Page 1

www.iOptron.com
Manual
SmartStarTM-G Series
Refractor, Newtonian and
Maksutov-Cassegrain Telescopes
www . iOptron . com
1
Page 2
www.iOptron.com
WARNING!
NEVER USE A SMARTSTAR
TELESCOPE TO LOOK AT THE SUN!
Looking at or near the Sun will cause instant
and irreversible damage to your eye.
Children should always have adult
supervision while observing.
2
Page 3
www.iOptron.com
G. Alignment Stars
TIP:
For beginner users
without a lot of
knowledge in astronomy
please refer to the Quick
Start Reference. It
contains enough
information to get you
started so you can enjoy
the night sky without
knowing all the jargon
and math.
CONTENTS
Chapter. 0 Quick Start Reference
0.1 Assembly
0.2 GoToNova
0.3 Getting Started
Chapter. 1 Set Up And Align
1.1 Basic Symbols
1.2 Set Up
1.3 Align
Chapter. 2 Select And Slew
2.1 Planets, sun, moon
2.2 Deep Sky Objects
2.3 Comets
2.4 Asteroids
2.5 Stars
2.6 User Objects
2.7 Enter Position
2.8 Land Marks
2.9 Watch List
Chapter. 3 Other Functions
3.1 Sync To Target
3.2 Electronic Focuser
3.3 PEC option
3.4 Set up tracking
3.5 User objects
3.6 Auto guide
3.7 Park scope
3.8 To park position
Chapter. 4 How to Observe
4.1 Observe manually
4.2 Observe using arrow keys
4.3 the Moon
4.4 Tracking
Appendix
A. Menu Structure
B. Messier Catalog
C. Modern Constellations
D. Celestial Coordinates
E. Specifications
F. Products List
TM
Features
3
Page 4

www.iOptron.com
TIP:
Learn some astronomy
basics
For beginner users without a lot of knowledge in
astronomy please refer to the Quick Start Menu. It
contains enough information to get you started so
you can enjoy the night sky without knowing all the
jargon and math.
For more serious users we assume that you know
some astronomy basics in reading this manual.
Please refer to Appendix A for a more detailed
menu structure.
4
Page 5
www.iOptron.com
NOTE:
Make sure that your
telescope is not too
heavy for your mount
Chapter 0 Quick Start Reference
0.1 Assembly
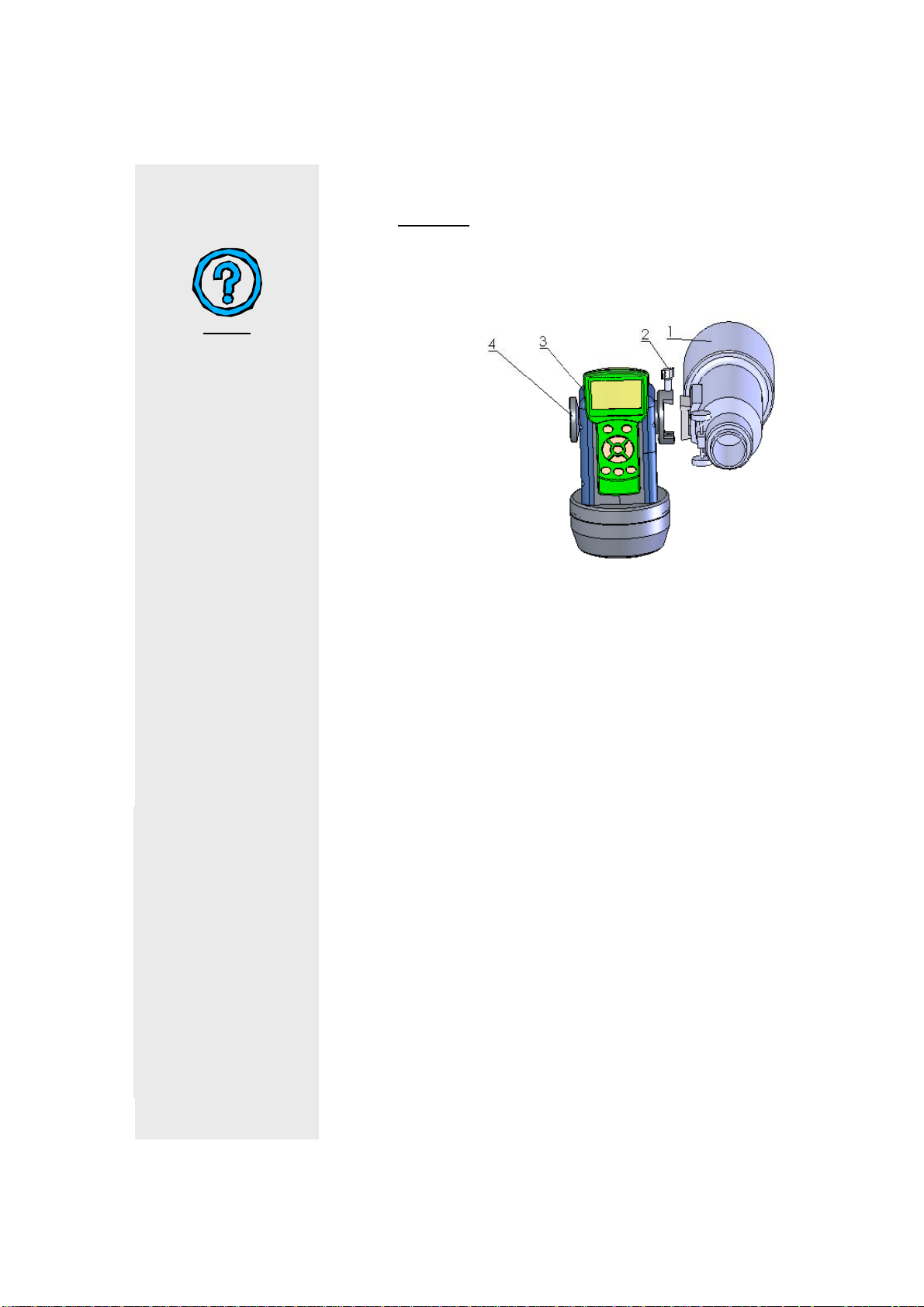
1. Telescope tube
2. Dovetail lock
3. Hand held controller
4. Altitude lock
FIG. 1
1. Unpack the package, take out all the parts.
2. Set up the tripod(6).
3. Put the mount(5) on the top of tripod(6), hold the
mount with one hand, put the supporting rod(7)
through the hole on the top of tripod with the other
hand, screw and tighten the mount on the top of
tripod(6).
4. Tighten the telescope tube(1) on the dovetail with lock
(2), point the tube upward vertically and tighten the
altitude lock (4).
5
Page 6

www.iOptron.com
TIP:
Alt-Az mode is easier to
set up, and easier to
operate. Adjust the
tripod and the mount,
check the bubble on the
mount, make sure it is
horizontal.
NOTE:
A-series can also work
in equatorial mode
5. Mount
6. Tripod
7. Inner support
8. Tray
9. Tray lock
FIG.2
TIP:
If you are not using the
AC adaptor, you need
eight AA batteries.
5. Fit the tray (8) to the lower end of the rod (7), also fit
the three indents to the three legs of tripod, tighten
the tray lock (9). To avoid any damage to the tray or
tripod, please do not use excessive strength.
6. Open the cover of battery box on the side of the
mount (below dovetail), install 8 AA batteries (not
included) appropriately. If you are using 12V AC
adapter, plug the connector to the socket on the other
side of the mount (below altitude lock). Connect hand
controller(3) and mount(5) with retractable cable
(provided). You can pick any one of the two socket s
below altitude lock to plug in.
7. Always adjust the tripod to center the bubble in the
circle on the mount. It is important that the tripod stay
horizontal.
6
Page 7

