Page 1

XL-VC2402F
VDSL Concentrator
User’s Guide
Page 2

XtendLan VC2402F – User’s Guide http://www.xtendlan.com
Introduction:
The XL-VC2402F has
1 x RJ-21(24 x POTS Ports) with splitter on board,
1 x RJ-21(24 x 10 Mbps VDSL Ports),
2 x 10/100/1000Mbps auto-sensing RJ-45,
1 x Giga miniGBIC SFP (fiber optic)
The XL-VC2402F is a rack-unit (1RU) high, 14-inches deep. It is a standard 19” Rack mounted size.
The XL-VC2402F delivers dedicated bandwidth per port at rates up to 15 Mbps. VDSL transmissions
coexist with POTS and ISDN, and can be compatible with ADSL/HomePNA traffic in the same building.
This VDSL concentrator can be configured on a per-switch basis to support the following modes:
4/1 asymmetrical, 5/10/15 Mbps symmetrical rate (up to 1900/ 1500 /1200 /1000 meters), our factory
default threshold is 10Mbps & Speed rate control from 100k up to 15Mbps.
The XL-VC2402F and VDSL Modem provide fast and easy connectivity into building patch panels with
RJ-21 connector.
The 10/100/1000 Ethernet ports can be used to connect servers, Ethernet switches. These connectivity
options provide multiple price/performance options to meet building and budget requirements.
The XL-VC2402F provides the important features necessary for robust networks:
Features:
• Quality of Service: Supports 802.1p QoS. Provides high-and low-priority queuing on a per-port
basis. Supports IGMP: Snooping by 512 IP multicast table for VOD (Video on demand) and
Video conference and Internet games application
• Scalability: Supports bandwidth control from 100k to 4/1, 5/10/15 Mbps symmetric performance
over single-pair wiring. Fast Ethernet Channel port aggregation.
• Security: 802.1Q Tag base and port-based virtual local-area network (VLAN) support. Private
VLAN access, assuring port security without requiring a VLAN per port, and also
• Supports MAC filtering to Lock MAC address
• In band Management: XL-VC2402F provides a console port for setup IP or other function
• Out Of Band Management: XL-VC2402F support remote control by Telnet and Web-based
Management easy-to-use configuration and ongoing monitoring. This software is embedded in the
XL-VC2402F and delivers remote, intuitive management of 24 ports VDSL concentrator and
connected VDSL CPE devices through a single IP address. The 24 ports VDSL concentrator is
easy-to-configured and deployed, and offering a compelling option in terms of cost, performance,
scalability and services compared to traditional ATM-based xDSL solutions
• Speed Rate Control: XL-VC2402F supports speed rate control function, from 100k to 4/1,
5/10/15Mbps
• IEEE-802.1x: port base network access control, this function for wireless users connecting
Authentication
• Spanning tree: Supports IEEE802.1d for MAC bridge and link redundant.
• DHCP Client: Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) for auto configuring management
IP.
• TFTP Protocol: Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) for new version firmware remote upgraded
• SNR indication: Signal to Noise Ratio (SNR) for check phone wiring quality and cross talk
for offering wiring information to engineer.
- 2 -
Page 3

XtendLan VC2402F – User’s Guide http://www.xtendlan.com
• FAN & Temperature Monitor: This is a monitoring function for the cooler FAN speed and
inner temperature status, if the FAN stops or the temperature is over 70 ℃, the alarm trap will be
sent via SNMP
• SNMP MIB Supports: RFC-1213 MIBII;RFC-1493 Bridge MIB; RFC-1643 Ether like MIB
RFC-1757 RMON MIB/ groups 1,2,3,9; Enterprise MIB
• Giga port auto link supports: This function can be auto sensing client interface media with
Copper or fiber optic and link one and supports hot swap.
• Alarm: In order to make sure the system is working normally, the XL-VC2402F provides Fan
and Temperature monitor and management, you can see through WEB or Telnet which shows the
internal temperature and fan speed, if the temperature exceeds 70℃ or the fan stops working, the
VDSL concentrator will send a SNMP trap to inform the Trap management server.
• Hacker prevention: To avoid hacker to enter management system through client side (CPE), the
XL-VC2402F will filter system IP from client side
• Supports multiple web browsers: IE, Mozilla & Netscape under Windows O/S, Mozilla &
Netscape under Linux O/S
- 3 -
Page 4

XtendLan VC2402F – User’s Guide http://www.xtendlan.com
Contents
1 Unpacking Information......................................................................................................................... 6
2 Product Description .............................................................................................................................. 7
2.1 General.......................................................................................................................................... 8
2.1.1 Front Panel............................................................................................................................ 8
2.1.2 miniGBIC SFP Fiber Optics.................................................................................................9
2.1.3 LED Indications.................................................................................................................... 9
2.1.4 Rear Panel............................................................................................................................. 9
3 Hardware Installation.......................................................................................................................... 10
4 Management Configuration................................................................................................................ 12
4.1 In-Band Management ................................................................................................................. 12
4.2 Remote Network Management ................................................................................................... 15
4.2.1 IP Setting ............................................................................................................................ 15
4.2.1.1 Remote control by “Telnet”............................................................................................ 15
4.2.1.2 Network control by “WEB”............................................................................................ 15
4.2.2 Port Status........................................................................................................................... 17
4.2.3 Port Statistics ...................................................................................................................... 18
5 Administrator...................................................................................................................................... 19
5.1 IP Address................................................................................................................................... 19
5.2 Switch Setting............................................................................................................................. 19
5.2.1 Basic Description................................................................................................................ 19
5.2.2 Advanced ............................................................................................................................ 20
5.2.2.1 Miscellaneous Settings: .................................................................................................. 20
5.2.2.2 Interleaver depths............................................................................................................ 21
5.3 Console Port Information ........................................................................................................... 23
5.4 Port Controls............................................................................................................................... 23
5.5 Trunking ..................................................................................................................................... 25
5.5.1 Aggregator setting .............................................................................................................. 25
5.5.2 Aggregator Information...................................................................................................... 26
5.5.3 State Activity ...................................................................................................................... 27
5.6 Filter Database ............................................................................................................................ 28
5.6.1 IGMP Snooping .................................................................................................................. 28
5.6.2 Static MAC Address ........................................................................................................... 29
5.6.3 MAC filtering ..................................................................................................................... 30
5.7 VLAN configurations ................................................................................................................. 31
5.7.1 Port Based VLAN............................................................................................................... 32
5.7.2 802.1Q VLAN .................................................................................................................... 33
5.7.2.1 Basic ............................................................................................................................... 33
5.7.2.2 Port VID Configure port VID settings............................................................................ 34
5.8 Spanning Tree............................................................................................................................. 35
5.9 Port Sniffer.................................................................................................................................. 37
5.10 SNMP ......................................................................................................................................... 37
5.11 Security Manager........................................................................................................................ 38
5.12 802.1X Configuration ................................................................................................................. 38
5.13 TFTP Update Firmware.............................................................................................................. 39
5.14 Configuration Backup................................................................................................................. 40
5.14.1 TFTP Restore Configuration .............................................................................................. 40
5.14.2 TFTP Backup Configuration .............................................................................................. 40
5.15 Reset System............................................................................................................................... 40
5.16 Reboot......................................................................................................................................... 41
6 Applications........................................................................................................................................ 42
6.1 Used as apartment for Internet access ........................................................................................ 43
- 4 -
Page 5

XtendLan VC2402F – User’s Guide http://www.xtendlan.com
6.2 Application for sharing a single internet account ....................................................................... 44
7 Appendix............................................................................................................................................. 45
7.1 Appendix A: Troubleshooting .................................................................................................... 45
7.1.1 Diagnosing VDSL Indicators ............................................................................................. 45
7.1.2 System Diagnostics............................................................................................................. 45
7.2 Appendix B:RJ-21 Telco ports distribution............................................................................. 47
7.3 Appendix C: VDSL Spectrum .................................................................................................... 49
7.4 Appendix D: Example of VLAN Setting.................................................................................... 50
7.4.1 Port Based VLAN............................................................................................................... 50
7.4.2 802.1Q Tag Vlan ................................................................................................................ 51
- 5 -
Page 6

XtendLan VC2402F – User’s Guide http://www.xtendlan.com
1 Unpacking Information
Check List
Carefully unpack the package and check its contents against the checklist.
Package Contents:
• XL-VC2402F
• Users manual CD
• AC Power Cord
• 2x Rack Mounting Brackets
• 4x Screws
• 4x Plastic feet
• 2x1.5m RJ-21 male-to-male Telco connector wire (Option Parts)
Please inform your dealer immediately for any missing, or damaged parts. If possible, retain the carton,
including the original packing materials. Use them to repack the unit in case there is a need to return for
repair.
- 6 -
Page 7

XtendLan VC2402F – User’s Guide http://www.xtendlan.com
2 Product Description
Key Specifications & Features:
• Compliant with IEEE 802.3 & 802.3u & 802.3z Ethernet Standards
• Compliant with ETSI, ITU, ANSI standards
• Provides 1 x 10/100/1000Mbps auto-sensing RJ-45 and 1 x 10/100/1000Mbps RJ-45/miniGBIC
SFP SFP (fiber) Auto-Link Ethernet port for Trunking or cascading
• Provides 24 x 4/1, 5/10/15M VDSL ports with RJ-21 connector for connecting client side
• Provides 24 POTS/ISDN filtering port with RJ-21 connector
• Splitter on board
• Performance: 8.8 Gbps switching fabric, 4.72 Gbps maximum forwarding bandwidth (Forwarding
rates based on 64byte packets), 6.5 Mbps forwarding rate
• Supports SNR (Signal to Noise Ratio) indications for checking phone wiring quality
• Supports bandwidth management (speed rate control) from 100Kbps to 4/1, 5/10/15Mbps for
VDSL port
• Supports MAC address table: 6K Entries
• Store-and-forward Switching method.
• Supports auto MDIX
• Supports flow control IEEE802.3x for Full Duplex & Back Pressure for Half Duplex
• Long driver capable 4/1:1.9Km / 5M:1.5Km / 10M:1.2Km / 15M:1Km
• Ethernet transport with POTS / ISDN traffic over single copper wire pair
• Spectral compatibility with xDSL, ISDN (2B1Q/4B3T), HomePNA
• Robust operation on severely distorted line
• Supports Port Base VLAN
• Supports GARP/GVRP 802.1p/q Tagging VLAN
• Supports IEEE802.1v protocol VLAN
• Supports IEEE802.1ad port trunking
• Supports port mirroring (sniffer)
• Supports IEEE802.1d Spanning trees
• Supports BOOTP/DHCP Client
• Supports IGMP snooping
• Supports 802.1p QOS
• Supports 802.1x Port Based Network Access Control
• Supports RS-232 console port for functions setup (DB-9Pin Female / 9600bps)
• Supports internal FAN and temperature monitor and management function
• Supports SNMP RFC-1493 Bridge MIBs & RFC-1213 MIB II & RFC-1643 Ethernet MIB &
Enterprise MIB
• Supports RMON groups 1,2,3,9(RFC-1757 RMON MIB)
• Supports MAC address filtering/learning limit for port security mode
• Supports broadcast storm filtering
• Provides surge protection for each VDSL ports
• Supports Telnet and WEB Base for remote control access
• Supports WEB Base for Management
- 7 -
Page 8

