W&T 58620 User Manual
Release 2.0, January 2010
Model 58620
Firmware 2.10 or higher
Manual
LAN-Modem
W&T

W&T
© 01/2010 by Wiesemann und Theis GmbH
Subject to error and alteration:
Since it is posssible that we make mistakes, you mustn’t use
any of our statements without verification. Please, inform us of
any error or misunderstanding you come about, so we can
identify and eliminate it as soon as possible.
Carry out your work on or with W&T products only to the extent
that they are described here and after you have completely read
and understood the manual or guide. We are not liable for
unauthorized repairs or tampering. When in doubt, check first
with us or with your dealer.
W&T
Introduction
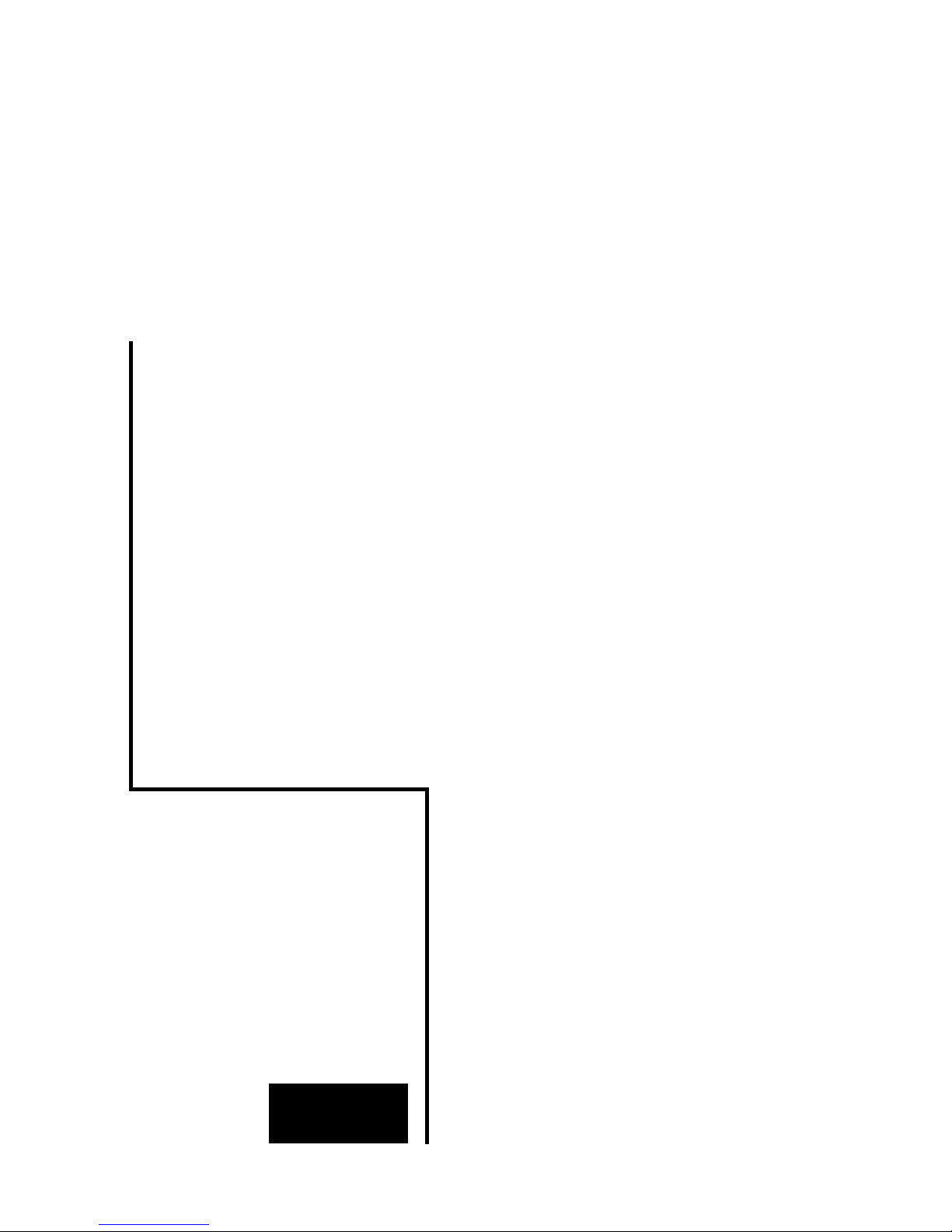
The LAN-Modem permits devices that require dial-up modems
for communicating to use the Intranet or Internet instead of the
telephone system. On a serial interface, the LAN-Modem
behaves in a way this is compatible with standard modems for
the telephone system; the only difference is that the dial-up
number is replaced by an IP address.
Modem
Intranet /
Internet
“ATDT <Tel. No.>”
RS232
RS232
RS232
RS232
before:
LAN Modem
LAN Modem
RS232
“RING”
now:
serial
device
serial
device
serial
device
RS232
Modem
Modem
Modem
RS232
“RING”
serial
device
serial
device
serial
device
“ATDT <IP. No.>”
RS232

