Xantrex XW-MPPT60-150 Owner's Guide

XW Series Solar
Charge Controller
XW-MPPT60-150
Owner’s Manual


XW Series Solar Charge
Controller
Owner’s Guide

About Xantrex
Xantrex Technology Inc. is a world-leading supplier of advanced power electronics and controls with products from
50 watt mobile units to one MW utility-scale systems for wind, solar, batteries, fuel cells, microturbines, and backup
power applications in both grid-connected and stand-alone systems. Xantrex products inclu de inverters, batt ery
chargers, programmable power supplies, and variable speed drives that convert, supply, control, clean, and distribute
electrical power.
Trademarks
Xantrex is a registered trademark of Xantrex International.
Other trademarks, registered trademarks, and product names are the property of their respective owners and are used
herein for identification purposes only.
Notice of Copyright
Solar Charge Controller Owner’s Manual © April 2007 Xantrex International. All rights reserved.
Exclusion for Documentation
UNLESS SPECIFICALLY AGREED TO IN WRITING, XANTREX TECHNOLOGY INC. (“XANTREX”)
(
A) MAKES NO WARRANTY AS TO THE ACCURACY, SUFFICIENCY OR SUITABILITY OF ANY TECHNICAL OR OTHER
INFORMATION PROVIDED IN ITS MANUALS OR OTHER DOCUMENTATION.
(
B) ASSUMES NO RESPONSIBILITY OR LIABILITY FOR LOSSES, DAMAGES, COSTS OR EXPENSES, WHETHER SPECIAL,
DIRECT, INDIRECT, CONSEQUENTIAL OR INCIDENTAL, WHICH MIGHT ARISE OUT OF THE USE OF SUCH INFORMATION.
T
HE USE OF ANY SUCH INFORMATION WILL BE ENTIRELY AT THE USER’S RISK; AND
(C) REMINDS YOU THAT IF THIS MANUAL IS IN ANY LANGUAGE OTHER THAN ENGLISH, ALTHOUGH STEPS HAVE BEEN
TAKEN TO MAINTAIN THE ACCURACY OF THE TRANSLATION, THE ACCURACY CANNOT BE GUARANTEED. APPROVED
X
ANTREX CONTENT IS CONTAINED WITH THE ENGLISH LANGUAGE VERSION WHICH IS POSTED AT www.xantrex.com.
Date and Revision
April 2007 Revision A
Part Number
975-0283-01-01
Product Number
865-1030
Contact Information
Telephone: 1 800 670 0707 (toll free North America)
1 360 925 5097 (direct)
Fax: 1 800 994 7828 (toll free North America)
1 360 925 5143 (direct)
Email: customerservice@xantrex.com
Web: www.xantrex.com

About This Guide
Purpose
The purpose of this Guide is to provide explanations and procedures for installing,
configuring, operating, and troubleshooting the XW Series Solar Charge
Controller.
Scope
This Guide provides safety guidelines, detailed planning and setup information,
procedures for installing the unit, as well as information about operating and
troubleshooting the unit. It does not provide details about particular brands of
photovoltaic (PV) panels. You need to consult individual PV manufacturers for
this information.
Audience
This Guide does not provide sufficient information for anyone but a qualified
installer to install this product. Installers should be electricians or technicians fully
educated on the hazards of installing electrical equipment. The monitoring and
operation information in this manual is intended for anyone who needs to operate
the Solar Charge Controller.
Organization
This Guide is organized into five chapters and two appendices.
Chapter 1 describes features and functions of the Solar Charge Controller.
Chapter 2 contains information and procedures to install the Solar Charge
Controller.
Chapter 3 contains information and procedures to configure the Solar Charge
Controller.
Chapter 4 contains information about the operation of the Solar Charge Controller.
Chapter 5 contains information about identifying and resolving possible problems
with systems using a Solar Charge Controller.
Appendix A provides the specifications for the Solar Charge Controller.
Appendix B is a guide to the Charge Controller monitoring and configuration
menus on the XW System Control Panel. The System Control Panel may be
installed if the Charge Controller is part of a power management system that
includes an inverter/charger.
975-0283-01-01 iii

About This Guide
Conventions Used
The following conventions are used in this guide.
WARNING
Warnings identify conditions that could result in personal injury or loss of life.
CAUTION
Cautions identify conditions or practices that could result in damage to the unit or to other
equipment.
Important:
attention to.
These notes describe an important action item or an item that you must pay
Abbreviations and Acronyms
AGM Absorbed Glass Mat
AWG American Wire Gauge
BTS Battery Temperature Sensor
EMC Electro-Magnetic Compatibility
Related Information
You can find more information about Xantrex Technology Inc. as well as its
products and services at www.xantrex.com.
iv 975-0283-01-01

Important Safety Instructions
WARNING
This manual contains important safety instructions that should be followed during the
installation and maintenance of this product. Be sure to read, understand, and save these
safety instructions.
General Safety Instructions
• All electrical work must be done in accordance with local, national, and/or
international electrical codes.
• Before installing or using this device, read all instructions and cautionary
markings located in (or on) this guide, the unit, the batteries, PV array, and
any other equipment used.
• This product is designed for indoor mounting only. Do not expose this unit to
rain, snow or liquids of any type.
• To reduce the chance of short-circuits, use insulated tools when installing or
working with the unit or any DC source (such as PV, hydro, wind, or
batteries).
• Remove all jewelry when installing or working with the unit or any DC
source. This will greatly reduce the chance of accidental exposure to live
circuits.
• The unit contains more than one live circuit (batteries and PV array). Power
may be present at more than one source.
• This product contains no user-serviceable parts.
WARNING: Limitations on use
The Solar Charge Controller is not intended for use in connection with life support
systems or other medical equipment or devices..
Battery Safety Information
WARNING
A battery can produce the following hazards to personal safety:
• electrical shock
• burn from high-short-circuit current
• fire or explosion from vented gasses.
Observe proper precautions when working with or around batteries.
975-0283-01-01 v

Safety
• Always wear eye protection, such as safety glasses, when working with
batteries.
• Remove all jewelry before working with batteries.
• Never work alone. Have someone assist you with the installation or be close
enough to come to your aid when working with batteries.
• Always use proper lifting techniques when handling batteries.
• Always use identical types of batteries.
• Never install old or untested batteries. Check each battery’s date code or label
to ensure age and type.
• Batteries should be installed in a well-vented area to prevent the possible
buildup of explosive gasses. If the batteries are installed inside an enclosure,
vent its highest point to the outdoors.
• When installing batteries, allow at least 1 inch of air space between batteries
to promote cooling and ventilation.
• NEVER smoke in the vicinity of a battery or generator.
• Always connect the batteries first, then connect the cables to the inverter or
controller. This will greatly reduce the chance of spark in the vicinity of the
batteries.
• Use insulated tools when working with batteries.
• When connecting batteries, always verify proper voltage and polarity.
• Do not short-circuit battery cables. Fire or explosion can occur.
• In the event of exposure to battery electrolyte, wash the area with soap and
water. If acid enters the eyes, flood them with running cold water for at least
15 minutes and get immediate medical attention.
• Always recycle old batteries. Contact your local recycling center for proper
disposal information.
vi 975-0283-01-01

Contents
Important Safety Instructions
1
Introduction
Features - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 1–2
Maximum Power Point Tracking - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 1–3
Charge Controlling - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 1–4
Three-Stage Battery Charging - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 1–4
Bulk Stage - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 1–4
Absorption Stage - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 1–5
Float Stage - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 1–5
Two-Stage Battery Charging - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 1–6
No Float Stage - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 1–6
Battery Temperature Compensation - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 1–7
Equalization Charging - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 1–7
Auxiliary Output Functions- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 1–8
Load Control - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 1–8
Vent Fan - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 1–8
Alarms - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 1–8
Automatic PV Array Night Disconnect - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 1–8
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -v
2
Installation
PV Array Requirements - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 2–2
Array Size - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 2–2
Array Voltage - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 2–2
Array Current - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 2–2
MPPT Voltage Range - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 2–3
Mounting - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -2–3
Choosing a Location - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 2–3
Removing the Wiring Terminals Cover - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 2–5
Removing Knockouts - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 2–5
Mounting the Charge Controller - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 2–7
Grounding - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 2–8
Wiring- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 2–9
DC Terminal Connector Locations - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 2–9
Wire Size and Over-current Protection Requirements - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 2–9
Current Rating - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 2–9
Minimum Wire Gauge - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 2–10
Over-current Protection - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 2–10
975-0283-01-01 vii

