Page 1

MULTI-WAN GATEWAY
Model X16-R
User’s Guide
Page 2

ii
Page 3

TABLE OF CONTENTS
1: INTRODUCTION ..............................................................................................................................1
Internet Features ..........................................................................................................................1
Other Features..............................................................................................................................3
Package Contents ........................................................................................................................5
Physical Details ............................................................................................................................5
2: BASIC SETUP..................................................................................................................................9
Overview........................................................................................................................................9
Procedure......................................................................................................................................9
LAN & DHCP……………………………………………………………………………………………..11
MAX WAN....................................................................................................................................14
Primary Setup .............................................................................................................................15
3: ADVANCED PORT ........................................................................................................................21
Overview......................................................................................................................................21
Port Options................................................................................................................................21
Load Balance ..............................................................................................................................22
Advanced PPPoE........................................................................................................................24
Advanced PPTP..........................................................................................................................25
4: ADVANCED SETUP.......................................................................................................................28
Overview......................................................................................................................................28
Host IP…………………………………………………………………………………………………….28
Routing …….………………………………………………………………………………………….….30
Virtual Server ..............................................................................................................................34
Special Application ....................................................................................................................37
Dynamic DNS..............................................................................................................................39
Multi DMZ ....................................................................................................................................41
UPnP Setup ................................................................................................................................42
NAT Setup ...................................................................................................................................43
Advanced Feature ......................................................................................................................45
5: SECURITY MANAGEMENT ………………………………………………………… …………………..48
Block URL ...................................................................................................................................48
Access Filter ...............................................................................................................................49
Session Limit ..............................................................................................................................52
SysFilter Exception……………………………………………………………………………….…… 53
6: QOS CONFIGURATION ………………………………………………………………………………….54
Overview ………………………………………………………………………………………………...54
QoS Setup ...................................................................................................................................54
Policy Configuration…...............................................................................................................55
7: MANAGEMENT ASSISTANT ........................................................................................................56
Overview......................................................................................................................................56
Admin. Setup ..............................................................................................................................56
Email Alert...................................................................................................................................58
SNMP ...........................................................................................................................................60
Syslog..........................................................................................................................................61
Upgrade Firmware......................................................................................................................64
i
Page 4

8: METWORK INFO ...........................................................................................................................65
Operation.....................................................................................................................................65
System Status.............................................................................................................................65
WAN Status.................................................................................................................................68
APPENDIX A SPECIFICATIONS.......................................................................................................69
APPENDIX B WINDOWS TCP/IP SETUP .........................................................................................70
Overview......................................................................................................................................70
TCP/IP Settings...........................................................................................................................70
APPENDIX C TROUBLESHOOTING.................................................................................................77
Overview......................................................................................................................................77
General Problems.......................................................................................................................77
Internet Access...........................................................................................................................78
Copyright ©2006 XiNCOM, LLC. All Rights Reserved.
All trademarks and trade names are the properties of their respective owners.
ii
Page 5
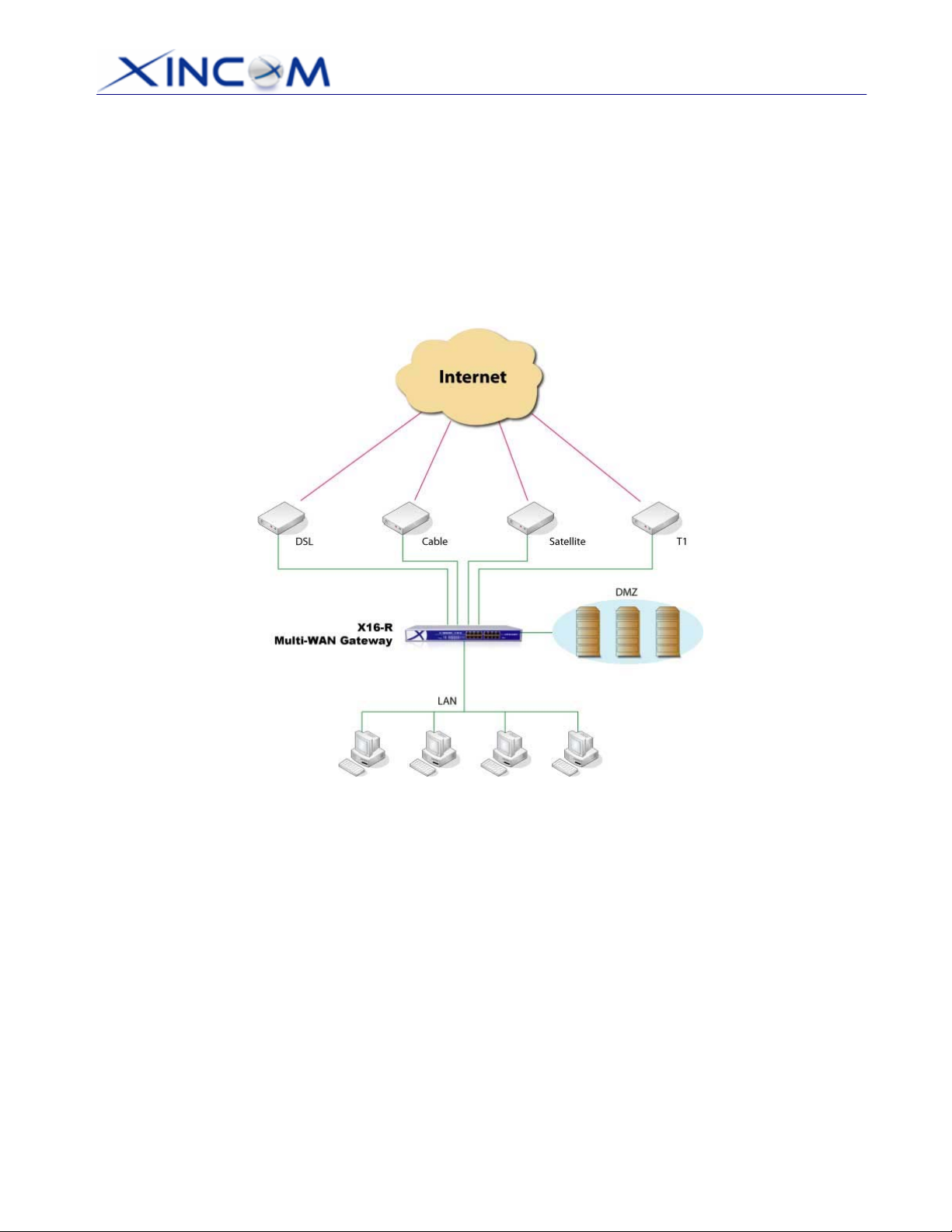
1: Introduction
Congratulations on the purchase of your new MULTI-WAN GATEWAY. The MULTI-WAN
GATEWAY not only provides a selection of 2~8 WAN ports – it also provides
Internet Access
for all LAN users.
Shared Broadband
Figure 1-1: MULTI-WAN GATEWAY
Internet Features
• Flexible use of WAN ports
There are up to 8 WAN ports available for use on the MULTI-WAN GATEWAY. The user can
decide how many WAN ports to use by changing settings in the web page setup area. (The
default setting is 2 WAN ports). This gives increased flexibility for Internet bandwidth access. If all
8 WAN ports are not used, the remaining WAN ports will be available as LAN Ports, but by
default, at least 2 of the ports will be used as WAN ports.
Page 1
Page 6

• Shared Broadband Internet Access
All LAN users can access the Internet through the MULTI-WAN GATEWAY by sharing from one
(1) up to eight (8) Broadband modems and connections.
High-Performance multi ADSL Modem Support
•
The MULTI-WAN GATEWAY has eight (8) WAN ports, allowing the connection of up to eight (8)
Broadband modems at the same time.
This can provide a greater increase in bandwidth than is allowed by a single modem.
This flexible configuration allows each port to use a different type of modem and connection
method. Also, the Internet traffic that is shared between the 8 modems can be pre-determined.
•
Support for all common Connection Methods
All popular DSL, Cable Modems and connection methods are supported. These include - Fixed
IP, Dynamic IP, PPPoE and PPTP.
Load Balancing and Failover
•
There are a variety of load balancing methods that allow administrators to manage the traffic from
LAN or WAN in order to maximize bandwidth - as well as smart health check methods to protect
against connection failure for failover.
PPPoE Session Management
•
Multiple PPPoE sessions are supported and you can choose “mapping” sessions to selected PCs
if desired.
• Multiple IP Address Support
If your ISP allocates you multiple IP addresses, these are also supported and you can “map” IP
addresses to selected PCs if desired.
• Special Application
This feature allows you to use some non-standard applications; for example, where the port
number used for the response is different to the port number used by the sender.
• Virtual Server
This feature allows Internet users to access Internet servers on your LAN. For standard servers
such as Web, FTP or E-Mail servers, only the IP address of the server PC is required. You can
also define your own Server types if required.
• Multiple DMZ
A "DMZ" PC will receive incoming connection requests which would otherwise be blocked. For
each IP address allocated by your ISP, a separate "DMZ" PC can be specified. So if your ISP has
given you multiple IP addresses, you can have multiple “DMZ” PCs. With the MULTI-WAN
GATEWAY, each “DMZ” PC has unrestricted 2-way Internet access, providing the ability to run
programs that are otherwise normally incompatible with NAT routers.
• Access Filter
The network Administrator can use the Access Filter to gain fine control over the Internet access
and applications available to LAN users. Five (5) user groups are available and each group can
be assigned unique access rights.
Page 2
Page 7

• Block URL
This feature can be used by the Administrator to block access to undesirable Web sites by LAN
users. You can even assign different settings for different groups of PCs.
• Session Limit
With the Session Limit feature, if the number of new sessions for the system exceeds the
maximum allowance set by the Administrator in the sampling time, any new session in the system
will be dropped.
• System Filter Exception
This feature ensures that every packet with an unrecognized port will be rejected so as to prevent
access to port scanning programs from hackers. However, in some situations this may incur
problems with some servers (e.g. SMTP server port 113) or WAN clients which require a
response packet to verify the availability of their communication peers.
Other Features
• 16-Port Switching Hub
The MULTI-WAN GATEWAY incorporates a 16-port 10 /100BaseT switching hub, making it easy
to create or extend your LAN as needed.
• DHCP Server Support
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol provides a dynamic IP address to PCs and other devices
upon request. The MULTI-WAN GATEWAY can act as a DHCP Server for devices on your local
LAN.
• Multi Segment LAN Support
LANs comprising of one or more segments or additional IPs are supported via the MULTI-WAN
GATEWAY's built-in static routing table.
• Easy Setup
Setup and configuration is easily accomplished through your favorite WEB browser.
• Remote Management
The MULTI-WAN GATEWAY can be managed from any PC on your LAN. Also, if an Internet
connection exists, it can (optionally) be configured via the Internet.
• Password - protected Configuration
Optional password protection is provided to prevent unauthorized users from modifying the
configuration data and settings.
Page 3
Page 8

