Page 1

EOM
Engineering
Operation &
Maintenance
P820/P830
FIT Metal Pump
Where Innovation Flows
wildenpump.com
Page 2

TABLE OF CONTENTS
SECTION 1 CAUTIONS—READ FIRST! ..............................................1
SECTION 2 WILDEN PUMP DESIGNATION SYSTEM .................................2
SECTION 3 HOW IT WORKS—PUMP & AIR DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM ................3
SECTION 4 DIMENSIONAL DRAWINGS .............................................4
SECTION 5 PERFORMANCE
P820/P830 Metal Rubber-Fitted ..............................................6
P820/P830 Metal EZ-Install TPE-Fitted .........................................6
P820/P830 Metal Reduced-Stroke PTFE-Fitted ..................................7
P820/P830 Metal Full-Stroke PTFE-Fitted ......................................7
Suction-Lift Curves ........................................................8
SECTION 6 SUGGESTED INSTALLATION, OPERATION & TROUBLESHOOTING .......10
SECTION 7 DISASSEMBLY / REASSEMBLY ........................................13
Air Valve / Center Section Disassembly ......................................16
Reassembly Hints & Tips ..................................................19
SECTION 8 EXPLODED VIEW & PARTS LISTING
P820/P830 Metal .........................................................20
SECTION 9 ELASTOMER OPTIONS .................................................22
Page 3
Section 1
CAUTIONS—READ FIRST!
CAUTION : Do not apply compressed air to the
exhaust port — pump will not function.
CAUTION: Do not over-lubricate air supply —
excess lub rication will reduce pump p erformance .
Pump is pre-lubed.
TEMPERATURE LIMITS:
Acetal –29°C to 82°C –20°F to 180°F
Buna-N –12°C to 82°C 10°F to 180°F
Geolast
®
–40°C to 82°C –40°F to 180°F
Neoprene –18°C to 93°C 0°F to 200°F
Nordel
®
EPDM –51°C to 138°C –60°F to 280°F
Nylon –18°C to 93°C 0°F to 200°F
PFA –7°C to 107°C 45°F to 225°F
Polypropylene 0°C to 79°C 32°F to 175°F
Polyurethane –12°C to 66°C 10°F to 150°F
PVDF –12°C to 107°C 10°F to 225°F
Saniflex™ –29°C to 104°C –20°F to 220°F
SIPD PTFE with EPDM-backed
SIPD PTFE with Neoprene-backed
PTFE
Viton
1
4°C to 104°C 40°F to 220°F
®
FKM –40°C to 177°C –40°F to 350°F
4°C to 137°C 40°F to 280°F
4°C to 93°C 40°F to 200°F
Wil-Flex™ –40°C to 107°C –40°F to 225°F
1
4°C to 149°C (40°F to 300°F) - 13 mm (1/2") and 25 mm (1") models only.
CAUTION: Do not exceed 82°C (180°F) air inlet
®
temperature for Pro-Flo
models.
CAUTION: Pumps should be thoroughly flushed
before installing into process lines. FDA- and
USDA-approved pumps should be cleaned and /
or sanitized before being used.
CAUTION: Always wear safety glasses when
operating pump. If diaphragm rupture occurs,
material being pumped may be forced out air
exhaust.
CAUTION: Before any maintenance or repair is
attempted, the compressed air line to the pump
should be disconnected and all air pressure
allowed to bleed from pump. Disconnect all
intake, discharge and air lines. Drain the pump
by turning it upside down and allowing any fluid
to flow into a suitable container.
CAUTION: Blow out air line for 10 to 20 seconds
before attaching to pump to make sure all pipeline
debris is clear. Use an in-line air filter. A 5μ
(micron) air filter is recommended.
NOTE:
Not all materials are available for all models.
Refer to Section 2 for material options for your pump.
CAUTION: When choosing pump materials, be
sure to check the temperature limits for all wet-
ted components. Example: Viton® has a maxi-
mum limit of 177°C (350°F), but polypropylene
has a maximum limit of only 79°C (175°F).
CAUTION: Maximum temperature limits are
based upon mechanical stress only. Certain
chemicals will significantly reduce maximum
safe operating temperatures. Please consult the
Wilden Chemical Resistance Guide.
WARNING : Prevent static sparking — If static
sparking occurs, fire or explosion could result.
Pump, valves and containers must be grounded
to a proper grounding point when handling
flammable fluids and whenever discharge of
static electricity is a hazard.
CAUTION: Do not exceed 8.6 bar (125 psig) air
supply pressure.
CAUTION: The process fluid and cleaning fluids
must be chemically compatible with all wetted
pump components. Please consult the Wilden
Chemical Resistance Guide.
NOTE: When installing PTFE diaphragms, it is
important to tighten outer pistons simultaneously
(turning in opposite directions) to ensure tight fit.
(See torque specifications in Section 7.)
