuit that can trigger Q905 from 16 input sources. (6 of
these are not operational in Standby mode). I903 is activated by Q905, applying gate voltage to Q901, which
grounds out the Vcc at pin (4) of I901, disabling the
power supply.
Audio Front 29V Regulator SW+29V indicated by D912:The
Audio Front 29V supply is generated from pin (17) of T901.
This output is protected by E992, rectified by D910 and
filtered by C918. This supply is routed to the Rear Audio
Output IC IC01. This voltage is what illuminates the Green
Visual Trouble Shooting LED, D912.
STBY+11V Regulator I906 indicated by D949: The STBY+11V
supply is generated from pin (11) of T901. This output is
rectified by D918 and filtered by C928. This supply is routed
to the Stand By +11 Regulator I906 pin (1). This voltage
is what illuminates the Green Visual Trouble Shooting LED,
D949.
STBY+7V Regulator I905 indicated by D927:The STBY+7V
supply is generated from pin (11) of T901. This output is
rectified by D918 and filtered by C928. This supply is routed
to the Stand By +7 Regulator I905 pin (1). This voltage is
what illuminates the Green Visual Trouble Shooting LED,
D927.
The sub power supply in theZP94 & 95 chassis works very
similar to the previous models, with some very significant
exceptions. This power supply runs at 50% efficiency when
the AC is applied with the set OFF. The use of the power
supply creating the STBY+11V supply eliminates the need
for a Standby transformer. The following explanation will
describe the Turning ON and OFF of the projection television.
POWER SUPPLY OPERATIONAL FREQUENCY DURING STANDBY:
When the Horizontal deflection is defeated, the power supply
no longer has a deflection load. This low current demand is
detected by the three resistors connected to the source of
the internal Switch MOS FET inside I901 via pin (2). Pin
(1) of I901 is the over current detection pin, however it is
also the current demand sensing pin. When the current
demand is low due to horizontal defeat, pin (1) will be less
than 1.4V and the internal frequency will switch to 200Khz.
This is caused by the Quasi Resonant circuit operation.
This reduction of power supply frequency will move the
frequency above the Bell of the power supply transformer
and all secondary voltages will reduce to approximately 1/
2 of their normal voltage.Due to the fact that the power
PV152 3-1 PROJO
Page 42

CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
supply is still operating at 1/2 voltage output, the Green
LEDs used for visual trouble sensing will reduce in intensity, however they will remain lit. With the exception of
the SW+12V and SW+5V regulator. Which are turned off in
Stand By.
POWER SUPPLY FREQUENCY OF OPERATION DURING RUN:
When the Horizontal deflection is in operation, the power
supply frequency fluctuates in accordance to screen brightness, causing differing demands for High Voltage replacement. The normal operational range for the power supply is
between 80 KHz to 100 KHz. The lower the frequency, the
higher the current supplied to the load. During Stand-By,
it operates at 200KHz.
AC LOSS DETECTION:
AC is monitored by the AC Loss detection circuit. The AC
input from PQS1 pin (10) is rectified by DN09. This charges
up C009 and through DN08 it charges C008. When AC is
first applied, C008 charges slightly be-hind C009 preventing activation of Q001. If AC is lost, C009 discharges rapidly pulling the base of Q001 low, however DN08 blocks
C008 from discharging and the emitter of Q001 is held
high. This action turns on Q001 and produces a high. This
high is routed through D029 to the base of Q022 turning
it ON. The collector goes low and pulls the base of Q023
low turning it ON. The emitter of Q023 is connected to
STBY +11V, so when it turns ON, its collector output goes
HIGH. This high is now called V Mute 1.
SW+9V AND SW+5V REGULATOR OPERATION IN STAND-BY:
Both of these ICs as well as the STBY+11V and the STBY+7V
regulators are DC to DC converters just like last year. This is
because of the wide range of input voltages from Stand-By
to Normal operation of the Power Supply. The SW+12V regulator (I908) and the SW+5V regulator (I907) are shut off
during Stand-By mode. This is accomplished by Q002 and
Q903. When the High for the power On/Off pin (53) of the
Microprocessor is inverted by the relay driver Q002, and
routed through the PQS1 connector pin (8). It is detected
by Q903, it’s collector will go low. This will pull pin (5) of
I907 and I908 low, turning off the two DC to DC converters.
SHUT DOWN CIRCUIT:
Shut down occurs when the shutdown SCR Q905 is activated by gate voltage. When Q905 receives gate voltage of
0.6V, the SCR fires and give a ground path for the emitter
of the LED inside I903. The light produced by turning on
this LED turns on the internal photo receiver and generates a high out of pin (3). This high is routed to the gate
of Q901 turning it on. This grounds pin (4) of I901 removing Vcc and the power supply stops working. The reason for the photo sensor I903 is to isolate hot and cold
ground.
SOME SHUT-DOWN DETECTION CIRCUITS SHUT OFF DURING STAND-BY:
During Stand-By, all of the secondary voltages are reduced
to approximately 50% of their normal voltage, except the
STBY voltages. This could cause a potential problem with
the Short Detection circuits for shutdown. To avoid accidental shut down, Q903 also controls the activity of Q908
and Q909. During Stand-By, Q903 is turned On. This allows
the Base of Q908 to be pulled through D945. This action
turns off Q908. When Q908 is off, it doesn’t supply emitter
voltage to the collector of Q909. The base of Q909 is connected to 6 Low Detection in-puts. When the power supply operates at 50%, the Short Detection circuit could
activate. By turning off Q909, no accidental shut down
operation can occur.
SUB POWER SUPPLY VISUAL LEDs:
ZP94 & 95 Chassis has 5 Green and 1 Red LED on Sub Power
Supply PWB. This chassis utilizes 5 Green LED’s in the power
supply cold side and a Red LED in the HOT side. The power
supply operates it two different modes, Standby and in
Projection On mode.
TURNING ON THE DEFLECTION POWER SUPPLY
When the Projection Television is turned on, the Microprocessor outputs a high for Pin (35) which is inverted by
Q002. This low is routed through the connector PQS1 pin
(8) on the signal PWB to the Sub Power Supply PWB. It is
then routed to Q903, its collector will go High. This will
pull up pin (5) of I907 and I908, turning ON the two DC to
DC converters. The output of both DC to DC converters
I907 and I908, are used by the relay which supplies AC
voltage to the Deflection Power Supply on the Power/Deflection PWB. The output of I907 SW+5V regulator supplies B+ for pin (3) of the relay S901. The output of I908
SW+12V drives the base of Q911 turning it On and grounding pin (4) of the relay S901. The relay now provides AC to
the bridge rectifier on the Deflection Power Supply.
HORIZONTAL B+ ON AND OFF CIRCUIT:
When the power supply goes into Stand-By mode (TV Off),
the Horizontal Drive signal for deflection is shut off This
is accomplished by Q002 and QP04. The Low out produced
from the Power On/Off pin 53 of the Microprocessor routed
through Q002 located on the Signal PWB. This Low is sent
through the PQS1 connector pin (8) to the Sub Power
Supply PWB and then through PQD2 connector pin (1) and
sent to the Deflection PWB. This Low is detected by the
base of QP04 turning it ON and the SBY +11V connected to
it’s emitter is made available at its collector. The collector
is connected to the Deflection B+ pin (22) of the Horizontal and Vertical Drive IC, I701 via pin (8). This action stop
I701 from producing a horizontal deflection drive signal.
PV152 3-2 PROJO
Page 43

CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
HIGH VOLTAGE DRIVE CIRCUIT:
When QN04 is turned on, the 11V standby will also be applied to the High Voltage Drive IC IH02 pin 14 via RN15
and DN13. When this occurs, the IC will stop generating
the drive signal that is used to produce High Voltage via
QH08, the High Voltage Driver. Again, this is done to prevent CRT burn, especially during sweep loss.
GREEN LED:
The Deflection B+ 120V supply is generated from pin (13)
of TP91. This output is rectified by DP11 and filtered by
CP17. This supply is routed to the Horizontal Drive Circuit
and the High Voltage generation circuit. This voltage is
what illuminates the Green Visual Trouble Shooting LED,
DP29
POWER SUPPLY SHUTDOWN EXPLANATION
This chassis utilizes IP01 as the Osc.\Driver \Switch for
the Deflection power supply, just as the previous chassis
have done. This IC is very similar to the previous versions,
however it does differ in Frequency (described previously).
The Shutdown circuit (cold ground side detection), is used
to turn off the Relay S901 via the following circuit, QP01
(the Shutdown SCR), Connector PQD2, Q911 the Relay Driver
and the Relay S901. The Power Supply utilizes a Shutdown
circuit that can trigger QP01 from 14 input sources. When
any of these inputs cause a high on the gate of QP01, the
relay disengages, disabling the deflection power supply.
All of the Power Supply Shutdown circuitry can be broken
down into the following five groups;
SHUT DOWN CIRCUIT:
Shut down occurs when the shutdown SCR QP01 is activated by gate voltage. When QP01 receives gate voltage of
0.6V, the SCR fires and give a ground path for the pin (5)
of Connector PQD2 called PROTECT. This Low is routed to
the Sub Power Supply PWB and is impressed on the base of
the Relay Driver Transistor Q911 turning it Off. When Q911
turns Off the Relay S901 will disengage and remove the AC
source from the Deflection Power Supply.
VOLTAGE LOSS DETECTION
1. Shorted 220V (DP31 and DP32) Inverted by QP03 then
through DP22 The cathode of DP31 is connected directly to the 220V line. If it shorts this circuit is activated and pulls the base of QP03 low. This output High
is routed through DP22 to the gate of the Shut Down
SCR QP01.
2. Shorted SW+8V (DP33) Inverted by QP03 then through
DP22 The cathode of DP33 is connected directly to the
SW+8V line. If it shorts this circuit is activated and
pulls the base of QP03 low. This output High is routed
through DP22 to the gate of the Shut Down SCR QP01.
3. Shorted 28V (DP30) Inverted by QP03 then through
DP22 The cathode of DP30 is connected directly to the
28V line. If it shorts this circuit is activated and pulls
the base of QP03 low. This output High is routed through
DP22 to the gate of the Shut Down SCR QP01.
4. Shorted Side Pin Cushion Circuit (D760 and Q754) then
through DP34 The Side Pin Cushion circuit is comprised
of I651, Q652 through Q657 If a problem occurred in
this circuit that creates a Low on the cathode of D760,
the low will be routed to the base of Q754, turning it
Off. This output High is routed through DP34 to the
gate of the Shut Down SCR QP01.
5. Shorted Deflection Transformer or Misoperation (D756
and Q754) then through DP34 The Deflection circuit
generates the actual Drive signal used in the High Voltage section. If a problem occurs in this circuit, the
CRTs could be damaged or burnt. D757 is connected to
D759 which is normally rectifying pulses off the Deflection Transformer T753. This rectified voltage is normally
sent through D757, D756 to the base of Q754 keeping
it On and it’s collector Low. If the Deflection circuit
fails to produce the pulses for rectification, the base
voltage of Q754 disappears and the transistor turns Off
generating a High on its collector. This output High is
routed through DP34 to the gate of the Shut Down SCR
QP01.
6. Heater Loss Detection (DH26, DH27,QH07 and DP34)
This voltage does not go to the CRTs.The Flyback Transformer TH01 generates a pulse called Heater. (Note: This
does not go to the CRTs as heater voltage, it’s used for
Excessive High Voltage Detection. If a problem occurs
in this circuit, the Ex-cessive High Voltage Detection
circuit wouldn’t operate. It would be possible for there
to be High Voltage but the circuit detecting Excessive
High Voltage couldn’t work. DH26 is connected to DH24
which is normally rectifying pulses off the Flyback Transformer TH01. This rectified voltage is nor-mally sent
through DH26, DH27 to the base of QH07 keeping it On
and its collector Low. If the Heater Pulse fails to produce the pulses for rectification, the base voltage of
Q754 disappears and the transistor turns Off generating
a High on its collector. This output High is routed
through DH30 to the anode of DP34 to the gate of the
Shut Down SCR QP01.
NEGATIVE VOLTAGE LOSS DETECTION:
7. -M28V Loss Detection (DP23, DP24) RP31 (18K ohm) is
connected to the negative –M28V line and RP30 (22K
ohm) is connected to the positive +29V line. The Cathode of DP23 monitors the neutral point where these
two resistors are connected. If the negative voltage disappears, the zener DP23 fires. This high is routed through
DP24 to the gate of the Shut Down SCR QP01 and Shut
Down occurs.
8. SW-8V Loss Detection (DP28, DP29) RP26 (3.3K ohm) is
PV152 3-3 PROJO
Page 44

CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
connected to the negative SW-8V line and RP25 (3.3K
ohm) is connected to the positive SW+8V line. The Cathode of DP28 monitors the neutral point where these
two resistors are connected. If the negative voltage disappears, the zener DP28 fires. This high is routed through
DP29 to the gate of the Shut Down SCR QP01 and Shut
Down occurs.
EXCESSIVE CURRENT DETECTION:
9. 120V Deflection Power Supply (RP17, QP02, DP15, DP16
and DP18) If an excessive current condition of the Deflection B+ is detected by RP17 a 0.47 ohm resistor, the
base of QP02 would drop. This would turn on QP02 and
the high produced at the collector would fire zener DP15.
This High would be routed through DP16 through DP18
to the gate of the Shut Down SCR QP01 and Shut Down
occurs.
10. 28V Vertical IC I601 Power Supply (R645, Q609, D615,
and DP34) If an excessive current condition of the Vertical B+ is detected by R645 a 0.68 ohm resistor, the
base of Q609 would drop. This would turn on Q609 and
the high produced at the collector would be routed
through D615 through DP34 to the gate of the Shut
Down SCR QP01 and Shut Down occurs.
VOLTAGE TOO HIGH DETECTION:
11. Excessive High Voltage Detection (DH31, RH54, RH55
and DH24). Sensed from the Heater Voltage generated
from pin (5) of the Flyback Transformer TH01. Also,
(DH42) sends a high command to the Horizontal Driver
IC IH02, to defeat Horizontal Drive Output The Flyback
Transformer TH01 generates a pulse called Heater. (Note:
This does not go to the CRTs as heater voltage, its used
for Excessive High Voltage Detection). If this voltage
goes too high indicating an excessive High Voltage
condition, the voltage divider comprised of RH54 and
RH55 would impress a high on the cathode of DH31.
This high is routed through DH34 to the gate of the
Shut Down SCR QP01 and a Shut Down occurs.
12. Side Pincushion failure generating a High. (D754, and
D753) The Side Pin Cushion circuit is comprised of I651,
Q652 through Q657 If a problem occurred in this circuit that creates a High on the cathode of D754, the
High will be routed through D753 to the gate of the
Shut Down SCR QP01.
13. Deflection B+ Too High. (DP17, RP21 and RP22 RP21
and RP22 form a voltage divider. The top side of RP22
is monitored by DP17. If this voltage goes too high,
zener DP17 will fire. This high is routed through DP18
to the gate of the Shut Down SCR QP01 and Shut Down
occurs.
14. Heater Voltage from the Deflection Power Supply Too
High Detection. (DP27 and DP28) The Heater Voltage
for the CRTs filament is generated in the Deflection Power
Supply. This voltage is monitored by DP27. If this voltage goes too high, zener DP27 will fire. This high is
routed through DP28 to the gate of the Shut Down SCR
QP01 and Shut Down occurs.
ABL CIRCIUT
The ABL voltage is generated from the ABL pin of the Flyback
transformer, TH01. The ABL pull-up resistors are RH58 and
RH59. They receive their pull up voltage from the B+
120V(V2 ) for Deflection line generated from the Power
Supply via TP91 pin 13, rectified by DP11, filtered by CP33
and then routed through the excessive current sensing
resistor RP17.
ABL VOLTAGE OPERATION:
The ABL voltage is determined by the current draw through
the Flyback transformer. As the picture brightness becomes
brighter or increases, the demand for replacement of the
High Voltage being consumed is greater. In this case, the
flyback will work harder and the current through the Flyback
increases. This in turn will decrease the ABL voltage. The
ABL voltage is inversely proportionate to screen brightness. Also connected to the ABL voltage line is DH33. This
zener diode acts as a clamp for the ABL voltage. If the ABL
voltage tries to increase above 12V due to a dark scene
which decreases the current demand on the flyback, the
ABL voltage will rise to the point that DH33 dumps the
excess voltage into the 12 line.
ACCL TRANSISTOR OPERATION:
The ABL voltage is routed through the PSD3 connector,
through the PSZ2 connector, to the base of QX13. Under
normal conditions, this transistor is nearly saturated. QX13
determines the voltage being supplied to the cathode of
DX05, which is connected to pin 45 of the Jungle IC, IX01.
During an ABL voltage decrease, due to an excessive bright
circumstance, the base of QX13 will go down, this will drop
the emitter voltage which in turn drops the cathode voltage of DX05. This in turn will pull voltage away from pin 45
of the jungle IC, IX01. Internally, this reduces the contrast
and brightness voltage which is being controlled by the I
C bus data communication from the Microprocessor arriving at pin 27 and 28 of the jungle IC and reduces the
overall brightness, preventing blooming.
SPOT CIRCUIT:
When QN04 is turned on, the 11V standby will be applied
to the anode of DN11, forward biasing it. This voltage will
then pass through DN11, get zenered by DN09, and go to
pin 2 of PSD3, where it will activate the Video Mute circuitry Q022 - Q024 on the Signal PWB. This is done to
prevent CRT burn. Another input to this circuit is the I701
DAC3 line. This will activate when accessing certain adjustment parameters in the service mode; i.e. turning off
vertical drive for making CRT drive or cut-off adjustments.
PV152 3-4 PROJO
Page 45

CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
SPOT PROTECT or SPOT KILLER:
As mentioned earlier, when the deflection power supply
goes into shutdown for whatever reason, a low potential
will be applied at the cathode of DN14, forward biasing it
and causing current flow through RN07. Once again, this
increase of current flow through RN07 will bias on QN04
and the events described previously will occur.
SWEEP LOSS DETECTION:
The key component in the Sweep Loss Detection circuit is
QN04. This transistor is normally biased off. When the base
becomes more negative, it will be turned on, causing the
Standby 11V to be applied to two different circuits, the
Spot circuit and the High Voltage Drive circuit.
VERTICAL / HORIZONTAL BLANKIN:
Loss of Vertical Blanking:
When the 24Vpp positive vertical blanking pulse is missing from the base of QN01, it will be turned off, which will
cause the collector to go high. This in turn will cause QN02
to turn on, creating an increase of current flow from emitter to collector and up through RN07, (which is located
across the emitter base junction of QN04), to the 11V
standby supply. This increase of current flow through RN07
will bias on QN04 and the events described previously will
occur.
Loss of Horizontal Blanking:
When the 11.6Vpp positive horizontal blanking pulse is
missing from the base of QN05, it will be turned off, which
will cause the collector to go high. This in turn will cause
QN03 to turn on, creating an increase of current flow from
emitter to collector, through RN06, and up through RN07.
Again, this increase of current flow through RN07 will bias
on QN04 and the events described previously will occur.
CONCERNING QN04:
There are several factors that can affect the operation of
QN04; namely loss of vertical or horizontal blanking and
spot killer or spot protect from a shutdown in the deflection power supply.
MICRO PROCESSOR DATA COMMUNICATION
The Microprocessor must keep in communication with the
Chassis to maintain control over the individual circuits.
Some of the circuits must return information as well so the
Microprocessor will know how to respond to different request. The Microprocessor uses a combination of I 2 C Bus
communication and the Standard Data, Clock and Load lines
for control. The I 2 C communication scheme only requires
2 lines for control. These lines are called SDA and SCL. System Data and System Clock respectively. The Microprocessor also requires the use of what are called Fan Out ICs or
DACs, (Digital to Analog Converters). This allows the Microprocessor to use only two lines to control many differ-
ent circuits. Also, due to the fact that this Microprocessor
operates at the new 3.3Vdc voltage, it requires a Level
Shift IC to bring up the DC level of the control lines to
make it compatible with the connected ICs.
ON THE SIGNAL PWB:
Main Tuner U201:
The Microprocessor controls the Main Tuner by Clock, Data
and Enable lines. Clock, Data and Enable lines for the Main
Tuner are output from the Microprocessor at pins (20 Clock,
21 Data and 44 FEENABLE1) respectively. Pin (44) FEENABLE1
goes directly to the Main Tuner at pin (6), where as the
Clock and Data lines must be routed through the Level
Shift IC I014 to be brought up to 5V. Clock and Data from
the Microprocessor arrive at I014 (Level Shift) at pins (2
and 3) and are output at pins (18 and 17). They arrive at
the Main Tuner at pins (4 and 5).
PIP Tuner U202:
The only difference for the PinP tuner control lines is related to the PinP Enable line. This is output from the Microprocessor pin (43 FEENABLE2) to the PinP Tuner at pin
(17). Clock and Data are the same as for the Main Tuner.
EEPROM I002:
The EEPROM is ROM for many different functions of the
Microprocessor. Channel Scan or Memory List, Customer set
ups for Video, Audio, Surround etc… are memorized as
well. Also, some of the Microprocessors internal sub routines have variables that are stored in the EEPROM, such as
the window for Closed Caption detection. Data and Clock
lines are SDA1 from pin (2) of the Microprocessor to pin
(5) of the EEPROM and SCL2 from pin (3) of the Microprocessor to pin (6) of the EEPROM. Data travels in both directions on the Data line.
Flex Converter U205:
The projection television is capable of two different horizontal frequencies. 31.75Khz for everything except HD and
33.75Khz for HD. (High Definition). The Flex Converter is
responsible for receiving any video input and converting
it to the related output. This output is controlled by sync
and by the customer’s menu and how it is set up. The set
up can be 4X3 or 16X9, sometimes called letterbox. The
Flex Converter can take any NTSC, S-In, Component in NTSC,
Progressive, Interlaced, 480I, 720P, 1080I signal. Control
for the Flex Converter is Clock, Data and Enable lines. Clock,
Data and Enable lines for the Flex Converter are output
from the Microprocessor at pins (20 Clock, 21 Data and 46
FCENABLE). FCENABLE Clock and Data lines must be routed
through the Level Shift IC I014 to be brought up to 5V.
They arrive at I014 at pins (2 Clock, 3 Data and 4 FCENABLE)
and are output at pins (18, 17 and 16) respectively.
PV152 3-5 PROJO
Page 46

CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
DAC1 I003 and DAC2 I004:
These Digital to Analog converter acts as an extensions of
the Microprocessor( Sometimes called an Expansion ICs).
The purpose of these ICs are to reduce the number of pins,
(fan out) of the Main Microprocessor I001. The Main Microprocessor send Clock and Data via I2C bus to the DAC1
IC. The output from the Microprocessor is pin (2 SDA1 and
3 SCL1) which arrives at the DAC1 and DAC2 ICs at pins (5
and 6) respectively.
Level Shift I014:
The Microprocessor operates at 3.3VDC. Most of the Circuits controlled by the Microprocessor operate at 5VDC.
The Level Shift IC steps up the DC voltage to accommodate.
ON THE DEFLECTION PWB:
Sweep Control I701:
The Sweep Control IC is responsible for generating Horizontal Drive and Vertical Drive signals. The Microprocessor
must tell the IC when certain things are done in the Service Menu. When Cut Off is performed, the Vertical is collapsed. The Microprocessor tells I701 to stop producing
Vertical Drive. At the same time, I701 must stop the Spot
Killer circuit from operating. This is accomplished by placing pin (24 DAC3) high which activates QN07 which inhibits spot killer high. Also, when H.Phase is adjusted, the
Microprocessor controls the H. Drive signals phase in relationship to H.Blk which is timed with video sync. This
gives the appearance that the horizontal centering is being moved. Communication from the Microprocessor via
pins (59 SDA2 and 60 SCL2) to the PSD2 connector pins (2
and 3) and then to I701 pins (16 and 17) respectively.
ON THE SUB VIDEO PWB (2H VIDEO):
Jungle IX01:
The Video Processing IC is responsible for controlling video/
chroma processing before the signal is made available to
the CRTs. Some of the emphasis circuits are controlled by
the customer’s menu. As well as some of them being controlled by AI, (Artificial Intelligence). Communication from
the Microprocessor via pins (59 SDA2 and 60 SCL2) to the
PSZ2 connector pins (1 and 2) and then to IX01 pins (27
and 26) respectively.
MICROPROCESSOR AS THE SOURCE FOR OSD:
The Microprocessor receives information related to timing
for H. Blanking and V. Blanking. These arrive at pins (49
and 55) respectively. The Microprocessor determines the
position for each display using these signals as a timing
pulse. When it’s necessary, the Microprocessor generates
1uSec pulses from pins (37 Red, 38 Green and 39 Blue)
that are routed through the PSZ1 connector pins (14 Red,
16 Green and 18 Blue) and then through (QX07 Red, QX08
Green and QX09 Blue) and then sent to the Jungle IC IX01
pins (39 Red, 38 Green and 37 Blue) as OSD signals. When
the OSD signals are high, they turn on the output of the
Red or Green or Blue chroma amps inside the jungle IC and
output a pulse to the CRTs to generate that particular character in the particular color. HALF TONE PIN (40): This pin
is responsible for controlling the background transparency
of the Main Menu. When the customer calls up the Main
Menu, they can select the CUSTOM section. Within the
CUSTOM section is MENU BACK-GROUND. There are three
selections for this, GRAY, SHADED, and CLEAR. · CLEAR:
Selection turns off any background for the Menu and video
is clearly seen behind the Menu. · SHADED: Selection add a
transparent background which makes the Menu easier to
see and also some of the video behind the Menu. · GRAY:
Selection generates a GRAY background for the MENU blocking video behind the Menu. This is accomplished by outputting any one of three different pulses from pin (40) of
the Microprocessor. This signal is then routed through the
PSZ1 connector pin (20) to the jungle IC IX01 pin (47) as
YM signal which does the following: · CLEAR: No output
during the display of the Menu. · SHADED: 1/2 Vcc pulse
equal to the timing of the Menu background. · GRAY: Full
Vcc equal to the timing of the Menu background.
OSD BLANKING PIN (51):
This pin is responsible for muting the video behind each
character produced by the Microprocessor. This pulse is in
exact time with the character, however it is slightly longer.
In other words, just before any character is produced, this
pin goes high and just after any character turns off, this
pin turns off. This clears up the video behind the OSD
character to make it easier to read. OSD Blk is produced
from pin (51) of the Microprocessor. This signal is then
routed through Q013, then through Q007, through the
PSZ1 connector pin (19) to the jungle IC IX01 pin (36) as
YS1 signal which mutes the video.
P Blk PICTURE BLANKING PIN (56):
This pin is responsible for muting the video when the Microprocessor deems it necessary. This would be during power
up or power off, child lock, channel change, or selecting a
video input with no video input available. P Blk is produced from pin (56) of the Microprocessor. This signal is
then routed through Q007, through the PSZ1 connector
pin (19) to the Jungle IC IX01 pin (36) as YS1 signal which
mutes the video.
PV152 3-6 PROJO
Page 47

