Page 1

XL-MB101M
MoCA Ethernet bridge
User’s Guide
Page 2

Preface
User Guide
This manual explains how t o use command line interface to configure XtendLan EOC products.
Reader
1. Network planner
2. Technical service person
3. Network management per son
Application Ra nge
The manual is for the EOC head end product XL-MB101M produced by XtendLan company.
Conventions Used in This Manual
command line keyword indicated in bold;
command line parameter indic at ed in italic.
Curly brackets “{ }” indic at e t he contents in them is mandatory ;
Center brackets “[ ] ” indic at e the contents in them is optional;
Angular brackets “< > ” indi cat e the contents in them will not be shown;
Square brackets “【】” indicate t he contents in them needs the notice of user;
Vert ica l l ine “|” is used to separate several options, indicates alternat iv e or multiple-choice;
Diagonal “/” is used to separate several options, it in dicates all the options can be selected by the same
time;
“ Notice ” Indicates t he user should pay attention to, it is the key point of system configuration, please
read carefully.
“ Note” Indicates the note for the mentioned co nt ent ;
“ Diagram” Indicates t he written explanation to th e dia gr am.
Statement
As the upgrade of the product or other uncertain reasons, t hi s m anual will be updated in the future. This
manual can only be used as the user guide, t he statements、information or construction do es not
guarantee anything, unless there is any other agreement.
Page 3

Catalogue
Chapter One System Ba si c
1.1 Configuration Method
1.2 XtendLan SHELL Introduction
1.2.1 Shell Function
1.2.2 Shell Mode
1.2.3 Get Help
1.2.4 Command Abbreviation
1.2.5 Common Prompting Message Meaning
1.2.6 Use History Command
1.2.7 Line Edit Shortcut Key
1.3 XtendLan EOC Products Functi on Introduction
1.4 T ypical Application of XtendLan EOC Product
Chapter Two S HE LL Rel at ing Co nfi gurat i on
2.1 Mode Shift Comm and
2.1.1 Common Description
2.2 Common Command under All Command Modes
2.2.1 Common Description
2.3 Virtual Terminal Configuration
2.3.1 Common Descript ion
2.4 Privileged Mode and TELNET Login Passw ord Conf igurat ion
2.4.1 Common Description
2.5 Application Program St art-up Prompting Message
2.5.1 Common Descriptio n
2.6 Start Script Configuration and Display
2.6.1 Common Description
2.7 System Miscellaneous
2.7.1 Common Descriptio n
Chapter Three Head End Configuration
3.1 Head End Configuration Com m and
3.1.1 Common Descriptio n
Page 4

Chapter Four User Database C onfiguration
4.1 User Database Configuration Com mand
4.1.1 Common Descriptio n
Chapter Five SNMP Parameter Configuration
5.1 User Database Configuration Com mand
5.1.1 Common Descriptio n
Chapter Six Configuration Exam ples
6.1 User Enter Control Function
6.1.1 Configuration Examples
6.2 Start -up SNMP Server
6.2.1 Configuration Examples
6.3 Remote Configuration for the VLA N of User CPE Port
6.3.1 Configuration Examples
Page 5

Chapter One System Base
This Chapter introduces the basic knowledge of XtendLan EOC(Ethernet Over Cable) system, i ncludi ng
the preparation of configuration and command line interface relating knowledge .
The content of this chapter:
1. EOC Configuration Method Introduction
2. XtendLan Shell Introduction
3. XtendLan EOC Product Funct ion Introduction
4. XtendLan EOC Product Typical Applicat ion
1.1 Configuration Method
XtendLan EOC products support the following t hr ee typical configuration methods:
1. Via console port, use Shell command to configure
2. Via Telnet remote login, use Shell to con figure
3. Use SNMP network management to configure
4. The manual explains the configuration method of console and telnet by login to Shell, the following
chapters will explain the d etail use of shell and EOC configuration command.
5. The manual does not include the relating content of SNMP network management, if need help, please
refer to network management manual.
1.2 XtendLan Shell Introduction
1.2.1 Shell Function
1. For the convenience of user management, the command processing subsystem (thereafter called
shell) are embedded in XtendLan EOC product, the command line operation interface is familiar to the
network engineer. The main function includes:
2. Command line edit
3. Command line help
4. Command grammar na vigation
5. Command parsing
6. Command execute
7. Command line edit. Edi t by line, multiple hotkeys are availabl e f or edit help.
Page 6

8. Command line help. User can type “?” to acquire the meaning of which are being typed and the use
mode when
to this
command to
quit and restart
command to
the command of
command under
command to
return to user
file system
debug
all kinds of
under this
Including the
commands of
“file system
mode” and
configure
command to
method help when editing.
9. Command gramm ar nav igation. This fu nction can help to input command fast, user input some pre fix
letters, then press TAB key, shell will search for relating commands according to the prefix letters
and guide the user to input the command.
10. Command parsing. Automatic check if the input command grammar is right or wrong, wrong
commands will not be processed by Shell.
1.2.2 Shell Mode
1. The Shell interface of XtendLan EOC equipmen t i s divided into several command modes (thereafter
called mode). Dif ferent modes have differe nt commands, for different function configuratio n.
2. Under different command modes, shell has different prompts. XtendLan EOC product has the
following command mod es (suppose hose name is the system defaul string “GD.LINK”):
Prompt Mode Enter Method Quit Method Function
GD.LINK> User Mode
GD.LINK#
Privileged
Mode
console:the defau lt
startup.
telnet:enter
mode when login in.
Execute enable
user mode
console:execute
exit
Display system
information and
the application.
telnet: execute
privileged
exit
mode.
break off telnet
connection。
Display、
Execute exit
commands
mode. Execute
mode.
configure terminal
command to enter
privileged mode.
Execute file
configuration
command to enter
to
“global
configuration
configuration
mode.
mode”.
GD.LINK(config)#
Global
Configuratio
Execute
terminal command
Execute exit
Configuration
system
Page 7