4
W&T
Inhalt
1 Quickstart 7
1.1 Installation in flow chart form 8
1.2 Factory Default setting 9
2 Assigning the IP address 11
2.1 Configuring network parameters with WuTility 12
2.2 Serial assigning of IP, subnet mask and gateway 15
2.3 Assigning the IP using DHCP protocol 17
2.3.1 Activating/Deactivating DHCP 17
2.4 Assigning the IP using BOOTP protocol 20
3 Interfaces and displays 23
3.1 Ethernet connection 24
3.2 RS232 interface 26
3.3 Supply voltage 27
3.4 LED displays 28
4 LAN-Modem operation settings 29
4.1 Standard mode LAN-Modem <> LAN-Modem 30
4.2 Mode LAN-Modem <> Virtueller Modemport 31
5 Modem Operation 35
5.1 Serial transmission parameters 36
5.2 Command syntax 37
5.3 Command and data mode 38
5.4 All AT commands 39
5.4.1 A (ATA) 40
5.4.2 D (ATD[IP address]) 41
5.4.3 E (ATE[0|1]) 44
5.4.4 H (ATH) 45
5.4.5 In (ATI[0–8]) 46
5.4.6 O (ATO) 47
5.4.7 Q (ATQ0|1) 48
5.4.8 Sn? (ATS[0-40]?) 49
5.4.9 Sn=x (AT[0–40]=[0–255]) 50
5.4.10 Vn (ATV[0|1]) 52
5.4.11 Zn (ATZ[0|1]) 53
5.4.12 &C (AT&C[0|1]) 54

5
W&T
Subject to error and alteration
5.4.13 &D (AT&C[0|1|2|3]) 55
5.4.14 &Fn (AT&F[0|1]) 56
5.4.15 &K (AT&K[0|3|4|5|6]) 57
5.4.16 &Sn (AT&S[0|1]) 58
5.4.17 &Vn (AT&V[0|1|2]) 59
5.4.18 &Wn(AT&W[0|1]) 60
5.4.19 &Yn (AT&Y[0|1]) 61
5.4.20 &Zn=x (AT&Z[0|1|2|3]=[IP address]) 62
5.4.21 %Bn (AT%B[2-8]) 63
5.4.22 %Dn (AT%D[7|8]) 64
5.4.23 %Pn (AT%P[0|1|2]) 65
5.4.24 %Sn (AT%S[1|2]) 66
5.4.25 %Nn (AT%N[0|1]) 67
5.4.26 ** (AT**) 68
Appendix 69
A1 Extended configuration of the LAN-Modem 70
A1.1 Starting the Telnet session 70
A1.2 Configuration of the TCP server port (Local Port) 71
A1.3 Configuration of the System Name 72
A1.4 Configuration of the System Password 72
A1.5 Configuration of Keep Alive Check 73
A1.6 Configuration of Link Speed 73
A2 Firmware update of the LAN-Modem 75
A3 Reading/Sending Configuration Profiles 82
A4 Software reset of the LAN-Modem 83
A5 The Modem Protocol on the TCP Level 84
A6 Used ports and network security 85
A7 Technical Data 88

