Winbond Electronics W83787IF Datasheet

W83787IF
WINBOND I/O WITH SERIAL-INFRARED SUPPORT
PRELIMINARY
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The W83787IF is a derivative product of W83787F with one of UARTs support HPSIR and ASKIR.
The W83787IF integrates a disk drive adapter ,two 16550 compatible UARTs, and one parallel port
with EPP mode, ECP mode, and joystick mode.
The disk drive adapter functions of the W83787IF is sames as W83787F which including a floppy
disk drive controller compatible with the industry standard 765, data separator, write precompensation circuit, decode logic, data rate selection, clock generator, drive interface control logic,
and interrupt and DMA logic. The wide range of functions integrated onto the W83787IF greatly
reduces the number of components required for interfacing with floppy disk drives. The W83787IF
supports four 360K, 720K, 1.2M, 1.44M disk drives and data transfer rates of 250Kb/S, 300Kb/S,
500Kb/S.
There are two high-speed serial communication ports (UARTs) on the W83787IF, one of them
support serial infrared communication. The UARTs include 16-byte send/receive FIFOs, a
programmable baud rate generator, complete modem control capability, and a processor interrupt
system.
The W83787IF supports three optional PC-compatible printer ports: 378h, 278h and 3BCh. Additional
bi-directional I/O capability is available by hardware control or software programming. The parallel
port also supports the Enhanced Parallel Port (EPP) and Extended Capabilities Port (ECP).
The W83787IF supports two embedded hard disk drive (AT bus) interfaces and a game port with
decoded read/write output.
The W83787IF's Extension FDD Mode and Extension 2FDD Mode allow one or two external floppy
disk drives to be connected to the computer through the printer interface pins in notebook computer
applications.
The Extension Adapter Mode of the W83787IF allows pocket devices to be installed through the
printer interface pins in notebook computer applications according to a protocol set by Winbond, but
with upgraded performance.
The JOYSTICK mode allows a joystick to be connected to a parallel port with a signal switching
cable.
The configuration register supports address selection, mode selection, function enable/disable, and
power down function selection.
Publication ReleaseDate:Sep 1995
- 1 - Revision A1

W83787IF
FEATURES
• 1.44MB Floppy Disk Controller
--- Support four 360K,720K,1.2M,1.44M floppy disk drives
--- Data Transfer Rate 250Kb/s,300Kb/s,500Kb/s
--- Single 24Mhz crystal input
--- FDD anti-virus function with software write protect and FDD write enable signal,
write data signal force inactive
• Serial Ports
--- Two high speed 16550 UART with 16 byte FIFO
--- Programmable baud rate generator
--- Modem Control Circuitry
--- Support IrDA(HPSIR) and Amplitude Shift Keyed IR(ASKIR) Infrared communication
--- MIDI compatible
• Parallel Port
--- Support Standard Parallel Port(SPP),Enhanced Parallel Port(EPP),
Enhanced Capability Port(ECP)
--- Joystick mode supports joystick through parallel port
--- Extension FDD mode support disk drive B through parallel port
--- Extension Adapter Mode support pocket devices through parallel port
--- Extension 2FDD mode support disk drive A and B through parallel port
--- Compatible with IBM Parallel Port
--- Support parallel port with bi-directional lines
• IDE Interface
--- Support two embedded hard disk drives(IDE AT BUS)
• Game Port Supported
• Based on pinout of W83777/787F
• Two General Purpose I/O pins
• 100 PQFP
Publication Release Date:Sep 1995
- 2 - Revision A1
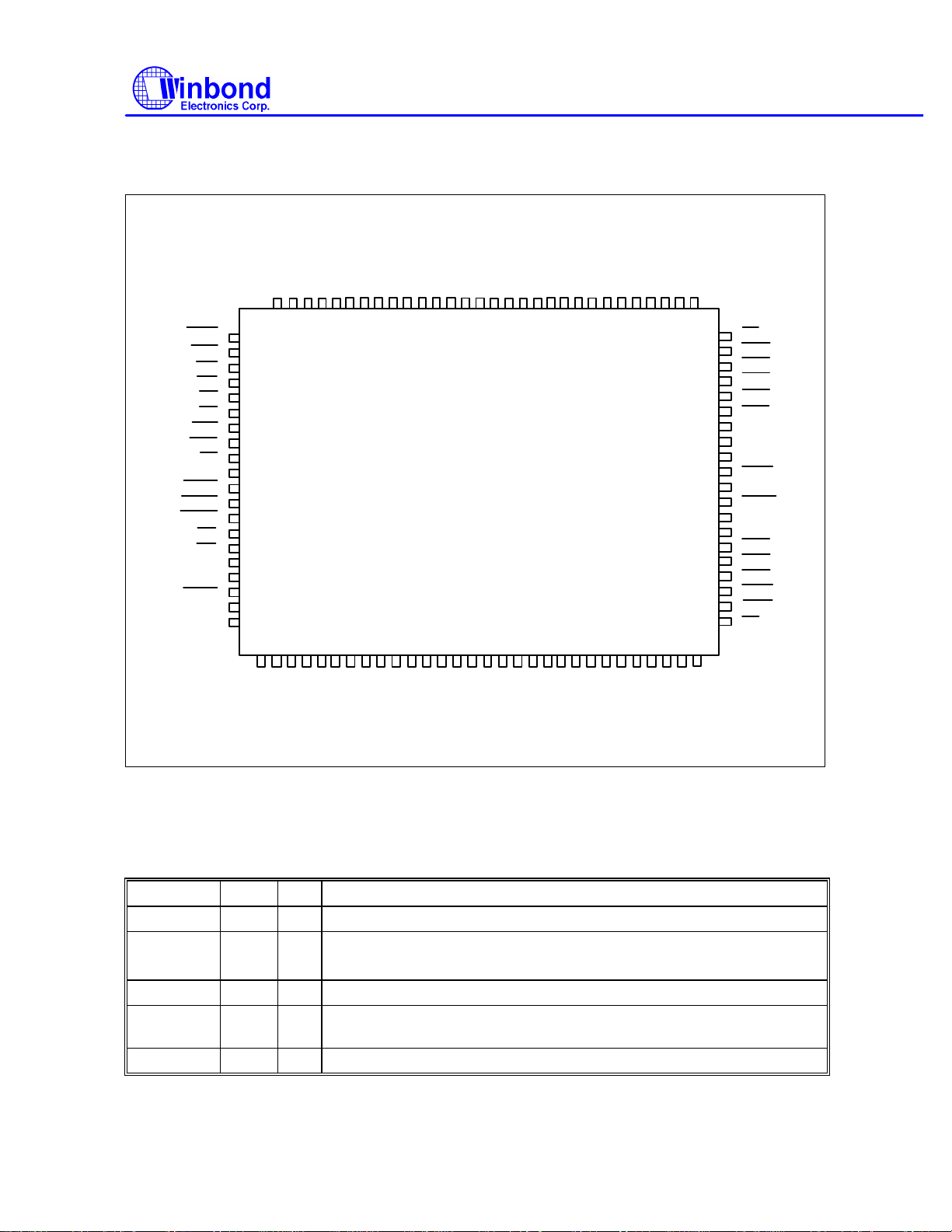
PIN CONFIGURATION
0
W
9
R
5
7
N
/
/
M
M
O
O
A
B
W83787IF
/
D
/
T
R
A
K
0
/
S
R
K
D
A
N
C
A
1
W
H
T
P
G
A
D
D
D
D
D
5
6
7
D
4
1
3D2
/
/
I
G
I
D
0
A
O
N
D
A
O
A8A7A
E
R
N
V
A
A
D
A2A
A
5
4
6
D
A
1
3
0
INDEX
STEP
DSA
DSB
WE
WD
RWC
HEAD
DIR
GND
DBENL
DBENH
IOCS16
CS0
CS1
IDED7
TC
DACK2
IRQ6
DRQ2
X X X X
80 79 78 77 76 75 74 73 72 71 70 69 68 67 66 65 64 63 62 61 60 59 58 57 56 55 54 53 52 51
X
81
X
82
X
83
X
84
X
85
X
86
X
87
X
88
X
89
X
90
X
91
X
92
X
93
X
94
95
X
X
96
X
97
X
98
X
99
X
100
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 1718 19 20 21 22 2324 25 26 27 28 29 30
/
P
P
P
R
D
D
D
E
C
R
B
S
I
Q
D
I
N
X
I
D
R
E
X
X
I
M
T
O
T
A
C
A
L
L
H
2
1
R
D
Y
X X X
X X X X X X X X XXX X X X XX X X X X X X X X X X X X
P
P
D
0
P
P
P
D
D
D
D
1
4
2
3
X X X X
P
P
V
P
D
D
D
D
6
D
XX X X X X
X X X X
X
/
/
/
/
/
S
P
T
R
B
T
O
E
I
S
A
I
R
L
F
N
Q
D
I
I
7
T
P
B
G
/
E
U
N
A
S
D
C
Y
K
X
RIB
50
X
DCDB
49
X
DSRB
48
X
CTSB
47
X
46
DTRB
X
45
RTSB
X
44
IRQ3
X
SOUTB
43
X
42
SINB
X
41
GMRD
X
40
GND
X
39
GMWR
X
38
SOUTA
X
IRQ4
37
X
36
RTSA
X
35
DTRA
X
34
CTSA
X
33
DSRA
X
32
DCDA
X
31
RIA
X
/
S
S
E
L
I
R
C
N
R
T
A
1.0 PIN DESCRIPTION
Note I: Input pin, O: Output pin, I/O: Bi-directional pin, OD: Open Drain pin.
1.1 Host Interface
SYMBOL PIN I/O FUNCTION
D0-D7 66-73 I/O System data bus bits 0-7
A0-A9 51-55
57-61
A10 75 I In ECP Mode, this pin is the A10 address input.
IOCHRDY 5 OD In EPP Mode, this pin is the IO Channel Ready output to extend the
MR 6 I Master Reset. Active high. MR is low during normal operations.
I System address bus bits 0-9
host read/write cycle.
Publication Release Date:Sep 1995
- 3 - Revision A1
W83787IF
IOR
IOW
DACK
2
PRTOE
PDACKX
Host Interface, continued
SYMBOL PIN I/O FUNCTION
AEN 62 I
63 I
64 I
DRQ2 100 O
98 I
TC 97 I
IRQ6 99 O
IRQ4 37 O Interrupt request generated by UART A or UART B when their addresses
IRQ3 44 O
IRQ7 23 O
PDRQX
HPRTM1
XTAL1 7 I
XTAL2 8 O
4 I/O In Extension Adapter mode this pin is a DMA Request generated by
18 I In printer mode, this pin is for data direction control. When it is set to low,
System address bus enable
CPU I/O read signal
CPU I/O write signal
When DRQ2 = 1, a DMA request is being made by the FDC
DMA Acknowledge. When this pin is active, a DMA cycle is underway
and the controller is executing a DMA transfer.
Terminal Count. When active, this pin indicates termination of a DMA
transfer.
Interrupt request generated by FDC
are COM1 or COM3.
This interrupt request can be tri-stated by setting bit 3 of HCR low.
This signal is at high impedance after each reset operation.
Interrupt request generated by UART A or UART B when their addresses
are COM2 or COM4.
Same as IRQ4
When IRQ7 = 1 and interrupt request is being made by the printer, this
pin is pulled high internally.
In EPP or ECP mode, IRQ7 is pulsed low, then released to allow sharing
of interrupts.
Extension Adapter. This request is output directly from XDRQ.
In ECP mode, this pin is the parallel port DMA Request output.
During power-on reset, this pin is pulled down internally and is defined as
HPRTM1, which is used for selecting the mode of the parallel port (see
Table 1-1).
the parallel port functions as an output port. When it is set to high, the
direction of the data bus is controlled by Bit 5 (DIR) of the printer control
register and Bit 7 (PRTBEN) of CR3. This pin is pulled up internally.
In Extension Adapter mode, this pin is the DMA acknowledge for the
Extension Adapter. When this pin is active, a DMA cycle is underway
and the controller is executing a DMA transfer.
In ECP mode, this pin is the parallel port DMA Acknowledge input.
24Mhz XTAL/Oscillator/Clock input
XTAL output
Publication Release Date:Sep 1995
- 4 - Revision A1

1.2 Serial Port Interface
CTSA
CTSB
DSRA
DSRB
DCDA
DCDB
RIA
RIB
DTRA
DTRB
SYMBOL PIN I/O FUNCTION
34
47
33
48
I Clear To Send is the modem control input.
The function of these pins can be tested by reading Bit 4 of the
handshake status register.
I Data Set Ready. An active low indicates the modem or data set is ready
to establish a communication link and transfer data to the UART.
W83787IF
SINA
SINB
IRRX1
SOUTA
HURAS1
SOUTB
HURBS1
IRTX1
HPRTAS0
HURAS0
32
49
31
50
30
42
38 I/O UART A Serial Output. Used to transmit serial data out to the
43 I/OOUART B Serial Output. Used to transmit serial data out to the
35 I/O UART A Data Terminal Ready. An active low informs the modem or
46 I/O UART B Data Terminal Ready. An active low informs the modem or
I Data Carrier Detect. An active low indicates the modem or data set has
detected a data carrier.
I Ring Indicator. An active low indicates that a ring signal is being
received by the modem or data set.
I Serial Input. Used to receive serial data from the communication link.
SINB can be programmed by CR0D register as input pin IRRX1 for
serial infrared communication
communication link.
During power-on reset, this pin is pulled up internally and is defined as
HURAS1, which is used for selecting the I/O address of the UART A.
(See Table 1-2.)
communication link. SOUTB can be programmed by CR0D register as
output pin IRTX1 for serial infrared communication.
During power-on reset, this pin is pulled up internally and is defined as
HURBS1, which is used for selecting the I/O address of UARTB. (See
Table 1-2.)
data set that the controller is ready to communicate.
During power-on reset, this pin is pulled down internally and is defined
as HPRTAS0. It is used for selecting the address of the parallel port.
(See Table 1-3.)
data set that controller is ready to communicate.
During power-on reset, this pin is pulled down internally and is defined
as HURAS0. It is used for setting the I/O address of UART A. (See
Table 1-2.)