MODEL PARTS LIST
The following information is for models in and
out of warranty. The ZP 94/95 models are module
level repair.
To Order Parts:call 1-888-3-ZENITH
fax 1-888-6-ZENITH
By Mail: ZENITH NATIONAL PARTS
SALES AND DISTRIBUTION CENTER
P O Box 240007
Huntsville, AL 35824-6407
CM152 4-1 PROJO - MODEL PARTS
Page 48

MODEL PARTS
IQC50M94W
ZPN LOC DESC
809-10543 POWER / DEFLECTION PWB
809-10542 SIGNAL PWB ASSY
809-10548 VIDEO CHROMA PWB
809-10533 CRT / PRT PWB ASSY
809-10532 AUDIO / MATRIX PWB
809-10546 TERMINAL / JACKPACK PWB ASSY
809-10547 STANDBY POWER SUPPLY
809-10565 COMB FILTER, 3 LINE
811-10034 A/C LINE
814-10160 PANEL W/RF SWITCH
812-10529 FOCUS BLOCK / BLEEDER ASSY
849-10013 SPEAKER
965-10001 CASTER
857-10194 01 KEYBOARD PANEL/PLASTIC
809-10545 01A REMOTE CONTROL PWB
NSP 02 LENS CRT METAL
992-10029 03 MIRROR
NSP 04 BARRIER BOARD
814-10150 05 REAR COVER, UPPER
NSP 06 FRONT COVER BOARD
NSP 07 BACK CENTER BAR
814-10152 08 BACK COVER, LOWER
857-10194 09 GRILLE
992-10031 10 MIRROR METAL A
992-10032 11 MIRROR METAL B
874-10023 12/13/14 SCREEN ASSY
900-10045 15 LIQUID COUPLER-RED
900-10046 16 LIQUID COUPLER-GREEN
900-10047 17 LIQUID COUPLER-BLUE
924-10092 900 REMOTE
971-10015 18/19/20 LENS & HOUSING ASSY (CPD78)
895-10116 21/22/23 YOKE RED, BLUE, GREEN
IQC60M94W
ZPN LOC DESC
809-10543 POWER / DEFLECTION PWB
809-10542 SIGNAL PWB ASSY
809-10548 VIDEO CHROMA PWB
809-10533 CRT / PRT PWB ASSY
809-10532 AUDIO / MATRIX PWB
809-10546 TERMINAL / JACKPACK PWB ASSY
809-10547 STANDBY POWER SUPPLY
809-10565 COMB FILTER, 3 LINE
811-10034 A/C LINE
814-10160 PANEL W/RF SWITCH
812-10529 FOCUS BLOCK / BLEEDER ASSY
849-10013 SPEAKER
965-10001 CASTER
857-10194 01 KEYBOARD PANEL/PLASTIC
809-10545 01A REMOTE CONTROL PWB
NSP 02 LENS CRT METAL
992-10029 03 MIRROR
NSP 04 BARRIER BOARD
814-10149 05 REAR COVER, UPPER
NSP 06 FRONT COVER BOARD
NSP 07 BACK CENTER BAR
814-10151 08 BACK COVER, LOWER
857-10196 09 GRILLE
992-10031 10 MIRROR METAL A
992-10032 11 MIRROR METAL B
874-10023 12/13/14 SCREEN ASSY
900-10045 15 LIQUID COUPLER-RED
900-10046 16 LIQUID COUPLER-GREEN
900-10047 17 LIQUID COUPLER-BLUE
924-10092 900 REMOTE
971-10015 18/19/20 LENS & HOUSING ASSY (CPD78)
895-10116 21/22/23 YOKE RED, BLUE, GREEN
PV152 4-2 PROJO
Page 49

MODEL PARTS
IQC50H95W
ZPN LOC DESC
809-10543 POWER / DEFLECTION PWB
809-10582 SIGNAL PWB ASSY
809-10548 VIDEO CHROMA PWB
809-10533 CRT / PRT PWB ASSY
809-10567 VELOCITY MODULATOR PWB
809-10532 AUDIO / MATRIX PWB
809-10546 TERMINAL / JACKPACK PWB ASSY
809-10547 STANDBY POWER SUPPLY
811-10034 A/C LINE
814-10160 PANEL W/RF SWITCH
812-10529 FOCUS BLOCK / BLEEDER ASSY
849-10013 SPEAKER
965-10001 CASTER
857-10194 01 KEYBOARD PANEL/PLASTIC
809-10545 01A REMOTE CONTROL PWB
NSP 02 LENS CRT METAL
992-10030 03 MIRROR
NSP 04 BARRIER BOARD
814-10150 05 REAR COVER, UPPER
NSP 06 FRONT CONVERGENCE COVER
NSP 07 BACK CONTROL BAR
814-10152 08 BACK COVER, LOWER
857-10194 09 GRILLE
992-10031 10 MIRROR METAL A
992-10032 11 MIRROR METAL B
874-10006 12/13/14 SCREEN ASSY
900-10045 15 LIQUID COUPLER-RED
900-10046 16 LIQUID COUPLER-GREEN
900-10047 17 LIQUID COUPLER-BLUE
924-10092 900 REMOTE
971-10015 18/19/20 LENS & HOUSING ASSY (D78)
895-10116 21/22/23 YOKE RED, BLUE, GREEN
IQC60H95W
ZPN LOC DESC
809-10543 POWER / DEFLECTION PWB
809-10582 SIGNAL PWB ASSY
809-10548 VIDEO CHROMA PWB
809-10533 CRT / PRT PWB ASSY
809-10567 VELOCITY MODULATOR PWB
809-10532 AUDIO / MATRIX PWB
809-10546 TERMINAL / JACKPACK PWB ASSY
809-10547 STANDBY POWER SUPPLY
811-10034 A/C LINE
814-10160 PANEL W/RF SWITCH
812-10529 FOCUS BLOCK / BLEEDER ASSY
849-10013 SPEAKER
965-10001 CASTER
857-10194 01 KEYBOARD PANEL/PLASTIC
809-10545 01A REMOTE CONTROL PWB
NSP 02 LENS CRT METAL
992-10030 03 MIRROR
NSP 04 BARRIER BOARD
814-10149 05 REAR COVER, UPPER
NSP 06 FRONT CONVERGENCE COVER
NSP 07 BACK CONTROL BAR
814-10151 08 BACK COVER, LOWER
857-10196 09 GRILLE
992-10031 10 MIRROR METAL A
992-10032 11 MIRROR METAL B
874-10006 12/13/14 SCREEN ASSY
900-10045 15 LIQUID COUPLER-RED
900-10046 16 LIQUID COUPLER-GREEN
900-10047 17 LIQUID COUPLER-BLUE
924-10092 900 REMOTE
971-10015 18/19/20 LENS & HOUSING ASSY (D78)
895-10116 21/22/23 YOKE RED, BLUE, GREEN
PV152 4-3 PROJO
Page 50

Page 51

PV152 5-1 PROJO
Page 52

SECTION 6
ZP95 Only
ZP94/95 Exploded View Front
CRITICAL SAFETY COMPONENTS ARE IDENTIFIED BY THE LETTER “X“ IN THEIR
COMPONENT DESIGNATORS. REPLACE ONLY WITH PART NUMBERS SPECIFIED.
5-3
ALL SYMBOLS WITH “M” ON END OF DESIGNATOR
INDICATE SURFACE MOUNTED COMPONENT
ZP94/94 SHEET 3
Page 53

ZP94/95 Exploded View Back
CRITICAL SAFETY COMPONENTS ARE IDENTIFIED BY THE LETTER “X“ IN THEIR
COMPONENT DESIGNATORS. REPLACE ONLY WITH PART NUMBERS SPECIFIED.
5-4
ALL SYMBOLS WITH “M” ON END OF DESIGNATOR
INDICATE SURFACE MOUNTED COMPONENT
ZP94/94 SHEET 4
Page 54

