
User Manual
June 2003 Rev 0
Software Version 3.1

Important
You can obtain the latest customer documentation for this product by visiting our web
site at www.wi-lan.com. Click on Support ➔ Customer Documentation. Updated
information will be posted regularly on this site and can be downloaded via the Internet.
WilLAN
2 Libra 5800 Series User Guide

Contents
Contents ........................................................................................................ 3
Important Information ................................................................................7
Safety considerations ..........................................................................................................7
Warning symbols used in this book 7
About this guide ..................................................................................................................8
Notices ........................................................................................................... 9
Copyright notice .................................................................................................................9
Regulatory notice ................................................................................................................9
Other notices .....................................................................................................................10
Warranty & repair .............................................................................................................10
Customer support contacts ................................................................................................10
Distributor technical support 10
Contacting Wi-LAN Technical Support 11
Wi-LAN product information 11
Publication history ............................................................................................................11
Description ..................................................................................................13
Overview ...........................................................................................................................13
Libra 5800 Series System Features ...................................................................................13
About W-OFDM ...............................................................................................................14
About Point-to-Multi-Point (P-MP) Systems ...................................................................15
Access Point (AP) Equipment 15
Customer Premise Equipment (CPE) 16
Long Range Customer Premise Equipment (LCPE) 16
Radio Operation Background 17
About Point-to-Point (P-P) Systems .................................................................................18
Rapid Deployment (RD) Equipment 18
Extened Range (ER) Equipment 19
June 2003 Rev 0 3

Contents
Hardware ...........................................................................................................................20
Specifications ....................................................................................................................24
Configuration ..............................................................................................27
Overview ...........................................................................................................................27
Accessing the Main Menus ...............................................................................................28
Access Methods 28
Setting VT100 Arrows 30
Powering up the unit .........................................................................................................32
Quick-Start Menu .............................................................................................................33
Exiting Setup 33
Unit Configuration: 34
Radio Configuration: 35
Communication Parameters: 35
Access Configuration: 37
OFDM Channel Statistics: 38
Link Test 38
PDA Setup Menu ..............................................................................................................39
Unit Configuration: 39
Radio Configuration: 40
Communication Parameters: 41
Setup Menu - Second Screen 42
Main System Menu ...........................................................................................................45
System Revision Information ...........................................................................................46
System Software ROM Images .........................................................................................48
Viewing system software ROM images 48
System Current Status .......................................................................................................48
Viewing system current status 48
System Security ................................................................................................................50
Setting Ethernet and wireless access to the TCP/IP Stack 50
Assigning Community Names 52
Setting Menu Passwords 53
Setting Auto Logout Timeout 59
System Commands ...........................................................................................................60
Setting Default System Image 60
Reboot Current Image 60
Rebooting a System Image 61
Restoring the Factory Configuration 62
Resetting MAC Layer Statistics 63
Network Configuration .....................................................................................................64
Setting the Internet IP Address 64
Setting the Internet IP Mask 65
VLAN Tagging 65
VLAN Tagging ID 67
4 Libra 5800 Series User Guide

VLAN Tagging User Priority 68
Setting Local Network MAC Filtering (LNMF) 68
Radio Configuration .........................................................................................................70
Setting the RF Station ID (P-MP Only) 70
Setting the Sector ID 71
Setting the Synchronization ID 72
Setting the RF Center Frequency 72
Setting Tx Power 74
Setting the Modulation Type 75
Remote Station Configuration Menu (P-MP Only) ..........................................................76
IP/MBR Filter Configuration ............................................................................................78
Setting the IP Filtering Option 78
Configuring the IP Filter 79
Setting the MBR Filtering Option 81
MAC Layer Statistics ........................................................................................................84
Using the Command Line .................................................................................................86
Field Installation ........................................................................................ 89
Introduction .......................................................................................................................89
Libra 5800 field installation ..............................................................................................90
Site preparation 90
Tools and equipment 91
Libra 5800 installation procedure 93
Troubleshooting ......................................................................................... 97
Preventative maintenance .................................................................................................97
Troubleshooting areas .......................................................................................................98
Troubleshooting chart 98
Appendix A: Upgrading Software .......................................................... 103
Background Information .................................................................................................103
Upgrading software via ftp .............................................................................................103
Rebooting the Unit Using Menu Commands 105
Rebooting the Unit Using FTP "Reboot" Files 105
Appendix B: SNMP MIB ......................................................................... 107
Overview .........................................................................................................................107
Obtaining SNMP Software .............................................................................................108
Using Wi-LAN MIB Object Identifier Nodes ................................................................108
System Commands 108
Network Configuration 109
Radio Configuration 110
June 2003 Rev 0 5

Contents
System Security 112
IP Filter Configuration 112
System Current Status 113
MAC Layer Statistics 114
Appendix C: Simple Link Planning Worksheet ....................................117
AP (for P-MP) or Base (for P-P) Information ................................................................117
CPE (for P-MP) or Remote (for P-P) Information .........................................................118
Appendix D: Linktest and Link Statistics ..............................................119
Overview .........................................................................................................................119
Performing a Linktest .....................................................................................................119
Linktest variables 120
Appendix E: Bench Configuration Testing ............................................123
Overview .........................................................................................................................123
Setup process ..................................................................................................................123
Tools and equipment .......................................................................................................124
Checking shipping package contents ..............................................................................124
Assembling the Libra Units ............................................................................................126
Configuring the units ......................................................................................................127
Configuring a P-MP System 127
Configuring a P-P System 128
Testing the units ..............................................................................................................129
Testing the RF link with Linktest 129
Performing simple network tests 131
Glossary .....................................................................................................133
Index ..........................................................................................................145
Menu Map .................................................................................................153
6 Libra 5800 Series User Guide

Important Information
Safety considerations
This document must be reviewed for familiarization with the product, instructions, and safety symbols
before operation.
Verify that local safety regulations are adhered to during installation with regard to grounding and
lightning protection.
Verify that the correct AC power source is available for the Power Inserter.
Disconnect the product from operating power before cleaning.
Warning symbols used in this book
WARNING: Injury or death may result from failure to heed a WARNING.
!
Do not proceed beyond a WARNING until the indicated conditions are fully understood and
met.
! CAUTION: Damage to equipment may result from failure to heed a caution.
Do not proceed beyond a ! CAUTION until the indicated conditions are understood and met.
Important: Indicates critical information to be aware of which may affect the completion of a task or
successful operation of equipment.
WARNING
!
All antennas must be installed by a knowledgeable and professional
installer.
! CAUTION
An antenna must be connected to the AP, LCPE or ER units before
powering up the equipment. Powering up equipment without an antenna
connected can permanently damage the unit or the RF transmission cable
June 2003 Rev 0 7

Important Information
! CAUTION
Change the passwords and community names as soon as possible. Default
community names and passwords given in this book are provided to all customers and
are not secure.
About this guide
This guide describes the common features of the Libra 5800-Series Broadband Wireless Access
System family of products from Wi-LAN Inc.
This guide is organized in the following sections.
Description,page 13, explains Broadband Wireless Access, the theory behind W-OFDM, how a BWS
system operates, and the function of the various parts.
Configuration,page 27, describes how to configure the units so they will function as part of their new
network.
Field Installation,page 89 guides you through the process of setting up Customer Premise
Equipment units.
Troubleshooting,page 97, explains how to fix some of the most common problems.
Appendix A: Upgrading Software,page 103, tells how to upgrade software.
Appendix B: SNMP MIB,page 107, explains the Simple Network Management Protocol software
used to remotely control the APs and CPEs.
Appendix C: Simple Link Planning Worksheet,page 117, gives a worksheet for calculating the link
budget for a simple situation.
Appendix E: Bench Configuration Testing,page 123, explains how to set up the BWS units in a
controlled environment such as a lab, configure them and test their basic operation.
Glossary,page 133, explains product terminology.
Index,page 145, can be used to quickly locate information on particular topics.
Menu Map,page 153, shows the Main System Menu and its submenus.
8 Libra 5800 Series User Guide

Notices
Copyright notice
Copyright© July 2003 Wi-LAN, Inc.
All rights reserved.
This guide and the application and hardware described herein are furnished under license and are
subject to a confidentiality agreement. The software and hardware can be used only in accordance
with the terms and conditions of this agreement.
No part of this guide may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means – electronic,
mechanical, or otherwise, including photocopying and recording – without the express written
permission of Wi-LAN, Inc.
While every effort has been made to ensure that the information contained in this guide is correct,
Wi-LAN, Inc. does not warrant the information is free of errors or omissions.
Information contained in this guide is subject to change without notice.
Regulatory notice
The specifications and parameters of the device described in this document are subject to change
without notice.
For Canadian regulatory information, go to www.ic.gc.ca. For American regulatory information, see
www.fcc.gov. For European regulatory information, see www.etsi.org.
This equipment generates, uses and radiates energy on radio frequencies and, if not installed and
used in accordance with this guide, may cause harmful interference to radio communications.
However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation.
June 2003 Rev 0 9
Notices
If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be
determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to correct the interference
by one or more of the following methods:
• reorient or relocate the receiving antenna
• move the equipment and receiver farther apart
• connect equipment to an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is
connected
Other notices
Changes or modifications to the equipment not expressly approved by Wi-LAN, Inc., could void the
user’s authority to operate the equipment.
Appropriately shielded remote I/O serial cable with the metal connector shell and cable shield
properly connected to chassis ground shall be used to reduce the radio frequency interference.
All antenna installation work shall be carried out by a knowledgeable and professional installer.
The parts in some Libra 5800 versions are Imperial sizes – inches and fractions of a inch. Do not
attempt to mix Imperial nuts, bolts and screws with similar metric hardware. This will strip the
threads.
Warranty & repair
Please contact the party from whom you purchased the product for warranty and repair information.
Wi-LAN provides no direct warranty to end users of this product.
Customer support contacts
Users of Wi-LAN equipment who require technical assistance must contact their reseller or
distributor. For information on distributors in your area, please visit www.wi-lan.com/channel.
Distributor technical support
Distributors may contact Wi-LAN’s Technical Support on Wi-LAN’s products.
When requesting support, please have the following information available
• configuration of the system, including models of Wi-LAN equipment, versions and serial
numbers
• antenna type and cable lengths
• site information, including possible RF path problems, such as trees, buildings and other RF
equipment in the area
• distance of the RF link
• configuration of unit.
• description of the problem
10 Libra 5800 Series User Guide

Publication history
Contacting Wi-LAN Technical Support
By Telephone Call: 1-403-273-9133
Business hours: 8:00 a.m. to 5:00 p.m. Mountain Standard Time (GMT - 7)
By e-mail Send an e-mail message to:
techsupport@wi-lan.com
Wi-LAN product information
To obtain information regarding Wi-LAN products, contact the Wi-LAN distributor in your region, or
call
1-403-273-9133 to speak with a Wi-LAN sales representative or visit our web site at www.wilan.com.
Publication history
Revision Date Description
Rev 1 July 2003 First public release of this manual.
June 2003 Rev 0 11

Notices
12 Libra 5800 Series User Guide

Description
Overview
This information in this guide applies to the "LIBRA 5800" Series products, including the following.
Data Rate / Channel Size BWS Model Frequency (TDD System)
32 Mbps, 12.5 MHz channel separation Libra 5800 CPE TX&RX:5725-5850
32 Mbps, 12.5 MHz channel separation Libra 5800 LCPE TX&RX:5725-5850
32 Mbps, 12.5 MHz channel separation Libra 5800 AP TX&RX:5725-5850
32 Mbps, 12.5 MHz channel separation Libra 5800 RD TX&RX:5725-5850
32 Mbps, 12.5 MHz channel separation Libra 5800 ER TX&RX:5725-5850
This chapter presents an overview of the LIBRA 5800 Series product.
Libra 5800 Series System Features
• Point-to-Point (P-P) system: Rapid Deployment (RD) units with integral 23 dBi antena or
Extended Range (ER) units with N-Type (F) RF connector for use with high gain external
antenna.
• Point-to-Multi-Point (P-MP) system: Access Point (AP) with N-Type (F) RF connector for use
with external sectoral, omni or other antennas, Customer Premise Equipment (CPE) with
integrated 23 dBi antenna and Long Range CPE (LCPE) with N-Type RF connector for use
with high gain external antenna
• fast transmission speeds–up to 32 Mbps raw data rate in 10 MHz channel (12.5 MHz
separation)
• Efficient use of spectrum
• cost-effective–wireless solution is inexpensive compared to wire line alternatives
• fast and easy to deploy
• enhanced multipath capabilities enable non-, near- and obstructed-line-of-sight operation
• operates in the unlicensed 5.8 GHz band
• advanced error recovery and signal processing
• easy-to-operate user interface and system configuration
June 2003 Rev 0 13
Description
About W-OFDM
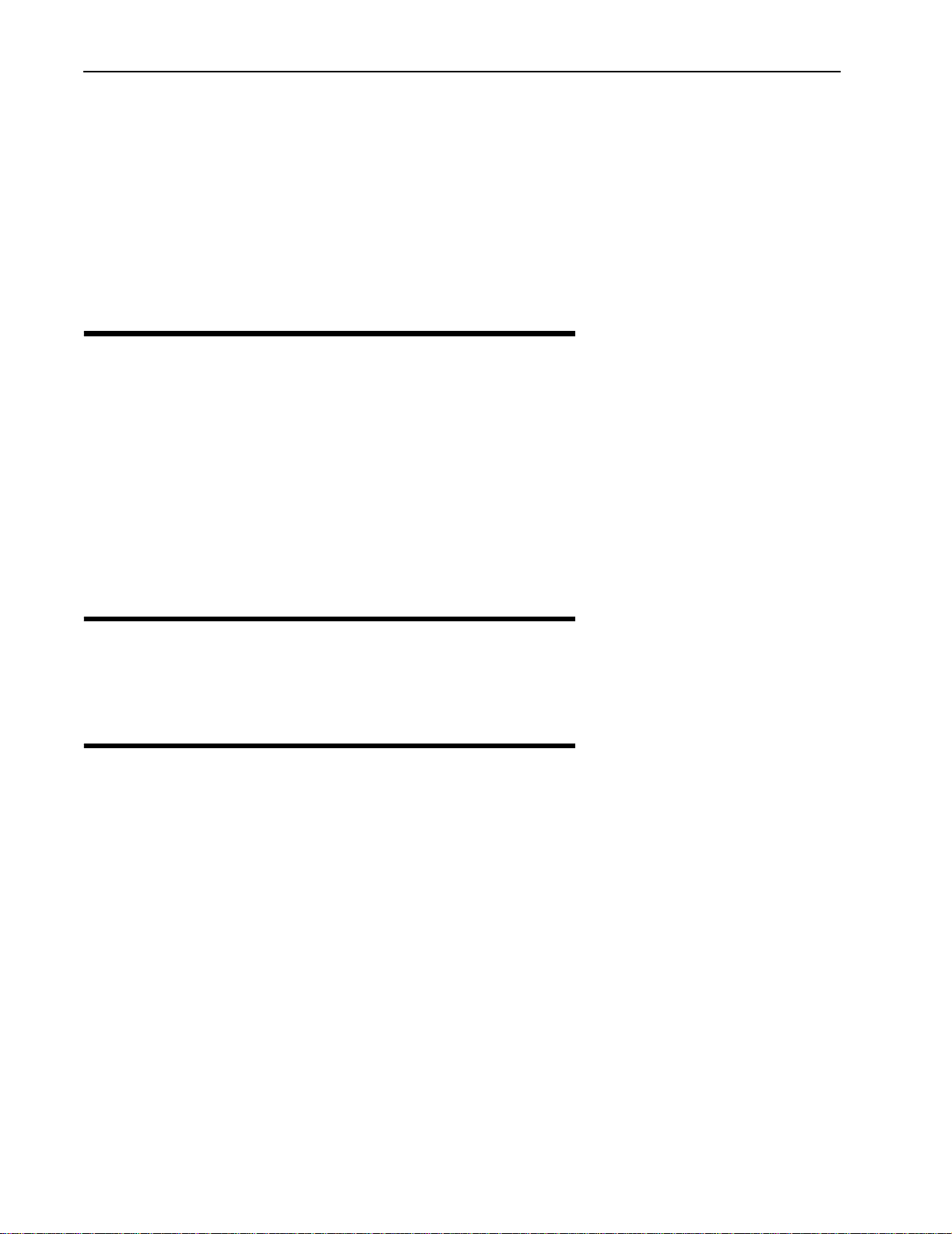
The Libra system uses Wi-LAN’s patented Wide-band Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing
(W-OFDM) technology to process, transmit and receive data in parallel fashion over the air. WOFDM divides a wide RF frequency band into several subchannels that work together to deliver
data, similar to splitting a road into several lanes that together can handle more traffic than a single
lane.
W-OFDM offers many advantages, including effective use of bandwidth, resistance to interference,
ability to take advantage of multipath characteristics, and advanced error correction and recovery.
Because data is spread across all the channels, interference usually affects only a few channels
rather than all channels, and lost data can be easily recovered. Since W-OFDM is insensitive to
interference, the amount of ongoing tuning, adjustment and maintenance is minimized. Both
multipoint networks and point-to-point backbone systems are supported.
The following diagram illustrates the main concept behind W-OFDM. The available frequency
spectrum is divided into subchannels. Each subchannel is orthogonal, meaning that the peak signal
strength of each signal occurs at the null or point of minimum signal strength of its neighbor, so
adjacent subchannels do not interfere with each other. Data is carried in parallel across the
subchannels.
Orthogonal Arrangement of W-OFDM Subchannels
Subchannel (shaded for clarity)
Signal Strength
Frequency
Null
Zone
Operating
Frequency Range
14 Libra 5800 Series User Guide

