Page 1

Page 2

Page 3

Page 4

CONTENTS
VOICE COMMON...................................................3
NAME................................................................5
CONFIGURATION.............................................5
EFFECT (Type & Depth)....................................5
PITCH BEND.....................................................6
WHEEL (Amplitude & Pitch Modulation)...........6
AFTER TOUCH (Amplitude &
Pitch Modulation, Pitch & Level Control).......7
ENVELOPE (Attack & Release Rates).................7
RANDOM (Element, Level & Detune)................8
VOICE VECTOR.....................................................9
LEVEL SPEED (Vector Rate)...........................11
LEVEL RECORD.............................................11
LEVEL EDIT (Step, X-axis, Y-axis & Time).....11
DETUNE SPEED (Vector Rate)........................13
DETUNE RECORD..........................................13
DETUNE EDIT
(Step, X-axis, Y-axis & Time).......................13
ELEMENT TONE................................................15
WAVE TYPE....................................................17
ELEMENT COPY.............................................19
FREQUENCY SHIFT........................................19
VOLUME.........................................................20
PAN..................................................................20
VELOCITY SENSITIVITY...............................20
AFTER TOUCH SENSITIVITY........................21
TONE (FM Elements B and D Only).................21
LFO (Low Frequency Oscillator) AM Depth,
PM Depth, Type, Delay, Rate & Speed..........22
MIDI RECEIVE CHANNEL.............................36
VOLUME.........................................................36
DETUNE..........................................................37
NOTE LIMIT (Low & High)............................37
NOTE SHIFT....................................................37
UTILITY SETUP.................................................39
MASTER TUNE...............................................41
TRANSPOSE....................................................41
MEMORY CARD
(Save, Load, Format, & Bank).......................41
VOICE INITIALIZE.........................................43
MULTI INITIALIZE........................................44
MEMORY PROTECT (Internal & Card)...........45
FACTORY VOICE & MULTI RESTORE..........45
UTILITY RECALL...............................................47
VOICE RECALL (Voice or Multi)....................49
UTILITY MIDI....................................................51
MIDI ON/OFF...................................................53
BASIC RECEIVE CHANNEL...........................53
TRANSMIT CHANNEL...................................53
LOCAL CONTROL ON/OFF.............................54
MIDI PROGRAM CHANGE.............................54
MIDI CONTROL CHANGE..............................54
AFTER TOUCH ON/OFF..................................55
PITCH BEND ON/OFF......................................55
EXCLUSIVE ON/OFF.......................................55
ALL V/M TRANSMIT......................................56
1 VOICE TRANSMIT.......................................56
ELEMENT ENVELOPE.......................................25
TYPE................................................................27
ENVELOPE COPY...........................................28
DELAY (Delay Rate & Element ON/OFF).........28
INITIAL LEVEL..............................................28
ATTACK (Level & Rate)..................................29
DECAY 1 (Level & Rate)..................................29
DECAY 2 (Level & Rate)..................................29
RELEASE RATE..............................................30
LEVEL SCALING............................................30
RATE SCALING..............................................31
MULTI.................................................................33
NAME..............................................................35
EFFECT (Type & Depth)..................................35
VOICE NUMBER.............................................35
APPENDIX...........................................................57
VOICE LIST.....................................................59
MULTI LIST....................................................66
WAVEFORM LIST...........................................67
SPECIFICATIONS............................................69
ERROR MESSAGES.........................................70
INDEX.............................................................71
MIDI DATA FORMAT.....................................73
MIDI IMPLEMENTATION CHART................76
i
Page 5

About This Manual
We recommend that you start by going through the Getting Started manual in
order to become familiar with the SY35 and the way it works, then you can
refer to the Feature Reference manual from time to time to get details on
functions you’ve never used before, or refresh your memory about functions
Each section of this manual has its own table of contents, so you should be
able to locate any particular function quickly and easily. Functions and refer-
The SY35 Feature Reference manual individually describes the SY35 functions in detail, providing a summary,
operating procedure, and additional details for each function. It is divided into eight main sections, each
describing the various functions within a particular SY35 edit or utility mode.
1. VOICE COMMON [Page 3]
2. VOICE VECTOR [Page 9]
3. ELEMENT TONE [Page 15]
4. ELEMENT ENVELOPE [Page 25]
5. MULTI [Page 33]
6. UTILITY SETUP [Page 39]
7. UTILITY RECALL [Page 47]
8. UTILITY MIDI [Page 51]
that you don’t use very often.
ences can also be located by referring to the index at the back of the manual.
ii
Page 6

Feature
Reference Manual
VOICE COMMON
1
Page 7

VOICE COMMON
2
Page 8

VOICE COMMON
VOICE COMMON
The VOICE COMMON mode provides access to a range of parameters that affect the
selected voice as a whole. Detailed programming of individual elements is provided by the
ELEMENT TONE and ELEMENT ENVELOPE edit modes.
NAME............................................................................................................................ 5
CONFIGURATION......................................................................................................... 5
EFFECT (Type & Depth)............................................................................................... 5
PITCH BEND................................................................................................................. 6
WHEEL (Amplitude & Pitch Modulation)...................................................................... 6
AFTER TOUCH (Amplitude & Pitch Modulation, Pitch & Level Control).................... 7
ENVELOPE (Attack & Release Rates)............................................................................ 7
RANDOM (Element, Level & Detune)........................................................................... 8
3
Page 9
Page 10

NAME
VOICE COMMON
VC>VOICE NAME
I23 Initial
Summary: Assigns a name of up to 8 characters to
the current voice.
Settings: The following characters are available for
use in voice names:
(Space) !"#¢%&'()*+,-./0123456789:;<=>?Å
ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ[Á]^_«
abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz“|‘Ÿ˚
CONFIGURATION
VC>CONFIGURATION
A-B-C-D
Summary: Selects the two-element (A-B) or four-
element (A-B-C-D) voice configuration.
Settings: A-B, A-B-C-D
Procedure: Use the [6] key to move the cursor to
the lower display line. Use the [–1/NO] and
[+1/YES] keys to select the desired configuration.
Procedure: Use the [4] and [6] cursor keys to place
the underline cursor under the character to be
changed. Use the [–1/NO] and [+1/YES] keys to
select the desired character. Continue until the
entire voice name has been programmed.
Details: It’s a good idea to give your voices names
that make them easily identifiable. If you’ve
created a new voice that combines piano and
organ elements, for example, you could call it
something like “PianOrg”.
When selecting characters, scrolling will pause at
the beginning of each character group (capitals,
lower case, numbers, and symbols).
Details: In the 2-element “A-B” configuration, ele-
ment A is AWM and element B is FM. In the 4element “A-B-C-D” configuration elements A
and B are the same as in the “A-B” configuration, while element C is AWM and element D is
FM.
A-B: A = AWM, B = FM.
A-B-C-D: A = AWM, B = FM, C = AWM, D = FM.
EFFECT (Type & Depth)
VC>VOICE EFFECT
Rev Hall Dep=1
Summary: Selects one of sixteen digital effects, and
sets the depth of the selected effect for the current voice.
5
Page 11
VOICE COMMON
Settings: Effect type:
Rev Hall (Reverb Hall)
Rev Room (Reverb Room)
Rev Plate (Reverb Plate)
Rev Club (Reverb Club)
Rev Metal (Reverb Metal)
Delay 1 (Short Single Delay)
Delay 2 (Long Delay)
Delay 3 (Long Delay)
Doubler (Doubler)
Ping-Pong (Ping Pong Delay)
Pan Ref (Panned Reflections)
Early Ref (Early Reflections)
Gate Rev (Gated Reverb)
Dly&Rev 1 (Delay & Reverb 1)
Dly&Rev 2 (Delay & Reverb 2)
Dist&Rev (Distortion & Reverb)
PITCH BEND
VC@PITCH BEND
Range= 2
Summary: Sets the range of the pitch bend wheel.
Settings: 0 … 12 max.*
Procedure: Use the [6] key to move the cursor to
the lower display line. Use the [–1/NO] and
[+1/YES] keys to select the desired pitch bend
range.
Depth: 0 … 7
Procedure: Use the [4] and [6] cursor keys to place
the underline cursor under the effect type or
depth parameter. Use the [–1/NO] and [+1/YES]
keys to select the desired effect or effect depth.
Details: Setting the depth parameter to “0” is
equivalent to turning the effect OFF. A depth
setting of “7” produces the greatest effect.
Details: Each increment from “0” to “12” repre-
sents a semitone. A setting of “0” produces no
pitch bend. A setting of “12” allows a
maximum pitch bend of plus or minus one
octave, while a setting of “4” allows a
maximum pitch bend of plus or minus a major
third.
* This range may be more limited in some cases.
An exclamation mark (!) will appear after the
range value when the limit is reached.
WHEEL (Amplitude & Pitch Modulation)
VC@WHEEL
AM=on PM=ON
Summary: Assigns the modulation wheel to ampli-
tude and/or pitch modulation.
Settings: AM (Amplitude Modulation): off, on
PM (Pitch Modulation): off, on
Procedure: Use the [4] and [6] cursor keys to place
the underline cursor under the AM or PM
parameter. Use the [–1/NO] and [+1/YES] keys
to turn the selected parameter on or off.
Details: Amplitude modulation produces a tremolo
effect while pitch modulation produced a
vibrato effect. This function allows the
modulation wheel to be assigned to produce
either or both. This is only an “off/on” switch,
however, and the maximum depth of
modulation to be applied must be set using the
LFO AM Depth and PM Depth parameters in
the ELEMENT TONE edit mode.
When the modulation wheel is assigned to
amplitude or pitch modulation, LFO modulation
can only be applied via the wheel.
If both WHEEL and AFTER TOUCH are assigned to modulation control, the controller via
which the highest modulation level is applied
will take priority when both are used simultaneously.
6
Page 12

VOICE COMMON
AFTER TOUCH (Amplitude & Pitch Modulation, Pitch & Level Control)
VC>AFTER TOUCH
AM=on PM=on ->
Summary: Assigns keyboard after-touch to ampli-
tude modulation, pitch modulation, pitch
control, or level control — or any combination
of the above.
Settings: AM (Amplitude Modulation): off, on
PM (Pitch Modulation): off, on
Pit (Pitch Control): –12 … 0 … +12 max.*
Lev (Level Control): off, on
Procedure: Use the [4] and [6] cursor keys to place
the underline cursor under the AM, PM, Pit, or
Lev parameter. The arrows at either end of the
display mean that more parameters can be
accessed by scrolling in the indicated direction.
Use the [–1/NO] and [+1/YES] keys to turn the
AM, PM, and/or Lev parameter on or off, or to
select the desired Pit control range.
Details: As with the modulation wheel, amplitude
modulation produces a tremolo effect while
pitch modulation produced a vibrato effect. The
harder you press a key, the deeper the
modulation. This is only an “off/on” switch,
however, and the maximum depth of
modulation to be applied must be set using the
LFO AM Depth and PM Depth parameters in
the ELEMENT TONE edit mode.
When after touch is assigned to amplitude or
pitch modulation, LFO modulation can only be
applied via after touch.
The Pit parameter allows keyboard after touch
to be used for note bending. The greater the key
pressure the greater the amount of pitch bend.
Positive values produce an upward bend when
key pressure is applied, and minus values produce a downward bend. Each increment from
represents a semitone. A setting of “0” produces no pitch bend. A setting of “12” allows a
maximum upward pitch bend of one octave,
while a setting of “–4” allows a maximum
downward pitch bend of a major third.
When the Lev parameter is turned on it becomes
possible to control the level of the sound over a
limited range by keyboard after touch. The
amount and direction (i.e. an increase or decrease) of level change depends on the setting of
the AFTER TOUCH SENSITIVITY parameter
in the ELEMENT TONE edit mode.
If both WHEEL and AFTER TOUCH are assigned to modulation control, the controller via
which the highest modulation level is applied
will take priority when both are used simultaneously.
* This range may be more limited in some cases.
An exclamation mark (!) will appear after the
range value when the limit is reached.
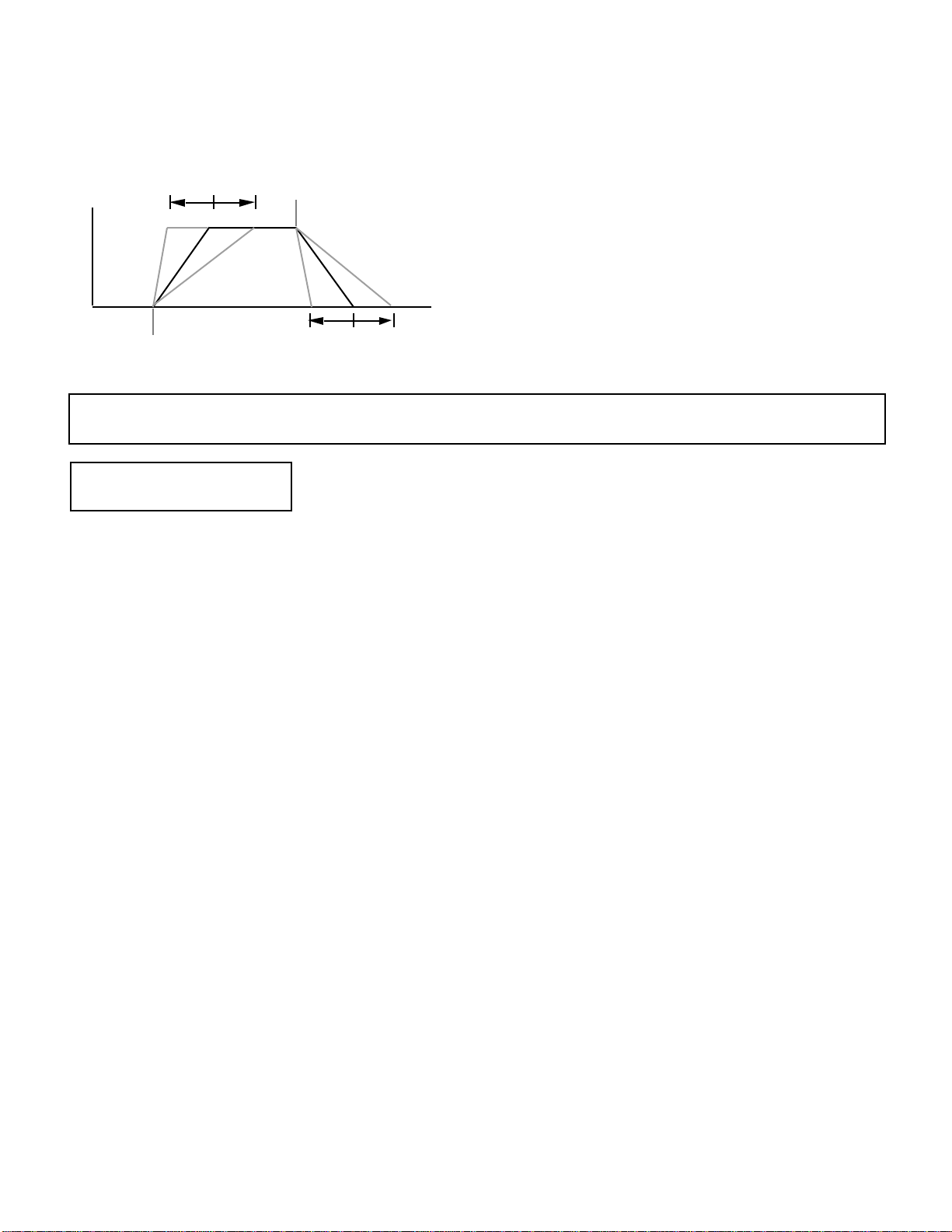
ENVELOPE (Attack & Release Rates)
VC>ENVELOPE
AR= 0 RR= 0
Summary: Sets the overall attack and release rates
for the current voice.
Settings: AR (Attack Rate): –99 … 0 … +99 max.*
RR (Release Rate): –99 … 0 … +99 max.*
Procedure: Use the [4] and [6] cursor keys to place
the underline cursor under the AR or RR
parameter. Use the [–1/NO] and [+1/YES] keys
to set the selected parameter as required.
Details: Although much more detailed envelope
programming capability is available for
individual elements (see the ELEMENT
ENVELOPE edit mode), these functions provide
an easy way to adjust the most important
envelope parameters for the overall voice.
Positive values produce a faster attack or release
time, while negative values produce a slower
attack or release time. You might want to
lengthen the release time of a voice, for
example, to produce a lingering sustain effect
after you release the keys.
7
Page 13
VOICE COMMON
Please note that the AR parameter will have no
effect on elements in which the INITIAL
LEVEL parameter (page 28) is set to 99.
LEVEL
Key ON
Faster
attack.
AR
0 –99+99
Envelope
TIME
Slower
attack.
Key OFF
Faster
release.
0 –99+99
RR
Slower
release
RANDOM (Element, Level & Detune)
VC>RANDOM
ELEMENT
Summary: Automatically produces random combi-
nations of elements, level vectors, or detune
vectors.
Settings: None.
Procedure: Use the [4] and [6] cursor keys to place
the left parameter on the lower display line, then
use the [–1/NO] and [+1/YES] keys to select
ELEMENT, LEVEL or DETUNE. Press the [6]
to move the cursor to “Y/N,” then press the
[+1/YES] key to generate random values of the
select type. A new set of random values is generated each time the [+1/YES] key is pressed
while the cursor is in this position. Pressing the
[–1/NO] returns the cursor to the left parameter.
* This range may be more limited in some cases.
An exclamation mark (!) will appear after the
range value when the limit is reached.
Details: This function is actually a very useful pro-
gramming aid. It allows you try out a virtually
unlimited variety of element combinations or
level/detune vectors by simply pressing a single
key. The random element combinations, in particular, can produce some very surprising and
often pleasant results.
When the “A-B” voice configuration is selected
(see CONFIGURATION on page 5), random
element combinations will always consist of only
two elements. When the “A-B-C-D” voice configuration is selected, random element generation will produce combinations of four
elements.
8
Page 14

