Winbond Electronics W83977TF-PW, W83977TF-P, W83977TF-AW, W83977TF-A Datasheet

W83977TF
WINBOND I/O
W83977TF Data Sheet Revision History
Pages Dates Versi
1 n.a. 05/20/97 0.50 First published.
IV,V,6,7,14,49,5
2
5,69-80,87-96,
103,113, 117,
118,122, 128,
149
3 III,3,68,134,
146,148; 64-67
4 P101,101.1,102 11/18/97 0.61 Register correction
P1,3,49,62,64,
5
67,71,73,74,
100,117,119,
120,129
6
7
8
07/01/97 0.51 Typo correction and data calibrated
07/20/97 0.60 Explanation of OnNow/ security wake-up
03/19/98 0.62 Typo correction and data calibrated
on
Version
on Web
Main Contents
functions; Repagenating
9
10
Please note that all data and specifications are subject to change without notice. All
the trade marks of products and companies mentioned in this data sheet belong to
their respective owners.
LIFE SUPPORT APPLICATIONS
These products are not designed for use in life support appliances, devices, or
systems where malfunction of these products can reasonably be expected to result
in personal injury. Winbond customers using or selling these products for use in such
applications do so at their own risk and agree to fully indemnify Winbond for any
damages resulting from such improper use or sales.

W83977TF
TABLE OF CONTENTS
GENERAL DESCRIPTION.......................................................................................................1
FEATURES....................................................................................................................................2
PIN CONFIGURATION .............................................................................................................4
1. PIN DESCRIPTION................................................................................................................5
1.1 HOST INTERFACE.....................................................................................................................................5
1.2 GENERAL PURPOSE I/O PORT...............................................................................................................7
1.3 SERIAL PORT INTERFACE......................................................................................................................8
1.4 INFRARED INTERFACE...........................................................................................................................9
1.5 MULTI-MODE PARALLEL PORT...........................................................................................................9
1.6 FDC INTERFACE......................................................................................................................................14
1.7 KBC INTERFACE......................................................................................................................................15
1.8 POWER PINS.............................................................................................................................................16
1.9 ACPI INTERFACE.....................................................................................................................................16
2. FDC FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION................................................................................17
2.1 W83977TF FDC.........................................................................................................................................17
2.1.1 AT INTERFACE.............................................................................................................................17
2.1.2 FIFO (DATA)..................................................................................................................................17
2.1.3 DATA SEPARATOR.....................................................................................................................18
2.1.4 WRITE PRECOMPENSATION ...................................................................................................18
2.1.5 PERPENDICULAR RECORDING MODE.................................................................................18
2.1.6 FDC CORE......................................................................................................................................19
2.1.7 FDC COMMANDS ........................................................................................................................19
2.2 REGISTER DESCRIPTIONS...................................................................................................................29
2.2.1 STATUS REGISTER A (SA REGISTER) (READ BASE ADDRESS + 0).............................29
2.2.2 STATUS REGISTER B (SB REGISTER) (READ BASE ADDRESS + 1) .............................31
2.2.3 DIGITAL OUTPUT REGISTER (DO REGISTER) (WRITE BASE ADDRESS + 2)............33
2.2.4 TAPE DRIVE REGISTER (TD REGISTER) (READ BASE ADDRESS + 3)........................33
2.2.5 MAIN STATUS REGISTER (MS REGISTER) (READ BASE ADDRESS + 4)....................34
Publication Release Date: March 1998
- I - Revision 0.62

W83977TF
2.2.6 DATA RATE REGISTER (DR REGISTER) (WRITE BASE ADDRESS + 4).......................34
2.2.7 FIFO REGISTER (R/W BASE ADDRESS + 5)..........................................................................36
2.2.8 DIGITAL INPUT REGISTER (DI REGISTER) (READ BASE ADDRESS + 7)....................38
2.2.9 CONFIGURATION CONTROL REGISTER (CC REGISTER)
(WRITE BASE ADDRESS + 7)...................................................................................................39
3. UART PORT............................................................................................................................40
3.1 UNIVERSAL ASYNCHRONOUS RECEIVER/TRANSMITTER (UART A, UART B)..................40
3.2 REGISTER ADDRESS..............................................................................................................................40
3.2.1 UART CONTROL REGISTER (UCR) (READ/WRITE)...........................................................40
3.2.2 UART STATUS REGISTER (USR) (READ/WRITE)...............................................................42
3.2.3 HANDSHAKE CONTROL REGISTER (HCR) (READ/WRITE) ............................................43
3.2.4 HANDSHAKE STATUS REGISTER (HSR) (READ/WRITE).................................................44
3.2.5 UART FIFO CONTROL REGISTER (UFR) (WRITE ONLY) .................................................45
3.2.6 INTERRUPT STATUS REGISTER (ISR) (READ ONLY).......................................................46
3.2.7 INTERRUPT CONTROL REGISTER (ICR) (READ/WRITE).................................................47
3.2.8 PROGRAMMABLE BAUD GENERATOR (BLL/BHL) (READ/WRITE) .............................47
3.2.9 USER-DEFINED REGISTER (UDR) (READ/WRITE).............................................................48
4. INFRARED (IR) PORT.........................................................................................................49
5. PARALLEL PORT ...............................................................................................................49
5.1 PRINTER INTERFACE LOGIC...............................................................................................................49
5.2 ENHANCED PARALLEL PORT (EPP)..................................................................................................50
5.2.1 DATA SWAPPER ..........................................................................................................................51
5.2.2 PRINTER STATUS BUFFER.......................................................................................................51
5.2.3 PRINTER CONTROL LATCH AND PRINTER CONTROL SWAPPER...............................52
5.2.4 EPP ADDRESS PORT...................................................................................................................52
5.2.5 EPP DATA PORT 0-3....................................................................................................................53
5.2.6 BIT MAP OF PARALLEL PORT AND EPP REGISTERS .......................................................53
5.2.7 EPP PIN DESCRIPTIONS ............................................................................................................54
5.2.8 EPP OPERATION..........................................................................................................................54
5.3 EXTENDED CAPABILITIES PARALLEL (ECP) PORT.....................................................................55
5.3.1 ECP REGISTER AND MODE DEFINITIONS...........................................................................55
5.3.2 DATA AND ECPAFIFO PORT....................................................................................................56
5.3.3 DEVICE STATUS REGISTER (DSR).........................................................................................56
5.3.4 DEVICE CONTROL REGISTER (DCR) ....................................................................................57
Publication Release Date: March 1998
- II - Revision 0.62

W83977TF
5.3.5 CFIFO (PARALLEL PORT DATA FIFO) MODE = 010...........................................................58
5.3.6 ECPDFIFO (ECP DATA FIFO) MODE = 011............................................................................58
5.3.7 TFIFO (TEST FIFO MODE) MODE = 110.................................................................................58
5.3.8 CNFGA (CONFIGURATION REGISTER A) MODE = 111 ....................................................58
5.3.9 CNFGB (CONFIGURATION REGISTER B) MODE = 111 .....................................................58
5.3.10 ECR (EXTENDED CONTROL REGISTER) MODE = ALL....................................................59
5.3.11 BIT MAP OF ECP PORT REGISTERS.......................................................................................60
5.3.12 ECP PIN DESCRIPTIONS............................................................................................................61
5.3.13 ECP OPERATION..........................................................................................................................62
5.3.14 FIFO OPERATION ........................................................................................................................62
5.3.15 DMA TRANSFERS........................................................................................................................63
5.3.16 PROGRAMMED I/O (NON-DMA) MODE................................................................................63
5.4 EXTENSION FDD MODE (EXTFDD)...................................................................................................63
5.5 EXTENSION 2FDD MODE (EXT2FDD)..............................................................................................63
6. KEYBOARD CONTROLLER.............................................................................................64
6.1 OUTPUT BUFFER ....................................................................................................................................64
6.2 INPUT BUFFER.........................................................................................................................................64
6.3 STATUS REGISTER.................................................................................................................................65
6.4 COMMANDS .............................................................................................................................................65
6.5 HARDWARE GATEA20/KEYBOARD RESET CONTROL LOGIC .................................................67
6.5.1 KB CONTROL REGISTER (LOGIC DEVICE 5, CR-F0).........................................................67
6.5.2 PORT 92 CONTROL REGISTER (DEFAULT VALUE = 0X24)............................................67
6.4 ONNOW / SECURITY KEYBOARD AND MOUSE WAKE-UP ......................................................68
7. GENERAL PURPOSE I/O....................................................................................................69
7.1 BASIC I/O FUNCTIONS...........................................................................................................................71
7.2 ALTERNATE I/O FUNCTIONS..............................................................................................................73