About Point-to-Multi-Point (P-MP) Systems
About Point-to-Multi-Point (P-MP) Systems
Two kinds of equipment are required for a wireless P-MP link: Access Point (AP) equipment and
Customer Premise Equipment (CPE). AP equipment is located at the service provider’s site and
CPE equipment is located at the customer’s site. The LIBRA 5800 P-MP product is available as an
AP, a CPE with integrated 23 dBi antenna or an LCPE for connection to higher gain external
antennas.
LIBRA 5800 P-MP System Components
Sectoral Antenna
CPE with
Integrated
Panel Antenna
Access Point
Outdoor CAT-5
Cable
Outdoor CAT-5
Power Inserter
Hub
Cable
Workstation
Computer
Power Inserter
Access Point (AP) Equipment
The AP controls communication within the wireless network and is the main access point to the
Ethernet.
The access point communicates with the CPE’s in the system to provide each CPE with Access to
the main network (ie Ethernet). The access point is typically located at a distance away from the CPE
that will provide adequate radio signal strength for the specified data rates.
June 2003 Rev 0 15

Description
The Access Point is responsible for any CPE data management functions.
The Libra 5800 AP consists of three parts: 1) AP radio unit, 2) Ethernet Power Inserter with CAT-5
cable (bought separately) and weatherproofing kit (included), and 3) the External Antenna and cable
(both bought separately).
• LIBRA 5800 AP– The AP is the main piece of radio equipment. It is designed for outdoor
installation but can also be installed indoors if needed. The AP is equipped with an N-type (F)
RF connector so that the external antenna can be connected to it. Thus many different types
of base stations can be deployed using sectoral, omni or other specialized antennas.
• Ethernet Power Inserter– This piece of equipment is a small box that connects between the
CPE and the P.C. This box also provides power for the AP equipment to run. A CAT-5 outdoor
cable is used to connect the Power inserter to the AP. The weatherproofing kit is used with
standard RJ-45 connector to ensure reliable connection for outdoor systems.
• Antenna and Cable– In order to accomodate different frequency re-use plans and scalability
of the base stations the AP is designed to be used with an external antenna. Antennas and
cables are selected by the user based on the network requirements.
Customer Premise Equipment (CPE)
The CP equipment connects customers to the AP via a wireless link. The link enables customers to
communicate with other users of the wireless network and the Ethernet.
Customer Premise Equipment has two parts: 1) CPE radio unit and 2) Ethernet Power Inserter with
CAT-5 cable (bought separately) and weatherproofing kit (included).
• LIBRA 5800 CPE– The CPE is the main piece of equipment that would normally be installed
outdoors (indoor installation is permitted when feasible) The CPE contains all of the
necessary radio equipment to provide a high-speed wireless link. The CPE also has an
integral antenna such that no RF cables are required for a typical installation.
• Ethernet Power Inserter– This piece of equipment is a small box that connects between the
CPE and the P.C. This box also provides power for the CPE equipment to run. A CAT-5
outdoor cable is used to connect the Power Inserter to the CPE. The weatherproofing kit is
used with standard RJ-45 connector to ensure reliable connection for outdoor systems.
Wireless network activity focuses on the AP, which is both the main access point to the Ethernet
(LAN or WAN) and the destination for CPE-originated communications (CPEs do not communicate
directly with other CPEs—they communicate only via the AP). CPEs complete the customer-end of a
wireless link.
Long Range Customer Premise Equipment (LCPE)
The LCP equipment also connects customers to the AP via a wireless link. The LCPE enables the
customer to reach longer ranges by allowing the connection to a higher gain external antenna. It can
also be used for indoor installation of the units should severe weather conditions require it. The
antenna is then mounted outdoors and connected via appropriate RF cables to the unit. One other
alternative which customers may want to consider is to use lower gain antennas with systems that
are very close to the Base Station to mitigate some interference concerns without recourse to
dynamic power control.
16 Libra 5800 Series User Guide

About Point-to-Multi-Point (P-MP) Systems
The Libra 5800 LCPE consists of three parts: 1) LCPE, 2) Ethernet Power Inserter with CAT-5 cable
(bought separately) and weatherproofing kit (included), and 3) the External Antenna and cable (both
bought separately).
• LIBRA 5800 LCPE– The LCPE is the main piece of equipment. It is designed for outdoor
installation but can also be installed indoors if needed. The LCPE is equipped with an N-type
connector so that the external antenna can be connected to it. Thus the range of the P-MP
system can be significantly increased by use of higher gain antennas. Also, in situations
where very severe conditions may be encountered outdoors the LCPE can be installed
indoors with cabling to the antenna outside.
• Ethernet Power Inserter– This piece of equipment is a small box that connects between the
LCPE and the P.C. This box also provides power for the LCPE equipment to run. A CAT-5
outdoor cable is used to connect the Power inserter to the LCPE. The weatherproofing kit is
used with standard RJ-45 connector to ensure reliable connection for outdoor systems.
• Antenna and Cable– In order to accomodate different range requirements for P-MP links,
the LCPE is designed to be used with an external antenna. Antennas and cables are selected
by the user based on the network requirements.
Radio Operation Background
The Libra 5800 communicates using a technique call Time Division Duplexing (TDD) in both the P-P
and P-MP configurations. TDD uses one frequency for both the Down Link (DL) Transmission (Base
to Remote in P-P, or AP to CPEs in P-MP), and for the Up Link (UL) (Remote to Base in PP or CPEs
to AP in P-MP). The DL and UL transmissions are performed at different times, therefore the system
is known as a Time Division Duplexing system. The available frequency band is therefore separated
into multiple TDD channels allowing for use of the whole frequency bands for very high capacity.
Time Division Duplexing Channels
F1 F2 F3
......
Fn
TDD Channels
In addition to using TDD, in a P-MP system, the AP and CPE also use Time Division Multiplexing
(TDM). TDM is a process of using time slots to allow the AP to transmit to multiple CPEs during a
single transmit cycle. During the Up Link cycle each CPE is polled and if it has data it transmits in
turn. This is known as Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA). All CPEs thus share the bandwidth
available by allocating time slots in turn to each of the units on both transmit and receive channels.
The following diagram shows TDM in a DL and TDMA in the UL. Each slot is allocated to a different
CPE. In the Wi-LAN system each slot may vary in time depending on traffic destined for each of the
CPEs. CPEs that are not very active will also be polled less frequently thus reducing the latency of
June 2003 Rev 0 17

Description
the system. Once they are ready to transmit or receive they will move up the polling list and will be
polled more often.
Time Division Multiplexing/Time Division Multiple Access (TDM/TDMA)
DL TDM
DL
slot1DLslot2
DL superframe
......
DL slot-n
UL SF1
UL TDMA
UL SF2 UL SFm
UL superframes
Antenna characteristics and placement are critical. Because of W-OFDM’s excellent Non-Line of
Sight performance and its resistance to frequency selective multipath fading CPE directional
antennas do not have to be pointed directly at the AP antenna. Having a clear line of sight is always
preferable, but is not necessary with the BWS series. There are cases in which the optimal
performance is acheived when the CPE antenna does not point directly to the AP (e.g. when using
reflection off a nearby structure to avoid an absorbing obstruction).
About Point-to-Point (P-P) Systems
For P-P systems Libra 5800 comes in two versions, the Rapid Deployment (RD) and the Extended
Range (ER) units. P-P links are used when only two locations are connected, for example for
backhaul purposes between P-MP Base Stations and the Network Operating Center for connection
to the Internet backbone, or in situations where throughput requirements between two locations are
such that the bandwidth can’t be shared.
Rapid Deployment (RD) Equipment
The RD equipment is intended for very rapid installation of a P-P link and can be used for links of up
to 16 kms (up to 12 kms at full 32 Mbps bandwidth).
RD Equipment has two parts: 1) RD and 2) Ethernet Power Inserter with CAT-5 cable (bought
separately) and weatherproofing kit (included).
• LIBRA 5800 RD– The RD is the main piece of equipment that is normally installed outdoors
(indoor installation is permitted when the range and link budget allows it) The RD contains all
of the necessary radio equipment to provide a high-speed wireless link. The RD also has an
integral 23 dBi antenna such that no RF cables are required for a typical installation.
• Ethernet Power Inserter– This piece of equipment is a small box that connects between the
RD and the Ethernet network. This box also provides power for the RD equipment to run. A
CAT-5 outdoor cable is used to connect the Power inserter to the RD. The weatherproofing kit
is used with standard RJ-45 connector to ensure reliable connection for outdoor systems.
18 Libra 5800 Series User Guide

About Point-to-Point (P-P) Systems
Extened Range (ER) Equipment
The ER Equipment allows for the use of different external antennas to achieve links of much longer
range (up to 66 kms). It can also be used for indoor installation of the units should severe weather
conditions require it. The antenna is then mounted outdoors and connected via appropriate RF
cables to the unit.
The Libra 5800 ER consists of three parts: 1) ER, 2) Ethernet Power Inserter with CAT-5 cable
(bought separately) and weatherproofing kit (included), and 3) the External Antenna and cable (both
bought separately).
• LIBRA 5800 ER– The ER is the main piece of equipment. It is designed for outdoor
installation but can also be installed indoors if needed. The ER is equipped with an N-type
connector so that the external antenna can be connected to it. Thus the range of the P-P
system can be significantly increased by use of higher gain antennas. Also, in situations
where very severe conditions may be encountered outdoors the ER can be installed indoors
with cabling to the antenna outside.
• Ethernet Power Inserter– This piece of equipment is a small box that connects between the
ER and the Ethernet network. This box also provides power for the ER equipment to run. A
CAT-5 outdoor cable is used to connect the Power inserter to the ER. The weatherproofing kit
is used with standard RJ-45 connector to ensure reliable connection for outdoor systems.
• Antenna and Cable– In order to accomodate different range requirements for P-P links, the
ER is designed to be used with an external antenna. Antennas and cables are selected by
the user based on the network requirements.
June 2003 Rev 0 19

Description
Hardware
This section describes the LIBRA 5800 hardware. Although antennas are part of the equipment in
general, antennas are not discussed here.
The LIBRA 5800 product has two connectors on the back panel. 1) Power/Ethernet Port 2) Serial
Port. The connectors are common for all types of Libra 5800 equipment. The AP, ER and LCPE units
also have a female N-Type connector on the front panel for connection to the antenna.
Libra 5800 Connection Panell
Power/Ethernet Port
Power/Ethernet Port Standard RJ 45 Ethernet Connector. A weatherproofing kit is provided
Serial Port 5-pin female connector. A matching connector and cable is available
CAT-5 Weatherproofing Kit
Serial Port
with the unit, so that standard outdoor CAT-5 cable can be used.
separately for local configuration
Power/Ethernet Port
Serial Port
20 Libra 5800 Series User Guide

Libra 5800 AP, ER and LCPE Front Panel RF Connector
Hardware
N-Type
Connector
Ethernet Power Inserter
Item Description
1
2
3
1 To Ethernet LAN
2 To Libra 5800 Radio
3 Main AC Power Cord
June 2003 Rev 0 21

