Page 1

5G CPE
UF51
Administrator Guide
Page 2

2
Preface
Document
Description
UF51 Datasheet
Datasheet for the UF51 5G CPE.
UF51 Installation Guide
Hardware descriptions and installation instructions for the UF51 5G
CPE.
Date
Doc Version
Description
June 21, 2021
V 1.0
Initial version
Thanks for choosing Yeastar UF51 5G CPE. The UF51 5G CPE delivers tenacious connection over
network with full-featured design such as automated failover/failback, extended operating
temperature, hardware watchdog, VPN, Gigabit Ethernet and beyond.
This guide describes how to configure and operate the UF51 5G CPE. You can refer to it for detailed
functionality and device configuration.
Readers
This guide is mainly intended for the following users:
- Network Planners
- On-site technical support and maintenance personnel
- Network administrators responsible for network configuration and maintenance
Related Documents
Declaration of Conformity
UF51 is in conformity with the essential requirements and other relevant provisions of the CE, FCC,
and RoHS.
For assistance, please contact
Yeastar technical support:
Email: support@yeastar.com
Tel: 86-592-5085280
Fax: 86-592-5023065
Revision History
Page 3

3
Contents
Chapter 1 Product Introduction
1.1 Overview
1.2 Advantages
1.3 Specifications
1.4 Dimensions (mm)
Chapter 2 Access to Web GUI
2.1 Wireless Access
2.2 Wired Access
Chapter 3 Web Configuration
3.1 Status
3.1.1 Overview
3.1.2 Cellular
3.1.3 Network
3.1.4 WLAN
3.1.5 VPN
3.1.6 Routing
3.1.7 Host List
3.1.8 GPS
3.2 Network
3.2.1 Interface
3.2.2 DHCP
3.2.3 Firewall
3.2.4 QoS
....................................................................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................
..................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................
.........................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................
.........................................................................................................................................
.......................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................
3.2.1.1 Link Failover
3.2.1.2 Cellular
3.2.1.3 Port
3.2.1.4 WAN
3.2.1.5 Bridge
3.2.1.6 WLAN
3.2.1.7 Switch
3.2.1.8 Loopback
............................................................................................................................................
3.2.2.1 DHCP Server/DHCPv6 Server
3.2.2.2 DHCP Relay
3.2.3.1 Security
3.2.3.2 ACL
3.2.3.3 Port Mapping
3.2.3.4 DMZ
3.2.3.5 MAC Binding
3.2.3.6 Custom Rules
3.2.3.7 SPI
...............................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................
..................................................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................................
................................................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................
..................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................
.........................................................................................................................
......................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
..................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................
..................................................................................................................
7
7
7
8
10
12
12
12
15
15
15
16
18
19
20
21
22
22
23
23
23
25
28
28
33
34
37
38
38
38
40
41
41
42
43
44
45
45
46
47
Page 4

4
3.2.5 VPN
..............................................................................................................................................
3.2.5.1 DMVPN
3.2.5.2 IPSec Server
3.2.5.3 IPSec
3.2.5.4 GRE
3.2.5.5 L2TP
3.2.5.6 PPTP
3.2.5.7 OpenVPN Client
3.2.5.8 OpenVPN Server
3.2.5.9 Certifications
3.2.6 IP Passthrough
3.2.7 Routing
........................................................................................................................................
3.2.7.1 Static Routing
3.2.7.2 RIP
.....................................................................................................................................
3.2.7.3 OSPF
3.2.7.4 Routing Filtering
3.2.8 VRRP
3.2.9 DDNS
3.3 System
............................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................................
3.3.1 General Settings
3.3.1.1 General
3.3.1.2 System Time
3.3.1.3 Email
3.3.2 Phone & SMS
3.3.2.1 Phone
3.3.2.2 SMS
3.3.3 User Management
3.3.3.1 Account
3.3.3.2 User Management
3.3.4 SNMP
...........................................................................................................................................
3.3.4.1 SNMP
3.3.4.2 MIB View
3.3.4.3 VACM
3.3.4.4 Trap
3.3.4.5 MIB
3.3.5 AAA
..............................................................................................................................................
3.3.5.1 Radius
3.3.5.2 TACACS+
3.3.5.3 LDAP
3.3.5.4 Authentication
3.3.6 Device Management
3.3.6.1 DeviceHub
3.3.6.2 Yeastar VPN
3.3.7 Events
..........................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................
................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................
.................................................................................................................................
.................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................
............................................................................................................
..................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
.................................................................................................................
.................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................
.................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................................
..................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................................
.........................................................................................................................
.................................................................................................................................
................................................................................................................
.................................................................................................................
.......................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................
48
48
49
53
55
57
59
61
62
64
67
67
67
68
71
77
77
79
81
81
81
82
84
85
85
86
88
88
89
90
90
91
91
92
93
93
93
94
95
96
96
96
97
99
Page 5

5
3.3.7.1 Events
...............................................................................................................................
3.3.7.2 Events Settings
3.4 Industrial Interface
3.4.1 I/O
...............................................................................................................................................
3.4.1.1 DI
3.4.1.2 DO
3.4.2 Serial Port
3.4.3 Modbus Slave
.............................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................
.................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
3.4.3.1 Modbus TCP
3.4.3.2 Modbus RTU
3.4.3.3 Modbus RTU Over TCP
3.4.4 Modbus Master
3.4.4.1 Modbus Master
3.4.4.2 Channel
3.4.5 GPS
3.4.5.1 GPS
............................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................
.................................................................................................................................
3.4.5.2 GPS IP Forwarding
3.4.5.3 GPS Serial Forwarding
3.5 Maintenance
3.5.1 Tools
3.5.1.1 Ping
........................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................
................................................................................................................................
3.5.1.2 Traceroute
3.5.1.3 Packet Analyzer
3.5.1.4 Qxdmlog
3.5.2 Debugger
........................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................
3.5.2.1 Cellular Debugger
3.5.2.2 Firewall Debugger
3.5.3 Log
.............................................................................................................................................
3.5.3.1 System Log
3.5.3.2 Log Download
3.5.3.3 Log Settings
3.5.4 Upgrade
.....................................................................................................................................
3.5.5 Backup and Restore
3.5.6 Reboot
3.6 APP
3.6.1 Python
........................................................................................................................................................
3.6.1.1 Python
.......................................................................................................................................
.......................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
3.6.1.2 App Manager Configuration
3.6.1.3 Python App
Chapter 4 Application Examples
4.1 Restore Factory Defaults
4.1.1 Via Web Interface
4.1.2 Via Hardware
4.2 Firmware Upgrade
............................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................
.................................................................................................................
.................................................................................................................
...............................................................................................
........................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................
.......................................................................................................
................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................
........................................................................................................
........................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................
..................................................................................................................
................................................................................................................
......................................................................................
....................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................
99
99
101
102
102
103
103
107
107
108
108
109
109
110
112
112
112
114
115
115
115
115
115
116
116
116
117
118
118
119
120
121
121
122
123
123
123
124
124
126
126
126
127
127
Page 6

6
4.3 Events Application Example
4.4 SNMP Application Example
4.5 Network Connection
...........................................................................................................................
4.5.1 Cellular Connection
4.5.2 Ethernet WAN Connection
4.6 Wi-Fi Application Example
4.6.1 AP Mode
4.6.2 Client Mode
....................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................
4.7 VRRP Application Example
4.8 NAT Application Example
.............................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................
.................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................
................................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................
..................................................................................................................
4.9 Access Control Application Example
4.10 QoS Application Example
4.11 DTU Application Example
4.12 PPTP Application Example
................................................................................................................
................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................
..............................................................................................
128
129
132
132
134
135
135
136
137
140
141
142
143
147
Page 7

7
Chapter 1 Product Introduction
1.1 Overview
Yeastar UF51 5G CPE is designed as a cost-effective solution providing for 5G wireless networking
application. Adopting high-performance industrial platform of quad-core CPU and 5G cellular module,
UF51 is capable of providing ultra-fast Internet connection and ultra-small packages to ensure the
extremely safe and reliable connection to the wireless network. With various kinds of installation
methods, IP67 waterproof enclosure and novel design, UF51 is applicable to indoor and outdoor
applications.
Meanwhile, the UF51 also supports 2-port Gigabit Ethernet switch, serial port (RS232/RS485) and I/O
(input/output), which allow you to scale up M2M application combining data and video in limited time
and budget.
The UF51 is particularly ideal for smart offices, video surveillance, digital media implementations,
industrial automation, traffic applications, robots and so on.
For details of hardware and installation, please check the UF51 Quick Start Guide.
1.2 Advantages
Benefits
- Built-in Qualcomm quad-core CPU and big memory
- 4G LTE/5G NR (NSA/SA) network with dual SIM cards for backup among multiple carriers
networking
- Gigabit Ethernets for fast data transmission
- Equipped with Ethernet, I/O, serial port, Wi-Fi, GPS for connecting diverse field assets
- Embedded Python SDK for second development
- Pole mounting, wall mounting, desktop, bottom magnetic or lock mounting for various
applications
- 3-year warranty included
Security & Reliability
- Automated failover/failback among Ethernet, Cellular and Wi-Fi
- Enable unit with security frameworks like IPsec/OpenVPN/GRE/L2TP/PPTP/ DMVPN
Embed hardware watchdog, automatically recovering from various failure, and ensuring highest
-
level of availability
- Establish a secured mechanism on centralized authentication and authorization of device access
by supporting AAA (TACACS+, Radius, LDAP, local authentication) and multiple levels of user
authority
Page 8

8
Easy Maintenance
Hardware System
CPU
Qualcomm Quad-core ARM Cortex A7, 716.8 MHz
Memory
8 GB Flash, 512 MB DDR3 RAM
Ethernet
Ports
2 × RJ-45
Physical Layer
10/100/1000 Base-T (IEEE 802.3)
Data Rate
10/100/1000 Mbps (Auto-Sensing)
Interface
Auto MDI/MDIX
Mode
Full or Half Duplex (Auto-Sensing)
PoE
1 × 802.3af PoE PD on WAN/LAN port
Cellular Interfaces
Network
5G/4G LTE
Antenna
8 × Internal Antennas
SIM Slot
1 (Mini SIM-2FF)
Wi-Fi Interface
Yeastar DeviceHub provides easy setup, mass configuration, and centralized management of
-
remote devices
- The user-friendly web interface design and several upgrade options help administrator to manage
the device as easy as pie
- Web GUI and CLI enable the admin to achieve simple management and quick configuration
among a large quantity of devices
- Efficiently manage the remote devices on the existing platform through the industrial standard
SNMP
Capabilities
- Link remote devices in an environment where communication technologies are constantly
changing
- It can be continuously running in a broken or weak network environment, and the latest data can
be synchronized to remote server after the network is restored
- Support rich protocols like SNMP, Modbus bridging, RIP, OSPF
- Support wide operating temperature ranging from -40°C to 70°C/-40°F to 158°F
1.3 Specifications
Page 9

9
Antenna
4 × Internal Antennas
Standards
IEEE 802.11 a/b/g/n/ac
Tx Power
2.4 GHz: 26dBm(max)
5 GHz: 26.4dBm(max)
Rx Sensitivity
2.4 GHz
5 GHz
802.11b: ≤ -92dBm@11Mbps
802.11g: ≤ -78dBm@54Mbps
802.11ac VHT20: ≤ -91dBm@MCS0
802.11ac VHT20: ≤ -66dBm@MCS8
802.11ac VHT40: ≤ -88.5dBm@MCS0
802.11ac VHT40: ≤ -64dBm@MCS8
802.11a: ≤ -91dBm@6Mbps
802.11a: ≤ -76dBm@54Mbps
802.11ac VHT20: ≤ -90dBm@MCS0
802.11ac VHT20: ≤ -68dBm@MCS8
802.11ac VHT40: ≤ -87dBm@MCS0
802.11ac VHT40: ≤ -65dBm@MCS9
802.11ac VHT80: ≤ -84dBm@MCS0
802.11ac VHT80: ≤ -60dBm@MCS9
Modes
AP and Client Mode
Security
WPA/WPA2 Authentication, WEP/TKIP/AES Encryption
IO
Connector
3.5 mm Terminal Block
Digital
1 × DI (Dry Contact) + 1 × DO (Wet Contact)
Serial Interface
Ports
1 × RS232 or 1 × RS485 (Switchable)
Connector
3.5 mm Terminal Block
Baud Rate
300bps to 230400bps
GNSS
1
Antenna
1 × Internal Antenna
Technology
GPS/GLONASS/Beidou/Galileo/QZSS
Software
1
GNSS is under development.
Page 10

10
Physical Characteristics
Ingress Protection
IP67
Housing
Polycarbonate + Metal
Dimensions
No Waterproof Connector: ф105 x 110 x 187 mm (ф4.13 x 4.33 x 7.36 in)
With Waterproof Connector: ф105 x 110 x 218 mm (ф4.13 x 4.33 x 8.58 in)
Mounting
Desktop, Wall Mounting, Pole Mounting, Bottom Magnetic/Lock Mounting
Others
Reset Button
1 × RESET
LED Indicators
1 × STATUS, 1 × Cellular Network
Built-in
Watchdog, Timer
Environmental
Operating
Temperature
-40°C to +70°C (-40°F to +158°F)
Reduced Cellular Performance above 60°C
Storage Temperature
-40°C to +85°C (-40°F to +185°F)
Ethernet Isolation
1.5 kV RMS
Relative Humidity
0% to 95% (Non-condensing) at 25°C/77°F
1.4 Dimensions (mm)
Network Protocols
IPv4/IPv6, PPP, PPPoE, SNMP v1/v2c/v3, TCP, UDP, DHCP, RIPv1/v2,
OSPF, DDNS, VRRP, HTTP, HTTPS, DNS, ARP, QoS, SNTP, Telnet, VLAN,
SSH, etc.
VPN Tunnel
DMVPN/IPsec/OpenVPN/PPTP/L2TP/GRE
Access Authentication
CHAP/PAP/MS-CHAP/MS-CHAPV2
Firewall
ACL/DMZ/Port Mapping/MAC Binding/SPI/DoS & DDoS Protection
/IP Passthrough
Management
Web, CLI, SMS, On-demand Dial up, DeviceHub
AAA
Radius, TACACS+, LDAP, Local Authentication
Multilevel Authority
Multiple Levels of User Authority
Reliability
VRRP, WAN Failover
Serial Port
Transparent (TCP Client/Server, UDP), Modbus Gateway (Modbus RTU to
Modbus TCP)
Power Supply and Consumption
Connector
2-pin 3.5 mm Terminal Block
Input Voltage
9-48 VDC or 802.3af PoE PD
Power Consumption
≤ 7 W
Page 11

