Page 1

WLAN 802.11a/b/g USB 2.0 Adapter
User’s Guide
Version: 1.0 — Sep. 2004
Page 2

Copyright Statement
No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or
transmitted in any form or by any means, whether electronic, mechanical,
photocopying, recording or otherwise without the prior writing of the publisher.
Windows™ 2000/XP are trademarks of Microsoft® Corp.
Atheros is a registered trademark of Atheros Communications, Inc.
All copyright reserved.
1
Page 3

Federal Communication Commission Interference Statement
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class
B digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are
designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a
residential installation. This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio
frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the
instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio communications.
However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular
installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or
television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and
on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one of the
following measures:
- Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
- Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
- Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that
to which the receiver is connected.
- Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the
following two conditions: (1) This device may not cause harmful interference,
and (2) this device must accept any interference received, including
interference that may cause undesired operation.
FCC Caution: Any changes or modifications not expressly approved by the
party responsible for compliance could void the user's authority to operate this
equipment.
IMPORTANT NOTE:
FCC Radiation Exposure Statement:
This equipment complies with FCC radiation exposure limits set forth for an
uncontrolled environment. End users must follow the specific operating
instructions for satisfying RF exposure compliance. To maintain compliance with
FCC RF exposure compliance requirements, please avoid direct contact to the
transmitting antenna during transmitting. For operation within 5.15 ~ 5.25GHz
frequency range, it is restricted to indoor environment. This transmitter must
not be co-located or operating in conjunction with any other antenna or
transmitter.
Wistron NeWeb Corp. declares that this product is limited in CH1~CH11 by
specified firmware controlled in the USA.
Highest SAR test value: 1.55W/kg
2
Page 4

Table of Contents
REGULATORY INFORMATION......................................................................錯誤! 尚未定義書籤。
1. WELCOME...............................................................................................................................................5
1.1 KIT CONTENTS......................................................................................................................................5
1.2 MAIN FEATURES OF 802.11A/B/G USB 2.0 ADAPTER.........................................................................5
1.3 WIRELESS NETWORKING SCENARIOS..................................................................................................6
2. QUICK START GUIDE..........................................................................................................................8
2.1 INSTALLATION.......................................................................................................................................8
2.2 CONNECTING TO AN EXISTING NETWORK...........................................................................................9
3. STEP-BY-STEP INSTRUCTIONS......................................................................................................10
3.1 INSTALLATION.....................................................................................................................................10
3.2 CONNECTING TO A NETWORK.............................................................................................................15
3.3 CREATING AN AD HOC NETWORK .....................................................................................................19
3.4 REMOVING YOUR 802.11A/B/G USB 2.0 ADAPTER...........................................................................21
3.5 UNINSTALLATION................................................................................................................................22
4. USING THE UTILITY..........................................................................................................................24
4.1 CURRENT STATUS ...............................................................................................................................24
4.2 DIAGNOSTICS ......................................................................................................................................25
4.3 PROFILE MANAGEMENT.....................................................................................................................27
4.3.1 Creating or Modifying a Configuration Profile................................................. 28
4.3.2 Removing a Profile......................................................................................... 30
4.3.3 Profile Auto Selection..................................................................................... 31
4.3.4 Switching Profiles...........................................................................................32
4.4 SECURITY............................................................................................................................................33
4.4.1 Using EAP-TLS Security................................................................................. 33
4.4.2 Enabling EAP-TLS Security............................................................................ 34
4.4.3 Using EAP-TTLS Security............................................................................... 35
4.4.4 Enabling EAP-TTLS Security.......................................................................... 36
4.4.5 Using PEAP(EAP-GTC) Security ....................................................................37
4.4.6 Enabling PEAP(EAP-GTC) Security................................................................38
4.4.7 Using PEAP-MSCHAP V2 Security................................................................. 39
4.4.8 Enabling PEAP- MSCHAP V2 Security............................................................40
4.4.9 Using LEAP Security......................................................................................41
4.4.10 Configuring LEAP........................................................................................ 41
3
Page 5