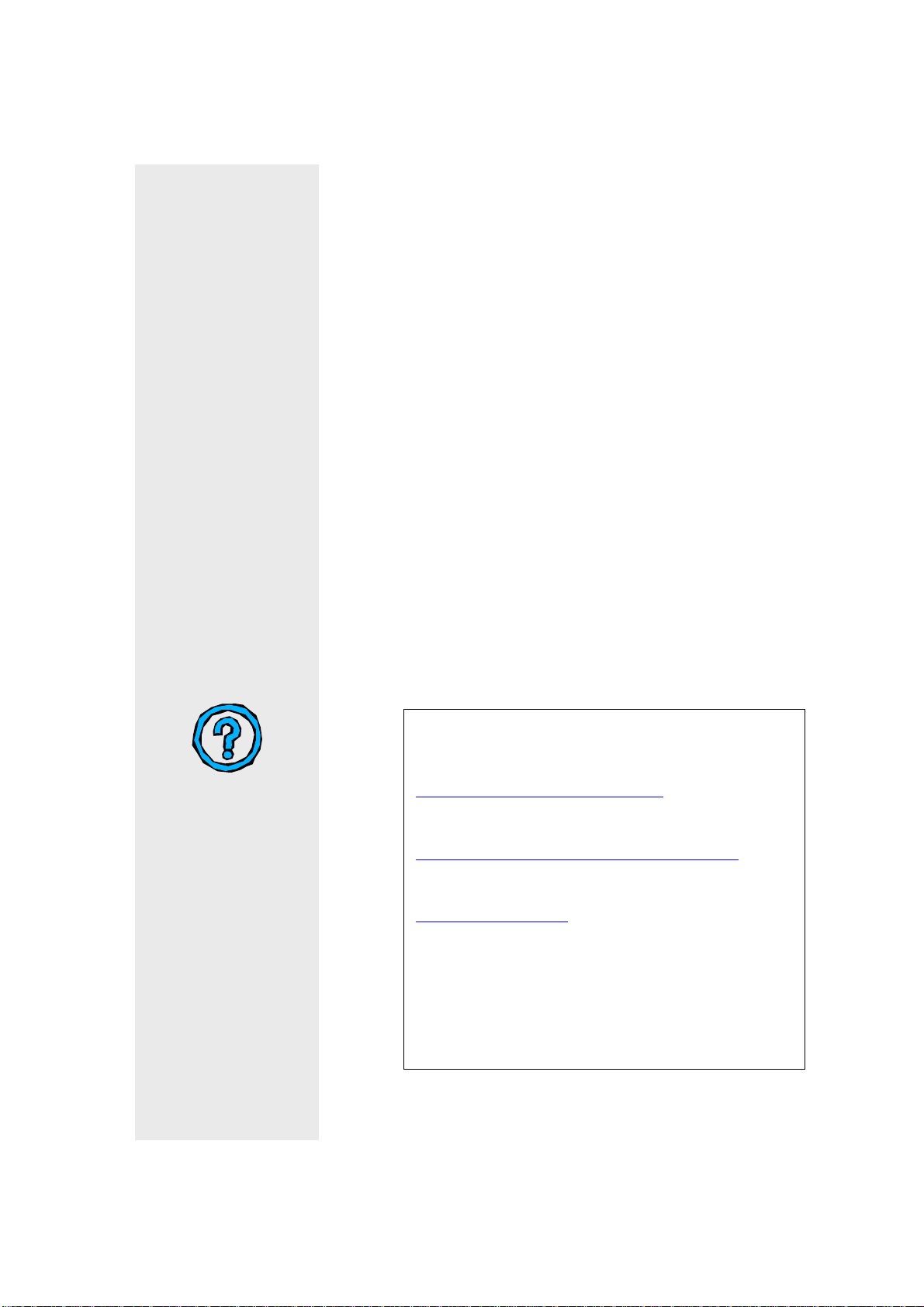
0.2 GoToNovaTM Features: (8402)
www.iOptron.com
LCD Display
Menu
Back
Up
Left
Right
Enter
Down
Help
Speed
Light
FIG.3
7
Page 8
www.iOptron.com
The 8402 GoToNova
SmartStar
and easy-to-learn, it can automatically move to any of the
50,000 objects stored in the database with the push of a
button.
LCD Display: 8-line big screen, it displays all the information
Back Key: Moves back to the previous screen.
Menu Key: Gets to the Main Menu.
Enter Key:
a choice, slews the telescope to a sele ct ed objec t.
Arrow Keys: Moves the cursor, adjusts numerical values,
moves the telescope in a specific direction.
Speed Key:
Light Key: Adjusts the light.
Help Key: For help.
TM
G series telescopes. Its user interface is simple
Confirms an input, goes to the n ext menu, sele cts
Adjusts the speed.
Sky and Telescope
http://www.skyandtelescope.com/
Astronomy
http://www.astronomy.com/asy/default.aspx
The Hubble Site
http://hubblesite.org/
TM
hand held controller controls
Useful Links
8
Page 9