11
Page 12

12
Chapter 2 Access to Web GUI
If you enter the username or password incorrectly more than 5 times, the login page will be
locked for 10 minutes.
This chapter explains how to access to Web GUI of the UF51 device.
Username: admin
Password: password
2.1 Wireless Access
1. Enable Wireless Network Connection on your computer and search for access point
“Router_******” to connect it.
2. Open a Web browser on your PC (Chrome is recommended) and type in the IP address 192.168.1.1
to access the web GUI.
3. Enter the username and password, and click “Login”.
4. After logging in the web GUI, you can view system information and perform configuration.
2.2 Wired Access
Connect PC to any LAN port directly or through PoE injector to access the web GUI of device. The
following steps are based on Windows 10 system for your reference.
1. Go to “Control Panel” → “Network and Internet” → “Network and Sharing Center”, then click
“Ethernet” (May have different names).
Page 13

13
2. Go to “Properties” → “Internet Protocol Version 4(TCP/IPv4) ”, select “Obtain an IP address
If you enter the username or password incorrectly more than 5 times, the login page will be
locked for 10 minutes.
automatically” or “Use the following IP address”, then assign a static IP manually within the same
subnet of the device.
3. Open a Web browser on your PC (Chrome is recommended) and type in the IP address
192.168.1.1 to access the web GUI.
4. Enter the username and password, click “Login”.
5. After logging in the web GUI, you can view system information and perform configuration of the
gateway.
Page 14

14
Page 15

15
Chapter 3 Web Configuration
System Information
Item
Description
Model
Show the model name of device.
Serial Number
Show the serial number of device.
Firmware Version
Show the currently firmware version of device.
Hardware Version
Show the currently hardware version of device.
System Status
Item
Description
Local Time
Show the currently local time of system.
Uptime
Show the information about how long the device has
been running.
CPU Load
Show the current CPU utilization of the device.
RAM (Available/Capacity)
Show the RAM capacity and the available RAM memory.
Flash (Available/Capacity)
Show the Flash capacity and the available Flash memory.
Cellular
Item
Description
Status
Show the real-time status of the SIM card.
3.1 Status
3.1.1 Overview
You can view the system information of the device on this page.
Figure 3-1-1-1
Table 3-1-1-1 System Information
Table 3-1-1-2 System Status
Page 16

16
Current SIM
Show the SIM card currently used for the data connection.
IPv4/IPv6
Show the IPv4/IPv6 address obtained from the mobile carrier.
Connection Duration
Show the connection duration of the currently-used SIM card.
Data Usage Monthly
Show the monthly data usage of currently used SIM card.
Table 3-1-1-3 Cellular Status
WAN
Item
Description
Status
Show the current status of WAN port.
IPv4/IPv6
The IPv4/IPv6 address of WAN port.
MAC
The MAC address of the Ethernet port.
Connection Duration
Show the connection duration of the WAN port.
WLAN
Item
Description
Status
Show the current status of WLAN.
IP
Show the WLAN mode (AP or client).
SSID
Show the SSID of the WLAN AP or client.
Connected Clients
Show the amount of connected devices when using AP
mode.
LAN
Item
Description
IPv4/IPv6
Show the IPv4/IPv6 address of the LAN port.
Connected Devices
The number of devices that connect to the device's LAN.
Table 3-1-1-4 WAN Status
Table 3-1-1-5 WLAN Status
Table 3-1-1-6 LAN Status
3.1.2 Cellular
You can view the cellular network status of device on this page.
Page 17

17
Figure 3-1-2-1
Modem Information
Item
Description
Status
Show corresponding detection status of module and SIM card.
Model
Show the model name of cellular module.
Version
Show the cellular module firmware version.
Signal Level
Show the cellular signal level.
Register Status
Show the registration status of SIM card.
IMEI
Show the IMEI of the module.
IMSI
Show IMSI of the SIM card.
ICCID
Show ICCID of the SIM card.
ISP
Show the network provider which the SIM card registers on.
Network Type
Show the connected network type, such as 5G NR, LTE, etc.
PLMN ID
Show the current PLMN ID, including MCC, MNC, LAC and Cell ID.
LAC
Show the location area code of the SIM card.
Cell ID
Show the Cell ID of the SIM card location.
CQI
Show the Channel Quality Indicator of the cellular network.
DL Bandwidth
Show the DL bandwidth of the cellular network.
UL Bandwidth
Show the UL bandwidth of the cellular network.
SINR
Show the Signal Interference + Noise Ratio of the cellular network.
PCI
Show the physical-layer cell identity of the cellular network.
RSRP
Show the Reference Signal Received Power of the cellular network.
RSRQ
Show the Reference Quality Received Power of the cellular network.
ECGI
Show the E-UTRAN Cell Global Identifier of the cellular network.
EARFCN
Show the E-UTRA Absolute Radio Frequency Channel Number.
Page 18

18
ENODEB ID
Show the eNodeB ID of the cellular network.
Table 3-1-2-1 Modem Information
Network
Item
Description
Status
Show the connection status of cellular network.
IPv4/IPv6 Address
Show the IPv4/IPv6 address and netmask of cellular network.
IPv4/IPv6 Gateway
Show the IPv4/IPv6 gateway and netmask of cellular network.
IPv4/IPv6 DNS
Show the DNS of cellular network.
Connection Duration
Show information on how long the cellular network has been
connected.
Data Usage Monthly
Item
Description
RX
Show monthly downlink data usage.
TX
Show monthly uplink data usage.
ALL
Show all monthly data usage.
WAN Status
Item
Description
Port
Show the name of WAN port.
Status
Show the status of WAN port. "Up" refers to a status that WAN is enabled
and Ethernet cable is connected. "Down" means Ethernet cable is
disconnected or WAN function is disabled.
Type
Show the dial-up connection type of WAN port.
IP Address
Show the IPv4 or IPv6 address of WAN port.
Netmask
Show the IPv4 netmask of WAN port.
Prefix-length
Show the IPv6 Prefix-length of WAN port.
Gateway
Show the gateway of WAN port.
Table 3-1-2-2 Network Status
Table 3-1-2-3 Data Usage Information
3.1.3 Network
On this page you can check the WAN and LAN status of the device.
Figure 3-1-3-1
Page 19

19
DNS
Show the DNS of WAN port.
Connection
Duration
Show the information about how long the Ethernet cable has been
connected to WAN port when WAN function is enabled. Once WAN function
is disabled or Ethernet connection is disconnected, the duration will stop
counting.
Table 3-1-3-1 WAN Status
Bridge
Item
Description
Name
Show the name of the bridge interface.
STP
Show if STP is enabled.
IPv4/IPv6
Show the IPv4/IPv6 address and netmask of the bridge interface.
Members
Show the members of the bridge interface.
WLAN Status
Item
Description
WLAN Status
Name
Show the name of the Wi-Fi interface .
Status
Show the status of the Wi-Fi interface.
Type
Show the Wi-Fi interface type (AP or client).
SSID
Show the SSID of AP device.
IPv4/IPv6 Address
Show the IPv4/IPv6 address and netmask of AP device.
Figure 3-1-3-2
Table 3-1-3-2 Bridge Status
3.1.4 WLAN
You can check Wi-Fi status on this page, including the information of access point and client.
Figure 3-1-4-1
Page 20

20
Associated Stations
SSID
Show the SSID of AP device.
MAC Address
Show the MAC address of the client which connected to the
device when the interface type is AP. Show the MAC address of
the AP which the device connected to when the interface type
is Client.
IPv4/IPv6 Address
Show the IPv4/IPv6 address of the client which connected to
the device when the interface type is AP. Show the IPv4/IPv6
address of the AP which the device connected to when the
interface type is Client.
Connection Duration
Show the connection duration between client device and device
when the interface type is AP. Show the connection duration
between device and the AP when the interface type is Client.
Table 3-1-4-1 WLAN Status
VPN Status
Item
Description
Clients
Name
Show the name of the enabled VPN clients.
Status
Show the status of client. "Connected" refers to a status that
client is connected to the server. "Disconnected" means client is
disconnected to the server.
Local IP
Show the local IP address of the tunnel.
Remote IP
Show the real remote IP address of the tunnel.
3.1.5 VPN
You can check VPN status on this page, including PPTP, L2TP, IPsec, OpenVPN and DMVPN.
Figure 3-1-5-1
Page 21

21
Server
Name
Show the name of the enabled VPN Server.
Status
Show the status of Server.
Connected List
Server Type
Show the type of the server.
Client IP
Show the IP address of the client which connected to the server.
Duration
Show the information about how long the client has been
connected to this server when the server is enabled. Once the
server is disabled or connection is disconnected, the duration will
stop counting.
Table 3-1-5-1 VPN Status
Item
Description
Routing Table
Destination
Show the IP address of destination host or destination network.
Netmask/Prefix
Length
Show the netmask or prefix length of destination host or
destination network.
Gateway
Show the IP address of the gateway.
Interface
Show the outbound interface of the route.
Metric
Show the metric of the route.
3.1.6 Routing
You can check routing status on this page, including the routing table and ARP cache.
Figure 3-1-6-1
Page 22

22
ARP Cache
IP
Show the IP address of ARP pool.
MAC
Show the IP address's corresponding MAC address.
Interface
Show the binding interface of ARP.
Table 3-1-6-1 Routing Information
Host List
Item
Description
DHCP Leases
IP Address
Show IP address of DHCP client
MAC/DUID
Show MAC address of DHCPv4 client or DUID of DHCPv6
client.
Lease Time Remaining
Show the remaining lease time of DHCP client.
MAC Binding
IP
Show the IP address set in the Static IP list of DHCP service.
MAC/DUID
Show the MAC address or DUID set in the Static IP list of DHCP
service.
3.1.7 Host List
You can view the host information on this page.
Figure 3-1-7-1
Table 3-1-7-1 Host List Description
3.1.8 GPS
When GPS function is enabled and the GPS information is obtained successfully, you can view the
latest GPS information including GPS Time, Latitude, Longitude and Speed on this page.
Page 23

23
GPS Status
Item
Description
Status
Show the status of GPS.
Time for Locating
Show the time for locating.
Satellites In Use
Show the quantity of satellites in use.
Satellites In View
Show the quantity of satellites in view.
Latitude
Show the Latitude of the location.
Longitude
Show the Longitude of the location.
Altitude
Show the Altitude of the location.
Speed
Show the speed of movement.
3.2 Network
3.2.1 Interface
3.2.1.1 Link Failover
Figure 3-1-8-1
Table 3-1-8-1 GPS Status Description
This section describes how to configure link failover strategies, their priority and the ping settings,
each rule owns its own ping rules by default. UF51 will follow the priority to choose the next available
interface to access the internet, make sure you have enable the full interface that you need to use
here. If priority 1 can only use IPv4, UF51 will select a second link which IPv6 works as main IPv6 link
and vice versa.
Page 24

24
Figure 3-2-1-1
Link Failover
Item
Description
Link Priority
Priority
Display the priority of each interface, you can modify it by the
operation’s up and down button.
Enable Rule
If enabled, the device will choose this interface into its switching
rule. For the Cellular interface, if it’s not enabled here, the
interface will be disabled as well.
Link In Use
Mark whether this interface is in use with green icon.
Interface
Display the name of the interface.
Connection type
Display how to obtain the IP address in this interface, like static
IP or DHCP.
IP
Display the IP address of the interface.
Operation
You can change the priority of the rules and configure the ping
detection rules here.
Settings
Revert Interval
Specify the number of seconds to waiting for switching to the
link with higher priority, 0 means to disable the function.
Emergency Reboot
Enable to reboot the device if no link is available.
Table 3-2-1-1 Link Failover Parameters
Page 25

25
Figure 3-2-1-2
Ping Detection
Item
Description
Enable
If enabled, the device will periodically detect the connection
status of the link.
IPv4/IPv6 Primary
Server
The device will send ICMP packet to the IPv4/IPv6 address or
hostname to determine whether the Internet connection is still
available or not.
IPv4/IPv6 Secondary
Server
The device will try to ping the secondary server if primary
server is not available.
Interval
Time interval (in seconds) between two Pings.
Retry Interval
Set the ping retry interval. When ping failed, the device will
ping again in every retry interval.
Timeout
The maximum amount of time the device will wait for a
response to a ping request. If it does not receive a response
for the amount of time defined in this field, the ping request
will be considered to have failed.
Max Ping Retries
The retry times of the device sending ping request until
determining that the connection has failed.
Table 3-2-1-2 Ping Detection Parameters
3.2.1.2 Cellular
This section explains how to set the related parameters for cellular network.
Page 26

26
Figure 3-2-1-3
Cellular Settings
Item
Description
Protocol
Select from "IPv4", "IPv6" and "IPv4/IPv6".
APN
Enter the Access Point Name for cellular dial-up connection provided
by local ISP.
Username
Enter the username for cellular dial-up connection provided by local
ISP.
Password
Enter the password for cellular dial-up connection provided by local
ISP.
PIN Code
Enter a 4-8 characters PIN code to unlock the SIM.
Access Number
Enter the dial-up center NO. For cellular dial-up connection provided
by local ISP.
Authentication Type
Select from "Auto", "PAP", "CHAP", "MS-CHAP", and "MS-CHAPv2".
Page 27

