XECOM XE3386L Datasheet
Compact 33,600 BPS Data and Fax Modem
XE3386L
12/00
Description
Xecom's XE3386L combines high-speed data and
Group III send/receive fax in a compact component.
Xecom designed the XE3386L to be embedded by OEM
designers. Xecom also offers pin compatible 2400 BPS
14,400 BPS and 56 KBPS alternatives to the XE3386L
for applications with other date rate requirements.
The XE3386L is not a modem chip but a complete
modem including the telephone interface integrated into
a compact module. It provides user transferable FCC
Part 68 registration and can connect directly to the
telephone line through an RJ11 jack. The modem
connects to the host through a TTL level serial interface.
The XE3386L also includes MNP2-4, MNP10 and
V.42 error control and MNP5 and V.42bis data
compression to provide an error free connection with the
greatest possible data throughput rate.
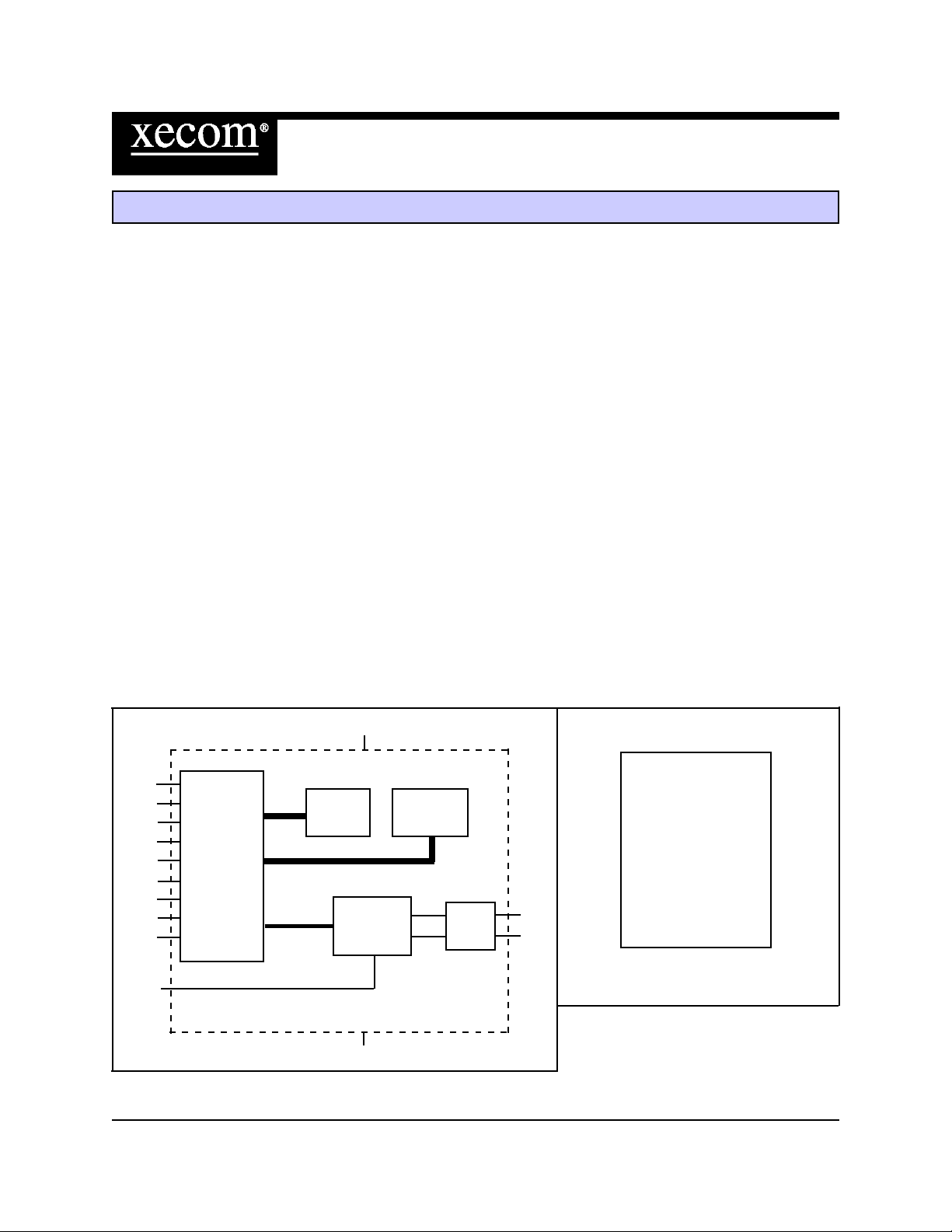
Block Diagram
Features
• Small Size; 1.385 " x 1.36" x 0.575"
• Modem control with "AT" commands
• Class 1 Fax commands
• Data transfer up to 33,600 bps
• Send and receive fax to 14,400 bps
• MNP and V.42 Error Control
• MNP10 Error Control for Cellular Links
• MNP5 Data Compression to 67,200 bps
• V.42bis Data Compression to 115,200 bps
• Low power, single +5V supply
Operating Power 800 mW (Typ.)
