
1
Using Security Certificates on Skype for
Business phones
This guide provides the detailed instructions on how to configure and use certificates on Skype
for Business phones. In addition, this guide provides step-by-step instructions on how to create
custom certificates for Skype for Business phones.
This guide applies to the MP56, T58A, T56A, T55A, T48S, T46S, T42S and T41S Skype for
Business phones running firmware version 9 or later and CP960 Skype for Business phones
running firmware version 8 or later.
Introduction
Certificate is an important element in deploying a solution that ensures the integrity and privacy
of communications involving Skype for Business phones.
Three types of certificates are pre-loaded on Skype for Business phones and comply with X.509
standard.
A unique device certificate: It is installed at the time of manufacture and is unique to a
Skype for Business phone (based on the MAC address) and issued by the Yealink
Certificate Authority (CA).
A generic device certificate: It is installed by default and is issued by the Yealink
Certificate Authority (CA). If no unique certificate exists, the Skype for Business phone
may send a generic certificate for authentication.
Trusted certificates (Certificate Authority certificates):
For MP56/T58A/T56A/ T55A/T48S/T46S/T42S/T41S/CP960 Skype for Business phones,
there are 51 trusted certificates installed by default. Refer to Appendix B: Trusted
Certificate Authority List on page 11 for more information.
Using Security Certificates on Skype for Business Phones
2
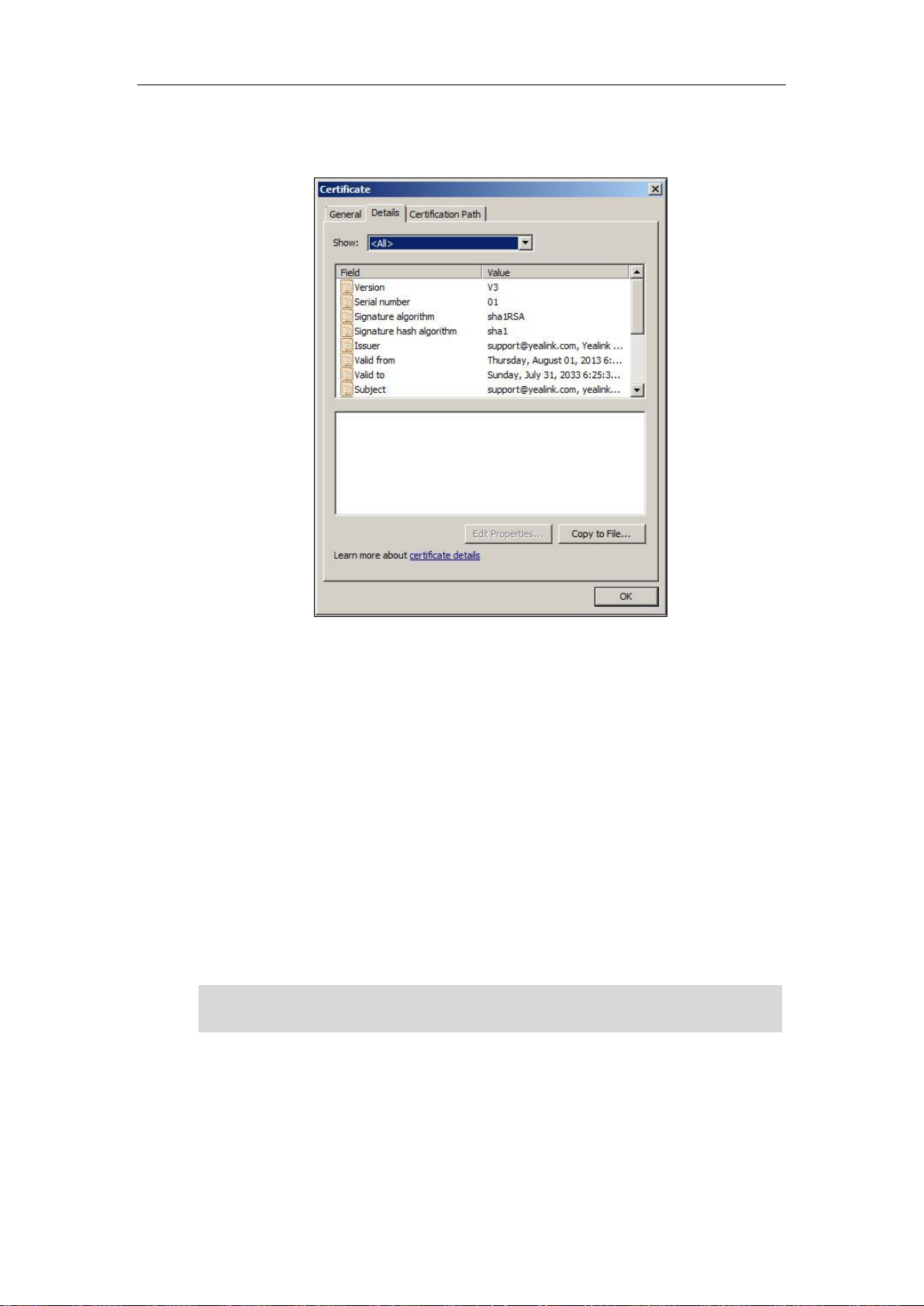
The following shows an example of a Yealink generic certificate. For the information on
fields of X.509 certificate, refer to Appendix A X.509 Certificate Structure on page 11.
