
IEEE 802.11g 54Mbps Wireless Router
1

Copyright
The contents of this publication may not be reproduced in any part or as a whole, stored,
transcribed in an information retrieval system, translated into any language, or transmitted in
any form or by any means, mechanical, magnetic, electronic, optical, photocopying, manual, or
otherwise, without the prior written permission.
Trademarks
All products, company, brand names are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective
companies. They are used for identification purpose only. Specifications are subject to be
changed without prior notice.
2

FCC Interference Statement
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device
pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable
protection against radio interference in a commercial environment. This equipment can
generate, use and radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance
with the instructions in this manual, may cause harmful interference to radio communications.
Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely to cause interference, in which case
the user, at his own expense, will be required to take whatever measures are necessary to
correct the interference.
CE Declaration of Conformity
This equipment complies with the requirements relating to electromagnetic compatibility, EN
55022/A1 Class B, and EN 50082-1. This meets the essential protection requirements of the
European Council Directive 89/336/EEC on the approximation of the laws of the member states
relation to electromagnetic compatibility.
3
Content
Chapter 1: Introduction.............................................................................................. 5
1.1 Five steps to success...................................................................................... 5
1.2 Functions and Features.................................................................................. 7
Chapter 2: Hardware Installation............................................................................... 9
2.1 Panel Layout.................................................................................................. 9
2.2 Procedure for hardware installation ............................................................ 10
Chapter 3: Network Settings.....................................................................................11
3.1 Client Network Settings ...............................................................................11
Chapter 4: Router Configuration ............................................................................. 14
4.1 Start-up and Log in...................................................................................... 14
4.2 System Status .............................................................................................. 14
4.3 Wizard ......................................................................................................... 15
4.4 Primary Setup.............................................................................................. 16
4
Chapter 1: Introduction
Congratulations on your purchase of the outstanding Wireless Broadband
Router. This product is specifically designed for Small Office and Home Office
needs. It provides a complete SOHO solution for Internet surfing, and is easy to
configure and operate even for non-technical users. Instructions for installing
and configuring the Router can be found in this manual. Before you install and
use this product, please read this manual carefully to ensure that you take full
advantage of it’s functionality.
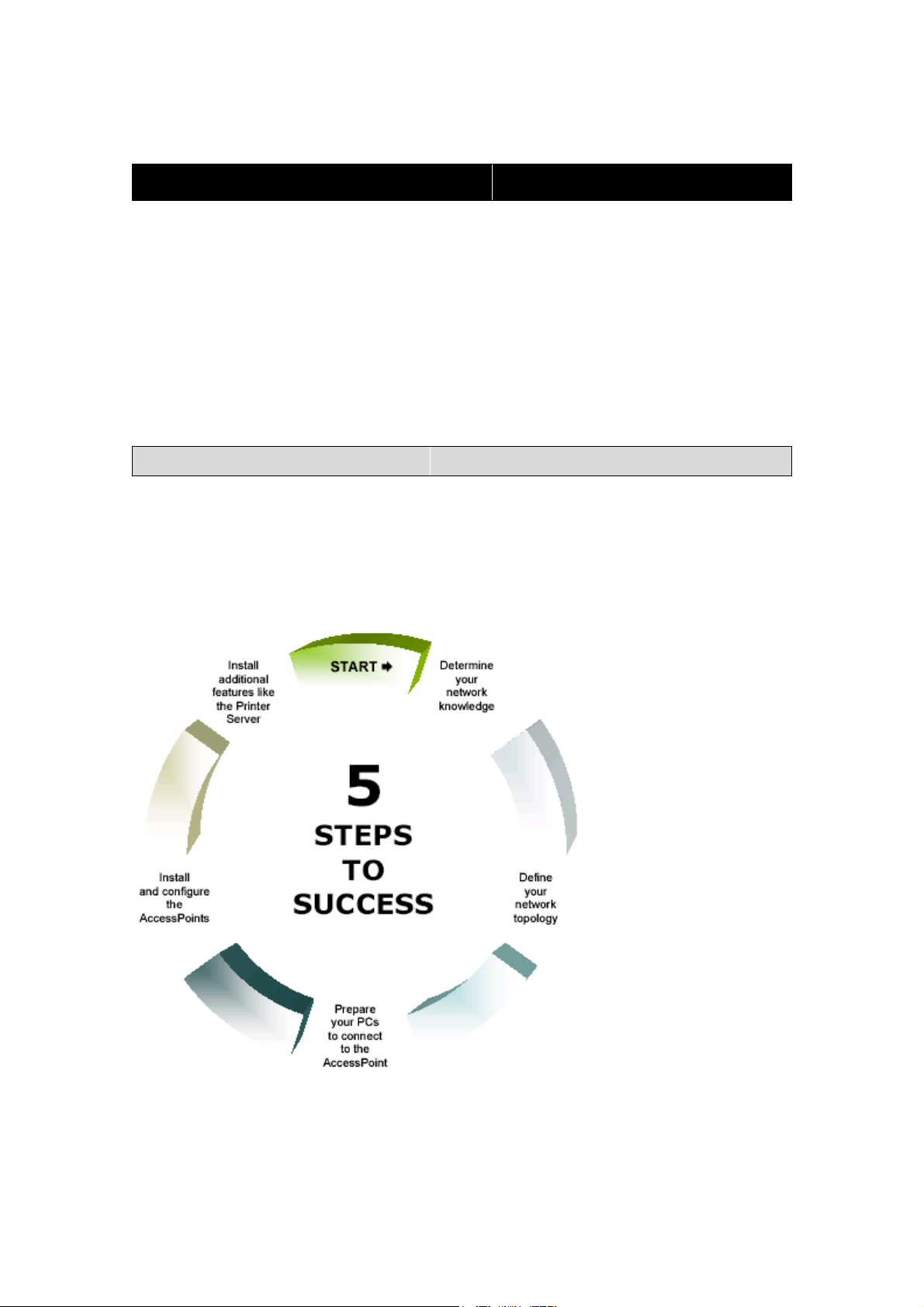
1.1 Five steps to success
To enable a smooth entry in to the world of the Wireless LAN, you will be
guided through the installation of the individual components by way of the “Five
steps to success”. In doing so your specific level of technical expertise will be
catered for. You decide which settings are doable for you.
1. Determine your network knowledge
The success of the installation of your Router and Wireless Clients is largely
5

