Page 1

ACCESS POINT
User Guide
Access Point
i
Page 2

ACCESS POINT
Table of Contents
1. INTRODUCTION ................................................................................ 1
1.1 P
RODUCT FEATURES .............................................................................................1
1.2 N
ETWORK OVERVIEW ...........................................................................................2
1.2.1 Infrastructure Mode ......................................................................................2
1.2.2 Microcells and Roaming...............................................................................3
ETWORK SERVICE SET IDENTIFICATION (SSID) OVERVIEW................................4
1.3 N
1.4 C
HANNEL SERVICES OVERVIEW ............................................................................5
1.5 R
EQUIREMENT FOR A WIRELESS CONNECTION.......................................................5
2. INSTALLATION AP ............................................................................ 6
2.1 P
ACKAGE CONTENTS .............................................................................................6
2.2 N
OTICE .................................................................................................................6
2.3 I
NSTALLATION DIAGRAM ......................................................................................6
2.4 P
HYSICAL DESCRIPTION........................................................................................7
2.5 C
ONNECTING TO THE NETWORK ...........................................................................7
2.6 AP C
2.7 D
ONFIGURATION (INSTALL THE SNMP MANAGER) ........................................7
EFAULT SETTING.................................................................................................8
3. SPECIFICATION ................................................................................. 9
3.1 H
ARDWARE SPECIFICATION...................................................................................9
3.2 IEEE 802.11 F
UNCTIONALITY SUPPORT.............................................................10
4. CONFIGURATION AP...................................................................... 11
4.1 S
ETTING UP ACCESS POINTS IP ADDRESS...........................................................11
5. INSTALLING SNMP MANAGER.................................................... 13
5.0.1 U
5.1 F
5.2 S
SING SNMP APPLICATION ............................................................................14
ILE MENU..........................................................................................................15
5.1.1 Connection to Access Point ........................................................................16
5.1.2 Find Access Point .......................................................................................17
ETUP MENU.......................................................................................................19
5.2.1 Bridge..........................................................................................................20
5.2.2 IP Configuration.........................................................................................21
ii
Page 3

ACCESS POINT
5.2.3 Wireless LAN...............................................................................................22
5.2.4 Privacy Options ..........................................................................................23
5.2.5 Operational Settings ...................................................................................24
5.2.6 Advance Operational Setting......................................................................26
5.2.7 Authorized MAC addresses .........................................................................29
5.2.8 SNMP Traps ................................................................................................30
5.2.9 Authorization ..............................................................................................31
5.3 C
OMMANDS MENU .............................................................................................32
5.4 I
NFORMATION MENU...........................................................................................33
5.4.1 Wireless Statistics........................................................................................34
5.4.2Ethernet Statistics ........................................................................................35
RAP MENU ........................................................................................................36
5.5 T
5.6 N
ETWORK MENU ................................................................................................38
5.7 W
INDOW MENU ..................................................................................................40
5.8 H
ELP MENU ........................................................................................................41
6. TUTORIAL ........................................................................................ 42
6.1 P
ACKET FRAGMENTATION ...................................................................................42
6.2 E
NCRYPTION .......................................................................................................43
Authentication Type .............................................................................................44
How is encryption key generated?.......................................................................44
UBNETTING .......................................................................................................45
6.3 S
7. TROUBLESHOOTING...................................................................... 46
7.1 C
HECKING VALID IP ADDRESSES........................................................................49
7.2 C
ONNECTION TROUBLESHOOTING ......................................................................50
7.3 R
ESETTING THE ACCESS POINT ...........................................................................51
7.4 E
NCRYPTION TROUBLESHOOTING .......................................................................52
7.5 T
ROUBLESHOOTING CHECK TABLE .....................................................................53
8. FAQ..................................................................................................... 54
9. WLAN GLOSSARY........................................................................... 56
FEDERAL COMMUNICATIONS COMMISSION INTERFERENCE STATEMENT......... 60
iii
Page 4

ACCESS POINT
Copyright © 2002 Manufacturer all rights reserved.
The information in this document is subject to change without notice. The statements,
configurations, technical data, and recommendations in this document are believed to be
accurate and reliable, but are presented without express or implied warranty. Users must
take full responsibility for their applications of any products specified in this document.
The information in this document is proprietary to Manufacturer.
Manufacturer reserves the right to make revisions to this publication without obligation to
notify any person or entity of any such changes.
Trademarks
Microsoft, Windows 98, Windows ME, Windows 2000, Windows XP are trademarks or
registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
Atmel and Atmel logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Atmel Corporation.
All other trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owner
iv
Page 5