Description
Hardware Mounting Kit for Libra 5800
Unit can be rotated by 90o to
operate in either vertical or
horizontal polarization. See
the arrow on the antenna for
proper direction before
connecting to mounting
hardware.
Large Pipe Diameter Mounting Configuration
22 Libra 5800 Series User Guide
Small Pipe Diameter Mounting Configuration
Hardware
Wall Mounting Configuration
Knuckle (allows for
Pan and Tilt; can be
used in all other
Configurations
To U n i t
To Wall
June 2003 Rev 0 23
Description
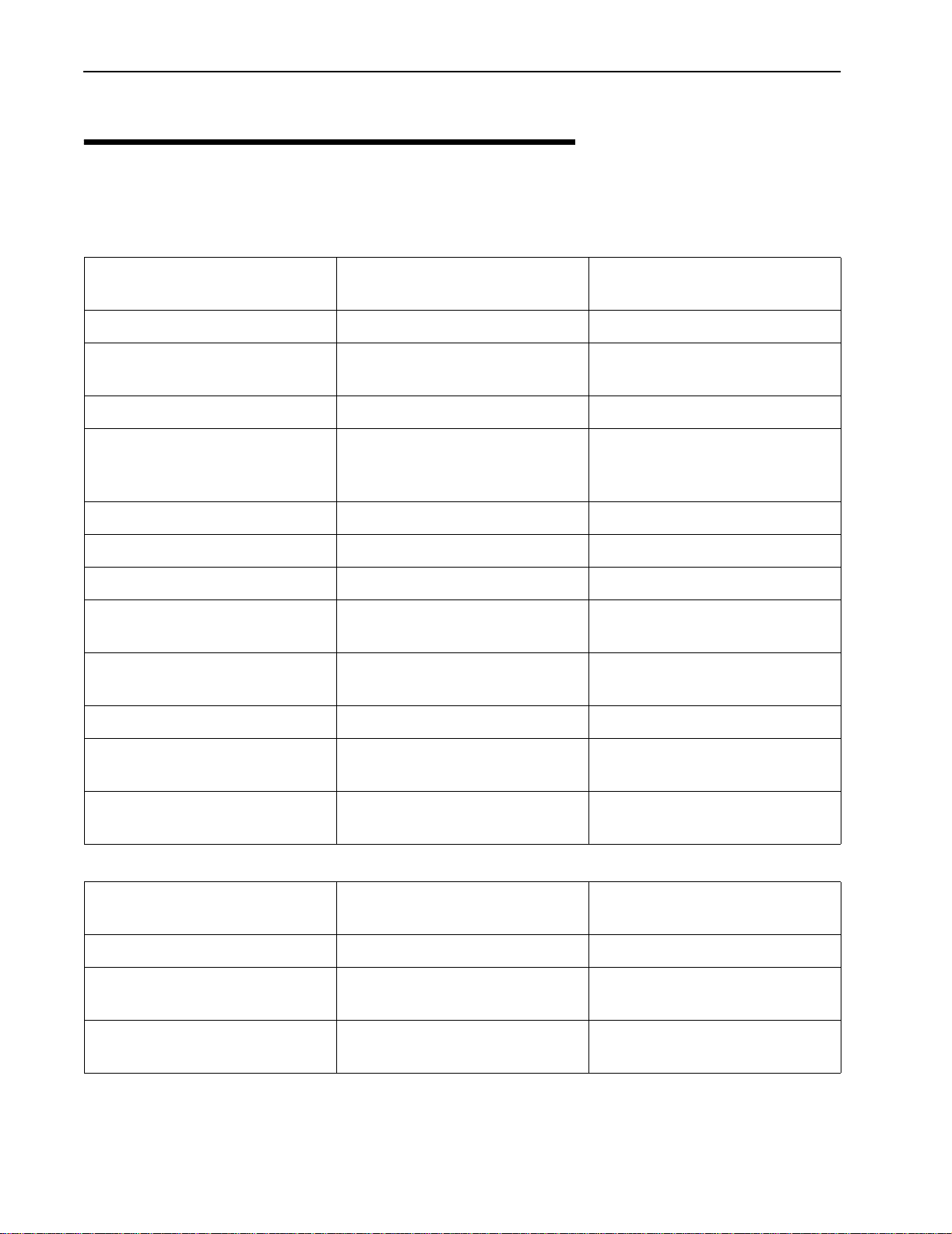
Specifications
Libra 5800 P-P
RD and ER
Radio Specifications:
Out put Power (average) +17dBm to -3dBm, all
channels
RF Frequency Band (Tx/Rx) 5725 MHz t o 5850 MHz 5725 MHz t o 5850 MHz
Channel Assignments Field Selectable in 0.25 MHz
steps
Channel Size/Separation 10MHz/12.5 MHz 10MHz/12.5 MHz
Rx Sensitivity at 1E-06 BER -84 dBm BPSK
-81 dBm QPSK
-75 dBm 16QAM
Data Rate Raw/Effective 32 Mbps/24 Mbps 32 Mbps/24 Mbps
Power / Ethernet Cable Length Max Length:40m Max Length: 40m
Integrated Antenna 23 dBi (RD Only) 23 dBi (CPE Only)
RF Connector N Type (Female, ER only) N Type (Female, AP/LCPE
+17dBm to -3dBm, all channel
Field Selectable in 0.25 MHz
steps
-84 dBm BPSK
-81 dBm QPSK
-75 dBm 16QAM
Only)
Libra 5800 P-MP
AP & CPE/LCPE
RF Technology W-OFDM (16 QAM, QPSK,
BPSK)
Duplexing Format TDD TDD
Certification FCC/IC/SRRC/Others on
demand
Range (@BER 1E-6, 99.95%
Availability)
Diagnostics:
Serial Port Diagnostic Accessl Weatherproof 5 Pin DIN RS-
Monitor /Control Via 5 Pin DIN RS-232 Via 5 Pin DIN RS-232
Network Connection 10/100 Base T with 802.3 &
MAC Address Filtering Prevents local MAC address
Up to 66 kms Up to 35 kms
232 Format
Ethernet II
packet from RF transmission.
W-OFDM (16 QAM, QPSK,
BPSK)
FCC/IC/SRRC/Others on
demand
Weatherproof 5 Pin DIN RS232 Format
10/100 Base T with 802.3 &
Ethernet II
Prevents local MAC address
packet from RF transmission.
24 Libra 5800 Series User Guide
Description
Libra 5800 P-P
RD and ER
Wireless Networking:
Libra 5800 P-MP
AP & CPE/LCPE
Network Topologies Point -to-Point Point -to-Multipoint
RF Collision Management Dynamic Polling with
Dynamic Time Allocation
Security:
Privacy Proprietary Phase
Randomization over RF Link
Dynamic Polling with
Dynamic Time Allocation
Proprietary Phase
Randomization over RF Link
Configuration security Password Protected Password Protected
Management:
Remote Management SNMP & Telnet SNMP & Telnet
Local Management Port RS-232 Serial Port, DB-9
Conn.
Management Port
Functionality
Support system configuration,
security access control,
wireless LAN diagnostics &
management, menu driven
ASCI I interface.
RS-232 Serial Port, DB-9
Conn.
Support system configuration,
security access control,
wireless LAN diagnostics &
management, menu driven
ASCI I interface.
Software Management FTP, Flash upgradeable in the
field
Configuration Access Remote: SNMP, Telnet
Local :RS-232,Telnet ,SNMP
Physical:
FTP, Flash upgradeable in the
field
Remote: SNMP, Telnet
Local :RS-232,Telnet ,SNMP
Power Consumption <30W <30W
Dimensions CPE (w/h/d) 12"x12"x3.5" (RD)
9"x9"x2.5" (ER)
Dimensions Power Inserter (w/
6.2/5/12.6cm 6.2/5/12.6cm
12"x12"x3.5" (CPE)
9"x9"x2.5" (AP/LCPE)
h/d)
Weight 2.5 kgs (RD)
2.0 kgs (ER)
2.5 kgs (CPE)
2.0 kgs (AP/LCPE)
Operating Temperature -45 to +50C -45 to +50C
25 Libra 5800 Series User Guide

Description
26 Libra 5800 Series User Guide

Configuration
Overview
This section explains how to access and use the configuration menus. Menu items are described in
the order that they appear in the main menu.
There are three different menu trees available to the user as follows:
• The Main System Menu - This is the normal menu used by the user and contains all of the
sub-menus and contains detailed information related to the operation of the unit.
• The Setup Menu - This menu is the one that comes up the first time the unit is powered up.
It displays configuration parameters that can be modified to allow the user to get the Libra
unit up and running quickly. When the user is done with the setup a command can be executed that will cause the Main System Menu to come up the next time the user logs in. The
Setup menu canbe brought up again at any time from the main menu by selecting the
"Setup" option.
• The PDA Setup Menu - This menu has its own logon id and like the Setup menu above is
used to allow the user to configure the Libra unit quickly. A PDA can be connected to the
serial port of the Libra unit using a special cable so that the installer can get the Libra unit
running where it is installed and not have to go to the user’s computer to determine if it is
communicating.
The menus described above are the starting points for all Libra configuration parameters. The Main
System Menu and the Setup Menu are accessed from a local PC connected via RS-232 to the Libra
unit. The PDA Setup Menu is accessed from a PDA device such as a Palm Pilot connected to the
Libra unit via RS-232 using a special Wi-LAN supplied cable.
The Libra 5800 is configured as either a P-MP system with AP, CPE or LCPE, or a P-P system with
base station and remote. The P-P units use a protocol optimized for P-P operation and therefore
cannot communicate with P-MP units. These configurations are factory set and cannot be changed
by the user. The description of the menus will highlight the differences between the different types of
units.
June 2003 Rev 0 27
Configuration
Accessing the Main Menus
Access Methods
There are several ways to access the configuration menu system on the Libra 5800. They are:
• Via Local PC RS 232 (Cable Required - 5 Pin DIN Connector)
• Via Telnet
• Via PDA RS-232 (Cable Required - 5 Pin DIN Connector - see note below
NOTE: When connecting to a PDA, a null modem or straight-through cable with a 5 pin DIN
connector is required. The Libra unit is configured as DCE so if the PDA is configured as DCE (most
typical), then a null modem cable is needed. If the PDA is configured as DTE then a straight-through
cable is needed.
➧
1. Connect the RS-232 (5 pin din to DB9) cable from the serial port on the PC to the serial port on
Connect the RS-232 Port
2. Start a terminal emulation program.
3. Set the emulation program to use the following settings. (This example is for HyperTerminal
To access the main system menu via Local PC on the the serial port
the CPE as shown below.
5 Pin DIN
DB9 Serial Connector
®
)
Bits per second 9600
Data bits 8
Parity None
Stop bits 1
Flow control None
28 Libra 5800 Series User Guide

Send line ends with line feeds No
Echo typed characters locally No
Line delay 0
Character delay 0
Accessing the Main Menus
Append line feeds to incoming line
No
ends
Force incoming data to 7-bit ASCII No
Wrap lines that exceed terminal
Yes
width
VT-100 Arrows On
4. Press Enter. The Libra 5800 login screen appears.
Started by Boot ROM (Power-On/Hard Reset)
Wi-LAN Libra Login Menu
Software: Rev 3.0.1 (Jun 27 2002 17:02:44)
Enter Password:
5. Type a default password (user, supervisor, or PDA) or your personal password if you have
one.
Login Account Default Password Privileges
User user Read Only
Supervisor supervisor Read and Write
PDA pda Read and Write
The main menu is displayed.
June 2003 Rev 0 29
Configuration
How to use the main menus
• To select an item from any of the menus, press the keyboard arrow
keys to move the cursor –> next to the item. Press the
key to open the data entry field. This will make the field
highlight in black.
• To scroll through items in the data entry field, press .
Press to select an item from the field.
• To exit from a menu without making changes, press the
Esc
➧
1. Ensure that the unit has an Internet IP address configured, the Ethernet connection is
2. Ensure that the VT100 Arrows feature in your telnet session is enabled. See Setting VT100
3. From a VT100 terminal emulation program, type telnet <IP address>, where
4. Press
5. Type the password (supervisor). The Main System Menu appears.
To access the main menu via telnet
operational, and wire and remote access are enabled (see Setting Ethernet and wireless access
to the TCP/IP Stack, page 50).
Arrows, page 30.
<IP address> is the address of the unit that you want to configure.
Enter. The login screen appears.
For more information about passwords, see Setting Menu Passwords, page 53.
Enter
Enter
Enter
Esc key.
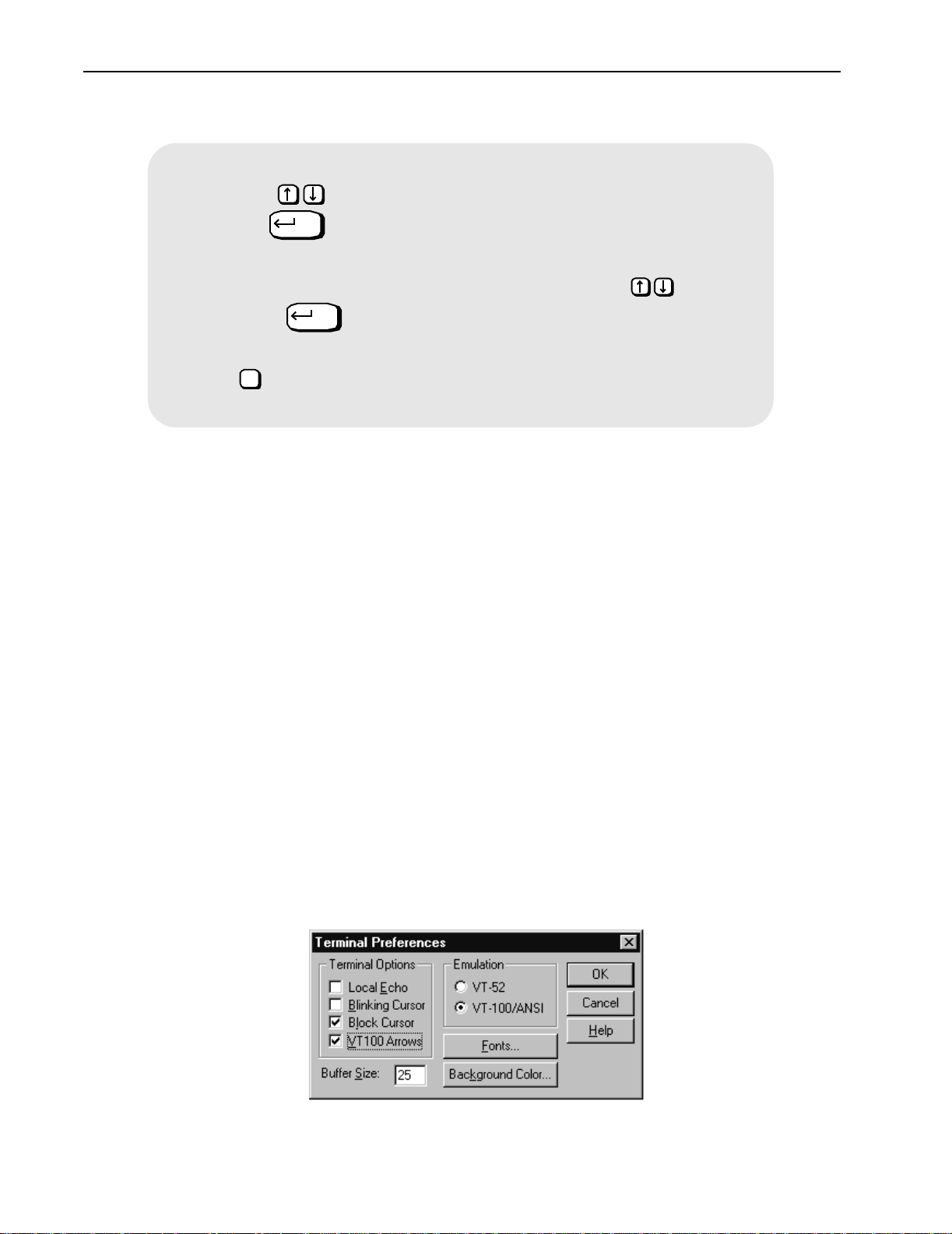
Setting VT100 Arrows
➧
1. Start a Microsoft telnet session.
2. Select Terminal, Preferences from the menu bar. The Terminal Preferences dialog box appears.
30 Libra 5800 Series User Guide
To set the VT100 arrows in Microsoft telnet

