
AWE 120-58
Advanced Wireless Ethernet Bridge
Installation &
Configuration Guide
APR 2001 Rev 3


Contents
Important Information ....................................................................vii
Notices ................................................................................................ix
Copyright Notice ..............................................................................................................................ix
Regulatory Notice .............................................................................................................................ix
Other Notices .....................................................................................................................................x
Warranty & Repair .............................................................................................................................x
Customer Support Contacts ...........................................................................................................x
Distributor Technical Support .......................................................................................................xi
Wi-LAN Product Information ........................................................................................................xi
Description ..........................................................................................1
Features ................................................................................................................................................1
About Spread Spectrum ....................................................................................................................1
About AWE Units 2
Some System Applications ................................................................................................................3
Making a Simple Wireless Bridge 3
Creating a Simple Wireless Network 3
Creating a Network with Cells 5
Using a Repeater Base 6
Building a WAN 6
Hardware Description ......................................................................................................................7
Shipping Package Contents 7
AWE 120-58 Unit 8
AWE 120–58 Specifications .......................................................................................................... 10
Installation .........................................................................................13
Overview ........................................................................................................................................... 13
Obtain Network Plan ..................................................................................................................... 14
APR 2001 Rev 03
i

Assemble Units .................................................................................................................................14
Checking the Shipping Contents 14
Assembling AWE Units 14
Checking the Power 16
Pre-Configure Units .........................................................................................................................16
Configuring a Base Station 16
Configuring a Remote Unit 19
Bench Test Units ..............................................................................................................................21
Establishing a Basic RF Link 21
Testing the Link and Adjusting Tx Power 23
Performing Simple Network Tests 25
Install Units ........................................................................................................................................29
Point-to-Multipoint Installation 30
Co-Location Installation 30
Test Network ...................................................................................................................................30
Adding to a Network ......................................................................................................................30
Preventative Maintenance
and Monitoring ..................................................................................................................................31
Configuration .................................................................................... 33
Overview ............................................................................................................................................33
Main Menu 33
Accessing the Main Menu ...............................................................................................................34
Accessing the Main Menu with HyperTerminal® 34
Accessing Units via telnet 35
Setting VT100 Arrows 35
Configuring with the Main Menu ..................................................................................................36
Unit Identification .............................................................................................................................37
Viewing Unit Identification 37
Assigning Unit Identification Information 38
Hardware/Software Revision .........................................................................................................39
Viewing System Revision Information 39
System Software ROM Images ......................................................................................................40
Viewing System Software ROM Images 40
System Current Status ....................................................................................................................41
Viewing System Current Status 41
Network Configuration ..................................................................................................................42
Viewing Internet IP Addresses and Subnet Mask 42
Setting the Internet IP Address 43
Setting the IP Subnet Mask 43
Setting the Default Gateway IP Address (future) 44
Setting the SNMP NMS Trap IP Address (future) 44
Setting the MAC Filter Entry Age Time Minutes 44
ii
AWE 120-58 Installation & Configuration Guide

IP Filter Configuration .................................................................................................................... 45
Viewing IP Filter Configuration 45
Enabling IP Packet Filtering 47
Enabling IP Address Filtering 47
Setting IP Address Filter Range 48
Setting the IP Filter Base Address 48
RF Station Configuration ............................................................................................................... 49
Viewing Current RF Station Configuration 49
Setting the Operating Mode 51
General Equipment Setup for Performing RF Tests 52
Setting Test Mode Timer Minutes 53
Performing Link Monitor Test (Normal Mode) 54
Performing Transmit and Receive Tests 57
Performing the RSSI Test 59
Setting the RF Transmit Status 60
Setting the Link Monitor Period 61
Setting Maximum Remote Distance (Base Station Only) 62
Setting Link Monitor Remote Station Rank 63
Adjusting Throttling (Remote Station Only) 64
Radio Module Configuration ......................................................................................................... 65
Viewing the Radio Module Configuration 65
Setting Config Test Minutes 67
Setting the Station Type 68
Setting the Station Rank 69
Setting the Center Frequency 70
Setting Security Passwords 73
Setting the Scrambling Code 74
Setting the Acquisition Code 75
Adjusting the Tx Power Level 76
Setting a Base to Repeater Mode (Base Station Only) 77
Setting System Symmetry Type (Base Station Only) 79
Setting Dynamic Polling Level (Base Station Only) 80
Setting Remote Unit RF Group 81
Rebooting and Saving RF Module Configurations 84
RF/Ethernet Statistics ...................................................................................................................... 86
Viewing RF/Ethernet Statistics 86
System Security ................................................................................................................................ 89
Viewing System Security 89
Assigning Community Names 91
Setting Menu Passwords 92
Allowing Remote Access and Configuration 94
Setting the Auto Logout Minutes 95
System Commands .......................................................................................................................... 96
Viewing System Command Menu 96
Setting Default System Image 97
Setting the Reboot System Image 98
Rebooting the Current Image 98
Restoring Factory Configurations 99
Resetting Radio and Ethernet Statistics 100
Link Monitor Display .................................................................................................................... 101
APR 2001 Rev 03
iii

Viewing Link Monitor Statistics 101
Logout .............................................................................................................................................. 102
Logging Out 102
Setting Operating Mode with the Mode Button .................................................................... 102
Selecting RF Tests with the Mode Button 103
Command Line Interface ............................................................................................................. 104
Troubleshooting ............................................................................. 105
Administrative Best Practices ..................................................................................................... 105
Troubleshooting Areas ................................................................................................................ 106
Troubleshooting Chart 107
Appendix A: Planning Your Wireless Link ..................................111
Planning the Physical Layout ....................................................................................................... 111
Determine the Number of Remotes 111
Ensure LOS and Determine Coverage Area 111
Measure the Distance Between Units 112
Determine Shelter, Power and Environmental Requirements 112
Determining Antenna
and Cable Requirements ............................................................................................................. 112
Determining Unit Configuration Settings ................................................................................ 113
Calculating a Link Budget ............................................................................................................. 113
Link Budget Example .................................................................................................................... 117
Antenna Basics ............................................................................................................................... 118
Antenna Parameters 118
Implementation Considerations 119
Wi-LAN Approved Antennas 120
Antenna Installation Factors 121
Installing Antennas 122
Fine-tuning Antennas 123
Co-locating Units 123
Appendix B: Using HyperTerminal .............................................. 125
Starting HyperTerminal ............................................................................................................... 125
Determining the Communications Port .................................................................................. 126
Appendix C: Configuring a Simple Data Network ..................... 127
iv
Checking Network Adaptor Installation .................................................................................. 127
Configuring the Network ............................................................................................................ 128
Enabling Sharing on the Hard Disk Drive ................................................................................ 131
AWE 120-58 Installation & Configuration Guide

Appendix D: SNMP ........................................................................133
About SNMP MIB .......................................................................................................................... 133
Wi-LAN Object Identifier Nodes .............................................................................................. 134
Using SNMP .................................................................................................................................... 134
Using Object Identifier Nodes ................................................................................................... 135
Appendix E: Technical Reference Information ...........................149
Front Panel LEDs ........................................................................................................................... 149
DC Power Plug Pinout ................................................................................................................. 150
Appendix F: Menu Map ..................................................................151
Appendix G: Upgrading Software .................................................153
Obtaining New Software Images ............................................................................................... 153
Downloading Image Software ..................................................................................................... 153
Activating New Software Images ............................................................................................... 155
Removing Old Software Images ................................................................................................. 155
Glossary ...........................................................................................157
Index ................................................................................................167
APR 2001 Rev 03
v

vi
AWE 120-58 Installation & Configuration Guide

Important Information
Please be aware of the following information about the AWE 120-58.
• Tx power can be adjusted (attenuated) from 0 dB to –31 dB through the configuration menu.
• Center frequency is typed into a data field (rather than selected from a list). Available center frequencies range from 5.7410 GHz to 5.8338 GHz in 400 kHz steps.
• Indoor antennas are not supplied with the shipping contents. To test and configure units you need
to purchase a Bench Test Kit (9000-0034). For bench testing, antennas must be separated by at
least 2 meters.
WARNING
Never operate a unit without an antenna, dummy load, or terminator
connected to the antenna port.
Operating a unit without an antenna, dummy load, or terminator connected
to the antenna port can permanently damage a unit.
Important
All antennas must be installed by a knowedgeable and professional installer.
Antennas must be selected from a list of Wi-LAN approved antennas.
See Wi-LAN Approved Antennas , page 120 for list.
APR 2001 Rev 03
vii

Important Information
viii
AWE 120-58 Installation & Configuration Guide

Notices
Copyright Notice
Copyright© 2001 Wi-LAN, Inc.
All rights reserved.
This guide and the application and hardware described herein are furnished under license and are subject to a
confidentiality agreement. The software and hardware can be used only in accordance with the terms and
conditions of this agreement.
No part of this guide may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means—electronic,
mechanical, or otherwise, including photocopying and recording—without the express written permission of
Wi-LAN, Inc.
While every effort has been made to ensure that the information contained in this guide is correct, Wi-LAN,
Inc. does not warrant the information is free of errors or omissions.
Information contained in this guide is subject to change without notice.
Regulatory Notice
The AWE 120-58 product presented in this guide complies with the following regulations and/or regulatory
bodies.
• RSS-210 of Industry Canada (www.ic.gov.ca)
• FCC Part 15 (www.fcc.gov)
Operation is subject to the following two conditions.
• This device may not cause interference
• This device must accept any interference, including interference that may cause undesired operation
of the device
This equipment generates, uses, and radiates radio frequency and, if not installed and used in accordance with
this guide, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that
interference will not occur in a particular installation.
APR 2001 Rev 03
ix