Configuring Trusted Certificates on Skype for Business
phones
When a Skype for Business phone requests an SSL connection with a server, the phone should
verify that whether the server can be trusted. The server sends its certificate to the phone and
the phone verifies this certificate based on its trusted certificates list.
The MP56/T58A/T56A/ T55A/T48S/T46S/T42S/T41S/CP960 Skype for Business phones have
51 built-in trusted certificates. For more information, refer to Appendix B: Trusted Certificate
Authority List on page 11. The phone supports uploading 10 custom trusted certificates (CA
certificates) at most. For more information on customizing a trusted certificate, refer to Appendix
C Creating Custom Certificates on page 13.
Note
Configuring Trusted Certificate via Web User Interface
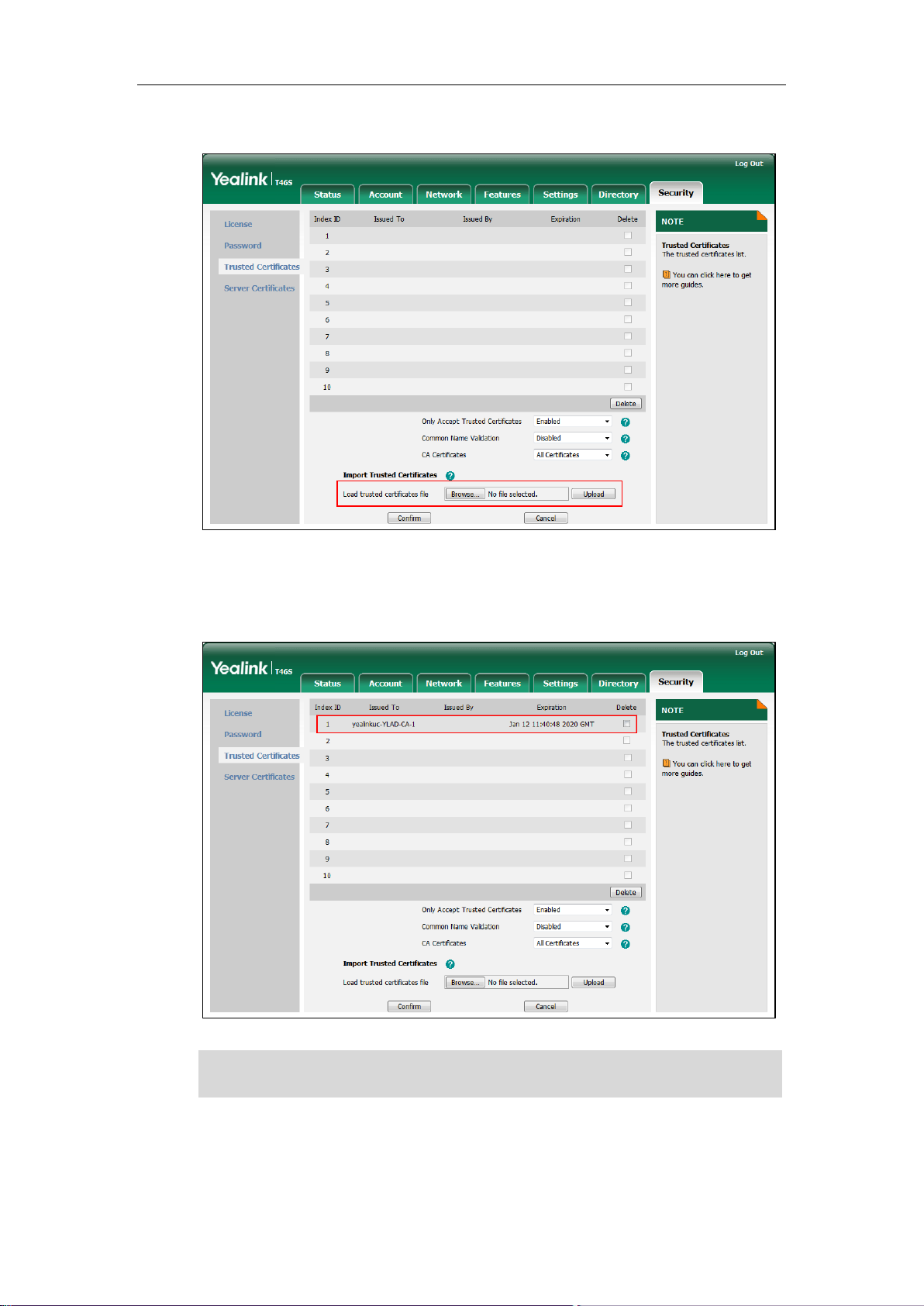
To upload a trusted certificate via web user interface:
1. Click on Security->Trusted Certificates.
To determine whether a certificate is within its valid time range, check that the time and date on
the phone are configured properly.