Contents
Long-distance wire runs - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -2–10
Maximum One-way Distance and Wire Size - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -2–11
Connecting the Charge Controller - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -2–12
Connecting Multiple Units- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -2–14
Aux Output Connections - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -2–15
Disconnecting the Charge Controller - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -2–16
Network Installation - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -2–17
Network Components - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -2–17
Ordering Network Components - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -2–19
Network Layout - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -2–20
Multi-Drop Backbone Layout - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -2–20
Daisy Chain Layout - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -2–21
Guidelines for Routing the Network Cables - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -2–22
Connecting Network Cable Between Multiple Units - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -2–22
Multi-Drop Backbone Layout - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -2–22
Daisy Chain Layout - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -2–23
Installing the Battery Temperature Sensor - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -2–24
Commissioning - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -2–26
Configuration Screens - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -2–26
Commissioning a Single Unit Without a System Control Panel - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -2–27
Commissioning Multiple Units Without a System Control Panel - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -2–28
Commissioning Units Using a System Control Panel - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -2–30
3
Configuration
Configuring the Charge Controller - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 3–2
Configuration Menus - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 3–3
Basic and Advanced Menus - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 3–3
Configuring Battery Characteristics and Battery Charging - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 3–5
Setting a Custom Battery Type - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 3–8
Battery Temperature Compensation - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -3–10
Configuring Charge Controller Input - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -3–11
Configuring the Auxiliary Output - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -3–12
Trigger Source Descriptions - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -3–14
Trigger Source Configurable Ranges - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -3–15
Configuring the LCD - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -3–16
Device Menu - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -3–18
Resetting to Factory Defaults - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -3–20
4
Operation
Viewing Operating Status - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 4–2
LCD Screens and What They Mean - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 4–2
Normal Operation - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 4–3
viii 975-0283-01-01

Charge Stages - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 4–5
Dynamic Text - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 4–6
Monitoring Charge Controller Operation- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 4–7
Viewing Active Faults and Warnings - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 4–8
Viewing Logged System Data - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 4–11
Daily Logs - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 4–12
Monthly Logs - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 4–12
Battery Equalization - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 4–13
5
Troubleshooting
PV Charge Control Troubleshooting- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 5–2
Replacing the Ground Fault Protection Fuse - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 5–3
A
Specifications
Electrical Specifications - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -A–2
Default Battery Charging Settings - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -A–2
Mechanical Specifications - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -A–3
Output Power Versus Ambient Temperature - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -A–3
Optional Accessories - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -A–4
Regulatory Approvals - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -A–4
Contents
B
XW System Control Panel Menus
Using the XW System Control Panel - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -B–2
System Control Panel Menu Map - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -B–3
Changing Settings Using the System Control Panel - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -B–5
Viewing the Select Device Menu - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -B–5
Viewing the Charge Controller Setup Menu - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -B–5
The Charge Controller Setup Menu - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -B–6
Configuration Settings - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -B–7
Monitoring the Charge Controller - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -B–10
Charge Controller Home Screen - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -B–10
Meters - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -B–11
Warranty and Return Information
Index
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - IX–1
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - WA–1
975-0283-01-01 ix

x

1
Introduction
Chapter 1 describes features and functions of the Solar Charge
Controller.
For information on: See:
“Features” page 1–2
“Maximum Power Point Tracking” page 1–3
“Charge Controlling” page 1–4
“Auxiliary Output Functions” page 1–8
“Automatic PV Array Night Disconnect” page 1–8
Introduction
Features
The Xantrex Solar Charge Controller is a phot ovoltaic (PV) char ge control ler that
tracks the maximum power point of a PV array to deliver the maximum available
current for charging batteries. The Charge Controller can be used with 12-, 24-,
36-, 48-, and 60-volt DC battery systems.
The Solar Charge Controller is designed to regulate PV input, but will also work
with other DC sources. The DC source must meet the specifications listed on
page A–2.
The Charge Controller can be installed (in single or multi-unit configurations)
with a Xantrex XW Series Inverter/Charger or in a stand-alone installation.
Figure 1-1
Standard features of the Solar Charge Controller include:
• Two- or three-stage charging process, with manual equalization to maximize
system performance and maintain expected battery life.
• True dynamic Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) to deliver the
maximum available power from a PV array to a bank of batteries. See
“Maximum Power Point Tracking” on page 1–3.
• Integrated PV Ground Fault Protection (PVGFP)
• Convection cooled (no internal or external fan) using aluminum die-cast
chassis and heat sink
• 60 amp capacity
• 150 volt open circut input voltage
• Configurable auxiliary output. See “Auxiliary Output Functions” on page 1–8.
• Two-line, 16-character liquid crystal display (LCD) and four buttons for
configuration and system monitoring.
• Input over-voltage and under -voltage protection, output ov er-current p rotection,
and backfeed (reverse current) protection. Warning and Fault messages appear
on the LCD when the unit shuts down as a protective measure.
Charge Controller
1–2 975-0283-01-01
• Over-temperature protection and power derating when output power and
ambient temperature are high.
• Battery Temperature Sensor (BTS) to provide automatically temperaturecompensated battery charging. If the BTS is lost or damaged, a replacement
can be ordered from Xantrex (part number 808-0232-02).
• Xanbus
®
-enabled. Xanbus is a network communications protocol developed
by Xantrex. The Charge Controller is able to communicate its settings and
activity to other Xanbus-enabled devices, such as the XW Series Inverter/
Charger, the XW System Control Panel (SCP), XW Automatic Generator
Start (XW-AGS), and other XW-MPPT60-150 Solar Charge Controllers.
• Five-year limited warranty .
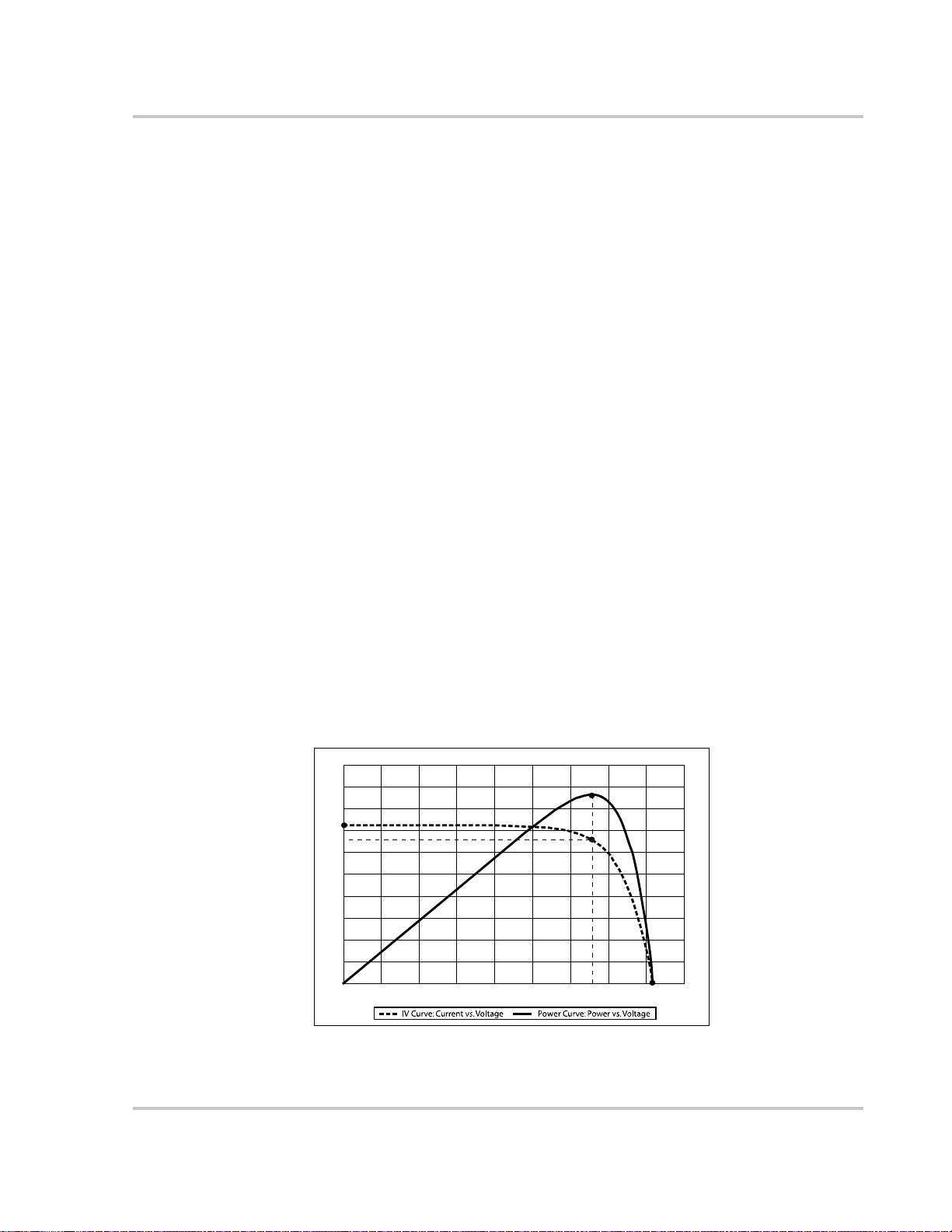
Maximum Power Point Tracking
Maximum Power Point Tracking allows the Charge Controller to harvest the
maximum energy available from the PV array and deliver it to the batteries.
The MPPT algorithm continuously adjusts the operating points in an attempt to
find the maximum power point of the array. The algorithm can then determine if it
is harvesting more or less power than the previous operating points.
The Charge Controller applies a variable load on the array—shown by the power
curve (solid line) in Figure 1-2—until it finds the maximum wattage (the point at
which both operating voltage and current can be maximized at the same time), as
indicated by “MPP” in Figure 1-2. The Charge Controller then holds the array at
this point for as long as the array continues to produce the maximum power
possible. As panel shading, cloud cover, and sunlight angle shift, the Charge
Controller finds the new maximum power point without interrupting its output
power flow.
Maximum Power Po int Tracking
20
18
16
I
sc
14
I
mp
12
10
8
Current (I) Amps
6
4
2
0
0102030405060708090
Figure 1-2
Maximum Power Point Curve
s
t
t
a
W
Voltag e (V) Volts
MPP
V
mp
V
oc
975-0283-01-01 1–3

