Yamaha 8D User Manual

OWNER’S MANUAL
8D
U.S.A.Edition
LIT-18626-05-81
6M8-F8199-18

EMU25060
Read this owner’s manual carefully before operating your outboard motor.
ZMU01690

Important manual information
EMU25100
To the owner
Thank you for choosing a Yamaha outboard
motor. This Owner’s Manual contains information needed for proper operation, maintenance and care. A thorough understanding
of these simple instructions will help you obtain maximum enjoyment from your new
Yamaha. If you have any question about the
operation or maintenance of your outboard
motor, please consult a Yamaha dealer.
In this Owner’s Manual particularly important
information is distinguished in the following
ways.
The Safety Alert Symbol means
ATTENTION! BECOME ALERT! YOUR
SAFETY IS INVOLVED!
EWM00780
WARNING
Failure to follow WARNING instructions
could result in severe injury or death
the machine operator, a bystander, or a
person inspecting or repairing the outboard motor.
ECM00700
CAUTION:
A CAUTION indicates special precautions
that must be taken to avoid damage to the
outboard motor.
to
al, please consult your Yamaha dealer.
NOTE:
The 8MH and the standard accessories are
used as a base for the explanations and illustrations in this manual. Therefore some
items may not apply to every model.
EMU25130
8D
OWNER’S MANUAL
©2004 by Yamaha Motor Corporation, USA
1st Edition, January 2004
All rights reserved.
Any reprinting or unauthorized use
without the written permission of
Yamaha Motor Corporation, USA
is expressly prohibited.
Printed in France
P/N LIT-18626-05-81
NOTE:
A NOTE provides key information to make
procedures easier or clearer.
Yamaha continually seeks advancements in
product design and quality. Therefore, while
this manual contains the most current product information available at the time of printing, there may be minor discrepancies
between your machine and this manual. If
there is any question concerning this manu-

Table of contents
General information .......................... 1
Identification numbers record.......... 1
Outboard motor serial number .......... 1
Emission control information ........... 1
North American models..................... 1
Safety information ........................... 2
Important labels............................... 3
Warning labels ..................................3
Basic boating rules (Rules of the
road) .............................................. 4
Steering and sailing rules and sound
signals............................................. 4
Rules when encountering vessels .... 4
Other special situations..................... 5
Fueling instructions ......................... 7
Gasoline............................................ 8
Engine oil ..........................................8
Propeller selection........................... 8
Start-in-gear protection ................... 9
Basic components ..........................10
Main components.......................... 10
Fuel tank .........................................10
Fuel joint ......................................... 11
Fuel gauge ...................................... 11
Fuel tank cap .................................. 11
Air vent screw ................................. 11
Tiller handle .................................... 11
Gear shift lever................................ 11
Throttle grip..................................... 11
Throttle indicator .............................12
Throttle friction adjuster................... 12
Engine stop lanyard switch .............12
Engine stop button .......................... 13
Choke knob for pull type .................13
Manual starter handle .....................13
Steering friction adjuster .................13
Trim rod (tilt pin).............................. 14
Shallow water lever......................... 14
Tilt support knob ............................. 14
Top cowling lock lever(s) (turn
type).............................................. 14
Operation .........................................16
Installation ..................................... 16
Mounting the outboard motor.......... 16
Clamping the outboard motor ......... 17
Breaking in engine ........................ 18
Gasoline and engine oil mixing
chart (25:1).................................... 18
Procedure for pre-mixed models..... 18
Preoperation checks ..................... 19
Fuel .................................................19
Oil.................................................... 19
Controls........................................... 19
Engine ............................................. 19
Filling fuel and engine oil .............. 19
Filling fuel for portable tank ............. 19
Gasoline and oil mixing (100:1)....... 20
Operating engine .......................... 20
Feeding fuel (portable tank) ............20
Starting engine ................................ 21
Warming up engine....................... 23
Choke start models .........................23
Shifting.......................................... 23
Forward (tiller handle and remote
control models) .............................23
Reverse (manual tilt and hydro tilt
models) ......................................... 24
Stopping engine............................ 24
Procedure........................................ 24
Trimming outboard motor.............. 25
Adjusting trim angle for manual tilt
models ..........................................26
Adjusting boat trim ..........................26
Tilting up and down....................... 27
Procedure for tilting up (manual tilt
models) ......................................... 28
Procedure for tilting down (manual
tilt models)..................................... 29
Cruising in shallow water .............. 29
Cruising in shallow water (manual
tilt models)..................................... 29
Cruising in other conditions........... 30
Maintenance .................................... 31
Specifications................................ 31
Transporting and storing
outboard motor ........................... 31
Clamp screw mounting models ....... 32
Storing outboard motor ...................32
Procedure........................................ 33
Lubrication (except oil injection

models) ......................................... 34
Cleaning and anticorrosion
measures ...................................... 34
Cleaning the outboard motor .......... 34
Checking painted surface of
motor............................................. 34
Periodic maintenance.................... 34
Replacement parts.......................... 35
Maintenance chart .......................... 36
Greasing ......................................... 37
Cleaning and adjusting spark plug.. 37
Checking fuel system...................... 38
Checking fuel filter .......................... 39
Inspecting idling speed ................... 39
Checking wiring and connectors ..... 40
Exhaust leakage ............................. 40
Water leakage................................. 40
Checking propeller .......................... 40
Removing the propeller................... 41
Installing the propeller..................... 41
Changing gear oil............................ 42
Cleaning fuel tank ...........................42
Inspecting and replacing anode(s).. 43
Checking top cowling ...................... 43
Coating the boat bottom.................. 44
Trouble Recovery............................ 45
Troubleshooting ............................ 45
Temporary action in emergency.... 48
Impact damage ...............................48
Starter will not operate .................... 48
Emergency starting engine .............49
Treatment of submerged motor..... 50
Procedure ....................................... 50
Consumer information.................... 52
Important warranty information for
U.S.A. and Canada ..................... 52
YAMAHA MOTOR
CORPORATION, U.S.A.