Notices
If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined
by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or
more of the following methods.
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna
• Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver
• Connect equipment to an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is connected
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help
• Selecting and testing different channels, if employing 5.8 GHz equipment
As the AWE 120-58 is used on a license-exempt, non-frequency coordinated, unprotected spectrum
allocation, and thus can be subject to random unidentified interference, applications must not be those of a
primary control where a lack of intercommunication could cause danger to property, process, or person. An
alternative fail-safe should be designed into any system to ensure safe operation or shut down, should
communication be lost for any reason.
Other Notices
• Changes or modifications to the equipment not expressly approved by Wi-LAN, Inc., could void the
user’s authority to operate the equipment.
• Appropriately shielded remote I/O serial cable with the metal connector shell and cable shield
properly connected to chassis ground shall be used to reduce the radio frequency interference.
• Radio frequency exposure limits may be exceeded at distances closer than 23 centimeters from the
antenna of this device.
• All antenna installation work shall be carried out by a knowledgeable and professional installer.
• Use only a power adapter approved by Wi-LAN.
Warranty & Repair
Please contact the party from whom you purchased the product for warranty and repair information.
Wi-LAN provides no direct warranty to end users of this product.
Customer Support Contacts
Users of Wi-LAN equipment who require technical assistance must contact their reseller or distributor. For
information on distributors in your area, please visit www.wi-lan.com/channel.
x
AWE 120-58 Installation & Configuration Guide
Distributor Technical Support
Distributor Technical Support
Distributors may contact Wi-LAN’s Technical Assistance Center (TAC) for technical support on Wi-LAN
products. When requesting support, please have the following information available:
• Description of the problem
• Configuration of the system, including equipment models, versions and serial numbers.
• Antenna type and transmission cable lengths
• Site information, including possible RF path problems (trees, buildings, other RF equipment in the
area)
• Configuration of units (base, remote, channels used, etc.) and Link Monitor statistics
Contact Wi-LAN’s Technical Assistance Center at the numbers listed below.
Canada and USA Call toll free: 1-866-702-3375
Business hours: 7:30 a.m. to 4:30 p.m. Mountain Standard Time (GMT-7:00)
International Call: 1-403-204-2767
Business hours: 7:30 a.m. to 4:30 p.m. Mountain Standard Time (GMT-7:00)
All locations Send an e-mail message to:
techsupport@wi-lan.com
Wi-LAN Product Information
To obtain information regarding Wi-LAN products, contact the Wi-LAN distributor in your region, call
1-800-258-6876 to speak with a Wi-LAN sales representative or visit our web site at www.wi-lan.com.
APR 2001 Rev 03
xi

Notices
xii
AWE 120-58 Installation & Configuration Guide

Description
Features
The AWE 120-58 advanced wireless Ethernet bridge provides high-speed, wireless connectivity at a fraction
of the cost of wired solutions. It operates over the license-exempt 5.7250 – 5.8500 GHz ISM radio band and
has a maximum raw wireless data rate of 12.0 Mbps.
• Provides wireless connectivity at speeds up to eight times faster than regular T1 lines, making the AWE 12058 ideal for providing high-speed Internet access or for wirelessly extending existing communications
infrastructures.
• Supports point-to-point, point-to-multipoint, and multipoint-to-multipoint networks (if all remotes have
clear line of sight to the base station). Contentionless polling ensures efficient access to remote data
networks.
• Is self-contained and easy to use. Simply connect a AWE 120-58 to each LAN segment, and the unit
automatically learns where nodes are located on the network and performs dynamic packet filtering to
ensure the local LAN traffic does not overload the wireless connection.
• Uses Wi-LAN's patented Multi-Code Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (MC-DSSS) technology, which
makes the unit spectrally efficient and resistant to interference. MC-DSSS technology increases data
throughput by as much as ten times compared to traditional spread spectrum technology.
• Other features include adjustable Tx power level, IP address filtering, throughput throttling and monitoring,
high security and reliability, and a flash-code upgrade path. SNMP, telnet and RS-232 management enable
users to manage, configure and monitor their wireless network with ease.
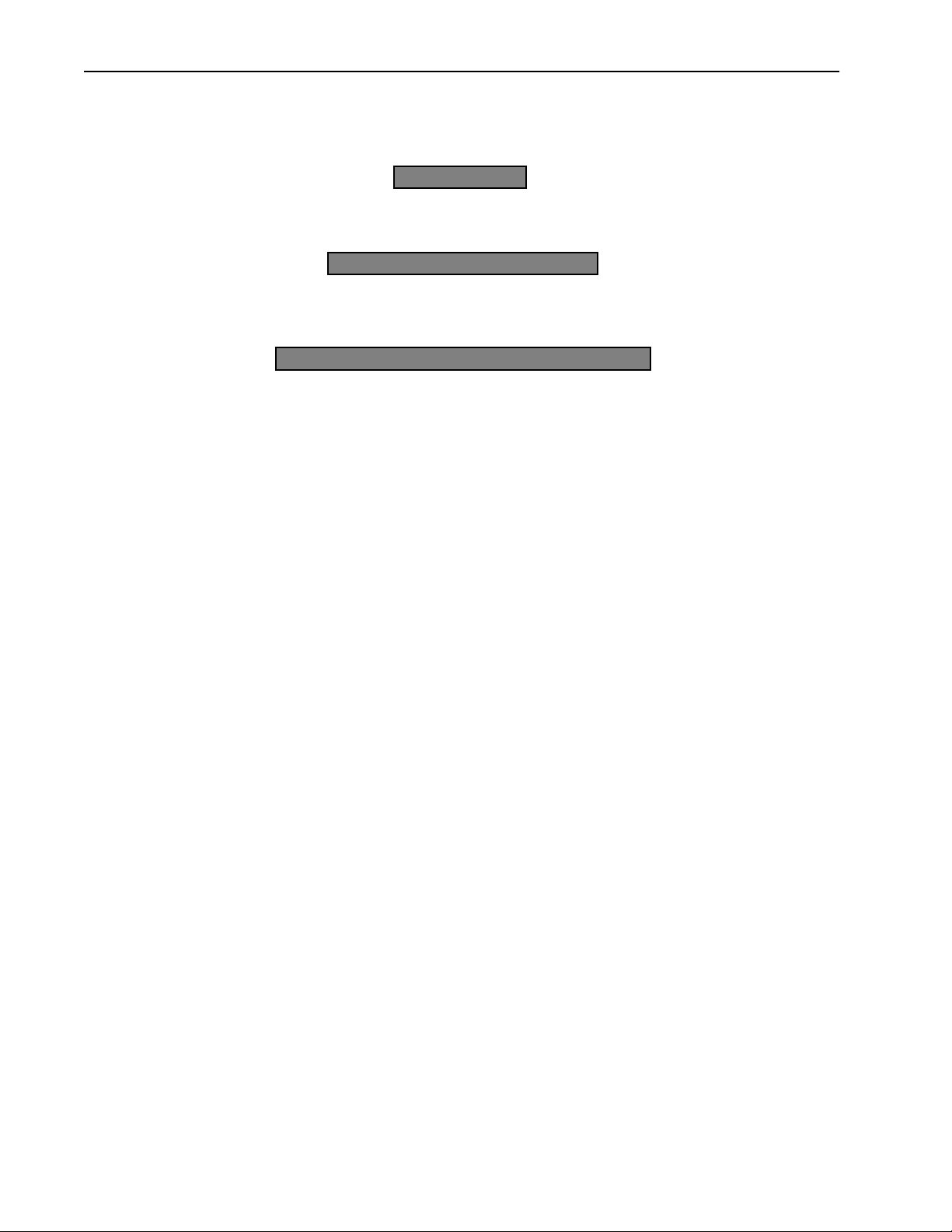
About Spread Spectrum
Three license-free frequency bands (called the ISM bands) are allocated in Canada and the United States to a
radio technique known as spread spectrum communication. The bands are located at 900MHz, 2.4 GHz, and
5.8 GHz (shown in the following illustration). The AWE 120-58 operates with spread spectrum technology
over the 5.7250 – 5.850 GHz band.
APR 2001 Rev 03
1
Description
License-Free ISM Bands
26 MHz Wide
900 MHz
902 MHz 928 MHz
83.5 MHz Wide
2.4 GHz
2.4 GHz 2.4835 GHz
125 MHz Wide
5.8 GHz
5.725 GHz 5.85 GHz
Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS) technology converts a data stream into packets and spreads the
packets across a broad portion of the RF band. The particular spread pattern depends upon a code. With
multi-code DSSS (MC-DSSS), multiple codes and spread patterns are employed. A spread spectrum receiver
reconstructs the signal and interprets the data.
Some advantages of DSSS are as follows:
• Fast throughput: A wide bandwidth means fast data throughput.
• Resistant to interference: DSSS overcomes medium levels of interference and multipath problems.
• Security: There must be a decoder at the receiving end to recover data (an AWE can only talk to
another AWE). Data is transmitted at irregular time intervals. Upon request, Wi-LAN can assign a
customer a data packet security code so that a customer can only receive transmissions from
another AWE with the same code.
• Low probability of detection: Due to a low amplitude signal and wide bandwidth.
• No license fee: A license fee is not required if used in the specified radio bands and the transmitter
power is limited.
About AWE Units
AWE 120-58 units can function as base stations, remote units or repeater bases.
Base Station: At least one unit in your wireless network must be configured as a base station. A base station
acts as the central control unit of the wireless network. The base station polls all remote units and controls
how traffic is routed to and from remotes. The base usually connects to a major access point of the wired
network. The antenna of the base station must be capable of transmitting and receiving radio signals to and
from all the remote units in a system. If remotes are spread over a large area, an omni-directional antenna is
usually required. See Configuring a Base Station , page 16 for information about setting up a base station.
2
AWE 120-58 Installation & Configuration Guide
Some System Applications
Remote Units: Remote units receive and transmit wireless data to the base station. You need at least one
remote unit for each wireless link. Remotes can limit the amount of data passed by the remote (a function
called throttling), and they can filter data packets based on their IP address. Because remote units
communicate only with the base station, their antennas can be more directional and have higher gains than
base antennas. See Configuring a Remote Unit , page 19 for information about setting up a remote unit.
Repeater Base: A base station can be configured as a repeater base. A repeater is needed when remote
units cannot communicate directly with each other, but direct transfers of data between them are necessary
(as in a true WAN). When configured as a repeater, the base station passes data packets between remote
stations based on the remote group status and a list of MAC (Media Access Control) addresses that the base
station automatically builds. A single repeater uses a method called "store and forward" to receive data from
the originating remote and to pass data to the destination remote. See Setting a Base to Repeater Mode (Base
Station Only) , page 77 for more information. Two units can also be employed as a dual unit repeater (back-to-
back) configuration that maximizes data throughput.
Some System Applications
You can build a wireless network from AWE units and various other components such as cables and antennas.
The following section shows some simple examples of AWE applications.
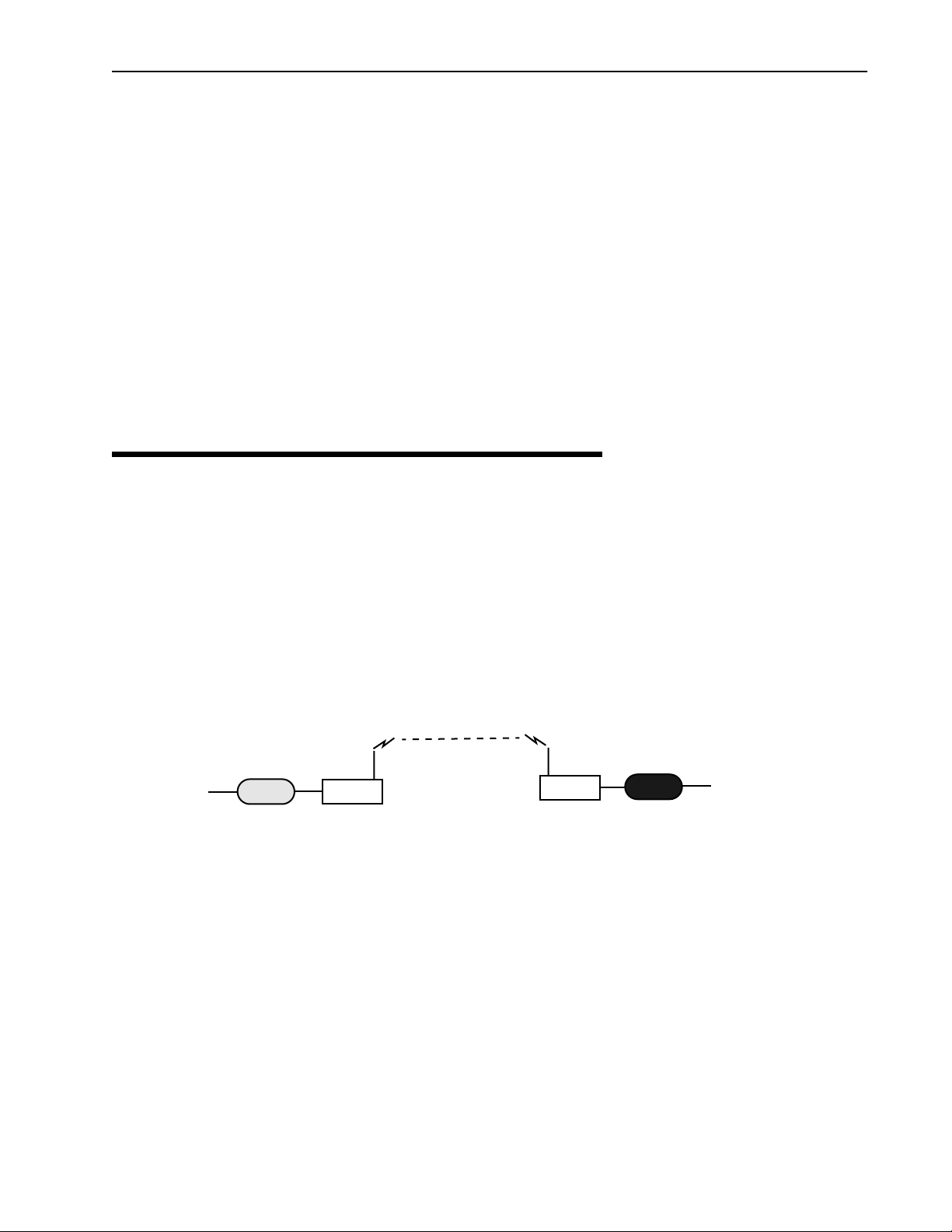
Making a Simple Wireless Bridge
The simplest example of using a AWE 120-58 is a point-to-point wireless bridge that connects two wired
network segments or LANs. Two AWE units are required: a base station and a remote unit.
Point-to-Point Wireless Bridge
Wireless Link
Wired Network
Switch
Hub
Firewall
RemoteRouter
Base
Main Wired Network
Router
Hub
Switch
Firewall
Creating a Simple Wireless Network
You can create a point-to-multipoint wireless network by adding several remote units to a base station. A
base station can support up to 1000 remotes, however, Wi-LAN recommends no more than 225 remotes per
base station to esnure high levels of data throughput. See Determine the Number of Remotes, page 111 for
more information.
APR 2001 Rev 03
3