6
W&T

7
W&T
Subject to error and alteration
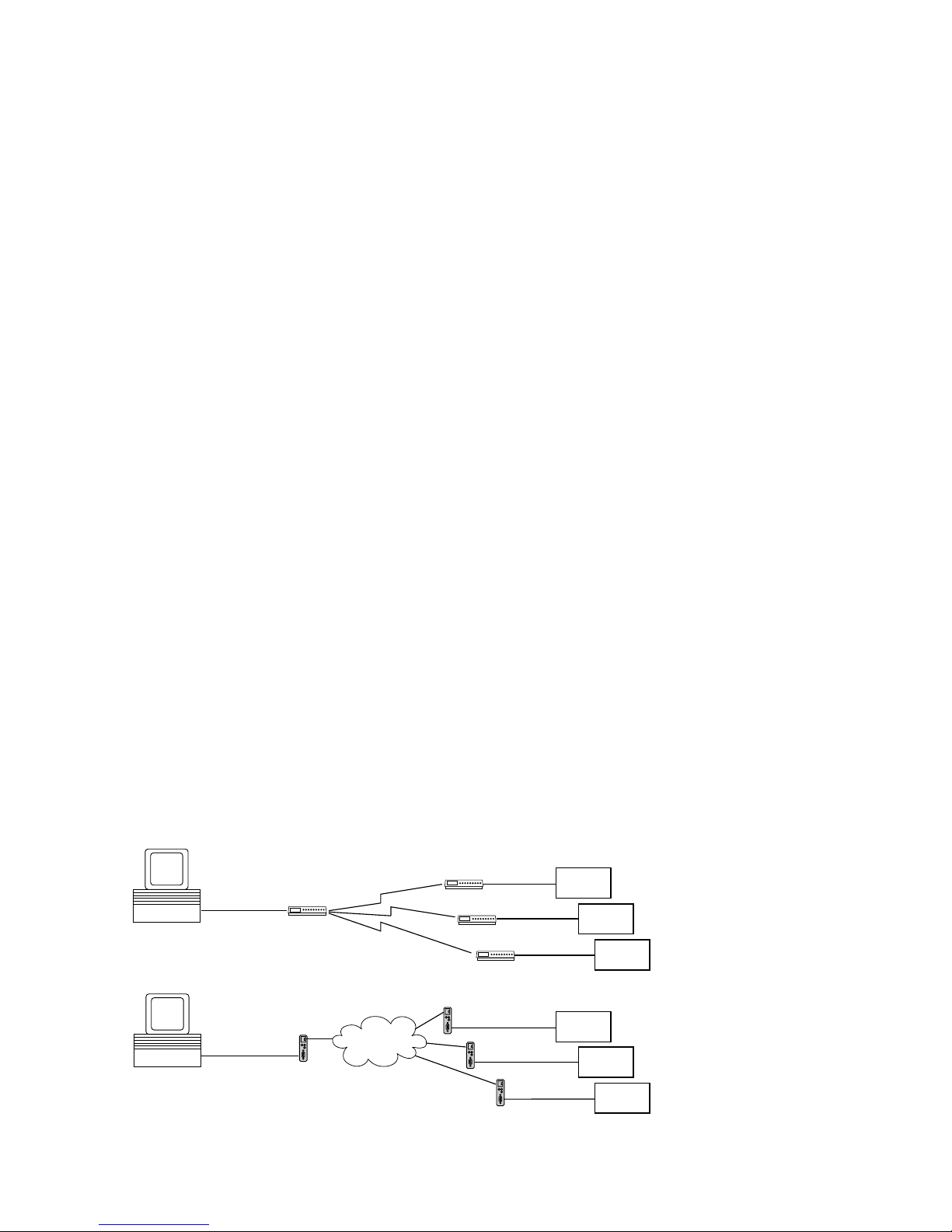
1 Quickstart
Already experienced users of LAN-Modems will find on the two following
pages a flow chart with the essential steps for start-up as well as the
configuration. Detailed information can be found then in the following
sections.
8
W&T Quickstart
1.1 Installation in flow chart form
Select site
Connect
supply voltage
LAN-Modem Windows PC
with TCP/IP
WuTility
installed?
yes
Connect
network cable
Finish
Network
no
Optain IP
address, subnet
mask, gateway
address
Install
WuTility with
product CD
Button:
IP address
Enter IP address,
subnet mask,
gateway
Start
WuTility
Select
LAN-Modem in
inventory list

9
W&T Quickstart
1.2 Factory Default setting
The list contains an overview of the most important settings.
Detailed information on the respective parameters can be found
in later sections of this manual.
Network settings
Hardware connection: Auto negotiating
IP address: 0.0.0.0
Gateway address: 0.0.0.0
Subnet mask: 255.0.0.0
DHCP: Active
TCP port for incoming calls: 8000
1
To prevent unintended address assignments or changes,
we recommend deactivating the DHCP, BOOTP and RARP
protocols if they are not expressly used in the respective
network environment.
Serial settings
Baud rate: 9600
Data bits: 8
Parity: NO
Stop bits: 1
Handshake: Hardware (RTS/CTS)