independent of your technical skills. The more advanced and familiar you
are with networking terminology, the more you will act intuitively. A beginner
will need more support in learning about his new networking equipment.
Some chapters are therefore supplemented with additional information,
designed for Beginners:
2. Define your network topology
Decide which PC and devices will be connected to your Network
PC
Laptop
PDA
Printer with parallel Port
Network Scanner
Network Printer
…
Chapter 2 ‘Hardware Installation’ will help you to connect these devices
properly.
3. Prepare your PCs and Devices to connect to the Router
Before an Router can be configured, an initial connection must be
established.
Chapter 3 ‘Network Settings’ will guide you through the settings.
4. Install and configure the Router
Your Router needs to be configured to work properly with each of your
networking components and your Internet connection. Security aspects and
special Router functionalities will also be covered.
see Chapter 5 ‘Router Configuration’.
5. Install additional features like Print Server
The Router is equipped with a Printer port which is wirelessly accessible by
any user in the network. Therefore a software needs to be installed on every
PC.
see Chapter 4.2 for the Software Installation and Chapter 6 for the Software
6

Configuration
1.2 Functions and Features
High speed wireless LAN connection
11Mbps data rate incorporating Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS).
Roaming
Seamless roaming within the IEEE 802.11g WLAN infrastructure.
IEEE 802.11g compatible
Allows interoperability between multiple vendors.
Auto fallback
11M, 5M, 2M, 1M data rate with auto fallback.
Broadband modem and NAT Router
Connects multiple computers to the internet through a broadband (cable or
DSL) modem or an Ethernet router.
Auto-sensing Ethernet Switch
Equipped with a 2-port auto-sensing Ethernet switch.
VPN supported
Supports multiple PPTP sessions and allows you to setup VPN server and
VPN clients.
Printer sharing
Embeds a print server to allow all of the networked computers to share one
printer.
DHCP server supported
All of the networked computers can retrieve their TCP/IP (network
communications protocol) settings automatically.
Web-based configuring
Configurable through any networked computer’s web browser using
Netscape or Internet Explorer.
Virtual Server supported
Enables you to open WWW, FTP and other services on your LAN to Internet
users.
User-Definable Application Sensing Tunnel
User definable attributes to support special applications that require multiple
connections, such as Internet gaming, video conferencing, Internet
telephony and so on. The product then senses the application type and
opens a multi-port tunnel for it.
7

Firewall
All unwanted network packets from outside intruders are blocked to protect
your Intranet. The access rule allows you to control access to a network by
analyzing the incoming and outgoing packets and letting them pass or
blocking them based on the source and destination IP Addresses.
8

Chapter 2: Hardware Installation
2.1 Panel Layout
2.1.1 Front Panel
Led Indicators
Reset Switch
To reset the system settings to factory defaults, please follow the steps:
1 Press the reset button for 10 seconds
2 Release the button
3
Watch the M1 LED, it will flash 8 times and then flash once per second
9

2.1.2 Back Panel
Ports:
2.2 Procedure for hardware installation
1. Decide where to place your Wireless Broadband Router.
You can place your Router on a desk or other flat surface, or mount it on a
wall. For optimal performance, place it in the center of your office (or your
home) and in a location that is away from any potential source of
interference, such as a metal wall or microwave oven. This location must be
close to a wall plug and a network connection.
2. Set up LAN connection
a) Wired LAN connection: connects an Ethernet cable from your
computer’s Ethernet port to one of the AP’s LAN ports
b)
Wireless LAN connection: locate this product at a proper position to
gain the best transmission performance.
3. Set up WAN connection
Prepare an Ethernet cable for connecting the AP to your cable/xDSL modem
or Ethernet backbone. Figure 2-3 illustrates the WAN connection.
4. Connecting the AP to your printer
10

Use the USB cable to connect your printer to the AP’s USB port .
5. Power on
Connect the power adapter to the power socket. Your Router then will
automatically enter the self-test phase. During the self-test, the M1 indicator
will be lit ON for about 10 seconds, and will then flash 3 times to indicate
that the self-test operation has completed. Finally, the M1 will flash
continuously once per second to indicate that the AP is in normal operation.
Chapter 3: Network Settings
In order to use your Router and the Printer Server functionality correctly, it will
be necessary to ensure the correct configuration of the network settings on your
computers and install the attached setup program on your Windows based
platform. (Windows 95 / 98 / ME / NT / 2000 / XP).
3.1 Client Network Settings
3.1.1 Networking for Beginners
Every PC or Device in a network is individually identified by a unique set of four
numbers, the so called IP Address. This IP Address is one of the key elements
in the opening of network communications between devices in order to
exchange data, such as the transfer of a file from one PC to another or simply
receiving E-Mails from your ISP. More precisely, an IP Address consists of a set
of 4 number, each 3 digits long, and separated by a decimal point: example:
192.168.100.200. These addresses can be set manually or be received from a
‘DHCP-Server’, which manages a pool of IP Addresses in a network. Each IP
Address is accompanied by a “default Subnet Mask”. The combination of these
addresses (IP Address and subnet mask) defines the segment of the network
where a specific device is located.
Your new router comes with a preset default IP Address (192.168.1.254) and
“default Subnet Mask” (255.255.255.0), which can be changed by the user as
required. These default values are used as a reference in this manual. If the
TCP/IP environment of your computer has not yet been configured, refer to
Appendix A to configure it.
11