ACCESS POINT
1. Introduction
This user guide provides an overview of the Wireless LAN Technology and
instruction for using the Access Point. Actually, Wireless LAN is a flexible data
communication system implemented as an extension to, or as an alternative for, a
wired LAN within a building or campus. Using electromagnetic waves, WLANs
transmit and receive data over the air, minimizing the need for wired connections.
Overall, we hope this document is helpful to give users a Clear View on the Access
Point and a better understanding of WLAN Technology.
1.1 Product Features
Flexible and standards-based (IEEE802.11b) interoperability.
64/128bits WEP key encryption for security.
MAC address registration function for security.
Communication between the Ethernet LAN and the wireless LAN.
AppleTalk protocol compatible.
Automatic Rate Fallback.
Association, Re-association and Disassociation.
Support three Operational Modes (Access Point, AP Client, Wireless Bridge).
Support Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP).
DHCP Client-Default Gateway.
IP Filtering.
1
Page 6
ACCESS POINT
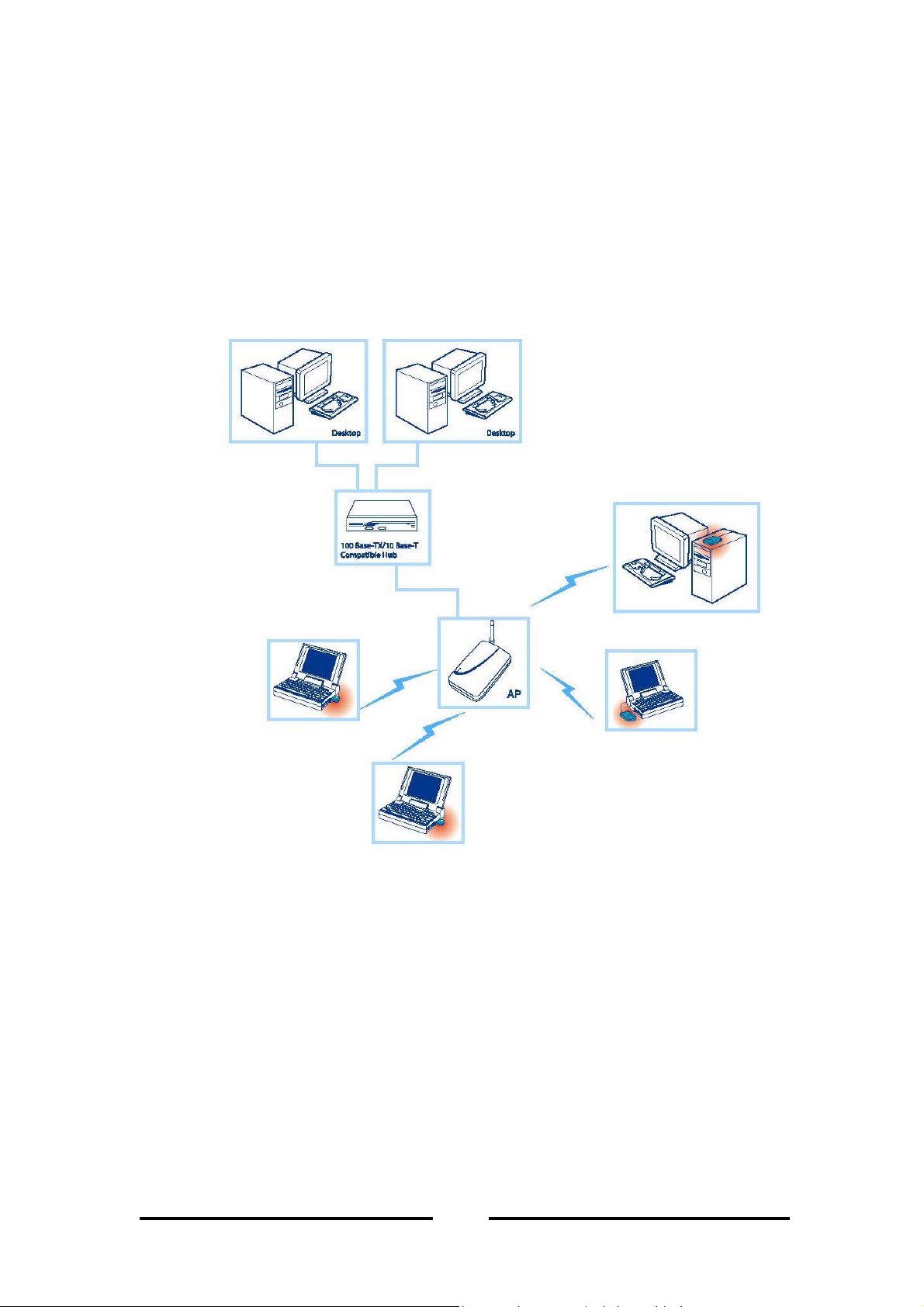
1.2 Network Overview
1.2.1 Infrastructure Mode
In an infrastructure network, the wireless device (such as Access Point) links the
WLAN to the wired network to offer users more mobilities in movement and
resources sharing within the network service area. It enables users to have freedom
from network cabling.
Figure 1 - Infrastructure mode
2
Page 7
ACCESS POINT
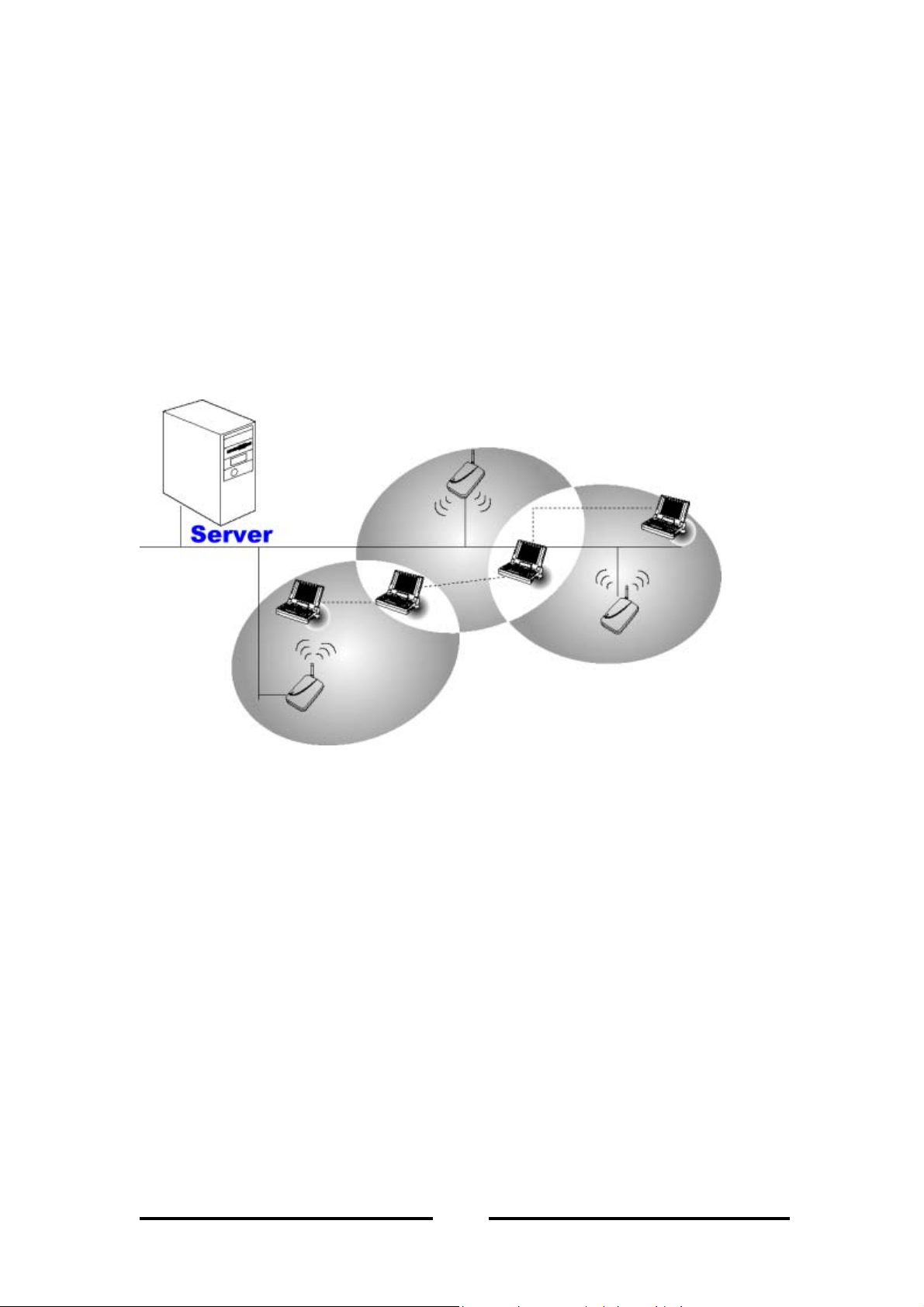
1.2.2 Microcells and Roaming
WLANs use cells, called microcells, similar to the cellular telephone system to extend
the range of wireless connectivity. At any point in time, a mobile PC equipped with a
WLAN adapter is associated with a single access point and its microcell, or area of
coverage. Individual microcells overlap to allow continuous communication within
wired network. They handle low-power signals and allow users to roam through a
given geographic area.
Figure 2 - Handling of WLAN connection between APs
3
Page 8
ACCESS POINT
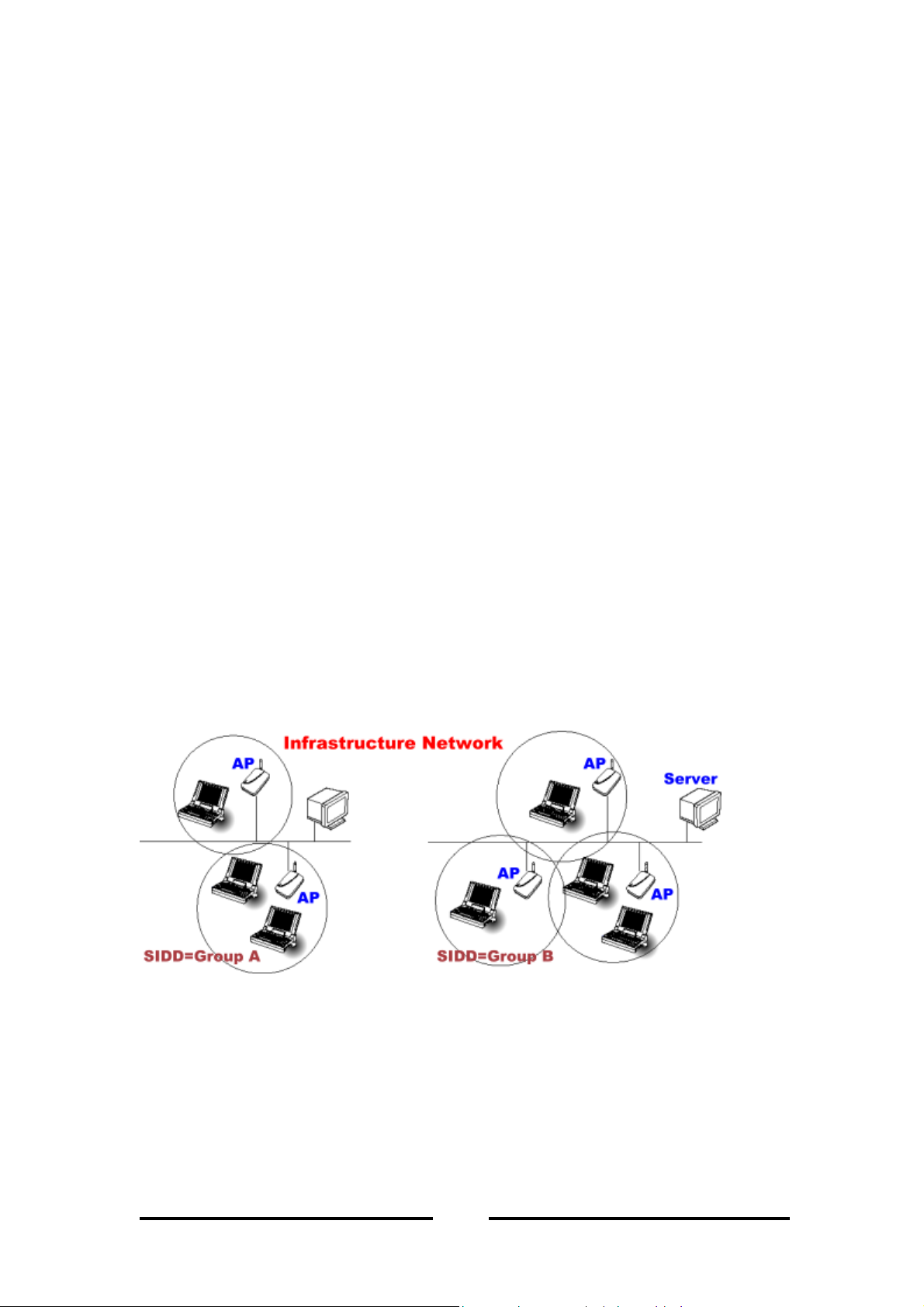
1.3 Network Service Set Identification (SSID) Overview
On a wireless network, a mobile user can roam freely within the service area of the
Access Point with the same service Set Identification SSIDs without losing
connection to the wired network. In order for a mobile unit to roam seamlessly from
one Access Point to another, the SSIDs of all Access Points and the wireless LAN
cards must be the same.
Assigning SSIDs, can provide the following security:
To avoid different user-groups from accessing network resources other than their
own.
Ensure each user-group has access within its own network.
Assure different user-group has the same access to Ethernet segment.
Figure 3 illustrates the use off SSIDs in an environment containing multiple
infrastructure network configured to communicate in the same Ethernet segment.
SSIDs assure the 3 users of Group A can only access each other, but not other
infrastructure, such as Group B.
Figure 3 – SSID Assignments
4
Page 9