10
W&T Quickstart

11
W&T
Subject to error and alteration
2 Assigning the IP address
The LAN-Modem is factory set to IP address 0.0.0.0. Before you can make
the entry in the LAN-Modem, you need to specify an IP address that is valid
for your network. You system administrator will provide you with this. If
you have only a small network with no routing, use the IP address of your
PC and simply change the last digit. The IP address must be unique within
the network!
. Assigning IP address, subnet mask and gateway address
using WuTility management tool
. Assigning IP address, subnet mask and gateway address
through the serial port
. Assigning IP address, subnet mask and gateway using
DHCP/BOOTP protocol
. Using the ARP command

12
W&T Assigning the IP address
2.1 Configuring network parameters with WuTility
The Windows tool WuTility version 3.0 and higher allows not
only inventorying of LAN-Modem, Com-Server and Web-IO
installations, but also convenient assignment of the following
network-side basic parameters:
• IP address
• Subnet mask, gateway address
• Activating/deactivating BOOTP/DHCP
Assigning requires that the PC and LAN-Modem be in the same
subnet. In firmware revisions 1.45/1.14 and higher the function
is independent of the current address settings in the LAN-Modem, i.e. even changes to parameters not matching the network
are easily made. Any system password which has been set must
however in this case be known.
Downloading and installing WuTility
The most current version can always be found at our Web site
under the following address:
http://www.wut.de
From there use the menu tree on the left side to navigate:
Downloads r Serial Com-Servers
After unzipping the ZIP file, begin installation by doubleclicking on the file wutility_xxxus.msi. WuTility is started from
Start r Programs r W&T Software Toolkit r WuTility
Starting the assignment dialog
First be sure that both the LAN-Modem and the computer you