3.1.2 Configuration of your Wireless Client
To open a wireless connection to your Router, it is necessary to configure the
wireless client device in your PC:
1. SSID: CONNECT2AIR
2. Channel: 10
3. WEP: disabled
These parameters can be entered in the User Interface of your network card.
Please refer to the documentation delivered with your device.
Note: Recent Client Configuration Utilities do detect the wireless settings
automatically. Your wireless Client has to be configured properly to
connect to the AP.
3.1.3 Network Settings
Regardless whether you are using a wireless or wired device to connect to your
Router, all the following Steps must be applied to your network adapter to
access your Router:
1. Setup your hardware network installation (see Chapter 2 – Hardware
Installation)
2. Configure your network computers (LAN server/client/host) to “Obtain an IP
address automatically.” (See Appendix A)
Note: By default the Router’s DHCP is enabled - so by setting your computer
to “Obtain and IP address automatically” - you can connect to the
Router automatically.
3. Launch your web browser and type the router’s default IP address (http://
192.168.1.254) into the browser’s address box and press Enter.
12

Note: If you have setup your computer to use a static IP address: Please
make sure your PC’s IP address is in the same network as the Router’s.
In windows 98SE you can type WINIPCFG and in windows 2000/XP
you can type IPCONFIG (see appendix) to find out if you are on the
same network.
13

Chapter 4: Router Configuration
This product is provided with a Web based configuration interface, that can be
accessed through your Web browser, such as Internet Explorer, Netscape
Communicator, or any other HTML compatible browsers. This interface can be
used in any MS Windows, Macintosh or UNIX based platforms.
4.1 Startup and Log in
To enter the Router configuration proceed, activate your browser, and type in
the IP Address of your AP in the Address field (for Internet Explorer) or in the
Location field (for Netscape) and press ENTER. For example:
http://192.168.1.254
After the connection is established, you will see the AP’s web user interface pop
up. You will now able to select one of file languages: English, German, French,
Italian or Spanish.
To log in, enter the system password (the factory setting is ”connect”) in the
System Password field and click the “Log in” button. If the password is correct,
the interface will switch to administrator configure mode. As listed in the main
menu at the top of the window, there are several system administration sections.
4.2 System Status
This section shows the AP’s working status:
WAN Port Status.
If you have selected a specific WAN type to connect to your ISP, the
corresponding connection type will be shown on this field by following the given
IP address.
LAN Port Status.
Shows you the settings of the local area network side of the Router
Wireless Settings Status.
14

Shows the status of the SSID, security setting and access control of the Router.
Printer Status.
The possible values of printer status include “Ready”, “Not ready”, “Printing…”,
and “Device error”.
4.3 Wizard
The Wizard section will guide you through the main settings of your Router. You
will be prompted to select your ISP (Internet Service Provider).
If you would like to use your device strictly as an Router only (no connection to
ISP) please select “No ISP”. You will then be able to use your AP to share your
printer as well as to access all networking equipment connected to the device.
4.3.1 How to connect to your Internet Service Provider (ISP)
1. Static IP Address
WAN IP Address, Subnet Mask, Gateway, Primary and Secondary DNS:
enter the settings provided by your ISP.
2. Dynamic IP Address
a) Host Name: optional. Required by some ISPs, for example, @Home.
b) Renew IP Forever: this feature enables the AP to renew your IP
Address automatically when the lease time expires -- even when the
system is idle.
3. PPP over Ethernet
a) PPPoE Account and Password: the account and password that your
ISP assigned to you. For security, this field appears blank. If you don't
want to change the password, leave it empty.
b) PPPoE Service Name: optional. Input the service name if your ISP
requires it. Otherwise, leave it blank.
c) Maximum Idle Time: the amount of time of inactivity before
disconnecting your PPPoE session. Set it to zero or enable Auto-
reconnect to disable this feature.
15