ZP95 Only
ZP94/95 Interconnect
CRITICAL SAFETY COMPONENTS ARE IDENTIFIED BY THE LETTER “X“ IN THEIR
COMPONENT DESIGNATORS. REPLACE ONLY WITH PART NUMBERS SPECIFIED.
5-5
ALL SYMBOLS WITH “M” ON END OF DESIGNATOR
INDICATE SURFACE MOUNTED COMPONENT
ZP94/94 SHEET 5
Page 55

ZP94/95 Wiring Diagram
CRITICAL SAFETY COMPONENTS ARE IDENTIFIED BY THE LETTER “X“ IN THEIR
COMPONENT DESIGNATORS. REPLACE ONLY WITH PART NUMBERS SPECIFIED.
5-6
ALL SYMBOLS WITH “M” ON END OF DESIGNATOR
INDICATE SURFACE MOUNTED COMPONENT
ZP94/94 SHEET 6
Page 56

SECTION 6
TO SHEET ?
TO SHEET 7
Jackpack
TO SHEET 5
Deflection
TO SHEET 7
Jackpack
TO SHEET 8
Comb Filter
TO SHEET ?
TO SHEET 2
Tuner
TO SHEET ?
TO SHEET 3
Power Supply
TO SHEET 11
Control Panel
TO SHEET 3
Power Supply
TO SHEET 12 Audio
TO SHEET 3 Power Supply
TO SHEET 3
Power Supply
I001-63
I001-62
I001-2
I001-3
I001-55
I001-23
I001-49
PIN RUN PIN RUN PIN RUN
10 10 10
2 4.8 2 -.7 2 4.2
3 4.9 3 -.7 3 5.0
43.4 4 0 45.0
53.2 54.8 57.0
61.8 64.9 PINRUN
72.1 7 .1 15.3
81.5 85.0 2 0
9 0 PIN RUN 3 2.5
10 3.6 1 .2 PIN RUN
11 3.6 2 4.5 1 5.3
12 1.6 3 4.6 2 0
13 1.6 4 4.0 3 3.3
14 1.6 5 4.0 PIN RUN
15 3.2 6 4.6 1 7.1
16 3.2 7 4.6 2 0
17 0 8 0 3 5.0
18 0 9 0 PIN RUN
19 0 10 5.0 1 5.0
20 3.0 11 0 2 2.9
21 3.0 12 0 3 2.9
22 3.8 13 4.9 4 2.9
23 1.3 14 4.9 5 .1
24 2.7 15 4.9 6 0
25 3.2 16 5.0 7 .1
26 2.2 PIN RUN 8 .1
27 2.3 1 5.0 9 0
28 1.4 2 5.0 10 0
29 0 3 .4 11 0
30 1.4 4 4.6 12 0
31 2.3 5 4.6 13 0
32 1.5 6 .4 14 0
33 3.2 7 .4 15 0
34 1.8 8 0 16 *
35 1.5 9 5.0 17 4.9
36 1.6 10 0 18 4.9
37 0 11 0 19 0
38 0 12 0 20 5.0
39 0 13 5.0 PIN RUN
40 0 14 4.9 E 3.3
41 1.4 15 4.9 B 3.8
42 1.4 16 5.0 C 5
43 0 PIN RUN
44 .3 1 5.0
45 0 2 5.0
46 2.9 3 4.8
47 1.8 4 5.1
48 1.8 5 5.3
49 2.8 6 0
50 3.0 7 0
51 0 8 0
52 3.0 9 0
53 2.8 10 0
54 3.2 11 0
55 3.1 12 2.6
56 0 13 2.3
57 3.2 14 2.6
58 3.2 15 5.0
59 4.8 16 9.1
60 4.8 PIN RUN
61 3.2 1 0
62 1.6 2 4.2
63 1.6 3 9.3
64 0 4 9.1
511.1
Main Micro Voltages
I001
I002
I003
I004
I005
I009
I010
I011
QO29
I012
I008
I014
ZP94/95 Main Microprocessor Circuit
1
2345678910
G
F
E
D
C
B
A
CRITICAL SAFETY COMPONENTS ARE IDENTIFIED BY THE SYMBOL .
REPLACE ONLY WITH PART NUMBERS SPECIFIED.
7-1
ZP94/95 SHEET 1
Page 57

ZP94/95 Small Signal/Tuner Circuit
PIN RUN PIN RUN PIN RUN PIN RUN PIN RUN
14.0 1 .2 14.8 1 0 12.4
24.0 2 4.9 24.8 2 0 22.4
34.0 3 4.9 34.1 33.9 3 0
42.1 4 .1 4 .4 4 0 4 .3
5 0 5 4.9 5 9.3 5 3.8 5 1.2
61.8 6 0 6 0 6 0 63.2
76.3 7 0 7 0 73.9 73.0
82.8 85.0 PINRUN 80 8.1
92.3 9 0 19.2 91.4 9 0
10 7.6 10 4.9 2 9.2 10 0 10 0
11 0 11 .2 3 0 11 2.5 11 0
12 6.0 12 .1 4 5.1 12 0 12 .5
13 4.9 13 4.9 5 5.1 13 2.5 13 2.0
14 .1 14 5.0 6 0 14 0 14 2.5
15 1.2 PIN RUN 7 0 15 4.8 15 0
16 0 1 9.2 8 0 16 0 16 4.3
17 .6 2 32.3 9 0 17 4.8 17 0
18 9.1 3 5.0 10 0 18 0 18 4.3
19 9.1 4 4.7 11 0 19 4.8 19 0
20 2.0 5 4.7 12 0 20 0 20 4.3
21 5.2 6 * 13 0 PIN RUN 21 9.2
22 5.4 7 3.08 14 0 1 4.9 22 N- C
23 0 8 0 15 0 2 4.9 PIN RUN
240 99.2 160 30 10
25 3.3 10 4.8 17 0 4 4.6 2 5.1
26 3.3 11 N/C 18 0 5 5 3 5.0
27 3.2 12 N/C 19 0.8 6 4.9 4 5.0
28 0 13 N/C 20 0 7 0 5 .5
29 3.3 14 N/C PIN RUN 8 1.9 6 9.3
30 3.1 15 N/C 1 4.9 9 1.9 7 2.5
31 3.2 16 N/C 2 4.9 10 0 8 0
32 0 17 N/C 3 0 11 4.6 9 2.4
33 4.8 18 4.8 4 4.7 12 4.5 10 0
34 4.9 19 0 5 11 13 0 11 4.3
35 1.5 20 1.0 6 0 14 6.4 12 0
36 0 21 0 7 0 15 0 13 3.8
37 .4 22 0 8 1.2 16 4.6 14 0
38 4.2 23 0 9 0 17 4.6 15 2.4
39 2.7 24 0 10 0.2 18 0 PIN RUN
40 2.7 25 0 11 0 19 1.1 1 4.7
41 4.9 26 4.6 12 0.5 20 0 2 4.8
42 4.9 27 4.6 13 0.3 PIN RUN 3 4.8
43 0 PIN RUN 14 0 1 5.0 4 - 2
44 3.0 1 11.3 15 4.2 2 0 5 0
45 .9 2 -.1 16 0 3 5.7 6 0
46 4.2 3 -.9 17 4.2 4 5.8 7 0
47 2.2 4 3.6 18 0.1 5 5.7 8 4.3
48 2.5 5 0 19 4.2 6 0 9 4.3
PIN RUN 6 1.5 20 0 7 .1 10 0
14.9 7 0 PINRUN 84.8 114.5
24.9 8 3.2 10.2 9 0 124.5
3.2 9 0 2 0 104.7 130
4 .2 10 .6 3 0.1 11 5.0 14 0
5 0 11 0 4 0 12 * 15 4.8
60 12 0 50 139.2 160
7 0 13 6.6v ac 6 0 14 .1 17 5.0
8 0 PIN RUN 7 0.1 15 4.9 18 0
94.2 1 0 8 0 16 0 199.3
10 4.2 2 0 9 9.1 17 5.8 20 9.3
11 4.2 3 0 10 9.2 18 5.8
12 2.5 4 0 11 0 19 5.8
13 2.6 5 5.0 12 0 20 0
14 2.6 6 0 13 9.2 21 3.3
15 4.9 7 0 14 9.2 22 3.3
16 5.0 15 0
16 0
17 5.1
18 5.1
19 0
20 0
I201
I202
I203
Small Sign al Voltages
U201
PSD3
PSD1
PSD2
PSZ1
PSZ2
PST3
PST2
PSU1
PST1
PFC1
PFC 2
PYC1
TO SHEET 8
Comb Filter
TO SHEET 8
Comb Filter
TO SHEET 5
Deflection
TO SHEET 7
Jackpack
TO SHEET 3
Power Supply
TO SHEET 5
Deflection
TO SHEET 5
Deflection
TO SHEET 7
Jackpack
TO SHEET 7
Jackpack
TO SHEET 3
Power Supply
1201-3
I201-12
PFC1-3,4,5
PFC1
10,11
PFC1
17,18,
19
1
2345678910
G
F
E
D
C
B
A
CRITICAL SAFETY COMPONENTS ARE IDENTIFIED BY THE SYMBOL .
REPLACE ONLY WITH PART NUMBERS SPECIFIED.
7-2
ZP94/95 SHEET 2
Page 58

