XICOR X24C16S8MB-3,5, X24C16S8MB-3, X24C16S8MB-2,7, X24C16S8M-3,5, X24C16S8MB Datasheet
...
X24C16
1
Serial E2PROM
© Xicor, 1991 Patents Pending Characteristics subject to change without notice
DESCRIPTION
The X24C16 is a CMOS 16,384 bit serial E2PROM,
internally organized 2048 X 8. The X24C16 features a
serial interface and software protocol allowing operation
on a simple two wire bus.
The X24C16 is fabricated with Xicor’s advanced CMOS
Textured Poly Floating Gate Technology.
The X24C16 utilizes Xicor’s proprietary Direct Write
TM
cell providing a minimum endurance of 100,000 cycles
and a minimum data retention of 100 years.
FEATURES
• 2.7V to 5.5V Power Supply
• Low Power CMOS
—Active Read Current Less Than 1 mA
—Active Write Current Less Than 3 mA
—Standby Current Less Than 50 µA
• Internally Organized 2048 x 8
• 2 Wire Serial Interface
—Bidirectional Data Transfer Protocol
• Sixteen Byte Page Write Mode
—Minimizes Total Write Time Per Byte
• Self Timed Write Cycle
—Typical Write Cycle Time of 5 ms
• High Reliability
—Endurance: 100,000 Cycles
—Data Retention: 100 Years
• 8 Pin Mini-DIP, 8 Pin SOIC and 14 Pin SOIC
Packages
16K X24C16 2048 x 8 Bit
Preliminary Information
FUNCTIONAL DIAGRAM
3840 FHD F01
START
STOP
LOGIC
CONTROL
LOGIC
SLAVE ADDRESS
REGISTER
+COMPARATOR
H.V. GENERATION
TIMING
& CONTROL
WORD
ADDRESS
COUNTER
XDEC
YDEC
D
OUT
ACK
E
2
PROM
128 X 128
DATA REGISTER
START CYCLE
(8) V
CC
R/W
PIN
(4) V
SS
(5) SDA
(6) SCL
(3) A
2
(2) A
1
(1) A
0
D
OUT
LOAD INC
CK
8
(7) TEST
3840-1.1 7/29/96 T1/C0/D0 SH

2
X24C16
NC
A
0
A
1
NC
A
2
V
SS
NC
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
NC
V
CC
TEST
NC
SCL
SDA
NC
X24C16
A
0
A
1
A
2
V
SS
1
2
3
4
8
7
6
5
V
CC
TEST
SCL
SDA
X24C16
PIN CONFIGURATIONPIN DESCRIPTIONS
Serial Clock (SCL)
The SCL input is used to clock all data into and out of the
device.
Serial Data (SDA)
SDA is a bidirectional pin used to transfer data into and
out of the device. It is an open drain output and may be
wire-ORed with any number of open drain or open
collector outputs.
An open drain output requires the use of a pull-up
resistor. For selecting typical values, refer to the Pull-Up
Resistor selection graph at the end of this data sheet.
Address (A0, A1, A
2)
The A0, A1 and A2 inputs are unused by the X24C16,
however, they must be tied to VSS to insure proper
device operation.
3840 FHD F02
3840 FHD F03
PIN NAMES
Symbol Description
A0–A
2
Address Inputs
SDA Serial Data
SCL Serial Clock
TEST Hold at V
SS
V
SS
Ground
V
CC
Supply Voltage
NC No Connect
3840 PGM T01
SOIC
DIP/SOIC

X24C16
3
DEVICE OPERATION
The X24C16 supports a bidirectional bus oriented protocol. The protocol defines any device that sends data
onto the bus as a transmitter, and the receiving device
as the receiver. The device controlling the transfer is a
master and the device being controlled is the slave. The
master will always initiate data transfers, and provide
the clock for both transmit and receive operations.
Therefore, the X24C16 will be considered a slave in all
applications.
Clock and Data Conventions
Data states on the SDA line can change only during SCL
LOW. SDA state changes during SCL HIGH are reserved for indicating start and stop conditions. Refer to
Figures 1 and 2.
Start Condition
All commands are preceded by the start condition,
which is a HIGH to LOW transition of SDA when SCL is
HIGH. The X24C16 continuously monitors the SDA and
SCL lines for the start condition and will not respond to
any command until this condition has been met.
Figure 1. Data Validity
3840 FHD F06
SCL
SDA
DATA STABLE DATA
CHANGE