OUTBOARD MOTOR TWO
YEAR LIMITED WARRANTY ...... 54
IMPORTANT WARRANTY
INFORMATION IF YOU USE
YOUR YAMAHA OUTSIDE
U.S.A. OR CANADA ...................57
Table of contents
General information
EMU25170
Identification numbers record
EMU25182
Outboard motor serial number
The outboard motor serial number is
stamped on the label attached to the port
side of the clamp bracket or the upper part of
the swivel bracket.
Record your outboard motor serial number in
the spaces provided to assist you in ordering
spare parts from your Yamaha dealer or for
reference in case your outboard motor is stolen.
1
ZMU02836
1. Outboard motor serial number location
engine for details.
EMU30390
Approval label of emission control certificate
This label is attached to the bottom cowling.
Existing Technology; N/A
1
ZMU02839
1. Approval label location
EMU25220
Emission control information
EMU25230
North American models
This engine conforms to U.S. Environmental
Protection Agency (EPA) regulations for marine SI engines. See the label affixed to your
1
ZMU02896
EMU25261
Manufactured date label
This label is attached to the clamp bracket or
the swivel bracket.

1
ZMU02838
1. Manufactured date label location
Manufactured:
ZMU04346
EMU25360
Safety information
●
Before mounting or operating the outboard
motor, read this entire manual. Reading it
should give you an understanding of the
motor and its operation
●
Before operating the boat, read any owner’s or operator’s manuals supplied with it
and all labels. Be sure you understand
each item before operating.
●
Do not overpower the boat with this outboard motor. Overpowering the boat could
result in loss of control. The rated power of
the outboard should be equal to or less
than the rated horsepower capacity of the
boat. If the rated horsepower capacity of
the boat is unknown, consult the dealer or
boat manufacturer.
General information
●
Do not modify the outboard. Modifications
could make the motor unfit or unsafe to
use.
●
Never operate after drinking alcohol or taking drugs. About 50% of all boating fatalities involve intoxication.
●
Have an approved personal flotation device (PFD) on board for every occupant. It
is a good idea to wear a PFD whenever
boating. At a minimum, children and nonswimmers should always wear PFDs, and
everyone should wear PFDs when there
are potentially hazardous boating conditions.
Gasoline is highly flammable, and its va-
●
pors are flammable and explosive. Handle
and store gasoline carefully. Make sure
there are no gas fumes or leaking fuel before starting the engine.
●
This product emits exhaust gases which
contain carbon monoxide, a colorless,
odorless gas which may cause brain damage or death when inhaled. Symptoms include nausea, dizziness, and drowsiness.
Keep cockpit and cabin areas well ventilated. Avoid blocking exhaust outlets.
Check throttle, shift, and steering for prop-
●
er operation before starting the engine.
●
Attach the engine stop switch lanyard cord
to a secure place on your clothing, or your
arm or leg while operating. If you accidentally leave the helm, the cord will pull from
the switch, stopping the engine.
●
Know the marine laws and regulations
where you will be boating—and obey
them. For basic boating rules, see “Rules
of the road” on page 4.
●
Stay informed about the weather. Check
weather forecasts before boating. Avoid
boating in hazardous weather.
●
Tell someone where you are going: leave
2
General information
a Float Plan with a responsible person. Be
sure to cancel the Float Plan when you return.
●
Use common sense and good judgment
when boating. Know your abilities, and be
sure you understand how your boat handles under the different boating conditions
you may encounter. Operate within your
limits, and the limits of your boat. Always
operate at safe speeds, and keep a careful
watch for obstacles and other traffic.
Always watch carefully for swimmers dur-
●
ing the engine operation.
●
Stay away from swimming areas.
When a swimmer is in the water near you
●
shift into neutral and shut off the engine.
Be informed about boating safety. Additional
publications and information can be obtained
from many organizations, including the following:
United States Coast Guard
Consumer Affairs Staff (G-BC)
Office of Boating, Public, and Consumer Affairs
U.S. Coast Guard Headquarters
Washington, D.C. 20593-0001
Boating Safety Hotline: 1-800-368-5647
National Marine Manufacturers Association (NMMA)
401 N. Michigan Ave.
Chicago, Il 60611
Marine Retailers Association of America
155 N. Michigan Ave.
Chicago, Il 60601
EMU25380
Important labels
EMU25395
Warning labels
ZMU02841
ZMU02842
EMU25401
Label
EWM01260
WARNING
●
Be sure shift control is in neutral before
starting engine. (except 2HP)
●
Do not touch or remove electrical parts
when starting or during operation.