www.iOptron.com
TIP:
GPS module makes life a
lot easier, it
automatically sets the
time and location for
you.
TIP:
The controller
automatically skips
those stars below the
horizon of your current
time and location.
0.3 Getting Started
For most beginner users who may not need a lot of
astronomical detail this chapter gives just enough information
to set up the controller. After the easy-to-follow setup you will
be ready to point your telescope to wherever you want in the
night sky.
After assembling the telescope [Refer to our Assembling
Chart], you need to level the mount. This is don e by centering
the bubble in the circle on the mount. Turn on the power
button located on the mount. You will see the iOptron logo
displayed for a few seconds. Then you will see the zero
position screen. By default, it works in Alt-Az mode:
TR.A. 1h36m 2s
TDEC 90°0’ 0”
R.A. 19h52m 5s
DEC 47°31’16” 64X
Lgst 7h52m38s Stop
Alt. 0°0’ 0”
Azi. 0°0’ 0”
2007-07-10 14:25:23 N
When the power is turned on, you will see “G_ON” (GPS
turned on) on the upper right corner o f the screen. In about a
minute, after the internal GPS communicate with the
satellites, you will see “G_OK” on the screen, both time and
location are automatically set.
Press MENU button, then you will see this screen:
Select and slew
Sync. To target
Electric Focuser
Set up GOTONOVA
Align
PEC option
Set up tracking
User objects
Auto guide
Park scope
To park position
From the main menu, select “Align”. The system provides
“one-star align” and “two-star align”.
Select “one-star align”. You will see this screen:
Alphard
A 39°43.3′ Z 221°20.0′
Center the target then
press “ENTER” 2X
Use “UP” and “DOWN” arrow buttons to select a star and
press ENTER. Use SPEED button to select a speed, and use
arrow buttons to center the star in your telescope. Press
ENTER when finished . Now your GoToNova
TM
is ready to
9
Page 10
www.iOptron.com
TIP:
Spend some time
familiarizing yourself
with these bright stars in
the night sky
direct you to any location in the night sky (provided that the
object is in the database and above the horizon). Simply
choose any object in the menu and press ENTER. Although
not required, we strongly suggest that you double check your
initial alignment with additional bright objects in the night sky,
For example, in the menu, select “Venus” (if it is indeed in the
sky) and press ENTER. When the motor stops check to see if
Venus is in the center of your eye piece. If your previous
steps were correct, it should be. You may need to m ake some
minor adjustments to center the object. Otherwise, use “twostar align”.
What’s Next?
Most beginner users are now ready to explore the night sky
without needing to refer to the manual any further. The
function you will need most is “Select and slew” in the main
menu. From there you can select and explore planets, stars,
galaxies, nebulae, comets, asteroids, etc.-- virtually all of the
most common celestial objects are included.
10
Page 11
www.iOptron.com
Appendix:
Check Appendix D for a
brief introduction of
celestial coordinate
systems
Chapter.1 Set Up And Alignment
1.0 Basic Symbols
R Right ascension
D Declination
A Altitude
Z Azimuth
Cele Sidereal speed
Sola Solar speed
Moon Lunar speed
Land Land mode
nnX Slewing speed
1.1 Set Up
By default, the mount works in Alt-az mode. Turn on the
power button located on the mount. You will see the iOptron
logo screen. Then you will see the zero position screen:
TR.A. 1h36m 2s
TDEC 90°0’ 0”
R.A. 19h52m 5s
DEC 47°31’16” 64X
Lgst 7h52m38s Stop
Alt. 0°0’ 0”
Azi. 0°0’ 0”
2007-07-10 14:25:23 N
When the power is turned on you will see “G_ON” (GPS
turned on) in the upper right corner of th e screen. In about a
minute, after the internal GPS communicate with the
satellites, you will see “G_OK” on the screen. Both time and
location are automatically set. Setup is finished in Alt-az
mode.
The mount can also work in equatorial mode. Tilt the mount to
the appropriate angle and point it to the polar star . Go to “Set
up GotoNova”, select “Set Mount Type”, and select Equatorial
mode.
1.2 Align
1.2.1 One-Star Align
From the main menu, select “Align”. The system pro vides for
“one-star align” and “two-star align”.
Select “one-star align”. You will see this screen:
11
Page 12

www.iOptron.com
Alphard
A 39°43.3′ Z 221°20.0′
Center the target then
press “ENTER” 2X
Use “UP” and “DOWN” arrow buttons to select a star and
press ENTER. Use SPEED button to select a speed, and u se
arrow buttons to center the star in your telescope. Press
ENTER when finished.
1.2.2 Two-Star Align
If your mount is not horizontal one-star align is usually not
accurate enough. You will need to do two-star align. Select
“Two-star align” from the previous menu. Select one bright
star from the menu. Use the arrow buttons to center it in the
telescope and press ENTER. Select a second bright star and
use the arrow keys to center the second star. Press ENTER.
Two-star align is finished.
12
Page 13

www.iOptron.com
Appendix:
Check Appendix B and
Appendix C for names of
galaxies and
constellations
WARNING:
NEVER LOOK DIRECTLY
AT THE SUN WITH THE
NAKED EYES OR WITH
A TELESCOPE(UNLESS
YOU HAVE THE
PROPER SOLAR
FILTER). PERMANENT
AND IRREVERSIBLE
EYE DAMAGE MAY
RESULT.
TIP:
You can define and save
new celestial objects in
the database.
Chapter. 2 Select And Slew
After you have finished the set up and align steps in chapter 1
go to the main menu. Select “Select and slew.” Now you can
select any celestial objects in the database and GoToNova
will take you there—whether it is a star, a planet, an asteroid,
a comet or a galaxy.
Check astronomy books and magazines such as “Sky and
Telescope.” Familiarize yourself with the names in the night
sky. Use the arrow buttons to move your cursor and press
ENTER to select an object.
2.1 Planets, sun, moon
This menu includes the Sun, the Moon, Mercury, Venus,
Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune.
WARNING: NEVER LOOK DIRECTLY AT THE SUN WITH
THE NAKED EYES OR WITH A TELESCOPE (UNLESS
YOU HAVE THE PROPER SOLAR FILTER). PERMANENT
AND IRREVERSIBLE EYE DAMAGE MAY RESULT.
2.2 Deep Sky Objects
This menu includes objects outside our Solar system such as
galaxies, star clusters, quasars, ne bulae , etc.
2.2.1 Named Deep Sky Objects
This menu contains 60 named deep sky objects. If you know
the names of the objects you can use this menu.
2.2.2 Messier Catalogue
Contains 110 objects from the Messier catalogue.
2.3 Comets
Contains up to 256 comets.
2.4 Asteroids
Contains up to 4096 asteroids.
2.5 Stars
2.5.1 Named Stars
Contains 191 stars.
2.5.2 Constellations
Contains 88 constellations.
2.5.3 Double Stars
Contains 40 double stars.
2.5.4 SAO Bright Stars
Contains up to 26,584 SAO bright stars.
2.6 Constellations
TM
13
Page 14

www.iOptron.com
TIP:
By specifying R.A. and
DEC numbers (or A and
Z ) , you can point your
telescope to anywhere
on the celestial sphere.
2.7 User Objects
User defined objects, user can define up to 128 objects
2.8 Enter R.A. DEC.
In Equatorial mode the user can target a location by
specifying its RA (Right Ascension) and DEC (Declination).
Use the arrow buttons to move the cursor and adjust the
values. Press ENTER.
In Altazimuth mode the user can target a location by
specifying its A (Altitude) and Z (Azimuth). Use the arrow
buttons to move the cursor and adjust the values. Press
ENTER.
14
Page 15

www.iOptron.com
Appendix:
Check Appendix A for
complete menu
structures
Chapter. 3 Other Functions
3.1 Sync To Target
Matches the telescope's current equatorial coordinates to
Target Right Ascension and Declination.
3.2 Electric Focuser
If you have an electric focuser in your system, use this option
to adjust the focuser.
3.3 PEC option
If you telescope is equipped with Periodic Error Correction,
use this option to adjust Periodic Error Correction.
3.4 Set up tracking
Set up tracking speed.
3.5 User objects
Add, edit or delete user objects.
3.6 Auto guide
If your telescope is equipped with auto guide use this option.
3.7 Park Scope
Park your telescope.
3.8 To Park position
Move your telescope to park position.
15
Page 16