Using Security Certificates on Skype for Business Phones
3
2. Click Browse to locate the certificate (*.pem, *.crt, *.cer or *.der) from your local system.
3. Click Upload to upload the certificate.
The information of the custom trusted certificate is displayed on the web user interface of
the Skype for Business phone.
Note
The information of built-in trusted certificates is not displayed on the web user interface of the
Skype for Business phone.
Using Security Certificates on Skype for Business Phones
4
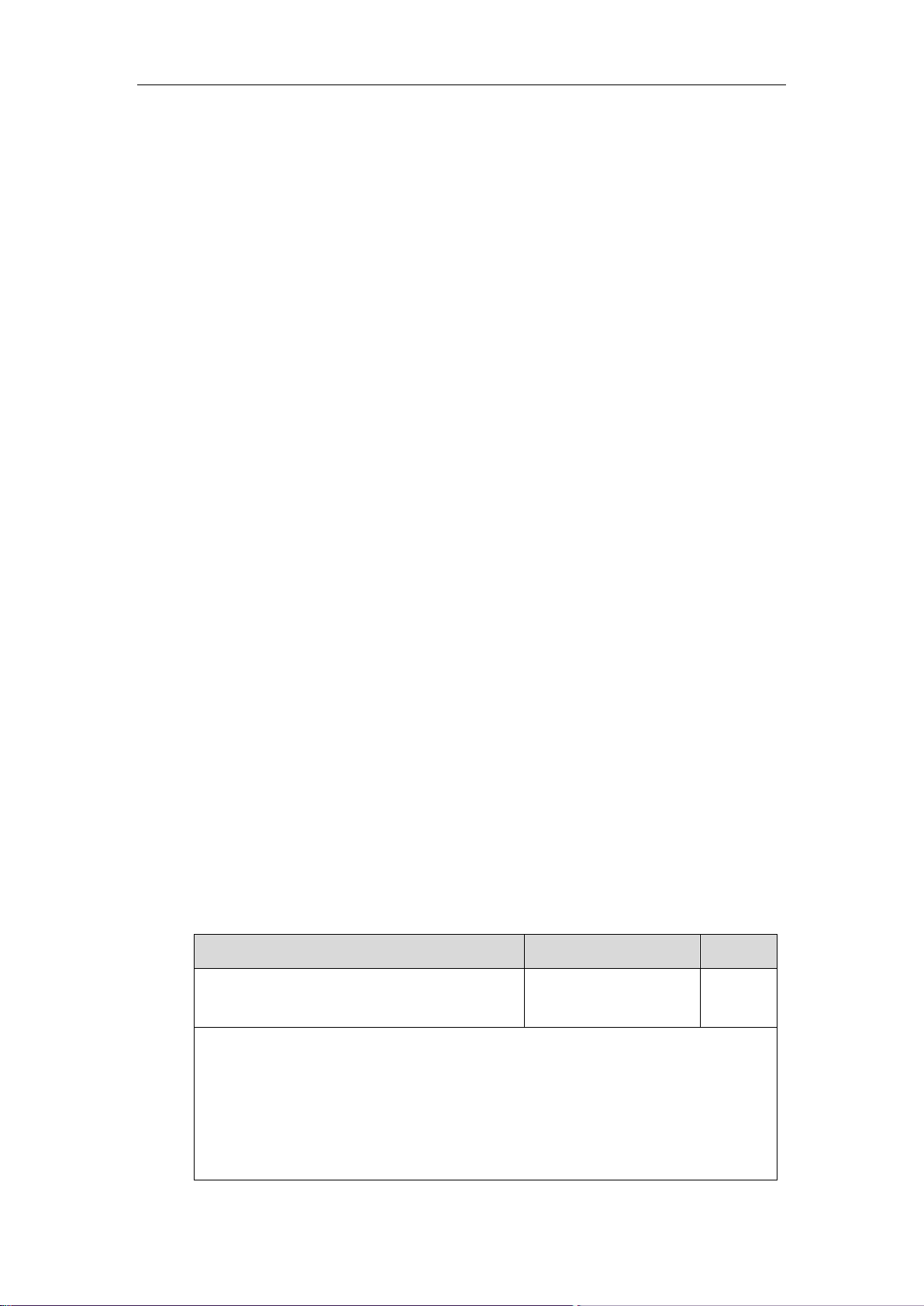
To configure trusted certificates via web user interface:
1. Click on Security->Trusted Certificates.
2. Select the desired value from the pull-down list of Only Accept Trusted Certificates.
If Enabled is selected, the Skype for Business phone will verify the server certificate
based on the trusted certificates list. Only when the authentication succeeds, the
Skype for Business phone will trust the server.