ZP94/95 Deflection Circuit
PIN RUN
A10.3
K0
G0.2
PIN RUN
E11.3
B10.6
C11.2
PIN RUN
12
20
3300.0vac
418.5
50
PIN RUN
17.8
26.3
30
45.5
PIN RUN
111.9
210.9
32
418.5
PIN RUN
1120.2
210.6
30
RUN RUN
-9.3 -28.5
RUN RUN
8.9 27.8
RUN
227.0
PIN STBY RUN
110.4 8
20 0
30 11.34
40 0
50 10.35
6-2 1.03
70 12.35
DP10
DP09
DP08
PQD2
QP01
QP04
Power Sup ply Voltages
IP01
IP02
IP04
IP03
DP13
DP12
TO SHEET 10
CRT
TO SHEET 4
TO SHEET 5
Deflection
To Power
IP01-3
IP01-1
IP01-2
TP91-10
TP91-16
TP91-17
TP91-13
TP91-14
TP91-15
IP04-2
IP04-3
anode
cathode
gate
QP01-PA
QP01-PG
1
2345678910
G
F
E
D
C
B
A
CRITICAL SAFETY COMPONENTS ARE IDENTIFIED BY THE SYMBOL .
REPLACE ONLY WITH PART NUMBERS SPECIFIED.
7-3
ZP94/95 SHEET 3
Page 59

ZP94/95 Stand By Power Supply Circuit
TO SHEET ?
TO SHEET ?
TO SHEET 5
Deflection
TO SHEET ?
TO SHEET ?
I901-3
I901-1
I901-2
TP91-17
TP91-14
TP91-11
I902-3
I903-3
I903-3
PQS1-10
PIN STBY RUN PIN STBY RUN
1 1.62 1.71 A 12.7 13.5
20 0.03 K 0 0
3 162 426 v ac G 0 0
4 12.87 13.7 PIN STBY RUN
50 0 E0.34.7
PIN STBY RUN B 0.6 4.9
1 12.3 12.3 C 4.9 4.9
2 11.3 11.76 PIN STBY RUN
3 3.02 2.7 E 0.3 4.7
4 13.81 14.6 B 0.2 4.5
PIN STBY RUN C -2 -3.1
1 12.3 12.3 PIN STBY RUN
2 12.7 13.5 E 0 0
30 0 B 00.86
4 13.8 14.6 C 0 0.77
PIN STBY RUN PIN STBY RUN
1 3.2 2.7 E 4.8 4.9
2 0.25 6.5 B 4.8 4.9
3 5.1 0.4 C -2.5 -3.1
4 12.3 12.3 PIN STBY RUN
PIN STBY RUN 1 0 31.9
1 2703 27.4 2 0 31.9
27.8 7.8 3 0 0
30 0 4 0 0
45 5 5 0-2.14
5 1.4 1.6 6 0 -1.02
PIN STBY RUN PIN STBY RUN
1 27.3 27.4 1 22.5 33.9
2 12.1 12.2 2 0 0
3 0 0 3 11.6 11.3
4 9.16 9.15 4 11.6 11.3
5 1.4 1.5 5 11.6 11.3
PIN STBY RUN 6 0 0
1 27.3 27.4 7 0 0
20 6.22 82.60
30 0 9 0 0
40 5 104.44.44
5 0 1.5 PIN STBY R UN
PIN STBY RUN 1 0 7.26
1 27.3 27.4 2 0 7.26
2 0.3 13.6 3 0 7.26
30 0 4 0 0
4 0.3 12.1 5 0 0
50 1.4 6 0 0
PIN STBY RUN 7 0 5.5
K0 0 8 0 5.5
A12.87 13.7 9 0 0
G0 0 10 02.36
PIN STBY RUN 11 0 3.4
E 2.34 2.1 STBY RUN
B3.02 2.7 0 32
C 13.81 14.6 STBY RUN
PIN STBY RUN 0 5.6
E 5.8 5.9 STBY RUN
B 5.9 5.9 2.3 41.5
C 11.3 11.7 STBY RUN
PIN STBY RUN 27.4 27.4
E0 0
B0.7 0
C0 6.8
D910
D914
D915
Q903
Q905
Q908
Q909
Q911
Q912
PQU1
PQS1
D918
PQS2
I908
Q901
Q910
Q902
I904
I905
I906
I907
SMPS Voltages
I901
I902
I903
1
2345678910
G
F
E
D
C
B
A
CRITICAL SAFETY COMPONENTS ARE IDENTIFIED BY THE SYMBOL .
REPLACE ONLY WITH PART NUMBERS SPECIFIED.
7-4
ZP94/95 SHEET 4
Page 60

PIN RUN PIN RUN PIN RUN PIN RUN
B 1.3 B 7 1 15.6 1 0.7
C6.7 C9.7 227.1 2 1.3
E0.7 E6.3 34.9 3 0.9
PIN RUN PIN RUN 4 6.7 4 0
B 6.7 B 16.8 5 4.6 5 3.1
C0.8 C 0 6 0 6 0.7
E7.1 E 0 73.8 7 1.8
PIN RUN PIN RUN 8 4.6 8 12.3
B0.8 B0.6 94.6 PINRUN
C 11.7 C 0 10 27.4 1 6.4
E 0.3 E 0 11 1.1 2 12.4
PIN RUN PIN RUN PIN RUN 3 0.9
B 12.3 B 0.7 B 0 4 2.5
C 395 C 0.1 C 12.1 5 1.6
E11.7 E 0 E 0 6 0
PIN RUN PIN RUN PIN RUN 7 0
B 383 B 0.4 B 11.2 8 0
C 981.6 C 16.3 C -3 9 7.2
E487.1 E 0 E11.2 10 7.2
PIN RUN PIN RUN PIN RUN 11 7.2
B 11.6 B 9.2 B 0 12 7.2
C 482.2 C 0.8 C -2.7 13 2.7
E 11.1 E 8.1 E 0 14 1.9
PIN RUN PIN RUN PIN RUN 15 4.9
E 11.5 B 1.1 B 11.4 16 0
B 11.5 C 12.3 C -0.7 PIN RUN
C 0 E 1.6 E 11.4 1 11.3
PIN RUN PIN RUN PIN RUN 2 -.1
B0.7 B 0 B1 3 -.9
C 0 C 116.9 C 0 4 3.6
E0 E0 E0 5 0
PIN RUN PIN RUN PIN RUN 6 1.5
B0.3 B 12 B 0 7 0
C8.7 C-0.2 C-0.1 8 3.2
E0 E10.5 E0 9 0
PIN RUN PIN RUN PIN RUN 10 .6
B 10.9 B 0.6 B 0.6 11 0
C7 C4 C0 12 0
E11.5 E 0 E 0 136.6vac
PIN RUN PIN RUN PIN RUN PIN RUN
B6.4 B 4 10.1 1 4.8
C 1 C 12.3 2 0.1 2 4.8
E6.9 E3.9 33.1 3 4.1
PIN RUN PIN RUN 4 3.2 4 .4
B5.6 B 4 5 0 5 9.3
C2.5 C 0 6 7 6 0
E6.1 E3.9 75.7 7 0
PIN RUN PIN RUN 8 9.7 PIN RUN
B 0.6 B 12.2 9 2.7 E 0
C 12.3 C 12 10 1.1 B 0
E1 E12.3 111.2 C6.6
PIN RUN PIN RUN 12 1.2 RUN
B0.7 B3.3 130 27.8
C 0 C 119.5 14 0 RUN
E 1 E 0.4 15 1.3 27.8
PIN RUN PIN RUN 16 4.9
B0 B0.3 174.9
C 100 C 2.5 18 6.3
E0 E0 192.2
PIN RUN PIN RUN 20 0.1
B0.1 B27.4 212.2
C7 C0 225.2
E0 E27.7 230.3
24 0.8
Deflection Voltages
D656
D657
QF09
PSD2
PSD3
I701
I651
IH02
QN04
QN05
QN07
QN08
I601
QN01
QN02
QN03
QH80
QH01
Q601
Q609
QH07
QH08
QH09
QH10
Q751
Q754
Q755
Q777
Q702
Q703
Q704
Q705
Q655
Q656
Q657
Q701
Q612
Q652
Q653
Q654
QF07
QF09
QF05
QF01
QF02
QF03
QF04
QF06
ZP94/95 Deflection Circuit
To Green Yoke
TO SHEET 3
Power
TO SHEET 2
Signal
TO SHEET 2
Signal
TO SHEET 6
Convergence
To Red Yoke
To Blue Yoke
To Focus Block
Assembly
To Red CPTAnode
To Green CPTAnode
To Blue CPTAnode
PSD3-1
PSD3-10
PSD3-2
PSD3-4
PSD3-8
B
B
C
E
E
C
C778-PE
Q751-PB
Q751-PC
Q777-PB
Q777-PC
B
E
C
QFO1-PC
C
QFO9-PC
QH01-PG
QH01-PE
QH01-PC
TH01-5
TH01-3
E
B
I601-3
I601-2
I601-1
I601-7
I601-11
1
2345678910
G
F
E
D
C
B
A
CRITICAL SAFETY COMPONENTS ARE IDENTIFIED BY THE SYMBOL .
REPLACE ONLY WITH PART NUMBERS SPECIFIED.
7-5
ZP94/95 SHEET 5
Page 61