Publication Release Date:Sep 1995
- 5 - Revision A1
W83787IF
RTSA
RTSB
GMRD
GMWR
Serial Port Interface, continued
SYMBOL PIN I/O FUNCTION
36 I/O UART A Request To Send. An active low informs the modem or data
HPRTAS1
45 I/O UART B Request To Send. An active low informs the modem or data
HURBS0
1.3 Game Port/Power Down Interface
Bit 4 of CR3 (GMODS0) determines whether the game port is in Adapter mode or Portable mode
(default is Adapter mode).
Game I/O port address is 201h.
set that the controller is ready to send data.
During power-on reset, this pin is pulled up internally and is defined as
HPRTAS1. It is used for setting the address of the parallel port. (See
Table 1-3.)
set that the controller is ready to send data.
During power-on reset, this pin is pulled down internally and is defined
as HURBS0. It is used for setting the I/O address of UART B. (See
Table 1-2.)
SYMBOL PIN I/O FUNCTION
41 O
PFDCEN
HEFERE
39 O
PEXTEN
HPRTM0
Adapter mode: Game port read control signal.
Portable mode: When parallel port is selected as Extension
O
FDD/Extension 2FDD mode, this pin will be active. The active state is
I
dependent on bit 7 of CRA (PFDCACT), and default is low active.
During power-on reset, this pin is pulled up internally and is defined as
HEFERE for determining whether Extended Function Enable Register
enable value is 88h or 89h. If the HEFERE= H (default) at power-on
reset, then EFER enable value is 89h. If HEFERE = L at power-on
reset, the enable value is 88h.
Adapter mode: Game port write control signal.
Portable mode: When a particular extended mode is selected for the
O
parallel port, this pin will be active. The extended modes include
I
Extension Adapter mode, EPP mode, ECP mode, and ECP/EPP mode,
which are selected using bit 3 - bit 0 of CRA. The active state is
dependent on bit 6 of CRA (PEXTACT); the default is low active.
During power-on reset, this pin is pulled down internally and is defined
as HPRTM0. It is used to determine the mode of the parallel port. (See
Table 1-1.)
Publication Release Date:Sep 1995
- 6 - Revision A1
Game Port/Power Down Interface, continued
MOB
2
MOB
MOB
2
MOB
W83787IF
PDCIN
IRRX2
3 I
This input pin controls the chip power down. When this pin is active, the
clock supply to the chip will be inhibited and the output pins will be tri-
I
stated as defined in CR4 and CR6. The PDCIN is pulled down
internally. Its active state is defined by bit 4 of CRA (PDCHACT).
Default is high active.
PDCIN can be programmed by CR0D register as input pin IRRX2 for
serial infrared communication.
1.4 Multi-Mode Parallel Port
The following pins have eight functions, which are controlled by bits PRTMOD0, PRTMOD1, and
PRTMOD2 of CR0 and CR9 (refer to section 6.0, Extended Functions).
SYMBOL PIN I/O FUNCTION
BUSY
24 I
PRINTER MODE: BUSY
An active high input indicates that the printer is not ready to receive
data. This pin is pulled high internally. Refer to the description of the
parallel port for the definition of this pin in ECP and EPP mode.
EXTENSION FDD MODE:
OD
This pin is for Extension FDD B; the function of this pin is the same as
that of the
EXTENSION ADAPTER MODE: XIRQ
I
This pin is an interrupt request generated by the Extension Adapter
and is an active high input.
pin.
EXTENSION 2FDD MODE:
OD
This pin is for Extension FDD A and B; the function of this pin is the
same as that of the
JOYSTICK MODE: NC pin.
_
- 7 - Revision A1
pin.
Publication Release Date:Sep 1995
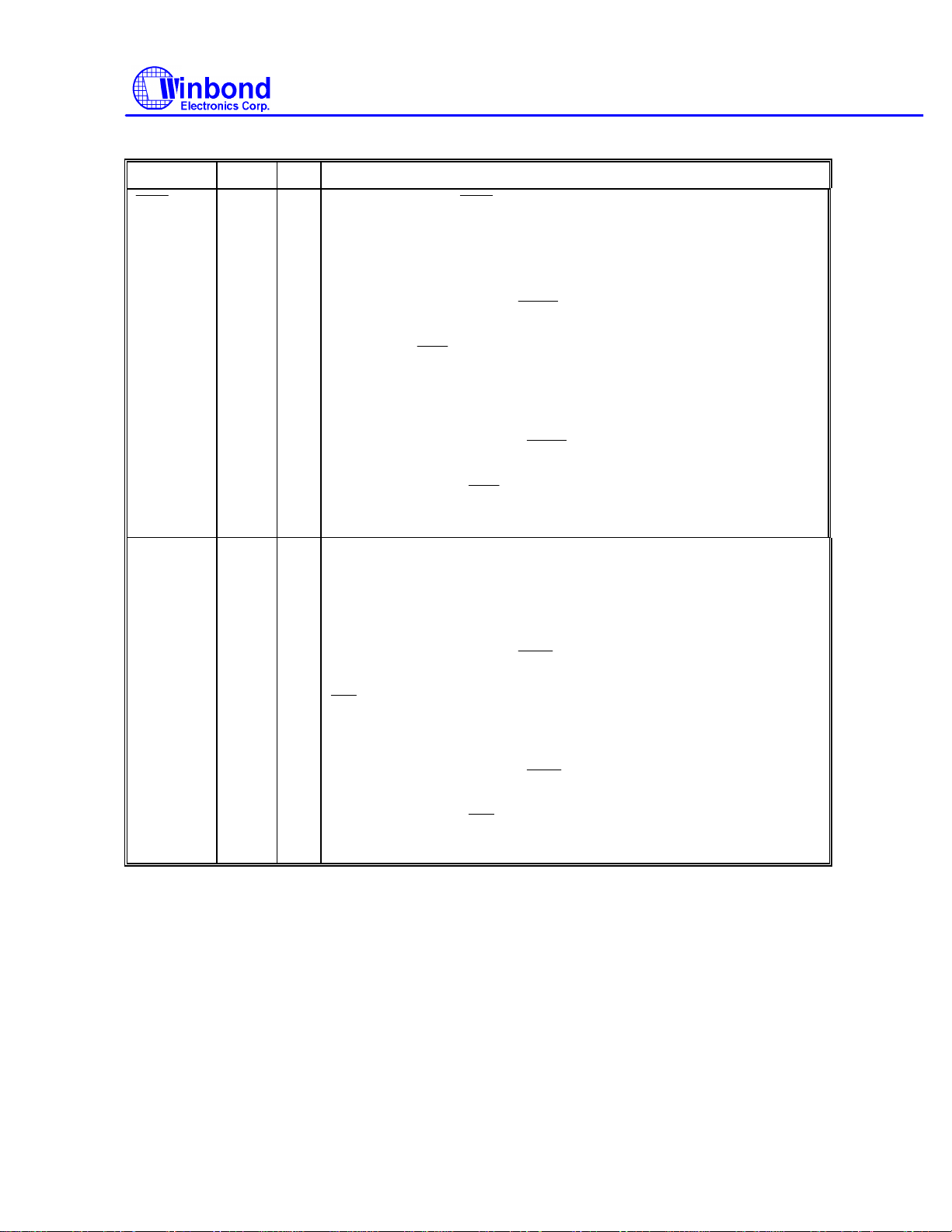
Multi-Mode Parallel Port, continued
ACK
ACK
DSB
2
DSB
DSB
2
DSB
WD
2
WD
WD
2
SYMBOL PIN I/O FUNCTION
W83787IF
PE
26 I
OD
OD
27 I
PRINTER MODE:
An active low input on this pin indicates that the printer has received
data and is ready to accept more data. This pin is pulled high
internally. Refer to the description of the parallel port for the definition
of this pin in ECP and EPP mode.
EXTENSION FDD MODE:
This pin is for the Extension FDD B; its functions are the same as
those of the
EXTENSION ADAPTER MODE: XDRQ
I
pin.
DMA request generated by the Extension Adapter. An active high
input.
EXTENSION 2FDD MODE:
This pin is for Extension FDD A and B; this function of this pin is the
same as that of the
JOYSTICK MODE: NC pin.
_
pin.
PRINTER MODE: PE
An active high input on this pin indicates that the printer has detected
the end of the paper. This pin is pulled high internally.
Refer to the description of the parallel port for the definition of this pin
in ECP and EPP mode.
EXTENSION FDD MODE:
OD
This pin is for Extension FDD B; its function is the same as that of the
pin.
EXTENSION ADAPTER MODE: XA0
O
This pin is system address A0 for the Extension Adapter.
EXTENSION 2FDD MODE:
OD
This pin is for Extension FDD A and B; this function of this pin is the
same as that of the WD pin.
JOYSTICK MODE: NC pin.
_
Publication Release Date:Sep 1995
- 8 - Revision A1
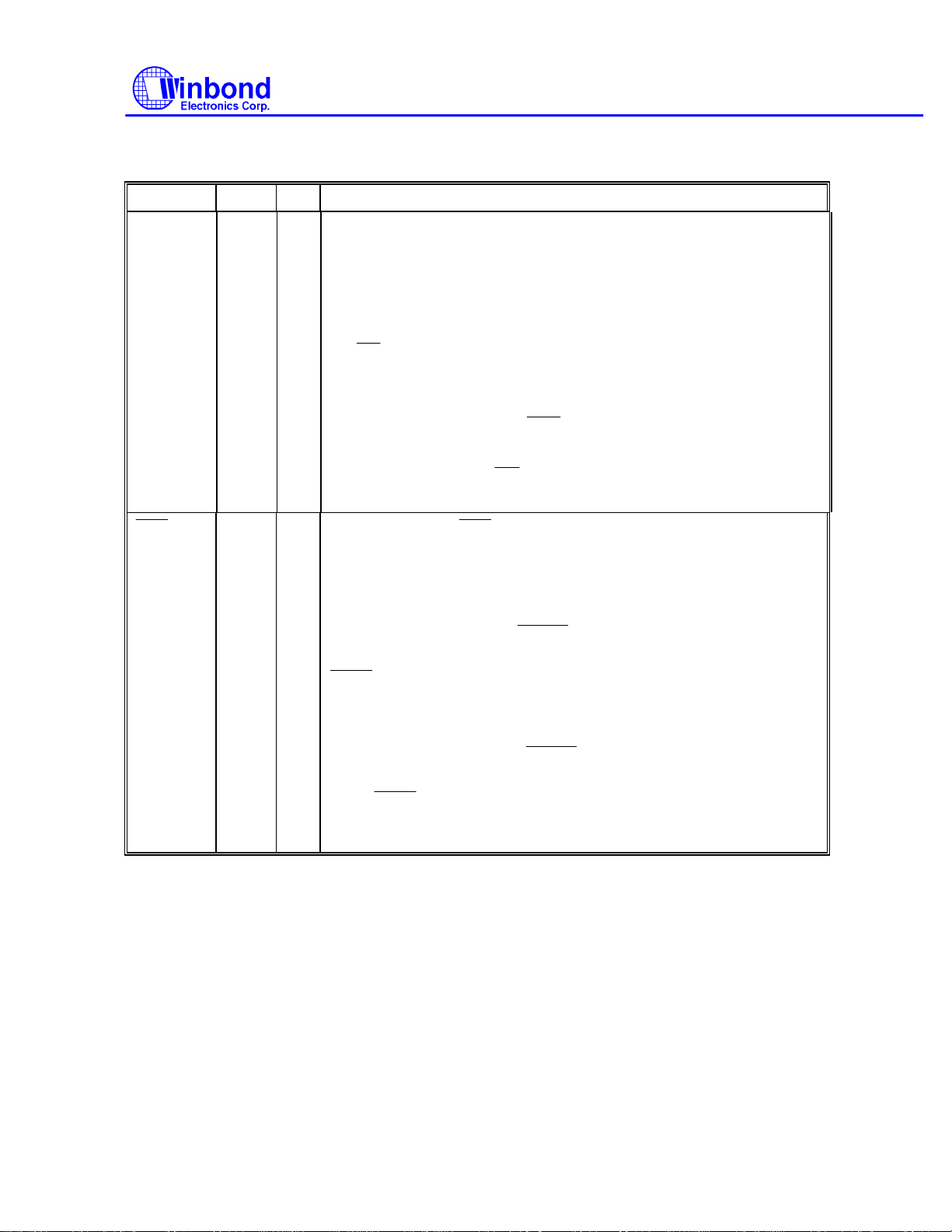
Multi-Mode Parallel Port, continued
WE
2
ERR
ERR
HEAD
2
HEAD
HEAD
2
HEAD
SYMBOL PIN I/O FUNCTION
SLCT
28 I
29 I
PRINTER MODE: SLCT
An active high input on this pin indicates that the printer is selected.
This pin is pulled high internally. Refer to the description of the parallel
port for the definition of this pin in ECP and EPP mode.
OD
EXTENSION FDD MODE: WE2
This pin is for Extension FDD B; its functions are the same as those of
the WE pin.
EXTENSION ADAPTER MODE: XA1
O
This pin is system address A1 for the Extension Adapter.
EXTENSION 2FDD MODE:
OD
This pin is for Extension FDD A and B; this function of this pin is
the same as that of the WE pin.
_
JOYSTICK MODE: NC pin.
PRINTER MODE:
An active low input on this pin indicates that the printer has
encountered an error condition. This pin is pulled high internally. Refer
to the description of the parallel port for the definition of this pin in
ECP and EPP mode.
W83787IF
EXTENSION FDD MODE:
OD
This pin is for Extension FDD B; its function is the same as that of the
pin.
EXTENSION ADAPTER MODE: XA2
O
This pin is system address A2 for the Extension Adapter.
EXTENSION 2FDD MODE:
OD
This pin is for Extension FDD A and B; its function is the same as that
of the
JOYSTICK MODE: NC pin.
_
pin.