4
X24C16
Stop Condition
All communications must be terminated by a stop condition, which is a LOW to HIGH transition of SDA when
SCL is HIGH. The stop condition is also used by the
X24C16 to place the device into the standby power
mode after a read sequence. A stop condition can only
be issued after the transmitting device has released the
bus.
Acknowledge
Acknowledge is a software convention used to indicate
successful data transfer. The transmitting device, either
master or slave, will release the bus after transmitting
eight bits. During the ninth clock cycle the receiver will
pull the SDA line LOW to acknowledge that it received
the eight bits of data. Refer to Figure 3.
The X24C16 will respond with an acknowledge after
recognition of a start condition and its slave address. If
both the device and a write operation have been selected, the X24C16 will respond with an acknowledge
after the receipt of each subsequent eight bit word.
In the read mode the X24C16 will transmit eight bits of
data, release the SDA line and monitor the line for an
acknowledge. If an acknowledge is detected and no
stop condition is generated by the master, the X24C16
will continue to transmit data. If an acknowledge is not
detected, the X24C16 will terminate further data transmissions. The master must then issue a stop condition
to return the X24C16 to the standby power mode and
place the device into a known state.
Figure 2. Definition of Start and Stop
SCL
SDA
START BIT STOP BIT
3840 FHD F07
Figure 3. Acknowledge Response From Receiver
SCL FROM
MASTER
DATA
OUTPUT
FROM
TRANSMITTER
1
89
DATA
OUTPUT
FROM
RECEIVER
START
ACKNOWLEDGE
3840 FHD F08

X24C16
5
Figure 4. Slave Address
DEVICE ADDRESSING
Following a start condition the master must output the
address of the slave it is accessing. The most significant
four bits of the slave address are the device type identifier
(see Figure 4). For the X24C16 this is fixed as 1010[B].
The next three bits of the slave address field are the bank
select bits. They are used by the host to toggle between
the eight 256 x 8 banks of memory. These are, in effect,
the most significant bits for the word address.
The next three bits of the slave address are an extension
of the array’s address and are concatenated with the
eight bits of address in the word address field, providing
direct access to the whole 2048 x 8 array.
Following the start condition, the X24C16 monitors the
SDA bus comparing the slave address being transmitted with its slave address (device type). Upon a correct
compare the X24C16 outputs an acknowledge on the
SDA line. Depending on the state of the R/W bit, the
X24C16 will execute a read or write operation.
WRITE OPERATIONS
Byte Write
For a write operation, the X24C16 requires a second
address field. This address field is the word address,
comprised of eight bits, providing access to any one of the
2048 words in the array. Upon receipt of the word address
the X24C16 responds with an acknowledge, and awaits
the next eight bits of data, again responding with an
acknowledge. The master then terminates the transfer by
generating a stop condition, at which time the X24C16
begins the internal write cycle to the nonvolatile memory.
While the internal write cycle is in progress the X24C16
inputs are disabled, and the device will not respond to any
requests from the master. Refer to Figure 5 for the
address, acknowledge and data transfer sequence.
3840 FHD F09
Figure 5. Byte Write
BUS ACTIVITY:
MASTER
SDA LINE
BUS ACTIVITY:
X24C16
S
T
A
R
T
SLAVE
ADDRESS
S
S
T
O
P
P
A
C
K
A
C
K
A
C
K
WORD
ADDRESS DATA
3840 FHD F10
101 0 A2 A1 A0 R/W
DEVICE TYPE
IDENTIFIER
HIGH
ORDER
WORD
ADDRESS