3. Click the VT100 Arrows checkbox.
4. Click OK. The VT100 arrows are enabled in the telnet session.
You can now use the keyboard arrow keys to navigate the configuration menus.
Accessing the Main Menus
June 2003 Rev 0 31

Configuration
Powering up the unit
If a CRT session is started on a laptop or PDA which is connected to the unit via an RS-232 cable,
the following power up sequence can be viewed on the screen.
Startup Self-Test Results
-------------------------
Flash CRC Test: PASSED
Traffic Connectivity: CONNECTED
I2C Communication Test: PASSED
Ethernet Loopback Test: PASSED
DSP Function Test: PASSED
FPGA Function Test: PASSED
BootROM Replacement Status: PASSED
Hit Enter to Continue
These tests should all pass for a unit deployed in the field. Traffic Connectivity may show
"DISCONNECTED" for a unit when it has just been installed and is not communicating with an
Access Point.
The BootROM Replacement Status field is not normally displayed except in the very rare occurrence
when the unit's bootROM code is updated.
32 Libra 5800 Series User Guide

Quick-Start Menu
Quick-Start Menu
When the Libra unit starts up for the very first time, it will start up in setup mode. This a single screen
as shown below that displays all of the parameters that the user needs to set up the unit and get it
talking with the base station.
Libra Model 5800 - 12.5 MHz Setup Menu
Unit Conf iguration
RF Statio n Id [1..2048] - > 2 Inte rn et IP Address 192. 16 8.1.100
Sector Id [0..31] 1 Internet IP Mask 255.255.255.0
Synchronization Id [0..1] 0 System Ethernet Access on
Local Network Mac Filter off
Radio Configuration
Modulation Type QAM 16 SNMP Priv Community netman
Tx Power [-14..17] 17 Super Password Press Enter to change pwd
Rx Center Freq (kHz) 5787000 Confirm Super Pwd Press Enter to confirm pwd
Tx Center Freq (kHz) 5787000 User Pwd Press Enter to change pwd
Confirm User Pwd Press Enter to confirm pwd
OFDM Chan nel Statistics
RSSI (dBm) -22 Confirm PDA Pwd Press Enter to confirm pwd
Null Depth (dB) 0
Fade Marg in (dB) 53 Link Test
RF Link Sta tus Not Connec te d Link Test Type Coarse (xE- 5)
Dest Radio Id [1..2048] 9
Start Link Test
Activate changes and reboot
Exit se tu p an d lo go ut
Commun ic at ion Parameter s
Access Con figuration
PDA Password Press Enter to change pwd
Many of the fields on this menu can be found in more detailed menus as discussed later on in this
section.
Exiting Setup
When the setup procedure is complete and the unit has been re-booted to activate all the changes
you can exit the setup procedure.
➧
1.
June 2003 Rev 0 33
To exit setup
Move the cursor to the Exit setup and logout field and press Enter.

Configuration
Unit Configuration:
Setting the RF Station ID
Each Libra unit requires a unique RF Station ID to identify it on the network. Every unit must have a
unique RF Station ID. No two units may have the same ID. In a P-P system you cannot access this
selection.
➧
1. Select
2. Type a unique number for the RF Station ID and press Enter. Zero is not a valid Station ID.
3. Record the RF Station ID you have assigned to the unit.You will need to know this number when
4. Reboot the system to effect the changes unless there are more changes you would like to make
Setting the Sector ID
Each Libra unit can have a Sector ID to identify its AP within the cell on the network. This prevents
Libra units from accessing different APs which may have the same Center Frequency.
➧
1. Move the cursor to the Sector Id [0..31] field and press Enter. The entry field highlights.
2. Type a unique number for the Sector ID and press Enter.
3. Reboot the system to effect the changes unless there are more changes you would like to make
To set the RF station ID
RF Station Id [1..2047] and press Enter. The entry field highlights.
you configure the polling list on the Access Point.
at this time. To do this move the cursor down to the line, "Activate changes and reboot" and press
Enter
To set the Sector ID
at this time. To do this move the cursor down to the line, "Activate changes and reboot" and press
Enter
Setting the Synchronization ID
Because of OFDM’s superior multipath performance it is possible for the Libra to falsely synchronize
on an AP from a different sector operating at the same frequency. In order to avoid this type of error,
the APs and Libras of each sector can have one of two possible OFDM synchronization patterns.
These patterns are orthogonal, thus a Libra with a given Synchronization ID will never synch to an
AP with the other synch. Every Libra in the sector must have the same Synchronization ID as the AP
of that sector.
➧
1. Move the cursor to the Synchronization Id [0..1] field and press Enter. The entry field
2. Type a 0 or 1 to select the Synchronization ID and press Enter. Factory default is zero (0).
3. Reboot the system to effect the changes unless there are more changes you would like to make
34 Libra 5800 Series User Guide
To set the Synchronization ID
highlights.
at this time. To do this move the cursor down to the line, "Activate changes and reboot" and press
Enter. Setting the Modulation Type

Quick-Start Menu
Radio Configuration:
Setting the Modulation Type
The OFDM Modulation Type can be selected from among the following possible values: "QAM 16",
"QPSK" and "BPSK". The selected type will be added to the next superframe transmitted.
➧
1. Move the cursor to the Modulation Type field and press Enter. The field highlights.
2. Select from the list using the up and down arrow keys the Modulation type and press Enter. The
Setting the Tx power
➧
1. This configuration allows the user to program the output power from -3dBm to +17dBm
2. Move the cursor to the Set Tx Power field and press Enter. The field highlights.
3. Type in the signal strength. The new signal strength is applied.
Setting the RF Center Frequency
Libra 5800 equipment uses Time Division Duplexing (TDD). In TDD, the units transmit and receive
on the same frequency. They alternate in time to provide the duplexing capability. The frequency of
these channels depend on the model of equipment used.
The center frequency is a frequency located in the middle of each set of transmit and receive
channels and it defines the group of frequencies situated around it.
To set the Modulation Type
possible options are: QAM 16, QPSK, and BPSK. The new modulation type is applied after the
next reboot.
To set the Tx power
➧
1. Move the cursor to the Set RF Center Frequency field and press Enter. The entry field is
2. Enter the frequency value assigned to this unit in kHz and press enter to effect the changes. The
To set the RF Center Frequency
highlighted.
unit does not require rebooting for this change to become effective.
Communication Parameters:
Setting the Internet IP Address
An IP address must be assigned to each Libra unit in the network. Changes takes effect on the next
reset. You will require the IP address assigned by your system network administrator to your Libra
unit for this procedure.
1. Move the cussor to the Internet IP Address field and press Enter. The data entry field
highlights.
2. Type the unique Internet IP address for the unit and press Enter. The Internet IP address is
assigned to the unit.
June 2003 Rev 0 35

Configuration
3. Reboot the system to effect the changes unless there are more changes you would like to make
at this time. To do this move the cursor down to the line, "Activate changes and reboot" and press
Enter.
Setting the Internet IP Mask
You can obtain an IP Mask value from your system administrator and configure it into the unit.
➧
1. Move the cursor to the Internet IP Mask and press Enter. The field highlights.
2. Type the Internet IP Mask for the unit and press Enter. The Internet IP Mask is assigned to the
3. Reboot the system to effect the changes unless there are more changes you would like to make
Setting Ethernet access to the TCP/IP Stack
Ethernet access to an Libra unit can be controlled by restricting the type of link that can be used to
make configuration changes. You can enable or disable the type of link independently with the two
different access settings. These settings do not affect the unit’s ability to carry traffic.
➧
4. Move the cursor to the System Ethernet Access field and press Enter.
5. Select the desired setting from the list by using the up and down arrow keys and press Enter.
To set the Internet IP mask
unit.
at this time. To do this move the cursor down to the line, "Activate changes and reboot" and press
Enter..
To enable Ethernet access to the TCP/IP
on Enable configuration access to the unit from
Ethernet
off Disable configuration access to the unit from
Ethernet
6. Press Enter. The change has been made.
Setting Local Network MAC Filtering
This is also known as LANCAM (Local Area Network Content Addressable Memory) filtering. A Local
network MAC filter is simply a list of MAC addresses of units that are located on the same LAN. Data
flowing between units in the list is not sent across the wireless link. The table shows up to eight local
MAC addresses that are automatically discovered by the unit when Local Network Mac filtering is on.
This filtering enables data to be handled more efficiently and saves radio bandwidth for traffic that
really needs it.
➧
1. Move the cursor to the Local Network Mac Filter field and press Enter. The entry field
36 Libra 5800 Series User Guide
To set software Local Network Mac filtering
highlights.

Quick-Start Menu
2. Select On or Off from the list by using the up and down arrow keys and press Enter. The change
appears on the screen.
Access Configuration:
Assigning the SNMP Private Community Name
Community names are used to control Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) access to the
Libra unit. The Private Community Name allows read and write access. The factory default for the
SNMP Private Community Name it is netman. Any SNMP manager can access and configure any
unit on the network as long as the unit has the correct community names and Ethernet access is
enabled
! CAUTION
The default community names are public knowledge. Ensure you change
names during installation and record the name changes.
➧
1. Move the cursor to the SNMP Private Community Name field and press Enter. The field
2. Type a new name and press Enter. The change has been made.
Setting Menu Passwords
You can control access to configuration submenus with passwords. The default passwords are
user, supervisor, and pda. A user has read-only access and a supervisor can modify
settings. A new password is hidden by asterisks on the screen when you type it in.
➧
1. Move the cusor to the desired Password field and press
2. Type the new password and press
3. Move to the desired "Confirm Password" field and press
4. Retype the new password to confirm it and press
To set the private community name
highlights.
Important
Default passwords are public knowledge. You should change the default
passwords at installation time and record them. When you restore the factory
configurations, the passwords revert to their defaults.
To change the passwords
Enter. The entry field changes to the edit
mode, meaning the field is highlighted in black and you can change the text there.
Enter.
Enter. The data field highlights.
Enter. The password change is complete when
Success
appears beside the confirmation field.
June 2003 Rev 0 37

Configuration
Note: If you retype the new password incorrectly, appears and you must start again at Step
Failure
2.
OFDM Channel Statistics:
The following values are displayed in real time on the Setup menu to help the installer determine how
well the Libra unit is communicating with the Access Point. These values are as follows:
OFDM Channel Statistics
RSSI (dBm)
Null Depth (dB)
Fade Margin (dB)
RF Link Status
Received Signal Strength Indicator in dBm
Difference in dB between the lowest signal sub carrier and the
highest signal sub carrier. This value is an indication of the level of
multi-path signals present in the link.
Signal-to-noise ratio of the signal; value in dB above the sensitivity
level of the modulation being used (e.g. -75dBm for 16QAM, see
Specifications, page 24 for the values).
This indicates whether any data is being transmitted from the Libra
unit.
Link Test
Once the unit has been configured as desired, the Link Test option can be selected from the setup
menu. This results in test data being transmitted to and from the Libra unit. Statistcs for RSSI and
BER (coarse and fine values) and shown in real-time to allow the person setting up the unit to adjust
it for the best performance (signal strength and BER).
Note: When the Libra-5800 is configured as a point-to-point unit, the "Dest Radio Id" field is not
selectable.
38 Libra 5800 Series User Guide

PDA Setup Menu
PDA Setup Menu
When logging into the unit using the PDA login, it will come up in setup mode. This is in the form of
two screens that display all of the parameters that the user needs to set up the unit and get it talking
with the base station.
Libra Setup
RF Station Id [1..2048] -> 244
Sector Id [0..31] 7
Synchronization Id [0..1] 0
Modulation Type QAM 16
Tx Power [-14..17] 17
Rx Center Freq (kHz) 5787000
Tx Center Freq (kHz) 5787000
Internet IP Address 192.168.1.100
System Ethernet Access on
Local Network Mac Filter off
Monitor Screen Logout
Activate changes and reboot
Many of the fields on this menu can be found in more detailed menus available when using a PC as
discussed later on in this section.
Unit Configuration:
Setting the RF Station ID
Each Libra unit in a P-MP network requires a unique RF Station ID to identify it on the network. Every
unit must have a unique RF Station ID. No two units may have the same ID. In P-P system you
cannot access this selection.
➧
1. Select
2. Type a unique number for the RF Station ID and press Enter. Zero is not a valid Station ID.
3. Record the RF Station ID you have assigned to the unit.You will need to know this number when
4. Reboot the system to effect the changes unless there are more changes you would like to make
To set the RF station ID
RF Station Id [1..2048] and press Enter. The entry field highlights.
you configure the polling list on the Access Point.
at this time. To do this move the cursor down to the line, "Activate changes and reboot" and press
Enter
June 2003 Rev 0 39

Configuration
Setting the Sector ID
Each Libra unit can have a Sector ID to identify its AP/Base within the network. This prevents Libra
units from accessing different APs which may have the same Center Frequency.
➧
1. Move the cursor to the Sector Id [0..31] field and press Enter. The entry field highlights.
2. Type a unique number for the Sector ID and press Enter.
3. Reboot the system to effect the changes unless there are more changes you would like to make
Setting the Synchronization ID
Because of OFDM’s superior multipath performance it is possible for the Libra to falsely synchronize
on an AP from a different sector operating at the same frequency. In order to avoid this type of error,
the APs and Libras of each sector can have one of two possible OFDM synchronization patterns.
These patterns are orthogonal, thus a Libra with a given Synchronization ID will never synch to an
AP with the other synch. Every Libra in the sector must have the same Synchronization ID as the AP
of that sector.
➧
1. Move the cursor to the Synchronization Id [0..1] field and press Enter. The entry field
2. Type a 0 or 1 to select the Synchronization ID and press Enter. Factory default is zero (0).
3. Reboot the system to effect the changes unless there are more changes you would like to make
To set the Sector ID
at this time. To do this move the cursor down to the line, "Activate changes and reboot" and press
Enter
To set the Synchronization ID
highlights.
at this time. To do this move the cursor down to the line, "Activate changes and reboot" and press
Enter.
Radio Configuration:
Setting the Modulation Type
The OFDM Modulation Type can be selected from among the following possible values: "QAM 16",
"QPSK" and "BPSK". The selected type will be added to the next superframe transmitted.
➧
1. Move the cursor to the Modulation Type field and press Enter. The field highlights.
2. Select from the list using the up and down arrow keys the Modulation type and press Enter. The
3. Reboot the system to effect the changes unless there are more changes you would like to make
40 Libra 5800 Series User Guide
To set the Modulation Type
possible options are: QAM 16, QPSK, and BPSK. The new modulation type is applied to the next
superframe to be transmitted.
at this time. To do this move the cursor down to the line, "Activate changes and reboot" and press
Enter