are using are connected to the same network and are in the
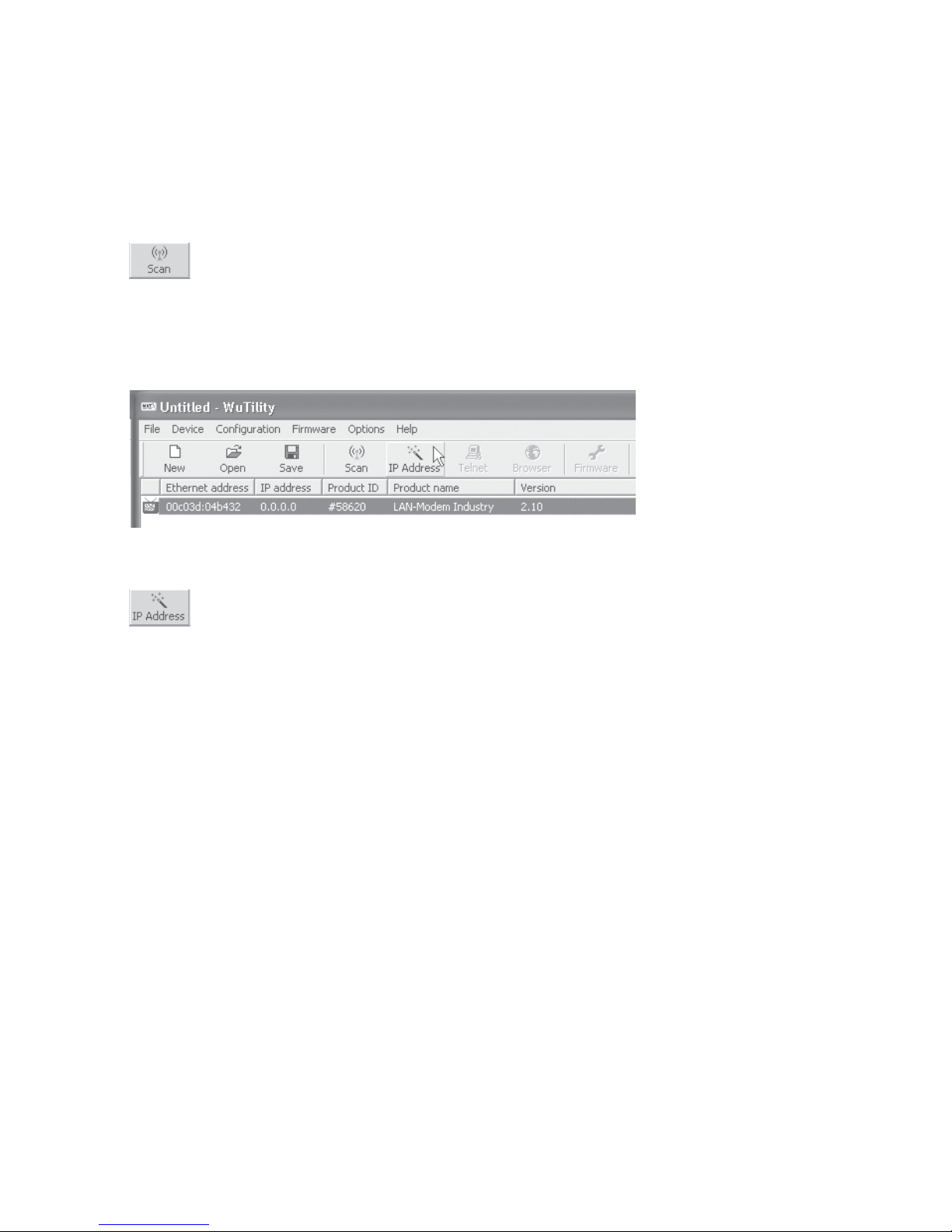
13
W&T Assigning the IP address
Subject to error and alteration
same subnet. When started, WuTility automatically searches the
local network for connected W&T network devices and creates
an inventory list. This search process can be repeated manually
as often as desired by clicking on the Scan button:
Within the inventory list you can identify the desired LAN-Modem based on its MAC address. For initial installations its IP
address is 0.0.0.0.
Select the LAN-Modem and click on the IP address button:
To use the LAN-Modem with dynamic IP parameters, select in
the following dialog box the corresponding option DHCP or
BOOTP and then click on the Next button. Detailed information
about these modes can be found in the section IP Assignment
using DHCP protocol and IP Assignment using BOOTP protocol.
The Static option allows you to assign fixed basic parameters
while simultaneously disabling DHCP and BOOTP protocols in
the LAN-Modem. Enter the desired values for IP address, subnet
mask and gateway address in the corresponding entry fields.
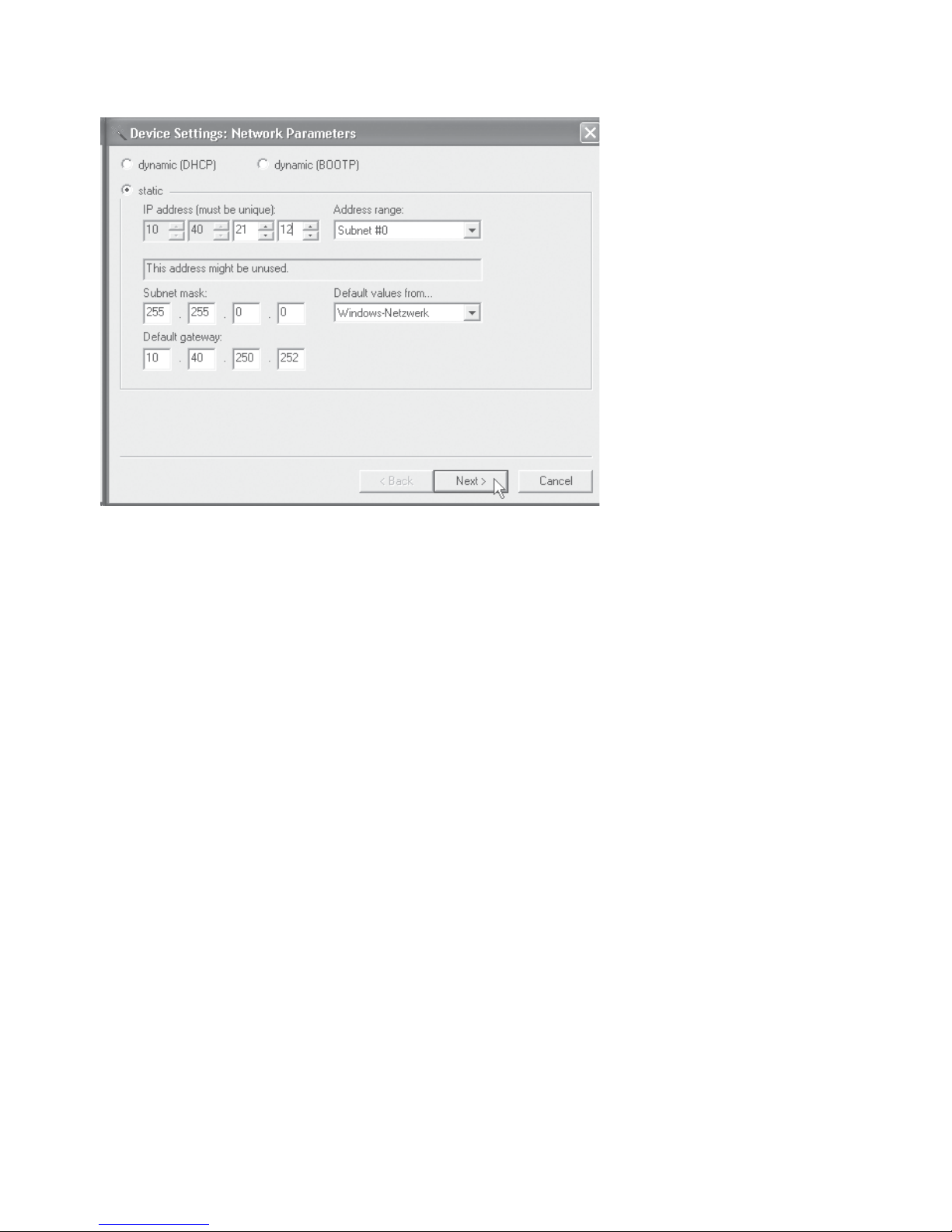
14
W&T Assigning the IP address
Clicking on the Next button assigns the network parameters to
the LAN-Modem. After acknowledging the resulting message,
all the columns in the WuTility device list are filled in with
information.
This concludes the network-side startup of the LAN-Modem.
With the exception of a few special settings, the rest of the
configuration is done as for a standard dial-up modem using
the serial port and AT commands.
1
Changing network parameters is protected by the
system password. To prevent improper access, we
recommend assigning a system password for any LAN-Modems
in use. Additional information can be found in the section
Extended configuration of the LAN-Modem.