7.2.1 INTERRUPT STEERING..............................................................................................................73
7.2.2 WATCH DOG TIMER OUTPUT.................................................................................................74
7.2.3 POWER LED...................................................................................................................................74
7.2.4 GENERAL PURPOSE ADDRESS DECODER..........................................................................74
7.2.5 GENERAL PURPOSE WRITE STROBE....................................................................................74
8. PLUG AND PLAY CONFIGURATION ............................................................................75
8.1 COMPATIBLE PNP...................................................................................................................................75
8.1.1 EXTENDED FUNCTION REGISTERS......................................................................................75
Publication Release Date: March 1998
- III - Revision 0.62

W83977TF
8.1.2 EXTENDED FUNCTIONS ENABLE REGISTERS (EFERS) .................................................76
8.1.3 EXTENDED FUNCTION INDEX REGISTERS (EFIRS), EXTENDED FUNCTION
DATA REGISTERS(EFDRS).......................................................................................................76
9. ACPI REGISTERS FEATURES.........................................................................................77
9.1 SMI TO SCI/SCI TO SMI AND BUS MASTER....................................................................................78
9.2 POWER MANAGEMENT TIMER..........................................................................................................79
9.3 ACPI REGISTERS (ACPIRS)...................................................................................................................80
9.3.1 POWER MANAGEMENT 1 STATUS REGISTER 1 (PM1STS1)..........................................80
9.3.2 POWER MANAGEMENT 1 STATUS REGISTER 2 (PM1STS2)..........................................81
9.3.3 POWER MANAGEMENT 1 ENABLE REGISTER 1(PM1EN1) ............................................82
9.3.4 POWER MANAGEMENT 1 ENABLE REGISTER 2 (PM1EN2)...........................................82
9.3.5 POWER MANAGEMENT 1 CONTROL REGISTER 1 (PM1CTL1)......................................83
9.3.6 POWER MANAGEMENT 1 CONTROL REGISTER 2 (PM1CTL2)......................................83
9.3.7 POWER MANAGEMENT 1 CONTROL REGISTER 3 (PM1CTL3)......................................84
9.3.8 POWER MANAGEMENT 1 CONTROL REGISTER 4 (PM1CTL4)......................................84
9.3.9 POWER MANAGEMENT 1 TIMER 1 (PM1TMR1) ................................................................85
9.3.10 POWER MANAGEMENT 1 TIMER 2 (PM1TMR2) ................................................................85
9.3.11 POWER MANAGEMENT 1 TIMER 3 (PM1TMR3) ................................................................86
9.3.12 POWER MANAGEMENT 1 TIMER 4 (PM1TMR4) ................................................................87
9.3.13 GENERAL PURPOSE EVENT 0 STATUS REGISTER 1 (GP0STS1)...................................87
9.3.14 GENERAL PURPOSE EVENT 0 STATUS REGISTER 2 (GP0STS2)...................................88
9.3.15 GENERAL PURPOSE EVENT 0 ENABLE REGISTER 1 (GP0EN1)....................................89
9.3.16 GENERAL PURPOSE EVENT 0 ENABLE REGISTER 2 (GP0EN2)....................................89
9.3.17 GENERAL PURPOSE EVENT 1 STATUS REGISTER 1 (GP1STS1)...................................90
9.3.18 GENERAL PURPOSE EVENT 1 STATUS REGISTER 2 (GP1STS2)...................................90
9.3.19 GENERAL PURPOSE EVENT 1 ENABLE REGISTER 1 (GP1EN1)....................................91
9.3.20 GENERAL PURPOSE EVENT 1 ENABLE REGISTER 2 (GP1EN2)....................................91
9.3.21 BIT MAP CONFIGURATION REGISTERS...............................................................................92
10. SERIAL IRQ.........................................................................................................................93
10.1 START FRAME .........................................................................................................................................94
10.2 IRQ/DATA FRAME...................................................................................................................................94
10.3 STOP FRAME............................................................................................................................................94
10.4 RESET AND INITIALIZATION..............................................................................................................95
11. CONFIGURATION REGISTER.......................................................................................96
Publication Release Date: March 1998
- IV - Revision 0.62

W83977TF
11.1 CHIP (GLOBAL) CONTROL REGISTER..............................................................................................96
11.2 LOGICAL DEVICE 0 (FDC)...................................................................................................................100
11.3 LOGICAL DEVICE 1 (PARALLEL PORT)..........................................................................................103
11.4 LOGICAL DEVICE 2 (UART A)¢) ........................................................................................................104
11.5 LOGICAL DEVICE 3 (UART B) ...........................................................................................................104
11.6 LOGICAL DEVICE 5 (KBC)..................................................................................................................106
11.7 LOGICAL DEVICE 7 (GP I/O PORT I).................................................................................................107
11.8 LOGICAL DEVICE 8 (GP I/O PORT II)...............................................................................................110
11.9 LOGICAL DEVICE 9 (GP I/O PORT III)..............................................................................................114
11.10 LOGICAL DEVICE A (ACPI)................................................................................................................117
12. SPECIFICATIONS............................................................................................................123
12.1 ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS ....................................................................................................123
12.2 DC CHARACTERISTICS.......................................................................................................................123
12.3 AC CHARACTERISTICS.......................................................................................................................127
12.3.1 FDC: DATA RATE = 1 MB, 500 KB, 300 KB, 250 KB/SEC...............................................127
12.3.2 UART/PARALLEL PORT........................................................................................................129
12.3.3 PARALLEL PORT MODE PARAMETERS..........................................................................129
12.3.4 EPP DATA OR ADDRESS READ CYCLE TIMING PARAMETERS..............................130
12.3.5 EPP DATA OR ADDRESS WRITE CYCLE TIMING PARAMETERS ............................131
12.3.6 PARALLEL PORT FIFO TIMING PARAMETERS..............................................................132
12.3.7 ECP PARALLEL PORT FORWARD TIMING PARAMETERS .........................................132
12.3.8 ECP PARALLEL PORT REVERSE TIMING PARAMETERS...........................................132
12.3.9 KBC TIMING PARAMETERS................................................................................................133
12.3.10 GPIO TIMING PARAMETERS................................................................................................134
13. TIMING WAVEFORMS..................................................................................................135
13.1 FDC............................................................................................................................................................135
13.2 UART/PARALLEL...................................................................................................................................136
13.2.1 MODEM CONTROL TIMING ................................................................................................137
13.3 PARALLEL PORT...................................................................................................................................138
13.3.1 PARALLEL PORT TIMING.....................................................................................................138
13.3.2 EPP DATA OR ADDRESS READ CYCLE (EPP VERSION 1.9)......................................139
13.3.3 EPP DATA OR ADDRESS WRITE CYCLE (EPP VERSION 1.9)....................................140
13.3.4 EPP DATA OR ADDRESS READ CYCLE (EPP VERSION 1.7)......................................141
13.3.5 EPP DATA OR ADDRESS WRITE CYCLE (EPP VERSION 1.7)....................................142
13.3.6 PARALLEL PORT FIFO TIMING...........................................................................................142
Publication Release Date: March 1998
- V - Revision 0.62

W83977TF
13.3.7 ECP PARALLEL PORT FORWARD TIMING......................................................................143
13.3.8 ECP PARALLEL PORT REVERSE TIMING........................................................................143
13.4 KBC............................................................................................................................................................144
13.4.1 WRITE CYCLE TIMING..........................................................................................................144
13.4.2 READ CYCLE TIMING...........................................................................................................144
13.4.3 SEND DATA TO K/B...............................................................................................................144
13.4.4 RECEIVE DATA FROM K/B ..................................................................................................145
13.4.5 INPUT CLOCK..........................................................................................................................145
13.4.6 SEND DATA TO MOUSE.......................................................................................................145
13.4.7 RECEIVE DATA FROM MOUSE..........................................................................................145
13.5 GPIO WRITE TIMING DIAGRAM.......................................................................................................146
13.6 MASTER RESET (MR) TIMING...........................................................................................................146
14. APPLICATION CIRCUITS.............................................................................................147
14.1 PARALLEL PORT EXTENSION FDD.................................................................................................147
14.2 PARALLEL PORT EXTENSION 2FDD...............................................................................................147
14.3 FOUR FDD MODE..................................................................................................................................148
15. ORDERING INFORMATION.........................................................................................148
16. HOW TO READ THE TOP MARKING .......................................................................148
17. PACKAGE DIMENSIONS...............................................................................................149
Publication Release Date: March 1998
- VI - Revision 0.62

W83977TF
SMI
SCI
WINBOND I/O
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The W83977TF is an evolving product from Winbond's most popular I/O chip W83877F --- which
integrates the disk drive adapter, serial port (UART), IrDA 1.0 SIR, parallel port, configurable plug-and-
play registers for the whole chip --- plus additional powerful features:
with PS/2 mouse support, 23 general purpose I/O ports, full 16-bit address decoding, OnNow keyboard
wake-up, OnNow mouse wake-up.