27
Network Type
Select from "Auto", “5G NSA”, “5G SA”, "4G Only" and "3G Only".
Auto: connect to the network with the strongest signal automatically.
4G Only: connect to 4G network only.
And so on.
SMS Center
Enter the local SMS center number for storing, forwarding, converting
and delivering SMS message.
Enable NAT
Enable or disable NAT function.
Roaming
Enable or disable roaming.
Data Limit
When you reach the specified data usage limit, the data connection of
currently used SIM card will be disabled. 0 means to disable the
function.
Billing Day
Choose the billing day of the SIM card, the device will reset the data
used to 0.
Table 3-2-1-3 Cellular Parameters
Connection Setting
Item
Description
Connection Mode
Select from "Always Online" and "Connect on Demand".
Re-dial Interval(s)
Set the interval to dial into ISP when it lost connection, the default value is 5s.
Max Idle Times
Set the maximum duration of device when current link is under idle status.
Range: 10-3600
Triggered by Call
The device will switch from offline mode to cellular network mode
automatically when it receives a call from the specific phone number.
Call Group
Select a call group for call trigger. Go to "System > Phone&SMS > Phone" to
set up phone group.
Triggered by SMS
The device will switch from offline mode to cellular network mode
automatically when it receives a specific SMS from the specific mobile
phone.
Figure 3-2-1-4
Page 28

28
SMS Group
Select an SMS group for trigger. Go to "System > Phone&SMS > SMS" to set
up SMS group.
SMS Text
Fill in the SMS content for trigger.
Triggered by IO
The device will switch from offline mode to cellular network mode
automatically when the DI status is changed. Go to "Industrial > I/O > DI" to
configure trigger condition.
Table 3-2-1-4 Cellular Parameters
Port Setting
Item
Description
Port
Users can define the Ethernet ports according to their needs.
Status
Set the status of Ethernet port; select "up" to enable and "down" to
disable.
Property
Show the Ethernet port's type, as a WAN port or a LAN port.
Speed
Ethernet port speed is fixed as “auto”.
Duplex
Ethernet port mode is fixed as “auto”.
Related Topics
Cellular Network Connection
Phone Group
DI Setting
3.2.1.3 Port
This section describes how to configure the Ethernet port parameters.
UF51 supports 2 Gigabit Ethernet ports.
Figure 3-2-1-5
Table 3-2-1-5 Port Parameters
3.2.1.4 WAN
WAN port can be connected with Ethernet cable to get Internet access. It supports 3 connection
types.
- Static IP: configure IP address, netmask and gateway for Ethernet WAN interface.
- DHCP Client: configure Ethernet WAN interface as DHCP Client to obtain IPv4 address
automatically.
- PPPoE: configure Ethernet WAN interface as PPPoE Client.
- DHCPv6 Client: configure Ethernet WAN interface as DHCP Client to obtain IPv6 address
automatically.
Page 29

29
- PPPoE v6: configure Ethernet WAN interface as PPPoEv6 Client.
WAN Basic Setting
Item
Description
Default
Enable
Enable WAN function.
Enable
Port
The port that is currently set as WAN port.
LAN1/WAN
Connection Type
Select from "Static IP", "DHCP Client", “DHCPv6
Client”, "PPPoE", “DHCPv6 Client”, "PPPoEv6", and
"Dual-Stack Lite".
Static IP
MTU
Set the maximum transmission unit.
1500
IPv4 Primary
DNS Server
Set the primary IPv4 DNS server.
114.114.114.
114
IPv4 Secondary
DNS Server
Set the secondary IPv4 DNS server.
8.8.8.8
IPv6 Primary
DNS Server
Set the primary IPv6 DNS server.
2001:4860:4
860:8888
IPv6 Secondary
DNS Server
Set the secondary IPv6 DNS server.
--
Enable NAT
Enable or disable NAT function. When enabled, a
private IP can be translated to a public IP.
Enable
- Dual-Stack Lite: use IPv4-in-IPv6 tunneling to send terminal device’s IPv4 packet through a tunnel on
the IPv6 access network to the ISP.
Figure 3-2-1-6
Table 3-2-1-6 WAN Parameters
Page 30

30
1. Static IP Configuration
Static IP
Item
Description
Default
IPv4
Address
Set the IPv4 address of the WAN port.
192.168.0.1
Netmask
Set the Netmask for WAN port.
255.255.255.0
IPv4
Gateway
Set the gateway for WAN port's IPv4 address.
192.168.0.2
IPv6
Address
Set the IPv6 address which can access Internet.
Generated from
Mac address
Prefix-length
Set the IPv6 prefix length to identify how many bits of a Global
Unicast IPv6 address are there in network part. For example, in
2001:0DB8:0000:000b::/64, the number 64 is used to identify
that the first 64 bits are in network part.
64
IPv6
Gateway
Set the gateway for WAN port's IPv6 address.
E.g.2001:DB8:ACAD:4::2.
--
Multiple IP
Address
Set the multiple IP addresses for WAN port.
Null
If the external network assigns a fixed IP for the WAN interface, user can select “Static IP” mode.
Figure 3-2-1-7
Table 3-2-1-7 Static Parameters
2. DHCP Client/DHCPv6 Client
If the external network has DHCP server enabled and has assigned IP addresses to the Ethernet WAN
interface, user can select “DHCP client” mode to obtain IP address automatically.
Page 31

31
Figure 3-2-1-8
DHCP Client
Item
Description
Use Peer DNS
Obtain peer DNS automatically during PPP dialing. DNS is
necessary when visiting domain name.
DHCPv6 Client
Request IPv6-address
Choose the ways to obtain the IPv6 address from the DHCP
Server. Select from try, force, none.
Try: The DHCP Server will assign specific address in priority.
Force: The DHCP Server assigns specific address only.
None: The DHCP Server will randomly assign address.The
specific address is relevant to the prefix length of IPv6 address
you set.
Request prefix length of
IPv6
Set the prefix length of IPv6 address which device is expected
to obtain from DHCP Server.
Figure 3-2-1-9
Table 3-2-1-8 DHCP Client Parameters
3. PPPoE/PPPoEv6
PPPoE refers to a point to point protocol over Ethernet. With PPPoE, remote access devices can get
control of each user. If type as PPPoEv6, UF51 can get both IPv4 and IPv6 address.
Page 32

32
Figure 3-2-1-10
PPPoE
Item
Description
Username
Enter the username provided by your Internet Service Provider (ISP).
Password
Enter the password provided by your Internet Service Provider (ISP).
Link Detection
Interval (s)
Set the heartbeat interval for link detection. Range: 1-600.
Max Retries
Set the maximum retry times after it fails to dial up. Range: 0-9.
Use Peer DNS
Obtain peer DNS automatically during PPP dialing. DNS is necessary
when visiting domain name.
Figure 3-2-1-11
Table 3-2-1-9 PPOE Parameters
4. Dual-Stack Lite
Dual-Stack Lite (DS-Lite) uses IPv4-in-IPv6 tunneling to send a subscriber’s IPv4 packet through a
tunnel on the IPv6 access network to the ISP. The IPv6 packet is decapsulated to recover the
Page 33

33
subscriber’s IPv4 packet and is then sent to the Internet after NAT address and port translation and
Dual-Stack Lite
Item
Description
IPv6 Gateway
Set the gateway for WAN port's IPv6 address.
DS-Lite AFTR
Address
Set the DS-Lite AFTR server address.
Local IPv6
Address
Set the WAN port IPv6 address which use the same subnet as IPv6
gateway.
other LSN related processing. The response packets traverse through the same path to the
subscriber.
Figure 3-2-1-12
Table 3-2-1-10 Dual-Stack Lite Parameters
Related Configuration Example
Ethernet WAN Connection
3.2.1.5 Bridge
Bridge setting is used for managing local area network devices which are connected to LAN ports of
the UF51, allowing each of them to access the Internet.
Page 34

34
Figure 3-2-1-13
Bridge
Item
Description
Default
Name
Show the name of bridge. "Bridge0" is set by default and
cannot be changed.
Bridge0
STP
Enable/disable STP.
Disable
IP Address
Set the IP address for bridge.
192.168.1.1
Netmask
Set the Netmask for bridge.
255.255.255.
0
IPv6 Address
Set the IPv6 address for bridge.
2004::1/64
MTU
Set the maximum transmission unit. Range: 68-1500.
1500
Multiple IP Address
Set the multiple IP addresses for bridge.
Null
Table 3-2-1-11 Bridge Settings
3.2.1.6 WLAN
This section explains how to set the related parameters for Wi-Fi network. UF51 supports both 2.4
GHz and 5 GHz Wi-Fi and it can work as AP or client mode at the same time.
Page 35
35
Figure 3-2-1-14
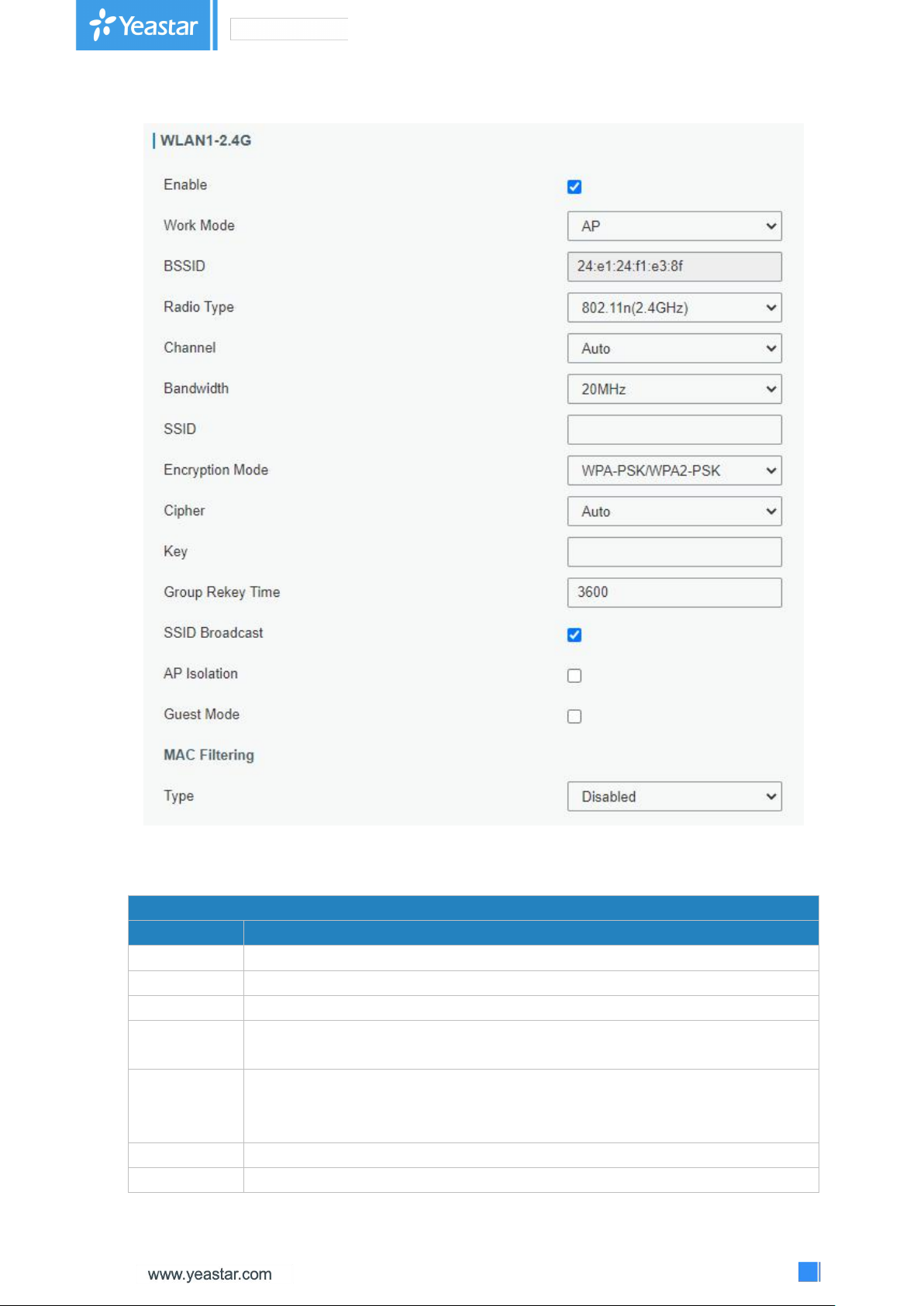
WLAN
Item
Description
Enable
Enable/disable WLAN.
Work Mode
The options are "Client" or "AP".
SSID
Fill in the SSID of the access point.
BSSID
Fill in the MAC address of the access point. Either SSID or BSSID can be filled
to joint the network.
Encryption
Mode
Select encryption mode. The options are “No Encryption", “WEP Open
System" , “WEP Shared Key", “WPA-PSK", “WPA2-PSK" and
“WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK".
Cipher
Select cipher. The options are “Auto", “AES", “TKIP" and “AES/TKIP".
Key
Fill in the key of access point.
Page 36