Publication Release Date:Sep 1995
- 9 - Revision A1
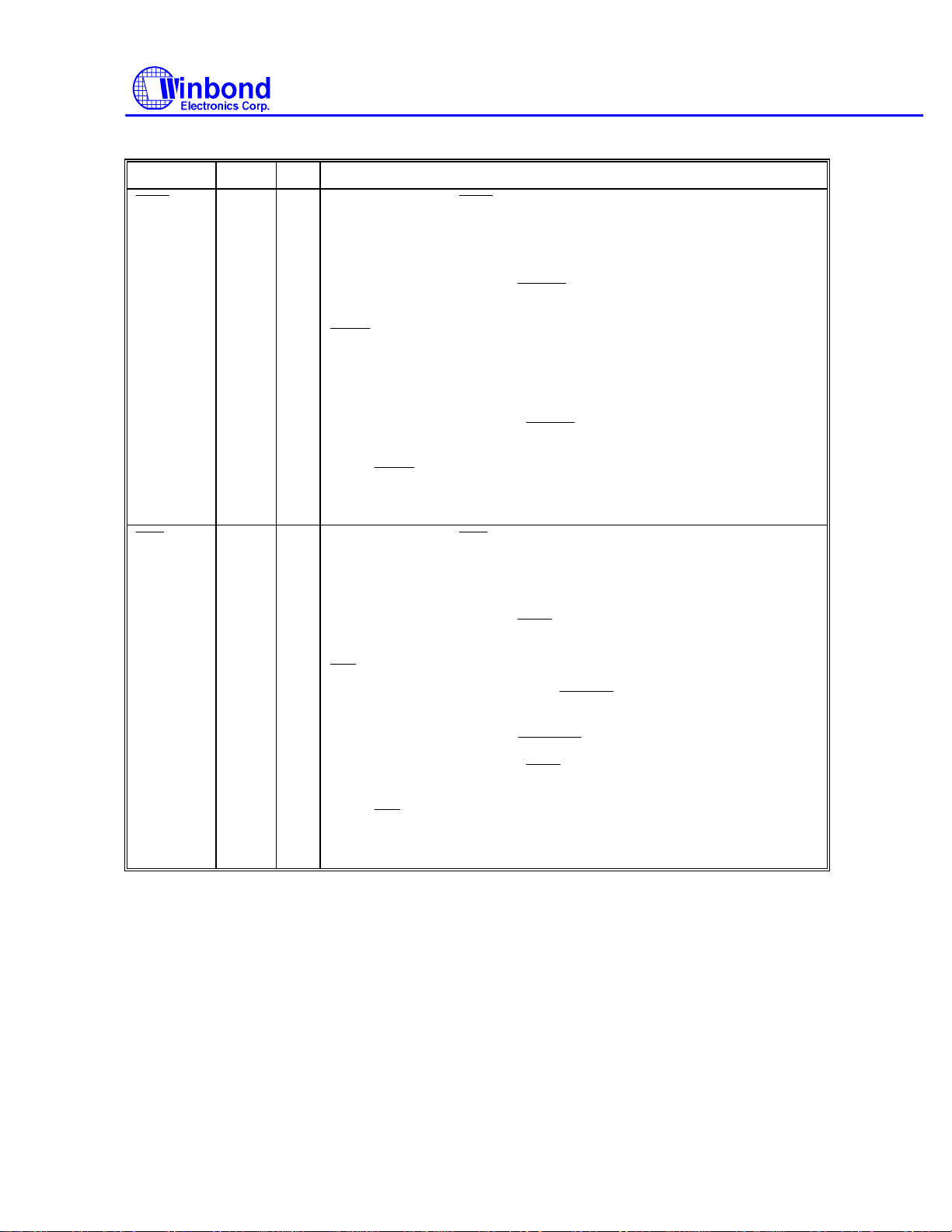
Multi-Mode Parallel Port, continued
SLIN
SLIN
STEP
2
STEP
STEP
2
STEP
INIT
INIT
DIR
2
DIR
XDACK
PDACKX
DIR
2
DIR
SYMBOL PIN I/O FUNCTION
W83787IF
22 OD
OD
O
OD
O
21 OD
OD
PRINTER MODE:
Output line for detection of printer selection. This pin is pulled high
internally. Refer to the description of the parallel port for the definition
of this pin in ECP and EPP mode.
EXTENSION FDD MODE:
This pin is for Extension FDD B; its function is the same as that of the
pin.
EXTENSION ADAPTER MODE: XTC
This pin is the DMA terminal count for the Extension Adapter. The
count is sent by TC directly.
EXTENSION 2FDD MODE:
This pin is for Extension FDD A and B; its function is the same as that
of the
JOYSTICK MODE: VDD for joystick.
PRINTER MODE:
Output line for the printer initialization. This pin is pulled high
internally. Refer to the description of the parallel port for the definition
of this pin in ECP and EPP mode.
EXTENSION FDD MODE:
This pin is for Extension FDD B; its function is the same as that of the
pin.
pin .
EXTENSION ADAPTER MODE:
O
This pin is the DMA acknowledge output for the Extension Adapter; the
output is sent directly from
EXTENSION 2FDD MODE:
OD
This pin is for Extension FDD A and B; its function is the same as that
of the
JOYSTICK MODE: VDD for joystick.
O
pin.
- 10 - Revision A1
.
Publication Release Date:Sep 1995
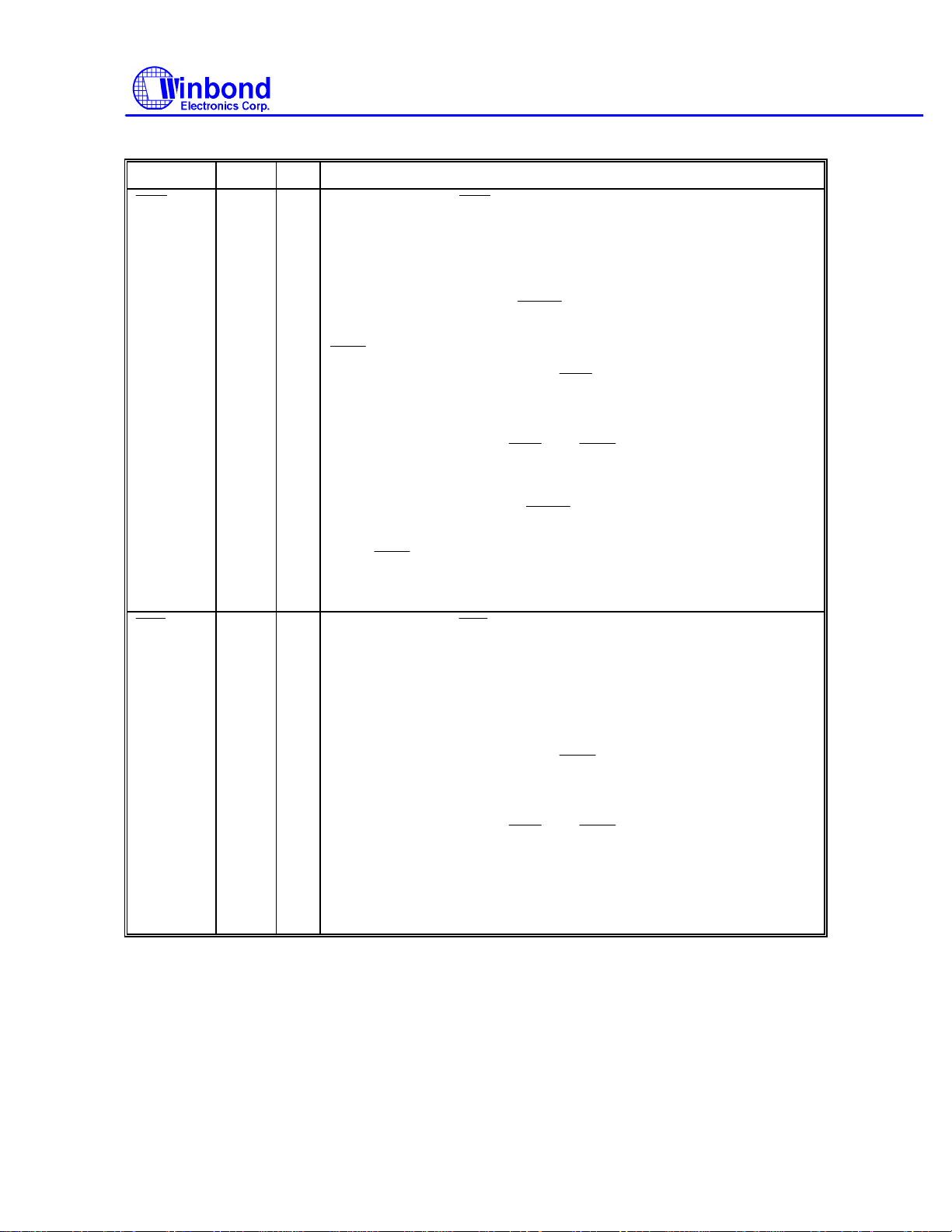
Multi-Mode Parallel Port, continued
AFD
AFD
RWC
2
RWC
XRD
XRD
XWR
RWC
2
RWC
STB
STB
XWR
XRD
XWR
SYMBOL PIN I/O FUNCTION
W83787IF
20 OD
OD
O
OD
O
19 OD
-
PRINTER MODE:
An active low output from this pin causes the printer to auto feed a line
after a line is printed. This pin is pulled high internally. Refer to the
description of the parallel port for the definition of this pin in ECP and
EPP mode.
EXTENSION FDD MODE:
This pin is for Extension FDD B; its function is the same as that of the
pin.
EXTENSION ADAPTER MODE:
This pin is the I/O read command for the Extension Adapter.
When the Extension Adapter base address is written to the Extension
Adapter address register,
that the command register on the Extension Adapter can latch the
same base address.
EXTENSION 2FDD MODE:
This pin is for Extension FDD A and B; its function is the same as that
of the
JOYSTICK MODE: VDD for joystick.
PRINTER MODE:
An active low output is used to latch the parallel data into the printer.
This pin is pulled high internally. Refer to the description of the parallel
port for the definition of this pin in ECP and EPP mode.
EXTENSION FDD MODE:
This pin is a tri-state output.
pin.
and
go low simultaneously so
EXTENSION ADAPTER MODE:
O
This pin is the I/O write command for the Extension Adapter.
When the Extension Adapter base address is written to the Extension
Adapter address register,
that the command register on the Extension Adapter can latch the
same base address.
EXTENSION 2FDD MODE: This pin is a tri-state output.
JOYSTICK MODE: VDD for joystick.
O
- 11 - Revision A1
and
go low simultaneously so
Publication Release Date:Sep 1995
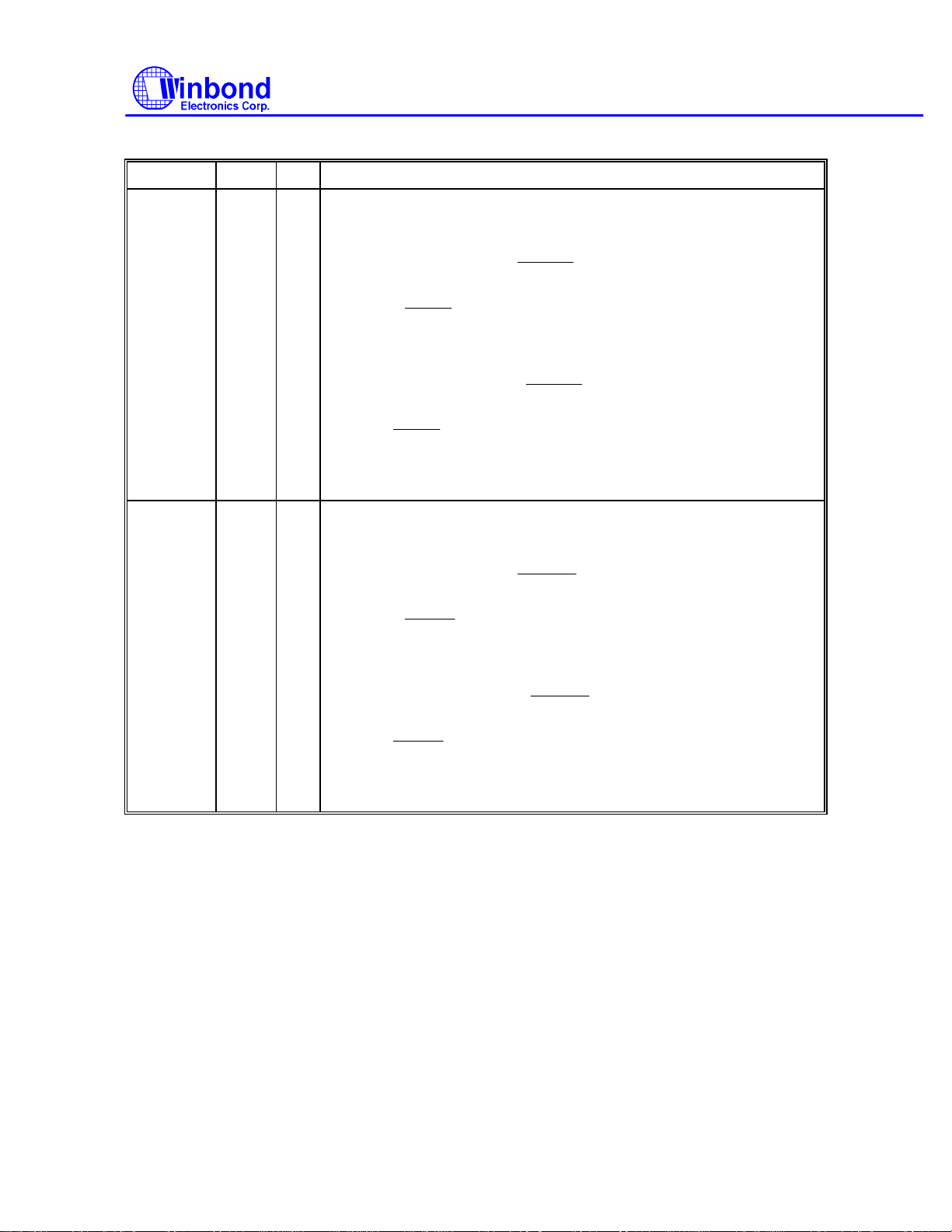
Multi-Mode Parallel Port, continued
INDEX
2
INDEX
INDEX
2
INDEX
TRAK
02
TRAK
0
TRAK
02
TRAK
0
SYMBOL PIN I/O FUNCTION
W83787IF
PD0
PD1
9 I/O
I
I/O
I
I/O
10 I/O
I
I/O
PRINTER MODE: PD0
Parallel port data bus bit 0. Refer to the description of the parallel port
for the definition of this pin in ECP and EPP mode.
EXTENSION FDD MODE:
This pin is for Extension FDD B; the function of this pin is the same as
that of the
EXTENSION ADAPTER MODE: XD0
This pin is system data bus D0 for the Extension Adapter.