XtendLan VC2402F – User’s Guide http://www.xtendlan.com
• Supports TFTP/XMODEM for firmware upgrade
• Supports In-Band/Out-of-Band Management
• Provides Power & POST (Power On Self Test) LED.
• Provides LED indication Link/Active/Speed/Duplex Status for Ethernet port.
• Provides LED indication Link for VDSL port.
• Internal switching power adapter Input: AC 85-265 volts/50-60Hz/2A.
• Dimensions: 444 x 362 x 44 mm
• Operating Temperature: 0°C ~ 50°C(32F ~ 122F).
• Storage Temperature: -20°C~ 65°C(-4F ~ 149F).
• Humidity: 10%~90% non-condensing.
• Rack mount size 19"/1U.
• EMI: FCC/CE
• Safety: EN60950
• Chipset: Infineon 10Base-S
• Power Consumption: 28W
2.1 General
This section describes the important parts of the XL-VC2402F, the front and rear panel drawings, LEDs,
connectors, and switches.
2.1.1 Front Panel
The following figure shows the front panel of the XL-VC2402F.
24x POTS
Front panel
(1) “PWR.”: Power LED light.
(2) “POST”: Power On Self Test
(3) 24x POTS Ports (RJ21)
(4) 24x VDSL Ports (RJ21)
(5) RS-232 Console Port
(6) 1x 10/100/1000Mbps RJ-45/miniGBIC SFP (fiber) Auto-Link and Hot Swappable trunk ports
(7) 1x 10/100/1000Mbps RJ-45 auto-sensing Ethernet expansion port
(8) Reset Button.
The XL-VC2402F has embedded Splitter between every VDSL side and POTS side. It permits you can
deliver broadband service on the same lines as Plain Old Telephone Service (POTS), PBX, ISDN traffic
and VDSL Signal. Several LED indicators for monitoring the device itself, and the network status. At a
quick glance of the front panel, the user would be knew if the product is receiving power; if it is
monitoring another VDSL concentrator or other devices; or if a problem exists on the network.
24x VDSL
Console
Gigabit port
Gigabit port
miniGBIC SFP
Reset
- 8 -
Page 9
XtendLan VC2402F – User’s Guide http://www.xtendlan.com
The 24-port XL-VC2402F provides one 10/100/1000Mbps auto-sensing RJ-45 Ethernet ports as Ethernet
expansion port and two trunk Ports (one 10/100/1000 RJ-45 or Giga miniGBIC SFP Interface with auto
link function, you can use RJ-45 or miniGBIC SFP interface, not simultaneously).
2.1.2 miniGBIC SFP Fiber Optics
A gigabit interface converter (miniGBIC SFP) is a transceiver that converts electric currents (digital highs
and lows) to optical signals, and optical signals to digital electric currents. The miniGBIC SFP is
typically employed in fiber optic and Ethernet systems as an interface for high-speed networking. The
data transfer rate is 1.25 gigabit per second. miniGBIC SFP modules allow technicians to easily configure
and upgrade electro-optical communications networks. The typical miniGBIC SFP transceiver is a
plug-in module that supports hot-plugging (it can be removed and replaced without turning off the
system). The devices are economical, because they eliminate the necessity for replacing entire boards at
the system level. Upgrading can be done with any number of units at a time, from an individual module to
all the modules in a system. miniGBIC SFP (mini Gigabit Interface Converter), meet the Gigabit
Interface Converter specification Rev. 5.4 (MOD_DEF4) industry standard.
Mode Wavelength Bit Rate Voltage Power Margin
1 LX-Single Mode 1310nm 1.25Gbps 5V 10.5db(10KM)
2 SX-Multi Mode 850nm 1.25Gbps 5V 8.5db(550m)
2.1.3 LED Indications
The following describes the function of each LED indicator.
LEDs Status Descriptions
PWR
(Power LED)
POST
(Power On Self Test)
ACT (Receiving
LEDs)
Speed100 Speed1000
(Speed LEDs)
FD (Full-Duplex) Steady
Steady
LINK LEDs Steady
Steady
Green
Steady
Green
Steady
Green
Flashing
Steady
Yellow
Yellow
Yellow
Green
This LED light is located at the left side on the front panel. It will light
up (ON) to show that the product is receiving power. Conversely, no
light (OFF) means the product is not receiving power.
Proceed function test to myself when power on.
Act Led if flashing to show data on Receiving status
Indicates that communications have been set 100 or 1000 Mbps. Each
port on the VDSL concentrator is assigned an LED light for 100 or
1000 Base-TX connecting, else on 10M speed.
Indicates that communications have been set to full-duplex operation
for the indicated port
The indicator lights up means working in Full Duplex And light down
means working in Half Duplex
RJ21 LED is lit up to show “Link”. The indicator both CO and CE
side connection OK, and light down which Meaning is no connection.
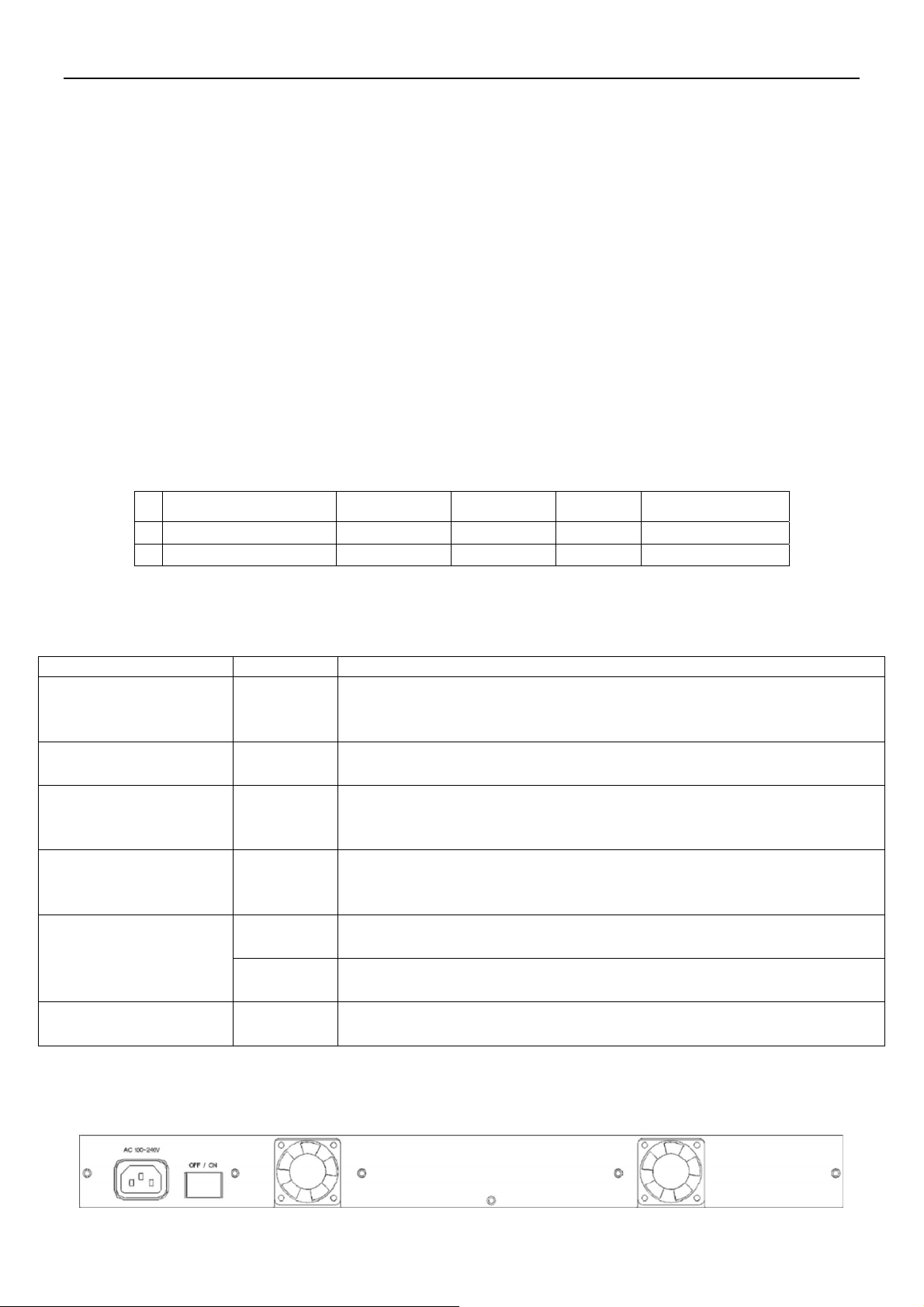
2.1.4 Rear Panel
The following figure shows the rear panel
Figure Chapter 2.3 Rear Panel
- 9 -
Page 10

XtendLan VC2402F – User’s Guide http://www.xtendlan.com
AC Power Socket
The power cord should be plugged into this socket. The AC Socket accepts AC power from 100 to 240
voltage.
3 Hardware Installation
This chapter describes how to install the XL-VC2402F and to establish network connection. You may
install the VDSL concentrator on any level surface (table, shelf, 19-inch rack or wall mounting). However,
please take note of the following minimum site requirements before you begin.
Pre-Installation Requirements
Before you start actual hardware installation, make sure you can provide the right operating environment,
including power requirements, sufficient physical space, and proximity to other network devices that are
to be connected.
Verify the following installation requirement:
• Power requirements: AC 100V to 240 V at 50 to 60 Hz. The Switch power supply automatically
adjusts to the input voltage level.
• The VDSL concentrator should be located in a cool dry place, with at least 10cm/4in of space at
the front and back for ventilation.
• Place the VDSL concentrator out of direct sunlight, and away from heat sources or areas with a
high amount of electromagnetic interference.
• Check if network cables and connectors needed for installation are available.
General Rules
Before making any connections to the VDSL concentrator, note the following rules:
• Ethernet Port (RJ-45): All network connections to the VDSL concentrator’s Ethernet port must be
made using Category 5 UTP for 100Mbps and Category 3,4 UTP for 10Mbps. No more than 100
meters (about 328 feet) of cabling may be use between VDSL concentrator’s or with HUB or an
end node.
• VDSL Port (RJ-21): All home network connections to the VDSL, 1 X RJ-21 Cable (Male to
Male)Using Pin 1~24, 26~49.
RJ-21 Pin 25 & 50 are not used!
Connecting the XL-VC2402F
The 24-port VDSL concentrator has 2 x Gigabit Ethernet supporting full or half-duplex operation. The
transmission mode is using auto-negotiation. Therefore, the devices attached to these ports must support
auto-negotiation unless they will always operate at half duplex. If transmissions must run at full duplex,
but the attached device does not support auto-negotiation, then you should upgrade this device to a newer
version that supports auto-negotiation. Use “25” port connect to devices such as server, bridge or router.
You can also cascade to another compatible MUX or hub by connecting the 26 port to the other device.
“Port 25” support 10/100/1000Giga RJ-45/miniGBIC SFP (fiber) Auto-Link. So you also can use Fiber
Optic wire connect to Port 25 miniGBIC SFP side.
Connecting Ethernet Port
Ethernet Port “25” and “26” support auto MDI/MDIX. You can connect the “25 or 26” port on the VDSL
concentrator to any device that uses a standard network interface such as a Cable modem, ADSL modem,
Ethernet Switch, workstation or server, or also to a network interconnection device such as a bridge or
router (depending on the port type implemented). Prepare straight through (or cross over) shielded or
unshielded twisted-pair cables with RJ-45 plugs on both ends. Use 100Ω Category 5 cable for
connections. Connect one end of the cable to “25” port of the VDSL concentrator, and the other end to a
standard RJ-45 station port on cable modem, ADSL router, wireless bridge, etc. When inserting an RJ-45
plug, be sure the tab on the plug clicks into position to ensure that it is properly seated.
Notes: Make sure the length of twisted-pair cable is not over 100 meters (328 feet).
- 10 -
Page 11

XtendLan VC2402F – User’s Guide http://www.xtendlan.com
Connecting VDSL Port
Prepare the network devices you wish to connect. Make sure you have installed suitable VDSL Modem
before making a connection to any of the VDSL concentrator (1-24) station ports. You also need to
prepare one 18 ~ 26 gauge twisted pair phone Line wiring with RJ21 plugs at both ends.
Connect one end of the cable to the RJ21 port of the Home Access network adapter, and the other end to
any available (1~24) station port on the VDSL.
Every port supports 4/1, 5/10/15 Mbps connections. When inserting an RJ21 plug, be sure the tab on the
plug clicks into position to ensure that it is properly seated.
Notes:
• Be sure each twisted-pair cable (RJ-45) is not over 100 meters (328 feet)
• VDSL port use 18 ~ 26 AWG, 28 AWG or above is not recommended.
- 11 -
Page 12
XtendLan VC2402F – User’s Guide http://www.xtendlan.com
4 Management Configuration
4.1 In-Band Management
Console port (RS-232) Configuration (Change IP Address By Terminal):
You can configure the product with the local serial console port, If one of the VDSL port is not in use,
you can disable it, that procedure is to connect a notebook computer to the RS-232 port, then boot
windows @95/98/ME/2000 system, and run “Hyper-terminal” program into terminal window, and setup
step are as follow.
Set “Bits per second” at 9600 to the content window.
Set “Flow control” at None
Connects PC with the VDSL concentrator, you will find login manual window on the screen then enter
Login name :”admin” ; password:”123” you will find user manual window on the screen of the
following :
Operation Button:
Tab=Next Item;
BackSpace=Previous Item
Enter=Select Item
- 12 -
Page 13

XtendLan VC2402F – User’s Guide http://www.xtendlan.com
To set IP Address: Please follow the following steps
(1)
Choose Switch Static Configuration you can enter to Switch Configuration page
(2) Choose Administration Configuration you can enter to Device Configuration page
Choose IP Configuration you can enter IP configuration page
- 13 -
Page 14

XtendLan VC2402F – User’s Guide http://www.xtendlan.com
(3)
1. Choose Edit item to Change IP address, Subnet Mask and Gateway
2. Use CTRL+A button to back actions choice
3. Choose Save item to save change and back to System Configuration page
4. Choose Previous Menu item to quit System Configuration page
5. Choose Main Menu item to quit Configuration page and back to Main Manual
6. Choose Reboot System item
7. Choose Restart item to reboot device
- 14 -
Page 15

XtendLan VC2402F – User’s Guide http://www.xtendlan.com
4.2 Remote Network Management
4.2.1 IP Setting
You must setup the “IP Address” with the local serial console port (RS-232 Port), and then you
can use this IP address to control this VDSL concentrator by Telnet and WEB. Or you can change
your computer’s IP domain same with VDSL SWITH. Then use the default IP address to control
this VDSL concentrator.
4.2.1.1 Remote control by “Telnet”
To enter Telnet, type the IP address of the VDSL switch to connect management system. And
type User name and
password.
Default User Name: admin
Default Password: 123
Note:
For security reason, we limit the user login number on Telnet and Console port. So you can’t
login Telnet and Console port in the same time. But you can login Telnet and Console port in the
different time. When you want to end console port control you must log-out to leave. Otherwise
you can’t login by Telnet.
WEB Login doesn’t have user login limitation.
4.2.1.2 Network control by “WEB”
1.The XL-VC2402F provides a WEB browser to manage and monitor the VDSL concentrator,
that default values are as follows: If you need change IP address in first time,you can use console
mode to modify it.
Default IP Address: 192.168.16.250
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
Default Gateway:192.168.16.1
User Name: admin Password: 123
2.You can browse
http://192.168.16.250,type user name and password as above.
- 15 -
Page 16