Introduction
Charge Controlling
The Charge Controller can regulate PV array current at 12, 24, 36, 48 or 60 volts
DC for charging batteries. It produces up to 3500 watts and 60 amps of charging
current for all battery voltages except 60 V.
Figure 1-3
The Charge Controller controls how the batteries are charged by the DC source
(the PV array). It can be configured to use a two-stage (“No Float”) or three-stage
charging process to maintain battery voltage at bulk or float levels.
When charging, the Char ge Controller regulates the battery voltage and the output
current based on the amount of DC power available from the PV array and the
state of charge of the battery.
The Charge Controller is able to charge a lower nominal-voltage battery from a
higher-nominal voltage array. For example, the Charge Controller can charge a
12-volt battery from a 36-volt array. This gives flexibility to installers to use
longer wiring runs without compromising efficiency on a higher-voltage array.
The Charge Controller is not able to charge a higher-volt age battery from a lo wervoltage array.
PV Charge Controller
Three-Stage Battery Charging
The three-stage charging process results in more efficient charging compared to
on-off relay type or constant voltage solid-state regulators. The final float stage
reduces battery gassing, minimizes electrolyte loss, and ensures complete battery
recharging. Battery voltage and current vary during the three-stage charging
process as shown in Figure 1-4 on page 1–5.
Bulk Stage
During the bulk stage, the Charge Controller sets its voltage limit to the bulk
voltage setting. If the batteries are discharged, the Charge Controller operates in
constant current mode, delivering its maximum current to the batteries. When the
battery voltage reaches the Float voltage setting, the controller will transition to
the absorption stage.
1–4 975-0283-01-01
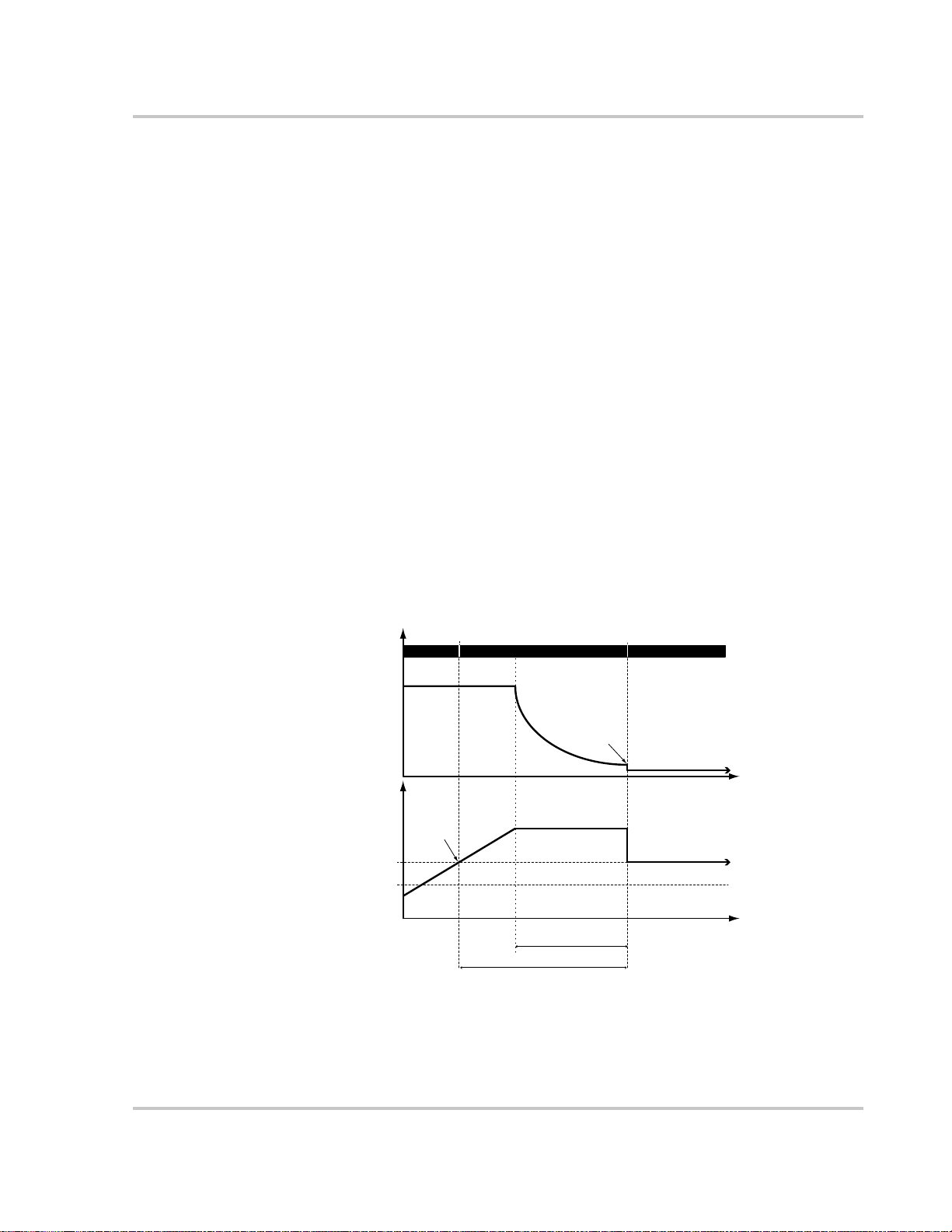
Absorption Stage
Float Stage
Charge Controlling
During the absorption stage, the Charge Controller continues to deliver its
maximum available current output until the battery voltage reaches the absorption
voltage setting. The Charge Controller then operates in constant voltage mode,
holding the battery voltage at the absorption voltage setting for a pre-set time limit
(the default time limit is three hours). During this time, current falls gradually as
the battery capacity is reached. The Charge Controller transitions to the float stage
if any one of three criteria are met:
1. The charge current allowed by the batteries falls below the exit current
threshold, which is equal to 2% of battery capacity (for a 500 Ah battery bank,
this would be 10 A), for one minute.
2. The battery voltage has been at or above the float voltage (which it reached
during the bulk stage) for eight hours.
3. The battery voltage has been at the bulk/absorption voltage setting for a preset time limit (the Max Absorb Time).
During the float stage, the voltage of the battery is held at the float voltage setting.
Full current can be provided to the loads connected to the battery during the float
stage from the PV array. When battery voltage drops below the ReCharge Volts
setting for 1 minute, a new bulk cycle will be triggered.
Figure 1-4
Bulk Stage
Bulk Stage Absorption Stage
Current
Max Current Limit
Voltage
Float voltage
Absorption—
constant current
Absorption Stage
Absorption—
constant voltage
Exit Current Threshold
Bulk/Absorption Voltage
Max Absorb Time—3 hours
(adjustable 2–6 hours)
Maximum 8 hours (fixed)
Three-stage Battery Charging Cycle
Float Stage
Float Stage
Float Voltage Threshold
ReCharge Voltage Threshold
a
Time
Time
a.An actual charging cycle for a PV-based system that is in use while it is being charged will
likely differ from the cycle represented in Figure 1-4. This is because a PV system’s output
is limited by the amount of solar energy available, and also because DC loads will affect the
charge current and the measured battery voltage.
975-0283-01-01 1–5
Introduction
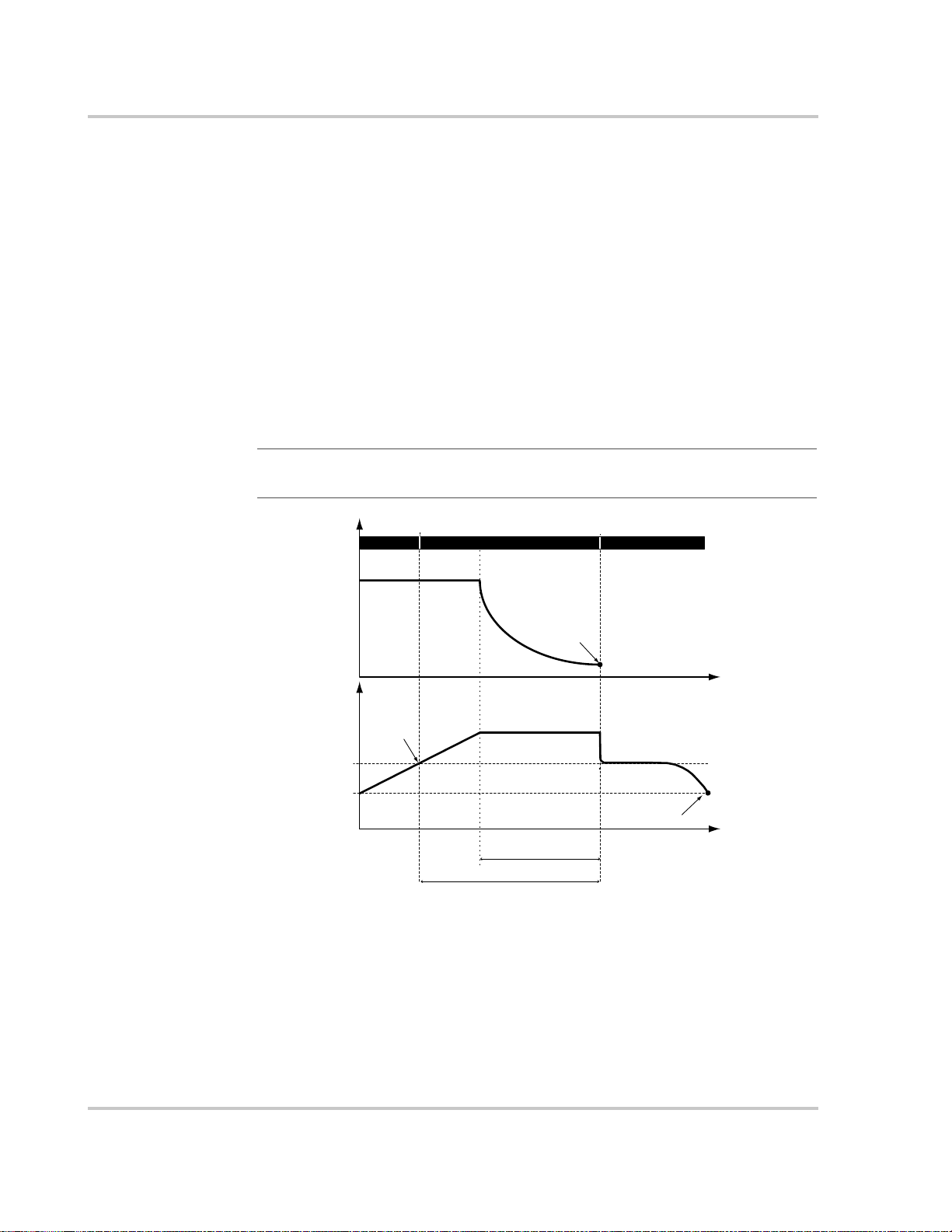
Two-Stage Battery Charging
The two-stage charging process includes the bulk and absorption stages, but uses a
“No Float” stage instead of “Float.” Two-stage charging is recommended for offgrid applications, where batteries are used more frequently and maintaining them
at the float voltage is both less important and less practical. Two-stage charging
can extend the life of most batteries. The relationship between charging current
and battery voltage during the two-stage charging process is shown in Figure 1-5.
No Float Stage
During the No Float stage the Charge Controller does not produce any charge
current. Instead the Charge Controller monitors the battery voltage and transitions
back to the bulk stage once the voltage drops below the ReCharge Volts setting for
one minute.
Note: For more information about battery charging settings, see Table 3-2, “Battery
Menu Values” on page 3–7 and Table 3-3, “Custom Battery Menu Values” on page 3–10.
Figure 1-5
Bulk Stage
Bulk Stage Absorption Stage
Current
Max Current Limit
Voltage
Float Voltage
Absorption—
constant current
Absorption Stage
Absorption—
constant voltage
Exit Current Threshold
Bulk/Absorption Voltage
Max Absorb Time—3 hours
(adjustable 2–6 hours)
Maximum 8 hours (fixed)
Two-Stage Battery Charging Cycle
No Float Stage
Float Stage
ReCharge Voltage Threshold
Return to Bulk Stage
Time
Time
1–6 975-0283-01-01