36
Client Mode
Scan
Click "Scan" button to search the nearby access point.
SSID
Show SSID.
Channel
Show wireless channel.
Signal
Show wireless signal.
BSSID
Show the MAC address of the access point.
Cipher
Show the cipher of the access point.
Security
Show the encryption mode.
Frequency
Show the frequency of radio.
Join Network
Click the button to join the wireless network.
AP Mode
Radio Type
Select Radio type. 2.4G radio types can only be selected in WLAN 1 and 5G
radio types can only be selected in WLAN2.
Channel
Select wireless channel. The options are "Auto", "1", "2"......"11".
Bandwidth
Select bandwidth. The options are "20MHz" and "40MHz".
Group Rekey
Time
Rekeytime is when you select PSK encryption mode.
SSID
Broadcast
When SSID broadcast is disabled, other wireless devices can't not find the
SSID, and users have to enter the SSID manually to access to the wireless
network.
AP Isolation
When AP isolation is enabled, all users that access to the AP are isolated
without communication with each other.
Guest Mode
The internal network is not allowed to visit if the guest mode is enabled.
IP Setting
Protocol
Set the IP address in wireless network.
IP Address
Set the IP address in wireless network.
Netmask
Set the netmask in wireless network.
Gateway
Set the gateway in wireless network.
Table 3-2-1-12 WLAN Parameters
MAC Filtering
Item
Description
Type
In this mode, you can choose the rule according to your security
Figure 3-2-1-15
Page 37

37
policy, which is ‘Allow and Block the Rest’ and ‘Block and Allow
the Rest’, the default value is Disabled.
Allow and Block the Rest
Only the listed MAC addresses are allowed to connect to the
device's wireless access point.
Block and Allow the Rest
The listed MAC addresses are not allowed to connect to the
device's wireless access point.
Table 3-2-1-13 MAC Filtering Parameters
Switch
Item
Description
LAN Settings
Name
Set interface name of VLAN.
VLAN ID
Select VLAN ID of the interface.
IP Address
Set IP address of LAN port.
Netmask
Set Netmask of LAN port.
MTU
Set the maximum transmission unit of LAN port. Range: 68-1500.
VLAN Settings
VLAN ID
Set the label ID of the VLAN. Range: 1-4094.
LAN 1/2
Make the VLAN bind with the corresponding ports and select status
from "Tagged", "Untagged" and "Close" for Ethernet frame on trunk link.
CPU
Control communication between VLAN and other networks.
Related Topic
Wi-Fi Application Example
3.2.1.7 Switch
VLAN is a kind of new data exchange technology that realizes virtual work groups by logically dividing
the LAN device into network segments.
Figure 3-2-1-16
Table 3-2-1-14 VLAN Trunk Parameters
Page 38

38
3.2.1.8 Loopback
Loopback
Item
Description
Default
IP Address
Unalterable
127.0.0.1
Netmask
Unalterable
255.0.0.0
Multiple IP
Addresses
Apart from the IP above, user can configure
other IP addresses.
Null
Loopback interface is used for replacing device's ID as long as it is activated. When the interface is
DOWN, the ID of the device has to be selected again which leads to long convergence time of OSPF.
Therefore, Loopback interface is generally recommended as the ID of the device.
Loopback interface is a logic and virtual interface on device. Under default conditions, there's no
loopback interface on device, but it can be created as required.
Figure 3-2-1-17
Table 3-2-1-15 Loopback Parameters
3.2.2 DHCP
DHCP adopts Client/Server communication mode. The Client sends configuration request to the
Server which feeds back corresponding configuration information and distributes IP address to the
Client so as to achieve the dynamic configuration of IP address and other information.
3.2.2.1 DHCP Server/DHCPv6 Server
UF51 can be set as a DHCP server or DHCPv6 server to distribute IP address when a host logs on and
ensures each host is supplied with different IP addresses. DHCP Server has simplified some previous
network management tasks requiring manual operations to the largest extent. UF51 only supports
stateful DHCPv6 when working as DHCPv6 server.
Page 39

39
Figure 3-2-2-1
DHCP Server/DHCPv6 Server
Item
Description
Default
Enable
Enable or disable DHCP server.
Enable
Interface
Select interface.
Bridge0
Start Address
Define the beginning of the pool of IP addresses which will
be leased to DHCP clients.
192.168.1.2
End Address
Define the end of the pool of IP addresses which will be
leased to DHCP clients.
192.168.1.2
54
Netmask
Define the subnet mask of IPv4 address obtained by DHCP
clients from DHCP server.
255.255.255
.0
Figure 3-2-2-2
Page 40

40
Table 3-2-2-1 DHCP Server Parameters
DHCP Relay
Item
Description
Enable
Enable or disable DHCP relay.
DHCP Server
Set DHCP server, up to 10 servers can be configured;
separate them by blank space or ",".
Prefix Length
Set the IPv6 prefix length of IPv6 address obtained by DHCP
clients from DHCP server.
64
Lease Time (Min)
Set the lease time on which the client can use the IP
address obtained from DHCP server. Range: 1-10080.
1440
Primary DNS Server
Set the primary DNS server.
192.168.1.1
Secondary DNS
Server
Set the secondary DNS server.
Null
Windows Name
Server
Define the Windows Internet Naming Service obtained by
DHCP clients from DHCP sever. Generally you can leave it
blank.
Null
Static IP
MAC Address
Set a static and specific MAC address for the DHCP client
(it should be different from other MACs so as to avoid
conflict).
Null
DUID
Set a static and specific DUID for the DHCPv6 client (it
should be different from other DUID so as to avoid conflict).
Null
IP Address
Set a static and specific IP address for the DHCP client (it
should be outside of the DHCP range).
Null
3.2.2.2 DHCP Relay
UF51 can be set as DHCP Relay to provide a relay tunnel to solve the problem that DHCP Client and
DHCP Server are not in the same subnet.
Figure 3-2-2-2
Table 3-2-2-2 DHCP Relay Parameters
Page 41

41
3.2.3 Firewall
Item
Description
Default
Prevent Attack
DoS/DDoS Protection
Enable/disable Prevent DoS/DDoS Attack.
Disable
Access Service Control
Port
Set port number of the services. Range: 1-65535.
--
Local
Access the device locally.
Enable
Remote
Access the device remotely.
Disable
HTTP
Users can log in the device locally via HTTP to
80
This section describes how to set the firewall parameters, including security, ACL, DMZ, Port Mapping,
MAC Binding and SPI.
The firewall implements corresponding control of data flow at entry direction (from Internet to local
area network) and exit direction (from local area network to Internet) according to the content
features of packets, such as protocol style, source/destination IP address, etc. It ensures that the
device operate in a safe environment and host in local area network.
3.2.3.1 Security
Figure 3-2-3-1
Page 42

42
access and control it through Web after the option
is checked.
HTTPS
Users can log in the device locally and remotely
via HTTPS to access and control it through Web
after option is checked.
443
TELNET
Users can log in the device locally and remotely
via Telnet after the option is checked.
23
SSH
Users can log in the device locally and remotely
via SSH after the option is checked.
22
FTP
Users can log in the device locally and remotely
via FTP after the option is checked.
21
Website Blocking
URL Blocking
Enter the HTTP address which you want to block.
Keyword Blocking
You can block specific website by entering keyword. The
maximum number of character allowed is 64.
Table 3-2-3-1 Security Parameters
3.2.3.2 ACL
Access control list, also called ACL, implements permission or prohibition of access for specified
network traffic (such as the source IP address) by configuring a series of matching rules so as to
filter the network interface traffic. When device receives packet, the field will be analyzed according to
the ACL rule applied to the current interface. After the special packet is identified, the permission or
prohibition of corresponding packet will be implemented according to preset strategy.
The data package matching rules defined by ACL can also be used by other functions requiring flow
distinction.
Figure 3-2-3-2
Page 43

43
Item
Description
ACL Setting
Default Filter Policy
Select from "Accept" and "Deny".
The packets which are not included in the access control list
will be processed by the default filter policy.
Access Control List
Type
Select type from "Extended" and "Standard".
ID
User-defined ACL number. Range: 1-199.
Action
Select from "Permit" and "Deny".
Protocol
Select protocol from "ip", "icmp", "tcp", "udp", and "1-255".
Source IP
Source network address (leaving it blank means all).
Source Wildcard Mask
Wildcard mask of the source network address.
Destination IP
Destination network address (0.0.0.0 means all).
Destination Wildcard
Mask
Wildcard mask of destination address.
Description
Fill in a description for the groups with the same ID.
ICMP Type
Enter the type of ICMP packet. Range: 0-255.
ICMP Code
Enter the code of ICMP packet. Range: 0-255.
Source Port Type
Select source port type, such as specified port, port range, etc.
Source Port
Set source port number. Range: 1-65535.
Start Source Port
Set start source port number. Range: 1-65535.
End Source Port
Set end source port number. Range: 1-65535.
Destination Port Type
Select destination port type, such as specified port, port range,
etc.
Destination Port
Set destination port number. Range: 1-65535.
Start Destination Port
Set start destination port number. Range: 1-65535.
End Destination Port
Set end destination port number. Range: 1-65535.
More Details
Show information of the port.
Interface List
Interface
Select network interface for access control.
In ACL
Select a rule for incoming traffic from ACL ID.
Out ACL
Select a rule for outgoing traffic from ACL ID.
Table 3-2-3-2 ACL Parameters
Related Configuration Example
Access Control Application Example
3.2.3.3 Port Mapping
Port mapping is an application of network address translation (NAT) that redirects a communication
request from the combination of an address and port number to another while the packets are
traversing a network gateway such as a router or firewall.
Page 44

44
Click to add a new port mapping rules.
Port Mapping
Item
Description
Source IP
Specify the host or network which can access local IP address.
0.0.0.0/0 means all.
Source Port
Enter the TCP or UDP port from which incoming packets are
forwarded. Range: 1-65535.
Destination IP
Enter the IP address that packets are forwarded to after being
received on the incoming interface.
Destination Port
Enter the TCP or UDP port that packets are forwarded to after
being received on the incoming port(s). Range: 1-65535.
Protocol
Select from "TCP" and "UDP" as your application required.
Description
The description of this rule.
Figure 3-2-3-3
Table 3-2-3-3 Port Mapping Parameters
Related Configuration Example
NAT Application Example
3.2.3.4 DMZ
DMZ is a host within the internal network that has all ports exposed, except those forwarded ports in
port mapping.
Page 45

45
Figure 3-2-3-4
DMZ
Item
Description
Enable
Enable or disable DMZ.
DMZ Host
Enter the IP address of the DMZ host on the internal network.
Source Address
Set the source IP address which can access to DMZ host.
"0.0.0.0/0" means any address.
MAC Binding List
Item
Description
MAC Address
Set the binding MAC address.
IP Address
Set the binding IP address.
Description
Fill in a description for convenience of recording the
meaning of the binding rule for each piece of MAC-IP.
Table 3-2-3-4 DMZ Parameters
3.2.3.5 MAC Binding
MAC Binding is used for specifying hosts by matching MAC addresses and IP addresses that are in
the list of allowed outer network access.
Figure 3-2-3-5
Table 3-2-3-5 MAC Binding Parameters
3.2.3.6 Custom Rules
In this page, you can configure your own custom firewall iptables rules.
Figure 3-2-3-6
Page 46

46
Custom Rules
Item
Description
Rule
Specify an iptables rule like the example shows.
Tips: You must reboot the device to take effect after modifying or
deleting the iptables rules.
Description
Enter the description of the rule.
3.2.3.7 SPI
SPI Firewall
Item
Description
Enable
Enable/disable SPI firewall.
Filter Proxy
Blocks HTTP requests containing the "Host": string.
Filter Cookies
Identifies HTTP requests that contain "Cookie": String and
mangle the cookie. Attempts to stop cookies from being used.
Filter ActiveX
Blocks HTTP requests of the URL that ends in ".ocx" or ".cab".
Filter Java Applets
Blocks HTTP requests of the URL that ends in ".js" or ".class".
Filter Multicast
Prevent multicast packets from reaching the LAN.
Filter IDENT(port 113)
Prevent WAN access to Port 113.
Block WAN SNMP access
Block SNMP requests from the WAN.
Filter WAN NAT Redirection
Prevent hosts on LAN from using WAN address of device to
connect servers on the LAN (which have been configured
using port redirection).
Block Anonymous WAN
Requests
Stop the device from responding to "pings" from the WAN.
Table 3-2-3-6 Custom Rules Parameters
Figure 3-2-3-7
Table 3-2-3-7 SPI Parameters
Page 47

47
3.2.4 QoS
QoS
Item
Description
Download/Upload
Enable
Enable or disable QoS.
Default Category
Select the default category from Service Category list.
Download/Upload
Bandwidth Capacity
The download/upload bandwidth capacity of the network
that the device is connected with, in kbps. Range:
1-8000000.
Service Category
Name
You can use characters such digits, letters and "-".
Percent (%)
Set percent for the service category. Range: 0-100.
Max BW(kbps)
The maximum bandwidth that this category is allowed to
consume, in kbps. The value should be less than the
"Download/Upload Bandwidth Capacity" when the traffic is
blocked.
Min BW(kbps)
The minimum bandwidth that can be guaranteed for the
category, in kbps.The value should be less than the "MAX
BW" value.
Service Category Rules
Item
Description
Name
Give the rule a descriptive name.
Source IP
Source address of flow control (leaving it blank means any).
Quality of service (QoS) refers to traffic prioritization and resource reservation control mechanisms
rather than the achieved service quality. QoS is engineered to provide different priority for different
applications, users, data flows, or to guarantee a certain level of performance to a data flow.
Figure 3-2-4-1
Page 48

48
Source Port
Source port of flow control. Range: 0-65535 (leaving it blank
means any).
Destination IP
Destination address of flow control (leaving it blank means
any).
Destination Port
Destination port of flow control. Range: 0-65535 (leaving it
blank means any).
Protocol
Select protocol from "ANY", "TCP", "UDP", "ICMP", and "GRE".
Service Category
Set service category for the rule.
Table 3-2-4-1 QoS (Download/Upload) Parameters
Related Configuration Example
QoS Application Example
3.2.5 VPN
Virtual Private Networks, also called VPNs, are used to securely connect two private networks
together so that devices can connect from one network to the other network via secure channels.
UF51 supports DMVPN, IPsec, GRE, L2TP, PPTP, OpenVPN, as well as GRE over IPsec and L2TP over
IPsec.
3.2.5.1 DMVPN
A dynamic multi-point virtual private network (DMVPN), combining mGRE and IPsec, is a secure
network that exchanges data between sites without passing traffic through an organization's
headquarter VPN server or router.
Figure 3-2-5-1
Page 49

