Page 1

Wireshark User’s Guide
For Wireshark 2.1
Ulf Lamping <ulf.lamping[AT]web.de>
Richard Sharpe, NS Computer Software and
Services P/L <rsharpe[AT]ns.aus.com>
Ed Warnicke <hagbard[AT]physics.rutgers.edu>
Page 2

Wireshark User’s Guide: For Wireshark 2.1
by Ulf Lamping, Richard Sharpe, and Ed Warnicke
Copyright © 2004-2014 Ulf Lamping, Richard Sharpe, Ed Warnicke
Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU General Public License, Version 2 or any later
version published by the Free Software Foundation.
All logos and trademarks in this document are property of their respective owner.
Page 3

Preface ............................................................................................................................. ix
1. Foreword ............................................................................................................... ix
2. Who should read this document? ............................................................................... ix
3. Acknowledgements ................................................................................................. ix
4. About this document ................................................................................................ x
5. Where to get the latest copy of this document? ............................................................. x
6. Providing feedback about this document ...................................................................... x
1. Introduction .................................................................................................................... 1
1.1. What is Wireshark? ............................................................................................... 1
1.1.1. Some intended purposes .............................................................................. 1
1.1.2. Features .................................................................................................... 1
1.1.3. Live capture from many different network media ............................................. 2
1.1.4. Import files from many other capture programs ................................................ 2
1.1.5. Export files for many other capture programs .................................................. 2
1.1.6. Many protocol dissectors ............................................................................. 2
1.1.7. Open Source Software ................................................................................. 2
1.1.8. What Wireshark is not ................................................................................. 2
1.2. System Requirements ............................................................................................. 3
1.2.1. Microsoft Windows .................................................................................... 3
1.2.2. UNIX / Linux ............................................................................................ 3
1.3. Where to get Wireshark ......................................................................................... 4
1.4. A brief history of Wireshark ................................................................................... 4
1.5. Development and maintenance of Wireshark .............................................................. 5
1.6. Reporting problems and getting help ........................................................................ 5
1.6.1. Website ..................................................................................................... 6
1.6.2. Wiki ......................................................................................................... 6
1.6.3. Q&A Site .................................................................................................. 6
1.6.4. FAQ ......................................................................................................... 6
1.6.5. Mailing Lists ............................................................................................. 6
1.6.6. Reporting Problems .................................................................................... 7
1.6.7. Reporting Crashes on UNIX/Linux platforms .................................................. 7
1.6.8. Reporting Crashes on Windows platforms ....................................................... 8
2. Building and Installing Wireshark ...................................................................................... 9
2.1. Introduction ......................................................................................................... 9
2.2. Obtaining the source and binary distributions ............................................................. 9
2.3. Installing Wireshark under Windows ........................................................................ 9
2.3.1. Installation Components ............................................................................. 10
2.3.2. Additional Tasks ....................................................................................... 10
2.3.3. Install Location ......................................................................................... 10
2.3.4. Installing WinPcap .................................................................................... 11
2.3.5. Windows installer command line options ...................................................... 11
2.3.6. Manual WinPcap Installation ...................................................................... 11
2.3.7. Update Wireshark ..................................................................................... 11
2.3.8. Update WinPcap ....................................................................................... 12
2.3.9. Uninstall Wireshark ................................................................................... 12
2.3.10. Uninstall WinPcap ................................................................................... 12
2.4. Installing Wireshark under OS X ........................................................................... 12
2.5. Building Wireshark from source under UNIX ........................................................... 12
2.6. Installing the binaries under UNIX ......................................................................... 13
2.6.1. Installing from RPM’s under Red Hat and alike ............................................. 13
2.6.2. Installing from deb’s under Debian, Ubuntu and other Debian derivatives ............ 13
2.6.3. Installing from portage under Gentoo Linux ................................................... 14
2.6.4. Installing from packages under FreeBSD ....................................................... 14
2.7. Troubleshooting during the install on Unix .............................................................. 14
iii
Page 4

Wireshark User’s Guide
2.8. Building from source under Windows ..................................................................... 14
3. User Interface ............................................................................................................... 15
3.1. Introduction ........................................................................................................ 15
3.2. Start Wireshark ................................................................................................... 15
3.3. The Main window ............................................................................................... 15
3.3.1. Main Window Navigation .......................................................................... 16
3.4. The Menu .......................................................................................................... 17
3.5. The “File” menu ................................................................................................. 18
3.6. The “Edit” menu ................................................................................................. 20
3.7. The “View” menu ............................................................................................... 22
3.8. The “Go” menu .................................................................................................. 26
3.9. The “Capture” menu ............................................................................................ 27
3.10. The “Analyze” menu .......................................................................................... 28
3.11. The “Statistics” menu ......................................................................................... 30
3.12. The “Telephony” menu ....................................................................................... 31
3.13. The “Tools” menu ............................................................................................. 32
3.14. The “Internals” menu ......................................................................................... 33
3.15. The “Help” menu .............................................................................................. 33
3.16. The “Main” toolbar ............................................................................................ 34
3.17. The “Filter” toolbar ............................................................................................ 38
3.18. The “Packet List” pane ....................................................................................... 39
3.19. The “Packet Details” pane ................................................................................... 40
3.20. The “Packet Bytes” pane .................................................................................... 40
3.21. The Statusbar .................................................................................................... 41
4. Capturing Live Network Data .......................................................................................... 43
4.1. Introduction ........................................................................................................ 43
4.2. Prerequisites ....................................................................................................... 43
4.3. Start Capturing .................................................................................................... 43
4.4. The “Capture Interfaces” dialog box ....................................................................... 44
4.5. The “Capture Options” dialog box .......................................................................... 45
4.5.1. Capture frame .......................................................................................... 45
4.5.2. Capture File(s) frame ................................................................................. 46
4.5.3. Stop Capture… frame ................................................................................ 47
4.5.4. Display Options frame ............................................................................... 47
4.5.5. Name Resolution frame ............................................................................. 47
4.5.6. Buttons ................................................................................................... 48
4.6. The “Edit Interface Settings” dialog box .................................................................. 48
4.7. The “Compile Results” dialog box ......................................................................... 49
4.8. The “Add New Interfaces” dialog box .................................................................... 49
4.8.1. Add or remove pipes ................................................................................. 50
4.8.2. Add or hide local interfaces ........................................................................ 50
4.8.3. Add or hide remote interfaces ..................................................................... 50
4.9. The “Remote Capture Interfaces” dialog box ............................................................ 50
4.9.1. Remote Capture Interfaces .......................................................................... 51
4.9.2. Remote Capture Settings ............................................................................ 51
4.10. The “Interface Details” dialog box ........................................................................ 52
4.11. Capture files and file modes ................................................................................ 52
4.12. Link-layer header type ........................................................................................ 53
4.13. Filtering while capturing ..................................................................................... 54
4.13.1. Automatic Remote Traffic Filtering ............................................................ 55
4.14. While a Capture is running … ............................................................................. 56
4.14.1. Stop the running capture ........................................................................... 56
4.14.2. Restart a running capture .......................................................................... 56
5. File Input, Output, and Printing ........................................................................................ 58
iv
Page 5

Wireshark User’s Guide
5.1. Introduction ........................................................................................................ 58
5.2. Open capture files ............................................................................................... 58
5.2.1. The “Open Capture File” dialog box ............................................................ 58
5.2.2. Input File Formats .................................................................................... 59
5.3. Saving captured packets ....................................................................................... 61
5.3.1. The “Save Capture File As” dialog box ........................................................ 61
5.3.2. Output File Formats .................................................................................. 62
5.4. Merging capture files ........................................................................................... 63
5.4.1. The “Merge with Capture File” dialog box .................................................... 63
5.5. Import hex dump ................................................................................................. 64
5.5.1. The “Import from Hex Dump” dialog box ..................................................... 64
5.6. File Sets ............................................................................................................ 65
5.6.1. The “List Files” dialog box ........................................................................ 66
5.7. Exporting data .................................................................................................... 66
5.7.1. The “Export as Plain Text File” dialog box ................................................... 67
5.7.2. The “Export as PostScript File” dialog box .................................................... 67
5.7.3. The "Export as CSV (Comma Separated Values) File" dialog box ...................... 67
5.7.4. The "Export as C Arrays (packet bytes) file" dialog box ................................... 68
5.7.5. The "Export as PSML File" dialog box ......................................................... 68
5.7.6. The "Export as PDML File" dialog box ........................................................ 68
5.7.7. The "Export selected packet bytes" dialog box ............................................... 68
5.7.8. The "Export Objects" dialog box ................................................................. 69
5.8. Printing packets .................................................................................................. 69
5.8.1. The “Print” dialog box ............................................................................... 69
5.9. The “Packet Range” frame .................................................................................... 70
5.10. The Packet Format frame .................................................................................... 71
6. Working with captured packets ........................................................................................ 72
6.1. Viewing packets you have captured ........................................................................ 72
6.2. Pop-up menus ..................................................................................................... 72
6.2.1. Pop-up menu of the “Packet List” column header ........................................... 72
6.2.2. Pop-up menu of the “Packet List” pane ......................................................... 73
6.2.3. Pop-up menu of the “Packet Details” pane .................................................... 75
6.3. Filtering packets while viewing .............................................................................. 78
6.4. Building display filter expressions .......................................................................... 79
6.4.1. Display filter fields ................................................................................... 79
6.4.2. Comparing values ..................................................................................... 79
6.4.3. Combining expressions .............................................................................. 80
6.4.4. Membership Operator. ............................................................................... 82
6.4.5. A common mistake ................................................................................... 82
6.5. The “Filter Expression” dialog box ......................................................................... 82
6.6. Defining and saving filters .................................................................................... 83
6.7. Defining and saving filter macros ........................................................................... 84
6.8. Finding packets ................................................................................................... 84
6.8.1. The “Find Packet” dialog box ..................................................................... 84
6.8.2. The “Find Next” command ......................................................................... 85
6.8.3. The “Find Previous” command .................................................................... 85
6.9. Go to a specific packet ......................................................................................... 85
6.9.1. The “Go Back” command .......................................................................... 85
6.9.2. The “Go Forward” command ...................................................................... 85
6.9.3. The “Go to Packet” dialog box .................................................................... 85
6.9.4. The “Go to Corresponding Packet” command ................................................ 86
6.9.5. The “Go to First Packet” command .............................................................. 86
6.9.6. The “Go to Last Packet” command .............................................................. 86
6.10. Marking packets ................................................................................................ 86
v
Page 6

Wireshark User’s Guide
6.11. Ignoring packets ................................................................................................ 86
6.12. Time display formats and time references .............................................................. 87
6.12.1. Packet time referencing ............................................................................ 87
7. Advanced Topics ........................................................................................................... 89
7.1. Introduction ........................................................................................................ 89
7.2. Following TCP streams ........................................................................................ 89
7.2.1. The “Follow TCP Stream” dialog box .......................................................... 89
7.3. Expert Information .............................................................................................. 90
7.3.1. Expert Info Entries .................................................................................... 90
7.3.2. “Expert Info” dialog .................................................................................. 91
7.3.3. “Colorized” Protocol Details Tree ................................................................ 92
7.3.4. “Expert” Packet List Column (optional) ........................................................ 92
7.4. Time Stamps ...................................................................................................... 92
7.4.1. Wireshark internals ................................................................................... 92
7.4.2. Capture file formats .................................................................................. 93
7.4.3. Accuracy ................................................................................................. 93
7.5. Time Zones ........................................................................................................ 93
7.5.1. Set your computer’s time correctly! .............................................................. 94
7.5.2. Wireshark and Time Zones ......................................................................... 95
7.6. Packet Reassembly .............................................................................................. 96
7.6.1. What is it? ............................................................................................... 96
7.6.2. How Wireshark handles it .......................................................................... 96
7.7. Name Resolution ................................................................................................. 97
7.7.1. Name Resolution drawbacks ....................................................................... 97
7.7.2. Ethernet name resolution (MAC layer) .......................................................... 97
7.7.3. IP name resolution (network layer) .............................................................. 98
7.7.4. TCP/UDP port name resolution (transport layer) ............................................. 98
7.8. Checksums ......................................................................................................... 98
7.8.1. Wireshark checksum validation ................................................................... 99
7.8.2. Checksum offloading ................................................................................. 99
8. Statistics ..................................................................................................................... 101
8.1. Introduction ...................................................................................................... 101
8.2. The Summary window ........................................................................................ 101
8.3. The "Protocol Hierarchy" window ........................................................................ 102
8.4. Conversations .................................................................................................... 102
8.4.1. The “Conversations” window .................................................................... 103
8.5. Endpoints ......................................................................................................... 103
8.5.1. The "Endpoints" window .......................................................................... 104
8.6. The "IO Graphs" window .................................................................................... 105
8.7. Service Response Time ....................................................................................... 106
8.7.1. The "Service Response Time DCE-RPC" window ......................................... 106
8.8. Compare two capture files ................................................................................... 106
8.9. WLAN Traffic Statistics ..................................................................................... 107
8.10. The protocol specific statistics windows ............................................................... 108
9. Telephony ................................................................................................................... 109
9.1. Introduction ...................................................................................................... 109
9.2. RTP Analysis .................................................................................................... 109
9.3. IAX2 Analysis .................................................................................................. 109
9.4. VoIP Calls ........................................................................................................ 109
9.5. LTE MAC Traffic Statistics ................................................................................ 109
9.6. LTE RLC Traffic Statistics .................................................................................. 110
9.7. The protocol specific statistics windows ................................................................ 110
10. Customizing Wireshark ............................................................................................... 111
10.1. Introduction ..................................................................................................... 111
vi
Page 7

Wireshark User’s Guide
10.2. Start Wireshark from the command line ............................................................... 111
10.3. Packet colorization ........................................................................................... 117
10.4. Control Protocol dissection ................................................................................ 118
10.4.1. The “Enabled Protocols” dialog box .......................................................... 118
10.4.2. User Specified Decodes .......................................................................... 119
10.4.3. Show User Specified Decodes ................................................................. 120
10.5. Preferences ..................................................................................................... 120
10.5.1. Interface Options ................................................................................... 120
10.6. Configuration Profiles ....................................................................................... 121
10.7. User Table ...................................................................................................... 123
10.8. Display Filter Macros ....................................................................................... 123
10.9. ESS Category Attributes .................................................................................... 123
10.10. GeoIP Database Paths ..................................................................................... 123
10.11. IKEv2 decryption table .................................................................................... 124
10.12. Object Identifiers ............................................................................................ 124
10.13. PRES Users Context List ................................................................................. 125
10.14. SCCP users Table ........................................................................................... 125
10.15. SMI (MIB and PIB) Modules ........................................................................... 125
10.16. SMI (MIB and PIB) Paths ............................................................................... 125
10.17. SNMP Enterprise Specific Trap Types ............................................................... 126
10.18. SNMP users Table .......................................................................................... 126
10.19. Tektronix K12xx/15 RF5 protocols Table ........................................................... 126
10.20. User DLTs protocol table ................................................................................ 127
A. Wireshark Messages .................................................................................................... 128
A.1. Packet List Messages ......................................................................................... 128
A.1.1. [Malformed Packet] ................................................................................ 128
A.1.2. [Packet size limited during capture] ........................................................... 128
A.2. Packet Details Messages .................................................................................... 128
A.2.1. [Response in frame: 123] ......................................................................... 128
A.2.2. [Request in frame: 123] ........................................................................... 129
A.2.3. [Time from request: 0.123 seconds] ........................................................... 129
A.2.4. [Stream setup by PROTOCOL (frame 123)] ................................................ 129
B. Files and Folders ......................................................................................................... 130
B.1. Capture Files .................................................................................................... 130
B.1.1. Libpcap File Contents ............................................................................. 130
B.1.2. Not Saved in the Capture File ................................................................... 130
B.2. Configuration Files and Folders ........................................................................... 131
B.2.1. Protocol help configuration ....................................................................... 135
B.3. Windows folders ............................................................................................... 136
B.3.1. Windows profiles .................................................................................... 136
B.3.2. Windows roaming profiles ....................................................................... 137
B.3.3. Windows temporary folder ....................................................................... 137
C. Protocols and Protocol Fields ........................................................................................ 138
D. Related command line tools .......................................................................................... 139
D.1. Introduction ..................................................................................................... 139
D.2. tshark: Terminal-based Wireshark ........................................................................ 139
D.3. tcpdump: Capturing with tcpdump for viewing with Wireshark ................................ 141
D.4. dumpcap: Capturing with dumpcap for viewing with Wireshark ............................... 141
D.5. capinfos: Print information about capture files ........................................................ 142
D.6. rawshark: Dump and analyze network traffic. ........................................................ 143
D.7. editcap: Edit capture files ................................................................................... 144
D.8. mergecap: Merging multiple capture files into one .................................................. 149
D.9. text2pcap: Converting ASCII hexdumps to network captures ..................................... 150
D.10. reordercap: Reorder a capture file ...................................................................... 152
vii
Page 8

Wireshark User’s Guide
11. This Document’s License (GPL) ................................................................................... 153
viii
Page 9

Preface
1. Foreword
Wireshark is one of those programs that many network managers would love to be able to use, but they are
often prevented from getting what they would like from Wireshark because of the lack of documentation.
This document is part of an effort by the Wireshark team to improve the usability of Wireshark.
We hope that you find it useful and look forward to your comments.
2. Who should read this document?
The intended audience of this book is anyone using Wireshark.
This book will explain all the basics and also some of the advanced features that Wireshark provides. As
Wireshark has become a very complex program since the early days, not every feature of Wireshark may
be explained in this book.
This book is not intended to explain network sniffing in general and it will not provide details about specific
network protocols. A lot of useful information regarding these topics can be found at the Wireshark Wiki
at https://wiki.wireshark.org/
By reading this book, you will learn how to install Wireshark, how to use the basic elements of the graphical
user interface (such as the menu) and what’s behind some of the advanced features that are not always
obvious at first sight. It will hopefully guide you around some common problems that frequently appear
for new (and sometimes even advanced) users of Wireshark.
3. Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the whole Wireshark team for their assistance. In particular, the authors
would like to thank:
• Gerald Combs, for initiating the Wireshark project and funding to do this documentation.
• Guy Harris, for many helpful hints and a great deal of patience in reviewing this document.
• Gilbert Ramirez, for general encouragement and helpful hints along the way.
The authors would also like to thank the following people for their helpful feedback on this document:
• Pat Eyler, for his suggestions on improving the example on generating a backtrace.
• Martin Regner, for his various suggestions and corrections.
• Graeme Hewson, for a lot of grammatical corrections.
The authors would like to acknowledge those man page and README authors for the Wireshark project
from who sections of this document borrow heavily:
• Scott Renfro from whose mergecap man page Section D.8, “mergecap: Merging multiple capture
files into one” is derived.
ix
Page 10

Preface
• Ashok Narayanan from whose text2pcap man page Section D.9, “text2pcap: Converting ASCII
hexdumps to network captures” is derived.
4. About this document
This book was originally developed by Richard Sharpe with funds provided from the Wireshark Fund. It
was updated by Ed Warnicke and more recently redesigned and updated by Ulf Lamping.
It was originally written in DocBook/XML and converted to AsciiDoc by Gerald Combs.
You will find some specially marked parts in this book:
This is a warning
You should pay attention to a warning, otherwise data loss might occur.
This is a note
A note will point you to common mistakes and things that might not be obvious.
This is a tip
Tips are helpful for your everyday work using Wireshark.
5. Where to get the latest copy of this document?
The latest copy of this documentation can always be found at https://www.wireshark.org/docs/.
6. Providing feedback about this document
Should you have any feedback about this document, please send it to the authors through wireshark-
dev[AT]wireshark.org.
x
Page 11

Chapter 1. Introduction
1.1. What is Wireshark?
Wireshark is a network packet analyzer. A network packet analyzer will try to capture network packets
and tries to display that packet data as detailed as possible.
You could think of a network packet analyzer as a measuring device used to examine what’s going on
inside a network cable, just like a voltmeter is used by an electrician to examine what’s going on inside
an electric cable (but at a higher level, of course).
In the past, such tools were either very expensive, proprietary, or both. However, with the advent of
Wireshark, all that has changed.
Wireshark is perhaps one of the best open source packet analyzers available today.
1.1.1. Some intended purposes
Here are some examples people use Wireshark for:
• Network administrators use it to troubleshoot network problems
• Network security engineers use it to examine security problems
• Developers use it to debug protocol implementations
• People use it to learn network protocol internals
Beside these examples Wireshark can be helpful in many other situations too.
1.1.2. Features
The following are some of the many features Wireshark provides:
• Available for UNIX and Windows.
• Capture live packet data from a network interface.
• Open files containing packet data captured with tcpdump/WinDump, Wireshark, and a number of other
packet capture programs.
• Import packets from text files containing hex dumps of packet data.
• Display packets with very detailed protocol information.
• Save packet data captured.
• Export some or all packets in a number of capture file formats.
• Filter packets on many criteria.
• Search for packets on many criteria.
• Colorize packet display based on filters.
1
Page 12