• HTTP Firmware Upgrade and backup
The web management feature allows you to use HTTP upgrade for new firmware and backup
system configuration from a local or even remote site, as long as “Remote upgrade” and “Remote
web-based setup” is enabled in the Advanced feature web page.
• Email Alert
The Email Alert will send a warning email message to the system administrator if any of the WAN
ports become disconnected when more than two WAN ports are enabled or if there is excessive
ping notification.
• Syslog
This is a very useful feature for monitoring the device in that it can generate real time system
information on the web page or on a particular machine.
• QoS Configuration.
This function will allow higher priority pass-through for specified packets such as real-time
applications like Internet phone, video conference, etc.
• UPnP
When UPnP (Universal Plug & Play), is set to “Enable” - the MULTI-WAN GATEWAY becomes a
network device. This feature is useful for detecting and controlling network devices such as
Internet gateways.
Page 4
Page 9
Package Contents
The following items are included in the MULTI-WAN GATEWAY package:
• MULTI-WAN GATEWAY Unit
• Power Cord
• Quick Installation Guide
• CD-ROM containing the on-line manual.
If any of the above items are damaged or missing, please contact your dealer immediately.
Physical Details
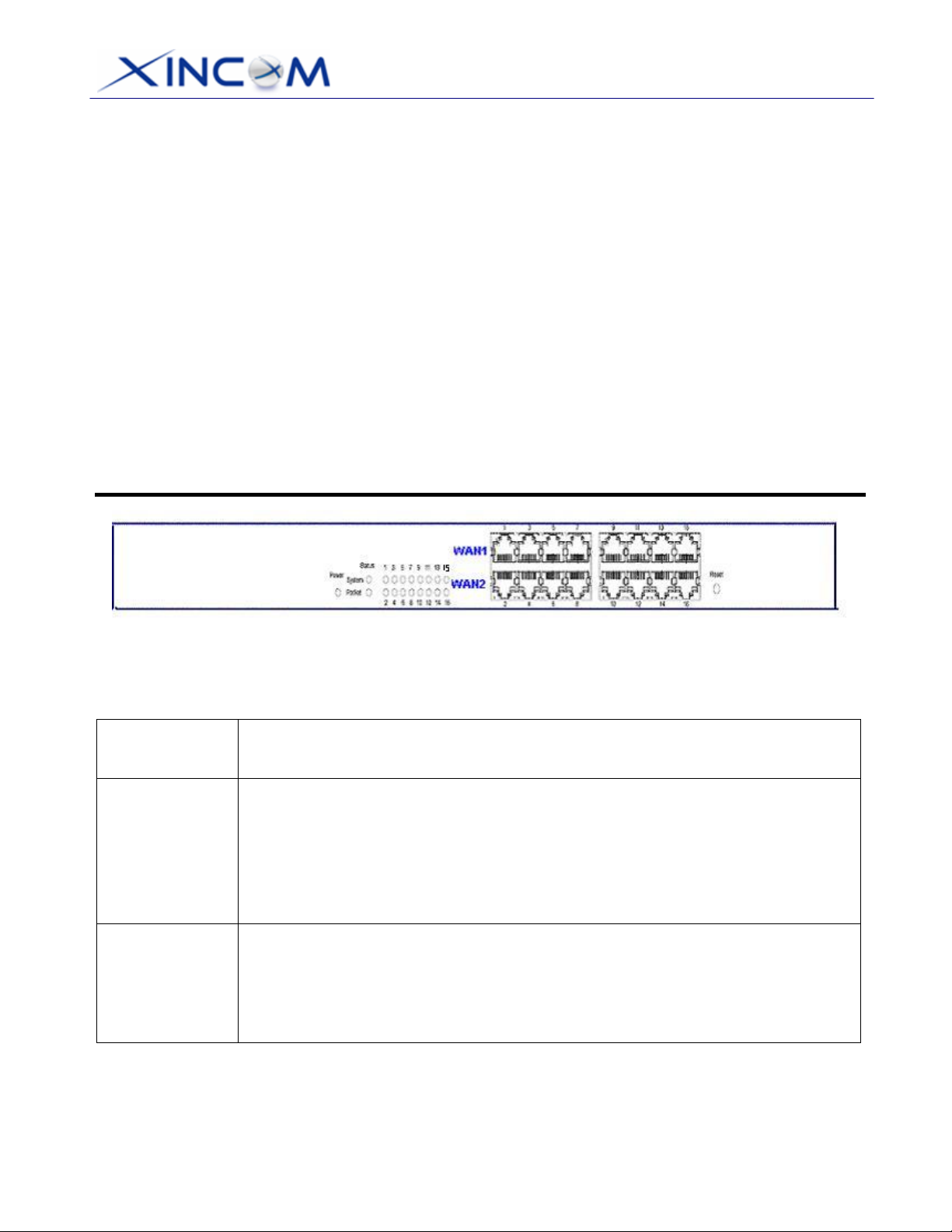
Front Panel
Figure 1-2: Front Panel
Front Panel LED indication is as follows:
Power
Status
System
Packets
Ethernet
OFF – No Power
ON – Normal Operation
Blinking – Normal Operation.
ON/OFF – Error
Blinking – Packets Active
ON/OFF – No Packet
Green ON – 100M Linked
Yellow ON – 10M Linked
Blinking – Data Transmit / Receive.
OFF – No Linked
Page 5
Page 10
Ethernet Ports and Reset Button
Ethernet Ports
WAN ports: 2 to 8 WAN ports (default is 2), using Port 1 to Port 8 for connecting
to Modem(s).
LAN ports: The remaining ports which are connected to PCs or a Hub.
Note:
Any port will automatically operate as an “Uplink” port if required. You can use a
normal LAN cable to connect to a normal port on another hub.
Reset Button
When pressed and released, the MULTI-WAN GATEWAY will reboot (restart)
within 1 second. It will reset to default when pushed and held for more than 3
seconds.
Some Status and Error conditions are indicated by the combinations of
LEDs, as shown below:
LED Action Condition
Status – System & Packets flash alternatively. Firmware Download in progress.
Status – System & Packets flash concurrently. MAC address not assigned.
Status – System (Solid Off) & Packets (Solid On) SDRAM error
Status – System (Solid On) & Packets (Solid On) Timer/Interrupt error
Page 6
Page 11
Rear Panel
Figure 1-3: Rear Panel
AC 100V ~ 240V
Connects to AC100~240V / 50~60Hz with supplied AC power cord.
Default Settings
When the MULTI-WAN GATEWAY has finished booting, all configuration settings will be set to the
factory defaults, including:
• IP Address set to its default value of 192.168.1.1, with a Network Mask of 255.255.255.0
• DHCP Server is enabled
• User Name: admin
• Password cleared (no password)
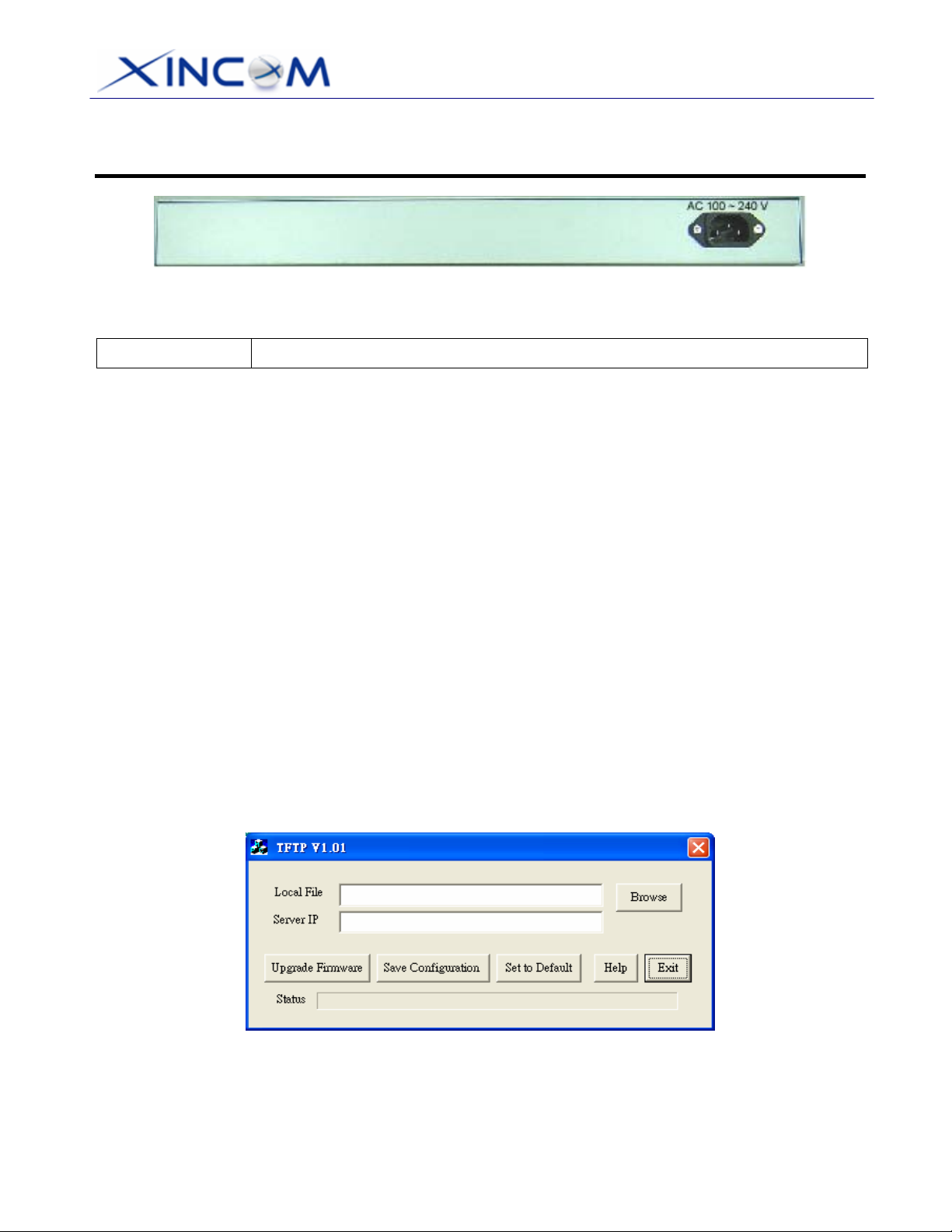
TFTP Download
This setting should be used only if your MULTI-WAN GATEWAY becomes unusable and you are
attempting to restore it by upgrading the firmware. Follow this procedure:
1. Power-On the MULTI-WAN GATEWAY.
2. Use the supplied Windows utility or a TFTP client program to apply the new firmware. If using the
supplied Windows TFTP program, the screen will look like the following example:
Figure 1-4: Windows TFTP utility
Page 7
Page 12

• Enter the name of the firmware upgrade file located on your PC, or click the "Browse" button
to locate the file.
• Enter the LAN IP address of the MULTI-WAN GATEWAY in the "Server IP" field.
• Click "Upgrade Firmware" to send the file to the MULTI-WAN GATEWAY.
3. When the upgrade is finished, the MULTI-WAN GATEWAY should work normally. The factory
default settings will be applied.
Note:
The supplied Windows TFTP utility also allows you to perform three (3) additional operations:
• Save the current configuration settings to your PC (use the "Save Configuration" button).
• Restore a previously saved configuration file to the MULTI-WAN GATEWAY (use the "Upgrade
Firmware" button).
• Set the MULTI-WAN GATEWAY to its default values (use the "Set to Default" button).
Page 8
Page 13

2: Basic Setup
Overview
Basic Setup of your MULTI-WAN GATEWAY involves the following steps:
1. Attach the MULTI-WAN GATEWAY to a PC using any LAN port (3 to16) and configure it for your
LAN.
2. Install your MULTI-WAN GATEWAY in your LAN and connect the Broadband Modem(s).
3. Configure your MULTI-WAN GATEWAY for Internet Access.
4. Configure PCs on your LAN to use the MULTI-WAN GATEWAY.
Requirements
• One (1) up to eight (8) DSL or Cable modems, each with an ISP Internet Access account.
• Network cables. Use standard 10/100BaseT network (UTP) cables with RJ45 connectors
• TCP/IP network protocol must be installed on all PCs.
Procedure
1: Configuring the MULTI-WAN GATEWAY for your LAN
1. Use a standard LAN cable to connect your PC to any LAN port (3 -16) on the MULTI-WAN
GATEWAY. (Default is 2 WAN ports from Port 1 – 2)
2. Connect the power cord into the power outlet on the rear panel of the MULTI-WAN GATEWAY.
3. Power-on your PC. If your PC is already running, restart it. It will then obtain an IP address from
the MULTI-WAN GATEWAY.
4. Open your WEB browser.
5. In the Address or Location box enter:
HTTP://192.168.1.1
6. You will be prompted for the User Name and password, as shown below:
Figure 2-1: Password Dialog
Page 9
Page 14
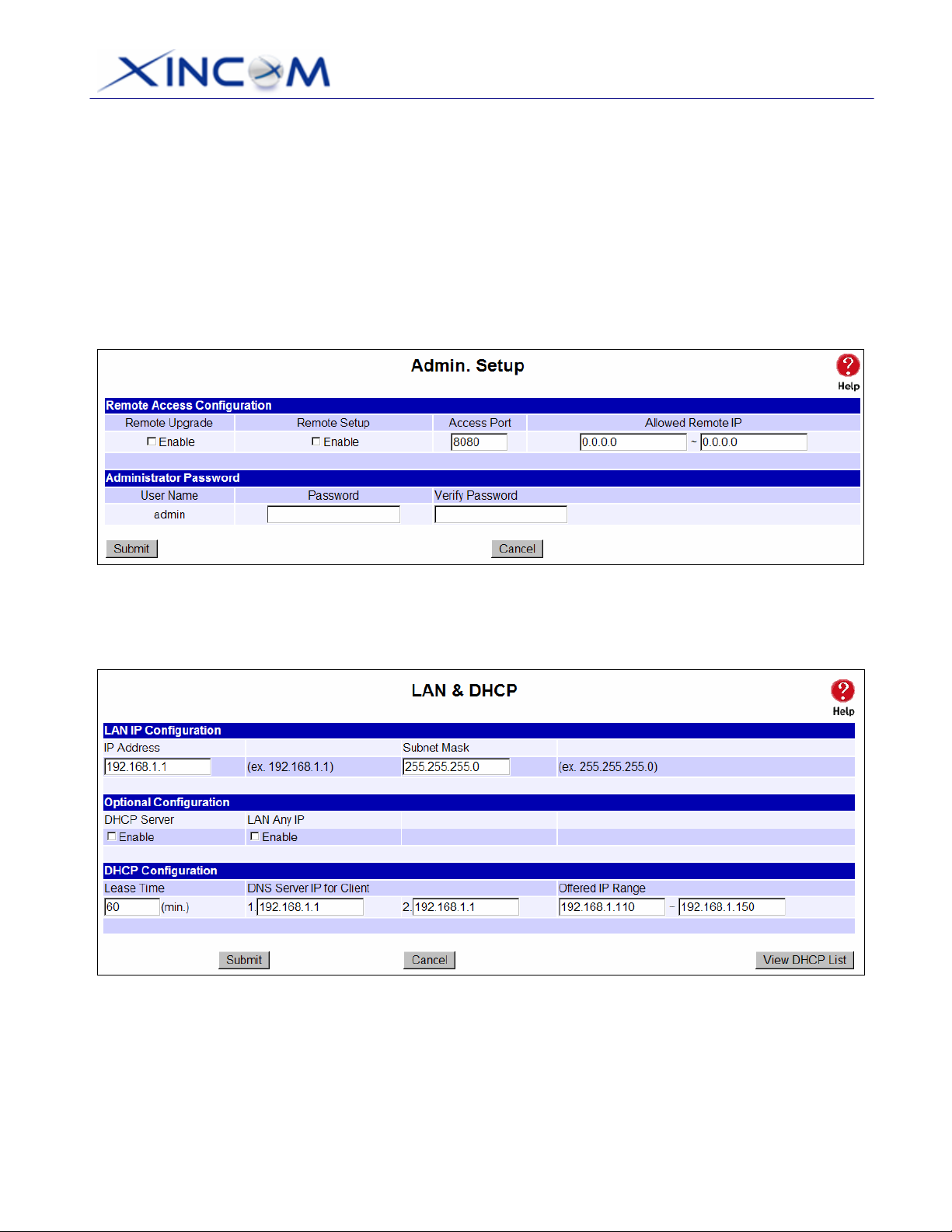
7. Enter admin for the "User Name" and leave the "Password" field blank.
• The "User Name" is always set as admin
• For security, it is highly recommended that you set a password. You may do this using the
Admin Setup screen.
8. After logging in, you will see the Administrator Password setup in the Admin Setup screen, as
shown below.
Assign a password by entering it in the "Password" and "Verify Password” Fields.
Figure 2-2: Home Screen (Admin. Setup)
9. Select LAN & DHCP from the menu. You will see a screen like in the example below.
Figure 2-3: LAN & DHCP Setup
Page 10
Page 15