XtendLan VC2402F – User’s Guide http://www.xtendlan.com
This is Web Management Home Overview
- 16 -
Page 17

XtendLan VC2402F – User’s Guide http://www.xtendlan.com
4.2.2 Port Status
This page can see every port status that depended on user setting and the negotiation result.
State:Display port statuses disable or enable. “unlink” will be treated as “off”.
Link Status:Down is “No Link”,UP is “Link”.
SNR: Signal to Noise ratio. The SNR can be used as an indication of the quality of the
Link. If SNR Value>25, it means Good Link.
Speed Status: Port 1-24 are4/1, 5/10/15Mbps VDSL,Port 25-26 are 10/100/1000Mbps.
Duplex Status: Display full-duplex or half-duplex mode.
Flow Control: Full:Display the flow control status is enable or disable in full mode.
Half:Display the backpressure is enable or disable in half mode.
Rate Control : Display the rate control setting.
Ingr:Display the Port effective ingress rate of user setting.
Egr:Display the Port effective egress rate of user setting.
Port Security:Display the port security is enable or disable.
Config:Display the state of user setting.
State:Display the negotiation result.
- 17 -
Page 18

XtendLan VC2402F – User’s Guide http://www.xtendlan.com
4.2.3 Port Statistics
The following information provides a view of the current status of the unit. Press “Reset” button
to clean all count.
- 18 -
Page 19
XtendLan VC2402F – User’s Guide http://www.xtendlan.com
5 Administrator
There are many management functions included:
• IP address
• Switch settings
• Interleaver depths
• Console port information
• Port controls
• Trunking
• Filter database
• VLAN configuration
• Spanning tree
• Port Sniffer
• SNMP
• Security Manager
• 802.1x configuration
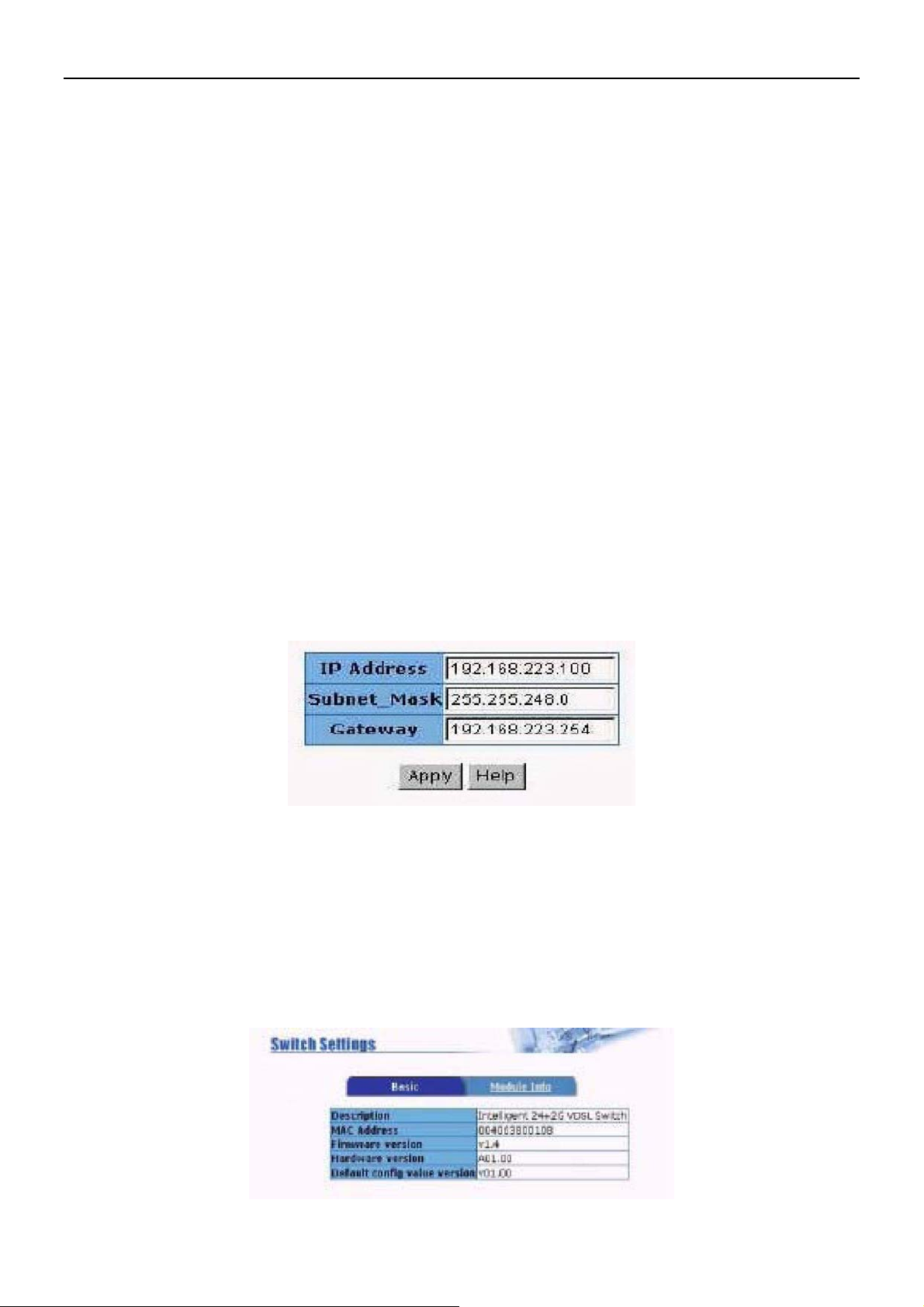
5.1 IP Address
User can configure the IP Setting and fill the new value,then clicks apply button. User must
reset and use new IP address to browser this web management.
5.2 Switch Setting
5.2.1 Basic Description
Display the name of device type.
MAC Address:The unique hardware address assigned by manufacturer(default)
Firmware Version:Display the switch’s Hardware version.
Hardware version:Display the switch’s Hardware version.
Default config value version:display write to default EEPROM value table version.
- 19 -
Page 20

XtendLan VC2402F – User’s Guide http://www.xtendlan.com
5.2.2 Advanced
5.2.2.1 Miscellaneous Settings
Mac Address Age-out Time: Type the number of seconds that an inactive MAC address
remains in the switch’s address table. The valid range is between 300∼ 765 seconds. Default is
300 seconds.
Max bridge transit delay bound control:Limit the packets queuing time in VDSL concentrator.
If enable,the packets queued exceed will be dropped. This valid value 1 sec、2 sec、4 sec and off.
Default is 1 seconds.
Broadcast Storm Filter:To configure broadcast storm control, enable it and set the upper
threshold for individual ports. The threshold is the percentage of the port's total bandwidth used
by broadcast traffic. When broadcast traffic for a port rises above the threshold you set, broadcast
storm control becomes active. The valid threshold values are 5%, 10%, 15%, 20%, 25% and off.
Priority Queue Service settings:
First Come First Service: The sequence of packets sent is depend on arrive order.
All High before Low: The high priority packets sent before low priority packets.
WRR: Weighted Round Robin. Select the preference given to packets in the switch's
high-priority queue.
These options represent the number of high priority packets sent before one low priority packet is
sent.
For example, 5 High: 2 Low means that the switch sends 5 high priority packets before sending 2
low priority packet.
Enable Delay Bound: Limit the low priority packets queuing time in switch.
Default Max Delay Time is 255ms. If the low priority packet stays in switch exceed Max Delay
Time, it will be sent. The valid range is 1~255 ms.
NOTE: Make sure of “Max bridge transit delay bound control” is enabled before enable Delay
Bound, Because Enable Delay Bound must be work under “Max bridge transit delay bound
control is enabled” situation.
QoS Policy: High Priority Levels: 0~7 priority level can map to high or low queue.
- 20 -
Page 21

XtendLan VC2402F – User’s Guide http://www.xtendlan.com
Protocol Enable Setting:
Enable Spanning Tree Protocol: enable STP protocol
Enable Internet Group Multicast Protocol: enable IGMP protocol
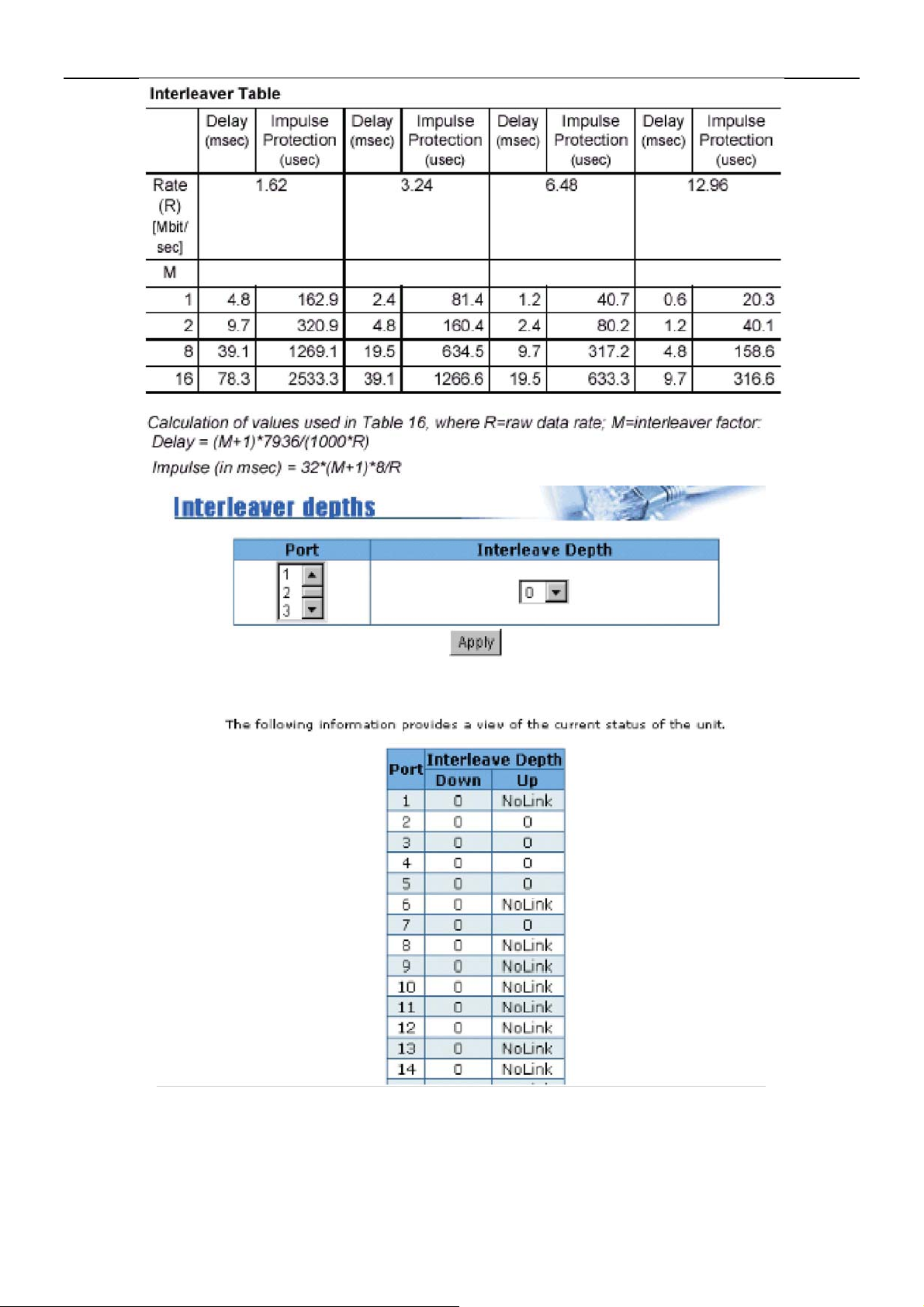
5.2.2.2 Interleaver depths
The Interleaving function reorganizes the bytes of the VDSL frames, dispersing them throughout
the frames over the line. As a result, impulse noise that would normally appear sequentially is
spread over several frames. This enables correction of a greater number of errors than would be
possible if the bytes had been concentrated in a single frame.
The protected portion of the VDSL frame can be passed through a convolutional
interleaver/deinterleaver. This protects the data, together with the RS coding, from impulse noise
with duration of up to 300 µs at full rate. The total latency of the device consists of the latency
caused by the RS encoding and the delay caused by interleaving. The parameter M is used to
define the length of protection supported by the interleaving function. The value of if0le defines
no use of the interleaver and the maximum value of 16 defines the maximum protection. The
values 0,1,2,8 and 16 are valid. The registers M_TX and M_RX are used for the depth of the
interleaver.
- 21 -
Page 22
XtendLan VC2402F – User’s Guide http://www.xtendlan.com
- 22 -
Page 23