VOICE VECTOR
VOICE VECTOR
The VOICE VECTOR edit mode allows recording and fine editing of dynamic level and
detune vectors.
LEVEL SPEED (Vector Rate)......................................................................................... 11
LEVEL RECORD............................................................................................................ 11
LEVEL EDIT (Step, X-axis, Y-axis & Time).................................................................. 11
DETUNE SPEED (Vector Rate)..................................................................................... 13
DETUNE RECORD........................................................................................................ 13
DETUNE EDIT (Step, X-axis, Y-axis & Time).............................................................. 13
9
Page 15
Page 16

LEVEL SPEED (Vector Rate)
VOICE VECTOR
VV>LEVEL SPEED
Vector Rate 30ms
Summary: Sets the time between level vector steps.
Settings: 10 … 160 milliseconds (in 10-millisecond
steps)
Procedure: Use the [6] key to move the cursor to
the lower display line. Use the [–1/NO] and
[+1/YES] keys to select the desired vector rate.
LEVEL RECORD
VV>LEVEL REC
STBY REC PLAY
Summary: Allows recording of a dynamic level
vector.
Settings: STBY, REC, PLAY
Details: Each dynamic vector is composed of up to
50 “steps” corresponding to points along the
path followed by the vector control. This
function sets the initial time between each step.
The Time parameter in the LEVEL EDIT
function, described later, allows the length of
individual steps to be edited. The vector rate
parameter can be changed even after recording
a vector, producing a corresponding change in
the spacing between the steps.
The LEVEL SPEED parameter can also be used
to change the playback speed of a pre-recorded
vector.
Move the cursor to REC. Recording will actually
begin as soon as you play a key on the keyboard. When you release the key or when 50
steps have been recorded (See “LEVEL
SPEED” above), recording will end and the cursor will move to the PLAY position. You can
now play the keyboard to hear how the vector
sweep you just recorded sounds.
Procedure: Use the [4] and [6] cursor keys to place
the underline cursor under STBY. The vector
control LEVEL mode will be automatically
selected and you can rehearse the vector sweep
you wish to record.
LEVEL EDIT (Step, X-axis, Y-axis & Time)
● Step
VV L.ED A B C D
1 X 0 Y 0 End
Summary: Selects any of the 50 steps in a recorded
level vector for editing.
Details: The amount of time available for recording
depends both on the vector rate setting and how
much the vector control is moved.
Settings: 1 … 50
Procedure: Use the [4] and [6] cursor keys to place
the underline cursor under the leftmost value on
the lower display line (Step). Use the [–1/NO]
and [+1/YES] keys to select the step to be edited.
11
Page 17
VOICE VECTOR
Details: Step 1 is the first step recorded and step 50
is the last. Experience will give you a feel for
relating specific points in a dynamic vector to
the corresponding steps.
● X-axis & Y-axis
VV L.ED A B C D
1 X 0 Y 0 End
Summary: These parameters define the position of
the currently selected step on the X and Y axes
of the level vector control range.
Settings: –31 … 0 … +31
Procedure: After selecting the step to be recorded
as described in the previous function, use the [4]
and [6] cursor keys to place the underline
cursor under the X or Y parameter. Use the
[–1/NO] and [+1/YES] keys to set the value as
required.
Details: On the X (D-C) axis, a setting of –31 places
the step as far as possible toward the D element
while a setting of +31 places it as far as possible
toward the C element. The Y (A-B) axis values
work in the same way: a setting of
–31 places the step as far as possible toward the
B element while a setting of +31 places it as far
as possible toward the A element. In both axes a
setting of 0 places the step at center position.
● Time
VV L.ED A B C D
1 X 0 Y 0 End
Summary: Multiplies the vector rate setting of the
current level vector step only. Also allows vectors to be looped or ended at the current step.
Settings: 1 … 254, Rep, End
Procedure: Use the [4] and [6] cursor keys to place
the underline cursor under the rightmost value
on the lower display line (Time). Use the
[–1/NO] and [+1/YES] keys to select the required time value, repeat, or end.
Details: Time values multiply the vector rate setting
for the current step. If the vector rate parameter
is set to 30ms, for example, setting the time
parameter to 2 results in a step length of 60ms,
setting it to 3 results in a step length of 90ms,
and so on. Since the maximum time value is
254, extremely long steps can be created.
If you select the “End” setting, the vector will
end at the current step.
The “Rep” setting causes the vector to loop
back to the first step from the current step, repeating continuously.
12
X axis
A
+31
D
0
–31
B
Y axis
C
+31–31
Page 18

DETUNE SPEED (Vector rate)
VOICE VECTOR
VV>DETUNE SPEED
Vector Rate 30ms
Summary: Sets the time between detune vector
steps.
Settings: 10 … 160 milliseconds
Procedure: Use the [6] key to move the cursor to
the lower display line. Use the [–1/NO] and
[+1/YES] keys to select the desired vector rate.
DETUNE RECORD
VV>DETUNE REC
STBY REC PLAY
Summary: Allows recording of a dynamic detune
vector.
Settings: STBY, REC, PLAY
Procedure: Use the [4] and [6] cursor keys to place
the STBY. The vector control DETUNE mode
will be automatically selected and you can
rehearse the vector sweep you wish to record.
Move the cursor to REC. Recording will actually
begin as soon as you play a key on the key
Details: Each automatic vector sweep is composed
of up to 50 “steps,” corresponding to equallyspaced points along the path followed by the
vector control. This function sets the initial time
between each step.
board. When you release the key or when all 50
steps have been recorded (See “DETUNE
SPEED” above), recording will end and the cursor will move to the PLAY position. You can
now play the keyboard to hear how the vector
sweep you just recorded sounds.
Details: The amount of time available for recording
depends both on the vector rate setting and how
much the vector control is moved.
Moving the vector control towards an element
raises the pitch of that element while lowering
the pitch of the others.
DETUNE EDIT (Step, X-axis, Y-axis & Time)
● Step
VV D.ED A B C D
1 X 0 Y 0 End
Summary: Selects any of the 50 steps in a recorded
detune vector for editing.
Settings: 1 … 50
Procedure: Use the [4] and [6] cursor keys to place
the underline cursor under the leftmost value on
the lower display line (Step). Use the [–1/NO]
and [+1/YES] keys to select the step to be edited.
Details: Step 1 is the first step recorded and step 50
is the last. Experience will give you a feel for
relating specific points in a dynamic vector to
the corresponding steps.
13
Page 19
VOICE VECTOR
● X-axis & Y-axis
VV D.ED A B C D
1 X 0 Y 0 End
Summary: These parameters define the position of
the currently selected step on the X and Y axes
of the detune vector control range.
Settings: –31 … 0 … +31
Procedure: Use the [4] and [6] cursor keys to place
the underline cursor under the X or Y
parameter. Use the [–1/NO] and [+1/YES] keys
to set the value as required.
Details: On the X (D-C) axis, a setting of –31 places
the step as far as possible toward the D element
while a setting of +31 places it as far as possible
toward the C element. The Y (A-B) axis values
work in the same way: a setting of
–31 places the step as far as possible toward the
B element while a setting of +31 places it as far
as possible toward the A element. In both axes a
setting of 0 places the step at center position.
A
+31
X axis
0
–31
CD
+31
● Time
VV D.ED A B C D
1 X 0 Y 0 End
Summary: Multiplies the vector rate setting of the
current detune vector step only. Also allows
vectors to be looped or ended at the current
step.
Settings: 1 … 254, Rep, End
Procedure: Use the [4] and [6] cursor keys to place
the underline cursor under the rightmost value
on the lower display line (Time). Use the
[–1/NO] and [+1/YES] keys to select the required time value.
Details: Time values multiply the vector rate setting
for the current step. If the vector rate parameter
is set to 30ms, for example, setting the time
parameter to 2 results in a step length of 60ms,
setting it to 3 results in a step length of 90ms,
and so on. Since the maximum time value is
254, extremely long steps can be created.
If you select the “End” setting, the vector will
end at the current step.
The “Rep” setting causes the vector to loop
back to the first step from the current step,
repeating continuously.
–31
B
Y axis
14
Page 20