EXTENSION 2FDD MODE:
This pin is for Extension FDD A and B; this function of this pin is the
same as
JOYSTICK MODE: JP0
This pin is the paddle 0 input for joystick.
PRINTER MODE: PD1
Parallel port data bus bit 1. Refer to the description of the parallel port
for the definition of this pin in ECP and EPP mode.
EXTENSION FDD MODE:
This pin is for Extension FDD B; the function of this pin is the same as
that of the
EXTENSION ADAPTER MODE: XD1
This pin is system data bus D1 for the Extension Adapter.
pin. This pin is pulled high internally.
pin. This pin is pulled high internally.
pin. This pin is pulled high internally.
EXTENSION. 2FDD MODE:
I
This pin is for Extension FDD A and B; this function of this pin is the
same as
JOYSTICK MODE: JP1
I/O
This pin is the paddle 1 input for joystick.
pin. This pin is pulled high internally.
Publication Release Date:Sep 1995
- 12 - Revision A1
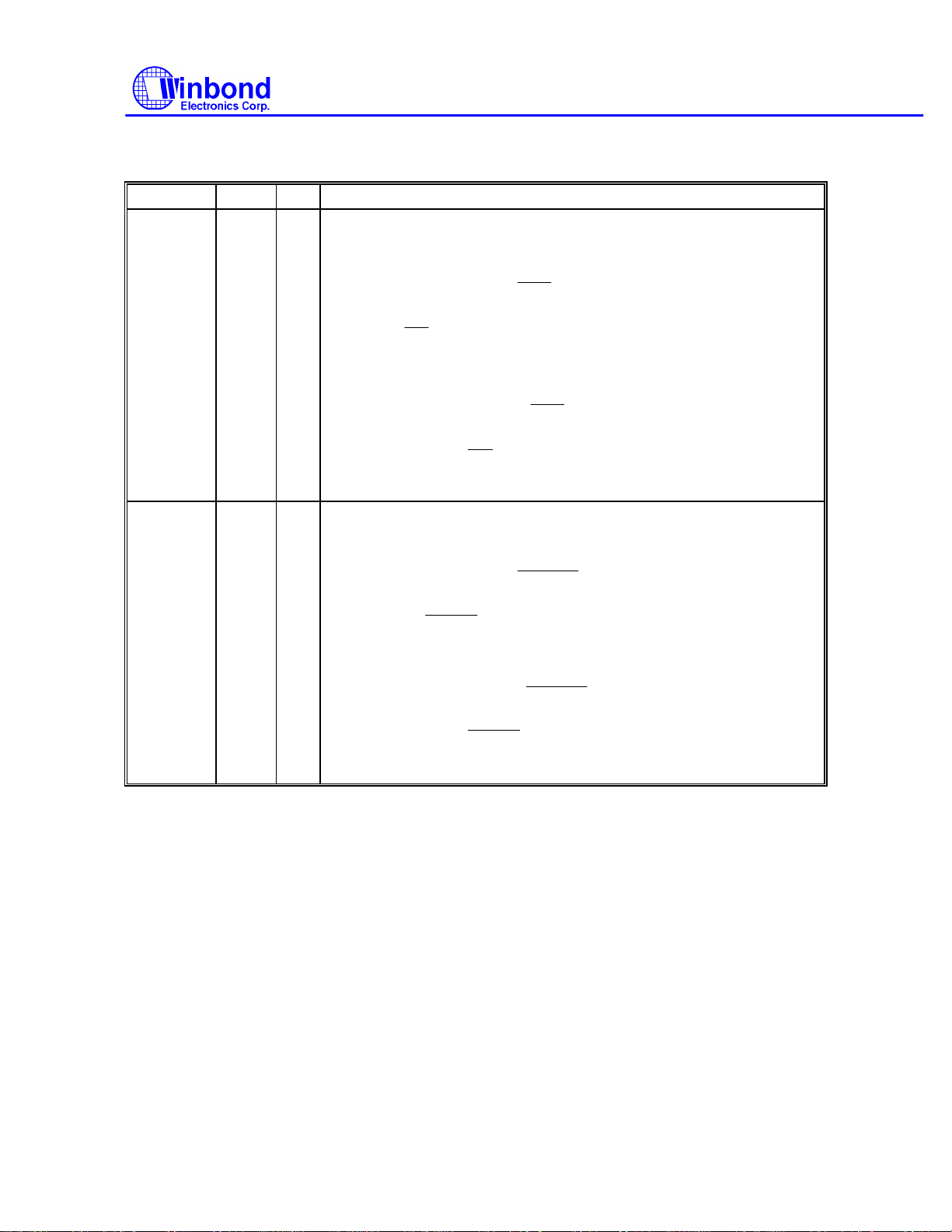
Multi-Mode Parallel Port, continued
WP
2
WP
2
RDATA
2
RDATA
RDATA
2
RDATA
SYMBOL PIN I/O FUNCTION
PD2
PD3 12 I/O
11 I/O
PRINTER MODE: PD2
Parallel port data bus bit 2. Refer to the description of the parallel port
for the definition of this pin in ECP and EPP mode.
EXTENSION FDD MODE:
I
This pin is for Extension FDD B; the function of this pin is the same as
that of the WP pin. This pin is pulled high internally.
EXTENSION ADAPTER MODE: XD2
I/O
This pin is system data bus D2 for the Extension Adapter.
EXTENSION. 2FDD MODE:
I
This pin is for Extension FDD A and B; this function of this pin is the
same as that of the WP pin. This pin is pulled high internally.
JOYSTICK MODE: NC pin
PRINTER MODE: PD3
Parallel port data bus bit 3. Refer to the description of the parallel port
for the definition of this pin in ECP and EPP mode.
I
EXTENSION FDD MODE:
Motor on B for Extension FDD B; the function of this pin is the same
as that of the
EXTENSION ADAPTER MODE: XD3
I/O
This pin is system data bus D3 for the Extension Adapter.
EXTENSION 2FDD MODE:
I
This pin is for Extension FDD A and B; this function of this pin is the
same as that of the
JOYSTICK MODE: NC pin
-
pin. This pin is pulled high internally.
pin. This pin is pulled high internally.
W83787IF
Publication Release Date:Sep 1995
- 13 - Revision A1
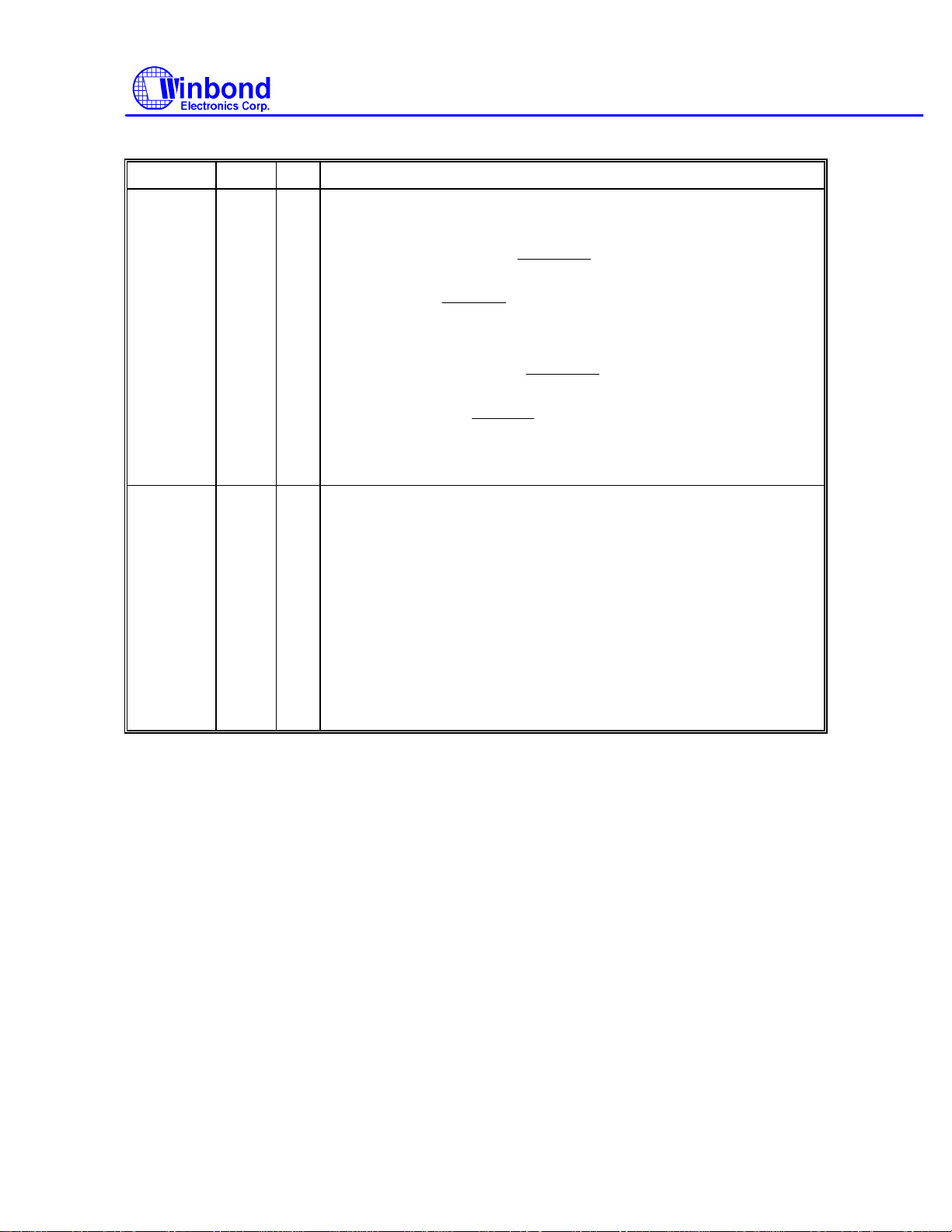
Multi-Mode Parallel Port, continued
DSKCHG
2
DSKCHG
DSKCHG
2
DSKCHG
SYMBOL PIN I/O FUNCTION
PD4 13 I/O
PD5 14 I/O
PRINTER MODE: PD4
Parallel port data bus bit 4. Refer to the description of the parallel port
for the definition of this pin in ECP and EPP mode.
I
EXTENSION FDD MODE:
Drive select B for Extension FDD B; the function of this pin is the
same as that of
EXTENSION ADAPTER MODE: XD4
I/O
This pin is system data bus D4 for the Extension Adapter.
EXTENSION 2FDD MODE:
I
This pin is for Extension FDD A and B; this function of this pin is the
same as that of the
JOYSTICK MODE: JB0
I
This pin is the button 0 input for the joystick.
PRINTER MODE: PD5
Parallel port data bus bit 5. Refer to the description of the parallel port
for the definition of this pin in ECP and EPP mode.
-
EXTENSION FDD MODE:
This pin is a tri-state output.
I/O
EXTENSION ADAPTER MODE: XD5
This pin is system data bus D5 for the Extension Adapter
-
EXTENSION 2FDD MODE:
This pin is a tri-state output.
I
JOYSTICK MODE: JB1
This pin is the button 1 input for the joystick.
pin. This pin is pulled high internally.
pin. This pin is pulled high internally.
W83787IF
Publication Release Date:Sep 1995
- 14 - Revision A1
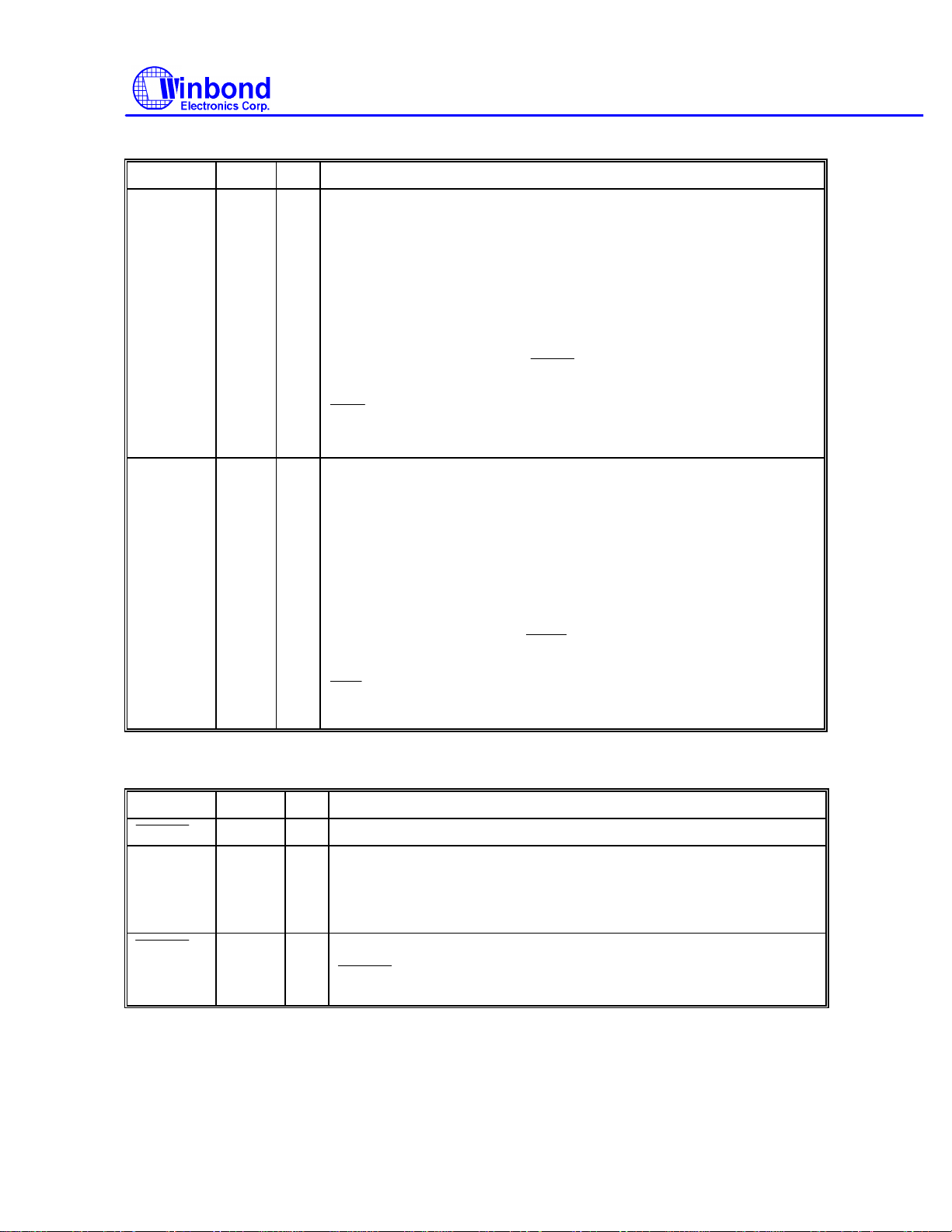
Multi-Mode Parallel Port, continued
MOA
2
MOA
DSA
2
DSA
IOCS
16
RESIDE
RESIDE
SYMBOL PIN I/O FUNCTION
W83787IF
PD6 16 I/O
-
I/O
OD
-
PD7 17 I/O
-
I/O
OD
-
PRINTER MODE: PD6
Parallel port data bus bit 6. Refer to the description of the parallel port
for the definition of this pin in ECP and EPP mode.