4.4.11 Using WPA Passphrase Security ....................................................................43
4.4.12 Using Pre-Shared Key (Static WEP) Security..................................................44
4.5 DISPLAY SETTING...............................................................................................................................45
4.6 ACTIONS TOOLS ..................................................................................................................................45
5. RIGHT CLICKING THE TRAY ICON .............................................................................................46
6. NETWORK APPLICATION................................................................................................................47
6.1 SURVEYING THE NETWORK NEIGHBORHOOD....................................................................................47
6.2 FILE SHARING.....................................................................................................................................48
6.3 USING THE SHARED FOLDER..............................................................................................................49
4
Page 6

1. Welcome
Thank you for purchasing our 802.11a/b/g USB 2.0 Adapter, and welcome to Wireless
LAN— the easy way to wireless networking.
This user’s guide introduces to you the 802.11a/b/g USB 2.0 Adapter and describes
the most common configurations, which will help you connect to your network easily.
Please read this manual to get familiar with the IEEE802.11a/b/g Wireless LAN. This
manual contains detailed instructions in operation of this product. Please keep this
manual for future reference.
As this product is designed to run under Microsoft Windows, it is recommended that
to be installed by people who are familiar with the installation procedures for network
operating systems under Microsoft Windows.
1.1 Kit Contents
The 802.11a/b/g USB 2.0 Adapter kit should include the following items: One
802.11a/b/g USB 2.0 Adapter with USB cable, one CD and one Quick Start Guide.
n One 802.11a/b/g USB 2.0 Adapter
n One Software CD including:
(1) Utility & Driver Installation Software
(2) User Manual PDF File
n Quick Start Guide
1.2 Main Features of 802.11a/b/g USB 2.0 Adapter
Status LED:
n Off: Power Off.
n Blinking: The USB adapter is powered on but no wireless connection is made
yet.
n Steady Green: Wireless connection is linked.
802.11a/b/g USB 2.0 Adapter features:
n Plug & Play
n Worldwide Radio Support
5
Page 7

n Super A/GTM and eXtended Range XRTM Technology
n Backward Compatible with 802.11b
n Roaming Support
n 802.1x Authentication
n AES-CCM & TKIP Encryption
n 64/128/152-bit WEP Encryption
n Driver Support OS Windows®2000/XP
802.11a/b/g USB 2.0 Adapter supports:
n Automatic load balancing for optimized bandwidth
n Advanced power management
n OS Windows® 2000/XP
1.3 Wireless Networking Scenarios
As our 802.11a/b/g USB 2.0 Adapter is interoperable and compatible with other IEEE
802.11a/b/g compliant products from other manufacturers, it offers you the most
freedom to establish your ideal wireless network. Therefore, after installing
802.11a/b/g USB 2.0 Adapter, you can connect your computer to:
n A Peer-to-Peer Workgroup of 802.11a/b/g compliant wireless devices.
n A LAN (Local Area Network) constructed by Access Point(s) or other
802.11a/b/g compliant systems.
n Share your Internet access by using just one connection, share printers and other
peripheral devices, share data and image files between networked PCs, play
multi-player games, and use other network enabled sharing resources.
6
Page 8

Peer-to-Peer Networking:
An Ad Hoc Network could be easily set up with some PCs and this 802.11a/b/g
USB 2.0 Adapter or our other WLAN devices. Therefore, it is very suitable to
build a network for temporary use, such as for demonstration in exhibition, for
new sales point/branch use and alike.
Cooperate LAN (Local Area Networking):
With some 802.11a/b/g USB 2.0 Adapters and Access Points, it is easy to
construct a LAN with access to Internet for enterprise use.
The construction is quite easy that the 802.11a/b/g USB 2.0 Adapter and Access
Point will automatically work at the most suitable frequency when Access Point is
set within the proper range.
In addition, commonly manufacturers will bundle the Site-Survey tool for users to
check the communication quality.
7
Page 9