15
W&T Assigning the IP address
Subject to error and alteration
2.2 Serial assigning of IP, subnet mask and gateway
After a LAN-Modem reset a time window of around 2 seconds is
available, during which you can assign a new IP address, subnet
mask and gateway address by entering at least 3 „x“.
1
This serial method functions regardless of whether the
LAN-Modem already has an IP address or not. The
procedure can be repeated as often as desired. Therefore use
this method if you don‘t know the IP address or have forgotten
it.
First connect the serial port of the LAN-Modem to a computer.
For a standard PC or laptop, you will need a 1:1 wired RS232
cable (=modem cable, see section RS232 interface).
The serial transmission parameters of the terminal program you
use should be set to 9600 baud, no parity, 8 bits, 1 stop bit, no
handshake. Reset the LAN-Modem by interrupting the power.
When the green status LED lights up, enter the letter „x“ at least
three times on the terminal, until the LAN-Modem returns the
prompt IPno.+<Enter>.
Use the usual format (xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx) to enter the IP
address, and end the entry by pressing <Enter>. If the entry
was accepted, the acknowledgement is the assigned IP address.
Otherwise you will get a FAIL message followed by the last
current IP address.
2.2.1 Assigning of subnet mask and gateway address
Together with the IP address, the subnet mask and gateway
address can also be assigned serially. The entry is separated
by commas and follows the IP address. Entering as shown in

16
W&T Assigning the IP address
the following example will assign IP address 172.17.231.99,
subnet mask 255.255.255.0 and gateway 172.17.231.52 to the
LAN-Modem.
xxx -> LAN-Modem
IP no.+<ENTER>: <- LAN-Modem
172.17.231.99,255.255.255.0,172.17.231.52 -> LAN-Modem
172.17.231.99,255.255.255.0,172.17.231.52-1 <- LAN-Modem
2.2.2 Activating/Deactivating DHCP, BOOTP/RARP
The DHCP and BOOTP/RARP function of the LAN-Modem can
be turned off as part of assigning the IP address serially. To
activate/deactivate the DHCP or BOOTP/RARP client enter one
of the following options directly appended (no space!) to the IP
address and confirm with <Enter>.
• -0
DHCP and BOOTP/RARP = OFF
• -1
DHCP = OFF,
BOOTP/RARP = ON
• -2
DHCP = ON
BOOTP/RARP = OFF
Example: Deactivation of DHCP and BOOTP/RARP
xxx -> LAN-Modem
IP no.+<ENTER>: <- LAN-Modem
172.17.231.99-0 -> LAN-Modem
172.17.231.99 <- LAN-Modem
1
To prevent unintended address assignments or changes,
we recommend deactivating the DHCP and BOOTP/RARP
protocols if they are not expressly used in the respective
network environment. LAN-Modems with incorrectly assigned IP
addresses can be easily found after the fact using the scan
function of the WuTility management tool and reconfigured.