Keep hands, hair, and clothes away
●
from flywheel and other rotating parts
while engine is running.
EMU25431
Label
EWM01300
WARNING
This engine is equipped with a neutral
●
3

General information
starting device.
●
The engine will not start unless the shift
control is in neutral position.
EMU25500
Basic boating rules (Rules of
the road)
Just as there are rules which apply when you
are driving on streets and high ways, there
are waterway rules which apply when you
are driving your boat. These rules are used
internationally, and are also enforced by the
United States Coast Guard and local agencies. You should be aware of these rules,
and follow them whenever you encounter
another vessel on the water.
Several sets of rules prevail according to
geographic location, but are all basically the
same as the International Rules of the Road.
The rules presented here in your Owner’s
Manual are condensed, and have been provided for your convenience only. Consult
your local U.S. Coast Guard Auxiliary or Department of Motor Vehicles for a complete
set of rules governing the waters in which
you will be using your boat.
EMU25510
Steering and sailing rules and sound
signals
Whenever two vessels on the water meet
one another, one vessel has the right-ofway; it is called the “stand-on” vessel. The
vessel which does not have the right-of-way
is called the “give-way” or “burdened” vessel.
These rules determine which vessel has the
right-of-way, and what each vessel should
do.
Stand-on vessel
The vessel with the right-of-way has the duty
to continue its course and speed, except to
avoid an immediate collision. When you
maintain your direction and speed, the other
vessel will be able to determine how best to
avoid you.
Give-way vessel
The vessel which does not have the right-ofway has the duty to take positive and timely
action to stay out of the way of the Stand-On
vessel. Normally, you should not cross in
front of the vessel with the right-of-way. You
should slow down or change directions briefly and pass behind the other vessel. You
should always move in such a way that the
operator of the other vessel can see what
you are doing.
“The general prudential rule”
This rule is called Rule 2 in the International
Rules and says,
“In obeying and construing these rules due
regard shall be had to all dangers of navigation and collision, and to any special circumstances, which may render a departure from
the above rules necessary in order to avoid
immediate danger.”
In other words, follow the standard rules except when a collision will occur unless both
vessels try to avoid each other. If that is the
case, both vessels become “Give-Way” vessels.
EMU25520
Rules when encountering vessels
There are three main situations which you
may encounter with other vessels which
could lead to a collision unless the Steering
Rules are followed:
Meeting:
sel head-on)
Crossing:
er vessel’s path)
Overtaking:
passed by another vessel)
In the following illustration, your boat is in the
center. You should give the right-of-way to
any vessels shown in white area (you are the
(you are approaching another ves-
(you are traveling across the oth-
(you are passing or being
4
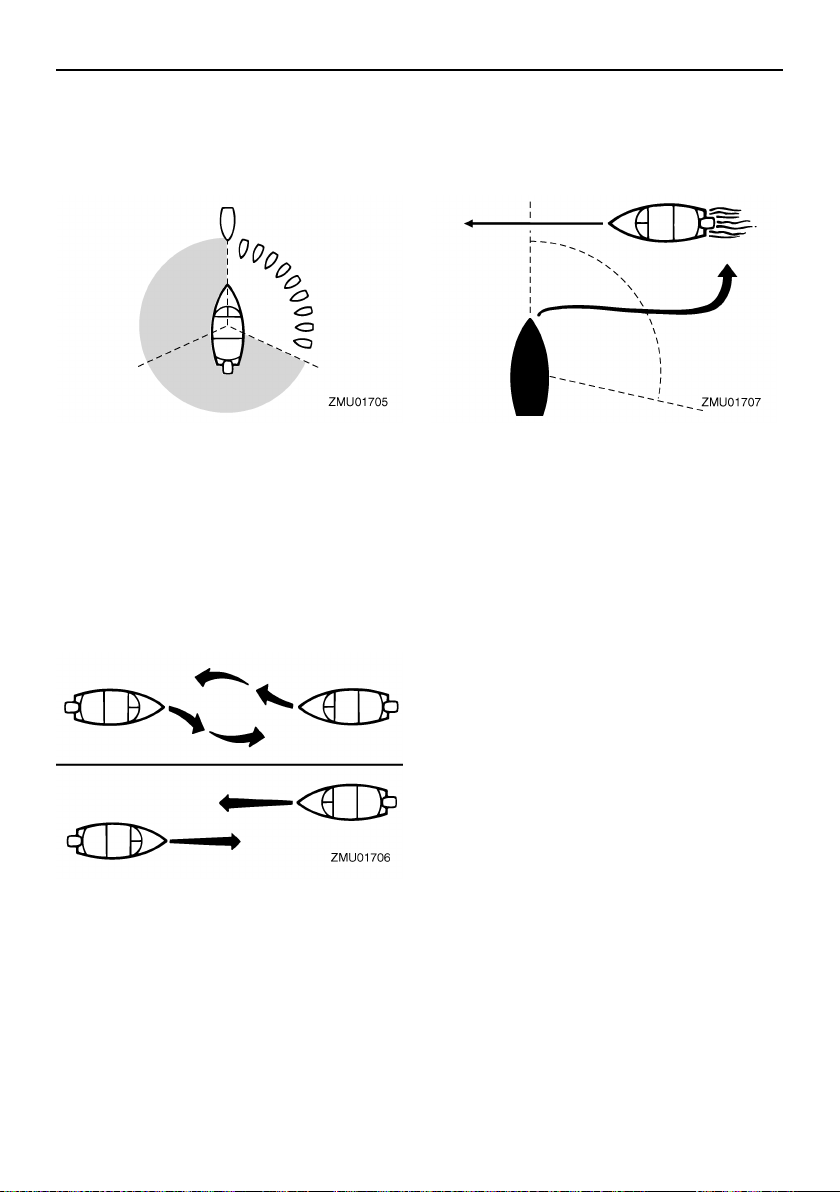
General information
Give-Way vessel). Any vessels in the shaded area must yield to you (they are the GiveWay vessels). Both you and the meeting
vessel must alter course to avoid each other.