10. If your LAN already has a DHCP Server and you wish to continue using it, the following
configuration is required:
• The DHCP Server function in the MULTI-WAN GATEWAY must be disabled. You will find
this setting in the LAN & DHCP screen.
• Your DHCP Server must be configured to provide the MULTI-WAN GATEWAY's LAN IP
Address as the "Default Gateway".
• Your DHCP Server must provide correct DNS addresses to any connected PCs.
11. Ensure these settings are suitable for your LAN:
• See the following table for details of each setting. For most situations, the default settings will
be suitable.
Page 11
Page 16
Settings – LAN & DHCP
LAN IP Configuration
Optional
Configuration
DHCP Configuration
• IP Address – IP address for the MULTI-WAN GATEWAY, as seen
from the Local LAN. Use the default value unless the address is
already in use or your LAN is using a different IP Address range.
• Subnet Mask –The default value 255.255.255.0 is standard for small
(class "C") networks. For other networks, use the Subnet Mask for
the LAN segment to which the MULTI-WAN GATEWAY is attached.
(The same value as the PCs on that LAN segment.)
• DHCP Server Setup – If set to “Enable”, the MULTI-WAN
GATEWAY will assign IP Addresses to the PCs (DHCP clients) on
your LAN when they start up. The default and recommended value is
"Enable". (Windows systems, by default, act as DHCP clients. This
setting in the Windows Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties is:
Obtain an IP address automatically.)
• LAN Any IP – By default this option is disabled. If you enable “LAN
Any IP”, then no matter what, the static IP address is held on the
client (your PC). The client does not need to change the IP address,
even though it has a different IP segment than the LAN segment. It
can still access the Internet through NAT.
• Lease Time – This is a finite period of time for a DHCP server to
lease an IP address to a client.
• DNS Server IP for Client – An IP address of the default DNS server
for the client requesting DNS service.
View DHCP List
• Offered IP Range – The fields set the values used by the DHCP
server when allocating IP addresses to DHCP clients. This range
also determines the number of DHCP clients supported.
This table shows the IP addresses which have been allocated by the
DHCP Server. For each address which has been allocated, the following
information is shown:
• Free Entry – Indicates how many IP addresses the DHCP server can
allocate to DHCP clients.
• Name – The "hostname" of the PC. In some cases, this may not be
known.
• MAC Address – The physical address (network adapter address) of
the PC.
• IP Address – The IP address that is allocated to this PC.
• Type – Indicates whether the IP address is to be dynamic or static.
• Status – If Dynamic, the IP address was allocated by this DHCP
Server. If Sniffed, the IP address was detected by examining the LAN
rather than allocated by the DHCP Server. In this case, the Name is
usually not known.
• Time Left – The time expired since the IP address was leased.
Page 12
Page 17

12. Save your data, then go to Step 2, Installing the MULTI-WAN GATEWAY in your LAN.
Page 13
Page 18
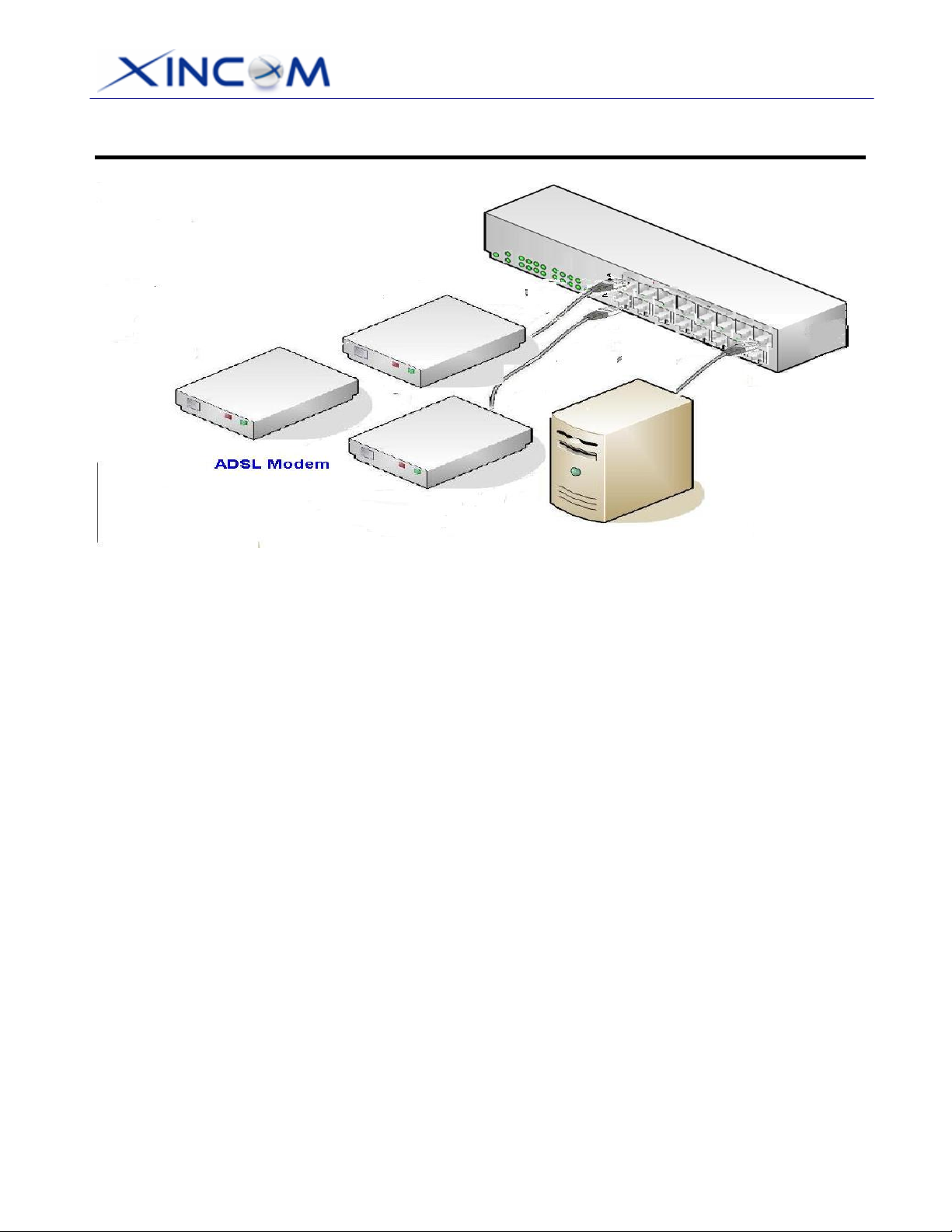
2. Installing the MULTI-WAN GATEWAY in your LAN
Figure 2-4: Installation Diagram
1. Ensure that the MULTI-WAN GATEWAY and any DSL/Cable modem(s) are powered-OFF.
Leave the modem or modems connected to their data lines.
2. Connect the Broadband modem(s) to the MULTI-WAN GATEWAY.
• If using only one (1) Broadband modem, connect it to port 1.
• Use the cable supplied with your DSL/Cable modem. If no cable was supplied, use a standard
cable.
3. Use standard LAN cables to connect PCs to the LAN ports on the MULTI-WAN GATEWAY.
• Both 10BaseT and 100BaseT connections can be used simultaneously.
• If you need to connect the MULTI-WAN GATEWAY to another Hub, just use a standard LAN
cable to connect any LAN port on the MULTI-WAN GATEWAY to a standard port on another
hub. Any LAN port on the MULTI-WAN GATEWAY will automatically act as an "Uplink" port
when required.
• If devices are connected to the 2 WAN ports (1 and 2), the remaining ports (3 to 16), are LAN
ports.
4. Power-Up
• Power-on the Cable or DSL modem(s).
• Connect the supplied power cord to the MULTI-WAN GATEWAY and power-up.
5. Check the LEDs
• The Power LED should be ON.
Page 14
Page 19
• The Link/ACT LED should be ON if the corresponding WAN port is connected to a
broadband modem.
• For each PC connected to the LAN ports, the corresponding LAN LED (either 10/Yellow or
100/Green) should be ON.
3. Configuring the MULTI-WAN GATEWAY for Internet Access
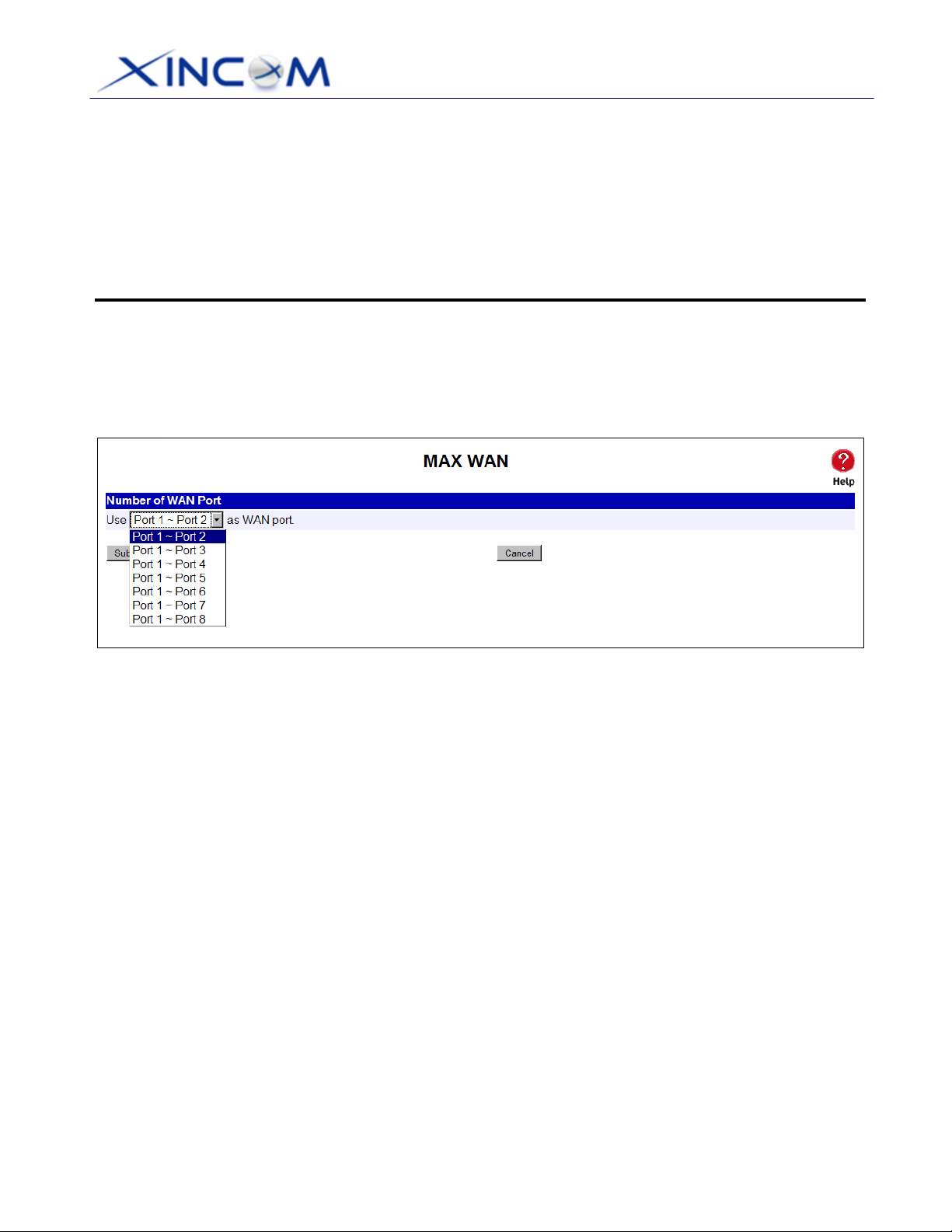
To configure access to the Internet, first decide how many WAN ports you are going to use. The
pull down menu on the MAX WAN web page (Figure 2-5) will let you setup the WAN port numbers.
You can choose from two (2), up to eight (8) WAN ports. Once you have selected how many ports
you are going to use, click on Submit. You may then proceed to the Primary Setup page.
Figure 2-5: MAX WAN
Select Primary Setup from the menu. You will see a screen like in the example below.
• Configure each WAN one by one through the Interface column pull-down menu.
• For any of the following situations, refer to Chapter 3: Advanced Port Setup, for any further
configuration which may be required:
• Using multiple WAN ports
• Enabling multiple IP addresses on each WAN port
• Enabling multiple PPPoE sessions
• PPTP connection method
Page 15
Page 20
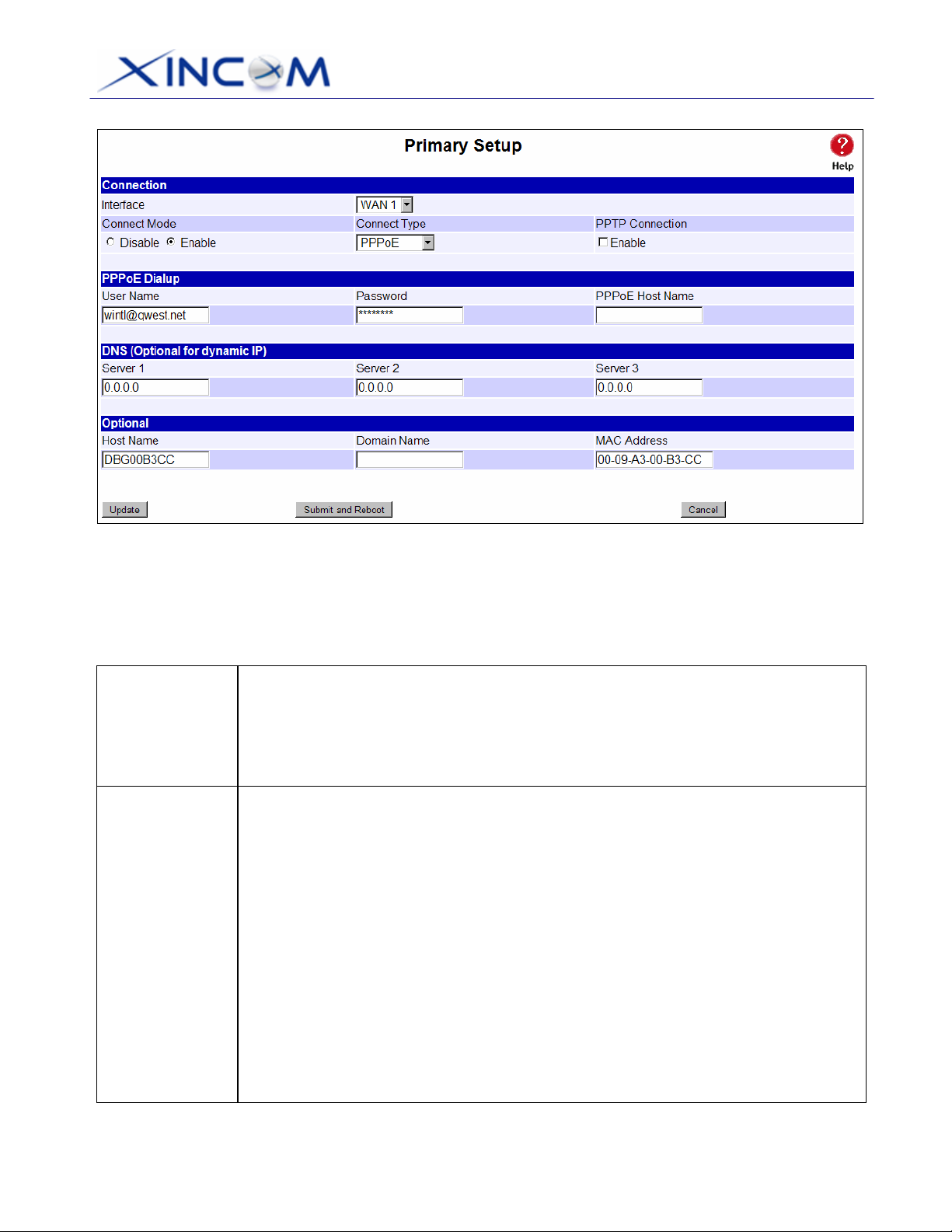
Figure 2-6: Primary Setup
Settings – Primary Setup
Connection
Mode
Connection
Type
• Interface – A pull down menu for each WAN port that you are going to
connect to the Internet.
• Connect Mode – Enable – Select this if you have connected a broadband
modem to this port. Disable – Select this if there is no broadband modem
connected to this port.
Check the data supplied by your ISP and select the appropriate option.
• Static IP – Select this if your ISP has provided a Fixed or Static IP address.
Enter the data into the Address Info fields.
• Dynamic IP – Select this if your ISP provides an IP address automatically
when you connect. You can ignore the Address Info fields.
• PPPoE – Select this if your ISP uses this method. (Usually, your ISP will
provide some PPPoE software; however, this software is not required and
should not be used.)
If this method is selected, you must complete the PPPoE dialup fields.
Note:
If using the PPTP connection method (enable PPTP Connection), select Static
IP or Dynamic IP as appropriate, according to the IP Address method used by
your ISP.
Page 16
Page 21
Address
Information
PPPoE / PPTP
Dialup
DNS
Optional
This is for Static IP users only. Enter the address information (IP Address,
Subnet Mask, Gateway) provided by your ISP. If your ISP provides multiple IP
address, you can use the Multi-DMZ screen to assign any additional IP
addresses.
This is for PPPoE or PPTP users only.
• Enter the Username and Password provided by your ISP.
• If using PPTP, enable the PPTP Connection checkbox and enter the IP
address of the PPTP server.
• PPPoE Host name (Optional) – This field is used by a Host to uniquely
associate an access concentrator with a particular Host request.
Note:
There are additional PPPoE/PPTP options on the Port Options screen.
To use multiple PPPoE sessions on either port, configure settings in the
Advanced PPPoE screen.
If using a Fixed IP address, you MUST enter at least 1 DNS address.
If using a Dynamic IP, PPPoE or PPTP; DNS information is optional.
• Host name – This is required by some ISPs. If your ISP provided a Host
Name, enter it here. Otherwise, you can use the default value.
• Domain name – This is required by some ISPs. If your ISP provided a
Domain Name, enter it here. Otherwise, you can use the default value.
• MAC address – Some ISP records your MAC address (also called "Physical
address" or "Network Adapter address"). If so, you can enter the MAC
address expected by your ISP in this field. Otherwise, this should be left at
the default value.
Setup of the MULTI-WAN GATEWAY is now complete. PCs on your LAN must now be configured.
See the following section for details.
Page 17
Page 22