XtendLan VC2402F – User’s Guide http://www.xtendlan.com
5.3 Console Port Information
Console is a standard UART interface to communicate with Serial Port. User can use
windows HyperTerminal program to link the switch.
Bits per seconds: 9600
Data bits: 8 Parity: none
Stop Bits: 1
Flow control: none
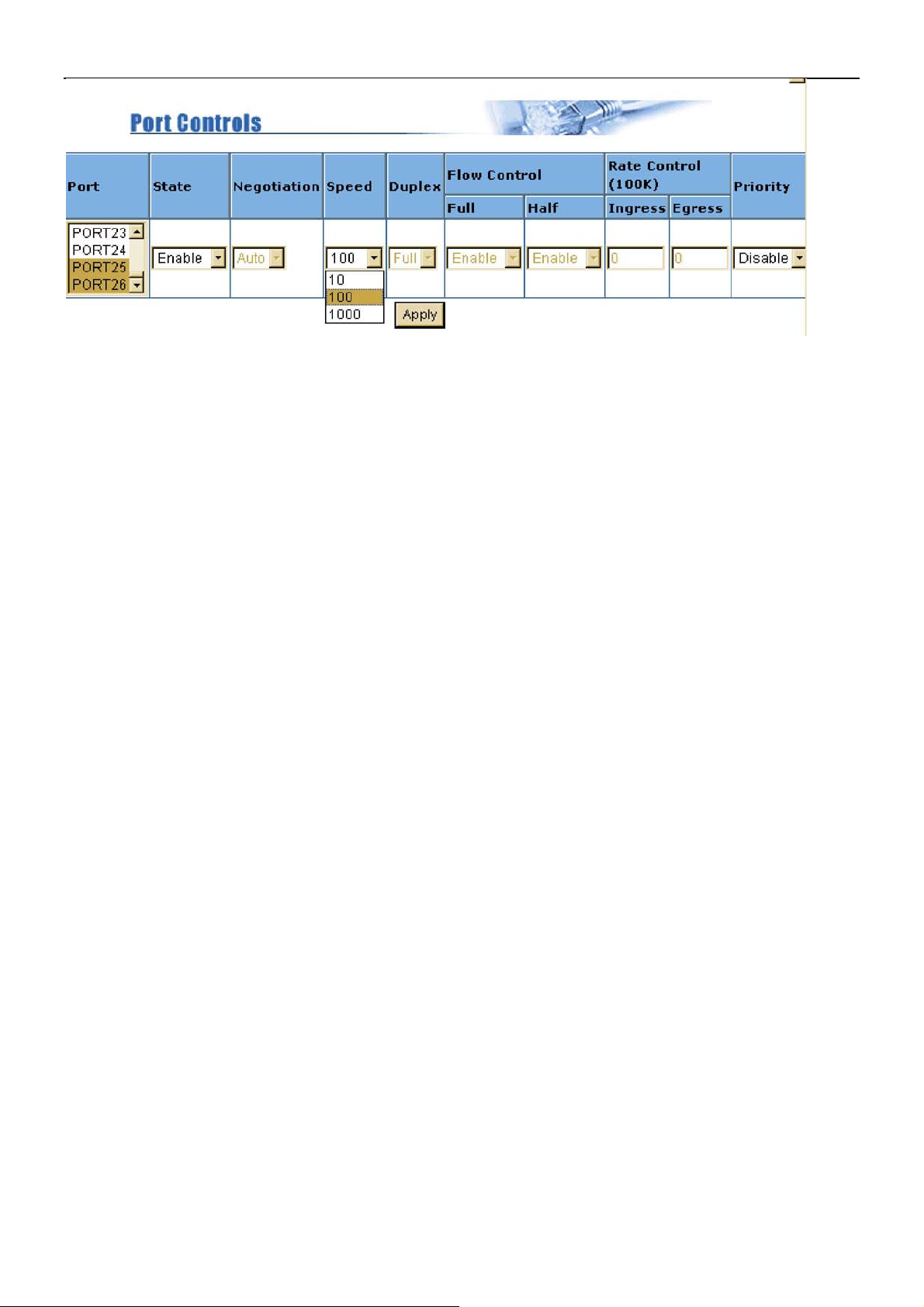
5.4 Port Controls
This section shows you how to change every port status and speed mode.
State: User can disable or enable this port control.
Auto Negotiation: User can set auto negotiation mode is Auto, Nway (specify the speed/duplex
on this port and enable auto-negotiation), Force of per port.
Speed: User can set 4/1, 5Mbps/10Mbps/15Mbps from port 1~24, 1000Mbps, 100Mbps or
10Mbps speed on Port25~Port26 (base on copper mode, when fiber mode force on
1000Base-SX/LX)
Distance between VDSL & VDSL modem when standard 24 Gauge 0.5mm cable is used:
4/1 Mbps -> 1.9km.
5 Mbps -> 1.5km
10 Mbps -> 1.2km
15 Mbps -> 1.0km
- 23 -
Page 24
XtendLan VC2402F – User’s Guide http://www.xtendlan.com
Duplex: User can set full-duplex or half-duplex mode of per port.
Flows control:
Full: User can set flow control function is enable or disable in full mode.
Half: User can set backpressure is enable or disable in half mode.
Change Speed procedures:
a. Confirm the VDSL port is linking which you want to change the speed mode.
b. Make sure VDSL port has been connecting to VDSL Modem and Link up OK.
c. Select the port (there are 26 ports available)
d. Select the speed mode
e. Click “Apply” to confirm the settings
f. The VDSL port will link down
g. Await 20 seconds the VDSL port will link up again with the new speed mode.
When the VDSL is linked up with the VDSL modem, both speed modes will be changed
correspondingly. If the VDSL is not linked up with the VDSL modem, only the speed mode of
the port selected from
VDSL will be changed.
Note: We do not suggest to change speed, unless necessary. Both VDSL & VDSL modem must
be in the same speed mode in order to be linked successfully.
Rate Control: XL-VC2402F, port 1 ~ port 24, supports by-port ingress and egress rate control.
For example, assume Port 1 is 10Mbps, users can set it’s effective egress rate is 1Mbps, ingress
rate is 500Kbps.
VDSL concentrator will be performed flow control or backpressure to confine the ingress rate to
meet the specified rate.
Ingress: Type the port effective ingress rate. The valid range is 0 ~ 100. The unit is 100K
0: disable rate control. 1 ~ 100: valid rate value (100=10Mbps)
Egress: Type the port effective egress rate. The valid range is 0~100. The unit is 100K.
0: disable rate control. 1 ~ 100: valid rate value.
Port Security: A port in security mode will be “locked” without permission of address learning.
Only the incoming packets with source MAC already existing in the address table can be
forwarded normally. User can disable the port from learning any new MAC addresses, and then
use the static MAC addresses screen to define a list of MAC addresses that can use the secure
port. Enter the settings, then click Apply button to changes on this page.
- 24 -
Page 25

XtendLan VC2402F – User’s Guide http://www.xtendlan.com
5.5 Trunking
The Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) provides a standardized means for exchanging
information between Partner Systems on a link to allow their Link Aggregation Control instances
to reach agreement on the identity of the Link Aggregation Group to which the link belongs,
move the link to that Link Aggregation Group, and enable its transmission and reception
functions in an orderly manner. In conclusion, Link aggregation lets you group up to eight
consecutive ports into a single dedicated connection. This feature can expand bandwidth to a
device on the network. LACP operation requires full-duplex mode, more detail information refers
to IEEE802.3ad.
5.5.1 Aggregator setting
System Priority: A value used to identify the active LACP. The switch with the lowest value has
the highest priority and is selected as the active LACP.
Group ID: There are seven trunk groups to provide configure. Choose the "group id" and click
"Get".
LACP: If enable, the group is LACP static trunking group. If disable, the group is local static
trunking group All ports support LACP dynamic trunking group. If connecting to the device that
also supports LACP, the LACP dynamic trunking group will be created automatically.
Work ports: Allow max four ports can be aggregated at the same time. If LACP static trunking
group, the exceed ports is standby and able to aggregate if work ports fail. If local static trunking
group, the number must be assame as the group member ports.
Select the ports to join the trunking group. Allow max four ports can be aggregated at the same
time.
If LACP enable, you can configure LACP Active/Passive status in each ports on State Activity
page.
- 25 -
Page 26

XtendLan VC2402F – User’s Guide http://www.xtendlan.com
5.5.2 Aggregator Information
When you are setting LACP aggregator, you can see relation information in here.
This page is no group active. LACP don’t working.
This page is Static Trunking group.
- 26 -
Page 27

XtendLan VC2402F – User’s Guide http://www.xtendlan.com
5.5.3 State Activity
Active (select): The port automatically sends LACP protocol packets.
Passive (no select): The port does not automatically sends LACP protocol packets, and responds
only if it receives LACP protocol packets from the opposite device.
A link having either two active LACP ports or one active port can perform dynamic LACP
trunking. A link has two passive LACP ports will not perform dynamic LACP trunking because
both ports are waiting for and LACP protocol packet from the opposite device.
If you are active LACP’s actor, when you are select trunking port, the active status will be
created automatically.
- 27 -
Page 28

XtendLan VC2402F – User’s Guide http://www.xtendlan.com
5.6 Filter Database
5.6.1 IGMP Snooping
The XL-VC2402F supports IP multicast, you can enable IGMP protocol on web management’s
switch setting advanced page, then display the IGMP snooping information in this page, you can
view difference multicast group, VID and member port in here, IP multicast addresses range from
224.0.0.0 through 239.255.255.255.
The Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) is an internal protocol of the Internet Protocol
(IP) suite. IP manages multicast traffic by using switches, routers, and hosts that support IGMP.
Enabling IGMP allows the ports to detect IGMP queries and report packets and manage IP
multicast traffic through the switch.
IGMP have three fundamental types of message as follows:
Message Description
Query
Report
Leave Group
A message sent from the carrier (IGMP router or switch) asking for a response
from each host belonging to the multicast group.
A message sent by a host to the carrier to indicate that the host wants to be or
is a member of a given group indicated in the report message.
A message sent by a host to the carrier to indicate that the host has quit to be a
m ember of a specific multicast group.
- 28 -
Page 29

XtendLan VC2402F – User’s Guide http://www.xtendlan.com
5.6.2 Static MAC Address
When you add a static MAC address, it remains in the switch's address table, regardless of whether the
device is physically connected to the switch. This saves the switch from having to re-learn a device's
MAC address when the disconnected or powered-off device is active on the network again.
1. From the main menu, click administrator → Filter Database →Static MAC Address.
2. In the MAC address box, enter the MAC address to and from which the port should permanently
forward traffic, regardless of the device’s network activity.
3. In the Port Number box, enter a port number.
4. If tag-based (IEEE 802.1Q) VLANS are set up on the switch, static addresses are associated with
individual VLANS. Type the VID (tag-based VLANS) to associate with the MAC address.
5. Click add.
- 29 -
Page 30

XtendLan VC2402F – User’s Guide http://www.xtendlan.com
5.6.3 MAC filtering
MAC address filtering allows the switch to drop unwanted traffic. Traffic is filtered based on the
destination addresses.
1. In the MAC Address box, enter the MAC address that wants to filter.
2. If tag-based (802.1Q) VLAN are set up on the switch, in the VLAN ID box, type the VID to
associate with the MAC address.
3. Click the Add.
- 30 -
Page 31

XtendLan VC2402F – User’s Guide http://www.xtendlan.com
5.7 VLAN configurations
A Virtual LAN (VLAN) is a logical network grouping that limits the broadcast domain. It allows you to
isolate network traffic so only members of the VLAN receive traffic from the same VLAN members.
Basically, creating a VLAN from a switch is logically equivalent of reconnecting a group of network
devices to another Layer 2 switch. However, all the network devices are still plug into the same switch
physically.
The VDSL concentrator support port-based and 802.1Q (tagged-based) VLAN in web management page.
In the default configuration VLAN support is disabled.
NOTE:
If you change VLAN Operation Mode from No VLAN to 802.1Q, you must wait 50 seconds. Change
VLAN mode for every time, you have to reboot the VDSL concentrator for valid value.
Support of Port-based VLAN :
Packets can go among only members of the same VLAN group. Note all unselected ports are treated as
belonging to another single VLAN. If the port-based VLAN enabled, the VLAN-tagging is ignored.
Support of Tag-based VLAN (IEEE 802.1Q VLAN):
Tagged-based VLAN is an IEEE 802.1Q specification standard. Therefore, it is possible to create a
VLAN across devices from different switch venders. IEEE 802.1Q VLAN uses a technique to insert a
“tag” into the Ethernet frames. Tag contains a VLAN Identifier (VID) that indicates the VLAN numbers.
In order to an end station to send packets to different VLANs, it itself has to be either capable of tagging
packets it sends with VLAN tags or attached to a VLAN-aware bridge that is capable of classifying and
tagging the packet with different VLAN ID based on not only default PVID but also other information
about the packet, such as the protocol.
- 31 -
Page 32

XtendLan VC2402F – User’s Guide http://www.xtendlan.com
5.7.1 Port Based VLAN
1. Click Add to create a new VLAN group.
2. Enter the VLAN name, group ID and select the members for the new VLAN.
3. Click Apply.
4. If there are many groups that over the limit of one page, you can click the “Next Page” to view
5. other VLAN groups.
NOTE: If the trunk groups exist, you can see it (ex: TRK1, TRK2…..) in select menu of ports, and you
can configure it is the member of the VLAN or not.
- 32 -
Page 33