The disk drive adapter functions of W83977TF include a floppy disk drive controller compatible with the
industry standard 82077/ 765, data separator, write pre-compensation circuit, decode logic, data rate
selection, clock generator, drive interface control logic, and interrupt and DMA logic. The wide range of
functions integrated into the W83977TF greatly reduces the number of components required for
interfacing with floppy disk drives. The W83977TF supports four 360K, 720K, 1.2M, 1.44M, or 2.88M
disk drives and data transfer rates of 250 Kb/s, 300 Kb/s, 500 Kb/s,1 Mb/s, and 2 Mb/s.
The W83977TF provides two high-speed serial communication ports (UARTs), one of which supports
serial Infrared communication. Each UART includes a 16-byte send/receive FIFO, a programmable
baud rate generator, complete modem control capability, and a processor interrupt system. Both
UARTs provide legacy speed with baud rate up to 115.2k bps and also advanced speed with baud rates
230k, 460k
of
The W83977TF supports one PC-compatible printer port (SPP), Bi-directional Printer port (BPP) and
also Enhanced Parallel Port (EPP) and Extended Capabilities Port (ECP). Through the printer port
interface pins, also available are: Extension FDD Mode and Extension 2FDD Mode allowing one or two
external floppy disk drives to be connected.
The configuration registers support mode selection, function enable/disable, and power down function
selection. Furthermore, the configurable PnP features are compatible with the plug-and-play feature
demand of Windows 95TM, which makes system resource allocation more efficient than ever.
W83977TF provides functions that comply with
which includes support of legacy and ACPI power management through
W83977TF also has auto power management to reduce power consumption.
The keyboard controller is based on 8042 compatible instruction set with a 2K Byte programmable ROM
and a 256-Byte RAM bank. Keyboard BIOS firmware is available with optional AMIKEY
MultiKey/42TM, or customer code.
The W83977TF provides a set of flexible I/O control functions to the system designer through a set of
General Purpose I/O ports. These GPIO ports may serve as simple I/O or may be individually
configured to provide a predefined alternate function.
W83977TF is made to fully comply with
I/O space resource are flexible to adjust to meet ISA PnP requirement. Moreover W83977TF is made to
meet the specification of PC97's requirement in the power management:
Power Management).
Another benifit is that W83977TF has the same pin assignment as W83977AF, W83977F, W83977ATF.
This makes the design very flexible.
921k bps
, or
which support higher speed modems.
ACPI (Advanced Configuration and Power Interface
Microsoft PC97 Hardware Design Guide
ACPI
, 8042 keyboard controller
or
ACPI
function pins.
TM
. IRQs, DMAs, and
DPM
and
-
2, Phoenix
(Device
),
Publication Release Date: April 1998
-1- Preliminary Revision 0.62

W83977TF
SCI
PRELIMINARY
FEATURES
General
•
Plug & Play 1.0A compatible
• Support 13 IRQs, 4 DMA channels, full 16-bit address decoding
•
Capable of ISA Bus IRQ Sharing
•
Compliant with
•
Support
•
Report ACPI status interrupt by
• Programmable configuration settings
•
Single 24/48 Mhz clock input
FDC
•
Compatible with IBM PC AT disk drive systems
•
Variable write pre-compensation with track selectable capability
• Support vertical recording format
•
DMA enable logic
•
16-byte data FIFOs
•
Support floppy disk drives and tape drives
•
Detects all overrun and underrun conditions
•
Built-in address mark detection circuit to simplify the read electronics
•
FDD anti-virus functions with software write protect and FDD write enable signal (write data signal was
forced to be inactive)
•
Support up to four 3.5-inch or 5.25-inch floppy disk drives
•
Completely compatible with industry standard 82077
•
360K/720K/1.2M/1.44M/2.88M format; 250K, 300K, 500K, 1M, 2M bps data transfer rate
•
Support
Microsoft PC97
DPM
(Device Power Management),
3-mode FDD, and its Win95 driver
Hardware Design Guide
ACPI
signal issued from any of the 13 IQRs pins or GPIO xx
UART
•
Two high-speed 16550 compatible UARTs with 16-byte send/receive FIFOs
•
MIDI compatible
•
Fully programmable serial-interface characteristics:
--- 5, 6, 7 or 8-bit characters
--- Even, odd or no parity bit generation/detection
--- 1, 1.5 or 2 stop bits generation
•
Internal diagnostic capabilities:
--- Loop-back controls for communications link fault isolation
--- Break, parity, overrun, framing error simulation
•
Programmable baud generator allows division of 1.8461 Mhz and 24 Mhz by 1 to (216-1)
Maximum baud rate up to
-2- Revision 0.62
921k bps
for 14.769 Mhz and 1.5M bps for 24 Mhz
Publication Release Date: April 1998

W83977TF
PRELIMINARY
Infrared
•
Support IrDA version 1.0 SIR protocol with maximum baud rate up to 115.2K bps
•
Support SHARP ASK-IR protocol with maximum baud rate up to 57,600 bps
• Support S/W driver for Windows95TM and Windows98TM (MemphisTM)
Parallel Port
•
Compatible with IBM parallel port
•
Support PS/2 compatible bi-directional parallel port
•
Support Enhanced Parallel Port (EPP) − Compatible with IEEE 1284 specification
•
Support Extended Capabilities Port (ECP) − Compatible with IEEE 1284 specification
•
Extension FDD mode supports disk drive B; and Extension 2FDD mode supports disk drives A and B
through parallel port
•