49
DMVPN
Item
Description
Enable
Enable or disable DMVPN.
Hub Address
The IP address or domain name of DMVPN Hub.
Local IP Address
DMVPN local tunnel IP address.
GRE Hub IP Address
GRE Hub tunnel IP address.
GRE Local IP Address
GRE local tunnel IP address.
GRE Netmask
GRE local tunnel netmask.
GRE Key
GRE tunnel key.
Negotiation Mode
Select from "Main" and "Aggressive".
Authentication
Algorithm
Select from "DES", "3DES", "AES128", "AES192" and
"AES256".
Encryption Algorithm
Select from "MD5" and "SHA1".
DH Group
Select from "MODP768_1", "MODP1024_2" and
"MODP1536_5".
Key
Enter the preshared key.
Local ID Type
Select from "Default", "ID", "FQDN", and "User FQDN"
IKE Life Time (s)
Set the lifetime in IKE negotiation. Range: 60-86400.
SA Algorithm
Select from "DES_MD5", "DES_SHA1", "3DES_MD5",
"3DES_SHA1", "AES128_MD5", "AES128_SHA1",
"AES192_MD5", "AES192_SHA1", "AES256_MD5" and
"AES256_SHA1".
PFS Group
Select from "NULL", "MODP768_1", "MODP1024_2" and
"MODP1536-5".
Life Time (s)
Set the lifetime of IPsec SA. Range: 60-86400.
DPD Interval Time (s)
Set DPD interval time
DPD Timeout (s)
Set DPD timeout.
Cisco Secret
Cisco Nhrp key.
NHRP Holdtime (s)
The holdtime of NHRP protocol.
Table 3-2-5-1 DMVPN Parameters
3.2.5.2 IPSec Server
IPsec is especially useful for implementing virtual private networks and for remote user access
through dial-up connection to private networks. A big advantage of IPsec is that security
arrangements can be handled without requiring changes to individual user computers.
IPsec provides three choices of security service: Authentication Header (AH), Encapsulating Security
Payload (ESP), and Internet Key Exchange (IKE). AH essentially allows authentication of the senders’
data. ESP supports both authentication of the sender and data encryption. IKE is used for cipher code
exchange. All of them can protect one and more data flows between hosts, between host and
gateway, and between gateways.
Page 50

50
Figure 3-2-5-2
IPsec Server
Item
Description
Enable
Enable IPsec tunnel. A maximum of 3 tunnels is allowed.
IPsec Mode
Select from "Tunnel" and "Transport".
IPsec Protocol
Select from "ESP" and "AH".
Local Subnet
Enter the local subnet IP address that IPsec protects.
Local Subnet Netmask
Enter the local netmask that IPsec protects.
Local ID Type
Select from "Default", "ID", "FQDN", and "User FQDN".
Remote Subnet
Enter the remote subnet IP address that IPsec protects.
Remote Subnet Mask
Enter the remote netmask that IPsec protects.
Remote ID type
Select from "Default", "ID", "FQDN", and "User FQDN".
Table 3-2-5-2 IPsec Parameters
Page 51

51
Figure 3-2-5-3
IKE Parameter
Item
Description
IKE Version
Select from "IKEv1" and "IKEv2".
Negotiation Mode
Select from "Main" and "Aggressive".
Encryption Algorithm
Select from "DES", "3DES", "AES128", "AES192" and "AES256".
Authentication Algorithm
Select from "MD5" and " SHA1"
DH Group
Select from "MODP768_1", "MODP1024_2" and "MODP1536_5".
Local Authentication
Select from "PSK" and "CA".
XAUTH
Enter XAUTH username and password after XAUTH is enabled.
Figure 3-2-5-4
Page 52

52
Lifetime (s)
Set the lifetime in IKE negotiation. Range: 60-86400.
XAUTH List
Username
Enter the username used for the xauth authentication.
Password
Enter the password used for the xauth authentication.
PSK List
Selector
Enter the corresponding identification number for PSK authentication.
PSK
Enter the pre-shared key.
SA Parameter
SA Algorithm
Select from "DES_MD5", "DES_SHA1", "3DES_MD5", "3DES_SHA1",
"AES128_MD5", "AES128_SHA1", "AES192_MD5", "AES192_SHA1",
"AES256_MD5" and "AES256_SHA1".
PFS Group
Select from "NULL", "MODP768_1" , "MODP1024_2" and
"MODP1536_5".
Lifetime (s)
Set the lifetime of IPsec SA. Range: 60-86400.
DPD Interval Time(s)
Set DPD interval time to detect if the remote side fails.
DPD Timeout(s)
Set DPD timeout. Range: 10-3600.
IPsec Advanced
Enable Compression
The head of IP packet will be compressed after it's enabled.
VPN Over IPsec Type
Select from "NONE", "GRE" and "L2TP" to enable VPN over IPsec
function.
Expert Options
User can enter some other initialization strings in this field and
separate the strings with “;”. For example, if more local or remote
subnet need to be added, users can add contents here.
Table 3-2-5-3 IPsec Server Parameters
Page 53

53
3.2.5.3 IPSec
IPsec
Item
Description
Enable
Enable IPsec tunnel. A maximum of 3 tunnels is allowed.
IPsec Gateway Address
Enter the IP address or domain name of remote IPsec
server.
IPsec Mode
Select from "Tunnel" and "Transport".
IPsec Protocol
Select from "ESP" and "AH".
Local Subnet
Enter the local subnet IP address that IPsec protects.
Local Subnet Netmask
Enter the local netmask that IPsec protects.
Local ID Type
Select from "Default", "ID", "FQDN", and "User FQDN".
Remote Subnet
Enter the remote subnet IP address that IPsec protects.
Remote Subnet Mask
Enter the remote netmask that IPsec protects.
Remote ID type
Select from "Default", "ID", "FQDN", and "User FQDN".
Figure 3-2-5-5
Table 3-2-5-4 IPsec Parameters
Page 54

54
Figure 3-2-5-6
IKE Parameter
Item
Description
IKE Version
Select from "IKEv1" and "IKEv2".
Negotiation Mode
Select from "Main" and "Aggressive".
Encryption Algorithm
Select from "DES", "3DES", "AES128", "AES192" and "AES256".
Authentication Algorithm
Select from "MD5" and " SHA1"
DH Group
Select from "MODP768_1", "MODP1024_2" and "MODP1536_5".
Local Authentication
Select from "PSK" and "CA".
Local Secrets
Enter the pre-shared key.
XAUTH
Enter XAUTH username and password after XAUTH is enabled.
Lifetime (s)
Set the lifetime in IKE negotiation. Range: 60-86400.
SA Parameter
SA Algorithm
Select from "DES_MD5", "DES_SHA1", "3DES_MD5", "3DES_SHA1",
"AES128_MD5", "AES128_SHA1", "AES192_MD5", "AES192_SHA1",
"AES256_MD5" and "AES256_SHA1".
Page 55

55
PFS Group
Select from "NULL", "MODP768_1" , "MODP1024_2" and
"MODP1536_5".
Lifetime (s)
Set the lifetime of IPsec SA. Range: 60-86400.
DPD Interval Time(s)
Set DPD interval time to detect if the remote side fails.
DPD Timeout(s)
Set DPD timeout. Range: 10-3600.
IPsec Advanced
Enable Compression
The head of IP packet will be compressed after it's enabled.
VPN Over IPsec Type
Select from "NONE", "GRE" and "L2TP" to enable VPN over IPsec
function.
Expert Option
User can enter some other initialization strings in this field and
separate the strings with “;”. For example, if more local or remote
subnet need to be added, users can add contents here.
Table 3-2-5-5 IPsec Parameters
3.2.5.4 GRE
Generic Routing Encapsulation (GRE) is a protocol that encapsulates packets in order to route other
protocols over IP networks. It’s a tunneling technology that provides a channel through which
encapsulated data message could be transmitted and encapsulation and decapsulation could be
realized at both ends.
In the following circumstances the GRE tunnel transmission can be applied:
GRE tunnel could transmit multicast data packets as if it were a true network interface. Single use
-
of IPSec cannot achieve the encryption of multicast.
A certain protocol adopted cannot be routed.
-
A network of different IP addresses shall be required to connect other two similar networks.
-
Page 56

56
Figure 3-2-5-7
GRE
Item
Description
Enable
Check to enable GRE function.
Remote IP Address
Enter the real remote IP address of GRE tunnel.
Local IP Address
Set the local IP address.
Local Virtual IP
Address
Set the local tunnel IP address of GRE tunnel.
Netmask
Set the local netmask.
Peer Virtual IP Address
Enter remote tunnel IP address of GRE tunnel.
Global Traffic
Forwarding
All the data traffic will be sent out via GRE tunnel when this
function is enabled.
Remote Subnet
Enter the remote subnet IP address of GRE tunnel.
Remote Netmask
Enter the remote netmask of GRE tunnel.
MTU
Enter the maximum transmission unit. Range: 64-1500.
Key
Set GRE tunnel key.
Enable NAT
Enable NAT traversal function.
Table 3-2-5-6 GRE Parameters
Page 57

57
3.2.5.5 L2TP
L2TP
Item
Description
Enable
Check to enable L2TP function.
Remote IP Address
Enter the public IP address or domain name of L2TP server.
Username
Enter the username that L2TP server provides.
Password
Enter the password that L2TP server provides.
Authentication
Select from "Auto", "PAP", "CHAP", "MS-CHAPv1" and
"MS-CHAPv2".
Global Traffic
Forwarding
All of the data traffic will be sent out via L2TP tunnel after
this function is enabled.
Remote Subnet
Enter the remote IP address that L2TP protects.
Remote Subnet Mask
Enter the remote netmask that L2TP protects.
Key
Enter the password of L2TP tunnel.
Layer Two Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) is an extension of the Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP)
used by an Internet service provider (ISP) to enable the operation of a virtual private network (VPN)
over the Internet.
Figure 3-2-5-8
Table 3-2-5-7 L2TP Parameters
Page 58

58
Figure 3-2-5-9
Advanced Settings
Item
Description
Local IP Address
Set tunnel IP address of L2TP client. Client will obtain
tunnel IP address automatically from the server when it's
null.
Peer IP Address
Enter tunnel IP address of L2TP server.
Enable NAT
Enable NAT traversal function.
Enable MPPE
Enable MPPE encryption.
Address/Control
Compression
For PPP initialization. User can keep the default option.
Protocol Field
Compression
For PPP initialization. User can keep the default option.
Asyncmap Value
One of the PPP protocol initialization strings. User can
keep the default value. Range: 0-ffffffff.
MRU
Set the maximum receive unit. Range: 64-1500.
MTU
Set the maximum transmission unit. Range: 64-1500
Link Detection Interval (s)
Set the link detection interval time to ensure tunnel
connection. Range: 0-600.
Max Retries
Set the maximum times of retry to detect the L2TP
connection failure. Range: 0-10.
Expert Options
User can enter some other PPP initialization strings in this
field and separate the strings with blank space.
Table 3-2-5-8 L2TP Parameters
Page 59

59
3.2.5.6 PPTP
PPTP
Item
Description
Enable
Enable PPTP client. A maximum of 3 tunnels is allowed.
Remote IP Address
Enter the public IP address or domain name of PPTP
server.
Username
Enter the username that PPTP server provides.
Password
Enter the password that PPTP server provides.
Authentication
Select from "Auto", "PAP", "CHAP", "MS-CHAPv1", and
"MS-CHAPv2".
Global Traffic
Forwarding
All of the data traffic will be sent out via PPTP tunnel once
enable this function.
Remote Subnet
Set the peer subnet of PPTP.
Remote Subnet Mask
Set the netmask of peer PPTP server.
Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP) is a protocol that allows corporations to extend their own
corporate network through private "tunnels" over the public Internet. Effectively, a corporation uses a
wide-area network as a single large local area network.
Figure 3-2-5-10
Table 3-2-5-9 PPTP Parameters
Page 60

60
Figure 3-2-5-11
PPTP Advanced Settings
Item
Description
Local IP Address
Set IP address of PPTP client.
Peer IP Address
Enter tunnel IP address of PPTP server.
Enable NAT
Enable the NAT faction of PPTP.
Enable MPPE
Enable MPPE encryption.
Address/Control
Compression
For PPP initialization. User can keep the default option.
Protocol Field
Compression
For PPP initialization. User can keep the default option.
Asyncmap Value
One of the PPP protocol initialization strings. User can keep
the default value. Range: 0-ffffffff.
MRU
Enter the maximum receive unit. Range: 0-1500.
MTU
Enter the maximum transmission unit. Range: 0-1500.
Link Detection Interval
(s)
Set the link detection interval time to ensure tunnel
connection. Range: 0-600.
Max Retries
Set the maximum times of retrying to detect the PPTP
connection failure. Range: 0-10.
Expert Options
User can enter some other PPP initialization strings in this
field and separate the strings with blank space.
Table 3-2-5-10 PPTP Parameters
Related Configuration Example
PPTP Application Example
Page 61

61
3.2.5.7 OpenVPN Client
OpenVPN Client
Item
Description
Enable
Enable OpenVPN client. A maximum of 3 tunnels is allowed.
OpenVPN is an open source virtual private network (VPN) product that offers a simplified security
framework, modular network design, and cross-platform portability.
Advantages of OpenVPN include:
Security provisions that function against both active and passive attacks.
-
Compatibility with all major operating systems.
-
High speed (1.4 megabytes per second typically).
-
Ability to configure multiple servers to handle numerous connections simultaneously.
-
All encryption and authentication features of the OpenSSL library.
-
Advanced bandwidth management.
-
A variety of tunneling options.
-
Compatibility with smart cards that support the Windows Crypt application program interface
-
(API).
Figure 3-2-5-12
Page 62