n Mode
under privileged
return to
privileged mode.
to interface
to EOC head end
to user database
line vty
to virtual terminal
operates the
required global
interface
lobal
command to
Configure and
Head
service
to stop forwad
service, and then
headend
global configuration
command to
return to global
head end
user
global configuration
d to
return to global
Configure EOC
mode.
Execute interface
manage-interface
command to enter
configuration
mode.
Execute headend
command to enter
configuration
mode.
Execute user
command to enter
configuration
mode.
parametes.r
GD.LINK(config-if)#
GD.LINK(config-headend)#
Interface
Configuratio
n Mode
EOC
End
Configuratio
n Mode
Execute
interface
manage-interface
under g
configuration mode.
Execute
stop
execute
command under
Execute
command to enter
configuration
mode.
Execute exit
return to global
configuration
mode.
Execute exit
configuration
mode.
manage
interface
parameter.
Configure EOC
parameter.
GD.LINK(config-user<n>)#
User
Database
Configuratio
n Mode
mode.
Execute
command under
mode.
Execute exit
comman
user database.
configuration
Page 8

mode.
File System
commande under
command to
return to
System remote
global configuration
command to
return to global
parameter
User can input this command to get shell
common operation help information under any
: check all the commands
Input of command prefix <?>: check the
: check the
Execute file
GD.LINK(file)#
GD.LINK(config-line)#
1.2.3 Get Help
User can input question mar k (?) under command prompt to list the com m ands of each function mode.
User can also use the following c ommand writing to acquire help inf or m at ion:
Command Explanation
Configuratio
n Mode
Virtual
Teminal
Configuratio
n Mode
privileged mode.
Execute line vty
command under
mode.
Execute exit
upgrade.
privileged mode.
Execute exit
Shell
configuration.
configuration
mode.
Help Command
?Command ?command includes the foll ow ing formats:
mode.
Direct input of ?
underthe running mode.
commands with the same prefix under running
mode.
Example: GD.LINK# s<?>
show show clink statics
system system control tools.
Input command keywords <?>
Command prefix <TAB> AutoFill command keyword.
subsequent param et er s of the running command.
Example: GD.LINK# ping <?>
A.B.C.D Host ip address
Example : GD.LINK# p<TAB>
Page 9

GD.LINK# ping
the about example, shell shows two
If a command prefix is corresponding to serveral
commands, shell will list all the options for user to
input.
Example : GD.LINK# s<TAB>
show system
In
commands with prefix of ‘s’.
1.2.4 Command Abbreviation
1. XtendLan Shell allows t he user t o i nput abbreviation command. S hell will find the correct com mand to
execute automatically as long as the abbreviation command is unique.
● For example, show running-config command can be shortened to :
● GD.LINK# show run
2. If shell finds more than one result for an i nput comm and, the syt em will print “% Ambig uous com mand”
to prompt the user.
● GD.LINK# s r
● % Ambiguous command.
1.2.5 Common Prompt Information Meaning
% Ambiguous command: system finds several commands corresponding to the abbrevation com m and
% Command incomplete: i nput commmand is incomplete.
% Unknown command: t he keyword of the input command is wr ong.
1.2.6 Use History Comm and
The system can remember the last ten input commands, use r can use Ctrl+P or upw ard arrow keyboar d,
and Ctrl+N or downward a r r ow keyboard to browse the the history com ma nds.
1.2.7 Line Edit Shortcut Keys
The following shortcut keys can be used to edit command line or to control cursor when editing the
command line:
Function Shortcut Key Explanation
Move cursor Left arrow or Ctrl+B Move cursor to the left
Right arow or Ctrl+F Move cursor to the right
Page 10