www.iOptron.com
TIP:
The earth’s axis of
rotation is tipped over
about 23.5° from the
vertical.
TIP:
People usually use alt-zi
mode to observe land
objects.
TIP:
People usually use
optics that produces
normal images (not
revered, or up-sidedown images) to
observe land objects.
TIP:
Use slower speed for
fine tuning.
Chapter. 4 How to Observe
4.1 Land Objects
If you want to observe land objects, such as a mountain top or
a bird, you should use “Land” mode. Simply point the
telescope to your target and look through the eye piece. For
certain models, such as Newtonian, the image you see in the
eye piece is up-side down.
If you don’t want to turn on power and use hand controller,
then you need to loosen the te lescop e’s trip od base lock knob
and Altitude lock so that the telescope can move freely in both
directions. Next, use the viewfinder to locate your target.
Center the target in your eyepiece and tighten the b ase and
Altitude locks. Then adjust focus.
You can also use the hand controller to observe land objects.
Turn on the power and from the main menu choose “Land
Objects”. If you already have land marks saved in your
system and you want to go to one of those land marks (this is
assuming that the tripod is not moved since you recorded
those land marks), select “GoTo Land Mark” and pick the land
mark you want to observe. If you want to record new land
marks, select “Record New Land Mark”, on the next screen,
use “SPEED” button to choose an appropriate speed, then
use arrow keys to move your telescope to your targ et. When
the target is centered, press “ENTER”, then give it a
name(with “UP” and “DOWN” arrows you can input alphabets,
with “LEFT” and “RIGHT” to move the cursor). Push “ENTER”
to confirm you input. Next time, you can go to this land mark
by selecting its name in the list under “GoTo Land Mark”
menu.
If you use “Land” mode to observe celestial objects in the
night sky, you will notice that stars drift away slowly from your
eyepiece field, and you have to keep adjusting your telescope
to re-center your target. This drift is caused by the rotation of
the Earth. This drift can be countered by using the automatic
tracking feature of GoToNova
4.2 Using Arrow Keys
On our GoToNova
You can use these keys to adjust and fine tune your
telescope. To use this function, make sure you tig hten both
the Altitude and base locks. Then turn on the power.
With the “User position” screen, press ENTER button to
switch betwe en “Land” and “Cele” mode (upper righ t corner).
Use SPEED button to adjust the speed (lo wer right corner).
Use higher speed for initial adjustment. Use lower speed for
fine tuning.
Center your target in your eye piece then adjust the focus.
User position Land
R:1h47.8m D:32°3.3’
A 89°58.5’ Z 179°11.8’
07-06-06 08:59:20 8x
TM
.
TM
controllers, there are four arrow keys.
16
Page 17

www.iOptron.com
TIP:
A Full Moon is not the
best time to watch the
Moon.
4.3 The Moon
The Moon, when visible in the night sky, is most likely the first
celestial object you want to watch with your new telescope. It
is also the most convenient object in the sky to test some of
the GoToNova
TM
functions. You can even use the Moon to
align your telescope.
There are a lot to explore on the surface of the Moon, such as
craters, mountain ranges and fault lines, etc. During full Moon,
however, no shadows are seen on the Moon surface and it
becomes too bright for the details to be seen. The best time to
observe the Moon is during its crescent or half phase.
A neutral density Moon filter is recommended when obse rving
the Moon. This filter cuts down on the bright glare and
enhances contrast. You will be amazed by the dramatic
image.
4.4 Tracking
The tracking function is used to counteract the r otation of the
earth. When the telescope is in tracking mode, the celestial
object will not drift away from your eye piece field. This
function is essential for astrophotography.
When you switch to “Cele” mode, the system is auto matically
in tracking mode. When you switch back to “ Land” mode, the
tracking stops.
A user can setup tracking in the main menu by selecting “Set
up tracking”. Then user can select “sidereal speed”, “Solar
speed”, “Lunar speed”, or user can define a speed using
“User defined speed”.
4.5 The First Night
With the convenience of SmartStar
TM
, star hunting is made
much easier. But this does not mean tha t you don’t need to
do any homework before you actually spend the night
watching the night sky, especially if you have never tried this
before.
You should play with SmartStar
TM
and familiarize yourself with
the components and functions during day time, check the
altitude and latitude of your location (where you are going to
use the SmartStar
TM
at night).
Spend sometime to study the current night sky, know what to
expect when you are out there. It will be extremely helpful if
you are able to identify some of the bright star s in the night
sky.
17
Page 18

APPENDIX A
MENU STRUCTURE
MENU
Select and sl ew
www.iOptron.com
Planets,sun,moon
Mer cury
Venus
Mars
Jupiter
Saturn
Uranus
Neptune
Sum
Moon
Deep sky objects
Na med de epsky objec t s
Messier Catalog
Comets
Asteroids
Land Objects
Sy n c. to targ et
Se t up controller
Align
User object list
Watch list
Set telescope cord.
Park telescope
Stars
User objects
Enter position
Wat ch list
Goto Land mark
Recor d now land mark
Add a new Land Ma rk
Edi t one data
Set up time and site
Se t dis pla y i nfo
Set key Beep
Rese t All
One star align
Two star align
RA a nd DE C
Comets
Asteriods
Add a wa tch l ist
De lete one da t a
Delete all
Browse the list
Name stars
Constellations
Double st ars
SA O br ight stars
18
Page 19

APPENDIX B
Messier Catalog
• Andromeda
o M31
o
o
• Aquarius
o
o M72
o M73
•
o M36
o M37
o
• Cancer
o M44
o
• Canes Venatici
o
o
o M63
o M94
o
• Canis Major
o
• Capricornus
o M30
• Cassiopeia
o M52
o M103
• Cetus
o M77
• Coma Berenices
o M53
o M64
o
o M88
o M91
o
o
o M100
•
o M29
o M39
•
o M102
•
o
•
o
o M92
•
o
Auriga
Cygnus
Draco
Gemini
Hercules
Hydra
The Andromeda Galaxy spiral galaxy (type Sb)
Satellite galaxy of M31 elliptical galaxy (type E2)
M32
Satellite galaxy of M31 elliptical galaxy (type E6pec)
M110
M2
globular cluster
globular cluster
system or asterism of 4 stars
open cluster
open cluster
M38
open cluster
Praesepe, the Beehive Cluster open cluster
open cluster
M67
globular cluster
M3
The Whirlpool Galaxy spiral galaxy
M51
Sunflower galaxy spiral galaxy
spiral galaxy
spiral galaxy
M106
open cluster
M41
globular cluster
open cluster
open cluster
spiral galaxy
globular cluster
Blackeye galaxy spiral galaxy
elliptical galaxy
M85
spiral galaxy
spiral galaxy
spiral galaxy
M98
spiral galaxy
M99
spiral galaxy
open cluster
open cluster
may be NGC 5866
open cluster
M35
Great Hercules Globular Cluster globular cluster
M13
globular cluster
open cluster
M48
www.iOptron.com
Spindle Galaxy
, a lenticular galaxy (type S0_3)
19
Page 20