62
Protocol
Select from "UDP" and "TCP".
Remote IP Address
Enter remote OpenVPN server's IP address or domain name.
Port
Enter the listening port number of remote OpenVPN server. Range:
1-65535.
Interface
Select from "tun" and "tap".
Authentication
Select from "None", "Pre-shared", "Username/Password", "X.509 cert",
and "X.509 cert+user".
Local Tunnel IP
Set local tunnel address.
Remote Tunnel IP
Enter remote tunnel address.
Global Traffic Forwarding
All the data traffic will be sent out via OpenVPN tunnel when this
function is enabled.
Enable TLS Authentication
Check to enable TLS authentication.
Username
Enter username provided by OpenVPN server.
Password
Enter password provided by OpenVPN server.
Enable NAT
Enable NAT traversal function.
Compression
Select LZO to compress data.
Link Detection Interval (s)
Set link detection interval time to ensure tunnel connection. Range:
10-1800.
Link Detection Timeout (s)
Set link detection timeout. OpenVPN will be reestablished after
timeout. Range: 60-3600.
Cipher
Select from "NONE", "BF-CBC", "DE-CBC", "DES-EDE3-CBC",
"AES-128-CBC", "AES-192-CBC" and "AES-256-CBC".
MTU
Enter the maximum transmission unit. Range: 128-1500.
Max Frame Size
Set the maximum frame size. Range: 128-1500.
Verbose Level
Select from "ERROR", "WARING", "NOTICE" and "DEBUG".
Expert Options
User can enter some other PPP initialization strings in this field and
separate the strings with blank space.
Local Route
Subnet
Set the local route's IP address.
Subnet Mask
Set the local route's netmask.
Table 3-2-5-11 OpenVPN Client Parameters
3.2.5.8 OpenVPN Server
UF51 supports OpenVPN server to create secure point-to-point or site-to-site connections in routed or
bridged configurations and remote access facilities.
Page 63
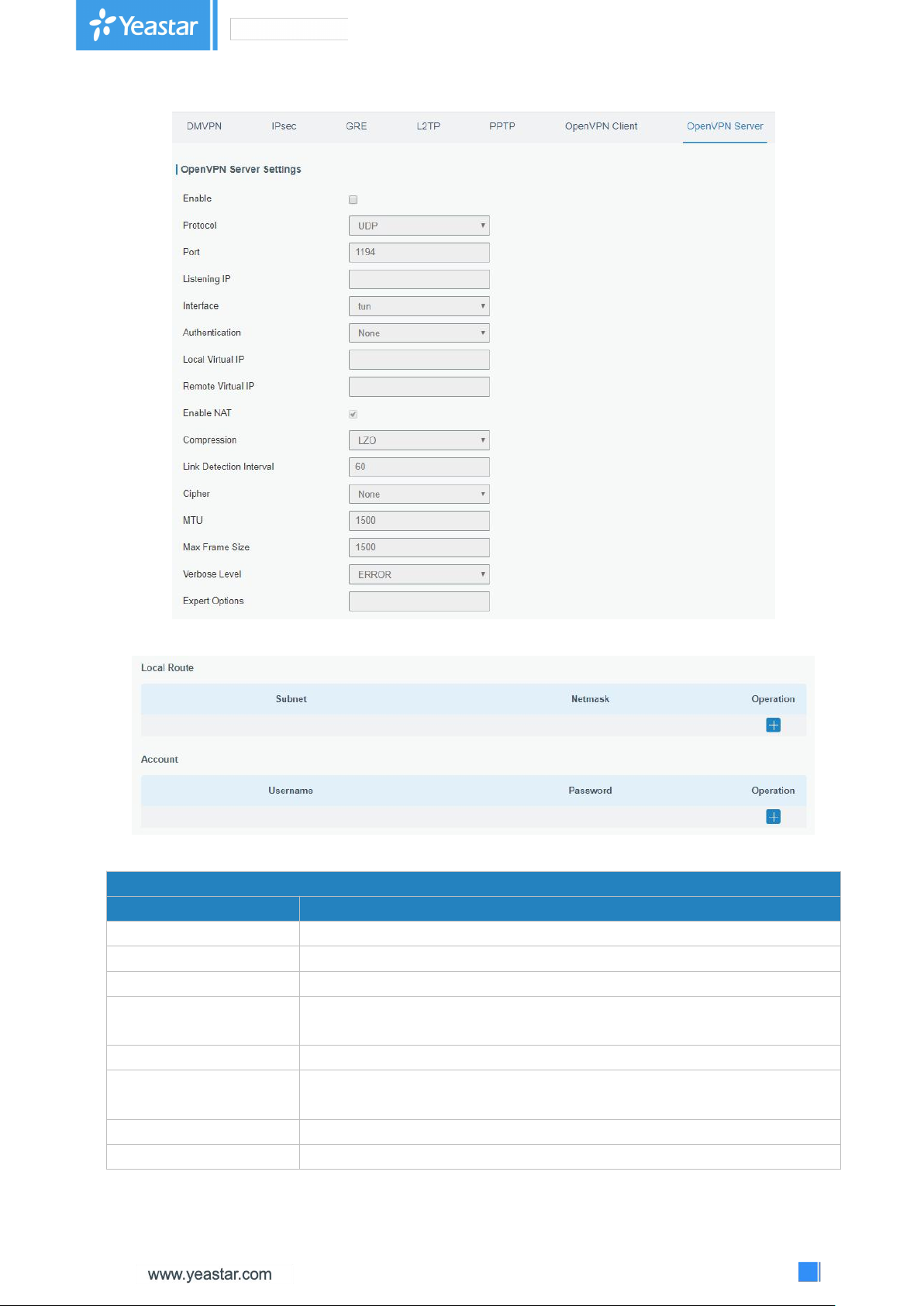
63
Figure 3-2-5-13
OpenVPN Server
Item
Description
Enable
Enable/disable OpenVPN server.
Protocol
Select from TCP and UDP.
Port
Fill in listening port number. Range: 1-65535.
Listening IP
Enter WAN IP address or LAN IP address. Leaving it blank refers to all
active WAN IP and LAN IP address.
Interface
Select from " tun" and "tap".
Authentication
Select from "None", "Pre-shared", "Username/Password", "X.509 cert"
and "X. 509 cert +user".
Local Virtual IP
The local tunnel address of OpenVPN's tunnel.
Remote Virtual IP
The remote tunnel address of OpenVPN's tunnel.
Figure 3-2-5-14
Page 64
64
Client Subnet
Local subnet IP address of OpenVPN client.
Client Netmask
Local netmask of OpenVPN client.
Renegotiation
Interval(s)
Set interval for renegotiation. Range: 0-86400.
Max Clients
Maximum OpenVPN client number. Range: 1-128.
Enable CRL
Enable CRL
Enable Client to Client
Allow access between different OpenVPN clients.
Enable Dup Client
Allow multiple users to use the same certification.
Enable NAT
Check to enable the NAT traversal function.
Compression
Select "LZO" to compress data.
Link Detection Interval
Set link detection interval time to ensure tunnel connection. Range:
10-1800.
Cipher
Select from "NONE", "BF-CBC", "DES-CBC", "DES-EDE3-CBC",
"AES-128-CBC", "AES-192-CBC" and "AES-256-CBC".
MTU
Enter the maximum transmission unit. Range: 64-1500.
Max Frame Size
Set the maximum frame size. Range: 64-1500.
Verbose Level
Select from "ERROR", "WARING", "NOTICE" and "DEBUG".
Expert Options
User can enter some other PPP initialization strings in this field and
separate the strings with blank space.
Local Route
Subnet
The real local IP address of OpenVPN client.
Netmask
The real local netmask of OpenVPN client.
Account
Username & Password
Set username and password for OpenVPN client.
Table 3-2-5-12 OpenVPN Server Parameters
3.2.5.9 Certifications
User can import/export certificate and key files for OpenVPN and IPsec on this page.
Figure 3-2-5-15
Page 65

65
OpenVPN Client
Item
Description
CA
Import/Export CA certificate file.
Public Key
Import/Export public key file.
Private Key
Import/Export private key file.
TA
Import/Export TA key file.
Preshared Key
Import/Export static key file.
PKCS12
Import/Export PKCS12 certificate file.
Table 3-2-5-13 OpenVPN Client Certification Parameters
OpenVPN Server
Item
Description
CA
Import/Export CA certificate file.
Public Key
Import/Export public key file.
Private Key
Import/Export private key file.
DH
Import/Export DH key file.
TA
Import/Export TA key file.
CRL
Import/Export CRL.
Preshared Key
Import/Export static key file.
Figure 3-2-5-16
Table 3-2-5-14 OpenVPN Server Parameters
Page 66

66
Figure 3-2-5-17
IPsec
Item
Description
CA
Import/Export CA certificate.
Client Key
Import/Export client key.
Server Key
Import/Export server key.
Private Key
Import/Export private key.
CRL
Import/Export certificate recovery list.
IPsec Server
Item
Description
CA
Import/Export CA certificate.
Local Certificate
Import/Export Local Certificate file.
Private Key
Import/Export private key.
CRL
Import/Export certificate recovery list.
Table 3-2-5-15 IPsec Parameters
Figure 3-2-5-18
Table 3-2-5-16 IPsec Server Parameters
Page 67

67
3.2.6 IP Passthrough
IP Passthrough
Item
Description
Enable
Enable or disable IP Passthrough.
Passthrough Mode
Select passthrough mode from “DHCPS-Fixed” and
“DHCPS-Dynamic”.
MAC
Set MAC address.
IP Passthrough mode shares or "passes" the Internet providers assigned IP address to a single LAN
client device connected to the device.
Figure 3-2-6-1
Table 3-2-6-1 IP Passthrough Parameters
3.2.7 Routing
3.2.7.1 Static Routing
A static routing is a manually configured routing entry. Information about the routing is manually
entered rather than obtained from dynamic routing traffic. After setting static routing, the package for
the specified destination will be forwarded to the path designated by user.
Page 68

68
Figure 3-2-7-1
T
Static Routing
Item
Description
Destination
Enter the destination IPv4/IPv6 address.
Netmask/Prefix
Length
Enter the subnet mask or prefix length of destination address.
Interface
The interface through which the data can reach the destination
address.
Gateway
IPv4/IPv6 address of the next router that will be passed by before the
input data reaches the destination address.
Distance
Priority, smaller value refers to higher priority. Range: 1-255.
Table 3-2-7-1 Static Routing Parameters
3.2.7.2 RIP
RIP is mainly designed for small networks. RIP uses Hop Count to measure the distance to the
destination address, which is called Metric. In RIP, the hop count from the router to its directly
connected network is 0 and the hop count of network to be reached through a router is 1 and so on. In
order to limit the convergence time, the specified metric of RIP is an integer in the range of 0 - 15 and
the hop count larger than or equal to 16 is defined as infinity, which means that the destination
network or host is unreachable. Because of this limitation, the RIP is not suitable for large-scale
networks. To improve performance and prevent routing loops, RIP supports split horizon function. RIP
also introduces routing obtained by other routing protocols.
Each router that runs RIP manages a routing database, which contains routing entries to reach all
reachable destinations.
Page 69

69
Figure 3-2-7-2
RIP
Item
Description
Enable
Enable or disable RIP.
Update Timer
It defines the interval to send routing updates. Range:
5-2147483647, in seconds.
Timeout Timer
It defines the routing aging time. If no update package on a routing
is received within the aging time, the routing's Routing Cost in the
routing table will be set to 16. Range: 5-2147483647, in seconds.
Garbage Collection Timer
It defines the period from the routing cost of a routing becomes 16
to it is deleted from the routing table. In the time of
Garbage-Collection, RIP uses 16 as the routing cost for sending
routing updates. If Garbage Collection times out and the routing
still has not been updated, the routing will be completely removed
from the routing table. Range: 5-2147483647, in seconds.
Version
RIP version. The options are v1 and v2.
Advanced Settings
Default Information Originate
Default information will be released when this function is enabled.
Default Metric
The default cost for the device to reach destination. Range: 0-16
Redistribute Connected
Check to enable.
Metric
Set metric after "Redistribute Connected" is enabled. Range: 0-16.
Redistribute Static
Check to enable.
Metric
Set metric after "Redistribute Static" is enabled. Range: 0-16.
Page 70

70
Redistribute OSPF
Check to enable.
Metric
Set metric after "Redistribute OSPF" is enabled. Range: 0-16.
Table 3-2-7-2 RIP Parameters
Item
Description
Distance/Metric Management
Distance
Set the administrative distance that a RIP route learns. Range:
1-255.
IP Address
Set the IP address of RIP route.
Netmask
Set the netmask of RIP route.
Figure 3-2-7-3
Page 71