2. Quick Start Guide
2.1 Installation
1. Insert the installation CD. It automatically starts the setup program for software
installation.
2. Follow the installation wizard to complete the software installation process.
3. Connect the WLAN 802.11a/b/g USB 2.0 Adapter to your laptop PC/desktop
PC during software installation.
4. Restart your PC.
NOTE! Select “Cancel” when Found New Hardware window appears.
NOTE! In Windows XP, it is recommended that you use the WLAN 802.11a/b/g
USB2.0 Utility.
8
Page 10
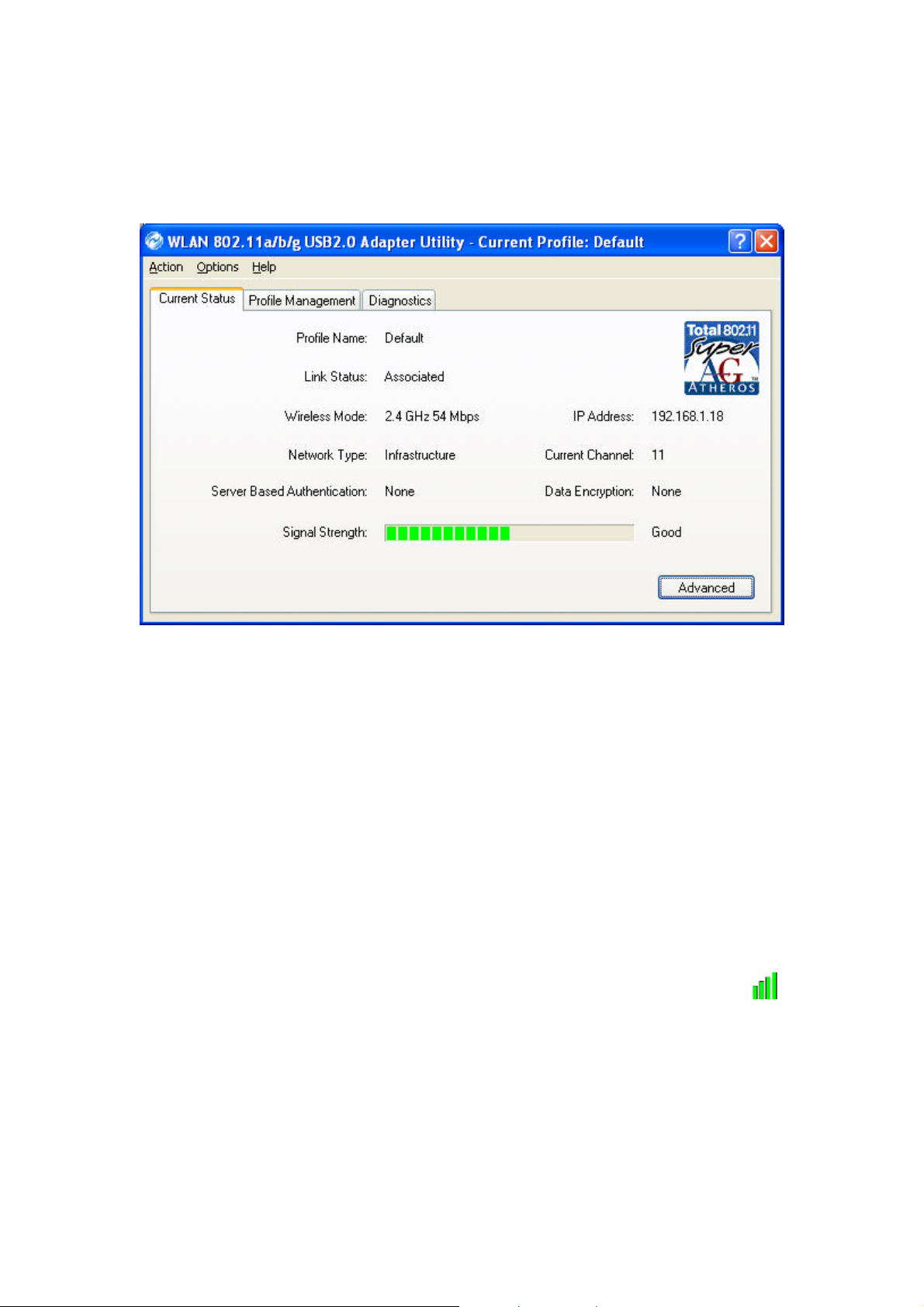
2.2 Connecting to an Existing Network
After restarting your PC, the adapter automatically connects to an unsecured network
that has the best signal strength(if there’s any). Profile Name shows Default.
You may also manually assign a network to connect with. Follow the steps below:
1. Open WLAN 802.11a/b/g USB 2.0 Adapter Utility (by double-clicking on the
shortcut icon on the desktop), and click Profile Management tab.
2. Click Scan, and Available Infrastructure and Ad Hoc Networks list appears.
3. Click the desired network SSID and click Activate.
4. Contact the network administrator for Profile Settings: General, Security and
Advanced.
5. Once connected, the configuration icon in the Windows System Tray appears .
You can click Current Status tab to check the connection status.
6. For details of each tab in WLAN 802.11a/b/g USB2.0 Adapter Utility, please read
Chapter 4.
9
Page 11

