ZARLINK SP5730 DATA SHEET
查询SP5730供应商
1.3 GHz Low Phase Noise Frequency Synthesiser
Features
• Complete 1·3 GHz Single Chip System for Digital
Terrestrial Television Applications
• Selectable Reference Division Ratio, Compatible with
DTT Requirements
• Optimised for Low Phase Noise, with Comparison
Frequencies up to 4 MHz
• No RF Prescaler
• Selectable Reference/Comparison Frequency Output
• Four Selectable I2C Addresses
•I2C Fast Mode Compliant with 3·3V and 5V Logic
Levels
• Four Switching Ports
• Functional Replacement for SP5659 (except ADC)
• Pin Compatible with SP5655
• Power Consumption 120mW with VCC = 5·5V , all Ports off
• ESD Protection 2kV min., MIL-STD-883B Method 3015
Cat.1 (Normal ESD handling procedures should be
observed)
SP5730
Data Sheet
November 2004
Ordering Information
SP5730A/KG/QP1T 16 Pin QSOP Tape & Reel
SP5730A/KG/QP1S 16 Pin QSOP Tubes
SP5730A/KG/MP1S 16 Pin SOIC Tubes
SP5730A/KG/MP2S 16 Pin SOIC* Tubes
SP5730A/KG/QP2T 16 Pin QSOP* Tape & Reel
SP5730A/KG/MP1T 16 Pin SOIC T ape & Reel
SP5730A/KG/MP2T 16 Pin SOIC* Tape & Reel
SP5730A/KG/QP2S 16 Pin QSOP* Tubes
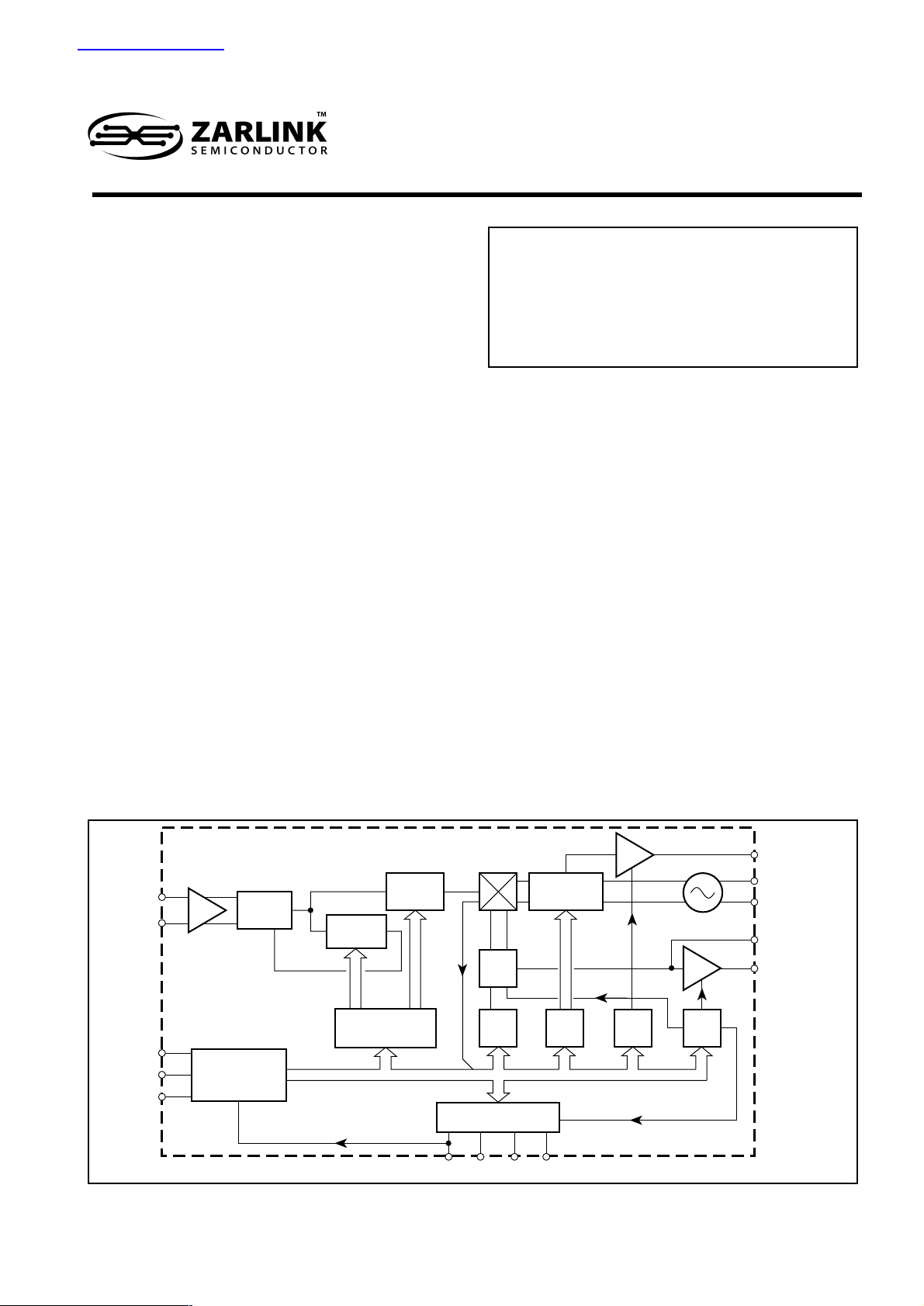
prescaler phase noise degradation over the full RF
operating range. The comparison frequency is obtained
either from an on-chip crystal controlled oscillator, or from
an external source. The oscillator frequency , f
comparator frequency , f
COMP output providing a reference for a second
frequency synthesiser. The synthesiser is controlled via
an 12C bus and is fast mode compliant. It can be hard