Description
Point-to-Multipoint Wireless Network
Wired Network
Switch
Hub
Firewall
Wired Network
Switch
Hub
Firewall
Wired Network
RemoteRouter
Wireless Links
Main Wired Network
RemoteRouter
Base
Router
Hub
Switch
Firewall
Base station polls
Remote Units
Hub
Switch
Firewall
RemoteRouter
Direct remote-to-remote communication can occur if a direct RF link can be established between remotes,
and if remotes are in the same RF group.
Remote-to-Remote Communication
Remote
Wireless Links
Main Wired Network
Remote
Base
Remotes must be in the same
RF group to communicate
directly
Remote
4 AWE 120-58 Installation & Configuration Guide
Some System Applications
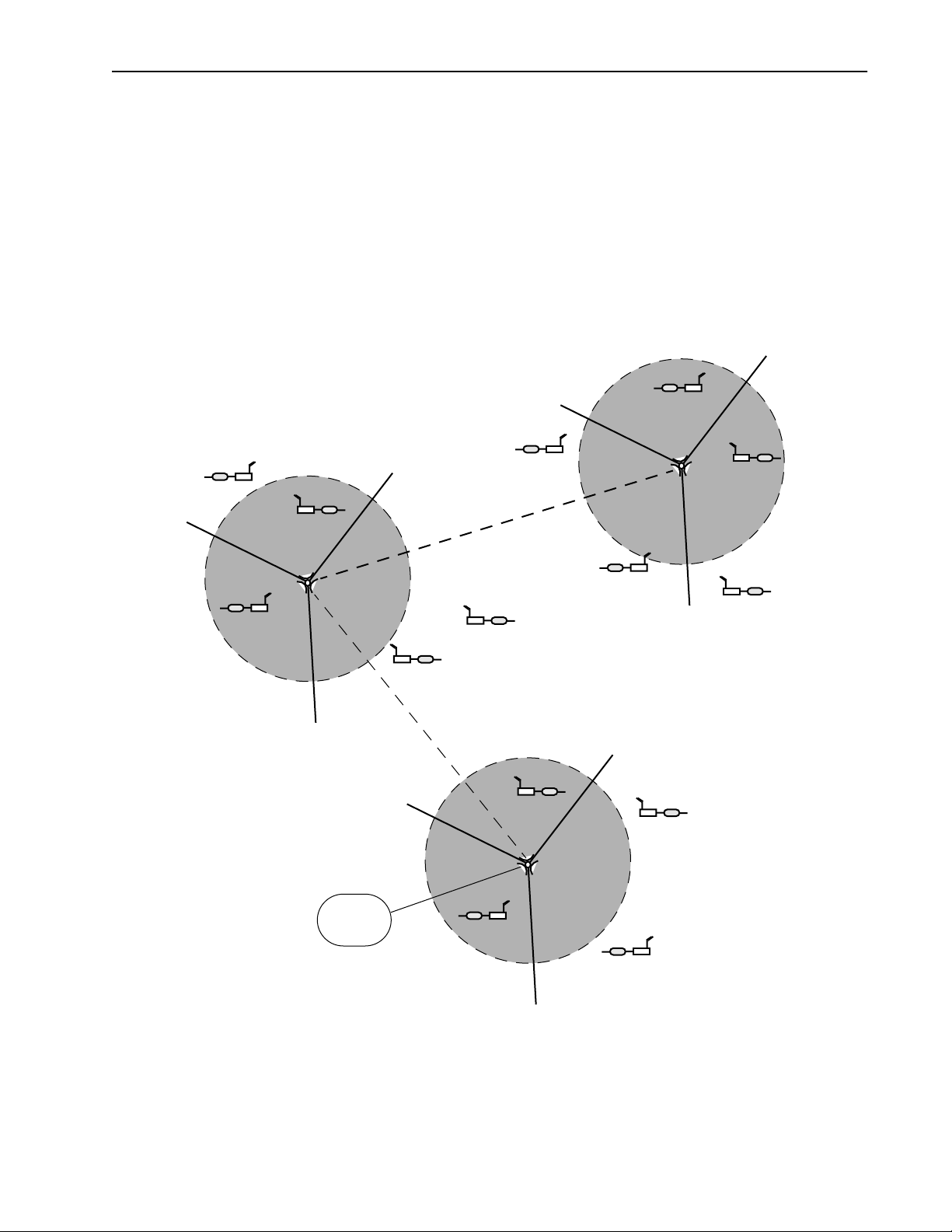
Creating a Network with Cells
Cells or data nodes can be created with AWE units to maxmimize coverage, minimize interference, and
increase data throughput. Directional antennas are mounted on a mast to divide cells into sectors.Each sector
is connected to an antenna and a base station. Directional antennas increase signal gain within the sector and
increase the distance possible between base stations and remotes. Center frequency, acquisition code and
antenna polarization techniques are used to isolate sectors. The increase in data rate depends on the number
of sectors. For example, the data rate of Cell 1 in the diagram below is 36 Mbps (12 Mbps x 3 sectors). Cells
are distributed across a service area and can be linked to each other via a wireless link or a fiber optic cable.
LAN with Cells and Sectors
Cell 2
Remote
Remote
Remote
Cell 1
Remote
Base
Stations (3)
Fiber Optiic Cable or
Remote
Remote
Fiber Optiic Cable or Wireless Link
In this example, cells are divided into120 degree sectors.
Cells are linked to other cells by a wired or wireless link.
Remote
Wireless Link
Cell 3
Remote
Base
Stations (3)
Remote
Remote
Base
Stations (3)
Remote
Remote
APR 2001 Rev 03
Internet
Remote
Remote
5
Description
Using a Repeater Base
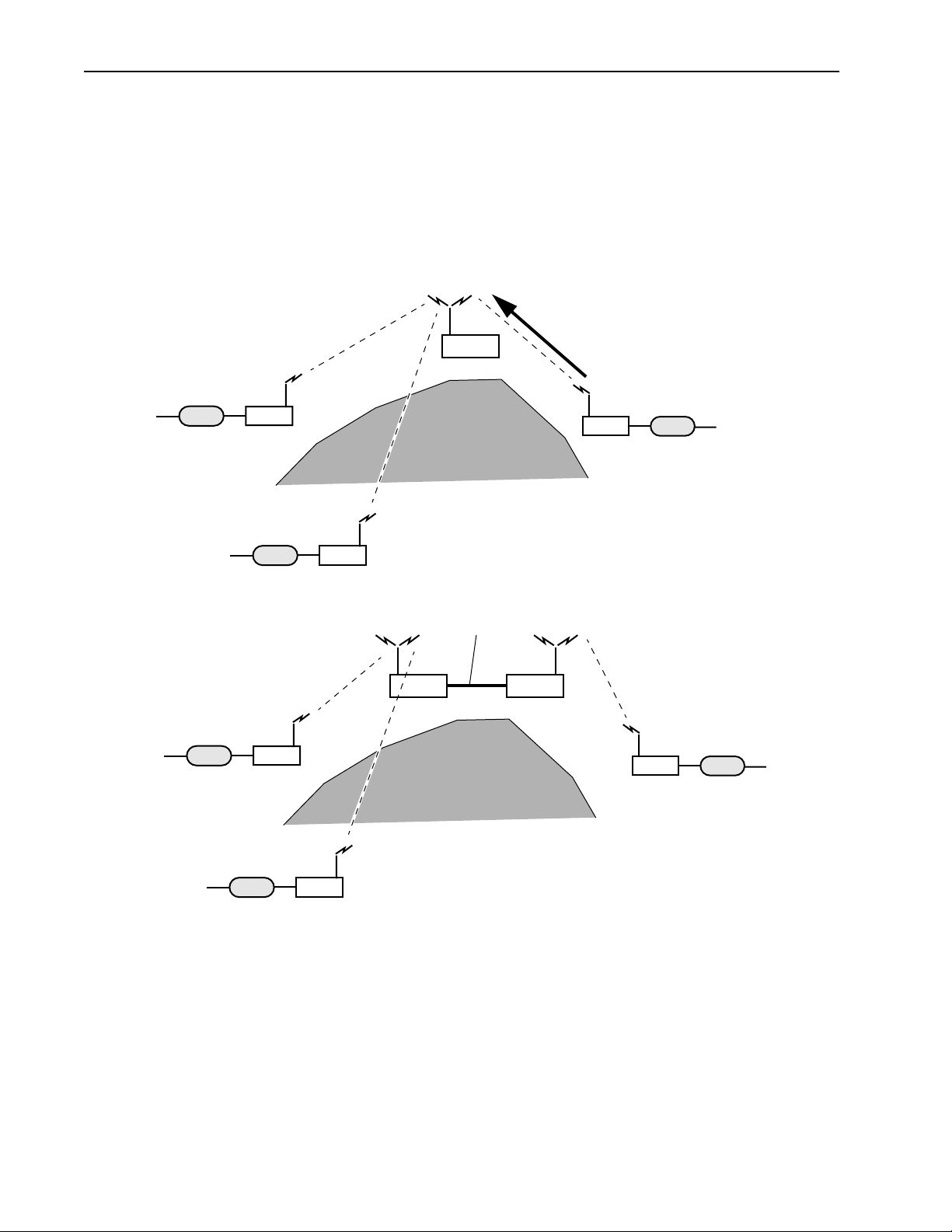
A base station can function as a repeater to enable wireless data communication around physical obstacles
such as tall buildings or mountains. The repeater passes data around the obstacle to any remote in the same
RF group. The single unit repeater slows data throughput due to the "store and foreward" process where
each packet is handled twice. A dual unit repeater does not slow data throughput.
Base Station as a Repeater
Single Unit Repeater
Wired Network
3
Remote
Wired Network
Dual Unit Repeater
Wired Network
3
Remote
Wireless Links
2
Remote
Wireless Links
Repeater
Mountain
Ethernet
Base Base
Mountain
Wired Network
1
Remote
Wired Network
1
Remote
Wired Network
2
Remote
Building a WAN
LAN segments can be linked with AWE units to build a WAN (Wide Area Network). Wi-LAN networks are
installed in many locations around the world. You can contact Wi-LAN for help designing your network.
6 AWE 120-58 Installation & Configuration Guide