4. PPTP
a) My IP Address and My Subnet Mask: the private IP Address and subnet
mask that your ISP assigned to you.
b) Server IP Address: the IP Address of the PPTP server.
c) PPTP Account and Password: the account and password that your ISP
assigned to you. If you don't want to change the password, leave the
field empty.
d) Connection ID: optional. Input the connection ID if your ISP requires it.
e) Maximum Idle Time: the time of no activity to disconnect your PPTP
session. Set it to zero or enable Auto-reconnect to disable this feature.
If Auto-reconnect is enabled, this product will automatically connect to
ISP after system is restarted or connection is dropped.
4.4 Primary Setup
These core options are essential to enable the AP to work properly. The
available settings and the interface depend on the WAN type. Choose correct
WAN type before you start.
4.4.1 LAN IP Settings
1. LAN IP Address Type:
Two selections are provided. If you plan to use any external DHCP server,
first enter the settings on the DHCP server page and disable the default
DHCP sever, and then return to this page and select Dynamic. Otherwise
set the LAN address to Static and make sure the IP address is in the range
of the DHCP server where the default DHCP server is usually enabled.
2. LAN IP Address:
The local IP Address of this device. Normally the computers on your network
use the LAN IP Address of your product as their Default Gateway. You can
change it if necessary.
3. Subnet Mask:
16

Whenever there is a request, the DHCP server will automatically allocate an
unused IP Address from the IP Address pool to the requesting computer.
You must specify the starting and ending address of the IP Address pool.
4. Gateway:
Optional, this information will be passed to the client. The Gateway Address
would be the IP Address of an alternate Gateway. This function enables you
to assign another gateway to your local PC, when the DHCP server assigns
an IP Address to your PC.
5. Secondary Address Selection:
Optional, the secondary address is providing a safe way for network
administrator to quickly access the Router where there is no DHCP server
present in the network. It will always come up with the setting where the
LAN Address Type is set on Dynamic. Click on the field of automatic IP,
Router will provide itself an automatic private IP, like Windows system does.
Note: Auto IP: When a system is configured for TCP/IP "to Obtain
an IP address automatically" via DHCP, it will first attempt
to locate a DHCP-server (which can takes some time). If
no DHCP server is found on the network, it will use the
build-in "Automatic Client Configuration" (sometimes
referred to as APIPA ) to assign itself an IP-address in the
address-range 169.254.x.x with Subnet- mask
255.255.0.0. The double x is calculated by the MAC
address of LAN port.
4.4.2 WAN Type Settings
WAN Type: select the WAN connection type of your ISP. You can click the
“Change” button to choose different settings:
17

1. Static IP Address
WAN IP Address, Subnet Mask, Gateway, Primary and Secondary DNS:
enter the settings provided by your ISP.
Clone MAC address: If your ISP requires a specific MAC address to
connect to the service, you can enter a specific MAC address or clone the
current computer’s MAC address through this link.
2. Dynamic IP Address
a) Host Name: optional. Required by some ISPs, for example, @Home.
b)
Renew IP Forever: this feature enables the AP to renew your IP
Address automatically when the lease time expires -- even when the
system is idle.
3. PPP over Ethernet
a) PPPoE Username and Password: the Username and password that
your ISP assigned to you. For security, this field appears blank. If you
don't want to change the password, leave it empty.
b) PPPoE Service Name: optional. Input the service name if your ISP
requires it. Otherwise, leave it blank.
c) IP Address: optional. The IP address your ISP assigned to you. Set it to
zero to disable this feature.
4. PPTP
a) PPTP Account and Password: the account and password that your ISP
assigned to you. If you don't want to change the password, leave the
field empty.
b) My IP Address and My Subnet Mask: the private IP Address and subnet
mask that your ISP assigned to you.
c) Server IP Address: the IP Address of the PPTP server.
4.4.3 DHCP Server Settings
DHCP Server:
The settings of a TCP/IP environment include host IP, Subnet Mask, Gateway,
18