6
X24C16
Flow 1. ACK Polling SequencePage Write
The X24C16 is capable of a sixteen byte page write
operation. It is initiated in the same manner as the byte
write operation, but instead of terminating the write cycle
after the first data word is transferred, the master can
transmit up to fifteen more words. After the receipt of
each word, the X24C16 will respond with an acknowledge.
After the receipt of each word, the four low order address
bits are internally incremented by one. The high order
seven bits of the address remain constant. If the master
should transmit more than sixteen words prior to generating the stop condition, the address counter will “roll
over” and the previously written data will be overwritten.
As with the byte write operation, all inputs are disabled
until completion of the internal write cycle. Refer to
Figure 6 for the address, acknowledge and data transfer
sequence.
Acknowledge Polling
The disabling of the inputs can be used to take advantage of the typical 5 ms write cycle time. Once the stop
condition is issued to indicate the end of the host’s write
operation the X24C16 initiates the internal write cycle.
ACK polling can be initiated immediately. This involves
issuing the start condition followed by the slave address
for a write operation. If the X24C16 is still busy with the
write operation no ACK will be returned. If the X24C16
has completed the write operation an ACK will be
returned and the host can then proceed with the next
read or write operation. Refer to Flow 1.
WRITE OPERATION
COMPLETED
ENTER ACK POLLING
ISSUE
STAR T
ISSUE SLAVE
ADDRESS AND R/W = 0
ACK
RETURNED?
NEXT
OPERATION
A WRITE?
ISSUE BYTE
ADDRESS
PROCEED
ISSUE STOP
NO
YES
YES
PROCEED
ISSUE STOP
NO
3840 FHD F11
Figure 6. Page Write
BUS ACTIVITY:
MASTER
SDA LINE
BUS ACTIVITY:
X24C16
S
T
A
R
T
SLAVE
ADDRESS
S
S
T
O
P
P
A
C
K
A
C
K
A
C
K
A
C
K
A
C
K
WORD
ADDRESS (n) DATA n DATA n+1 DATA n+15
NOTE: In this example n = xxxx 000 (B); x = 1 or 0
3840 FHD F12

X24C16
7
READ OPERATIONS
Read operations are initiated in the same manner as
write operations with the exception that the R/W bit of the
slave address is set to a one. There are three basic read
operations: current address read, random read and
sequential read.
It should be noted that the ninth clock cycle of the read
operation is not a “don’t care.” To terminate a read
operation, the master must either issue a stop condition
during the ninth cycle or hold SDA HIGH during the ninth
clock cycle and then issue a stop condition.
Current Address Read
Internally the X24C16 contains an address counter that
maintains the address of the last word accessed,
incremented by one. Therefore, if the last access (either
a read or write) was to address n, the next read operation
would access data from address n + 1. Upon receipt of
the slave address with the R/W bit set to one, the
X24C16 issues an acknowledge and transmits the eight
bit word. The read operation is terminated by the master;
by not responding with an acknowledge and by issuing
a stop condition. Refer to Figure 7 for the sequence of
address, acknowledge and data transfer.
Random Read
Random read operations allow the master to access any
memory location in a random manner. Prior to issuing
the slave address with the R/W bit set to one, the master
must first perform a “dummy” write operation. The master issues the start condition, and the slave address
followed by the word address it is to read. After the word
address acknowledge, the master immediately reissues
the start condition and the slave address with the R/W bit
set to one. This will be followed by an acknowledge from
the X24C16 and then by the eight bit word. The read
operation is terminated by the master; by not responding
with an acknowledge and by issuing a stop condition.
Refer to Figure 8 for the address, acknowledge and data
transfer sequence.
Figure 7. Current Address Read
BUS ACTIVITY:
MASTER
SDA LINE
BUS ACTIVITY:
X24C16
S
T
A
R
T
SLAVE
ADDRESS
S
S
T
O
P
P
A
C
K
DATA
3840 FHD F13
Figure 8. Random Read
BUS ACTIVITY:
MASTER
SDA LINE
BUS ACTIVITY:
X24C16
S
T
A
R
T
SLAVE
ADDRESS
S
S
T
O
P
P
A
C
K
A
C
K
A
C
K
WORD
ADDRESS n
SLAVE
ADDRESS DATA n
S
T
A
R
T
S
3840 FHD F14

8
X24C16
Sequential Read
Sequential reads can be initiated as either a current
address read or random access read. The first word is
transmitted as with the other read modes, however, the
master now responds with an acknowledge, indicating it
requires additional data. The X24C16 continues to output data for each acknowledge received. The read
operation is terminated by the master; by not responding
with an acknowledge and by issuing a stop condition.
The data output is sequential, with the data from address
n followed by the data from n + 1. The address counter
for read operations increments all address bits, allowing
the entire memory contents to be serially read during
one operation. At the end of the address space (address
2047), the counter “rolls over” to 0 and the X24C16
continues to output data for each acknowledge received. Refer to Figure 9 for the address, acknowledge
and data transfer sequence.
Figure 9. Sequential Read
BUS ACTIVITY:
MASTER
SDA LINE
BUS ACTIVITY:
X24C16
SLAVE
ADDRESS
A
C
K
A
C
K
DATA n+x
S
T
O
P
P
DATA n
A
C
K
DATA n+1
A
C
K
DATA n+2
3840 FHD F15
Figure 10. Typical System Configuration
MASTER
TRANSMITTER/
RECEIVER
SLAVE
RECEIVER
SLAVE
TRANSMITTER/
RECEIVER
MASTER
TRANSMITTER
MASTER
TRANSMITTER/
RECEIVER
PULL-UP
RESISTORS
SDA
SCL
V
CC
3840 FHD F16