3. Step-by-Step Instructions
3.1 Installation
1. Insert the installation CD into your CD-ROM drive. Click Next.
2. Select “I accept the terms of the license agreement” and click Next.
10
Page 12

3. Click Next. You can highlight different items to choose different setup.
4. Click Yes. System reminds you the reboot step.
11
Page 13

5. Click Next. Or click Browse to select the destination folder you prefer.
6. Click Next. Edit the Program Folder name if necessary.
12
Page 14

7. Read the notice and click Next.
8. Click Next. WLAN 802.11a/b/g USB2.0 Adapter Utility is recommended.
13
Page 15

9. Insert the adapter and click OK.
10. Click OK and your PC will restart.
11. A short-cut icon appears on the desktop of your PC.
NOTE! Select “Cancel” when Found New Hardware window appears.
NOTE! In Windows XP, it is recommended that you use the WLAN 802.11a/b/g
USB2.0 Utility.
14
Page 16

3.2 Connecting to a network
NOTE! For details of Utility Configuration, please refer to Chapter 4.
Status Icons
: Low Signal Strength
: Medium Signal Strength
: High Signal Strength
: No Signal Strength
: Radio Off
After restarting your PC, the adapter automatically connects to an unsecured network
that has the best signal strength (if there’s any). Profile Name shows Default.
: Ad Hoc Network
: Infrastructure Network
: Infrastructure Network Connected
: Profile Activated
: Secured
You may also manually assign a network to connect with. Follow the steps below:
15
Page 17

1. Open WLAN 802.11a/b/g USB 2.0 Adapter Utility (by double-clicking on the
shortcut icon on the desktop), and click Profile Management tab.
2. Click Scan, and Available Infrastructure and Ad Hoc Networks list appears.
16
Page 18

3. Click the desired network SSID and click Activate.
4. Contact the network administrator for Profile Settings: General, Security and
Advanced.
General Tab: Enter a Profile Name and SSID (if necessary).
17
Page 19

Security Tab: If the connected network is secured, contact the network
administrator for Security Settings.
Advanced Tab: Click Advanced for other network settings.
5. Once connected, the status icon in the Windows System Tray appears. You
can click Current Status tab to check the connection status.
18
Page 20