Introduction
• Create various statistics.
• …and a lot more!
However, to really appreciate its power you have to start using it.
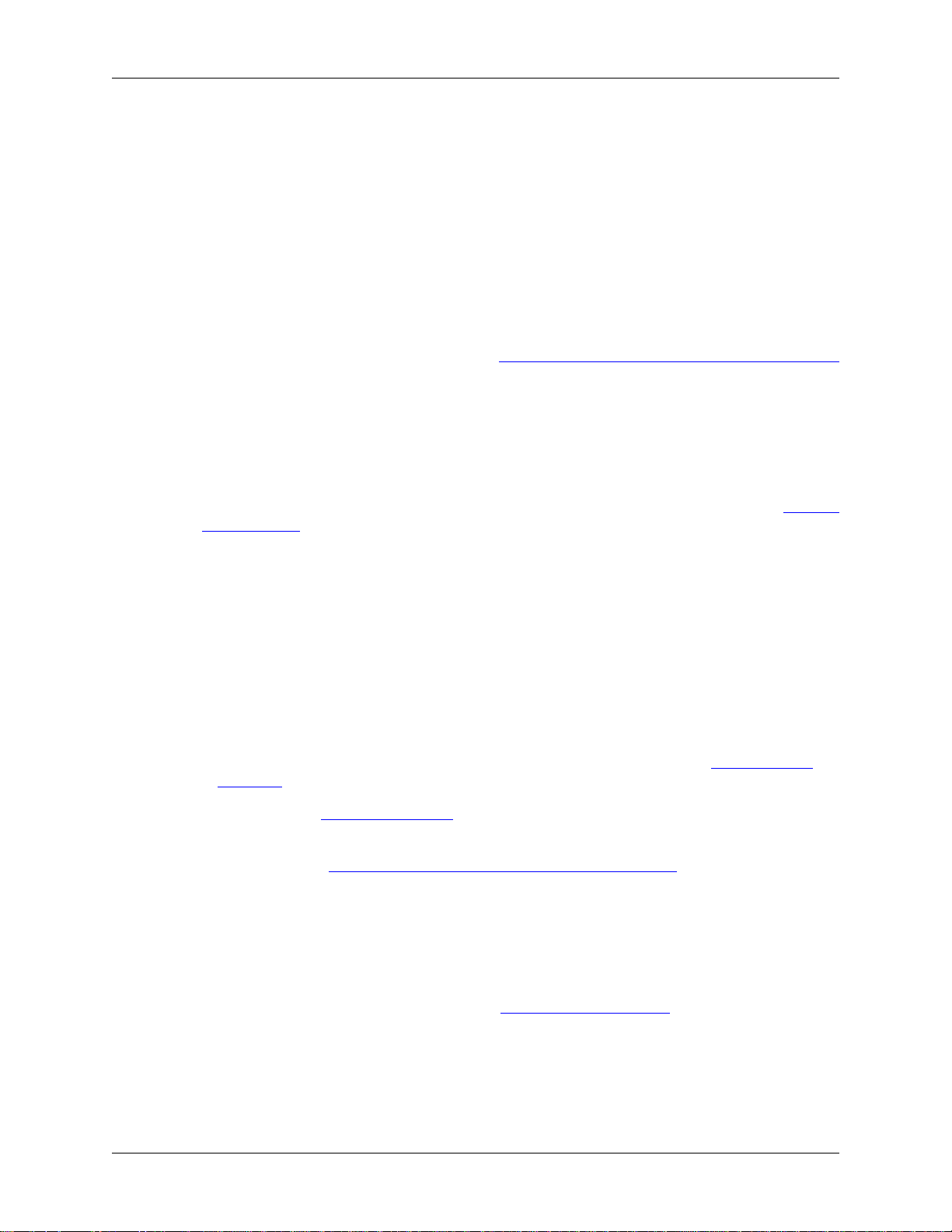
Figure 1.1, “Wireshark captures packets and lets you examine their contents.” shows Wireshark having
captured some packets and waiting for you to examine them.
Figure 1.1. Wireshark captures packets and lets you examine their contents.
1.1.3. Live capture from many different network media
Wireshark can capture traffic from many different network media types - and despite its name - including
wireless LAN as well. Which media types are supported, depends on many things like the operating system
you are using. An overview of the supported media types can be found at https://wiki.wireshark.org/
CaptureSetup/NetworkMedia.
1.1.4. Import files from many other capture programs
Wireshark can open packets captured from a large number of other capture programs. For a list of input
formats see Section 5.2.2, “Input File Formats”.
1.1.5. Export files for many other capture programs
Wireshark can save packets captured in a large number of formats of other capture programs. For a list of
output formats see Section 5.3.2, “Output File Formats”.
1.1.6. Many protocol dissectors
There are protocol dissectors (or decoders, as they are known in other products) for a great many protocols:
see Appendix C, Protocols and Protocol Fields.
1.1.7. Open Source Software
Wireshark is an open source software project, and is released under the GNU General Public License
(GPL). You can freely use Wireshark on any number of computers you like, without worrying about license
keys or fees or such. In addition, all source code is freely available under the GPL. Because of that, it is
very easy for people to add new protocols to Wireshark, either as plugins, or built into the source, and
they often do!
1.1.8. What Wireshark is not
Here are some things Wireshark does not provide:
• Wireshark isn’t an intrusion detection system. It will not warn you when someone does strange things
on your network that he/she isn’t allowed to do. However, if strange things happen, Wireshark might
help you figure out what is really going on.
• Wireshark will not manipulate things on the network, it will only "measure" things from it. Wireshark
doesn’t send packets on the network or do other active things (except for name resolutions, but even
that can be disabled).
2
Page 13
Introduction
1.2. System Requirements
The amount of resources Wireshark needs depends on your environment and on the size of the capture file
you are analyzing. The values below should be fine for small to medium-sized capture files no more than
a few hundred MB. Larger capture files will require more memory and disk space.
Busy networks mean large captures
Working with a busy network can easily produce huge capture files. Capturing on a gigabit
or even 100 megabit network can produce hundreds of megabytes of capture data in a short
time. A fast processor, lots of memory and disk space is always a good idea.
If Wireshark runs out of memory it will crash. See https://wiki.wireshark.org/KnownBugs/OutOfMemory
for details and workarounds.
Although Wireshark captures packets using a separate process the main interface is single-threaded and
won’t benefit much from multi-core systems.
1.2.1. Microsoft Windows
• The current version of Wireshark should support any version of Windows that is still within its extended
support lifetime. At the time of writing this includes Windows 10, 8, 7, Vista, Server 2016, Server 2012,
Server 2008 R2, and Server 2008.
• Any modern 64-bit AMD64/x86-64 or 32-bit x86 processor.
• 400 MB available RAM. Larger capture files require more RAM.
• 300 MB available disk space. Capture files require additional disk space.
• 1024×768 (1280×1024 or higher recommended) resolution with at least 16 bit color. 8 bit color should
work but user experience will be degraded. Power users will find multiple monitors useful.
• A supported network card for capturing
• Ethernet. Any card supported by Windows should work. See the wiki pages on Ethernet capture and
offloading for issues that may affect your environment.
• 802.11. See the Wireshark wiki page. Capturing raw 802.11 information may be difficult without
special equipment.
• Other media. See https://wiki.wireshark.org/CaptureSetup/NetworkMedia
Older versions of Windows which are outside Microsoft’s extended lifecycle support window are no longer
supported. It is often difficult or impossible to support these systems due to circumstances beyond our
control, such as third party libraries on which we depend or due to necessary features that are only present
in newer versions of Windows (such as hardened security or memory management).
Wireshark 1.12 was the last release branch to support Windows Server 2003. Wireshark 1.10 was the last
branch to officially support Windows XP. See the Wireshark release lifecycle page for more details.
1.2.2. UNIX / Linux
Wireshark runs on most UNIX and UNIX-like platforms including OS X and Linux. The system
requirements should be comparable to the Windows values listed above.
3
Page 14

Introduction
Binary packages are available for most Unices and Linux distributions including the following platforms:
• Apple OS X
• Debian GNU/Linux
• FreeBSD
• Gentoo Linux
• HP-UX
• Mandriva Linux
• NetBSD
• OpenPKG
• Red Hat Enterprise/Fedora Linux
• Sun Solaris/i386
• Sun Solaris/SPARC
• Canonical Ubuntu
If a binary package is not available for your platform you can download the source and try to build it.
Please report your experiences to wireshark-dev[AT]wireshark.org.
1.3. Where to get Wireshark
You can get the latest copy of the program from the Wireshark website at https://www.wireshark.org/
download.html. The download page should automatically highlight the appropriate download for your
platform and direct you to the nearest mirror. Official Windows and OS X installers are signed by the
Wireshark Foundation.
A new Wireshark version typically becomes available each month or two.
If you want to be notified about new Wireshark releases you should subscribe to the wireshark-announce
mailing list. You will find more details in Section 1.6.5, “Mailing Lists”.
1.4. A brief history of Wireshark
In late 1997 Gerald Combs needed a tool for tracking down network problems and wanted to learn more
about networking so he started writing Ethereal (the original name of the Wireshark project) as a way to
solve both problems.
Ethereal was initially released after several pauses in development in July 1998 as version 0.2.0. Within
days patches, bug reports, and words of encouragement started arriving and Ethereal was on its way to
success.
Not long after that Gilbert Ramirez saw its potential and contributed a low-level dissector to it.
In October, 1998 Guy Harris was looking for something better than tcpview so he started applying patches
and contributing dissectors to Ethereal.
4
Page 15

Introduction
In late 1998 Richard Sharpe, who was giving TCP/IP courses, saw its potential on such courses and started
looking at it to see if it supported the protocols he needed. While it didn’t at that point new protocols could
be easily added. So he started contributing dissectors and contributing patches.
The list of people who have contributed to the project has become very long since then, and almost all of
them started with a protocol that they needed that Wireshark or did not already handle. So they copied an
existing dissector and contributed the code back to the team.
In 2006 the project moved house and re-emerged under a new name: Wireshark.
In 2008, after ten years of development, Wireshark finally arrived at version 1.0. This release was the first
deemed complete, with the minimum features implemented. Its release coincided with the first Wireshark
Developer and User Conference, called Sharkfest.
In 2015 Wireshark 2.0 was released, which featured a new user interface.
1.5. Development and maintenance of Wireshark
Wireshark was initially developed by Gerald Combs. Ongoing development and maintenance of Wireshark
is handled by the Wireshark team, a loose group of individuals who fix bugs and provide new functionality.
There have also been a large number of people who have contributed protocol dissectors to Wireshark,
and it is expected that this will continue. You can find a list of the people who have contributed code to
Wireshark by checking the about dialog box of Wireshark, or at the authors page on the Wireshark web site.
Wireshark is an open source software project, and is released under the GNU General Public License
(GPL) version 2. All source code is freely available under the GPL. You are welcome to modify Wireshark
to suit your own needs, and it would be appreciated if you contribute your improvements back to the
Wireshark team.
You gain three benefits by contributing your improvements back to the community:
1. Other people who find your contributions useful will appreciate them, and you will know that you have
helped people in the same way that the developers of Wireshark have helped people.
2. The developers of Wireshark might improve your changes even more, as there’s always room for
improvement. Or they may implement some advanced things on top of your code, which can be useful
for yourself too.
3. The maintainers and developers of Wireshark will maintain your code as well, fixing it when API
changes or other changes are made, and generally keeping it in tune with what is happening with
Wireshark. So if Wireshark is updated (which is done often), you can get a new Wireshark version from
the website and your changes will already be included without any effort for you.
The Wireshark source code and binary kits for some platforms are all available on the download page of
the Wireshark website: https://www.wireshark.org/download.html.
1.6. Reporting problems and getting help
If you have problems or need help with Wireshark there are several places that may be of interest to you
(well, besides this guide of course).
5
Page 16

1.6.1. Website
You will find lots of useful information on the Wireshark homepage at https://www.wireshark.org/.
1.6.2. Wiki
The Wireshark Wiki at https://wiki.wireshark.org/ provides a wide range of information related to
Wireshark and packet capture in general. You will find a lot of information not part of this user’s guide.
For example, there is an explanation how to capture on a switched network, an ongoing effort to build a
protocol reference and a lot more.
And best of all, if you would like to contribute your knowledge on a specific topic (maybe a network
protocol you know well) you can edit the wiki pages by simply using your web browser.
1.6.3. Q&A Site
The Wireshark Q&A site at https://ask.wireshark.org/ offers a resource where questions and answers come
together. You have the option to search what questions were asked before and what answers were given
by people who knew about the issue. Answers are graded, so you can pick out the best ones easily. If your
question hasn’t been discussed before you can post one yourself.
Introduction
1.6.4. FAQ
The Frequently Asked Questions lists often asked questions and their corresponding answers.
Read the FAQ
Before sending any mail to the mailing lists below, be sure to read the FAQ. It will often
answer any questions you might have. This will save yourself and others a lot of time. Keep
in mind that a lot of people are subscribed to the mailing lists.
You will find the FAQ inside Wireshark by clicking the menu item Help/Contents and selecting the FAQ
page in the dialog shown.
An online version is available at the Wireshark website: https://www.wireshark.org/faq.html. You might
prefer this online version, as it’s typically more up to date and the HTML format is easier to use.
1.6.5. Mailing Lists
There are several mailing lists of specific Wireshark topics available:
wireshark-announce This mailing list will inform you about new program releases, which
wireshark-users This list is for users of Wireshark. People post questions about building
usually appear about every 4-8 weeks.
and using Wireshark, others (hopefully) provide answers.
wireshark-dev This list is for Wireshark developers. If you want to start developing a
protocol dissector, join this list.
You can subscribe to each of these lists from the Wireshark web site: https://www.wireshark.org/lists/.
From there, you can choose which mailing list you want to subscribe to by clicking on the Subscribe/
6
Page 17

Unsubscribe/Options button under the title of the relevant list. The links to the archives are included on
that page as well.
The lists are archived
You can search in the list archives to see if someone asked the same question some time
before and maybe already got an answer. That way you don’t have to wait until someone
answers your question.
1.6.6. Reporting Problems
Note
Before reporting any problems, please make sure you have installed the latest version of
Wireshark.
When reporting problems with Wireshark please supply the following information:
1. The version number of Wireshark and the dependent libraries linked with it, such as Qt or GLib. You
can obtain this from Wireshark’s about box or the command wireshark -v.
Introduction
2. Information about the platform you run Wireshark on.
3. A detailed description of your problem.
4. If you get an error/warning message, copy the text of that message (and also a few lines before and after
it, if there are some) so others may find the place where things go wrong. Please don’t give something
like: "I get a warning while doing x" as this won’t give a good idea where to look.
Don’t send large files
Do not send large files (> 1 MB) to the mailing lists. Just place a note that further data
is available on request. Large files will only annoy a lot of people on the list who are not
interested in your specific problem. If required you will be asked for further data by the
persons who really can help you.
Don’t send confidential information!
If you send capture files to the mailing lists be sure they don’t contain any sensitive or
confidential information like passwords or personally identifiable information (PII).
1.6.7. Reporting Crashes on UNIX/Linux platforms
When reporting crashes with Wireshark it is helpful if you supply the traceback information along with
the information mentioned in "Reporting Problems".
You can obtain this traceback information with the following commands on UNIX or Linux (note the
backticks):
$ gdb `whereis wireshark | cut -f2 -d: | cut -d' ' -f2` core >& backtrace.txt
backtrace
^D
If you do not have gdb available, you will have to check out your operating system’s debugger.
7
Page 18

Introduction
Mail backtrace.txt to wireshark-dev[AT]wireshark.org.
1.6.8. Reporting Crashes on Windows platforms
The Windows distributions don’t contain the symbol files (.pdb) because they are very large. You
can download them separately at https://www.wireshark.org/download/win32/all-versions and https://
www.wireshark.org/download/win64/all-versions
8
Page 19

Chapter 2. Building and Installing Wireshark
2.1. Introduction
As with all things there must be a beginning and so it is with Wireshark. To use Wireshark you must
first install it. If you are running Windows or OS X you can download an official release at https://
www.wireshark.org/download.html, install it, and skip the rest of this chapter.
If you are running another operating system such as Linux or FreeBSD you might want to install from
source. Several Linux distributions offer Wireshark packages but they commonly ship out-of-date versions.
No other versions of UNIX ship Wireshark so far. For that reason, you will need to know where to get the
latest version of Wireshark and how to install it.
This chapter shows you how to obtain source and binary packages and how to build Wireshark from source
should you choose to do so.
The following are the general steps you would use:
1. Download the relevant package for your needs, e.g. source or binary distribution.
2. Compile the source into a binary if needed. This may involve building and/or installing other necessary
packages.
3. Install the binaries into their final destinations.
2.2. Obtaining the source and binary distributions
You can obtain both source and binary distributions from the Wireshark web site: https://
www.wireshark.org/. Select the download link and then select the desired binary or source package.
Download all required files
If you are building Wireshark from source you will In general, unless you have already
downloaded Wireshark before, you will most likely need to download several source
packages if you are building Wireshark from source. This is covered in more detail below.
Once you have downloaded the relevant files, you can go on to the next step.
2.3. Installing Wireshark under Windows
Windows installers contain the platform and version, e.g. Wireshark-winxx-2.1.x.exe. The Wireshark
installer includes WinPcap which is required for packet capture.
Simply download the Wireshark installer from: https://www.wireshark.org/download.html and execute it.
Official packages are signed by the Wireshark Foundation. You can choose to install several optional
9
Page 20

Building and Installing Wireshark
components and select the location of the installed package. The default settings are recommended for
most users.
2.3.1. Installation Components
On the Choose Components page of the installer you can select from the following:
• Wireshark - The network protocol analyzer that we all know and mostly love.
• TShark - A command-line network protocol analyzer. If you haven’t tried it you should.
• Wireshark 1 Legacy - The old (GTK+) user interface in case you need it.
• Plugins & Extensions - Extras for the Wireshark and TShark dissection engines
• Dissector Plugins - Plugins with some extended dissections.
• Tree Statistics Plugins - Extended statistics.
• Mate - Meta Analysis and Tracing Engine - User configurable extension(s) of the display filter
engine, see https://wiki.wireshark.org/Mate for details.
• SNMP MIBs - SNMP MIBs for a more detailed SNMP dissection.
• Tools - Additional command line tools to work with capture files
• Editcap - Reads a capture file and writes some or all of the packets into another capture file.
• Text2Pcap - Reads in an ASCII hex dump and writes the data into a pcap capture file.
• Reordercap - Reorders a capture file by timestamp.
• Mergecap - Combines multiple saved capture files into a single output file.
• Capinfos - Provides information on capture files.
• Rawshark - Raw packet filter.
• User’s Guide - Local installation of the User’s Guide. The Help buttons on most dialogs will require
an internet connection to show help pages if the User’s Guide is not installed locally.
2.3.2. Additional Tasks
• Start Menu Shortcuts - Add some start menu shortcuts.
• Desktop Icon - Add a Wireshark icon to the desktop.
• Quick Launch Icon - add a Wireshark icon to the Explorer quick launch toolbar.
• Associate file extensions to Wireshark - Associate standard network trace files to Wireshark.
2.3.3. Install Location
By default Wireshark installs into %ProgramFiles%\Wireshark on 32-bit Windows and
%ProgramFiles64%\Wireshark on 64-bit Windows. This expands to C:\Program Files
\Wireshark on most systems.
10
Page 21

Building and Installing Wireshark
2.3.4. Installing WinPcap
The Wireshark installer contains the latest WinPcap installer.
If you don’t have WinPcap installed you won’t be able to capture live network traffic but you will still be
able to open saved capture files. By default the latest version of WinPcap will be installed. If you don’t
wish to do this or if you wish to reinstall WinPcap you can check the Install WinPcap box as needed.
For more information about WinPcap see https://www.winpcap.org/ and https://wiki.wireshark.org/
WinPcap.
2.3.5. Windows installer command line options
For special cases, there are some command line parameters available:
• /S runs the installer or uninstaller silently with default values. The silent installer will not install
WinPCap.
• /desktopicon installation of the desktop icon, =yes - force installation, =no - don’t install,
otherwise use default settings. This option can be useful for a silent installer.
• /quicklaunchicon installation of the quick launch icon, =yes - force installation, =no - don’t
install, otherwise use default settings.
• /D sets the default installation directory ($INSTDIR), overriding InstallDir and InstallDirRegKey. It
must be the last parameter used in the command line and must not contain any quotes even if the path
contains spaces.
• /NCRC disables the CRC check. We recommend against using this flag.
Example:
> Wireshark-win64-wireshark-2.0.5.exe /NCRC /S /desktopicon=yes /quicklaunchicon=no /D=C:\Program Files\Foo
Running the installer without any parameters shows the normal interactive installer.
2.3.6. Manual WinPcap Installation
As mentioned above, the Wireshark installer takes care of installing WinPcap. The following is only
necessary if you want to use a different version than the one included in the Wireshark installer, e.g.
because a new WinPcap version was released.
Additional WinPcap versions (including newer alpha or beta releases) can be downloaded from the main
WinPcap site: https://www.winpcap.org/. The Installer for Windows supports modern Windows operating
systems.
2.3.7. Update Wireshark
By default the offical Windows package will check for new versions and notify you when they are
available. If you have the Check for updates preference disabled or if you run Wireshark in an isolated
environment you should subcribe to the wireshark-announce mailing list. See Section 1.6.5, “Mailing
Lists” for details on subscribing to this list.
New versions of Wireshark are usually released every four to six weeks. Updating Wireshark is done the
same way as installing it. Simply download and start the installer exe. A reboot is usually not required and
all your personal settings remain unchanged.
11
Page 22

Building and Installing Wireshark
2.3.8. Update WinPcap
New versions of WinPcap are less frequently available. You will find WinPcap update instructions the
WinPcap web site at https://www.winpcap.org/. You may have to reboot your machine after installing a
new WinPcap version.
2.3.9. Uninstall Wireshark
You can uninstall Wireshark using the Programs and Features control panel. Select the "Wireshark" entry
to start the uninstallation procedure.
The Wireshark uninstaller provides several options for removal. The default is to remove the core
components but keep your personal settings and WinPcap. WinPcap is left installed by default in case
other programs need it.
2.3.10. Uninstall WinPcap
You can uninstall WinPcap independently of Wireshark using the WinPcap entry in the Programs and
Features control panel. Remember that if you uninstall WinPcap you won’t be able to capture anything
with Wireshark.
2.4. Installing Wireshark under OS X
The official OS X packages are distributed as disk images (.dmg) containing the application installer. To
install Wireshark simply open the disk image and run the enclosed installer.
The installer package includes Wireshark, its related command line utilities, and a launch daemon that
adjusts capture permissions at system startup. See the included Read me first file for more details.
2.5. Building Wireshark from source under UNIX
Building Wireshark requires the proper build environment including a compiler and many supporting
libraries. See the Developer’s Guide at https://www.wireshark.org/docs/ for more information.
Use the following general steps to build Wireshark from source under UNIX or Linux:
1. Unpack the source from its compressed tar file. If you are using Linux or your version of UNIX uses
GNU tar you can use the following command:
$ tar xaf wireshark-2.0.5.tar.bz2
In other cases you will have to use the following commands:
$ bzip2 -d wireshark-2.0.5.tar.bz2
$ tar xf wireshark-2.0.5.tar
2. Change directory to the Wireshark source directory.
$ cd wireshark-2.0.5
3. Configure your source so it will build correctly for your version of UNIX. You can do this with the
following command:
12
Page 23

Building and Installing Wireshark
$ ./configure
If this step fails you will have to rectify the problems and rerun configure. Troubleshooting hints
are provided in Section 2.7, “Troubleshooting during the install on Unix”.
4. Build the sources.
$ make
5. Install the software in its final destination.
$ make install
Once you have installed Wireshark with make install above, you should be able to run it by entering
wireshark.
2.6. Installing the binaries under UNIX
In general installing the binary under your version of UNIX will be specific to the installation methods
used with your version of UNIX. For example, under AIX, you would use smit to install the Wireshark
binary package, while under Tru64 UNIX (formerly Digital UNIX) you would use setld.
2.6.1. Installing from RPM’s under Red Hat and alike
Building RPMs from Wireshark’s source code results in several packages (most distributions follow the
same system):
• The wireshark package contains the core Wireshark libraries and command-line tools.
• The wireshark-qt package contains the Qt-based GUI.
• The wireshark-gtk (formerly wireshark-gnome) package contains the legacy Gtk+ based GUI.
Many distributions use yum or a similar package management tool to make installation of software
(including its dependencies) easier. If your distribution uses yum, use the following command to install
Wireshark together with the Qt GUI:
yum install wireshark wireshark-qt
If you’ve built your own RPMs from the Wireshark sources you can install them by running, for example:
rpm -ivh wireshark-2.0.0-1.x86_64.rpm wireshark-qt-2.0.0-1.x86_64.rpm
If the above command fails because of missing dependencies, install the dependencies first, and then retry
the step above.
2.6.2. Installing from deb’s under Debian, Ubuntu and other Debian derivatives
If you can just install from the repository then use
$ aptitude install wireshark
Aptitude should take care of all of the dependency issues for you.
Use the following command to install downloaded Wireshark deb’s under Debian:
13
Page 24