XtendLan VC2402F – User’s Guide http://www.xtendlan.com
5.7.2 802.1Q VLAN
This page, user can create Tag-based VLAN, and enable or disable GVRP protocol.
There are 256 VLAN groups to provide configure. Enable 802.1Q VLAN, the all ports on the switch
belong to default VLAN, VID is 1. The default VLAN can’t be deleted.
GVRP (GARP [Generic Attribute Registration Protocol] VLAN Registration Protocol):
GVRP allows automatic VLAN configuration between the switch and nodes. If the XL-VC2402F is
connected to a device with GVRP enabled, you can send a GVRP request using the VID of a VLAN
defined on the XL-VC2402F, the concentrator will automatically add that device to the existing VLAN.
5.7.2.1 Basic
Create a VLAN and add tagged member ports to it:
1. From the main menu, click administrator → VLAN configuration, click Add then you will see the
page as follow.
2. Type a name for the new VLAN.
3. Type a VID (between 2-4094). The default is 1.
4. Choose the protocol type.
5. From the Available ports box, select ports to add to the switch and click “Add >>”. If the trunk
groups exist, you can see itin here (ex:TRK1,TRK2…), and you can configure it is the member of
the VLAN or not.
6. Click Next. Then you can view the page as follow.
- 33 -
Page 34

XtendLan VC2402F – User’s Guide http://www.xtendlan.com
7.Using this page to set the outgoing frames of VLAN-Tagged frames or not. Then click Apply.
Tag: outgoing frames with VLAN-Tagged.
Un-tag: outgoing frames without VLAN-Tagged.
5.7.2.2 Port VID Configure port VID settings
From the main Tag-based (IEEE 802.1Q) VLAN page, click Port VID Settings.
Port VID (PVID)
Set the port VLAN ID that will be assigned to untagged traffic on a given port. This feature is useful for
accommodating devices that you want to participate in the VLAN but that don’t support tagging. VDSL
- 34 -
Page 35
XtendLan VC2402F – User’s Guide http://www.xtendlan.com
concentrator each port allows user to set one PVID, the range is 1~4094, default PVID is 1. The PVID
must as same as the VLAN ID that the port belong to VLAN group, or the untagged traffic will be
dropped.
Ingress Filtering
Ingress filtering lets frames belonging to a specific VLAN to be forwarded if the port belongs to that
VLAN.
VDSL concentrator have two ingress filtering rule as follows:
Ingress Filtering Rule 1: Forward only packets with VID matching this port's configured VID.
Ingress Filtering Rule 2: Drop Untagged Frame.
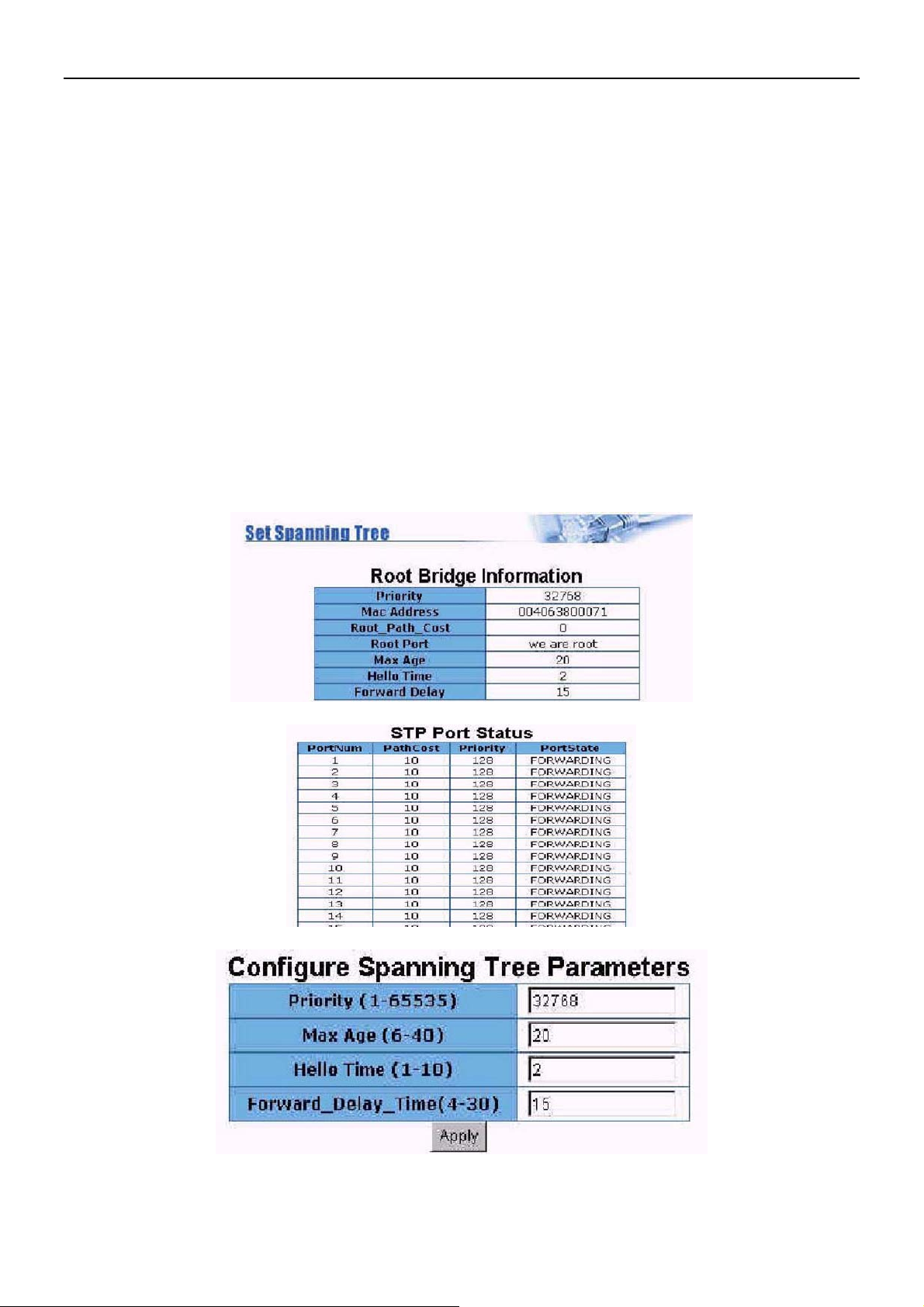
5.8 Spanning Tree
The Spanning-Tree Protocol (STP) is a standardized method (IEEE 802.1D) for avoiding loops in
switched networks. When STP enabled, to ensure that only one path at a time is active between any two
nodes on the network. You can enable Spanning-Tree Protocol on web management’s switch setting
advanced item, select enable Spanning-Tree protocol. We are recommended that you enable STP on all
XL-VC2402F to ensure a single active path on the network.
1. You can view spanning tree information about the Root Bridge.
2. You can view spanning tree status about the switch as the following screen.
3. You can set new value for STP parameter, then click set Apply button to modify.
- 35 -
Page 36

XtendLan VC2402F – User’s Guide http://www.xtendlan.com
Parameter Description
You can change priority value, A value used to identify the root bridge.The
Priority
bridgewith the lowest value has the highest priority and is selected as the root.
Enter a number 1 through 65535.
You can change Max Age value, The number of seconds a bridge waits
Max Age
without receiving Spanning-Tree Protocol configuration messages before
attempting areconfiguration. Enter a number 6 through 40.
You can change Hello time value, the number of seconds between the
Hello Time
transmission of Spanning-Tree Protocol configuration messages. Enter a
number 1 through 10.
Forward Delay
time
4.The following parameter can be configured on each port, click set Apply button to modify.
You can change forward delay time, The number of seconds a port waits
before changing from its Spanning-Tree Protocol learning and listening states
to the forwarding state. Enter a number 4 through 30.
Parameter Description
Port Priority
You can make it more or less likely to become the root port, the rage is
0-255,default setting is 128 the lowest number has the highest priority.
Specifies the path Cost of the port that switch uses to determine which port are
the forwarding ports the lowest number is forwarding ports, the rage is
Path Cost
1-65535 and default value base on IEEE802.1D
10Mb/s = 50-600
100Mb/s = 10-60
1000Mb/s = 3-10
- 36 -
Page 37
XtendLan VC2402F – User’s Guide http://www.xtendlan.com
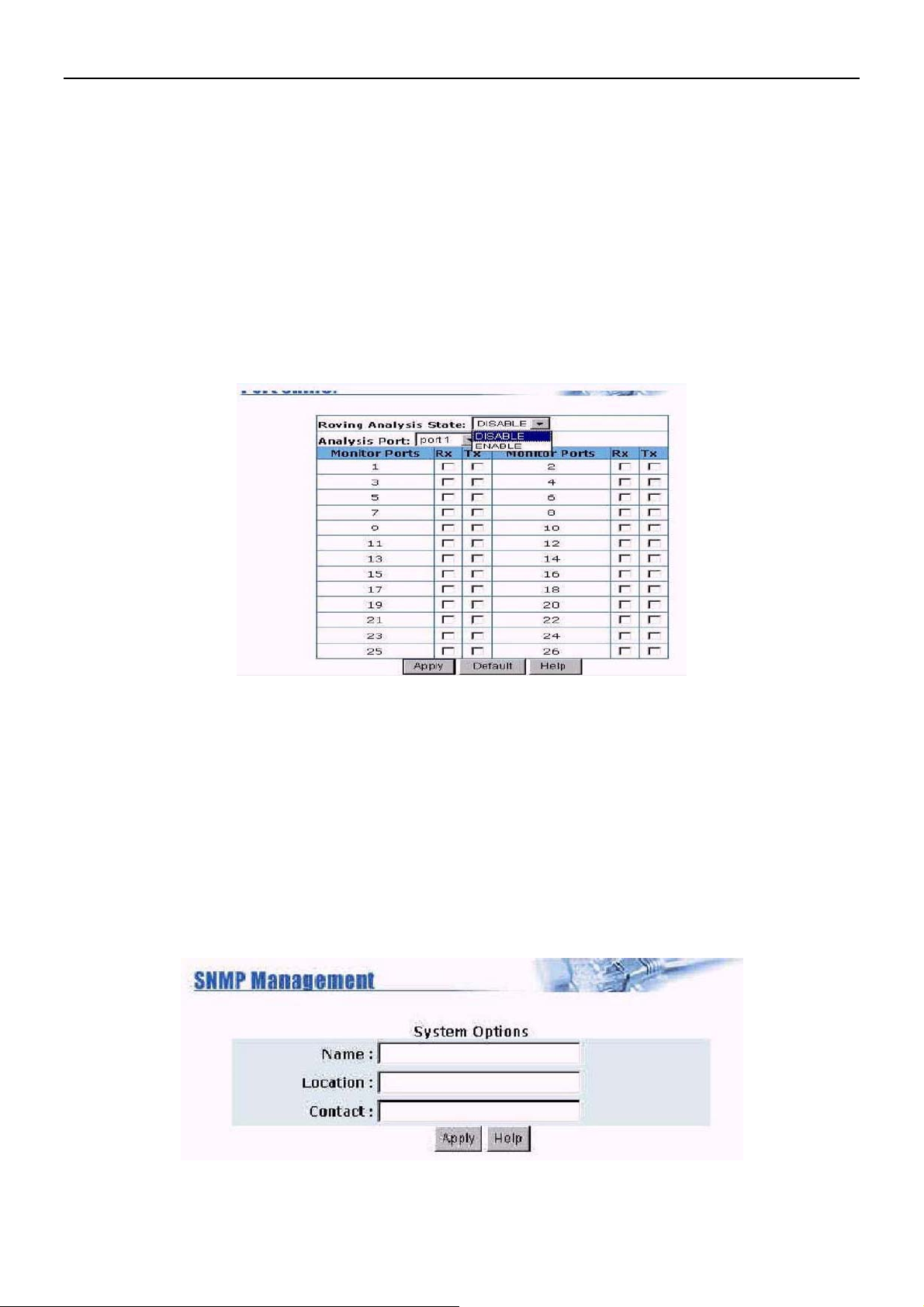
5.9 Port Sniffer
The Port Sniffer is a method for monitor traffic in switched networks. Traffic through ports can be
monitored by one specific port. That is, traffic goes in or out monitored ports will be duplicated into
sniffer port.
1. Sniffer Mode: Press Space key to set sniffer mode: Disable/Rx/Tx/Both.
2. Monitoring Port: It’s mean sniffer port can be used to see all monitor port traffic. You can connect
sniffer port to lan analyzer.
3. Monitored Port: The ports you want to monitor. All monitor port traffic will be copied to sniffer
port. You can select max 25 monitoring ports in the switch. User can choose which port will be
monitored in only one sniffer mode.
If you want to disable the function, you must select monitor port to none!
5.10 SNMP
Any Network Management running the simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) can manage the
switch, Provided the Management Information Base (MIB) is installed correctly on the management
station. The SNMP is a Protocol that governs the transfer of information between management and agent.
Use this page to define management stations as trap managers and to enter SNMP community strings.
User can also define a name, location, and contact person for the switch. Fill in the system options data,
then click Apply to update the changes on this page.
Name: Enter a name to be used for the switch.
Location: Enter the location of the switch.
Contact: Enter the name of a person or organization.
Community strings serve as passwords and can be entered as one of the following:
- 37 -
Page 38