Meeting
If you are meeting another power vessel
head on, and are close enough to run the risk
of collision, neither of you has the right-ofway! Both of you should alter course to avoid
an accident. You should keep the other vessel on your port (left) side. This rule doesn’t
apply if both of you will clear one another if
you continue on your set course and speed.
Crossing
When two power driven vessels are crossing
each other’s path close enough to run the
risk of collision, the vessel which has the other on the starboard (right) side must keep out
of the way of the other. If the other vessel is
on your right, you must keep out of its way;
you are the Give-Way vessel. If the other
vessel is on your port (left) side, remember
that you should maintain course and direction, provided the other vessel gives you the
right-of-way as it should.
Overtaking
If you are passing another vessel, you are
the “Give-Way” vessel. This means that the
other vessel is expected to maintain its
course and speed. You must stay out of its
way until you are clear of it. Likewise, if another vessel is passing you, you should
maintain your speed and direction so that the
other vessel can steer itself around you.
EMU25530
Other special situations
There are three other rules you should be
aware of when driving your boat around other vessels.
Narrow channels and bends
When navigating in narrow channels, you
should keep to the right when it is safe and
practical to do so. If the operator of a powerdriven vessel is preparing to go around a
bend that may obstruct the view of other water vessels, the operator should sound a prolonged blast on the whistle (4 to 6 seconds).
If another vessel is around the bend, it too
should sound the whistle. Even if no reply is
heard, however, the vessel should still proceed around the bend with caution. If you
navigate such waters with your boat, you will
5

General information
need to carry a portable air horn, available
from local marine supply stores.
Fishing vessel right-of-way
All vessels which are fishing with nets, lines
or trawls are considered to be “fishing vessels” under the International Rules. Vessels
with trolling lines are not considered fishing
vessels. Fishing vessels have the right-ofway regardless of position. Fishing vessels
cannot, however, impede the passage of
other vessels in narrow channels.
Sailing vessel right-of-way
Sailing vessels should normally be given the
right-of-way. The exceptions to this are:
1. When the sailing vessel is overtaking
the power-driven vessel, the power-driven vessel has the right-of-way.
2. Sailing vessels should keep clear of any
fishing vessel.
3. In a narrow channel, a sailing vessel
should not hamper the safe passage of
a power-driven vessel which can navigate only in such a channel.
Reading buoys and other markers
The waters of the United states are marked
for safe navigation by the lateral system of
buoyage. Simply put, buoys and markers
have an arrangement of shapes, colors,
numbers and lights to show which side of the
buoy a boater should pass on when navigating in a particular direction. The markings on
these buoys are oriented from the perspective of being entered from seaward (the boater is going towards the port). This means that
red buoys are passed on the starboard
(right) side when proceeding from open water into port, and black buoys are to port (left)
side. When navigating out of port, your position with respect to the buoys should be reversed; red buoys should be to port and
black buoys to starboard.
Many bodies of water used by boaters are
entirely within the boundaries of a particular
state. The Uniform State Waterway Marking
System has been devised for these waters.
This system uses buoys and signs with distinctive shapes and colors to show regulatory or advisory information. These markers
are white with black letters and orange
boarders. They signify speed zones, restricted areas, danger areas, and general information.
Remember, markings may vary by geographic location. Always consult local boating authorities before driving your boat in
unfamiliar waters.
6

General information
EMU25540
Fueling instructions
EWM00010
WARNING
GASOLINE AND ITS VAPORS ARE HIGHLY FLAMMABLE AND EXPLOSIVE!
●
Do not smoke when refueling, and keep
7
ZMU01708
away from sparks, flames, or other
sources of ignition.
●
Stop engine before refueling.
●
Refuel in a well-ventilated area. Refuel
portable fuel tanks off the boat.
●
Take care not to spill gasoline. If gasoline spills, wipe it up immediately with

General information
dry rags.
●
Do not overfill the fuel tank.
Tighten the filler cap securely after re-
●
fueling.
●
If you should swallow some gasoline,
inhale a lot of gasoline vapor, or get
gasoline in your eyes, get immediate
medical attention.
If any gasoline spills onto your skin, im-
●
mediately wash with soap and water.
Change clothing if gasoline spills on it.
Touch the fuel nozzle to the filler open-
●
ing or funnel to help prevent electro-
static sparks.