PDA Setup Menu
Setting Tx Power
The Radio Frequency (RF) Board power setting enables you to adjust the strength of the transmit
signal sent from the Libra unit to the antenna. The range is -3dBm to +17dBm.
➧
1. Move the cursor to the Set Tx Power field and press Enter. The field highlights.
2. Type in the signal strength. The new signal strength is applied.
Setting the RF Center Frequency
Libra 5800 equipment uses Time Division Duplexing (TDD). In TDD, the units transmit and receive
on the same frequency. They alternate in time to provide the duplexing capability. The frequency of
these channels depend on the model of equipment used.
The center frequency is a frequency located in the middle of each set of transmit and receive
channels and it defines the group of frequencies situated around it.
➧
1. Move the cursor to the Set RF Center Frequency field and press Enter. The entry field is
2. Enter the frequency value assigned to this unit in kHz and press enter to effect the changes. The
To set the Tx power
To set the RF Center Frequency
highlighted.
unit does not require rebooting for this change to become effective.
Communication Parameters:
Setting the IP Address
An IP address must be assigned to each Libra unit in the network. Changes takes effect on the next
reset. You will require the IP address of yourLibra unit for this procedure. Your system administrator
should be able to provide it.
➧
1. Move the cussor to the Internet IP Address field and press Enter. The data entry field
2. Type the unique Internet IP address for the unit and press Enter. The Internet IP address is
3. Reboot the system to effect the changes unless there are more changes you would like to make
Setting Ethernet access to the TCP/IP Stack
Ethernet access to an Libra unit can be controlled by restricting the type of link that can be used to
make configuration changes. You can enable or disable the type of link independently with the two
different access settings. These settings do not affect the unit’s ability to carry traffic.
To set the IP Address
highlights.
assigned to the unit.
at this time. To do this move the cursor down to the line, "Activate changes and reboot" and press
Enter.
June 2003 Rev 0 41

Configuration
➧
4. Move the cursor to the System Ethernet Access field and press Enter.
5. Select the desired setting from the list by using the up and down arrow keys and press Enter.
6. Press Enter. The change has been made.
Setting Local Network MAC Filtering
This is also known as LANCAM (Local Area Network Content Addressable Memory) filtering. A Local
network MAC filter is simply a list of MAC addresses of units that are located on the same LAN. Data
flowing between units in the list is not sent across the wireless link. The table shows up to eight local
MAC addresses that are automatically discovered by the unit when Local Network MAC filtering is
on. This filtering enables data to be handled more efficiently and saves radio bandwidth for traffic that
really needs it.
➧
To enable Ethernet access to the TCP/IP
on Enable configuration access to the unit from
Ethernet
off Disable configuration access to the unit from
Ethernet
To set software Local Network MAC filtering
1. Move the cursor to the Local Network MAC Filter field and press Enter. The entry field
highlights.
2. Select On or Off from the list by using the up and down arrow keys and press Enter. The change
appears on the screen.
Setup Menu - Second Screen
The following set of parameters are available on page 2 of the setup screen. Move the cursor to the
Monitor field on the first screen and press the Enter key to get to the second screen as depicted
below.
42 Libra 5800 Series User Guide

OFDM Channel Statistics:
OFDM Channel Statistics
RSSI (dBm) -22
Null Depth (dB) 25
Fade Margin (dB) 45
RF Link Status Connected
Link Test
Link Test Type -> Coarse (xE-5)
Dest Radio Id 26
Start Link Test
Logout
Press ESC to go to setup screen
PDA Setup Menu
The following values are displayed in real time on the Setup menu to help the installer determine how
well the Libra unit is communicating with the Access Point. These values are as follows:
OFDM Channel Statistics
RSSI (dBm)
Null Depth (dB)
Received Signal Strength Indicator in dBm
Difference in dB between the lowest signal sub carrier and the
highest signal sub carrier. This value is an indication of the level of
multi-path signals present in the link.
Fade Margin (dB)
Signal-to-noise ratio of the signal; value in dB above the rated
sensitivity of the modulation type (e.g. -75 dBm for 16QAM)
RF Link Status
This indicates whether any data is being transmitted from the Libra
unit.
Link Test:
Once the unit has been configured as desired, the Link Test option can be selected from either setup
screen. This results in test data being transmitted to and from the Libra unit. Statistcs for RSSI and
BER (coarse and fine values) and shown in real-time to allow the person setting up the unit’s
antenna to adjust it for the best performance in terms of signal strenght, BER and Fade Margin.
Note: When the Libra-5800 is configured as a point-to-point unit, the "Dest Radio Id" field is not
selectable.
June 2003 Rev 0 43

Configuration
44 Libra 5800 Series User Guide

Main System Menu
Main System Menu
This is main menu used during normal operation of the unit when not in setup mode. It displays a set
up sub-menus that allow the user to set configuration parameters (if logged in as supervisor) or read
statistics related to the operation of the unit. At the bottom of the menu the Libra RF Board Model
name and Bandwidth are displayed. These are associated with the type of RF Board plugged into the
unit.
AP - Main System Menu
-> System Revision Information
System Software ROM Images
System Current Status
System Security
System Commands
Network Configuration
Radio Configuration
Remote Station Configuration
MAC Layer Statistics
RF Statistics
Setup
Logout
Libra Model 5800 Bandwidth 12.5 MHz
June 2003 Rev 0 45

Configuration
System Revision Information
The System Revision Information screen displays information about the Libra unit such as software
revision, firmware version and RF board model.
➧
To view system revision information
1. From the Main System Menu, select System Revision Information and press Enter. The
System Revision Information screen appears. This screen is view-only.
System Revision Information
Hardware Revision 0x01 RS Version 0x3001001
CPLD Revision 0x04 FE Version 0x86001001
DSP Revision 0x20507 BootROM Version 0
RF Board Model: 13748-003
RF Board Serial Number: 7233-455
File Name lib5800-3-2-2-bws.wil
Software Rev 3-2-2 (Wi-LAN Ethernet/OFDM)
Software Date Aug 08 2003 17:20:02
File Size 2097152
Hardware Revision Static Integer Identifies the hardware revision.
CPLD Revision Static Integer Identifies the CPLD revision. The
revision register is implemented
starting with CPLD revision 0xB4.
DSP Revision Static Integer Revision number of the DSP
image running on the unit.
RS Version Static Integer Version of Reed Solomon FPGA
running on the unit.
FE Version Static Integer Version of Front End FPGA
running on the unit.
BootROM Version Static Integer Version of the BootROM code
running on the unit.
RF Board Model Static Integer Model number of RF board as
displayed on the board in the unit
46 Libra 5800 Series User Guide

System Revision Information
RF Board Serial Number Static Integer Serial number of RF board as
displayed on the board in the unit
File Name Static Text (0..31) File name of the master system
image running on the unit. The
message "No Flash Images
Found" is displayed if no system
images are found in flash.
Software Rev Static Text Revision number of the master
system image running on the unit.
.
Software Date Static Text Timestamp of the master system
image running on the unit.
File Size Static Integer Size of the master system image
running on the unit as reported by
the dir command.
2. Press Esc to exit.
June 2003 Rev 0 47

Configuration
System Software ROM Images
Viewing system software ROM images
The System Software ROM Images screen lists all the images available in a unit. An image is the
software stored in Flash ROM that a unit uses to operate. This example lists only the Factory Image.
More than one image may be displayed. As new images become available, Wi-LAN places them on
their web site for downloading by customers.
➧
1. From the Main System Menu, select System Software ROM Images and press
System Software ROM Images
File Name Revision Date Time Size Default Current
------------------- -------- ----------- -------- ------- ------- -------
lib5800-3-2-2-bws.wil 3.2.2 Aug 08 2003 12:48:45 2097152 No No
lib5800-3-2-1-bws.wil 3.2.1 Aug 02 2003 17:20:02 1835008 Yes Yes
To view system software ROM images
Enter.
The System Software ROM Images screen appears. This screen is view-only.
File Name Name(s) of system image files stored in the unit
Revision Revision number of the system image file.
Date Date the image file was created
Time Time the image file was created
Size Size of the image file in bytes
Default Indicates which image file is the default. This is the image used at power up.
See Setting Default System Image, page 60. Possible values are Yes and
No.
Current Indicates if the image file is currently operating on the unit. Possible values
are Yes and No.
System Current Status
Viewing system current status
The System Current Status screen displays administrative information, such as the time a unit has
been running and login statistics. This information enables you to view the current state of the
system and, if you are troubleshooting system problems, provides historical information.
48 Libra 5800 Series User Guide

System Current Status
Note:You can reset the Current Run-Time statistics to zero by resetting the system.
➧
1. From the Main System Menu, select System Current Status and press
To view current system status
Enter.
The System Current Status screen appears. The screen is view-only.
System Current Status
Cumulative Run-Time Days: 0 Hours: 3
Current Run-Time Days: 0 Hours: 00:14:25
Power Cycles 6
Successful Logins 34
Unsuccessful Logins 1
Local User Logged In Supervisor
Telnet User Logged In None
FTP User Logged In None
No RF Activity Reboot 0
Cumulative Run-Time Number of hours the system has run since the first power-up. This
information is required for maintenance. Loading new images resets
this value. This field has a resolution of one hour.
Current Run-Time Approximate time since the unit was last reset.
Power Cycles Number of times that the unit has been turned off and on again
Successful Logins Number of successful login attempts
Unsuccessful Logins Number of failed login attempts
Local User Logged In Identifies the user currently logged into the configuration menus via
the serial port: None, User or Supervisor
Telnet User Logged In Identifies the user currently logged into the configuration menus via
telnet: None, User or Supervisor
FTP User Logged In Identifies the user currently logged into the configuration menus via
FTP: None, User or Supervisor
June 2003 Rev 0 49

Configuration
System Security
The System Security menu enables you to control access to the Libra 5800 system. You can control
remote access, assign community names and set passwords and the timeout period.
Setting Ethernet and wireless access to the TCP/IP Stack
Access to a Libra unit can be controlled by restricting the type of link that can be used to make
configuration changes: wired (Ethernet) or wireless access. You can enable or disable the type of link
independently with the two different access settings. These settings do not affect the unit’s ability to
carry traffic just access to the unit’s local management functions.
➧
1. From the Main System Menu, select System Security and press Enter.
To enable Ethernet access to the TCP/IP
The System Security menu appears.
2. Select System Ethernet Access and press Enter.
3. Select the desired setting from the list by using the up and down arrow keys and press Enter.
on Enable configuration access to the unit from
Ethernet
off Disable configuration access to the unit from
Ethernet
4. Press Enter. The change has been made.
50 Libra 5800 Series User Guide

System Security
➧
1. From the Main System Menu, select System Security and press Enter.
To enable wireless access to the TCP/IP Stack
The System Security menu appears.
2. Select System Wireless Access. The field highlights.
3. Select the desired setting with the up and down arrow keys.
on Enable configuration access to the unit from the air
off Disable configuration access to the unit from the air
4. Press Enter. The change has been made.
June 2003 Rev 0 51

Configuration
Assigning Community Names
Community names are used to control Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) access to the
AP and CPE unit. The Public Community Name allows read-only access. The Private Community
Name allows read and write access. The factory default for the SNMP Public Community Name is
public and for the Private Community Name it is netman. Any SNMP manager can access and
configure any unit on the network as long as the unit has the correct community names and Ethernet
access is enabled (see Setting Ethernet and wireless access to the TCP/IP Stack, page 50).
! CAUTION
The default community names are public knowledge. Ensure you change
names during installation and record the name changes. If you restore
units to factory configurations, you also restore the default (public) names.
➧
1. From the Main System Menu, select System Security and press
To set the public community name
The System Security menu appears.
Enter.
2. Select SNMP Public Community Name and press Enter.
3. Type a new community name and press Enter. The change has been made.
52 Libra 5800 Series User Guide

System Security
➧
1. From the Main System Menu, select System Security and press
To set the private community name
The System Security menu appears.
Enter.
2. Select SNMP Private Community Name and press Enter. The field highlights.
3. Type a new name and press Enter. The change has been made.
Setting Menu Passwords
You can control access to configuration submenus with passwords. The default passwords are user
and supervisor. A user has read-only access and a supervisor can modify settings. A new
password is hidden by asterisks on the screen when you type it in.
! CAUTION
Default passwords are public knowledge. You should change the default passwords
at installation time and record them. When you restore the factory configurations,
the passwords revert to their defaults.
June 2003 Rev 0 53

Configuration
➧
1. From the Main System Menu, select System Security and press
To change the user password
The System Security menu appears.
Enter.
2. Select Change User Password and press
meaning the field is highlighted in black and you can change the text there.
3. Type the new password and press
Enter.
Enter. The entry field changes to the edit mode,
54 Libra 5800 Series User Guide

System Security
4. Select Confirm User Password and press
Enter. The data field highlights.
5. Retype the new password to confirm it and press
Success
Note: If you retype the new password incorrectly, appears and you must start again at Step
appears beside the confirmation field.
Enter. The password change is complete when
Failure
2.
June 2003 Rev 0 55

Configuration
➧
1. From the Main System Menu, select System Security and press
To change the supervisor password
The System Security menu appears.
Enter.
2. Select Change Supervisor Password and press
3. Type the new password and press
Enter.
Enter. The data field highlights.
56 Libra 5800 Series User Guide

System Security
4. Select Confirm Supervisor Password and press
Enter.
5. Retype the new password and press Enter. The change is saved when appears beside
the confirmation field. If you retype the new password incorrectly, appears and you must
Success
Failure
start again at Step 2.
June 2003 Rev 0 57

Configuration
To change the PDA password
1. From the Main System Menu, select System Security and press
The System Security menu appears.
Enter.
2. Select Change PDA Password and press
3. Type the new password and press
Enter.
4. Select Confirm PDA Password and press
Enter. The data field highlights.
Enter.
58 Libra 5800 Series User Guide

System Security
5. Retype the new password and press
the confirmation field. If you retype the new password incorrectly, appears and you must
start again at Step 2.
Enter. The change is saved when appears beside
Success
Failure
Setting Auto Logout Timeout
You can specify the maximum time the system can remain idle before a local, telnet or ftp session
automatically ends and the login menu reappears. This security feature ensures that the
configuration menus close when a user forgets to exit. You can enter any value from zero minutes,
meaning the system never times out, to 9,999 minutes – six days, 22 hours, 39 minutes.
➧
1. From the Main System Menu, select System Security and press
To set the automatic logout timeout period
Enter.
The System Security menu appears.
2. From the System Security menu, select Auto Logout Timeout (Minutes) and press
Enter. The entry field highlights.
3. Type the period, in minutes, that you want to wait before the configuration menus close.
4. Press Enter. The change has been made.
June 2003 Rev 0 59