XtendLan VC2402F – User’s Guide http://www.xtendlan.com
RO: Read only. Enables requests accompanied by this string to display MIB-object information. RW:
Read write. Enables requests accompanied by this string to display MIB-object information and to set
MIB objects.
Trap Manager
A trap manager is a management station that receives traps, the system alerts generated by the switch. If
no trap manager is defined, no traps are issued. Create a trap manager by entering the IP address of the
station and a community string.
5.11 Security Manager
Using this page, user can change web management user name and password.
User name: Type the new user name.
Password: Type the new password.
Reconfirm password: Retype the new password.
Click Apply.
5.12 802.1X Configuration
802.1x makes using of the physical access characteristics of IEEE802 LAN infrastructures in order to
provide a means of authenticating and authorizing devices attached to a LAN port that has point-to-point
connection characteristics, and of preventing access to that port in cases in which the authentication and
authorization process fails.
To enable 802.1x, you still to fill in the authentication server information:
Radius Server IP Address: the IP address of the authentication server.
Server Port: The UDP port number used by the authentication server to authenticate.
Accounting Port: The UDP port number used by the authentication server to retrieve accounting
information.
- 38 -
Page 39

XtendLan VC2402F – User’s Guide http://www.xtendlan.com
Shared Key: A key shared between this switch and authentication server.
NAS Identifier: A string used to identify this switch.
Per port Configuration:
In this page, you can select the specific port and configure the authorization state. Each port can
select four kinds of authorization state:
Fu: force the specific port to be unauthorized.
Fa: force the specific port to be authorized.
Au: the state of the specific port was determined by the outcome of the authentication.
No: the specific port didn't support 802.1x function.
Misc Configuration
In this page, you can change the default configuration for the 802.1x standard:
Quiet Period: used to define periods of time during which it will not attempt to acquire a
supplicant (Default time is 60 seconds).
Tx Period: used to determine when an EAPOL PDU is to be transmitted (Default value is 30
seconds).
Supplicant Timeout: used to determine timeout conditions in the exchanges between the
supplicant and authentication server (Default value is 30 seconds).
Server Timeout: used to determine timeout conditions in the exchanges between the
authenticator and authentication server (Default value is 30 seconds).
ReAuthMax: used to determine the number of re-authentication attempts that are permitted
before the specific port becomes unauthorized (Default value is 2 times).
ReAuth Period: used to determine a nonzero number of seconds between periodic
re-authentication of the supplications (Default value is 3600 seconds).
5.13 TFTP Update Firmware
The following menu options provide some system control functions to allow a user to update
firmware and remote boot switch system:
1. Install TFTP Turbo98 and execution.
2. Copy firmware update version image.bin to TFTP Turbo98 directory.
3. In web management select administrator—TFTP update firmware.
4. Download new image.bin file then in web management press <update firmware>.
5. After update finished, press <reboot> to restart switch.
- 39 -
Page 40

XtendLan VC2402F – User’s Guide http://www.xtendlan.com
5.14 Configuration Backup
5.14.1 TFTP Restore Configuration
Use this page to set TFTP server address. You can restore EEPROM value from here, but you
must put back image in TFTP server, switch will download back flash image.
5.14.2 TFTP Backup Configuration
Use this page to set TFTP server IP address. You can save current EEPROM value from here,
then go to the TFTP restore configuration page to restore the EEPROM value.
5.15 Reset System
Reset XL-VC2402F to default configuration, default value as below.
- 40 -
Page 41

XtendLan VC2402F – User’s Guide http://www.xtendlan.com
5.16 Reboot
Reboot the XL-VC2402F in software reset.
- 41 -
Page 42

XtendLan VC2402F – User’s Guide http://www.xtendlan.com
6 Applications
The VDSL provides home network architecture. Transforming an apartment into a
Multiple-Family Home network area, sharing a single internet account for multiple users with
Router & Cable Modem, it can provide unlimited access time in the internet at a reasonable low
price.
Bridging Functions – The XL-VC2402F provides full transparent bridging function. It
automatically connects node addresses, that are later used to filter and forward all traffic based on
the destination address. When traffic passes between devices attached to the shared collision
domain, those packets are filtered from the VDSL concentrator. But when traffic must be passed
between unique segments (i.e., different ports of the VDSL concentrator), a temporary link is set
up between the VDSL concentrator’s port in order to pass this traffic, XL-VC2402F (the
high-speed VDSL fabric).
Transceiver function - The XL-VC2402F supports Ethernet to VDSL convert, It can be transmit
or receive packet from Ethernet port to the RJ21 port. Or VDSL port to Ethernet port.
Flexible Configuration –The XL-VC2402F is not only designed to segment your network, but
also to provide a wide range of options in the configuration of Home network connections. It can
be used as a simple stand-alone VDSL concentrator; or can be connected with another VDSL
concentrator, Cable modem, Router, XDSL, ISDN, gateway or other network interconnection
devices in various configurations. Some of the common applications of the VDSL concentrator
are described in this chapter.
- 42 -
Page 43

XtendLan VC2402F – User’s Guide http://www.xtendlan.com
6.1 Used as apartment for Internet access
The XL-VC2402F provides a high speed, 4/1, 5/10/15Mbps transmission over existing home
telephone wiring over a single Internet account to provide simultaneous independent Internet
access to multiple users. No mater ISDN Telephone system or POTS Telephone system you are.
VDSL Technology let you can use telephone system and VDSL network system in the same time.
- 43 -
Page 44

XtendLan VC2402F – User’s Guide http://www.xtendlan.com
6.2 Application for sharing a single internet account
If multiple users would like to share a single internet account using the XL-VC2402F, which is to
be connected to a IP sharing device, then to a xDSL or Cable Modem.
Note: For network applications that actually require Router (e.g., Interconnecting dissimilar
network types), attaching the VDSL concentrator directly to a router can significantly improve
overall home networking performance.
High bandwidth backbone ready The XL-VC2402F provides 10/100/1000Mbps auto sensing for
external trunk device (Fiber optics, Wireless Bridge, xDSL & other WAN services)
- 44 -
Page 45

XtendLan VC2402F – User’s Guide http://www.xtendlan.com
7 Appendix
7.1 Appendix A: Troubleshooting
7.1.1 Diagnosing VDSL Indicators
The VDSL can be easily monitored through its comprehensive panel indicators. These indicators
assist the network manager in identifying problems of the VDSL concentrator may encounter.
This section describes common problems you may encounter and possible solutions
Symptom: POWER indicator does not light up (green) after power on. Cause: Defective power
outlet, power cord, internal power supply
Solution: Cheek the power outlet by trying another outlet that is functioning properly. Check the
power cord with another device. If these measures fail to resolve the problem, have the unit
power supply replaced by a qualified distributor.
Symptom: Link indicator does not light up (green) after making a connection.
Cause: Network interface (e.q., a network adapter card on the attached device), network cable, or
switch port is defective.
Solution:
1. Verifies the switch and attached device are powered on.
2. Be sure the cable is plug into both the switch and corresponding device.
3. Verify that the proper cable type is used and its length does not exceed specified
limits.
4. Check the adapter on the attached device and cable connections for possible
defects.
5. Replace the defective adapter or cable if necessary.
Symptom: VDSL Link can not be established.
Cause: Rusted phone wire, not standard 24 gauge phone wire, not twisted-pair phone wire, wrong
speed mode.
Solution: Check if speed of CO and CPE is in the same speed mode
depth value to 8 or above.
else please increase interleaver
7.1.2 System Diagnostics
Power and Cooling Problems
If the POWER indicator does not turn on when the power cord is plugged in, you may have a
problem with the power outlet, power cord, or internal power supply as explained in the previous
section. However, if the unit should turn itself off after running for a while, check for loose power
connections, power losses or surges at the power outlet, and verify that the fan on back of the unit
is unobstructed and running prior to shutdown. If you still cannot isolate the problem, then the
internal power supply may be defective. In this case, contact your supplier for assistance.
Installation
- 45 -
Page 46

XtendLan VC2402F – User’s Guide http://www.xtendlan.com
Verify that all system components have been properly installed. If one or more components
appear to be malfunctioning (e.g., the power cord or network cabling), test them in an alternate
environment where you are sure that all the other components are functioning properly.
Transmission Mode
The selections of the transmission mode for the RJ-45 ports are auto-negotiation using the default
method. Therefore, if the Link signal is disrupted (e.g., by unplugging the network cable and
plugging it back in again, or by resetting the power), the port will try to re-establish
communications with the attached device (auto-negotiation). If auto-negotiation fails, then
communications are set to half duplex by default. Based on this type of industry-standard
connection policy, if you are using a full-duplex device that does not support auto-negotiation,
communications can be easily lost (i.e., reset to the wrong mode) whenever the attached device is
reset or experiences a power fluctuation. The best way to resolve this problem is to upgrade these
devices to version that will support auto-negotiation.
Cabling
Verify that the cable type is correct. Be sure RJ-45 cable connectors are securely seated in the
required ports. Use 100Ω straight-through cables for all standard connections. Use Category 5
cable for 100/1000Mbps Fast Ethernet connections, or Category 3, 4 or 5 cables for standard
10Mbps Ethernet connections. Be sure RJ21 phone wiring, use 18~26 gauge.
Make sure all devices are connected to the network. Equipment any have been unintentionally
disconnected from the network.
When cascading two devices using RJ-45 station ports at both ends of the cable (XL-VC2402F)
supports auto MDIX), without crossover cable can be used.
Physical Configuration
If problems occur after altering the network configuration, restore the original connections, and
try to track the problem down by implementing the new changes, one step at a time. Ensure that
cable distances and other physical aspects of the installation do not exceed recommendations
System Integrity
As a last resort verify the switch integrity with a power-on reset. Turn the power to the switch off
and then on several times. If the problem still persists and you have completed all the preceding
diagnoses, contact your dealer for assistance.
- 46 -
Page 47
XtendLan VC2402F – User’s Guide http://www.xtendlan.com
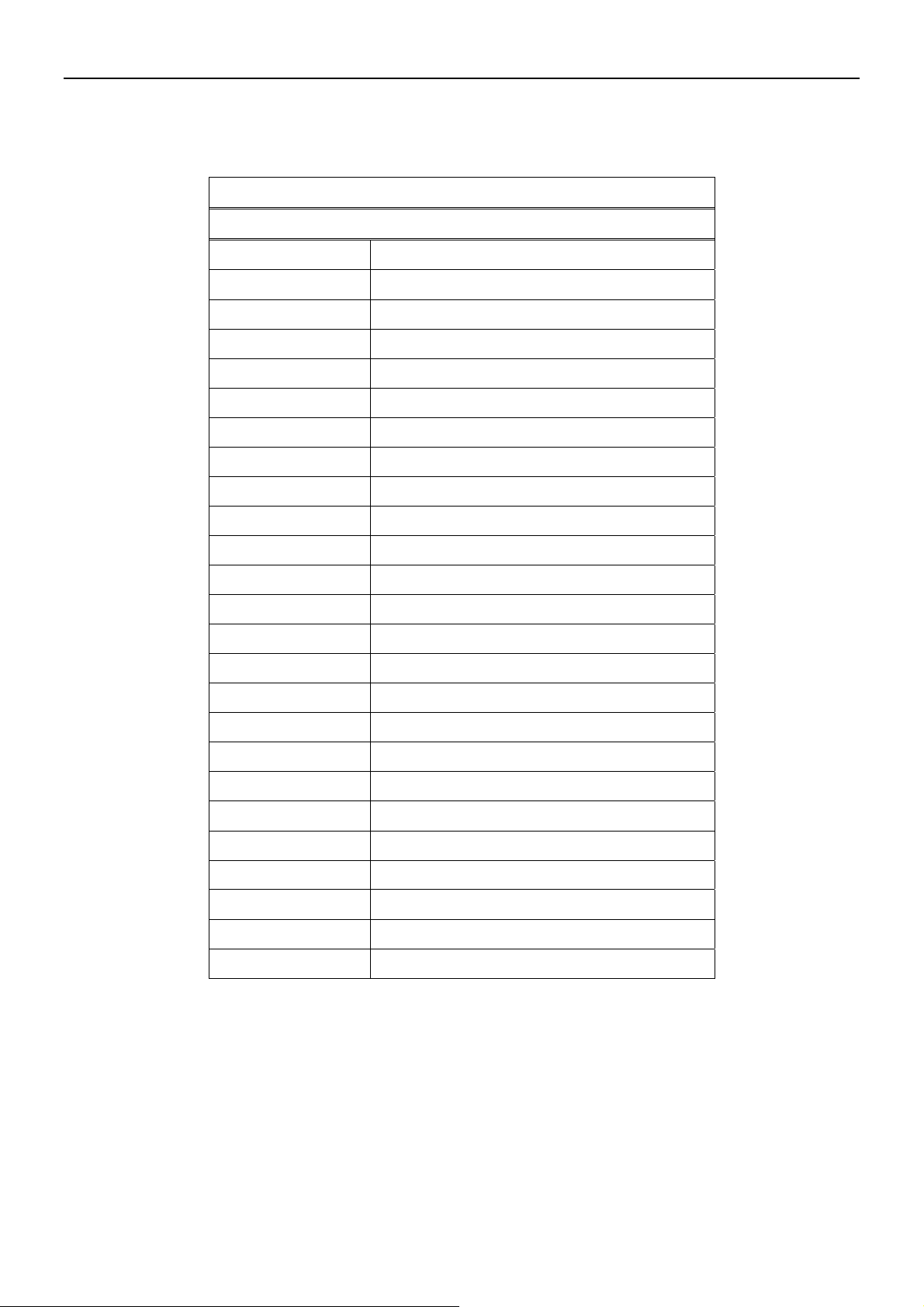
7.2 Appendix B:RJ-21 Telco ports distribution
RJ-21 Pin and VDSL port contrast list Note: RJ-21 Pin25 & 50 are not used
VDSL 50 Pin RJ-21 Cable Connector List
Cable Characteristic = 24 AWG twist wire
VDSL Port No. RJ-21 Cable No.
1 24 & 49
2 23 & 48
3 22 & 47
4 21 & 46
5 20 & 45
6 19 & 44
7 18 & 43
8 17 & 42
9 16 & 41
10 15 & 40
11 14 & 39
12 13 & 38
13 12 & 37
14 11 & 36
15 10 & 35
16 9 & 34
17 8 & 33
18 7 & 32
19 6 & 31
20 5 & 30
21 4 & 29
22 3 & 28
23 2 & 27
24 1 & 26
- 47 -
Page 48