ZP94/95 Convergence Power Supply
PIN RUN PIN RUN
18.8 1 0
20 2.1
35 30
PIN RUN 4 0
13.6 5 .5
25 64.2
30 70
PIN RUN 8 .3
18.8 93.6
2 0 PIN RUN
35 10
PIN RUN 2 0
E-9.3 3-31.3
B-8.7 4-32.3
C-5.3 5 33
PIN RUN 6 0
E0.6 7 0
B0 828.2
C0 91.0
PIN RUN 10 27.1
E0.6 11 0
B 0 12 -28.3
C-8.0 13 0
PIN RUN 14 0
E0 15.2
B0 16.3
C 9.0 17 - 28.3
PIN RUN 18 .3
E 0 PIN RUN
B0 1 0
C5.0 2 0
PIN RUN 3 -31.3
E0 4-32.3
B0 533
C5.0 6 0
PIN RUN 7 0
E0 828.2
B0 91.0
C 5.0 10 27.1
PIN RUN 11 0
1 -5.3 12 -28.3
20 130
35.5 14 0
4 4.8 15 .2
5 0.6 16 .3
6 0 17 -28.3
7 0.1 18 .3
80
95.0
10 0
11 0
12 0
13 0
14 5.0
15 5.0
QK01
QK02
QK03
IK01
IK02
Convergence Voltages
PDG
PDC
IK04
IK05
QK71
QK06
QK07
QK08
IK03
TO SHEET 2
Signal
To Digital
Convergence Unit
To Red Yoke
TO SHEET 5
Deflection
To Green Yoke
To Blue Yoke
1
2345678910
G
F
E
D
C
B
A
CRITICAL SAFETY COMPONENTS ARE IDENTIFIED BY THE SYMBOL .
REPLACE ONLY WITH PART NUMBERS SPECIFIED.
7-6
ZP94/95 SHEET 6
Page 62

ZP94/95 Jackpack Terminal Circuit
PIN RUN PIN RUN PIN RUN PIN RUN
1 4 1 2.6 B 4.5 B 8.5
24.5 24.9 C 9 C5.5
3 4 3 1.8 E 3.9 E 9.1
4 4.5 4 0 PIN RUN PIN RUN
54.5 51.8 B4.5 B5.5
60.2 60.7 C 9 C9.1
74.9 74.9 E3.8 E4.8
8 4 8 2.1 PIN RUN PIN RUN
94.5 92.1 B4.6 B0.7
104 100 C9 C0
11 4.5 11 2.5 E 3.9 E 1.4
12 4.5 12 4.9 PIN RUN PIN RUN
13 0.2 13 5 B 5.9 B 1.8
14 4.9 14 2.6 C 9.1 C 2.4
15 4 15 0 E 5.3 E 0
16 4.5 16 2.5 PIN RUN PIN RUN
17 4 PIN RUN B 4.6 B 1.8
18 4.5 1 4 C 9 C 2.5
19 4.5 2 4 E 3.9 E 0
20 0.2 3 4 PIN RUN PIN RUN
21 5 4 2.2 B 3.7 B 2.5
22 4 5 0 C 9 C 5
23 4.5 6 1.8 E 3.1 E 1.9
24 4.1 7 6.3 PIN RUN PIN RUN
25 4.5 8 3 B 4.5 B 2.5
26 4.5 9 0.1 C 9.1 C 5
27 0.2 10 7.5 E 3.9 E 1.9
28 5 11 0 PIN RUN PIN RUN
29 4.5 12 5.9 B 0 B 3.2
304 130 C0 C5
31 4.5 14 0.2 E 0.7 E 2.5
32 0.1 15 1.2 PIN RUN PIN RUN
33 5 16 0 B 2.4 B 3.1
345 179 C3 C5
35 0 18 9.1 E 0 E 2.5
36 4.5 19 9.1 PIN RUN PIN RUN
37 4.5 20 1.1 B 2.5 B 3.1
38 4.6 21 4.8 C 0 C 5
39 3.7 22 2.4 E 3.1 E 2.5
40 4.6 23 9.1 PIN RUN PIN RUN
41 4.5 24 0 B 3.7 B 3.1
42 9 25 0.5 C 3.1 C 5
43 4.6 26 0.3 E 8.5 E 2.5
44 0 27 0.4 PIN RUN PIN RUN
45 3.9 28 0 B 8.5 B 3.1
46 3.7 29 1.4 C 5.5 C 5
47 4.5 30 1.3 E 9.1 E 2.5
48 0.1 31 1.4 PIN RUN PIN RUN
49 5 32 0 B 5.5 B 3.1
50 4.6 33 4.9 C 9.1 C 5
51 4.5 34 4.9 E 4.8 E 2.5
52 4.6 35 0.3 PIN RUN PIN RUN
53 4.6 36 0 B 3.7 B 0.7
54 4.6 37 0.1 C 8.5 C 0.1
55 3.7 38 5 E 3.1 E 0
56 4.3 39 4.9 PIN RUN PIN RUN
57 0 40 2.7 B 8.5 B 4.2
58 4.5 41 5 C 5.5 C 9.1
59 4.5 42 5 E 9.1 E 4.8
60 4.4 43 0 PIN RUN PIN RUN
61 4.5 44 3.2 B 5.5 B 4.2
62 4.5 45 0 C 9.1 C 9.1
63 4.4 46 3.8 E 4.9 E 4.8
64 4.5 47 2.4 PIN RUN PIN RUN
PIN RUN 48 2.5 B 0 B 4.2
16.5 C3.1 C9.1
2 0 E 8.5 E 4.8
34.1
45.1
59.1
Q446
Q439
Q443
Q444
Q445
Q423
Q424
Q425
Q426
Q427
Q431
Q433
Q434
Q435
Q436
Q437
Q438
Q414
Q416
Q417
Q422
Q418
Q419
Q420
Q421
Q410
Q411
Q412
Q413
Jackpack Voltages
I401
I402
I406
I403
Q401
Q402
Q403
Q406
Q409
TO SHEET 11
Control Panel
TO SHEET 2
Signal
Video 2 Out
S2 In
Component In 2Component In 1
Video 1 Out
S1 In
Monitor Out
S-Monitor Outl
TO SHEET 2
Signal
TO SHEET 2
Signal
1
2345678910
G
F
E
D
C
B
A
CRITICAL SAFETY COMPONENTS ARE IDENTIFIED BY THE SYMBOL .
REPLACE ONLY WITH PART NUMBERS SPECIFIED.
7-7
ZP94/95 SHEET 7
Page 63