X24C16
9
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS*
Temperature Under Bias.................. –65°C to +135°C
Storage Temperature ....................... –65°C to +150°C
Voltage on any Pin with
Respect to V
SS
................................
–1.0V to +7.0V
D.C. Output Current ............................................5 mA
Lead Temperature
(Soldering, 10 Seconds) ............................. 300°C
*COMMENT
Stresses above those listed under “Absolute Maximum
Ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device.
This is a stress rating only and the functional operation of
the device at these or any other conditions above those
indicated in the operational sections of this specification is
not implied. Exposure to absolute maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
D.C. OPERATING CHARACTERISTICS (Over the recommended operating conditions, unless otherwise specified)
Limits
Symbol Parameter Min. Max. Units Test Conditions
l
CC1
VCC Supply Current (read) 1 SCL = VCC x 0.1/VCC x 0.9 Levels
l
CC2
VCC Supply Current (write) 3 mA @ 100 KHz, SDA = Open, All Other
Inputs = GND or VCC – 0.3V
I
SB1
(1)
VCC Standby Current 150 µA SCL = SDA = VCC – 0.3V, All Other
Inputs = GND or VCC, VCC = 5.5V
I
SB2
(1)
VCC Standby Current 50 µA SCL = SDA = VCC – 0.3V, All Other
Inputs = GND or VCC, VCC = 3.3V +10%
I
LI
Input Leakage Current 10 µAVIN = GND to V
CC
I
LO
Output Leakage Current 10 µAV
OUT
= GND to V
CC
V
lL
(2)
Input Low Voltage –1.0 VCC x 0.3 V
V
IH
(2)
Input High Voltage VCC x 0.7 VCC + 0.5 V
V
OL
Output Low Voltage 0.4 V IOL = 3 mA
3840 PGM T03
CAPACITANCE TA = 25°C, f = 1.0 MHz, VCC = 5V
Symbol Parameter Max. Units Test Conditions
C
I/O
(3)
Input/Output Capacitance (SDA) 8 pF V
I/O
= 0V
C
IN
(3)
Input Capacitance (A0, A1, A2, SCL) 6 pF V
IN
= 0V
3840 PGM T05
Notes: (1) Must perform a stop command prior to measurement.
(2) VIL min. and VIH max. are for reference only and are not tested.
(3) This parameter is periodically sampled and not 100% tested.
RECOMMENDED OPERATING CONDITIONS
Temperature Min. Max.
Commercial 0°C70°C
Industrial –40°C +85°C
Military –55°C +125°C
3840 PGM T09
Supply Voltage Limits
X24C16 4.5V to 5.5V
X24C16–3.5 3.5V to 5.5V
X24C16–3 3V to 5.5V
X24C16–2.7 2.7V to 5.5V
3840 PGM T10