Building and Installing Wireshark
$ dpkg -i wireshark-common_2.0.5.0-1_i386.deb wireshark_wireshark-2.0.5.0-1_i386.deb
dpkg doesn’t take care of all dependencies, but reports what’s missing.
Capturing requires privileges
By installing Wireshark packages non-root users won’t gain rights automatically to capture
packets. To allow non-root users to capture packets follow the procedure described in /usr/
share/doc/wireshark-common/README.Debian
2.6.3. Installing from portage under Gentoo Linux
Use the following command to install Wireshark under Gentoo Linux with all of the extra features:
$ USE="adns gtk ipv6 portaudio snmp ssl kerberos threads selinux" emerge wireshark
2.6.4. Installing from packages under FreeBSD
Use the following command to install Wireshark under FreeBSD:
$ pkg_add -r wireshark
pkg_add should take care of all of the dependency issues for you.
2.7. Troubleshooting during the install on Unix
A number of errors can occur during the installation process. Some hints on solving these are provided here.
If the configure stage fails you will need to find out why. You can check the file config.log in
the source directory to find out what failed. The last few lines of this file should help in determining the
problem.
The standard problems are that you do not have a required development package on your system or that
the development package isn’t new enough. Note that installing a library package isn’t enough. You need
to install its development package as well. configure will also fail if you do not have libpcap (at least
the required include files) on your system.
If you cannot determine what the problems are, send an email to the wireshark-dev mailing list explaining
your problem. Include the output from config.log and anything else you think is relevant such as a
trace of the make stage.
2.8. Building from source under Windows
We strongly recommended that you use the binary installer for Windows unless you want to start
developing Wireshark on the Windows platform.
For further information how to build Wireshark for Windows from the sources see the Developer’s Guide
at https://www.wireshark.org/docs/
You may also want to have a look at the Development Wiki (https://wiki.wireshark.org/Development) for
the latest available development documentation.
14
Page 25
Chapter 3. User Interface
3.1. Introduction
By now you have installed Wireshark and are most likely keen to get started capturing your first packets.
In the next chapters we will explore:
• How the Wireshark user interface works
• How to capture packets in Wireshark
• How to view packets in Wireshark
• How to filter packets in Wireshark
• … and many other things!
3.2. Start Wireshark
You can start Wireshark from your shell or window manager.
Power user tip
When starting Wireshark it’s possible to specify optional settings using the command line.
See Section 10.2, “Start Wireshark from the command line” for details.
In the following chapters a lot of screenshots from Wireshark will be shown. As Wireshark runs on
many different platforms with many different window managers, different styles applied and there are
different versions of the underlying GUI toolkit used, your screen might look different from the provided
screenshots. But as there are no real differences in functionality these screenshots should still be well
understandable.
3.3. The Main window
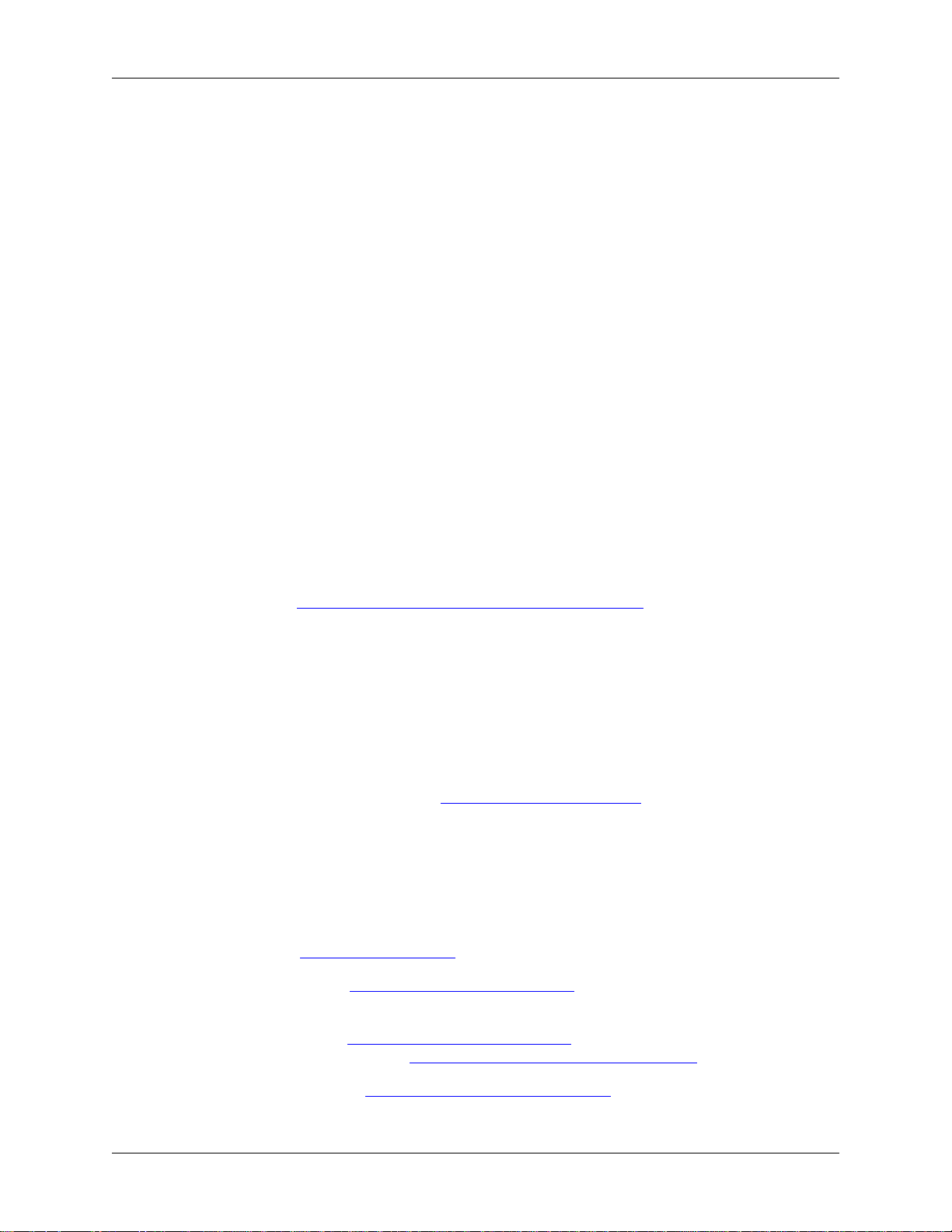
Let’s look at Wireshark’s user interface. Figure 3.1, “The Main window” shows Wireshark as you would
usually see it after some packets are captured or loaded (how to do this will be described later).
Figure 3.1. The Main window
Wireshark’s main window consists of parts that are commonly known from many other GUI programs.
1. The menu (see Section 3.4, “The Menu”) is used to start actions.
2. The main toolbar (see Section 3.16, “The “Main” toolbar”) provides quick access to frequently used
items from the menu.
3. The filter toolbar (see Section 3.17, “The “Filter” toolbar”) provides a way to directly manipulate the
currently used display filter (see Section 6.3, “Filtering packets while viewing”).
4. The packet list pane (see Section 3.18, “The “Packet List” pane”) displays a summary of each packet
captured. By clicking on packets in this pane you control what is displayed in the other two panes.
15
Page 26

User Interface
5. The packet details pane (see Section 3.19, “The “Packet Details” pane”) displays the packet selected
in the packet list pane in more detail.
6. The packet bytes pane (see Section 3.20, “The “Packet Bytes” pane”) displays the data from the packet
selected in the packet list pane, and highlights the field selected in the packet details pane.
7. The statusbar (see Section 3.21, “The Statusbar”) shows some detailed information about the current
program state and the captured data.
Tip
The layout of the main window can be customized by changing preference settings. See
Section 10.5, “Preferences” for details!
3.3.1. Main Window Navigation
Packet list and detail navigation can be done entirely from the keyboard. Table 3.1, “Keyboard Navigation”
shows a list of keystrokes that will let you quickly move around a capture file. See Table 3.5, “Go menu
items” for additional navigation keystrokes.
Table 3.1. Keyboard Navigation
Accelerator Description
Tab, Shift+Tab Move between screen elements, e.g. from the
toolbars to the packet list to the packet detail.
Down Move to the next packet or detail item.
Up Move to the previous packet or detail item.
Ctrl+Down, F8 Move to the next packet, even if the packet list
isn’t focused.
Ctrl+Up, F7 Move to the previous packet, even if the packet list
isn’t focused.
Ctrl+. Move to the next packet of the conversation (TCP,
UDP or IP)
Ctrl+, Move to the previous packet of the conversation
(TCP, UDP or IP)
Left In the packet detail, closes the selected tree item. If
it’s already closed, jumps to the parent node.
Right In the packet detail, opens the selected tree item.
Shift+Right In the packet detail, opens the selected tree item
and all of its subtrees.
Ctrl+Right In the packet detail, opens all tree items.
Ctrl+Left In the packet detail, closes all tree items.
Backspace In the packet detail, jumps to the parent node.
Return, Enter In the packet detail, toggles the selected tree item.
Help → About Wireshark → Keyboard Shortcuts will show a list of all shortcuts in the main window.
Additionally, typing anywhere in the main window will start filling in a display filter.
16
Page 27

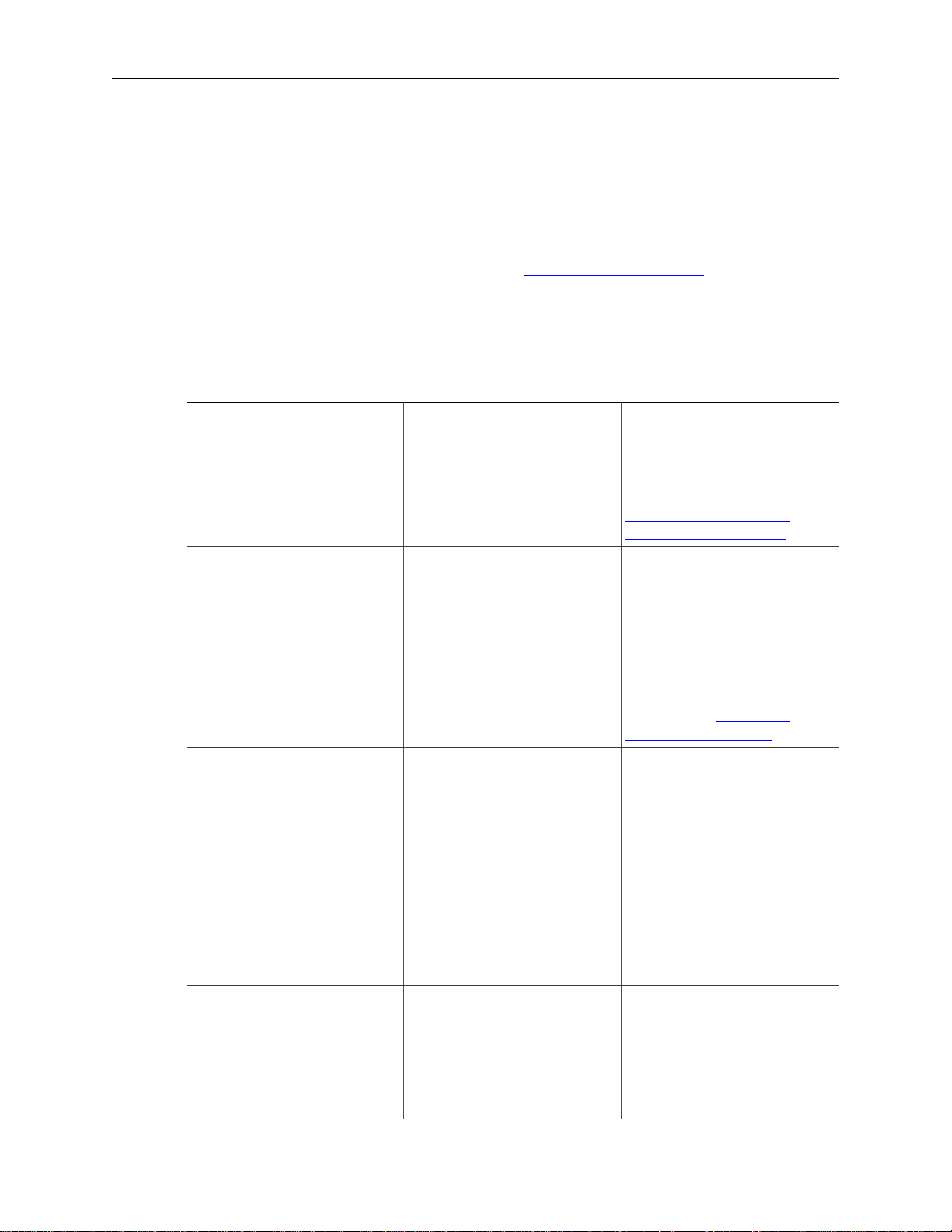
3.4. The Menu
Wireshark’s main menu is located either at the top of the main window (Windows, Linux) or at the top of
your main screen (OS X). An example is shown in Figure 3.2, “The Menu”.
Note
Some menu items will be disabled (greyed out( if the corresponding feature isn’t available.
For example, you cannot save a capture file if you haven’t captured or loaded any packets.
Figure 3.2. The Menu
The main menu contains the following items:
File This menu contains items to open and merge capture files, save, print, or export
Edit This menu contains items to find a packet, time reference or mark one or more packets,
User Interface
capture files in whole or in part, and to quit the Wireshark application. See Section 3.5,
“The “File” menu”.
handle configuration profiles, and set your preferences; (cut, copy, and paste are not
presently implemented). See Section 3.6, “The “Edit” menu”.
View This menu controls the display of the captured data, including colorization of packets,
zooming the font, showing a packet in a separate window, expanding and collapsing
trees in packet details, …. See Section 3.7, “The “View” menu”.
Go This menu contains items to go to a specific packet. See Section 3.8, “The “Go”
menu”.
Capture This menu allows you to start and stop captures and to edit capture filters. See
Section 3.9, “The “Capture” menu”.
Analyze This menu contains items to manipulate display filters, enable or disable the dissection
of protocols, configure user specified decodes and follow a TCP stream. See
Section 3.10, “The “Analyze” menu”.
Statistics This menu contains items to display various statistic windows, including a summary
of the packets that have been captured, display protocol hierarchy statistics and much
more. See Section 3.11, “The “Statistics” menu”.
Telephony This menu contains items to display various telephony related statistic windows,
including a media analysis, flow diagrams, display protocol hierarchy statistics and
much more. See Section 3.12, “The “Telephony” menu”.
Wireless The items in this menu show Bluetooth and IEEE 802.11 wireless statistics.
Tools This menu contains various tools available in Wireshark, such as creating Firewall
ACL Rules. See Section 3.13, “The “Tools” menu”.
Help This menu contains items to help the user, e.g. access to some basic help, manual
pages of the various command line tools, online access to some of the webpages, and
the usual about dialog. See Section 3.15, “The “Help” menu”.
Each of these menu items is described in more detail in the sections that follow.
17
Page 28
Shortcuts make life easier
Most common menu items have keyboard shortcuts. For example, you can press the Control
(or Strg in German) and the K keys together to open the “Capture Options” dialog.
3.5. The “File” menu
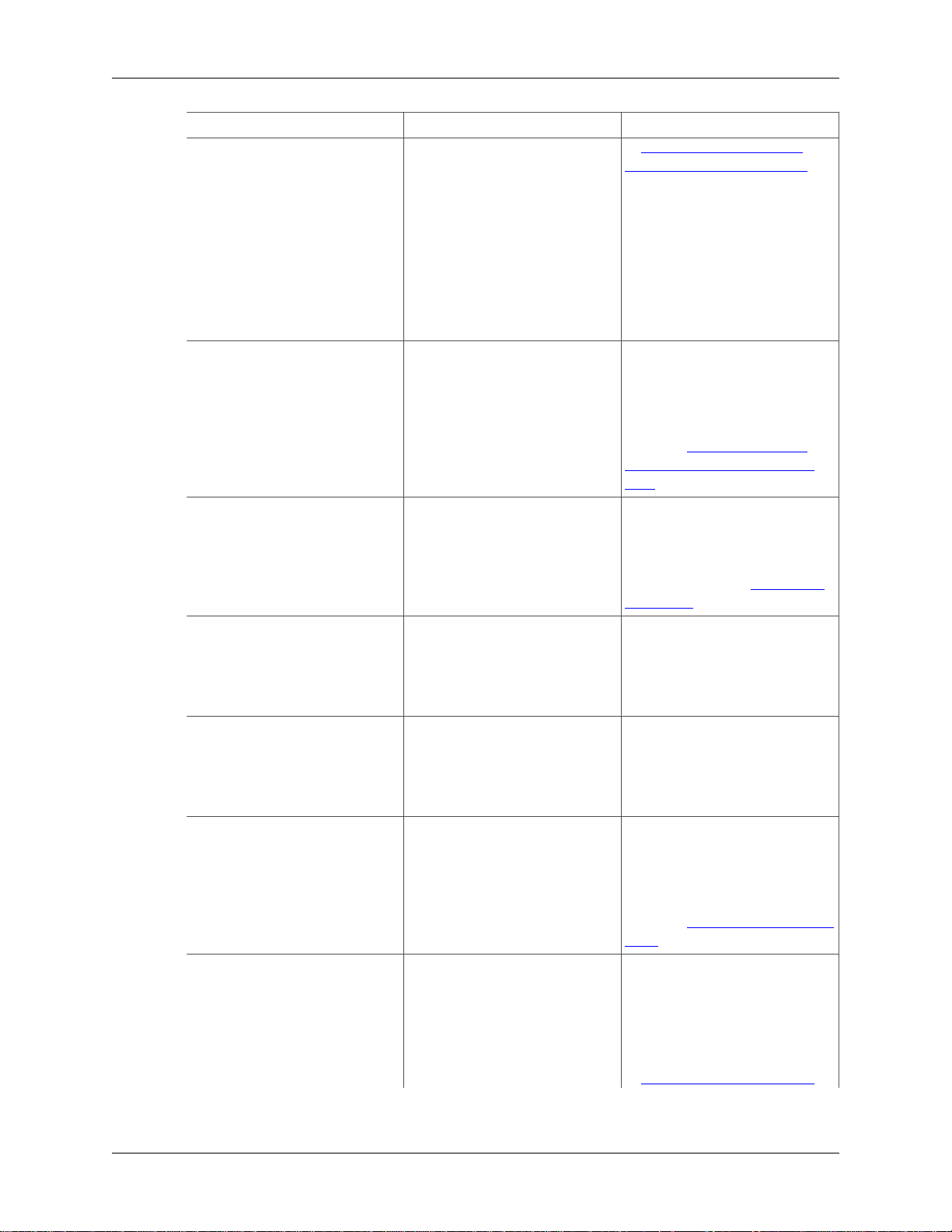
The Wireshark file menu contains the fields shown in Table 3.2, “File menu items”.
Figure 3.3. The “File” Menu
Table 3.2. File menu items
Menu Item Accelerator Description
Open… Ctrl+O This shows the file open dialog
Open Recent This lets you open recently
Merge… This menu item lets you merge
Import from Hex Dump… This menu item brings up the
Close Ctrl+W This menu item closes the current
Save Ctrl+S This menu item saves the current
User Interface
box that allows you to load
a capture file for viewing. It
is discussed in more detail in
Section 5.2.1, “The “Open
Capture File” dialog box”.
opened capture files. Clicking on
one of the submenu items will
open the corresponding capture
file directly.
a capture file into the currently
loaded one. It is discussed in
more detail in Section 5.4,
“Merging capture files”.
import file dialog box that
allows you to import a text file
containing a hex dump into
a new temporary capture. It
is discussed in more detail in
Section 5.5, “Import hex dump”.
capture. If you haven’t saved the
capture, you will be asked to do
so first (this can be disabled by a
preference setting).
capture. If you have not set
a default capture file name
(perhaps with the -w <capfile>
option), Wireshark pops up the
Save Capture File As dialog
box (which is discussed further
18
Page 29
User Interface
Menu Item Accelerator Description
in Section 5.3.1, “The “Save
Capture File As” dialog box”).
If you have already saved the
current capture, this menu item
will be greyed out.
You cannot save a live capture
while the capture is in progress.
You must stop the capture in
order to save.
Save As… Shift+Ctrl+S This menu item allows you to
save the current capture file to
whatever file you would like. It
pops up the Save Capture File As
dialog box (which is discussed
further in Section 5.3.1, “The
“Save Capture File As” dialog
box”).
File Set → List Files
File Set → Next File
File Set → Previous File
Export Specified Packets… This menu item allows you
Export Packet Dissections… Ctrl+H These menu items allow you
This menu item allows you to
show a list of files in a file set.
It pops up the Wireshark List
File Set dialog box (which is
discussed further in Section 5.6,
“File Sets”).
If the currently loaded file is part
of a file set, jump to the next file
in the set. If it isn’t part of a file
set or just the last file in that set,
this item is greyed out.
If the currently loaded file is part
of a file set, jump to the previous
file in the set. If it isn’t part of a
file set or just the first file in that
set, this item is greyed out.
to export all (or some) of the
packets in the capture file to file.
It pops up the Wireshark Export
dialog box (which is discussed
further in Section 5.7, “Exporting
data”).
to export the currently selected
bytes in the packet bytes pane
to a text file file in a number of
formats including plain, CSV,
and XML. It is discussed further
in Section 5.7.7, “The "Export
19
Page 30
User Interface
Menu Item Accelerator Description
selected packet bytes" dialog
box”.
Export Objects These menu items allow you to
export captured DICOM, HTTP,
SMB, or TFTP objects into local
files. It pops up a corresponding
object list (which is discussed
further in Section 5.7.8, “The
"Export Objects" dialog box”)
Print… Ctrl+P This menu item allows you to
print all (or some) of the packets
in the capture file. It pops up
the Wireshark Print dialog box
(which is discussed further in
Section 5.8, “Printing packets”).
Quit Ctrl+Q This menu item allows you to
quit from Wireshark. Wireshark
will ask to save your capture
file if you haven’t previously
saved it (this can be disabled by a
preference setting).
3.6. The “Edit” menu
The Wireshark Edit menu contains the fields shown in Table 3.3, “Edit menu items”.
Figure 3.4. The “Edit” Menu
Table 3.3. Edit menu items
Menu Item Accelerator Description
Copy These menu items will copy
Find Packet… Ctrl+F This menu item brings up a
Find Next Ctrl+N This menu item tries to find the
Find Previous Ctrl+B This menu item tries to find the
the packet list, packet detail,
or properties of the currently
selected packet to the clipboard.
toolbar that allows you to find a
packet by many criteria. There
is further information on finding
packets in Section 6.8, “Finding
packets”.
next packet matching the settings
from “Find Packet…”.
previous packet matching the
settings from “Find Packet…”.
20
Page 31