Ctrl+A Move cursor to the beginning of the line.
Delete the input
Screen Scroll
Ctrl+E Move cursor to the end of the line.
Backspace key Delete one letter on the left of the cursor.
letter
Delete key Delete the letter where the curso r is at.
Any key Page down
Control
Q key Quit scrol
1.3 XtendLan EOC products f unc t ion introction
XtendLan EOC products are the enter equipments based on EOC technique in MOCA (MultiMedia Over
Coax Alliance). The function is to m odulate the baseband si gnals to 800~1500MHz fre quency by the way
of OFDM, and to transmit in HFC network after mixing the signals with TV signals, which can rebuild the
unidirectional normal CATV network to a bilateral network that can transmit ethernet data without large
change of the existing TV network equipemnt and layout. XtendLan EOC products includes two main
types: the station device network coordinator (NC) and the end customer premise equipment (CPE).
Each of the function are:
Function of Station Device:
● MOCA network control, for controlling the CPEs in MOCA network to receive ether messages. MOCA
network adopts TDMA work mode and CPE time-sharing data transmission. In addition, NC can also be
used to control the acess CP E.
● Modulation-demodulation process. OFDM modulation-demodulation, data frequency signal convert,
automatic gain control an d aut omatic power control can be realiz ed.
● Ethernet Layer 2 switching, finishing ethenet message layer 2 transmission.
● SNMP server, for accepting romote management of the SNMP network manage software.
● TELNET server, users can login to NC via TELNET client remote, thus the remote management can be
processed by command li ne m ode.
● VTY terminal server, which is communicated with the hyperterminal of a computer by using 115200
baudrate serial interface s o as t o set t he local information of NC.
Function of CPE :
● Modulation-demodulation process. Finishing OFDM modulation-demodulation, data frequency signal
Page 11
convert, automatic gain control and automatic power cont r ol.
● Ethernet Layer 2 switching, finish ethenet message layer 2 transmission.
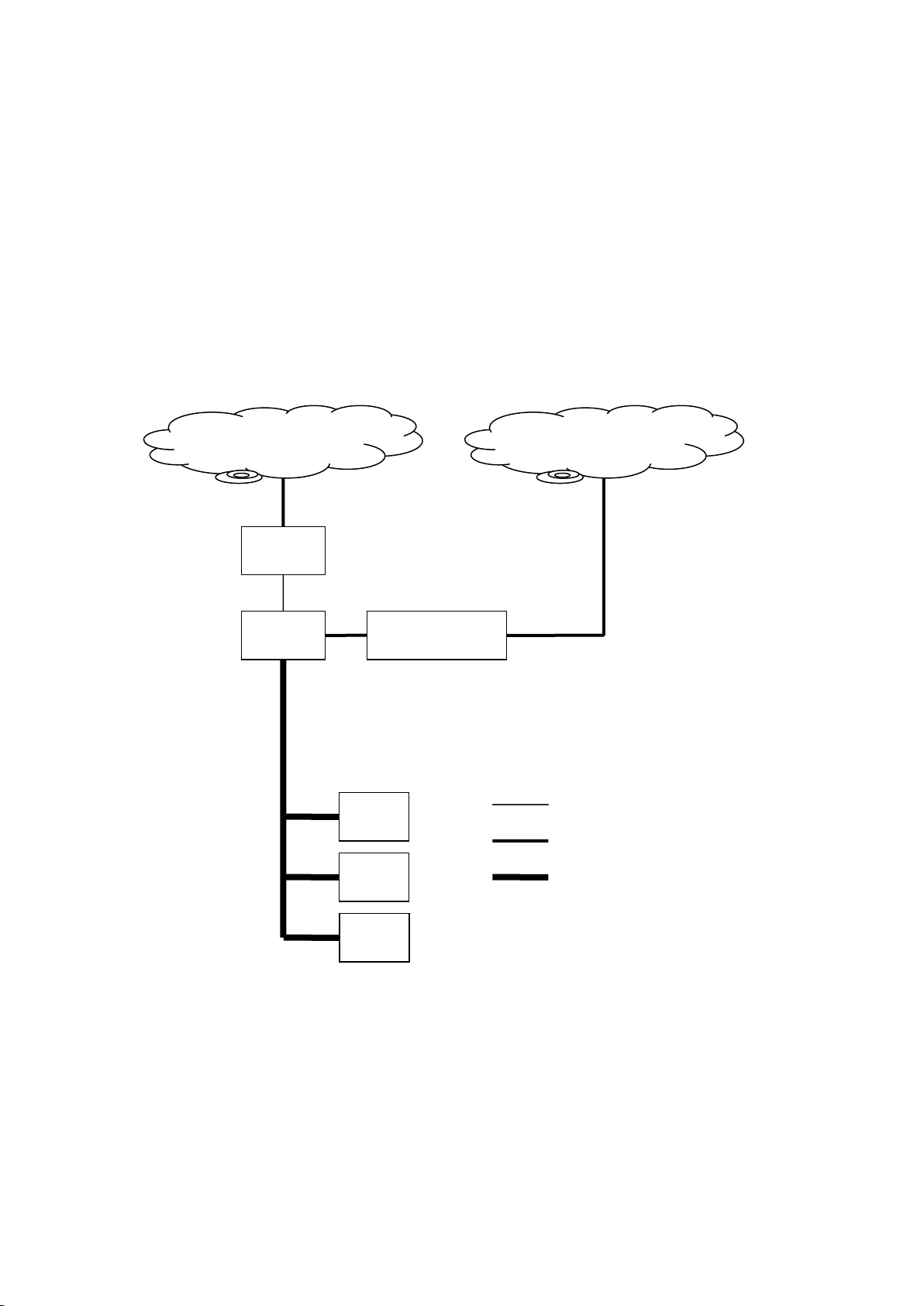
1.4 XtendLan EOC Products Typical Application
XtendLan EOC products are designed for the network bidirectional rebuilding, mainly used to solve the
last 300 enter proble m in catv data net work. NC and CPE can co ntinuou sly work under t he conditio n that
the link attenuation is less than 75db (the transmission distance can be more than 300m under the
condition that the standard 5mm coaxial cable is in direct enter). The typical application enviroment
diagram is shown as follo wing:
Data Network
ONU
NC
Analog Optical Receiver
CPE
CPE
HFC Network
Ethernet Cable
Fiber Cable
Coaxial Cable
CPE
Page 12