Hardware Description
Hardware Description
Shipping Package Contents
The shipping package contains the following items.
• AWE unit
• Power supply, table top adapter (12 Vdc)
• Ferrite Block
• Power supply cord
• Installation and Configuration Guide
• Warranty Card
If any of the above items are not included in the AWE 120-58 shipping package, contact Wi-LAN customer
support.
You may also require the following items.
• Bench Test Kit (9000-0034) for unit testing and configuration (kit contains two indoor planar
antennas, test cables, and adapters)
• Cable, straight-through ethernet RJ45, when connecting a unit to a hub
• Cable, crossover ethernet cable RJ45, when connecting directly to the Ethernet port of a PC
• Cable adapter, DB25F to DB9M
• RS-232 DB25 serial cable
You can purchase any of these items directly from Wi-LAN or any authorized supplier. Please contact WiLAN for information about obtaining parts from you local supplier or ordering parts from Wi-LAN.
APR 2001 Rev 03
7
Description
AWE 120-58 Unit
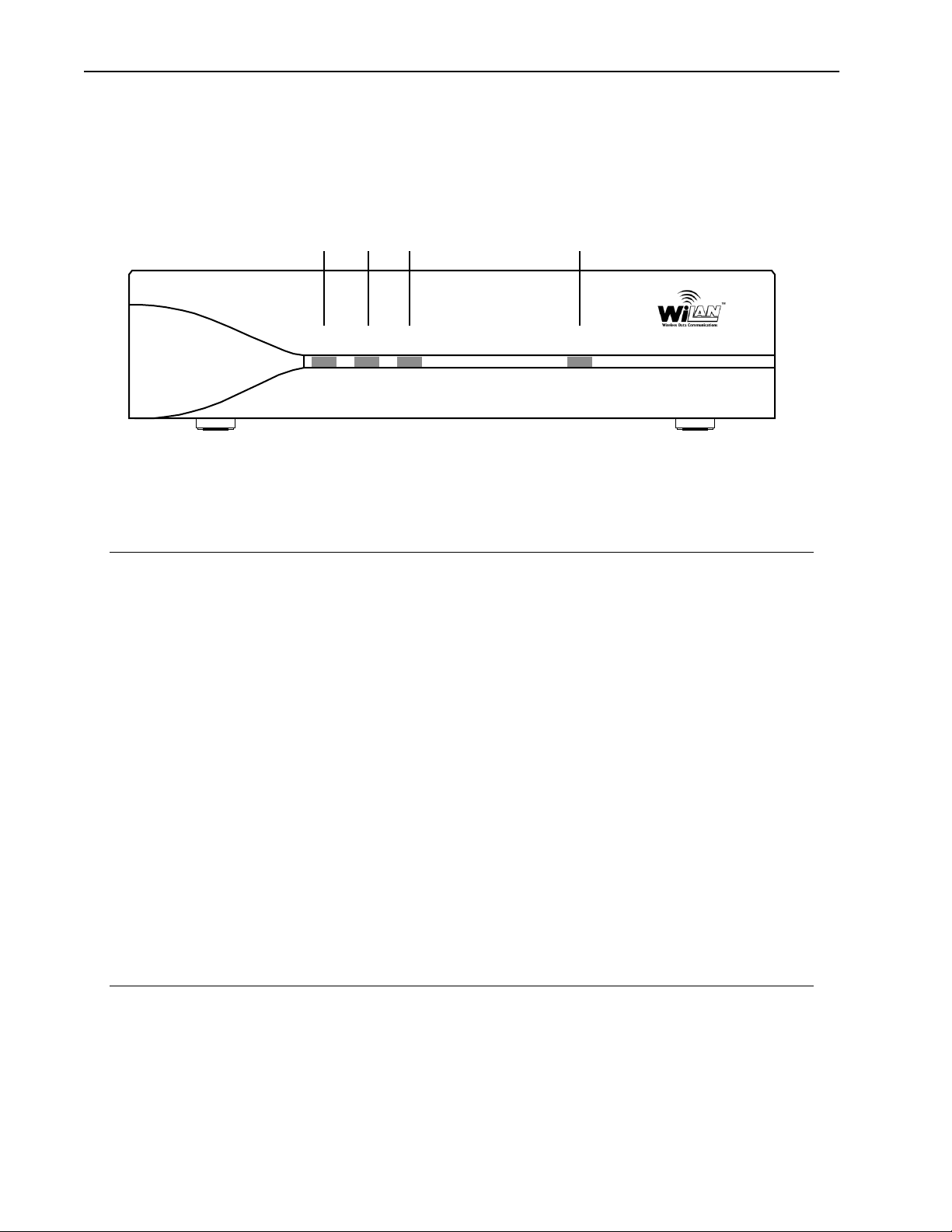
The AWE 120-58 has indicator LEDs on the front panel.
Front Panel
Air Mode Wire Power
Air
Mode Wire Power
The front panel connector and LEDs are described below. The color of a LED indicates its status. See Front
Panel LEDs, page 149 for detailed information.
Air LED Color of LED indicates the transmit/receive status of the wireless link:
Red = transmitting data to the air
Green = receiving data from the air
Orange = transmitting and receiving approximately equal amounts of
data over the air
Off = listening to the air
Mode LED Color of LED indicates the operating mode of a unit:
Green = Receive Test mode
Red = Transmit Test mode
Orange= RSSI Test mode (measures fade margin, which is indicated by
LED color)
Off = Normal mode
Wire LED Color of LED indicates the transmit/receive status of the wire link:
Green = receiving data from wire
Red = transmitting data to wire
Orange = transmitting and receiving data on the wire
Off = listening to wire or no wire connected
Power LED Green = power is connected to transceiver
Off = no power is connected to transceiver
Connectors for power, antenna and wired network are located on the rear panel, as well as a mode button
and a Link LED.
8 AWE 120-58 Installation & Configuration Guide
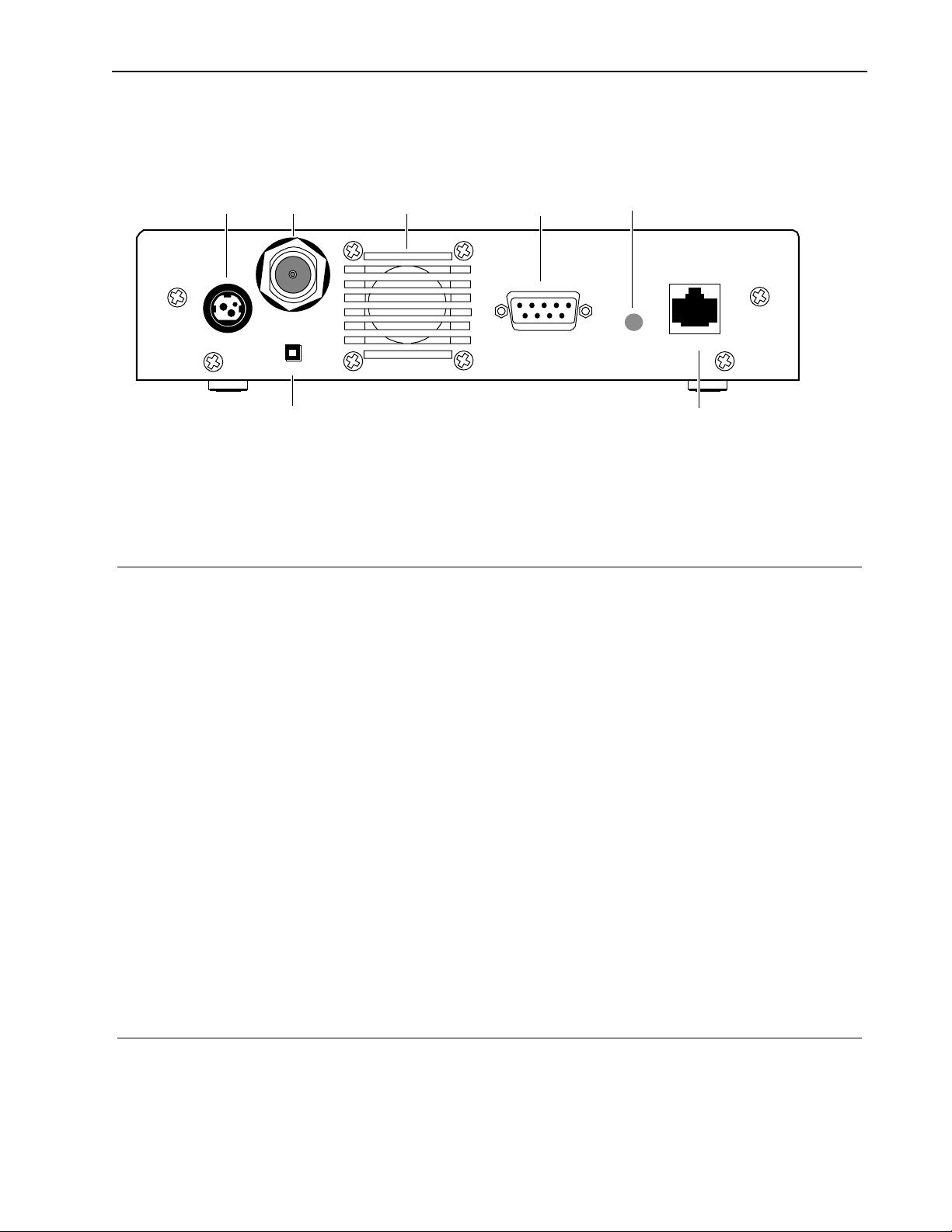
Rear Panel
Hardware Description
Power
Power
Antenna
Port
Antenna
Mode
Mode Button
Air Vent
Serial Port
Serial Port
Link LED
Link
Ethernet
Ethernet
Items located on the back panel are described below:
Antenna N-type female connector antenna port is located at the top left of the rear
panel. This port should always be connected to an antenna directly or
through a 50 ohm coaxial cable
Serial Port RS-232, DB9 connector used to communicate with a PC. Use this port to
locally configure and test a AWE
Power 3-pin power connector. See DC Power Plug Pinout, page 148 for detailed
pinout illustration
Mode Button Mode button can be used to set the operating mode of a unit without a
terminal. See Setting Operating Mode with the MODE Button, page 97 for
information about the mode button
Ethernet Standard RJ45 female ethernet connector. To connect to a PC Ethernet card,
you must use the crossover twisted-pair cable. To connect to a hub, use a
straight-through twisted-pair cable
Link LED Color of LED indicates the data rate and status of the twisted-pair
connection:
green = 10BaseT link, functioning properly
orange = 100BaseT link, functioning properly
off = No link
Air Vent Air vent for unit’s internal cooling fan
APR 2001 Rev 03
9