ECM00010
CAUTION:
Use only new clean gasoline which has
been stored in clean containers and is not
contaminated with water or foreign matter.
EMU25570
Gasoline
If knocking or pinging occurs, use a different
brand of gasoline or premium unleaded fuel.
Recommended gasoline:
Regular unleaded gasoline with a minimum octane rating of 86 (Pump Octane Number) = (R+M)/2
Gasohol
There are two types of gasohol: gasohol containing ethanol and that containing methanol. Gasohol containing ethanol can be used
if ethanol content does not exceed 10% and
the fuel meets minimum octane ratings.
Yamaha does not recommended gasohol
containing methanol because it can cause
fuel system damage or engine performance
problems.
EMU25640
Engine oil
If the recommended engine oil is not available, another 2-stroke engine oil with an
NMMA-certified TC-W3 rating may be used.
Recommended engine oil:
YAMALUBE 2-stroke outboard motor
oil
EMU25741
Propeller selection
The performance of your outboard motor will
be critically affected by your choice of propeller, as an incorrect choice could adversely
affect performance and could also seriously
damage the motor. Engine speed depends
on the propeller size and boat load. If engine
speed is too high or too low for good engine
performance, this will have an adverse effect
on the engine.
Yamaha outboard motors are fitted with propellers chosen to perform well over a range
of applications, but there may be uses where
a propeller with a different pitch would be
more appropriate. For a greater operating
load, a smaller-pitch propeller is more suitable as it enables the correct engine speed
to be maintained. Conversely, a larger-pitch
propeller is more suitable for a smaller operating load.
Yamaha dealers stock a range of propellers,
and can advise you and install a propeller on
your outboard that is best suited to your application.
8

General information
—
×
9
1
1. Propeller diameter in inches
2. Propeller pitch in inches
3. Type of propeller (propeller mark)
NOTE:
Select a propeller which will allow the engine
to reach the middle or upper half of the operating range at full throttle with the maximum
boat load. If operating conditions such as
light boat loads then allow the engine r/min to
rise above the maximum recommended
range, reduce the throttle setting to maintain
the engine in the proper operating range.
7
2
N
3
ZMU02844
For instructions on propeller removal and installation, see page 40.
EMU25770
Start-in-gear protection
Yamaha outboard motors or Yamaha-approved remote control units are equipped
with start-in-gear protection device(s). This
feature permits the engine to be started only
when it is in neutral. Always select neutral
before starting the engine.
9

Basic components
EMU25795
Main components
NOTE:
* May not be exactly as shown; also may not be included as standard equipment on all models.
8D
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
1. Manual starter handle
2. Engine stop button/Engine stop lanyard
switch
3. Choke knob
4. Throttle grip
5. Throttle friction adjuster
6. Clamp screw
7. Cooling water inlet
8. Anti-cavitation plate
9. Trim rod
10. Shallow water lever
11. Rope attachment
12. Tilt support knob
13. Cooling water pilot hole
14. Gear shift lever
1
3
4
5
2
6
16
ZMU04490
15. Top cowling
16. Fuel tank*
EMU25802
Fuel tank
If your model was equipped with a portable
fuel tank, its function is as follows.
EWM00020
WARNING
The fuel tank supplied with this engine is
its dedicated fuel reservoir and must not
be used as a fuel storage container. Commercial users should conform to relevant
licensing or approval authority regula-
10
Basic components
tions.
1. Air vent screw
2. Fuel gauge
3. Fuel joint
4. Fuel tank cap
EMU25830
4
3
1
2
ZMU01992
Fuel joint
This joint is used to connect the fuel line.
EMU25841
Fuel gauge
This gauge is located on either the fuel tank
cap or on the fuel joint base. It shows the approximate amount of fuel remaining in the
tank.
EMU25850
Fuel tank cap
This cap seals the fuel tank. When removed,
the tank can be filled with fuel. To remove the
cap, turn it counterclockwise.
EMU25860
Air vent screw
This screw is on the fuel tank cap. To loosen
the screw, turn it counterclockwise.