3.3 Creating an Ad Hoc Network
If you have more computers and only want to place them in a local area network, or
you want to communicate directly without using an Access Point or any connection to
a wired network, you can create a new Ad Hoc Network.
1. In Profile Management tab, click New button to create a profile.
19
Page 21

2. Click Advanced to switch Network Type to Ad Hoc.
3. Click General to edit the Profile and SSID1 names.
20
Page 22

4. Click Security to configure security options.
5. Click OK button.
3.4 Removing your 802.11a/b/g USB 2.0 Adapter
You can remove the device after you finished the action with the device. However, in
Windows XP and Windows 2000, please follow the safe removal procedure. You can
find a safe removal icon in your computer’s notification area.
1. Double click the Safely Remove Hardware icon.
2. The “Safely Remove Hardware” window will pop up. You can select the device
you want to remove. Then, click the “Stop” button.
NOTE! When removing the WLAN 802.11a/b/g USB 2.0 Adapter, you will lose your
connection to the network. Make sure you have closed all files and network
applications (such as e-mail) before removing the WLAN 802.11a/b/g USB
2.0 Adapter.
21
Page 23

3.5 Uninstallation
1. Make sure the Utility is closed.
2. Go to Star → Programs → WLAN 802.11a+b+g USB2.0 Adapter → Uninstall
Utility.
3. Choose “Uninstall the previous installation” and click Next.
4. Click Yes.
5. Click OK.
22
Page 24

6. Click Yes.
7. Click OK, and your PC will restart. Uninstallation is finished.
23
Page 25

4. Using the Utility
4.1 Current Status
The Current Status tab contains general information about the program and its
operations.
n Profile Name: The name of the current selected configuration profile. If you see
Default in Profile Name, it is because you do not assign a specific SSID, and the
adapter automatically searches and connects to the most suitable network. You
can configure the profile name through Profile Management gModifygGeneral.
n Link Status: Shows whether or not the station is associated to the wireless
network.
n Wireless Mode: Displays the wireless mode. You can configure the wireless
mode through Profile Management gModifygAdvanced.
n IP Address: Displays the computer's IP address.
n Network Type: The type of network the station is connected to. The options
include infrastructure and Ad Hoc. You can configure the network type through
Profile Management gModifygAdvanced.
n Current Channel: Shows the currently connected channel.
n Server Based Authentication: Shows whether server based authentication is
used.
n Data Encryption: Displays the encryption type the driver is using. You can
configure Data Encryption through Profile Management gModifygSecurity.
n Signal Strength: Shows the strength of the signal.
24
Page 26

4.2 Diagnostics
In Diagnostics tab, you can check Transmit and Receive Data: Multicast Packets,
Broadcast Packets, Unicast Packets and Total Bytes.
Adapter Information
n Card Name: The name of the wireless network adapter.
n MAC Address: The MAC address of the wireless network adapter.
n Driver: The driver name and path of the wireless network adapter driver.
n Driver Version: The version of the wireless network adapter driver.
n Driver Date: The creation date of the wireless network adapter driver.
n Client Name: The name of the client computer.
25
Page 27

Advanced Statistics: Shows receive and transmit statistical information for the
following receive and transmit diagnostics for frames received by or transmitted to the
wireless network adapter:
Transmitted Frames:
n Frames transmitted OK
n Frames retried
n Frames dropped
n No ACK frames
n ACK frames
n RTS Frames
n Clear-to-send (CTS) Frames
n No CTS frames
n Retried RTS frames
n Retried data frames
Received Frames:
n Frames received OK
n Beacons
n Frames with errors
26
Page 28

n CRC errors
n Encryption errors
n Duplicate frames
n AP mismatches
n Data rate mismatches
n Authentication time-out
n Authentication rejects: the number of AP authentication failures received by the
wireless network adapter
n Association time-out
n Association rejects: the number of access point authentication rejects received by
the wireless network adapter
n Standard MIC OK
n Standard MIC errors
n CKIP MIC OK
n CKIP MIC errors
4.3 Profile Management
n Network Type: Indicates whether the current activated network type is
Infrastructure or Ad Hoc mode.
n Security Mode: Indicates current connected network’s security mode.
n Network Name: Indicates current connected network’s name.
n New: To create new profile.
27
Page 29