wired to respond to one of four addresses to enable two
or more synthesisers to be used on a common bus. The
device contains four switching ports P0 - P3.
*Pb Free Matte Tin
, can be switched to the REF/
COMP
, or phase
REF
Applications
• Digital Satellite, Cable and T errestrial Tuning Systems
• Communications Systems
Description
The SP5730 is a single chip frequency synthesiser
designed for tuning systems up to 1·3GHz and is
optimised for digital terrestrial applications. The RF
preamplifier interfaces direct with the RF programmable
divider, which is of MN1A construction so giving a step
size equal to the loop comparison frequency and no
12-BIT
COUNT
LOCK
fPD/2
4-BIT LATCH AND
PORT INTERFACE
P3
RF
INPUT
ADDRESS
SDA
SCL
13
14
10
4
I2C BUS
TRANSCEIVER
5
48/9
3-BIT
COUNT
15-BIT LATCH
Absolute Maximum Ratings
All voltages are referred to VEE = 0V
Supply voltage, V
RF differential input voltage
All I/O port DC offsets
SDA and SCL DC offset
Storage temperature
Junction temperature
QP16 thermal resistance
Chip to ambient, θ
Chip to case, θ
REFERENCE
DIVIDER
PUMP
2 BIT 5 BIT 2 BIT 2 BIT
6
789
P2 P1 P0
CC
JC
CP MODE
f
PD
JA
ENABLE/
SELECT
/2 SELECT
-0·3V to +7V
-0·3 to VCC +0·3V
-55°C to +150°C
11
REF/COMP
2
CRYSTAL CAP
3
CRYSTAL
1
CHARGE PUMP
16
DRIVE
DISABLE
2·5Vp-p
-0·3 to 6V
+150°C
80°C/W
20°C/W
Figure 1 - SP5730 block diagram
Zarlink, ZL and the Zarlink Semiconductor logo are trademarks of Zarlink Semiconductor Inc.
Copyright 2001-2004, Zarlink Semiconductor Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Zarlink Semiconductor Inc.