to global configuration
Chapter Two Shell Relat i ng Co nfi gur ati on
This chapter describes shell relating configuration, including the following function configuration
command:
Mode shift command.
The common command u nder al l command modes.
Virtual terminal co nf iguration.
Privileged mode and Telnet enter passw or k configu rat ion
Application startup prompt information.
Star t up script configuration and display.
System miscellaneous.
2.1 Mode Shift Command
This section indicates the enter methods of the command modes of XtendLan EOC products.
2.1.1 Command Description
Configuration
Command Description
Mode
enable Enter to privileged mode User Mode
configure terminal Enter
Privileged Mode
mode
file Enter to file configuration mode Privileged Mode
headend Enter to head end configuration
mode
user Enter to user database
configuration mode
interface Enter to interface configuration
Global Configuration
Mode
Global Configuration
Mode
Global Configuration
mode
line vty Enter to virtual terminal
configuration mode
■ Enable
From user mode to privile ged mode.
Mode
Global Configuration
Mode
Page 13
enable
rivileged mode needs correct password. The
global configuration mode to head end
Grammar Description
enable from user mode to privileged mode, to enter
p
system defult passw or d is admin.
■configure terminal
Command for shifting from privileged mo de t o global configuration mode.
configure terminal
Grammar Description
configure terminal
from privileged mode to global configuration mode.
file
From user mode to file conf iguration mode.
file
Grammar Description
file From user mode to file conf iguration mode.
headend
From global configuration mode to head end configuration mode.
headend
Grammar Description
headend From
Note: user should use service stop to stop EOC headend farward service under the globle
configuratio n mode bef or e enter to headend mode.
user
From global configuratio n mo de t o use r database configurat ion mo de.
user number
Grammar Description
configuration mode.
Page 14

user number
global configuration mode to user database
indicates the logic
From global configuration mode to interface
name indicates the interface names of
global configuration mode to virtual terminal
e and
All modes except
Print shell basic help
interface
From global configuratio n mo de t o int erface configuration mode.
interface interface-name
Grammar Description
interface interface-name
line
From
configuration mode. Number
number of user.
configuration mode.
interface-
three layers.
From global configuratio n mo de t o virtual terminal configuratio n mode.
line vty
Grammar Description
line vty
2.2 The common command under all command modes
This section introduces the common command under all c ommand modes.
2.2.1 Command Description
Command Description
exit Quit the running mod
From
configuration mode
Configuration
Mode
All modes
end Quit to privileged mode directly.
help
quit The same as exit command All modes
exit
return to the previous mode.
user mode
All modes
information.
Page 15
mode and return to the previous
Use this command can quit to privileged mode under
mode and return to the previous
Quit the running mode and return to the prev ious m ode.
exit
Grammar Description
exit
Quit the running
mode.
end
Quit to privileged mode directly.
end
Grammar Description
end
any command mode.
Notice: User mode do es not includes this command.
help
Print shell basic help information.
help
Grammar Description
help
print shell basic help information.
quit
Quit the running mode and return to the prev ious command mode.
quit
Grammar Description
quit Quit the running
command mode.
Notice: the co m m and is another name of exit.
2.3 Virtual Terminal Configuration
This section describes the virtual terminal configurati on of XtendLan EOC products.
2.3.1 Command Description
Page 16

Command Description
nal timeout
virtual terminal
virtual terminal
inal timeout period. Minutes
indicates the expired minutes, seconds indicates the
Recover the terminal timeout period to the defult
to telnet. The
exec-timeout Configure the termi
Configuration
Mode
period.
login Configure if a passwor d c heck is
needed when enter to telnet.
exec-timeout
Configure the terminal timeout per iod. When the terminal no str oke time is longger than the confi guratio n
value, console terminal will quit back to user mode automatically, telnet terminal will cut connection
automatically.
exec-timeout minutes seconds
no exec-timeout
Grammar Description
exec-timeout minutes seconds
Configure the term
expired seconds.
configuration mode
configuration mode
no exec-timeout
value. The defult v alue i s 1 m inut es timeout period.
login
Configure if a passwor d check is needed when enter to telnet.
login
no login
Grammar Description
login
no login
2.4 Privileged Mode and Telnet Login Password Configur ati on
This section explains the method of how EOC products enter to privileged mode and Telnet login
Password check is needed when enter
default is need passwor d check.
Password check is not required when enter to telnet.
password configuration.
2.4.1 Command Description
Command Description Configuration
Page 17
Mode
Configure privileged mode
to Telnet.
parameter indicates the configured
parameter indicates the user
Recover the login password to privileged mode to be
thedefault value. The system defult password is
command, the privileged mode password and Telnet
password Configure telnet login password Global mode
enable password
password
enable password-encryption Start encrypted passwor d Global mode
password
Configure the login password when enter to Telnet.
password login_password
no password
Grammar Description
password enable_password
no password
enable passwo rd
Configure the login password when enter
login_password
password.
Cancel Telnet login password.
Global mode
Configure the login password for enable command when enter to privileged mode.
enable password ena ble_password
no enable password
Grammar Description
enable password enable_password Configure the login password to privileged mode.
enable_password
configuredpassword.
no enable password
“admin”.
enable passwo rd-encryption
Star t t he encr ypted password funct ion.
nable password-encryption
no enable password-encryption
Grammar Description
enable password-encryption
Start the encrypted password. After execute the
Page 18

login password will be stored in start script
after
er execute
the command, Telnet password will be deleted, the
privileged mode password will become to the default
Print edition information when
No print of edition information
when the
No print of the prompt information when the
encryption.
no enable password-encryption
2.5 Appli cat i on Program Start-up Prompting Mes sag e
This section introduces the configuration method of the prompting message when XtendLan EOC
products start -up.
2.5.1 Command Description
Command Description
banner motd default
Cancel password encryption function. Aft
value of “admin.”
Configuration
Mode
Global mode
the application is started up.
no banner motd
when the application is started
up.
banner motd
Configure if the print of pr om pt in formation when the application is started up.
banner motd default
no banner motd default
Grammar Description
banner motd default
no banner motd
Print the default prompt information
application is starte d up.
application is starte d up.
Global mode
2.6 St ar t Script Config ur ation and Display
This section explains the con fig ur at i on and display command of script start for XtendLan EOC products.
2.6.1 Command Description
Page 19