User Interface
Menu Item Accelerator Description
Mark/Unmark Packet Ctrl+M This menu item marks the
currently selected packet. See
Section 6.10, “Marking packets”
for details.
Mark All Displayed Packets Shift+Ctrl+M This menu item marks all
displayed packets.
Unmark All Displayed Packets Ctrl+Alt+M This menu item unmarks all
displayed packets.
Next Mark Shift+Alt+N Find the next marked packet.
Previous Mark Shift+Alt+B Find the previous marked packet.
Ignore/Unignore Packet Ctrl+D This menu item marks the
currently selected packet as
ignored. See Section 6.11,
“Ignoring packets” for details.
Ignore All Displayed Shift+Ctrl+D This menu item marks all
displayed packets as ignored.
Unignore All Displayed Ctrl+Alt+D This menu item unmarks all
ignored packets.
Set/Unset Time Reference Ctrl+T This menu item set a time
reference on the currently
selected packet. See
Section 6.12.1, “Packet
time referencing” for more
information about the time
referenced packets.
Unset All Time References Ctrl+Alt+T This menu item removes all time
references on the packets.
Next Time Reference Ctrl+Alt+N This menu item tries to find the
next time referenced packet.
Previous Time Reference Ctrl+Alt+B This menu item tries to find the
previous time referenced packet.
Time Shift Ctrl+Shift+T This will show the Time Shift
dialog, which allows you to
adjust the timestamps of some or
all packets.
Packet Comment… This will let you add a comment
to a single packet. Note that the
ability to save packet comments
depends on your file format. E.g.
pcapng supports comments, pcap
does not.
Configuration Profiles… Shift+Ctrl+A This menu item brings up
a dialog box for handling
configuration profiles. More
detail is provided in Section 10.6,
“Configuration Profiles”.
21
Page 32

Menu Item Accelerator Description
Preferences… Shift+Ctrl+P or Cmd+ (OS X) This menu item brings up a
3.7. The “View” menu
The Wireshark View menu contains the fields shown in Table 3.4, “View menu items”.
Figure 3.5. The “View” Menu
User Interface
dialog box that allows you to set
preferences for many parameters
that control Wireshark. You can
also save your preferences so
Wireshark will use them the next
time you start it. More detail
is provided in Section 10.5,
“Preferences”.
Table 3.4. View menu items
Menu Item Accelerator Description
Main Toolbar This menu item hides or
shows the main toolbar, see
Section 3.16, “The “Main”
toolbar”.
Filter Toolbar This menu item hides or
shows the filter toolbar, see
Section 3.17, “The “Filter”
toolbar”.
Wireless Toolbar This menu item hides or shows
the wireless toolbar. May not be
present on some platforms.
Statusbar This menu item hides or shows
the statusbar, see Section 3.21,
“The Statusbar”.
Packet List This menu item hides or
shows the packet list pane, see
Section 3.18, “The “Packet List”
pane”.
Packet Details This menu item hides or shows
the packet details pane, see
Section 3.19, “The “Packet
Details” pane”.
Packet Bytes This menu item hides or shows
the packet bytes pane, see
Section 3.20, “The “Packet
Bytes” pane”.
22
Page 33

User Interface
Menu Item Accelerator Description
Time Display Format → Date
and Time of Day: 1970-01-01
01:02:03.123456
Time Display Format → Time of
Day: 01:02:03.123456
Time Display Format → Seconds
Since Epoch (1970-01-01):
1234567890.123456
Time Display Format → Seconds
Since Beginning of Capture:
123.123456
Time Display Format → Seconds
Since Previous Captured Packet:
1.123456
Time Display Format → Seconds
Since Previous Displayed Packet:
1.123456
Time Display Format →
Automatic (File Format
Precision)
Selecting this tells Wireshark
to display the time stamps in
date and time of day format,
see Section 6.12, “Time display
formats and time references”.
The fields "Time of Day", "Date
and Time of Day", "Seconds
Since Beginning of Capture",
"Seconds Since Previous
Captured Packet" and "Seconds
Since Previous Displayed
Packet" are mutually exclusive.
Selecting this tells Wireshark
to display time stamps in time
of day format, see Section 6.12,
“Time display formats and time
references”.
Selecting this tells Wireshark to
display time stamps in seconds
since 1970-01-01 00:00:00, see
Section 6.12, “Time display
formats and time references”.
Selecting this tells Wireshark
to display time stamps in
seconds since beginning of
capture format, see Section 6.12,
“Time display formats and time
references”.
Selecting this tells Wireshark
to display time stamps in
seconds since previous captured
packet format, see Section 6.12,
“Time display formats and time
references”.
Selecting this tells Wireshark
to display time stamps in
seconds since previous displayed
packet format, see Section 6.12,
“Time display formats and time
references”.
Selecting this tells Wireshark
to display time stamps with
the precision given by the
capture file format used, see
Section 6.12, “Time display
formats and time references”.
23
Page 34

User Interface
Menu Item Accelerator Description
The fields "Automatic",
"Seconds" and "…seconds" are
mutually exclusive.
Time Display Format →
Seconds: 0
Time Display Format → …
seconds: 0….
Time Display Format → Display
Seconds with hours and minutes
Name Resolution → Resolve
Name
Name Resolution → Enable for
MAC Layer
Name Resolution → Enable for
Network Layer
Name Resolution → Enable for
Transport Layer
Colorize Packet List This item allows you to control
Selecting this tells Wireshark
to display time stamps with a
precision of one second, see
Section 6.12, “Time display
formats and time references”.
Selecting this tells Wireshark
to display time stamps with
a precision of one second,
decisecond, centisecond,
millisecond, microsecond or
nanosecond, see Section 6.12,
“Time display formats and time
references”.
Selecting this tells Wireshark to
display time stamps in seconds,
with hours and minutes.
This item allows you to trigger
a name resolve of the current
packet only, see Section 7.7,
“Name Resolution”.
This item allows you to control
whether or not Wireshark
translates MAC addresses into
names, see Section 7.7, “Name
Resolution”.
This item allows you to control
whether or not Wireshark
translates network addresses into
names, see Section 7.7, “Name
Resolution”.
This item allows you to control
whether or not Wireshark
translates transport addresses into
names, see Section 7.7, “Name
Resolution”.
whether or not Wireshark should
colorize the packet list.
Enabling colorization will slow
down the display of new packets
while capturing / loading capture
files.
Auto Scroll in Live Capture This item allows you to specify
that Wireshark should scroll the
packet list pane as new packets
24
Page 35

User Interface
Menu Item Accelerator Description
come in, so you are always
looking at the last packet. If you
do not specify this, Wireshark
simply adds new packets onto the
end of the list, but does not scroll
the packet list pane.
Zoom In Ctrl++ Zoom into the packet data
(increase the font size).
Zoom Out Ctrl+- Zoom out of the packet data
(decrease the font size).
Normal Size Ctrl+= Set zoom level back to 100% (set
font size back to normal).
Resize All Columns Shift+Ctrl+R Resize all column widths so the
content will fit into it.
Resizing may take a significant
amount of time, especially if a
large capture file is loaded.
Displayed Columns This menu items folds out with
a list of all configured columns.
These columns can now be
shown or hidden in the packet
list.
Expand Subtrees Shift+
Collapse Subtrees Shift+
Expand All Ctrl+
Collapse All Ctrl+
Colorize Conversation This menu item brings up a
→
←
→
←
This menu item expands the
currently selected subtree in the
packet details tree.
This menu item collapses the
currently selected subtree in the
packet details tree.
Wireshark keeps a list of all
the protocol subtrees that are
expanded, and uses it to ensure
that the correct subtrees are
expanded when you display a
packet. This menu item expands
all subtrees in all packets in the
capture.
This menu item collapses the tree
view of all packets in the capture
list.
submenu that allows you to color
packets in the packet list pane
based on the addresses of the
currently selected packet. This
makes it easy to distinguish
packets belonging to different
25
Page 36

User Interface
Menu Item Accelerator Description
conversations. Section 10.3,
“Packet colorization”.
Colorize Conversation → Color
1-10
Colorize Conversation → Reset
coloring
Colorize Conversation → New
Coloring Rule…
Coloring Rules… This menu item brings up a
Show Packet in New Window This menu item brings up the
Reload Ctrl+R This menu item allows you to
These menu items enable one of
the ten temporary color filters
based on the currently selected
conversation.
This menu item clears all
temporary coloring rules.
This menu item opens a
dialog window in which a new
permanent coloring rule can be
created based on the currently
selected conversation.
dialog box that allows you to
color packets in the packet
list pane according to filter
expressions you choose. It
can be very useful for spotting
certain types of packets,
see Section 10.3, “Packet
colorization”.
selected packet in a separate
window. The separate window
shows only the tree view and
byte view panes.
reload the current capture file.
3.8. The “Go” menu
The Wireshark Go menu contains the fields shown in Table 3.5, “Go menu items”.
Figure 3.6. The “Go” Menu
Table 3.5. Go menu items
Menu Item Accelerator Description
Back Alt+
Forward Alt+
←
→
Jump to the recently visited
packet in the packet history,
much like the page history in a
web browser.
Jump to the next visited packet in
the packet history, much like the
page history in a web browser.
26
Page 37

User Interface
Menu Item Accelerator Description
Go to Packet… Ctrl+G Bring up a window frame that
allows you to specify a packet
number, and then goes to that
packet. See Section 6.9, “Go to a
specific packet” for details.
Go to Corresponding Packet Go to the corresponding packet
of the currently selected protocol
field. If the selected field doesn’t
correspond to a packet, this item
is greyed out.
Previous Packet Ctrl+
Next Packet Ctrl+
First Packet Ctrl+Home Jump to the first packet of the
Last Packet Ctrl+End Jump to the last packet of the
Previous Packet In Conversation Ctrl+, Move to the previous packet
Next Packet In Conversation Ctrl+. Move to the next packet in the
↑
↓
Move to the previous packet in
the list. This can be used to move
to the previous packet even if the
packet list doesn’t have keyboard
focus.
Move to the next packet in the
list. This can be used to move to
the previous packet even if the
packet list doesn’t have keyboard
focus.
capture file.
capture file.
in the current conversation.
This can be used to move to
the previous packet even if the
packet list doesn’t have keyboard
focus.
current conversation. This can
be used to move to the previous
packet even if the packet list
doesn’t have keyboard focus.
3.9. The “Capture” menu
The Wireshark Capture menu contains the fields shown in Table 3.6, “Capture menu items”.
Figure 3.7. The “Capture” Menu
Table 3.6. Capture menu items
Menu Item Accelerator Description
Interfaces… Ctrl+I This menu item brings up a
27
dialog box that shows what’s
Page 38

User Interface
Menu Item Accelerator Description
going on at the network
interfaces Wireshark knows of,
see Section 4.4, “The “Capture
Interfaces” dialog box”) .
Options… Ctrl+K This menu item brings up the
Capture Options dialog box
(discussed further in Section 4.5,
“The “Capture Options” dialog
box”) and allows you to start
capturing packets.
Start Ctrl+E Immediately start capturing
packets with the same settings
than the last time.
Stop Ctrl+E This menu item stops the
currently running capture, see
Section 4.14.1, “Stop the running
capture”) .
Restart Ctrl+R This menu item stops the
currently running capture
and starts again with the
same options, this is just for
convenience.
Capture Filters… This menu item brings up a
dialog box that allows you to
create and edit capture filters.
You can name filters, and you
can save them for future use.
More detail on this subject
is provided in Section 6.6,
“Defining and saving filters”
3.10. The “Analyze” menu
The Wireshark Analyze menu contains the fields shown in Table 3.7, “Analyze menu items”.
Figure 3.8. The “Analyze” Menu
Table 3.7. Analyze menu items
Menu Item Accelerator Description
Display Filters… This menu item brings up a
28
dialog box that allows you to
create and edit display filters.
You can name filters, and you
can save them for future use.
More detail on this subject
is provided in Section 6.6,
“Defining and saving filters”
Page 39

User Interface
Menu Item Accelerator Description
Display Filter Macros… This menu item brings up a
dialog box that allows you to
create and edit display filter
macros. You can name filter
macros, and you can save them
for future use. More detail
on this subject is provided in
Section 6.7, “Defining and
saving filter macros”
Apply as Column This menu item adds the selected
protocol item in the packet
details pane as a column to the
packet list.
Apply as Filter → …
Prepare a Filter → …
Enabled Protocols… Shift+Ctrl+E This menu item allows the
Decode As… This menu item allows the user
User Specified Decodes… This menu item allows the user
Follow TCP Stream This menu item brings up a
These menu items will change
the current display filter
and apply the changed filter
immediately. Depending on the
chosen menu item, the current
display filter string will be
replaced or appended to by the
selected protocol field in the
packet details pane.
These menu items will change
the current display filter but
won’t apply the changed filter.
Depending on the chosen
menu item, the current display
filter string will be replaced
or appended to by the selected
protocol field in the packet
details pane.
user to enable/disable protocol
dissectors, see Section 10.4.1,
“The “Enabled Protocols” dialog
box”
to force Wireshark to decode
certain packets as a particular
protocol, see Section 10.4.2,
“User Specified Decodes”
to force Wireshark to decode
certain packets as a particular
protocol, see Section 10.4.3,
“Show User Specified Decodes”
separate window and displays
all the TCP segments captured
29
Page 40

User Interface
Menu Item Accelerator Description
that are on the same TCP
connection as a selected packet,
see Section 7.2, “Following TCP
streams”
Follow UDP Stream Same functionality as “Follow
TCP Stream” but for UDP
streams.
Follow SSL Stream Same functionality as “Follow
TCP Stream” but for SSL
streams. See the wiki page on
SSL for instructions on providing
SSL keys.
Expert Info Open a dialog showing some
expert information about the
captured packets. The amount of
information will depend on the
protocol and varies from very
detailed to non-existent. XXX add a new section about this and
link from here
Conversation Filter → …
In this menu you will find
conversation filter for various
protocols.
3.11. The “Statistics” menu
The Wireshark Statistics menu contains the fields shown in Table 3.8, “Statistics menu items”.
Figure 3.9. The “Statistics” Menu
All menu items will bring up a new window showing specific statistical information.
Table 3.8. Statistics menu items
Menu Item Accelerator Description
Summary Show information about the data
Protocol Hierarchy Display a hierarchical tree
Conversations Display a list of conversations
Endpoints Display a list of endpoints
captured, see Section 8.2, “The
Summary window”.
of protocol statistics, see
Section 8.3, “The "Protocol
Hierarchy" window”.
(traffic between two endpoints),
see Section 8.4.1, “The
“Conversations” window”.
(traffic to/from an address), see
30
Page 41

User Interface
Menu Item Accelerator Description
Section 8.5.1, “The "Endpoints"
window”.
Packet Lengths… See Section 8.10, “The protocol
specific statistics windows”
IO Graphs Display user specified graphs
(e.g. the number of packets in the
course of time), see Section 8.6,
“The "IO Graphs" window”.
Service Response Time Display the time between a
request and the corresponding
response, see Section 8.7,
“Service Response Time”.
ANCP See Section 8.10, “The protocol
specific statistics windows”
Colledtd… See Section 8.10, “The protocol
specific statistics windows”
Compare… See Section 8.10, “The protocol
specific statistics windows”
Flow Graph… See Section 8.10, “The protocol
specific statistics windows”
HTTP HTTP request/response statistics,
see Section 8.10, “The protocol
specific statistics windows”
IP Addresses… See Section 8.10, “The protocol
specific statistics windows”
IP Destinations… See Section 8.10, “The protocol
specific statistics windows”
IP Protocol Types… See Section 8.10, “The protocol
specific statistics windows”
ONC-RPC Programs See Section 8.10, “The protocol
specific statistics windows”
Sametime See Section 8.10, “The protocol
specific statistics windows”
TCP Stream Graph See Section 8.10, “The protocol
specific statistics windows”
UDP Multicast Streams See Section 8.10, “The protocol
specific statistics windows”
WLAN Traffic See Section 8.9, “WLAN Traffic
Statistics”
BOOTP-DHCP See Section 8.10, “The protocol
specific statistics windows”
3.12. The “Telephony” menu
The Wireshark Telephony menu contains the fields shown in Table 3.9, “Telephony menu items”.
31
Page 42

User Interface
Figure 3.10. The “Telephony” Menu
All menu items will bring up a new window showing specific telephony related statistical information.
Table 3.9. Telephony menu items
Menu Item Accelerator Description
IAX2 See Section 9.7, “The protocol
specific statistics windows”
SMPP Operations… See Section 9.7, “The protocol
specific statistics windows”
SCTP See Section 9.7, “The protocol
specific statistics windows”
ANSI See Section 9.7, “The protocol
specific statistics windows”
GSM See Section 9.7, “The protocol
specific statistics windows”
H.225… See Section 9.7, “The protocol
specific statistics windows”
ISUP Messages… See Section 9.7, “The protocol
specific statistics windows”
LTE See Section 9.5, “LTE MAC
Traffic Statistics”
MTP3 See Section 9.7, “The protocol
specific statistics windows”
RTP See Section 9.2, “RTP Analysis”
SIP… See Section 9.7, “The protocol
specific statistics windows”
UCP Messages… See Section 9.7, “The protocol
specific statistics windows”
VoIP Calls… See Section 9.4, “VoIP Calls”
WAP-WSP… See Section 9.7, “The protocol
specific statistics windows”
3.13. The “Tools” menu
The Wireshark Tools menu contains the fields shown in Table 3.10, “Tools menu items”.
Figure 3.11. The “Tools” Menu
Table 3.10. Tools menu items
Menu Item Accelerator Description
Firewall ACL Rules This allows you to create
command-line ACL rules for
32
Page 43

User Interface
Menu Item Accelerator Description
Lua These options allow you to
3.14. The “Internals” menu
many different firewall products,
including Cisco IOS, Linux
Netfilter (iptables), OpenBSD
pf and Windows Firewall
(via netsh). Rules for MAC
addresses, IPv4 addresses, TCP
and UDP ports, and IPv4+port
combinations are supported.
It is assumed that the rules will
be applied to an outside interface.
work with the Lua interpreter
optionally build into Wireshark.
See the “Lua Support in
Wireshark” in the Wireshark
Developer’s Guide.
The Wireshark Internals menu contains the fields shown in Table 3.11, “Help menu items”.
Figure 3.12. The “Internals” Menu
Table 3.11. Help menu items
Menu Item Accelerator Description
Dissector tables This menu item brings up a
Supported Protocols (slow!) This menu item brings up
3.15. The “Help” menu
The Wireshark Help menu contains the fields shown in Table 3.12, “Help menu items”.
Figure 3.13. The “Help” Menu
dialog box showing the tables
with subdissector relationships.
a dialog box showing the
supported protocols and protocol
fields.
Table 3.12. Help menu items
Menu Item Accelerator Description
Contents F1 This menu item brings up a basic
help system.
33
Page 44

User Interface
Menu Item Accelerator Description
Manual Pages → …
Website This menu item starts a
FAQ’s This menu item starts a Web
Downloads This menu item starts a
Wiki This menu item starts a Web
Sample Captures This menu item starts a
About Wireshark This menu item brings up
This menu item starts a Web
browser showing one of the
locally installed html manual
pages.
Web browser showing the
webpage from: https://
www.wireshark.org/.
browser showing various FAQ’s.
Web browser showing the
downloads from: https://
www.wireshark.org/.
browser showing the front page
from: https://wiki.wireshark.org/.
Web browser showing the
sample captures from: https://
wiki.wireshark.org/.
an information window that
provides various detailed
information items on Wireshark,
such as how it’s build, the
plugins loaded, the used folders,
…
Note
Opening a Web browser might be unsupported in your version of Wireshark. If this is the
case the corresponding menu items will be hidden.
If calling a Web browser fails on your machine, nothing happens, or the browser starts but
no page is shown, have a look at the web browser setting in the preferences dialog.
3.16. The “Main” toolbar
The main toolbar provides quick access to frequently used items from the menu. This toolbar cannot be
customized by the user, but it can be hidden using the View menu, if the space on the screen is needed
to show even more packet data.
As in the menu, only the items useful in the current program state will be available. The others will be
greyed out (e.g. you cannot save a capture file if you haven’t loaded one).
Figure 3.14. The “Main” toolbar
34
Page 45

Table 3.13. Main toolbar items
User Interface
Toolbar Icon Toolbar Item Corresponding Menu
Item
Interfaces…
Options…
Start
Stop
Restart
Open…
Save As…
Capture → Interfaces…
Capture → Options…
Capture → Start
Capture → Stop
Capture → Restart
File → Open…
File → Save As…
Description
This item brings up the
Capture Interfaces List
dialog box (discussed
further in Section 4.3,
“Start Capturing”).
This item brings up the
Capture Options dialog
box (discussed further
in Section 4.3, “Start
Capturing”) and allows
you to start capturing
packets.
This item starts
capturing packets with
the options form the last
time.
This item stops the
currently running
live capture process
Section 4.3, “Start
Capturing”).
This item stops the
currently running live
capture process and
restarts it again, for
convenience.
This item brings up the
file open dialog box that
allows you to load a
capture file for viewing.
It is discussed in more
detail in Section 5.2.1,
“The “Open Capture
File” dialog box”.
This item allows you to
save the current capture
file to whatever file you
would like. It pops up
the Save Capture File
As dialog box (which
is discussed further in
Section 5.3.1, “The
“Save Capture File As”
dialog box”).
35
If you currently have a
temporary capture file,
Page 46

User Interface
Toolbar Icon Toolbar Item Corresponding Menu
Item
Close
Reload
Print…
Find Packet…
Go Back
Go Forward
Go to Packet…
Go To First Packet
Go To Last Packet
Colorize
Auto Scroll in Live
Capture
File → Close
View → Reload
File → Print…
Edit → Find Packet…
Go → Go Back
Go → Go Forward
Go → Go to Packet…
Go → First Packet
Go → Last Packet
View → Colorize
View → Auto Scroll in
Live Capture
Description
the Save icon will be
shown instead.
This item closes the
current capture. If you
have not saved the
capture, you will be
asked to save it first.
This item allows you
to reload the current
capture file.
This item allows you
to print all (or some
of) the packets in the
capture file. It pops up
the Wireshark Print
dialog box (which is
discussed further in
Section 5.8, “Printing
packets”).
This item brings up
a dialog box that
allows you to find a
packet. There is further
information on finding
packets in Section 6.8,
“Finding packets”.
This item jumps back in
the packet history.
This item jumps forward
in the packet history.
This item brings up a
dialog box that allows
you to specify a packet
number to go to that
packet.
This item jumps to
the first packet of the
capture file.
This item jumps to the
last packet of the capture
file.
Colorize the packet list
(or not).
Auto scroll packet
list while doing a live
capture (or not).
36
Page 47