Enhanced printer port back-drive current protection
Keyboard Controller
TM
•
8042 based with optional F/W from AMIKKEYTM-2, Phoenix MultiKey/42
with 2K bytes of programmable ROM, and 256 bytes of RAM
•
Asynchronous Access to Two Data Registers and One status Register
•
Software compatibility with the 8042 and PC87911 microcontrollers
•
Support PS/2 mouse
•
Support port 92
• Support both interrupt and polling modes
•
Fast Gate A20 and Hardware Keyboard Reset
•
8 Bit Timer/ Counter
•
Support binary and BCD arithmetic
• 6MHz, 8 MHz, 12 MHz, or 16 MHz operating frequency
or customer code
General Purpose I/O Ports
•
23 programmable general purpose I/O ports; 3 dedicate, 20 optional
•
General purpose I/O ports can serve as simple I/O ports, interrupt steering inputs, watching dog timer
output, power LED output, infrared I/O pins, general purpose address decoder, KBC control I/O pins
OnNow Funtions
•
Keyboard wake-up by programmable keys
•
Mouse wake-up by programmable buttons
Package
•
128-pin PQFP
Publication Release Date: April 1998
-3 - Revision 0.62
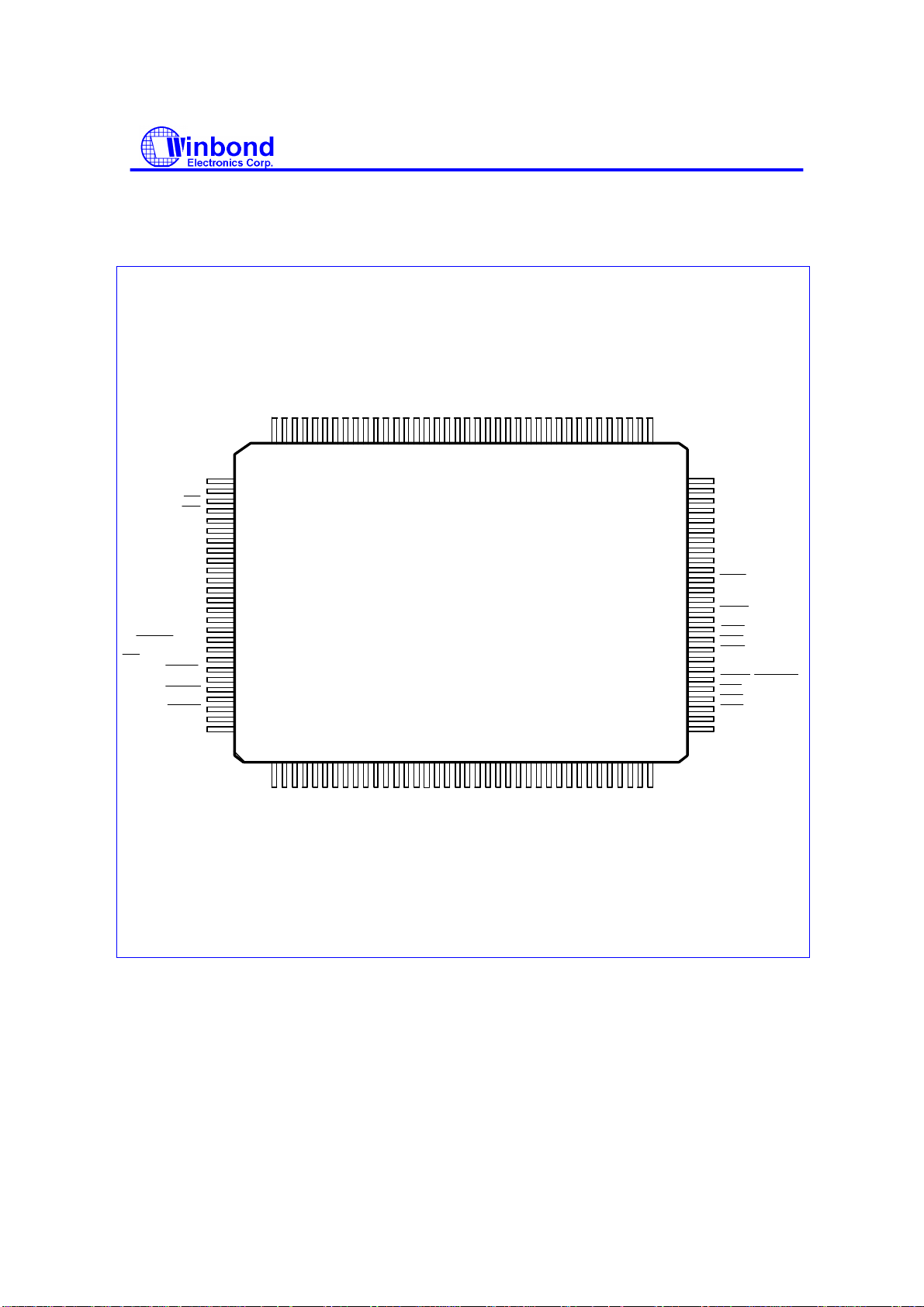
W83977TF
PIN CONFIGURATION
I
I
I
R
I
R
R
Q
R
Q
Q
1
Q
1
1
2
1
0
1
1
1
1
9
0
0
0
9
2
1
IRQ14/GP14
IRQ15/GP15
IOR
IOW
AEN
IOCHRDY
D0
D1
D2
D3
VCC
D7
DACK0/GP16
SCI/DRQ0/GP17
VSS
DACK1
DRQ1
DACK2
DRQ2
DACK3
DRQ3
TC
D4
D5
D6
MR
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
0
1 2 345
I
R
Q
3
989
I
R
Q
4
7
I
I
R
R
Q
Q
6
5
969
5949392
678 9
I
I
R
R
Q
Q
8
7
I
R
A
Q
1
9
5
9
1
1
0111213
A
A
V
1
1
S
3
4
S
9089888
1
415161718
PRELIMINARY
/
/
P
A
P
N
A
N
S
S
W
/
W
O
S
U
I
M
N
T
,
I
,
,
G
G
G
A
A
A
V
1
1
C
C
011
2
868
8
5
7
4
1
920
9
838
281807978
2
1
A
5
222
324252627
777
6
A1A2A3A4A6A7A8A
7
5
282
P
P
2
2
A
3
2
0
747
7
3
271
9303132
V
S
B
G
P
2
1
3
3
706
/
K
M
/
P
R
C
C
R
2
I
L
L
I
0
B
K
K
A
6
6
6
9
6
867
5
64
VBAT
63
XTAL1
62
VSS
61
XTAL2
MDATA
60
KDATA
59
KBLOCK/GP13
58
KBRST/GP12
57
56
GA20/GP11
VCC
55
54
DCDB
53
SOUTB/PEN48
52
SINB
51
DTRB
50
RTSB
49
DSRB
48
CTSB
47
DCDA
46
SOUTA/PENKBC
45
SINA
44
DTRA/PNPCSV
43
RTSA/HEFRAS
42
DSRA
41
CTSA
40
GP24
39
3
3
3
3
3
5
4
6
8
7
GP25
D
D
/
/
C
L
K
I
N
//
R
R
V
V
D
D
E
E
N
N
1
0
,
G
P
1
0
,
/
S
C
I
/
D
H
T
R
W
S
P
E
R
D
K
A
A
A
C
D
K
T
H
0
A
G
/
/
/
/
/
/
M
D
S
W
W
D
O
I
T
E
D
S
B
E
R
A
P
P
/
/
S
/
I
M
L
D
N
O
C
S
D
A
T
B
E
X
P
/
P
V
B
E
C
U
C
S
Y
P
V
D
D
A
D
S
7
C
6
S 5
K
P
P
/
P
P
P
D
D
S
D
D
D
0
1
L
2
3
4
I
N
I
/
I
N
I
T
I
/
/
/
R
A
E
R
S
T
F
T
R
R
X
D
B
R
X
Publication Release Date: April 1998
-4- Revision 0.62
W83977TF
IOR
IOW
1. PIN DESCRIPTION
Note: Please refer to Section 11.2 DC CHARACTERISTICS for details.
I/O6t - TTL level bi-directional pin with 6 mA source-sink capability
I/O8t - TTL level bi-directional pin with 8 mA source-sink capability
I/O8 - CMOS level bi-directional pin with 8 mA source-sink capability
I/O
- TTL level bi-directional pin with 12 mA source-sink capability
12t
I/O12 - CMOS level bi-directional pin with 12 mA source-sink capability
I/O
- CMOS level bi-directional pin with 16 mA source-sink capability with internal pull-up resistor
16u
I/OD
- CMOS level bi-directional pin open drain output with 16 mA sink capability with internal pull-up resistor
16u
I/O
- TTL level bi-directional pin with 24 mA source-sink capability
24t
OUT8t - TTL level output pin with 8 mA source-sink capability
OUT
- TTL level output pin with 12 mA source-sink capability
12t
OD12 - Open-drain output pin with 12 mA sink capability
OD24 - Open-drain output pin with 24 mA sink capability
INt - TTL level input pin
INc - CMOS level input pin
INcu - CMOS level input pin with internal pull-up resitor
INcs - CMOS level Schmitt-triggered input pin
INts - TTL level Schmitt-triggered input pin
IN
- TTL level Schmitt-triggered input pin with internal pull-up resistor
tsu
PRELIMINARY
1.1 Host Interface
SYMBOL PIN I/O FUNCTION
I/O
I/O
IN
IN
System address bus bits 0-10
t
System address bus bits 11-14
t
System address bus bit 15
t
System data bus bits 0-5
12t
System data bus bits 6-7
12t
CPU I/O read signal
ts
CPU I/O write signal
ts
System address bus enable
ts
In EPP Mode, this pin is the IO Channel Ready output to extend
24
the host read/write cycle.
Master Reset; Active high; MR is low during normal operations.
ts
Publication Release Date: April 1998
A0−A10
A11-A14 86-89
A15 91 IN
D0−D5
74-84
109-
114
D6−D7
116-
117
105 IN
106 IN
AEN 107 IN
IOCHRDY 108 OD
MR 118 IN
-5 - Revision 0.62
W83977TF
DACK0
SCI
DACK1
DACK2
DACK3
1.1 Host Interface, continued
SYMBOL PIN I/O FUNCTION
I/O
OUT
DMA Channel 0 Acknowledge signal. (CR2C bit 5_4 = 00, default)
tsu
General purpose I/O port 1bit 6. (CR2C bit 5_4 = 01)
12t
Alternate function from GP16: Watch dog timer output
KBC P15 I/O port. (CR2C bit 5_4 = 10)
12t
DMA Channel 0 request signal. (CR2C bit 7_6 = 00, default)
12t
General purpose I/O port 1bit 7. (CR2C bit 7_6 = 01)
12t
Alternate Function from GP17: Power LED output.
KBC P14 I/O port (CR2C bit 7_6 = 10)
12t
System Control Interrupt (CR2C bit 7_6 = 11)
12t
DMA Channel 1 Acknowledge signal
ts
DMA Channel 1 request signal
12t
DMA Channel 2 Acknowledge signal
ts
DMA Channel 2 request signal
12t
DMA Channel 3 Acknowledge signal
ts
DMA Channel 3 request signal
12t
Terminal Count. When active, this pin indicates termination of a
ts
119 IN
I/O
I/O
121 OUT
I/O
122 IN
GP16
(WDTO)
P15
DRQ0
GP17
(PLEDO)
P14
DRQ1 123 OUT
124 IN
DRQ2 125 OUT
126 IN
DRQ3 127 OUT
TC 128 IN
DMA transfer.