Sleep Mode 200 mW (Typ.)
• NVRAM for modem configuration storage
XE3386L Pin Configuration
RST
TXD
RXD
/DCD
/CTS
/DSR
/DTR
/RTS
/V-D
Modem
Controller
VCC
ROM NVRAM
Analog
Front End
DAA
Tip
Ring
RING
TIP
N/C
N/C
SPK
N/C
N/C
N/C
N/C
TXD
RXD
(Top View)
oo
1
oo
2
oo
3
oo
4
oo
5
oo
6
oo
7
oo
8
oo
9
oo
10
o
11
22
RTS
21
RST
o
20
GND
19
VCC
18
N/C
17
/DCD
16
/CTS
15
/RI
14
/DSR
13
/DTR
12
/V-D
Spk
Gnd
XECOM (1) XE3386L
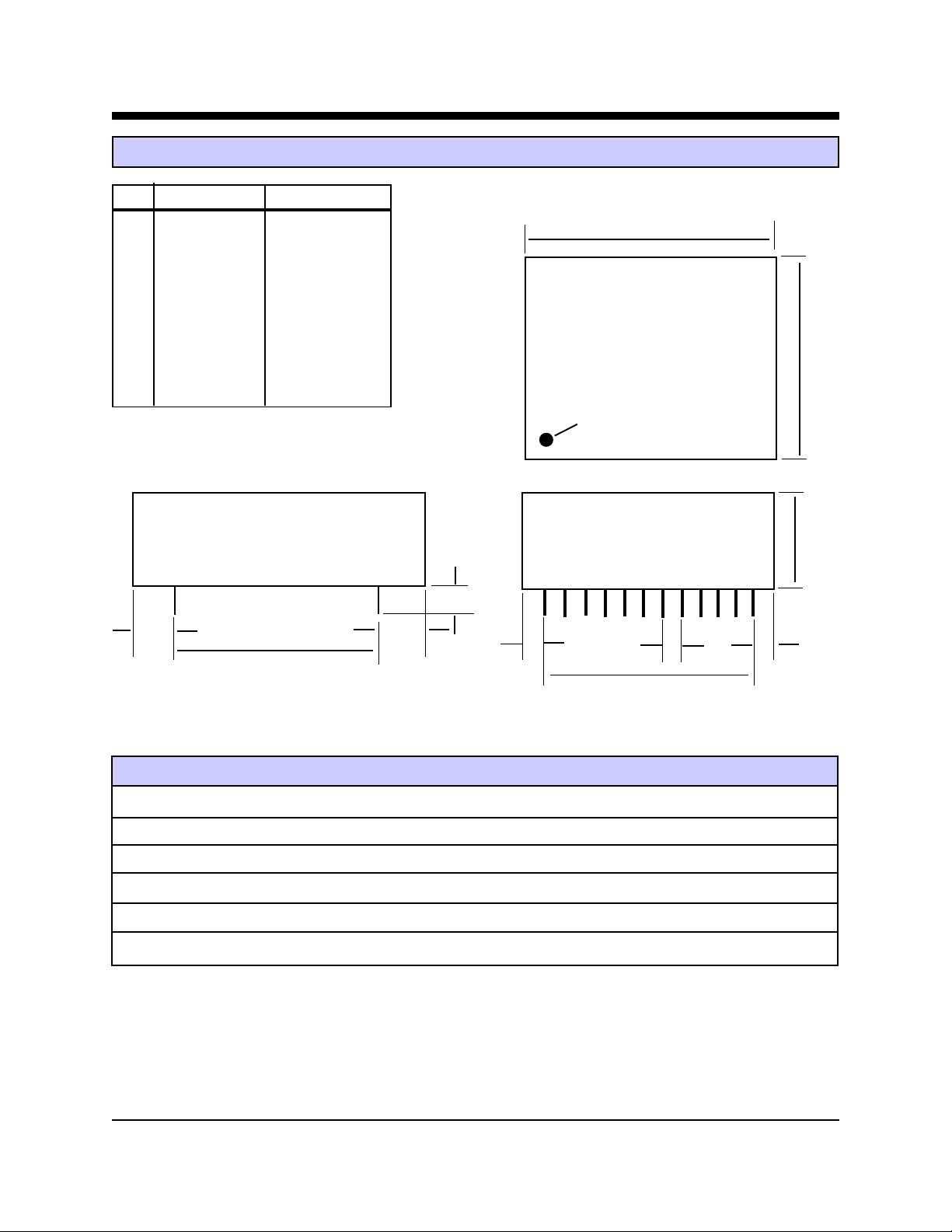
XE3386L Mechanical Specifications
INCHES METRIC(MM)
Dim Min Max Min Max
A 1.350 1.370 34.29 34.80
B 1.375 1.395 34.92 35.43
C 0.555 0.585 14.10 14.86
D 0.190 0.210 4.83 5.33
E 0.090 0.110 2.29 2.79
F 0.115 0.135 2.92 3.43
G 0.280 0.300 7.11 7.62
H 0.790 0.810 20.07 20.57
J 1.090 1.110 27.69 28.19
Pins = 0.025 inches Square
A
B
Denotes Pin 1
C
D
G
G
F
E
H
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS*
SUPPLY VOLTAGE - Vcc +6.5 Volts
DC INPUT VOLTAGE -0.6 Volts to +6.5 Volts
STORAGE TEMPERATURE RANGE -25° C TO +85° C
LEAD TEMPERATURE (Soldering, 2 sec per wave) 260° C
OPERATING TEMPERATURE RANGE 0 TO 70° C
*Exceeding these values may result in permanent damage to the device.
F
J
XECOM (2) XE3386L
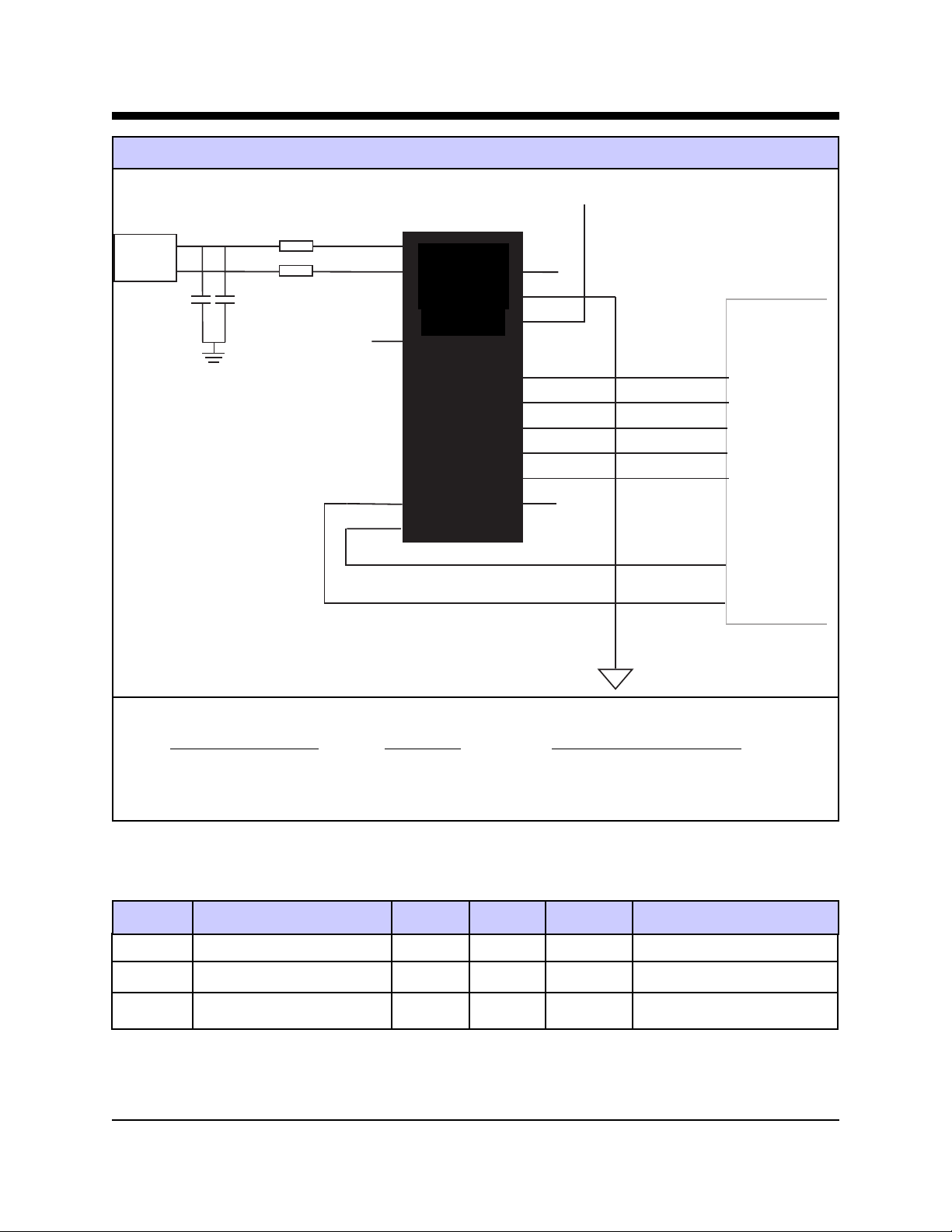
XE3386L Typical Connection Diagram
VCC
RJ11
3
4
C1 C2
FB1
FB2
Ring
Tip
AMP
TXD
RXD
XE1486
XE3386L
RST
Gnd
VCC
/DCD
/CTS
/RI
/DSR
/DTR