Battery Temperature Compensation
The Battery T emperature Se nsor (BTS) automatically adjusts the charging process
of the Charge Controller. With the BTS installed, the Charge Controller increases
or decreases the battery charging voltage depending on the temperature of the
battery to optimize the charge to the battery and to protect it from over-charge or
damage. Using the BTS can extend battery life and improve overall charging.
The BTS plugs into the BTS jack located inside the wiring compartment of the
Charge Controller. The BTS can be installed on the negative battery post or on the
side of the battery.
Charge Controlling
Figure 1-6
If the BTS is not installed, the voltage settings for charging are based on one of
three temperature settings (Cold, Warm, or Hot) available on the Charge
Controller configuration menu. See “Configuring Battery Characteristics and
Battery Charging” on page 3–5.
Only one BTS is required if multiple Charge Controllers or a complete XW Power
System with XW Inverter/Chargers are networked together using Xanbus. All
networked XW Series devices share battery temperature information, and the BTS
can be connected to a Charge Controller or an XW Inverter/Charger.
Equalization Charging
The Charge Controller can be used to provide the battery bank with an equalize
charge.
Equalization is a deliberate overcharge designed to return each battery cell to
optimum condition by reducing sulfation and stratification in the battery. The
equalization charge is generally performed only on flooded, vented (non-sealed or
“wet”) lead-acid batteries, as recommended by the battery manufacturer.
To avoid damaging your batteries, be sure to read all cautions and warnings
concerning equalization charging. For more information, see “Battery
Equalization” on page 4–17.
Battery Temperature Sensor
Important:
60 V battery system, which is the bulk voltage setting for 60 V batteries. Because of this
output limit, the Charge Controller does not equalize 60 V batteries.
975-0283-01-01 1–7
The Charge Controller maximum output voltage is limited to 72 V for a