If Disabled is selected, the Skype for Business phone will trust the server no matter
whether the certificate received from the server is valid or not.
3. Select the desired value from the pull-down list of Common Name Validation.
If Enabled is selected, the Skype for Business phone will verify the CommonName or
subjectAltName of the server certificate.
If Disabled is selected, the Skype for Business phone will not verify the
CommonName or subjectAltName of the server certificate.
4. Select the desired value from the pull-down list of CA Certificates.
If Default Certificates is selected, the Skype for Business phone will verify the server
certificate based on the built-in trusted certificates list.
If Custom Certificates is selected, the Skype for Business phone will verify the server
certificate based on the custom trusted certificates list.
If All Certificates is selected, the Skype for Business phone will verify the server
certificate based on the trusted certificates list, which contains built-in and custom
trusted certificates.
5. Click Confirm to accept the change.
Configuring Trusted Certificate Using Configuration Files
To configure trusted certificates using configuration files:
1. Add/Edit trusted certificates parameters in configuration files.
The following table lists the information of parameters:
Parameters
Permitted Values
Default
Static.trusted_certificates.url
URL within 511
characters
Blank
Description:
Configures the access URL of the custom trusted certificate used to authenticate the
connecting server.
Note: The certificate you want to upload must be in *.pem, *.crt, *.cer or *.der format.
Web User Interface:
Using Security Certificates on Skype for Business Phones
5
Parameters
Permitted Values
Default
Security->Trusted Certificates->Load trusted certificates file
Phone User Interface:
None
Static.security.trust_certificates
0 or 1
1
Description:
Enables or disables the Skype for Business phone to only trust the server certificates in the
Trusted Certificates list.
0-Disabled
1-Enabled
Web User Interface:
Security->Trusted Certificates->Only Accept Trusted Certificates
Phone User Interface:
None
Static.security.cn_validation
0 or 1
0
Description:
Enables or disables the Skype for Business phone to mandatorily validate the
CommonName or SubjectAltName of the certificate sent by the server.
0-Disabled
1-Enabled
Web User Interface:
Security->Trusted Certificates->Common Name Validation
Phone User Interface:
None
Static.security.ca_cert
0, 1 or 2
2
Description:
Configures the type of certificates in the Trusted Certificates list for the Skype for Business
phone to authenticate for TLS connection.
0-Default Certificates
1-Custom Certificates
2-All Certificates
Web User Interface:
Security->Trusted Certificates->CA Certificates
Phone User Interface:
None
Using Security Certificates on Skype for Business Phones
6
The following shows an example of failover configurations for account 1 in the
<y0000000000xx.cfg> configuration file:
static.trusted_certificates.url = http://192.168.1.20/tc.crt
static.security.trust_certificates = 1
static.security.cn_validation = 0
static.security.ca_cert = 2
2. Upload configuration files to the root directory of the provisioning server and trigger Skype
for Business phones to perform an auto provisioning for configuration update.
For more information on auto provisioning, refer to
Yealink_Skype_for_Business_HD_IP_Phones_Auto_Provisioning_Guide.
Configuring Device Certificates on Skype for Business
phones
When a client requests an SSL connection with a Skype for Business phone, the phone sends a
device certificate to the client for authentication.
The phones have two built-in device certificates: a unique and a generic device certificate. The
Skype for Business phone supports uploading one custom device certificate at most. The old
custom device certificate will be overridden by the new one. For more information on
customizing a device certificate, refer to Appendix C Creating Custom Certificates on page 13.