User Interface
Toolbar Icon Toolbar Item Corresponding Menu
Item
Zoom In
Zoom Out
Normal Size
Resize Columns
Capture Filters…
Display Filters…
Coloring Rules…
Preferences…
View → Zoom In
View → Zoom Out
View → Normal Size
View → Resize
Columns
Capture → Capture
Filters…
Analyze → Display
Filters…
View → Coloring
Rules…
Edit → Preferences
Description
Zoom into the packet
data (increase the font
size).
Zoom out of the packet
data (decrease the font
size).
Set zoom level back to
100%.
Resize columns, so the
content fits into them.
This item brings up a
dialog box that allows
you to create and edit
capture filters. You can
name filters, and you
can save them for future
use. More detail on this
subject is provided in
Section 6.6, “Defining
and saving filters”.
This item brings up a
dialog box that allows
you to create and edit
display filters. You can
name filters, and you
can save them for future
use. More detail on this
subject is provided in
Section 6.6, “Defining
and saving filters”.
This item brings up a
dialog box that allows
you to color packets
in the packet list pane
according to filter
expressions you choose.
It can be very useful for
spotting certain types of
packets. More detail on
this subject is provided
in Section 10.3, “Packet
colorization”.
This item brings up a
dialog box that allows
you to set preferences
for many parameters
that control Wireshark.
You can also save
37
Page 48

User Interface
Toolbar Icon Toolbar Item Corresponding Menu
Help
3.17. The “Filter” toolbar
The filter toolbar lets you quickly edit and apply display filters. More information on display filters is
available in Section 6.3, “Filtering packets while viewing”.
Figure 3.15. The “Filter” toolbar
Table 3.14. Filter toolbar items
Toolbar Icon Toolbar Item Description
Filter: Brings up the filter construction
Filter input The area to enter or edit
Item
Help → Contents
Description
your preferences so
Wireshark will use them
the next time you start it.
More detail is provided
in Section 10.5,
“Preferences”
This item brings up help
dialog box.
dialog, described in Figure 6.8,
“The “Capture Filters” and
“Display Filters” dialog boxes”.
a display filter string, see
Section 6.4, “Building display
filter expressions”. A syntax
check of your filter string is
done while you are typing. The
background will turn red if you
enter an incomplete or invalid
string, and will become green
when you enter a valid string.
You can click on the pull down
arrow to select a previously-
entered filter string from a list.
The entries in the pull down list
will remain available even after a
program restart.
38
After you’ve changed something
in this field, don’t forget to press
the Apply button (or the Enter/
Return key), to apply this filter
string to the display.
This field is also where the
current filter in effect is
displayed.
Page 49

User Interface
Toolbar Icon Toolbar Item Description
Expression… The middle button labeled "Add
Clear Reset the current display filter
Apply Apply the current value in the
3.18. The “Packet List” pane
The packet list pane displays all the packets in the current capture file.
Expression…" opens a dialog
box that lets you edit a display
filter from a list of protocol
fields, described in Section 6.5,
“The “Filter Expression” dialog
box”
and clears the edit area.
edit area as the new display filter.
Applying a display filter on large
capture files might take quite a
long time.
Figure 3.16. The “Packet List” pane
Each line in the packet list corresponds to one packet in the capture file. If you select a line in this pane,
more details will be displayed in the “Packet Details” and “Packet Bytes” panes.
While dissecting a packet, Wireshark will place information from the protocol dissectors into the columns.
As higher level protocols might overwrite information from lower levels, you will typically see the
information from the highest possible level only.
For example, let’s look at a packet containing TCP inside IP inside an Ethernet packet. The Ethernet
dissector will write its data (such as the Ethernet addresses), the IP dissector will overwrite this by its own
(such as the IP addresses), the TCP dissector will overwrite the IP information, and so on.
There are a lot of different columns available. Which columns are displayed can be selected by preference
settings, see Section 10.5, “Preferences”.
The default columns will show:
• No. The number of the packet in the capture file. This number won’t change, even if a display filter
is used.
• Time The timestamp of the packet. The presentation format of this timestamp can be changed, see
Section 6.12, “Time display formats and time references”.
• Source The address where this packet is coming from.
• Destination The address where this packet is going to.
• Protocol The protocol name in a short (perhaps abbreviated) version.
• Info Additional information about the packet content.
39
Page 50

User Interface
There is a context menu (right mouse click) available, see details in Figure 6.4, “Pop-up menu of the
“Packet List” pane”.
3.19. The “Packet Details” pane
The packet details pane shows the current packet (selected in the “Packet List” pane) in a more detailed
form.
Figure 3.17. The “Packet Details” pane
This pane shows the protocols and protocol fields of the packet selected in the “Packet List” pane. The
protocols and fields of the packet are displayed using a tree, which can be expanded and collapsed.
There is a context menu (right mouse click) available, see details in Figure 6.5, “Pop-up menu of the
“Packet Details” pane”.
Some protocol fields are specially displayed.
• Generated fields Wireshark itself will generate additional protocol fields which are surrounded by
brackets. The information in these fields is derived from the known context to other packets in the
capture file. For example, Wireshark is doing a sequence/acknowledge analysis of each TCP stream,
which is displayed in the [SEQ/ACK analysis] fields of the TCP protocol.
• Links If Wireshark detected a relationship to another packet in the capture file, it will generate a link
to that packet. Links are underlined and displayed in blue. If double-clicked, Wireshark jumps to the
corresponding packet.
3.20. The “Packet Bytes” pane
The packet bytes pane shows the data of the current packet (selected in the “Packet List” pane) in a
hexdump style.
Figure 3.18. The “Packet Bytes” pane
As usual for a hexdump, the left side shows the offset in the packet data, in the middle the packet data is
shown in a hexadecimal representation and on the right the corresponding ASCII characters (or . if not
appropriate) are displayed.
Depending on the packet data, sometimes more than one page is available, e.g. when Wireshark has
reassembled some packets into a single chunk of data, see Section 7.6, “Packet Reassembly”. In this case
there are some additional tabs shown at the bottom of the pane to let you select the page you want to see.
Figure 3.19. The “Packet Bytes” pane with tabs
Note
The additional pages might contain data picked from multiple packets.
40
Page 51

The context menu (right mouse click) of the tab labels will show a list of all available pages. This can be
helpful if the size in the pane is too small for all the tab labels.
3.21. The Statusbar
The statusbar displays informational messages.
In general, the left side will show context related information, the middle part will show the current number
of packets, and the right side will show the selected configuration profile. Drag the handles between the
text areas to change the size.
Figure 3.20. The initial Statusbar
This statusbar is shown while no capture file is loaded, e.g. when Wireshark is started.
Figure 3.21. The Statusbar with a loaded capture file
• The colorized bullet on the left shows the highest expert info level found in the currently loaded capture
file. Hovering the mouse over this icon will show a textual description of the expert info level, and
clicking the icon will bring up the Expert Infos dialog box. For a detailed description of expert info,
see Section 7.3, “Expert Information”.
User Interface
• The left side shows information about the capture file, its name, its size and the elapsed time while it
was being captured.
• The middle part shows the current number of packets in the capture file. The following values are
displayed:
• Packets: the number of captured packets
• Displayed: the number of packets currently being displayed
• Marked: the number of marked packets
• Dropped: the number of dropped packets (only displayed if Wireshark was unable to capture all
packets)
• Ignored: the number of ignored packets (only displayed if packets are ignored)
• The right side shows the selected configuration profile. Clicking in this part of the statusbar will
bring up a menu with all available configuration profiles, and selecting from this list will change the
configuration profile.
Figure 3.22. The Statusbar with a configuration profile menu
For a detailed description of configuration profiles, see Section 10.6, “Configuration Profiles”.
Figure 3.23. The Statusbar with a selected protocol field
41
Page 52

User Interface
This is displayed if you have selected a protocol field from the “Packet Details” pane.
Tip
The value between the brackets (in this example arp.opcode) can be used as a display
filter string, representing the selected protocol field.
Figure 3.24. The Statusbar with a display filter message
This is displayed if you are trying to use a display filter which may have unexpected results. For a detailed
description, see Section 6.4.5, “A common mistake”.
42
Page 53

Chapter 4. Capturing Live Network Data
4.1. Introduction
Capturing live network data is one of the major features of Wireshark.
The Wireshark capture engine provides the following features:
• Capture from different kinds of network hardware such as Ethernet or 802.11.
• Stop the capture on different triggers such as the amount of captured data, elapsed time, or the number
of packets.
• Simultaneously show decoded packets while Wireshark is capturing.
• Filter packets, reducing the amount of data to be captured. See Section 4.13, “Filtering while capturing”.
• Save packets in multiple files while doing a long term capture, optionally rotating through a fixed
number of files (a “ringbuffer”). See Section 4.11, “Capture files and file modes”.
• Simultaneously capture from multiple network interfaces.
The capture engine still lacks the following features:
• Stop capturing (or perform some other action) depending on the captured data.
4.2. Prerequisites
Setting up Wireshark to capture packets for the first time can be tricky. A comprehensive guide “How To
setup a Capture” is available at https://wiki.wireshark.org/CaptureSetup.
Here are some common pitfalls:
• You may need special privileges to start a live capture.
• You need to choose the right network interface to capture packet data from.
• You need to capture at the right place in the network to see the traffic you want to see.
If you have any problems setting up your capture environment you should have a look at the guide
mentioned above.
4.3. Start Capturing
The following methods can be used to start capturing packets with Wireshark:
• You can double-click on an interface in the main window.
• You can get an overview of the available interfaces using the “Capture Interfaces” dialog box (Capture
→ Options…). See Figure 4.1, “The “Capture Interfaces” dialog box on Microsoft Windows” or
Figure 4.2, “The “Capture Interfaces” dialog box on Unix/Linux” for more information. You can start
a capture from this dialog box using the Start button.
43
Page 54

Capturing Live Network Data
•
You can immediately start a capture using your current settings by selecting Capture → Start or by
cliking the first toolbar button.
• If you already know the name of the capture interface you can start Wireshark from the command line:
$ wireshark -i eth0 -k
This will start Wireshark capturing on interface eth0. More details can be found at Section 10.2, “Start
Wireshark from the command line”.
4.4. The “Capture Interfaces” dialog box
When you select Capture → Options… from the main menu Wireshark pops up the “Capture Interfaces”
dialog box as shown in Figure 4.1, “The “Capture Interfaces” dialog box on Microsoft Windows” or
Figure 4.2, “The “Capture Interfaces” dialog box on Unix/Linux”.
Both you and your OS can hide interfaces
This dialog box will only show the local interfaces Wireshark can access. It will also hide
interfaces marked as hidden in Section 10.5.1, “Interface Options”. As Wireshark might not
be able to detect all local interfaces and it cannot detect the remote interfaces available there
could be more capture interfaces available than listed.
It is possible to select more than one interface and capture from them simultaneously.
Figure 4.1. The “Capture Interfaces” dialog box on Microsoft Windows
Figure 4.2. The “Capture Interfaces” dialog box on Unix/Linux
Device (Unix/Linux only) The interface device name.
Description The interface description provided by the operating system, or the
user defined comment added in Section 10.5.1, “Interface Options”.
IP The first IP address Wireshark could find for this interface. You can
click on the address to cycle through other addresses assigned to it,
if available. If no address could be found “none” will be displayed.
Packets The number of packets captured from this interface, since this
dialog was opened. Will be greyed out, if no packet was captured
in the last second.
Packets/s Number of packets captured in the last second. Will be greyed out,
if no packet was captured in the last second.
Stop Stop a currently running capture.
Start Start a capture on all selected interfaces immediately, using the
settings from the last capture or the default settings, if no options
have been set.
44
Page 55

Capturing Live Network Data
Options Open the Capture Options dialog with the marked interfaces
selected. See Section 4.5, “The “Capture Options” dialog box”.
Details (Microsoft Windows only) Open a dialog with detailed information about the interface. See
Section 4.10, “The “Interface Details” dialog box”.
Help Show this help page.
Close Close this dialog box.
4.5. The “Capture Options” dialog box
When you select Capture → Options… (or use the corresponding item in the main toolbar), Wireshark
pops up the “Capture Options” dialog box as shown in Figure 4.3, “The “Capture Options” dialog box”.
Figure 4.3. The “Capture Options” dialog box
Tip
If you are unsure which options to choose in this dialog box just try keeping the defaults as
this should work well in many cases.
4.5.1. Capture frame
The table shows the settings for all available interfaces:
• The name of the interface and its IP addresses. If no address could be resolved from the system, “none”
will be shown.
Note
Loopback interfaces are not available on Windows platforms.
• The link-layer header type.
• The information whether promicuous mode is enabled or disabled.
• The maximum amount of data that will be captured for each packet. The default value is set to the
65535 bytes.
• The size of the kernel buffer that is reserved to keep the captured packets.
• The information whether packets will be captured in monitor mode (Unix/Linux only).
• The chosen capture filter.
By marking the checkboxes in the first column the interfaces are selected to be captured from. By doubleclicking on an interface the “Edit Interface Settings” dialog box as shown in Figure 4.4, “The “Edit
Interface Settings” dialog box” will be opened.
Capture on all interfaces As Wireshark can capture on multiple interfaces it is possible to
choose to capture on all available interfaces.
45
Page 56

Capturing Live Network Data
Capture all packets in promiscuous
mode
Capture Filter This field allows you to specify a capture filter for all interfaces
Compile selected BPFs This button allows you to compile the capture filter into BPF code
This checkbox allows you to specify that Wireshark should put all
interfaces in promiscuous mode when capturing.
that are currently selected. Once a filter has been entered in this
field, the newly selected interfaces will inherit the filter. Capture
filters are discussed in more details in Section 4.13, “Filtering while
capturing”. It defaults to empty, or no filter.
You can also click on the Capture Filter button and Wireshark will
bring up the Capture Filters dialog box and allow you to create
and/or select a filter. Please see Section 6.6, “Defining and saving
filters”
and pop up a window showing you the resulting pseudo code. This
can help in understanding the working of the capture filter you
created. The Compile Selected BPFs button leads you to Figure 4.5,
“The “Compile Results” dialog box”.
Tip
Linux power user tip
The execution of BPFs can be sped up on Linux by turning on BPF JIT by executing
$ echo 1 >/proc/sys/net/core/bpf_jit_enable
if it is not enabled already. To make the change persistent you can use sysfsutils.
Manage Interfaces The Manage Interfaces button opens the Figure 4.6, “The “Add New
Interfaces” dialog box” where pipes can be defined, local interfaces
scanned or hidden, or remote interfaces added (Windows only).
4.5.2. Capture File(s) frame
An explanation about capture file usage can be found in Section 4.11, “Capture files and file modes”.
File This field allows you to specify the file name that will be used for
the capture file. This field is left blank by default. If the field is
left blank, the capture data will be stored in a temporary file. See
Section 4.11, “Capture files and file modes” for details.
You can also click on the button to the right of this field to browse
through the filesystem.
Use multiple files Instead of using a single file Wireshark will automatically switch
to a new one if a specific trigger condition is reached.
Use pcap-ng format This checkbox allows you to specify that Wireshark saves the
captured packets in pcap-ng format. This next generation capture
file format is currently in development. If more than one interface
is chosen for capturing, this checkbox is set by default. See https://
wiki.wireshark.org/Development/PcapNg for more details on pcap-
ng.
46
Page 57

Capturing Live Network Data
Next file every n megabyte(s) Multiple files only. Switch to the next file after the given number
of byte(s)/kilobyte(s)/megabyte(s)/gigabyte(s) have been captured.
Next file every n minute(s) Multiple files only: Switch to the next file after the given number
of second(s)/minutes(s)/hours(s)/days(s) have elapsed.
Ring buffer with n files Multiple files only: Form a ring buffer of the capture files with the
given number of files.
Stop capture after n file(s) Multiple files only: Stop capturing after switching to the next file
the given number of times.
4.5.3. Stop Capture… frame
… after n packet(s) Stop capturing after the given number of packets have been
captured.
… after n megabytes(s) Stop capturing after the given number of byte(s)/kilobyte(s)/
megabyte(s)/gigabyte(s) have been captured. This option is greyed
out if “Use multiple files” is selected.
… after n minute(s) Stop capturing after the given number of second(s)/minutes(s)/
hours(s)/days(s) have elapsed.
4.5.4. Display Options frame
Update list of packets in real time This option allows you to specify that Wireshark should update the
packet list pane in real time. If you do not specify this, Wireshark
does not display any packets until you stop the capture. When you
check this, Wireshark captures in a separate process and feeds the
captures to the display process.
Automatic scrolling in live capture This option allows you to specify that Wireshark should scroll the
packet list pane as new packets come in, so you are always looking
at the last packet. If you do not specify this Wireshark simply adds
new packets onto the end of the list but does not scroll the packet
list pane. This option is greyed out if “Update list of packets in real
time” is disabled.
Hide capture info dialog If this option is checked, the capture info dialog described in
Section 4.14, “While a Capture is running …” will be hidden.
4.5.5. Name Resolution frame
Enable MAC name resolution This option allows you to control whether or not Wireshark
translates MAC addresses into names. See Section 7.7, “Name
Resolution”.
Enable network name resolution This option allows you to control whether or not Wireshark
translates network addresses into names. See Section 7.7, “Name
Resolution”.
Enable transport name resolution This option allows you to control whether or not Wireshark
translates transport addresses into protocols. See Section 7.7,
“Name Resolution”.
47
Page 58

Capturing Live Network Data
4.5.6. Buttons
Once you have set the values you desire and have selected the options you need, simply click on Start to
commence the capture or Cancel to cancel the capture.
If you start a capture, Wireshark allows you to stop capturing when you have enough packets captured,
for details see Section 4.14, “While a Capture is running …”.
4.6. The “Edit Interface Settings” dialog box
If you double-click on an interface in Figure 4.3, “The “Capture Options” dialog box” the following dialog
box pops up.
Figure 4.4. The “Edit Interface Settings” dialog box
You can set the following fields in this dialog box:
IP address The IP address(es) of the selected interface. If no address could be
resolved from the system “none” will be shown.
Link-layer header type Unless you are in the rare situation that requires this keep the default
setting. For a detailed description. See Section 4.12, “Link-layer
header type”
Wireless settings (Windows only) Here you can set the settings for wireless capture using the AirPCap
adapter. For a detailed description see the AirPCap Users Guide.
Remote settings (Windows only) Here you can set the settings for remote capture. For a detailed
description see Section 4.9, “The “Remote Capture Interfaces”
dialog box”
Capture packets in promiscuous
mode
This checkbox allows you to specify that Wireshark should put
the interface in promiscuous mode when capturing. If you do not
specify this Wireshark will only capture the packets going to or
from your computer (not all packets on your LAN segment).
Note
If some other process has put the interface in promiscuous mode you may be capturing in
promiscuous mode even if you turn off this option.
Even in promiscuous mode you still won’t necessarily see all packets on your LAN segment.
See the Wireshark FAQ for more information.
Limit each packet to n bytes This field allows you to specify the maximum amount of data that
will be captured for each packet, and is sometimes referred to as the
snaplen. If disabled the value is set to the maximum 65535 which
will be sufficient for most protocols. Some rules of thumb:
• If you are unsure just keep the default value.
• If you don’t need or don’t want all of the data in a packet - for
example, if you only need the link-layer, IP, and TCP headers you might want to choose a small snapshot length, as less CPU
48
Page 59

Capturing Live Network Data
time is required for copying packets, less buffer space is required
for packets, and thus perhaps fewer packets will be dropped if
traffic is very heavy.
• If you don’t capture all of the data in a packet you might find
that the packet data you want is in the part that’s dropped or that
reassembly isn’t possible as the data required for reassembly is
missing.
Buffer size: n megabyte(s) Enter the buffer size to be used while capturing. This is the size of
the kernel buffer which will keep the captured packets, until they
are written to disk. If you encounter packet drops, try increasing
this value.
Capture packets in monitor mode
(Unix/Linux only)
This checkbox allows you to setup the Wireless interface to capture
all traffic it can receive, not just the traffic on the BSS to which it
is associated, which can happen even when you set promiscuous
mode. Also it might be necessary to turn this option on in order
to see IEEE 802.11 headers and/or radio information from the
captured frames.
Note
In monitor mode the adapter might disassociate itself from the network it was associated to.
Capture Filter This field allows you to specify a capture filter. Capture filters are discussed in
more details in Section 4.13, “Filtering while capturing”. It defaults to empty,
or no filter.
You can also click on the Capture Filter button and Wireshark will bring up
the “Capture Filters” dialog box and allow you to create and/or select a filter.
Please see Section 6.6, “Defining and saving filters”
Compile BPF This button allows you to compile the capture filter into BPF code and pop up a
window showing you the resulting pseudo code. This can help in understanding
the working of the capture filter you created.
4.7. The “Compile Results” dialog box
This figure shows the compile results of the selected interfaces.
Figure 4.5. The “Compile Results” dialog box
In the left window the interface names are listed. The results of an individual interface are shown in the
right window when it is selected.
4.8. The “Add New Interfaces” dialog box
As a central point to manage interfaces this dialog box consists of three tabs to add or remove interfaces.
Figure 4.6. The “Add New Interfaces” dialog box
49
Page 60

Capturing Live Network Data
4.8.1. Add or remove pipes
Figure 4.7. The “Add New Interfaces - Pipes” dialog box
To successfully add a pipe, this pipe must have already been created. Click the New button and type the
name of the pipe including its path. Alternatively, the Browse button can be used to locate the pipe. With
the Save button the pipe is added to the list of available interfaces. Afterwards, other pipes can be added.
To remove a pipe from the list of interfaces it first has to be selected. Then click the Delete button.
4.8.2. Add or hide local interfaces
Figure 4.8. The “Add New Interfaces - Local Interfaces” dialog box
The tab “Local Interfaces” contains a list of available local interfaces, including the hidden ones, which
are not shown in the other lists.
If a new local interface is added, for example, a wireless interface has been activated, it is not automatically
added to the list to prevent the constant scanning for a change in the list of available interfaces. To renew
the list a rescan can be done.
One way to hide an interface is to change the preferences. If the “Hide” checkbox is activated and the
Apply button clicked, the interface will not be seen in the lists of the “Capture Interfaces” dialog box any
more. The changes are also saved in the preferences file.
4.8.3. Add or hide remote interfaces
Figure 4.9. The “Add New Interfaces - Remote Interfaces” dialog box
In this tab interfaces on remote hosts can be added. One or more of these interfaces can be hidden. In
contrast to the local interfaces they are not saved in the preferences file.
To remove a host including all its interfaces from the list, it has to be selected. Then click the Delete button.
For a detailed description see Section 4.9, “The “Remote Capture Interfaces” dialog box”
4.9. The “Remote Capture Interfaces” dialog box
Besides doing capture on local interfaces Wireshark is capable of reaching out across the network to a so
called capture daemon or service processes to receive captured data from.
Microsoft Windows only
This dialog and capability is only available on Microsoft Windows. On Linux/Unix you can
achieve the same effect (securely) through an SSH tunnel.
50
Page 61