Description
AWE 120–58 Specifications
General Specifications
Modulation Method: Multi-Code Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (MC-DSSS), time
division duplexing (TDD)
Wireless Data Rate: 12 Mbps raw data rate/up to 9 Mbps operational
RF Frequency Range: 5.725 - 5.850 MHz (unlicensed ISM band)
Power Requirements: 12Vdc (via 110/240 VAC 50/60 Hz adaptor)
30W (2.5A) maximum power consumption
Physical: Size: 19.3 x 4.4 x 25.5 centimeters
(7.6 x 1.75 x 10.0 inches)
Weight: 1.49 kg (3.27 lb)
Radio Specifications
Antenna Connector: N-type female
Output Power: +21 dBm to –10 dBm
Receiver Sensitivity:
Processing Gain: >10 dB
Center Frequency 5.7410 GHz–5.8338 GHz in 400 kHz steps
Channel Width 33 MHz
Network Support
Packet Format: IEEE 802.3 and Ethernet II
LAN Connection: 10/100BaseT (autonegotiates)
Bridge Functionality: Local Packet Filtering (self-learning)
–80 dBm (1 x e
(High-level protocol transparent)
Static IP address filtering
Dynamic polling of remotes
User configurable data rate (throttling)
Software is upgradeable online via ftp
–6
BER)
10 AWE 120-58 Installation & Configuration Guide

AWE 120–58 Specifications
Wireless Networking
Protocols
Network Topologies: Point-to-Point, Point-to-Multipoint, Multipoint-to-Multipoint
Repeater Mode: User Configurable
Private Network User configurable using repeater and RF Group
RF Collision Management: Dynamic Polling with Dynamic Time Allocation
Security
Data Scrambling: User Configurable
Data Security Password: Security password of up to 20 bytes in length
48
combinations)
(10
Configuration, Management, and Diagnostics
Configuration Methods: SNMP, telnet and RS-232 Serial Port
SNMP: Version I compliant (RFC 1157), MIB standard and enterprise
(RFC 1213)
Management Port Functionality: Supports system configuration, security, access control,
wireless LAN diagnostics and management, menu-driven
ASCII interface via RS-232 DB-9 connector
Environment
Units must be operated in a weatherproof environment with
an ambient temperature from 0 to 40º Celsius and
humidity 0 – 95% non-condensing
APR 2001 Rev 03
11