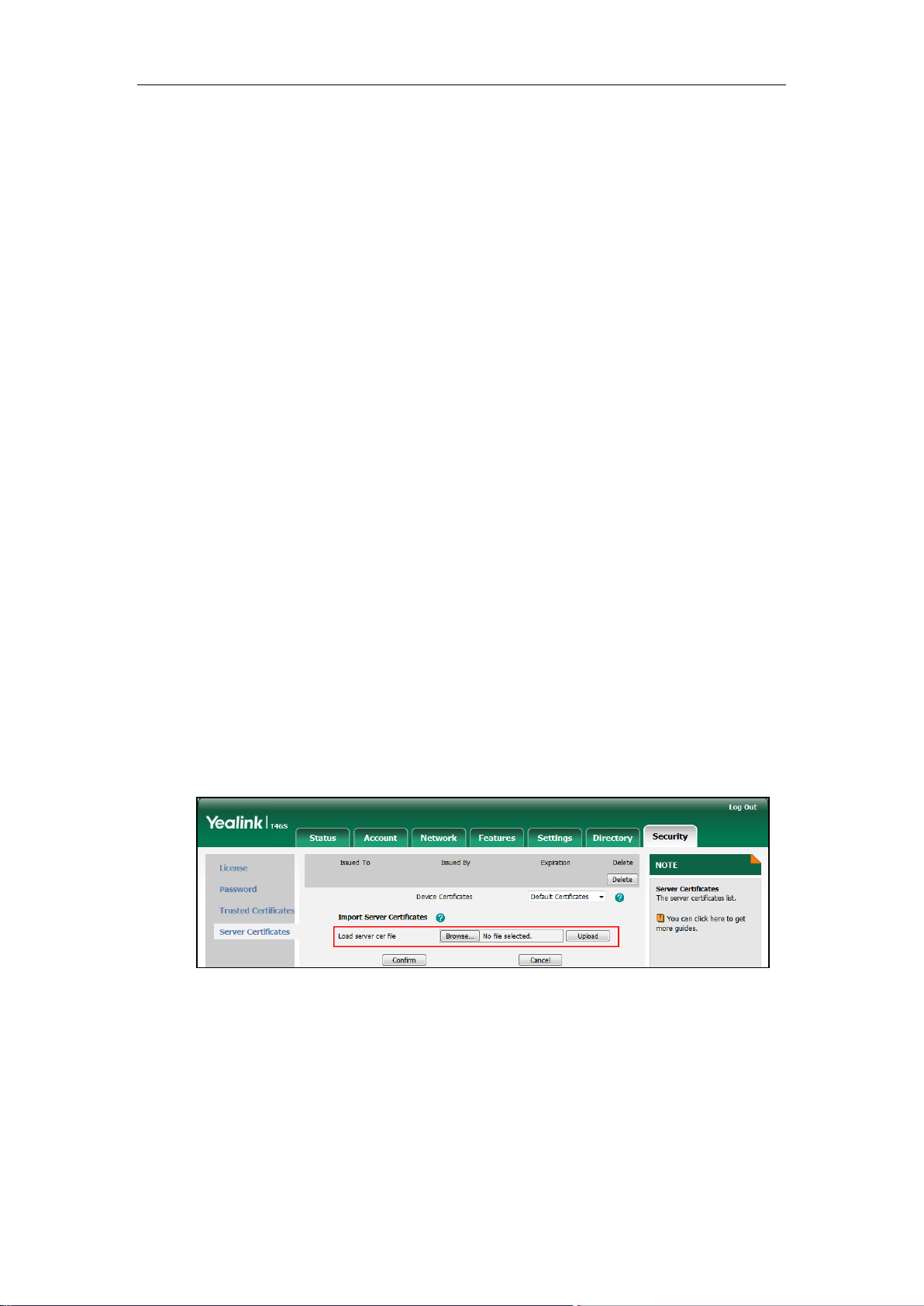
To upload a device certificate via web user interface:
1. Click on Security->Server Certificates.
2. Click Browse to locate the certificate (*.pem and *.cer) from your local system.
3. Click Upload to upload the certificate.

Using Security Certificates on Skype for Business Phones
7
The information of the custom device certificate is displayed on the web user interface of
the Skype for Business phone.
Note
To configure device certificates via web user interface:
1. Click on Security->Server Certificates.
2. Select the desired value from the pull-down list of Device Certificates.
If Default Certificates is selected, the Skype for Business phone will send the unique
or the generic device certificate to clients for authentication.
If Custom Certificates is selected, the Skype for Business phone will send custom
certificates to clients for authentication.
3. Click Confirm to accept the change.
Configuring Device Certificates Using Configuration Files
To configure device certificates using configuration files:
1. Add/Edit device certificates parameters in the configuration file (e.g., y000000000066.cfg).
The following table lists the information of parameters:
Parameters
Permitted Values
Default
static.server_certificates.url
URL within 511
characters
Blank
Description:
Configures the access URL of the certificate the Skype for Business phone sends for
authentication.
Note: The certificate you want to upload must be in *.pem or *.cer format.
Web User Interface:
Security->Server Certificates->Load server cer file
The information of built-in device certificates is not displayed on the web user interface of the
Skype for Business phone.

Using Security Certificates on Skype for Business Phones
8
Parameters
Permitted Values
Default
Phone User Interface:
None
static.security.dev_cert
0 or 1
0
Description:
Configures the type of the device certificates for the Skype for Business phone to send for
TLS authentication.