EXTENSION FDD MODE:
This pin is a tri-state output.
EXTENSION ADAPTER MODE: XD6
This pin is system data bus D6 for the Extension Adapter
EXTENSION. 2FDD MODE:
This pin is for Extension FDD A; its function is the same as that of the
pin.
JOYSTICK MODE: NC pin
PRINTER MODE: PD7
Parallel port data bus bit 7. Refer to the description of the parallel port
for the definition of this pin in ECP and EPP mode.
EXTENSION FDD MODE:
This pin is a tri-state output.
EXTENSION ADAPTER MODE: XD7
This pin is system data bus D7 for the Extension Adapter.
EXTENSION 2FDD MODE:
This pin is for Extension FDD A; its function is the same as that of the
pin.
JOYSTICK MODE: NC pin
1.5 IDE and FDC Interface
SYMBOL PIN I/O FUNCTION
93 I 16-bit I/O indication from IDE interface
IDED7
GIO1
IRRX3
96 I/O
1 OIReset signal for IDE, active low to initialize the IDE
IDE data bus bit 7
I/O
GIO1:General Purpose I/O pin 1.If pin #91 GIOSEL=1,this pin act as
GIO1.If GIOSEL=0,this pin act as IDED7.It can also be programmed
by CR0C register bit 2.
can be programmed by CR0D register as input pin IRRX3
for serial infrared communication.
- 15 - Revision A1
Publication Release Date:Sep 1995
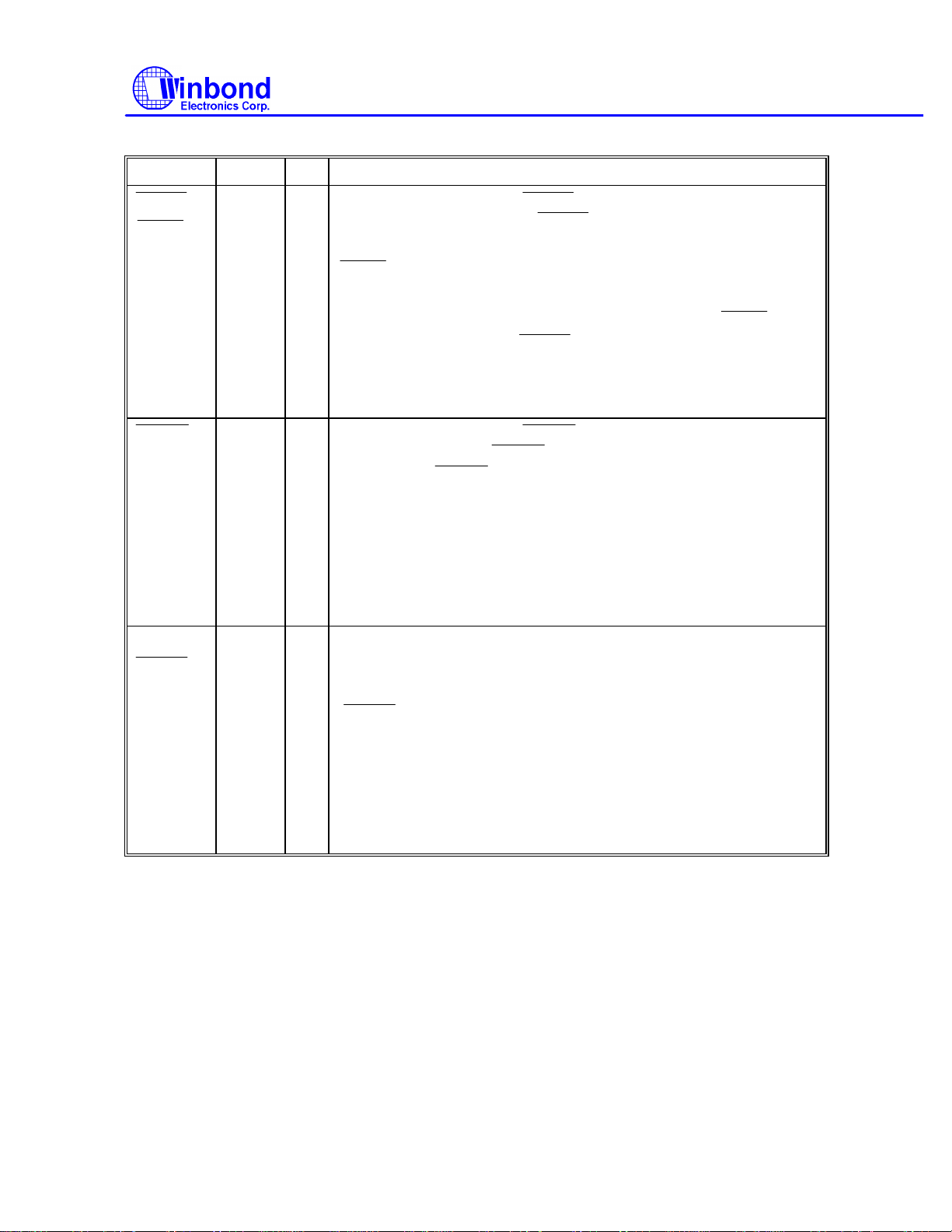
IDE and FDC Interface, continued
DBENL
IDBEN
DBENL
DBENL
IDBEN
IDBEN
DBENL
DBENH
DBENH
DBENH
DBENH
FDCEN
FDCEN
SYMBOL PIN I/O FUNCTION
W83787IF
GIOSEL
GIO0
URIRSEL
PDBDIR
IRTX2
91 O
92 O
I/O
2 I/O
During normal operations,
buffer of the IDE bus. When
O
addresses 1F0H - 1F7H (170H-177H) and 3F6-3F7H (376H-377H).
I
:IDE Data Bus Enable(Low Active). If I/O address 1F0~1F7H
and 2F7H is access, the pin will activate.
During power on reset,if GIOSEL=1,then this pin act as
GIOSEL=0,this pin act as
CR0C register bit 2.
GIOSEL:General Purpose I/O pin select at power on setting. (See
Table 1-4)
During normal operations,
buffer of the IDE bus.
When active,
I
(170H-177H).
GIO0:General Purpose I/O pin0. If pin #91 GIOSEL=1,this pin act as
GIO0.If GIOSEL=0,this pin act as nDBENH.It can also be
programmed by CR0C register bit 2.
URIRSEL:UART/IR Selection.During power on reset,if
URIRSEL=1,then UARTB act as UART function. If URIRSEL=0,then
UARTB act as IR function.
During normal operation, this pin (PDBDIR) is an output that
indicates the direction of the parallel port data bus. If bit 5 of CRA
(PDIRHISOP) is low, then PDBDIR = 0 means output/write, PDBDIR
O
= 1 means input/read (default). During power-on reset, this pin
(
4.7K resistor is recommend in order to pullup the pin at power on
reset to disable the FDC function.
When set to low, it enables the FDC port (default).
When set to high, it disables the FDC port.
PDBDIR can be programmed by CR0D register as output pin IRTX2
for serial infrared communication.
) is pulled down internally and is used to enable the FDC. A
selects I/O port address range 1F0-1F7H
is used to enable the low byte
is active, it accesses I/O
.It can also be programmed by
is used to enable the high byte
is active only when /IOCS16 is active.
.If
Publication Release Date:Sep 1995
- 16 - Revision A1
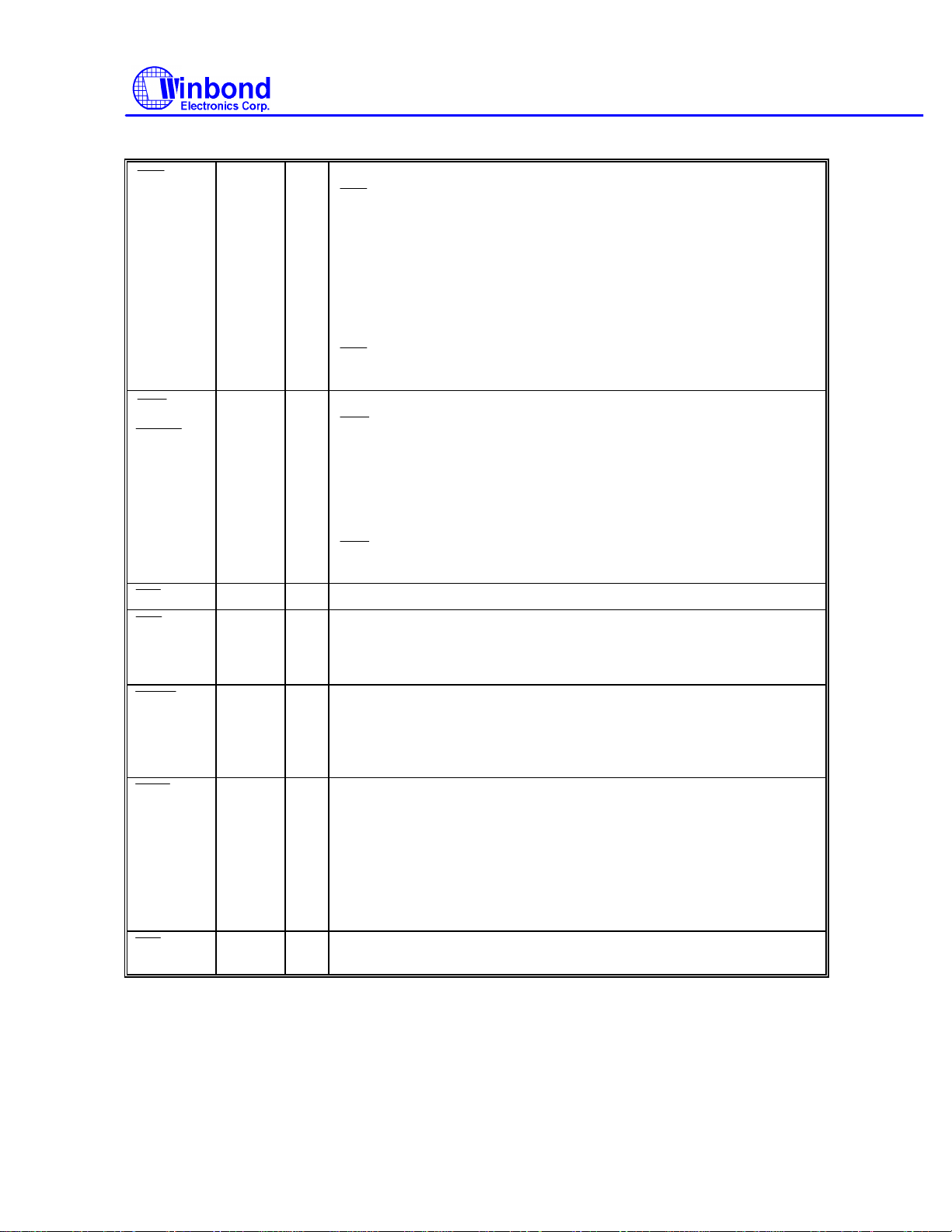
IDE and FDC Interface, continued
CS1
CS1
CS1
CS0
IDEEN
CS0
CS0
WE
DIR
HEAD
RWC
WD
W83787IF
HADSEL
IRTX3
IRRX4
95 I/O
O
94 O
I
I
85 OD
89 OD
88 OD
87 OD
86 OD
During normal operations this pin is used to select the IDE controller.
decodes the HDC addresses 3F6H and 3F7H (376H, 377H).
During power-on reset this pin selects the HDC address and is pulled
up internally.
When set to high, it selects I/O port address range 1F0H-1F7H
(3F6H-3F7H) (default).
When set to low, it selects I/O port address ranges 376H-377H and
170H-177H.
can be programmed by CR0D register as output pin IRTX3 for
serial infrared communication.
During normal operation this pin is used to select the IDE controller.
decodes HDC addresses 1F0H-1F7H (170H-177H).
During power-on reset this pin is pulled down internally and used to
enable or disable the IDE.
When it is set to high, IDE is disabled.
When it is set low, IDE is enabled (default).
can be programmed by CR0D register as input pin IRRX4 for
serial infrared communication.
Write enable. An open drain output.
Direction of the head step motor. An open drain output.
Logic 1 = outward motion
Logic 0 = inward motion
Head select. This open drain output determines which disk drive
head is active.
Logic 1 = side 0
Logic 0 = side 1
Reduced write current. This signal can be used on two-speed disk
drives to select the transfer rate. An open drain output.
Logic 0 = 250Kbps
Logic 1 = 500Kbps
When bit 5 of CR9 (EN3MODE) is set to high, the three-mode FDD
function is enabled, and the pin will have a different definition. Refer
to the EN3MODE bit in CR9.
Write data. This logic low open drain writes precompensation serial
data to the selected FDD. An open drain output.