IRQ1 99 OUT
IRQ3 98 OUT
IRQ4 97 OUT
IRQ5 96 OUT
IRQ6 95 OUT
IRQ7 94 OUT
IRQ8 93 OUT
IRQ9 92 OUT
IRQ10 100 OUT
IRQ11 101 OUT
IRQ12 102 OUT
Interrupt request 1
12t
Interrupt request 3
12t
Interrupt request 4
12t
Interrupt request 5
12t
Interrupt request 6
12t
Interrupt request 7
12t
Interrupt request 8
12t
Interrupt request 9
12t
Interrupt request 10
12t
Interrupt request 11
12t
Interrupt request 12
12t
PRELIMINARY
Publication Release Date: April 1998
-6- Revision 0.62
W83977TF
GPACS
GPAWE
SMI
SMI
SCI
PANSWOUT
PANSWIN
1.1 Host Interface, continued
SYMBOL PIN I/O FUNCTION
IRQ14 103 OUT
GP14 I/O
(
)
Alternate Function 1 from GP14: General purpose address
Interrupt request 14. (CR2C bit 1_0 = 00, default)
12t
General purpose I/O port 1 bit 4. (CR2C bit 1_0 = 01)
12t
decode output.
(P17)
PLEDO OUT
IRQ15
GP15
(
)
(P12)
WDT
CLKIN 1 IN
Alternate Function 2 from GP14: KBC P17 I/O port.
Power LED output. (CR2C bit 1_0 = 10)
12t
104 OUT
I/O
Interrupt request 15.(CR2C bit 3_2 = 00, default)
12t
General purpose I/O port 1 bit 5. (CR2C bit 3_2 = 01)
12t
Alternate Function 1 from GP15: General purpose address write
enable output.
Alternate Function 2 from GP15: KBC P12 I/O port.
OUT
Watch-Dog timer output. (CR2C bit 3_2 = 10)
12t
24 or 48 MHz clock input, selectable through bit 5 of CR24.
t
1.2 General Purpose I/O Port
SYMBOL PIN I/O FUNCTION
GP20
(KBRST)
GP21
69 I/O
70 OUT
I/O
(P13) Alternate Function from GP21: KBC P13 I/O port.
P16
I/O
72 OUT
GP22
(P14)
GP23
(P15)
Alternate Function from GP22: KBC P14 I/O port.
73 IN
Alternate Function from GP23: KBC P15 I/O port
GP24 40 I/O
(P16) Alternate Function from GP24: KBC P16 I/O port
P13
GP25
(GA20)
39 I/O
Alternate Function from GP25: GATE A20 (KBC P21)
I/O
I/O
I/O
General purpose I/O port 2 bit 0.
12t
Alternate Function from GP20: Keyboard reset (KBC P20)
12t
For the power management, the
is active low by the power
management events, that generate and
(CR2B bit 4_3 = 00, default)
General purpose I/O port 2 bit 1. (CR2B bit 4_3 = 01)
12t
KBC P16 I/O port. (CR2B bit 4_3 = 10)
12t
Panel Switch output. (CR2B bit 5 = 0, default)
12t
General purpose I/O port 2 bit 2. (CR2B bit 5 = 1)
12t
Panel Switch input. (CR2B bit 7_6 = 00, default)
12t
General purpose I/O port 2 bit 3. (CR2B bit 7_6 = 01)
12t
General purpose I/O port 2 bit 4 (CR2A bit 5_4 = 01)
12t
KBC P13 I/O port. (CR2A bit 5_4 = 10)
12t
General purpose I/O port 2 bit 5.
12
in ACPI mode.
PRELIMINARY
Publication Release Date: April 1998
-7 - Revision 0.62
W83977TF
CTSA
CTSB
DSRA
DSRB
RTSA
RTSB
DTRA
PNPCSV
PNPCSV
PNPCSV
DTRB
DCDA
DCDB
1.3 Serial Port Interface
SYMBOL PIN I/O FUNCTION
HEFRAS
41
48
42
49
43
During power-on reset, this pin is pulled down internally and is
50
44
IN
IN
I/O
I/O
I/O
Clear To Send is the modem control input.
t
The function of these pins can be tested by reading Bit 4 of the
handshake status register.
Data Set Ready. An active low signal indicates the modem or data
t
set is ready to establish a communication link and transfer data to
the UART.
UART A Request To Send. An active low signal informs the
8t
modem or data set that the controller is ready to send data.
defined as HEFRAS, which provides the power-on value for CR26
bit 6 (HEFRAS). A 4.7 kΩ is recommended if intends to pull up.
(select 370H as configuration I/O port′s address)
UART B Request To Send. An active low signal informs the
8t
modem or data set that the controller is ready to send data.
UART A Data Terminal Ready. An active low signal informs the
8t
modem or data set that the controller is ready to communicate.
During power-on reset, this pin is pulled down internally and is
defined as
bit 0 (
, which provides the power-on value for CR24
). A 4.7 kΩ is recommended if intends to pull up.
(clear the default value of FDC, UARTs, and PRT)
PRELIMINARY
51
SINA
SINB
SOUTA
45, 52
46
PENKBC
I/O
IN
I/O
UART B Data Terminal Ready. An active low signal informs the
8t
modem or data set that controller is ready to communicate.
Serial Input. Used to receive serial data through the
t
communication link.
UART A Serial Output. Used to transmit serial data out to the
8t
communication link.
During power-on reset, this pin is pulled down internally and is
defined as PENKBC, which provides the power-on value for CR24
bit 2 (ENKBC). A 4.7 kΩ resistor is recommended if intends to pull
up. (enable KBC)
SOUTB
PEN48
53
I/O
UART B Serial Output. During power-on reset, this pin is pulled
8t
down internally and is defined as PEN48, which provides the
power-on value for CR24 bit 6 (EN48). A 4.7 kΩ resistor is
recommended if intends to pull up.
47
54
IN
Data Carrier Detect. An active low signal indicates the modem or
t
data set has detected a data carrier.
Publication Release Date: April 1998
-8- Revision 0.62
W83977TF
RIA RIB
WE2
WE2
WD2
WD
WD2
PRELIMINARY
1.3 Serial Port Interface, continued
SYMBOL PIN I/O FUNCTION
65
66
IN
Ring Indicator. An active low signal indicates that a ring signal is
t
being received from the modem or data set.
1.4 Infrared Interface
SYMBOL PIN I/O FUNCTION
IRRX 37 IN
IRTX 38 OUT
Infrared Receiver input.
cs
Infrared Transmitter Output.
12t
1.5 Multi-Mode Parallel Port
The following pins have alternate functions, which are controlled by CR28 and L3-CRF0.
SYMBOL PIN I/O FUNCTION
PRINTER MODE: SLCT
SLCT 18 IN
OD
OD
PE
19 IN
OD
OD
t
An active high input on this pin indicates that the printer is selected.
This pin is pulled high internally. Refer to description of the
parallel port for definition of this pin in ECP and EPP mode.
EXTENSION FDD MODE:
12
This pin is for Extension FDD B; its function is the same as the WE
pin of FDC.
EXTENSION 2FDD MODE:
12
This pin is for Extension FDD A and B; it function is the same as
the WE pin of FDC.
PRINTER MODE: PE
t
An active high input on this pin indicates that the printer has
detected the end of the paper. This pin is pulled high internally.
Refer to description of the parallel port for definition of this pin in
ECP and EPP mode.
12
EXTENSION FDD MODE:
This pin is for Extension FDD B; its function is the same as the
12
pin of FDC.
EXTENSION 2FDD MODE:
This pin is for Extension FDD A and B; its function is the same as
the WD pin of FDC.
Publication Release Date: April 1998
-9 - Revision 0.62
W83977TF
MOB2
MOB
MOB2
MOB
ACK
ACK
DSB2
DSB
DSB2
DSB
ERR
ERR
HEAD
2
HEAD
HEAD
2
HEAD
1.5 Multi-Mode Parallel Port, continued
SYMBOL PIN I/O FUNCTION
BUSY
21 IN
22 IN
34
PRINTER MODE: BUSY
t
OD
OD
OD
OD
IN
OD
OD
An active high input indicates that the printer is not ready to receive
data. This pin is pulled high internally. Refer to description of the
parallel port for definition of this pin in ECP and EPP mode.
EXTENSION FDD MODE:
12
This pin is for Extension FDD B; the function of this pin is the same
as the
12
EXTENSION 2FDD MODE:
pin of FDC.
This pin is for Extension FDD A and B; the function of this pin is the
same as the
t
PRINTER MODE:
pin of FDC.
An active low input on this pin indicates that the printer has
received data and is ready to accept more data. This pin is pulled
high internally. Refer to description of the parallel port for
definition of this pin in ECP and EPP mode.