0-Default Certificates
1-Custom Certificates
Web User Interface:
Security->Server Certificates->Device Certificates
Phone User Interface:
None
The following shows an example of failover configurations for account 1 in the
<y0000000000xx.cfg> configuration file:
static.server_certificates.url = http://192.168.1.20/ca.pem
static.security.dev_cert = 0
2. Upload configuration files to the root directory of the provisioning server and trigger Skype
for Business phones to perform an auto provisioning for configuration update.
For more information on auto provisioning, refer to
Yealink_Skype_for_Business_HD_IP_Phones_Auto_Provisioning_Guide.
Using Certificates on Skype for Business phones
Certificates are used in mutual TLS authentication. It allows the server and the Skype for
Business phone to authenticate each other. This could be used for tasks like HTTPS
provisioning or SIPs signaling.
If you intend to use certificates on Skype for Business phones, they must exist on the Skype for
Business phones. Certificates issued by Yealink Certificate Authority (CA) are pre-loaded on
Skype for Business phones and a custom certificate can be uploaded to Skype for Business
phones. You can check whether a built-in device certificate is installed on your phone via phone
user interface only. A built-in device certificate can be either a unique certificate (based on the
MAC address) or a generic certificate. Each certificate is issued by the Yealink Certificate
Authority (CA), so a server can verify that a device is truly a Yealink device (not a malicious
device or software masquerading as a Yealink device).
To check whether a built-in device certificate is installed on your phone via phone user
interface:
1. Press Menu->Status->Phone.

Using Security Certificates on Skype for Business Phones
9
2. Press to scroll to Device Cert and read status.
If the status is Factory Installed, it means there is a valid device certificate installed
on your phone and the valid certificate is a unique certificate.
If the status is Not Installed, it means there is no valid device certificate installed on
your phone.
Note
When the Skype for Business phone initiates an SSL connection, we consider it as a client. The
server will send its certificate to the Skype for Business phone and the Skype for Business
phone verifies this certificate. If “Mutual TLS Authentication Required” is enabled on your server,
the Skype for Business phone should send its certificate to the server as well. The client
certificate is the same as the server certificate.
The following shows a scenario of a mutual TLS authentication. In this scenario, the Skype for
Business phone acts as a client and connects to the HTTPS server for provisioning.
To use custom device certificates for mutual TLS authentication:
1. Create CA, server and client certificates. For more information, refer to Appendix C
Creating Custom Certificates on page 13.
2. Install CA and server certificates on your server. For more information, refer to the online
resource.
3. Upload a CA certificate (trusted certificate) and a client certificate (device certificate) on
your Skype for Business phone. For more information, refer to Configuring Trusted
Certificates on Skype for Business phones on page 2 and Configuring Device Certificates
on Skype for Business phones on page 6.
The followings you need to know:
It is not possible to modify or delete the built-in device certificates.
Resetting the phone to factory defaults will not affect the built-in device certificates at all.
The built-in device certificates and associated private keys are stored on the phone in its
non-volatile memory as part of the manufacturing process.
Resetting the phone to factory defaults will delete custom certificates by default. But this
feature is determined by the value of the parameter “phone_setting.reserve_certs_enable”.
For more information on the configuration parameter, refer to
Yealink_Skype_for_Business_Edition_HD_IP_Phones_Description_of_Configuration_Paramete
rs_in_CFG_Files
.

Using Security Certificates on Skype for Business Phones
10
4. Check if Only Accept Trusted Certificates option has been enabled on the Skype for
Business phone.
- If Yes, go to step 5.
- If No, please enable Only Accept Trusted Certificates option. For more information,
refer to Configuring Trusted Certificates on Skype for Business phones on page 2.
5. Check if CA Certificates option has been configured as Custom Certificates or All
Certificates on the Skype for Business phone.
- If Yes, go to step 6.
- If No, please configure CA Certificates option. For more information, refer to
Configuring Trusted Certificates on Skype for Business phones on page 2.
6. Check if Device Certificates option has been configured as Custom Certificates on the
Skype for Business phone.
- If Yes, go to step 7.
- If No, please configure Device Certificates option. For more information, refer to
Configuring Device Certificates on Skype for Business phones on page 6.
7. Make sure that “Mutual TLS Authentication Required” is enabled on your server.
8. Make sure that auto provisioning URL on the Skype for Business phone begins with https,
e.g., “https://mydomain.com/autop/”.
9. Configure auto provisioning settings. For example, mark the On radio box in the Power On
field, and then reboot the Skype for Business phone. The Skype for Business phone will
perform auto provisioning with mutual TLS authentication.
For more information on auto provisioning, refer to
Yealink_Skype_for_Business_HD_IP_Phones_Auto_Provisioning_Guide
.

Using Security Certificates on Skype for Business Phones
11
Appendix A X.509 Certificate Structure
An X.509 digital certificate is a digitally signed statement. The X.509 standard defines what
information can go into a certificate.