www.iOptron.com
o
o
• Leo
o
o M66
o M95
o M96
o
• Lepus
o
• Lyra
o M56
o
• Monoceros
o
• Ophiuchus
o M9
o
o M12
o M14
o M19
o
o M107
•
o
o M43
o M78
• Pegasus
o M15
•
o M34
o M76
• Pisces
o M74
•
o M46
o M47
o
• Sagitta
o M71
• Sagittarius
o M8
o
o
o M20
o M21
o
o M23
o M24
o
o
o M54
o M55
o
o
Orion
Perseus
Puppis
M68
M83
M65
M105
M79
M57
M50
globular cluster
M10
M62
M42
M93
The Lagoon Nebula diffuse nebula
M17
M18
M22
M25
M28
M69
M70
globular cluster
spiral galaxy
spiral galaxy
spiral galaxy
spiral galaxy
spiral galaxy
elliptical galaxy
globular cluster
globular cluster
The Ring Nebula planetary nebula
open cluster
globular cluster
globular cluster
globular cluster
globular cluster
globular cluster
globular cluster
The Great Orion Nebula diffuse nebula
part of the Orion Nebula (de Mairan's Nebula) diffuse nebula
diffuse nebula
globular cluster
open cluster
The Little Dumbell, Cork, or Butterfly planetary nebula
spiral galaxy
open cluster
open cluster
open cluster
globular cluster
The Omega or Swan or Horseshoe Nebula diffuse nebula
open cluster
The Trifid Nebula diffuse nebula
open cluster
globular cluster
open cluster
Milky Way Patch star cloud with open cluster (NGC 6603)
open cluster
globular cluster
globular cluster
globular cluster
globular cluster
globular cluster
20
Page 21

www.iOptron.com
o
• Scorpius
o M4
o
o M7
o M80
•
o M11
o M26
•
o M5
•
o M16
•
o
o M45
•
o M33
•
o
o M81
o M82
o
o M101
of M101)
o M108
o
• Virgo
o
o
o M59
o M60
o
o M84
o M86
o M87
o
o M90
o M104
•
o M27
Scutum
Serpens Caput
Serpens Cauda
Taurus
Triangulum
Ursa Major
Vulpecula
M75
globular cluster
M6
The Butterfly Cluster open cluster
Ptolemy's Cluster
globular cluster
The Crab Nebula supernova remnant
M1
M40
M97
M109
M49
M58
M61
M89
globular cluster
open cluster
globular cluster
The Wild Duck Cluster
open cluster
open cluster associated with the
Subaru, the Pleiades--the Seven Sisters open cluster
The Triangulum Galaxy
Double Star Winecke 4 (WNC 4)
Bode's Galaxy (nebula) spiral galaxy (type Sb)
The Cigar Galaxy irregular galaxy
The Owl Nebula planetary nebula
The Pinwheel Galaxy
spiral galaxy (type Sc(s)III)
spiral galaxy (type SBb(rs)I)
elliptical galaxy (type E1 or S0_1(1))
spiral galaxy (type Sab(s)II)
elliptical galaxy (type E5)
elliptical galaxy (type E2 or S0_1(2))
spiral galaxy (type Sc(s)I.2)
elliptical or lenticular galaxy (type SB0_2/3(r)(3))
elliptical galaxy (type E3 or S0_1(3))
Virgo A elliptical galaxy (type E0), with Smoking Gun
elliptical galaxy (type E0)
spiral galaxy (type Sab(s)I-II)
The Sombrero Galaxy spiral galaxy (type Sa+/Sb-)
The Dumbbell Nebula planetary nebula
open cluster
Eagle Nebula (IC 4703)
(also Pinwheel) spiral galaxy
spiral galaxy (type Sc) (M102 may be a Duplication
21
Page 22

APPENDIX C
Modern Constellations
constellation abbreviation genitive origin
Andromeda And Andromedae ancient (Ptolemy)
Antlia Ant Antliae 1763, Lacaille
www.iOptron.com
Apus Aps Apodis
Aquarius Aqr Aquarii ancient (Ptolemy)
Aquila Aql Aquilae ancient (Ptolemy)
Ara Ara Arae ancient (Ptolemy)
Aries Ari Arietis ancient (Ptolemy)
Auriga Aur Aurigae ancient (Ptolemy)
Boötes Boo Boötis ancient (Ptolemy)
Caelum Cae Caeli 1763, Lacaille
1603, Uranometria, created by Keyser and de
Houtman
Camelopardalis Cam Camelopardalis 1624, Bartsch
Cancer Cnc Cancri ancient (Ptolemy)
Canes Venatici CVn
Canis Major CMa Canis Majoris ancient (Ptolemy)
Canum
Venaticorum
1690, Firmamentum Sobiescianum, Hevelius
22
[2]
Page 23

www.iOptron.com
Canis Minor CMi Canis Minoris ancient (Ptolemy)
Capricornus Cap Capricorni ancient (Ptolemy)
Carina Car Carinae 1763, Lacaille, split from Argo Navis
Cassiopeia Cas Cassiopeiae ancient (Ptolemy)
Centaurus Cen Centauri ancient (Ptolemy)
Cepheus Cep Cephei ancient (Ptolemy)
Cetus Cet Ceti ancient (Ptolemy)
Chamaeleon Cha Chamaeleontis
Circinus Cir Circini 1763, Lacaille
Columba Col Columbae 1679, Royer, split from Canis Major
Coma Berenices Com Comae Berenices 1603, Uranometria, split from Leo
Corona
Australis
Corona Borealis CrB Coronae Borealis ancient (Ptolemy)
Corvus Crv Corvi ancient (Ptolemy)
[3]
Crater Crt Crateris ancient (Ptolemy)
CrA Coronae Australis ancient (Ptolemy)
1603, Uranometria, created by Keyser and de
Houtman
Crux Cru Crucis 1603, Uranometria, split from Centaurus
23
Page 24

www.iOptron.com
Cygnus Cyg Cygni ancient (Ptolemy)
Delphinus Del Delphini ancient (Ptolemy)
Dorado Dor Doradus
Draco Dra Draconis ancient (Ptolemy)
Equuleus Equ Equulei ancient (Ptolemy)
Eridanus Eri Eridani ancient (Ptolemy)
Fornax For Fornacis 1763, Lacaille
Gemini Gem Geminorum ancient (Ptolemy)
Grus Gru Gruis
Hercules Her Herculis ancient (Ptolemy)
1603, Uranometria, created by Keyser and de
Houtman
1603, Uranometria, created by Keyser and de
Houtman
Horologium Hor Horologii 1763, Lacaille
Hydra Hya Hydrae ancient (Ptolemy)
Hydrus Hyi Hydri
Indus Ind Indi
Lacerta Lac Lacertae 1690, Firmamentum Sobiescianum, Hevelius
Leo Leo Leonis ancient (Ptolemy)
1603, Uranometria, created by Keyser and de
Houtman
1603, Uranometria, created by Keyser and de
Houtman
24
Page 25