XtendLan VC2402F – User’s Guide http://www.xtendlan.com
RJ-21 Cable Drawing (150 cm Male to Male)
- 48 -
Page 49
XtendLan VC2402F – User’s Guide http://www.xtendlan.com
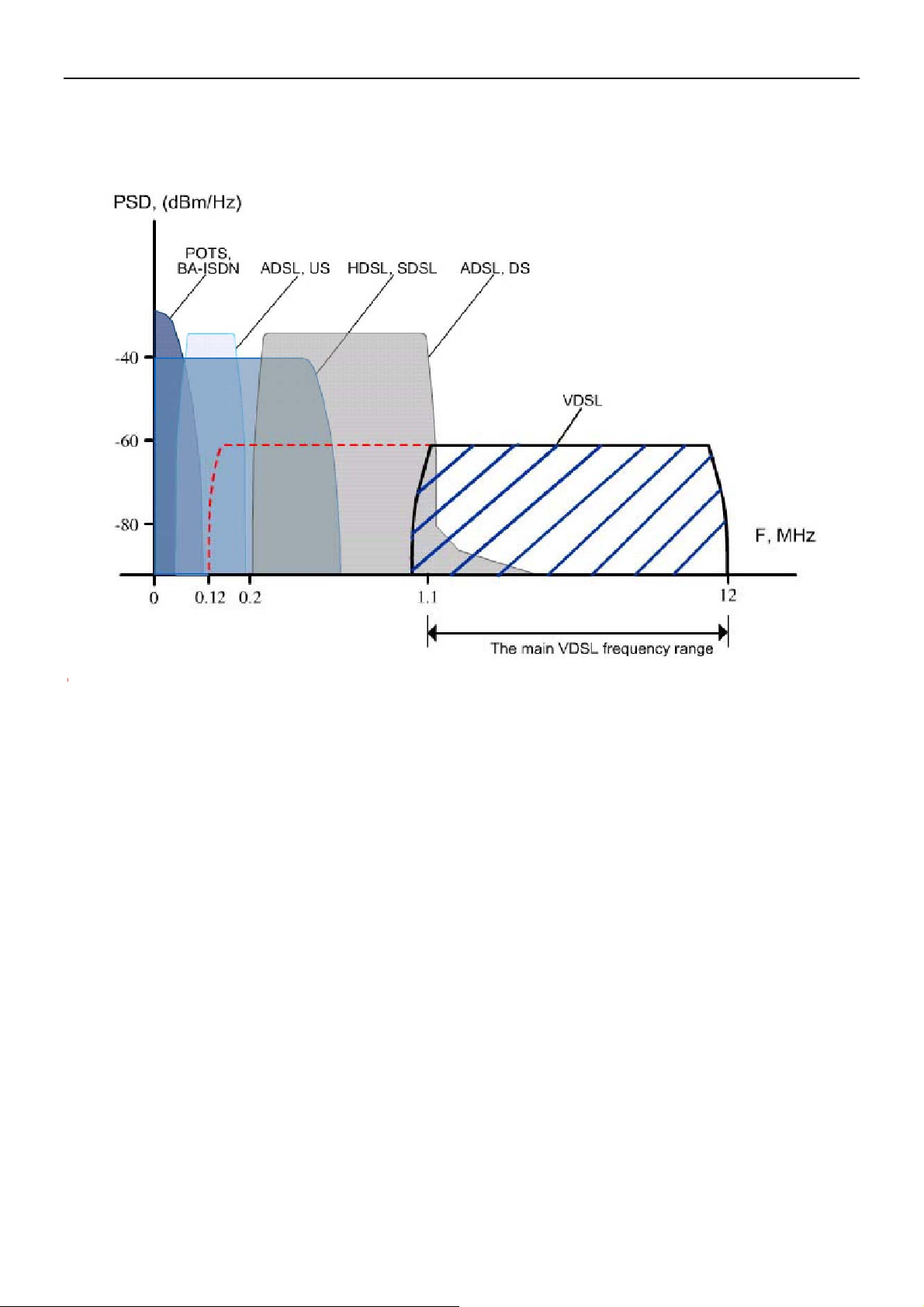
7.3 Appendix C: VDSL Spectrum
VDSL Technology – Requirements & Definitions Spectral Allocation
• Co-exists with legacy Voice and ISDN services
• Co-exists with other xDSL technologies
- 49 -
Page 50

XtendLan VC2402F – User’s Guide http://www.xtendlan.com
7.4 Appendix D: Example of VLAN Setting
XL-VC2402F supports Port Based VLAN and 802.1Q Tag VLAN:
VLAN Select: From Web Management→Switch setting→Advanced : Select VLAN Operation
Mode by Port Based VLAN or 802.1Q Tag VLAN
7.4.1 Port Based VLAN
Packets can go among only members of the same VLAN group. Note all unselected ports are
treated as belonging to another single VLAN. If the port-based VLAN enabled, the
VLAN-tagging is ignored.
- 50 -
Page 51

XtendLan VC2402F – User’s Guide http://www.xtendlan.com
1. Click Add to create a new VLAN group.
2. Enter the VLAN name, group ID and select the members for the new VLAN.
3. Click Apply.
4. If there are many groups that over the limit of one page, you can click the “Next Page” to
view other VLAN groups. NOTE: If the trunk groups exist, you can see it (ex: TRK1,
TRK2…..) in select menu of ports, and you can configure it is the member of the VLAN
or not.
7.4.2 802.1Q Tag Vlan
Tagged-based VLAN is an IEEE 802.1Q specification standard. Therefore, it is possible to create
a VLAN across devices from different switch venders. IEEE 802.1Q VLAN uses a technique to
insert a “tag” into the Ethernet frames. Tag contains a VLAN Identifier (VID) that indicates the
VLAN numbers. In order to an end station to send packets to different VLANs, it itself has to be
either capable of tagging packets it sends with VLAN tags or attached to a VLAN-aware bridge
that is capable of classifying and tagging the packet with different VLAN ID based on not only
default PVID but also other information about the packet, such as the protocol.
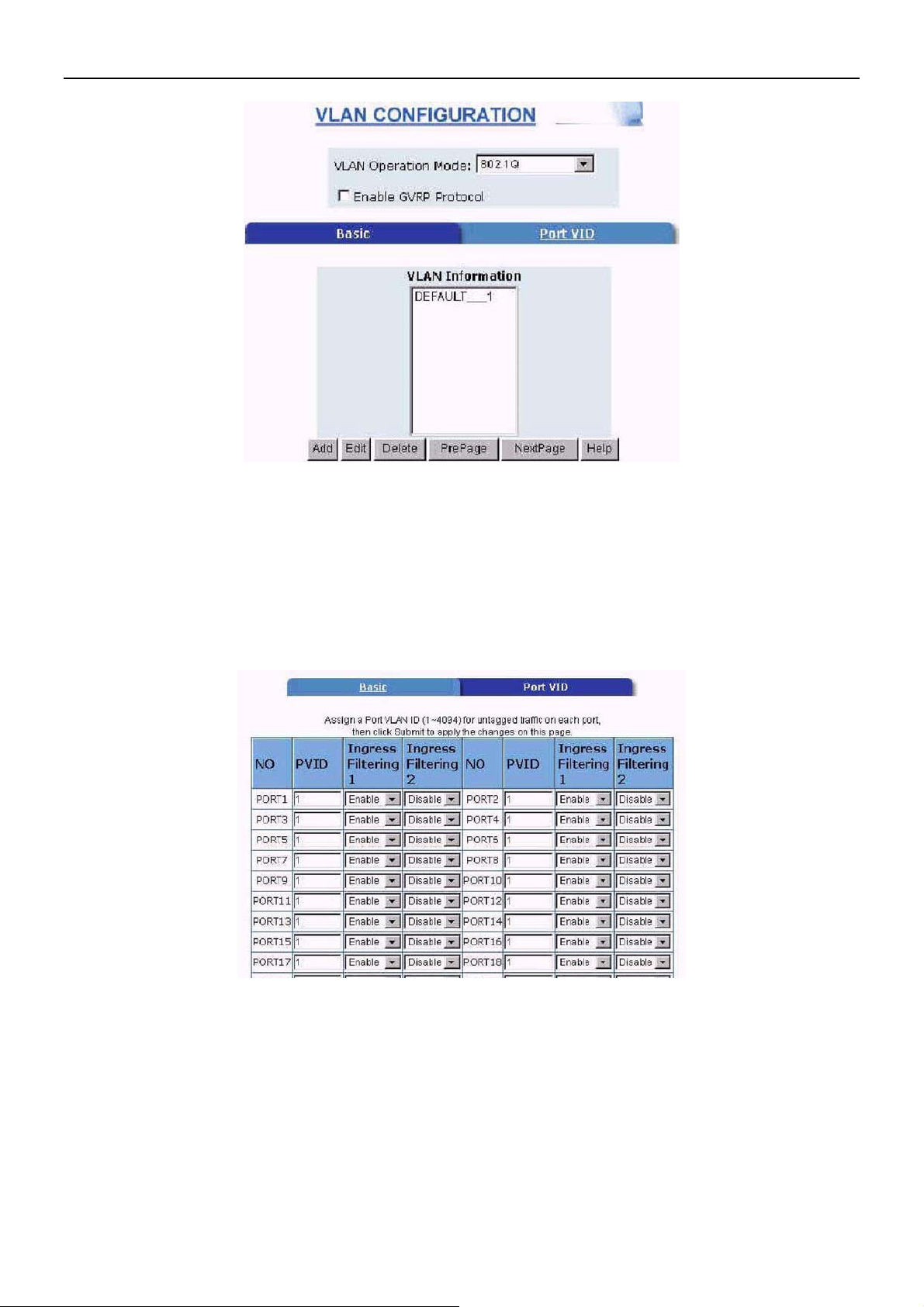
This page, user can create Tag-based VLAN, and enable or disable GVRP protocol. There are
256 VLAN groups to provide configure. Enable 802.1Q VLAN, the all ports on the switch belong
to default VLAN,VID is 1. The default VLAN can’t be deleted and modified.
- 51 -
Page 52
XtendLan VC2402F – User’s Guide http://www.xtendlan.com
GVRP (GARP [Generic Attribute Registration Protocol] VLAN Registration Protocol)
GVRP allows automatic VLAN configuration between the switch and nodes. If the VDSL
concentrator is connected to a device with GVRP enabled, you can send a GVRP request using
the VID of a VLAN defined on the VDSL concentrator, the VDSL concentrator will
automatically add that device to the existing VLAN.
Port VID Configure port VID settings
From the main Tag-based (IEEE 802.1Q) VLAN page, click Port VID Settings.
Port VID (PVID)
Set the port VLAN ID that will be assigned to untagged traffic on a given port. This feature is
useful for accommodating devices that you want to participate in the VLAN but that don’t
support tagging. VDSL SWITCH each port allows user to set one PVID, the range is 1~4094,
default PVID is 1. The PVID must as same as the VLAN ID that the port belong to VLAN group,
or the untagged traffic will be dropped. The 24-ports VDSL concentrator has 16 PVID ranges.
PVID of Port 1 ~ Port 26 must be in the same range.
- 52 -
Page 53