Configuration
System Commands
Master image files contain the software that runs the Libra. When a master image is rebooted, the
unit copies the MPC CPU code out of the master image in memory and runs it. It will also use the
DSP and FPGA code from the master image to boot those devices. If the master image also contains
a newer version of the BootROM code this will be updated as well.
When you first power up the unit, it runs from the default image loaded in at the factory. With the
System Commands menu you can control which master image file a unit uses to power up, and
which master image file a unit uses to reboot. These are typically the same except in the case where
you want to test an image before setting it as the default.
Note:Wi-LAN will make new images available on its website as they are developed.
Setting Default System Image
The default master image is the file used at power up. If you have more than one image saved on a
unit, you can change the default image. This default image is displayed in the System Revision
Information screen.
➧
1. From the Main System Menu, select System Commands and press
2. Select Set Default System Image. The field highlights.
3. Press the up and down arrows to select the default image and press Enter. The new image file
To set the default image
Enter.
The System Commands menu appears.
System Commands
Set Default System Image lib5800-3-2-0.wil
Reboot Current Image Press Enter to Execute
Reboot a System Image lib5800-3-2-1.wil
Restore Factory Configuration Press Enter to Execute
Restore Poweron Configuration Press Enter to Execute
Reset MAC Layer Statistics Press Enter to Execute
will be used each time the Libra 5800 unit is powered up.
Reboot Current Image
Always use the Reboot Current Image command when the IP address changes or any other
parameter that requires an unit reboot to take effect. See Setting the Internet IP Address, page 64.
60 Libra 5800 Series User Guide

System Commands
➧
1. From the Main System Menu, select System Commands and press Enter.
2. Select Reboot Current Image and press Enter. The Libra 5800 unit reboots using the
To reboot the current image
The System Commands menu appears.
System Commands
Set Default System Image lib5800-3-2-0.wil
Reboot Current Image Press Enter to Execute
Reboot a System Image lib5800-3-2-1.wil
Restore Factory Configuration Press Enter to Execute
Restore Poweron Configuration Press Enter to Execute
Reset MAC Layer Statistics Press Enter to Execute
current image.
Rebooting a System Image
Any image in the System Software ROM Images menu including the current one may be used for
rebooting. When you reboot a system image, the system reboots with a new image of your choice,
but this does not change the default image. This is useful for testing an upgrade. If a new image fails
to boot the last running image will be booted.
➧
1. From the Main System Menu, select System Commands and press Enter.
2. Select Reboot a System Image. The field highlights.
3. Use the up and down arrows to select the image you want to use and press Enter. The Libra
To reboot a system image
The System Commands menu appears.
System Commands
Set Default System Image lib5800-3-2-0.wil
Reboot Current Image Press Enter to Execute
Reboot a System Image lib5800-3-2-1.wil
Restore Factory Configuration Press Enter to Execute
Restore Poweron Configuration Press Enter to Execute
Reset MAC Layer Statistics Press Enter to Execute
5800 unit reboots using the selected system image.
June 2003 Rev 0 61

Configuration
Restoring the Factory Configuration
You can restore a unit to its factory configuration to put it into a known state for troubleshooting or to
remove customized configurations when decommissioning a unit.
➧
1. From the Main System Menu, select System Commands and press
2. Select
To restore the factory configuration
Enter.
The System Commands menu appears.
System Commands
Set Default System Image lib5800-3-2-0.wil
Reboot Current Image Press Enter to Execute
Reboot a System Image lib5800-3-2-1.wil
Restore Factory Configuration Press Enter to Execute
Restore Poweron Configuration Press Enter to Execute
Reset MAC Layer Statistics Press Enter to Execute
Restore Factory Configuration and press Enter.The factory configuration
settings are restored.
Important
When you restore factory configurations, many settings revert automatically to
their default values, including passwords, IP Address, radio and configuration
settings.
➧
1. From the Main System Menu, select System Commands and press Enter.
2. Select Restore Poweron Configuration and press Enter. The configuration settings
To restore the power-on configuration
The System Commands menu appears.
System Commands
Set Default System Image lib5800-3-2-0.wil
Reboot Current Image Press Enter to Execute
Reboot a System Image lib5800-3-2-1.wil
Restore Factory Configuration Press Enter to Execute
Restore Poweron Configuration Press Enter to Execute
Reset MAC Layer Statistics Press Enter to Execute
change back to what they were the last time the unit powered up.
62 Libra 5800 Series User Guide

System Commands
Resetting MAC Layer Statistics
Statistics displayed in the MAC Layer Statistics screen are cumulative, but can be reset to track
specific events. See MAC Layer Statistics, page 84, for a list of these statistics and instructions on
how to view them.
➧
1. From the Main System Menu, select System Commands and press Enter.
2. Select Reset MAC Layer Statistics and press Enter. appears, indicating that
To reset the MAC layer statistics
The System Commands menu appears.
System Commands
Set Default System Image lib5800-3-2-0.wil
Reboot Current Image Press Enter to Execute
Reboot a System Image lib5800-3-2-1.wil
Restore Factory Configuration Press Enter to Execute
Restore Poweron Configuration Press Enter to Execute
Reset MAC Layer Statistics Press Enter to Execute
Success
values in the MAC Layer Statistics Menu have been reset to 0.
June 2003 Rev 0 63

Configuration
Network Configuration
To enable the Libra to communicate via TCP/IP you need to assign an Internet IP address and IP
mask.
Important
When you change the IP address, you must reboot the current image for the
changes to take effect. See Reboot Current Image, page 60, for more information.
Note: The menu shown here is the one for the CPE or LCPE (in a P-MP system) and the remote in a
P-P system. The only difference for AP and base station is that VLAN tagging entries do not
appear.
Setting the Internet IP Address
An IP address must be assigned to each Libra unit in the network. Changes takes effect on the next
reset. You will require the IP address of your Libra unit for this procedure. Your system administrator
should be able to provide it.
➧
1. From the Main System Menu, select Network Configuration and press Enter.
To set the Internet IP address
The Network Configuration menu appears.
2. Select Internet IP Address and press Enter. The data entry field highlights.
3. Type the unique Internet IP address for the unit and press Enter. The Internet IP address is
assigned to the unit.
4. Reboot the current image to make changes take effect. See Reboot Current Image, page 60.
64 Libra 5800 Series User Guide

Setting the Internet IP Mask
You can obtain an IP Mask value from your system administrator.
Network Configuration
➧
1. From the Main System Menu, select Network Configuration.
To set the Internet IP mask
The Network Configuration menu appears.
2. Select Internet IP Mask and press Enter. The field highlights.
3. Type the Internet IP Mask for the unit and press Enter. The Internet IP Mask is assigned to the
unit.
4. Reboot the current image to make the changes take effect. See Reboot Current Image, page 60.
VLAN Tagging
Libra supports 802.1Q VLAN compatibility. In Libra the user can enable the VLAN Tagging option.
Under this option, ethernet packets received from the wired ethernet interface will be tagged with the
VLAN ID and user priority before being transmitted out to the RF interface (uplink tagging), and
ethernet packets received from the RF interface will be untagged before being transmitted out to the
wired ethernet interface (downlink untagging). Packets arriving over the air with different VLAN tags
than the VLAN ID configured on the CPE will be dropped before being sent on the local wire
interface.
Having VLAN tagging enabled can be used when the Libra and AP are under one VLAN domain;
however, the Libra unit does not require a VLAN switch to be connected to the ethernet network. If
the VLAN Tagging option is disabled, the Libra unit will transparently bridge 802.1Q tagged ethernet
June 2003 Rev 0 65

Configuration
packets between the wired ethernet interface and the RF interface. A sample scenario of this is when
both Libra and AP units are connected to VLAN switches.
There is no VLAN setting available on the AP. The AP transparently bridges VLAN packets in a
trunking fashion. If users plan to use VLAN functionality on their network, it is advisable to have a
VLAN switch located between the AP and its ethernet network.
Note: All packets with CFI=1 (Canonical Format Inidicator) in the 802.1Q VLAN tag control
information field will be discarded.
➧
Note: VLAN Tagging can only be set for the CPE and LCPE in a P-MP system and on the remote in
1. From the Main System Menu, select Network Configuration and press Enter.
To set VLAN Tagging
a P-P system. This item does not appear in the Network configuration menu for the AP or for
the base station.
The Network Configuration menu appears.
2. Select VLAN Tagging and press Enter. The entry field highlights.
3. Type Enable or Disable and press Enter. The change appears on the screen.
66 Libra 5800 Series User Guide

VLAN Tagging ID
Network Configuration
➧
1. From the Main System Menu, select Network Configuration and press Enter.
To set VLAN Tagging ID
The Network Configuration menu appears.
2. Select VLAN Id and press Enter. The entry field highlights.
3. Type the VLAN ID value (valid values are 1...4096) and press Enter. The change appears on the
screen.
June 2003 Rev 0 67

Configuration
VLAN Tagging User Priority
➧
1. From the Main System Menu, select Network Configuration and press Enter.
To set VLAN Tagging User Priority
The Network Configuration menu appears.
2. Select User Priority and press Enter. The entry field highlights.
3. Type the priority value and press Enter. The change appears on the screen.
Setting Local Network MAC Filtering (LNMF)
Local Network MAC Filtering also known as LAN CAM (Local Area Network Content Addressable
Memory) filtering enables you to filter MAC addresses so that data traffic is handled more efficiently.
A LNMF filter is simply a list of MAC address of units that are located on the same wired LAN. Data
flowing between units in the list is not sent across the wireless link. The table shows up to eight local
MAC addresses that are automatically discovered by the unit when LNMF filtering is on. LNMF
filtering enables data to be handled more efficiently and saves radio bandwidth for traffic that really
needs it.
68 Libra 5800 Series User Guide

Network Configuration
➧
1. From the Main System Menu, select Network Configuration and press Enter.
To set LNMF filtering
The Network Configuration menu appears.
2. Select Local Network Mac Filter and press Enter. The entry field highlights.
3. Type On or Off and press Enter. The change appears on the screen.
June 2003 Rev 0 69

Configuration
Radio Configuration
You can configure radio settings such as RF station IDs, Sector ID, Synchronization ID, center
frequencies transmit power and Base Station modulation type with the Radio Configuration menu.
Setting the RF Station ID (P-MP Only)
Each AP, CPE or LCPE unit requires a unique RF Station ID to identify it on the network. Every unit
must have a unique RF Station ID. No two units in a single sector (i.e. one controlled by a single AP)
may have the same ID.
➧
1. From the Main System Menu, select Radio Configuration and press Enter.
Radio Configuration
OFDM Station Type Base Station
RF Station Id [1..2047] -> 2
Sector Id [0..31] 1
Synchronization Id [0..1] 0
Base Station Tx Disable
Center Freq (kHz) 5787000
Set Tx Power (dBm) [-3...17] 17
Modulation Type QAM 16
Note: Changes on this menu aside from Tx Power require that the
unit be rebooted to take effect.
To set the RF station ID
The Radio Configuration menu appears.
2. Select
3. Type a unique number for the RF Station ID and press Enter. Zero is not a valid Station ID.
4. Record the RF Station ID you have assigned to the unit.You will need to know this number when
you configure the polling list on the Access Point.
5. Reboot the system to effect the changes. See Reboot Current Image, page 60.
70 Libra 5800 Series User Guide
RF Station Id [1..2048] and press Enter. The entry field highlights.

Radio Configuration
Setting the Sector ID
Each Libra unit can have a Sector ID to identify its AP within the cell on the network. This prevents
Libra units from connecting to different APs which may have the same Center Frequency.
➧
1. From the Main System Menu, select Radio Configuration and press Enter.
To set the Sector ID
The Radio Configuration menu appears.
Radio Configuration
OFDM Station Type Base Station
RF Station Id [1..2047] -> 2
Sector Id [0..31] 1
Synchronization Id [0..1] 0
Base Station Tx Disable
Center Freq (kHz) 5787000
Set Tx Power (dBm) [-3...17] 17
Modulation Type QAM 16
Note: Changes on this menu aside from Tx Power require th at
the unit be rebooted to take effect.
2. Select
3. Type a unique number for the Sector ID and press Enter. Zero is not a valid Sector ID.
4. Reboot the system to effect the changes. See Reboot Current Image, page 60.
June 2003 Rev 0 71
Sector Id [0..31] and press Enter. The entry field highlights.

Configuration
Setting the Synchronization ID
Because of OFDM’s superior multipath performance it is possible for the CPE to falsely synchronize
on an AP from a different sector operating at the same frequency. In order to avoid this type of error,
the APs and CPEs of each sector can have one of two possible OFDM synchronization patterns.
These patterns are orthogonal, thus a CPE with a given Synchronization ID will never synch to an AP
with the other synch. Every CPE in the sector must have the same Synchronization ID as the AP of
that sector.
➧
1. From the Main System Menu, select Radio Configuration and press Enter.
To set the Synchronization ID
The Radio Configuration menu appears.
Radio Configuration
OFDM Station Type Base Station
RF Station Id [1..2047] -> 2
Sector Id [0..31] 1
Synchronization Id [0..1] 0
Base Station Tx Disable
Center Freq (kHz) 5787000
Set Tx Power (dBm) [-3...17] 17
Modulation Type QAM 16
Note: Changes on this menu aside from Tx Power require that
the unit be rebooted to take effect.
2. Select
3. Type a 0 or 1 to select the Synchronization ID and press Enter. Factory default is zero (0).
4. Reboot the system to effect the changes. See Reboot Current Image, page 60.
Synchronization Id [0..1] and press Enter. The entry field highlights.
Setting the RF Center Frequency
Libra 5800 equipment uses Time Division Duplexing (TDD). In TDD, the units transmit and receive
on the same frequency. They alternate in time to provide the duplexing capability. The frequency of
these channels depend on the model of equipment used.
72 Libra 5800 Series User Guide

Radio Configuration
The center frequency is a frequency located in the middle of each set of transmit and receive
channels and it defines the group of frequencies situated around it.
➧
1. Move the cursor to the Set RF Center Frequency field and press Enter. The entry field is
2. Enter the frequency value assigned to this unit in kHz and press enter to effect the changes. The
To set the RF Center Frequency
highlighted.
unit does not require rebooting for this change to become effective.
Radio Configuration
OFDM Station Type Base Station
RF Station Id [1..2047] -> 2
Sector Id [0..31] 1
Synchronization Id [0..1] 0
Base Station Tx Disable
Center Freq (kHz) 5787000
Set Tx Power (dBm) [-3...17] 17
Modulation Type QAM 16
Note: Changes on this menu aside from Tx Power require that
the unit be rebooted to take effect.
June 2003 Rev 0 73