17
W&T Assigning the IP address
Subject to error and alteration
2.3 Assigning the IP using DHCP protocol
Many networks use DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration
Protocol) or its predecessor BOOTP described in the following
section for centralized and dynamic assignment of the network
parameters. DHCP protocol is activated by the factory default
settings, so that in network environments dynamic IP
assignment is sufficient for connecting the LAN-Modem to the
network. The following parameters can be assigned using
DHCP:
• IP address
• Subnet mask
• Gateway address
• Lease time
1
To prevent unintended address assignments or changes,
we recommend deactivating the DHCP and BOOTP/RARP
protocols if they are not expressly used in the respective
network environment. LAN-Modems with incorrectly assigned IP
addresses can be easily found after the fact using the scan
function of the WuTility management tool and reconfigured.
2.3.1 Activating/Deactivating DHCP
The factory default setting is for DHCP protocol active. To
deactivate it or to enable it again later, use one of the following
options.
• Management-Tool WuTility
Select the desired LAN-Modem in the device list and click
on the IP Address button. In the following dialog box enter
the desired option DHCP, BOOTP or Static. Clicking on
Continue then sends the new configuration data to the LANModem.

18
W&T Assigning the IP address
• Serial port
As part of serial IP assignment, the following options for
deactivating/activating DHCP and BOOTP can be selected
directly following the address string:
-0 r Deactivates DHCP and BOOTP/RARP
-1 r Activates BOOTP/RARP
-2 r Activates DHCP
A detailed description of the procedure can be found in the
section on Serial assignment of IP, subnet mask and
gateway.
2.3.2 System Name
To support any automatic updating of the DNS system by the
DHCP server, the LAN-Modem identifies itself within the DHCP
protocol with its system name. The factory default setting for
this is LanModem- followed by the last three places of the
Ethernet address. For example the factory set system name of
a LAN-Modem with the Ethernet address 00:c0:3d:01:02:03 is
LanModem_010203. The system name of the LAN-Modem can
be changed in the configuration. For additional information
refer to the section Extended configuration of the Lan-Modem.
2.3.3 Lease-Time
The lease time determined and transmitted by the DHCP server
specifies the Time-To-Live of the assigned IP address. After half
the lease time has expired, the LAN-Modem attempts to extend
the time for the assigned DHCP server and up update the
address. If this is not possible by the time the lease time
expires, for example because the DHCP server can no longer
be reached, the LAN-Modem deletes the IP address and starts a
new cyclical search for alternate DHCP servers for the purpose
of assigning a new IP address.
Because of the absent clock, the lease time associated with the
current IP address is no longer available after a reset. After the

19
W&T Assigning the IP address
Subject to error and alteration
restart therefore a corresponding update request is issued with
the original DHCP server. If the latter is not resolvable at this
point in time, the LAN-Modem deletes the IP address and starts
a new cyclical search for alternate DHCP servers.
1
If after the assigned lease time has expired the DHCP
server is not reachable, the LAN-Modem deletes its IP
address. All existing network connections with other network
clients are thereby closed. To prevent such events, we
recommend configuring the assigned lease time in the DHCP
server to infinite if possible.
2.3.4 Reserved IP addresses
A LAN-Modem provides services which other clients in the
network can make use of as needed. To open a connection, they
of course need the current IP address for the LAN-Modem, so
that in such situations it makes sense to reserve a particular IP
address for the LAN-Modem on the DHCP server. This is
generally done by linking the IP address to the unique Ethernet
address of the LAN-Modem, which can be found on the sticker
attached to the housing.
58xxx [Model]
EN=00c03d004a05
OK xxxxxx
Ethernet address
2.3.5 Dynamic IP addresses
Operation with dynamic address assignment, whereby the LAN
modem receives a different IP address after each restart of after
the lease time has expired, is not recommended, since the AT
dial-up command can be used only with numeric IP addresses.