Description
12 AWE 120-58 Installation & Configuration Guide
Installation
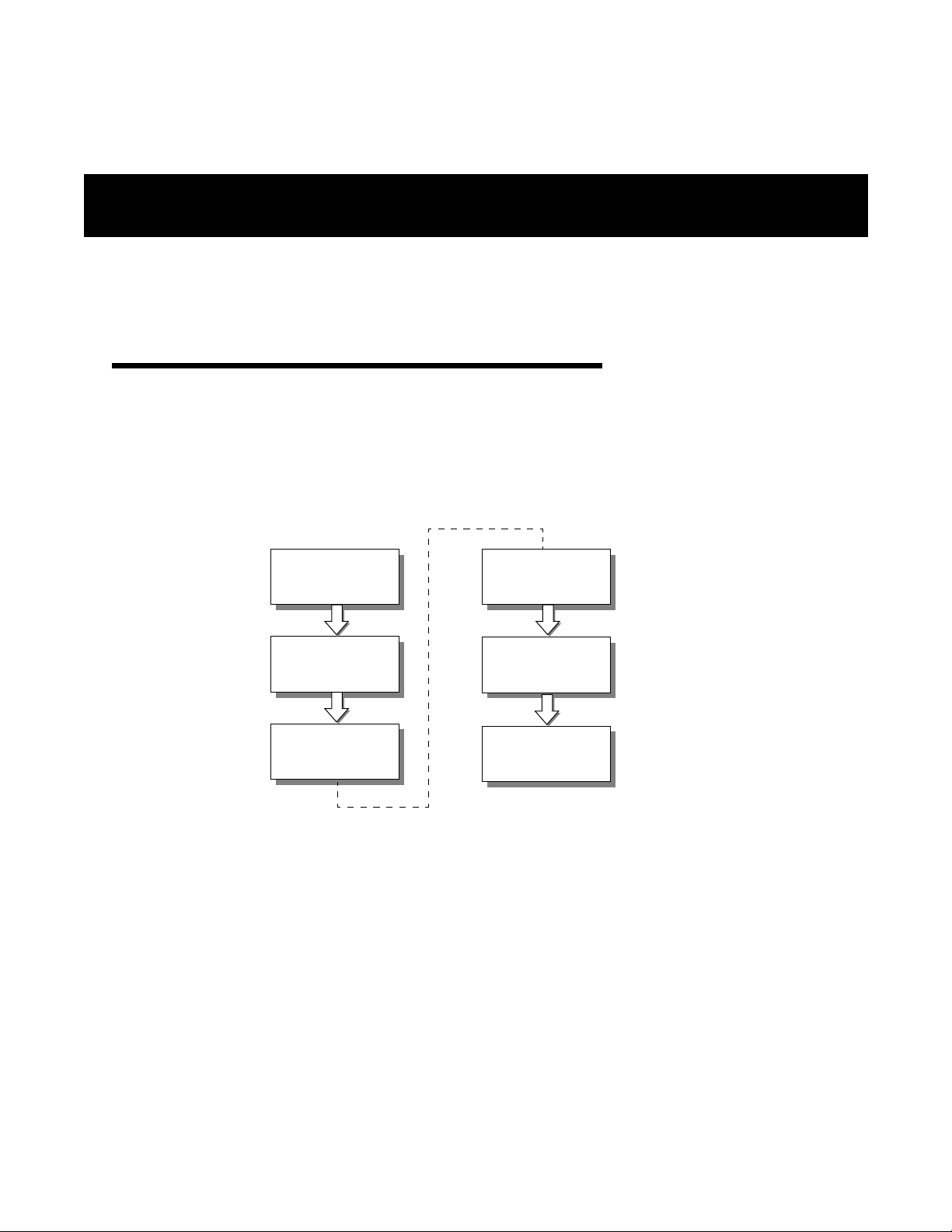
Overview
This section explains how to install AWE units. You will first assemble, configure and test units in a controlled
environment so that any problems can be solved easily, and then install units in the field. By going through this
process, you will ensure a successful installation, save time spent on-site, and reduce travel from site to site.
The following basic process should be followed.
1
2
3
Obtain
Network Plan
Assemble
Units
Pre-Configure
Units
4
5
6
Bench Test
Units
Install
Units
Test
Network
1. Obtain the network plan, equipment and tools.
2. Assemble units.
—Check the contents of each AWE shipping package to ensure that you have received the required parts.
—Connect an indoor antenna or dummy load, connect the power supply unit and check the power.
3. Pre-configure units—Configure units according to the network plan.
4. Bench test units—Test basic RF and network operation of units in a controlled environment.
5. Install units—Place the tested units in their field locations and connect them to antennas, the wired
network, and power. Install the ferrite block around the 10/100BaseT Ethernet cable.
6. Test Network—Test the operation of the installed network.
APR 2001 Rev 03 13

Installation
Obtain Network Plan
The network plan describes the network in detail, including the following:
• Type and number of units
• Physical layout
• Configuration settings for each unit
• Site names, IP addresses and links
• Antenna types, RF cables and cable lengths, surge suppressors, terminators
• Network cable types and lengths
• Grounding kits and backup power requirements
• Link budget
• Floor plans and equipment cabinet requirements.
The network plan must be completed before any equipment is installed. See Appendix A: Planning Your Wireless
Link, page 111 for more information about network plans.
Check your equipment and tools: Ensure that you have all the required parts and equipment specified in
the network plan. You will require a Bench Test Kit (9000-0034) and some tools to install and configure units–
in addition to a standard tool kit, you will require a laptop PC with HyperTerminal® or other terminal
emulation software and RS-232 cable. You may require a spectrum analyzer, Site Master® communication test
set, digital multimeter, 2-way radios, binoculars, strobe lights, ladder, and weatherproof caulking.
Assemble Units
Checking the Shipping Contents
Check the contents of each AWE shipping package to ensure that you have received all the materials. See
Shipping Package Contents, page 7 for a list.
Assembling AWE Units
To assemble a unit
➧
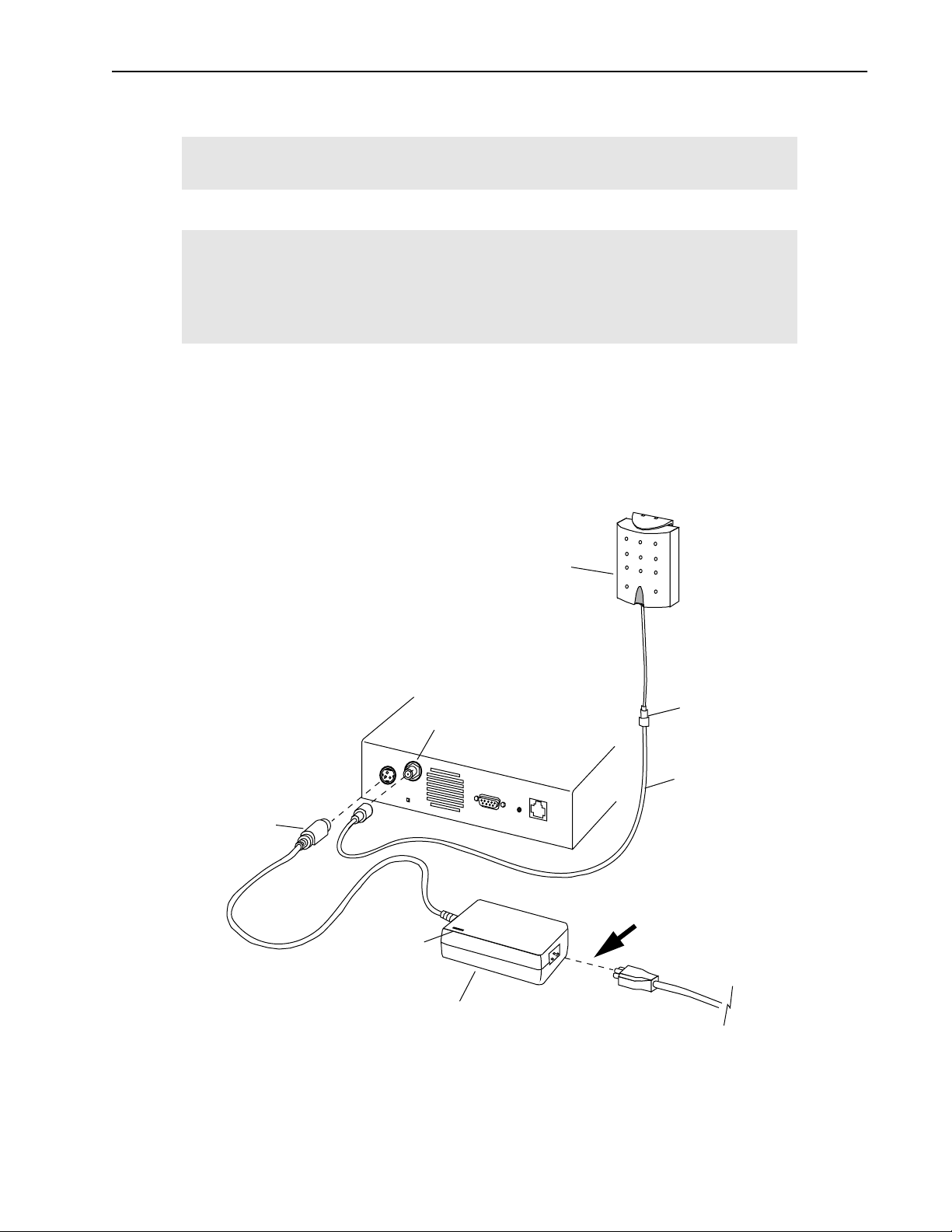
1. Connect an indoor antenna (included with Bench Test Kit) to the antenna port at the back of the unit.
Important
An indoor antenna is required for each unit for testing and configuration
purposes. Indoor antennas must be separated by at least 2 m.
Indoor antenna may differ from illustration.
14 AWE 120-58 Installation & Configuration Guide
Assemble Units
Important
Antennas must be installed by a knowedgeable and professional installer.
WARNING
Never operate a unit without an antenna, dummy load, or terminator
connected to the antenna port.
Operating a unit without an antenna, dummy load, or terminator connected
to the antenna port can permanently damage a unit.
2. Connect the power supply unit to the Power connector at the back of the unit. The AWE 120-58 must be
connected only to a Wi-LAN approved power supply unit with an output of 12 Vdc. See DC Power Plug
Pinout, page 150 for pinout information.
Antenna and Power Connections
DC Power
Plug
12 Vdc
Power LED
Antenna port
Indoor
Antenna
SMA to N-type
Adaptor
Coaxial
Cable
Hint: To turn unit
power ON or OFF,
connect or
disconnect the power
cord here.
APR 2001 Rev 03
Power Supply Unit
AC Power Cord
15