Configuration
Setting Tx Power
The transmitter power setting enables you to adjust the strength of the transmit signal sent from the
Libra unit to the antenna. The range is -3 dBm to 17 dBm.
➧
1. From the Main System Menu, select Radio Configuration and press Enter.
To set the Tx power
The Radio Configuration menu appears.
Radio Configuration
OFDM Station Type Base Station
RF Station Id [1..2047] -> 2
Sector Id [0..31] 1
Synchronization Id [0..1] 0
Base Station Tx Disable
Center Freq (kHz) 5787000
Set Tx Power (dBm) [-3...17] 17
Modulation Type QAM 16
Note: Changes on this menu aside from Tx Power require that
the unit be rebooted to take effect.
2. Select Set Tx Power and press Enter. The field highlights.
3. Type in the signal strength. The new signal strength is applied.
74 Libra 5800 Series User Guide

Radio Configuration
Setting the Modulation Type
The OFDM Modulation Type can be selected from among the following possible values: "QAM 16",
"QPSK" and "BPSK". The selected type will be added to the next superframe transmitted.
➧
1. From the Main System Menu, select Radio Configuration and press Enter.
To set the Modulation Type
The Radio Configuration menu appears.
Radio Configuration
OFDM Station Type Base Station
RF Station Id [1..2047] -> 2
Sector Id [0..31] 1
Synchronization Id [0..1] 0
Base Station Tx Disable
Center Freq (kHz) 5787000
Set Tx Power (dBm) [-3...17] 17
Modulation Type QAM 16
Note: Changes on this menu aside from Tx Power require that
the unit be rebooted to take effect.
2. Select Modulation Type and press Enter. The field highlights.
3. Use the up/down arrows to select the desired modulation type from the pull down list, and press
enter again. This change requires a reboot to take effect.
June 2003 Rev 0 75

Configuration
Remote Station Configuration Menu (P-MP Only)
This menu only appears on the Libra 5800 when set up as an AP. When setup as a P-P unit there is
only one unit to poll with an id of zero so this menu is not needed. It displays a portion of a larger
table. The table row order determines the polling sequence of the units. Changes to the table take
effect immediately.
The table cannot contain zeros between valid radio ids. If a radio Id within the table is set to zero
(hence removing the entry from the polling list), all values following this entry will be moved one entry
toward the beginning of the table.
Remote Station Configuration
Maximum Remote Distance (Km) (1...50) -> 10
Remote Radio Id Remote Radio Id Remote Radio Id
Number 0..2047 Number 0..2047 Number 0..2047
1 1 9 0 17 0
2 2 10 0 18 0
3 0 11 0 19 0
4 0 12 0 20 0
5 0 13 0 21 0
6 0 14 0 22 0
7 0 15 0 23 0
8 0 16 0 24 0
Field Name Type Comments
Maximum Remote
Distance (Km)
Static Integer
(1..50)
Sets the distance to the CPE farthest from
the AP. This value determines the timeout
for detecting late poll responses. Factory
default is 10.
Remote Number Static Integer
Sequential number for reference only.
(1..2048)
76 Libra 5800 Series User Guide

Remote Station Configuration Menu (P-MP Only)
Field Name Type Comments
Radio Id Variable Integer
(1..2048)
Identifies a unit to be polled. Values
correspond to the RF Station Id field in the
Radio Configuration Menu (see page 28). A
given ID may be listed more than once, in
which case that unit is polled more than
once in a single polling cycle. A value of
zero (an invalid RF Station ID) means the
table entry is not polled. Factory default is 1
for remote number 1, 2 for remote number
2, and zero for all other remotes.
June 2003 Rev 0 77

Configuration
IP/MBR Filter Configuration
IP filters help ensure that only valid subscribers use the wireless link. IP address filters are actually
tables that contain lists of IP addresses and masks on the local Ethernet. If an address is listed in the
table, the CPE will pass data packets to and from it. If the address is not defined by one of the filters,
the unit will not pass data packets to it or from it.
IP Address Filter Table
xxx.xx.xx.x
xxx.xx.xx.x
xxx.xx.xx.x
IP
Addresses
WireAir
Data packets pass only
if the IP address is
listed in the IP filter table
An IP address filter is defined by a range and a base value. IP address filtering improves system
security and helps manage data throughput.
The IP filter is created by combining the Subnet Mask and the IP Network address such that a binary
'1' in the subnet mask will preserve the corresponding digit in the IP Network address. For example
to filter on the range of addresses 192.8.62.0-255, a value of 192.8.62.0 would be entered as the IP
Network address and a value of 255.255.255.0 as the Subnet Mask. Alternatively to filter specifically
on the address 192.8.62.8, the values of 192.8.62.8 for the IP Network Address and
255.255.255.255 for the Subnet Mask would be entered.
The Maximum Burst Rate (MBR) option provides a means of limiting the maximum data rate on
individual CPE's. Use of this feature allows efficient management of the network by ensuring that
specific CPE's receive the level of service to which they are entitled.
Since the downstream Air link is broadcast, it is necessary to use MBR in conjunction with IP filtering.
This ensures that the maximum burst rate limit is applied only to data streams associated with the
particular CPE to which it is intended.Libra Unit
Setting the IP Filtering Option
You can set the IP Filtering Option to Disable to enable all data to pass through a CPE, or you can
set it to Filter to filter out certain IP address ranges defined in the IP Filter Configuration Menu.
The factory default is Disable. When set to IP Filtering, any packets other than IP and ARP
are rejected. When set to IP Filtering with MBR, the maximum burst rate for the CPE is
enforced in addition to filtering.
Note: IP Filtering is always set to disable on AP units. It can be set to Disable or IP Filtering
on CPEs.
78 Libra 5800 Series User Guide

IP/MBR Filter Configuration
➧
1. From the Main System Menu, select IP/MBR Filter Configuration and press Enter.
To set the IP Filtering option
The IP/MBR Filter Configuration menu appears.
2. Select
3. Use the up and down arrow keys to select one of the following options.
4. Press Enter to select the option.
IP Filtering Option. The field highlights.
Disable Enables the passage of all received data through the remote unit
Filter This prevents data destined for particular IP addresses from going through
particular remotes. This option does not appear on a base unit.
Filter with
MBR
This option will enforce filtering and enforce the maximum burst rate
Configuring the IP Filter
To define an IP filter, you indicate host and mask IP addresses on the local Ethernet and set the filter
to On. Data packets sent to these addresses or originating from them will be passed by the CPE.
Packets coming from or bound for addresses not defined in the filters will be dropped by the CPE.
This provides privacy in two directions, by allowing only authorized users to send or receive. Only
remote units can have IP filters and the IP Filter Configuration option appears only on the menus of
the remote units.
If you set the IP Filtering Option to Filter as described in Setting the IP Filtering Option, page 78, but
set all the filters to off, as described in this section, then no IP packets can pass through the unit.
June 2003 Rev 0 79

Configuration
Note: If you turn on IP filtering and want to allow broadcast traffic to flow through the unit, enter the
IP Broadcast address into the list; i.e.
Host/Net Address = 255.255.255.255 and
Host/Net Mask = 255.255.255.255.
➧
1. Follow the procedure in the previous section to enable IP Filtering Option by setting it to Filter.
To configure the remote IP filter
Filter A numbered list of the filters
Type Filter type can be Off or On
Host/Net
Address
Host/Net
Mask
2. Select On in the filter row you are defining and press Enter. The entry field highlights.
3. Use the arrow keys to select the desired filter type where
Off Do not filter the packets. This is the factory default
On Filter the packets
80 Libra 5800 Series User Guide
IP Filter net or host IP Address
Mask applied to the filter host or net address. Address and Mask = host and net
number

IP/MBR Filter Configuration
4. Press the right arrow key on the keyboard to move to the
Enter.
The entry field highlights.
5. Type the IP Address of the Host/Net and press Enter. You have defined the IP Address.
6. Press the right arrow key on the keyboard to move to the Host/Net Mask field and press Enter.
The entry field highlights.
7. Type the IP Address of the Host/Net Mask and press Enter.
8. Repeat steps to create additional IP filters.
Host/Net Address field and press
Setting the MBR Filtering Option
You can set the IP Filtering Option to IP Filtering with MBR to enforce a maximum allowable
burst rate for a given CPE. The factory default is Disable. When set to IP Filtering with
MBR, any packets other than IP and ARP are rejected and the maximum burst rate for the CPE is
enforced.
➧
1. From the Main System Menu, select IP/MBR Filter Configuration and press Enter.
To set the MBR Filtering option
The IP/MBR Filter Configuration menu appears.
2. Select
June 2003 Rev 0 81
IP Filtering Option. The field highlights.

Configuration
3. Use the up and down arrow keys to select the following option.
Filter with
This option will enforce filtering and enforce the maximum burst rate
MBR
4. Press Enter to select the option.
5. Select the
Uplink (Kbits/s) [0...2500]option to set the MBR from the CPE to the AP.
6. Type in the MBR allowed for that CPE. Note: entering zero in that field means that maximum
burst rate is NOT enforced for that CPE.
82 Libra 5800 Series User Guide

IP/MBR Filter Configuration
7. Select the
Downlink (Kbits/s) [0...2500]option to set the MBR from the AP to the CPE.
8. Type in the MBR allowed for that CPE. Note: entering zero in that field means that maximum
burst rate is NOT enforced for that CPE.
June 2003 Rev 0 83

Configuration
MAC Layer Statistics
The MAC Layer Statistics screen displays various statistics about a unit’s performance, including
Ethernet receive statistics, OFDM decoder statistics, OFDM channel statistics, approximated BERs,
Ethernet transmit statistics, OFDM encoder statistics, OFDM unpacking statistics and throughput
statistics. The statistics for an AP and a CPE may not match exactly because of link quality. MAC
layer statistics are not automatically updated when viewed via telnet.
➧
1. From the Main System Menu, select MAC Layer Statistics and press Enter.
To view the MAC layer statistics
The MAC Layer Statistics screen appears. The screen is view-only.
Ethernet Receive Statistics
Ethernet Receive
Statistics
Total Frames
Received
Frames For Local
Host
Receive Errors
Frames Dropped
84 Libra 5800 Series User Guide
Describes the data received at the Libra Unit from the Ethernet (10/
100 BaseT connection)
Number of Ethernet frames received
Number of Ethernet frames received and destined for the unit
Number of Ethernet frames received with errors
Number of Ethernet frames dropped because the wireless link is
running at capacity

OFDM Decoder Statistics
MAC Layer Statistics
OFDM Decoder
Statistics
Total Superframes
Decoded
Ethernet Frames
For Local
Uncorrected
Superframes
Corrected Bytes
Describes Reed Solomon decoder statistics
Number of superframes decoded by the Reed Solomon decoder
Number of Ethernet frames, destined for the unit, that went through
the Reed Solomon decoder without uncorrectable errors
Number of superframes received by the Reed Solomon decoder that
have uncorrected errors
Number of bytes through the Reed Solomon decoder that have been
corrected
Total Words
Decoded (x1E6)
Number of words received by the Reed Solomon decoder that have
been decoded
OFDM Channel Statistics
RSSI (dBm)
Null Depth (dB)
Received Signal Strength Indicator in dBm
Difference in dB between the lowest signal sub carrier and the
highest signal sub carrier. This value is an indication of the level of
multi-path signals present in the link.
Fade Margin (dB)
Signal-to-noise ratio of the signal; value in dB above the sensitivity
threshold.
Approximated BERs
FEC BER (x1E-9)
BER (x1E-9)
LFEC BER
LBER
Bit error rate after forward error correction, multiplied by 10
Bit error rate before Reed Solomon coding, multiplied by 10
Lifetime FEC BER multiplied by 10-9. Cumulative from the last reboot
Lifetime BER, multiplied by 10-9. Cumulative from the last reboot
Ethernet Transmit Statistics
Ethernet Transmit
Statistics
Total Frames
Transmitted
Frames From Local
Host
Frames Dropped
Describes the data sent from the Libra UnitLibra Unit to the Ethernet
Number of frames sent to the wire from the Libra UnitLibra Unit
Number of Ethernet frames transmitted to the 10/100 Base-T
connection which originated from the unit
Number of frames not transmitted because of an error
-9
-9
June 2003 Rev 0 85

Configuration
OFDM Encoder Statistics
OFDM Encoder
Statistics
Total Superframes
Encoded
Ethernet Frames
From Local
Describes Reed Solomon encoder statistics
Number of superframes encoded by the Reed Solomon encoder
Number of Ethernet frames sent to the Reed Solomon encoder that
originated from the unit’s local stack
OFDM Unpacking Statistics
OFDM Unpacking
Statistics
Superframe Header
Errors
Ethernet Header
Errors
Synch Errors
Late Poll
Responses
Describes statistics on synchronization of OFDM superframes
For Wi-LAN use only
For Wi-LAN use only
For Wi-LAN use only
A Poll was sent to a CPE, but either there was no response or the
response was late.
Throughput Statistics
Average Throughput
Total throughput in bits per second (bps) with no overhead from the
Libra Unit; this measurement is made over a ten-second average
Maximum Throughput
Highest throughput in bps since the last statistics reset, with no
overhead
Using the Command Line
Libra 5800 units have a command line interface you can use to perform basic tasks while logged into
the configuration menus.
➧
1. Log onto a Libra 5800 and press Esc until the wilan> command line prompt appears.
2. Type the command after the prompt and press Enter.
3. Press Esc to return to the main menu.
To use the command line interface
86 Libra 5800 Series User Guide

Using the Command Line
➧
To display a list of available commands
Type help to display a list of commands.
wilan> help
Command Summary:
menu cls dir del ping linktest
logout exit quit
display help for a specific command:
help <name>
wilan>
List of Commands
Command Explanation Example
help Shows the following command summary list:
menu cls dir del ping linktest logout exit quit
menu Returns to the configuration menus wilan>menu
wilan>help menu
cls Clears the terminal screen wilan>cls
dir Shows a file directory wilan>dir
del <name> Deletes a file called <name> wilan>del sample.txt
ping <name> Pings a remote IP address called <name> wilan>ping 198.168.200.5
linktest Runs the Linktest utility wilan>linktest 2
logout Logs out of the command line interface
or terminates a remote telnet session
peek Displays the contents of a block of memory wilan>peek 9000
rebootnewest Reboot the latest master image downloaded
onto the unit (in regards to time, not image
version)
rebootcurr Reboot the current master image running on the
unit
crc Displays CRC values for Wi-LAN image files. If
the file is a master image the CRC for each
component sub-section is displayed.
exit Leaves the command line interface or
terminates a remote telnet session
wilan>logout
wilan>rebootnewest
wilan>rebootcurr
wilan>crc
wilan>exit
quit Logs out of the command line interface or
terminates a remote telnet session
wilan>quit
June 2003 Rev 0 87

Configuration
The show command displays some additional information not available from the menu interface.
The following information is available:
wilan>help show Displays a list of the show commands
wilan>show arp Displays a list of the ARP cache
wilan>show exception Displays post-mortem exception information
wilan>show images Displays the system images files stored in the flash file system
wilan>show memory Displays the system memory map
wilan>show time Displays the current system time, measured in seconds, from the last reboot
wilan>show versions Displays the processor type, part and mask numbers
wilan>show wdog Displays the number of times the watchdog timer has reset the unit since the
system image was installed
88 Libra 5800 Series User Guide