NOTE: Some PTFE-fitted pumps come standard
from the factory with expanded PTFE gaskets
installed in the diaphragm bead of the liquid
chamber. PTFE gaskets cannot be re-used.
NOTE: Before starting disassembly, mark a line
from each liquid chamber to its corresponding air
chamber. This line will assist in proper alignment
during reassembly.
CAUTION: Pro-Flo® pumps cannot be used
in submersible applications. Pro-Flo® SHIFT
pumps do have a single-point exhaust option
for submersible applications. Do not use
®
standard Pro-Flo
SHIFT models in submersible
applications.
CAUTION : Tighten all hardware prior to installation.
WIL-115 9 0 -E- 01 1 WILDEN PUMP & ENGINEERING, LLC
Page 4
Section 2
WILDEN PUMP DESIGNATION SYSTEM
P820/P830 METAL
51 mm (2") Pump
Maximum Flow Rate:
609 lpm (161 gpm)
MATERIAL CODES
LEGEND
MODEL
XP 8 2 0 = PRO-FLO® THREADED
XP83 0 = PRO-FLO® FL ANGED
WETTED PARTS/OUTER PISTON
AA = ALUMINUM / ALUMINUM
SS = STAINLESS ST EEL /
STAINLESS STEEL
WW
AIR CHAMBERS
A = ALUMINUM
CENTER BLOCK
P = POLYPROP YLENE
AIR VALVE
P = POLYPROPYL ENE
PORTS
PORTS
= DUC TILE IRON /
DUCTILE IRON
P820 / XXX XX / XXX / XX / XXX / XXXX
MODEL
DIAPHRAGMS
VALVE BALLS
AIR VALVE
CENTER BLOCK
AIR CHAMBERS
WETTED PARTS & OUTER PISTON
DIAPHRAGMS
BNS = BUNA-N (Red Dot)
EPS = EPDM (Blue Dot)
FWS = SANITARY WIL-FLEXTM,
EZ-INSTALL [Santoprene®
(Two Black Dots)]
NES = NEOPRENE (Green Dot)
TEU = PTFE W/EPDM BACKUP
(White)
TNU = PTFE W/NEOPRENE
BACKUP (White)
TSS = FULL-STROKE PTFE W/
SANIFLEX™ BACK-UP
TSU = PTFE W/SANIFLEX™
BACKUP (White)
TWS = FULL-STROKE PTFE W/WIL-
FLEX™ BACKUP
VTS = VITON® (White Dot)
XBS = CONDUCTIVE BUNA-N
(Two Red Dots)
ZGS = GEOLAST®, EZ-INSTALL
(Black)
ZPS = POLYURETHANE, EZ-INSTALL
(Clear)
ZSS = SANIFLEX™, EZ-INSTALL
[Hytrel® (Cream)]
ZWS = WIL-FLEX™, EZ-INSTALL
[Santoprene® (Three Black
Dots)]
O-RINGS
VALVE SE ATS
VALVE BALLS
BN = BUNA-N (Red Dot)
FS = SANIFLEX™ [Hytrel® (Cream)]
FW = SANITARY WIL-FLEXTM
[Santoprene®
(Two Black Dots)]
EP = EPDM (Blue Dot)
NE = NEOPRENE (Green Dot)
PU = POLYURETHANE (Brown)
TF = PTFE (White)
VT = VITON® (Silver or White Dot)
WF = WIL-FLEX™ [Santoprene®
VALVE SEATS
A = ALUMINUM
BN = BUNA-N (Red Dot)
EP = EPDM (Blue Dot)
FS = SANIFLEX™ [Hytrel® (Cream)]
FW = SANITARY WIL-FLEXTM
[Santoprene®
(Two Black Dots)]
M = MILD STEEL
NE = NEOPRENE (Green Dot)
PU = POLYURETHANE (Brown)
S = STAINLESS STEEL
VT = VITON® (White Dot)
WF = WIL-FLEX™ [Santoprene®
SPECIALT Y
CODE
(if applicable)
(Three Black Dots)]
(Three Black Dots)]
SPECIALTY CODES
0014 BSPT
0100 Wil-Gard 110V
0102 Wil-Gard sensor wires ONLY
0103 Wil-Gard 220V
NOTE: Most elastomeric materials use colored dots for identification.
NOTE: Not all models are available with all material options.
Viton® is a registered trademark of DuPont Dow Elastomers.
WILDEN PUMP & ENGINEERING, LLC 2 WIL-115 9 0 -E- 01
0480 Pump Cycle Monitor (sensor & wires)
0483 Pump Cycle Monitor (module, sensor & wires)
0485 Pump Cycle Monitor (module, sensor & wires), DIN flange
0504 DIN flange
VALVE SEAT O-RINGS
TF = PTFE
Page 5
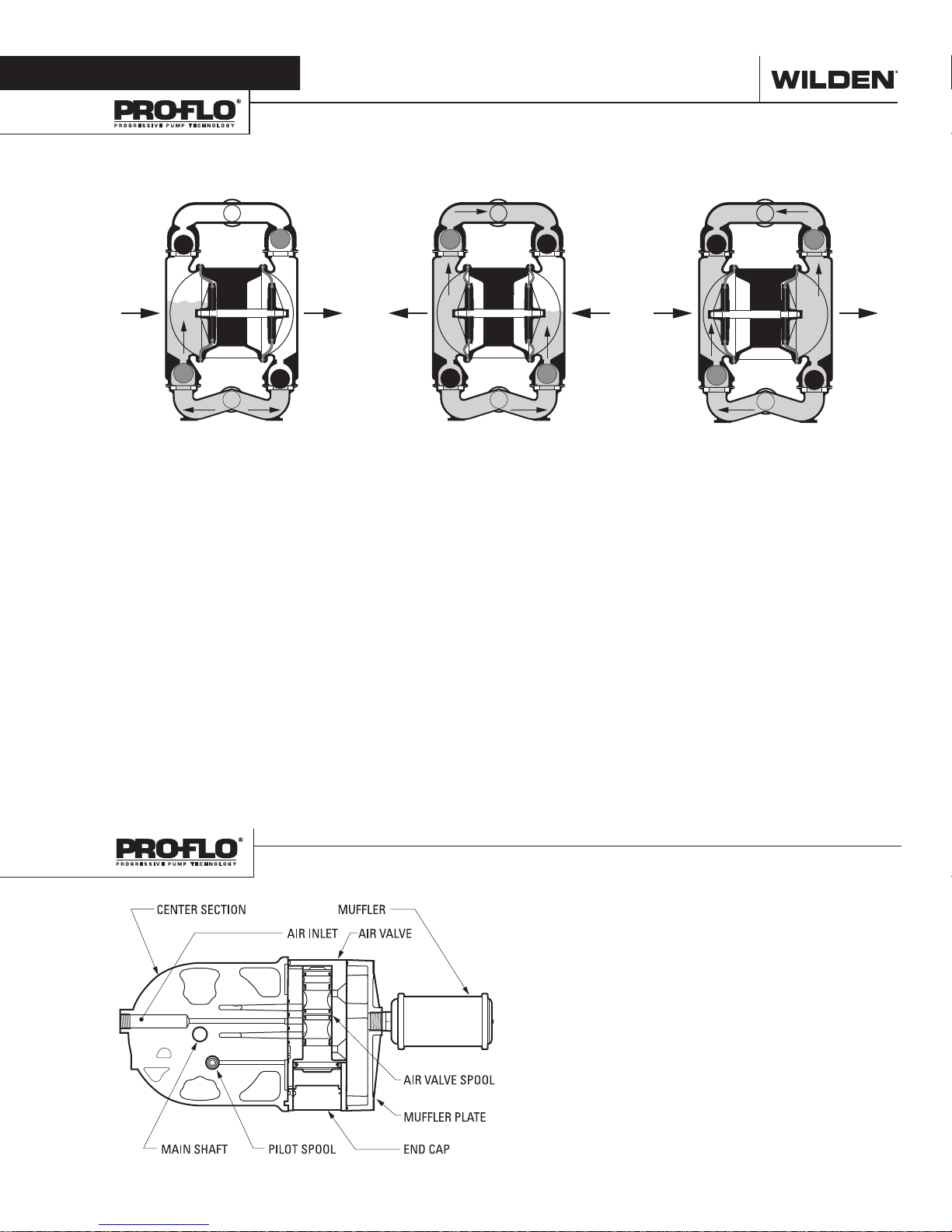
Section 3
HOW IT WORKS—PUMP
The Wilden diaphragm pump is an air-operated, positive displacement, self-priming pump. These drawings show flow pattern
through the pump upon its initial stroke. It is assumed the pump has no fluid in it prior to its initial stroke.
CLOSED
OUTLET
OPEN
B A
INLET
FIGUR E 1 The air valve dire cts pre ssurized
air to the back side of diaphragm A. The
compressed air is applied directly to the
liquid column separated by elastomeric
diaphragms. The diaphragm ac ts as
a separation membrane bet ween the
compressed air and liquid; a balanced
load removes mechanical stress from the
diaphragm. The compressed air moves
the diaphragm away from the center
of the pump. The opposite diaphragm
is pulled in by the shaft connected to
the pressurized diaphragm. Diaphragm
B is on its suction stroke; air behind
the diaphragm has been forced out to
atmosphere through the exhaust port of
the pump. The movement of diaphragm
B toward the center of the pump creates
a vacuum within chamber B. A tmosphe ric
pressure forces fluid into the inlet
manifold forcing the inlet valve ball off its
seat. Liquid is free to move past the inlet
valve ball and fill the liquid chamber (see
shaded area).
CLOSEDOPEN
OPEN
OUTLET
CLOSED
B A
CLOSED OPEN
FIGURE 2
phragm
, diaphragm A, reaches the limit
of its discharge stroke, the air valve