SP5730 Datasheet
CHARGE PUMP
CRYSTAL CAP
CRYSTAL
SDA
SCL
PORT P3/LOGLEV
PORT P2
PORT P1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
SP
5730
MP16
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
DRIVE
V
EE
RF INPUT
RFINPUT
V
CC
REF/COMP
ADDRESS
PORTP0
CHARGE PUMP
CRYSTAL CAP
CRYSTAL
SDA
SCL
PORT P3/LOGLEV
PORT P2
PORT P1
1
2
3
4
SP
5730
5
6
7
8
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
DRIVE
V
EE
RF INPUT
RFINPUT
V
CC
REF/COMP
ADDRESS
PORTP0
QP16
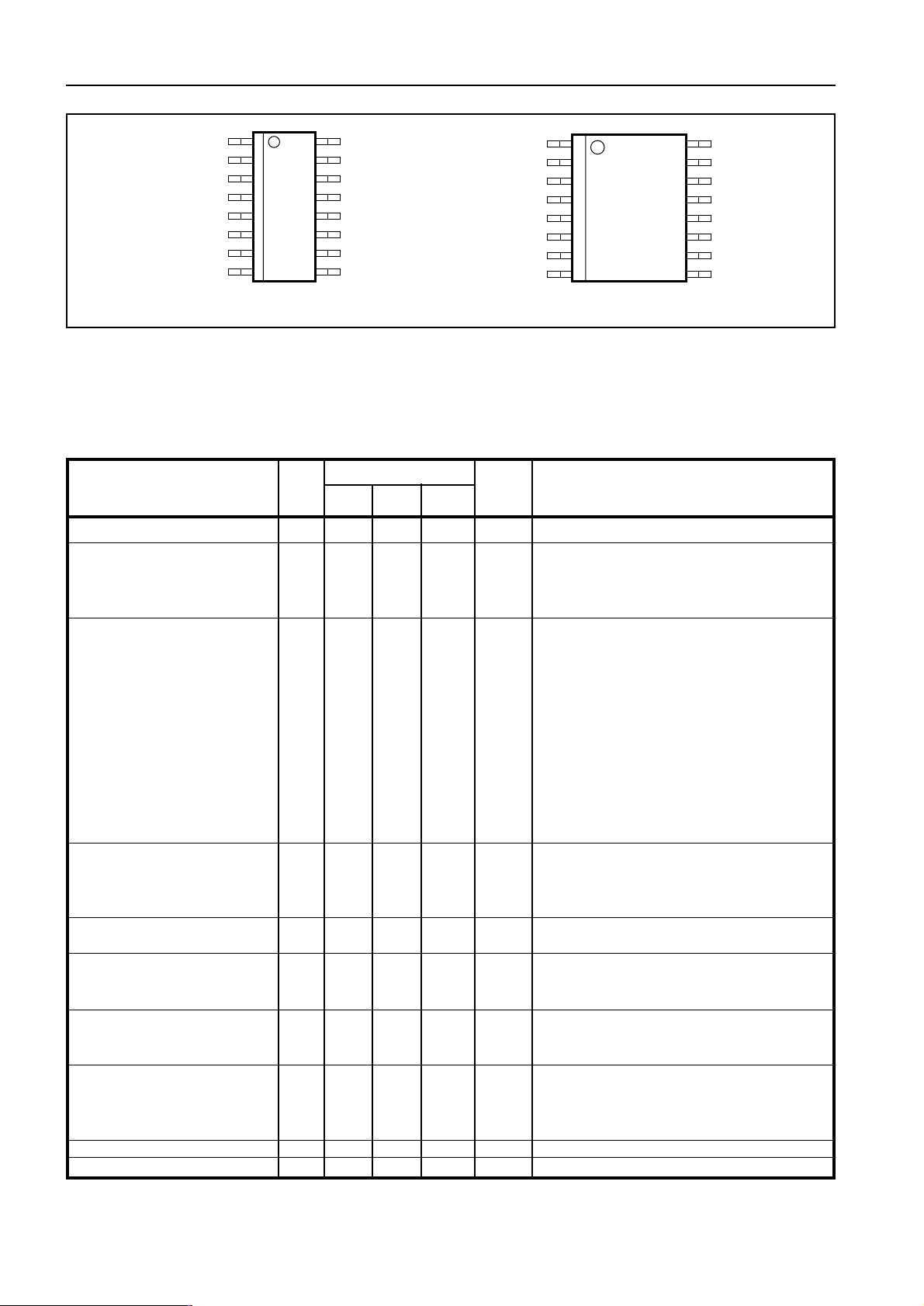
Figure 2 - Pin connections - top view
Table 1 - Electrical Characteristics
Test Conditions: T
production test or design. They apply within the specified ambient temperature and supply voltage ranges unless
otherwise stated.