Field Installation
Introduction
The information in this chapter is intended for qualified installers only.
WARNING
!
All antennas and equipment must be installed by a knowledgeable and
professional installer.
NOTE: WI-LAN RECOMMENDS THE USE OF LIGHTNING SUPRESSORS IN
ALL INSTALLATION.
Before you begin to install equipment in the field, you should develop a network plan, prepare the
customer site, and configure the equipment. The network plan describes the proposed system,
including a link budget, detailed list of all required hardware, Libra units (RD & ER for P-P links;
LCPE, CPE and Access Point for P-MP), antenna locations, cable routing, equipment configuration
settings, and other network requirements. (Wi-LAN offers Network Planning and Site Preparation
support. For more information on services and fees contact your Sales Representative or visit http://
www.wi-lan.com). Network planning should include visits to proposed sites to verify the feasibility of
the network plan and work out the details. Installers will use the network plan document to guide
them through final site preparation, installation, configuration and field testing of each unit. You can
see that a large amount of planning and preparation work is required before equipment is ready to
install. The better the preparation work, the more problem-free the field installation will be.
June 2003 Rev 0 89

Field Installation
Installation Process
Network
Plan
Site
Preparation
Configuration
Field
Installation
Testi ng
Libra 5800 field installation
This section discusses how to install, configure and test a Libra 5800 in the field.
Before you can install Libra equipment in the field
• All units should be configured as described in Configuration, page 27
• Site preparation work must be complete
• Ensure all necessary tools and equipment are available
Site preparation
Site preparation involves checking actual customer site conditions and ensuring that the site is ready
for Libra installation. Each site is unique, however the following guidelines are provided.
1. Obtain a customer site plan or make a site plan. This document should describe where to place
the Libra unit, what kind of equipment to use, and the required configuration settings of the unit.
2. Cables should always be connected without exceeding their recommended bend radius.
3. Ensure that there is enough room for ventilation.
4. Confirm that AC power and Ethernet access are available.
5. Inspect the recommended Libra location to determine the following.
• the mounting structure is suitable
• LOS and Fresnel Zone clearances can be met. Because of OFDM’s superior Non Line of Sight
performance these requirements will not be as stringent as for other systems.
• location of the Libra is acceptable
6. Check cable routes and entry and exit points to ensure that they are practical.
90 Libra 5800 Series User Guide

Libra 5800 field installation
Tools and equipment
You will require the following tools and equipment
Standard tool kit Test equipment, PDA with serial cable
and power
Drill and bits Libra Unit
Weatherproofing materials Libra mounting hardware
Ladder Cables: Outdoor CAT-5 Cable, AC
power cable.
Compass or GPS Customer acceptance form and
Installation record, if required
Binoculars
Libra 5800 Package Checklist
The CPE shipping package should contains the following items:
• 1x Libra 5800 Unit (with Integrated Antenna (CPE, RD units) or without (AP, LCPE, ER))
• 1x Power Cord
• 1x Power Inserter
• 1x Libra 5800 User Manual (CD ROM)
• 1x Mounting Kit
• 1x Mounting base
• 1x Wall Mount Clamp
•1x Clamp
•1x Arm
• 4x Washer Flat M5
• 4x Washer Spring M5
•4x Nut M5
• 4x Screw Hex Cap M5x0.8 16mm
• 6 x Washer Flat M8
• 4x Washer Spring M8
•2x Nut M8
• 4x Screw Hex Cap M8x40 (for 1 3/4" dia pole)
• 4x Screw Hex Cap M8x70 (for greater than 1 3/4" dia pole)
• 1x Weather Proof Kit
•1x O Ring
• 1x Insert
• 1x Coupling Nut
June 2003 Rev 0 91

Field Installation
• 1x Shell
• 1x RJ 45 Connector
Do not "hot plug" the power inserter into the Libra to power up the unit—the
Libra CAT-5/Power connector should first be plugged into the unit at the DIN
connector, and into the "TO RADIO" jack of the power inserter. Next, the
power supply cord should be plugged into the AC outlet to power up the unit.
Do NOT plug the LAN RJ45 cable into the power inserter marked "TO RADIO",
as this port has power and may damage external equipment.
! CAUTION
WARNING
!
92 Libra 5800 Series User Guide

Libra 5800 field installation
Libra 5800 installation procedure
Installing the CPE requires assembling the mounting hardware, finding a suitable mounting location,
configuration, and then a link test to check the RF link integrity.
Libra 5800 assembly diagram.
➧
1. Mount the clamps without the Libra unit to the pole or wall as required. The versatile mounting
2. Connect the four pointed star bracket to the unit. Assemble the mounting kit. Ensure that this
NOTE: IF YOU NEED HORIZONTAL OR VERTICAL POLARIZATION. MOUNT THE LIBRA
3. For the AP, ER and LCPE mount the external antenna. Connect the antenna to the unit.
4. Point the antenna (Integrated or external) towards the desired location.
June 2003 Rev 0 93
Mounting the Libra Unit
hardware can be used with large diameter and small diameter poles or as a wall mount.
Additionally an optional knuckle is provided that allows for both pan and tilt functionality while the
mounting clamp is firmly fixed to the pole or wall. See Hardware, page 20 for detailed diagrams of
the mounting hardware.
connection is in the right direction so that the antenna polarization is as specified in the network
plan for the CPE and RD units and that the connectors are on the lower side of the unit when
mounted to the clamp.
ACCORDING TO THE POLARIZATION STICKER LOCATED ON THE BACK OF THE
ANTENNA.

Field Installation
5. For the CPE or RD, if Up or Down tilt is required, adjust the unit accordingly such that the face of
the antenna is pointed as directly to the Access Point or the other unit in the P-P link as possible.
6. Lightly tighten the bracket bolts to hold the unit in place.
➧
1. Insert the end of the CAT-5/Power cable into the provided weatherproofing attachment.
2. Connect the CAT-5 / Power cable to the connector located on the back panel of the Libra Unit
3. Plug the RJ-45 end of the Libra CAT-5 cable into the power inserter in the "TO RADIO" jack.
4. Connect the "TO LAN" side of the power inserter to the PC or network.
5. Locate the AC power cord for the power inserter and plug AC power cord in, and to the AC wall
➧
1. Connect a laptop or PDA to the RS-232 port on the Libra. (See Configuration, page 27)
2. Configure unit to the proper center frequencies, etc if you have not done that previously (See
3. Run a "Link Test" for a minute or two (See Appendix D: Linktest and Link Statistics, page 119) to
Connecting the Libra
and screw in the weatherproofing attachment.
socket.
Configuration & Link Test
Quick-Start Menu, page 33 or PDA Setup Menu, page 39).
verify RF link performance.
From the MAC Layer statistics screen (see MAC Layer Statistics, page 84):
• The Late Poll Response number should not change
• The fade margin should be adequate for the link conditions and availability requirements.
• The uncorrected codewords and superframes figures should be zero.
From the Linktest result screen:
• LBER and BER should both be zero
• LFade Margin and Fade margin should be similar to the one calculated from link availability
requirements
4. If the link results are satisfactory, proceed to Step 6 below.
If the link is unsatisfactory first turn the antenna in different directions to benefit from beneficial
multi-paths. If still unsuccessful look for another antenna location with better line-of-sight until you
find a location that is satisfactory.
5. Refer to the troubleshooting guidelines, Troubleshooting, page 97, if problems persist.
6. Adjust antenna position to achieve the best Link Test performance.
7. When Link test performance is satisfactory, tighten mounting hardware.
➧
1. Call up the Network Operations Center (NOC).
2. “Ping” the NOC from the CPE.
Test network connectivity
The next step is to verify that a computer attached to the Libra can communicate with a computer
on the other side of the wireless link.
94 Libra 5800 Series User Guide

Libra 5800 field installation
3. Have the NOC “ping” the CPE from the NOC. A successful ping test means that the network
“sees” the CPE on the network.
4. Connect the CPE Ethernet Port to the customer LAN or PC.
5. Ping from the Customer LAN or PC to the NOC.
6. Use ftp to send some larger test files from the NOC to the PC or other IP device on the LAN.
7. Measure file transfer rates in both directions.
➧
Finish up the installation by doing the following.
1. Secure all the cables and weatherproof outside cable connection points.
2. Clean up all boxes, cables and other materials.
3. Record installation information as required by the service provider such as
4. Demonstrate to the customers that the installation works and that they can contact sites on the
5. Have the customers sign a document to indicate their acceptance of the installation.
Secure the installation
• Link Distance
• Site Locations (GPS coordinates)
• Unit configuration
• Link quality statistics
• Antenna cable configuration
• Unit model, Unit serial number, MAC address, IP address and IP submasks
• Unit password
• Antenna azimuth.
far side of the wireless link and upload and download data.
June 2003 Rev 0 95

Field Installation
96 Libra 5800 Series User Guide

Troubleshooting
Preventative maintenance
Administering and maintaining your system properly can prevent many problems and alert you to
minor problems before they become serious. Some recommendations follow.
• Measure and document system performance at the time of the original installation.
• Change menu passwords so that only authorized people can reconfigure the system. See
Setting Menu Passwords, page 53.
• Maintain the integrity of the system design when adding to or changing a system.
The introduction of new elements to a system can cause problems unless you revise the
network plan to take into account the changes. For example, improper installation of a colocated antenna can add unwanted system interference.
• Keep records of all changes. Especially document the addition of units, hardware and
software changes, and changes to configuration settings. Configuration errors often cause
other problems. Current records can be compared with original installation records and
function as benchmarks to help in troubleshooting.
• Keep a log of past and present problems and solutions. Store the log on-site for easy
reference, if possible. The log identifies common failure points and fixes.
• Before contacting Wi-LAN’s Technical Assistance Center, document the symptoms of the
fault and the steps taken to diagnose and fix the problem. Record the current configuration of
the system.
• Perform preventive maintenance at a regular interval, for example every six months. See
Appendix D: Linktest and Link Statistics, page 119 for information.
• Perform link monitor tests to verify the system after periods of extreme weather, and inspect
towers, antennas, ODUs, cables, and connectors for damage.
• Monitor system performance regularly. Environmental change as well as normal wear and
tear on components can affect system performance.
• In some cases a bench test is a useful tool in diagnosing problems. See Appendix E: Bench
Configuration Testing, page 123 for information on how to perform a bench test.
June 2003 Rev 0 97

Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting areas
There are five areas to keep in mind when troubleshooting:
1. Network integrity: The continued performance and reliability of a network depend upon
maintaining the integrity of the network. If you change a network’s design, you will affect its
operation. Be aware of recent changes to your network.
2. Quality of RF links: Data communication depends first on good RF links. If you establish and
maintain high-quality RF links, then you can be sure the links will carry high-speed data. If the
quality of the RF links degrades for some reason, the quality of the data and the associated
performance will also degrade.
3. Radio Hardware: This consists of three parts: Main unit, antenna, and mounting hardware..
• To verify the radio performance, you can run diagnostic tests, such as RSSI and link monitor
test.
4. Correct Unit Configuration: Units must be configured properly, according to the network plan.
Configuration errors can cause an inability to communicate or poor performance. The addition of
units or other changes to your system may require you to change configuration settings.
5. Embedded Software: Operate with a proven software image. Download new software if you
suspect that a unit’s software is corrupted. Software images are available from the Wi-LAN
website: http://www.wi-lan.com.
Troubleshooting chart
The following chart provides answers to some of the more common problems that can occur.
Indication Possible Cause Corrective Action
High BER Signal strength is too
low
Signal strength is too
high
Interference Change center frequency
Radio
Performance(Tx/Rx)
Perform an RSSI test to determine fade margin
Check for RF absorbent obstacles in the antenna path
Search for indirect RF paths between antennas (i.e.
ones that use beneficial reflections or multipaths)
Check and replace cables
Reposition IODU or if possible remove obstruction
Adjust antennas
Increase distance between units to add attenuation
Adjust Tx Power level
Increase RF power
Change polarization of antennas
Increase separation or change location of antenna
Increase separation between co-located antennas
Contact Wi-LAN technical support)
No Ethernet
connection
98 Libra 5800 Series User Guide
Bad CAT-5 cable Visually inspect cable
Change cable

Indication Possible Cause Corrective Action
Bad connectors Visually inspect connectors
Change cable/connectors
Temperature Determine if ambient operating temperature is too high
or low
Change ambient temperature to specified range.
Troubleshooting areas
Low signal
strength/fade
margin
High packet
loss
Bad radio Bench test system
Change IDU or IODU
Poor antenna
Use RF diagnostics to realign antenna
alignment
Bad cable Visually inspect cables/connectors
Sweep cable
Change cable/connectors
Incorrect radio
configuration
No Fresnel zone
clearance
Bench test the radio to confirm configuration
Reconfigure radio
Increase antenna height to obtain clearance
Relocate antenna
Remove obstacles to LOS
Power supply
problems
Try a different AC circuit
Measure the power at the AC outlet
Measure the output from the power supply unit
Replace Power Supply
Signal strength too
low
Perform RSSI test to determine fade margin
Check for obstacles in RF path
Check for interference
Point antenna in different directions to take advantage
of beneficial multipaths
Reposition IODU to establish better LOS
Replace IODU
Interference Change center frequency
Increase RF power
Change polarization of antennas
Get separation or change physical location of antenna
Temperature Determine if ambient operating temperature is too high
or low
Increase or reduce ambient temperature
No
communicatio
Configuration
problems
Check the following configuration settings:
n between
units
June 2003 Rev 0 99

Troubleshooting
Indication Possible Cause Corrective Action
Station ID–Each unit must have a unique RF Station ID
Access code–Only units with the same access code
can communicate
Scrambling code–Base station and remote units must
use the same scrambling codes to decode messages
Acquisition code–All units must have the same
acquisition code to communicate
Center frequency–Units must have the same center
frequency to communicate
IP address/subnet mask–Incorrectly configured IP
addresses result in units being unable to communicate.
Check that IP addresses are unique for each unit within
a subnet and that the correct subnet mask is being
used.
Poor link
performance
SNMP can’t
be activated
IF cable failure or
damage
Visually inspect cables for damage
Sweep cables and replace if necessary
Distance Check the maximum remote distance configuration
setting
Excessive Bit errors
and processing errors
Multipath interference–Align or relocate antennas or
radio.
Signal absorption Check LOS for obstacles such as trees
Change alignement of antenna to take advantage of
beneficial multipath signals
Move antenna to better location or remove obstacle if
possible
Center frequency Set units from different systems in the same
geographical area to different center frequencies–
overlapping wavelengths from other systems will
degrade performance
Overpowering colocated unit
Output power from one unit can overpower another, colocated, radio, even if units operate on different
channels
IP filtering configured
Change IP filtering to enable SNMP
incorrectly for SNMP
New
configuration
Incorrectly upgraded
software
Reload the software image using ftp
will not take
100 Libra 5800 Series User Guide
 Loading...
Loading...