XtendLan VC2402F – User’s Guide http://www.xtendlan.com
PVID Range:
Num. PVID
Range
Num. PVID
Range
Num. PVID
Range
Num. PVID
Range
1 1~255 5 1024~1279 9 2048~2303 13 3072~3327
2 256~511 6 1280~1535 10 2304~2559 14 3328~3583
3 512~767 7 1536~1791 11 2560~2815 15 3584~3839
4 768~1023 8 1792~2047 12 2816~3071 16 3840~4094
Basic
1. Create a VLAN and add tagged member ports to it.
2. From the main menu, click administrator →VLAN configuration, click Add then you will see the
page as follow.
3. Type a name for the new VLAN.
4. Type a VID (between 2-4094). The default is 1.
5. Choose the protocol type.
6. From the Available ports box, select ports to add to the switch and click “Add >>”. If the trunk
groups exist, you can see it
in here (ex:TRK1,TRK2…), and you can configure it is the member of the VLAN or
not.
7. Click Next. Then you can view the page as follow.
8. Using this page to set the outgoing frames are VLAN-Tagged frames or no. Then click Apply.
Tag: outgoing frames with VLAN-Tagged.
Un-tag: outgoing frames without VLAN-Tagged.
- 53 -
Page 54
XtendLan VC2402F – User’s Guide http://www.xtendlan.com
Ingress Filtering
Ingress filtering lets frames belonging to a specific VLAN to be forwarded if the port belongs to that
VLAN. The XL-VC2402F has two ingress filtering rules as following:
Ingress Filtering Rule 1: Forward only packets with VID matching this port's configured VID.
Ingress Filtering Rule 2: Drop Untagged Frame.
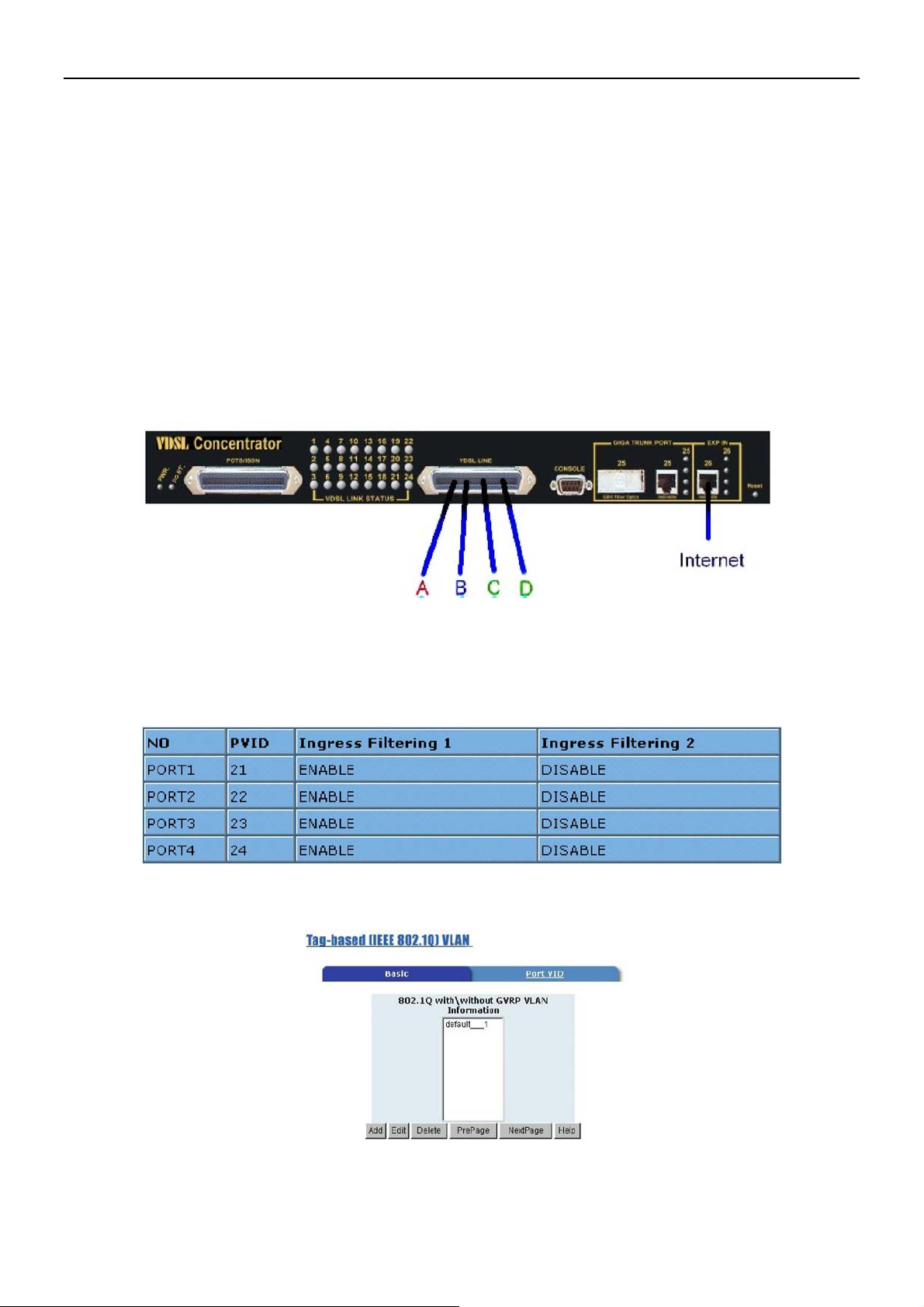
Example 1:
4 users join to Internet by VDSL system like following drawing, and have 7 demands.
1) User A connect to port 1 and join to Internet through port 26
2) User B connect to port 2 and join to Internet through port 26
3) User C connect to port 3 and join to Internet through port 26
4) User D connect to port 4 and join to Internet through port 26
5) User A isolate with Users B, C and D 6) User B isolate with Users A, C and D
7) User C and D in same Group and isolate with Users A and B
Setup Procedure:
Setup Port VID: Assign a Port VLAN ID (1~4094) for untagged traffic on each port like following: Port 1
PVID=21, Port 2 PVID=22, Port 3,4 PVID=23
Add VLAN Group:
1) Do not change the default_1 group.
2) Add a VLAN Group VID=21 member ports = port 1 & port 26
2.1) Setup VLAN Name=UserA, VID=21, select member ports 1 & 26
- 54 -
Page 55

XtendLan VC2402F – User’s Guide http://www.xtendlan.com
2.2) Select Untag or Tag Setup. Unless the device( computer or switch) which connect to port 1 or
port 26 can support Tagging VLAN, otherwise select Untag.
3) Add a VLAN Group Name=UserB, VID=22 member ports = port 2 & port 26 4) Add a VLAN Group
Name=UserCD, VID=23 member ports = port 3, port 4 & port 26
- 55 -
Page 56
XtendLan VC2402F – User’s Guide http://www.xtendlan.com
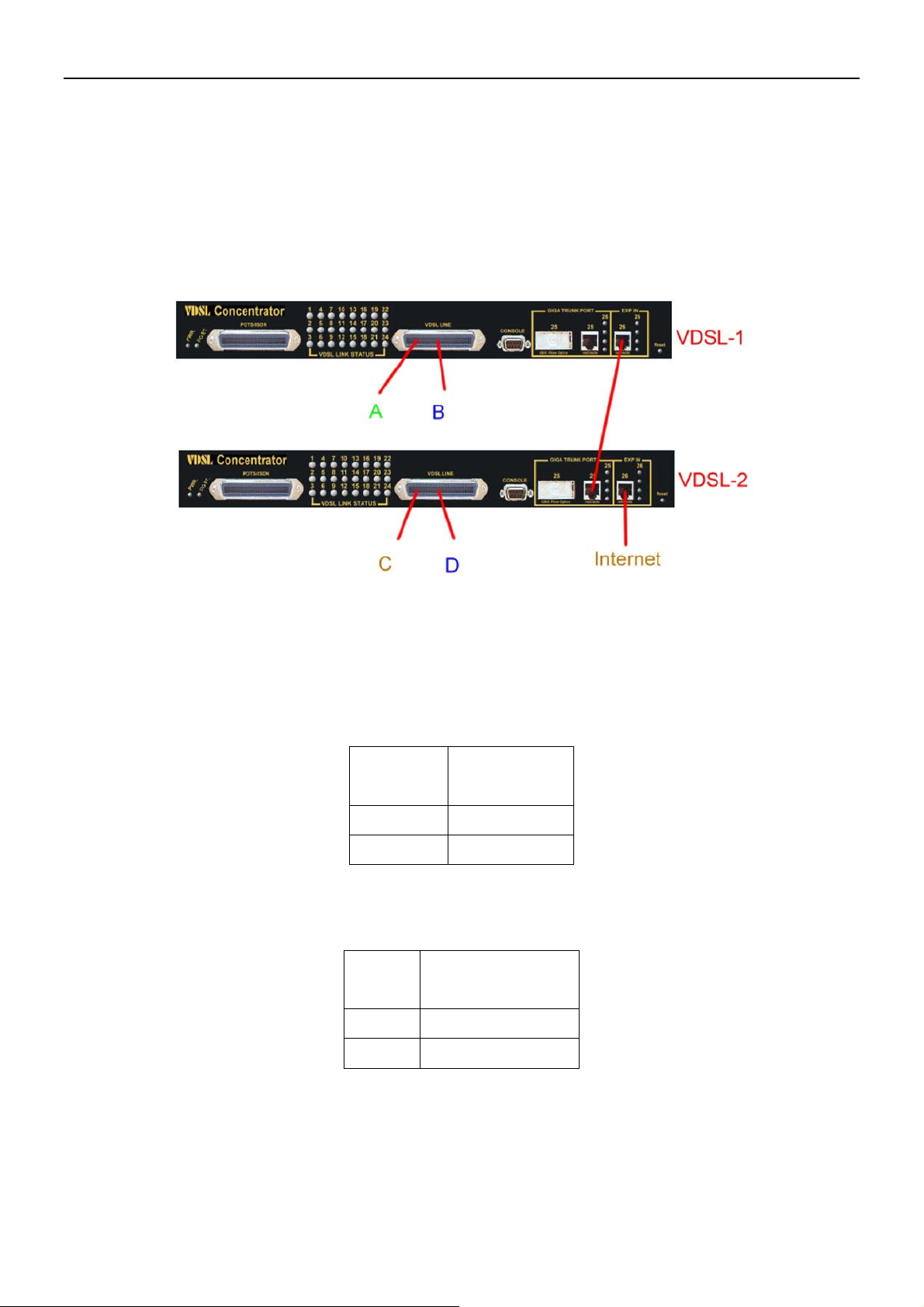
Example 2:
4 users join to Internet through 2 VDSL concentrators like the following drawing, and have 7 demands.
1) User A connect to port 1 of VDSL-1 and join to Internet through port 26 of VDSL-2
2) User B connect to port 2 of VDSL-1 and join to Internet through port 26 of VDSL-2
3) User C connect to port 1 of VDSL-2 and join to Internet through port 26 of VDSL-2
4) User D connect to port 2 of VDSL-2 and join to Internet through port 26 of VDSL-2
5) User A isolate with Users B, C and D
6) User C isolate with Users A, B and D
7) User B and D in same Group and isolate with Users A and B
Setup Procedure:
1. VDSL-1 SETUP:
a. Setup Port VID: Port 1 PVID=11, Port 2 PVID=12
b. Add VLAN Group:
ii. Add a VLAN Group, Group name=UserA VID=11 member ports = port 1 & port
iii. Select Untag or Tag Setup for VID=11 group:
iv. Add a VLAN Group, Group name=UserBD VID=12, member ports = port 2 & port
v. Select Untag or Tag Setup for VID=12 group:
i. Do not change the default_1 group.
26
Port Untag/Tag
Number Select
1 Untag
26 Tag
26
Port
Numbe
Untag/Tag Select
2 Untag
26 Tag
- 56 -
Page 57

XtendLan VC2402F – User’s Guide http://www.xtendlan.com
2. VDSL-2 SETUP:
a. Setup Port VID: Port 1 PVID=21, Port 2 PVID=12
b. Add VLAN Group:
i. Do not change the default_1 group.
ii. Add a VLAN Group, Group name=UserA VID=11 member ports = port 25 & port
26
iii. Select Untag or Tag Setup for VID=11 group:
Port Untag/Tag
Number Select
25 Tag
26 Untag
iv. Add a VLAN Group, Group name=UserBD VID=12 member ports = port 2 & port
25 & port 26
v. Select Untag or Tag Setup for VID=12 group:
Port Untag/Tag
Number Select
2 Untag
25 Tag
26 Untag
vi. Add a VLAN Group, Group name=UserC VID=21 member ports = port 1 & port
26
vii. Select Untag or Tag Setup for VID=21 group:
Port Untag/Tag
Number Select
1 Untag
26 Untag
- 57 -
Page 58

XtendLan VC2402F – User’s Guide http://www.xtendlan.com
FCC Warning
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital device, pursuant
to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful
interference when the equipment is operated in a commercial environment. This equipment generates,
uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the
instruction manual, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. Operation of this
equipment in a residential area is likely to cause harmful interference in which case the user will be
required to correct the interference at his/her own expense.
CE Mark Warning
This is a CE class A product. In a domestic environment, this product may cause radio interference in
which case the user may be required to take adequate measures.
Warranty
The original owner that the product delivered in this package will be free from defects in material and
workmanship for one year parts after purchase.
There will be a minimal charge to replace consumable components, such as fuses, power transformers,
and mechanical cooling devices. The warranty will not apply to any products which have been subjected
to any misuse, neglect or accidental damage, or which contain defects which are in any way attributable
to improper installation or to alteration or repairs made or performed by any person not under control of
The original owner.
The above warranty is in lieu of any other warranty, whether express, implied, or statutory, including but
not limited to any warranty of merchantability, fitness for a particular purpose, or any warranty arising
out of any proposal, specification, or sample. Shall not be liable for incidental or consequential damages.
We neither assumes nor authorizes any person to assume for it any other liability.
Note: Please do not tear off or remove the warranty sticker as shown, otherwise the warranty will be void.
- 58 -
 Loading...
Loading...