Characteristic Conditions
Supply current
RF input
Input voltage
Input impedance
SDA, SCL
Input high voltage
Input low voltage
Input high current
Input low current
Leakage current
Input hysteresis
SDA output voltage
SCL clock rate
Charge pump
Output current
Output leakage
Drive output current
Crystal
Frequency
External reference
Input frequency
Drive level
Buffered REF/COMP
Output amplitude
Output impedance
Phase Detector
Comparison frequency
Equivalent phase noise at
phase detector
RF division ratio
Reference division ratio
= -40°C to +85°C, VCC = 4·5V to 5·5V. These characteristics are guaranteed by either
AMB
Value
12
Min.
Typ.
16
Max.
22
UnitsPin
mA
13,14
12·5
40
300
300
mVrms
mVrms
100MHz to 1·3GHz, see Figure 3
50MHz to 100MHz, see Figure 3
See Figure 4
4,5
5V I2C logic selected
V
3·3V I2C logic selected
V
5V I2C logic selected
V
3·3V I2C logic selected
V
Input voltage = V
Input voltage = V
V
= V
CC
EE
V
I
V
V
SINK
I
SINK
= 3mA
= 6mA
See Table 7, V
V
= 2V, VCC = 15·0V, T
PIN1
V
= 0·7V
PIN16
See Figure 5 for application
PIN1
CC
EE
= 2V
AMB
4
5
1
1
16
2,3
3
2·3
0
0
0·4
0·5
2
±3
5·5
3·5
1·5
1
10
-10
10
0·4
0·6
400
±10
20
µA
µA
µA
kHz
nA
mA
MHz
3
Sinewave coupled via 10nF blocking capacitor
Sinewave coupled via 10nF blocking capacitor
AC coupled, see Note 2
0·5 to 20MHz
Enabled by bit RE = 1
Ω
f
= 2MHz, SSB, See Note 4
COMP
f
= 125kHz, SSB, See Note 4
COMP
11
2
0·2
56
0.35
250
4
-152
-158
20
0·5
32767
MHz
Vp-p
Vp-p
MHz
dBc/Hz
dBc/Hz
See Table 2
= 25°C
cont…
2
Table 1 - Electrical Characteristics (continued)
Value
Characteristic
Pin
Min.
Typ.
Max.
Units
SP5730Datasheet
Conditions
Output Ports P3 - P0
Sink current
Leakage current
Address select
Input high current
Input low current
Logic level select
Input high level
Input low level
Input current
NOTES
1. Output ports high impedance on power-up, with SDA and SCL at logic ‘0’.
2. If the REF/COMP output is not used, the output should be left open circuit or connected to V
3. Bi-dectional port. When used as an output, the input logic state is ignored. When used as an input, the port should be switched
into high impedance (off) state.
4. Figures measured at 2kHz deviation, SSB (within loop bandwidth).
6-9
10
6
2
3
0
-10
10
1
-0·5
V
CC
1·5
10
mA
µA
mA
µA
V
V
µA
V
= 0·7V
PORT
V
= V
PORT
See Note 1
CC
See Table 5
VIN = V
VIN = V
CC
EE
See Note 3
5V I2C logic level selected
3·3V I2C logic level selected
VIN = V
to V
EE
CC
and disabled by setting RE = ‘0’.
CC
Functional Description
The SP5730 contains all the elements necessary, with
the exception of a frequency reference, loop filter and
external high voltage transistor, to control a varactor tuned
local oscillator, so forming a complete PLL frequency
synthesised source. The device allows for operation with
a high comparison frequency and is fabricated in high
speed logic, which enables the generation of a loop with
good phase noise performance. It can also be operated
with comparison frequencies appropriate for frequency
offsets as required in digital terrestrial television (DTT)
receivers.
The RF input signal is fed to an internal preamplifier, which
provides gain and reverse isolation from the divider
signals. The output of the preamplifier interfaces with the
15-bit fully programmable divider which is of MN1A
architecture, where the dual modulus prescaler is 48/9,
the A counter is 3 bits, and the M counter is 12 bits.
The output of the programmable divider is applied to the
phase comparator where it is compared in both phase
and frequency domains with the comparison frequency.
This frequency is derived either from the on-chip crystal
controlled oscillator or from an external reference source.
In both cases the reference frequency is divided down to
the comparison frequency by the reference divider which
is programmable into 1 of 29 ratios as detailed inT able 2.