redirects pressurized air to the back side of
diaphragm B. The pressurized air forces
diaphragm B away from the center
while pulling diaphragm A to the center.
Diaphragm B is now on its discharge
stroke. Diaphragm B forces the inlet valve
ball onto its seat due to the hydraulic
forces developed in the liquid chamber
and manifold of the pump. These same
hydraulic forces lift the discharge valve
ball off its seat, while the opposite
discharge valve ball is forced onto its seat,
forcing fluid to flow through the pump
discharge. The movement of diaphragm A
toward the center of the pump creates a
vacuum within liquid chamber A. Atmospheric pressure forces fluid into the inlet
manifold of the pump. The inlet valve ball
is forced off its seat allowing the fluid
being pumped to fill the liquid chamber.
INLET
When the pressurized dia-
CLOSED OPEN
OUTLET
B A
OPEN
FIGURE 3 At completion of the stroke,
the air valve again redirects air to the
back side of diaphragm A, which starts
diaphragm B on its exhaust stroke. As
the pump reaches its original star ting
point, each diaphragm has gone through
one exhaust and one discharge stroke.
This constitutes one complete pumping
cycle. The pump may take several cycles
to completely prime depending on the
conditions of the application.
INLET
CLOSED
HOW IT WORKS—AIR DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM
WIL-115 9 0 -E- 01 3 WILDEN PUMP & ENGINEERING, LLC
The Pro-Flo® patented air distribution system incorporates
two moving par ts : the air valve spool and the pilot spool. The
heart of the system is the air valve spool and air valve. This
valve design incorporates an unbalanced spool. The smaller
end of the spool is pressurized continuously, while the large
end is alternately pressurized then exhausted to move the
spool. The spool directs pressurized air to one air chamber
while exhausting the other. The air causes the main shaft/
diaphragm assembly to shif t to one side — discharging liquid
on that side and pulling liquid in on the other side. When the
shaft reaches the end of its stroke, the inner piston actuates
the pilot spool, which pressurizes and exhausts the large end
of the air valve spool. The repositioning of the air valve spool
routes the air to the other air chamber.
Page 6
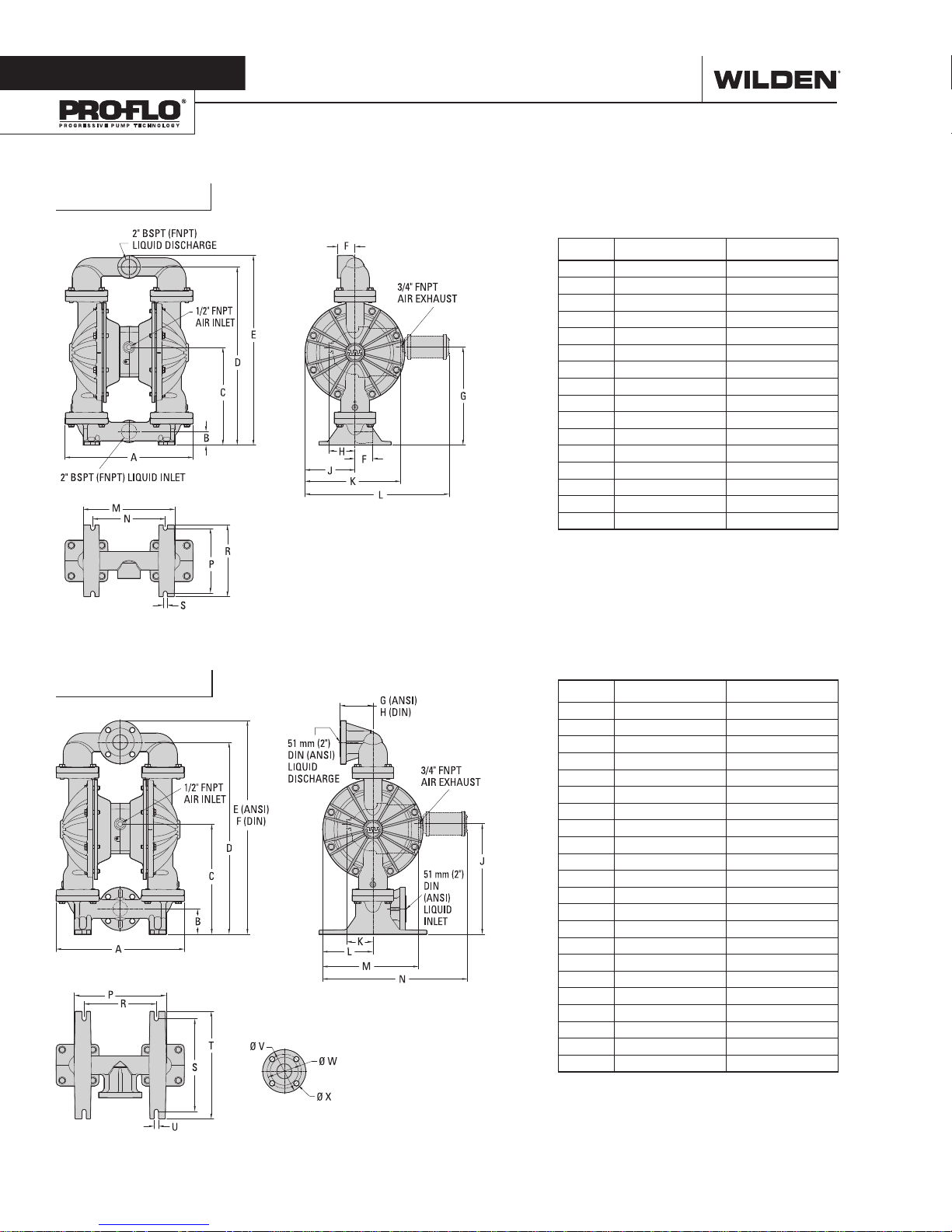
Section 4
P820 Metal
DIMENSIONAL DRAWINGS
DIMENSIONS
ITEM METRIC (mm) STANDARD (Inch)
A 453 17.9
B 48 1.9
C 346 13.6
D 630 24.8
E 670 26.4
F 62 2.4
G 347 13.7
H 93 3.7
J 177 7.0
K 338 13.3
L 510 20.1
M 324 12.8
N 257 10.1
P 229 9.0
R 254 10.0
S 14 0.6
LW0369 REV. A
P830 Metal
DIMENSIONS
ITEM METRIC (mm) STANDARD (Inch)
A 452 17.8
B 89 3.5
C 387 15.3
D 675 26.6
E 752 29.6
F 758 29.8
G 116 4.6
H 117 4.6
J 389 15.3
K 93 3.7
L 177 7.0
M 338 13.3
N 510 20.1
P 324 12.8
R 254 10.0
S 326 12.8
T 378 14.9
U 16 0.6
DIN (mm) ANSI (Inch)
V 165 DIA. 6.0 DIA.
W 125 DIA. 4.8 DIA.
X 18 DIA. 0.8 DIA.
LW0370 REV. A
WILDEN PUMP & ENGINEERING, LLC 4 WIL-115 9 0 -E- 01
Page 7
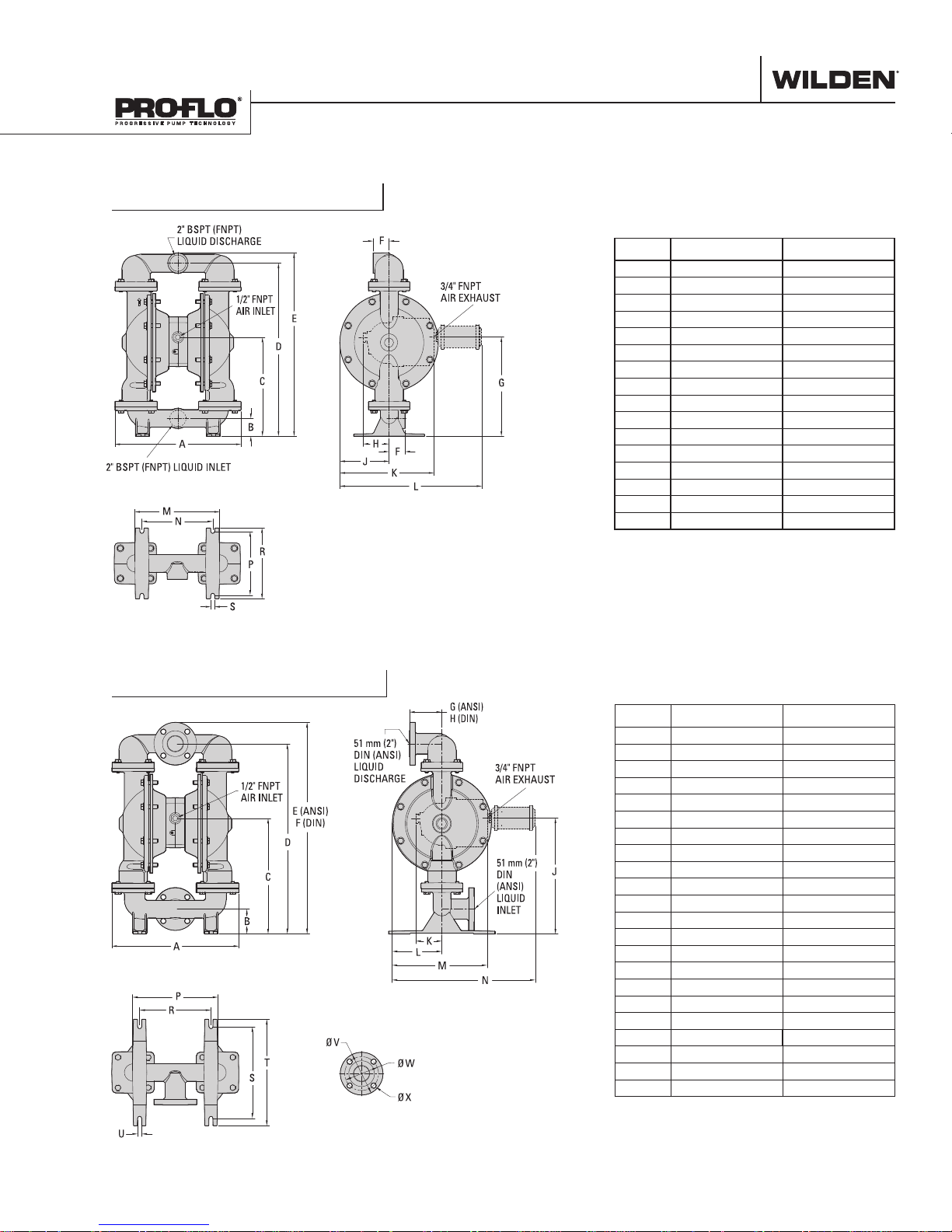
DIMENSIONAL DRAWINGS
P820 Stainless Steel
DIMENSIONS
ITEM METRIC (mm) STANDARD (Inch)
A 452 17.8
B 64 2.5
C 354 14.0
D 620 24.4
E 658 25.9
F 58 2.3
G 356 14.0
H 93 3.7
J 178 7.0
K 338 13.3
L 510 20.1
M 305 12.0
N 254 10.0
P 229 9.0
R 254 10.0
S 15 0.6
LW0371 REV. A
P830 Stainless Steel
DIMENSIONS
ITEM METRIC (mm) STANDARD (Inch)
A 452 17.8
B 89 3.5
C 412 16.2
D 678 26.7
E 754 29.7
F 760 29.9
G 116 4.6
H 115 4.5
J 413 16.3
K 93 3.7
L 177 7.0
M 338 13.3
N 510 20.1
P 304 12.0
R 254 10.0
S 325 12.8
T 379 14.9
U 14 0.6
DIN (mm) ANSI (Inch)
V 165 DIA. 6.0 DIA.
W 125 DIA. 4.8 DIA.
X 18 DIA. 0.8 DIA.
LW0372 REV. A
WIL-115 9 0 -E- 01 5 WILDEN PUMP & ENGINEERING, LLC
Page 8
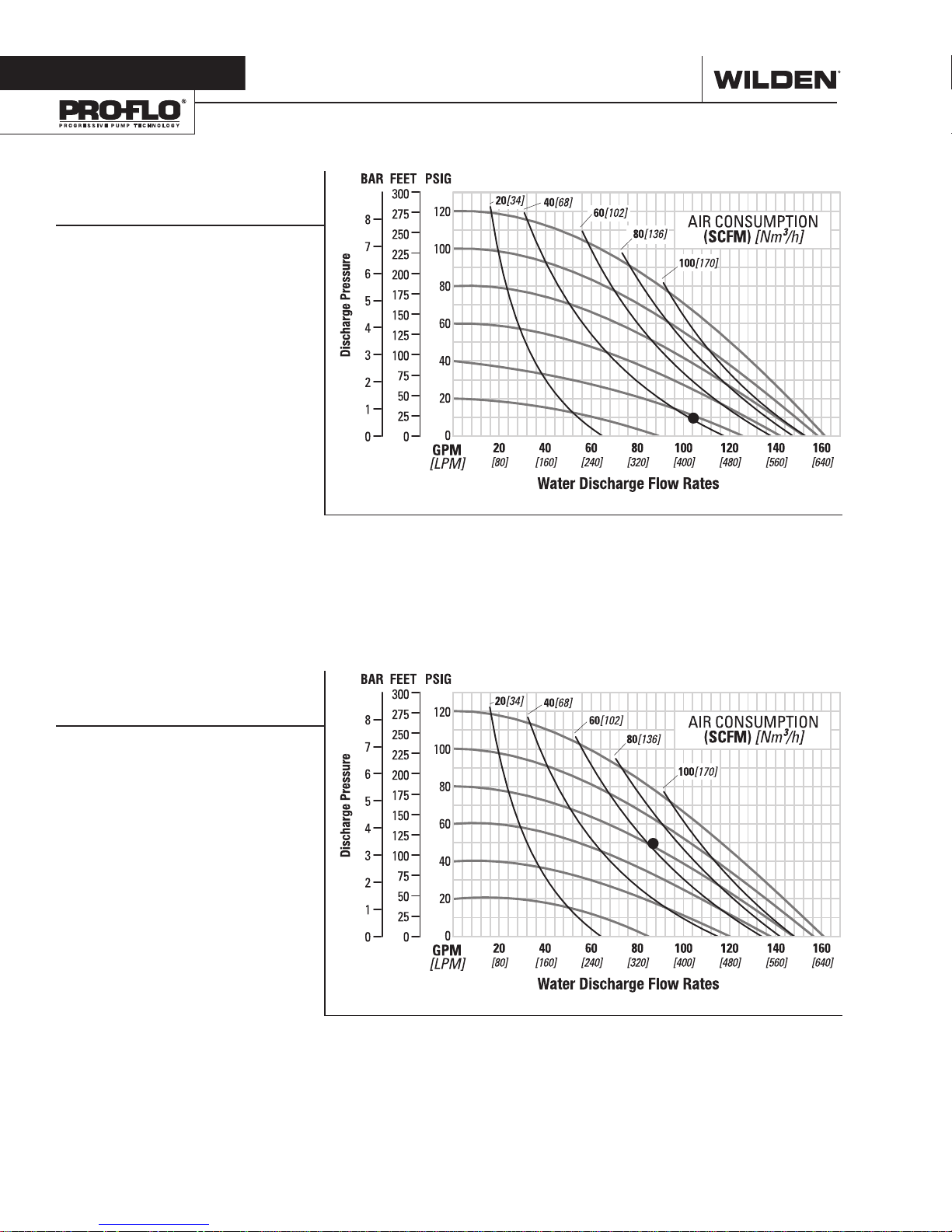
Section 5
PERFORMANCE
P820/P830 METAL
RUBBER-FITTED
Ship Weight ... 820 Threaded AL 47 kg (104 lb)
820 Threaded SS 73 kg (161 lb)
820 Threaded Iron 71 kg (156 lb)
830 Flanged AL 54 kg (118 lb)
830 Flanged SS 81 kg (178 lb)
830 Flanged Iron 82 Kg (181 lb)
Air Inlet ........................................19 mm (3/4”)
Inlet .................................................51 mm (2”)
Outlet ..............................................51 mm (2”)
Suction Lift .............................7.4 m Dry (24.3’)
9.0 m Wet (29.5’)
Disp. per Stroke1 ...................... 2.8 L (0.74 gal)
Max. Flow Rate ................. 609 lpm (161 gpm)
Max. Size Solids .........................6.4 mm (1/4”)
1
Displacement per stroke was calculated at