ELEMENT TONE
ELEMENT TONE
The ELEMENT TONE edit mode allows editing many of the most important sound-determining parameters of each individual element — A and B in a 2-element voice; A, B, C and
D in a 4-element voice.
WAVE TYPE................................................................................................................. 17
ELEMENT COPY.......................................................................................................... 19
FREQUENCY SHIFT...................................................................................................... 19*
VOLUME....................................................................................................................... 20
PAN............................................................................................................................... 20*
VELOCITY SENSITIVITY............................................................................................. 20
AFTER TOUCH SENSITIVITY..................................................................................... 21
TONE (FM Elements B and D Only).............................................................................. 21*
LFO (Low Frequency Oscillator) AM Depth, PM Depth, Type,
Delay, Rate & Speed.................................................................................................. 22*
* These four parameters are not available for an AWM element in which wave number 127
(Drum Set) is selected — “Cannot edit” display appears.
15
Page 21
ELEMENT TONE
➯
➯
➯
➯
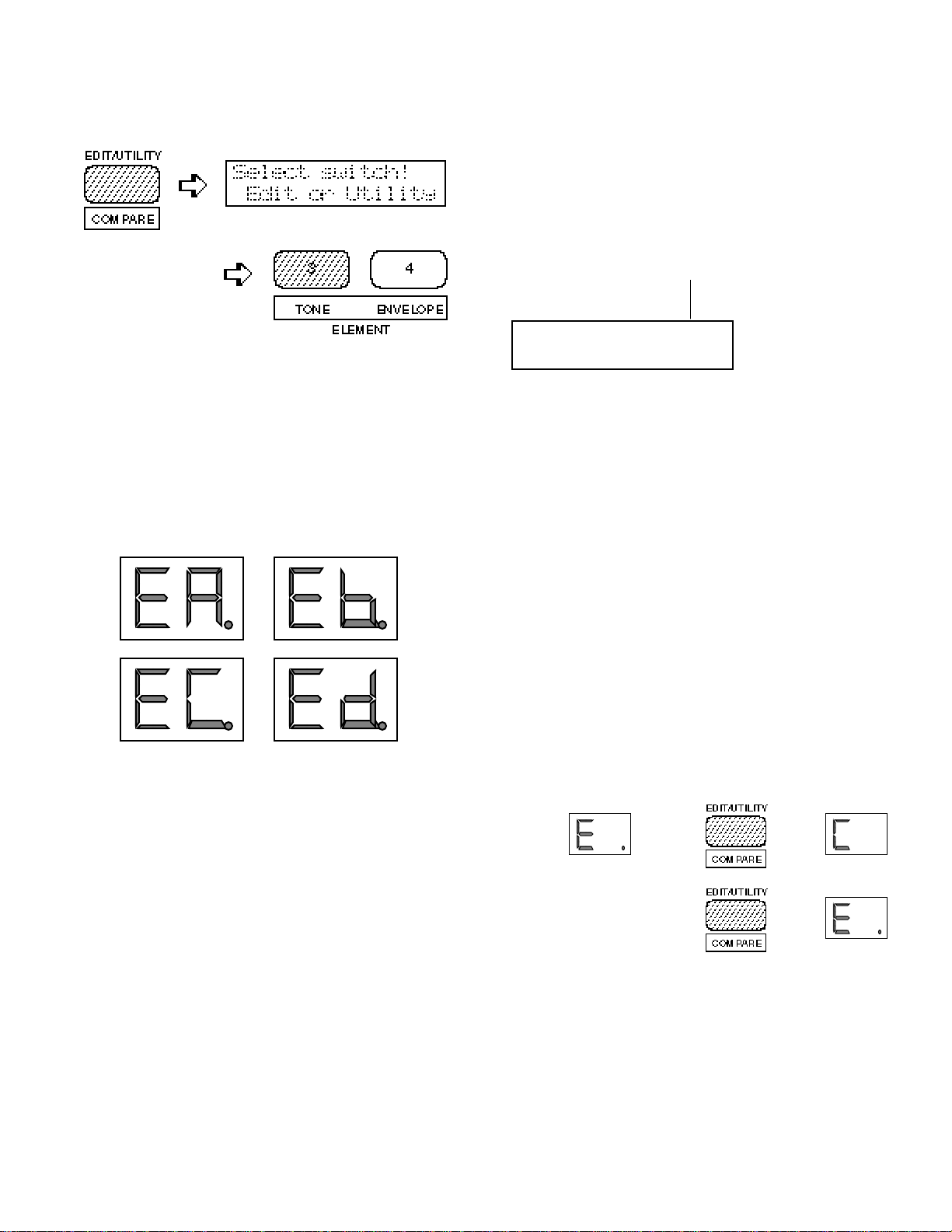
Selecting the ELEMENT TONE Edit Mode
From the VOICE or MULTI mode:
From another edit or utility mode simply press
[ELEMENT TONE].
An “E” will appear to the left of the LED display to indicate that an edit mode is selected,
and the element selected for editing will be displayed to the right of the display — “A”, “b”,
“C”, or “d”. A dot will appear to the right of
the element character as soon as any parameter
has been edited.
ON, if a dash appears in place of the element
character, that element is OFF. The ability to
turn elements on or off while editing makes it
easier to hear the effect of parameter changes on
a single element. The currently selected element
is also shown on the LCD as a reversed (white on
black) character.
In this example elements A, B and D are ON, while
element C is OFF. Element A is currently selected
for editing.
ET>WAVE 000 ÅB-D
Piano:Piano
Selecting the ELEMENT TONE Edit Mode
Functions
The various ELEMENT TONE edit mode functions can be selected in sequence by pressing the
[ELEMENT TONE] key, or by using the
[–1/NO] and [+1/YES] keys when the cursor
(6)is located immediately before the function
name on the upper display line.
Different elements can be selected for editing by
pressing the appropriate [ELEMENT SELECT]
key — [A], [B], [C] or [D]. If a 2-element voice
is being edited, only elements A and B can be
selected.
Any of the available elements can also be turned
on or off by pressing the appropriate
[ELEMENT ON/OFF] key. Each key alternately
turns the associated element on and off, and the
on/off status of the elements is shown to the
right of the upper LCD line. If the element
character is showing, the associated element is
The COMPARE Function
You can compare the sound of the edited voice
with the sound of the voice before it was edited
by pressing the [EDIT/COMPARE] key to activate the COMPARE function. A “C” will
appear on the LED display while the COMPARE
function is active, and the sound of the voice
prior to editing will be heard when you play the
keyboard. Press the [EDIT/COMPARE] key
again to return to the edit mode.
16
Page 22
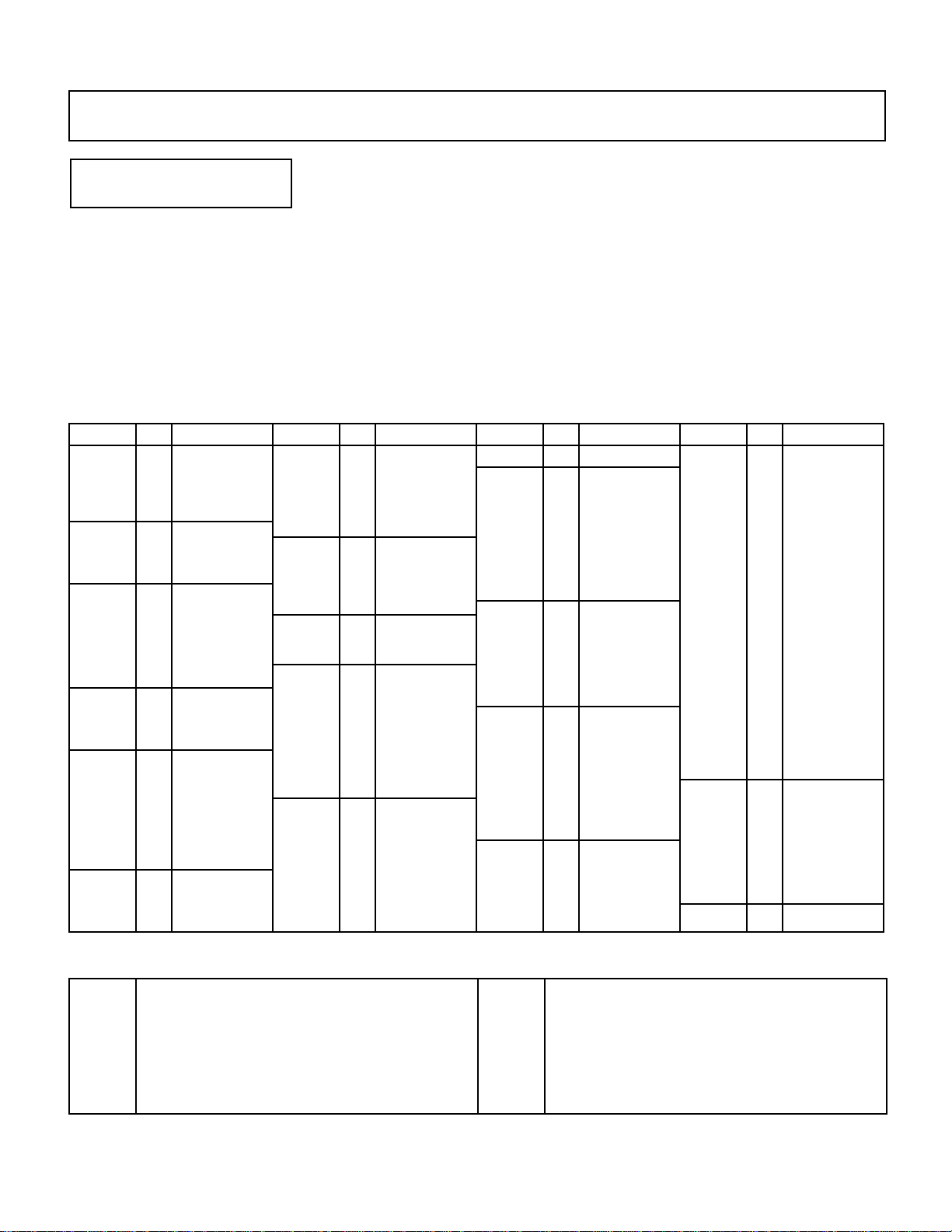
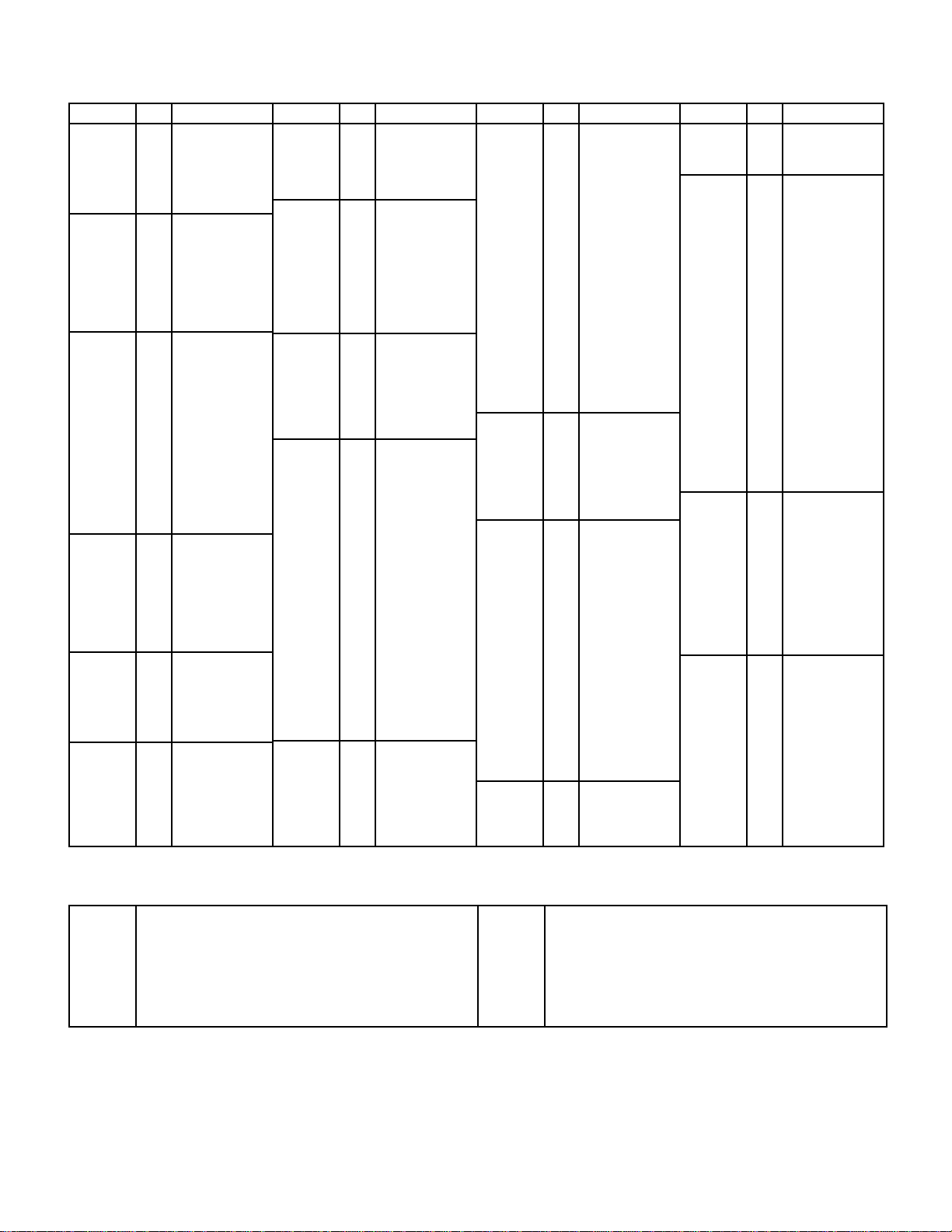
WAVE TYPE
161718
3233343536
383940
41
43
44
46474849505152
53
55565758596061
62
65666768697071
72
7475767778
79
96979899100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
ELEMENT TONE
ET>WAVE 000 !BCD
Piano:Piano
Summary: Assigns a preset wave to the selected
element.
Settings: Elements A and C (AWM): 0 … 127
Elements B and D (FM): 0 … 255
Procedure: Use the [4] and [6] cursor keys to place
the underline cursor under the left
AWM WAVEFORM LIST
Category No. Name
Piano 0
Organ 5
Brass 9
Wood
Gtr 20
Bass 28
1
2
3
4
6
7
8
10
11
12
13
14
15
19
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
29
30
31
Piano
E.Piano
Clavi
Cembalo
Celesta
P.Organ
E.Organ1
E.Organ2
Bandneon
Trumpet
Mute Trp
Trombone
Flugel
Fr Horn
BrasEns
SynBrass
Flute
Clarinet
Oboe
Sax
Gut
Steel
E.Gtr 1
E.Gtr 2
Mute Gtr
Sitar
Pluck 1
Pluck 2
Wood B 1
Wood B 2
E.Bass 1
E.Bass 2
Category No. Name
Bass
Str.
Vocal
Perc.
Synth
37
42
45
54
63
E.Bass 3
E.Bass 4
Slap
Fretless
SynBass1
SynBass2
Strings
Vn.Ens.
Cello
Pizz.
Syn Str
Choir
Itopia
Choir pa
Vibes
Marimba
Bells
Timpani
Tom
E. Tom
Cuica
Whistle
ThumbStr
SynPad
Harmonic
SynLead1
SynLead2
Bell Mix
Sweep
HumanAtk
Noise 1
Noise 2
parameter on the lower display line to directly
select the different wave categories, or under the
right parameter to select individual waves. Use
the [–1/NO] and [+1/YES] keys to select the
desired wave (refer to the wave list, below).
Details: The number of waves available depends on
whether the currently selected element is an
AWM element (A or C) or an FM element (B or
D). The SY35 has 128 preset AWM waves (0 …
127) and 256 preset FM waves (0 … 255).
Category No. Name
Synth 64 PopsHit
SFX
Hits
Tran. 81
OSC 90
73
80
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
91
92
93
94
95
NoisPad1
NoisPad2
NoisPad3
Coin
Crash
Bottle
BotleOpn
Cracker
Scratch
Metal 1
Metal 2
Metal 3
Metal 4
Wood
Bamboo
Slam
Tp. Body
Tb. Body
HornBody
Fl. Body
Str.Body
AirBlown
Reverse1
Reverse2
Reverse3
EP wv
Organ wv
M.Tp wv
Gtr wv
Str wv 1
Str wv 2
Category No. Name
OSC
SEQ
Drum 127 Drum set
118
126
Pad wv
Digital1
Digital2
Digital3
Digital4
Digital5
Saw 1
Saw 2
Saw 3
Saw 4
Square 1
Square 2
Square 3
Square 4
Pulse 1
Pulse 2
Pulse 3
Pulse 4
Pulse 5
Pulse 6
Tri
Sin8’
Sin8’+4’
SEQ 1
SEQ 2
SEQ 3
SEQ 4
SEQ 5
SEQ 6
SEQ 7
SEQ 8
AWM Waveform Category Descriptions
Piano
Organ
Brass
Wood
Gtr
Bass
Str.
Vocal
Perc.
Piano, clavi, and other decay-type keyboard sounds.
Pipe, electric and reed organs.
Acoustic and synthesized brass sounds.
Flute, sax and other woodwind sounds.
Acoustic and electric guitars.
Acoustic, electric, and synth bass.
Violin ensemble and other strings.
Choir and other vocal-type sounds.
Vibes, timpani, etc.
Synth
SFX
Hits
Tran.
OSC
SEQ
Drum
A range of synth sounds (including noise).
Special effects – crash, bottle, etc.
Struck metal and woods.
Transient attack waves and some reverse sounds.
Standard synth waveforms and the basic waveforms
from some actual instruments.
Sequences of sampled sounds.
Drum set waves.
17
Page 23
ELEMENT TONE
101112
14151617181920212223242526
28293031323334
3637383940
4243444546
47
495051
52
54555657585960
61
6364656667
68
70717273747576777879808182838485868788
89
9192939495
96
9899100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
118
119
120
121
122
123
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
143
144
145
147
148
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
172
173
174
175
176
177
220
221
223
224
225
250
251
252
253
254
FM WAVEFORM LIST
Category No. Name
Piano 0
Organ 6
Brass
Wood
Reed
Pluck
1
2
3
4
5
7
8
9
13
27
35
41
48
E.Piano1
E.Piano2
E.Piano3
E.Piano4
E.Piano5
E.Piano6
E.Organ1
E.Organ2
E.Organ3
E.Organ4
E.Organ5
E.Organ6
E.Organ7
E.Organ8
Brass 1
Brass 2
Brass 3
Brass 4
Brass 5
Brass 6
Brass 7
Brass 8
Brass 9
Brass 10
Brass 11
Brass 12
Brass 13
Brass 14
Wood 1
Wood 2
Wood 3
Wood 4
Wood 5
Wood 6
Wood 7
Wood 8
Reed 1
Reed 2
Reed 3
Reed 4
Reed 5
Reed 6
Clavi 1
Clavi 2
Clavi 3
Clavi 4
Guitar 1
Guitar 2
Guitar 3
Category No. Name
Pluck
Bass.
Str.
Perc.
Syn.S
53
62
69
90
97
Guitar 4
Guitar 5
Guitar 6
Guitar 7
Guitar 8
Bass 1
Bass 2
Bass 3
Bass 4
Bass 5
Bass 6
Bass 7
Bass 8
Bass 9
Str 1
Str 2
Str 3
Str 4
Str 5
Str 6
Str 7
Vibes 1
Vibes 2
Vibes 3
Vibes 4
Marimba1
Marimba2
Marimba3
Bells 1
Bells 2
Bells 3
Bells 4
Bells 5
Bells 6
Bells 7
Bells 8
Metal 1
Metal 2
Metal 3
Metal 4
Metal 5
Metal 6
Lead 1
Lead 2
Lead 3
Lead 4
Lead 5
Lead 6
Lead 7
Category No. Name
Syn.S
Syn.M
Syn.D
SFX
117
124
142
146
Sus. 1
Sus. 2
Sus. 3
Sus. 4
Sus. 5
Sus. 6
Sus. 7
Sus. 8
Sus. 9
Sus. 10
Sus. 11
Sus. 12
Sus. 13
Sus. 14
Sus. 15
Attack 1
Attack 2
Attack 3
Attack 4
Attack 5
Move 1
Move 2
Move 3
Move 4
Move 5
Move 6
Move 7
Decay 1
Decay 2
Decay 3
Decay 4
Decay 5
Decay 6
Decay 7
Decay 8
Decay 9
Decay 10
Decay 11
Decay 12
Decay 13
Decay 14
Decay 15
Decay 16
Decay 17
Decay 18
SFX 1
SFX 2
SFX 3
SFX 4
Category No. Name
SFX
OSC 1
OSC 2
OSC 3
149
171
222
255
SFX 5
SFX 6
SFX 7
Sin 16’
Sin 8’
Sin 4’
Sin2 2/3
Sin 2’
Saw 1
Saw 2
Square
LFOnoise
Noise 1
Noise 2
Digi 1
Digi 2
Digi 3
Digi 4
Digi 5
Digi 6
Digi 7
Digi 8
Digi 9
Digi 10
Digi 11
wave1-1
wave1-2
wave1-3
wave2-1
wave2-2
wave2-3
:
:
wave17-1
wave17-2
wave17-3
wave18-1
wave18-2
wave18-3
:
:
wave27-1
wave27-2
wave27-3
wave28
wave29
wave30
FM Voice Category Descriptions
Piano
Organ
Brass
Wood
Reed
Pluck
Bass
Str.
Electric pianos.
Electric organs.
A variety of brass sounds.
Woodwind instrument sounds.
Sax, oboe and other reed instruments.
Guitar, clavi, and other plucked instrument sounds.
Bass sounds.
Strings.
If the TYPE parameter in the ELEMENT
ENVELOPE edit mode (page 27) is set to
PRESET, selecting a WAVE TYPE also selects
18
Perc.
Syn.S
Syn.M
Syn.D
SFX
OSC1
OSC2
OSC3
Vibes, marimba, bells and other percussion sounds.
Sustained lead synth sounds.
Synth sounds that vary with time.
Decay-type synth sounds.
A range of sound-effect type synth sounds.
Sine, sawtooth, and other standard synth waveforms.
Basic FM timbres, group 1.
Basic FM timbres, group 2.
the corresponding preset envelope. If a different
envelope type is selected, the preset envelope is
not selected together with the wave.
Page 24