EXTENSION FDD MODE:
12
This pin is for the Extension FDD B; its functions is the same as the
pin of FDC.
EXTENSION 2FDD MODE:
12
This pin is for Extension FDD A and B; it functions is the same as
the
t
PRINTER MODE:
pin of FDC.
An active low input on this pin indicates that the printer has
encountered an error condition. This pin is pulled high internally.
Refer to description of the parallel port for definition of this pin in
ECP and EPP mode.
EXTENSION FDD MODE:
12
This pin is for Extension FDD B; its function is the same as the
12
pin of FDC.
EXTENSION 2FDD MODE:
This pin is for Extension FDD A and B; its function is the same as
the
pin of FDC.
PRELIMINARY
Publication Release Date: April 1998
-10- Revision 0.62
W83977TF
SLIN
SLIN
STEP
2
STEP
STEP
2
STEP
INIT
INIT
DIR2
DIR
DIR2
DIR
AFD
AFD
1.5 Multi-Mode Parallel Port, continued
SYMBOL PIN I/O FUNCTION
32 OD
33 OD
35 OD
12
PRINTER MODE:
Output line for detection of printer selection. This pin is pulled high
OD
OD
OD
OD
OD
OD
internally. Refer to description of the parallel port for definition of
this pin in ECP and EPP mode.
EXTENSION FDD MODE:
12
This pin is for Extension FDD B; its function is the same as the
pin of FDC.
EXTENSION 2FDD MODE:
12
This pin is for Extension FDD A and B; its function is the same as
the
12
PRINTER MODE:
pin of FDC.
Output line for the printer initialization. This pin is pulled high
internally. Refer to description of the parallel port for definition of
this pin in ECP and EPP mode.
EXTENSION FDD MODE:
12
This pin is for Extension FDD B; its function is the same as the
pin of FDC.
EXTENSION 2FDD MODE:
12
This pin is for Extension FDD A and B; its function is the same as
the
12
PRINTER MODE:
pin of FDC.
An active low output from this pin causes the printer to auto feed a
line after a line is printed. This pin is pulled high internally. Refer
to description of the parallel port for definition of this pin in ECP and
EPP mode.
EXTENSION FDD MODE: DRVDEN0
12
This pin is for Extension FDD B; its function is the same as the
DRVDEN0 pin of FDC.
EXTENSION 2FDD MODE: DRVDEN0
12
This pin is for Extension FDD A and B; its function is the same as
the DRVDEN0 pin of FDC.
PRELIMINARY
Publication Release Date: April 1998
-11 - Revision 0.62
W83977TF
STB
STB
INDEX
2
INDEX
INDEX
2
INDEX
TRAK
02
TRAK
0
TRAK
02
TRAK
0
WP2
WP2
1.5 Multi-Mode Parallel Port, continued
SYMBOL PIN I/O FUNCTION
36 OD
12
PRINTER MODE:
An active low output is used to latch the parallel data into the
printer. This pin is pulled high internally. Refer to description of the
parallel port for definition of this pin in ECP and EPP mode.
PD0
31 I/O
- EXTENSION FDD MODE: This pin is a tri-state output.
- EXTENSION 2FDD MODE: This pin is a tri-state output.
PRINTER MODE: PD0
24t
Parallel port data bus bit 0. Refer to description of the parallel port
for definition of this pin in ECP and EPP mode.
IN
IN
t
EXTENSION FDD MODE:
This pin is for Extension FDD B; the function of this pin is the same
as the
t
EXTENSION 2FDD MODE:
pin of FDC. It is pulled high internally.
This pin is for Extension FDD A and B; the function of this pin is the
PD1
same as the
30 I/O
PRINTER MODE: PD1
24t
IN
IN
Parallel port data bus bit 1. Refer to description of the parallel port
for definition of this pin in ECP and EPP mode.
EXTENSION FDD MODE:
t
This pin is for Extension FDD B; the function of this pin is the same
as the
EXTENSION. 2FDD MODE:
t
pin of FDC. It is pulled high internally.
pin of FDC. It is pulled high internally.
This pin is for Extension FDD A and B; the function of this pin is the
PD2
same as the
29 I/O
PRINTER MODE: PD2
24t
IN
IN
Parallel port data bus bit 2. Refer to description of the parallel port
for definition of this pin in ECP and EPP mode.
EXTENSION FDD MODE:
t
This pin is for Extension FDD B; the function of this pin is the same
as the WP pin of FDC. It is pulled high internally.
EXTENSION. 2FDD MODE:
t
pin of FDC. It is pulled high internally.
This pin is for Extension FDD A and B; the function of this pin is the
same as the WP pin of FDC. It is pulled high internally.
PRELIMINARY
Publication Release Date: April 1998
-12- Revision 0.62

W83977TF
RDATA
2
RDATA
RDATA
2
RDATA
DSKCHG
2
DSKCHG
DSKCHG
2
DSKCHG
MOA2
MOA
1.5 Multi-Mode Parallel Port, continued
SYMBOL PIN I/O FUNCTION
PD3
28 I/O
IN
IN
24t
PRINTER MODE: PD3
Parallel port data bus bit 3. Refer to description of the parallel port
for definition of this pin in ECP and EPP mode.
t
EXTENSION FDD MODE:
This pin is for Extension FDD B; the function of this pin is the same
as the
t
EXTENSION 2FDD MODE:
pin of FDC. It is pulled high internally.
This pin is for Extension FDD A and B; this function of this pin is the
PD4
same as the
27 I/O
IN
IN
24t
PRINTER MODE: PD4
Parallel port data bus bit 4. Refer to description of the parallel port
for definition of this pin in ECP and EPP mode.
EXTENSION FDD MODE:
t
This pin is for Extension FDD B; the function of this pin is the same
as the
EXTENSION 2FDD MODE:
t
pin of FDC. It is pulled high internally.
pin of FDC. It is pulled high internally.
This pin is for Extension FDD A and B; this function of this pin is the
PD5
PD6
same as the
26 I/O
24 I/O
OD
-
-
-
PRINTER MODE: PD5
24t
Parallel port data bus bit 5. Refer to description of the parallel port
for definition of this pin in ECP and EPP mode.
EXTENSION FDD MODE: This pin is a tri-state output.
EXTENSION 2FDD MODE: This pin is a tri-state output.
PRINTER MODE: PD6
24t
Parallel port data bus bit 6. Refer to description of the parallel port
for definition of this pin in ECP and EPP mode.
EXTENSION FDD MODE: This pin is a tri-state output.
EXTENSION. 2FDD MODE:
24
This pin is for Extension FDD A; its function is the same as the
pin of FDC. It is pulled high internally.
pin of FDC.
PRELIMINARY
Publication Release Date: April 1998
-13 - Revision 0.62
W83977TF
DSA2
DSA
SCI
HEAD
WE
WD
STEP
DIR
MOB
DSA
DSB
1.5 Multi-Mode Parallel Port, continued
SYMBOL PIN I/O FUNCTION
PD7
23 I/O
OD
PRINTER MODE: PD7
24t
Parallel port data bus bit 7. Refer to description of the parallel port
for definition of this pin in ECP and EPP mode.
EXTENSION FDD MODE: This pin is a tri-state output.
EXTENSION 2FDD MODE:
24
This pin is for Extension FDD A; its function is the same as the
pin of FDC.
1.6 FDC Interface
SYMBOL PIN I/O FUNCTION
DRVDEN0 2 OD
DRVDEN1
GP10
(IRQIN1)
P12
3 OD
IO
Alternate Function from GP10: Interrupt channel input.
IO
OUT
5 OD
9 OD
10 OD
11 OD
12 OD
13 OD
14 OD
15 OD
Drive Density Select bit 0.
24
Drive Density Select bit 1. (CR2A bit 1_0 = 00, default)
24
General purpose I/O port 1 bit 0. (CR2A bit 1_0 = 01)
24t
KBC P12 I/O port. (CR2A bit 1_0 = 10)
24t
System Control Interrupt (CR2A bit 1_0 = 11)
12t
Head select. This open drain output determines which disk drive
24
head is active.
Logic 1 = side 0
Logic 0 = side 1
Write enable. An open drain output.
24
Write data. This logic low open drain writes pre-compensation
24
serial data to the selected FDD. An open drain output.
Step output pulses. This active low open drain output produces a
24
pulse to move the head to another track.
Direction of the head step motor. An open drain output.
24
Logic 1 = outward motion
Logic 0 = inward motion
Motor B On. When set to 0, this pin enables disk drive 1. This is
24
an open drain output.
Drive Select A. When set to 0, this pin enables disk drive A. This
24
is an open drain output.
Drive Select B. When set to 0, this pin enables disk drive B. This
24
is an open drain output.