71
ACL Name
Set ACL name of RIP route.
Metric
The metric of received route or sent route from the interface.
Range: 0-16.
Policy in/out
Select from "in" and "out".
Interface
Select interface of the route.
ACL Name
Access control list name of the route strategy.
Filter Policy
Policy Type
Select from "access-list" and "prefix-list".
Policy Name
User-defined prefix-list name.
Policy in/out
Select from "in" and "out".
Interface
Select interface from "cellular0", "WAN" and "Bridge0".
Passive Interface
Passive Interface
Select interface from "cellular0" and "WAN", "Bridge0".
Interface
Interface
Select interface from "cellular0", "WAN" and "Bridge0".
Send Version
Select from "default", "v1" and "v2".
Receive Version
Select from "default", "v1" and "v2".
Split-Horizon
Select from "enable" and "disable".
Authentication Mode
Select from "text" and "md5".
Authentication String
The authentication key for package interaction in RIPV2.
Authentication
Key-chain
The authentication key-chain for package interaction in RIPV2.
Neighbor
IP Address
Set RIP neighbor's IP address manually.
Network
IP Address
The IP address of interface for RIP publishing.
Netmask
The netmask of interface for RIP publishing.
3.2.7.3 OSPF
OSPF, short for Open Shortest Path First, is a link status based on interior gateway protocol
developed by IETF.
If a router wants to run the OSPF protocol, there should be a Router ID that can be manually
configured. If no Router ID configured, the system will automatically select an IP address of interface
as the Router ID. The selection order is as follows:
If a Loopback interface address is configured, then the last configured IP address of Loopback
-
interface will be used as the Router ID;
If no Loopback interface address is configured, the system will choose the interface with the
-
Table 3-2-7-3
Page 72

72
biggest IP address as the Router ID.
OSPF
Item
Description
Enable
Enable or disable OSPF.
Router ID
Router ID (IP address) of the originating LSA.
ABR Type
Select from cisco, ibm, standard and shortcut.
RFC1583 Compatibility
Enable/Disable.
Five types of packets of OSPF:
Hello packet
-
DD packet (Database Description Packet)
-
LSR packet (Link-State Request Packet)
-
LSU packet (Link-State Update Packet)
-
LSAck packet (Link-Sate Acknowledgment Packet)
-
Neighbor and Neighboring
After OSPF router starts up, it will send out Hello Packets through the OSPF interface. Upon receipt of
Hello packet, OSPF router will check the parameters defined in the packet. If it’s consistent, a
neighbor relationship will be formed. Not all matched sides in neighbor relationship can form the
adjacency relationship. It is determined by the network type. Only when both sides successfully
exchange DD packets and LSDB synchronization is achieved, the adjacency in the true sense can be
formed. LSA describes the network topology around a router, LSDB describes entire network
topology.
Figure 3-2-7-4
Page 73

73
OSPF Opaque-LSA
Enable/Disable
LSA: a basic communication means of the OSPF routing
protocol for the Internet Protocol (IP).
SPF Delay Time
Set the delay time for OSPF SPF calculations.
Range: 0-6000000, in milliseconds.
SPF Initial-holdtime
Set the initialization time of OSPF SPF.
Range: 0-6000000, in milliseconds.
SPF Max-holdtime
Set the maximum time of OSPF SPF.
Range: 0-6000000, in milliseconds.
Reference Bandwidth
Range: 1-4294967, in Mbit.
Table 3-2-7-4 OSPF Parameters
Item
Description
Interface
Interface
Select interface from "cellular0",”WAN”and "Bridge0".
Hello Interval (s)
Send interval of Hello packet. If the Hello time between two adjacent
routers is different, the neighbour relationship cannot be established.
Range: 1-65535.
Dead Interval (s)
Dead Time. If no Hello packet is received from the neighbours within the
dead time, then the neighbour is considered failed. If dead times of two
adjacent routers are different, the neighbour relationship cannot be
established.
Retransmit Interval (s)
When the device notifies an LSA to its neighbour, it is required to make
acknowledgement. If no acknowledgement packet is received within the
retransmission interval, this LSA will be retransmitted to the neighbour.
Range: 3-65535.
Transmit Delay (s)
It will take time to transmit OSPF packets on the link. So a certain delay
time should be increased before transmission the aging time of LSA. This
configuration needs to be further considered on the low-speed link.
Range: 1-65535.
Figure 3-2-7-5
Page 74

74
Interface Advanced Options
Interface
Select interface.
Network
Select OSPF network type.
Cost
Set the cost of running OSPF on an interface. Range: 1-65535.
Priority
Set the OSPF priority of interface. Range: 0-255.
Authentication
Set the authentication mode that will be used by the OSPF area.
Simple: a simple authentication password should be configured and
confirmed again.
MD5: MD5 key & password should be configured and confirmed again.
Key ID
It only takes effect when MD5 is selected. Range 1-255.
Key
The authentication key for OSPF packet interaction.
Table 3-2-7-5 OSPF Parameters
Item
Description
Passive Interface
Passive Interface
Select interface from "cellular0", "WAN" and "Bridge0".
Network
IP Address
The IP address of local network.
Netmask
The netmask of local network.
Area ID
The area ID of original LSA's router.
Area
Area ID
Set the ID of the OSPF area (IP address).
Area
Select from "Stub" and "NSSA".
The backbone area (area ID 0.0.0.0) cannot be set as "Stub" or "NSSA".
No Summary
Forbid route summarization.
Authentication
Select authentication from "simple" and "md5".
Figure 3-2-7-6
Table 3-2--7-6 OSPF Parameters
Page 75

75
Figure 3-2-7-7
Area Advanced Options
Item
Description
Area Range
Area ID
The area ID of the interface when it runs OSPF (IP address).
IP Address
Set the IP address.
Netmask
Set the netmask.
No Advertise
Forbid the route information to be advertised among different areas.
Cost
Range: 0-16777215
Area Filter
Area ID
Select an Area ID for Area Filter.
Filter Type
Select from "import", "export", "filter-in", and "filter-out".
ACL Name
Enter an ACL name which is set on "Routing > Routing Filtering" webpage.
Area Virtual Link
Area ID
Set the ID number of OSPF area.
ABR Address
ABR is the router connected to multiple outer areas.
Authentication
Select from "simple" and "md5".
Key ID
It only takes effect when MD5 is selected. Range 1-15.
Key
The authentication key for OSPF packet interaction.
Hello Interval
Set the interval time for sending Hello packets through the interface. Range:
1-65535.
Dead Interval
The dead interval time for sending Hello packets through the interface. Range:
1-65535.
Retransmit
Interval
The retransmission interval time for re-sending LSA. Range: 1-65535.
Transmit Delay
The delay time for LSA transmission. Range: 1-65535.
Table 3-2-7-7 OSPF Parameters
Page 76

76
Figure 3-2-7-8
Item
Description
Redistribution
Redistribution Type
Select from "connected", "static" and "rip".
Metric
The metric of redistribution router. Range: 0-16777214.
Metric Type
Select Metric type from "1" and "2".
Route Map
Mainly used to manage route for redistribution.
Redistribution Advanced Options
Always Redistribute
Default Route
Send redistribution default route after starting up.
Redistribute Default
Route Metric
Send redistribution default route metric. Range:
0-16777214.
Redistribute Default
Route Metric Type
Select from "0", "1" and "2".
Distance Management
Area Type
Select from "intra-area", "inter-area" and "external".
Distance
Set the OSPF routing distance for area learning. Range:
1-255.
Table 3-2-7-8 OSPF Parameters
Page 77

77
3.2.7.4 Routing Filtering
Routing Filtering
Item
Description
Access Control List
Name
User-defined name, need to start with a letter. Only letters, digits and underline (_)
are allowed.
Action
Select from "permit" and "deny".
Match Any
No need to set IP address and subnet mask.
IP Address
User-defined.
Netmask
User-defined.
IP Prefix-List
Name
User-defined name, need to start with a letter. Only letters, digits and underline (_)
are allowed.
Sequence
Number
A prefix name list can be matched with multiple rules. One rule is matched with
one sequence number. Range: 1-4294967295.
Action
Select from "permit" and "deny".
Match Any
No need to set IP address, subnet mask, FE Length, and LE Length.
IP Address
User-defined.
Netmask
User-defined.
FE Length
Specify the minimum number of mask bits that must be matched. Range: 0-32.
LE Length
Specify the maximum number of mask bits that must be matched. Range: 0-32.
Figure 3-2-7-9
Table 3-2-7-9 Routing Filtering Parameters
3.2.8 VRRP
The Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP) is a computer networking protocol that provides
automatic assignment of available Internet Protocol (IP) routers for participating hosts. This
increases the availability and reliability of routing paths via automatic default gateway selections in
Page 78

78
an IP sub-network.
Increasing the number of exit gateway is a common method for improving system reliability. VRRP
adds a group of routers that undertake gateway function into a backup group so as to form a virtual
router. The election mechanism of VRRP will decide which router undertakes the forwarding task, and
the host in LAN is only required to configure the default gateway for the virtual router.
In VRRP, routers need to be aware of failures in the virtual master router. To achieve this, the virtual
master router sends out multicast “alive” announcements to the virtual backup routers in the same
VRRP group.
The VRRP router who has the highest number will become the virtual master router. The VRRP router
number ranges from 1 to 255 and usually we use 255 for the highest priority and 100 for backup.
If the current virtual master router receives an announcement from a group member (Router ID) with a
higher priority, then the latter will pre-empt and become the virtual master router.
VRRP has the following characteristics:
The virtual router with an IP address is known as the Virtual IP address. For the host in LAN, it is
-
only required to know the IP address of virtual router, and set it as the address of the next hop of
the default route.
The network Host communicates with the external network through this virtual router.
-
A router will be selected from the set of routers based on its priority to undertake the gateway
-
function. Other routers will be used as backup routers to perform the duties of gateway for the
gateway router in the case of any malfunction, so as to guarantee uninterrupted communication
between the host and external network.
When interface connected with the uplink is at the state of Down or Removed, the router actively
lowers its priority so that priority of other routers in the backup group will be higher. Thus the router
with the highest priority becomes the gateway for the transmission task.
Figure 3-2-8-1
Page 79

79
VRRP
Item
Description
Default
Enable
Enable or disable VRRP.
Disable
Interface
Select the interface of Virtual Router.
None
Virtual Router ID
User-defined Virtual Router ID. Range: 1-255.
None
Virtual IP
Set the IP address of Virtual Router.
None
Priority
The VRRP priority range is 1-254 (a bigger number indicates
a higher priority). The device with higher priority will be
more likely to become the gateway.
100
Advertisement Interval
(s)
Heartbeat package transmission time interval between
devices in the virtual ip group. Range: 1-255.
1
Preemption Mode
If the device works in the preemption mode, once it finds
that its own priority is higher than that of the current
gateway, it will send VRRP notification package, resulting in
re-election of gateway and eventually replacing the original
gateway. Accordingly, the original gateway will become a
Backup device.
Disable
IPV4 Primary Server
The device will send ICMP packet to the IP address or host
name to determine whether the Internet connection is still a
vailable or not.
8.8.8.8
IPV4 Secondary Server
The router will try to ping the secondary server name if prim
ary server is not available.
114.114.
114.114
Interval
Time interval (in seconds) between two Pings.
300
Retry Interval
Set the ping retry interval. When ping failed, the device will p
ing again every retry interval.
5
Timeout
The maximum amount of time the device will wait for a res
ponse to a ping request. If it does not receive a response fo
r the amount of time defined in this field, the ping request w
ill be considered as failure.
3
Max Ping Retries
The retry times of the device sending ping request until dete
rmining that the connection has failed.
3
Table 3-2-8-1 VRRP Parameters
Related Configuration Example
VRRP Application Example
3.2.9 DDNS
Dynamic DNS (DDNS) is a method that automatically updates a name server in the Domain Name
System, which allows user to alias a dynamic IP address to a static domain name.
DDNS serves as a client tool and needs to coordinate with DDNS server. Before starting configuration,
user shall register on a website of proper domain name provider and apply for a domain name.
Page 80

80
Figure 3-2-9-1
DDNS
Item
Description
Status
Show connection status of DDNS.
Enable
Enable/disable DDNS.
Name
Give the DDNS a descriptive name.
Service Type
Select the DDNS service provider.
Username
Enter the username for DDNS register.
User ID
Enter User ID of the custom DDNS server.
Password
Enter the password for DDNS register.
Server
Enter the name of DDNS server.
Server Path
By default the hostname is appended to the path.
Hostname
Enter the hostname for DDNS.
Append IP
Append your current IP to the DDNS server update path.
Use HTTPS
Enable HTTPS for some DDNS providers.
Table 3-2-9-1 DDNS Parameters
Page 81

81
3.3 System
General
Item
Description
Default
System
Hostname
User-defined device name, needs to start with a letter.
ROUTER
Web Login Timeout
(s)
You need to log in again if it times out. Range: 100-3600.
1800
Encrypting Cleartext
Passwords
This function will encrypt all of cleartext passwords into
ciphertext passwords.
Enable
HTTPS Certificates
Certificate
Click "Browse" button, choose certificate file on the PC,
and then click "Import" button to upload the file into
device. Click "Export" button will export the file to the PC.
Click "Delete" button will delete the file.
--
Key
Click "Browse" button, choose key file on the PC, and then
click "Import" button to upload the file into device. Click
"Export" button will export file to the PC.
Click "Delete" button will delete the file.
--
This section describes how to configure general settings, such as administration account, access
service, system time, common user management, SNMP, AAA, event alarms, etc.
3.3.1 General Settings
3.3.1.1 General
General settings include system info and HTTPS certificates.
Figure 3-3-1-1
Table 3-3-1-1 General Setting Parameters
Page 82

82
3.3.1.2 System Time
This section explains how to set the system time including time zone and time synchronization type.
Note: to ensure that the device runs with the correct time, it’s recommended that you set the system
time when configuring the device.
Figure 3-3-1-2
Figure 3-3-1-3
Page 83

83
Figure 3-3-1-4
System Time
Item
Description
Current Time
Show the current system time.
Time Zone
Click the drop down list to select the time zone you are in.
Sync Type
Click the drop down list to select the time synchronization type.
Sync with Browser
Synchronize time with browser.
Browser Time
Show the current time of browser.
Set up Manually
Manually configure the system time.
GPS Time
Synchronization
Synchronize time with GPS.
Primary NTP Server
Enter primary NTP Server's IP address or domain name.
Secondary NTP Server
Enter secondary NTP Server's IP address or domain name.
NTP Server
Enable NTP Server
NTP client on the network can achieve time synchronization with device
after "Enable NTP Server" option is checked.
Figure 3-3-1-5
Table 3-3-1-2 System Time Parameters
Page 84