www.iOptron.com
Leo Minor LMi Leonis Minoris 1690, Firmamentum Sobiescianum, Hevelius
Lepus Lep Leporis ancient (Ptolemy)
Libra Lib Librae ancient (Ptolemy)
Lupus Lup Lupi ancient (Ptolemy)
Lynx Lyn Lyncis 1690, Firmamentum Sobiescianum, Hevelius
Lyra Lyr Lyrae ancient (Ptolemy)
Mensa Men Mensae 1763, Lacaille
Microscopium Mic Microscopii 1763, Lacaille
Monoceros Mon Monocerotis 1624, Bartsch
Musca Mus Muscae
Norma Nor Normae 1763, Lacaille
Octans Oct Octantis 1763, Lacaille
Ophiuchus Oph Ophiuchi ancient (Ptolemy)
Orion Ori Orionis ancient (Ptolemy)
Pavo Pav Pavonis
1603, Uranometria, created by Keyser and de
Houtman
1603, Uranometria, created by Keyser and de
Houtman
Pegasus Peg Pegasi ancient (Ptolemy)
25
Page 26

www.iOptron.com
Perseus Per Persei ancient (Ptolemy)
Phoenix Phe Phoenicis
Pictor Pic Pictoris 1763, Lacaille
Pisces Psc Piscium ancient (Ptolemy)
Piscis Austrinus PsA Piscis Austrini ancient (Ptolemy)
Puppis Pup Puppis 1763, Lacaille, split from Argo Navis
Pyxis Pyx Pyxidis 1763, Lacaille
Reticulum Ret Reticuli 1763, Lacaille
Sagitta Sge Sagittae ancient (Ptolemy)
1603, Uranometria, created by Keyser and de
Houtman
Sagittarius Sgr Sagittarii ancient (Ptolemy)
Scorpius Sco Scorpii ancient (Ptolemy)
Sculptor Scl Sculptoris 1763, Lacaille
Scutum Sct Scuti 1690, Firmamentum Sobiescianum, Hevelius
Serpens
Sextans Sex Sextantis 1690, Firmamentum Sobiescianum, Hevelius
Telescopium Tel Telescopii 1763, Lacaille
[4]
Ser Serpentis ancient (Ptolemy)
Taurus Tau Tauri ancient (Ptolemy)
26
Page 27

www.iOptron.com
Triangulum Tri Trianguli ancient (Ptolemy)
Triangulum
Australe
Tucana Tuc Tucanae
Ursa Major UMa Ursae Majoris ancient (Ptolemy)
Ursa Minor UMi Ursae Minoris ancient (Ptolemy)
Vela Vel Velorum 1763, Lacaille, split from Argo Navis
Virgo Vir Virginis ancient (Ptolemy)
Volans Vol Volantis
Vulpecula Vul Vulpeculae 1690, Firmamentum Sobiescianum, Hevelius
TrA Trianguli Australis
1603 Uranometria, created by Keyser and de
Houtman
1603 Uranometria, created by Keyser and de
Houtman
1603, Uranometria, created by Keyser and de
Houtman
27
Page 28

APPENDIX D
Celestial Coordinates
www.iOptron.com
Celestial
North Pole
East
North South
Observer’s horizon
Zenith
Median of the location
Altitude
Azimuth
West
Celestial
Nadir
South Pole
FIG.D1
28
Page 29

www.iOptron.com
Celestial
Zenith
North Pole
median of
location
δ, declination
t, hour angle
East
M, midpoint
North South
Observer’s horizon
star hour
circle
Celestial Equator
West
axis of
rotation
Nadir
FIG.D2
South Pole
Celestial
29
Page 30

www.iOptron.com
γ
Celestial
Zenith
North Pole
median of
location
δ
, declination
circle
hour
Celestial
Equator
α
, right
ascension
East
North South
Observer’s horizon
star hour
West
axis of
rotation
circle
gamma point
Nadir
FIG. D3
South Pole
Celestial
30
Page 31

www.iOptron.com
TIP:
Celestial sphere is an
imaginary sphere of
infinite radius.
NOTE:
You need two numbers
to define a position on
the celestial sphere.
To understand the celestial coordinate systems there are
several concepts that should be clarified.
The Celestial s phere is an imaginary sphere of infinite radius
concentric with the earth on which all celestial bodies are
assumed to be projected. Celestial coordinates are used to
define a point on the celestial sphere. A great circle, a.k.a.,
orthodrome, is the intersection of a sphere and a plane
through its center. For the celestial sphere, a great circle is
the intersection of a plane through the observer (on the earth)
and the celestial sphere. Celestial pole is either of the two
points of intersection of the celestial sphere and the extended
axis of the earth. There are two celestial poles--the north
celestial pole
the point of the celestial sphere vertically overhead. The
Nadir is the point on the celestial sphere vertically below the
observer, or 180 degrees from the zenith. A horizon is a
great circle on the celestial sphere midway between the
zenith and nadir. Celestial meridian is a great circle of the
celestial sphere through the celestial poles and the zenith.
Celestial equator
the equator and the celestial sphere. It is the primary great
circle of the celestial sphere in the equatorial system,
everywhere 90-degree from the celestial poles.
We will talk about two different kinds of celestial coordinate
systems. One is the altazimuth system. And the other is the
equatorial system. The major difference between them is the
referencing great circle. In altazimuth it is the celestial
horizon, while in equatorial it is the celestial equator.
To define a position on the celestial sphere, we need two
angles. In the altazimuth system (FIG. D1) these two angles
are altitude (A) and azimuth (Z). Imagine a vertical plane
perpendicular to the observer’s horizon that passes through
the observer and the star. The intersection of the vertical
plane and the observer’s plane of horizon defines the
azimuth. It is measured from the south (or the north) to the
intersection (in the direction of motion of the star, in degrees,
0°~360°). In GoToNova
On the vertical plane,
intersection to the direction of the star (also in degrees, 90°~90°).
In the equatorial system (FIG. D2 and D3), hour angle (t) is
measured on the equator from the point of intersection of the
celestial equator and the local meridian in the direction of
motion of the star. The value of hour angle is measured in
hours, minutes and seconds instead of degrees.
and the
south celestial pole
is the intersection of the extended plane of
TM
azimuth is measured from the north.
altitude
is measured from the
. The
Zenith
is
31
Page 32