/V-D
Host Serial
Interface
Recommended Parts
Reference Designation Description Recommended Part Number
FB1, FB2 Ferrite Beads TDK CB30-1812
C1, C2 Capacitors Sprague 30GAT47, 470 pfd, 3000 Volts
Power Supply Characteristics(T
Symbol Parameter Typ Max Units Comments
Vcc Supply Voltage 5.0 5.25 Volts
Icc Vcc Supply Current 160 180 mA Active, On Line
= 0 - 70°C, Vcc = 5v ±5%)
A
40 60 mA Sleep Mode
XECOM (3) XE3386L
XE3386L Pin Descriptions
PIN NAME DESCRIPTION
1 Ring Ring provides half of the two-wire connection to the telephone network, RJ-11 Pin 4.
A 1500 volt barrier isolates Ring from all other circuits. This isolation must be preserved throughout the system. The battery voltage on Ring may be positive or negative
with respect to Tip.
2 Tip Tip provides half of the two-wire connection to the telephone network, RJ-11 Pin 3. A
1500 volt barrier isolates Tip from all other circuits. This isolation must be preserved
throughout the system. The battery voltage on Tip may be positive or negative with respect to Ring.
3, 4 Not Used No Connection should be made to these pins.
5 SPK SPK provides the audio output to a speaker. Speaker output is controlled by the ATL
and ATM commands. The input impedance to the speaker driver must be greater than
300 ohms.
6-9 N/C No Connection
10 TXD TXD provides serial data input from the host. A logic high represents a "Mark" and a
low represents a "Space".
11 RXD RXD provides serial data output to the host. A logic high represents a "Mark" and a
low represents a "Space".
12 /V-D The Voice-Data output can be used to drive an external relay for switching between the
modem and handset connected to the same telephone line.
13 /DTR Data Terminal Ready is an active low input to the modem. The AT&D command sets
the function of DTR.
14 /DSR Data Set Ready is an active low output from the modem. Its operation is determined by
the AT&S command.
15 /RI Ring Indicator is an active low output which marks the presence of a ring on the line.
16 /CTS The XE3386L uses Clear to Send for hardware flow control. With hardware flow con-
trol active the modem raises \CTS to signal the host that the modem's transmit data
buffer is nearly full. When the buffer empties, the modem reactivates CTS.
17 /DCD Data Carrier Detect goes low to indicate receipt of a valid incoming carrier. The
AT&C1 command enables the carrier detect function.
18 N/C No Connection
19 VCC VCC provides the +5 volt power required by the modem.
20 GND Ground provides the common reference for the XE3386L.
21 RST This active high input causes a hardware reset in the XE3386L. The reset pulse must be held
high for at least 10 milliseconds to correctly reset the modem.