4.8 bar (70 psig) air inlet pressure against
2 bar (30 psig) head pressure.
Example: To pump 394 lpm (104 gpm) against
a discharge head of 0.69 bar (10 psig) requires
2.8 bar (40 psig) and 63 Nm3/h (40 scfm) air
consumption.
Caution: Do not exceed 8.6 bar (125 psig) air
supply pressure.
Flow rates indicated on chart were determined by pumping water.
For optimum life and performance, pumps should be specified so that daily operation
parameters will fall in the center of the pump's performance curve.
P820/P830 METAL
EZ-INSTALL TPE-FITTED
Ship Weight ... 820 Threaded AL 47 kg (104 lb)
820 Threaded SS 73 kg (161 lb)
820 Threaded Iron 71 kg (156 lb)
830 Flanged AL 54 kg (118 lb)
830 Flanged SS 81 kg (178 lb)
830 Flanged Iron 82 Kg (181 lb)
Air Inlet ........................................19 mm (3/4”)
Inlet .................................................51 mm (2”)
Outlet ..............................................51 mm (2”)
Suction Lift ............................ 6.7 m Dry (21.9’)
9.0 m Wet (29.5’)
Disp. per Stroke
Max. Flow Rate ................. 605 lpm (160 gpm)
Max. Size Solids .........................6.4 mm (1/4”)
1
Displacement per stroke was calculated at
4.8 bar (70 psig) air inlet pressure against
2 bar (30 psig) head pressure.
Example: To pump 326 lpm (86 gpm) against
a discharge head of 3.4 bar (50 psig) requires
5.5 bar (80 psig) and 98 Nm3/h (62 scfm) air
consumption.
Caution: Do not exceed 8.6 bar (125 psig) air
supply pressure.
1
...................... 2.5 L (0.67 gal)
Flow rates indicated on chart were determined by pumping water.
For optimum life and performance, pumps should be specified so that daily operation
parameters will fall in the center of the pump's performance curve.
WILDEN PUMP & ENGINEERING, LLC 6 WIL-115 9 0 -E- 01
Page 9
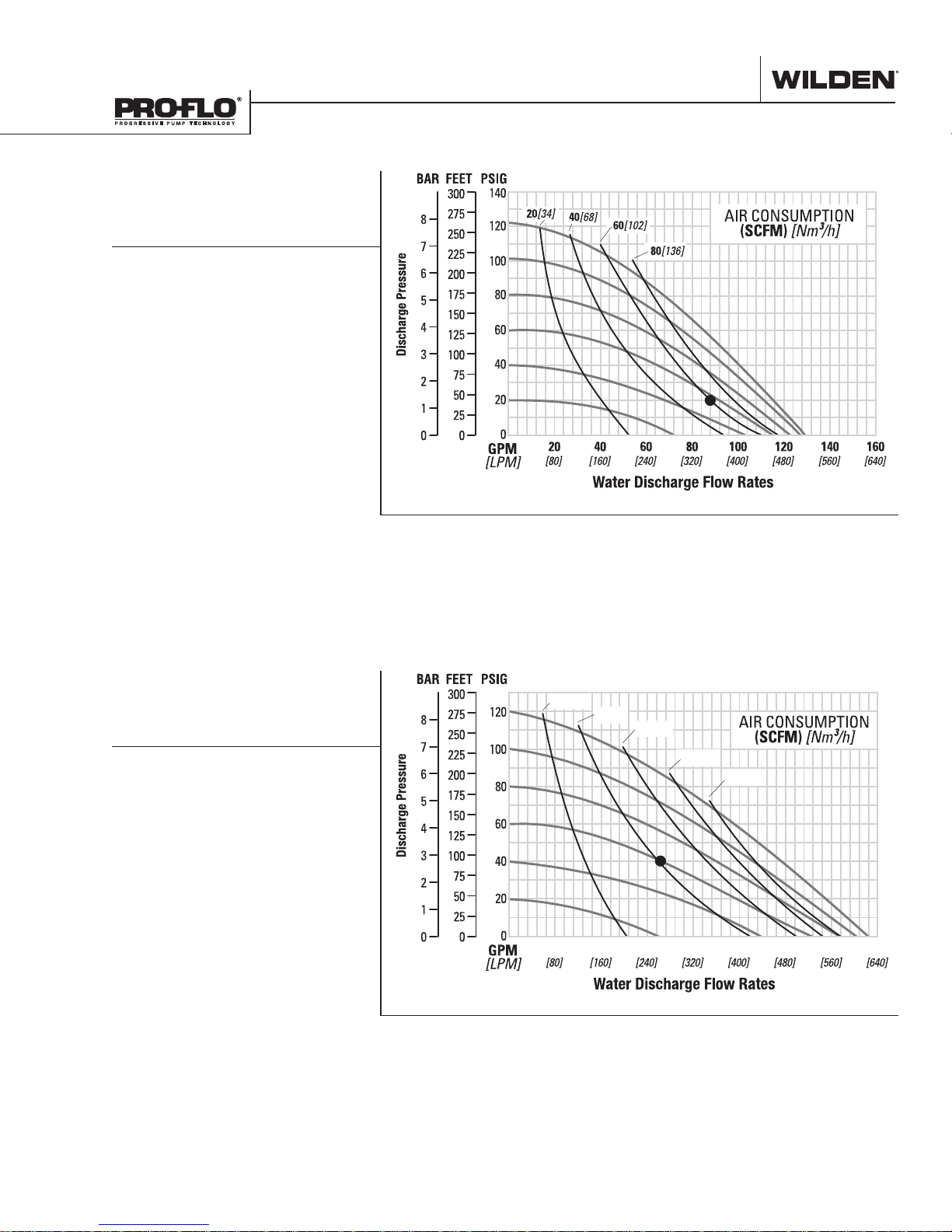
PERFORMANCE
P820/P830 METAL
REDUCED-STROKE
PTFE-FITTED
Ship Weight ... 820 Threaded AL 47 kg (104 lb)
820 Threaded SS 73 kg (161 lb)
820 Threaded Iron 71 kg (156 lb)
830 Flanged AL 54 kg (118 lb)
830 Flanged SS 81 kg (178 lb)
830 Flanged Iron 82 Kg (181 lb)
Air Inlet ........................................19 mm (3/4”)
Inlet .................................................51 mm (2”)
Outlet ..............................................51 mm (2”)
Suction Lift ............................ 4.6 m Dry (15.1’)
9.0 m Wet (29.5’)
Disp. per Stroke
Max. Flow Rate ................. 492 lpm (130 gpm)
Max. Size Solids .........................6.4 mm (1/4”)
1
Displacement per stroke was calculated at
4.8 bar (70 psig) air inlet pressure against
2 bar (30 psig) head pressure.
Example: To pump 326 lpm (86 gpm) against
a discharge head of 1.4 bar (20 psig) requires
4.1 bar (60 psig) and 95 Nm3/h (60 scfm) air
consumption.
Caution: Do not exceed 8.6 bar (125 psig) air
supply pressure.
1
.......................1.7 L (0.46 gal)
Flow rates indicated on chart were determined by pumping water.
For optimum life and performance, pumps should be specified so that daily operation
parameters will fall in the center of the pump's performance curve.
P820/P830 METAL
FULL-STROKE
PTFE-FITTED
Ship Weight ... 820 Threaded AL 47 kg (104 lb)
820 Threaded SS 73 kg (161 lb)
820 Threaded Iron 71 kg (156 lb)
830 Flanged AL 54 kg (118 lb)
830 Flanged SS 81 kg (178 lb)
830 Flanged Iron 82 Kg (181 lb)
Air Inlet ........................................19 mm (3/4”)
Inlet .................................................51 mm (2”)
Outlet ..............................................51 mm (2”)
Suction Lift ............................6.9 m Dry (22.6’)
9.0 m Wet (29.5’)
Disp. per Stroke1 ...................... 2.5 L (0.65 gal)
Max. Flow Rate ................. 590 lpm (156 gpm)
Max. Size Solids .........................6.4 mm (1/4”)
1
Displacement per stroke was calculated at
4.8 bar (70 psig) air inlet pressure against
2 bar (30 psig) head pressure.
Example: To pump 250 lpm (66 gpm) against
a discharge head of 2.8 bar (40 psig) requires
4.1 bar (60 psig) and 65 Nm3/h (41 scfm) air
consumption.
Caution: Do not exceed 8.6 bar (125 psig) air
supply pressure.
20[34]
40[68]
60[102]
80[136]
100[170]
20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160
Flow rates indicated on chart were determined by pumping water.
For optimum life and performance, pumps should be specified so that daily operation
parameters will fall in the center of the pump's performance curve.
WIL-115 9 0 -E- 01 7 WILDEN PUMP & ENGINEERING, LLC
Page 10