www.iOptron.com
TIP:
Don’t be intimidated by
the geometry. Hands-on
experience will help you
understand the concepts
better.
Since the celestial sphere completes a full rotation in 24 hours,
it follows that: 24 h = 360°, 1 h = 15°, 1 min = 15’, and 1 sec =
15”. The declination (δ, DEC, or D) is measured along the
hour circle (perpendicular to the equator, passing through the
celestial poles) passing through the star from the point it
intersects the equator, it is in degrees. The right ascension
(α, RA or R) is measured on the equator from the gamma
point in the direction opposite to the direction of the motion of
the star. It is in hours, minutes and seconds. Gamma point is
the intersection of the hour circle and the celestial equator.
32
Page 33

www.iOptron.com
Appendix E
SPECIFICATIONS
A-Series Specifications
LCD Display…………………………8-line
Mount….…………………………….The Cube
Alignment……………………………Altazimuth/Equatorial
GPS………………………………….32-channel GPS included
CPU………………………………….32 bit
USB Port…………………………….Yes
RS232 Port………………………….Yes
Slewing Speeds…………………….9-Speed (1x, 2x, 8x, 16x, 64x,
128x, 256x, 512x, MAX)
Tripod………………………………..Stainless Steel(6.0 lbs)
Batteries(User-Supplied)…………..8 x AA
GoToNova
Objects in database………………..50000+
Weight……………………………….4.0lbs
A-R80
Optical Design………………………Refractor
Clear Aperture………………………80mm
Focal Length………………………...400mm
Focal Ratio…………………………..f/5
Resolving Power……………………1.4 arc secs
Finder……………………….………..5x24
Weight………………………………..2.2lbs
A-N114
Optical Design………………………Reflector
Clear Aperture………………………114mm
Focal Length………………………...1000mm
Focal Ratio…………………………..f/8.8
Resolving Power……………………1 arc secs
Finder……………………….………..Red dot
Weight………………………………..6lbs
A-MC90
Optical Design……………………… Maksutov-Cassegrain
Clear Aperture………………………90mm
Focal Length………………………...1200mm
Focal Ratio…………………………..f/13.3
Resolving Power……………………1.3 arc secs
Finder……………………….………..red dot
Weight………………………………..4.4lbs
A-MC100
Optical Design……………………… Maksutov-Cassegrain
Clear Aperture………………………109mm
Focal Length………………………...1400mm
Focal Ratio…………………………..f/14
Resolving Power……………………1.2 arc secs
Finder…………………….…………..red dot
Weight………………………………..4.5lbs
TM
Version………………8402
33
Page 34

www.iOptron.com
Appendix F
Products List
Item # Product Product Description Components
SmartStar
#8500 SmartSta
#8502 SmartStar
#8503 SmartStarTM-E-N114 Automatic Newtonian GOTO Telescope #8500, #8732
#8504 SmartStar
#8501 1"Stainless Steel Tripod For SmartStarTM-E 26 .
SmartStar
#8600 SmartStarTM-A Fully Automatic AltAzi/EQ #8411, #8402,
#8602 SmartStar
#8603 SmartStarTM-A-N114 Fully Automatic Newtonian GOTO Telescope #8600, #8734
#8604 SmartStar
#8605 SmartStarTM-A-MC100 Fully Automatic Maksutov-Cassegrain #8600, #8741
#8601 1" AltAzi/EQ Stainless Steel Tripod
#8606 1.5kg Counter Weight .
#8419 SmartStar
#8400 GOTONovaTM #8401
GOTONova
#8401 GOTONovaTM Controller AltAzi/EQ Controller with 130,000 objects in database
#8402 GOTONova
#8403 GOTONovaTM Controller AltAzi/EQ Controller with 5,000 objects in database
Accessories
#8411 GPS Module Compatible with all GOTONovaTM Models
#8412 Electronic Focuser Module
#8413 2" Stainless Steel tripod For EQ、CG5、GPD、LX75 Mounts
#8414 EQ5 Equatorial Mount
#8415 Controller Cable Compatible with all GOTONovaTM Models
#8416 USB Cable For #8401, #8402 Controllers
#8417 AC Adaptor Compatible with all GOTONovaTM Models
#8418 12V Car Recharger
TM
-E Series
TM
-A Series
Dual-Axis Motor Kit For EQ、CG5、GPD、LX75 Mounts Dual-Axis Motor
TM
and Cable
rTM
-E GOTO Mount AltAzi Mount, #1403, #1501
TM
-E-R80 Automatic Refractor GOTO Telescope #8500, #8701
TM
-E-MC90 Automatic Maksutov GOTO Telescope #8500, #8740
TM
-A-R80 Fully Automatic Refractor GOTO Telescope #8600, #8701
TM
-A-MC90 Fully Automatic Maksutov-Cassegrain
GOTO Mount with GPS #8601
GOTO Telescope #8600, #8740
GOTO Telescope
For SmartStar
TM
-PR GOTO Equatorial Mount #8400, #8413,
TM
-A
#8414
Controllers
TM
Controller AltAzi/EQ Controller with 50,000 objects in database
(for SmartStarTM-E)
34
Page 35