ELEMENT COPY
ELEMENT TONE
ET>COPYfrom ABCD
any Voice? ->
Summary: Copies all element parameters from an
element of the same type (AWM or FM) in
another voice to the current element of the current voice.
Settings: Source: I, C, P
Bank: 1 … 8
Number: 1 … 8
Element: A/C or B/D
Procedure: Use the [4] and [6] cursor keys to move
the cursor to the source, bank, or number of the
source voice (the voice from which the element
parameters are to be copied) to the left of the
lower display line. Use the [–1/NO] and
[+1/YES] keys to set the selected parameter as
necessary.
Next move the cursor to the element type
parameter to the right of the lower display line,
and select the element from which the data is to
be copied using the [–1/NO] and [+1/YES] keys.
Press the [6] cursor key one more time and the
“Are you sure?” display will appear. Press
[+1/YES] to execute the element copy operation
or [–1/NO] to cancel. “>>Completed!!<<” will
appear briefly when the copy operation has
finished.
Details: In this display the source, bank and number
parameters are shown in the standard SY35
voice number format. “P12,” for example, is
preset bank 1, number 2; “I35” is internal bank
3, number 5, etc.
Data can only be copied between elements of
the same type. If the element currently being
edited is an AWM element (A or C), only element A or C of the source voice can be copied
from. the same applies to FM elements.
The data for all parameters contained in the
ELEMENT TONE mode will be copied.
FREQUENCY SHIFT
ET>FREQ. ABCD
Shift= 0
Summary: Shifts the frequency (pitch) of the
selected element up or down in semitone steps.
Settings: –12 ... 0 … +12.
Procedure: Use the [6] key to move the cursor to
the lower display line. Use the [–1/NO] and
[+1/YES] keys to select the desired amount of
frequency shift.
Details: A setting of “–12,” for example, shifts the
pitch of the selected element down by one octave; a setting of “+4” shifts the pitch up by a
major third.
The Frequency Shift function can be used to
transpose an element to its most useful range, or
to create harmony (intervals) between different
elements.
19
Page 25

ELEMENT TONE
VOLUME
ET>VOLUME ABCD
Level= 0
Summary: Adjusts the volume of the selected ele-
ment.
Settings: 0 ... 99
Procedure: Use the [6] key to move the cursor to
the lower display line. Use the [–1/NO] and
[+1/YES] keys to select the desired volume level.
ET>PAN ÅBCD
L--|--R
Summary: Determines the position in the stereo
sound field in which the sound from selected
element will be heard (left to right).
Settings: Graphic Display: L--+--R, 5 positions from
left to right.
Procedure: Use the [6] key to move the cursor to
the lower display line. Use the [–1/NO] and
[+1/YES] keys to select the desired pan position.
Details: A setting of “0” produces no sound while
a setting of “99” produces maximum volume.
The ability to independently adjust the volume
of each element makes it simple to set up the
optimum balance or “mix” between elements.
PAN
Details: The lower line of the display shows a
graphic representation of the stereo sound field
with “L” representing “left” and “R” representing “right.” As you edit the pan parameter
the position indicator will appear at the corresponding position on the graphic display. A
total of five different positions are available,
corresponding to left, left-center, center, rightcenter, and right.
Interesting stereo effects can be produced by
placing the output from different elements at
different locations in the stereo sound field.
VELOCITY SENSITIVITY
ET>VELOCITY ABCD
Sense= 0 ---
Summary: Determines how the output level of the
selected element changes in response to velocity
changes (keyboard initial touch response).
Settings: –5 ... 0 … +5
Procedure: Use the [6] key to move the cursor to
the lower display line. Use the [–1/NO] and
[+1/YES] keys to select the desired velocity
sensitivity.
20
Details: Plus “+” settings produce higher output
level in response to higher velocity values — i.e.
the harder a key is played, the louder the sound.
Minus “–” settings produce the opposite effect:
lower level in response to higher velocity. A
setting of “0” results in no level variation.
0 No response.
+1 Narrow change between medium-hard and
hard velocity.
Page 26
ELEMENT TONE
+2 Broader change between medium and hard
velocity.
+3 Smooth change all the way from soft to hard
velocity.
+4 Large change over small velocity range.
+5 Sudden change from no sound to maximum
level at about medium velocity.
AFTER TOUCH SENSITIVITY
ET>AFTER ABCD
Sense= 0 ---
Summary: Determines how the output level of the
selected element changes in response to keyboard after touch pressure changes when the
Lev (Level) parameter of the AFTER TOUCH
function in the VOICE COMMON mode is set
to “on” (see page 7).
Settings: –3 ... 0 … +3
Procedure: Use the [6] key to move the cursor to
the lower display line. Use the [–1/NO] and
[+1/YES] keys to select the desired after touch
sensitivity.
Details: Plus “+” settings produce higher output
level in response to higher after touch pressure.
Minus “–” settings produce the opposite effect:
“–” Settings have the same effect, but the
sound level decreases rather than increasing with
increased key velocity. A graphic display to the
right of the sensitivity value provides a visual
indication as to the type of change produced by
each setting.
lower level in response to higher pressure. A
setting of “0” results in no level variation.
0 No response.
+1 Narrow change between medium-high and
high pressure.
+2 Broader change between medium and high
pressure.
+3 Smooth change all the way from low to high
pressure.
“–” Settings have the same effect, but the
sound level decreases rather than increasing with
increased after touch pressure. A graphic
display to the right of the sensitivity value provides a visual clue as to the type of change produced by each setting.
TONE (FM Elements B and D Only)
ET>TONE A>CD
Lev= 0 FB=0
Summary: Adjusts the tone of the selected FM
element — B or D.
Settings: Lev (Level): 0 … 99
FB (Feedback): 0 … 7
Procedure: Use the [4] and [6] cursor keys to place
the underline cursor under the Lev or FB
parameter. Use the [–1/NO] and [+1/YES] keys
to set the level or feedback as required.
Details: The Lev parameter adjusts the modulation
level of the select FM element, so higher values
produce a brighter, sharper tone while lower
values produce a rounder, more mellow tone.
The effect of the feedback parameter varies
from element to element, but in general higher
values make the sound more brassy or noisy,
while lower values make the sound smoother.
21
Page 27

ELEMENT TONE
LFO (Low Frequency Oscillator) AM Depth, PM Depth, Type, Delay, Rate & Speed
● AM (Amplitude Modulation Depth)
ET LFO ABCD
AM= 0 PM= 0
Summary: Determines the maximum amount of
amplitude modulation that can be applied to the
selected element by the modulation wheel or
keyboard after touch.
Settings: 0 ... 15
Procedure: Use the [
the AM parameter. Use the [–1/NO] and
[+1/YES] keys to set the desired degree of
amplitude modulation.
Details: A “0” setting produces no modulation
while a setting of “15” produces maximum
modulation. Amplitude modulation produces a
periodic variation in the volume of the sound,
thus creating a tremolo effect.
Please note that the AM parameter of the
WHEEL and/or AFTER TOUCH function in the
VOICE COMMON edit mode must be set to
“on” before amplitude modulation can be
applied manually (see page 7). Amplitude
modulation is applied automatically when these
parameters are off.
● PM (Pitch Modulation Depth)
4] and [6] cursor keys to select
Details: A “0” setting produces no modulation
while a setting of “31” produces maximum
modulation. Pitch modulation produces a
periodic pitch variation, thereby creating a
vibrato effect.
Please note that the PM parameter of the
WHEEL and/or AFTER TOUCH function in the
VOICE COMMON edit mode must be set to
“on” before pitch modulation can be applied
manually. Pitch modulation is applied automatically when these parameters are off.
● Type
ET LFO ABCD
AM= 0 PM= 0
Summary: Determines the waveform of the LFO
for the selected element.
Settings:
SAW UP SAW DOWN TRIANGLE
SQUARE SAMPLE&HOLD
Procedure: Use the [4] and [6] cursor keys to select
the waveform parameter. Use the
[–1/NO] and [+1/YES] keys to select the desired
LFO waveform.
ET LFO ABCD
AM= 0 PM= 0
Summary: Determines the maximum amount of
pitch modulation that can be applied to the
selected element by the modulation wheel or
keyboard after touch.
Settings: 0 ... 31
Procedure: Use the [
the PM parameter. Use the [–1/NO] and
[+1/YES] keys to set the desired degree of pitch
modulation.
22
4] and [6] cursor keys to select
Details:
= Upward sawtooth.
= Downward sawtooth.
= Triangle.
= Square.
= Sample and hold.
Page 28

ELEMENT TONE
● Dly (Delay)
ET LFO ABCD
˚Dly= 0 Rate= 0->
Summary: Sets the delay time between the begin-
ning of a note and the beginning of LFO operation for the selected element when the WHEEL
and AFTER TOUCH parameters in the VOICE
COMMON edit mode are both turned off.
Settings: 0 ... 99
Procedure: Use the [
the Dly parameter. Use the [–1/NO] and
[+1/YES] keys to set the desired LFO delay.
Details: The minimum setting “0” results in no
delay, while the maximum setting of “99” produces maximum delay before the LFO begins
operation.
● Rate
4] and [6] cursor keys to select
ET LFO ÅBCD
˚Dly= 0 Rate= 0->
Summary: Sets the rate of LFO “fade in” for the
selected element when the WHEEL and AFTER
TOUCH parameters in the VOICE COMMON
edit mode are both turned off.
Procedure: Use the [
the Rate parameter. Use the [–1/NO] and
[+1/YES] keys to set the desired LFO fade-in
rate.
Details: “0” is the fastest rate, causing the LFO to
start operation at full depth immediately. A setting of 99 produces the longest LFO fade in.
● Spd (Speed)
4] and [6] cursor keys to select
ET LFO ABCD
˚Spd= 0
Summary: Sets the speed of the LFO for the
selected element.
Settings: 0 ... 31
Procedure: Use the [
the Spd parameter. Use the [–1/NO] and
[+1/YES] keys to set the desired LFO speed.
Details: “0” is slowest LFO speed setting; “31” is
the fastest.
The speed parameter can not be edited when the
sample-and-hold (
4] and [6] cursor keys to select
) LFO TYPE is selected.
º–º
Settings: 0 ... 99
23
Downloaded from:
Page 29

ELEMENT TONE
24
Page 30

ELEMENT ENVELOPE
ELEMENT ENVELOPE
The ELEMENT ENVELOPE edit mode allows detailed programming of the amplitude
envelopes for each element in the selected voice.
TYPE............................................................................................................................. 27
ENVELOPE COPY......................................................................................................... 28
DELAY (Delay Rate & ON/OFF).................................................................................... 28
INITIAL LEVEL............................................................................................................ 28
ATTACK (Level & Rate)............................................................................................... 29
DECAY 1 (Level & Rate)............................................................................................... 29
DECAY 2 (Level & Rate)............................................................................................... 29
RELEASE RATE............................................................................................................ 30
LEVEL SCALING........................................................................................................... 30
RATE SCALING............................................................................................................. 31
25
Page 31

ELEMENT ENVELOPE
➯
➯
➯
➯
Selecting the ELEMENT ENVELOPE Edit Mode
From the VOICE or MULTI mode:
From another edit or utility mode simply press
[ELEMENT ENVELOPE].
An “E” will appear to the left of the LED display to indicate that an edit mode is selected,
and the element selected for editing will be displayed to the right of the display — “A”, “b”,
“C”, or “d”. A dot will appear to the right of
the element character as soon as any parameter
has been edited.
ON, if a dash appears in place of the element
character, that element is OFF. The ability to
turn elements on or off while editing makes it
easier to hear the effect of parameter changes on
a single element. The currently selected element
is also shown on the LCD as a reversed (white on
black) character.
In this example elements A, B and D are ON, while
element C is OFF. Element A is currently selected
for editing.
ET@TYPE ÅB-D
USER
Selecting the ELEMENT ENVELOPE Edit Mode
Functions
The various ELEMENT ENVELOPE edit mode
functions can be selected in sequence by pressing the [ELEMENT ENVELOPE] key, or by
using the [–1/NO] and [+1/YES] keys when the
cursor (6)is located immediately before the
function name on the upper display line.
Different elements can be selected for editing by
pressing the appropriate [ELEMENT SELECT]
key — [A], [B], [C] or [D]. If a 2-element voice
is being edited, only elements A and B can be
selected.
Any of the available elements can also be turned
on or off by pressing the appropriate
[ELEMENT ON/OFF] key. Each key alternately
turns the associated element on and off, and the
on/off status of the elements is shown to the
right of the upper LCD line. If the element
character is showing, the associated element is
The COMPARE Function
You can compare the sound of the edited voice
with the sound of the voice before it was edited
by pressing the [EDIT/COMPARE] key to activate the COMPARE function. A “C” will
appear on the LED display while the COMPARE
function is active, and the sound of the voice
prior to editing will be heard when you play the
keyboard. Press the [EDIT/COMPARE] key
again to return to the edit mode.
26
Page 32

TYPE
ELEMENT ENVELOPE
EE>TYPE ÅBCD
USER
Summary: Selects a user or preset amplitude enve-
lope for the selected element.
Settings: PRESET, PIANO, GUITAR, PLUCK,
BRASS, STRINGS, ORGAN, USER
Procedure: Use the [6] key to move the cursor to
the lower display line. Use the [–1/NO] and
[+1/YES] keys to select the desired envelope.
Details: When “PRESET” is selected, the original
envelope of the wave selected for the current
element is used. For example, if the current uses
a guitar wave corresponding guitar envelope will
be selected.
When “PIANO,” “GUITAR,” “PLUCK,”
“BRASS,” “STRINGS,” or “ORGAN” is
selected, a generic envelope of the appropriate
type is used. Then piano, organ and strings
envelopes are roughly as shown below:
PLUCK
LEVEL
TIME
BRASS
LEVEL
TIME
STRINGS
LEVEL
PIANO
LEVEL
LEVEL
GUITAR
TIME
TIME
TIME
ORGAN
LEVEL
TIME
Editing any of the envelope parameters for one
of the above types turns the envelope into a
“USER” type.
When “USER” is selected, an original envelope
can be programmed using the attack, decay, and
release parameters described on pages 29, 30.
27
Page 33

ELEMENT ENVELOPE
ENVELOPE COPY
EE>COPYfrom ÅBCD
any Element? ->
Summary: Copies envelope parameters from a
selected element to the current element.
Settings: Element: A, B, C, D
Procedure: Use the [4] and [6] cursor keys to move
the cursor to the “from” element parameter.
Use the [–1/NO] and [+1/YES] keys to select the
element from which the envelope data is to be
copied.
DELAY (Delay Rate & ON/OFF)
EE>DELAY ÅBCD
Rate= 0 off
Summary: Sets a delay before the envelopes of all
elements begin.
Settings: Delay: 0 … 99
Mode: on/off
Procedure: Use the [4] and [6] cursor keys to move
the cursor to the “Rate” parameter. Use
Press the [6] cursor key one more time and the
“Are you sure?” display will appear. Press
[+1/YES] to execute the copy operation or
[–1/NO] to cancel. “>>Completed!!<<” will
appear briefly when the copy operation has
finished.
Details: This function can save a lot of
programming time by allowing easy copying of
complex USER type envelope data between
elements.
the [–1/NO] and [+1/YES] keys to select the
desired delay rate.
Press the [6] cursor key one more time to move
to the on/off mode parameter, and use the
[–1/NO] and [+1/YES] keys to set as required.
Details: The envelope delay rate parameter affects
all envelopes simultaneously. A setting of “0”
produces almost no delay while a setting of
“99” produces maximum delay.
INITIAL LEVEL
EE>INITIAL ÅBCD
Level= 0
Summary: Sets the starting level of the amplitude
envelope for the current element.
Settings: 0 … 99
Procedure: Use the [6] cursor key to move the cur-
sor to the lower display line. Use the [–1/NO]
and [+1/YES] keys to set the initial level.
Details: A setting of “0” means that the envelope
will begin from zero (minimum) level, while a
setting of “99”causes the envelope to begin
28
immediately from maximum level. The highest
setting produces the sharpest attack.
Attack rate
Attack
level
•
Initial
level
LEVEL
•
Key ON (Delay off) Key OFF
Decay
1 rate
•
Decay
1 level
Decay
2 rate
TIME
Decay 2
level
•
Release
rate
Page 34