10
X24C16
A.C. CHARACTERISTICS LIMITS (Over the recommended operating conditions unless otherwise specified.)
Read & Write Cycle Limits
Symbol Parameter Min. Max. Units
f
SCL
SCL Clock Frequency 0 100 KHz
T
I
Noise Suppression Time Constant at SCL, SDA Inputs 100 ns
t
AA
SCL Low to SDA Data Out Valid 0.3 3.5 µs
t
BUF
Time the Bus Must Be Free Before a 4.7 µs
New Transmission Can Start
t
HD:STA
Start Condition Hold Time 4.0 µs
t
LOW
Clock Low Period 4.7 µs
t
HIGH
Clock High Period 4.0 µs
t
SU:STA
Start Condition Setup Time (for a Repeated Start Condition) 4.7 µs
t
HD:DAT
Data In Hold Time 0 µs
t
SU:DAT
Data In Setup Time 250 ns
t
R
SDA and SCL Rise Time 1 µs
t
F
SDA and SCL Fall Time 300 ns
t
SU:STO
Stop Condition Setup Time 4.7 µs
t
DH
Data Out Hold Time 300 ns
3840 PGM T06
POWER-UP TIMING
Symbol Parameter Max. Units
t
PUR
(4)
Power-up to Read Operation 1 ms
t
PUW
(4)
Power-up to Write Operation 5 ms
3840 PGM T07
Bus Timing
t
SU:STA
t
HD:STAtHD:DAT
t
SU:DAT
t
LOW
t
SU:STO
t
R
t
BUF
SCL
SDA IN
SDA OUT
t
DH
t
AA
t
F
t
HIGH
3840 FHD F04
Notes: (4) t
PUR
and t
PUW
are the delays required from the time VCC is stable until the specified operation can be initiated. These parameters
are periodically sampled and not 100% tested.
A.C. CONDITIONS OF TEST
Input Pulse Levels VCC x 0.1 to VCC x 0.9
Input Rise and
Fall Times 10 ns
Input and Output
Timing Levels VCC x 0.5
3840 PGM T02
EQUIVALENT A.C. LOAD CIRCUIT
5.0V
1533Ω
100pF
Output
3840 FHD F18

X24C16
11
WRITE CYCLE LIMITS
Symbol Parameter Min. Typ.
(5)
Max. Units
t
WR
(6)
Write Cycle Time 5 10 ms
3840 PGM T08
The write cycle time is the time from a valid stop
condition of a write sequence to the end of the internal
erase/program cycle. During the write cycle, the X24C16
bus interface circuits are disabled, SDA is allowed to
remain high, and the device does not respond to its slave
address.
Write Cycle Timing
3840 FHD F05
SDA 8th BIT
WORD n
ACK
t
WR
STOP
CONDITION
START
CONDITION
X24C16
ADDRESS
SCL
120
100
80
40
60
20
20 40 60 80
100
120
0
0
RESISTANCE (KΩ)
BUS CAPACITANCE (pF)
MIN.
RESISTANCE
MAX.
RESISTANCE
R
MAX
=
C
BUS
t
R
R
MIN
=
I
OL MIN
V
CC MAX
=1.8KΩ
3840 FHD F17
Guidelines for Calculating Typical Values of
Bus Pull-Up Resistors
SYMBOL TABLE
Must be
steady
Will be
steady
May change
from Low to
High
Will change
from Low to
High
May change
from High to
Low
Will change
from High to
Low
Don’t Care:
Changes
Allowed
Changing:
State Not
Known
N/A
Center Line
is High
Impedance
OUTPUTSINPUTSWAVEFORM
Notes: (5) Typical values are for TA = 25°C and nominal supply voltage (5V)
(6) tWR is the minimum cycle time from the system perspective when polling techniques are not used. It is the maximum time the
device requires to perform the internal write operation.

12
X24C16
3926 FHD F01
NOTE:
1. ALL DIMENSIONS IN INCHES (IN PARENTHESES IN MILLIMETERS)
2. PACKAGE DIMENSIONS EXCLUDE MOLDING FLASH
0.020 (0.51)
0.016 (0.41)
0.150 (3.81)
0.125 (3.18)
0.110 (2.79)
0.090 (2.29)
0.430 (10.92)
0.360 (9.14)
0.300
(7.62) REF.
PIN 1 INDEX
0.145 (3.68)
0.128 (3.25)
0.025 (0.64)
0.015 (0.38)
PIN 1
SEATING
PLANE
0.065 (1.65)
0.045 (1.14)
0.260 (6.60)
0.240 (6.10)
0.060 (1.52)
0.020 (0.51)
TYP. 0.010 (0.25)
0°
15°
8-LEAD PLASTIC DUAL IN-LINE PACKAGE TYPE P
HALF SHOULDER WIDTH ON
ALL END PINS OPTIONAL
0.015 (0.38)
MAX.
0.325 (8.25)
0.300 (7.62)