4: Configure PCs on your LAN
Overview
For each PC, the following settings may need to be configured:
• TCP/IP network settings
• Internet Access configuration
TCP/IP Settings
If using the default MULTI-WAN GATEWAY settings and the default Windows
95/98/ME/2000/XP TCP/IP settings, no changes need to be made. Just start (or restart) your
PC.
• By default, the MULTI-WAN GATEWAY will act as a DHCP Server, automatically providing a
suitable IP Address (and related information) to each PC when the PC boots.
• For all non-Server versions of Windows, the default TCP/IP setting is to act as a DHCP client. In
Windows, this setting is: Obtain an IP address automatically.
Just start (or restart) your PC and it will automatically obtain an IP address from the MULTI-WAN
GATEWAY.
• If using fixed IP addresses on your LAN, or if you wish to check your TCP/IP settings, refer to
Appendix B – Windows TCP/IP Setup.
Internet Access
To configure your PCs to use the MULTI-WAN GATEWAY for Internet access, follow this procedure:
For Windows 9x/2000
1. Select Start Menu - Settings - Control Panel - Internet Options.
2. Select the Connection tab and then click the Setup button.
3. Select "I want to set up my Internet connection manually”, or “I want to connect through a local
area network (LAN)" and click Next.
4. Select "I connect through a local area network (LAN)" and click “Next”.
5. Ensure that all of the boxes on the following Local area network Internet Configuration screen are
unchecked.
6. Check the "No" option when prompted "Do you want to set up an Internet mail account now?"
7. Click Finish to close the Internet Connection Wizard.
Setup is now completed.
For Windows XP
1. Select Start Menu - Control Panel - Network Connections.
2. Select Create a new connection.
3. Click Next on the "New Connection Wizard" screen.
Page 18
Page 23

4. Select "Connect to the Internet" and click “Next”.
5. Select "Set up my connection manually" and click “Next”.
6. Check "Connect using a broadband connection that is always on" and click Next.
7. Click Finish to close the New Connection Wizard.
Setup is now completed.
Accessing AOL
To access AOL (America On Line) through the MULTI-WAN GATEWAY, the AOL for Windows
software must be configured to use TCP/IP network access rather than a dial-up connection. The
configuration process is as follows:
• Start the AOL for Windows communication software. Ensure that it is Version 2.5, 3.0 or later.
This procedure will not work with earlier versions.
• Click the Setup button.
• Select Create Location and change the location name from "New Locality" to " MULTI-WAN
GATEWAY".
• Click Edit Location. Select TCP/IP for the Network field. (Leave the Phone Number field blank.)
• Click Save, then OK.
Configuration is now complete.
• Before clicking "Sign On", always ensure that you are using the "MULTI-WAN GATEWAY"
location.
Macintosh Clients
For Macintosh users, the procedure for accessing the Internet via the MULTI-WAN GATEWAY is as
follows.
1. Open the TCP/IP Control Panel.
2. Select Ethernet from the Connect via pop-up menu.
3. Select Using DHCP Server from the Configure pop-up menu. The DHCP Client ID field can be left
blank.
4. Close the TCP/IP panel, saving your settings.
Note:
If using manually assigned IP addresses instead of DHCP, the required changes are:
• Set the Router Address field to the MULTI-WAN GATEWAY’s IP Address.
• Ensure your DNS settings are correct.
Linux Clients
To access the Internet via the MULTI-WAN GATEWAY using Linux, it is only necessary to set the
MULTI-WAN GATEWAY as the "Gateway" and ensure your Name Server settings are correct.
Ensure you are logged in as "root" before attempting any changes.
Page 19
Page 24

Fixed IP Address
By default, most Unix installations use a fixed IP Address. If you wish to continue using a fixed IP
Address, make the following changes to your configuration.
• Set your Default Gateway to the IP Address of the MULTI-WAN GATEWAY.
• Ensure your DNS (Name server) settings are correct.
To act as a DHCP Client (recommended)
The procedure below may vary depending on your version of Linux and X -windows shell.
1. Start your X Windows client.
2. Select Control Panel - Network
3. Select the "Interface" entry for your Network card. Normally this will be called "eth0".
4. Click the Edit button, set the "protocol" to "DHCP" and save this data.
5. To apply your changes, use the "Deactivate" and "Activate" buttons if available. Otherwise, restart
your system.
Page 20
Page 25
3: Advanced Port
Overview
• Port Options contains some options which can be set on any WAN port. For most situations, the
default values are satisfactory.
• Load Balance is only functional if you are using multiple WAN ports. It allows you to determine
the proportion of WAN traffic sent through each port.
• Advanced PPPoE setup is required if you wish to use multiple sessions on each WAN port. It
can also be used to manually connect or disconnect a PPPoE session. Otherwise, this screen
can be ignored.
• Advanced PPTP setup is required if using the PPTP connection method.
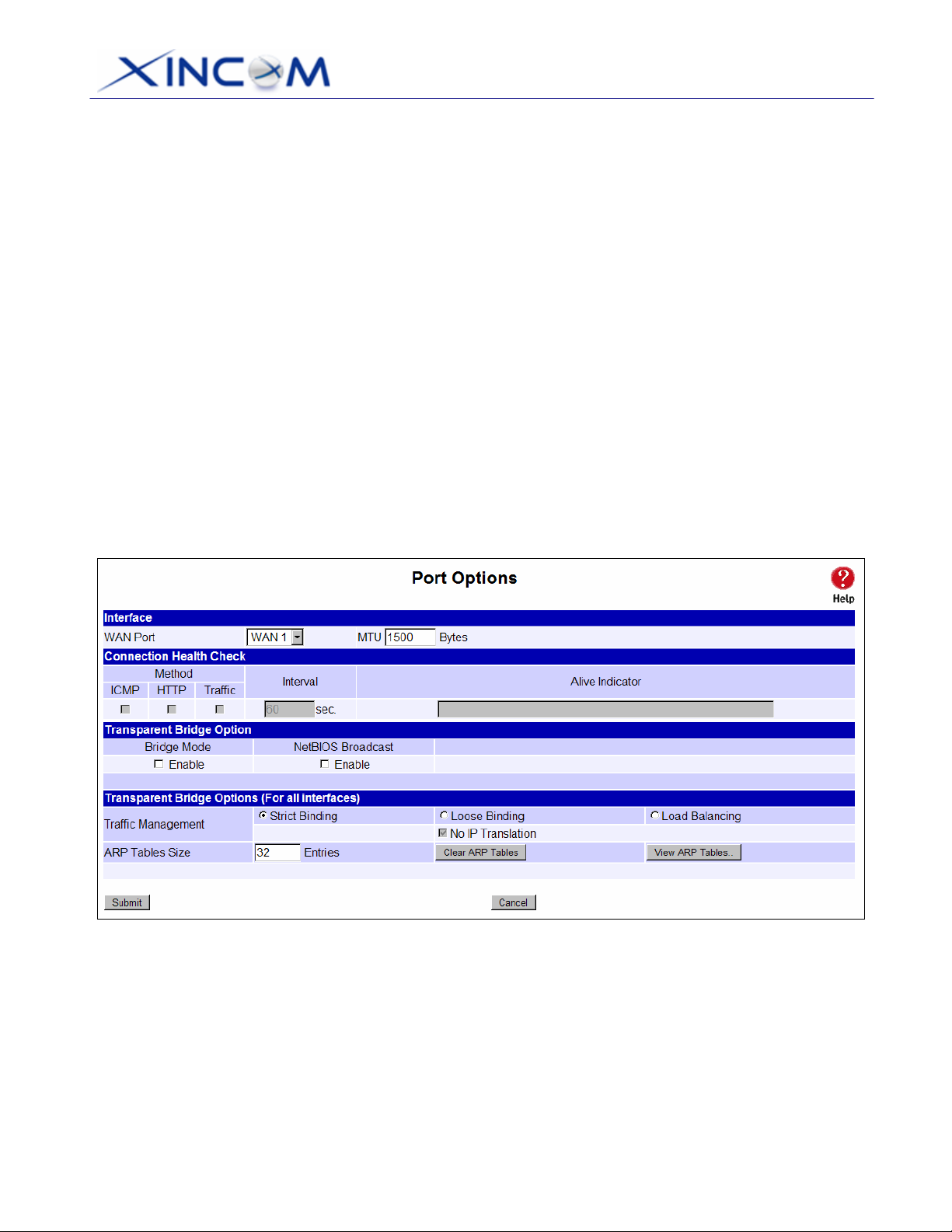
Port Options
Figure 3-1: Port Options
Page 21
Page 26