Publication Release Date:Sep 1995
- 17 - Revision A1
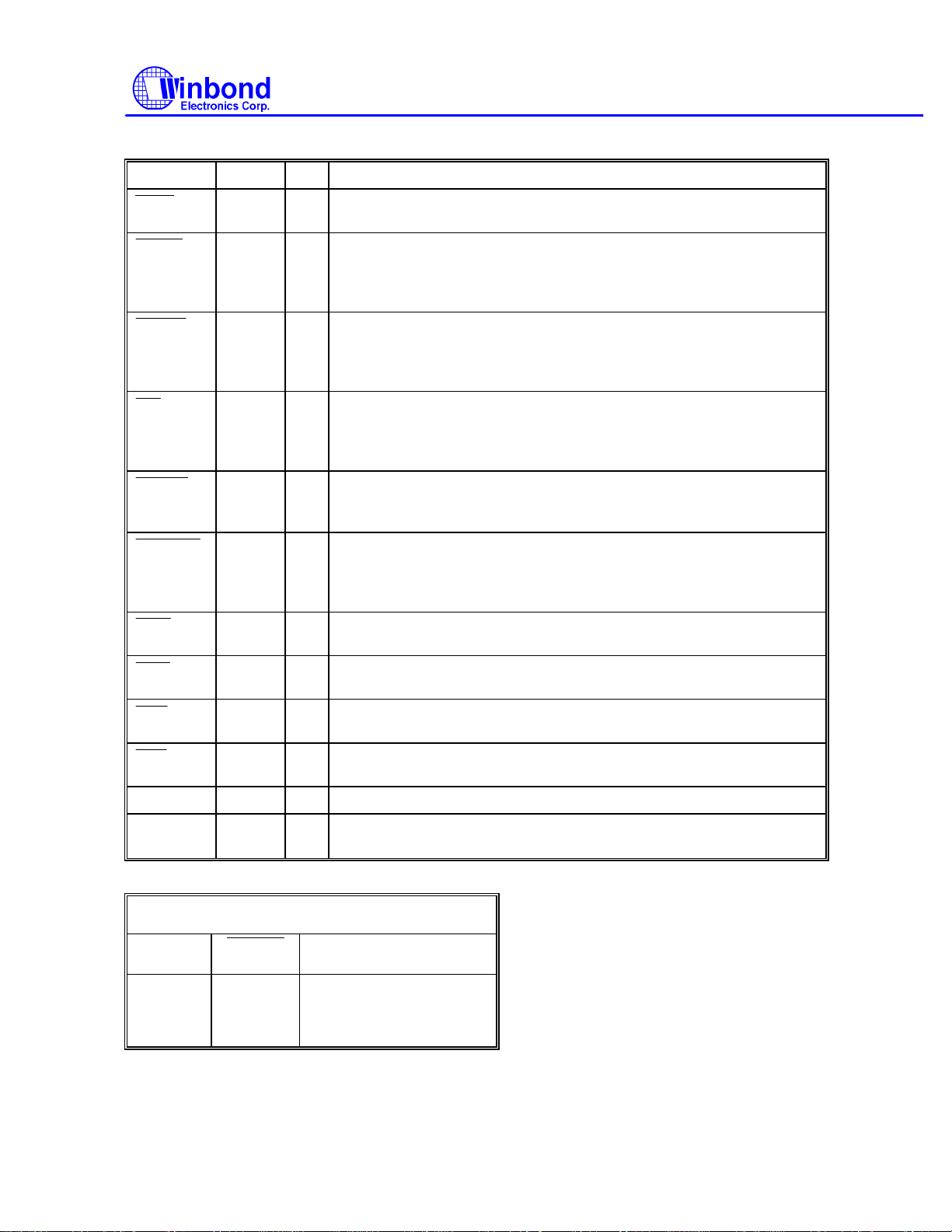
IDE and FDC Interface, continued
STEP
INDEX
TRAK
0
WP
RDATA
DSKCHG
MOA
MOB
DSA
DSB
GMWR
SYMBOL PIN I/O FUNCTION
W83787IF
82 OD
81 I
78 I
77 I
74 I
76 I
79 OD
80 OD
83 OD
84 OD
VDD 15, 56
Step output pulses. This active low open drain output produces a
pulse to move the head to another track.
This schmitt input from the disk drive is active low when the head is
positioned over the beginning of a track marked by an index hole.
This input pin is pulled up internally by an approximately 1K ohm
resistor. The resistor can be disabled by bit 4 of CR6 (FIPURDWN).
Track 0. This schmitt input from the disk drive is active low when the
head is positioned over the outermost track. This input pin is pulled
up internally by an approximately 1K ohm resistor. The resistor can
be disabled by bit 4 of CR6 (FIPURDWN).
Write protected. This active low schmitt input from the disk drive
indicates that the diskette is write-protected. This input pin is pulled
up internally by an approximately 1K ohm resistor. The resistor can
be disabled by bit 4 of CR6 (FIPURDWN).
The read data input signal from the FDD. This input pin is pulled up
internally by an approximately 1K ohm resistor. The resistor can be
disabled by bit 4 of CR6 (FIPURDWN).
Diskette change. This signal is active low at power on and whenever
the diskette is removed. This input pin is pulled up internally by an
approximately 1K ohm resistor. The resistor can be disabled by bit 4
of CR6 (FIPURDWN).
Motor A On. When set to 0, this pin enables disk drive 0. This is an
open drain output.
Motor B On. When set to 0, this pin enables disk drive 1. This is an
open drain output.
Drive Select A. When set to 0, this pin enables disk drive A. This is
an open drain output.
Drive Select B. When set to 0, this pin enables disk drive B. This is
an open drain output.
+5 power supply for the digital circuitry
GND 25, 40
65, 90
Table 1-1:
PARALLEL PORT FUNCTION MODE
POWER-ON SETTING
PDRQX
HPRTM1
L L Printer Mode (Default)
L H ECP/EPP
H L EPP
H H EXT2FDD
HPRTM0
Ground
Publication Release Date:Sep 1995
- 18 - Revision A1
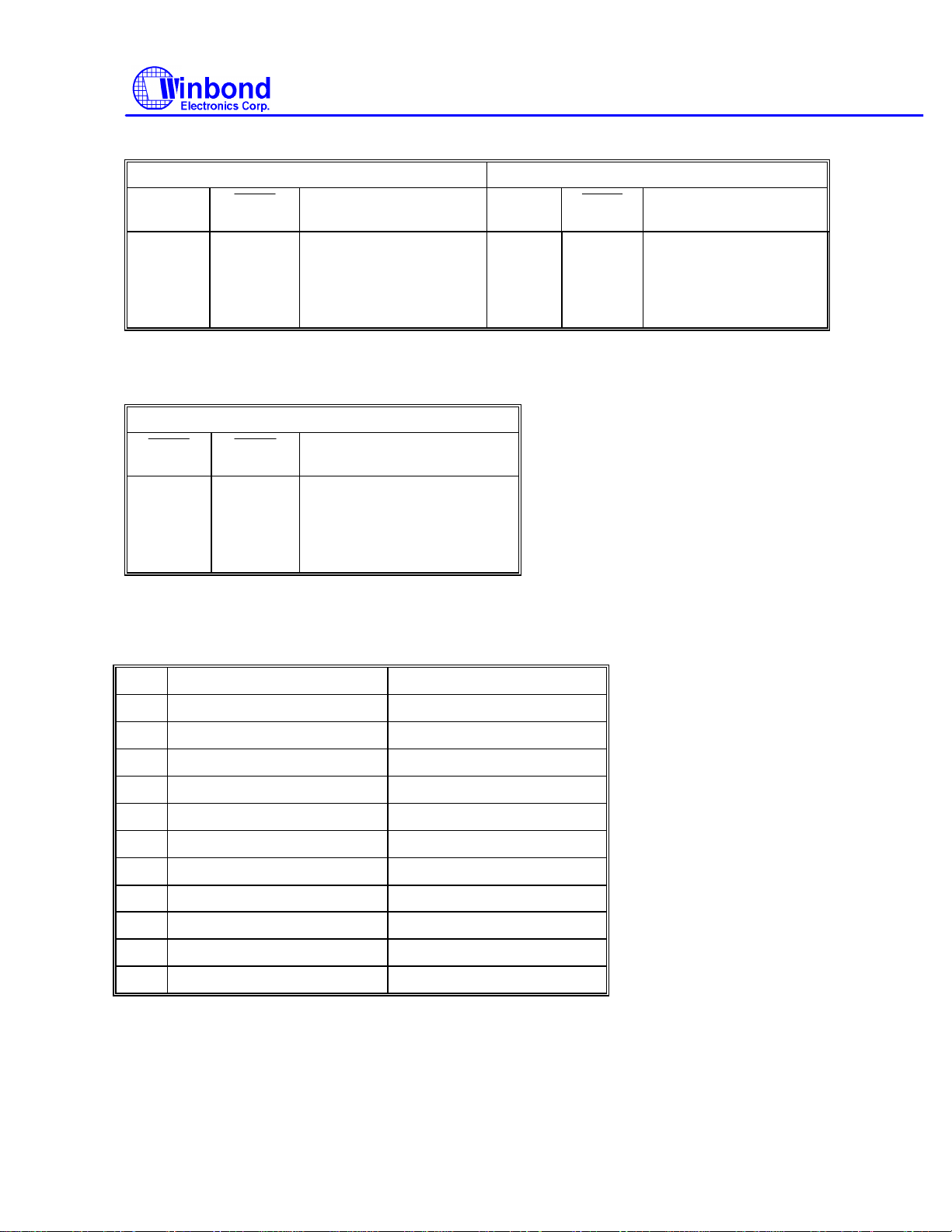
Table 1-2:
DTRB
RTSB
RTSA
DTRA
UART A UART B
SOUTA
HURAS1
L L COM4 (2E8) L L COM3 (3E8)
L H COM3 (3E8) L H COM4 (2E8)
H L COM1 (3F8) (Default) H L COM2 (2F8) (Default)
H H Disabled H H Disabled
Table 1-3 :
HURAS0
PARALLEL PORT
SOUTB
HURBS
HURBS0
W83787IF
HPRTS1
L L LPT3 (3BC)
L H LPT2 (278)
H L LPT1 (378) (Default)
H H Disabled
Note: When the parallel port is disabled, the eight function modes (W83757 mode, EXTFDD mode, EXTADP mode, EXT2FDD
mode, JOYSTICK mode, EPP mode, ECP mode, and ECP/EPP mode) are all inhibited.
Table 1-4 :
PIN W83787F/777F W83787IF
1 nRESIDE
2 PDBDIR/nFDCEN
3 PDCIN
42 SINB
43 SOUTB/HURBS1
91 nDBENL/ABCHG
92 nDBENH/FADSEL
93 nIOCS16 nIOCS16
HPRTS0
nRESIDE/IRRX3
PDBDIR/IRTX2/nFDCEN
PDCIN/IRRX2
SINB/IRRX1
SOUTB/IRTX1/HURBS1
nDBENL/nIDBEN/GIOSEL
nDBENH/GIO0/URIRSEL
94 nCS0/nIDEEN
95 nCS1/HADSEL
96 IDED7
nCS0/IRRX4/nIDEEN
nCS1/IRTX3/HADSEL
IDED7/GIO1
Publication Release Date:Sep 1995
- 19 - Revision A1

W83787IF
2.0 FDC FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
2.1 W83787IF FDC
The floppy disk controller of the W83787IF integrates all of the logic required for floppy disk
control.The FDC includes the following blocks: AT interface, Precompensation, Data Rate Selection,
Digital Data Separator, and FDC Core.
2.1.1 AT interface
The interface consists of the standard asynchronous signals: /RD, /WR, A0-A3, IRQ, DMA control,
and a data bus. The address lines select between the configuration registers, the FIFO and
control/status registers.
2.1.2 Data Separator
The function of the data separator is to lock onto the incoming serial read data. When a lock is
achieved the serial front end logic of the chip is provided with a clock which is synchronized to the
read data. The synchronized clock, called the Data Window, is used to internally sample the serial
data portion of the bit cell, and the alternate state samples the clock portion. Serial to parallel
conversion logic separates the read data into clock and data bytes.
The Digital Data Separator (DDS) has three parts: control logic, error adjustment, and speed tracking.
The DDS circuit cycles once every 12 clock cycles ideally. Any data pulse input will be synchronized
and then adjusted by immediate error adjustment. The control logic will generate RDD and RWD for
every pulse input. During any cycle where no data pulse is present, the DDS cycles are based on
speed. A digital integrator is used to keep track of the speed changes in the input data stream.
2.1.3 Write Precompensation
The write precompensation logic is used to minimize bit shifts in the RDDATA stream from the disk
drive. Shifting of bits is a known phenomenon in magnetic media and is dependent on the disk media
and the floppy drive.
The FDC monitors the bit stream that is being sent to the drive. The data patterns that require
precompensation are well known. Depending upon the pattern, the bit is shifted either early or late
relative to the surrounding bits.
2.1.4 FDC Core
The W83787IF FDC is capable of performing sixteen commands. Each command is initiated by a
multi-byte transfer from the microprocessor. The result can also be a multi-byte transfer back to the
microprocessor. Each command consists of three phases: command, execution, and result.
Command
The microprocessor issues all required information to the controller to perform a specific operation.
Execution
The controller performs the specified operation.
Result
After the operation is completed, status information and other housekeeping information is provided
to the microprocessor.