ZP94/95 3 Line Comb Filter
PIN RUN PIN RUN PIN RUN PIN RUN
B0 B0 11.6 12.6
C 0.1 C 4.9 2 4.4 2 4.7
E 0.7 E 0.9 3 4.1 3 1.9
PIN RUN PIN RUN 4 3.1 4 0.1
B 0 B 8.5 5 2.5 5 1.9
C 0.7 C 4.6 6 2.3 6 0.7
E 0 E 9.1 7 0.1 7 0
PIN RUN PIN RUN 8 4.1 8 2.2
B 0 B 8.5 9 4.1 9 2.2
C0 C0 104.1 100
E 0.7 E 9.2 11 1.6 11 2.6
PIN RUN PIN RUN 12 5 12 5
B 0 B 2.6 13 2.5 13 5.1
C0 C0.1 140 142.6
E 0.2 E 3.2 15 2.6 15 0
PIN RUN PIN RUN 16 0.1 16 2.6
B 0 B 6.9 17 0.1 PIN RU N
C 0 C 3.2 18 0.1 1 9.2
E 0.7 E 7.6 19 0.1 2 9.2
PIN RUN PIN RUN 20 6.7 3 0
B 0.1 B 2.7 21 0 4 5.1
C 0.1 C 0 22 9.1 5 5.1
E 0.2 E 3.3 23 9.1 6 0
PIN RUN PIN RUN 24 1.7 7 0
B 7.3 B 6.9 25 1.3 8 0
C9.2 C3.3 26 1 9 0
E 6.6 E 7.6 27 4.9 10 0
PIN RUN PIN RUN 28 4.9 11 0
B 0.2 B 2.8 29 5 12 0
C9.1 C0.1 30 5 13 0
E 0.2 E 3.4 31 0.1 14 0
PIN RUN PIN RUN 32 0 15 0
B 9.1 B 1.3 33 3.7 16 0
C0.3 C0.6 343.7 17 0
E 9.1 E 1.3 35 3.7 18 0
PIN RUN PIN RUN 36 0.2 19 0.8
B 1.2 B 3.5 37 3.6 20 0
C 0 C 9.2 38 3.6 PIN RUN
E 1.7 E 2.8 39 3.6 1 4.9
PIN RUN PIN RUN 40 9.1 2 4.9
B 0.6 B 4.9 41 2.8 3 0
C 0 C 0.1 42 2.6 4 4.7
E 1.3 E 4.3 43 2.6 5 11
PIN RUN PIN RUN 44 0.1 6 0
B 0.8 B 4.6 45 5.7 7 0
C1.6 C9.1 469.1 8 1.2
E 0.7 E 3.9 47 0 9 0
PIN RUN PIN RUN 48 3.4 10 0.2
B 5.3 B 4.6 49 5.5 11 0
C9.1 C8.5 505.1 120.5
E 4.6 E 4 51 5.1 13 0.3
PIN RUN PIN RUN 52 5.1 14 0
B 5.3 B 4.9 53 6.6 15 4.2
C9.1 C8.5 54 7 16 0
E 4.6 E 4.3 55 5.2 17 4.2
PIN RUN 56 0.2 18 0.1
B 7.7 19 4.2
C9.1 20 0
E7.1
Comb Filter Voltages
QX01
QX02
QX03
QX25
QX26
QX27
QX07
QX08
QX09
QX13
QX15
QX16
QX17
QX18
QX21
QX22
QX23
QX24
QX52
QX31
QX32
QX36
QX37
QX53
QX54
PSZ2
QX55
IX01
IX02
PSZ1
QX41
QX42
QX46
TO SHEET 2
Signal
TO SHEET 10
CRT
TO SHEET 2
Signal
1
2345678910
G
F
E
D
C
B
A
CRITICAL SAFETY COMPONENTS ARE IDENTIFIED BY THE SYMBOL .
REPLACE ONLY WITH PART NUMBERS SPECIFIED.
7-8
ZP94/95 SHEET 8
Page 64

ZP94/95 YC Circuit
TO SHEET ?
PYC1-11
PYC1-7
PYC1-9
PYC1-15
1
2345678910
G
F
E
D
C
B
A
CRITICAL SAFETY COMPONENTS ARE IDENTIFIED BY THE SYMBOL .
REPLACE ONLY WITH PART NUMBERS SPECIFIED.
7-9
ZP94/95 SHEET 9
Page 65

PIN RUN
B3.4
C12.7
E2.7
PIN RUN
B12
C27.9
E12.7
PIN RUN
B13.4
C22.3
E12.7
PIN RUN
B22.3
C27.9
E21.6
PIN RUN
B2.3
C15.4
E1.6
PIN RUN
B15.6
C0
E16.2
PIN RUN
B16.1
C27.9
E15.5
PIN RUN
B15.5
C27.9
E14.9
PIN RUN
B14
C0
E14.6
PIN RUN
B211.6
C10.7
E212.1
PIN RUN
B210.2
C187.7
E210.7
PIN RUN
B187
C0
E187.8
PIN RUN
B25.1
C117
E24.6
PIN RUN
B1.4
C24.6
E0.9
PIN RUN
B12.4
C139.5
E11.9
PIN RUN
B12.5
C27.9
E11.9
QE36
QE24
QE25
QE26
QE35
QE10
QE11
QE22
QE23
QE04
QE05
QE07
QE08
Velocity Modulator
Voltages
QE01
QE02
QE03
ZP95 Velocity Modulator
G
F
E
D
C
B
A
1
CRITICAL SAFETY COMPONENTS ARE IDENTIFIED BY THE SYMBOL .
REPLACE ONLY WITH PART NUMBERS SPECIFIED.
2345678910
7-10
*ZP 95 Only*
ZP94/95 SHEET 10
Page 66

ZP94/95 CRT/CPT Circuit
PIN RUN PIN RUN
B3.4 B2.5
C8.4 C9.2
E2.9 E1.9
PIN RUN PIN RUN
B8.6 B1.8
C9.2 C1.1
E8.4 E1.1
PIN RUN PIN RUN
B9.1 B3.5
C172 C 8.3
E8.6 E 3
PIN RUN PIN RUN
B172 B 8.6
C1 C9.2
E 172.7 E 8.3
PIN RUN PIN RUN
B1.7 B164.5
C1 C1.1
E1 E164.9
PIN RUN PIN RUN
B3.4 B165.9
C8.3 C222
E2.9 E165.3
PIN RUN PIN RUN
B8.6 B3.1
C9.2 C 0
E8.3 E2.9
PIN RUN PIN RUN
B9.1 B3.7
C 159.6 C 9.2
E8.6 E3.1
PIN RUN PIN RUN
B159.6 B 0
C1.1 C9.1
E160.3 E 0
PIN RUN PIN RUN
B 161.3 B 1.7
C222 C 1.1
E160.9 E 1
PIN RUN
B1.9
C0
E2.5
Q803
Q804
Q854
Q855
Q858
Q859
Q812
Q851
Q852
Q853
Q801
Q802
CRT Voltages
Q8C2
Q862
Q8A1
Q8A2
Q8A4
Q8A5
Q8A6
Q8A7
Q8C1
TO SHEET 8
Comb Filter
TO SHEET 3
Power Supply
TO SHEET5
Deflection
Test
Point
1
2345678910
G
F
E
D
C
B
A
CRITICAL SAFETY COMPONENTS ARE IDENTIFIED BY THE SYMBOL .
REPLACE ONLY WITH PART NUMBERS SPECIFIED.
7-11
ZP94/95 SHEET 11
Page 67

ZP94/95 Control Panel Circuit
PIN RUN
B0.12
C0
E0
PIN RUN
11.5
21.24
-- --
PIN RUN
B0
C0
E0
PIN RUN
B0
C0
E0
PIN RUN
B0
C0.8
E0
Control Panel
Volt ages
QM04
QM05
QM01
QM02
QM03
TO SHEET 2
Signal
TO SHEET 7
Jackpack
1
2345678910
G
F
E
D
C
B
A
CRITICAL SAFETY COMPONENTS ARE IDENTIFIED BY THE SYMBOL .
REPLACE ONLY WITH PART NUMBERS SPECIFIED.
7-12
ZP94/95 SHEET 12
Page 68

ZP94/95 Audio Circuit
PIN RUN PIN RUN
15.1 14.7
24.9 24.7
34.9 34.7
40.1 44.7
50.1 54.7
60.1 64.7
75.1 74.7
80 84.7
95.1 99.2
10 0 10 0
11 5.1 11 0.1
12 0.1 12 0.1
13 0.1 13 4.7
14 0.1 14 4.7
15 0.1 15 4.7
16 5.1 16 4.7
17 5.1 17 0
18 5.1 18 4.7
19 5.1 19 4.6
20 5.1 20 4.7
PIN RUN 21 4.6
10.1 224.7
2 0 PIN RUN
3 4.2 B 1.1
4 4.2 C 8.6
5 4.2 E 0.4
6 4.2 PIN RUN
70 B8.6
80 C4.1
90 E9.2
10 4.9 PIN RUN
11 4.9 B 1.1
12 0.1 C 8.6
13 0.1 E 0.4
14 3 PIN RUN
15 2.7 B 8.6
16 8.5 C 4.2
17 4.2 E 9.2
18 4.2 PIN RUN
19 4.2 B 0.1
20 0 C 0
21 4.2 E 0
22 0 PIN RUN
PIN RUN B 0
1 4.7 C 0.1
21.3 E 0
34.7
49.2
54.7
60
70.1
84.7
95.7
10 4.6
QA10
SIS Voltag es
IA01
IA05
IA02
IA03
QA11
QA12
QA07
QA08
QA09
TO SHEET 1
Micro
1
2345678910
G
F
E
D
C
B
A
CRITICAL SAFETY COMPONENTS ARE IDENTIFIED BY THE SYMBOL .
REPLACE ONLY WITH PART NUMBERS SPECIFIED.
7-13
ZP94/95 SHEET 13
 Loading...
Loading...