Capturing Live Network Data
The Remote Packet Capture Protocol service must first be running on the target platform before Wireshark
can connect to it. The easiest way is to install WinPcap from https://www.winpcap.org/install/ on the
target. Once installation is completed go to the Services control panel, find the Remote Packet Capture
Protocol service and start it.
Note
Make sure you have outside access to port 2002 on the target platform. This is the port where
the Remote Packet Capture Protocol service can be reached by default.
To access the Remote Capture Interfaces dialog use the “Add New Interfaces - Remote” dialog. See
Figure 4.9, “The “Add New Interfaces - Remote Interfaces” dialog box” and select Add.
4.9.1. Remote Capture Interfaces
Figure 4.10. The “Remote Capture Interfaces” dialog box
You have to set the following parameters in this dialog:
Host Enter the IP address or host name of the target platform where
the Remote Packet Capture Protocol service is listening. The drop
down list contains the hosts that have previously been successfully
contacted. The list can be emptied by choosing “Clear list” from
the drop down list.
Port Set the port number where the Remote Packet Capture Protocol
service is listening on. Leave open to use the default port (2002).
Null authentication Select this if you don’t need authentication to take place for a
remote capture to be started. This depends on the target platform.
Configuring the target platform like this makes it insecure.
Password authentication This is the normal way of connecting to a target platform. Set
the credentials needed to connect to the Remote Packet Capture
Protocol service.
4.9.2. Remote Capture Settings
The remote capture can be further fine tuned to match your situation. The Remote Settings button in
Figure 4.4, “The “Edit Interface Settings” dialog box” gives you this option. It pops up the dialog shown
in Figure 4.11, “The “Remote Capture Settings” dialog box”.
Figure 4.11. The “Remote Capture Settings” dialog box
You can set the following parameters in this dialog:
Do not capture own RPCAP traffic This option sets a capture filter so that the traffic flowing back
from the Remote Packet Capture Protocol service to Wireshark isn’t
captured as well and also send back. The recursion in this saturates
the link with duplicate traffic.
51
Page 62

Capturing Live Network Data
You only should switch this off when capturing on an interface
other than the interface connecting back to Wireshark.
Use UDP for data transfer Remote capture control and data flows over a TCP connection. This
option allows you to choose an UDP stream for data transfer.
Sampling option None This option instructs the Remote Packet Capture Protocol service
to send back all captured packets which have passed the capture
filter. This is usually not a problem on a remote capture session with
sufficient bandwidth.
Sampling option 1 of x packets This option limits the Remote Packet Capture Protocol service to
send only a sub sampling of the captured data, in terms of number
of packets. This allows capture over a narrow band remote capture
session of a higher bandwidth interface.
Sampling option 1 every x
milliseconds
This option limits the Remote Packet Capture Protocol service to
send only a sub sampling of the captured data in terms of time.
This allows capture over a narrow band capture session of a higher
bandwidth interface.
4.10. The “Interface Details” dialog box
When you select Details from the Capture Interface menu, Wireshark pops up the “Interface Details”
dialog box as shown in Figure 4.12, “The “Interface Details” dialog box”. This dialog shows various
characteristics and statistics for the selected interface.
Microsoft Windows only
This dialog is only available on Microsoft Windows
Figure 4.12. The “Interface Details” dialog box
4.11. Capture files and file modes
While capturing the underlying libpcap capturing engine will grab the packets from the network card and
keep the packet data in a (relatively) small kernel buffer. This data is read by Wireshark and saved into
the capture file(s) the user specified.
Different modes of operation are available when saving this packet data to the capture file(s).
Tip
Working with large files (several hundred MB) can be quite slow. If you plan to do a long
term capture or capturing from a high traffic network, think about using one of the “Multiple
files” options. This will spread the captured packets over several smaller files which can be
much more pleasant to work with.
Using Multiple files may cut context related information. Wireshark keeps context information of the
loaded packet data, so it can report context related problems (like a stream error) and keeps information
52
Page 63

Capturing Live Network Data
about context related protocols (e.g. where data is exchanged at the establishing phase and only referred to
in later packets). As it keeps this information only for the loaded file, using one of the multiple file modes
may cut these contexts. If the establishing phase is saved in one file and the things you would like to see
is in another, you might not see some of the valuable context related information.
Information about the folders used for capture files can be found in Appendix B, Files and Folders.
Table 4.1. Capture file mode selected by capture options
“File” option “Use multiple
files” option
- - - Single temporary
foo.cap - - Single named file foo.cap
foo.cap x - Multiple files,
foo.cap x x Multiple files, ring
Single temporary file A temporary file will be created and used (this is the default).
Single named file A single capture file will be used. If you want to place the new
Multiple files, continuous Like the “Single named file” mode, but a new file is created and
“Ring buffer with
n files” option
After capturing is stopped this file can be saved later under a user
specified name.
capture file in a specific folder choose this mode.
used after reaching one of the multiple file switch conditions (one
of the “Next file every …” values).
Mode Resulting
filename(s) used
wiresharkXXXXXX
file
continuous
buffer
(where XXXXXX
is a unique
number)
foo_00001_20100205110102.cap,
foo_00002_20100205110318.cap,
…
foo_00001_20100205110102.cap,
foo_00002_20100205110318.cap,
…
Multiple files, ring buffer Much like “Multiple files continuous”, reaching one of the multiple
files switch conditions (one of the “Next file every …” values) will
switch to the next file. This will be a newly created file if value of
“Ring buffer with n files” is not reached, otherwise it will replace
the oldest of the formerly used files (thus forming a “ring”).
This mode will limit the maximum disk usage, even for an unlimited
amount of capture input data, only keeping the latest captured data.
4.12. Link-layer header type
In most cases you won’t have to modify link-layer header type. Some exceaptions are as follows:
If you are capturing on an Ethernet device you might be offered a choice of “Ethernet” or “DOCSIS”. If
you are capturing traffic from a Cisco Cable Modem Termination System that is putting DOCSIS traffic
onto the Ethernet to be captured, select “DOCSIS”, otherwise select “Ethernet”.
If you are capturing on an 802.11 device on some versions of BSD you might be offered a choice of
“Ethernet” or “802.11”. “Ethernet” will cause the captured packets to have fake (“cooked”) Ethernet
53
Page 64

Capturing Live Network Data
headers. “802.11” will cause them to have full IEEE 802.11 headers. Unless the capture needs to be read
by an application that doesn’t support 802.11 headers you should select “802.11”.
If you are capturing on an Endace DAG card connected to a synchronous serial line you might be offered
a choice of “PPP over serial” or “Cisco HDLC”. If the protocol on the serial line is PPP, select “PPP over
serial” and if the protocol on the serial line is Cisco HDLC, select “Cisco HDLC”.
If you are capturing on an Endace DAG card connected to an ATM network you might be offered a choice
of “RFC 1483 IP-over-ATM” or “Sun raw ATM”. If the only traffic being captured is RFC 1483 LLCencapsulated IP, or if the capture needs to be read by an application that doesn’t support SunATM headers,
select “RFC 1483 IP-over-ATM”, otherwise select “Sun raw ATM”.
4.13. Filtering while capturing
Wireshark uses the libpcap filter language for capture filters. A brief overview of the syntax follows.
Complete documentation can be found in the pcap-filter man page. You can find a lot of Capture Filter
examples at https://wiki.wireshark.org/CaptureFilters.
You enter the capture filter into the “Filter” field of the Wireshark “Capture Options” dialog box, as shown
in Figure 4.3, “The “Capture Options” dialog box”.
A capture filter takes the form of a series of primitive expressions connected by conjunctions (and/or) and
optionally preceded by not:
[not] primitive [and|or [not] primitive ...]
An example is shown in Example 4.1, “A capture filter for telnet that captures traffic to and from a
particular host”.
Example 4.1. A capture filter for telnet that captures traffic to and from a particular
host
A capture filter for telnet that captures traffic to and from a particular host
tcp port 23 and host 10.0.0.5
This example captures telnet traffic to and from the host 10.0.0.5, and shows how to use two primitives
and the and conjunction. Another example is shown in Example 4.2, “Capturing all telnet traffic not from
10.0.0.5”, and shows how to capture all telnet traffic except that from 10.0.0.5.
Example 4.2. Capturing all telnet traffic not from 10.0.0.5
Capturing all telnet traffic not from 10.0.0.5
tcp port 23 and not src host 10.0.0.5
A primitive is simply one of the
following: [src|dst] host <host>
This primitive allows you to filter on a host IP address or name.
You can optionally precede the primitive with the keyword src|
dst to specify that you are only interested in source or destination
addresses. If these are not present, packets where the specified
address appears as either the source or the destination address will
be selected.
ether [src|dst] host <ehost> This primitive allows you to filter on Ethernet host addresses. You
can optionally include the keyword src|dst between the keywords
ether and host to specify that you are only interested in source or
54
Page 65

Capturing Live Network Data
destination addresses. If these are not present, packets where the
specified address appears in either the source or destination address
will be selected.
gateway host <host> This primitive allows you to filter on packets that used host as a
gateway. That is, where the Ethernet source or destination was host
but neither the source nor destination IP address was host.
[src|dst] net <net> [{mask
<mask>}|{len <len>}]
[tcp|udp] [src|dst] port <port> This primitive allows you to filter on TCP and UDP port numbers.
less|greater <length> This primitive allows you to filter on packets whose length was less
ip|ether proto <protocol> This primitive allows you to filter on the specified protocol at either
This primitive allows you to filter on network numbers. You
can optionally precede this primitive with the keyword src|dst
to specify that you are only interested in a source or destination
network. If neither of these are present, packets will be selected
that have the specified network in either the source or destination
address. In addition, you can specify either the netmask or the CIDR
prefix for the network if they are different from your own.
You can optionally precede this primitive with the keywords src|dst
and tcp|udp which allow you to specify that you are only interested
in source or destination ports and TCP or UDP packets respectively.
The keywords tcp|udp must appear before src|dst.
If these are not specified, packets will be selected for both the TCP
and UDP protocols and when the specified address appears in either
the source or destination port field.
than or equal to the specified length, or greater than or equal to the
specified length, respectively.
the Ethernet layer or the IP layer.
ether|ip broadcast|multicast This primitive allows you to filter on either Ethernet or IP
broadcasts or multicasts.
<expr> relop <expr> This primitive allows you to create complex filter expressions that
select bytes or ranges of bytes in packets. Please see the pcap-filter
man page at http://www.tcpdump.org/manpages/pcap-filter.7.html
for more details.
4.13.1. Automatic Remote Traffic Filtering
If Wireshark is running remotely (using e.g. SSH, an exported X11 window, a terminal server, …), the
remote content has to be transported over the network, adding a lot of (usually unimportant) packets to
the actually interesting traffic.
To avoid this, Wireshark tries to figure out if it’s remotely connected (by looking at some specific
environment variables) and automatically creates a capture filter that matches aspects of the connection.
The following environment variables are analyzed:
SSH_CONNECTION (ssh) <remote IP> <remote port> <local IP> <local port>
SSH_CLIENT (ssh) <remote IP> <remote port> <local port>
55
Page 66

Capturing Live Network Data
REMOTEHOST (tcsh, others?) <remote name>
DISPLAY (x11) [remote name]:<display num>
SESSIONNAME (terminal server) <remote name>
On Windows it asks the operating system if it’s running in a Remote Desktop Services environment.
4.14. While a Capture is running …
While a capture is running, the following dialog box is shown:
Figure 4.13. The “Capture Info” dialog box
This dialog box will inform you about the number of captured packets and the time since the capture was
started. The selection of which protocols are counted cannot be changed.
Tip
This “Capture Info” dialog box can be hidden using the “Hide capture info dialog” option
in the Capture Options dialog box.
4.14.1. Stop the running capture
A running capture session will be stopped in one of the following ways:
1. Using the button:[Stop[ button from the “Capture Info” dialog box.
Note
The “Capture Info” dialog box might be hidden if the “Hide capture info dialog” option is
used.
1.
Using the Capture → Stop menu item.
2. Using the Stop toolbar button.
3. Pressing Ctrl+E.
4. The capture will be automatically stopped if one of the Stop Conditions is met, e.g. the maximum
amount of data was captured.
4.14.2. Restart a running capture
A running capture session can be restarted with the same capture options as the last time, this will remove
all packets previously captured. This can be useful, if some uninteresting packets are captured and there’s
no need to keep them.
Restart is a convenience function and equivalent to a capture stop following by an immediate capture start.
A restart can be triggered in one of the following ways:
1.
Using the Capture → Restart menu item.
56
Page 67

Capturing Live Network Data
2. Using the Restart toolbar button.
57
Page 68

Chapter 5. File Input, Output, and Printing
5.1. Introduction
This chapter will describe input and output of capture data.
• Open capture files in various capture file formats
• Save/Export capture files in various capture file formats
• Merge capture files together
• Import text files containing hex dumps of packets
• Print packets
5.2. Open capture files
Wireshark can read in previously saved capture files. To read them, simply select the File → Open menu
or toolbar item. Wireshark will then pop up the “File Open” dialog box, which is discussed in more detail
in Section 5.2.1, “The “Open Capture File” dialog box”.
It’s convenient to use drag-and-drop
You can open a file by simply dragging it in your file manager and dropping it onto
Wireshark’s main window. However, drag-and-drop may not be available in all desktop
environments.
If you haven’t previously saved the current capture file you will be asked to do so to prevent data loss.
This warning can be disabled in the preferences.
In addition to its native file format (pcapng), Wireshark can read and write capture files from a large
number of other packet capture programs as well. See Section 5.2.2, “Input File Formats” for the list of
capture formats Wireshark understands.
5.2.1. The “Open Capture File” dialog box
The “Open Capture File” dialog box allows you to search for a capture file containing previously captured
packets for display in Wireshark. The following sections show some examples of the Wireshark “Open
File” dialog box. The appearance of this dialog depends on the system. However, the functionality should
be the same across systems.
Common dialog behaviour on all systems:
• Select files and directories.
• Click the Open or OK button to accept your selected file and open it.
• Click the Cancel button to go back to Wireshark and not load a capture file.
58
Page 69

File Input, Output, and Printing
Wireshark extensions to the standard behaviour of these dialogs:
• View file preview information such as the filesize and the number of packets in a selected a capture file.
• Specify a display filter with the Filter button and filter field. This filter will be used when opening the
new file. The text field background becomes green for a valid filter string and red for an invalid one.
Clicking on the Filter button causes Wireshark to pop up the “Filters” dialog box (which is discussed
further in Section 6.3, “Filtering packets while viewing”).
• Specify which type of name resolution is to be performed for all packets by clicking on one of the “…
name resolution” check buttons. Details about name resolution can be found in Section 7.7, “Name
Resolution”.
Save a lot of time loading huge capture files
You can change the display filter and name resolution settings later while viewing the
packets. However, loading huge capture files can take a significant amount of extra time if
these settings are changed later, so in such situations it can be a good idea to set at least the
filter in advance here.
Figure 5.1. “Open” on Microsoft Windows
This is the common Windows file open dialog - plus some Wireshark extensions.
Specific for this dialog:
• The Help button will lead you to this section of this “User’s Guide”.
Figure 5.2. “Open” - Linux and UNIX
This is the common Gimp/GNOME file open dialog plus some Wireshark extensions.
Specific for this dialog:
• The + button allows you to add a directory selected in the right-hand pane to the favorites list on the
left. These changes are persistent.
• The - button allows you to remove a selected directory from the list. Some items (such as “Desktop”)
cannot be removed from the favorites list.
• If Wireshark doesn’t recognize the selected file as a capture file it will grey out the Open button.
5.2.2. Input File Formats
The following file formats from other capture tools can be opened by Wireshark:
• pcapng. A flexible, etensible successor to the libpcap format. Wireshark 1.8 and later save files as pcapng
by default. Versions prior to 1.8 used libpcap.
• libpcap. The default format used by the libpcap packet capture library. Used by tcpdump, _Snort, Nmap,
Ntop, and many other tools.
59
Page 70

File Input, Output, and Printing
• Oracle (previously Sun) snoop and atmsnoop
• Finisar (previously Shomiti) Surveyor captures
• Microsoft Network Monitor captures
• Novell LANalyzer captures
• AIX iptrace captures
• Cinco Networks NetXray captures
• Network Associates Windows-based Sniffer and Sniffer Pro captures
• Network General/Network Associates DOS-based Sniffer (compressed or uncompressed) captures
• AG Group/WildPackets/Savvius EtherPeek/TokenPeek/AiroPeek/EtherHelp/PacketGrabber captures
• RADCOM’s WAN/LAN Analyzer captures
• Network Instruments Observer version 9 captures
• Lucent/Ascend router debug output
• HP-UX’s nettl
• Toshiba’s ISDN routers dump output
• ISDN4BSD i4btrace utility
• traces from the EyeSDN USB S0
• IPLog format from the Cisco Secure Intrusion Detection System
• pppd logs (pppdump format)
• the output from VMS’s TCPIPtrace/TCPtrace/UCX$TRACE utilities
• the text output from the DBS Etherwatch VMS utility
• Visual Networks' Visual UpTime traffic capture
• the output from CoSine L2 debug
• the output from Accellent’s 5Views LAN agents
• Endace Measurement Systems' ERF format captures
• Linux Bluez Bluetooth stack hcidump -w traces
• Catapult DCT2000 .out files
• Gammu generated text output from Nokia DCT3 phones in Netmonitor mode
• IBM Series (OS/400) Comm traces (ASCII & UNICODE)
• Juniper Netscreen snoop captures
60
Page 71

File Input, Output, and Printing
• Symbian OS btsnoop captures
• Tamosoft CommView captures
• Textronix K12xx 32bit .rf5 format captures
• Textronix K12 text file format captures
• Apple PacketLogger captures
• Captures from Aethra Telecommunications' PC108 software for their test instruments
New file formats are added from time to time.
It may not be possible to read some formats dependent on the packet types captured. Ethernet captures
are usually supported for most file formats but it may not be possible to read other packet types such as
PPP or IEEE 802.11 from all file formats.
5.3. Saving captured packets
You can save captured packets simply by using the File → Save As… menu item. You can choose which
packets to save and which file format to be used.
Not all information will be saved in a capture file. For example, most file formats don’t record the number
of dropped packets. See Section B.1, “Capture Files” for details.
5.3.1. The “Save Capture File As” dialog box
The “Save Capture File As” dialog box allows you to save the current capture to a file. The following
sections show some examples of this dialog box. The appearance of this dialog depends on the system.
However, the functionality should be the same across systems.
Figure 5.3. “Save” on Microsoft Windows
This is the common Windows file save dialog with some additional Wireshark extensions.
Specific behavior for this dialog:
• If available, the “Help” button will lead you to this section of this "User’s Guide".
• If you don’t provide a file extension to the filename (e.g. .pcap) Wireshark will append the standard
file extension for that file format.
Figure 5.4. “Save” on Linux and UNIX
This is the common Gimp/GNOME file save dialog with additional Wireshark extensions.
Specific for this dialog:
• Clicking on the + at "Browse for other folders" will allow you to browse files and folders in your file
system.
61
Page 72

File Input, Output, and Printing
With this dialog box, you can perform the following actions:
1. Type in the name of the file you wish to save the captured packets in, as a standard file name in your
file system.
2. Select the directory to save the file into.
3. Select the range of the packets to be saved. See Section 5.9, “The “Packet Range” frame”.
4. Specify the format of the saved capture file by clicking on the File type drop down box. You can choose
from the types described in Section 5.3.2, “Output File Formats”.
Some capture formats may not be available depending on the packet types captured.
Wireshark can convert file formats
You can convert capture files from one format to another by reading in a capture file and
writing it out using a different format.
1. Click the Save or OK button to accept your selected file and save to it. If Wireshark has a problem
saving the captured packets to the file you specified it will display an error dialog box. After clicking
OK on that error dialog box you can try again.
2. Click on the Cancel button to go back to Wireshark without saving any packets.
5.3.2. Output File Formats
Wireshark can save the packet data in its native file format (pcapng) and in the file formats of other protocol
analyzers so other tools can read the capture data.
Different file formats have different time stamp accuracies
Saving from the currently used file format to a different format may reduce the time stamp
accuracy; see the Section 7.4, “Time Stamps” for details.
The following file formats can be saved by Wireshark (with the known file extensions):
• pcapng (*.pcapng). A flexible, etensible successor to the libpcap format. Wireshark 1.8 and later save
files as pcapng by default. Versions prior to 1.8 used libpcap.
• libpcap, tcpdump and various other tools using tcpdump’s capture format (*.pcap,*.cap,*.dmp)
• Accellent 5Views (*.5vw)
• HP-UX’s nettl (*.TRC0,*.TRC1)
• Microsoft Network Monitor - NetMon (*.cap)
• Network Associates Sniffer - DOS (*.cap,*.enc,*.trc,*fdc,*.syc)
• Network Associates Sniffer - Windows (*.cap)
• Network Instruments Observer version 9 (*.bfr)
• Novell LANalyzer (*.tr1)
62
Page 73

File Input, Output, and Printing
• Oracle (previously Sun) snoop (*.snoop,*.cap)
• Visual Networks Visual UpTime traffic (*.*)
New file formats are added from time to time.
Whether or not the above tools will be more helpful than Wireshark is a different question ;-)
Third party protocol analyzers may require specific file
extensions
Wireshark examines a file’s contents to determine its type. Some other protocol analyzers
only look at a filename extensions. For example, you might need to use the .cap extension
in order to open a file using Sniffer.
5.4. Merging capture files
Sometimes you need to merge several capture files into one. For example, this can be useful if you have
captured simultaneously from multiple interfaces at once (e.g. using multiple instances of Wireshark).
There are three ways to merge capture files using Wireshark:
•
Use the File → Merge menu to open the “Merge” dialog. See Section 5.4.1, “The “Merge with Capture
File” dialog box”. This menu item will be disabled unless you have loaded a capture file.
• Use drag-and-drop to drop multiple files on the main window. Wireshark will try to merge the packets
in chronological order from the dropped files into a newly created temporary file. If you drop only a
single file it will simply replace the existing capture.
• Use the mergecap tool, a command line tool to merge capture files. This tool provides the most options
to merge capture files. See Section D.8, “mergecap: Merging multiple capture files into one” for details.
5.4.1. The “Merge with Capture File” dialog box
This dialog box let you select a file to be merged into the currently loaded file. If your current data has
not been saved you will be asked to save it first.
Most controls of this dialog will work the same way as described in the “Open Capture File” dialog box,
see Section 5.2.1, “The “Open Capture File” dialog box”.
Specific controls of this merge dialog are:
Prepend packets to existing file Prepend the packets from the selected file before the currently
loaded packets.
Merge packets chronologically Merge both the packets from the selected and currently loaded file
in chronological order.
Append packets to existing file Append the packets from the selected file after the currently loaded
packets.
Figure 5.5. “Merge” on Microsoft Windows
63
Page 74