PRELIMINARY
Publication Release Date: April 1998
-14- Revision 0.62
W83977TF
MOA
DSKCHG
RDATA
WP
TRAK0
INDEX
1.6 FDC Interface, continued
SYMBOL PIN I/O FUNCTION
Motor A On. When set to 0, this pin enables disk drive 0. This is
24
an open drain output.
Diskette change. This signal is active low at power on and
cs
whenever the diskette is removed. This input pin is pulled up
16 OD
4 IN
internally by a 1 KΩ resistor. The resistor can be disabled by bit 7
of L0-CRF0 (FIPURDWN).
6 IN
The read data input signal from the FDD. This input pin is pulled
cs
up internally by a 1 KΩ resistor. The resistor can be disabled by
bit 7 of L0-CRF0 (FIPURDWN).
7 IN
Write protected. This active low Schmitt input from the disk drive
cs
indicates that the diskette is write-protected. This input pin is
pulled up internally by a 1 KΩ resistor. The resistor can be
disabled by bit 7 of L0-CRF0 (FIPURDWN).
8 IN
Track 0. This Schmitt-triggered input from the disk drive is active
cs
low when the head is positioned over the outermost track. This
input pin is pulled up internally by a 1 KΩ resistor. The resistor
can be disabled by bit 7 of L0-CRF0 (FIPURDWN).
17 IN
This Schmitt-triggered input from the disk drive is active low when
cs
the head is positioned over the beginning of a track marked by an
index hole. This input pin is pulled up internally by a 1 KΩ resistor.
The resistor can be disabled by bit 7 of L0-CRF0 (FIPURDWN).
PRELIMINARY
1.7 KBC Interface
SYMBOL PIN I/O FUNCTION
KDATA 59 I/OD
MDATA 60 I/OD
KCLK 67 I/OD
MCLK 68 I/OD
GA20 56 I/O
GP11 I/O
(IRQIN2) Alternate Function from GP11: Interrupt channel input.
KBRST 57 I/O
GP12 I/O
(WDTO) Alternate Function 1 from GP12 : Watchdog timer output.
Keyboard Data
16u
PS2 Mouse Data
16u
Keyboard Clock
16u
PS2 Mouse Clock
16u
KBC GATE A20 (P21) Output. (CR2A bit 6 = 0, default)
12t
General purpose I/O port 1 bit 1. (CR2A bit 6 = 1)
12t
W83C45 Keyboard Reset (P20) Output. (CR2A bit 7 = 0, default)
12t
General purpose I/O port 1 bit 2. (CR2A bit 7 = 1)
12t
Publication Release Date: April 1998
-15 - Revision 0.62
W83977TF
1.7 KBC Interface, continued
SYMBOL PIN I/O FUNCTION
KBLOCK 58 IN
GP13 I/O
W83C45 KINH (P17) Input. (CR2B bit 0 = 0, default)
ts
General purpose I/O port 1 bit 3. (CR2B bit 0 = 1)
16t
1.8 POWER PINS
SYMBOL PIN FUNCTION
VCC 20, 55, 85,
115
VSB 71 +5V stand-by power supply for the digital circuitry
GND 25, 62, 90,
120
+5V power supply for the digital circuitry
Ground
1.9 ACPI Interface
SYMBOL PIN I/O FUNCTION
VBAT 64 NA
XTAL1 63 IN
XTAL2 61 O
battery voltage input
32.768Khz Clock Input
C
32.768Khz Clock Output
8t
PRELIMINARY
Publication Release Date: April 1998
-16- Revision 0.62
W83977TF
PRELIMINARY
2. FDC FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
2.1 W83977TF FDC
The floppy disk controller of the W83977TF integrates all of the logic required for floppy disk control.
The FDC implements a PC/AT or PS/2 solution. All programmable options default to compatible
values. The FIFO provides better system performance in multi-master systems. The digital data
separator supports up to 2 M bits/sec data rate.
The FDC includes the following blocks: AT interface, Precompensation, Data Rate Selection, Digital
Data Separator, FIFO, and FDC Core.
2.1.1 AT interface
The interface consists of the standard asynchronous signals: RD, WR, A0-A3, IRQ, DMA control, and
a data bus. The address lines select between the configuration registers, the FIFO and control/status
registers. This interface can be switched between PC/AT, Model 30, or PS/2 normal modes. The PS/2
register sets are a superset of the registers found in a PC/AT.
2.1.2 FIFO (Data)
The FIFO is 16 bytes in size and has programmable threshold values. All command parameter
information and disk data transfers go through the FIFO. Data transfers are governed by the RQM and
DIO bits in the Main Status Register.
The FIFO defaults to disabled mode after any form of reset. This maintains PC/AT hardware
compatibility. The default values can be changed through the CONFIGURE command. The advantage
of the FIFO is that it allows the system a larger DMA latency without causing disk errors. The following
tables give several examples of the delays with a FIFO. The data are based upon the following formula:
THRESHOLD # × (1/DATA/RATE) *8 - 1.5 µS = DELAY
FIFO THRESHOLD MAXIMUM DELAY TO SERVICING AT 500K BPS
1 Byte
2 Byte
8 Byte
15 Byte
FIFO THRESHOLD MAXIMUM DELAY TO SERVICING AT 1M BPS
Data Rate
1 Byte
2 Byte
8 Byte
15 Byte
-17 - Revision 0.62
Data Rate
1 × 16 µS - 1.5 µS = 14.5 µS
2 × 16 µS - 1.5 µS = 30.5 µS
8 × 16 µS - 1.5 µS = 6.5 µS
15 × 16 µS - 1.5 µS = 238.5 µS
1 × 8 µS - 1.5 µS = 6.5 µS
2 × 8 µS - 1.5 µS = 14.5 µS
8 × 8 µS - 1.5 µS = 62.5 µS
15 × 8 µS - 1.5 µS = 118.5 µS
Publication Release Date: April 1998

W83977TF
DACK
DACK
PRELIMINARY
At the start of a command the FIFO is always disabled and command parameters must be sent based
upon the RQM and DIO bit settings in the main status register. When the FDC enters the command
execution phase, it clears the FIFO of any data to ensure that invalid data are not transferred.
An overrun and underrun will terminate the current command and the data transfer. Disk writes will
complete the current sector by generating a 00 pattern and valid CRC. Reads require the host to
remove the remaining data so that the result phase may be entered.
DMA transfers are enabled with the SPECIFY command and are initiated by the FDC by activating the
DRQ pin during a data transfer command. The FIFO is enabled directly by asserting
addresses need not be valid.
Note that if the DMA controller is programmed to function in verify mode a pseudo read is performed by
the FDC based only on
mode (FIFO disabled) and is programmed to do a read. With the FIFO enabled the above operation is
performed by using the new VERIFY command. No DMA operation is needed.
2.1.3 Data Separator
The function of the data separator is to lock onto the incoming serial read data. When a lock is achieved
the serial front end logic of the chip is provided with a clock which is synchronized to the read data. The
synchronized clock, called the Data Window, is used to internally sample the serial data portion of the
bit cell, and the alternate state samples the clock portion. Serial to parallel conversion logic separates
the read data into clock and data bytes.
The Digital Data Separator (DDS) has three parts: control logic, error adjustment, and speed tracking.
The DDS circuit cycles once every 12 clock cycles ideally. Any data pulse input will be synchronized and
then adjusted by immediate error adjustment. The control logic will generate RDD and RWD for every
pulse input. During any cycle where no data pulse is present, the DDS cycles are based on speed. A
digital integrator is used to keep track of the speed changes in the input data stream.
. This mode is only available when the FDC has been configured into byte
and
2.1.4 Write Precompensation
The write precompensation logic is used to minimize bit shifts in the RDDATA stream from the disk
drive. Shifting of bits is a known phenomenon in magnetic media and is dependent on the disk media
and the floppy drive.
The FDC monitors the bit stream that is being sent to the drive. The data patterns that require
precompensation are well known. Depending upon the pattern, the bit is shifted either early or late
relative to the surrounding bits.
2.1.5 Perpendicular Recording Mode
The FDC is also capable of interfacing directly to perpendicular recording floppy drives. Perpendicular
recording differs from the traditional longitudinal method in that the magnetic bits are oriented vertically.
This scheme packs more data bits into the same area.
FDCs with perpendicular recording drives can read standard 3.5" floppy disks and can read and write
perpendicular media. Some manufacturers offer drives that can read and write standard and
perpendicular media in a perpendicular media drive.
A single command puts the FDC into perpendicular mode. All other commands operate as they
normally do. The perpendicular mode requires a 1 Mbps data rate for the FDC. At this data rate the
FIFO eases the host interface bottleneck due to the speed of data transfer to or from the disk.