Introduction
Auxiliary Output Functions
The Charge Controller has a configurable auxiliary output (producing 5 to 13
volts and up to 200 milliamps) to drive a relay for load control or to turn on
devices such as vent fans or indicator alarms. The auxiliary output can be
configured to perform only one function at a time.
See “Configuring the Auxiliary Output” on page 3–14 for information about
auxiliary output trigger sources and how to enable and configure the auxiliary
output for your application.
CAUTION
The auxiliary output is intended only to energize a low-current circuit such as a relay coil.
Connection to a high-amperage device will open the fuse in the common line and possibly
damage the unit.
Load Control
The Charge Controller auxiliary output can be configured to drive a relay to
disconnect or reconnect loads depending on battery voltage. This load control
function enables the Charge Controller to help prevent damage to the battery from
over-discharge during periods of poor charging (due to ambient temperature, for
example) or excessive loads.
Vent Fan
The Charge Controller auxiliary output can be configured to power a small DC
fan to clear a battery compartment of harmful gases. The Charge Controller
auxiliary output must be configured to activate when the batteries reach their
gassing voltage.
Alarms
The auxiliary output can be configured to trigger an alarm or indicator light when
a pre-set condition occurs, such as low or high battery voltage, high PV array
voltage, or a Charge Controller fault.
Automatic PV Array Night Disconnect
At night, or when the PV array voltage is less than the battery voltage, the Charge
Controller opens an internal relay to prevent battery current from flowing back to
the PV array. In this mode of operation the Charge Controller draws minimal
power from the battery.
This automatic night-time disconnect eliminates the need for a blocking diode
between the battery and the PV array. If the PV array consists of thin-film or
amorphous solar modules, diodes may still be required to prevent damage during
times of partial shading of the array. Check the documentation provided with the
PV modules.
1–8 975-0283-01-01