ACCESS POINT
1.4 Channel Services Overview
The Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS) modulation has the effect of
suppressing radio frequency interference in the same frequency bands.
The IEEE 802.11b DSSS service is a channelized service, listed as Table 1.
Table 1 - Channel Usage by Country
Country Channels Used by the Access Point
United States 1 through 11
Canada 1 through 11
Europe 1 through 13
France 10 through 13
Spain 10 through 11
Japan 14
1.5 Requirement for a wireless connection
To install an Access Point, the hardware requirements are:
A supported LAN protocol stack (IPX/SPX or TCP/IP or AppleTalk)
For a 100 Base-TX / 10 Base-T Ethernet connection, a modular data cable with a
dual twisted pair cable terminated with a male RJ-45 modular jack
5
Page 10
ACCESS POINT
2. Installation AP
2.1 Package contents
Before using the Access point, please make sure that all the items listed below are
present in your package.
Wireless Access Point
5V DC power adapter
Installation CD
Quick Installation Guide
If any items are missing or damaged, please contact your dealer immediately.
2.2 Notice
1. Keep the Number of Wall and ceilings to a minimum. Each of Wall or Ceiling will
reduce 20-30% transmission range.
2. Make sure having the direct line among the Client WLAN card.
3. Keep your product away from electronic devices
4. Make sure that the antenna is positioned for best reception
5. Building Material make a difference. Normally a solid metal door or aluminum
studs may have a negative effect on range.
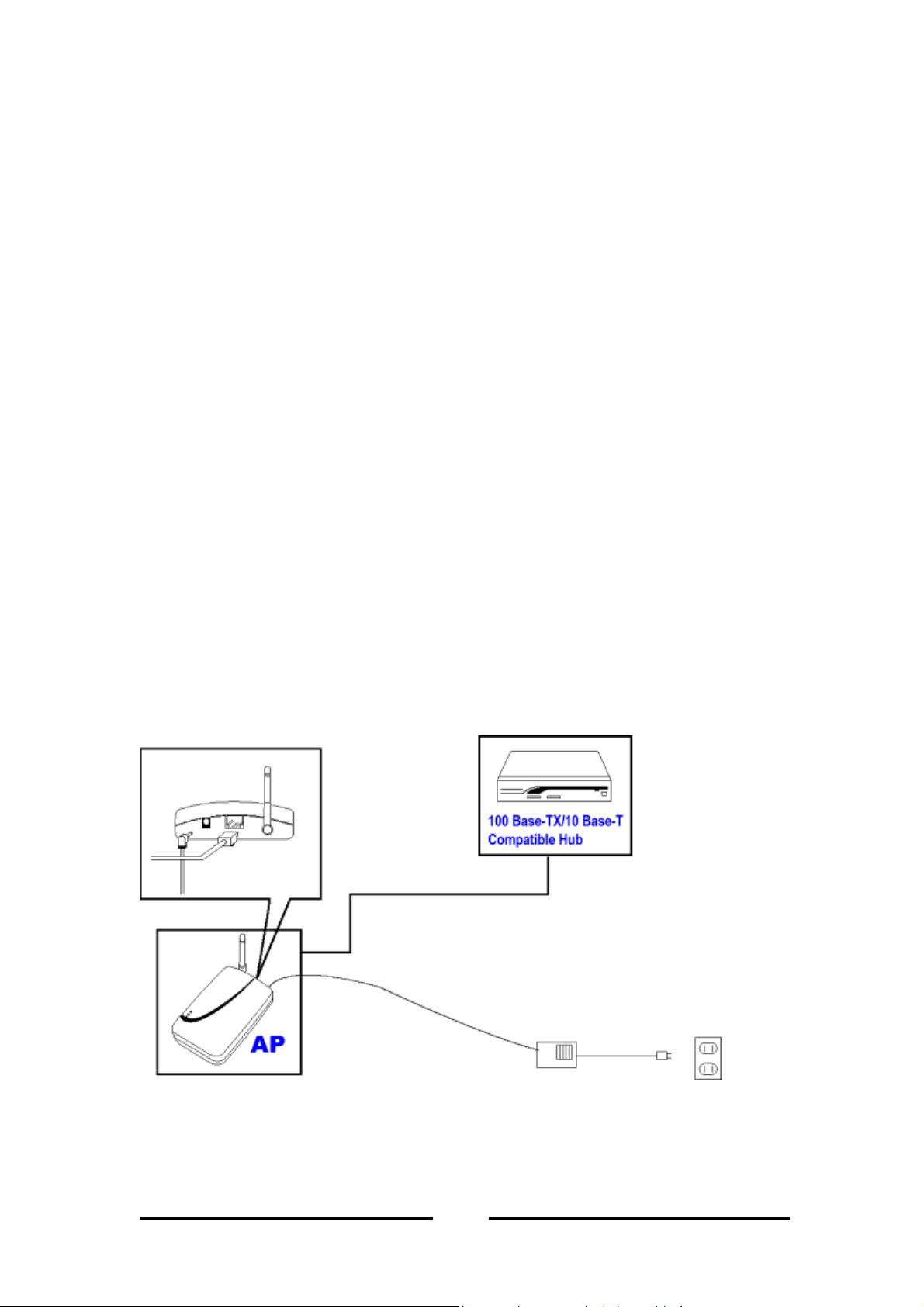
2.3 Installation Diagram
Figure 4 - Installation Diagram
6
Page 11
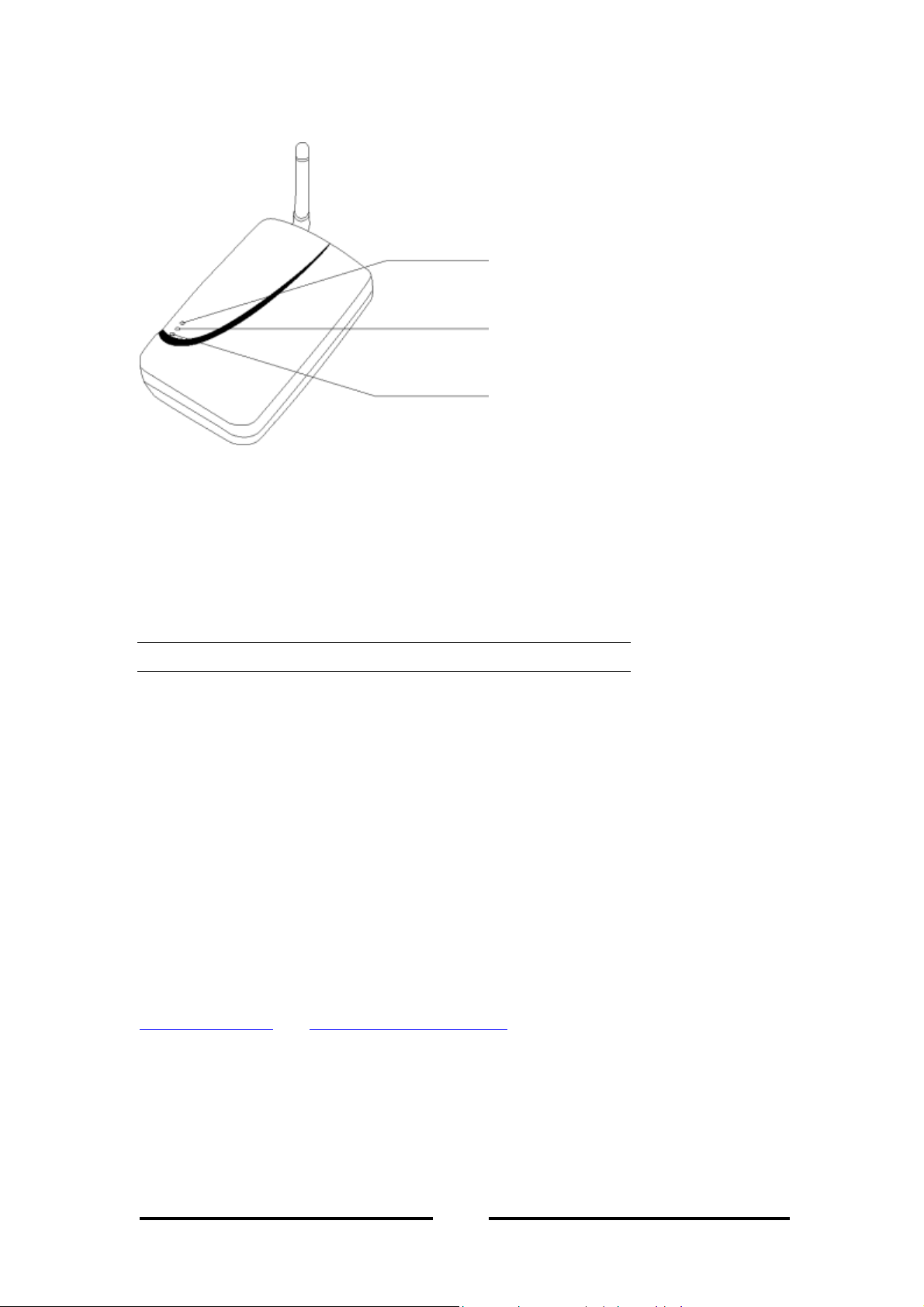
ACCESS POINT
2.4 Physical Description
1st – WLAN
(Wireless LAN lamp)
2nd – LAN
(LAN lamp)
3rd – PWR
(POWER lamp)
Figure 5 - Access Point Diagram
To install your Access Point, plug the power cord into the Access Point. When power
is applied and the network system has been loaded, please refer to Table 2 for the
LED activity:
Tab l e 2
LED Activity Description
1st Flashing (Green) Communicating with the wireless
LAN
2nd
On (Green)
Flashing (Green)
LAN connection is active
Communicating with the LAN
3rd On (Red) Power is on
2.5 Connecting to the Network
After installing the AP you can connect to the network when you have completed
network configuration of your wireless adapter.
2.6 AP Configuration (Install the SNMP Manager)
If you want to configure the AP (e.g.: Setting the AP’s IP address*), please refer to
Configuration AP and Installing SNMP Manager section. The electronic user manual
will guide you on how to install the
AP through the
Access Point SNMP Manager
Access Point SNMP Manager
.
and configure the
* You can connect to network without setting the AP’s IP address
7
Page 12
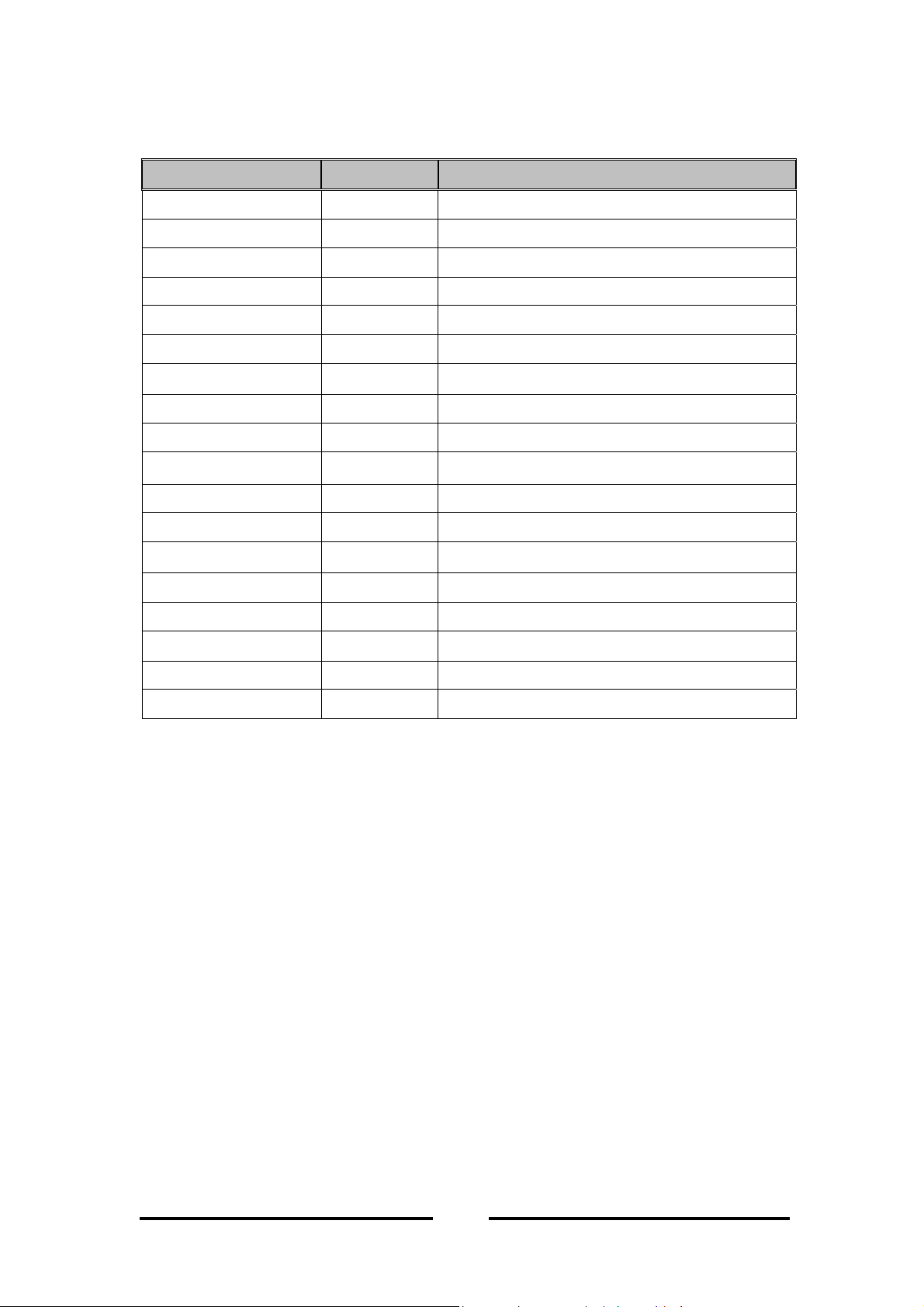
2.7 Default Setting
Functions Default
ACCESS POINT
Options
IP Address
Subnet Mask
Gateway
DHCP
Access Point Name
ESSID
SSID Broadcasting
Channel
Fragmentation Threshold
RTS Threshold
Rates
Authentication Type
Preamble Type
Rx Antenna
Tx Antenna
Operational Mode
192.168.100.2
255.255.255.0
0.0.0.0
Disable Enable/ Disable
AP-xxxxxx*
AP-xxxxxx*
Enable Enable/ Disable
10 1~14 (Depend on Regulatory Domain)
2346 256 ~ 2346
2346 0 ~ 2347
1/ 2/ 5.5/ 11 1, 2, 5.5, 11 Mbps
Both Open System/ Shared Key/ Both
Long Short/ Long
Diversity Left/ Right/ Diversity
Left Left/ Right/ Diversity
Access Point Access Point/ Access Point Client/ Wireless Bridge
User Password
Administrator Password
public
public
* Where xxxxxx are the last 6 digits of your devices MAC address.
8
Page 13
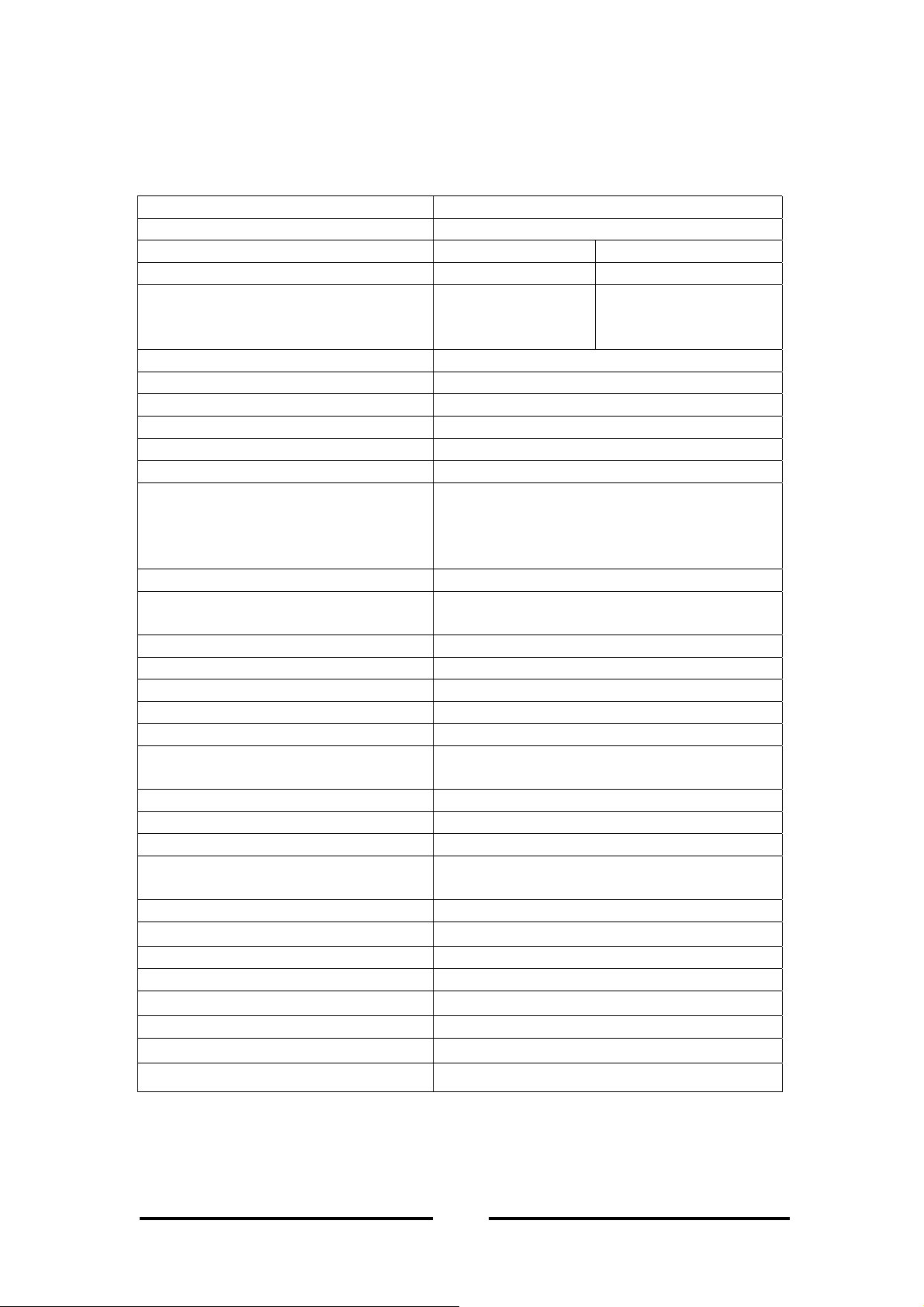
ACCESS POINT
3. Specification
3.1 Hardware Specification
Item Description
Data transfer rate 1, 2, 5.5, 11 Mbps and auto selective
Data Rates, Distance Range Indoor Range Outdoor Range
without
AP
with
AP
(May vary depending on operation
environmental)
Network Interface
Ethernet 10 Base-T / 100Base-TX (RJ45)*
Radio Specification
Modulation Technique Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum
Wireless LAN Standard Compliant with IEEE 802.11b
Frequency range 2.4-2.4835 GHz unlicensed ISM Band
Channels: USA and Canada 11 channels
Output Power MAX 14dBm(25mW)
EMC certification: U.S.: FCC part 15 class B
Modulation
@ 11 Mbps DQPSK (CCK)
@ 5.5 Mbps DQPSK (CCK)
@ 2 Mbps DQPSK
@ 1 Mbps DBPSK
Configuration & Management
Utility
Watching dog
Security 64/128 bit WEP Encryption
Power
LED indicators 3 LED for Ethernet Activity (green), Wireless
Size & Weight
Dimensions (L/W/H)
Weight (include box) 120g (body and cable, no box)
Environment
Operating temperature
Storage
Temperature
Supported Protocol
external Antenna 35 ~ 40m 80 ~ 100m
external Antenna
50 ~ 80m 180 ~ 300m
European 13 channels
France 4 channels
Japan 1 channel
Europe: ETSI 300.328 and CE EMC-EEC
Included
DC 5V, 1A
Activity (green), Power (red)
108.5mm × 71.2mm × 22mm
0℃-40℃
0℃-75℃
TCP/IP, NETBEUI, IPX/SPX, AppleTalk
*To ensure problem-free connection, avoid connecting the AP to a pure 100 Base-T Ethernet adapters
or hubs.
9
Page 14