20
W&T Assigning the IP address
2.4 Assigning the IP using BOOTP protocol
Many networks use BOOTP as predecessor of DHCP protocol
for centralized and dynamic assignment of IP addresses. The
factory default setting is for BOOTP turned off. You can activate
it e.g. by using WuTility The following parameters can be
assigned:
• IP address
• Subnet mask
• Gateway address
1
To prevent unintended address assignments or changes,
we recommend deactivating the DHCP and BOOTP/RARP
protocols if they are not expressly used in the respective
network environment. LAN-Modem with incorrectly assigned IP
addresses can be easily found after the fact using the scan
function of the WuTility management tool and reconfigured.
2.4.1 Address reservation
BOOTP protocol is based on fixed reservations of fixed IP
addresses for particular Ethernet addresses. This means a LANModem connected to the network only gets an IP address if the
latter was previously stored in the BOOTP server. Check with
your system administrator for creating this reservation. The
Ethernet address of the LAN-Modem can be found on the
housing sticker.
58xxx [Model]
EN=00c03d004a05
OK xxxxxx
Ethernet address

21
W&T Assigning the IP address
Subject to error and alteration
Once the administrator has made the necessary entries, the
LAN-Modem obtains the desired IP address automatically after
each reset. To ensure accessibility of the LAN-Modem even
should the BOOTP server go down, the previous IP address is
retained should there be no reply.

22
W&T Assigning the IP address

23
W&T
Subject to error and alteration
3 Interfaces and displays
. Ethernet interface
. Serial interface
. Supply voltage
. LED displays

24
W&T Interfaces and Displays
3.1 Ethernet connection
The LAN-Modem incorporates an IEEE 802.3-compatible
network interface.
Link-Status
The current link status of all models is indicated by the Error
LED on the device front panel. Flashing at a rate of approx. 1
second indicates that there is no connection to the hub or that
the connection is faulted.
3.1.1 10/100BaseT on RJ45
The LAN-Modem has a 10/100BaseT network interface on a
shielded RJ45 connector. The pin assignments shown below
correspond to an MDI interface, so that the connection to the
hub or switch is made using a max. 100m long 1:1 shielded
patch cable.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Direction
Out
Out
In
In
In
In
In
In
Signal
Tx+
Tx-
Rx+
nc
nc
Rx-
nc
nv
Pin
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
The network connection is galvanically isolated with respect to
the supply voltage as well as the serial interface(s) for at least
500V
rms
.
Auto Negotiation: 10/100BaseT, Full/Half Duplex
LAN-Modems are factory set to operate in Auto-Negotiation
mode on the network side. The data transmission speed and
duplex are automatically negotiated with the connected switch/
hub and set accordingly.

25
W&T Interfaces and Displays
Subject to error and alteration
In addition to the Auto-Negotiation mode, both the LAN-Modems as well as many switches can be configured for fixed
transmission parameters with respect to speed and duplex. To
prevent communications problems (duplex mismatch), only the
following two combinations are permissible:
• Both parties (switch and LAN-Modem) are operated in Auto-
Negotiation mode.
• Both parties (switch and LAN-Modem) are configured for the
same (fixed) transmission speeds and duplex mode.
Information on toggling between Auto Negotiation and fixed
transmission speeds can be found in the section Expanded
LAN Modem Settings.
1
Managable switches often have special protocols
(spanning tree, port trunking, ...) as required for
example for uplinks to other switches or broad-band connection
of servers. These protocols are not generally required for
connecting a normal terminal device such as the LAN-Modem,
and they do under some circumstances significantly delay
opening of communication after a new start. We recommend
deactivating these protocols and functions on the port used for
the LAN-Modem. Please consult here with the responsible
network administrator.

26
W&T Interfaces and Displays
3.2 RS232 interface
The pin assignments for the RS232 port are identical with that
of a dialup modem, which means that standard cable can be
used. Make sure that the ports for the LAN-Modem and the
serial terminal device are configured for identical transmission
parameters and handshake procedures.
The following table shows the factory configured functions for
the individual signals. These can be modified using the
respective AT commands.
Factory setting
Active for existing connection
Data output
Data input
If deactive, break connection and do not
accept new connection until active again
---
Always active
Hardware handshake input
Data output only when active
Hardware handshake output
active = ready to receive data
deactive = not ready to receive data
For incoming connection alternately 1s
active, 4s deactive until connection is
established; then deactive
Direction
Output
Output
Input
Input
GND
Output
Input
Output
Output
Pin
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
AT command
AT&Cn
---
---
AT&Dn
AT&Sn
AT&Kn
AT&Kn
---

27
W&T Interfaces and Displays
Subject to error and alteration
3.3 Supply voltage
The supply voltage for the LAN-Modem can be brought in on
the adjacent screw terminals on the underside of the housing.
DC voltage of any polarity or AC voltage may be used. The
reverse polarity protection results in the following various
maximum and minimum values for the supply voltage:
• AC: 9Vrms (- 10%) - 30Vrms (+10%)
• DC: 12V (-10%) - 48V (+10%)
The current draw is indicated in the technical appendix.
 Loading...
Loading...