84
3.3.1.3 Email
SMTP Client Settings
Item
Description
Enable
Enable or disable SMTP client function.
Email Address
Enter the sender's email account.
Password
Enter the sender's email password.
SMTP Server Address
Enter SMTP server's domain name.
Port
Enter SMTP server port. Range: 1-65535.
Encryption
Select from: None, TLS/SSL, STARTTLS.
None: No encryption. The default port is 25.
STARTTLS: STARTTLS is a way to take an existing insecure
connection and upgrade it to a secure connection by using
SSL/TLS. The default port is 587.
TLS/SSL: SSL and TLS both provide a way to encrypt a
communication channel between two computers (e.g. your
computer and our server). TLS is the successor to SSL and
the terms SSL and TLS are used interchangeably unless
you're referring to a specific version of the protocol.The
default port is 465.
SMTP, short for Simple Mail Transfer Protocol, is a TCP/IP protocol used in sending and receiving
e-mail. This section describes how to configure email settings and add email groups for alarms and
events.
Table 3-3-1-3 SMTP Setting
Figure 3-3-1-6
Page 85
85
Item
Description
Email List
Email Address
Enter the Email address.
Description
The description of the Email address.
Email Group List
Group ID
Set number for email group. Range: 1-100.
Description
The description of the Email group.
List
Show the Email address list.
Selected
Show the selected Email address.
Related Topics
DI Setting
Events Setting
Events Application Example
Figure 3-3-1-7
Table 3-3-1-4 Email Settings
3.3.2 Phone&SMS
3.3.2.1 Phone
Phone settings involve in call/SMS trigger, SMS control and SMS alarm for events.
Page 86

86
Phone
Item
Description
Phone Number List
Number
Enter the telephone number. Digits, "+" and "-" are allowed.
Description
The description of the telephone number.
Phone Group List
Group ID
Set number for phone group. Range: 1-100.
Description
The description of the phone group.
List
Show the phone list.
Selected
Show the selected phone number.
Related Topic
Connect on Demand
3.3.2.2 SMS
Figure 3-3-2-1
Table 3-3-2-1 Phone Settings
SMS settings involve in remote SMS control, sending SMS and SMS receiving and sending status.
Page 87

87
Figure 3-3-2-2
SMS Settings
Item
Description
SMS Mode
Select SMS mode from "TEXT" and "PDU".
SMS Remote
Control
Enable/disable SMS Remote Control.
Authentication
Type
You can choose “phone number” or ”password + phone number”.
Phone number: Use phone number for authentication.
Password + phone number: Use both ""Password"" and ""Phone
number"" for authentication.
Password
Set password for authentication.
Phone Group
Select the Phone group which used for remote control. User can
click the Phone Group and set phone number.
Table 3-3-2-2 SMS Remote Control Parameters
Page 88

88
Figure 3-3-2-3
SMS
Item
Description
Send SMS
Phone Number
Enter the number to receive the SMS.
Content
SMS content.
Inbox/Outbox
Sender
SMS sender from outside.
Recipient
SMS recipient which UF51 send to.
From
Select the start date.
To
Select the end date.
Table 3-3-2-3 SMS Settings
3.3.3 User Management
3.3.3.1 Account
Here you can change the login username and password of the administrator.
Note: it is strongly recommended that you modify them for the sake of security.
Page 89

89
Figure 3-3-3-1
Account
Item
Description
Username
Enter a new username. You can use characters such as a-z,
0-9, "_", "-", "$". The first character can't be a digit.
Old Password
Enter the old password.
New Password
Enter a new password.
Confirm New Password
Enter the new password again.
User Management
Item
Description
Username
Enter a new username. You can use characters such as a-z, 0-9, "_", "-", "$". The first
Table 3-3-3-1 Account Settings
3.3.3.2 User Management
This section describes how to create common user accounts.
The common user permission includes Read-Only and Read-Write.
Figure 3-3-3-2
Page 90

90
character can't be a digit.
Password
Set password.
Permission
Select user permission from “Read-Only” and “Read-Write”.
-
Read-Only: users can only view the configuration of device in this level.
-
Read-Write: users can view and set the configuration of device in this level.
Table 3-3-3-2 User Management
SNMP Settings
3.3.4 SNMP
SNMP is widely used in network management for network monitoring. SNMP exposes management
data with variables form in managed system. The system is organized in a management information
base (MIB) which describes the system status and configuration. These variables can be remotely
queried by managing applications.
Configuring SNMP in networking, NMS, and a management program of SNMP should be set up at the
Manager.
Configuration steps are listed as below for achieving query from NMS:
1. Enable SNMP setting.
2. Download MIB file and load it into NMS.
3. Configure MIB View.
4. Configure VCAM.
Related Configuration Example
SNMP Application Example
3.3.4.1 SNMP
UF51 supports SNMPv1, SNMPv2c and SNMPv3 version. SNMPv1 and SNMPv2c employ community
name authentication. SNMPv3 employs authentication encryption by username and password.
Figure 3-3-4-1
Page 91

91
Item
Description
Enable
Enable or disable SNMP function.
Port
Set SNMP listened port. Range: 1-65535.
The default port is 161.
SNMP Version
Select SNMP version; support SNMP v1/v2c/v3.
Location Information
Fill in the location information.
Contact Information
Fill in the contact information.
Table 3-3-4-1 SNMP Parameters
MIB View
Item
Description
View Name
Set MIB view's name.
View Filter
Select from "Included" and "Excluded".
View OID
Enter the OID number.
Included
You can query all nodes within the specified MIB node.
Excluded
You can query all nodes except for the specified MIB node.
3.3.4.2 MIB View
This section explains how to configure MIB view for the objects.
Figure 3-3-4-2
Table 3-3-4-2 MIB View Parameters
3.3.4.3 VACM
This section describes how to configure VCAM parameters.
Figure 3-3-4-3
Page 92

92
VACM
Item
Description
SNMP v1 & v2 User List
Community
Set the community name.
Permission
Select from "Read-Only" and "Read-Write".
MIB View
Select an MIB view to set permissions from the MIB view list.
Network
The IP address and bits of the external network accessing the MIB view.
Read-Write
The permission of the specified MIB node is read and write.
Read-Only
The permission of the specified MIB node is read only.
SNMP v3 User Group
Group Name
Set the name of SNMPv3 group.
Security Level
Select from "NoAuth/NoPriv", "Auth/NoPriv", and " Auth/Priv".
Read-Only View
Select an MIB view to set permission as "Read-only" from the MIB view list.
Read-Write View
Select an MIB view to set permission as "Read-write" from the MIB view list.
Inform View
Select an MIB view to set permission as "Inform" from the MIB view list.
SNMP v3 User List
Username
Set the name of SNMPv3 user.
Group Name
Select a user group to be configured from the user group.
Authentication
Select from "MD5", "SHA", and "None".
Authentication
Password
The password should be filled in if authentication is "MD5" and "SHA".
Encryption
Select from "AES", "DES", and "None".
Encryption
Password
The password should be filled in if encryption is "AES" and "DES".
Table 3-3-4-3 VACM Parameters
SNMP Trap
3.3.4.4 Trap
This section explains how to enable network monitoring by SNMP trap.
Figure 3-3-3-4
Page 93

93
Item
Description
Enable
Enable or disable SNMP Trap function.
SNMP Version
Select SNMP version; support SNMP v1/v2c/v3.
Server Address
Fill in NMS's IP address or domain name.
Port
Fill in UDP port. Port range is 1-65535. The default port is 162.
Name
Fill in the group name when using SNMP v1/v2c; fill in the username when using
SNMP v3.
Auth/Priv Mode
Select from "NoAuth & No Priv", "Auth & NoPriv", and "Auth & Priv".
Table 3-3-4-4 Trap Parameters
MIB
Item
Description
MIB File
Select the MIB file you need.
Download
Click "Download" button to download the MIB file to PC.
3.3.4.5 MIB
This section describes how to download MIB files. The last MIB file “LTE-ROUTER-MIB.txt” is for the
UF51 device.
Figure 3-3-4-5
Table 3-3-4-5 MIB Download
3.3.5 AAA
AAA access control is used for visitors control and the available corresponding services once access
is allowed. It adopts the same method to configure three independent safety functions. It provides
modularization methods for following services:
Authentication: verify if the user is qualified to access to the network.
-
Authorization: authorize related services available for the user.
-
Charging: record the utilization of network resources.
-
3.3.5.1 Radius
Using UDP for its transport, Radius is generally applied in various network environments with higher
requirements of security and permission of remote user access.
Page 94

94
Figure 3-3-5-1
Radius
Item
Description
Enable
Enable or disable Radius.
Server IP Address
Fill in the Radius server IP address/domain name.
Server Port
Fill in the Radius server port. Range: 1-65535.
Key
Fill in the key consistent with that of Radius server in order to
get connected with Radius server.
Table 3-3-5-1 Radius Parameters
3.3.5.2 TACACS+
Using TCP for its transport, TACACS+ is mainly used for authentication, authorization and charging of
the access users and terminal users by adopting PPP and VPDN.
Figure 3-3-5-2
Page 95

95
TACACS+
Item
Description
Enable
Enable or disable TACACS+.
Server IP Address
Fill in the TACACS+ server IP address/domain name.
Server Port
Fill in the TACACS+ server port. Range: 1-65535.
Key
Fill in the key consistent with that of TACACS+ server in
order to get connected with TACACS+ server.
Table 3-3-5-2 TACACS+ Parameters
LDAP
Item
Description
Enable
Enable or Disable LDAP.
Server IP Address
Fill in the LDAP server's IP address/domain name. The
maximum count is 10.
Server Port
Fill in the LDAP server's port. Range: 1-65535
Base DN
The top of LDAP directory tree.
Security
Select secure method from "None", "StartTLS" and "SSL".
3.3.5.3 LDAP
A common usage of LDAP is to provide a central place to store usernames and passwords. This
allows many different applications and services to connect the LDAP server to validate users.
LDAP is based on a simpler subset of the standards contained within the X.500 standard. Because of
this relationship, LDAP is sometimes called X.500-lite as well.
Figure 3-3-5-3
Page 96

96
Username
Enter the username to access the server.
Password
Enter the password to access the server.
Table 3-3-5-3 LDAP Parameters
Authentication
Item
Description
Console
Select authentication for Console access.
Web
Select authentication for Web access.
Telnet
Select authentication for Telnet access.
SSH
Select authentication for SSH access.
3.3.5.4 Authentication
AAA supports the following authentication ways:
None: uses no authentication, generally not recommended.
-
Local: uses the local username database for authentication.
-
Advantages: rapidness, cost reduction.
Disadvantages: storage capacity limited by hardware.
Remote: has user’s information stored on authentication server. Radius, TACACS+ and LDAP
-
supported for remote authentication.
When radius, TACACS+, and local are configured at the same time, the priority level is: 1 >2 >3.
Figure 3-3-5-4
Table 3-3-5-4 Authentication Parameters
3.3.6 Device Management
3.3.6.1 DeviceHub
You can connect the device to the Yeastar DeviceHub on this page so as to manage the device
centrally and remotely. For more details please refer to DeviceHub User Guide.
Page 97

97
DeviceHub
Item
Description
Status
Show the connection status between the device and the
DeviceHub.
Disconnected
Click this button to disconnect the device from the
DeviceHub.
Server Address
IP address or domain of the device management server.
Activation Method
Select activation method to connect the device to the
DeviceHub server, options are "By Authentication Code" and
"By Account name".
Authentication Code
Fill in the authentication code generated from the
DeviceHub.
Account Name
Fill in the registered DeviceHub account (email) and
password.
Password
3.3.6.2 Yeastar VPN
Figure 3-3-6-1
Table 3-3-6-1
You can connect the device to the Yeastar VPN on this page so as to manage the device and
connected devices centrally and remotely. For more details please refer to YeastarVPN User Guide.
Page 98

98
Figure 3-3-6-2
Yeastar VPN
Item
Description
Yeastar VPN Settings
Server
Enter the IP address or domain name of Yeastar VPN.
Port
Enter the HTTPS port number.
Authorization Code
Enter the authorization code which generated by Yeastar VPN.
Device Name
Enter the name of the device.
Yeastar VPN Status
Status
Show the connection information about whether the device is
connected to the Yeastar VPN.
Local IP
Show the virtual IP of the device.
Remote IP
Show the virtual IP of the Yeastar VPN.
Duration
Show the information on how long the device has been
connected to the Yeastar VPN.
Table 3-3-6-2
Page 99

99
3.3.7 Events
Events
Item
Description
Mark as Read
Mark the selected event alarm as read.
Delete
Delete the selected event alarm.
Mark All as Read
Mark all event alarms as read.
Delete All Alarms
Delete all event alarms.
Status
Show the reading status of the event alarms, such as “Read”
and “Unread”.
Type
Show the event type that should be alarmed.
Time
Show the alarm time.
Message
Show the alarm content.
Event feature is capable of sending alerts by Email when certain system events occur.
3.3.7.1 Events
You can view alarm messages on this page.
Figure 3-3-7-1
Table 3-3-7-1 Events Parameters
3.3.7.2 Events Settings
In this section, you can decide what events to record and whether you want to receive email and SMS
notifications when any change occurs.
Page 100

100
Figure 3-3-7-2
Event Settings
Item
Description
Enable
Check to enable "Events Settings".
Phone Group List
Select phone group to receive SMS alarm.
Email Group List
Select email group to receive alarm.
Record
The relevant content of event alarm will be recorded on
"Event" page if this option is checked.
Email
The relevant content of event alarm will be sent out via email
if this option is checked.
Figure 3-3-7-3
 Loading...
Loading...