The output of the phase detector feeds a charge pump
and loop amplifier section, which when used with an
external high voltage transistor and loop filter, integrates
the current pulses into the varactor line voltage.
The programmable divider output fPD/2 can be switched
to port P0 by programming the device into test mode.
The test modes are described inTable 6.
Programming
The SP5730 is controlled by an I2C data bus and is
compatible with both standard and fast mode formats and
with I2C data generated from nominal 3·3V and 5V
sources. The I2C logic level is selected by the bi-directional
port P3/ LOGLEV. 5V logic levels are selected by
connecting P3/ LOGLEV to VCC or leaving it open circuit;
3·3V logic levels are set by connecting P3/LOGLEV to
ground. If this port is used as an input the P3 data should
be programmed to high impedance. If used as an output
only 5V logic levels can be used, in which case the logic
state imposed by the port on the input is ignored.
Data and clock are fed in on the SDA and SCL lines
respectively as defined by I2C bus format . The synthesiser
can either accept data (write mode), or send data (read
mode). The LSB of the address byte (R/W) sets the device
into write mode if it is low, and read mode if it is high.
T ables 3 and 4 illustrate the format of the data. The device
can be programmed to respond to several addresses,
which enables the use of more than one synthesiser in
an I2C bus system. Table 5 shows how the address is
selected by applying a voltage to the address input.
When the device receives a valid address byte, it pulls
the SDA line low during the acknowledge period, and
during following acknowledge periods after further data
bytes are received.
When the device is programmed into read mode, the
controller accepting the data must be pulled low during
all status byte acknowledge periods to read another status
byte. If the controller fails to pull the SDA line low during
this period, the device generates an internal STOP
condition, which inhibits further reading.
3
SP5730 Datasheet
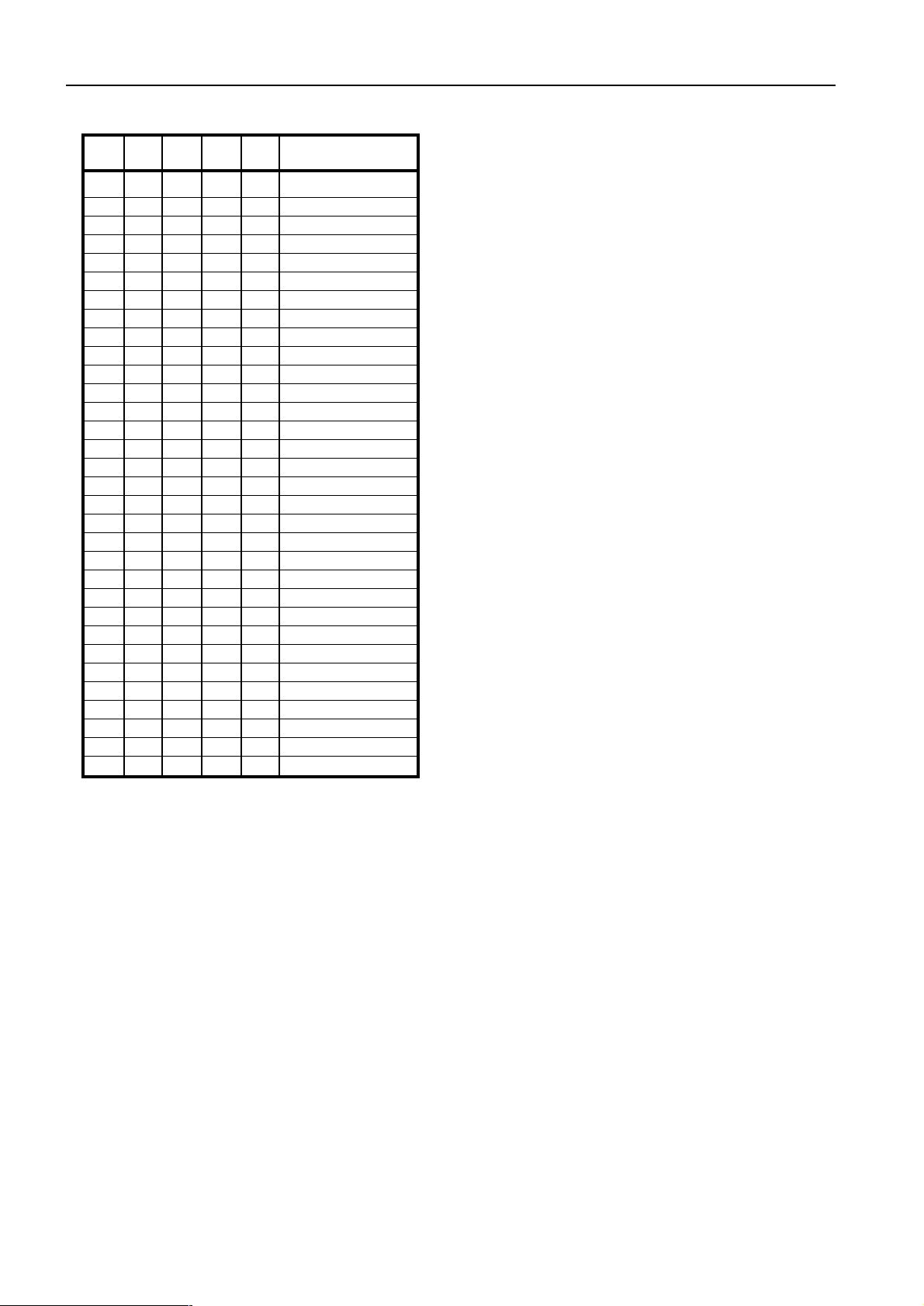
Table 2 - Reference division ratios
R2
R1
R4
R3
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
1
0
0
1
0
1
0
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
Write mode
With reference to T able 3, bytes 2 and 3 contain frequency
information bits 214-20 inclusive. Bytes 4 and 5 control
the reference divider ratio (see Table 2), charge pump
setting (see Table 7), REF/COMP output (see Table 8),
output ports and test modes (see Table 6).
