Wright Medical Technology Salvation User Manual

SALVATION™ Midfoot Reconstruction System
English (en)
For additional languages, visit our website www.wright.com. Then click on the Prescribing Use option.
For additional information and translations please contact the manufacturer or local distributor.
M
Wright Medical Technology, Inc.
1023 Cherry Road
Memphis, TN 38117
U.S.A.
The following languages are included in this packet:
153910-1
December 2018
Printed in U.S.A.


Attention Operating Surgeon
IMPORTANT MEDICAL INFORMATION
OUTLINE:
DEFINITIONS
I. GENERAL PRODUCT INFORMATION
A. PATIENT SELECTION
B. CONTRAINDICATIONS
C. POTENTIAL COMPLICATIONS AND ADVERSE REACTIONS
D. PRECAUTIONS
E. MRI SAFETY INFORMATION
F. HANDLING AND STERILIZATION
G. STORAGE CONDITIONS
II. SPECIFIC PRODUCT INFORMATION
A. SALVATION™ MIDFOOT RECONSTRUCTION SYSTEM
WRIGHT MEDICAL
SALVATION™ FUSION SYSTEMS
(153910-1)
EN
1
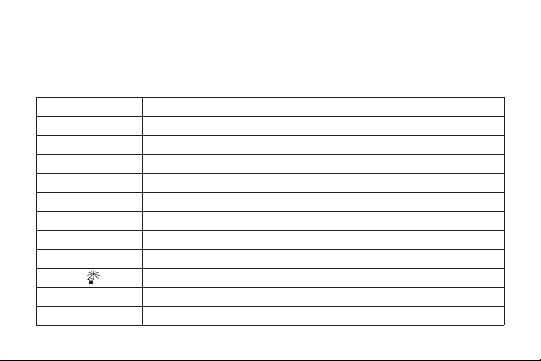
DEFINITIONS
Symbols and abbreviations may be used on the package label. The following table provides the
definition of these symbols and abbreviations.
Table 1. Definitions of Symbols and Abbreviations
Symbol Definition
g
h
D
Y
i
H
l
p
N
M
Batch code
Catalog number
Do not re-use
Caution, consult accompanying documents
Consult operating instructions
Use by
Temperature limitation
Keep dry
Keep away from sunlight
Date of manufacture
Manufacturer
2
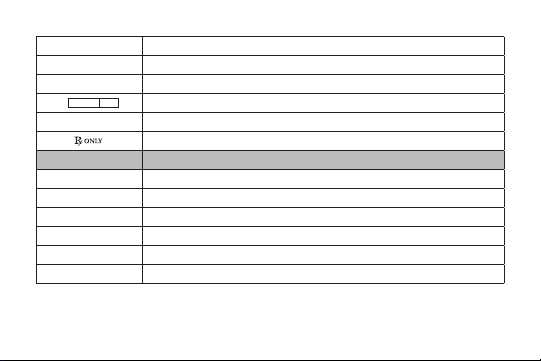
P[]\
I
K
STERILE GAS
J
Abbreviation Material
Ti Titanium
Ti6Al4V Titanium Alloy
CoCr Cobalt Chrome Alloy
SS Stainless Steel
UHMWPE Ultra High Molecular Weight Polyethylene
Authorized EC Representative in the European Community
Sterilized using ethylene oxide
Sterilized using radiation
Sterilized using gas plasma
Sterilized using aseptic processing techniques
For prescription use only
3

I. GENERAL PRODUCT INFORMATION
Through the advancement of surgical fusion hardware, the surgeon has been provided
a means of correcting deformity and reducing pain for many patients. While the implants
used are largely successful in attaining these goals, it must be recognized that they are
manufactured from metal, and that no implant can be expected to withstand the activity levels
and loads as would normal, healthy bone after fusion occurs.
Each patient must be evaluated by the surgeon to determine the risk/benefit relationship.
In using fusion implants, the surgeon should be aware of the following:
• The correct selection and sizing of the implant is extremely important. Selection of
the proper size, shape, and design of the implant increases the potential for success. The
implants require careful seating and adequate bone support.
• In selecting patients for surgery, the following factors can be critical to the
eventual success of the procedure:
1. Patient’s occupation or activity. If the patient is involved in an occupation or activity
which includes substantial lifting or muscle strain, the resultant forces can cause
failure of the fixation, the device, or both. The implant will not restore function to the
level expected with normal healthy bone, and the patient should not have unrealistic
functional expectations.
2. Condition of senility, mental illness, or alcoholism. These conditions, among
others, may cause the patient to ignore certain necessary limitations and precautions
in the use of the implant, leading to failure or other complications.
3. Foreign body sensitivity. Where material sensitivity is suspected, appropriate tests
should be made prior to material selection or implantation.
4

A. PATIENT SELECTION
Use of surgical fusion hardware requires consideration of the following general
indications:
• Good condition of the patient
• Good neurovascular status
• Adequate skin coverage
• Possibility of a functional musculotendinous system
• Adequate bone stock to receive implant
• Availability of post-operative therapy
• Cooperative patient
See Section II for specific product information.
B. GENERAL SURGICAL CONTRAINDICATIONS
• Infection
• Physiclogically or psychologically inadequate patient
• Inadequate skin, bone, or neurovascular status
• Irreparable tendon system
• Possibility for conservative treatment
• Growing patients with open epiphyses
• Patients with high levels of activity
5

C. POTENTIAL COMPLICATIONS AND ADVERSE REACTIONS
In any surgical procedure, the potential for complications exists. The risks and
complications with these implants include:
• Infection or painful, swollen or inflamed implant site
• Fracture of the implant
• Loosening or dislocation of the implant requiring revision surgery
• Bone resorption or over-production
• Allergic reaction(s) to implant material(s)
• Untoward histological responses posibly involving macrophages and/or fibroblasts
• Migration of particle wear debris possibly resulting in a bodily response
• Embolism
See Section II for specific product information.
D. PRECAUTIONS
Following the instructions for use provided in product literature can minimize the potential
for complications or adverse reactions with any implant.
It is the responsibility of each surgeon using implants to consider the clinical and
medical status of each patient and to be knowledgeable about all aspects of implant
procedure and the potential complications that may occur. The benefits derived from
implant surgery may not meet the patient’s expectations or may deteriorate with
time, necessitating revision surgery to replace the implant or to carry out alternative
procedures. Revision surgeries with implants are common. The patient’s mental status
6
 Loading...
Loading...