Appendix G
s
Alignment Stars
Stars for Alignment (iOptron SmartStar, GoToNova)
www.iOptron.com
StarName Constellation RA DEC Additional Information
Achernar Eri 1.6285685 -57.2367575 TYC 8478-1395-1 PPM 331199 SAO 232481 HD 10144 CPD -57 00334
Acrux Cru 12.443056 -63.098611 TYC 8979-3464-1 PPM 359410 SAO 251904 HD 108248 CPD -62 02745
Al Na'ir Gru 22.136944 -46.960833 TYC 8438-1959-1 PPM 327928 SAO 230992 HD 209952 CPD -47 09830
Albireo Cyg 19.511944 27.959167 TYC 2133-2964-1 PPM 109139 SAO 87301 HD 183912 BD +27 3410
Aldebaran Tau 4.598611 16.508889 TYC 1266-1416-1 PPM 120061 SAO 94027 HD 29139 BD +16 0629
Alphard
Alphecca CoB 15.578056 26.714444 TYC 2029-1690-1 PPM 104146 SAO 83893 HD 139006 BD +27 2512
Alpheratz And 0.139444 29.090278 TYC 1735-3180-1 PPM 89441 SAO 73765 HD 358 BD +28 0004
Altair Aql 19.846111 8.868333 TYC 1058-3399-1 PPM 168779 SAO 125122 HD 187642 BD +8 4236
Antares Sco 16.489722 -26.431667 TYC 6803-2158-1 PPM 265579 SAO 184415 HD 148478 CD -26 11359 CPD -26 05648
Arcturus
Betelgeuse Ori 5.919519 7.406944 TYC 129-1873-1 PPM 149643 SAO 113271 HD 39801 BD +7 1055
Canopus Car 6.399167 -52.695556 TYC 8534-2277-1 PPM 335149 SAO 234480 HD 45348 CPD -52 00914
Capella Aur 5.277778 45.997500 TYC 3358-3141-1 SAO 40186 HD 34029 BD +45 1077
Deneb Cyg 20.690000 45.280000 TYC 3574-3347-1 PPM 60323 SAO 49941 HD 197345 BD +44 3541
Denebola Leo 11.817500 14.571667 TYC 870-988-1 PPM 128576 SAO 99809 HD 102647 BD +15 2383
Deneb Kaitos Cet 0.726111 -17.986389 TYC 5847-2333-1 PPM 209214 SAO 147420 HD 4128 BD -18 0115
Dubhe UMa 11.061667 61.750556 TYC 4146-1274-1 PPM 17705 SAO 15384 HD 95689 BD +62 1161
Fomalhaut PsA 22.960833 -29.622222 TYC 6977-1267-1 PPM 274426 SAO 191524 HD 216956 CD -30 19370 CPD -30 06685
Hamal Ari 2.119444 23.462222 TYC 1758-2416-1 PPM 91373 SAO 75151 HD 12929 BD +22 0306
Markab Peg 23.078889 15.205000 TYC 1711-2475-1 PPM 142158 SAO 108378 HD 218045 BD +14 4926
Hya 9.459790 -8.658602 TYC 5460-1592-1 PPM 192393 SAO 136871 HD 81797 BD -8 2680
Boo 14.260833 19.182222 TYC 1472-1436-1 PPM 130442 SAO 100944 HD 124897 BD +19 2777
Mirfak Per 3.405000 49.861111 TYC 3320-2808-1 PPM 46127 SAO 38787 HD 20902 BD +49 0917
Mizar UMa 13.398333 54.925278 TYC 3850-1385-1 PPM 34007 SAO 28737 HD 116656 BD +55 1598
Nunki Sgr 18.920833 -26.296667 TYC 6868-1829-1 PPM 269078 SAO 187448 HD 175191 CD -26 13595 CPD -26 06590
Pollux Gem 7.754722 28.025833 TYC 1920-2194-1 PPM 97924 SAO 79666 HD 62509 BD +28 1463
Procyon CMa 7.655000 5.224444 TYC 187-2184-1 SAO 115756 HD 61421 BD +5 1739
Rasalhague
Regulus Leo 10.139444 11.967222 TYC 833-1381-1 PPM 127140 SAO 98967 HD 87901 BD +12 2149
Rigel
Rigel Kentauru
Schedar Cas 0.675000 56.536944 TYC 3663-2668-1 PPM 25578 SAO 21609 HD 3712 BD +55 0139
Sirius CMa 6.752222 -16.716111 YC 5949-2777-1 SAO 151881 HD 48915 BD -16 1591
Spica Vir 13.419722 -11.161111 TYC 5547-1518-1 PPM 227262 SAO 157923 HD 116658 BD -10 3672
Suhail Vel 9.133056 -43.432222 TYC 7689-2617-1 PPM 313999 SAO 220878 HD 78647 CD -42 04990 CPD -42 03366
Vega
Oph 17.581944 12.560000 TYC 1000-2508-1 PPM 133563 SAO 102932 HD 159561 BD +12 3252
Ori 5.241944 -8.201389 TYC 5331-1752-1 PPM 187839 SAO 131907 HD 34085 BD -8 1063
Cen 14.660138 -60.833958 TYC 9007-5849-1 SAO 252838 HD 128620 CPD -60 05483
Lyr 18.615556 38.783611 YC 3105-2070-1 SAO 67174 HD 172167 BD +38 3238
Page 36

www.iOptron.com
IOPTRON TWO YEAR TELESCOPE, MOUNT, AND CONTROLLER
WARRANTY
A. iOptron warrants your telescope, mount, or controller to be free from defects in materials and workmanship for two
years. iOptron will repair or replace such product or part which, upon inspection by iOptron, is found to be defective in
materials or workmanship. As a condition to the obligation of iOptron to repair or replace such product, the product must
be returned to iOptron together with proof-of-purchase satisfactory to iOptron.
B. The Proper Return Authorization Number must be obtained from iOptron in advance of return. Call iOptron at
1.866.399.4587 to receive the number to be displayed on the outside of your shipping container.
All returns must be accompanied by a written statement stating the name, address, and daytime telephone number of the
owner, together with a brief description of any claimed defects. Parts or product for which replacement is made shall
become the property of iOptron.
The customer shall be responsible for all costs of transportation and insurance, both to and from the factory of iOptron,
and shall be required to prepay such costs.
iOptron shall use reasonable efforts to repair or replace any telescope, mount, or controller covered by this warranty
within thirty days of receipt. In the event repair or replacement shall require more than thirty days, iOptron shall notify the
customer accordingly. iOptron reserves the right to replace any product which has been discontinued from its product line
with a new product of comparable value and function.
This warranty shall be void and of no force of effect in the event a covered product has been modified in design or
function, or subjected to abuse, misuse, mishandling or unauthorized repair. Further, product malfunction or deterioration
due to normal wear is not covered by this warranty.
IOPTRON DISCLAIMS ANY WARRANTIES, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, WHETHER OF MERCHANTABILITY OF FITNESS
FOR A PARTICULAR USE, EXCEPT AS EXPRESSL Y SET FORTH HERE. THE SOLE OBLIGATION OF IOPTRON
UNDER THIS LIMITED WARRANTY SHALL BE TO REPAIR OR REPLACE THE COVERED PRODUCT, IN
ACCORDANCE WITH THE TERMS SET FORTH HERE. IOPTRON EXPRESSLY DISCLAIMS ANY LOST PROFITS,
GENERAL, SPECIAL, INDIRECT OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES WHICH MAY RESULT FROM BREACH OF ANY
WARRANTY, OR ARISING OUT OF THE USE OR INABIL ITY TO USE ANY IOPTRON PRODUCT. AN Y WARRAN TIES
WHICH ARE IMPLIED AND WHICH CANNOT BE DISCLAI MED SHALL BE LIMITED IN DURATION TO A TERM OF
TWO YEARS FROM THE DATE OF ORIGINAL RETAIL PURCHASE.
Some states do not allow the exclusion or limitation of incidental or consequential damages or limitation on how long an
implied warranty lasts, so the above limitations and exclusions may not apply to you.
This warranty gives you specific legal rights, and you may also have other rights which vary from state to state.
iOptron reserves the right to modify or discontinue, without prior notice to you, any model or style telescope.
If warranty problems arise, or if you need assistance in using your telescope, mount, or controller contact:
NOTE: This warranty is valid to U.S.A. and Canadian customers who have purchased this product from an authorized
iOptron dealer in the U.S.A. or Canada or directly from iOptron. Warranty outside the U.S.A. and Canada is valid only to
customers who purchased from an iOptron Distributor or Authorized iOptron Dealer in the specific country. Please contact
them for any warranty service.
iOptron Corporation
Customer Service Department
6X Gill Street
Woburn, MA 01801
www.ioptron.com
Tel. (866)399-4597
Fax. (781)935-2860
Monday-Friday 9AM-5PM EST
35
 Loading...
Loading...