SUCTION-LIFT CURVES
P820/P830 METAL
SUCTION-LIFT
CAPABILITY
Suction-lift curves are calibrated
for pumps operating at 305 m
(1,000') above sea level. This
chart is meant to be a guide
only. There are many variables
that can affect your pump's
operating characteristics. The
number of intake and discharge
elbows, viscosity of pumping
fluid, elevation (atmospheric
pressure) and pipe friction loss
all affect the amount of suction
lift your pump will attain.
WILDEN PUMP & ENGINEERING, LLC 8 WIL-115 9 0 -E- 01
Page 11

NOTES
Page 12

Section 6
SUGGESTED INSTALLATION
Wilden pumps are designed to meet the performance
requirements of even the most demanding pumping
applications. They have been designed and manufactured
to the highest standards and are available in a variety of
liquid-path materials to meet your chemical-resistance
needs. Refer to the performance section of this manual for
an in-depth analysis of the performance characteristics of
your pump. Wilden offers the widest variety of elastomer
options in the industry to satisfy temperature, chemicalcompatibility, abrasion-resistance and flex concerns.
The suction pipe size should be at least the equivalent or
larger than the diameter size of the suction inlet on your
Wilden pump. The suction hose must be non-collapsible,
reinforced type as these pumps are capable of pulling a high
vacuum. Discharge piping should also be the equivalent
or larger than the diameter of the pump discharge which
will help reduce friction losses. It is critical that all fittings
and connections are airtight or a reduction or loss of pump
suction capability will result.
INSTALLATION: Months of careful planning, study
and selection efforts can result in unsatisfactory pump
performance if installation details are left to chance.
Premature failure and long-term dissatisfaction can be
avoided if reasonable care is exercised throughout the
installation process.
LOCATION: Noise, safety and other logistical factors usually
dictate where equipment will be situated on the production
floor. Multiple installations with conflicting requirements
can result in congestion of utility areas, leaving few choices
for additional pumps.
Within the framework of these and other existing conditions,
every pump should be located in such a way that six key
factors are balanced against each other to maximum
advantage.
ACCESS: First of all, the location should be accessible. If
it’s easy to reach the pump, maintenance personnel will
have an easier time carrying out routine inspections and
adjustments. Should major repairs become necessary, ease
of access can play a key role in speeding the repair process
and reducing total downtime.
AIR SUPPLY: Every pump location should have an air line
large enough to supply the volume of air necessary to
achieve the desired pumping rate. Use air pressure up to
a maximum of 8.6 bar (125 psig) depending on pumping
requirements.
For best results, the pumps should use a 5µ (micron) air
filter, needle valve and regulator. The use of an air filter
before the pump will ensure that the majority of any pipeline
contaminants will be eliminated.
SOLENOID OPERATION: When operation is controlled by a
solenoid valve in the air line, three-way valves should be
used. This valve allows trapped air between the valve and
the pump to bleed off which improves pump performance.
Pumping volume can be estimated by counting the number
of strokes per minute and then multiplying the figure by the
displacement per stroke.
MUFFLER: Sound levels are reduced below OSHA
specifications using the standard Wilden muffler. Other
mufflers can be used to further reduce sound levels, but
they usually reduce pump performance.
ELEVATION: Selecting a site that is well within the pump’s
dynamic-lift capability will ensure that loss-of-prime issues will
be eliminated. In addition, pump efficiency can be adversely
affected if proper attention is not given to site location.
PIPING: Final determination of the pump site should not be
made until the piping challenges of each possible location
have been evaluated. The impact of current and future
installations should be considered ahead of time to make
sure that inadvertent restrictions are not created for any
remaining sites.
The best choice possible will be a site involving the
shortest and straightest hookup of suction and discharge
piping. Unnecessary elbows, bends and fittings should
be avoided. Pipe sizes should be selected to keep friction
losses within practical limits. All piping should be supported
independently of the pump. In addition, the piping should
be aligned to avoid placing stress on the pump fittings.
Flexible hose can be installed to aid in absorbing the forces
created by the natural reciprocating action of the pump. If the
pump is to be bolted down to a solid location, a mounting
pad placed between the pump and the foundation will assist
in minimizing pump vibration. Flexible connections between
the pump and rigid piping will also assist in minimizing
pump vibration. If quick-closing valves are installed at any
point in the discharge system, or if pulsation within a system
becomes a problem, a surge suppressor (SD Equalizer
should be installed to protect the pump, piping and gauges
from surges and water hammer.
If the pump is to be used in a self-priming application, make
sure that all connections are airtight and that the suction lift is
within the model’s ability. NOTE: Materials of construction and
elastomer material have an effect on suction lift parameters.
Please refer to the performance section for specifics.
When pumps are installed in applications involving flooded
suction or suction head pressures, a gate valve should be
installed in the suction line to permit closing of the line for
pump service.
Pumps in service with a positive suction head are most efficient
when inlet pressure is limited to 0.5–0.7 bar (7–10 psig).
Premature diaphragm failure may occur if positive suction
is 0.7 bar (10 psig) and higher.
NOT FOR SUBMERSIBLE APPLICATIONS: Pro-Flo
cannot be used in submersible applications.
ALL WILDEN PUMPS ARE CAPABLE OF PASSING SOLIDS.
A STRAINER SHOULD BE USED ON THE PUMP INTAKE TO
ENSURE THAT THE PUMP'S RATED SOLIDS CAPACITY IS
NOT EXCEEDED.
CAUTION: DO NOT EXCEED 8.6 BAR (125 PSIG) AIR
SUPPLY PRESSURE.
®
pumps
®
)
WILDEN PUMP & ENGINEERING, LLC 10 WIL-115 9 0 -E- 01
Page 13