ATTACK (Level & Rate)
ELEMENT ENVELOPE
EE>ATTACK ÅBCD
AL= 0 AR= 0
Summary: Sets the rate and peak level of the attack
of the amplitude envelope for the current element.
Settings: AL (Attack Level): 0 … 99
AR (Attack Rate): 0 … 99
Procedure: Use the [4] and [6] cursor keys to move
the cursor to the “AL” or “AR” parameter.
Use the [–1/NO] and [+1/YES] keys to set the
selected level or rate parameter.
DECAY 1 (Level & Rate)
EE>DECAY1 ÅBCD
D1L= 0 D1R= 0
Summary: Sets the rate and final level of the first
decay of the amplitude envelope for the current
element.
Settings: D1L (Decay 1 Level): 0 … 99
D1R (Decay 1 Rate): 0 … 99
Procedure: Use the [4] and [6] cursor keys to move
the cursor to the “D1L” or “D1R” parameter.
Details: Refer to the INITIAL LEVEL function for
a complete envelope diagram.
A rate setting of “0” produces the slowest
attack, and a setting of “99” produces the
fastest attack.
A level setting of “0” produces the lowest
attack level, while a setting of “99” produces
the highest level.
Please note that the attack may be “biased” by
the ENVELOPE Attack Rate parameter in the
VOICE COMMON edit mode.
Use the [–1/NO] and [+1/YES] keys to set the
selected level or rate parameter.
Details: Refer to the INITIAL LEVEL function for
a complete envelope diagram.
A rate setting of “0” produces the slowest decay, and a setting of “99” produces the fastest
decay.
A level setting of “0” produces the lowest decay level, while a setting of “99” produces the
highest level.
DECAY 2 (Level & Rate)
EE>DECAY2 ÅBCD
D2L= 0 D2R= 0
Summary: Sets the rate and final level of the
second decay of the amplitude envelope for the
current element.
Settings: D2L (Decay 2 Level): 0 … 99
D2R (Decay 2 Rate): 0 … 99
Procedure: Use the [4] and [6] cursor keys to move
the cursor to the “D2L” or “D2R” parameter.
Use the [–1/NO] and [+1/YES] keys to set the
selected level or rate parameter.
Details: Refer to the INITIAL LEVEL function for
a complete envelope diagram.
A rate setting of “0” produces the slowest decay, and a setting of “99” produces the fastest
decay.
A level setting of “0” produces the lowest decay level, while a setting of “99” produces the
29
Page 35

Page 36

Page 37

ELEMENT ENVELOPE
32
Page 38

MULTI
The MULTI edit mode allows 8 different voices to be assigned to different MIDI channels.
The assigned voices can then be individually controlled over the appropriate channels from
an external MIDI sequence recorder or other controller. If a number of these channel/voice
“parts” are assigned to the MIDI transmit channel of the SY35, they can all be played
simultaneously from the SY35 keyboard. Individual characteristics of each voice, such as
volume and detune, can also be programmed.
NAME............................................................................................................................ 35
EFFECT (Type & Depth)............................................................................................... 35
VOICE NUMBER........................................................................................................... 35
MIDI RECEIVE CHANNEL........................................................................................... 36
VOLUME....................................................................................................................... 36
DETUNE........................................................................................................................ 37
NOTE LIMIT (Low & High).......................................................................................... 37
NOTE SHIFT................................................................................................................. 37
MULTI
33
Page 39

Page 40

NAME
MULTI
MU>NAME
P11 Initial
Summary: Assigns a name of up to 8 characters to
the current multi-play setup.
Settings: The following characters are available for
use in multi-play names:
(Space) !"#¢%&'()*+,-./0123456789:;<=>?Å
ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ[Á]^_«
abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz“|‘Ÿ˚
EFFECT (Type & Depth)
MU>EFFECT
Rev Hall Dep=1
Summary: Selects one of sixteen digital effects, and
sets the depth of the selected effect for the current multi-play setup.
Procedure: Use the [4] and [6] cursor keys to place
the underline cursor under the character to be
changed. Use the [–1/NO] and [+1/YES] keys to
select the desired character. Continue until the
entire multi-play name has been programmed.
Details: It’s a good idea to give your multi-play se-
tups names that make them easily identifiable.
If you’ve created a new setup using three voices
intended for rock music, you could call it something like “RockTrio”.
Depth: 0 … 7
Procedure: Use the [4] and [6] cursor keys to place
the underline cursor under the effect type or
depth parameter. Use the [–1/NO] and [+1/YES]
keys to select the desired effect or effect depth.
Settings: Effect type:
Rev Hall (Reverb Hall)
Rev Room (Reverb Room)
Rev Plate (Reverb Plate)
Rev Club (Reverb Club)
Rev Metal (Reverb Metal)
Delay 1 (Short Single Delay)
Delay 2 (Long Delay)
Delay 3 (Long Delay)
Doubler (Doubler)
Ping-Pong (Ping Pong Delay)
Pan Ref (Panned Reflections)
Early Ref (Early Reflections)
Gate Rev (Gated Reverb)
Dly&Rev 1 (Delay & Reverb 1)
Dly&Rev 2 (Delay & Reverb 2)
Dist&Rev (Distortion & Reverb)
MU>VOICE NUMBER
I11 Initial
Details: Setting the depth parameter to “0” is
equivalent to turning the effect OFF. A depth
setting of “7” produces the greatest effect.
VOICE NUMBER
Summary: Assigns a preset, card or internal voice
to the selected multi-play part.
35
Page 41

MULTI
Settings: Source: I, C, P
Bank: 1 … 8
Number: 1 … 8
Procedure: Press the [NUMBER/MULTI PART
SELECT] key corresponding to the desired
multi-play part.
Use the [4] and [6] cursor keys to move the cursor to the source, bank, or number parameter.
Use the [–1/NO] and [+1/YES] keys to set the
selected parameter as necessary.
MIDI RECEIVE CHANNEL
MU>MIDI Rcv.ch
channel= 1
Summary: Sets the MIDI receive channel for the
selected multi-play part to any channel between
1 and 16, or off.
Settings: 0 ... 16, off
Procedure: Press the [NUMBER/MULTI PART
SELECT] key corresponding to the desired
multi-play part.
Details: In this display the source, bank and number
parameters are shown in the standard SY35
voice number format. “P12,” for example, is
preset bank 1, number 2; “I35” is internal bank
3, number 5, etc.
Use the [6] cursor key to move the cursor to the
lower display line. The [–1/NO] and [+1/YES]
keys are used to select the desired MIDI channel
or turn MIDI reception for that part off.
Details: The most logical and easy-to-follow set-
tings for multi-play parts 1 through 8 are, naturally, MIDI channels 1 through 8. Turn MIDI
reception “off” for parts you do not intend to
use.
VOLUME
MU>VOLUME
Level= 0
Summary: Adjusts the volume of the selected
multi-play part.
Settings: 0 ... 99
Procedure: Press the [NUMBER/MULTI PART
SELECT] key corresponding to the desired
multi-play part.
Use the [6] cursor key to move the cursor to the
lower display line. Use the [–1/NO] and
[+1/YES] keys to select the desired volume level.
Details: A setting of “0” produces no sound while
a setting of “99” produces maximum volume.
The ability to independently adjust the volume
of each multi-play part makes it simple to set up
the optimum balance or “mix” between parts.
36
Page 42

DETUNE
MULTI
MU>DETUNE
0cent
Summary: Allows slight upward or downward pitch
adjustment of the selected multi-play part.
Settings: –50 ... 0 … +50
Procedure: Press the [NUMBER/MULTI PART
SELECT] key corresponding to the desired
multi-play part.
Use the [6] cursor key to move the cursor to the
lower display line. Use the [–1/NO] and
[+1/YES] keys to select the desired amount of
detuning.
NOTE LIMIT (Low & High)
MU>NOTE LIMIT
Low= C-2 High= G8
Summary: Sets the low and high note limits for the
selected multi-play part.
Settings: C-2 ... G8
Procedure: Press the [NUMBER/MULTI PART
SELECT] key corresponding to the desired
multi-play part.
Use the [4] and [6] cursor keys to select the Low
or High parameter. The [–1/NO] and [+1/YES]
keys are used to set the low or high note limit.
Details: The Detune function allows different parts
in a multi-play setup to be slightly detuned in
relation to each other, thereby “thickening” the
overall sound.
Detuning occurs in 3 or 4-cent steps. Since 100
cents equals one semitone, the overall detune
range is approximately one semitone. Plus settings tune upward from normal pitch, and minus
settings tune downward. A setting of “0” produces normal pitch.
This function allows the sound from a multiplay part to be limited to a specific region of the
keyboard. If the Low Note Limit is set to C3 and
the High Note Limit is set to C4, for example,
the sound from that part will only be produced
between C3 and C4 — the octave immediately
above middle C. This makes it simple to
produce split voices.
If the High Note Limit is set to a note that is
lower than the Low Note Limit, the keys between
the limits will produce no sound while all others
will operate normally.
Details: The C-2 to G8 range of this function covers
a full 10-1/2 octaves. “C3” corresponds to
“middle C” on a keyboard.
MU>NOTE SHIFT
0
NOTE SHIFT
Summary: Shifts the pitch of the selected multi-
play part up or down in semitone steps.
37
Page 43

MULTI
Settings: –24 ... 0 … +24.
Procedure: Press the [NUMBER/MULTI PART
SELECT] key corresponding to the desired
multi-play part.
Use the [6] cursor key to move the cursor to the
lower display line. Use the [–1/NO] and
[+1/YES] keys to select the desired degree of
note shift.
Details: A setting of “–12,” for example, shifts the
pitch of the selected voice down by one octave;
a setting of “+4” shifts the pitch up by a major
third. The maximum range is plus or minus two
octaves.
The Note Shift function can be used to
transpose a voice to its most useful range, or to
create harmony (intervals) between different
parts in a multi-play setup.
38
Page 44

UTILITY SETUP
UTILITY SETUP
The UTILITY SETUP mode provides access to a range of basic utility functions that are
essential for general operation of the SY35.
MASTER TUNE............................................................................................................. 41
TRANSPOSE.................................................................................................................. 41
MEMORY CARD (Save, Load, Format, & Bank)............................................................ 41
VOICE INITIALIZE....................................................................................................... 43
MULTI INITIALIZE..................................................................................................... 44
MEMORY PROTECT (Internal & Card)........................................................................ 45
FACTORY VOICE & MULTI RESTORE....................................................................... 45
39
Page 45

Page 46

MASTER TUNE
UTILITY SETUP
SU>MASTER TUNE
0cent
Summary: Tunes the overall pitch of the SY35 over
approximately a 100-cent range.
Settings: –50 ... 0 … +50
Procedure: Use the [6] key to move the cursor to
the lower display line. Use the [–1/NO] and
[+1/YES] keys to set the desired degree of
tuning.
TRANSPOSE
SU>TRANSPOSE
0
Summary: Transposes the overall pitch of the SY35
up or down in semitone steps.
Settings: –12 ... 0 … +12
Details: Tuning occurs in 3 or 4-cent steps. Since
100 cents equals one semitone, the overall tuning range is approximately one semitone — i.e.
plus or minus a quarter tone. Plus settings tune
upward from normal pitch, and minus settings
tune downward. A setting of “0” produces normal pitch.
Procedure: Use the [6] key to move the cursor to
the lower display line. Use the [–1/NO] and
[+1/YES] keys to set the desired degree of
transposition.
Details: A setting of “–12,” for example, trans-
poses down by one octave; a setting of “+4”
transposes up by a major third.
MEMORY CARD (Save, Load, Format, & Bank)
● Save
SU CARD
>SAVE
Summary: Saves all internal voice and multi-play
data to a memory card.
Settings: SAVE
Procedure: Use the [6] key to move the cursor to
the lower display line, then use the [–1/NO] and
[+1/YES] keys to select “SAVE.” Now press the
[6] key again and the “SAVE TO CARD?”
display will appear. Press the [+/YES] key to
start the save operation, or the [–1/NO] key to
cancel. “****SAVE NOW****” will appear
on the display while the operation is in progress,
and “>>Completed!!<<” will appear briefly
when the save operation has finished.
Details: The SAVE operation can only be executed
if the CARD parameter of the MEMORY
PROTECT function described on page 45 is
turned “off,” and the WRITE PROTECT switch
of the MCD32 or MCD64 Memory Card loaded
in into the CARD slot is turned “off.”
When an MCD64 Memory Card is used, the
bank to which the data is to be save can be
selected using the BANK function described on
page 42.
41
Page 47

UTILITY SETUP
Exercise caution when saving data to a memory
card — the previous card data will be erased and
completely replaced by the saved data.
● Load
SU CARD
>LOAD
Summary: Loads voice and multi-play data from a
memory card into the SY35 internal memory.
Settings: LOAD
Procedure: Use the [6] key to move the cursor to
the lower display line, then use the [–1/NO] and
[+1/YES] keys to select “LOAD.” Now press
the [6] key again and the “LOAD from
CARD?” display will appear. Press the [+1/YES]
key to start the load operation, or the [–1/NO]
key to cancel. “****LOAD NOW****” will
appear on the display while the operation is in
progress, and “>>Completed!!<<” will appear
briefly when the load operation has finished.
Summary: Formats MCD64 or MCD32 Memory
Cards so that they can be used by the SY35 to
save and load voice and multi-play data.
Settings: FORMAT
Procedure: Use the [6] key to move the cursor to
the lower display line, then use the [–1/NO] and
[+1/YES] keys to select “FORMAT.” Now press
the [6] key again and the “FORMAT ?”
display will appear. Press the [+1/YES] key to
start the format operation, or the [–1/NO] key to
cancel. “>>Completed!!<<” will appear briefly
when the format operation has finished.
Details: Formatting can only be carried out if the
memory card WRITE PROTECT switch is
turned OFF (refer to your MCD64 or MCD32
Memory Card instructions for details).
● Bank
SU CARD
>BANK 1
Details: The LOAD operation can only be executed
if the INTERNAL parameter of the MEMORY
PROTECT function described on page 45 is
turned “off.”
When an MCD64 Memory Card is used, the
bank from which the data is to be loaded can be
selected using the BANK function described on
this page.
Exercise caution when loading data from a
memory card — the corresponding internal
SY35 data will be erased and completely
replaced by the loaded data.
● Format
SU CARD
>FORMAT
Summary: Selects bank 1 or bank 2 of a Yamaha
MCD64 type memory card prior to formatting
or load/save operations.
Settings: 1, 2
Procedure: Use the [6] key to move the cursor to
the lower display line, then use the [–1/NO] and
[+1/YES] keys to select “BANK.” Now press
the [6] key again to move the cursor to the bank
number. Use the [–1/NO] and [+1/YES] keys to
select the desired bank.
Details: MCD32 memory cards only have a single
bank, so bank 2 cannot be selected if this type
of card is used. MCD64 memory cards allow
selection of bank 1 or 2. Each bank holds 64
voices and 16 multi-play setups.
42
Page 48