The following table describes fields of a X.509 certificate:
Field
Description
Version
Identifies the version of the certificate. It must be version 3 if extensions
are present. Most currently valid X.509 certificates follow version 3.
Serial number
Identifies a unique serial number per certificate.
Signature
Identifies the algorithm used by the Certificate Authority (CA) to sign
the certificate.
Issuer
Identifies the entity that has issued the certificate.
Validity
Identifies a period during which the CA warrants that it will maintain
information about the status of the certificate.
Subject
Identifies the entity associated with the public key stored in the subject
public key information field.
Subject Public Key
Information
Carries the public key and identifies the algorithm with which the key is
used.
Extensions
Define a sequence of one or more certificate extensions that cover
information about keys and procedures, attributes of owners and
issuers, and constraints of the certificate path. They appear only if the
version is 3.
Appendix B: Trusted Certificate Authority List
Yealink Skype for Business phones trust the following CAs by default:
DigiCert High Assurance EV Root CA
Deutsche Telekom AG Root CA-2
Equifax Secure Certificate Authority
Equifax Secure eBusiness CA-1
Equifax Secure Global eBusiness CA-1
GeoTrust Global CA
GeoTrust Global CA2
GeoTrust Primary CA
GeoTrust Primary CA G2 ECC

Using Security Certificates on Skype for Business Phones
12
GeoTrust Universal CA
GeoTrust Universal CA2
Thawte Personal Freemail CA
Thawte Premium Server CA
Thawte Primary Root CA - G1 (EV)
Thawte Primary Root CA - G2 (ECC)
Thawte Primary Root CA - G3 (SHA256)
Thawte Server CA
VeriSign Class 1 Public Primary Certification Authority
VeriSign Class 1 Public Primary Certification Authority - G2
VeriSign Class 1 Public Primary Certification Authority - G3
VeriSign Class 2 Public Primary Certification Authority - G2
VeriSign Class 2 Public Primary Certification Authority - G3
VeriSign Class 3 Public Primary Certification Authority
VeriSign Class 3 Public Primary Certification Authority - G2
VeriSign Class 3 Public Primary Certification Authority - G3
VeriSign Class 3 Public Primary Certification Authority - G4
VeriSign Class 3 Public Primary Certification Authority - G5
VeriSign Class 4 Public Primary Certification Authority - G2
VeriSign Class 4 Public Primary Certification Authority - G3
VeriSign Universal Root Certification Authority
Microsoft_IT_SSL_SHA2.cer
CNNIC_Root.cer
baltimoreCyberTrust.cer
UserTrust.cer
AAA Certificate Services.cer
DigiCert Assured ID Root CA.cer
Entrust.net Certification Authority (2048).cer
Entrust Root Certification Authority
Entrust.net Secure Server Certification Authority
GTE CyberTrust Global Root.cer
Starfield Class 2 Certification Authority.cer
AddTrust External CA Root
Go Daddy Class 2 Certification Authority
StartCom Certification Authority
DST Root CA X3
ISRG Root X1 (intermediate certificates: Let’s Encrypt Authority X1 and Let’s Encrypt

Using Security Certificates on Skype for Business Phones
13
Authority X2 are signed by the root certificate ISRG Root X1.)
Baltimore CyberTrust Root
DigiCert Cloud Services CA-1
D-Trust Root Class 3 CA 2 2009
AddTrust External CA Root
Starfield Root Certificate Authority - G2
Note
Appendix C Creating Custom Certificates
You can create and use your own CA to issue certificates. This requires a tool that supports SSL
and TLS protocols. We recommend you to use OpenSSL on Linux. The OpenSSL software is
available for free online:
http://www.openssl.org/source/
. If Windows is required, we recommend
you to use the apache server with OpenSSL. The software is available for free online:
http://httpd.apache.org/download.cgi
. Be sure to install OpenSSL before you read the following
instructions. For more information, refer to the network resource.
This appendix includes information on:
Creating a self-signed CA
Issuing certificates
To create a self-signed CA:
1. Open a terminal window.
2. Execute the following command to create a RSA private key for your CA:
[root@localhost openssl-0.9.8k]#openssl genrsa -out ca.key 1024
Generating RSA private key, 1024 bit long modulus
..........++++++
............++++++
e is 65537 (0x10001)
The command will generate a ca.key file.
3. Execute the following command to create a self-signed CA certificate with the RSA private
key:
[root@localhost openssl-0.9.8k]#openssl req -new -x509 -days 3650 -key ca.key -out ca.crt
You are about to be asked to enter information that will be incorporated into your certificate
Yealink endeavors maintain a built-in list of the most commonly used CA Certificates. Due to
memory constraints, we cannot ensure a complete set of certificates. If you are using a certificate
from a commercial Certificate Authority not in the list above, you can send a request to your local
distributor. At this point, you can upload your particular CA certificate into your phone. For more
information on uploading a custom CA certificate, refer to Configuring Trusted Certificates on
Skype for Business phones on page 2.