FOOTPAD
DISCHARGE
SUGGESTED INSTALLATION
This illustration is a generic
representation of an air-operated
double-diaphragm pump.
MUFFLER
FLEXIBLE
CONNECTION
SUCTION
EQUALIZER
SURGE DAMPENER
(OPTIONAL)
GAUGE
(OPTIONAL)
SHUT-OFF
VALVE
FLEXIBLE
CONNECTION
COMBINATION
FILTER & REGULATOR
AIR SHUT-OFF VALVE
NOTE: In the event of a power failure, the shut-off
valve should be closed, if the restarting of the pump is
not desirable once power is regained.
AIR-OPERATED PUMPS: To stop the pump from
operating in an emergency situation, simply close
the shut-off valve (user-supplied) installed in the air
supply line. A properly functioning valve will stop the
air supply to the pump, therefore stopping output. This
shut-of f valve should be located far enough away from
the pumping equipment such that it can be reached
safely in an emergency situatioVn.
WIL-115 9 0 -E- 01 11 WILDEN PUMP & ENGINEERING, LLC
Page 14

SUGGESTED OPERATION & MAINTENANCE
OPERATION: The Pro-Flo® pumps are pre-lubricated
and do not require in-line lubrication. Additional
lubrication will not damage the pump; however if the
pump is heavily lubricated by an external source, the
pump’s internal lubrication may be washed away. If the
pump is then moved to a non-lubricated location, it may
need to be disassembled and re-lubricated as described
in the DISASSEMBLY/REASSEMBLY INSTRUCTIONS.
Pump discharge rate can be controlled by limiting
the volume and/or pressure of the air supply to the
pump. An air regulator is used to regulate air pressure.
A needle valve is used to regulate volume. Pump
discharge rate can also be controlled by throttling
the pump discharge by partially closing a valve in
the discharge line of the pump. This action increases
friction loss which reduces flow rate. (See Section
5.) This is useful when the need exists to control
the pump from a remote location. When the pump
discharge pressure equals or exceeds the air supply
pressure, the pump will stop; no bypass or pressure
relief valve is needed, and pump damage will not
occur. The pump has reached a “deadhead” situation
and can be restarted by reducing the fluid discharge
pressure or increasing the air inlet pressure. Wilden
Pro-Flo® pumps run solely on compressed air and
do not generate heat; therefore, your process fluid
temperature will not be affected.
MAINTENANCE AND INSPECTIONS: Since each
application is unique, maintenance schedules may
be different for every pump. Frequency of use, line
pressure, viscosity and abrasiveness of process fluid
all affect the parts life of a Wilden pump. Periodic
inspections have been found to offer the best
means for preventing unscheduled pump downtime.
Personnel familiar with the pump’s construction and
service should be informed of any abnormalities that
are detected during operation.
RECORDS: When service is required, a record should
be made of all necessary repairs and replacements.
Over a period of time, such records can become a
valuable tool for predicting and preventing future
maintenance problems and unscheduled downtime. In
addition, accurate records make it possible to identify
pumps that are poorly suited to their applications.
TROUBLESHOOTING
Pump will not run or runs slowly.
1. Ensure that the air inlet pressure is at least 0.4 bar
(5 psig) above startup pressure and that the differential
pressure (the difference between air inlet and liquid
discharge pressures) is not less than 0.7 bar (10 psig).
2. Check air inlet filter for debris (see SUGGESTED
INSTALLATION).
3. Check for extreme air leakage (blow by) that would
indicate worn seals /bores in the air valve, pilot
spool and main shaft.
4. Disassemble pump and check for obstructions in
the air passageways or objects that would obstruct
the movement of internal parts.
5. Check for sticking ball check valves. If material being
pumped is not compatible with pump elastomers,
swelling may occur. Replace ball check valves and
seals with proper elastomers. Also, as the check
valve balls wear out, they become smaller and can
become stuck in the seats. In this case, replace balls
and seats.
6. Check for broken inner piston that would cause the
air valve spool to be unable to shift.
7. Remove plug from pilot spool exhaust.
Pump runs but little or no product flows.
1. Check for pump cavitation; slow pump speed down
to allow thick material to flow into liquid chambers.
2. Verify that vacuum required to lift liquid is not
greater than the vapor pressure of the material
being pumped (cavitation).
3. Check for sticking ball check valves. If material being
pumped is not compatible with pump elastomers,
swelling may occur. Replace ball check valves and
seats with proper elastomers. Also, as the check
valve balls wear out, they become smaller and can
become stuck in the seats. In this case, replace balls
and seats.
Pump air valve freezes.
1. Check for excessive moisture in compressed
air. Either install a dryer or hot air generator for
compressed air. Alternatively, a coalescing filter
may be used to remove the water from the
compressed air in some applications.
Air bubbles in pump discharge.
1. Check for ruptured diaphragm.
2. Check tightness of outer pistons (refer to Section 7).
3. Check tightness of fasteners and integrity of
O-rings and seals, especially at intake manifold.
4. Ensure pipe connections are airtight.
Product comes out air exhaust.
1. Check for diaphragm rupture.
2. Check tightness of outer pistons to shaft.
WILDEN PUMP & ENGINEERING, LLC 12 WIL-115 9 0 -E- 01
Page 15

Section 7
PUMP DISASSEMBLY
Tools Required:
• 1” Socket Wrench
• 3/4” Socket Wrench
• Snap-Ring Pliers
• Vise equipped w/
soft jaws (such as
plywood, plastic
or other suitable
material)
CAUTION: Before any maintenance or repair is attempted, the compressed air line
to the pump should be disconnected and all air pressure allowed to bleed from the
pump. Disconnect all intake, discharge, and air lines. Drain the pump by turning it
upside down and allowing any fluid to flow into a suitable container. Be aware of
any hazardous effects of contact with your process fluid.
NOTE: The model photographed is an aluminum PX820 51 mm (2”) pump. Your
specific pump model may vary from the configuration shown; however, pump
disassembly procedure will be the same.
Step 1
Step 1
Before starting disassembly, mark
Before starting disassembly, mark
a line from each liquid chamber to
a line from each liquid chamber to
its corresponding air chamber. This
its corresponding air chamber. This
line will assist in proper alignment
line will assist in proper alignment
during reassembly.
during reassembly.
WIL-115 9 0 -E- 01 13 WILDEN PUMP & ENGINEERING, LLC
Step 2
Step 2
Using the appropriate-sized wrench
Using the appropriate-sized wrench
for your pump size, loosen the
for your pump size, loosen the
discharge manifold from the liquid
discharge manifold from the liquid
chambers.
chambers.
Step 3
Step 3
Lift the discharge manifold to
Lift the discharge manifold to
expose discharge valve balls and
expose discharge valve balls and
valve seats. Inspect ball cage area
valve seats. Inspect ball cage area
of manifold for excessive wear or
of manifold for excessive wear or
damage.
damage.
Page 16

PUMP DISASSEMBLY
Step 4
Remove the discharge valve balls
and valve seats from the liquid
chambers and inspect for nicks,
gouges, chemical attack or abrasive
wear. Replace worn parts with
genuine Wilden parts for reliable
performance.
Step 5
Using the appropriate-sized wrench,
loosen the inlet manifold from the
liquid chambers. NOTE: Inverting
the pump will facilitate removal of
inlet manifold.
Step 6
Remove the inlet manifold to expose
the valve balls and valve seats.
Step 7
Remove the inlet valve balls and
valve seats from the inlet manifold
and liquid chambers and inspect for
nicks, gouges, chemical attack or
abrasive wear.
NOTE: Replace worn parts with
genuine Wilden parts for reliable
performance.
WILDEN PUMP & ENGINEERING, LLC 14 WIL-115 9 0 -E- 01
Step 8
Using an appropriately-sized
wrench, remove the liquid chamber
from the center section.
Step 9
The liquid chamber should be
removed to expose the diaphragm
and outer piston using an adjustable
wrench. Remove the diaphragm
assembly from the center section.
Repeat for opposite side.
Page 17

PUMP DISASSEMBLY
Step 10
Inspect the diaphragm assembly for
wear, damage or chemical attack.
Replace any damaged components
with genuine Wilden parts for
reliable performance.
Step 11
To remove diaphragm assembly
from shaft, secure shaft with
soft jaws (aluminum, plastic or
plywood) to ensure the shaft is
not damaged. Using an adjustable
wrench, remove the diaphragm
assembly from the shaft.
Step 12
Remove outer piston and stud if
equipped. Inspect for wear and
replace if necessary.
WIL-115 9 0 -E- 01 15 WILDEN PUMP & ENGINEERING, LLC
Page 18