After reception and acknowledgement of a correct
address (byte 1), the first bit of the following byte
determines whether the byte is interpreted as a byte 2 or
R0 Division ratio
0
0
0
1
1
0
1
1
0
0
0
1
1
0
1
1
0
0
0
1
1
0
1
1
0
0
0
1
1
0
1
1
0
0
0
1
1
0
1
1
0
0
0
1
1
0
1
1
0
0
0
1
1
0
1
1
0
0
0
1
1
0
1
1
Illegal state
Illegal state
Illegal state
2
4
8
16
32
64
128
256
5
10
20
40
80
160
320
6
12
24
48
96
192
384
7
14
28
56
112
224
448
4, a logic ‘0’ indicating byte 2, and a logic ‘1’ indicating
byte 4. Having interpreted this byte as either byte 2 or 4,
the following data byte will be interpreted as byte 3 or 5
respectively. Having received two complete data bytes,
additional data bytes can be entered, where byte
interpretation follows the same procedure, without readdressing the device. This procedure continues until a
STOP condition is received. The STOP condition can be
generated after any data byte; if, however, it occurs during
a byte transmission, the previous byte data is retained.
To facilitate smooth fine tuning, the frequency data bytes
are only accepted by the device after all 15 bits of
frequency data have been received, or after the generation
of a STOP condition.
Read mode
When the device is in read mode, the status byte read
from the device takes the form shown in Table 4.
Bit 1 (POR) is the power-on reset indicator , and this is set
to a logic ‘1’ if the VCC supply to the device has dropped
below 3V (at 25°C ), e.g. when the device is initially turned
on. The POR is reset to ‘0’ when the read sequence is
terminated by a STOP command. When POR is set high
this indicates the programmed information may be
corrupted and the device reset to power up condition.
Bit 2 (FL) indicates whether the device is phase locked, a
logic’1’is present if the device is locked, and a logic ‘0’ if it
is not.
Programable features
• RF programmable divider Function as described
above.
• Reference programmable divider Function as
described above.
• Charge pump current The charge pump current can
be programmed by bits C1 and C0 within data byte 5,
as defined in Table 7.
• T est mode The test modes are invoked by setting bits
RE, RS, T1 and T0 as described in Table 6.
• Reference/Comparison frequency output The
reference frequency f
f
can be switched to the REF/COMP output,
COMP
function as defined in Table 8. RE and RS default to
logic’1’during device power up, thus enabling the
comparison frequency f
or comparison frequency
REF
at the REF/COMP output.
COMP
4
 Loading...
Loading...