VOICE INITIALIZE
+
+
+
+
UTILITY SETUP
SU>INIT. VOICE
Summary: Initializes all parameters of the current
voice.
Settings: None.
Procedure: Select the UTILITY SETUP mode from
the VOICE play mode. Then, after selecting the
“INIT. VOICE” display, press the [6] key.
INITIAL VOICE
COMMON
VOICE NAME
CONFIGURATION
EFFECT
Dep
PITCH BEND
WHEEL AM
PM
AFTER TOUCH AM
PM
Pit
Lev
ENVELOPE AR
RR
VECTOR
VECTOR LEVEL SPEED
STEP/X/Y/TIME
Initial
A–B–C–D
Rev. Hall
1
2
off
on
off
off
0
off
0
0
30 ms
1 0 0 End
“Are you sure?” will appear on the lower line
of the display. Press the [+1/YES] to initialize or
[–1/NO] to cancel the initialize operation.
“>>Completed!!<<” will appear briefly when
the initialization is finished.
Details: When Voice Initialize is executed, the voice
parameters are initialized to the following
values:
VECTOR DETUNE SPEED
STEP/X/Y/TIME
ELEMENT TONE
WAVE
FREQ. shift
VOLUME
PAN
VELOCITY Sense
AFTER Sense
TONE Lev
TONE FB
LFO AM
LFO PM
LFO TYPE
LFO Dly
LFO Rate
LFO Spd
30 ms
1 0 0 End
A B C D
000:PIANO:PIANO
0
99
L-- --R
2
0
—
—
0
16
0
99
20
151:OSC1:sin8’
0
99
L-- --R
2
0
92
0
0
16
0
99
20
039:Str:Vn.Ens
0
99
L-- --R
2
0
—
—
0
16
0
99
20
152:OSC1:sin4’
0
99
L-- --R
2
0
92
0
0
16
0
99
20
43
Page 49

UTILITY SETUP
A B C D
ELEMENT ENV
TYPE
DELAY Rate
DELAY ELE.
INITIAL Level
ATTACK AL
ATTACK AR
DECAY1 D1L
DECAY1 D1R
DECAY2 D2L
DECAY2 D2R
RELEASE Rate
SCALING Lev Type
Rate Type
PRESET
99
off
67
99
99
99
0
0
26
60
2
3
The voice initialize function is useful if you
want to begin programming a voice “from
scratch.”
MULTI INITIALIZE
PRESET
99
off
0
92
99
92
0
92
0
76
1
1
PRESET
99
off
90
97
64
95
32
95
0
52
4
2
PRESET
99
off
0
92
99
92
0
92
0
76
1
1
SU>INIT. MULTI
“Are you sure?” will appear on the lower line
of the display. Press the [+1/YES] to initialize or
[–1/NO] to cancel the initialize operation.
Summary: Initializes all parameters of the current
multi-play setup.
Settings: None.
“>>Completed!!<<” will appear briefly when
the initialization is finished.
Details: When multi-play Initialize is executed, the
multi-play setup parameters are initialized to the
Procedure: Select the UTILITY SETUP mode from
following values:
the MULTI play mode. Then, after selecting the
“INIT. MULTI” display, press the [6] key.
INITIAL MULTI
PART1 PART2 PART3 PART4 PART5 PART6 PART7 PART8
NAME Initial
EFFECT Rev Hall
EFFECT Dep 1
VOICE NUMBER P11 AP:Rock P11 AP:Rock P11 AP:Rock P11 AP:Rock P11 AP:Rock P11 AP:Rock P11 AP:Rock P11 AP:Rock
MIDI Rcv.ch 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
VOLUME 99 99 99 99 99 99 99 99
DETUNE 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
NOTE LIMIT Low c-2 c-2 c-2 c-2 c-2 c-2 c-2 c-2
NOTE LIMIT High G8 G8 G8 G8 G8 G8 G8 G8
NOTE SHIFT 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
The multi initialize function is useful if you
want to begin programming a voice “from
44
scratch.”
Page 50

MEMORY PROTECT (Internal & Card)
UTILITY SETUP
SU>MEM.PROTECT
INT=on CARD=on
Summary: Turns internal or card memory
protection on or off.
Settings: INT: on, off
CARD: on, off
Procedure: Use the [4] and [6] cursor keys to select
the INT or CARD parameter. Use
[–1/NO] and [+1/YES] keys to turn memory
protection on or off.
FACTORY VOICE & MULTI RESTORE
SU>FACTORY V&M
Summary: Restores the factory-preset voices and
multi-play setups in the INTERNAL VOICE and
MULTI memory areas.
Procedure: Make sure the internal memory protect
function is turned OFF before using this
function (see “MEMORY PROTECT” above).
From the initial “SU>FACTORY V&M” display press [6] cursor key. “Are you sure?” will
appear on the display. Press the [+1/YES] key if
you want to go ahead with the factory voice and
multi restore operation, or press
[–1/NO] to cancel. If you press [+1/YES],
“>>Completed!!<<” will appear on the display
when the restore operation has finished.
Details: When INT memory protection is “on,” the
internal memory is protected and voice store
operations to the internal memory cannot be
carried out. The same applies to card memory:
when protection is “on” memory card save
operations will be blocked even if the memory
card WRITE PROTECT switch is turned OFF.
Details: When the factory voice and multi restore
operation is executed, all data in the SY35 internal voice and multi memory areas is overwritten
by the factory preset data. Make sure you save
important voice and multi data to memory card
or an external MIDI data filer prior to restoring
the factory preset data.
If you attempt to execute the factory voice and
multi restore operation when internal memory
protect is turned ON, “Memory Protected” will
appear on the display and the restore operation
will be aborted.
45
Page 51

UTILITY SETUP
46
Page 52

UTILITY RECALL
UTILITY RECALL
The UTILITY RECALL mode accesses the VOICE or MULTI recall function, depending
on whether the VOICE or MULTI play mode is selected when the RECALL function is
called. RECALL makes it possible to recover a voice or multi-play setup that has been
“lost” through failure to store the voice or multi-play setup prior to selecting a different
voice or multi-play setup.
Voice Recall (Voice or Multi).......................................................................................... 49
47
Page 53

Page 54

VOICE RECALL (Voice or Multi)
UTILITY RECALL
RC RECALL VOICE
Are you sure?
Summary: Recalls the last voice or multi-play setup
edited from the SY35 edit buffer memory.
Settings: None
Procedure: The “RECALL VOICE” function is
selected if called from the VOICE play mode,
while “RECALL MULTI” function is selected
if called from the MULTI play mode. “Are you
sure?” appears on the lower display line. Press
the [+1/YES] key to recall or [–1/NO] to cancel
the recall operation.
Details: Even if you’ve exited the edit mode and
called a different voice or multi-play setup, this
function will recall the last voice or multi-play
setup edited with all parameters as they were at
the time the edit mode was exited.
49
Page 55

UTILITY RECALL
50
Page 56

UTILITY MIDI
UTILITY MIDI
The UTILITY MIDI mode provides access to all of the SY35’s MIDI control functions.
MIDI ON/OFF................................................................................................................ 53
BASIC RECEIVE CHANNEL.......................................................................................... 53
TRANSMIT CHANNEL................................................................................................. 53
LOCAL CONTROL ON/OFF.......................................................................................... 54
MIDI PROGRAM CHANGE........................................................................................... 54
MIDI CONTROL CHANGE............................................................................................ 54
AFTER TOUCH ON/OFF............................................................................................... 55
PITCH BEND ON/OFF................................................................................................... 55
EXCLUSIVE ON/OFF..................................................................................................... 55
ALL V/M TRANSMIT.................................................................................................... 56
1 VOICE TRANSMIT..................................................................................................... 56
51
Page 57

Page 58

MIDI ON/OFF
UTILITY MIDI
MD>MIDI
midi=on
Summary: Turns all MIDI control functions on or
off.
Settings: on, off
Procedure: Use the [6] cursor key to move the cur-
sor to the lower display line. Use the [–1/NO]
and [+1/YES] keys to turn MIDI control on or
off.
BASIC RECEIVE CHANNEL
MD>BASIC Rcv.CH
channel= 1
Summary: Sets the SY35 MIDI receive channel to
any channel between 1 and 16, or the “omni”
mode for reception on all channels.
Settings: 1 ... 16, omni
Details: MIDI control can be turned “off” to
prevent unwanted interference from external
MIDI devices connected to the SY35, and/or to
prevent the SY35 from affecting operation of
the external equipment.
and [+1/YES] keys are used to select the desired
MIDI channel or the omni mode.
Details: When the SY35 is to receive data from an
external MIDI device such as a sequencer, make
sure that the SY35 MIDI receive channel is
either set to the channel that the external device
is transmitting on, or the omni mode.
Procedure: Use the [6] cursor key to move the
cursor to the lower display line. The [–1/NO]
TRANSMIT CHANNEL
MD>TRANSMIT CH
channel= 1
Summary: Sets the MIDI transmit channel for the
SY35.
Settings: 1 … 16.
Procedure: Use the [6] cursor key to move the cur-
sor to the lower display line. Use the [–1/NO]
and [+1/YES] keys to select the desired MIDI
transmit channel number.
Details: The MIDI transmit channel job is used
primarily to match the transmit channel of the
SY35 with the receive channel of an external
MIDI device being driven by the SY35. When a
multi-play setup is selected, however, the MIDI
transmit channel setting also determines which
of the setup’s voices is played via the SY35
keyboard.
53
Page 59

UTILITY MIDI
LOCAL CONTROL ON/OFF
MD>LOCAL
Local=on
Summary: Determines whether the SY35 keyboard
controls the internal tone generator system or
not.
Settings: on, off.
Procedure: Use the [6] cursor key to move the cur-
sor to the lower display line. Use the [–1/NO]
and [+1/YES] keys to turn local control on or
off.
MIDI PROGRAM CHANGE
MD>PROG.CHANGE
=off
Summary: Determines how the SY35 will respond
to MIDI program change messages for remote
voice/multi selection.
Settings: off, common, individual
Procedure: Use the [6] cursor key to move the
cursor to the lower display line. The [–1/NO]
and [+1/YES] keys are used to select the desired
MIDI program change mode.
Details: The “off” setting turns MIDI program
change reception and transmission off, so MIDI
program change messages received from external equipment will not cause the corresponding
SY35 voice to be selected, and no program
change messages will be transmitted by the
SY35 when one of its voices are selected.
Details: Normally, local control will be turned
“on” so that the SY35 keyboard plays its own
internal tone generator system. If you want to
control an external MIDI tone generator or
other device from the SY35 keyboard without
playing the internal tone generator, turn local
control “off.” One possibility is to drive the
SY35 tone generator system from an external
sequencer while independently playing a
separate external tone generator from the SY35
keyboard.
In the “common” mode, program change
numbers 0 through 63 received from external
equipment will select SY35 voices 1.1 through
8.8, and program change numbers 64 through
79 select multi-play setups 1.1 through 2.8. The
card, internal or preset voice banks cannot be
selected via MIDI control. The corresponding
program change number will also be transmitted
by the SY35 when one of its voices are selected.
The “individual” mode allows individual voice
selection for each multi-play part when the
MULTI play mode is active. Program change
between 0 and 63 received in a specific MIDI
channel will change only the voice for the multiplay part assigned to that channel.
MIDI CONTROL CHANGE
MD>CTRL.CHANGE
=off
54
Summary: Determines whether or not the SY35 will
receive and transmit MIDI control change messages.
Settings: off, on
Page 60

UTILITY MIDI
Procedure: Use the [6] cursor key to move the
cursor to the lower display line. The [–1/NO]
and [+1/YES] keys are used to turn control
change reception/transmission on or off.
AFTER TOUCH ON/OFF
MD>AFTER TOUCH
=on
Summary: Turns keyboard after touch on or off.
Settings: on, off.
Procedure: Use the [6] cursor key to move the cur-
sor to the lower display line. Use the [–1/NO]
and [+1/YES] keys to turn after touch on or off.
Details: The “off” setting turns MIDI control
change reception and transmission off so that
control change messages corresponding to
modulation, volume and other functions will be
ignored by the SY35 when received, and the
SY35 will not transmit any control change
messages.
Details: When after touch is turned “off,” internal
SY35 after touch will function normally but no
MIDI after touch data will be transmitted or
received.
Keyboard after touch generates a tremendous
amount of MIDI data, so you might want to turn
after touch “off” when recording to a MIDI
sequencer in order to preserve memory
capacity.
PITCH BEND ON/OFF
MD>PITCH BEND
=on
Summary: Turns pitch bend control on or off.
Settings: on, off.
EXCLUSIVE ON/OFF
MD>EXCLUSIVE
=on
Summary: Turns transmission/reception of MIDI
system exclusive data on or off.
Procedure: Use the [6] cursor key to move the cur-
sor to the lower display line. Use the [–1/NO]
and [+1/YES] keys to turn pitch bend control on
or off.
Details: When pitch bend control is turned “off,”
the SY35 pitch bend wheel will function
normally but no MIDI pitch bend wheel data
will be transmitted or received.
Procedure: Use the [6] cursor key to move the cur-
sor to the lower display line. Use the [–1/NO]
and [+1/YES] keys to exclusive transmission/reception on or off.
Settings: on, off.
55
Page 61

UTILITY MIDI
Details: MIDI system exclusive data is transmitted
by the SY35 when one of the voice transmit
functions described below is used. The same
type of data will also be automatically loaded
into the SY35 memory when received from a
second SY35 or other MIDI device, thus erasing
ALL V/M TRANSMIT
MD>ALL V/M TRANS
ALL Voice&Multi
Summary: Initiates MIDI bulk transmission of all
voice and multi-play data.
Settings: None
Procedure: Use the [6] key to move the cursor to
the lower display line. “Are you sure?” will
appear on the display. Press the [+1/YES] key to
begin transmission, or the [–1/NO] key to
cancel. “Transmitting!!” will appear on the display during transmission, and
“>>Completed!!<<” will appear briefly when
transmission has finished.
previous data. This function can be turned
“off” to prevent accidental erasure of the
internal memory, or the memory of external
equipment, do to mistaken data reception or
transmission.
Details: This function is useful for transferring all
the voice and multi-play data in the INTERNAL
memory from one SY35 to another. If the MIDI
OUT of the transmitting SY35 is connected to
the MIDI IN of the receiving SY35 via a MIDI
cable, the receiving unit will automatically
receive and load the data as long as its internal
memory protect function is turned “off” and
EXCLUSIVE ON/OFF is turned “on.” Another
possibility is to transfer the data to a MIDI bulk
data storage device for long-term storage.
1 VOICE TRANSMIT
MD>1 VOICE TRANS
I11 Yes/No ?
Summary: Initiates bulk transmission of the data
for a specified SY35 voice.
Settings: Source: I, C, P
Bank: 1 … 8
Number: 1 … 8
Procedure: Use the [4] and [6] cursor keys are
used to move the cursor to the source, bank, or
number parameter. Use the [–1/NO] and
[+1/YES] keys to set the selected parameter as
necessary. When the desired voice number has
been selected, move the cursor to the Yes/No?
parameter and press the [+1/YES] key to begin
transmission.
“Transmitting!!” will appear on the display
during transmission, and “>>Completed!!<<”
will appear briefly when transmission has
finished.
Details: Like the ALL V/M TRANSMIT function
described above, the 1 VOICE TRANSMIT
function is ideal for transferring voice from one
SY35 to another, or to a MIDI bulk storage
device for long-term storage.
In this display the source, bank and number
parameters are shown in the standard SY35
voice number format. “P12,” for example, is
preset bank 1, number 2; “I35” is internal bank
3, number 5, etc.
56
Page 62