AIR VALVE / CENTER SECTION DISASSEMBLY
Tools Required:
• 3/16” Hex-Head
Wrench
• Snap-Ring Pliers
• O-Ring Pick
CAUTION: Before any maintenance or repair is attempted, the compressed air line
to the pump should be disconnected and all air pressure allowed to bleed from the
pump. Disconnect all intake, discharge and air lines. Drain the pump by turning it
upside down and allowing any fluid to flow into a suitable container. Be aware of
hazardous effects of contact with your process fluid.
®
The Wilden P820 and P830 metal pumps utilize a revolutionary Pro-Flo
distribution system. Proprietary composite seals reduce the coefficient of friction
and allow the pumps to run lube-free. The Pro-Flo® air distribution system is
designed to perform in on/off, non-freezing, non-stalling, tough-duty applications.
air
Step 1
Using a 3/16" hex-head wrench,
loosen air valve bolts.
WILDEN PUMP & ENGINEERING, LLC 16 WIL-115 9 0 -E- 01
Step 2
Remove muffler plate and air valve
bolts from air valve assembly
exposing muffler gasket for
inspection. Replace if necessary.
Step 3
Lift away air valve assembly
and remove air valve gasket for
inspection. Replace if necessary.
Page 19

AIR VALVE / CENTER SECTION DISASSEMBLY
Step 4
Remove air valve end cap to expose
air valve spool by simply lifting up
on end cap once air valve bolts are
removed.
Step 5
Remove the air valve spool from
the air valve body by threading one
air valve bolt into the end of the
air valve spool and gently sliding
the spool out of the air valve body.
Inspect seals for signs of wear and
replace entire assembly if necessary.
Use caution when handling air
valve spool to prevent damaging
seals. NOTE: Seals should not be
removed from assembly. Seals are
not sold separately.
Step 6
Remove pilot sleeve retaining snap
ring on both sides of center section
with snap ring pliers.
Step 7
Remove pilot spool sleeve from
center section.
WIL-115 9 0 -E- 01 17 WILDEN PUMP & ENGINEERING, LLC
Step 8
Using an o-ring pick, gently remove the o-ring from the opposite side of the
“notched end“ on one side of the pilot spool. Gently remove the pilot spool
from pilot spool sleeve and inspect for nick, gouges and wear. Replace
pilot sleeve or outer sleeve o-rings if necessary. During re-assembly, never
insert the pilot spool into the sleeve with the “notched end“ first, this end
incorporates the urethane o-ring and will be damaged as it slides over the
ports cut in the sleeve. NOTE: Seals should not be removed from pilot
spool. Seals are not sold separately.
Page 20

AIR VALVE / CENTER SECTION DISASSEMBLY
Step 9
Check center section seals for signs
of wear. If necessary, remove seals
with o-ring pick and replace.
WILDEN PUMP & ENGINEERING, LLC 18 WIL-115 9 0 -E- 01
Page 21

REASSEMBLY HINTS & TIPS
RE A S SE M B LY:
Upon performing applicable maintenance to the air
distrib ution system, t he pump can now be re assembled .
Please refer to the disassembly instructions for photos
and parts placement. To reassemble the pump, follow
the disassembly instructions in reverse order. The air
distribution system needs to be assembled first, then
the diaphragms and finally the wetted path. Please
find the applicable torque specifications on this page.
The following tips will assist in the assembly process.
• Lubricate air valve bore, center section shaft
and pilot spool bore with NLGI grade 2 white EP
bearing grease or equivalent.
• Clean the inside of the center section shaft bore to
ensure no damage is done to new shaft seals.
• A small amount of NLGI grade 2 white EP bearing
grease can be applied to the muffler and air valve
gaskets to lubricate gaskets during assembly.
• Make sure that the exhaust port on the muffler plate
is centered between the two exhaust ports on the
center section.
• Stainless steel bolts should be lubed to reduce the
possibility of seizing during tightening.
PRO-FLO® MAXIMUM TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
Description of Part Torque
Air Valve 13.6 N•m (120 in-lb)
Air Chamber/Center Block 2 7.1 N•m (20 ft-lb)
Liquid Chamber/Air Chamber,
Aluminum Bolted Only
Liquid Chamber/Air Chamber,
Stainless-Steel Bolted Only
Outer Pistons, Rubber & PTF E,
Excluding Stainless-Steel Inner Pistons
Outer Pistons, Rubber & PTF E,
Stainless-Steel Inner Pistons
Outer Pistons, Ultra-Flex™ 74.6 N•m (55 ft-lb)
Figure A
SHA FT SE AL
27.1 N•m (20 ft-lb)
54.2 N•m (40 ft-lb)
109 N•m (80 ft-lb)
119 N•m (88 ft-lb)
SHAFT SEAL INSTALLATION:
PRE-INSTALLATION
• Once all of the old seals have been removed, the
inside of the bushing should be cleaned to ensure
no debris is left that may cause premature damage
to the new seals.
INSTALLATION
The following tools can be used to aid in the installation
of the new seals:
Needle-Nose Pliers
Phillips Screwdriver
Electrical Tape
• Wrap electrical tape around each leg of the needle-nose
pliers (heat shrink tubing may also be used). This is done
to prevent damaging the inside surface of the new seal.
• With a new seal in hand, place the two legs of the
needle-nose pliers inside the seal ring. (See Figure A.)
• Open the pliers as wide as the seal diameter will allow,
then with two fingers pull down on the top portion of
the seal to form a kidney shape. (See Figure B.)
• Lightly clamp the pliers together to hold the seal into
the kidney shape. Be sure to pull the seal into as tight
of a kidney shape as possible, this will allow the seal to
travel down the bushing bore with greater ease.
• With the seal clamped in the pliers, insert the seal into
the bushing bore and position the bottom of the seal
into the correct groove. Once the bottom of the seal is
seated in the groove, release the clamp pressure on the
pliers. This will allow the seal to partially snap back to its
original shape.
• After the pliers are removed, you will notice a slight
bump in the seal shape. Before the seal can be properly
resized, the bump in the seal should be removed as
much as possible. This can be done with either the
Phillips screwdriver or your finger. With either the side
of the screwdriver or your finger, apply light pressure
to the peak of the bump. This pressure will cause the
bump to be almost completely eliminated.
• Lubricate the edge of the shaft with NLGI grade 2
white EP bearing
• Slowly insert the center shaft with a rotating motion.
This will complete the resizing of the seal.
• Perform these steps for the remaining seals.
Figure B
grease.
NEEDLE-NOSE
PLIERS
TAPE
WIL-115 9 0 -E- 01 19 WILDEN PUMP & ENGINEERING, LLC
SHA FT SE AL
TAPE
Page 22

Section 8
EXPLODED VIEW & PARTS LISTING
P820/P830 METAL
EXPLODED VIEW
FULL-STROKE PTFE
REDUCED-STROKE PTFE
WILDEN PUMP & ENGINEERING, LLC 20 WIL-115 9 0 -E- 01
FLANGED
ALL CIRCLED PART IDENTIFIERS ARE INCLUDED IN REPAIR KITS
PLASTIC ADS
LW0373 REV. B
Page 23