Publication Release Date:Sep 1995
- 20 - Revision A1

2.1.5 FDC Commands
Command Symbol Descriptions:
C: Cylinder number 0 - 256
D: Data Pattern
DIR: Step Direction
DIR = 0, step out
DIR = 1, step in
DS0: Disk Drive Select 0
DS1: Disk Drive Select 1
DTL: Data Length
EC: Enable Count
EOT: End of Track
EFIFO: Enable FIFO
EIS: Enable Implied Seek
EOT: End of track
FIFOTHR: FIFO Threshold
GAP: Gap length selection
GPL: Gap Length
H: Head number
HDS: Head number select
HLT: Head Load Time
HUT: Head Unload Time
LOCK: Lock EFIFO, FIFOTHR, PTRTRK bits prevent affected by software reset
MFM: MFM or FM Mode
MT: Multitrack
N: The number of data bytes written in a sector
NCN: New Cylinder Number
ND: Non-DMA Mode
OW: Overwritten
PCN: Present Cylinder Number
POLL: Polling Disable
PRETRK: Precompensation Start Track Number
R: Record
RCN: Relative Cylinder Number
R/W: Read/Write
SC: Sector/per cylinder
SK: Skip deleted data address mark
SRT: Step Rate Time
ST0: Status Register 0
ST1: Status Register 1
ST2: Status Register 2
ST3: Status Register 3
WG: Write gate alters timing of WE
W83787IF
Publication Release Date:Sep 1995
- 21 - Revision A1
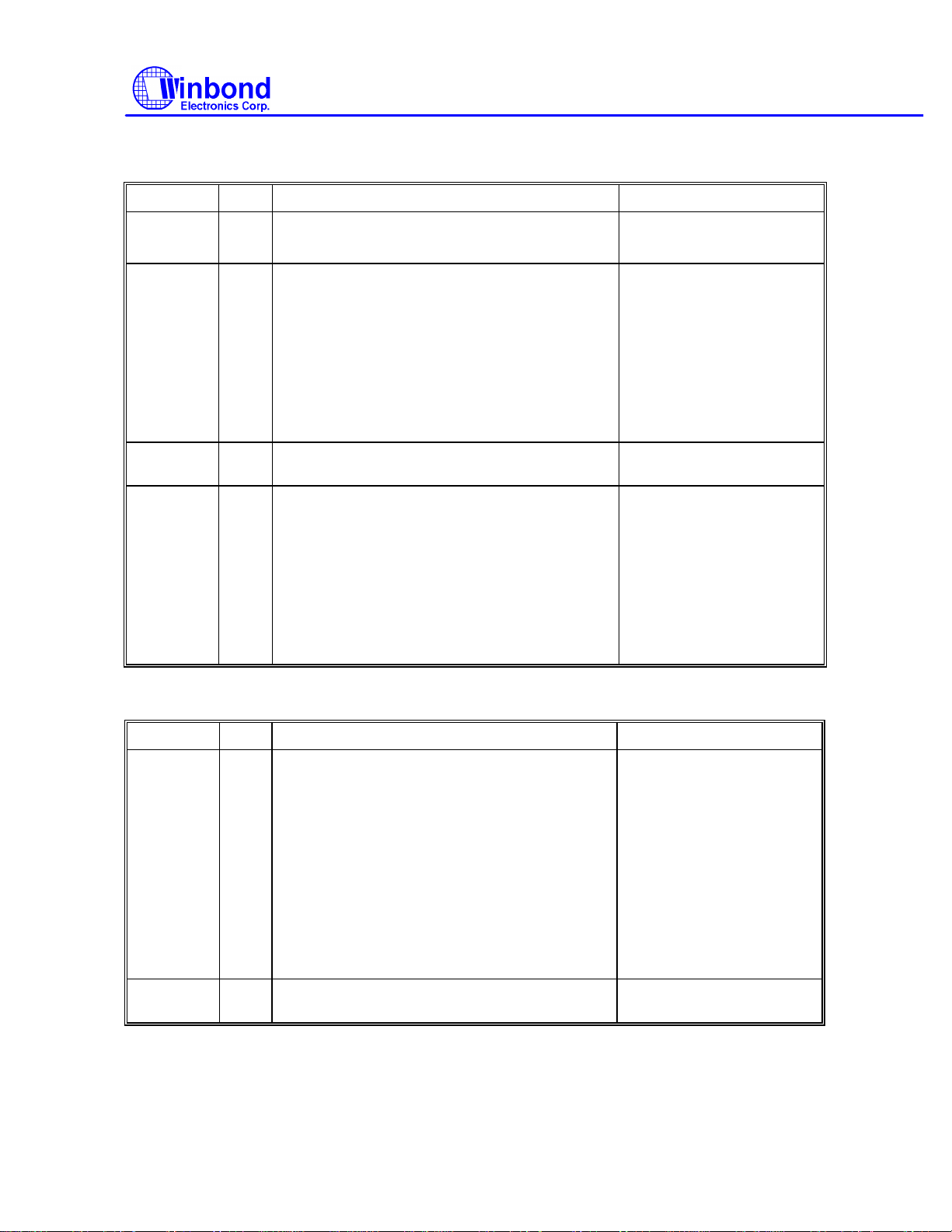
(1) Read Data
PHASE R/W D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 REMARKS
W83787IF
Command
Execution Data transfer between the
Result
W MT MFM SK 0 0 1 1 0
W 0 0 0 0 0 HDS DS1 DS0
W
W
W
W
W
W
W -------------------- DTL -----------------------
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
---------------------- C ------------------------
---------------------- H ------------------------
---------------------- R ------------------------
---------------------- N ------------------------
-------------------- EOT -----------------------
-------------------- GPL -----------------------
-------------------- ST0 -----------------------
-------------------- ST1 -----------------------
-------------------- ST2 -----------------------
---------------------- C ------------------------
---------------------- H ------------------------
---------------------- R ------------------------
---------------------- N ------------------------
Command codes
Sector ID information prior
to command execution
FDD and system
Status information after
command execution
Sector ID information after
command execution
(2) Read Deleted Data
PHASE R/W D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 REMARKS
Command
Execution Data transfer between the
W MT MFM SK 0 1 1 0 0
W
W
W
W
W
W
W
W -------------------- DTL -----------------------
0 0 0 0 0 HDS DS1 DS0
---------------------- C ------------------------
---------------------- H ------------------------
---------------------- R ------------------------
---------------------- N ------------------------
-------------------- EOT -----------------------
-------------------- GPL -----------------------
- 22 - Revision A1
Command codes
Sector ID information prior
to command execution
FDD and system
Publication Release Date:Sep 1995
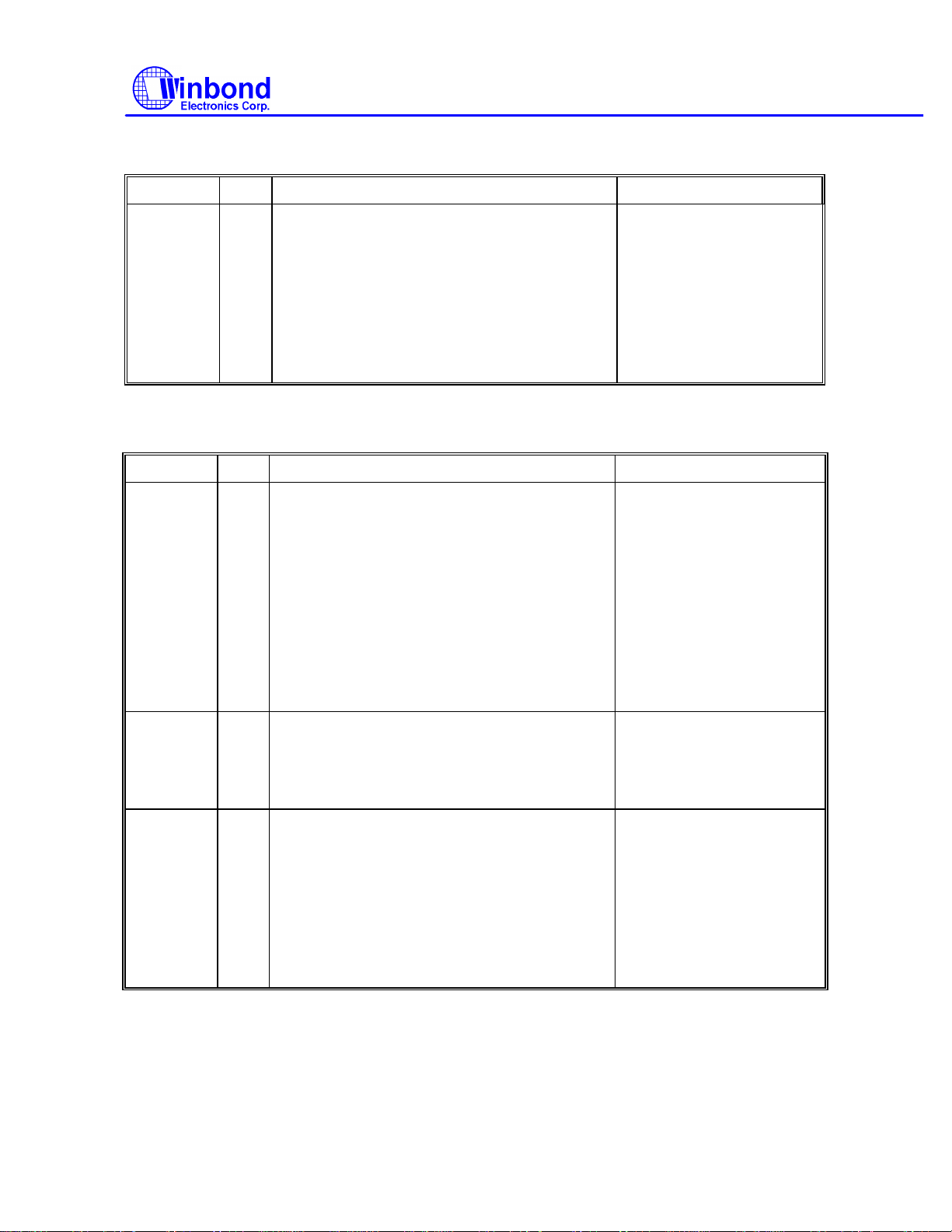
Read Deleted Data,Continued
PHASE R/W D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 REMARKS
W83787IF
Result
(3) Read A Track
PHASE R/W D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 REMARKS
Command
Execution Data transfer between the
Result
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
W 0 MFM 0 0 0 0 1 0
W 0 0 0 0 0 HDS DS1 DS0
W
W
W
W
W
W
W -------------------- DTL -----------------------
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
-------------------- ST0 -----------------------
-------------------- ST1 -----------------------
-------------------- ST2 -----------------------
---------------------- C ------------------------
---------------------- H ------------------------
---------------------- R ------------------------
---------------------- N ------------------------
---------------------- C ------------------------
---------------------- H ------------------------
---------------------- R ------------------------
---------------------- N ------------------------
-------------------- EOT -----------------------
-------------------- GPL -----------------------
-------------------- ST0 -----------------------
-------------------- ST1 -----------------------
-------------------- ST2 -----------------------
---------------------- C ------------------------
---------------------- H ------------------------
---------------------- R ------------------------
---------------------- N ------------------------
Status information after
command execution
Sector ID information after
command execution
Command codes
Sector ID information prior
to command execution
FDD and system; FDD
reads contents of all
cylinders from index hole to
EOT
Status information after
command execution
Sector ID information after
command execution
Publication Release Date:Sep 1995
- 23 - Revision A1
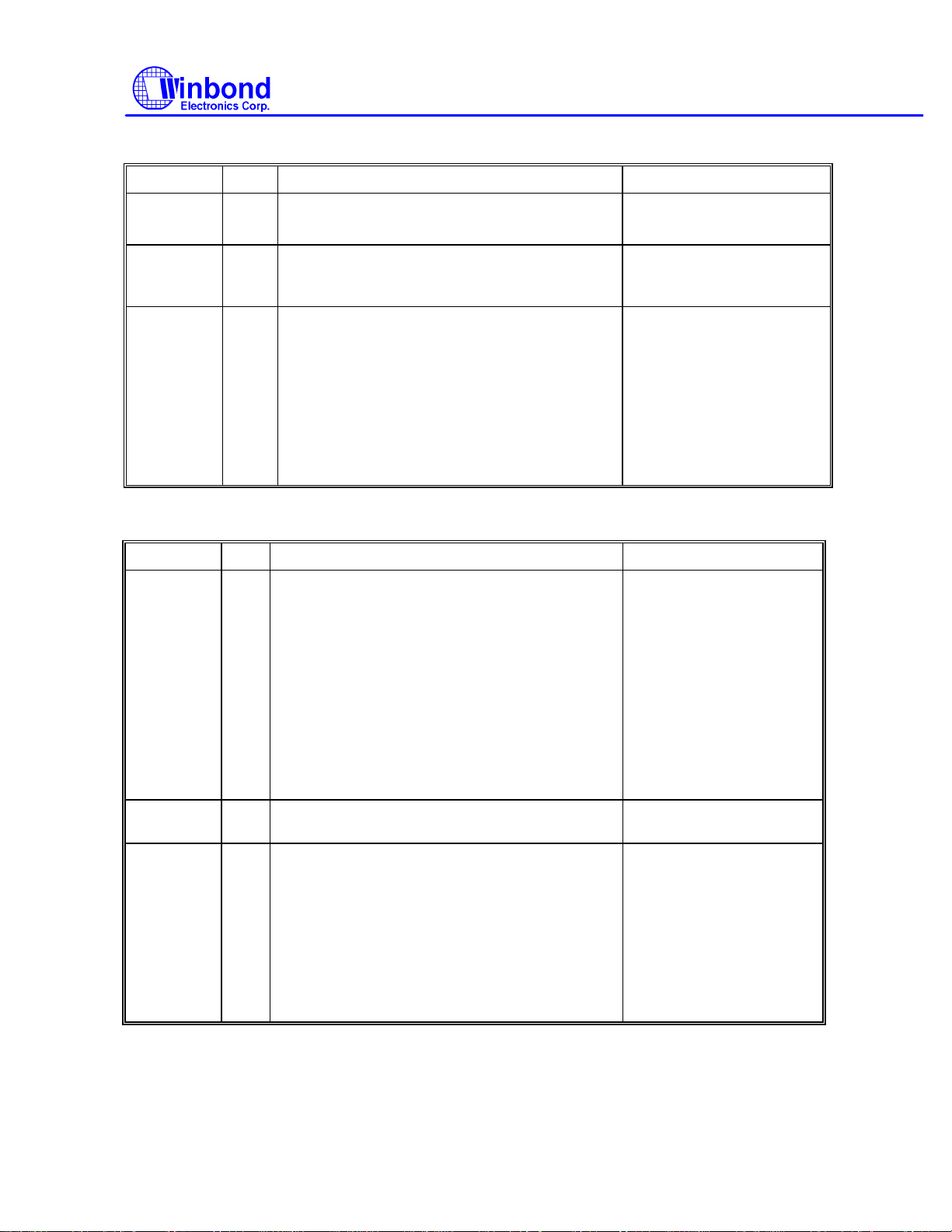
(4) Read ID
PHASE R/W D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 REMARKS
W83787IF
Command
Execution The first correct ID
Result
(5) Write Data
PHASE R/W D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 REMARKS
Command
Execution Data transfer between the
Result
W 0 MFM 0 0 1 0 1 0
W 0 0 0 0 0 HDS DS1 DS0
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
W MT MFM 0 0 0 1 0 1
W 0 0 0 0 0 HDS DS1 DS0
W
W
W
W
W
W
W -------------------- DTL -----------------------
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
-------------------- ST0 -----------------------
-------------------- ST1 -----------------------
-------------------- ST2 -----------------------
---------------------- C ------------------------
---------------------- H ------------------------
---------------------- R ------------------------
---------------------- N ------------------------
---------------------- C ------------------------
---------------------- H ------------------------
---------------------- R ------------------------
---------------------- N ------------------------
-------------------- EOT -----------------------
-------------------- GPL -----------------------
-------------------- ST0 -----------------------
-------------------- ST1 -----------------------
-------------------- ST2 -----------------------
---------------------- C ------------------------
---------------------- H ------------------------
---------------------- R ------------------------
---------------------- N ------------------------
Command codes
information on the cylinder
is stored in Data Register
Status information after
command execution
Disk status after the
command has been
completed
Command codes
Sector ID information prior
to Command execution
FDD and system
Status information after
Command execution
Sector ID information after
Command execution
Publication Release Date:Sep 1995
- 24 - Revision A1
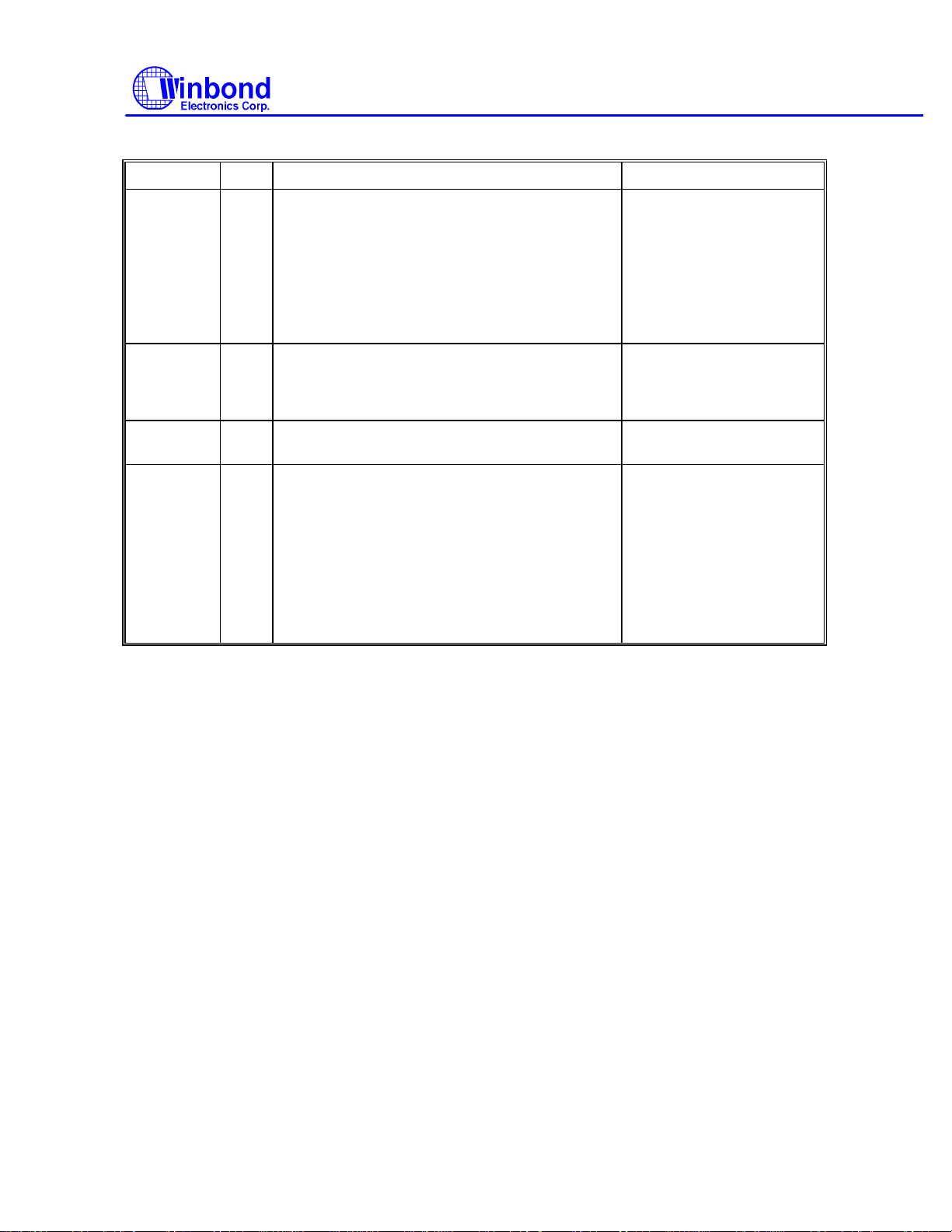
(6) Write Deleted Data
PHASE R/W D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 REMARKS
W83787IF
Command W MT MFM 0 0 1 0 0 1
W 0 0 0 0 0 HDS DS1 DS0
W
W
W
W
W
W
W
Execution
Result R
R
R
R
R
R
R
---------------------- C ------------------------
---------------------- H ------------------------
---------------------- R ------------------------
---------------------- N ------------------------
-------------------- EOT -----------------------
-------------------- GPL -----------------------
-------------------- DTL -----------------------
-------------------- ST0 -----------------------