Settings – Port Options
Interface
Connection Health
Check
• WAN Port – Select a particular WAN port from the pull-down menu to
setup WAN port configuration.
• MTU – The Maximum Transmission Unit for the Ethernet data. This
is used to determine the packet size to be used on the WAN
interface. Normally, this does not need to be changed but if your ISP
advises you to use a particular MTU, enter it here. The default MTU
value is 1500 Bytes.
• Method – There are three methods available for checking if a WAN
port is alive or not. Multiple choices can be selected when using it.
• Disable will not perform an Alive Indicator Check. By default, Health
Check is set to Enable. If the “Alive Indicator” input box is left blank,
Health Check performs an ICMP echo packet request to the specific
destination. This could be either a URL or an IP Address specified
by users in the “Alive Indicator” input box or WAN interface
gateway.
• Interval – The interval time for device health check. The default
interval time is 60 seconds.
• Alive Indicator – This is the IP address used to check if the WAN
connection is operating. The MULTI-WAN GATEWAY will contact
this system to check if the WAN connection is working or not. You
may change this address if you wish. Default is the gateway IP.
Note: This is not used for PPPoE connections.
Transparent Bridge
Option
• Bridge Mode – If set to Enable, this WAN port doesn’t use NAT &
Load Balance function when the LAN/WAN IP have the real IP
addresses on the same network segment.
• NetBIOS Broadcast – If you enable the NetBIOS Broadcast, this
will allow you to access files through the Microsoft network
neighborhood.
Page 22
Page 27

Transparent Bridge
Options (For all
interfaces)
• Traffic Management –
Strict Binding: Traffic from bridge hosts (eg. transparent to
WAN1) can only go through the specified WAN interface
(eg. WAN1).
Loose Binding: This acts as a failover mechanism for transparent
bridge mode.
WAN1) can go through any WAN interface (eg. WAN2 or
other) when bind interface (eg. WAN1) is down.
Load Balancing: This acts as a load balancing mechanism for
transparent bridge mode. Traffic from bridge hosts (eg. transparent
to WAN1) can go through any WAN interface (eg. WAN1, 2 or
other) based on the loading mechanism specified in the load
balance section.
• ARP Table – The ARP Table is used by the device to determine
the bridge hosts’ location (e.g. inside/outside WAN and which
WAN). Its size can be adjusted if needed. View ARP Tables
displays ON/OFF selection of bridge mode on each WAN port.
Clear ARP Tables disables bridge mode on all WAN ports.
Traffic from bridge hosts (eg. transparent to
Load Balance
This screen is only operational if using Internet connections on multiple WAN ports
Figure 3-2: Load Balance
Page 23
Page 28

Only functional when using two (2) or more WAN ports - these settings determine the proportion of
traffic sent over each port.
Settings – Load Balance
Load Balance
Configuration
• Enable – This enables your Load Balance setting options and must be
checked for other settings on this screen to be effective.
• Balance Type – You can select the Balance types based on:
• Bytes Tx + Rx – Traffic is measured by Bytes. (Least load)
• Packets Tx + Rx – Traffic is measured by Packets. (Least load)
• Sessions established – Traffic is measured by Sessions. (Least load)
• IP Address – Traffic is measured by IP address. (Least load)
• Auto Learning – The largest unused upload/outgoing bandwidth.
• Fastest – The largest upload bandwidth.
• Priority – The highest priority.
• Round Robin – Continuously repeating sequence.
• Weight Round Robin – In sequence with weight placed accordingly.
• Loading Share – Enter the percentage (%) of traffic to be sent over each
WAN port. If one WAN port connection has a greater bandwidth than another,
the one with the greater bandwidth is given a higher percentage of traffic than
the other.
Click the "submit" button to save your changes.
NAT
Statistics
Interface
Statistics
Buttons
This section displays the current data about any WAN port. You can use this
information to help you "fine-tune" the settings above.
This section displays cumulative statistics.
Use the "Restart Counters" button to restart the counters when required.
• Refresh – Update the data entered on the screen.
• Restart Counters – Restart the counters used in the "Interface Statistics"
section.
Page 24
Page 29

Advanced PPPoE
The Advanced PPPoE screen is required in order to use multiple PPPoE sessions on the same WAN
port.
It can also be used to manually connect or disconnect a PPPoE session.
Settings – Advanced PPPoE
Select WAN Port
& Session
WAN Port – Selected WAN port only using PPPoE connection
PPPoE Session – ISPs can usually provide multiple floating real IPs for
PPPoE. Each WAN port can have up to eight (8) PPPoE sessions, each with
a different IP address if your WAN port is using PPPoE connectivity.
PPPoE Session MTU – The Maximum Transfer Unit for PPPoE packet data.
Leave it as default unless the ISP provides a different PPPoE packet data
size. The default MTU value is 1492 bytes.
Figure 3-3: Advanced PPPoE
Page 25
Page 30

WAN IP Account
Options
PPPoE Auto
Dialup
• User Name – Enter the PPPoE user name assigned by your ISP.
• Password – Enter the PPPoE password assigned by your ISP.
• Verify Password – Re-enter the PPPoE password assigned by your ISP.
• Specified Fix IP Address – If you have a fixed IP address, enter if here.
Otherwise, this field should be left at 0.0.0.0.
• Assigned Host Name –This field is used by a Host to uniquely associate
an access concentrator with a particular Host request.
• Auto Dialup (connect-on-demand) – If set to Enable, a connection will be
established whenever outgoing WAN traffic is detected. If not enabled,
you must establish a connection manually.
• Disconnect after Idle – This determines when an idle connection will be
terminated. Enter the required time period. (-1: Always on)
• Echo Time – This determines how often an Echo request is sent to the
PPPoE server. The Echo request is used to determine if the connection is
still alive. Normally, there is no need to change the default value.
• Echo Retry – The number of times the Echo request will be sent, if there
is no response to the first request. Normally, there is no need to change
the default value.
Connection
Status
This displays the current connection status for each session.
Advanced PPTP
This Advanced PPTP screen is only useful if using the PPTP connection method.
Figure 3-4: Advanced PPTP
Page 26
Page 31

Settings – Advanced PPTP
WAN Port
WAN IP Account
PPTP Auto Dialup
Select the desired WAN port (click desired WAN on Connection Status). The
data of the selected port will then be displayed in the WAN IP Account
section.
PPTP MTU – Maximum transfer unit for PPTP. The default value is 1460
• User Name – The PPTP user name (login name) assigned by your ISP.
• Password – The PPTP password associated with the User Name above.
This is assigned by your ISP, and used to login to the PPTP Server.
• Verify Password – Re-enter the PPTP password assigned by your ISP.
• Server IP Address – Enter the IP address of the PPTP Server, as
provided by your ISP.
• Static IP Address – If you have a fixed IP address, enter if here.
Otherwise, this field should be left at 0.0.0.0.
• Auto Dialup (connect-on-demand) – If set to Enable, a connection will be
established whenever outgoing WAN traffic is detected. If not enabled,
you must establish a connection manually.
• Disconnect after Idle – This determines when an idle connection will be
terminated. Enter the required time period. (-1: Always on)
• Echo Time – This determines how often an Echo request is sent to the
PPTP server. The Echo request is used to determine if the connection is
still alive. Normally, there is no need to change the default value.
Connection
Status
• Echo Retry – The number of times the Echo request will be sent, if there
is no response to the first request. Normally, there is no need to change
the default value.
This displays the current PPTP connection status.
Page 27
Page 32

4: Advanced Setup
Overview
The following features are provided in Advanced Setup:
• Host IP
• Routing
• Virtual Server
• Special Application
• Dynamic DNS
• Multi DMZ
• UPnP Setup
• NAT Setup
• Advanced Feature
This chapter contains details on the configuration and use of each of these features.
Host IP
This feature is used in the following situations:
• You have Multi-Session PPPoE and wish to bind each session to a particular PC on your LAN.
• You wish to use the Access Filter feature. This requires that each PC is identified by using the
Host IP screen.
• You wish to have different Block URL settings for different PCs. This requires that each PC is
identified by using the Host IP screen. (You do not have to use the Host IP feature to apply the
same Block URL settings to all PCs.)
• You wish to reserve a particular (LAN) IP address for a particular PC on your LAN. This allows the
PC to use DHCP (In Windows this setting is configured as: "Obtain an IP address automatically")
while gaining the benefits of a fixed IP address. The PC's IP address will never change, allowing it
to be provided to other users and applications.
Page 28
Page 33

Figure 4-1: Host IP
Settings – Host IP
Host Network
Identity
This section identifies each Host (PC)
• Host name – Enter a suitable name. Generally, you should use the
• MAC Address – Also called Physical Address or Network Adapter Address.
• Select Group – Select the group you wish this Host to be included in.
• Reserve in DHCP – Select Enable to reserve a particular (LAN) IP address
• Reserved IP Address – Enter the IP address you wish to reserve, if the
"Hostname" (computer name) as defined on the Host itself.
Enter the MAC address of this Host.
for a particular PC on your LAN. This allows the PC to use DHCP (In Windows
this setting is configured as: "Obtain an IP address automatically") while
retaining an IP address that never changes.
setting above (Reserve in DHCP) is set to Enable. Otherwise, ignore this field.
Page 29
Page 34

Host Network
Binding
Buttons
• Binding WAN Port / Session – Select Enable if you wish to associate this
PC with a particular PPPoE session. All traffic for that PC will then use the
selected PPPoE port and session.
• Binding Method – Suppose your PC is bound to WAN1 port and you select
“Strict Binding.” If WAN1 port is disconnected, your packets cannot go
through another WAN port, if it is still alive. If you select “Loose Binding” then
if WAN1 port becomes disconnected, your packets will automatically go to
another WAN port, if it is alive.
• Select WAN Port / Select PPPoE session – If the Binding Method setting
above is set to Enable, select the desired Port and Session. Otherwise, ignore
these settings.
Note: Multiple PPPoE sessions are defined on the Advanced PPPoE screen.
• Add – Use this to add a new entry to the database, using the data shown on
screen.
• Delete – Click this to delete the selected entry.
• Update – After making the desired changes, use this to update the selected
entry
• Reset – Reverse any changes you have made since loading the data from the
MULTI-WAN GATEWAY.
Host & Group
List
This table shows the current bindings.
Routing
This section is only relevant if your LAN has other Routers or Gateways.
• If you don't have other Routers or Gateways on your LAN, you can ignore the Static Routing
page completely.
• If your LAN has other Gateways and Routers, you must configure the Static Routing screen as
described below. You also need to configure the other Routers.
Page 30
Page 35

Figure 4-2: Routing
Note:
If there is an entry or entries in the Routing table with an Index of zero (0), these are System entries.
You cannot modify or delete these entries.
Settings – Routing
Dynamic
Routing
Static
Routing
• RIP v2 – This acts as a “master” switch. If enabled, the selected WAN or LAN
will run RIPv1/v2, otherwise RIP function will not be available.
• Interface – If LAN or other WAN are enabled, the specified WAN or LAN can
execute RIP function.
• Network Address – The network address of the remote LAN segment. For
standard class "C" LANs, the network address is the first 3 fields of the
Destination IP Address. The 4th (last) field can be left at 0.
• Netmask –The Network Mask for the remote LAN segment. For class "C"
networks, the default mask is 255.255.255.0
• Gateway – The IP Address of the Gateway or Router that the MULTI-WAN
GATEWAY must use to communicate with the destination IP address entered
above. (NOT the router attached to the remote segment.)
• Interface – Select the correct interface - usually "LAN". The "WAN" interface
is only available if NAT (Network Address Translation) is disabled.
Routing List
• Metric – The number of "hops" (routers) to pass through to reach the remote
LAN segment. The shortest path will be used.
This shows the current routing table set by the user.
Page 31
Page 36

1
Configuring Other Routers on your LAN
All traffic for devices not on the local LAN must be forwarded to the MULTI-WAN GATEWAY so that it
can be forwarded to the Internet. This is done by configuring other Routers to use the MULTI-WAN
GATEWAY as the Default Route or Default Gateway, as illustrated by the example below.
Static Routing - Example
Segment
(192.168.2.xx)
(192.168.2.80)
Router B
(192.168.1.100)
Router A
Segment 0
(192.168.1.xx)
(192.168.1.1)
(192.168.2.90)
(192.168.3.70)
Segment 2
(192.168.3.xx)
Figure 4-3: Routing Example
For the MULTI-WAN GATEWAY Gateway's Routing Table
For the LAN shown above, with 2 routers and 3 LAN segments - the MULTI-WAN GATEWAY requires
2 entries as follows:
Entry 1 (Segment 1)
Destination IP
Address
Network Mask 255.255.255.0
Gateway IP Address 192.168.1.100
Interface LAN
192.168.2.0
Metric 2
Entry 2 (Segment 2)
Destination IP 192.168.3.0
Page 32
Page 37