Installation
Checking the Power
To check the power
➧
1. Plug the AC power cord into the AC power outlet.
2. Plug the DC power plug (12 Vdc) to the unit’s power connector.
3. Plug the AC power cord into the power supply unit.
The green Power LED on the front of the unit turns ON and the Air, Mode and Wire LEDs turn ON
briefly then turn OFF.
The green Power LED stays ON. The Mode LED stays OFF (indicating Normal mode). The Air LED is
orange, green, red or OFF. See Front Panel LEDs, page 149 for more information about LEDs.
If the green Power LED does not turn ON, check your AC power source and the power supply unit. Measure
the power supply unit voltage at the DC Power Plug between pins 1 and 2. See DC Power Plug Pinout, page 150.
The output should be 12 Vdc and the power supply unit power LED should be ON.
Pre-Configure Units
This section describes how to pre-configure a base station and a remote unit, which are the basic units
required for a point-to-point wireless link. Once you have configured and tested this basic equipment, you
can configure and test all remaining units. See Configuration, page 33 for detailed information about
configuration settings.
Configuring a Base Station
When you configure a unit as a base station, you need to perform the following tasks.
• Check the Network Configuration information of the unit.
• Set the Station Type of the unit to "Base Station"
• Assign the Station Rank (# equal to or greater than the number of remote units)
• Choose a Center Frequency (must be the same for all units in network)
• Select an Acquistion Code (must be the same for all units in network)
• Set Tx Power Level Adjust intially to "0 dB"
• Set the security passwords (must be the same for all units in network)
• Change the default menu passwords
These tasks are described below in detail.
To configure a unit as a base station
➧
1. Connect a PC to the AWE unit that will be the base station. Connect the COM port of the PC to the
serial port of the AWE with the adapter plug and straight through RS-232 cable.
16 AWE 120-58 Installation & Configuration Guide

Connecting PC to Serial Port
Pre-Configure Units
Detail
AWE
Serial
Port (DB9)
RS-232
DB 25 to 9 pin
Adapter
RS 232 Serial
Cable to
PC COM port
Serial Port
(See detail)
RS-232 Serial Cable
to PC COM port
AWE Unit
PC
2. Start HyperTerminal® (see Appendix B: Using HyperTerminal, page 125 for details) or another terminal
emulation program such as Tera Term™. Use the following communication settings: 9600 bps, 8 bits, no
parity, 1 stop bit, no flow control.
3. Press
Enter. The AWE 120-58 Login window is displayed.
Wi-LAN AWE 120-58 Login
Software: Rev 0.0.0 (Aug 25 2000 10:13:37)
Hardware: Rev 0.0.0 (4MB SDRAM, 4MB Intel Flash)
Enter Password:
4. Type the default password (supervisor) and press
Enter. The Main Menu is displayed.
Note: supervisor enables you to change the configuration settings with the Main Menu. See Setting Menu
Passwords, page 87 for more information about menu passwords.
APR 2001 Rev 03
17

Installation
Main Menu
Wi-LAN AWE 120-58 Main Menu
How to Use the Main Menu
• To select an item from the Main
Menu or a sub-menu, press the
-> Unit Identification
Hardware/Software Revision
System Software ROM Images
Current System Status
Network Configuration
IP Filter Configuration
RF Station Configuration
Radio Module Configuration
RF/Ethernet Statistics
System Security
System Commands
Link Monitor Display
Logout
keyboard arrow keys to
move the cursor –> next to the
item.
Press the
Enter key to
Enter
open the data entry field.
• To scroll through items in the data
entry field, press .
Press to select an item
Enter
from the field.
• To exit from a menu, press the
Esc
key.
Esc
5. Select Network Configuration. Check the network configuration information, the IP address and
subnet mask settings. If necessary, change settings to match the network plan.
6. From the Main Menu, select Radio Module Configuration and press
Enter. The Radio Module
Configuration window is displayed.
Radio Module Configuration
New Current Flash
Station Type -> Remote Unit Remote Unit Remote Unit
Station Rank (1-1000) 1 1 1
Center Frequency (57410-58338) 5.7874 GHz 5.7874 GHz 5.7874 GHz
Security Password 1 (Hex) 1 1 1
Security Password 2 (Hex) 10 10 10
Security Password 3 (Hex) 100 100 100
Security Password 4 (Hex) 1000 1000 1000
Security Password 5 (Hex) 10000 10000 10000
Scrambling Code (Hex) 0 0 0
Acquisition Code (0-15) 1 1 1
Config Test Minutes (1-120) 30 30 30
Tx Power Level Adjust 0 dB 0 dB 0 dB
Base Station Only Parameters
Repeater Mode off off off
System Symmetry Type Asymmetric Asymmetric Asymmetric
Dynamic Polling Level (1-100) 1 1 1
Remote Station Only Parameters
Remote Unit RF Group (0-63) 0 0 0
Reboot New RF configuration Press Enter to Execute
Save Current Config to Flash Press Enter to Execute
• Select Station Type. Choose Base Station.
18 AWE 120-58 Installation & Configuration Guide

• Select Station Rank. Enter the total number of remote units in your wireless network. For
Success
example, if you have only one remote unit, enter "1". If there are 20 remote units, enter "20".
• Choose a Center Frequency. Enter the value of the center frequency (range is 57410–58338
in 400 kHz steps). All wireless units must be set to the same center frequency.
• Select Security Password x. Type security passwords in hexadecimal for the unit. All units in
the same network must have the same set of security passwords.
• Select Scrambling Code. Enter a hexadecimal value or leave the default at "0". All units in the
same network must have the same scambling code.
• Select Acquistion Code. Enter a value from 0–15. (All units in the same network must have
the same acquisiton code.)
• Select Config Test Minutes. Enter a time in minutes, for example, 10. The unit will automatically reboot when this time period expires, and uses the settings stored in flash memory instead of
current settings.
• Select Tx Power Level Adjust. Choose an initial value of 0 dB, which means no Tx power
attenuation.
• Select Reboot New RF configuration and press
Enter. The unit reboots and the Login
window is displayed.
7. Log in to the unit. (Type supervisor for the password). The Main Menu is displayed.
8. Select Radio Module Configuration and press
Enter. The Radio Module Configuration window
is displayed.
Pre-Configure Units
• Select Save Current Config to Flash and press
Enter. The new settings are stored in flash
memory and displayed on the menu. The word appears on the screen.
9. Press Esc to go back to the Main Menu.
10. Select Logout to exit or press
Note: At this time you may want to finish configuring the base station according to the network plan. See
Esc.
Configuration, page 33 for instructions about viewing and changing various settings.
Configuring a Remote Unit
When you configure a unit as a remote unit, you need to do the following tasks.
• Check the Network Configuration information of the unit
• Set the Station Type of the unit to "Remote Unit"
• Assign the Station Rank (polling ID # of the remote unit)
• Select a Center Frequency (must be the same for all units in network)
• Select an Acquistion Code (must be the same for all units in network)
• Set Tx Power Level Adjust intially to "0 dB"
• Set the security passwords (must be the same for all units in network)
• Change the default menu passwords
These tasks are described below in detail.
APR 2001 Rev 03
19

Installation
To configure a unit as a remote unit
➧
1. Connect a PC to a AWE remote unit. Connect the COM port of the PC to the Serial port of the remote
unit using an adapter plug and RS-232 cable. See Configuring a Base Station, page 16 for cabling diagram.
2. Start HyperTerminal® or other terminal emulation program (see Appendix B: Using HyperTerminal, page
125). Use the following commnication settings: 9600 bps, 8 bits, no parity, 1 stop bit, no flow control.
3. Press
4. Type the default password supervisor and press
Enter. The AWE 120-58 Login window is displayed.
Enter. The Main Menu is displayed.
5. Select Network Configuration. Check the IP settings. If necessary, change the settings to match
the network plan.
6. From the Main Menu, select Radio Module Configuration and press
Enter. The Radio Module
Configuration window is displayed.
Radio Module Configuration
New Current Flash
Station Type -> Remote Unit Remote Unit Remote Unit
Station Rank (1-1000) 1 1 1
Center Frequency (57410-58338) 5.7874 GHz 5.7874 GHz 5.7874 GHz
Security Password 1 (Hex) 1 1 1
Security Password 2 (Hex) 10 10 10
Security Password 3 (Hex) 100 100 100
Security Password 4 (Hex) 1000 1000 1000
Security Password 5 (Hex) 10000 10000 10000
Scrambling Code (Hex) 0 0 0
Acquisition Code (0-15) 1 1 1
Config Test Minutes (1-120) 30 30 30
Tx Power Level Adjust 0 dB 0 dB 0 dB
Base Station Only Parameters
Repeater Mode off off off
System Symmetry Type Asymmetric Asymmetric Asymmetric
Dynamic Polling Level (1-100) 1 1 1
Remote Station Only Parameters
Remote Unit RF Group (0-63) 0 0 0
Reboot New RF configuration Press Enter to Execute
Save Current Config to Flash Press Enter to Execute
• Select Station Type. Choose Remote Unit.
• Select Station Rank. Enter the rank number of the remote unit. Enter a number from 1–1000.
• Choose a Center Frequency. Enter the value of the center frequency (range is 57410–58338
in 400 kHz steps). All wireless units must be set to the same center frequency.
• Select Security Password x. Type security passwords in hexadecimal for the unit. All units in
the same network must have the same set of security passwords.
• Select Scrambling Code. Enter a hexadecimal value or leave the default at "0". All units in the
same network must have the same scambling code.
• Select Acquistion Code. Enter a value from 0–15. (All units in the same network must have
the same acquisiton code.)
• Select Config Test Minutes. Enter a time in minutes, for example, 10. The unit will automatically reboot when this time period expires, and uses the settings stored in flash memory instead of
current settings.
20 AWE 120-58 Installation & Configuration Guide