2
Installation
Chapter 2 contains information and procedures to install the XW
Series Solar Charge Controller.
For information on: See:
“PV Array Requirements” page 2–2
“Mounting” page 2–3
“Grounding” page 2–8
“Wiring” page 2–9
“Installing the Battery Temperature Sensor” page 2–24
“Commissioning” page 2–26
Installation
PV Array Requirements
Each Charge Controller must be connected to its own PV array. For optimum
performance, each individual array must be composed of the same type of solar
panel, with the same V
Note: The following information provides only general guidelines. The installation and
rated performance of your PV array is subject to inspection and approval by the authority
having jurisdiction.
Array Size
For PV array sizing guidelines, use the XW Solar Charge Controller PV array
sizing tool accessible from www.xantrex.com/support.
Although the Solar Charge Controller can harvest a maximum of 3500 W, the PV
array size can be as high as 6720 W (based on 48 A × 140 Vdc = 6720 W).
Array Voltage
and V
oc
specifications.
mpp
Array Current
CAUTION: Equipment damage
The PV array voltage must never exceed 150 Voc (open circuit voltage) under any
conditions.
The maximum V
140 Vdc. The difference between V
When calculating PV array size for the Solar Charge Controller you should
consider the expected V
increases with decreasing temperature. The array needs to be sized so that
150 Vdc does not occur, even at the lowest expected panel temperature during
open circuit. The panel manufacturer provides a V
usually rated at 25
Important:
input current rating of the Charge Controller at any time.
Panels rated up to 48 A at 25 °C (77 °F) are recommended to allow for increases
at low panel temperatures and at solar noon. Ensure that the Isc rating under
in I
sc
all conditions does not exceed 60 A. A factor of 1.25 is applied to the rated I
25 °C when the panel is colder than -21 °C.
(PV array voltage for Charge Controller MPPT operation) is
mpp
and Voc is shown in Figure 1-2 on page 1–3.
mpp
of the array under all possible conditions. Panel voltage
oc
rating per panel, but it is
oc
°C (77 °F).
The Isc (short circuit current) rating of the array must not exceed the 60 A
at
sc
2–2 975-0283-01-01
MPPT Voltage Range
The Charge Controller maximum power point tracking algorithm maximizes the
output energy of PV arrays as long as the operating voltage is within the MPPT
operational window. Ensure that the PV array used in the system operates within
the MPPT operational window.
Effects of array voltages outside of the MPPT operational window are shown in
Table 2-1.
Mounting
Mounting
Table 2-1
Voltage Effect of Array Voltage Charge Controller Mode
V
< V
oc
(system battery voltage)
V
MPP
V
MPP
120 Vdc < V
V
MPP
(or V
MPPT Operational Window
batt
< V
batt
= V
to 120 Vdc Maximum harvest of solar
batt
< 140 Vdc Charge Controller reduces the
MPP
> 140 Vdc
> 140 Vdc)
oc
Charge Controller not
operating.
Harvest of solar energy less
than optimal.
energy.
output current limit to protect
the unit from voltage spikes.
Charge Controller shuts down.
Unit may be damaged if V
150 V.
>
oc
Low Light
Charging
Charging
(MPPT window)
Input voltage derating
Over-voltage fault
The instructions in this chapter are applicable to the typical stand-alone
installation. Installation procedures will vary according to your specific
application. For special applications, consult a qualified electrician or your
Xantrex Certified Dealer.
If installing the Charge Controller as part of an XW System, see the XW Power
System Installation Guide for additional information.
Important:
of this equipment should only be performed by a qualified electrician or by a Certified
Renewable Energy (RE) System installer.
Installations must be compliant with all local electrical codes. Installation
Choosing a Location
The Charge Controller must be mounted vertically and installed indoors in a dry,
protected location away from flammable materials, sources of high temperature,
moisture, and vibration. The location must also be sheltered from direct sunlight,
rain, snow, and wind-blown debris.
975-0283-01-01 2–3
Installation
CAUTION: Equipment damage
Never install the Charge Controller where it is exposed to salt water spray. Exposure to
salt water will void the warranty and may cause a shock hazard.
WARNING: Explosion/corrosion hazard
To reduce the risk of fire or explosion, do not install the Charge Controller in sealed
compartments containing batteries or in locations that require ignition-protected
equipment.
To reduce the risk of corrosion from hydrogen-sulfide gas vented by batteries, do not
install the Charge Controller in sealed compartments containing batteries.
If using “sealed” batteries, the Charge Controller can be mounted in the same
enclosure as long as it is adequately ventilated.
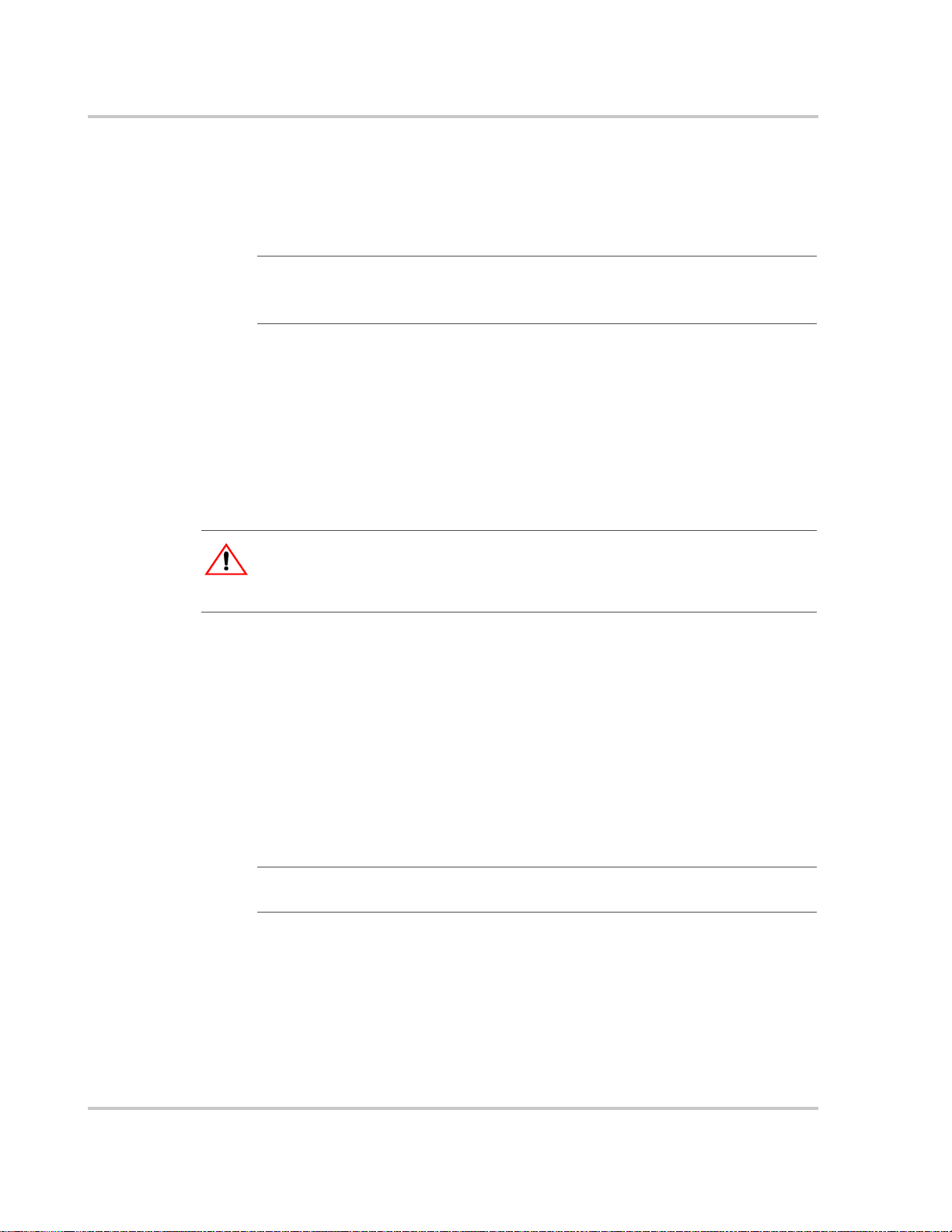
For optimal and safe operation, ensure there is adequate clearance around the
Charge Controller. See Table 2-2 and Figure 2-1. If clearances are reduced below
these minimums, rated performance may not be achieved.
Table 2-2
Location Minimum Clearance
Above 150 mm (6 inches). When units are mounted in a vertical stack, the topmost
In front Sufficient room to allow for easy access to read the display, to prevent