X24C16
13
0.150 (3.80)
0.158 (4.00)
0.228 (5.80)
0.244 (6.20)
0.014 (0.35)
0.019 (0.49)
PIN 1
PIN 1 INDEX
0.010 (0.25)
0.020 (0.50)
0.050 (1.27)
0.188 (4.78)
0.197 (5.00)
0.004 (0.19)
0.010 (0.25)
0.053 (1.35)
0.069 (1.75)
(4X) 7°
0.016 (0.410)
0.037 (0.937)
0.0075 (0.19)
0.010 (0.25)
0° – 8°
X 45°
3926 FHD F22
8-LEAD PLASTIC SMALL OUTLINE GULL WING PACKAGE TYPE S
NOTE: ALL DIMENSIONS IN INCHES (IN PARENTHESIS IN MILLIMETERS)
0.250"
0.050" TYPICAL
0.050"
TYPICAL
0.030"
TYPICAL
8 PLACES
FOOTPRINT

14
X24C16
0.150 (3.80)
0.158 (4.00)
0.228 (5.80)
0.244 (6.20)
0.014 (0.35)
0.020 (0.51)
PIN 1
PIN 1 INDEX
0.010 (0.25)
0.020 (0.50)
0.050 (1.27)
0.336 (8.55)
0.345 (8.75)
0.004 (0.10)
0.010 (0.25)
0.053 (1.35)
0.069 (1.75)
(4X) 7°
0.016 (0.41)
0.037 (0.937)
0.0075 (0.19)
0.010 (0.25)
0° – 8°
X 45°
3926 FHD F10
14-LEAD PLASTIC SMALL OUTLINE GULL WING PACKAGE TYPE S
NOTE: ALL DIMENSIONS IN INCHES (IN PARENTHESES IN MILLIMETERS)
0.250"
0.050" Typical
0.050" Typical
0.030" Typical
14 Places
FOOTPRINT
X24C16
15
ORDERING INFORMATION
Device
VCC Range
Blank = 4.5V to 5.5V
3.5 = 3.5V to 5.5V
3 = 3V to 5.5V
2.7 = 2.7V to 5.5V
Temperature Range
Blank = Commercial = 0°C to +70°C
I = Industrial = –40°C to +85°C
M = Military = –55°C to +125°C
MB = MIL-STD-883
Package
P = 8-Lead Plastic DIP
S8 = 8-Lead SOIC
S14 = 14-Lead SOIC
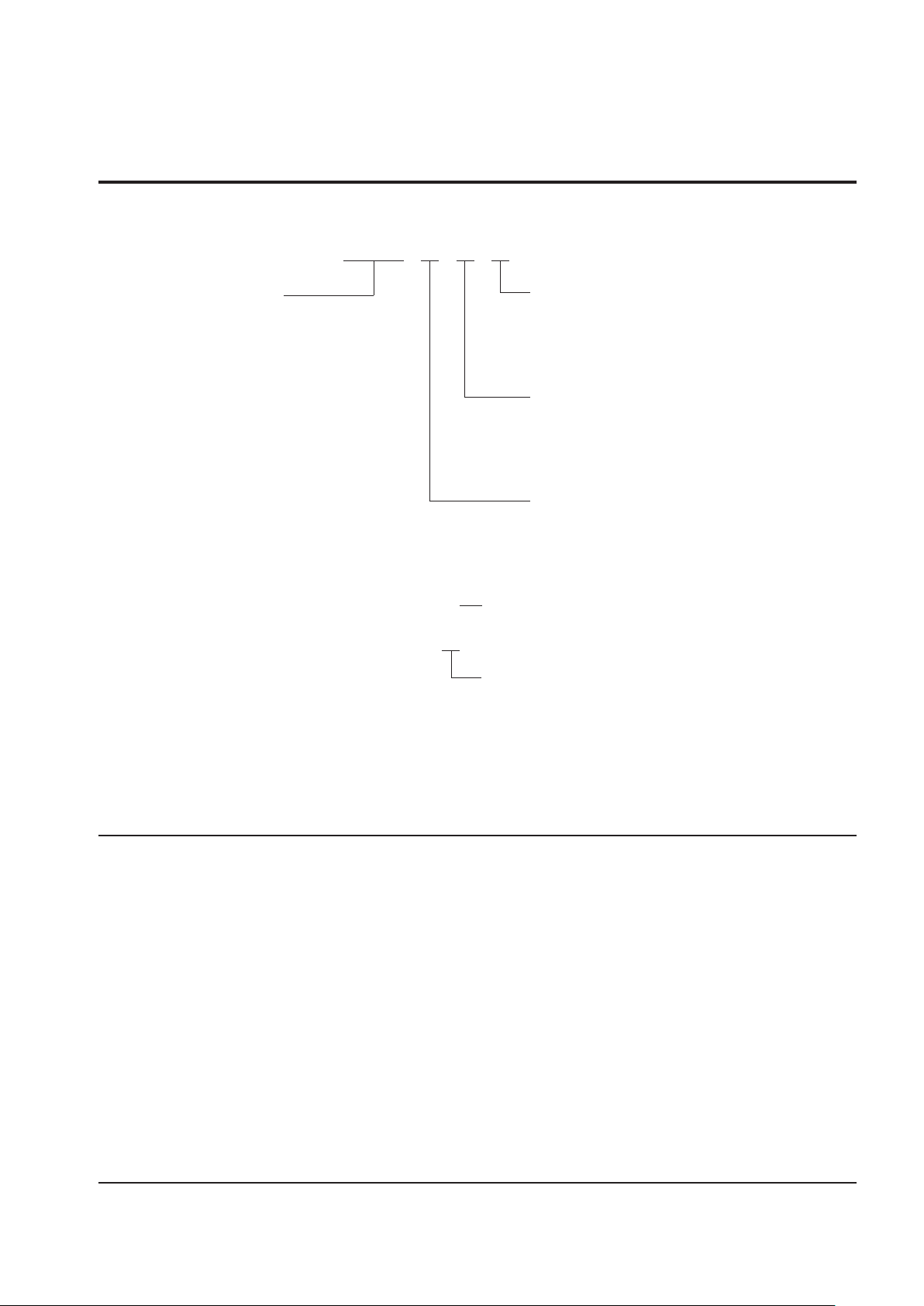
X24C16 X X -X
LIMITED WARRANTY
Devices sold by Xicor, Inc. are covered by the warranty and patent indemnification provisions appearing in its Terms of Sale only. Xicor, Inc. makes
no warranty, express, statutory, implied, or by description regarding the information set forth herein or regarding the freedom of the described
devices from patent infringement. Xicor, Inc. makes no warranty of merchantability or fitness tor any purpose. Xicor, Inc. reserves the right to
discontinue production and change specifications and prices at any time and without notice.