Address
Network Mask 255.255.255.0 (Standard Class C)
Gateway IP Address 192.168.1.100
Interface LAN
Metric 3
For Router A's Default Route
Destination IP
Address
Network Mask 0.0.0.0
Gateway IP Address 192.168.1.1
Metric 2
For Router B's Default Route
Destination IP
Address
Network Mask 0.0.0.0
Gateway IP Address 192.168.2.80
Interface LAN
Metric 3
0.0.0.0
0.0.0.0
Page 33
Page 38

Virtual Server
This feature allows you to make Servers on your LAN accessible to Internet users. Normally, Internet
users would not be able to access a server on your LAN because:
• Your Server's IP address is only valid on your LAN, not on the Internet.
• Attempts to connect to devices on your LAN are blocked by the firewall in the MULTI-WAN
GATEWAY.
The "Virtual Server" feature solves these problems and allows Internet users to connect to your
servers, as illustrated below.
Web Server
(192.168.1.45)
PC using FTP Server
(ftp://205.20.45.34)
FTP Server
(192.168.1.20)
205.20.45.34 (WAN)
PC using Web Server
(http://205.20.45.34)
Note that, in this illustration, both Internet users are connecting to the same IP Address but using
different protocols.
Figure 4-4: Virtual Server
Multi-WAN Load Balancer
192.168.1.1 (LAN)
Connecting to the Virtual Server
Once configured, anyone on the Internet can connect to your Virtual Servers. They must use the
MULTI-WAN GATEWAY's Internet IP Address (the IP Address allocated by your ISP).
e.g.
http://205.20.45.34
ftp://205.20.45.34
• To Internet users, all virtual Servers on your LAN have the same IP Address. This IP Address is
allocated by your ISP.
• This address should be static, rather than dynamic, to make it easier for Internet users to connect
to your Servers. However, you can use the Dynamic DNS feature (explained later in this chapter)
Page 34
Page 39

to allow users to connect to your Virtual Servers using a URL, instead of an IP Address.
e.g.
http://my_domain_name.dyndns.org
ftp://my_domain_name.dyndns.org
This screen allows you to define your own Server types.
Settings – Virtual Server
Virtual Server
Configuration
• Enable – The enable checkbox is to Enable or Disable each Virtual
server as required.
• Server Name – Enter a suitable name for this server. (By default, 12
well-known virtual servers have been listed on the Custom Virtual
Server List)
• Protocol – Select the network protocol (TCP/UDP) used by this sever.
• IP Address – LAN, Enter the IP address of the server on your LAN
which is running the required Server software.
Each Host (server) should have a fixed IP address, or have a reserved
IP address. (See the Host IP section earlier in this Chapter for details
on reserving an IP address.)
Figure 4-5: Virtual Server
Page 35
Page 40

Each Host (server) must be running the appropriate Server software
WAN – This selection allows this server to bind to any WAN port (1-8),
or even bind to all WAN ports together.
• LAN Port Range – Enter the range of port number used for outgoing
traffic from this Server. If only a single port is required, enter it in both
fields.
• WAN Port Range -– Enter the range of port numbers used for incoming
traffic to this Server. If only a single port is required, enter it in both fields
• Allowed Remote IP – It allows only a range of remote side IP
addresses to access the virtual servers. The default entry 0.0.0.0 ~
0.0.0.0, means all remote side IP address can access it.
Buttons
Virtual Server List
• Add – Create a new Virtual Server entry.
• Delete – Delete the selected entry.
• Update – Save any changes you have made to the current entry.
• Cancel – Cancel any changes you have made since the last saved
operation.
This table shows the details of all Custom Virtual Servers configuration data
which have been defined. You can modify their configuration data by
selecting and clicking on a row.
Page 36
Page 41

Special Application
If you use Internet applications which have non-standard connections or port numbers, you may find
that they do not function correctly because they are blocked by the firewall in the MULTI-WAN
GATEWAY. In this case, you can define the application as a "Special Application" in order to make it
work.
Note that the terms "Incoming" and "Outgoing" on this screen refer to traffic from the client (PC)
viewpoint
Figure 4-6: Special Application
Settings – Special Application
Special Application
Configuration
• Enable – Use this to Enable or Disable the Special Application as
required
• Name – Enter a descriptive name to identify the Special Application.
• Outgoing Protocol –Select the protocol used by the application when
sending data to the remote server or PC.
• Outgoing Port Range – Enter the beginning and end of the range of
port numbers used by the application server for data you send. If the
application uses a single port number, enter it in both fields.
• Incoming Protocol – Select the protocol used by the application when
receiving data from the remote server or PC.
• Incoming Port Range –Enter the beginning and end of the range of
port numbers used by the application server for data you receive. If the
application uses a single port number, enter it in both fields.
Page 37
Page 42

Buttons
Special Application
List
• Add – Create a new Special Application entry.
• Delete – Delete the selected entry.
• Update – Save any changes you have made to the current entry.
• Cancel – Cancel any changes you have made since the last saved
operation.
This shows the details of all Special Applications which are currently
defined. You can modify its configuration data by selecting and clicking on
a row.
Using a Special Application on your PC
• Once the Special Applications screen is configured correctly, you can use the application on your
PC normally. Remember that only one (1) PC can use each Special application at any time.
• Also, when 1 PC is finished using a particular Special Application, there may need to be a "Timeout" period before another PC can use the same Special Application.
• If an application still cannot function correctly, try using the "DMZ" feature, if possible.
Page 38
Page 43

Dynamic DNS
Dynamic DNS is very useful when combined with the Virtual Server feature. It allows Internet users to
connect to your Virtual Servers using a URL, rather than an IP Address.
This also solves the problem of having a dynamic IP address. With a dynamic IP address, your IP
address may change each time you connect to your ISP, making it difficult to connect to you.
You must register for the Dynamic DNS service. The MULTI-WAN GATEWAY supports 3 types of
service providers:
• Standard client, available at http://www.dyndns.org
(Other sites may offer the same service, but can not be guaranteed to work)
• TZO at http://www.tzo.com
• 3322 is available in China at http://www.3322.org
To use the Dynamic DNS feature
1. Register for the service from your preferred service provider.
2. Follow the service provider's procedure to have a Domain Name (Host name) allocated to you.
3. Configure the Dynamic DNS screen, as described below.
4. The MULTI-WAN GATEWAY will then automatically update your IP Address recorded by the
Dynamic DNS service provider.
5. From the Internet, users will now be able to connect to your Virtual Servers (or DMZ PC) using
your Domain name.
Figure 4-7: Dynamic DNS
Page 39
Page 44

Settings – Dynamic DNS
Dynamic DNS
Service
Additional
Settings
This pull-down menu can Enable/Disable the Dynamic DNS feature and select
the required service provider.
• Disable – Dynamic DNS is not used.
• TZO – Select this to use the TZO service (www.tzo.com). You must
configure the TZO section of this screen.
• DynDNS – Select this to use the standard service (from www.dyndns.org
or other provider). You must configure the Standard Client section of this
screen.
• 3322(in China) – This is available in China. It is similar to “DynDNS”
• User Defined DDNS Server – This is the user defined DDNS server. If the
DDNS provider is other than TZO, dyndns.org or 3322.
These options are available if using the standard client.
• Enable Wildcard – If selected, traffic sent to sub-domains (of your Domain
name) will also be forwarded to you.
• Enable backup MX – If enabled, you must enter the Mail Exchanger
address below.
• Mail Exchanger – If the setting above is enabled, enter the address of the
backup Mail Exchanger.
WAN Port
Binding
• Select the WAN port used by the Dynamic DNS.
• The "Force Update" button will update your record on the Dynamic DNS
Server immediately.
Page 40
Page 45

Multi DMZ
This feature allows each WAN port IP address to be associated with one (1) computer on your LAN.
All outgoing traffic from that PC will be associated with that WAN port IP address. Any traffic sent to
that IP address will be forwarded to the specified PC, allowing unrestricted 2-way communication
between the "DMZ PC" and other Internet users or Servers.
Note:
The "DMZ PC" is effectively outside the Firewall, making it more vulnerable to hacker attacks or other
intrusions. For this reason, you should only enable the DMZ feature when required.
Settings – Multi DMZ
Multi DMZ Edit
• Enable – Use this to enable or disable the DMZ setting, as required.
• WAN – Select the desired WAN port binding with a particular LAN host.
• Name – Enter a name to assist you to remember this setting. This name
• Private IP Address (LAN) – Enter the IP address of the PC you wish to
• Access Group –You can decide which users will have authorization to
• Direction –For DMZ, you can allow inbound only, outbound only, or both
Figure 4-8: Multi DMZ
(There are a maximum 8 WAN ports which can be available.) Its
connection type may change based on your WAN connection type
(Static/DHCP/PPPoE/PPTP).
can be anything you choose and will have no effect on the operation.
associate with this WAN port IP address. This IP address should be fixed,
or reserved. (See the Host IP section for details on reserving an IP
address.)
use DMZ by defining the groups (Host IP web page)
inbound and outbound traffic.
Multi DMZ List
Multi DMZ List shows the details of all DMZ configuration data which are
currently defined. You can modify its configuration data by selecting and
clicking on a row.
Page 41
Page 46

UPnP Setup
With the UPnP (Universal Plug & Play) function, you can easily setup and configure an entire network
as well as enable detection and control of networked devices and services.
Figure 4-9: UPnP Setup
Settings – UPnP Setup
UPnP Option
UPnP Port
Mapping List
If set to Enable UPnP, this device will register on the local network. You will
find that there is an icon showing on the My Network Places in Window XP.
Each time you add a new service with port mapping, the new service will
appear on the mapping list.
If UPnP is set to Enable, this table shows the details of all Custom Virtual
Servers configuration data which have been defined.
Page 42
Page 47

NAT Setup
NAT (Network Address Translation) is the technology which allows one (1) WAN (Internet) IP address
to be used by multiple LAN users.
Settings – NAT Setup
NAT
Configuration
• NAT Routing – You can enable or disable NAT through the check box. If
you disable the NAT checkbox, it will act as a bridge or Static Router. Most
features will be unavailable.
• TCP Timeout – Enter the desired value to use on each WAN port. The
default is 300
• UDP Timeout – Enter the desired value to use on each WAN port. The
default is 120
• TCP Window Limit – Enter the desired value to use on each WAN port.
The default is 0 (no limit).
• TCP MSS Limit – Enter the required MSS (Maximum Segment Size) to
use on each WAN port. The default is 0 (no limit).
Figure 4-10: NAT Setup
Page 43
Page 48

Non-Translation
Port Range
NAT Alias
NAT Alias List
Check NAT
Detail
NAT Connection
List
If some packets whose port number cannot be translated for special
applications, you must set state to “Enable” and input value in port range.
Alternatively, if its port cannot be translated in the specified time period, you
must set Enable and enter a seconds value in Timeout.
For each alias entry, the WAN IP acts as an alias of the host with Local LAN IP
accessing the Internet via the specified WAN port for the specified protocol
packets, i.e. 1-1 NAT.
NAT Alias List shows the list of all NAT alias configuration data which are
currently defined. You can modify its configuration data by selecting and
clicking on a row.
Shows all detailed NAT configuration data.
This shows the current details of all NAT entries which include interface,
protocol, state, destination IP, WAN IP, local IP, idle time and in/out packets.
Page 44
Page 49

Advanced Feature
• External Filters Configuration – These settings determine whether the MULTI-WAN GATEWAY
should respond to ICMP (ping) requests received from the WAN port or not.
• Interface Binding – Use these settings to ensure that certain traffic is sent by a particular WAN
port and thereby a particular ISP account. These settings are only useful on some WAN ports.
• Protocol & Port Binding – This allows you to bind any WAN port by selecting the protocol type
you want.
Figure 4-11: Advanced Feature
Page 45
Page 50

Settings – Advanced Feature
External Filters
Configuration
DNS Loopback
Interface
Binding
• IDENT Port – Port 113 is associated with the Internet's (Identification /
Authentication) service. When a client program in your computer contacts a
remote server for services such as POP, IMAP, SMTP, that remote server
sends back a query to the "Ident" server running in many systems listening
for these queries on port 113. This means that hackers can probe port 113
as a rich source of your personal information. The default value of this
check box is “Disable”
• Block Selected ICMP Types – These settings determine whether or not
this device should respond to ICMP requests received from the WAN port.
If checked, the selected packet types are blocked. Otherwise, the packets
are accepted.
Used when you have some servers on the LAN and their domain names have
already been registered on public DNS. To avoid DNS loop back problems,
please enter the following fields:
• Domain Name – Enter the domain name specified by you for the local
server.
• Private IP – Enter the private IP address of your local server.
SMTP (Simple Mail Transport Protocol) Binding
Unless you are using E-mail accounts from different ISPs on each port, you
can ignore these settings.
Protocol & Port
Binding
Some ISPs configure their E-mail Servers so they will not accept E-mail from
IP addresses not allocated by them. If you are using accounts from different
ISPs, sending E-mail over the wrong WAN port may result in the mail not being
accepted. In this case, you can use these settings to correct the problem:
• Enable - If enabled, the WAN port you specify below will be used for all
outgoing SMTP traffic. If not enabled, either WAN port will be used.
• WAN – Select the desired WAN port to be bound.
Protocol and Port Binding
Use these settings if you wish to ensure that particular traffic is sent by a
specific WAN port, and thereby a particular ISP account.
• Enable - Enable or disable each item as required.
• Source IP - IP address of source from which packets are sent.
• Destination IP – IP address of destination to which packets are sent.
• Subnet Mask – With a subnet mask other than 255.255.255.255, you can
make an IP sub-network as your destination.
• Protocol – Select protocol type used by the traffic you wish to configure.
• Port Range - Enter the beginning and end of the port range used by the
traffic you wish to configure. If only a single port is used, enter the port
number in both fields.
• WAN - Select the WAN port you wish this traffic to use.
Page 46
Page 51