EMU25911
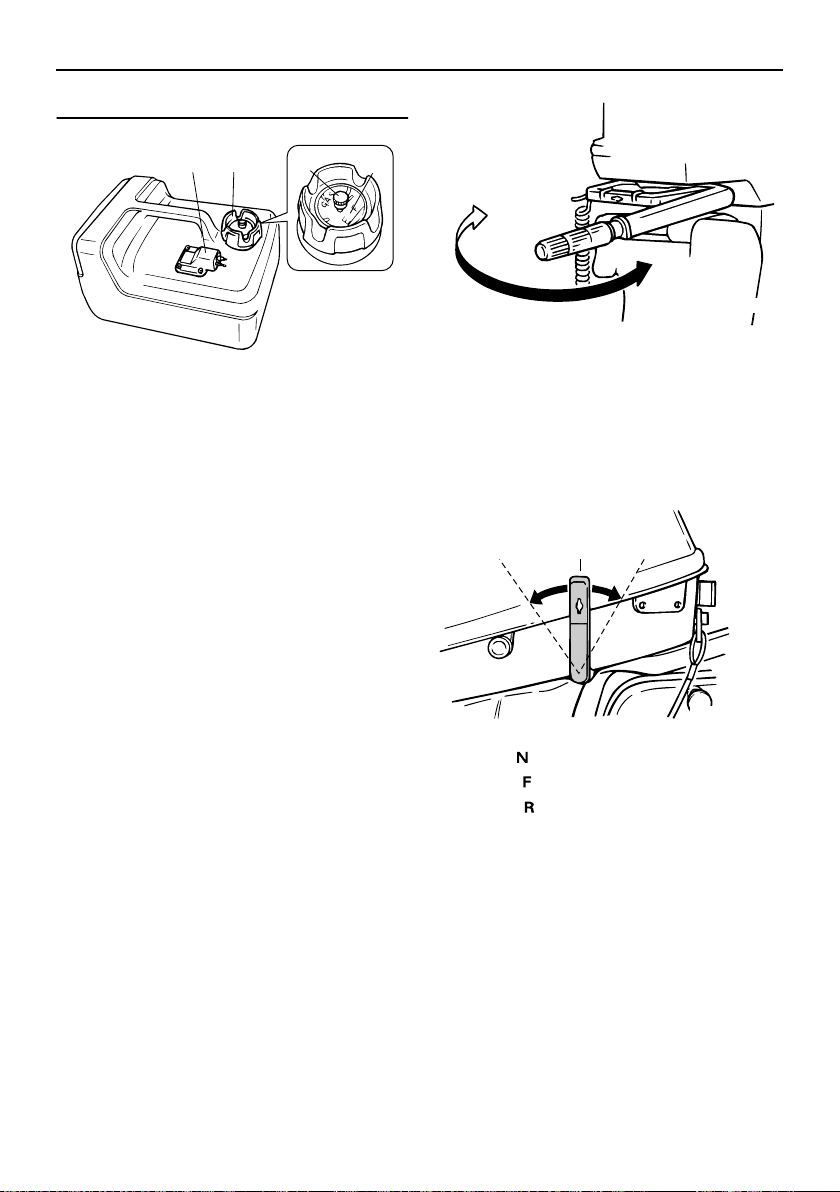
Tiller handle
To change direction, move the tiller handle to
the left or right as necessary.
ZMU02846
EMU25921
Gear shift lever
Pulling the gear shift lever towards you puts
the engine in forward gear so that the boat
moves ahead. Pushing the lever away from
you puts the engine in reverse gear so that
the boat moves astern.
R
N
F
123
ZMU02847
1. Neutral “”
2. Forward “”
3. Reverse “”
EMU25941
Throttle grip
The throttle grip is on the tiller handle. Turn
the grip counterclockwise to increase speed
and clockwise to decrease speed.
11
ZMU02848
EMU25961
Throttle indicator
The fuel consumption curve on the throttle
indicator shows the relative amount of fuel
consumed for each throttle position. Choose
the setting that offers the best performance
and fuel economy for the desired operation.
1
ZMU02849
1. Throttle indicator
EMU25970
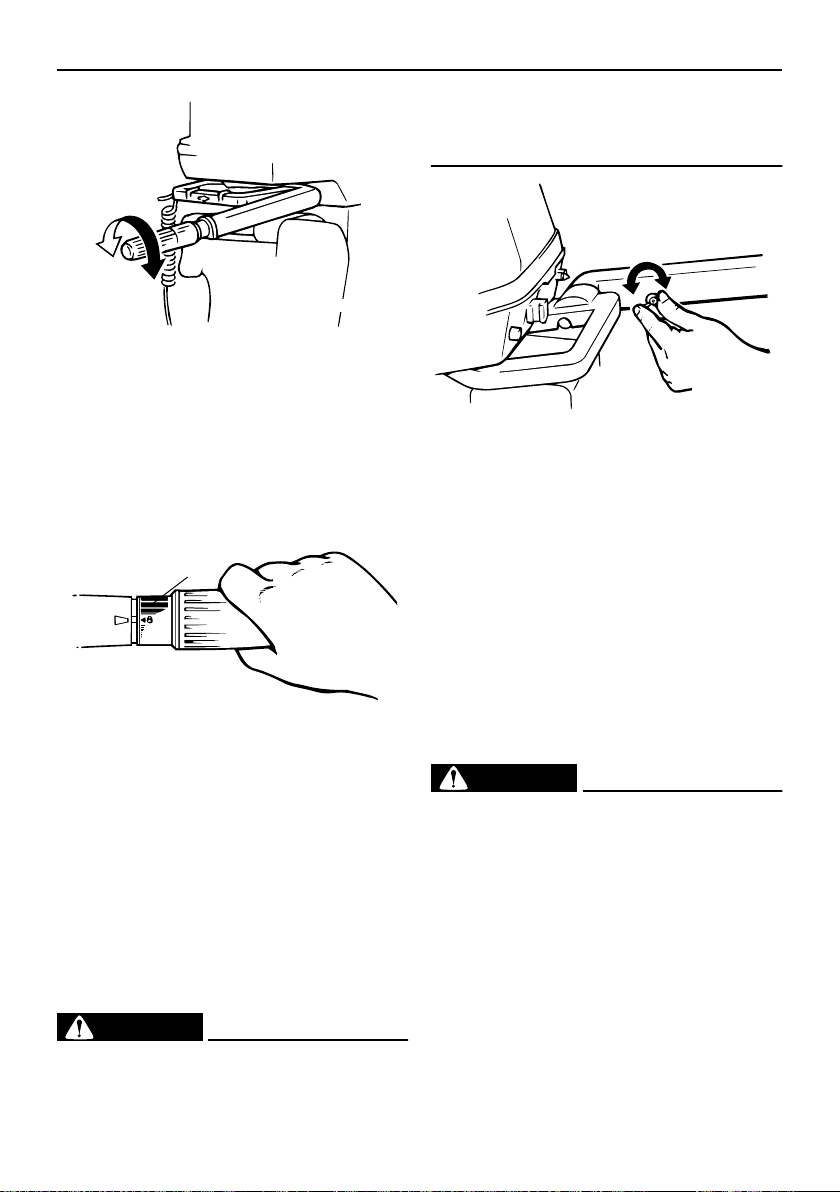
Throttle friction adjuster
A friction device provides adjustable resistance to movement of the throttle grip or the
remote control lever, and can be set according to operator preference.