APPENDIX
APPENDIX
57
Page 63

APPENDIX
58
Page 64

VOICE LIST
Preset Voice List
No. Voice Name Wave Effect Ct Comment
11
AP:Rock
(Rock)
12
AP:Clsic
(Classic)
13
AP Chors
(Chorus)
14 AP:HTonk
15 AP:Soft
16 AP Pf&St
17 AP:Blend
18
21
22
23
24 EP Malet
25 KY Clav1
26 KY:Clav2
27 KY:Celst
28
31
32
33
34 BR:Flugl
35 BR:FrHrn
36 BR Sect1
37 BR Sect2
: = 2 elements, * = 4 elements
(HonkyTonk)
(Soft)
(PF&Strings)
(Blend)
AP Bell
(Bell)
EP Tine
(Tine)
EP:Light
(Light)
EP:Old
(Old)
(Malet)
(Clavi1)
(Clavi2)
(Celesta)
KY:Hrpsi
(Harpsichord)
BR:Trmpt
(Trumpet)
BR:Mute
(MuteTrumpet)
BR:Tromb
(Trombone)
(FlugelHorn)
(FrenchHorn)
(Section1)
(Section2)
MW = Modulation Wheel effective
AT = Aftertouch effective
000 Piano
071 Vibes 2
000 Piano
002 E.Piano3
000 Piano∞2
005 E.Piano6∞2
000 Piano
057 B as s 4
000 Piano
002 E.Piano3
000 Piano 085 Str.Body
002 E.Piano3 064 Str 2
000 Piano
073 Vibes 4
000 Piano 001 E.Piano
079 Bells 3 070 Vibes 1
001 E.Piano∞2
070 Vibes 1∞2
001 E.Piano
000 E.Piano1
001 E.Piano
002 E.Piano3
001 E.Piano∞2
071 Vibes 2∞2
002 Clavi 083 HornBody
057 Bas s 4 242 Wave2 4- 2
083 HornBody
057 B as s 4
004 Celesta
152 Sin 4’
003 Cembalo
044 C la vi 3
009 Trumpet
018 B ras s 5
010 MuteTrp
099 Sus. 2
011 Trombone
017 B ras s 4
012 Flugel
018 B ras s 5
013 FrHorn
020 Bras s 7
014 BrasEns∞2
016 Bras s 3 017 Brass 4
019 Sax 014 BrasEns
038 Reed 3 016 Brass 3
Dly&Re v2 MW Basic rock piano
Rev Hall MW Standard classical piano
Rev Hall A chorused piano
Dly&Rev2 MW G in joint honky-t o nk pi ano
Dly&Rev2 MW Mild piano, tone changes with velocity.
Rev Hall Acoustic piano with orchestral strings
Rev Hall Blended acoustic and electric pianos
Rev Hall Acoustic piano with bell attack
Rev Hall DX-like electric piano
Rev Club MW Electric piano with light metal attack
Rev Hall MW Electric piano from the ’70s
Rev Hall MW Bright electric piano with mallet attack
Dly&Rev2 MW A standard clavinet
Dly&Rev2 MWATSlightly different clavinet, aftertouch produces vibrato.
Rev Hall MW Delicate celesta
Dly&Rev2 MW The classic harpsichord
Rev Hall
Rev Hall
Rev Room
Rev Hall MWATFlugelhorn with aftertouch vibrato
Rev Hall MWATFrench horn with aftertouch vibrato
Rev Club Bright pops brass section
Rev Club MWATLow brass section with sax
Trumpet with aftertouch vibrato
MW
AT
Muted trumpet
MW
AT
Trombone, attack goes brassy when played hard.
MW
APPENDIX
59
Page 65

APPENDIX
No. Voice Name Wave Effect Ct Comment
38
BR Fanfr
(Fanfare)
41
ST Arco1
(Arco1)
42
ST:Arco2
(Arco2)
43 ST:Cello
44 ST SlwAt
45 ST Pizz
46 ST Treml
47 ST OrchB
48
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
61
62
63
64 WN:Oboe
65 WN PanFl
66 WN SaxEm
67 WN Ensmb
68 WN Orch
: = 2 elements, * = 4 elements
(Cello)
(SlowAtack)
(Pizzicato)
(Tremolo)
(OrchestraBrass)
ST OrchS
(OrchestraStrings)
BA:Wood
(Wood)
BA:Frtls
(Fretless)
BA Slap
(Slap)
BA:Fingr
(Finger)
BA:Pick
(Pick)
BA:Synth
(Synth)
BA:Tchno
(Techno)
BA:Groov
(Groove)
WN:Sax
(Sax)
WN:Flute
(Flute)
WN:Clari
(Clarinet)
(Oboe)
(PanFlute)
(SaxEnsemble)
(WindEnsemble)
(Orchestra)
MW = Modulation Wheel effective
AT = Aftertouch effective
011 Trombone∞2
017 Bras s 4 016 Brass 3
038 Strings∞2
155 Saw 1∞2
039 Vn.Ens.
063 Str 1
040 Cello
065 Str 3
038 Strings 039 Vn.Ens
068 Str 6∞2
041 Pizz∞2
052 Guitar 7∞2
039 Vn.Ens.∞2
156 Saw 2∞2
038 Strings∞2
027 Bras s 14 02 3 B ras s 10
038 Strings∞2
127 Decay 3∞2
028 Wood B 1
055 Bas s 2
035 Fretless
055 Bas s 2
031 E. Bass 2 054 TumbStr
006 E.Organ1 043 Clavi 2
030 E.Bass 1
055 Bas s 2
031 E.Bass 2
056 Bas s 3
104 Saw 3
062 Bas s 9
037 SynBass2
138 Decay 14
111 Pulse 2
061 Bas s 8
019 Sax
038 Reed 3
016 Flute
028 Wood 1
017 Clarinet
032 Wood 5
018 Oboe
037 Reed 2
066 NoisPad2 070 Bottle
034 Wood 7∞ 2
019 Sax∞ 2
038 Reed 3∞2
016 Flute 017 Clarinet
110 Sus. 13 108 Sus. 11
016 Flute 085 Str.Body
121 Move 4 108 Sus. 11
Rev Hall
Rev Hall Full orchestral strings
Rev Room Cham ber strings
Rev Room MWATA cello, good played stacatto or with aftertouch.
Rev Hall MWATSlow attack strings, level changes with aftertouch.
Rev Hall MW Pizzicato strings
Rev Hall Tremolo strings
Rev Hall Orchestral strings, brass appear when played hard.
Rev Hall Orchestral strings
Rev Room
Rev Hall
Rev Hall MW Slapped bass, thumps when played hard.
Rev Plate MW Fingered electric bass
Rev Club MW Picked electric bass
Delay 1
Delay 1
Gate Rev
Rev Room
Rev Hall
Rev Hall
Rev Hall MWATOboe
Rev Hall Pan flute
Rev Club MWATSaxophone ensemble
Early Ref MWATWind ensemble, tone varies with velocity.
Rev Hall An orchestra, featuring the wind instruments
Classic fanfare brass
MW
AT
Wood bass
MW
AT
Fretless bass
MW
AT
Synth bass
MW
AT
Technorock-oriented synth bass
MW
AT
Fat synth bass with resonance
MW
AT
A bright alto sax
MW
AT
Flute with aftertouch vibrato
MW
AT
Clarinet
MW
AT
60
Page 66

No. Voice Name Wave Effect Ct Comment
71
PL:Gypsy
(Gypsy)
72
PL:Folk
(Folk)
73
PL Wide
(Wide)
74 PL Mute
75 PL:Rock
76 PL Dist
77 PL:Chrng
78 PL:Sitar
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
: = 2 elements, * = 4 elements
(Mute)
(Rock)
(Distortion)
(Charango)
(Sitar)
CH Pure
(Pure)
CH Itopy
(Itopy)
CH Uhh--
(Uhh)
CH Angel
(Angel)
CH Bell
(Bell)
CH Snow
(Snow)
CH Vcodr
(Vocorder)
CH Marin
(Marin)
MW = Modulation Wheel effective
AT = Aftertouch effective
020 Gut
179 Wave3-2
021 Steel
044 C la vi 3
021 Steel∞2
048 Guitar 3∞2
026 Pluck 1 024 MuteGtr
052 Guitar 7 050 Guitar 5
026 Pluck 1
048 Guitar 3
022 E.Gtr 1 098 Digital2
157 Square 193 Wave8-1
021 Steel
048 Guitar 3
025 Sitar
053 Guitar 8
067 NoisPad3 043 Choir
130 Decay 6∞2
044 Itopia∞2
030 Wood 3∞ 2
043 Choir∞2
125 Decay 1∞2
065 NoisPad1∞2
028 Wood 1∞ 2
043 Choir∞2
079 Bells 3∞2
066 NoisPad2 044 Itopia
131 Decay 7∞2
045 Choir Pa∞2
109 Sus. 12∞2
043 Choir∞2
028 Wood 1 152 Sin 4’
Rev Hall MW Nylon guitar
Rev Hall MW Steel-string folk guitar
Rev Room 12-string guitar
Dly&Rev2 MW Muted guitar, tone changes with velocity.
Dist&Rev MW Rock guitar
Dist&Rev MW Distorted guitar, vectoring produces feedback
Rev Hall MW Charango
Rev Room Sitar
Rev Hall Choir with a clear high tone
Rev Hall Itopia-style synth chorus
Rev Room Chorus with a strong attack
Rev Hall Heavenly female synth chorus
Rev Hall AT Chorus with a bell attack
Rev Hall A cold choir
Dly&Rev2 Vocoder-like chorus
Rev Hall Mysterious choir sound
APPENDIX
61
Page 67

APPENDIX
In t e rn al Voi ce Lis t
No. Voice Name Wave Effect Ct Comment
11
SP Warm
(Warm)
12
SP Resnc
(Resonance)
13
SP Full!
(Full)
14 SP Bell
15 SP Filtr
16 SP Deep
17 SP Fog
18 SP Dyna
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
31
32
33
34
35 SL Whstl
36 SL 2VCO
37 SL Fat
38 SL AnaSy
41 OR:Tango
: = 2 elements, = 4 elements
(Bell)
(Filter)
(Deep)
(Fog)
(Dynamic)
SC Dgcrd
(Digichord)
SC Elgnt
(Elegant)
SC sFz<
(Sforzando)
SC Coin
(Coin)
SC Brash
(Brash)
SC:Water
(Water)
SC Sand
(Sand)
SC Reso
(Resonance)
SL Saw
(Saw)
SL:Squar
(Square)
SL Sync
(Sync)
SL Power
(Power)
(Whistle)
(2VCO)
(Fat)
(AnalogSynth)
(Tango)
MW = Modulation Wheel effective
AT = Aftertouch effective
055 SynPad∞2
111 Sus. 14∞2
102 Saw 1 081 Tp.Body
061 B as s 8∞ 2
042 Syn Str∞2
063 Str 1∞2
059 Bell Mix 055 SynPad
104 Sus. 7∞2
060 Sweep∞2
121 Move 4∞2
046 Vibes∞2
078 Bells 2∞2
067 NoisPad3∞2
101 Sus. 4∞2
044 Itopia 066 NoisPad 2
111 Sus. 14 122 Move 5
101 Digital5∞2
045 Cla vi 4∞2
059 Bell Mix∞2
106 Sus. 9∞2
015 SynBrass∞2
121 Move 4∞2
068 Coin∞2
073 Vibes 4∞2
015 SynBrass∞2
026 Bras s 13 01 7 B ras s 4
056 Harmonic
090 Metal 6
067 NoisPad3∞2
044 Cla vi 3∞2
058 SynLoad2∞2
140 Decay 16∞2
102 Saw 1∞ 2
091 Lead 1∞ 2
107 Squar e 2
093 Lead 3
058 SynLead2 116 Tri
061 Bas s 8∞2
067 NoisPad3∞2
098 Sus. 1∞2
066 NoisPad2∞2
073 Vibes 4∞2
108 Square 3 095 Str wv 2
135 Decay 11 124 Move 7
102 Saw 1∞ 2
095 Lead 5∞ 2
057 SynLead1∞2
096 Lead 6∞ 2
008 Bandneon
038 Reed 3
Rev Hall Warm synth pad on a grand scale
Rev Room
Rev Hall Analog-like fat synth sound
Rev Hall MWATSynth pad with metal attack and aftertouch vibrato
Rev Hall Synth pad with filter EG tone change
Rev Hall Deep sea synth, best played low.
Rev Hall Pad with a touch of London fog
Pan Ref The SY35’s theme sound, dynamic and big
Rev Hall Digichord, a buzzy low-range comping synth
Rev Hall Soft comping synth, sizzles w hen held.
Dly&Rev 2 MW Comping with filter EG and distinctive attack
Delay 3 Bell-like comping synth
Rev Club Comping synth with brass attack
Rev Hall Wet synth with water drops
Gate Rev Comping synth, good for sequencing.
Rev Club
Delay 3
Rev Plate
Rev Hall
Delay 3
Rev Plate The sound of two lips whistling
Delay 3 MWATLead synth with noisy attack and aftertouch
Rev Hall MWATPowerful fat lead synth with aftertouch vibrato
Rev Hall MWATAnalog wind synth lead with aftertouch vibrato
Rev Room Bandneon
Resonant synth pad with aftertouch vibrato
MW
AT
Resonant synth with aftertouch vibrato
MW
AT
Typical sawtooth lead with aftertouch vibrato
MW
AT
Typical square wave lead with aftertouch vibrato
MW
AT
MWATLead synth with unique attack and aftertouch
vibrato
Buzzy, powerful lead synth with aftertouch vibrato
MW
AT
vibrato
62
Page 68

No. Voice Name Wave Effect Ct Comment
42
OR:Paris
(Paris)
43
OR Rock1
(Rock1)
44
OR Rock2
(Rock2)
45 OR Rock3
46 OR Cat
47 OR Big
48 OR Combo
51 BR Punch
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
61
62
63
64
65
66 SE Elect
67 SE GoUp!
68 SE and>?
71 ME Wide!
72 ME Drama
: = 2 elements, = 4 elements
(Rock3)
(Cat)
(Big)
(Combo)
(Punch)
BR Power
(Power)
BR Fat
(Fat)
BR:Lite
(Light)
ST Modrn
(Modern)
ST Soft
(Soft)
ST Mild
(Mild)
ST:Lite
(Light)
SE Hit
(Hit)
SE Start
(Start)
SE Who?
(Who)
SE Open
(Open)
SE Emgsy
(Emergensy)
(Electric)
(GoUp)
(and>?)
(Wide)
(Drama)
MW = Modulation Wheel effective
AT = Aftertouch effective
008 Bandneon
094 Lead 4
006 E.Organ1 007 E.Organ2
006 E.Organ1 007 E.Organ2
006 E.Organ1∞2
008 E.Organ3 006 E.Organ1
007 E.Organ2∞2
153 Sin2 2/3∞2
090 EP wv 117 Sin8’
153 Sin2 2/3 152 Sin 4’
005 P.Organ∞2
011 E.Organ6250 Wave27-1
117 Sin8’ 090 EP wv
037 Reed 2 153 Sin2 2/3
015 SynBrass∞2
062 Bas s 9∞2
057 SynLead1 015 SynBrass
014 Bras s 1∞2
015 SynBrass∞2
022 Bras s 9∞2
104 Saw 3
096 Lead 6
042 Syn Str∞2
063 Str 1∞2
038 Strings∞2
091 Lead 1∞ 2
039 Vn.Ens.∞2
067 Str 5∞2
085 Str.Body
155 Saw 1
064 PopsHit 069 Crash
255 Wave30x2
044 Itopia 060 Sweep
150 Sin 16’ x2
060 Sweep 059 Bell Mix
144 SFX 2 121 Move 4
068 Coin∞2
120 Move 3 118 Move 1
055 SynPad 056 Harmonic
156 Saw 2 145 SFX 3
100 Digital4 098 Digital2
152 Sin 4’ 162 Digi 2
121 SEQ 3 125 SEQ 7
254 Wave29 121 Move 4
056 Harmonic 071 BotleOpn
123 Move 6 145 SFX 3
066 NoisPad2 x2
124 Move 7x2
055 SynPad 121 SEQ 3
145 SFX 3 091 Lead 1
Rev Room
Pan Ref
Rev Room
Rev Room MW Rock organ with sampled rotary speaker sound
Rev Room Jazz organ with a percussive attack
Rev Hall MW A huge cathedral pipe organ
Rev Room MW Combo organ
Gate Rev MWATSynth brass with a punched attack and aftertouch
Rev Hall Powerful synth brass
Rev Club
Rev Club Bright synth brass
Rev Hall Modern-sounding synth strings
Rev Hall Ve ry basic synth strigns
Rev Hall Mild synth strings
Rev Hall Bright synth strings
Rev Hall Pops hit with crash cymbal
Rev Metal Sweep attack followed by an uncanny pitch change
Rev Hall MW A bell sound appears when held.
Delay 3 Play a lot of keys while holding the sustain pedal.
Dly&Rev1 Emergency! A crisis is approaching …
Rev Room MW The sound of old-fashioned electric machines
Rev Hall Pitch and tone vary when held.
Rev Hall The final sound effect: hold it for a long time.
Rev Hall Grand scale and a distinctive sizzle
Rev Hall MW Dramatic sound, tone changes often when held.
An accordion you might hear at a Paris sidewalk
cafe
Heavy rock organ
MW
AT
Slightly br i ght er rock organ
MW
AT
vibrato
Fat synth brass with aftertouch vibrato
MW
AT
APPENDIX
63
Page 69