Protocol & Port
Binding List
This list shows the details of all protocol and port configuration data which are
currently defined. You can modify them by clicking on a selected row.
Page 47
Page 52

5: Security Management
Overview
• Block URL – Ability to block a specific website by configuring IP address, URL or Keywords.
• Access Filter – Ability to block all Internet access, a known port or user defined ports by group
access.
• Session Limit – Ability to limit users Internet access when the device detects new sessions that
exceed the maximum value in the sampling time, for example, virus, syn flood, etc.
• SysFilter Exception – This feature allows you to configure an unrecognized port, allowing those
packets to be processed, enabling some programs to run more smoothly. This is also applicable
for some future applications that may need this mechanism in order to work well.
Block URL
This feature allows you to block access to undesirable Web sites. You can block by URL, IP address,
or Keyword. You can also have different blocking settings for different groups of PCs.
• In operation, every URL is searched to see if it matches or contains any of the URLs or keywords
entered here. Then, after a DNS lookup, it determines the IP address of the requested site and
checks it against IP address entries on this screen.
• Note that a single IP address may host many Web sites (shared IP). Entering an IP address on
this screen will block all Web sites that may be hosted on that IP address.
Figure 5-1: Block URL
Page 48
Page 53

Settings – Block URL
Access Group
Access Item
Internet Access
List
This allows you to have different blocking rules for different Groups of PCs.
• All PCs (users) are in the Default Group unless moved to another specified
group on the Host IP screen.
• If you want the same restrictions to apply to everyone, select Default for the
Group. In this case, there is no need to enter any Hosts in the Host IP
screen.
• If you wish to apply different restrictions on different Groups, select the
desired Group, and click the "Select" button. The screen will update the
data for the selected Group.
• URL List Type – Black List: If you select Black List, It will block the URL
that you keep it on Access Item. White List: If you are select White List
type, it will block the entire URL except you keep it on the Access Item.
• Set Type Button – Button to submit Black List or White List.
• Enable/Disable – Use this to Enable or Disable each setting as required.
• Block URL/IP/Keyword – Enter the URL, IP address or Keyword you wish
to block.
The list will display all block rules that you have setup. You can modify it by
clicking on a selected row.
Access Filter
The network Administrator can use the Access Filter to gain fine control over the Internet access and
applications available to LAN users.
• Five (5) user groups are available and each group can have different access rights assigned to
them.
• All PCs (users) are in the Default group, unless assigned to another group on the Host IP screen.
Page 49
Page 54

Figure 5-2: Access Filter
Page 50
Page 55

Settings – Access Filter
Access Group
Filter Setting
ICMP Filters
User-Defined Filter
This allows you have different access rights for different Groups of PCs.
• If you want the same restrictions to apply to everyone, select Default
for the Group. In this case, there is no need to enter any Hosts on
the Host IP screen.
• If you wish to apply different restrictions to different Groups, select
the desired Group. The screen will update data for the selected
Group.
Select the desired option for this Group:
• No filtering – Nothing is blocked, Internet access is not restricted.
• Block All Access – Everything is blocked, Internet access is not
available.
• Block selected items – Items selected on this screen are blocked.
You can block known services by using the checkboxes, or you may
define your own filters.
If you enable ICMP Filter that means it will block ICMP request packet
types specified by users from local host to remote side.
This section is optional. It allows you to define your own filters as
required. For each filter, the following information is required:
• Filter Name – Enter a name for this filter.
User-Defined Filter List
• Protocol Type – Select a protocol type you wish to block.
• Port No. Range – Enter the range of port numbers used that you
wish to block. If only a single port is required, enter it in both fields.
This List shows the details of all User-Defined Filter configurations which
are currently defined. You can modify its configuration data by clicking
on a selected row.
Page 51
Page 56

Session Limit
This new feature allows to drop the new sessions from both WAN and LAN side, if the number of
new sessions exceeds the maximum value set by you in the Sampling Time field.
Figure 5-3: Session Limit
Settings – Session Limit
Sampling Time
Maximum of Total New
session
Maximum of New
Sessions for Host
Maximum of Dropped
New Sessions for Host
Pause Time for Host
while exceeding limit
on Dropped New
Sessions
The time interval specified by you for new sessions. Only the new
sessions that have recently occurred are counted according to the
sampling time entered. (Default is 400 mil-sec)
The maximum total number of new sessions in the system which is
acceptable in the sampling time. Any new incoming sessions will be
dropped after the number of new sessions has been exceeded.
(Default: 65535 session/sec)
The maximum number of new sessions from the host which is
acceptable in the sampling time. Any new incoming sessions will be
dropped from this host after the number of new sessions has been
exceeded. (Default: 100 session/sec)
If the number of dropped new sessions from the host exceeds the
Maximum in the sampling time, any new session from the host will be
dropped in the pause time period. (Default: 25 session/sec)
Within the pause time period, new session from the suspended host will
not be served by the system when the number of dropped new
sessions exceeds the defined Maximum. (Default is 5 minutes)
Page 52
Page 57

S
SysFilter Exception
System Filter Exception - This will reject every packet with an unrecognized port to block port scan
programs from hackers. This, however, also incurs problems in some situations where servers (e.g.
SMTP server port 113) or WAN clients need to send a response packet to verify the activity of their
communication peers.
Figure 5-4: SysFilter Exception
Settings –SysFilter Exception
System Filter Exception
Rules
ystem Filter Exception
Rules List
• Enable – If check box is marked, it will enable System Filter
Exception
• Interface – You can select LAN, any WAN port or ALL interfaces
from which a packet originates.
• Protocol – The packet type (selected in the above Interface) which
will be directly processed by this device.
• Foreign Port Range – Enter the beginning and end of the foreign
port range used by the traffic you wish to configure. If only a single
port is used, enter the port number in both fields.
• Device Port Range – Enter the beginning and end of the device port
range used by the traffic you wish to configure. If only a single port is
used, enter the port number in both fields.
The list will display the details of all System Filter Exception Rules that
you have setup. You can modify data by clicking on a selected row.
Page 53
Page 58

6: QoS Configuration
Overview
The MULTI-WAN GATEWAY incorporates a QoS (Quality of Service) utility to provide high quality
network support service.
Because it classifies outgoing packets based on policies defined by users, real-time applications
should respond or perform better.
QoS Setup
The following web page instructs you on setting up and enabling QoS.
Settings – QoS Setup.
QoS Feature
Enable QoS – Checkbox allows users enable QoS mechanism. If set to
"enable" QoS. QoS will allocate Inbound/Outbound bandwidth to pass through
the device.
• WAN Inbound / Outbound Bandwidth –This allows you to set the maximum
inbound or outbound bandwidth, maximizing your network's performance. This
information can be obtained from your ISP
• Set Policy Button –Setting the policy can allocate Inbound/Outbound
bandwidth (based on your configuration) to pass through this device.
Figure 6-1: QoS Setup
Page 54
Page 59

Policy Configuration
Setting the QoS policy can allocate Inbound/Outbound bandwidth (based on your configuration) to
pass through this device. You can define some policies which classify received packets based on
Local/Remote IP, MAC, port and protocol type. This feature is useful when the WAN link is very busy
or congested or when using special applications that need real time services such as Internet phone,
video conference...etc.
.
Settings – QoS Policy
WAN Inbound
/ Outbound
Policy
• Policy Name –The name of a policy which is used to classify the received
packets based on the following types for your memory
• Local / Remote Address, Port –Specify a packet based on Local/Remote
address or port. Address has two types: IP address and MAC address. By
default, the IP address is 0.0.0.0 for all IP Addresses but the MAC address is
00-00-00-00-00-00 which cannot be used to classify.
Port and Protocol Type define all packets for special applications
• Protocol Type – The field defines traffic packet type, i.e. IP, TCP and UDP.
• Maximum Guaranteed Bandwidth –This device supports Bandwidth
queues. When a packet meets a policy rule requirement, it will be put into the
responding queue. The queue will send them use the guaranteed bandwidth.
If the rest bandwidth is enough it will try to arrive the maximum bandwidth.
Figure 6-2: Policy Configuration
Page 55
Page 60

7: Management Assistant
Overview
The following advanced features are provided:
• Admin. Setup
• Email Alert
• SNMP
• Syslog
• Upgrade Firmware
This chapter contains details of the configuration and use of each of these features.
Admin. Setup
Remote Access Configuration – This feature allows you to manage the MULTI-WAN GATEWAY via
the Internet. You can restrict access to a specified IP address or address range.
Administrator Password – This feature allows you to assign a password for remote upgrade and
access to the MULTI-WAN GATEWAY.
Figure 7-1: Admin. Setup
Page 56
Page 61

Settings – Admin. Setup
Remote Access
Configuration
Administrator
Password
• Remote Upgrade – If enabled, you can use the supplied Windows
utility to remotely upgrade the firmware. If not enabled, the upgrade
must be performed by a PC on the LAN.
• Remote Setup – If enabled, access to the web-based interface is
available via the Internet (See below for details). If not enabled, access
is only available by a PC on the LAN.
• Access port – The port number used when connecting remotely. The
default port number is 8080.
• Allowed Remote IP – Remote access is only available to the IP
address entered here.
1. Leaving these fields blank (0.0.0.0 ~ 0.0.0.0), will allow access by
all PCs.
2. These addresses must be Internet IP addresses; not addresses on
the local LAN.
3. To specify a single address, enter it in both fields.
You can modify the device password in this field. The default entry is
“ “ (no password).
Page 57
Page 62

Email Alert
This feature will send a warning Email to the system administrator when any WAN port is
disconnected, has received excessive ping flooding, exceeded session limitation, etc.
Settings – Email Alert
Global Setting:
Notification on
• Link Down – If set to Enable, it will send a warning email to alert the
• Excessive Ping – This feature is useful to prevent ICMP attacks from
Figure 7-2: Email Alert
administrator when any WAN port is disconnected.
WAN or LAN. It will drop the packets if the ping packets exceed the
threshold value. If enabled, an email alert is sent to the administrator.
Page 58
Page 63

Email Alert
Configuration
Email Alert
Configuration List
• Email (SMTP) Server Address – An email sever to which a warning
email will be sent, if email alert has been enabled. For example:
mail.domain.com
• User Name – An email account name for the sender.
• Password – A password for the sender.
• Sender Address – An email address that sends a warning email to a
recipient.
• Recipient Address – An email address that a warning email will be
sent to. Usually this is a system administrator email address. For
example:
This lists all email alert configuration data that you have entered. You can
modify these details by clicking on a selected row.
admin@mail.domain.com
Page 59
Page 64

SNMP
This section is only useful if you have SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) software on
your PC. If you have SNMP software, you can use a standard MIB II file with the MULTI-WAN
GATEWAY.
Settings – SNMP
System
Information
Community
Trap Targets
• Contact Person – The name of the person responsible for this device.
• Device name – The name of this device.
• Physical Location – The location of the device.
• Community Name – This is a password or key used between this device and
• Access Control – Access privileges which allow the management station to
Enter the IP addresses of any targets (PCs running SNMP software) to which you
want traps to be sent. All traps are level 1.
Figure 7-3: SNMP
the management station. The administrator/manager must use the same
name when monitoring the device.
manage this device. This value may be: Read/Write, Read Only or No Access.
Page 60
Page 65

Syslog
This feature can send the real time system information to a web page or to specified PCs.
Syslog Configuration – Syslog Configuration allows you to select whether to send the system
information to another machine or not. Up to three machines can be chosen to send the system log to.
Message Status – Messages are only sent and kept when “Keep Sent Message” is enabled.
Currently 100 messages are retained in RAM and will be cleared when the system is rebooted or
powered off.
Figure 7- 4: Syslog
Page 61
Page 66

Settings – Syslog
Syslog Delivery
Log Priority for
Modules
SNTP (Simple
Network Time
Protocol)
Configuration
• Sending Out – Set to “Enable”, if you want to send system log messages
to other machines (PCs).
• Keep Sent Message – If set to Enable, it means you want to keep sent
messages; otherwise the sent messages will be deleted.
• Syslog Server – Up to 3 syslog servers can be used.
• IP Address: The IP address(es) of the syslog server(s) that you want to
send to.
• Port: If your syslog server does not use the default port, you can
change it.
• Log Priority Level: The syslog messages are divided into 8 levels from
Emergency to Debug. The lower the level, the more messages will be
generated. Emergency is the highest priority level and Debug is the
lowest.
By pressing the “Expand” button, selection can be made as to which syslog
module and level should be sent to the syslog server. You can arrange all items
on a line by pressing the “Collapse” button.
SNTP is an Internet protocol to synchronize the computer (device) clock. You
can select your location from the pull-down menu and fill in the SNTP server’s
IP address. The local clock will then synchronize with your device which
updates with the correct time received from the SNTP server, then adds the
Time Zone.
Page 62
Page 67