configuration to the startup
configuration to the startup
y system configuration to the
startup script file of file system. The startup script file
is saved in a non volatile memory, shell will execute
the commands in the startup script line by line to
onfiguration to the startup
script file of file system. The startup script file is
non volatile memory, shell will execute
the commands in the startup script line by line to
Configuration
Command Description
Mode
write Save the running system
privileged mode
script.
copy running-config st artup-config Save the running system
privileged mode
script.
show running-config Display the running system
privileged mode
configuration.
show startup-config Display startup script file. privileged mode
write
Save the running syste m configuration to the startup script file of file system.
write
Grammar Description
write Save the running
copy running-config sta rtup-config
Save the running system configuration to the startup script file of file system.
copy running-config st artup-config
Grammar Description
copy running-config st artup-config Save the running system c
Notice: this command i s anot her na me o f write.
configure the system automatically.
saved in the
configure the system automatically.
Page 20

show running-config
how the saved script file
content in the non volatile memory. The shown
content is the command which wi ll be executed w he n
Online terminal information
Show the ruuning configur at ion.
show running-config
Grammar Description
show running-config Show the ruuning configur at ion.
Notice: This command can only generate script according the running system configuration, the
configuration only exist in t he system memory, not saved in the startup script file.
show startup-config
show the saved script file cont ent i n t he non volatile memory.
show startup-config
Grammar Description
show startup-config
The command is used to s
the application be start ed up again.
2.7 System Miscellaneous
This section introduces the commands of system reload, debugging, terminal print control, online
terminal information dis pl ay, network tool and so on other funct ion.
2.7.1 Command Description
Configuration
Command Description
Mode
system reload reload system privileged mode
debug Debug command privileged mode
terminal monitor Terminal monitor privileged mode
who
ping Ping tool privileged mode
fast-ping Fast ping tool privileged mode
system reload
privileged mode
show
Page 21

system reload
n the application is started
up, it will execute the last saved startup cript, the
parameter
indicates the function module needs debug, after
information when
This command is only valid for Telnet, it is used to
the virtual
terminal does not have IP address, the address bar
Grammar Description
system reload
debug
Debug command, for t he t echn ique ser vic e man to chec k th e debug in form atio n of the fun ctio n mod ules.
It’s no need for nor ma l users to pay attention to the se commands.
debug function
undebug function
Grammar Description
debug function
Reload the system. Whe
unsaved running configuration information will lost.
Start the debug of a function. Function
execute, it will print on the debug
the module is executing.
undebug function
terminal monitor
Star t t he debug information of the Telnet terminal.
terminal monitor
Grammar Description
terminal monitor
Who
Check the connected terminal information to this device.
Grammar Description
who
Close the debug of a function. function parameter
indicates the function mod ule needs debug.
control the output of some pr int information.
This command is used to show all
terminals information on the device. As Console
ping
shows NULL.
Page 22

ping tool.
r indicates the IP
indicates
parameter indicates
ping ip-address
Grammar Description
ping ip-address
Ping tool, ip-address paramete
address of the target host
fast-ping
fast ping packet t ool. This tool uses 1400 bit s big packet to fast ping the target host.
fast-ping ip-address
fast-ping ip-address packet-number
Grammar Description
fast-ping ip-address
fast ping pack et to ol. ip-address parameter
the IP address of target IP.
fast-ping ip-address packet-number
fast ping packe t to ol. ip-address
the IP address of target IP. spacket-number
parameter indicate s t he ping package.
Page 23

Configure the start operation
automatic power
Head end
Head end
Configure the allocation of
Head end
Head end
Head end
Chapter Three Head En d Conf igur at ion
This chapter describes the head end con figurat ion method o f EOC prod uct. Before enter to the head e nd
configuration mode, please run service stop under to stop station equipment (NC) global mode.
Execute service start command to start the service to make the parameters effective. The Chapter
includes the following configuration command:
Automatic power control c onf iguration.
Head end work mode configuration.
System buffer con f iguration.
Work frequency configur ation.
IGMP-SNOOPING configurat ion.
Min connection establishment parameter configuration.
Modulation density p ar ameter configuration.
Noise gate configuration.
Transmit power configuration.
Notice: As the above stat ed commands are important t o pr oper operation of the equipment, to make
sure the proper operation, user should use the defual configuration by the manufacturer before
understanding the fu nctions.
3.1 Head End Conf i guration Comm and
1. this section elaborates the meanings of the head end parameters and the usage of configuration
command.
3.1.1 Command Description
Configuration
Command Description
Mode
apc-begin-phyrate
point of
configuration mode
authentication Configure the enter control way.
buffer
frequency Configure NC work frequency.
igmp-snooping Configure IGMP-SNOOPING
control.
buffer area in the chip.
configuration mode
configuration mode
configuration mode
Page 24