ACCESS POINT
3.2 IEEE 802.11 Functionality Support
Distributed Coordination Function (DCF)
CSMA/CA
Backoff Procedure
NAV Management
ACK procedure
Retransmission of unacknowledged frames
RTS/CTS Handshake
Duplicate detection and recovery
Beacon generation
Probe response
Fragmentation and reassembly
Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP 64/128 bits)
Authentication algorithm (Open system and Shared key)
Power Management
Short preamble
10
Page 15

ACCESS POINT
4. Configuration AP
The first step to configure the AP is to set its IP Address. This procedure can be done
through the Ethernet/Wireless port by using a combination of ARP/ PING commands
and the SNMP Manager, or by the network DHCP server.
4.1 Setting up Access Points IP Address
You can use ARP/PING commands to set the access point IP address or let the
network DHCP server set the address automatically. Before starting, get the MAC
address of the access point, which is indicated on the back of the AP housing. Follow
the steps below to give the access point a temporary address (Step A) and saving the
IP address through the SNMP Manager (Step B).
Note
: Setting the IP address of the access point using the ARP/PING command will
only work within the first three minute from the time the AP first power on.
Step A
:
1. Connect an Ethernet station and the access point on the same LAN. The simplest
way to accomplish this is to connect the access point and the Ethernet station to the
same hub. Check the station IP and the subnet mask address configurations to see if
they are properly set. New IP address for the access point must correspond to the
subnet mask.
2. Open an MS-DOS prompt window and enter a static route in the ARP table for the
new IP you want to assign. To assign IP address, use the ARP -s command:
> arp -s "new-IP-address" "AP-MAC-address"
For example:
> arp -s 192.168.1.105 00-03-E1-F2-00-01
(The MAC-address of the AP is indicated on the back of the AP housing.)
Note: A valid IP address must be specified, otherwise communication to and
from AP will not work
. Refer to checking valid IP address section to check which
IP are valid.
3. Use its new IP address to
ping
the Access Point.
For example:
> ping 192.168.1.105 -t
If you receive replies, then the IP address has been temporarily set. In order to set it
permanently you need to proceed to Step B
without
11
powering off the access point.
Page 16