To increase resistance, turn the adjuster
clockwise. To decrease resistance, turn the
adjuster counterclockwise.
EWM00030
WARNING
Do not overtighten the friction adjuster. If
Basic components
there is too much resistance, it could be
difficult to move throttle lever or grip,
which could result in an accident.
ZMU02850
When constant speed is desired, tighten the
adjuster to maintain the desired throttle setting.
EMU25990
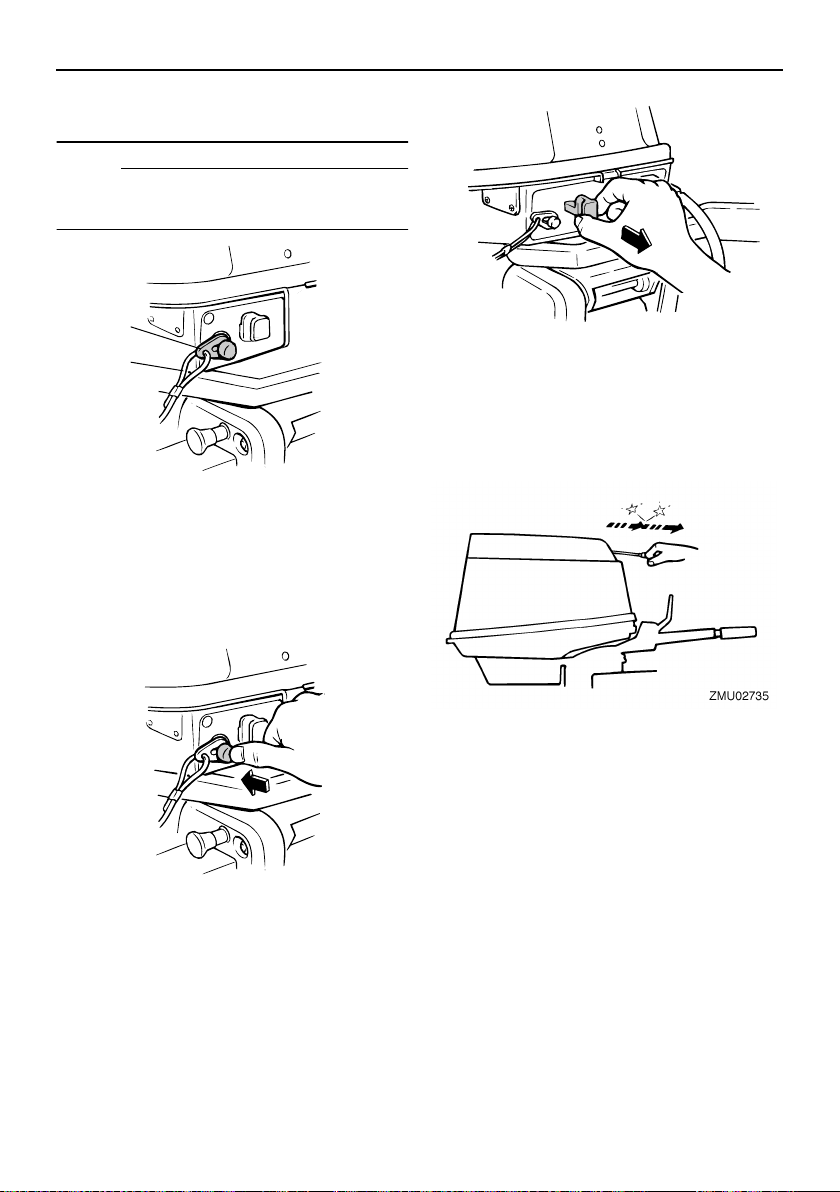
Engine stop lanyard switch
The lock plate must be attached to the engine stop switch for the engine to run. The
lanyard should be attached to a secure place
on the operator’s clothing, or arm or leg.
Should the operator fall overboard or leave
the helm, the lanyard will pull out the lock
plate, stopping ignition to the engine. This
will prevent the boat from running away under power.
EWM00120
WARNING
Attach the engine stop switch lanyard
●
to a secure place on your clothing, or
your arm or leg while operating.
Do not attach the lanyard to clothing
●
that could tear loose. Do not route the
lanyard where it could become entangled, preventing it from functioning.