function switch. con figurati on mode
Head end
Head end
Head end
Head end
Configure forward service
Global configuration
Configure the start operation point PHY rate of
automatic power control. The value range is from 50
int PHY rate of aut omati c
min-link-threshold Configure the lowest enter PHY
rate.
phy-bit-mask Configure modulation density.
phy-margin Configure noise gate.
transmit-power Configure transmit pow er
service
start/stop
apc-begin-phyrate
XtendLan EOC adopts OFDM modulation mode with 256 subcarriers, it can work between
QAM2~QAM128 according to the physical channel condition near each of the subcarriers. When
physical link is in good condition, all the subcarriers are negotiated as QAM128, the PHY rate at the
coaxial cable end can r each to 25 0-270Mbp s at the time. When ther e is inter fering s ignal on a subcarrier ,
configuration mode
configuration mode
configuration mode
configuration mode
mode
the QAM number will reduce, the PHY rate will reduce accordingly. When APC module tested that the
PHY rate is lower than the configuration, it will increase the transmit power to cover the interfere
automatically to keep the per f ect PHY rate.
apc-begin-phyrate <50-270>
no apc-begin-phyrate
Grammar Description
apc-begin-phyrate <50-270>
to 270Mbps. System defaul value is 250Mbps.
no apc-begin-phyrate
authentication
Configure enter control way. When a connect request to NC sent from a CPE, NC will locate the user
Reset the start operat ion po
power control to be the default value.
database according to the globally unique indentity Identifier (UID), and then initially connect according
to the configuration value in the user database. When the parameter of authentication is configured as
on, the CPE in the database to be located are not allowed to enter. When the parameter of
authentication is configured as off, the CPE to be loc at ed in the database are allowed to enter.
authentication <on | off>
Page 25

Grammar Description
control way. The defaul value is off,
to NC by default
Configure the allocation of buffer area in the chip.
he system
Reset the allocation of buffer area in the chip to the
975 | 1000 | 1025 | 1050 | 1075 |
1100 | 1125 | 1150 | 1175 | 1200 | 1225 | 1250 |
1275 | 1300 | 1325 | 1350 | 1375 | 1400 | 1425 |
Configure the work frequency of NC. The default of
authentication <on | off>
Configure enter
allow the unfound CPE to enter
parameter.
buffer
Configure the allocation of buffer area in the chip. Therein, be means service the queue best, af means
ensure forwad service queue, ef means expedited forwardin g ser vice queue.
buffer be <0-37> af <0-37> ef <0-37>
no buffer
Grammar Description
buffer be <0-37> af <0-37> ef <0-37>
The summation should equal to 37. T
default value is be 31 af 6 ef 0.
no buffer
default value.
frequency
Configure the work freque ncy of NC.
frequency <950 | 975 | 1000 | 1025 | 1050 | 1075 | 1100 | 1125 | 1150 | 1175 | 1200 | 1225 | 1250 |
1275 | 1300 | 1325 | 1350 | 1375 | 1400 | 1425 | 1450 | 1475 | 1500>
no frequency
Grammar Description
frequency <950 |
work frequency is 1000Mhz.
1450 | 1475 | 1500>
no frequency
Reset the work frequency of NC to the default value.
igmp-snooping
Start/stop NC IGMP-SNOOPING function. NC will sniff IGMP protocol message when L2 is forwarding,
NC will only forward message to the CPE multicast group. After the function is closed, NC will forward
multicast messages to all the online CPE.
Page 26

igmp-snooping <enable | disable>
SNOOPING function. System
default
to NC.
qam |
ystem default
Reset allowable max NC modulation density to
no igmp-snooping
Grammar Description
igmp-snooping <enable | disable>
no igmp-snooping
min-link-threshold
Configure allowable min PHY rate enter to NC. When the receiving PHY rate of the CPE requesting to
connect to NC is lower than t he m in value, NC will stop the enter o f the C PE.
min-link-threshold <18-200>
no min-link-threshold
Grammar Description
min-link-threshold <18-200>
no min-link-threshold
Start/stop IGMPdefault value is disable.
Reset IGMP-SNOOPING configuration to
value.
Configure allowable min PHY rate enter
System default value is 18Mbps.
Reset allowable min PHY rate enter to NC to system
default value.
phy-bit-mask
Configure max NC modulation density. The configuration limits the max modulation density of OFDM
subcarriers.
phy-bit-mask <0-qam | 2-qam | 4-qam | 8-qam | 16-qam | 32-qam | 64-qam | 128-qam>
no phy-bit-mask
Grammar Description
phy-bit-mask <0-qam | 2-qam | 4-qam | 8-
16-qam | 32-qam | 64-qam | 128-qam>
no phy-bit-mask
phy-margin
Configure NC noise gate. The value is used to control the quantification of QAM data.
Configure max NC modulation density.
value is 128-qam.
system default value.
phy-margin <-6 | -5 | -4 | -3 | -2 | -1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6>
no phy-margin
Page 27

Grammar Description
1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4
5dB, the
10
25
Configure NC transmit power, the system default
Start/Stop NC to forward message. System default
phy-margin <-6 | -5 | -4 | -3 | -2 | -
Configure NC noise gate. The unit is 0.
system default value is 2 (1dB).
| 5 | 6>
no phy-margin
Reset NC noise gate to system d ef ault value.
transmit-power
Configure transmit power bet ween NC and CPE when commu ni ca t e.
transmit-power <0dbm | -3 dbm | -7 db m | -10 db m | -13 dbm | -16 db m | -19 dbm | -22 dbm | -25 dbm
| -28 dbm | -31 dbm >
no transmit-power
Grammar Description
transmit-power <0dbm | -3 dbm | -7 dbm | -
value is 0dbm.
dbm | -13 dbm | -16 dbm | -19 dbm | -22 dbm | dbm | -28 dbm | -31 dbm >
no transmit-power
service
Star t/Stop NC to forward message.
service <start | stop>
Grammar Description
service <start | stop>
Reset NC transmit power t o system default value.
value is forward.
Page 28