Using Remote Web-based Setup
To connect to the MULTI-WAN GATEWAY from a remote PC via the Internet:
1. Ensure that both your PC and the MULTI-WAN GATEWAY are connected to the Internet.
2. Open your Web Browser.
3. In the "Address" bar, enter "HTTP://" followed by the Internet IP Address of the MULTI-WAN
GATEWAY. If the port number is not 80, then the port number is also required. (After the IP
Address, enter ":" followed by the port number.)
e.g.
HTTP://123.123.123.123:8080
• This example assumes that the WAN IP Address is 123.123.123.123 and the port number is
8080.
• If using the Dynamic DNS feature, you can connect using the domain name allocated to you.
e.g.
HTTP://my_domain_name.dyndns.org:8080
Management password
Enter the desired password, re-enter it in the Verify Password field, then save it.
When you connect to the MULTI-WAN GATEWAY with your Browser, you will be prompted for the
password when you connect, as shown below:
Figure 7-5: Password Dialog
• Enter "Admin" for the User Name.
• Enter the password for the MULTI-WAN GATEWAY.
Page 63
Page 68

Upgrade Firmware
The Upgrade Firmware Screen allows you to upgrade the firmware or backup the system
configuration.
Figure 7-6: Upgrade Firmware
You can backup your system configuration by pressing the Save System Configuration “Save”
button. This will save the system configuration for future use.
You also can upgrade the firmware by inputting the correct password, browsing to the firmware
upgrade file and then pressing the “Upgrade” button. Do not reset or restart the device while
updating the firmware as this may cause the system to crash.
Pressing the “Factory Settings” button will reset the configuration data to its default value.
Page 64
Page 69

8: Network Info
Operation
Once the MULTI-WAN GATEWAY and the PCs are configured, operation is automatic.
However, there are some situations where additional Internet configuration may be required.
Refer to Chapter 4 - Advanced Setup for further details.
System Status
Use the System Status link on the main menu to view this screen.
Figure 8-1: System Status
Page 65
Page 70

Data – System Status
WAN Interface
LAN Interface
• Connection Type – The type of connection used – DHCP, Fixed IP, PPPoE
or PPTP.
• Connection Status – Either "Connected" or "Disconnected”.
• "Force Renew" button– Only available if using a dynamic IP address
(DHCP). Clicking this button will perform a DHCP "Renew" transaction with
the ISP's DHCP server. This will extend the period for which the current
WAN IP address is allocated to you.
• Connect/Disconnect – Used for dial-up/connection of PPPoE or PPTP.
• IP Address – The IP address of the MULTI-WAN GATEWAY, as seen from
the Internet. This IP Address is allocated by the ISP (Internet Service
Provider).
• Subnet Mask – The Network Mask (Subnet Mask) for the IP Address above.
• Domain Name IP Address – The address of the current DNS (Domain
Name Server)
• Gateway – The address of the MULTI-WAN GATEWAY gateway.
• MAC Address – The MAC (physical) address of the MULTI-WAN
GATEWAY, as seen from the Internet.
• IP Address – The LAN IP Address of the MULTI-WAN GATEWAY.
Device
Information
• Subnet Mask – The Network Mask (Subnet Mask) for the IP Address above.
• MAC Address – The MAC (physical) address of the MULTI-WAN
GATEWAY, as seen from the local LAN.
• DHCP Server – The status of the DHCP Server function - either "Enabled"
or "Disabled".
• Hardware ID – The manufacturers ID for this particular device.
• Firmware Version – Version of the Firmware currently installed.
• NAT – Status of the NAT feature – either “Enable” or “Disable”.
• Load Balance – Status of the Load Balance feature – either “Enable” or
“Disable”.
• Virtual Server – Status of the Virtual Server feature – either "Enabled" or
"Disabled".
• Special Applications – Status of the Special Applications feature – either
"Enabled" or "Disabled".
• Multi DMZ – Status of the Multi DMZ feature – either "Enabled" or
"Disabled".
• Block URL – Status of the Block URL feature – either “Enable” or “Disable”.
Page 66
Page 71

Device
Statistics
Buttons
• System UpTime – The time since the device system was last reinitialized.
• CPU Usage – The current CPU percentage usage.
• Memory Heap – The current Memory percentage usage (Heap & Queue).
• Packet Queue – The current Packet Queue percentage usage.
• Refresh – Updates the on-screen data.
• Restart – Restarts (reboots) the MULTI-WAN GATEWAY.
• Restore Factory Defaults – This will delete all existing settings and restore
the factory default settings. See below for details.
Restore Factory Defaults
When the "Restore Factory Defaults" button on the Status screen above is clicked, the following
screen is displayed:
Figure 8-2: Restore Factory Defaults
If the "Restore” button on this screen is clicked:
• ALL of your settings will be erased.
• The default IP address, password and all other settings will be restored to the factory default
values.
• The DCHP server function will be enabled.
These changes may mean that the current connection is invalid and you will have to re-connect to
the MULTI-WAN GATEWAY using its default IP address (192.168.1.1).
Page 67
Page 72

WAN Status
Use the WAN Status link on the main menu to view this screen.
Figure 8-3: WAN Status
Data – WAN Status
NAT
Statistics
Interface
Statistics
This section displays data for each WAN port.
• Status – This will display either Connected or Disconnected.
• Default Loading Share - The default traffic loading on each WAN port.
• Current Loading Share – The current traffic loading on each WAN port.
• Current Loading – The number of current traffic Sessions, Bytes and
Packets being processed on each WAN port.
• Current Bandwidth – The current Download and Upload speed on each
WAN port.
• Refresh – Updates the on-screen data.
• Restart Counters – Restarts the counters used in the "Interface Statistics".
• Check NAT Detail – Displays the NAT Status screen, described below.
This section displays cumulative statistics.
Use the "Restart Counter" button to restart these counters when required.
Page 68
Page 73

Appendix A
Specifications
Model MULTI-WAN GATEWAY
Dimensions 423mm (W) x 155mm (D) x 43mm (H)
Operating
Temperature
Storage
Temperature
Network
Protocol:
Network
Interface:
LEDs 1 power LED.
Power Supply Internal AC 100V ~ 240V / 50 ~ 60 Hz
0° C to 40° C
-10° C to 70° C
TCP/IP
16 *10/100 BaseT (RJ45) Auto-switching Hub ports for WAN / LAN devices.
2 status LEDs.
16 LEDs for WAN/LAN
FCC Statement
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two
conditions:
(1) This device may not cause harmful interference.
(2) This device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause
undesired operation.
Tested to comply with FCC Standards for Home or Office use.
CE Marking Warning
This is a Class B product. In a domestic environment this product may cause radio interference in
which case the user may be required to take adequate measures.
Page 69
Page 74

Appendix B
Windows TCP/IP Setup
Overview
TCP/IP Settings
If using the default MULTI-WAN GATEWAY settings and the default Windows
95/98/ME/2000 TCP/IP settings, no changes need to be made.
• By default, the MULTI-WAN GATEWAY will act as a DHCP Server, automatically providing a
suitable IP Address (and related information) to each PC when the PC boots.
• For all non-Server versions of Windows, the default TCP/IP setting is to act as a DHCP client.
• If you wish to check your TCP/IP settings, the procedure is described in the following sections.
• If your LAN has a router, it must be reconfigured by the LAN Administrator.
Checking TCP/IP Settings - Windows 9x/ME:
1. Select Control Panel - Network. You should see a screen like the following:
Figure B-1: Network Configuration
2. Select the TCP/IP protocol for your network card.
3. Click on the Properties button. You should then see a screen like the following:
Page 70
Page 75

Figure B-2: IP Address (Win 95)
Ensure your TCP/IP settings are correct as follows:
Using DHCP
To use DHCP, select the radio button Obtain an IP Address automatically. This is the default
Windows setting.
Restart your PC to ensure it obtains an IP Address from the MULTI-WAN GATEWAY.
Using "Specify an IP Address"
If your PC is already configured, check with your network administrator before making the following
changes:
• If the DNS Server fields are empty, select Use the following DNS server addresses, and enter the
DNS address or addresses provided by your ISP, then click OK.
• On the Gateway tab, enter the MULTI-WAN GATEWAY's IP address in the New gateway field
and click Add, as shown below. (Your LAN administrator can advise you of the IP Address
assigned to the MULTI-WAN GATEWAY.)
Page 71
Page 76

Figure B-3: Gateway Tab (Win 95/98)
• On the DNS Configuration tab, ensure Enable DNS is selected. If the DNS Server Search Order
list is empty, enter the DNS address provided by your ISP in the field beside the Add button, then
click Add.
Figure B-4: DNS Tab (Win 95/98)
Checking TCP/IP Settings - Windows 2000:
1. Select Control Panel - Network and Dial-up Connection.
2. Right click the Local Area Connection icon and select Properties. You should see a screen like
the following:
Page 72
Page 77

Figure B-5: Network Configuration (Win 2000)
3. Select the TCP/IP protocol for your network card.
4. Click on the Properties button. You should then see a screen like the following:
Page 73
Page 78

Figure B-6: TCP/IP Properties (Win 2000)
5. Ensure your TCP/IP settings are correct:
Using DHCP
To use DHCP, select the radio button Obtain an IP Address automatically. This is the default
Windows setting.
Restart your PC to ensure it obtains an IP Address from the MULTI-WAN GATEWAY.
Using a fixed IP Address ("Use the following IP Address")
If your PC is already configured, check with your network administrator before making the following
changes:
• Enter the MULTI-WAN GATEWAY's IP address in the Default gateway field and click OK. (Your
LAN administrator can advise you of the IP Address assigned to the MULTI-WAN GATEWAY.)
• If the DNS Server fields are empty, select Use the following DNS server addresses, and enter the
DNS address or addresses provided by your ISP, then click OK.
Page 74
Page 79

Checking TCP/IP Settings - Windows XP:
1. Select Control Panel - Network Connection.
2. Right click the Local Area Connection and choose Properties. You should see a screen like the
following:
Figure B-7: Network Configuration (Windows XP)
3. Select the TCP/IP protocol for your network card.
4. Click on the Properties button. You should then see a screen like the following:
Page 75
Page 80

Figure B-8: TCP/IP Properties (Windows XP)
5. Ensure your TCP/IP settings are correct.
Using DHCP
To use DHCP, select the radio button Obtain an IP Address automatically. This is the default
Windows setting.
Restart your PC to ensure it obtains an IP Address from the MULTI-WAN GATEWAY.
Using a fixed IP Address ("Use the following IP Address")
If your PC is already configured, check with your network administrator before making the following
changes.
• Enter the MULTI-WAN GATEWAY's IP address in the Default gateway field and click OK. (Your
LAN administrator can advise you of the IP Address assigned to the MULTI-WAN GATEWAY.)
• If the DNS Server fields are empty, select Use the following DNS server addresses, and enter the
DNS address or addresses provided by your ISP, then click OK.
Page 76
Page 81

Appendix C
Troubleshooting
Overview
This chapter covers some common problems that may be encountered while using the MULTI-WAN
GATEWAY and some possible solutions to them. If you follow the suggested steps and the MULTIWAN GATEWAY still does not function properly, contact your dealer for further advice.
General Problems
Problem 1: Can't connect to the MULTI-WAN GATEWAY to configure it.
Solution 1:
Check the following:
• The MULTI-WAN GATEWAY is properly installed, LAN connections are OK,
and it is powered ON. By default, Port 1-2 of this device are WAN ports, the
others are LAN ports. Otherwise you have changed Maximum WAN ports.
• Ensure that your PC and the MULTI-WAN GATEWAY are on the same
network segment. (If you don't have a router, this must be the case.)
• If your PC is set to "Obtain an IP Address automatically" (DHCP client), restart
it.
• If your PC uses a Fixed (Static) IP address, ensure that it is using an IP
Address within the range 192.168.1.2 to 192.168.1.254 and thus compatible
with the MULTI-WAN GATEWAY’s default IP Address of 192.168.1.1.
Also, the Network Mask should be set to 255.255.255.0 to match the MULTIWAN GATEWAY. In Windows, you can check these settings by accessing
Control Panel-Network to check the Properties for the TCP/IP protocol.
Page 77
Page 82

Internet Access
Problem 1: When I enter a URL or IP address I get a time out error.
Solution 1:
Problem 2: Some applications do not run properly when using the MULTI-WAN
Solution 2:
A number of things could be causing this. Try the following troubleshooting steps.
• Check if other PCs are working. If they are, ensure that your PC’s IP settings
are correct. If using a Fixed (Static) IP Address, check the Network Mask,
Default gateway and DNS as well as the IP Address.
• If the PCs are configured correctly, but still not working, check the MULTI-WAN
GATEWAY. Ensure that it is connected and ON. Connect to it and check its
settings. (If you can't connect to it, check the LAN and power connections.)
• If the MULTI-WAN GATEWAY is configured correctly, check your Internet
connection (DSL/Cable modem etc.) to see if it is working correctly.
GATEWAY.
The MULTI-WAN GATEWAY processes the data passing through it, so it is not
transparent.
Use the Special Applications feature to allow the use of Internet applications which
are not functioning correctly.
If this does solve the problem, you can use the DMZ function. This should work with
most applications, however:
• It is a security risk, since the firewall is disabled for the DMZ PC.
• Only one (1) PC can use this feature.
Page 78
 Loading...
Loading...