●
Avoid accidentally pulling the lanyard
during normal operation. Loss of engine power means the loss of most
steering control. Also, without engine
power, the boat could slow rapidly. This
12
Basic components
could cause people and objects in the
boat to be thrown forward.
NOTE:
The engine cannot be started with the lock
plate removed.
1
2
ZMU02851
1. Lock plate
2. Lanyard
EMU26001
Engine stop button
To open the ignition circuit and stop the engine, push this button.
ZMU02860
EMU26070
Manual starter handle
To start the engine, first gently pull the handle out until resistance is felt. From that position, then pull the handle straight out quickly
to crank the engine.
ZMU02852
EMU26011
Choke knob for pull type
To supply the engine with the rich fuel mixture required to start, pull out this knob.
13
EMU26121
Steering friction adjuster
A friction device provides adjustable resistance to the steering mechanism, and can be
set according to operator preference. An adjusting screw or bolt is located on the swivel
bracket.

Basic components
ZMU04508
To increase resistance, turn the adjuster
clockwise.
To decrease resistance, turn the adjuster
counterclockwise.
EWM00040
WARNING
Do not overtighten the friction adjuster. If
there is too much resistance, it could be
difficult to steer, which could result in an
accident.
EMU26261
Trim rod (tilt pin)
The position of the trim rod determines the
minimum trim angle of the outboard motor in
relation to the transom.
ZMU02854
EMU26320
Tilt support knob
To keep the outboard motor in the tilted up
position, push the tilt support knob under the
swivel bracket.
ZMU02855
EMU26371
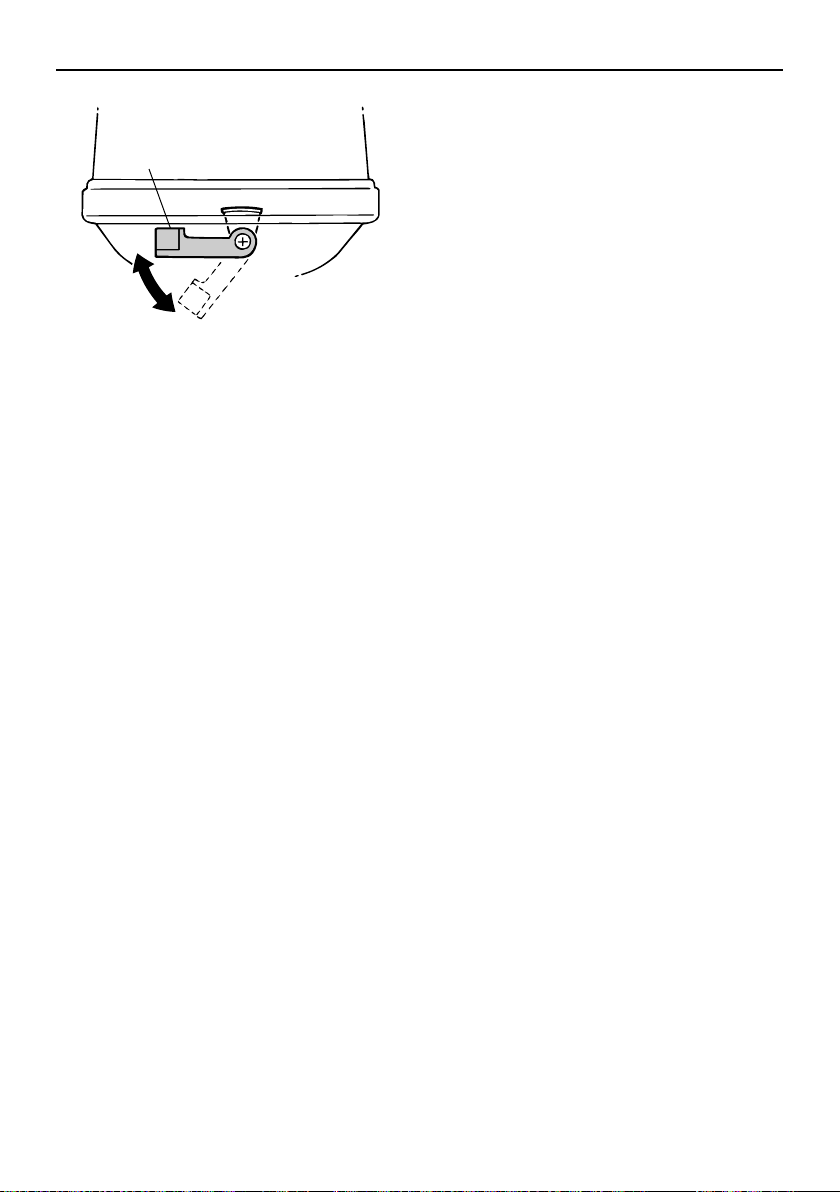
Top cowling lock lever(s) (turn type)
To remove the engine top cowling, turn the
lock lever(s) and lift off the cowling. When installing the cowling, check to be sure it fits
properly in the rubber seal. Then lock the
cowling again by returning the lever(s) to the
lock position.
ZMU02853
EMU26280
Shallow water lever
Pushing this lever down will tilt the motor up
partially to provide more clearance when operating in shallow water.
14
Basic components
1
ZMU02862
1. Top cowling lock lever(s)
15
 Loading...
Loading...