-------------------- ST1 -----------------------
-------------------- ST2 -----------------------
---------------------- C ------------------------
---------------------- H ------------------------
---------------------- R ------------------------
---------------------- N ------------------------
Command codes
Sector ID information prior
to command execution
Data transfer between the
FDD and system
Status information after
command execution
Sector ID information after
command execution
Publication Release Date:Sep 1995
- 25 - Revision A1
(7) Format A Track
PHASE R/W D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 REMARKS
W83787IF
Command
Execution
for Each
Sector
Repeat:
Result
W 0 MFM 0 0 1 1 0 1
W 0 0 0 0 0 HDS DS1 DS0
W
W
W
W
W
W
W
W
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
---------------------- N ------------------------
--------------------- SC -----------------------
--------------------- GPL ---------------------
---------------------- D ------------------------
---------------------- C ------------------------
---------------------- H ------------------------
---------------------- R ------------------------
---------------------- N ------------------------
-------------------- ST0 -----------------------
-------------------- ST1 -----------------------
-------------------- ST2 -----------------------
---------------- Undefined -------------------
---------------- Undefined -------------------
---------------- Undefined -------------------
---------------- Undefined -------------------
Command codes
Bytes/Sector
Sectors/Cylinder
Gap 3
Filler Byte
Input Sector Parameters
Status information after
command execution
(8) Recalibrate
PHASE R/W D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 REMARKS
Command
Execution Head retracted to Track 0
(9) Sense Interrupt Status
PHASE R/W D7 76 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 REMARKS
Command
Result
W 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1
W 0 0 0 0 0 0 DS1 DS0
W 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0
R
R
---------------- ST0 -------------------------
---------------- PCN -------------------------
Command codes
Interrupt
Command code
Status information at the
end of each seek operation
Publication Release Date:Sep 1995
- 26 - Revision A1
(10) Specify
PHASE R/W D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 REMARKS
W83787IF
Command
(11) Seek
PHASE R/W D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 REMARKS
Command
Execution
(12) Sense Drive Status
PHASE R/W D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 REMARKS
Command
Result R ---------------- ST3 -------------------------
W 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1
W
W
W 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 Command codes
W
W
R
| ---------SRT ----------- | --------- HUT ---------- |
|------------ HLT ----------------------------------| ND
0 0 0 0 0 HDS DS1 DS0
-------------------- NCN -----------------------
W 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0
W 0 0 0 0 0 HDS DS1 DS0
Command codes
Head positioned over
proper cylinder on diskette
Command Code
Status information about
disk drive
(13) Invalid
PHASE R/W D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 REMARKS
Command
Result
W ------------- Invalid Codes -----------------
R -------------------- ST0 ----------------------
- 27 - Revision A1
Invalid codes (no operation
- FDC goes into standby
state)
ST0 = 80H
Publication Release Date:Sep 1995
(14) Scan Equal
PHASE R/W D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 REMARKS
W83787IF
Command
PHASE R/W D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 REMARKS
Execution Data compare between the
Result
W MT MFM SK 1 0 0 0 1
W 0 0 0 0 0 HDS DS1 DS0
W
W
W
W
W
W
W -------------------- DTL -----------------------
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
---------------------- C ------------------------
---------------------- H ------------------------
---------------------- R ------------------------
---------------------- N ------------------------
-------------------- EOT -----------------------
-------------------- GPL -----------------------
-------------------- ST0 -----------------------
-------------------- ST1 -----------------------
-------------------- ST2 -----------------------
---------------------- C ------------------------
---------------------- H ------------------------
---------------------- R ------------------------
---------------------- N ------------------------
Command codes
Sector ID information prior
to command execution
FDD and system
Status information after
command execution
Sector ID information after
command execution
Publication Release Date:Sep 1995
- 28 - Revision A1
(15) Scan Low or Equal
PHASE R/W D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 REMARKS
W83787IF
Command
Execution Data compare between
Result
W MT MFM SK 1 1 0 0 1
W 0 0 0 0 0 HDS DS1 DS0
W
W
W
W
W
W
W -------------------- DTL -----------------------
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
---------------------- C ------------------------
---------------------- H ------------------------
---------------------- R ------------------------
---------------------- N ------------------------
-------------------- EOT -----------------------
-------------------- GPL -----------------------
-------------------- ST0 -----------------------
-------------------- ST1 -----------------------
-------------------- ST2 -----------------------
---------------------- C ------------------------
---------------------- H ------------------------
---------------------- R ------------------------
---------------------- N ------------------------
Command codes
Sector ID information prior
to command execution
the FDD and system
Status information after
command execution
Sector ID information after
command execution
Publication Release Date:Sep 1995
- 29 - Revision A1
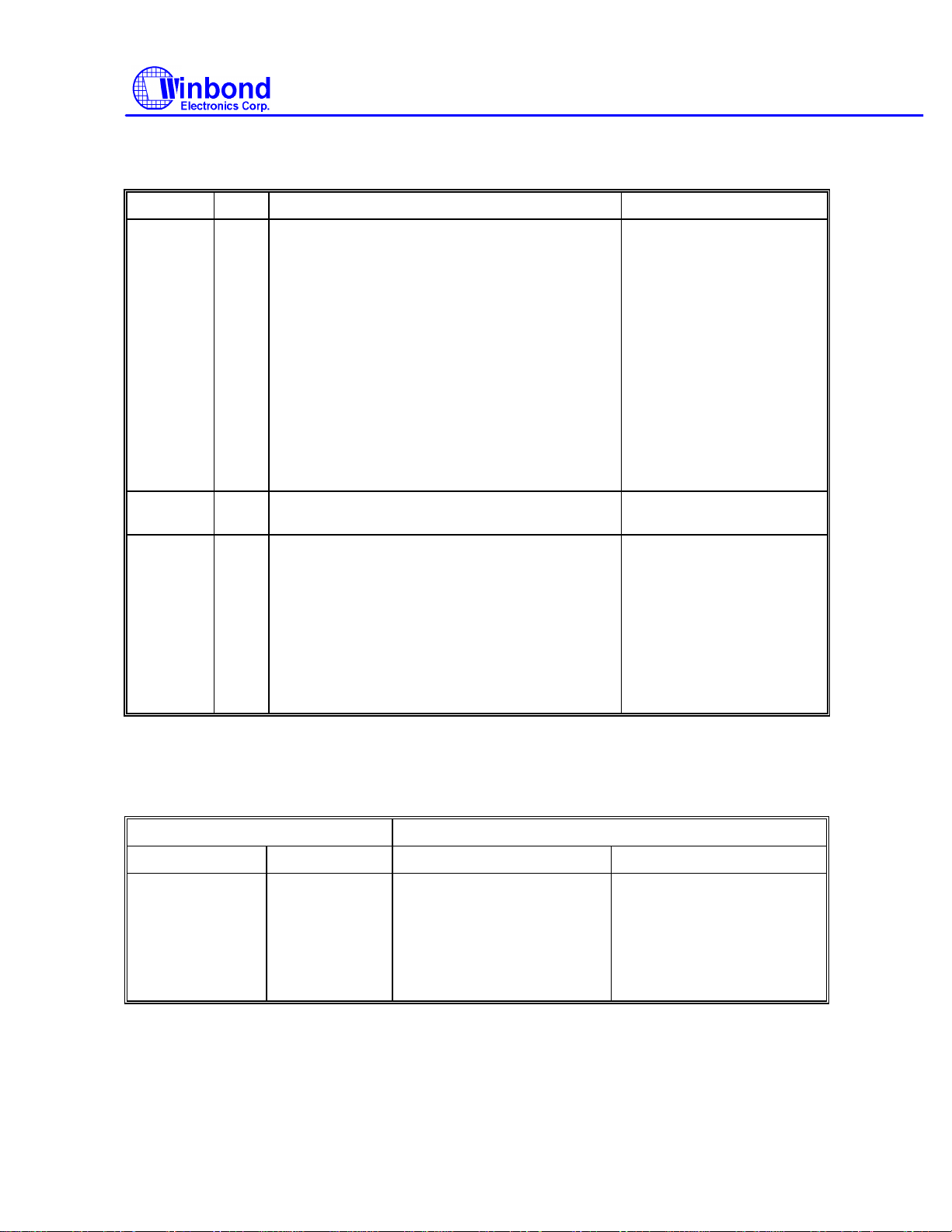
(16) Scan High or Equal
PHASE R/W D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 REMARKS
W83787IF
Comman
d
Execution Data compare between the
Result
W MT MFM SK 1 1 1 0 1
W 0 0 0 0 0 HDS DS1 DS0
W
W
W
W
W
W
W -------------------- DTL -----------------------
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
---------------------- C ------------------------
---------------------- H ------------------------
---------------------- R ------------------------
---------------------- N ------------------------
-------------------- EOT -----------------------
-------------------- GPL -----------------------
-------------------- ST0 -----------------------
-------------------- ST1 -----------------------
-------------------- ST2 -----------------------
---------------------- C ------------------------
---------------------- H ------------------------
---------------------- R ------------------------
---------------------- N ------------------------
Command codes
Sector ID information prior
to command execution
FDD and system
Status information after
command execution
Sector ID information after
command execution
2.3 Register Descriptions
There are status, data, and control registers in the W83787IF. The addresses of these registers are
defined below:
ADDRESS REGISTER
PRIMARY SECONDARY READ WRITE
3F2
3F3
3F4 374 MS REGISTER Reserved
3F5 375 DT REGISTER DT REGISTER
3F7 377 DI REGISTER CC REGISTER
372
373
DO REGISTER
TD REGISTER
Publication Release Date:Sep 1995
- 30 - Revision A1
 Loading...
Loading...