On sides 150 mm (6 inches) on at least one side of the overall assembly. A maximum
Minimum Clearance Requirements
unit must maintain the minimum clearance to the nearest surface.
Note: Minimum clearances can be ignored when mounting two units on the
side of the XW Power Distribution Panel
information,
XW Hybrid Inverter/Charger. Other installations must follow the guidelines
in this Owner’s Guide.
accidental contact with the heat sink, and to perform maintenance.
of two u
Power Distribution Panel. In both configurations, the minimum clearance
around the outermost unit must be maintained.
see the XW Power System Installation Guide, available with the
nits can be mounted side by side or side mounted against an XW
(part number 865-1015). For more
2–4 975-0283-01-01
150 mm (6 inches) on top and side(s)
Mounting
Figure 2-1
Minimum Clearance Requirements
Removing the Wiring Terminals Cover
Before mounting, remove the wiring terminals cover to access the mounting holes
and the wiring terminals. The wiring terminals cover is secured with two Phillips
#8-32 × 2 ½-inch screws on the front cover of the unit. See Figure 2-2.
Figure 2-2
Removing the Wiring Terminals Cover
Removing Knockouts
Six dual and two single knockouts are provided for routing battery, PV array,
BTS, and network cables into the Charge Controller. Use bushings or conduits to
protect the wiring from damage from rough edges around the knockout holes.
When removing knockouts, ensure that no metal shavings or fragments fall into
the wiring compartment.
Remove screws to access
the wiring terminals.
Important:
knockouts provided for conduit entry.
975-0283-01-01 2–5
Do not drill, cut, or punch holes in the Charge Controller. Use only the
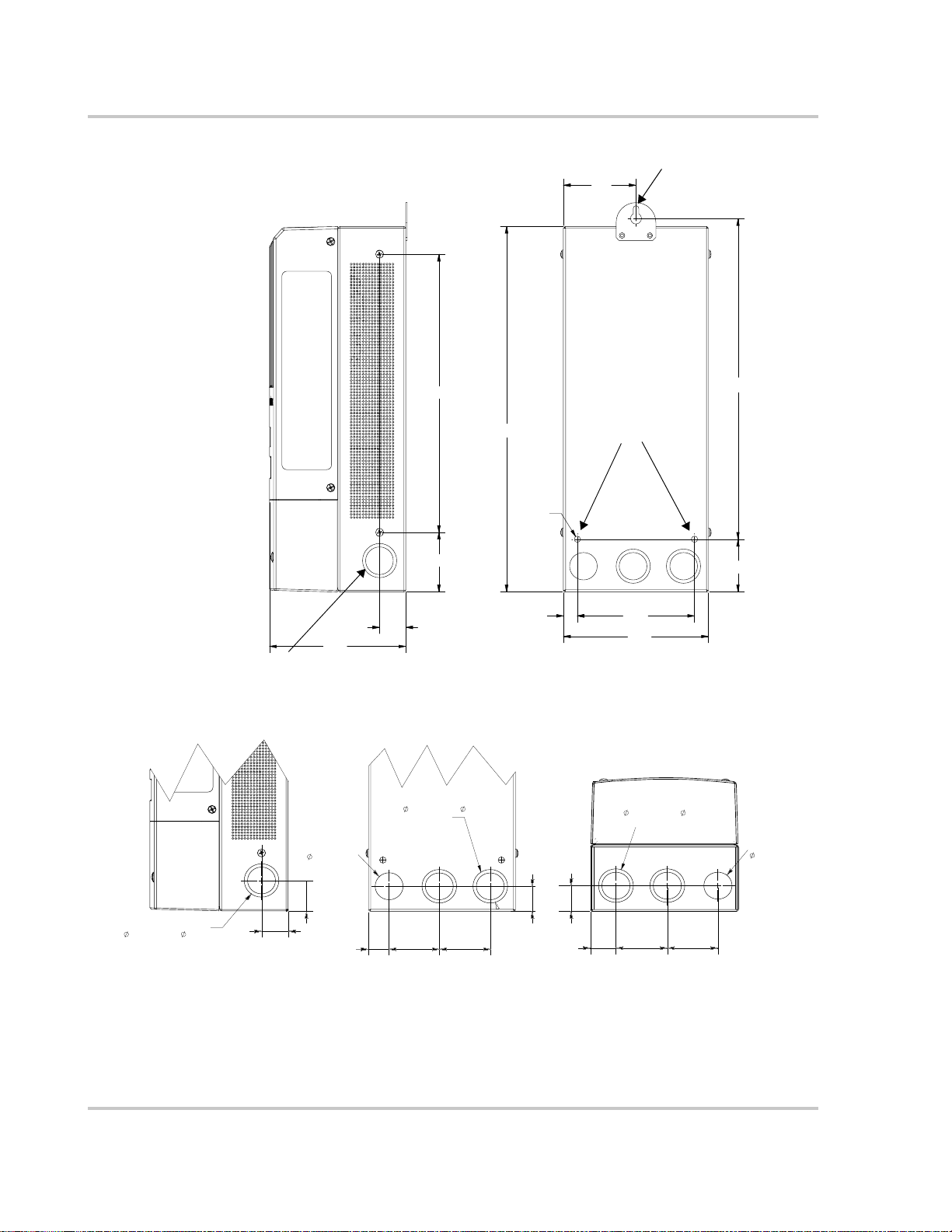
Installation
Keyhole slot for wall mounting
73
(2 7/8)
Figure 2-3
KNOCKOUT
27.78 (1 1/16)
280 (11)
368 (14 1/2)
Ø 6.35
(1/4)
60 (2 3/8)
14 (9/16)
138
(5 7/16)
26.5
(1)
Dimensions and Knockout Locations
DUAL KNOCKOUT
34.52 (1 3/16) & 27.78 (1 1/16)
2 PL
323 (12 3/4)
Additional
mounting holes
53 (2 1/16)
118
(4 5/8)
146
(5 3/4)
All measurements in mm (in.)
Single knockouts intended
for BTS and network cables
DUAL KNOCKOUT
34.52 (1 3/16) & 27.78 (1 1/16)
2 PL
KNOCKOUT
27.78 (1 1/16)
DUAL KNOCKOUT
34.52 (1 3/16) & 27.78 (1 1/16)
26.47
(1)
31.50 (1¼)
20.20
(¾)
50.00 (2) 50.80 (2)
25.9 (1)
26.47 (1)
25.0 (1)
50.80 (2)
50.00 (2)
All measurements in mm (in.)
Figure 2-4
Knockout Dimensions
2–6 975-0283-01-01
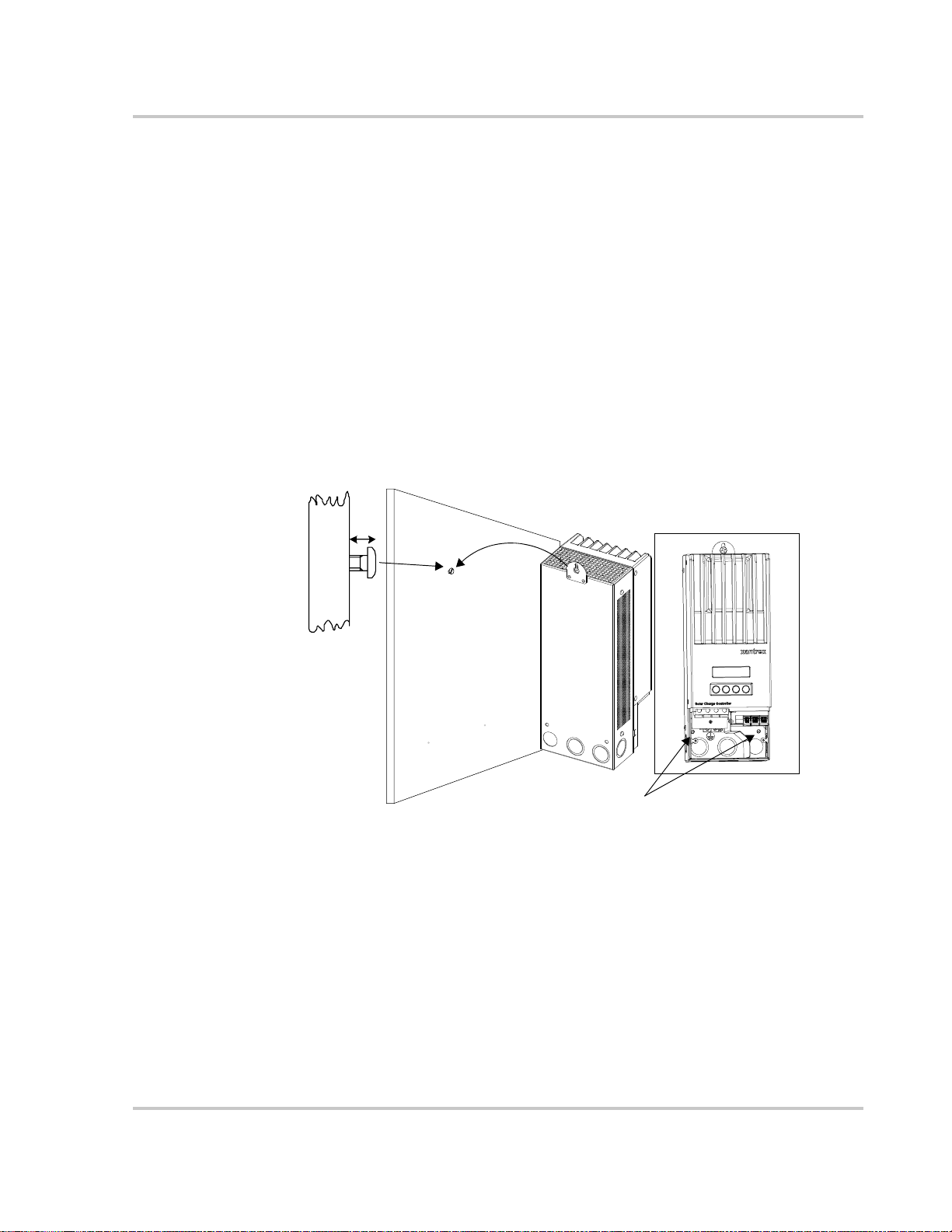
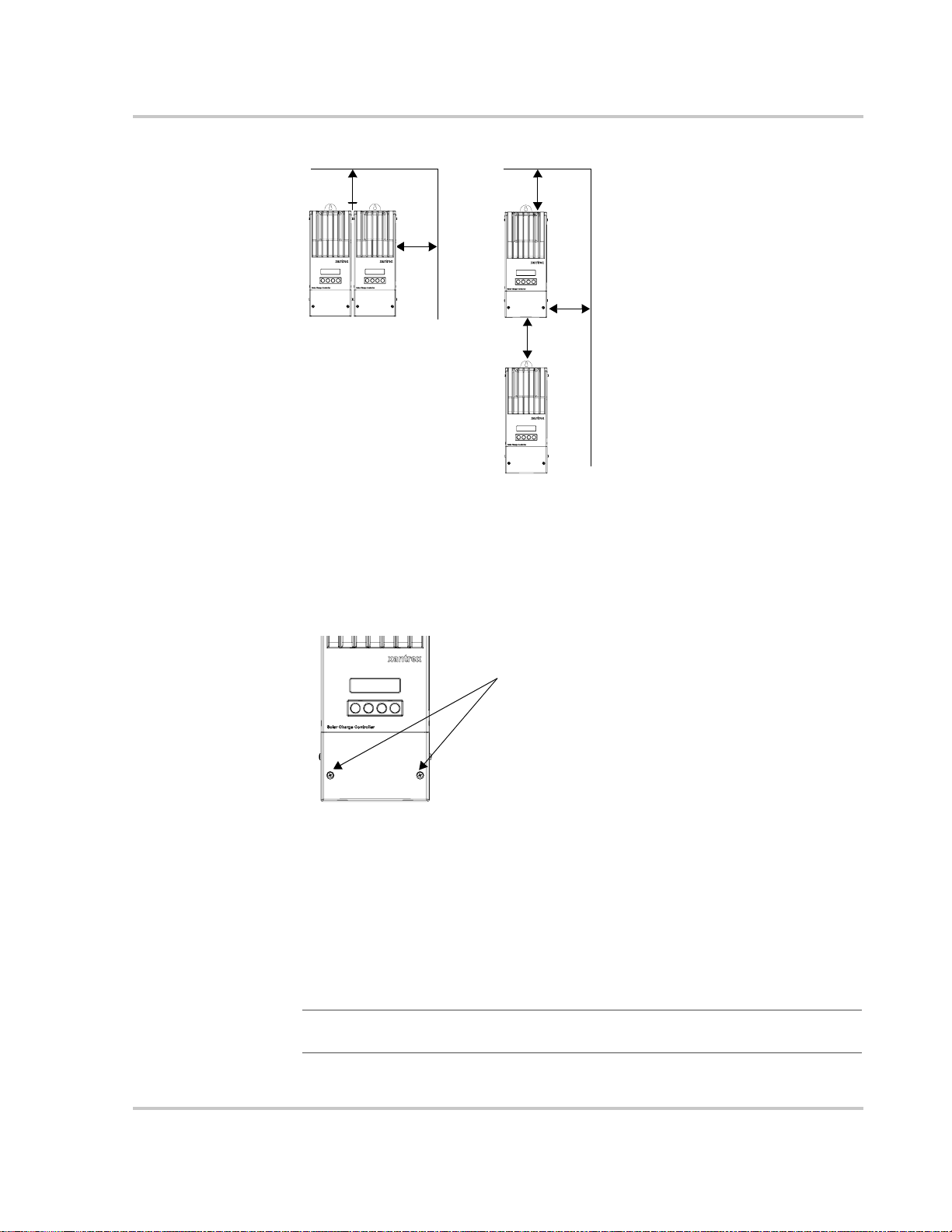
Mounting the Charge Controller
The Charge Controller is vertically mounted using three #10 × ½-inch or #12 × ½inch pan-head screws.
To mount the Charge Controller:
1. Remove the wiring terminals cover.
2. Mark the location of the keyhole slot on the wall.
3. Secure the top mounting screw in the location marked. Leave the screw head
backed out approximately ¼ inch (6 mm).
4. Place the controller onto the screw and pull it down into the keyhole slot.
5. Insert two screws in the two mounting holes provided to secure the unit to the
wall.
6. Provide strain-relief clamps or conduit to prevent damage to the circuit board
and terminal block from pulling on the wires.
¼"
Mounting
Figure 2-5
Place keyhole
slot over the
mounting screw.
Secure with two
more screws.
Mounting the Solar Charge Controller
975-0283-01-01 2–7
Installation
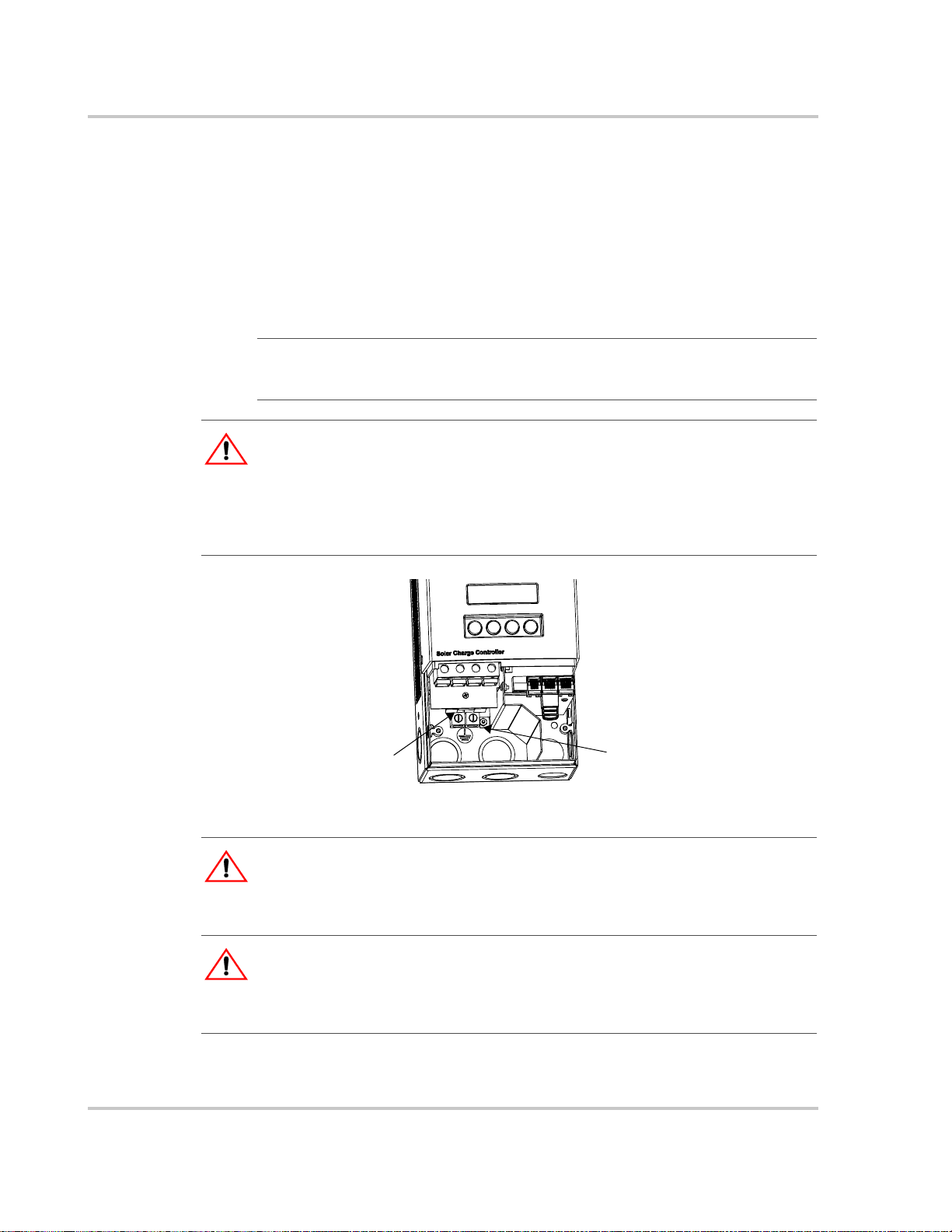
Grounding
The Charge Controller is designe d to work only with negative-grounded electrical
systems. Grounding for both PV and battery circuits is provided inside the wiring
compartment. Each ground connection can accommodate up to #6 AWG wire
size.
A fuse rated at 1 A, 600 V (accessible from inside the wiring compartment)
grounds the negative conductor of the PV array and provides PV ground-fault
protection (PV-GFP). Replace with Littelfuse KLKD 1 or equivalent.
Important:
installations with multiple parallel Charge Controllers. Before mounting and connecting
the Charge Controllers, remove the PV-GFP fuse from each unit except one.
Only one Charge Controller is to have the PV-GFP fuse installed in
WARNING: Shock hazard
Do not connect the battery negative to ground. NEC requirements specify that the battery
negative ground must be done only through the 1A PV-GFP fuse. Bonding the battery
negative to ground disables PV ground-fault protection and causes improper unit
operation. The battery compartment must only be grounded if it is metal. See Figure 2-9
on page 2–13 for correct routing of the battery negative.
This symbol identifies the
protective conductor
Ground fault protection
fuse (behind wiring
terminals)
(grounding) connection.
Chassis ground terminals (2)
Figure 2-6
Charge Controller Safety Ground Connector
WARNING: Shock and fire hazard
Fuses must only be replaced by qualified service personnel, such as a certified electrician
or technician. For continued protection again risk of fire, replace only with the same type
and rating of fuse.
WARNING: Shock hazard
Disconnect PV and battery circuits before removing the grounding connections or before
removing or installing the PV-GFP fuse. Wait at least 5 minutes for the internal circuitry to
discharge before servicing the unit.
2–8 975-0283-01-01