22 RTS The modem uses Request to Send for hardware flow control. The modem stops sending data to
the host when the hosts raises /RTS. The modem resumes transferring data to the host when the
host activates /RTS
XECOM (4) XE3386L
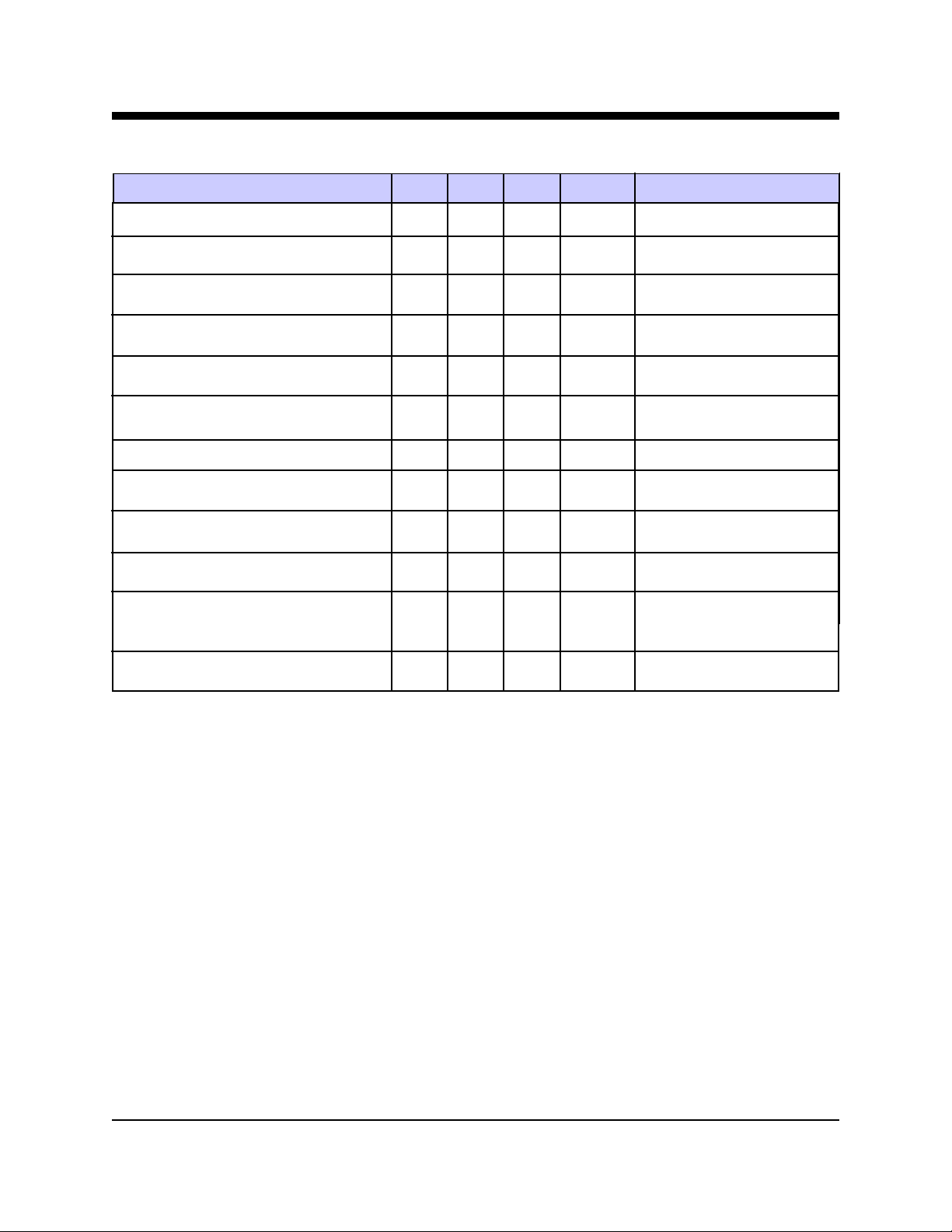
XE3386L Electrical Specifications (T
= 0 - 70°C, Vcc = 5v ±5%)
A
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Comments
DTMF Level -2.2 0 dBm 3 second average
Modem Transmit Level -12 -10.5 -9.0 dBm 600 ohm line
Pulse Dialing Rate 10 pps
Pulse Dialing Make/Break 39/61 % USA
Billing Delay Interval 2.0 sec.
Phone Line Impedance Match 600 ohms
Ring Detect Sensitivity 38 150 VRMS Type B Ringer
Telephone Loop Current 20 100 milliamps Off-hook
Input High Voltage (TXD, RTS, DTR) 2.0 Volts
Input Low Voltage (TXD, RTS, DTR) 0.8 Volts
Output High Voltage 2.4 Volts RXD -100 microamps;
(DCD, DSR, CTS, RXD, RI, OH) DCD, RI, OH - 1.6 milliamps
Output Low Voltage 0.4 Volts RXD - 1.6 milliamps;
XECOM (5) XE3386L
 Loading...
Loading...