ACCESS POINT
Step B
1. Open the SNMP Manager application. If you haven’t installed SNMP Manager
application, please refer to the Installing SNMP Manager section.
2. Connect to the access point by selecting
File
menu. Type the IP address of the access point (which has been temporarily set
in Step A) in the panel that appears. Type “
Administrator
“
manager will inform you that the access point has been found and that all the
configuration values have been retrieved.
3. Under the
that was set up in
validity of the other values (MAC Address and subnet mask), and select the
primary port that determines the access point’s MAC Address and IP, then press
“OK”.
4. Save the configuration by selecting “Download Changes” under the
IP address of the access point has now been set permanently.
DHCP client
If DHCP client is enabled, the IP address field displays the IP address that was
dynamically assigned to the access point by the DHCP server. The
Setup
” in the
⇒
Step A
authority
Bridge
submenu, select
in the configuration window that appears. Confirm the
combo-box and then press “OK”. The SNMP
Connect AP
public
IP Configuration
,
which is a submenu under
” at the
password
. Type the IP address
field; select
File
Subnet Mask
menu. The
field
displays the subnet mask utilized by the network DHCP server. Select the primary
port that is the interface which determines the DHCP server and press “OK”. If the
network server failed to give an IP address to the access point, then the default IP
address will be assigned to the access point.
If you have problem in configuring your AP correctly, then follow the appropriate
link(s) above to seek further information regarding setting and configuring your AP.
Otherwise, you may proceed to the Using SNMP Application usage section on
information describing on how to use the application utility.
12
Page 17
ACCESS POINT
5. Installing SNMP Manager
Insert your installation CD into your CD-ROM. Auto run screen will appear. Click on
SNMP Utility Installation
“
” to start the installation process. Follow the instructions of
the setup program to finish installation. Refer to the Using SNMP Application
for information regarding how to use the SNMP manager.
section
Figure 6 - Autorun screen
13
Page 18
ACCESS POINT
5.0.1 Using SNMP Application
This section describes how to use your SNMP application. You can open up SNMP
application from the start menu as shown below.
Figure 7 - SNMP Application
When you start up the application, there will be only two menus available, namely
File
will become available. Refer to
and
Help
. You will need to connect to an access point first before other menus
Connection to AP
section if you need help with
establishing connection with AP. SNMP application has the following menu options:
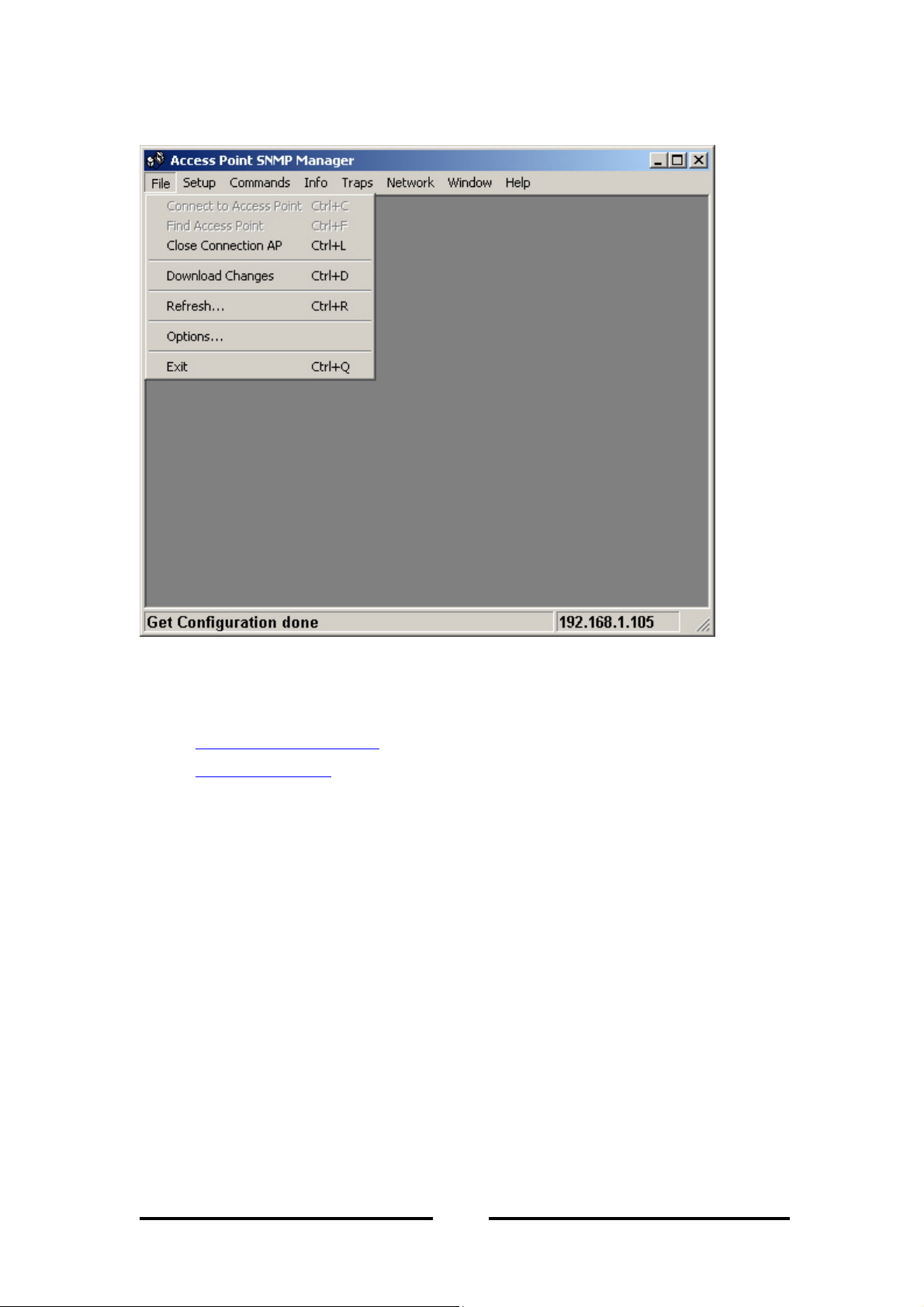
File – Download/upload information to the access point.
Setup – Provide setup configurations for the access point.
Commands – Provide reset and default functions.
Info – Provides statistical values for the access point.
Traps – Provides trap records.
Network – Provide network information regarding to AP.
Window – Provide functions to organize your window views.
Help – Provides help facilities on using SNMP application and application
version.
14
Page 19
5.1 File Menu
ACCESS POINT
Figure 8 - File Menu
Click on the topics below to see a full detail description of each submenu.
Connect to Access Point – Connect to a known AP.
Find Access Point – Search for an available AP to connect to.
Exit – Exit SNMP application.
The following menus will be enabled once connection to the AP has been made.
Close Connection AP – close the current connection with the AP.
Download changes – Upload configuration changes to the access point.
Refresh – Get the current AP configuration.
Options – Defines the polling interval according to which the SNMP manager
polls the access point in order to update statistics and associated stations list.
15
Page 20
ACCESS POINT
5.1.1 Connection to Access Point
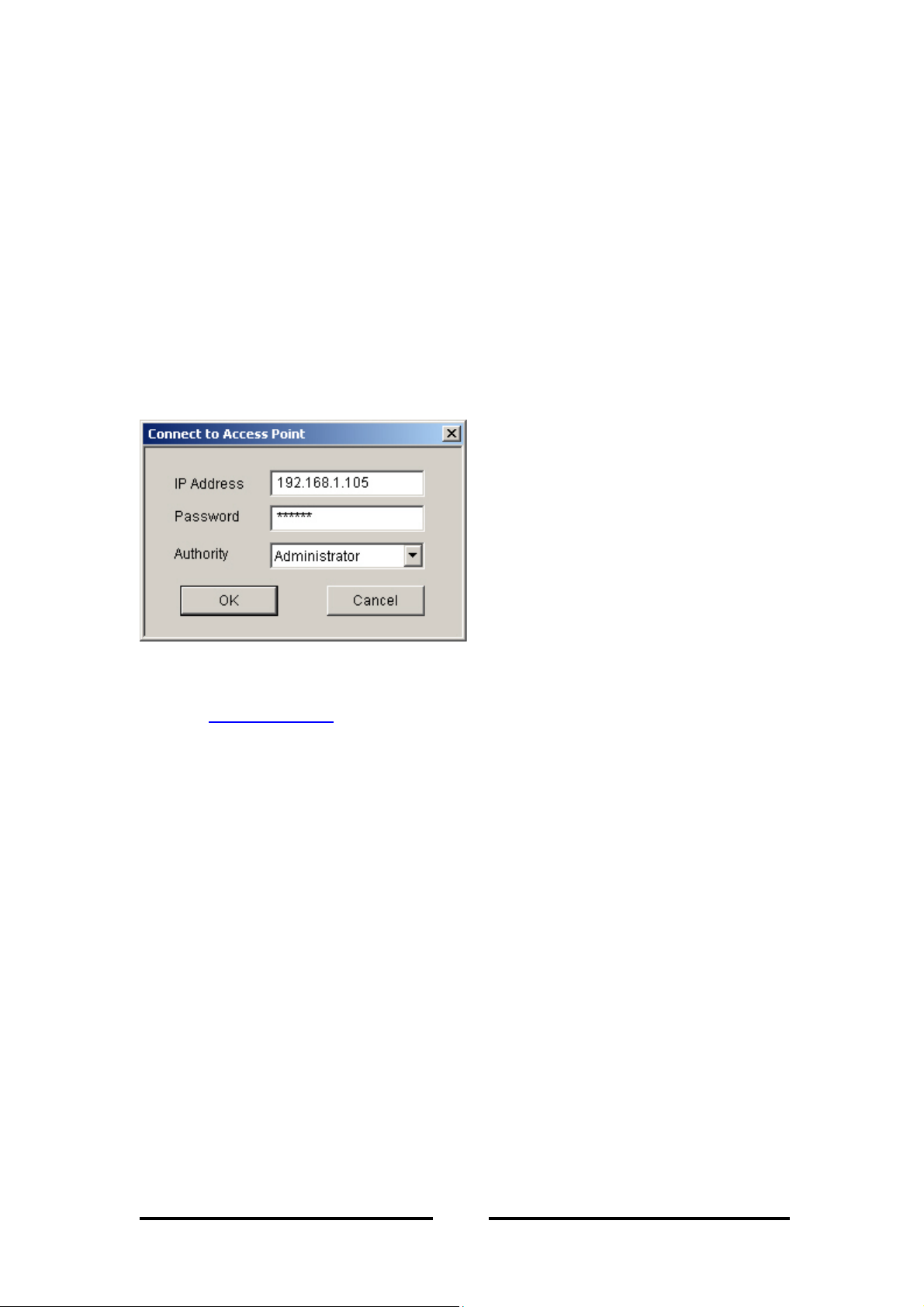
To connect to the access point, you need to do the following:
1. Type the access points IP address in the
2. Type in the appropriate password in the
is “
3. In
public
Authority
Note
”.)
: Password is case sensitive.
combo-box, choose either
authority allows you only to view and not set or save changes to the access
point configuration, while administrator authority allows you to view and
change AP configurations.
4. Click “OK”.
IP Address
Password
field.
field. (The default password
Administrator
User Authority.
or
User
Figure 9 - Connecting to AP
Refer to troubleshooting section if you have trouble connecting to the AP.
16
Page 21

ACCESS POINT
5.1.2 Find Access Point
This option allows you to find and connect with an access point without the necessity
of knowing its IP. Choose this option in order to find the access points available for
connection. Select one of the available access points and press “Connect”.
Figure 10 - Available Access Points
The following screen will appear indicating the IP address of the selected access point
and prompting you to select
Password
field. Then press “Ok”.
authority
and to input the appropriate password at the
Figure 11 - Connecting to AP
17
Page 22

ACCESS POINT
If connection to the access points is successful, then the following window will
appear.
Figure 12 - Connection successful
When the connection has been successfully established, a message in the bottom left
hand corner of the screen indicating, “Get Configuration done” will appear. IP address
of the connected AP will appear at the bottom right hand corner of the screen.
Refer to troubleshooting section if you have trouble connecting to the AP.
18
Page 23