n Modify: To edit settings of chosen profile.
n Remove: To remove the chosen profile from the list.
n Activate: To activate the chosen profile.
n Import: To import a pre-set profile (pre-saved as a Config File *.prf)
n Export: To export the chosen profile, so you can save the profile as a Config File
(*.prf) for future use.
n Scan: To scan all available network in vicinity.
n Order Profiles: To place the order of preferred profiles.
4.3.1 Creating or Modifying a Configuration Profile
1. To add a New configuration profile, click New on the Profile Management tab. To
modify a configuration profile, select the configuration from the Profile list and
click the Modify button.
2. The Profile Management dialog box displays the General, Security and
Advanced tabs.
3. Edit the fields in the General tab to configure the configuration profile.
n Profile Name: Identifies the configuration profile. This name should be
unique. Profile names are not case sensitive.
n Client Name: Identifies the client machine.
n Network Names (SSIDs): The IEEE 802.11 wireless network name. This
field has a maximum limit of 32 characters. Configure up to three SSIDs
(SSID1, SSID2, SSID3).
28
Page 30

4. Edit the fields in the Security tab to configure the configuration profile.
n WPA: Enables the use of Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA).
n WPA Passphrase: Enables WPA Passphrase security. Click on the
Configure button and fill in the WPA Passphrase.
n 802.1x: Enables 802.1x security. This option requires IT administration.
n Pre-Shared Key (Static WEP): Enables the use of pre-shared keys that are
defined on both the access point and the station.
n None: No security (not recommended).
5. Edit the fields in the Advanced tab to configure the configuration profile.
29
Page 31

n Power Save Mode: Specify:
ü Maximum mode: causes the access point to buffer incoming messages for
the wireless adapter. The adapter up periodically polls the access point to
see if any messages are waiting.
ü Normal mode: uses maxim when retrieving a large number of packets, then
switches back to power save mode after retrieving the packets.
ü Off: turns power saving off, thus powering up the wireless adapter
continuously for a short message response time.
n Network Type: Specifies the network as either Infrastructure or Ad Hoc.
n 802.11b Preamble: Specifies the preamble setting in 802.11b. The default
setting is Short & Long (access point mode), which allows both short and
long headers in the 802.11b frames. The adapter can only use short radio
headers if the access point supports and uses them. Set to Long Only to
override allowing short frames.
n Wireless Mode: Specifies 5GHz 54Mbps, 2.4GHz 54Mbps, 2.4GHz 11Mbps,
or Super A/G operation in an access point network. The wireless adapter must
match the wireless mode of the access point it associates to.
n Wireless Mode when Starting Ad Hoc Network: Specifies 5GHz 54Mbps,
5GHz 108Mbps, or 2.4GHz 54/11Mbps, to start an Ad Hoc network if no
matching network name is found after scanning all available modes. This
mode also allows selection of the channel the wireless adapter uses. The
channels available depend on the regulatory domain. If the adapter finds no
other ad hoc adapters, this selection specifies which channel with the adapter
starts the Ad Hoc network with. The wireless adapter must match the wireless
mode of the access point it associates to.
n 802.11 Authentication Mode: Select what mode the wireless adapter uses to
authenticate to an access point:
ü Auto: causes the adapter to attempt authentication using shared, but
switches it to open authentication if shared fails.
ü Open: enables an adapter to attempt authentication regardless of its WEP
settings. It will only associate with the access point if the WEP keys on both
the adapter and the access point match.
ü Shared: only allows the adapter to associate with access points that have
the same WEP key.
4.3.2 Removing a Profile
1. Go to the Profile Management tab.
30
 Loading...
Loading...