File Input, Output, and Printing
This is the common Windows file open dialog with additional Wireshark extensions.
Figure 5.6. “Merge” on Linux and UNIX
This is the common Gimp/GNOME file open dialog with additional Wireshark extensions.
5.5. Import hex dump
Wireshark can read in an ASCII hex dump and write the data described into a temporary libpcap capture
file. It can read hex dumps with multiple packets in them, and build a capture file of multiple packets. It
is also capable of generating dummy Ethernet, IP and UDP, TCP, or SCTP headers, in order to build fully
processable packet dumps from hexdumps of application-level data only.
Wireshark understands a hexdump of the form generated by od -Ax -tx1 -v. In other words, each
byte is individually displayed and surrounded with a space. Each line begins with an offset describing the
position in the file. The offset is a hex number (can also be octal or decimal), of more than two hex digits.
Here is a sample dump that can be imported:
000000 00 e0 1e a7 05 6f 00 10 ........
000008 5a a0 b9 12 08 00 46 00 ........
000010 03 68 00 00 00 00 0a 2e ........
000018 ee 33 0f 19 08 7f 0f 19 ........
000020 03 80 94 04 00 00 10 01 ........
000028 16 a2 0a 00 03 50 00 0c ........
000030 01 01 0f 19 03 80 11 01 ........
There is no limit on the width or number of bytes per line. Also the text dump at the end of the line
is ignored. Byte and hex numbers can be uppercase or lowercase. Any text before the offset is ignored,
including email forwarding characters >. Any lines of text between the bytestring lines are ignored. The
offsets are used to track the bytes, so offsets must be correct. Any line which has only bytes without a
leading offset is ignored. An offset is recognized as being a hex number longer than two characters. Any
text after the bytes is ignored (e.g. the character dump). Any hex numbers in this text are also ignored.
An offset of zero is indicative of starting a new packet, so a single text file with a series of hexdumps
can be converted into a packet capture with multiple packets. Packets may be preceded by a timestamp.
These are interpreted according to the format given. If not the first packet is timestamped with the current
time the import takes place. Multiple packets are read in with timestamps differing by one microsecond
each. In general, short of these restrictions, Wireshark is pretty liberal about reading in hexdumps and has
been tested with a variety of mangled outputs (including being forwarded through email multiple times,
with limited line wrap etc.)
There are a couple of other special features to note. Any line where the first non-whitespace character is
# will be ignored as a comment. Any line beginning with #TEXT2PCAP is a directive and options can be
inserted after this command to be processed by Wireshark. Currently there are no directives implemented.
In the future these may be used to give more fine grained control on the dump and the way it should be
processed e.g. timestamps, encapsulation type etc. Wireshark also allows the user to read in dumps of
application-level data, by inserting dummy L2, L3 and L4 headers before each packet. The user can elect to
insert Ethernet headers, Ethernet and IP, or Ethernet, IP and UDP/TCP/SCTP headers before each packet.
This allows Wireshark or any other full-packet decoder to handle these dumps.
5.5.1. The “Import from Hex Dump” dialog box
This dialog box lets you select a text file, containing a hex dump of packet data, to be imported and set
import parameters.
64
Page 75

File Input, Output, and Printing
Figure 5.7. The “Import from Hex Dump” dialog
Specific controls of this import dialog are split in two sections:
Input Determine which input file has to be imported and how it is to be interpreted.
Import Determine how the data is to be imported.
The input parameters are as follows:
Filename / Browse Enter the name of the text file to import. You can use Browse to browse
for a file.
Offsets Select the radix of the offsets given in the text file to import. This is usually
hexadecimal, but decimal and octal are also supported.
Date/Time Tick this checkbox if there are timestamps associated with the frames in
the text file to import you would like to use. Otherwise the current time is
used for timestamping the frames.
Format This is the format specifier used to parse the timestamps in the text
file to import. It uses a simple syntax to describe the format of the
timestamps, using %H for hours, %M for minutes, %S for seconds, etc. The
straightforward HH:MM:SS format is covered by %T. For a full definition
of the syntax look for strptime(3).
The import parameters are as follows:
Encapsulation type Here you can select which type of frames you are importing. This all
Dummy header When Ethernet encapsulation is selected you have to option to prepend
Maximum frame length You may not be interested in the full frames from the text file, just
Once all input and import parameters are setup click OK to start the import. If your current data wasn’t
saved before you will be asked to save it first.
When completed there will be a new capture file loaded with the frames imported from the text file.
5.6. File Sets
depends on from what type of medium the dump to import was taken.
It lists all types that Wireshark understands, so as to pass the capture
file contents to the right dissector.
dummy headers to the frames to import. These headers can provide
artificial Ethernet, IP, UDP or TCP or SCTP headers and SCTP data
chunks. When selecting a type of dummy header the applicable entries
are enabled, others are grayed out and default values are used.
the first part. Here you can define how much data from the start of the
frame you want to import. If you leave this open the maximum is set
to 65535 bytes.
When using the "Multiple Files" option while doing a capture (see: Section 4.11, “Capture files and file
modes”), the capture data is spread over several capture files, called a file set.
65
Page 76

File Input, Output, and Printing
As it can become tedious to work with a file set by hand, Wireshark provides some features to handle
these file sets in a convenient way.
How does Wireshark detect the files of a file set?
A filename in a file set uses the format Prefix_Number_DateTimeSuffix which might look
something like test_00001_20060420183910.pcap. All files of a file set share the same
prefix (e.g. “test”) and suffix (e.g. “.pcap”) and a varying middle part.
To find the files of a file set, Wireshark scans the directory where the currently loaded file resides
and checks for files matching the filename pattern (prefix and suffix) of the currently loaded file.
This simple mechanism usually works well but has its drawbacks. If several file sets were captured
with the same prefix and suffix, Wireshark will detect them as a single file set. If files were renamed
or spread over several directories the mechanism will fail to find all files of a set.
The following features in the File → File Set submenu are available to work with file sets in a convenient
way:
• The “List Files” dialog box will list the files Wireshark has recognized as being part of the current file set.
• Next File closes the current and opens the next file in the file set.
• Previous File closes the current and opens the previous file in the file set.
5.6.1. The “List Files” dialog box
Figure 5.8. The "List Files" dialog box
Each line contains information about a file of the file set:
• Filename the name of the file. If you click on the filename (or the radio button left to it), the current file
will be closed and the corresponding capture file will be opened.
• Created the creation time of the file
• Last Modified the last time the file was modified
• Size the size of the file
The last line will contain info about the currently used directory where all of the files in the file set can
be found.
The content of this dialog box is updated each time a capture file is opened/closed.
The Close button will, well, close the dialog box.
5.7. Exporting data
Wireshark provides several ways and formats to export packet data. This section describes general ways to
export data from the main Wireshark application. There are more specialized functions to export specific
data which are described elsewhere.
66
Page 77

File Input, Output, and Printing
5.7.1. The “Export as Plain Text File” dialog box
Export packet data into a plain ASCII text file, much like the format used to print packets.
Tip
If you would like to be able to import any previously exported packets from a plain text file
it is recommended that you:
• Add the “Absolute date and time” column.
• Temporarily hide all other columns.
•
Disable the Edit → Preferences → Protocols → Data “Show not dissected data on new
Packet Bytes pane” preference. More details are provided in Section 10.5, “Preferences”
• Include the packet summary line.
• Exclude column headings.
• Exclude packet details.
• Include the packet bytes.
Figure 5.9. The “Export as Plain Text File” dialog box
• The “Export to file:” frame chooses the file to export the packet data to.
• The “Packet Range” frame is described in Section 5.9, “The “Packet Range” frame”.
• The “Packet Details” frame is described in Section 5.10, “The Packet Format frame”.
5.7.2. The “Export as PostScript File” dialog box
Figure 5.10. The "Export as PostScript File" dialog box
• Export to file: frame chooses the file to export the packet data to.
• The Packet Range frame is described in Section 5.9, “The “Packet Range” frame”.
• The Packet Details frame is described in Section 5.10, “The Packet Format frame”.
5.7.3. The "Export as CSV (Comma Separated Values) File" dialog box
Export packet summary into CSV, used e.g. by spreadsheet programs to im-/export data.
• Export to file: frame chooses the file to export the packet data to.
• The Packet Range frame is described in Section 5.9, “The “Packet Range” frame”.
67
Page 78

File Input, Output, and Printing
5.7.4. The "Export as C Arrays (packet bytes) file" dialog box
Export packet bytes into C arrays so you can import the stream data into your own C program.
• Export to file: frame chooses the file to export the packet data to.
• The Packet Range frame is described in Section 5.9, “The “Packet Range” frame”.
5.7.5. The "Export as PSML File" dialog box
Export packet data into PSML. This is an XML based format including only the packet summary. The
PSML file specification is available at: http://www.nbee.org/doku.php?id=netpdl:psml_specification.
Figure 5.11. The "Export as PSML File" dialog box
• Export to file: frame chooses the file to export the packet data to.
• The Packet Range frame is described in Section 5.9, “The “Packet Range” frame”.
There’s no such thing as a packet details frame for PSML export, as the packet format is defined by the
PSML specification.
5.7.6. The "Export as PDML File" dialog box
Export packet data into PDML. This is an XML based format including the packet details. The PDML file
specification is available at: http://www.nbee.org/doku.php?id=netpdl:pdml_specification.
Note
The PDML specification is not officially released and Wireshark’s implementation of it is
still in an early beta state, so please expect changes in future Wireshark versions.
Figure 5.12. The "Export as PDML File" dialog box
• Export to file: frame chooses the file to export the packet data to.
• The Packet Range frame is described in Section 5.9, “The “Packet Range” frame”.
There’s no such thing as a packet details frame for PDML export, as the packet format is defined by the
PDML specification.
5.7.7. The "Export selected packet bytes" dialog box
Export the bytes selected in the "Packet Bytes" pane into a raw binary file.
Figure 5.13. The "Export Selected Packet Bytes" dialog box
68
Page 79

File Input, Output, and Printing
• Name: the filename to export the packet data to.
• The Save in folder: field lets you select the folder to save to (from some predefined folders).
• Browse for other folders provides a flexible way to choose a folder.
5.7.8. The "Export Objects" dialog box
This feature scans through HTTP streams in the currently open capture file or running capture and
takes reassembled objects such as HTML documents, image files, executables and anything else that
can be transferred over HTTP and lets you save them to disk. If you have a capture running, this list is
automatically updated every few seconds with any new objects seen. The saved objects can then be opened
with the proper viewer or executed in the case of executables (if it is for the same platform you are running
Wireshark on) without any further work on your part. This feature is not available when using GTK2
versions below 2.4.
Figure 5.14. The "Export Objects" dialog box
• Packet num: The packet number in which this object was found. In some cases, there can be multiple
objects in the same packet.
• Hostname: The hostname of the server that sent the object as a response to an HTTP request.
• Content Type: The HTTP content type of this object.
• Bytes: The size of this object in bytes.
• Filename: The final part of the URI (after the last slash). This is typically a filename, but may be a
long complex looking string, which typically indicates that the file was received in response to a HTTP
POST request.
• Help: Opens this section in the user’s guide.
• Close: Closes this dialog.
• Save As: Saves the currently selected object as a filename you specify. The default filename to save as
is taken from the filename column of the objects list.
• Save All: Saves all objects in the list using the filename from the filename column. You will be asked
what directory / folder to save them in. If the filename is invalid for the operating system / file system
you are running Wireshark on, then an error will appear and that object will not be saved (but all of
the others will be).
5.8. Printing packets
To print packets, select the File → Print… menu item. When you do this Wireshark pops up the “Print”
dialog box as shown in Figure 5.15, “The “Print” dialog box”.
5.8.1. The “Print” dialog box
Figure 5.15. The “Print” dialog box
69
Page 80

File Input, Output, and Printing
The following fields are available
in the Print dialog box: Printer
This field contains a pair of mutually exclusive radio buttons:
• Plain Text specifies that the packet print should be in plain text.
• PostScript specifies that the packet print process should use
PostScript to generate a better print output on PostScript aware
printers.
• Output to file: specifies that printing be done to a file, using the
filename entered in the field or selected with the browse button.
This field is where you enter the file to print to if you have
selected Print to a file, or you can click the button to browse the
filesystem. It is greyed out if Print to a file is not selected.
• Print command specifies that a command be used for printing.
Note!
These Print command fields are not available on
windows platforms.
This field specifies the command to use for printing. It is typically
lpr. You would change it to specify a particular queue if you
need to print to a queue other than the default. An example might
be:
$ lpr -Pmypostscript
This field is greyed out if Output to file: is checked above.
Packet Range Select the packets to be printed, see Section 5.9, “The “Packet
Range” frame”
Packet Format Select the output format of the packets to be printed. You can
choose, how each packet is printed, see Figure 5.17, “The “Packet
Format” frame”
5.9. The “Packet Range” frame
The packet range frame is a part of various output related dialog boxes. It provides options to select which
packets should be processed by the output function.
Figure 5.16. The “Packet Range” frame
If the Captured button is set (default), all packets from the selected rule will be processed. If the Displayed
button is set, only the currently displayed packets are taken into account to the selected rule.
• All packets will process all packets.
• Selected packet only process only the selected packet.
• Marked packets only process only the marked packets.
• From first to last marked packet process the packets from the first to the last marked one.
70
Page 81

File Input, Output, and Printing
• Specify a packet range process a user specified range of packets, e.g. specifying 5,10-15,20- will process
the packet number five, the packets from packet number ten to fifteen (inclusive) and every packet from
number twenty to the end of the capture.
5.10. The Packet Format frame
The packet format frame is a part of various output related dialog boxes. It provides options to select which
parts of a packet should be used for the output function.
Figure 5.17. The “Packet Format” frame
• Packet summary line enable the output of the summary line, just as in the “Packet List” pane.
• Packet details enable the output of the packet details tree.
• All collapsed the info from the “Packet Details” pane in “all collapsed” state.
• As displayed the info from the “Packet Details” pane in the current state.
• All expanded the info from the “Packet Details” pane in “all expanded” state.
• Packet bytes enable the output of the packet bytes, just as in the “Packet Bytes” pane.
• Each packet on a new page put each packet on a separate page (e.g. when saving/printing to a text file,
this will put a form feed character between the packets).
71
Page 82

Chapter 6. Working with captured packets
6.1. Viewing packets you have captured
Once you have captured some packets or you have opened a previously saved capture file, you can view
the packets that are displayed in the packet list pane by simply clicking on a packet in the packet list pane,
which will bring up the selected packet in the tree view and byte view panes.
You can then expand any part of the tree to view detailed information about each protocol in each packet.
Clicking on an item in the tree will highlight the corresponding bytes in the byte view. An example with
a TCP packet selected is shown in Figure 6.1, “Wireshark with a TCP packet selected for viewing”. It
also has the Acknowledgment number in the TCP header selected, which shows up in the byte view as
the selected bytes.
Figure 6.1. Wireshark with a TCP packet selected for viewing
You can also select and view packets the same way while Wireshark is capturing if you selected “Update
list of packets in real time” in the “Capture Preferences” dialog box.
In addition you can view individual packets in a separate window as shown in Figure 6.2, “Viewing a
packet in a separate window”. You can do this by double-clicking on an item in the packet list or by
selecting the packet in which you are interested in the packet list pane and selecting View → Show Packet
in New Window. This allows you to easily compare two or more packets, even across multiple files.
Figure 6.2. Viewing a packet in a separate window
Along with double-clicking the packet list and using the main menu there are a number of other ways to
open a new packet window:
• Hold down the shift key and double-click on a frame link in the packet details.
• From Table 6.2, “The menu items of the “Packet List” pop-up menu”.
• From Table 6.3, “The menu items of the “Packet Details” pop-up menu”.
6.2. Pop-up menus
You can bring up a pop-up menu over either the “Packet List”, its column header, or “Packet Details” pane
by clicking your right mouse button at the corresponding pane.
6.2.1. Pop-up menu of the “Packet List” column header
Figure 6.3. Pop-up menu of the “Packet List” column header
The following table gives an overview of which functions are available in this header, where to find the
corresponding function in the main menu, and a short description of each item.
72
Page 83

Working with captured packets
Table 6.1. The menu items of the “Packet List” column header pop-up menu
Item Identical to main menu’s item: Description
Sort Ascending Sort the packet list in ascending
order based on this column.
Sort Descending Sort the packet list in descending
order based on this column.
No Sort Remove sorting order based on
this column.
Align Left Set left alignment of the values in
this column.
Align Center Set center alignment of the
values in this column.
Align Right Set right alignment of the values
in this column.
Column Preferences… Open the Preferences dialog box
on the column tab.
Resize Column Resize the column to fit the
values.
Rename Column Title Allows you to change the title of
the column header.
Displayed Column View This menu items folds out with
a list of all configured columns.
These columns can now be
shown or hidden in the packet
list.
Hide Column Allows you to hide the column
from the packet list.
Remove Column Allows you to remove the
column from the packet list.
6.2.2. Pop-up menu of the “Packet List” pane
Figure 6.4. Pop-up menu of the “Packet List” pane
The following table gives an overview of which functions are available in this pane, where to find the
corresponding function in the main menu, and a short description of each item.
Table 6.2. The menu items of the “Packet List” pop-up menu
Item Identical to main menu’s item: Description
Mark Packet (toggle) Edit Mark/unmark a packet.
Ignore Packet (toggle) Edit Ignore or inspect this packet
while dissecting the capture file.
Set Time Reference (toggle) Edit Set/reset a time reference.
73
Page 84

Working with captured packets
Item Identical to main menu’s item: Description
Manually Resolve Address Allows you to enter a name to
resolve for the selected address.
Apply as Filter Analyze Prepare and apply a display filter
based on the currently selected
item.
Prepare a Filter Analyze Prepare a display filter based on
the currently selected item.
Conversation Filter This menu item applies a
display filter with the address
information from the selected
packet. E.g. the IP menu entry
will set a filter to show the traffic
between the two IP addresses of
the current packet. XXX - add
a new section describing this
better.
Colorize Conversation This menu item uses a
display filter with the address
information from the selected
packet to build a new colorizing
rule.
SCTP Allows you to analyze and
prepare a filter for this SCTP
association.
Follow TCP Stream Analyze Allows you to view all the data
on a TCP stream between a pair
of nodes.
Follow UDP Stream Analyze Allows you to view all the data
on a UDP datagram stream
between a pair of nodes.
Follow SSL Stream Analyze Same as “Follow TCP Stream”
but for SSL. XXX - add a new
section describing this better.
Copy/ Summary (Text) Copy the summary fields as
displayed to the clipboard, as tabseparated text.
Copy/ Summary (CSV) Copy the summary fields as
displayed to the clipboard, as
comma-separated text.
Copy/ As Filter Prepare a display filter based on
the currently selected item and
copy that filter to the clipboard.
Copy/ Bytes (Offset Hex Text) Copy the packet bytes to the
clipboard in hexdump-like
format.
Copy/ Bytes (Offset Hex) Copy the packet bytes to the
clipboard in hexdump-like
74
Page 85

Working with captured packets
Item Identical to main menu’s item: Description
format, but without the text
portion.
Copy/ Bytes (Printable Text
Only)
Copy/ Bytes (Hex Stream) Copy the packet bytes to the
Copy/ Bytes (Binary Stream) Copy the packet bytes to the
Decode As… Analyze Change or apply a new relation
Print… File Print packets.
Show Packet in New Window View Display the selected packet in a
Copy the packet bytes to
the clipboard as ASCII text,
excluding non-printable
characters.
clipboard as an unpunctuated list
of hex digits.
clipboard as raw binary. The
data is stored in the clipboard as
MIME-type “application/octetstream”.
between two dissectors.
new window.
6.2.3. Pop-up menu of the “Packet Details” pane
Figure 6.5. Pop-up menu of the “Packet Details” pane
The following table gives an overview of which functions are available in this pane, where to find the
corresponding function in the main menu, and a short description of each item.
Table 6.3. The menu items of the “Packet Details” pop-up menu
Item Identical to main menu’s item: Description
Expand Subtrees View Expand the currently selected
subtree.
Collapse Subtrees View Collapse the currently selected
subtree.
Expand All View Expand all subtrees in all packets
in the capture.
Collapse All View Wireshark keeps a list of all
the protocol subtrees that are
expanded, and uses it to ensure
that the correct subtrees are
expanded when you display a
packet. This menu item collapses
the tree view of all packets in the
capture list.
Apply as Column Use the selected protocol item
to create a new column in the
packet list.
75
Page 86

Working with captured packets
Item Identical to main menu’s item: Description
Apply as Filter Analyze Prepare and apply a display filter
based on the currently selected
item.
Prepare a Filter Analyze Prepare a display filter based on
the currently selected item.
Colorize with Filter This menu item uses a display
filter with the information from
the selected protocol item to
build a new colorizing rule.
Follow TCP Stream Analyze Allows you to view all the data
on a TCP stream between a pair
of nodes.
Follow UDP Stream Analyze Allows you to view all the data
on a UDP datagram stream
between a pair of nodes.
Follow SSL Stream Analyze Same as “Follow TCP Stream”
but for SSL. XXX - add a new
section describing this better.
Copy/ Description Edit Copy the displayed text of the
selected field to the system
clipboard.
Copy/ Fieldname Edit Copy the name of the selected
field to the system clipboard.
Copy/ Value Edit Copy the value of the selected
field to the system clipboard.
Copy/ As Filter Edit Prepare a display filter based on
the currently selected item and
copy it to the clipboard.
Copy/ Bytes (Offset Hex Text) Copy the packet bytes to the
clipboard in hexdump-like
format; similar to the Packet List
Pane command, but copies only
the bytes relevant to the selected
part of the tree (the bytes selected
in the Packet Bytes Pane).
Copy/ Bytes (Offset Hex) Copy the packet bytes to the
clipboard in hexdump-like
format, but without the text
portion; similar to the Packet List
Pane command, but copies only
the bytes relevant to the selected
part of the tree (the bytes selected
in the Packet Bytes Pane).
Copy/ Bytes (Printable Text
Only)
Copy the packet bytes to
the clipboard as ASCII text,
excluding non-printable
characters; similar to the Packet
76
Page 87