5.2 Setup Menu
ACCESS POINT
Figure 13 - Setup menu
Under the setup menu are the following submenus:
Bridge – Provides routing setup for your AP.
Wireless LAN – Provides configurations for your APs wireless activities.
Enable SNMP Traps – Provides trap messages.
Authorization – Let your AP accept/decline packets from authorized remote
APs.
19
Page 24

5.2.1 Bridge
ACCESS POINT
Figure 14 - Bridge configuration
There are two menus under bridge menu. They are:
1. IP Configuration – Let you modified AP IP settings.
2. Filtering – If filtering is enabled, then only the IP protocol packets will pass
through the WLAN and other protocol packets will get filtered out.
Note
: If you change any of the settings, remember to save your changes by choosing
Download Changes
under the
file
menu. Otherwise, the values that you altered will be
discarded!
20
Page 25

ACCESS POINT
5.2.2 IP Configuration
The IP address and subnet mask can be modified through “IP Configuration”. If
DHCP client is enabled the
dynamically assigned to AP and the
IP Address
Subnet Mask
field displays the IP address that was
field displays the subnet mask
utilized by the network DHCP server. In addition, you have to select the primary port
that determines the DHCP server.
Table 3 - Bridge IP Configuration Parameters
Parameters Description
MAC Address
IP Address
Subnet Mask Four sets of three digits that divide a network into sub networks.
Unique 48-bit, hard-coded physical address known as the station identifier.
Network-assigned Internet Protocol address of the
access point
.
Bridge IP Configuration dialog box
Figure 15 - IP Configurations
21
Page 26

5.2.3 Wireless LAN
ACCESS POINT
Figure 16 - Wireless LAN
Under Wireless LAN are the following sub-menus:
•
Privacy Options – Specifies whether to use encryption or not.
•
Operational Settings – Specifies AP operational settings
•
Authorized MAC Addresses – Specifies which APs are allowed to
communicate with you.
Note
: If you change any of the settings, remember to save your changes by choosing
Download Changes
under the
file
menu. Otherwise, the values that you altered will be
discarded!
22
Page 27

ACCESS POINT
5.2.4 Privacy Options
Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) is an authentication algorithm that protects
authorized wireless LAN users against eavesdroppers. Ten hexadecimal digits must
be supplied in keys 1 to 4 if 64 bits encryption selected. If 128 bits encryption
selected, then 26 hexadecimal digits must be supplied in keys 1 to 4. Choosing disable
will disable WEP encryption and every packet will be send without any encryption.
Finally, if you are using encryption, choose a default key to use.
Figure 17 - Privacy option
Refer to tutorial section if you are unfamiliar with encryptions.
23
Page 28

ACCESS POINT
5.2.5 Operational Settings
Using this option you can either view or modify the wireless LAN parameters of the
access point. These parameters are described below:
Figure 18 - Operational settings
Access Point Name:
Specifies the name of your access point.
ESSID:
Up to 32 ASCII characters used to identify a wireless LAN. It prevents the
unintentional merging of two co-located WLANs. The ESSID value must be the same
in all stations and access point in the extended WLAN.
SSID broadcasting
: Setting broadcasting on will allow the access point to broadcast
its SSID.
24
Page 29

ACCESS POINT
Channel:
There are 14 channels available. Select the channel to be used. Refer to
radio channel selection table to see which channels are available in your region.
Fragmentation threshold:
setting within a range of 256 to 2346 bytes. Refer to tutorial
The size at which packets will be fragmented. Choose a
section if you are
unfamiliar with fragmentations.
RTS Threshold:
Minimum packet size to require an RTS (Request To Send).
Authentication Type:
authentication type to
point either with or without data encryption. Refer to the tutorial
Select Open System, Shared Key, or Both. Setting
both
will enable your AP to communicate with other access
section if you are
unfamiliar with authentication type.
Preamble Type (Short/Long):
Preamble is the first sub field of PPDU, which is the
appropriate frame format for transmission to physical layer. There are two options,
Short Preamble
Long Preamble
and
. The short preamble option improves throughput
performance while long preamble provides better synchronization.
Rate:
By default the unit adoptively selects the highest possible rate for transmission.
Alternatively, you can choose the rate at which the AP will transmit its data at.
Available transmission rates are 1, 2, 5.5 and 11 Mbps.
Auto Rate Fall Back:
System will automatically reduce the transmission rate if
traffic in network is heavy. This will result in better network performance and
minimize packet loss.
Regulatory Domain:
Specify the regulatory domain that you are in.
Click on the
advanced
button to configure advanced settings.
25
Page 30

ACCESS POINT
5.2.6 Advance Operational Setting
Figure 19 - Operating modes
Access Point:
This mode provides access for wireless stations to wired LANs and
from wired LANs to wireless stations. Furthermore, wireless stations within the range
of the access point device may communicate with each other via the access point.
Access Point Client:
This mode allows the connection of one or more remote LANs
with a central LAN, creating thus an extended single virtual LAN. In this way, any
station of the remote LAN can successfully communicate with any station of the
central LAN, as if all of them belonged to the same physical LAN. Wireless stations
can’t associate with access point clients. The access point conducts the designated
traffic to the appropriate wired or wireless station. Figure below illustrate this:
Figure 20 - Access Point Client environment
26
Page 31

ACCESS POINT
To connect to a central LAN, tick the
Preferred BSS
check box and enter the MAC
address of the central LANs AP. If you don’t know the MAC address of the central
LANs AP, click on
Site Survey
and then on
“Get / Refresh”
button. A list of the
available APs will appear. Click on the SSID of the AP you wish to connect to and
click the
make sure that the remote AP has the
Connect
button. In addition to setting the preferred BSS, you also need to
same ESSID
as yours.
Figure 21 - Access Point Client setting
Wireless Bridge:
Two types of connection are available under this mode.
a. Point to Point: The wireless bridge can communicate with a specific remote
MAC address.
b. Point to Multipoint: The wireless bridge can communicate with any wireless
bridge available in the
same channel
. When authorization algorithm is enabled,
the wireless bridge can communicate with any wireless bridge whose MAC
addresses exists in the
authorization table
.
27
Page 32

ACCESS POINT
Figure 22 - Wireless Bridge environment
28
Page 33

5.2.7 Authorized MAC addresses
ACCESS POINT
Figure 23 - Authorized MAC address
For security reasons, the access points have the ability to associate with authorized
MAC address stations. To activate this option, click on the
Enable
check box.
Authorization Table
Load file:
Load a file with the authorized MAC addresses. To create
load file
,
compose a file with MAC addresses, (12 consecutive digits, no ‘-‘) one per line.
Download:
Download the authorized MAC addresses to the access point.
Get:
Get the authorized MAC addresses from AP.
Note
: Make sure that you download the changes to the AP, otherwise the MAC
addresses you specified will not be validated.
29
Page 34

ACCESS POINT
5.2.8 SNMP Traps
SNMP traps are messages that are displayed in the bottom right hand corner of the
main window specifying AP actions. Available trap messages are:
• Trap Re-association
: This trap message is sent when a Station’s re-association
request is received from the AP - Bridge.
• Trap Association
: Indicates the reception of an association request packet and
the sender station's successful association with the wireless bridge.
• Trap Disassociation
: This trap message is sent when a disassociation
notification packet is received from a station.
• Trap Reset
: This trap message is sent when the AP-Bridge resets.
• Trap Setting IP Address with Ping
AP-Bridge IP address is set with the transmission of a ping message.
• Trap Start Up
: This trap message is sent when bridge starts up.
• Trap Failed To Erase Flash
: This trap message is sent when the
: This trap message is sent when bridge fails to
erase flash.
30
Page 35

5.2.9 Authorization
ACCESS POINT
This menu let the administrator change the password that referred to the
field for the user and also the fields in
Administrator
Authority.
Password
Type in the password in the appropriate field and again in the confirm field to confirm
password. Click “
Apply”
to save settings.
Figure 24 - Authority configuration
31
Page 36

5.3 Commands Menu
ACCESS POINT
Figure 25 - Command options
Reset Device – Reset the AP
Restore Defaults – Restore AP configurations to factory defaults.
32
Page 37

5.4 Information Menu
ACCESS POINT
Figure 26 - Information menu
Wireless Statistics – Displays several statistical values on your wireless
activities.
Ethernet Statistics – Displays statistical data on your Ethernet activities
33
Page 38

ACCESS POINT
5.4.1 Wireless Statistics
Report statistics concerning the unit’s wireless activities.
Figure 27 - Short wireless statistics view
Field name Description
Unicast Transmitted Packets The number of unicast packets successfully transmitted
Broadcast transmitted packets The number of broadcast packets transmitted
Multicast transmitted packets The number of multicast packets transmitted
Unicast Received Packets The number of unicast packets that were successfully received
Broadcast Received The number of broadcast packets that were successfully received.
Multicast Received The number of multicast packets that were successfully received
34
Page 39

ACCESS POINT
5.4.2Ethernet Statistics
Report statistics concerning the unit’s Ethernet port activity.
Figure 28 - Basic Ethernet statistics
Field Description
Received Packets
Total Bytes The number of bytes in the frames that were received
Total Packets Total number of received packets
Packet CRC Errors The number of packets with CRC Errors
Transmitted Packets
Total Bytes The number of bytes in the frames that were transmitted
Total Packets Total number of transmitted packets
Packet CRC Errors The number of packets with CRC Errors
35
Page 40

5.5 Trap Menu
ACCESS POINT
Figure 29 – Traps menu
36
Page 41

ACCESS POINT
Figure 30 - Trap recorder
Trap menu contains trap records of your AP.
37
Page 42

5.6 Network Menu
ACCESS POINT
Figure 31 - Network menu
Associated stations shows you the MAC addressees of access points you are
associated (connected) with.
38
Page 43

ACCESS POINT
Figure 32 - Associated stations
39
Page 44

5.7 Window Menu
ACCESS POINT
Figure 33 - Window menu
Under this menu there are the following submenus
• Cascade -
All opened windows are arranged on the desktop in a cascade
fashion.
• Tile
- All open windows are visible on the desktop.
40
Page 45

5.8 Help Menu
ACCESS POINT
Figure 34 - Help menu
Help Topics
: Display quick listing of help topics.
About SNMP Manager
: Displays the manger version.
41
Page 46