User database
service upward
User database
User database
Configure af upward traffic
User database
User database
Configure ef service upward
User database
User database
User database
CPE port parameter
User database
Chapter Four User Database Configuration
This chapter describes the configure method of XtendLan EOC products user database. This section
includes the following conf igure commands:
User CPE globally unique identifier.
User traffic policin g.
User comment informati on.
Work frequency configur ation.
User enter denied configu r at ion.
User CPE port parameter configurat ion.
4.1 User datab ase configuration comma nd
XtendLan terminal device includes 31 databases, when the uid property configuration of each entry is
not 00:00:00:00:00:00, the entry is effective.
4.1.1 Command Description
Command Description
uid Configure user CPE GUID.
be-service-upstream Configure be
traffic policing.
be-service-downstream Configure be service downward
traffic policing.
af-service-upstream
policing.
af-service-downstream Configure af service downward
traffic policing.
ef-service-upstream
traffic policing.
ef-service-downstream Configure ef service downward
Configuration
Mode
configuration mode
configuration mode
configuration mode
configuration mode
configuration mode
configuration mode
User database
remark Configure comment information.
shutdown User enter delied.
cpe-port
traffic policing.
configuration.
configuration mode
configuration mode
configuration mode
configuration mode
Page 29

uid
Configure the CPE UID of a user, system default is
Configure the upstream limit of be service, system
Configure the CPE GUID of a user, the number can be checked on the bottom side of Xtendlan CPE
equipment.
uid <user_id>
no uid
Grammar Description
uid <user_id>
00:00:00:00:00:00, show ing no uid is configured.
no uid
Cancel the UID of the user.
service-stream
Configure the upward and downward stream parameter of be, af and ef services. The corresponding
802.1p priority value is 0-3 of be serv ice, the co rre sp onding 8 02.1p prior ity v alue is 4-5 of af service, and
the corresponding 802.1p priority value is 6-7 of ef service, among XtendLan EOC products. Normally,
the ef is corresponding to interactive service, af is corresponding to video traffic, be is corresponding to
normal network service. C ir p ara meter is used t o configure stream committed rate, pir parameter is used
to configure stream peak rate. The following comma nds are for t he stream policing of the three serv ices.
be-service-upstream cir <0-100> pir <0-100>
be-service-downstream cir <0-100> pir <0-100>
af-service-upstream cir <0-64> pir <0-64>
af-service-downstream cir <0-64> pir <0-64>
ef-service-upstream cir <0-10> pir <0-10>
ef-service-downstream cir <0-10> pir <0-10>
no be-service-upstream
no be-service-downstream
no af-service-upstream
no af-service-downstream
no ef-service-upstream
no ef-service-downstream
Grammar Description
be-service-upstream cir <0-100> pir <0-100>
default is 100Mbps.
Page 30

be-service-downstream cir <0-100> pir <0-100> Configure the downstre
am limit of be service, system
Configure the upstream limit of af service, system
stem
Configure the upstream limit of ef service, system
Configure the downstream limit of af service, system
information, system default is empty
default is 100Mbps.
af-service-upstream cir <0-64> pir <0-64>
default is 0Mbps.
af-service-downstream cir <0-64> pir <0-64> Configure the downstream limit of af service, sy
default is 0Mbps.
ef-service-upstream cir <0-10> pir <0-10>
default is 0Mbps.
ef-service-downstream cir <0-10> pir <0-10>
default is 0Mbps.
no be-service-upstream Reset upstream limit of b e service to default.
no be-service-downstream Reset downstream limit of be ser vice to default.
no af-service-upstream Reset upstream limit of a f se r vice to default.
no af-service-downstream Reset downstream limit of af service to default.
no ef-service-upstream
Reset upstream limit of e f se r vice to default.
no ef-service-downstream Reset downstream limit of ef service to default.
Note: only pir value is effective of current XtendLan EOC product, the configured cir value is
not effective. To reserve ci r par ameter i s to make the com mand c omp atibl e with the c hip set in the
future.
remark
Configure user comment i nformation.
remark <remark_string>
no remark
Grammar Description
remark <remark_string>
user comment
string.
no remark
shutdown
Configure user status as enter barred.
shutdown
no shutdown
Delete user comment in fo r mation.
Page 31
Grammar Description
barred. System default
|
Configure the VLAN number, port mode, port priority
and port storm control parameter of user CPE port.
System default VLAN is 0, 0 indicats the
user CPE works at hub
shutdown
enter
enter barred.
no shutdown
Reset user status to de fa ult.
cpe-port
Configure the CPE port attribute of a user. When the CPE user get online, the IP address of NC
management interface is cor rectly conf igured, and th e configur ation of port 1 and 2 of CPE are co mplete d,
NC will transmit port configuration information to user CPE, and configure the two ports of user CPE as
specified value.
cpe-port <1-2> enter-vlan <vlan_id> <enter | trunk> dot1p < 0-7> storm-control <on | off>
no cpe-port
Grammar Description
cpe-port <1-2> enter-vlan <vlan_id> <enter
trunk> dot1p <0-7> storm-control <on | off>
no cpe-port
configuration is not effective,
mode.
Reset user CPE port attribute to default.
Chapter Five SNMP Parameter Configuration
This chapter describes the configuration method of XtendLan EOC product SNMP server parameter.
This chapter contain the following configuration c ommand:
Configure community name.
Page 32