APPENDIX
No. Voice Name Wave Effect Ct Comment
73
ME SlwSg
(SlowSong)
74
ME Grand
(Grand)
75
ME Typhn
(Typhoon)
76 ME Tzone
77 ME Space
78 ME Memry
81 PC:Vibe
82 PC Marim
83
84
85
86
87
88
: = 2 elements, = 4 elements
(Tzone)
(Space)
(Memory)
(Vibraphone)
(Marimba)
PC:M.Box
(MusicBox)
PC:Timp
(Timpani)
PC Batl
(Battle)
PC Human
(Human)
DR Auto
(Auto)
DR:Kit
(Kit)
MW = Modulation Wheel effective
AT = Aftertouch effective
046 Vibes 083 HornBody
073 Vibes 4 102 Sus. 5
048 Bells 122 SEQ 4
121 Move 4 122 Move 5
059 Bell Mix 044 Itopia
102 Sus. 5 144 SFX 2
062 N oi se 1∞ 2
154 Sin 2’ 153 Sin2 2/3
065 NoisPad1∞2
122 Move 5∞2
119 SEQ 1121 SEQ 3
121 Move 4 112 Sus. 15
046 Vibes
151 Sin 8’
047 Marimba∞2
075 Marimba2∞2
046 Vibes
088 Metal 4
049 Timpani
184 Wave5-1
080 Slam∞ 2
000 E.Piano1∞2
087 Reverse1 061 HumanAtk
151 Sin 8’ 152 Sin 4’
124 SEQ 6 051 E.Tom
160 Noi se 2 151 Sin 8’
127 Drum Set Rev Plate Drum set voice
Rev Club Typical vector effect sound
Rev Hall
Rev Hall Mysterious chorus sound, broadens when held.
Rev Hall A mysterious, somehow sorrowful sound
Rev Hall Outer space synth pad
Rev Hall Two wave sequences appear.
Rev Club A cool vibraphone
Rev Hall Marimba
Rev Room MW An old-time music box
Dly&Rev2 MW Timpani
Rev Hall
Rev Hall Human voice attack and its reverse, combined
Rev Club Drum pattern below C2, electric toms above G3
Large-sca le s ound with a bell attac k
MW
AT
TNT below B1, cannon around C3, machine guns
at E4
Sound Category List
AP = Acoustic Piano WN = Wind OR = Organ
EP = Electric Piano PL = Plucked SE = Sound Effect
KY = Keyboard CH = Chorus ME = Musical Effect
BR = Brass SP = Synth Pad PC = Percussive
ST = Strings SC = Synth Comp DR = Drums
BA = Bass SL = Synth Lead
64
Page 70

Page 71

APPENDIX
MULTI LIST
PR ESET M U LT I LIS T
No. MULTI Name Type Voice Numbers Comments
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
Orchstra
BigBand
SuperClv
PianoStr
VoiceBs
FullBrs
PanLead
Str&Cho
DistLead
Wb/Piano
B/BrsSec
Celo/Flt
<Pop>
<Rock>
<Jazz>
<Demo>
Layer
Layer
Layer
Layer
Layer
Layer
Layer
Layer
Layer
Split
Split
Split
MIDI Multi
MIDI Multi
MIDI Multi
MIDI Multi
P47
P36
P25
P15
P52
P35
P63
P42
P76
P51
P54
P43
P12
P11
P15
P72
P41
P37
P26
P42
P87
P38
P63
P85
P76
P12
P37
P62
P22
I43
I46
P42
P65
P76
P74
P74
P71
P61
P65
P76
P36
P37
P32
P58
P76
P61
P61
P61
P12
P76
P42
P41
P42
I35
P76
P54
P55
P51
I64
Big orchestra.
Big-band brass section.
Layered clavi sound.
Layered piano and strings.
Layered bass and human voice.
Powerful brass.
Pan-flu te type le ad v oic e.
Layered strings and choir.
Distorti on le ad v oic e.
P76
Wood bass and piano split.
Electric bass and brass split.
Cello and flute split.
Pop music ensemble.
I88
Rock group.
I88
Jazz ensemble.
I88
SY35 demo multi.
I88
INTERNAL MULTI LIST
No. MULTI Name Type Voice Numbers Comments
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
SyncLead
SuperSaw
BellPad
SunBeam
WideDcy
AnaPad1
AnaPad2
AnaPad3
FatBrass
HyuhPad
Reggae
Mikado
Prologue
Epilogue
SolidSet
RytmSec.
Layer
Layer
Layer
Layer
Layer
Layer
Layer
Layer
Layer
Layer
Layer
Layer
Layer
Layer
Split
Split
I33
I31
I11
I22
I25
I13
I15
I13
I51
I71
I46
I67
I62
I64
I37
I87
I33
I31
I14
I24
I27
I51
I23
I55
I53
I76
I82
I18
I18
I72
I31
I36
I33
I31
PRESET Multi setups 25 through 28 (labelled “MIDI”
in the above list) are designed for use with an external
I33
I31 I31 I31 I31 I31
MIDI sequencer. Each has 8 voices assigned to
differ ent MIDI channels as shown in the chart below.
Fat “sync” lead.
Extra-fat sawtooth lead.
Filter swe ep s ynt h pad.
“Sunny” sound for backing.
Bright backing layer.
Analog synth pad 1.
Analog synth pad 2.
Analog synth pad 3.
Fat analog synth brass.
Synth pad with wind effect.
Ideal for Reggae music.
Musical effect.
Musical effect.
Musical effect.
Bass and synth lead split.
Auto drum and bass pattern.
PRESET MULTI MIDI CHANNEL ASSIGNMENTS
No. MULTI Name Ch1 Ch2 Ch3 Ch4 Ch5 Ch6 Ch7 Ch8 Ch16
I88
25
26
27
28
<Pop>
<Rock>
<Jazz>
<Demo>
P12
P11
P15
P72
P22
I43
I46
P42
P74
P74
P71
P61
P36
P37
P32
P58
P61
P61
P61
P12
P42
P41
P42
I35
P54
P55
P51
I64
—
—
—
I88
I88
I88
—
66
Page 72

AWM W AVEFORM LIST
Category No. Name
Piano 0
Organ 5
Brass
Wood
Gtr
Bass
1
2
3
4
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
Piano
E.Piano
Clavi
Cembalo
Celesta
P.Organ
E.Organ1
E.Organ2
Bandneon
Trumpet
Mute Trp
Trombone
Flugel
Fr Horn
BrasEns
SynBrass
Flute
Clarinet
Oboe
Sax
Gut
Steel
E.Gtr 1
E.Gtr 2
Mute Gtr
Sitar
Pluck 1
Pluck 2
Wood B 1
Wood B 2
E.Bass 1
E.Bass 2
WAVEFORM LIST
Category No. Name
Bass 32
Str.
Vocal 43
Perc. 46
Synth 55
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
44
45
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
E.Bass 3
E.Bass 4
Slap
Fretless
SynBass1
SynBass2
Strings
Vn.Ens.
Cello
Pizz.
Syn Str
Choir
Itopia
Choir pa
Vibes
Marimba
Bells
Timpani
Tom
E. Tom
Cuica
Whistle
ThumbStr
SynPad
Harmonic
SynLead1
SynLead2
Bell Mix
Sweep
HumanAtk
Noise 1
Noise 2
Category No. Name
Synth 64 PopsHit
SFX 65
Hits
Tran.
OSC 90
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
91
92
93
94
95
NoisPad1
NoisPad2
NoisPad3
Coin
Crash
Bottle
BotleOpn
Cracker
Scratch
Metal 1
Metal 2
Metal 3
Metal 4
Wood
Bamboo
Slam
Tp. Body
Tb. Body
HornBody
Fl. Body
Str.Body
AirBlown
Reverse1
Reverse2
Reverse3
EP wv
Organ wv
M.Tp wv
Gtr wv
Str wv 1
Str wv 2
Category No. Name
OSC 96
SEQ
Drum 127 Drum set
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
APPENDIX
Pad wv
Digital1
Digital2
Digital3
Digital4
Digital5
Saw 1
Saw 2
Saw 3
Saw 4
Square 1
Square 2
Square 3
Square 4
Pulse 1
Pulse 2
Pulse 3
Pulse 4
Pulse 5
Pulse 6
Tri
Sin8’
Sin8’+4’
SEQ 1
SEQ 2
SEQ 3
SEQ 4
SEQ 5
SEQ 6
SEQ 7
SEQ 8
AWM Waveform Category Descriptions
Piano
Organ
Brass
Wood
Gtr
Bass
Str.
Vocal
Perc.
Piano, clavi, and other decay-type keyboard sounds.
Pipe, electric and reed organs.
Acoustic and synthesized brass sounds.
Flute, sax and other woodwind sounds.
Acoustic and electric guitars.
Acoustic, electric, and synth bass.
Violin ensemble and other strings.
Choir and other vocal-type sounds.
Vibes, timpani, etc.
Synth
SFX
Hits
Tran.
OSC
SEQ
Drum
A range of synth sounds (including noise).
Special effects – crash, bottle, etc.
Struck metal and woods.
Transient attack waves and some reverse sounds.
Standard synth waveforms and the basic waveforms
from some actual instruments.
Sequences of sampled sounds.
Drum set waves.
67
Page 73

APPENDIX
FM WAVEFO RM LIST
Category No. Name
Piano 0
Organ 6
Brass 14
Wood
Reed 36
Pluck
1
2
3
4
5
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
E.Piano1
E.Piano2
E.Piano3
E.Piano4
E.Piano5
E.Piano6
E.Organ1
E.Organ2
E.Organ3
E.Organ4
E.Organ5
E.Organ6
E.Organ7
E.Organ8
Brass 1
Brass 2
Brass 3
Brass 4
Brass 5
Brass 6
Brass 7
Brass 8
Brass 9
Brass 10
Brass 11
Brass 12
Brass 13
Brass 14
Wood 1
Wood 2
Wood 3
Wood 4
Wood 5
Wood 6
Wood 7
Wood 8
Reed 1
Reed 2
Reed 3
Reed 4
Reed 5
Reed 6
Clavi 1
Clavi 2
Clavi 3
Clavi 4
Guitar 1
Guitar 2
Guitar 3
Category No. Name
Pluck 49
Bass.
Str.
Perc. 70
Syn.S 91
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
92
93
94
95
96
97
Guitar 4
Guitar 5
Guitar 6
Guitar 7
Guitar 8
Bass 1
Bass 2
Bass 3
Bass 4
Bass 5
Bass 6
Bass 7
Bass 8
Bass 9
Str 1
Str 2
Str 3
Str 4
Str 5
Str 6
Str 7
Vibes 1
Vibes 2
Vibes 3
Vibes 4
Marimba1
Marimba2
Marimba3
Bells 1
Bells 2
Bells 3
Bells 4
Bells 5
Bells 6
Bells 7
Bells 8
Metal 1
Metal 2
Metal 3
Metal 4
Metal 5
Metal 6
Lead 1
Lead 2
Lead 3
Lead 4
Lead 5
Lead 6
Lead 7
Category No. Name
Syn.S
Syn.M
Syn.D
SFX
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
Sus. 1
Sus. 2
Sus. 3
Sus. 4
Sus. 5
Sus. 6
Sus. 7
Sus. 8
Sus. 9
Sus. 10
Sus. 11
Sus. 12
Sus. 13
Sus. 14
Sus. 15
Attack 1
Attack 2
Attack 3
Attack 4
Attack 5
Move 1
Move 2
Move 3
Move 4
Move 5
Move 6
Move 7
Decay 1
Decay 2
Decay 3
Decay 4
Decay 5
Decay 6
Decay 7
Decay 8
Decay 9
Decay 1 0
Decay 1 1
Decay 1 2
Decay 1 3
Decay 1 4
Decay 1 5
Decay 1 6
Decay 1 7
Decay 1 8
SFX 1
SFX 2
SFX 3
SFX 4
Category No. Name
SFX
OSC 1 150
OSC 2
OSC 3 223
147
148
149
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
220
221
222
224
225
250
251
252
253
254
255
SFX 5
SFX 6
SFX 7
Sin 16’
Sin 8’
Sin 4’
Sin2 2/3
Sin 2’
Saw 1
Saw 2
Square
LFOnoise
Noise 1
Noise 2
Digi 1
Digi 2
Digi 3
Digi 4
Digi 5
Digi 6
Digi 7
Digi 8
Digi 9
Digi 10
Digi 11
wave1-1
wave1-2
wave1-3
wave2-1
wave2-2
wave2-3
:
:
wave17-1
wave17-2
wave17-3
wave18-1
wave18-2
wave18-3
:
:
wave27-1
wave27-2
wave27-3
wave28
wave29
wave30
FM Voice Cat eg or y De script io n s
Piano
Organ
Brass
Wood
Reed
Pluck
Bass
Str.
Electric pianos.
Electric organs.
A variety of brass sounds.
Woodwind instrument sounds.
Sax, oboe and other reed instruments.
Guitar, clavi, and other plucked instrument sounds.
Bass soun ds.
Strings.
If the TYPE parameter in the ELEMENT
ENVELOPE edit mode (page 27) is set to
PRESET, selecting a WAVE TYPE also selects
68
Perc.
Syn.S
Syn.M
Syn.D
SFX
OSC1
OSC2
OSC3
Vibes, marimba, bells and other percussion sounds.
Sustained lead synth sounds.
Synth sounds that vary with time.
Decay-type synth sounds.
A range of sound-effect type synth sounds.
Sine, sawtooth, and other standard synth waveforms.
Basic FM timbres, group 1.
Basic FM timbres, group 2.
the corresponding preset envelope. If a different
envelope type is selected, the preset envelope is
not sele cted together with the wave.
Page 74

SPECIFICATIONS
APPENDIX
Ke yboa r d: 61 keys, initial and after-touch response.
Tone Generator Systems: AWM (Advanced
Wave Memory) & FM (Frequency Modulation).
Internal Memory:
Wave ROM; 128 preset AWM & 256 preset FM
waveforms.
Preset ROM; 64 preset voices.
Internal RAM; 64 us er voices.
External Memory: Voice & Multi data; MCD64
or MCD32 memory cards + write & read.
Displ ays:
16-character ∞ 2-li ne backlit LCD.
7-segment 2-digit LED display.
Controls: VOLUME, VECTOR CONTROL,
PITCH BEND, MODULATION.
Key & Swit ch e s: POWER ; VECTOR PLAY ON /
OFF, LEVEL/DETUNE; CURSOR 4 and 6;
MODE VOICE and MULTI; –1/NO and +1/YES;
EDIT/ UTILITY/COMPARE; STORE;
INTERNAL, CARD, PRESET; BANK 1–8
(VOICE COMMON and VECTOR; ELEMENT
TONE and ENVELOPE; MULTI; UTILITY
RECALL, SETUP and MIDI); NUMBER/
MULTI PART SELECT 1–8 (ELEMENT
SELECT A–D, ELEMENT ON/OFF A–D);
DEMO.
UL, CSA: 120V
Europe , WG, Australia, B S: 220–240V
Power consumption:
7W (with PA-3 AC Adaptor)
Dimensions (W ∞ D ∞ H) :
976 ∞ 28 5 ∞ 93 mm (37-7/8" ∞ 11-1/4" ∞ 3-5/8")
Weigh t: 6.8 kg (14 lbs 16 oz)
Connectors: DC 10V–12V IN; PHONES;
OUTPUT R & L/MONO, FOOT VOLUME,
SUSTAIN.
MIDI Connectors:
IN, OUT, THRU.
Power requirements:
69
Page 75

Page 76

Page 77

Page 78

Page 79

Page 80

Page 81

Page 82

Page 83

Page 84

documentation manual, user maintenance, brochure, user reference, pdf manual
This file has been downloaded from:
User Manual and User Guide for many equipments like mobile phones, photo cameras, monther board, monitors, software, tv, dvd, and othes..
Manual users, user manuals, user guide manual, owners manual, instruction manual, manual owner, manual owner's, manual guide,
manual operation, operating manual, user's manual, operating instructions, manual operators, manual operator, manual product,
 Loading...
Loading...