Publication Release Date: April 1998
-18- Revision 0.62

W83977TF
PRELIMINARY
2.1.6 FDC Core
The W83977TF FDC is capable of performing twenty commands. Each command is initiated by a multibyte transfer from the microprocessor. The result can also be a multi-byte transfer back to the
microprocessor. Each command consists of three phases: command, execution, and result.
Command
The microprocessor issues all required information to the controller to perform a specific operation.
Execution
The controller performs the specified operation.
Result
After the operation is completed, status information and other housekeeping information is provided to
the microprocessor.
2.1.7 FDC Commands
Command Symbol Descriptions:
C: Cylinder number 0 - 256
D: Data Pattern
DIR: Step Direction
DIR = 0, step out
DIR = 1, step in
DS0: Disk Drive Select 0
DS1: Disk Drive Select 1
DTL: Data Length
EC: Enable Count
EOT: End of Track
EFIFO: Enable FIFO
EIS: Enable Implied Seek
EOT: End of track
FIFOTHR: FIFO Threshold
GAP: Gap length selection
GPL: Gap Length
H: Head number
HDS: Head number select
HLT: Head Load Time
HUT: Head Unload Time
LOCK: Lock EFIFO, FIFOTHR, PTRTRK bits prevent affected by software reset
MFM: MFM or FM Mode
MT: Multitrack
N: The number of data bytes written in a sector
NCN: New Cylinder Number
ND: Non-DMA Mode
OW: Overwritten
PCN: Present Cylinder Number
POLL: Polling Disable
PRETRK: Precompensation Start Track Number
Publication Release Date: April 1998
-19 - Revision 0.62
W83977TF
W
W
PRELIMINARY
R: Record
RCN: Relative Cylinder Number
R/W: Read/Write
SC: Sector/per cylinder
SK: Skip deleted data address mark
SRT: Step Rate Time
ST0: Status Register 0
ST1: Status Register 1
ST2: Status Register 2
ST3: Status Register 3
WG: Write gate alters timing of WE
(1) Read Data
PHASE R/W D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 REMARKS
Command W MT MFM SK 0 0 1 1 0 Command codes
W
W
W
Execution Data transfer between the
Result R
R
W 0 0 0 0 0 HDS DS1 DS0
W
W
R
R
R
R
R
---------------------- C ------------------------
---------------------- H ------------------------
---------------------- R ------------------------
---------------------- N ------------------------
-------------------- EOT -----------------------
-------------------- GPL -----------------------
-------------------- DTL -----------------------
-------------------- ST0 -----------------------
-------------------- ST1 -----------------------
-------------------- ST2 -----------------------
---------------------- C ------------------------
---------------------- H ------------------------
---------------------- R ------------------------
---------------------- N ------------------------
Sector ID information prior
to command execution
FDD and system
Status information after
command execution
Sector ID information after
command execution
Publication Release Date: April 1998
-20- Revision 0.62
W83977TF
W
W
W
PRELIMINARY
(2) Read Deleted Data
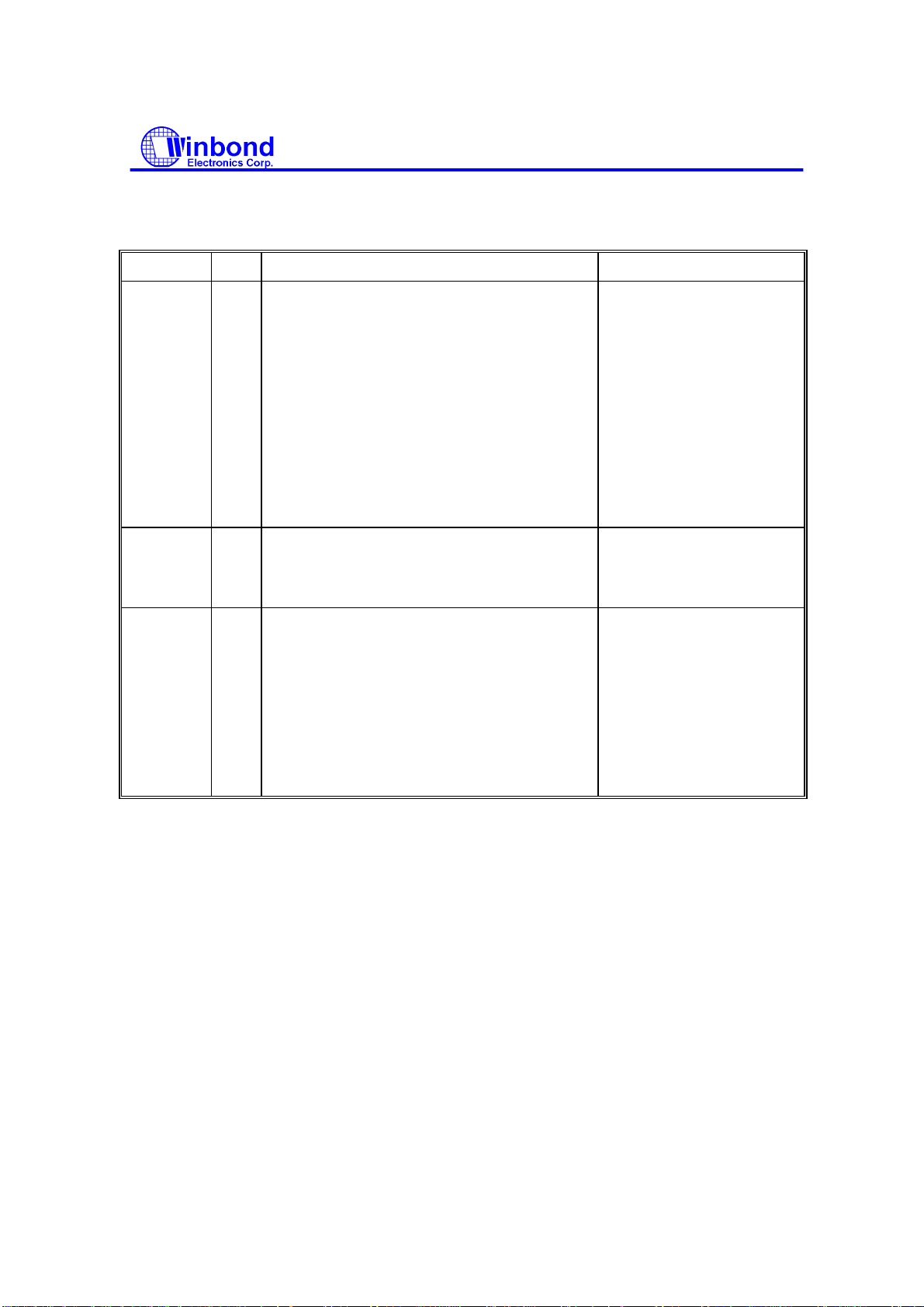
PHASE R/W D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 REMARKS
Command W MT MFM SK 0 1 1 0 0 Command codes
W
W
Execution Data transfer between the
Result R
W 0 0 0 0 0 HDS DS1 DS0
---------------------- C ------------------------
W
W
R
---------------------- H ------------------------
---------------------- R ------------------------
---------------------- N ------------------------
-------------------- EOT -----------------------
-------------------- GPL -----------------------
-------------------- DTL -----------------------
-------------------- ST0 -----------------------
-------------------- ST1 -----------------------
Sector ID information prior
to command execution
FDD and system
Status information after
command execution
R
R
R
R
R
-------------------- ST2 -----------------------
---------------------- C ------------------------
---------------------- H ------------------------
---------------------- R ------------------------
---------------------- N ------------------------
Sector ID information after
command execution
Publication Release Date: April 1998
-21 - Revision 0.62
W83977TF
W
W
PRELIMINARY
(3) Read A Track
PHASE R/W D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 REMARKS
Command W 0 MFM 0 0 0 0 1 0 Command codes
W 0 0 0 0 0 HDS DS1 DS0
W
W
W
W
W
Execution
Result R
R
---------------------- C ------------------------
---------------------- H ------------------------
---------------------- R ------------------------
---------------------- N ------------------------
-------------------- EOT -----------------------
-------------------- GPL -----------------------
-------------------- DTL -----------------------
Data transfer between the
-------------------- ST0 -----------------------
-------------------- ST1 -----------------------
Sector ID information prior to
command execution
FDD and system; FDD reads
contents of all cylinders from
index hole to EOT
Status information after
command execution
R
R
R
R
R
-------------------- ST2 -----------------------
---------------------- C ------------------------
---------------------- H ------------------------
---------------------- R ------------------------
---------------------- N ------------------------
Sector ID information after
command execution
Publication Release Date: April 1998
-22- Revision 0.62
 Loading...
Loading...