and DNS configurations. It is not easy to manually configure all the computers
and devices in your network. Fortunately, DHCP Server provides a rather
simple approach to handle all these settings. This product supports the function
of DHCP server. If you enable the DHCP server and configure your computers
as “automatic IP allocation” mode, then when your computer is powered on, it
will automatically load the proper TCP/IP settings from the AP. The DHCP
server settings include the following items and can be “Disabled” or “Enabled”.
4.4.4 WLAN Settings
Your wireless settings will have influence on the coverage and the performance
of your wireless LAN. The wireless settings allow you to set the following
configuration items:
1. Regulatory Domain: This is the organization that certifies the Router for
use in your country. It determines which radio channels can be used to
transmit and receive signals.
2. IAPP: Optional. The draft Inter Router Protocol implies that registration and
address information is determined by communicating with an external IAPP-
aware RADIUS server.
3. Wireless Network name (SSID): Network ID is used for identifying the
Wireless LAN (WLAN). Client stations can roam freely using this product
and other Routers that have the same Network ID. (The factory setting is
“CONNECT2AIR”)
4. Band: Operate the Router at three different scenarios, high rate, low rate
and a mix of both under 2.4GHz ISM band.
B/G Mixed Mode: A mixed network in which high rate and low rate
devices share the same wireless medium takes the vantage of
complete backward compatibility with 802.11g devices. This is quite
essential for those applications that significant bases of legacy 11g
equipments have been installed and hunt out a smooth migration path
to higher date rates for users.
Note: Due to the fact that dramatic reductions in throughput will be
caused by simply joining legacy 802.11g clients into the 802.11g
network, a new, powerful and flexible technology is placed additionally
to bring protection and performance enhancement. Please kindly refer
to the Turbo mode for detail. Enable Turbo function when select mixed
19

mode for your network environment is strongly recommendated.
G only Mode: Come up with a pure high speed 11g network. All
802.11g clients are initiated and operating at high rate.
B only Mode: The similar situation as G only mode, except it will create
a pure low rate wireless network. All clients are all operates at low rate
that legacy 802.11g network introduced..
5. Radio Channel: The radio channel number. The permissible channels
range from Channel 1 to 11 (default is 13). For restrictions please refer to
the first page of this manual.
6. Turbo mode / NitroTM mode: A technology delivers throughput
enhancement in both mixed and g-only networks. By introducing Intersil’s
packet bursting technology, administrator can easily enrich network
performance and stability in higher speed.
4.4.5 WLAN Security Settings
To protect your intellectual property, secure your wireless connection! This
Router is equipped with a sophisticated security algorithm to protect intruders
from entering your system or listening to what you are transferring on your
network. It is called WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access). Also provided with a legacy
WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) and standardwise authentication enhancement
(802.1x). In the meantime, you may want to experiment with the security we
provided to understand its benefits and implications.
Below is a chart that the operations of Router in different security level were
displayed.
Security WEP 802.1x WPA-PSK WPA-EAP RADIUS
None
Low
Middle1
Middle2
N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A
Yes N/A N/A N/A N/A
Yes Yes N/A N/A Yes
N/A Yes
N/A N/A Yes
(Dynamic WEP)
High1
High2
N/A N/A Yes N/A N/A
N/A N/A N/A Yes Yes
In most cases, security level will be revealed as
20