EXPLODED VIEW & PARTS LISTING
P820/P830 METAL
Item
Air Valve Assembly, Pro-Flo
1
2 O-Ring, End Cap (-225, Ø1.859" x Ø.139") 1 04-2390-52-700 04-2390-52-700 04-2390-52-700
3 End Cap, Pro-Flo
4 Screw, SHC, Air Valve (1/4"-20 x 4-1/2") 4 01-6000-03 01-6000-03 01-6000-03
5 Screw, Self Tapping, SHC (10-16 x 1-3/4") 2 04-6351-03 04-6351-03 04-6351-03
6 Nut, Square (1/4"-20) 4 00-6505-03 00-6505-03 00-6505-03
7 Muffler Plate, Pro-Flo
8 Gasket, Muffler Plate, Pro-Flo
Gasket, Air Valve, Pro-Flo
9
10 Center Block Assembly, Pro-Flo
11 Sleeve, Threaded, Center Block 4 04-7710-08 04-7710-08 04-7710-08
12 Pilot Sleeve Assembly 1 04-3880-99 04-3880-99 04-3880-99
13 O-Ring, Pilot Spool Retaining (-009, Ø.208" x Ø.070") 2 04-2650-49-700 04-2650-49-700 04-2650-49-700
14 Seal, Shaft 2 08-3210-55-225 08-3210-55-225 08-3210-55-225
15 Gasket, Center Block Pro-Flo
16 Air Chamber, Advanced FIT Pro-Flo
17 Screw, HSFHS (3/8"-16 x 1") 8 71-6250-08 71-6250-08 71-6250-08
18 Retaining Ring 2 04-3890-03 04-3890-03 04-3890-03
19 Bushing, Reducer 3/4" MNPT to 1/2" FNPT 1 04-6950-20-700 04-6950-20-700 04-6950-20-700
20 Muffler 3/4" MNPT 1 08-3510-99R 08-3510-99R 08-3510-99R
Description Qty.
® 1
®
®
®
®
® 2
®
®
AIR DISTRIBUTION COMPONENTS
P820/830/AAAPP/…/
P/N
1 04-2000-20-700 04-2000-20-700 04-2000-20-700
1 04-2330-20-700 04-2330-20-700 04-2330-20-700
1 04-3180-20-700 04-3180-20-700 04-3180-20-700
1 04-3500-52-700 04-3500-52-700 04-3500-52-700
1 04-2600-52-700 04-2600-52-700 04-2600-52-700
1 04-3110-20 04-3110-20 04-3110-20
2 04-3526-56 04-3526-56 04-3526-56
2 08-3687-01 08-3687-01 08-3687-01
P820/830/SSAPP/…/
P/N
PARTS LISTING
P820/830/WWAPP/…/
P/N
WETTED PATH COMPONENTS
21 Liquid Chamber, Bolted 2 08-5015-01 08-5015-03 08-5015-02
22 Manifold, Discharge (NPT) 1 08-5035-01 08-5035-03 08-5035-02
Manifold, Discharge (BSPT) 1 08-5036-01 08-5036-03 08-5036-02
Manifold, Discharge (ANSI) 1 08-5045-01 08-5045-03 08-5045-02
Manifold, Discharge (DIN) 1 08-5046-01 08-5046-03 08-5046-02
23 Manifold, Inlet (NPT) 1 08-5095-01 08-5095-03 08-5095-02
Manifold, Inlet (BSPT) 1 08-5096-01 08-5096-03 08-5096-02
Manifold, Inlet (ANSI) 1 08-5125-01 08-5125-03 08-5125-02
Manifold, Inlet (DIN) 1 08-5126-01 08-5126-03 08-5126-02
24 Washer, Flat (Ø.531" x Ø1.062" x .095") 32 04-6730-08 04-6730-03 04-6730-08
25 Screw, HHC (1/2"-13 x 1-3/4") 16 08-6190-08 N/A 08-6190-08
Screw, HHC (1/2"-13 x 1-1/2") 16 N/A 04-6180-03 N/A
26 Screw, HHC (1/2"-13 x 2") 16 04-6210-08 04-6210-03 04-6210-08
GASKETS/VALVE BALLS/VALVE SEATS/VALVE O-RINGS
27 Ball, Valve 4 * * *
28 Seat, Valve 4 * * *
29
O-Ring, Valve Seat PTFE Fitted, (-347, Ø4.225 x Ø.210) (not shown)
4 08-1209-55 08-1209-55 08-1209-55
FULL-STROKE RUBBER/TPE/PTFE/COMPONENTS
30 Shaft (Rubber) 1 08-3810-09 08-3810-09 08-3810-09
Shaft (EZ TPE/PTFE) 1 08-3812-03 08-3812-03 08-3812-03
32 Piston, Inner 2 08-3700-01 08-3700-01 08-3700-01
33 Diaphragm, Primary 2 * * *
Diaphragm, Backup 2 * * *
34 Piston, Outer 2 08-4550-01 08-4550-03 08-4550-02
35 Piston, Outer 2 08-4550-01 08-4550-03 08-4550-02
REDUCED-STROKE PTFE COMPONENTS
30 Shaft, Pro-Flo® PTFE 1 08-3840-09 08-3840-09 08-3840-09
31 Shaft Stud, 1/2"-20 X 2-1/8" 2 08-6152-08 08-6152-08 08-6152-08
32 Piston, Inner, PTFE 2 08-3750-01 08-3750-01 08-3750-01
33 Diaphragm, Primary PTFE 2 08-1010-55-42 08-1010-55-42 08-1010-55-42
34 Diaphragm, Backup 2 * * *
35 Piston, Outer, PTFE 2 08-4600-01 08-4600-03 08-4600-03
*Refer to Elastomer Chart
1
Air Valve Assembly includes items 2 and 3.
2
Plastic Center Block Assembly includes items 6, 11, 12, 14 and 19.
All boldface items are primary wear parts.
LW0374 REV. D
WIL-115 9 0 -E- 01 21 WILDEN PUMP & ENGINEERING, LLC
Page 24

Section 9
ELASTOMER OPTIONS
P820/P830 Metal
MATERIAL
Polyurethane
Neoprene
®
Buna-N
Conductive Buna-N
Geolast
EPDM
®
Viton
PTFE
Saniflex™
FDA Wil-Flex™
Wil-Flex™
Aluminum
Mild Steel
Stainless Steel
1
Used in conjunction with metallic valve seat.
DIAPHRAGMS
(2)
N/A N/A N/A N/A 08-1022-50 08-1080-50 08-1128-50 N/A
08-1010-51 08-1060-51 N/A N/A N/A 08-1080-51 08-1128-51 N/A
08-1010-52 N/A N/A N/A N/A 08-1080-52 08-1128-52 N/A
08-1010-86 N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A
N/A N/A N/A N/A 08-1022-15 N/A N/A N/A
08-1010-54 08-1060-54 N/A N/A N/A 08-1080-54 08-1128-54 N/A
08-1010-53 N/A N/A N/A N/A 08-1080-53 08-1128-53 N/A
08-1010-55-42 N/A 08-1040-55-42 N/A N/A 08-1080-55 N/A 08-1209-55
N/A 08-1060-56 N/A 08-1065-56 08-1022-56 08-1080-56 08-1128-56 N/A
N/A N/A N/A 08-1065-57 08-1022-57 08-1080-57 08-1128-57
N/A N/A N/A N/A 08-1022-58 08-1080-58 08-1128-58 N/A
N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A 08-1129-01 N/A
N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A 08-1129-08 N/A
N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A 08-1129-03 N/A
REDUCED-
STROKE BACKUP
DIAPHRAGMS
(2)
FULL-STROKE
DIAPHRAGMS
(2)
FULL-STROKE
BACKUP
DIAPHRAGMS
(2)
EZ-INSTALL
DIAPHRAGMS
(2)
VALVE
BALLS
(4)
VALVE
SEATS
(4)
VALVE SEAT
O-RINGS
(4)
1
N/A
LW0374 REV. D
WILDEN PUMP & ENGINEERING, LLC 22 WIL-115 9 0 -E- 01
Page 25

NOTES
Page 26

NOTES
Page 27

WARRANTY
Each and every product manufactured by Wilden Pump and Engineering, LLC is built to meet the highest
standards of quality. Every pump is functionally tested to insure integrity of operation.
Wilden Pump and Engineering, LLC warrants that pumps, accessories and parts manufactured or supplied by
it to be free from defects in material and workmanship for a period of five (5) years from date of installation or
six (6) years from date of manufacture, whichever comes first. Failure due to normal wear, misapplication, or
abuse is, of course, excluded from this warranty.
Since the use of Wilden pumps and parts is beyond our control, we cannot guarantee the suitability of any pump
or part for a particular application and Wilden Pump and Engineering, LLC shall not be liable for any consequential
damage or expense arising from the use or misuse of its products on any application. Responsibility is limited
solely to replacement or repair of defective Wilden pumps and parts.
All decisions as to the cause of failure are the sole determination of Wilden Pump and Engineering, LLC.
Prior approval must be obtained from Wilden for return of any items for warranty consideration and must be
accompanied by the appropriate MSDS for the product(s) involved. A Return Goods Tag, obtained from an
authorized Wilden distributor, must be included with the items which must be shipped freight prepaid.
The foregoing warranty is exclusive and in lieu of all other warranties expressed or implied (whether written or oral)
including all implied warranties of merchantability and fitness for any particular purpose. No distributor or other
person is authorized to assume any liability or obligation for Wilden Pump and Engineering, LLC other than expressly
provided herein.
PLEASE PRINT OR TYPE AND FAX TO WILDEN
PUMP INFORMATION
Item # Serial #
Company Where Purchased
YOUR INFORMATION
Company Name
Industry
Name Title
Street Address
City State Postal Code Country
Telephone Fax E-mail Web Address
Number of pumps in facility? Number of Wilden pumps?
Types of pumps in facility (check all that apply): Diaphragm
Media being pumped?
Other
Centrifugal
Gear
Submersible
Lobe
How did you hear of Wilden Pump?
Other
OR GO TO PSGDOVER.COM > WILDEN > SUPPORT TO COMPLETE THE WARRANTY REGISTRATION ONLINE
NOTE: WARRANTY VOID IF PAGE IS NOT FA XED TO WILDEN OR SUBMIT TED ONLINE VIA THE PSGDOVER.COM WEBSITE
Trade Journal
Trade Show
ONCE COMPLETE, FAX TO (909) 783-3440
WILDEN PUMP & ENGINEERING, LLC
Internet/ E-mail
Distributor
Page 28

PSG
22069 Van Buren St., Grand Terrace, CA 92313-5607
P: +1 (909) 422-1730
• F: +1 (909) 783-3440
wildenpump.com
Where Innovation Flows
PSG® reserves the right to modify the information and illustrations contained in this document without prior notice. This is a non-contractual document. 09-2017
Authorized PSG Representative:
Copyrigh t ©20 17, P S G®, A Dover Compa ny
WI L-115 90 -E -0 1
 Loading...
Loading...