Using Security Certificates on Skype for Business Phones
14
request.
What you are about to enter is what is called a Distinguished Name or a DN.
There are quite a few fields but you can leave some blank. For some fields there will be a
default value,
If you enter '.', the field will be left blank.
-----
Country Name (2 letter code) [US]:CN
State or Province Name (full name) [Wisconsin]:FJ
Locality Name (eg, city) [Madison]:XM
Organization Name (eg, company) [My Company Ltd]: Yealink
Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) []:
Common Name (eg, your name or your server's hostname) []:Yealink CA
Email Address []:support@yealink.com
You will be prompted to enter a few attributes (e.g., State, organization or Common Name
(CN)). The command will generate a self-signed X.509 certificate valid for ten years (3650
days).
You can execute the following command to see the details of this certificate.
[root@localhost openssl-0.9.8k]#openssl x509 -noout -text -in ca.crt
A server certificate is a digital certificate issued to a server by a CA. It verifies the server’s
identity for the client so that the client can securely browse the server. After the server certificate
is issued, you need to install the certificate on the server.
To issue a server certificate:
1. Open a terminal window.
2. Execute the following command to create a RSA private key for your server:
[root@localhost openssl-0.9.8k]#openssl genrsa -out server.key 1024
Generating RSA private key, 1024 bit long modulus
..............................................++++++
........++++++
e is 65537 (0x10001)
The command will generate a server.key file.
3. Execute the following command to create a server Certificate Signing Request (CSR) with
the server RSA private key:
[root@localhost openssl-0.9.8k]# openssl req -new -key server.key -out server.csr
You are about to be asked to enter information that will be incorporated into your certificate
request.
What you are about to enter is what is called a Distinguished Name or a DN.
There are quite a few fields but you can leave some blank. For some fields there will be a
default value,
If you enter '.', the field will be left blank.

Using Security Certificates on Skype for Business Phones
15
-----
Country Name (2 letter code) [US]:CN
State or Province Name (full name) [Wisconsin]:FJ
Locality Name (eg, city) [Madison]:XM
Organization Name (eg, company) [My Company Ltd]:Yealink
Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) []:
Common Name (eg, your name or your server's hostname) []:server.yealink.com
Email Address []:support@yealink.com
Please enter the following 'extra' attributes
to be sent with your certificate request
A challenge password []:1234567890
An optional company name []:
You will be prompted to enter a few attributes (e.g., State, organization or Common Name
(CN)). The command will generate a server.csr file.
Note
4. Execute the following command to issue your server certificate with ca.crt and ca.key
generated above:
[root@localhost openssl-0.9.8k]#openssl x509 -days 365 -CA ca.crt -CAkey ca.key -req
-CAcreateserial -CAserial ca.srl -in server.csr -out server.crt
Signature ok
subject=/C=CN/ST=FJ/L=XM/O=Yealink/CN=server.yealink.com/emailAddress=support@
yealink.com
Getting CA Private Key
The command will generate a X.509 server certificate valid for one year (365 days).
You can execute the following command to view the details of this certificate.
[root@localhost openssl-0.9.8k]#openssl x509 -text -in server.crt
A client certificate is a digital certificate issued to a client by a CA. Client certificate issue steps
are very similar to server certificate. Remember to specify a unique CN.
Execute the following commands to issue a client certificate:
[root@localhost openssl-0.9.8k]#openssl genrsa -out client.key 1024
[root@localhost openssl-0.9.8k]#openssl req -new -key client.key -out client.csr
[root@localhost openssl-0.9.8k]#openssl x509 -days 365 -CA ca.crt -CAkey ca.key -req
-CAcreateserial -CAserial ca.srl -in client.csr -out client.crt
These commands will generate a client.key file, a client.csr file and a client.crt file.
If the mutual TLS authentication is required, you need to generate a *.pem certificate and upload
The Common Name (CN) in the server certificate must match the name supplied as the server.
This is because the Skype for Business phone does not perform a DNS lookup, but only performs
a simple string comparison. The use of an IP address is also valid.

Using Security Certificates on Skype for Business Phones
16
it to the Skype for Business phone.
Execute the following command to generate a client.pem file with client.crt and client.key files
generated above:
[root@localhost openssl-0.9.8k]#cat client.crt client.key > client.pem

Using Security Certificates on Skype for Business Phones
17
Customer Feedback
We are striving to improve our documentation quality and we appreciate your feedback. Email your
opinions and comments to DocsFeedback@yealink.com.
 Loading...
Loading...