Star tup SNM P server.
User database
Configure the upstream control
User database
5.1 User Database Confi guratio n Comm and
XtendLan station device is embeded with SNMP server, user can use XtendLan network management
system or the third network ma nagement equipment to configure and manage remotely the dev ices.
5.1.1 Command Description
Configuration
Command Description
Mode
snmp community Configure user CPE globa l UID
configuration mode
snmp server
snmp communi t y
Configure community name.
snmp community <community_name>
Grammar Description
snmp community <community_name>
snmp server
Star t or st op SNMP server.
Grammar Description
snmp server <start | st op>
of be service
configuration mode
Configure community name.
Star t or st op SNMP server. System defau lt is st op.
This chapter describes the configuration method of commonly used function for EOC products. The
section includes the following configuration examples:
Configure NC to control u ser enter.
Configure SNMP server.
Configure the VLAN of us er CP E por t .
6.1 Use user enter control function
XtendLan station device can work under the work mode of “authentication” or “non-authentication”. The
Chapter Six Configuration Example
Page 33

difference between the two work modes is that if the CPE cannot be found UID is allowed to enter, under
the work mode of authentication, the CPE is not allowed to enter, while the CPE is allowed to enter by
system default parameter under the work mode o f n on-authentication.
6.1.1 Configuration Examples
Example: the user with the UID of 00:23:1f:10:16:ad is al low ed to enter to a NC.
GD.LINK# config terminal /*enter global configuration mode*/
GD.LINK(config)# service st op /*stop NC*/
GD.LINK(config)# head end /*enter headend configuration mode*/
GD.LINK(config-headend)# authentication on /*configure NC work under authent ication mode*/
GD.LINK(config-headend)# exit /*return to global configur at ion mode*/
GD.LINK(config)# service st ar t /*start NC*/
GD.LINK(config)# user 1 /*use user database item 1 and binding UID*/
GD.LINK(config-user<01>)# uid 00:23:1f:10:16:ad /*configure the UID attribute of the item*/
GD.LINK(config-user<01>)#end /*return to privileged mod e* /
GD.LINK#write /*save configuration to start script* /
6.2 Start-up SNMP Server
Gungda station device is embeded with SNMP server, user can use XtendLan network management
system or the third network management system to configure and manage the equipments remotely.
Before using the function, user should configure the SNMP server parameter and start SNMP service on
the station device first.
6.2.1 Configuration Examples
Example: start SNMP server on a NC so as to adopt network software man agement.
GD.LINK# config terminal /*enter global configuration mode*/
GD.LINK(config)# interfac e manage-interface /*enter interface configurat ion mode*/
GD.LINK(config-if)# ip-address 10.10.10.1/ 24 /*configure IP address*/
GD.LINK(config-if)# vlan 10 /*manage interface enter to VLAN10*/
GD.LINK(config-if)# exit /*return t o global configuration mode*/
GD.LINK(config)# sn mp c om m unity test /*configure SNMP communit y name as test*/
GD.LINK(config)# sn mp s er ver start /*start SNMP server*/
Page 34

GD.LINK(config-user<01>)#end /*return to privileged mode*/
GD.LINK#write /*save configuration to start script*/
6.3 Remote Conf iguration for the VLAN of User CPE Por t
XtendLan EOC support remote (by network management software, Console port, Telnet) and user
terminal (by CPE configure port) to configure CPE port attribute. Here we introduce remote configuration
method. The configured CPE port attributes are saved in the user database, NC will transmit the port
parameter to the user CPE when get online, CPE will compare the received the parameter with the
configured data, if there is any difference, CPE will update the local configuration and restart to make
effective.
When use remote configuration function, the followi ng co nditions are indispensable:
The IP address of man agement interface are correctly configured.
cpe-port 1、cpe-port 2 are correct ly configured in the user dat abase.
NC will transmit the config ure infor mation by management interfa ce when th e above conditi ons are read y.
6.3.1 Configuration Examples
Example: the user with the UID of 00:23:1f:10:16:ad is allowed to enter to a NC, and configure VLAN of
port 1 as 10, VLAN of port 2 as 20.
GD.LINK# config terminal /*enter global configuration mode*/
GD.LINK(config)# service st op /*stop NC*/
GD.LINK(config)# head end /*enter headend configuration mode */
GD.LINK(config-headend)# authentication on /*configure NC under privileged mo de* /
GD.LINK(config-headend)# exit /*return to global configur at ion mode*/
GD.LINK(config)# service st ar t /*start NC*/
GD.LINK(config)# user 1 /*user user databas e it em 1 and binding UID*/
GD.LINK(config-user<01>)# uid 00:23:1f:10:16:ad /*configure the UID attribute of the item*/
GD.LINK(config-user<01>)#cpe-port 1 enter-vlan 10 enter dot1p 0 storm-control on
/*enter port 1 to vlan 10, port is under enter mode, port priority is 0, st or m control on*/
GD.LINK(config-user<01>)# cpe-port 2 enter-vlan 20 enter dot1p 0 storm-control on
/*enter port 2 to vlan 20, port is under enter mode, port priority is 0, st or m control on*/
GD.LINK(config-user<01>)#end /*return to privileged mode* /
GD.LINK#write /*save configuration to start script* /
Page 35

 Loading...
Loading...