ACCESS POINT
6. Tutorial
This section explains some of the simple network concepts concerning wireless
LAN’s and networking in general.
Topics covered are:
Packet Fragmentation
Encryption
Subnetting
6.1 Packet Fragmentation
Packet fragmentation means splitting a data packet into several smaller packets.
We need to fragment packets because of:
o
Hardware limits – some hardware do not support packets up to certain
threshold.
o
Operating system buffer constraints – depending on the system memory,
buffer overflow means lost of data and waste bandwidth in unnecessary
retransmissions. Breaking packets into smaller segment means system will
have extra memory and extra time in processing those smaller data packets.
o
Protocol limits – some protocol specify maximum permitted size of a packet.
E.g. an ATM cell packet is restricted to 53 bytes.
o
Reduce channel occupancy – routers can process smaller packets faster than
larger packets, result in smaller packet stays in router shorter time. This will
result in more throughputs and reduce the likelihood router dropping packets.
Advantages of packet fragmentation:
Easier and faster processing time for routers.
Less delay compare to larger packets
Less likelihood of routers dropping packets when traffic in network is heavy.
This is because the processing time for fragmented packets is lower.
Disadvantages for packet fragmentation:
Additional header information in the packet header result in less data can be
stored in a single packet.
Unnecessary packet fragmentation if traffic in network is low.
Reassemble fragmented packets requires extra time.
42
Page 47

ACCESS POINT
Setting fragmentation threshold can be a tricky business. Getting the best performance
out of fragmentation depends on the network traffic condition.
6.2 Encryption
•
All users throughout the Internet can read unencrypted data, illustrated below
with a simple wired network.
Figure 35 - Intercepted data
•
B want to send some data to A, but the data was intercepted by C.
Figure 36 - Retransmitted data
•
C then modifies the data and transmits it to A. A is unaware of C’s presents and
thinks the data originates from B.
With wireless networks, data is even more vulnerable to such attacks since everyone
within your radio transmitting range can intercept your data.
43
Page 48

ACCESS POINT
Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) provides techniques to prevent intruders invading
your data.
With the current IEEE specification, WEP encryption has two types, 64 and 128 bits1
encryption.
For 64bits encryption, 10 hexadecimal
2
values must be presented in the key field.
While 128 bits encryption, 26 hexadecimal values must be in the key field.
Authentication Type
Share Key:
Encryption algorithm used on each of the computers or access points
might different. Hosts must discover which algorithm other remote hosts use before
proper communication could be established.
Open System:
The IEEE 802.11 default authentication method, which is a very simple,
two-step process. First the station wanting to authenticate with another station sends
an authentication management frame containing the sending station’s identity. The
receiving station then sends back a frame alerting whether it recognizes the identity of
the authenticating station.
WEP standard did not specify which algorithm or the procedure to be used. In
practice, most installation uses a single algorithm that is shared between all mobile
stations and access points.
How is encryption key generated?
Firstly, 24bits IV is generated. This IV is then pass through an encryption algorithm
generator with your data. The generator will generate the appropriate length of bits
that represents your encrypt data.
1
Other manual may specify 40 or 104bits encryption, this is because the manual didn’t include 24 bits
Initialization Vector (IV).
2
Hexadecimal numbers range from 0 ~ 9 and A ~ F.
44
Page 49

ACCESS POINT
6.3 Subnetting
Subnetting allows an organization to use one network address to span many small
physical networks, illustrated below.
Figure 37 - Example of subnet configuration
Subnetting breaks up host ID portion of the IP address and separate it into
host ID.
and
Without subnet With subnet
subnet ID
Net id Host id Net id Host id
Subnet id
Figure 38 - Class B IP address using subnetting
Subnet mask
is used to identify a particular network within the organization. Subnet
mask can be variable and it is determined by how the organization divides its network.
From the example above, to find a particular network within this organization, we can
use the first three portion of the IP address. Thus, its subnet mask is defined as
255.255.255.0
45
Page 50

ACCESS POINT
7. Troubleshooting
Problem 1: I can’t find an access point through the wireless LAN adapter.
Answer:
i) Check the following
Access point is powered on.
Make sure the operational mode of the AP is in
Access Point
mode. (Please
refer to operational settings section and advance operational setting for more
details.)
The AP is within the valid transmission range.
Keep the number of wall and ceilings to a minimum.
Keep the AP away from electronic devices.
If you still can’t find any access points through your WLAN adaptor, then you need to
reset your AP. Refer to resetting the access point section to see how to reset and
reconfigure your AP.
Problem 2: I can’t establish connection between an access point and a wired
network.
Answer:
To ensure problem-free connection, we recommend avoiding connecting the
AP to a pure 100 Base-TX Ethernet adapters or hubs. Also check the network settings
on both devices to ensure they are correct.
Problem 3: I can’t connect to an access point.
Answer
: There are few possible answers to this problem. Refer to connection
troubleshooting section for more details.
Problem 4: I have trouble with setting/using encryption.
Answer
: If you receive error when setting encryption or you can’t communicate with
other parties when you enable your encryption, check your settings against those
listed in the encryption troubleshooting section.
Problem 5: I can’t send other protocol packets except for IP.
Answer
: If you are using other protocols (e.g. NetBEUI) other then IP and have IP
filtering on, then all the packets apart from IP packets will get filtered out. In other
word, your AP will drop every packet other then IP data packets. To turn IP filtering
off, de-select the
IP filtering
check box in the bridge menu.
46
Page 51

ACCESS POINT
Problem 6: I forgot my password
Answer:
If you have forgotten your password, then you need to reset your AP so it
can restore factory settings and therefore restore default password as well. The default
password is “
public
”. Refer to resetting the access point
section to see how to reset
and reconfigure your AP.
Problem 7: I receive this error message when I try to set my AP to “Access Point
Client” mode.
Solution:
This error is caused by the fact that your AP cannot detect other APs within
its range. Make sure other AP is powered on and connected. Then try again.
Problem 8: I received this error message.
Some settings are restricted and can only be modified by administrators. If you want
to change these settings, then you have to log in as
administrator
rather than
user
.
Problem 9: I receive “Get Configuration failed” error message.
Answer:
This problem is usually caused by the connection between you and the
access point has been broken. Try to reconnect to the access point. If reconnection
fails, then check the network setting and also if the AP is powered on and connected
to the network.
47
Page 52

ACCESS POINT
Problem 10: I receive the following error message
:
Answer:
This error arises because you try to open up two SNMP Manager
applications. Only one SNMP Manager application can be run at one computer at any
time.
Problem 11: I have set authorized MAC addresses but then realize the addresses
I entered are wrong, and I can’t connect to the AP now.
Answer:
Your AP will only be allowed to communicate with
wireless
LANs/APs that
the MAC specifies. If you set MAC wrongly, then you have to find other wireless
LAN or AP who is authorized to communicate with the given AP. Otherwise you will
need to reset the access point. Refer to resetting the AP for further details.
Note: Authorized MAC address only restricts communication to the
You can still communicate with the access point if you are using a
wireless
wired
LAN.
LAN.
48
Page 53

ACCESS POINT
7.1 Checking Valid IP Addresses
There are restrictions on which IP addresses you can and cannot use. Some IP
addresses are reserved for testing, multicasting and some IP are restricted by your ISP.
Following IP addresses
cannot
be used:
•
127.X.X.X – this is a loop back address, used for testing
•
0.0.0.0 – this IP address represent the host address.
•
255.255.255.255 – this is local broadcast address
•
First portion of IP cannot exceed 224, that is, IP addresses which is in the
range of 224~239.X.X.X is not valid. This range of IP is for multicasting. IP
range from 240~255.X.X.X are reserved IP addresses and cannot be used.
•
0 or 255 in host ID portion of your IP are not valid. This represent local host
or broadcast address for your class of IP (explained in the next paragraph).
IP has five classes, namely class A, B, C, D and E. For each class, the host ID portion
in the IP field is different for each of the classes. Figure below illustrate this.
Class A: 1~127
Class B: 128~191
Class C: 192~223
.
X
.
.
X
.
X
.
.
Host ID
Host ID
Host ID
Class D: 224~239
Class E: 240~255
Used for Multicasting (no Host ID)
.
Reserved IP address
.
Host ID cannot be all 0’s or all 255’s. For example, the following are not valid IP’s:
1~127.0.0.0 – invalid class A address
1~127.255.255.255 – invalid class A address
128~191.X.0.0 – invalid class B address
128~191.X.255.255 – invalid class B address
192~223.X.X.0 – invalid class C address
192~223.X.X.255 – invalid class C address
Note
: X denote
don’t cares
in the above example
49
Page 54

ACCESS POINT
7.2 Connection Troubleshooting
VI receive this error message when I try to find access point.
Solution
: Check the following:
AP is powered on and connected
If AP is powered on but you still can’t find the access point, then you have
probably have or set the APs IP address to one of the invalid addresses. To fix the
problem, you need to
reset
the AP. Refer to resetting AP section for more
information on how to reset your AP.
Note
: If you are using wireless LAN to connect to the access point, then there is a
higher chance of you not able to detect the AP. Try to use Ethernet to connect to
the access point.
V I can’t connect to an AP.
Solution
: Check the following:
Access point is powered on and connected.
Access point is connected to the
same
subnet as your Ethernet station. Refer to
tutorial section if you are unfamiliar with subnet and subnet settings.
Both you and the access point have a valid IP address. Refer to validating IP
address section to check if you have a valid IP address.
50
Page 55

ACCESS POINT
7.3 Resetting the Access Point
Resetting the access point will restore the factory settings.
WARNING: All the settings you made to the access point will be lost after
resetting the device
.
To reset the AP, use a pin or something small to push and hold the reset button. Reset
button is located on the reverse side of the AP. Resetting procedure should take no
more then 10 seconds. After the device has been reset, you need to reconfigure its IP
and saving it again. Refer to configure AP
if you have problems setting APs IP using
ARP command.
The Bottom of the AP Diagram
51
Page 56

ACCESS POINT
7.4 Encryption Troubleshooting
Following discusses problems that may arise when setting your encryption keys.
VI got error messages when I press the set button
Error message type:
Unable to Set Privacy Configuration. Possibly Access Point is not connected.
This problem arises because you have typed in a non-hexadecimal digit.
That is, you have typed a key outside the range 0 ~ 9 and A ~ F.
VI cannot communicate with other parties.
This is probably the most common error when setting encryption. Try one of the
suggestions below to solve your dilemma.
1. Make sure you and the other party (either access point or wireless LAN) is
using the same encryption type, that is, 64 bits or 128 bits.
2. Make sure the WEP key you are using matches the corresponding key the
other party (either access point or wireless LAN) is using and vice versa. That
is, if you are using Key 1, other parties value of Key 1 must be the same as
yours, and vice versa.
3. Make sure all parties are using the same
both (automatic).
to
authentication type
. If uncertain, set it
4. If you set your encryption key under the required length, the system will set it
default
to
. Check your encryption keys again to see if they are set to what you
intended to.
52
Page 57