High2>high1>Middle2>Middle1>Low>None.
1. Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) Settings
WEP (128 or 64-bit) is used here.
WEP Key 1, 2, 3 & 4: When you enable the 128 or 64 bit WEP algorithm,
please select one WEP key to be used. If you are using a 128 bit key, you have
to enter a 26 digit hexadecimal key (0, 1, 2…8, 9, A, B…F) into the appropriate
field:
Example 128 bit: FEDCBA01234567890123456789 26 digits
Example 64 bit: FEDCBA0123 10 digits
Pass-phase generator: Since hexadecimal characters are not easily
memorable, this device offers a conversion utility from a simple word into the
hexadecimal code. Enter your Passphrase and press “Generate”. You can now
copy the hexadecimal entries in the WEP Key fields, if your wireless Clients do
not support the “Passphrase generator”.
2. RADIUS / Requires RADIUS
The RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service) plays a key role in
serving as a center in the network to provide the capabilities of authenticating,
authorizing, accounting, auditing and alarming…etc and allows an organization
to maintain user profiles in a central database that all remote servers can share.
Since RADIUS needs a relatively complex explanation, here we will focus on
how it acts as an 802.1x-Authentication Server (EAP-aware RADIUS) and
assist coming up with a security enhancement.
Te RADIUS performs the authentication function necessary to check the
credentials of the Users and intermediate Routers, and indicates whether the
Users are authorized to access the Routers. Therefore, setting a RADIUS
becomes the first step for building up an 802.1x-capable environment. Even
more, it is also a must-do to accommodate the latest introduced Wi-Fi protected
access (WPA-EAP) to wireless network.
Setting up RADIUS information in your Router is quite simple, just to input the
21

associated IP address of RADIUS and port number, which usually set in 1812,
and the secret key which is identified with the given key in RADIUS.
After finish adding RADIUS information, return to the page of Wireless Security
Settings, you will be allowed to do further configuration of 802.1x as the picture
shows up. Hereby you can choose to have either 802.1x with static WEP, with
dynamic WEP and WPA-EAP to even more secure your wireless network.
3. 802.1x Security
22

IEEE 802.1x is a standard for network access control (port based), especially
introduced for a distribution of encryption keys in a wireless network. The
Router supports 802.1x will keep out unauthorized users and perform
verification of credentials with RADIUS to allow authorized users to access the
network and services. To use 802.1x, you will need at least one common
Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) method on your authentication server,
APs (authenticator) and stations (Supplicant). Also, 802.1x is used to perform
generation and distribution of encryption keys from AP to the station as part of,
or after the authentication process, the whole story is also aware by Dynamic
WEP, which is based on legacy RC4 WEP encryption and available in this
Router under the setting, which enable 802.1x security by coming with
disabled Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) Settings, there are two options for
key length, 40 and 104bits. Longer the key length is, the more secure it will
bring to.
4. Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA)
A standard with highest level of security currently wireless network can achieve.
Wi-Fi Protected Access is a subset of security specification and has been
introduced as intermediate result that solves most known security weakness
related to plain WEP. Enterprises that already have RADIUS authentication in
place can use WPA with 802.1x (WPA-EAP). Small business and home wireless
LAN can use WPA without 802.1x (WPA-PSK).
WPA-PSK:
Instead of using RADIUS for authentication, systems with WPA-PSK will be
configured with secret passphrases. Enter your passphrases and press
“Generate”. You can now create a pre-shared key in Router and copy the
23

characters you input to stations’ WPA-PSK entry.
WPA-EAP:
Working with RADIUS, systems with WPA-EAP will be employed with an new
encryption method called Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP)
implementation with 802.1x dynamic
24

4.4.6 WDS Settings
Peer AP's for Wireless Distribution System (WDS): Normally, Routers are linked
to each other via cables. With WDS, you can link Routers via a wireless link
instead. This way you can extend the range of your network without having to
use cables to link the Routers.
When you click Add, you can enter the MAC address of an Router to link to.
You also need to enter the peer MAC address in the other Router.
You can use up to eight Routers in a WDS.
25

FCC Caution
1. The device complies with Part 15 of the FCC rules. Operation is subject to
the following two conditions:
(1)This device may not cause harmful interference.
(2)This device must accept any interference received,
including interference that may cause undesired operation.
2. FCC RF Radiation Exposure Statemen t: The equipment complies with
FCC RF radiation exposure limits set forth for an uncontrolled
environment. This equipment should be installed and operated with a
minimum distance of 20 centimeters between the radiator and your body.
3. This Transmitter must not be co-located or operating in conjunction with
any other antenna or transmitter.
4. Changes or modifications to this unit not expressly approved by the party
responsible for compliance could void the user authority to operate the
equipment.
 Loading...
Loading...