Wiring
Wiring
Important:
equipment should only be performed by a qualified electrician or a Certified Renewable
Energy (RE) System Installer.
Installations must meet all local electrical codes. Installations of this
WARNING: Shock hazard
Disconnect PV and battery circuits before wiring.
DC Terminal Connector Locations
Terminal connectors for DC wiring are located inside the wiring compartment.
The labels above the DC wiring terminals and inside the wiring compartment
identify all the connection points. See Figure 2-7.
CONNECTIONS DIAGRAM
TERMINAL TORQUE REQUIREMENTS
15lbf.in (1.7 Nm) FOR #14- 10 AWG WI RE
18lbf.in (2.0 Nm) FOR #8 AWG WI RE
20lbf.in (2.2 Nm) FOR #6 AWG WI RE
BATTERY
BATTERY
++
--
PV PV
AUX
+
BTS
XANBUS
XANBUS
-
Figure 2-7
DC Connection Terminals
Wire Size and Over-current Protection Requirements
The wiring, over-current protection devices (fuses and circuit breakers), and
installation methods used must conform to all national and local electrical code
requirements.
Wiring must be protected from physical damage with conduit or a strain relief
clamp.
To preserve signal integrity on communication cables, the BTS, auxiliary output,
and network cables must pass through a different conduit than the conduits used
for PV wiring and battery cables. You should pull the BTS cable through the
conduit first as the connector may not fit if other wires have been pulled first.
Current Rating
The Charge Controller PV inpu t is rated for 60 A maximum Isc. Since PV outputs
can vary due to the array size or sunlight angle, the safe minimum wire size must
be chosen for maximum array short-circuit current. Consult PV array
manufacturer specifications.
975-0283-01-01 2–9
Installation
Minimum Wire Gauge
For installations where the PV array output is the maximum allowable 60 A Isc,
the minimum allowable wire gauge is #6 AWG (13.3 mm
90 °C (194 °F) insulation rating. This wire gauge is determined by electrical code
requirements regarding conduit knockout sizes, wire bending radius, and space
available within the Charge Controller wiring compartment.
No crimp-on terminals or lugs are required.
Over-current Protection
Over-current protection must be installed to protect the Charge Controller from
short circuits and to provide a means of disconnecting the Charge Controller.
Battery Circuit
The NEC requires the battery circuit to be protected with a device rated for 125%
of the rating of the circuit. The DC-rated fuse or circuit breaker between the
battery and the Charge Controller must have a maximum size of 1.25 × 60 A (the
maximum current rating of the Charge Controller). That is, the fuse or circuit
breaker must be rated equal to or above 75 A.
PV Circuit
A PV disconnect device between the PV array and the Charge Controller must be
rated for the I
2
of the array but will not exceed the 60 A rating.
sc
) copper wire with a
Long-distance wire runs
If there is a significant distance between the PV array and the Charge Controller
or between the Charge Controller and the battery, larger wires can be used to
reduce the voltage drop and improve performance. Refer to Table 2-8.
WARNING: Equipment damage
Do not connect an array capable of delivering over 60 A Isc to the Charge Controller.
Wires larger than #6 AWG can be used only to reduce power loss in the wiring.
To use a larger size wire, use a splicer block (terminal block) approved and rated
for this application. This allows the larger cable size from the batteries to be
“spliced” to the #6 AWG wire connected to the Charge Controller. The splicer
block must be installed outside of the Charge Controller wiring compartment.
Follow manufacturer’s reco mmendations for torque and mounti ng. Splicer blocks
and split-bolt kerneys are available from renewable energy suppliers.
2–10 975-0283-01-01
 Loading...
Loading...