Working with captured packets
Item Identical to main menu’s item: Description
List Pane command, but copies
only the bytes relevant to the
selected part of the tree (the bytes
selected in the Packet Bytes
Pane).
Copy/ Bytes (Hex Stream) Copy the packet bytes to the
clipboard as an unpunctuated
list of hex digits; similar to the
Packet List Pane command, but
copies only the bytes relevant to
the selected part of the tree (the
bytes selected in the Packet Bytes
Pane).
Copy/ Bytes (Binary Stream) Copy the packet bytes to
the clipboard as raw binary;
similar to the Packet List Pane
command, but copies only the
bytes relevant to the selected part
of the tree (the bytes selected
in the Packet Bytes Pane). The
data is stored in the clipboard as
MIME-type “application/octetstream”.
Export Selected Packet Bytes… File This menu item is the same as
the File menu item of the same
name. It allows you to export raw
packet bytes to a binary file.
Wiki Protocol Page Show the wiki page
corresponding to the currently
selected protocol in your web
browser.
Filter Field Reference Show the filter field reference
web page corresponding to the
currently selected protocol in
your web browser.
Protocol Preferences… The menu item takes you to the
properties dialog and selects
the page corresponding to the
protocol if there are properties
associated with the highlighted
field. More information on
preferences can be found in
Figure 10.7, “The preferences
dialog box”.
Decode As… Analyze Change or apply a new relation
between two dissectors.
Disable Protocol Allows you to temporarily
disable a protocol dissector,
77
Page 88

Working with captured packets
Item Identical to main menu’s item: Description
which may be blocking the
legitimate dissector.
Resolve Name View Causes a name resolution to
be performed for the selected
packet, but NOT every packet in
the capture.
Go to Corresponding Packet Go If the selected field has a
corresponding packet, go to
it. Corresponding packets will
usually be a request/response
packet pair or such.
6.3. Filtering packets while viewing
Wireshark has two filtering languages: One used when capturing packets, and one used when displaying
packets. In this section we explore that second type of filter: Display filters. The first one has already been
dealt with in Section 4.13, “Filtering while capturing”.
Display filters allow you to concentrate on the packets you are interested in while hiding the currently
uninteresting ones. They allow you to select packets by:
• Protocol
• The presence of a field
• The values of fields
• A comparison between fields
• … and a lot more!
To select packets based on protocol type, simply type the protocol in which you are interested in the Filter:
field in the filter toolbar of the Wireshark window and press enter to initiate the filter. Figure 6.6, “Filtering
on the TCP protocol” shows an example of what happens when you type tcp in the filter field.
Note
All protocol and field names are entered in lowercase. Also, don’t forget to press enter after
entering the filter expression.
Figure 6.6. Filtering on the TCP protocol
As you might have noticed, only packets of the TCP protocol are displayed now (e.g. packets 1-10 are
hidden). The packet numbering will remain as before, so the first packet shown is now packet number 11.
Note
When using a display filter, all packets remain in the capture file. The display filter only
changes the display of the capture file but not its content!
78
Page 89

Working with captured packets
You can filter on any protocol that Wireshark understands. You can also filter on any field that a dissector
adds to the tree view, but only if the dissector has added an abbreviation for the field. A list of such fields
is available in Wireshark in the Add Expression… dialog box. You can find more information on the Add
Expression… dialog box in Section 6.5, “The “Filter Expression” dialog box”.
For example, to narrow the packet list pane down to only those packets to or from the IP address
192.168.0.1, use ip.addr==192.168.0.1.
Note
To remove the filter, click on the Clear button to the right of the filter field.
6.4. Building display filter expressions
Wireshark provides a simple but powerful display filter language that allows you to build quite complex
filter expressions. You can compare values in packets as well as combine expressions into more specific
expressions. The following sections provide more information on doing this.
Tip
You will find a lot of Display Filter examples at the Wireshark Wiki Display Filter page at:
https://wiki.wireshark.org/DisplayFilters.
6.4.1. Display filter fields
Every field in the packet details pane can be used as a filter string, this will result in showing only the
packets where this field exists. For example: the filter string: tcp will show all packets containing the tcp
protocol.
There is a complete list of all filter fields available through the menu item Help → Supported Protocols in
the page “Display Filter Fields” of the “Supported Protocols” dialog.
6.4.2. Comparing values
You can build display filters that compare values using a number of different comparison operators. They
are shown in Table 6.4, “Display Filter comparison operators”.
Tip
You can use English and C-like terms in the same way, they can even be mixed in a filter
string.
Table 6.4. Display Filter comparison operators
English C-like Description and example
eq == Equal. ip.src==10.0.0.5
ne != Not equal. ip.src!
=10.0.0.5
gt > Greater than. frame.len >
10
79
Page 90

Working with captured packets
English C-like Description and example
lt < Less than. frame.len < 128
ge >= Greater than or equal to.
frame.len ge 0x100
le <= Less than or equal to.
frame.len <= 0x20
In addition, all protocol fields have a type. Table 6.5, “Display Filter Field Types” provides a list of the
types and example of how to express them.
Table 6.5. Display Filter Field Types
Type Example
Unsigned integer (8-bit, 16-bit, 24-bit, 32-bit) You can express integers in decimal, octal, or
hexadecimal. The following display filters are
equivalent: ---- ip.len le 1500 ip.len le 02734 ip.len
le 0x436 ---Signed integer (8-bit, 16-bit, 24-bit, 32-bit)
Boolean A boolean field is present in the protocol decode
only if its value is true. For example, tcp.flags.syn
is present, and thus true, only if the SYN flag is
present in a TCP segment header.
Ethernet address (6 bytes) Separators can be a colon (:), dot (.) or dash (-) and
IPv4 address ip.addr == 192.168.0.1
IPv6 address ipv6.addr == ::1
String (text) http.request.uri == "https://www.wireshark.org/"
6.4.3. Combining expressions
Thus the filter expression tcp.flags.syn will select
only those packets for which this flag exists,
that is, TCP segments where the segment header
contains the SYN flag. Similarly, to find source-
routed token ring packets, use a filter expression of
tr.sr.
can have one or two bytes between separators: ----
eth.dst == ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff eth.dst == ff-ff-ff-ff-ff-ff
eth.dst == ffff.ffff.ffff ----
Classless InterDomain Routing (CIDR) notation
can be used to test if an IPv4 address is in a certain
subnet. For example, this display filter will find all
packets in the 129.111 Class-B network:
ip.addr == 129.111.0.0/16
You can combine filter expressions in Wireshark using the logical operators shown in Table 6.6, “Display
Filter Logical Operations”
80
Page 91

Working with captured packets
Table 6.6. Display Filter Logical Operations
English C-like Description and example
and && Logical AND.
ip.src==10.0.0.5 and
tcp.flags.fin
or || Logical OR.
ip.scr==10.0.0.5 or
ip.src==192.1.1.1
xor ^^ Logical XOR. tr.dst[0:3]
== 0.6.29 xor
tr.src[0:3] == 0.6.29
not ! Logical NOT. not llc
[…] Substring Operator. Wireshark
allows you to select
subsequences of a sequence in
rather elaborate ways. After a
label you can place a pair of
brackets [] containing a comma
separated list of range specifiers.
---- eth.src[0:3] == 00:00:83 ---The example above uses the n:m
format to specify a single range.
In this case n is the beginning
offset and m is the length of
the range being specified. ---eth.src[1-2] == 00:83 ---- The
example above uses the n-m
format to specify a single range.
In this case n is the beginning
offset and m is the ending offset.
---- eth.src[:4] == 00:00:83:00
---- The example above uses
the :m format, which takes
everything from the beginning
of a sequence to offset m. It is
equivalent to 0:m ---- eth.src[4:]
== 20:20 ---- The example
above uses the n: format, which
takes everything from offset
n to the end of the sequence.
---- eth.src[2] == 83 ---- The
example above uses the n format
to specify a single range. In
this case the element in the
sequence at offset n is selected.
This is equivalent to n:1. ---eth.src[0:3,1-2,:4,4:,2] ==
00:00:83:00:83:00:00:83:00:20:20:83
---- Wireshark allows you to
string together single ranges in
a comma separated list to form
81
Page 92

Working with captured packets
English C-like Description and example
6.4.4. Membership Operator.
Wireshark allows you to test a field for membership in a set of values or fields. After the field name, use
the in operator followed by the set items surrounded by braces {}.
tcp.port in {80 443 8080}
This can be considered a shortcut operator, as the previous expression could have been expressed as:
tcp.port == 80 || tcp.port == 443 || tcp.port == 8080
6.4.5. A common mistake
Using the != operator on combined expressions like eth.addr, ip.addr, tcp.port, and udp.port will probably
not work as expected.
Often people use a filter string to display something like ip.addr == 1.2.3.4 which will display
all packets containing the IP address 1.2.3.4.
compound ranges as shown
above.
Then they use ip.addr != 1.2.3.4 to see all packets not containing the IP address 1.2.3.4 in it.
Unfortunately, this does not do the expected.
Instead, that expression will even be true for packets where either source or destination IP address equals
1.2.3.4. The reason for this, is that the expression ip.addr != 1.2.3.4 must be read as “the packet
contains a field named ip.addr with a value different from 1.2.3.4”. As an IP datagram contains both a
source and a destination address, the expression will evaluate to true whenever at least one of the two
addresses differs from 1.2.3.4.
If you want to filter out all packets containing IP datagrams to or from IP address 1.2.3.4, then the correct
filter is !(ip.addr == 1.2.3.4) as it reads “show me all the packets for which it is not true that
a field named ip.addr exists with a value of 1.2.3.4”, or in other words, “filter out all packets for which
there are no occurrences of a field named ip.addr with the value 1.2.3.4”.
6.5. The “Filter Expression” dialog box
When you are accustomed to Wireshark’s filtering system and know what labels you wish to use in your
filters it can be very quick to simply type a filter string. However if you are new to Wireshark or are
working with a slightly unfamiliar protocol it can be very confusing to try to figure out what to type. The
“Filter Expression” dialog box helps with this.
Tip
The “Filter Expression” dialog box is an excellent way to learn how to write Wireshark
display filter strings.
Figure 6.7. The “Filter Expression” dialog box
When you first bring up the Filter Expression dialog box you are shown a tree of field names, organized
by protocol, and a box for selecting a relation.
82
Page 93

Working with captured packets
Field Name Select a protocol field from the protocol field tree. Every protocol with filterable fields
is listed at the top level. (You can search for a particular protocol entry by entering
the first few letters of the protocol name). By expanding a protocol name you can get
a list of the field names available for filtering for that protocol.
Relation Select a relation from the list of available relation. The is present is a unary relation
which is true if the selected field is present in a packet. All other listed relations are
binary relations which require additional data (e.g. a Value to match) to complete.
When you select a field from the field name list and select a binary relation (such as the equality relation
==) you will be given the opportunity to enter a value, and possibly some range information.
Value You may enter an appropriate value in the Value text box. The Value will
also indicate the type of value for the field name you have selected (like
character string).
Predefined values Some of the protocol fields have predefined values available, much like
enum’s in C. If the selected protocol field has such values defined, you can
choose one of them here.
Range A range of integers or a group of ranges, such as 1-12 or
39-42,98-2000.
OK When you have built a satisfactory expression click OK and a filter string
will be built for you.
Cancel You can leave the “Add Expression…” dialog box without any effect by
clicking the Cancel button.
6.6. Defining and saving filters
You can define filters with Wireshark and give them labels for later use. This can save time in remembering
and retyping some of the more complex filters you use.
To define a new filter or edit an existing one, select Capture → Capture Filters… or Analyze → Display
Filters…. Wireshark will then pop up the Filters dialog as shown in Figure 6.8, “The “Capture Filters”
and “Display Filters” dialog boxes”.
The mechanisms for defining and saving capture filters and display filters are almost identical. Both will
be described here but the differences between these two will be marked as such.
Warning
You must use Save to save your filters permanently. OK or Apply will not save the filters
and they will be lost when you close Wireshark.
Figure 6.8. The “Capture Filters” and “Display Filters” dialog boxes
New This button adds a new filter to the list of filters. The currently entered values
from Filter name and Filter string will be used. If any of these fields are empty,
it will be set to “new”.
Delete This button deletes the selected filter. It will be greyed out, if no filter is
selected.
83
Page 94

Working with captured packets
Filter You can select a filter from this list (which will fill in the filter name and filter
string in the fields down at the bottom of the dialog box).
Filter name: You can change the name of the currently selected filter here.
The filter name will only be used in this dialog to identify the filter for your
convenience, it will not be used elsewhere. You can add multiple filters with
the same name, but this is not very useful.
Filter string: You can change the filter string of the currently selected filter here. Display
Filter only: the string will be syntax checked while you are typing.
Add Expression… Display Filter only: This button brings up the Add Expression dialog box
which assists in building filter strings. You can find more information about
the Add Expression dialog in Section 6.5, “The “Filter Expression” dialog
box”
OK Display Filter only: This button applies the selected filter to the current display
and closes the dialog.
Apply Display Filter only: This button applies the selected filter to the current
display, and keeps the dialog open.
Save Save the current settings in this dialog. The file location and format is
explained in Appendix B, Files and Folders.
Close Close this dialog. This will discard unsaved settings.
6.7. Defining and saving filter macros
You can define filter macros with Wireshark and give them labels for later use. This can save time in
remembering and retyping some of the more complex filters you use.
6.8. Finding packets
You can easily find packets once you have captured some packets or have read in a previously saved
capture file. Simply select the Find Packet… menu item from the Edit menu. Wireshark will pop up the
dialog box shown in Figure 6.9, “The “Find Packet” dialog box”.
6.8.1. The “Find Packet” dialog box
Figure 6.9. The “Find Packet” dialog box
You might first select the kind of thing to search for:
• Display filter
Simply enter a display filter string into the Filter: field, select a direction, and click on OK.
For example, to find the three way handshake for a connection from host 192.168.0.1, use the following
filter string:
ip.src==192.168.0.1 and tcp.flags.syn==1
84
Page 95

Working with captured packets
For more details on display filters, see Section 6.3, “Filtering packets while viewing”
• Hex Value
Search for a specific byte sequence in the packet data.
For example, use “00:00” to find the next packet including two null bytes in the packet data.
• String
Find a string in the packet data, with various options.
The value to be found will be syntax checked while you type it in. If the syntax check of your value
succeeds, the background of the entry field will turn green, if it fails, it will turn red.
You can choose the search direction:
• Up
Search upwards in the packet list (decreasing packet numbers).
• Down
Search downwards in the packet list (increasing packet numbers).
6.8.2. The “Find Next” command
“Find Next” will continue searching with the same options used in the last “Find Packet”.
6.8.3. The “Find Previous” command
“Find Previous” will do the same thing as “Find Next”, but in the reverse direction.
6.9. Go to a specific packet
You can easily jump to specific packets with one of the menu items in the Go menu.
6.9.1. The “Go Back” command
Go back in the packet history, works much like the page history in current web browsers.
6.9.2. The “Go Forward” command
Go forward in the packet history, works much like the page history in current web browsers.
6.9.3. The “Go to Packet” dialog box
Figure 6.10. The “Go To Packet” dialog box
This dialog box will let you enter a packet number. When you press OK, Wireshark will jump to that packet.
85
Page 96

Working with captured packets
6.9.4. The “Go to Corresponding Packet” command
If a protocol field is selected which points to another packet in the capture file, this command will jump
to that packet.
As these protocol fields now work like links (just as in your Web browser), it’s easier to simply doubleclick on the field to jump to the corresponding field.
6.9.5. The “Go to First Packet” command
This command will simply jump to the first packet displayed.
6.9.6. The “Go to Last Packet” command
This command will simply jump to the last packet displayed.
6.10. Marking packets
You can mark packets in the “Packet List” pane. A marked packet will be shown with black background,
regardless of the coloring rules set. Marking a packet can be useful to find it later while analyzing in a
large capture file.
The packet marks are not stored in the capture file or anywhere else. All packet marks will be lost when
you close the capture file.
You can use packet marking to control the output of packets when saving, exporting, or printing. To do
so, an option in the packet range is available, see Section 5.9, “The “Packet Range” frame”.
There are three functions to manipulate the marked state of a packet:
• Mark packet (toggle) toggles the marked state of a single packet.
• Mark all displayed packets set the mark state of all displayed packets.
• Unmark all packets reset the mark state of all packets.
These mark functions are available from the “Edit” menu, and the “Mark packet (toggle)” function is also
available from the pop-up menu of the “Packet List” pane.
6.11. Ignoring packets
You can ignore packets in the “Packet List” pane. Wireshark will then pretend that this packets does not
exist in the capture file. An ignored packet will be shown with white background and gray foreground,
regardless of the coloring rules set.
The packet ignored marks are not stored in the capture file or anywhere else. All “packet ignored” marks
will be lost when you close the capture file.
There are three functions to manipulate the ignored state of a packet:
• Ignore packet (toggle) toggles the ignored state of a single packet.
• Ignore all displayed packets set the ignored state of all displayed packets.
86
Page 97

Working with captured packets
• Un-Ignore all packets reset the ignored state of all packets.
These ignore functions are available from the “Edit” menu, and the “Ignore packet (toggle)” function is
also available from the pop-up menu of the “Packet List” pane.
6.12. Time display formats and time references
While packets are captured, each packet is timestamped. These timestamps will be saved to the capture
file, so they will be available for later analysis.
A detailed description of timestamps, timezones and alike can be found at: Section 7.4, “Time Stamps”.
The timestamp presentation format and the precision in the packet list can be chosen using the View menu,
see Figure 3.5, “The “View” Menu”.
The available presentation formats are:
• Date and Time of Day: 1970-01-01 01:02:03.123456 The absolute date and time of the day when the
packet was captured.
• Time of Day: 01:02:03.123456 The absolute time of the day when the packet was captured.
• Seconds Since Beginning of Capture: 123.123456 The time relative to the start of the capture file or the
first “Time Reference” before this packet (see Section 6.12.1, “Packet time referencing”).
• Seconds Since Previous Captured Packet: 1.123456 The time relative to the previous captured packet.
• Seconds Since Previous Displayed Packet: 1.123456 The time relative to the previous displayed packet.
• Seconds Since Epoch (1970-01-01): 1234567890.123456 The time relative to epoch (midnight UTC of
January 1, 1970).
The available precisions (aka. the number of displayed decimal places) are:
• Automatic The timestamp precision of the loaded capture file format will be used (the default).
• Seconds, Deciseconds, Centiseconds, Milliseconds, Microseconds or Nanoseconds The timestamp
precision will be forced to the given setting. If the actually available precision is smaller, zeros will be
appended. If the precision is larger, the remaining decimal places will be cut off.
Precision example: If you have a timestamp and it’s displayed using, “Seconds Since Previous Packet”, :
the value might be 1.123456. This will be displayed using the “Automatic” setting for libpcap files (which
is microseconds). If you use Seconds it would show simply 1 and if you use Nanoseconds it shows
1.123456000.
6.12.1. Packet time referencing
The user can set time references to packets. A time reference is the starting point for all subsequent packet
time calculations. It will be useful, if you want to see the time values relative to a special packet, e.g. the
start of a new request. It’s possible to set multiple time references in the capture file.
The time references will not be saved permanently and will be lost when you close the capture file.
Time referencing will only be useful if the time display format is set to “Seconds Since Beginning of
Capture”. If one of the other time display formats are used, time referencing will have no effect (and will
make no sense either).
87
Page 98

Working with captured packets
To work with time references, choose one of the Time Reference items in the Edit menu or from the popup menu of the “Packet List” pane. See Section 3.6, “The “Edit” menu”.
• Set Time Reference (toggle) Toggles the time reference state of the currently selected packet to on or off.
• Find Next Find the next time referenced packet in the “Packet List” pane.
• Find Previous Find the previous time referenced packet in the “Packet List” pane.
Figure 6.11. Wireshark showing a time referenced packet
A time referenced packet will be marked with the string *REF* in the Time column (see packet number
10). All subsequent packets will show the time since the last time reference.
88
Page 99

Chapter 7. Advanced Topics
7.1. Introduction
This chapter some of Wireshark’s advanced features.
7.2. Following TCP streams
If you are working with TCP based protocols it can be very helpful to see the data from a TCP stream in
the way that the application layer sees it. Perhaps you are looking for passwords in a Telnet stream, or you
are trying to make sense of a data stream. Maybe you just need a display filter to show only the packets of
that TCP stream. If so, Wireshark’s ability to follow a TCP stream will be useful to you.
Simply select a TCP packet in the packet list of the stream/connection you are interested in and then select
the Follow TCP Stream menu item from the Wireshark Tools menu (or use the context menu in the packet
list). Wireshark will set an appropriate display filter and pop up a dialog box with all the data from the
TCP stream laid out in order, as shown in Figure 7.1, “The “Follow TCP Stream” dialog box”.
Note
Opening the “Follow TCP Stream” installs a display filter to select all the packets in the TCP
stream you have selected.
7.2.1. The “Follow TCP Stream” dialog box
Figure 7.1. The “Follow TCP Stream” dialog box
The stream content is displayed in the same sequence as it appeared on the network. Traffic from A to B
is marked in red, while traffic from B to A is marked in blue. If you like, you can change these colors in
the “Colors” page if the “Preferences” dialog.
Non-printable characters will be replaced by dots.
The stream content won’t be updated while doing a live capture. To get the latest content you’ll have to
reopen the dialog.
You can choose from the following actions:
1. Save As: Save the stream data in the currently selected format.
2. Print: Print the stream data in the currently selected format.
3. Direction: Choose the stream direction to be displayed (“Entire conversation”, “data from A to B only”
or “data from B to A only”).
4. Filter out this stream: Apply a display filter removing the current TCP stream data from the display.
5. Close: Close this dialog box, leaving the current display filter in effect.
You can choose to view the data in one of the following formats:
89
Page 100

Advanced Topics
1. ASCII: In this view you see the data from each direction in ASCII. Obviously best for ASCII based
protocols, e.g. HTTP.
2. EBCDIC: For the big-iron freaks out there.
3. HEX Dump: This allows you to see all the data. This will require a lot of screen space and is best used
with binary protocols.
4. C Arrays: This allows you to import the stream data into your own C program.
5. Raw: This allows you to load the unaltered stream data into a different program for further examination.
The display will look the same as the ASCII setting, but “Save As” will result in a binary file.
7.3. Expert Information
The expert infos is a kind of log of the anomalies found by Wireshark in a capture file.
The general idea behind the following “Expert Info” is to have a better display of “uncommon” or just
notable network behaviour. This way, both novice and expert users will hopefully find probable network
problems a lot faster, compared to scanning the packet list “manually” .
Expert infos are only a hint
Take expert infos as a hint what’s worth looking at, but not more. For example, the absence
of expert infos doesn’t necessarily mean everything is OK.
The amount of expert infos largely depends on the protocol being used. While some common protocols like
TCP/IP will show detailed expert infos, most other protocols currently won’t show any expert infos at all.
The following will first describe the components of a single expert info, then the User Interface.
7.3.1. Expert Info Entries
Each expert info will contain the following things which will be described in detail below.
Table 7.1. Some example expert infos
Packet # Severity Group Protocol Summary
1 Note Sequence TCP Duplicate ACK
2 Chat Sequence TCP Connection reset
8 Note Sequence TCP Keep-Alive
9 Warn Sequence TCP Fast retransmission
(#1)
(RST)
(suspected)
7.3.1.1. Severity
Every expert info has a specific severity level. The following severity levels are used, in parentheses are
the colors in which the items will be marked in the GUI:
• Chat (grey): information about usual workflow, e.g. a TCP packet with the SYN flag set
90
 Loading...
Loading...