ACCESS POINT
7.5 Troubleshooting Check Table
If you can’t establish connection, please check the configurations below.
Item
Operational
mode
Access Point
SSID Channel Encryption Key
#1~4
*
Disable
64 Bit or 128 Bit
Authentication
Type
N/A Open System or
Both
**
***
Protocol
&
Network
Domain
AP Client
N/A
Disable
N/A Open System or
Both
Wireless
N/A
64 Bit or 128 Bit
Bridge
Disable
N/A Open System or
Both
64 Bit or 128 Bit
Note:
* Encryption must be set to the same type.
** Value of encryption keys must be the same for all users but can choose
different key to use when communicating.
*** The
authentication type
Shared Key
. Select
setting must be the same, either O
Both
for communication with clients with different
pen System
or
settings.
53
Page 58

ACCESS POINT
8. FAQ
Q1: What is an Access Point (AP)?
Answer:
wireless 802.11b. It can be used as the center of a wireless infrastructure, providing
connections to your wired networks. Or, it can act as a repeater, increasing wireless
communication range. The maximum communication range is based on how you
configure your wireless infrastructure. If your purpose is merely to transfer files
between two nearby computers, you can connect these two PCs by two WLAN cards
through ad-hoc mode without using an AP.
Q2: Why can’t my wireless LAN detect an access point?
An AP is the bridge to connect two different protocols, Ethernet 802.3 and
Answer
an access point is configured to be
: Wireless LAN cannot detect access point under some AP configurations. If
access point client or wireless bridge
then
detection cannot be made with a wireless LAN. Although communication to the
access point through Ethernet is still possible.
Q3: What is the difference between point-to-point wireless bridge setting and
access point setting?
Answer
any other APs, but it
: Setting your AP to
cannot
point-to-point wireless bridge
bridge
mode will be able to communicate with any other APs which are in wireless
bridge mode, but it cannot communicate with any AP which are configured to
point
mode.
access point
mode will enable it to communicate with
communicate with any APs which are configured to
. Similarly, APs which are set to
point-to-point wireless
access
Q4: Can my wireless LAN communicate with an AP that is configured to access
point client?
Answer
: You can communicate to an AP that is configured to
access point client
mode if and only if communication is done through another AP that is configured to
access point
mode and that AP can communicate with the
access point client
AP.
Q5: Why does the APs SSID field empty why I try to detect it through my
wireless LAN?
Answer
: If the access point didn’t broadcast its SSID, then the SSID field will be
empty when you try to detect the AP using a wireless LAN. To turn the SSID
broadcasting on, select
SSID broadcasting
field in the
operational settings
menu.
54
Page 59

ACCESS POINT
Q6: How can I remove the SNMP Manager utility in Windows?
Answer
: You can uninstall the manager utility by executing the un-installation
program, which is located under the following path:
Start ⇒ Programs ⇒ Atmel Utilities ⇒ AP Configuration ⇒ Uninstall AP Configuration
Q7: Can I select any of the 14 channels to use?
Answer
channel usage by country table
: There are regulations to which channels that can be used. Refer to the
to see which channel is available in your region.
Q8: Does the radio wave emitted from the AP have any threat to human health?
Answer:
Now scientific studies have been unable to attribute adverse health effects to
AP transmissions. As with other wireless technologies, AP must meet strict
government and industry standards for safety.
Q9: What is the maximum transmission rate of the access point?
Answer:
In 802.11b, the maximum transmission rate is 11Mbps. It also supports
1Mbps, 2Mbps, and 5.5Mbps rates when the transmission condition is not desirable. If
the AP is connected to other APs or wireless LANs, then the 11Mbps bandwidth is
shared among these devices.
55
Page 60

ACCESS POINT
9. WLAN Glossary
Access Point (AP)
A device that transports data between a wireless network and a wired network
(infrastructure).
Ad-hoc network
A wireless network composed only of stations (no access point). Also known as peer
to peer network
Authentication
The process a station uses to announce its identity to another station. IEEE 802.11
specifies two forms of authentication: open and shared key.
Basic Service Set (BSS)
A set of 802.11-compliant stations that operates as a fully connected, wireless
network.
BSSID
A 6-byte address that distinguishes a particular AP from others. Also known as a
network ID or the MAC address of the AP.
Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC)
An error-detection process that (at the transmitting station) divides the data being sent
by a particular polynomial and appends the resulting remainder to the transmitted
data.
Data link layer
The bottom second layer of the OSI layers. It provides synchronization and
transmission error control to packets. In 802.11 LANs, it encompasses the logical link
control (LLC) and medium access control (MAC) layers.
Differential quadrature phase shift keying (DQPSK)
A modulation process that the IEEE 802.11 direct sequence physical layer uses to
transmit data. It operates at a specific center frequency and varies the phase of the
signal to represent double-bit symbols.
56
Page 61

ACCESS POINT
Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS)
Combines a data signal at the sending station with a higher data rate bit sequence,
which many refer to as a chip sequence (processing gain). A high processing gain
increases the signal’s resistance to interference.
Extended Service Set (ESS)
A collection of basic service sets tied together via a distribution system.
Frequency hopping spread spectrum (FHSS)
Takes the data signal and modulates it with a carrier signal that hops from frequency
to frequency as a function of time over a wide band of frequencies.
Independent Basic Service Set Network (IBSS Network)
A 802.11-based wireless network that has no backbone infrastructure and consists of
at least two wireless stations. This type of network is often referred to as an ad hoc
network because it can be constructed quickly without much planning.
Industrial, Scientific, and Medicine bands (ISM bands)
Radio frequency bands that the Federal Communications Commission (FCC)
authorized for wireless LANs. The ISM bands are located at 902 MHz, 2.400 GHz,
and 5.7 GHz.
Logical Link Control (LLC) layer
The highest layer of the IEEE 802 reference model, providing similar functions of a
traditional data link control protocol.
Medium Access Control (MAC) layer
Provides medium access services for IEEE 802 LANs.
Microcell
A bounded physical space in which a number of wireless devices can communicate.
Because it is possible to have overlapping cells as well as isolated cells, the
boundaries of the cell are established by some rule or convention.
57
Page 62

ACCESS POINT
Open system authentication
The IEEE 802.11 default authentication method, which is a very simple, two-step
process. First the station wanting to authenticate with another station sends an
authentication management frame containing the sending station’s identity. The
receiving station then sends back a frame alerting whether it recognizes the identity of
the authenticating station.
Open System Interconnection (OSI)
An ISO standard specifying an open system capable of enabling the communications
between diverse systems. It has the following seven layers of distinction: physical,
data link, network, transport, session, and application. These layers provide the
functions necessary to allow standardized communications between two application
processes.
Physical layer
Provides the transmission of bits through a communication channel by defining
electrical, mechanical, and procedural specifications.
Point Coordination Function (PCF)
An IEEE 802.11 mode that enables contention-free frame transfer based on a priority
mechanism. Enables time-bounded services that support the transmission of voice and
video.
Quadrature Phase Shift Keying (QPSK)
A modulation technique that changes the phase of a signal to represent different,
four-bit binary words.
Radio Frequency (RF) Terms: GHz, MHz, Hz
The international unit for measuring frequency is Hertz (Hz), which is equivalent to
the older unit of cycles per second. One Mega-Hertz (MHz) is one million Hertz. One
Giga-Hertz (GHz) is one billion Hertz. For reference: the standard US electrical
power frequency is 60 Hz, the AM broadcast radio frequency band is 0.55 -1.6 MHz,
the FM broadcast radio frequency band is 88-108 MHz, and microwave ovens
typically operate at 2.45 GHz.
Roaming
Movement of a wireless node between two microcells. Roaming usually occurs in
infrastructure networks built around multiple access points.
58
Page 63

ACCESS POINT
Shared key authentication
A type of authentication that assumes each station has received a secret shared key
through a secure channel independent from an 802.11 network. Stations authenticate
through shared knowledge of the secret key. Use of shared key authentication requires
implementation of the 802.11 WEP algorithms.
Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP)
An optional IEEE 802.11 function that offers frame transmission similar to a wired
network. The WEP generates secret shared encryption keys that both source and
destination stations can use to alter frame bits to avoid disclosure to eavesdroppers.
59
Page 64

ACCESS POINT
Federal Communications Commission Interference Statement
FCC Class B Certification
The device complies with Part 15 of the FCC rules. Operation is subject to the
following conditions:
1. This device may not cause harmful interference.
2. This device must accept any interference received, including interference that
may cause undesired operation.
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B
digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to
provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential installation.
This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not
installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference
to radio communications However, there is no guarantee that interference will not
occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to
radio or television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off
and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the
following measures:
Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from the one which the
receiver is connected.
Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
CAUTION:
To assure continued FCC compliance:
(1) The user must use shielded interface cable and shielded power cord.
(2) Any changes or modifications not expressly approved by the grantee of this
device could void the user's authority to operate the equipment.
FCC RF Radiation Exposure Statement
This equipment complies with FCC RF radiation exposure limits set forth for an
uncontrolled environment. This equipment should be installed and operated with a
minimum distance of 20cm between the radiator and your body.
CE Market Declaration of Conformance
This is to certify that this product complies with ISO/IEC Guide 22 and EN45014. It
conforms to the following specifications:
EMC: EN55022(1988)/CISPR-22(1985) Class B
IEC 61000-4-2(2000) 4kVCD/8k VAD
IEC 61000-3-3(2000) 3V/m
IEC 61000-4-4(2000) 1kV-(power line)
IEC 61000-4-6(2000) 3Vrms
IEC 61000-4-11(2000) 3Vrms
The product complies with the requirements of the Low Voltage Directive 73/23/EEC
and the EMC Directive 89/336/EEC, and carries the CE Mark accordingly.
60
Page 65

Radio Channel Selection Table
Channel
ID
1 2412 yes yes yes yes
2 2417 yes yes yes yes
3 2422 yes yes yes yes
4 2427 yes yes yes yes
5 2432 yes yes yes yes
6 2437 yes yes yes yes
7 2442 yes yes yes yes
8 2447 yes yes yes yes
9 2452 yes yes yes yes
10 2457 yes yes yes yes yes yes
11 2462 yes yes yes yes yes yes
12 2467 yes
Center
Frequency
(MHz)
FCC DOC ETSI MKK
MKK1
U.S.A Canada
ㄨ ㄨ
Regulator domains
Most of
Europe
yes
Spain France
ㄨ ㄨ ㄨ
ㄨ ㄨ ㄨ
ㄨ ㄨ ㄨ
ㄨ ㄨ ㄨ
ㄨ ㄨ ㄨ
ㄨ ㄨ ㄨ
ㄨ ㄨ ㄨ
ㄨ ㄨ ㄨ
ㄨ ㄨ ㄨ
ㄨ
yes
Japan
ㄨ
ㄨ
ㄨ
13 2472 yes
14 2484 yes
ㄨ ㄨ
ㄨ ㄨ ㄨ ㄨ ㄨ
yes
ㄨ
yes
ㄨ
yes
 Loading...
Loading...