Xicor, Inc assumes no responsibility for the use of any circuitry other than circuitry embodied in a Xicor, Inc. product. No other circuits, patents,
licenses are implied.
US. PATENTS
Xicor products are covered by one or more of the following U.S. Patents: 4,263,664; 4,274,012; 4,300,212; 4,314,265; 4,326,134; 4,393,481;
4,404,475; 4,450,402; 4,486,769; 4,488,060; 4,520,461; 4,533,846; 4,599,706; 4,617,652; 4,668,932; 4,752,912; 4,829,482; 4,874,967;
4,883,976; 4,980,859; 5,012,132; 5,003,197; 5,023,694. Foreign patents and additional patents pending.
LIFE RELATED POLICY
In situations where semiconductor component failure may endanger life, system designers using this product should design the system with
appropriate error detection and correction, redundancy and back-up features to prevent such an occurrence.
Xicor’s products are not authorized for use as critical components in life support devices or systems.
1. Life support devices or systems are devices or systems which, (a) are intended for surgical implant into the body, or (b) support or sustain life,
and whose failure to perform, when properly used in accordance with instructions for use provided in the labeling, can be reasonably expected
to result in a significant injury to the user.
2. A critical component is any component of a life support device or system whose failure to perform can be reasonably expected to cause the failure
of the life support device or system, or to affect its satety or effectiveness.
Part Mark Convention
P = 8-Lead Plastic DIP
S8 = 8-Lead SOIC
S14 = 14-Lead SOIC
Blank = 4.5V to 5.5V, 0°C to +70°C
I = 4.5V to 5.5V, –40°C to +85°C
B = 3.5V to 5.5V, 0°C to +70°C
C = 3.5V to 5.5V, –40°C to +85°C
D = 3.0V to 5.5V, 0°C to +70°C
E = 3.0V to 5.5V, –40°C to +85°C
F = 2.7V to 5.5V, 0°C to +70°C
G = 2.7V to 5.5V, –40°C to +85°C
M = 4.5V to 5.5V, –55°C to +125°C
X24C16 X
X
 Loading...
Loading...