Bench Test Units
• Select Tx Power Level Adjust. Choose an initial value of 0 dB, which means no Tx power
attenuation.
• Select Remote Unit RF Group. Enter a value from 0–63. (For testing purposes, you may leave
the value = 0.)
• Select Reboot New RF configuration and press
Enter. The unit reboots and the Login
window is displayed.
7. Log in to the unit. (Type supervisor for the password). The Main Menu is displayed.
8. Select Radio Module Configuration and press
Enter. The Radio Module Configuration window
is displayed. The settings under Current change to values that were in the New column.
9. Select Save Current Config to Flash and press
memory and displayed on the menu. The word appears on the screen.
Success
Enter. The new settings are stored in flash
10. Press Esc to go back to the Main Menu.
11. Select Logout to exit or press Esc.
Note: At this time you may want finish configuring the unit according to the network plan. See Configuration,
page 33 for instructions about viewing and changing various settings.
Bench Test Units
In this section, you will perform the following tasks:
• Ensure that a basic RF link exists between a base station and a remote unit.
• Test the basic link with Link Monitor and adjust Tx power level.
• Perform some simple network tests.
Establishing a Basic RF Link
This test ensures that a basic RF link exists between a base station and a remote unit.
IMPORTANT
The quality of your digital data transmission depends greatly on the quality of your RF
link. Always try to establish a high-quality RF link first. A high-quality RF link will
result in high-quality data transmissions and a low BER. A low-quality RF link will result
in low-quality data transmissions and a high bit error rate (BER). Digital data can always
be sent across a high-quality RF link. If the RF link is of poor quality, data either cannot
be sent at all or will contain too many errors to be useful..
Tip: First configure one unit as a base station, and then use it to test all the remote units.
To establish a basic RF link
1. Ensure that one unit is configured to a base station, select a center frequency and set the test minutes.
See Configuring a Base Station, page 16.
2. Ensure that the other unit(s) are configured as remote units with the center frequency the same as the
base station. See Configuring a Remote Unit, page 19.
APR 2001 Rev 03
21

Installation
3. Place the base station and a remote unit at least two meters apart with a clear line of sight between
antennas. Point the antennas toward each other.
Basic Test Setup
Indoor
Antenna
Coax Adapter Cable
Air
Mode Wire Power
Air LED = orange
Base Unit Remote Unit
2 m
minimum
Air
Air LED = orange
Mode Wire Power
Indoor
Antenna
Coax Adapter Cable
4. Power up the base station. The green Power LED is ON. The Air LED of the base unit is red. This Air LED
color indicates that the unit is transmitting data but is not receiving a response. (The reason is that the
remote is powered off.)
5. Power up the remote unit. The green Power LED is ON. The Air LED of the remote unit turns orange
and the Air LED of the base station also turns orange as both units send and receive data from each
other. Orange is the normal Air LED color.
The color of the Air LED during this step indicates the following conditions.
Orange (both stations) Units are continuously sending and receiving sync packets
Red (base station) Stations are configured incorrectly, and the base station is
transmitting without receiving acknowledgment
Green (remote station) Stations are configured incorrectly, and the remote station is
receiving packets to which it cannot respond
Off Nothing is being received (by the remote) or transmitted (from the
base)
Note: If antennas are placed too close together, the strong transmit signal will saturate the receiving unit.
Fine-tune antennas by changing antenna orientations until the Air LED is orange.
Next, you will test the link with the Link Monitor test and adjust the Tx power level to obtain a fade margin
of 15–30 dB. .
22 AWE 120-58 Installation & Configuration Guide

Bench Test Units
Testing the Link and Adjusting Tx Power
A basic RF link is established when the base station and remote unit can receive and transmit data to each
another (indicated by orange Air LEDs on both units). Once you have established a basic RF link, you test the
link by running the Link Monitor test and viewing the link statistics. Finally, you adjust the Tx Power of the
base and remote units to obtain a 15–30 dB fade margin.
To test the RF link and adjust Tx power
➧
1. Connect the test PC to the serial port of the base station or remote unit. See Connecting PC to Serial Port,
page 17.
2. Log in to the unit and go to the Main Menu.
3. Select RF Station Configuration and press
displayed.
RF Station Configuration
Operating Mode -> Normal Mode
RF Transmit Status unblocked
Link Monitor Period (0=OFF, 1-10000) 0
Test Mode Timer Minutes (1-1000) 5
Enter. The RF Station Configuration window is
Base Station Only Parameters
Maximum Remote Distance 5 Km
Link Monitor Remote Station Rank 1
Remote Station Only Parameters
Throttle Enable off
Throttle Level (1-50) 1
• Select Operating Mode. Press the arrow keys to select Normal mode.
• Select RF Transmit Status. Select unblocked.
• Select Link Monitor Remote Station Rank. Enter the rank of the unit that you want to
link test. (The rank is the identification number of the unit. The rank of a remote can be any number from 1 – 1000. The rank number of the the base station is always 0. See Setting the Station Rank,
page 69.)
• Select Link Monitor Period. Enter a link monitor period of 1. (A value of 1 means that 50%
of available data packets will carry test data. The higher the period number, the fewer the number
of data packets that will carry test data. See Setting the Link Monitor Period, page 61 for more information.) The Link Monitor test starts as soon as a non-zero value is entered in the field.
Next, you view the link statistics and adjust Tx power level.
APR 2001 Rev 03
23

Installation
4. From the Main Menu select Link Monitor Display and press Enter. The RF Background Link
Monitor Statistics window is displayed.
RF Background Link Monitor Statistics
Link Monitor Rank 1
Base to Remote BER 0.0E+00
Remote to Base BER 0.0E+00
Missed Packet Count 0
Base to Remote Env Power 27
Base to Remote Corr Power 28
Remote to Base Env Power 29
Remote to Base Corr Power 30
5. Check for the following statistics:
• Base to Remote BER = 0.0E+00
• Remote to Base BER = 0.0E+00
• Base to Remote Corr Power between 15 – 50 dB
• Remote to Base Corr Power between 15 – 50 dB
If the Corr Power is <15 dB the receive signal is probably too weak to be useful. If the power is
>55 dB the receiving unit is probably being saturated.
6. Adjust Tx power of both units to obtain a fade margin (Corr Power) of 15–30 dB, as displayed by the Link
Monitor Statistics window. See Adjusting the Tx Power Level, page 76 and Performing Transmit and Receive
Tests, page 57.
7. When you are finished viewing link monitor statistics, disable Link Monitor to remove the overhead test
data from the wireless link. To disable Link Monitor, select
RF Station Configuration from the Main Menu and press Enter. The RF Station Configuration
window is displayed.
8. Select Link Monitor Period and press Enter. The field is highlighted.
9. Type 0 in the field and press Enter. The link monitor test ends.
10. Press Esc to exit.
You have now established an RF link between two units, tested the ability of the link to carry test data, and
adjusted the Tx power level to 15–30 dB. Next, you connect the units to a network and perform some simple
network tests.
24 AWE 120-58 Installation & Configuration Guide

Bench Test Units
2
Performing Simple Network Tests
To test units within a simple network you require two AWE 120-58 units, a LAN connection, a PC and a
crossover ethernet cable or hub connection. A ferrite block is placed around the 10/100BaseT Ethernet cable
to prevent electromagnetic interference (EMI) from transferring from a unit to the Ethernet cable, and from
the Ethernet cable to the unit. The ferrite block is included with the contents of the shipping box. Install a
ferrite block when testing units, and ensure that a ferrite block is in place when units are installed in the field.
To install the ferrite block
➧
1. Remove the ferrite block from the plastic packaging.
2. Pull the clip and open the ferrite block. See
1
Ferrite Block
1
Clip
3. Place the Ethernet cable in the center of the open ferrite block. Locate the block approximately 4 cm
from the cable connector end that plugs into the unit’s Ethernet port. See
4. Close the ferrite block around the Ethernet cable, making sure that the block snaps together. See
2
3
3
4 cm
4
APR 2001 Rev 03
25

Installation
5. Plug the Ethernet cable into the unit. See
4
4
Ethernet port
Ethernet
26 AWE 120-58 Installation & Configuration Guide

Bench Test Units
To perform a simple network test
➧
1. Connect the Ethernet port of the base station to the internet port of the PC. You can either connect to
a network hub or connect directly using an RJ45 crossover ethernet cable.
Simple Network Test Setup
2 m
minimum
Cable connects to
Ethernet port
Base Unit
10/100 BaseT
Cable
(Straight
Through)
Direct 10/100 BaseT Cable (Crossover)
10/100 BaseT HUB
Air
Mode Wire Power
10/100 BaseT Cable
PC
Air
2. Power up both AWE units. Initially the LEDs should appear as follows.
Power LED Green
Mode LED Off
Air LED Orange
Mode Wire Power
LAN
3. Configure the AWE units within your network. See Network Configuration, page 42 for information about
AWE Internet addresses. See Appendix C: Configuring a Simple Data Network, page 127 for information
about configuring simple peer-to-peer networks.
4. Create some network traffic to test the wireless link. For example, use ping or ftp put and get to
transfer a large test files, in both directions, across the link. The Wire LED on the AWE indicates link file
transfer activity to the wired LAN. When the file transfer is done, ftp displays the size of the file and the
time it took to transfer the file. This information can be used to measure the data throughput of the
wireless link, and is very useful for troubleshooting.
APR 2001 Rev 03
27

Installation
Using ping and ftp
ping
From the command line prompt, type:
C:> ping IP Address
Example:
ping 192.163.2.88
ftp
To connect to the node, from the DOS prompt, type:
C:> ftp IP Address
For instructions about using ftp, type "help"
at the ftp prompt.
ftp> help
5. Test all units in the network.
Follow the instructions.
28 AWE 120-58 Installation & Configuration Guide

Install Units
Install Units
This section provides some guidelines about installing units in the field.
• Install the units at locations identified in the network plan.
WARNING
All antennas must be professionally installed following accepted safety, grounding,
electrical, and civil engineering standards. An antenna (indoor or outdoor), dummy load,
or terminator must be connected to the antenna port of a unit before a unit is powered
up to avoid damaging the unit.
• Verify that there is no interference at the site by performing spectrum sweeps with a spectrum
analyzer. Perform sweeps at various times of the day (for example, 9AM, noon, and 3 PM are peak
telephone traffic times.) If there are problems, contact the network planner, who may need to change
the system configuration or design.
• Sweep antennas and cables with the Site Master® communications test set before securing antennas
and cables to towers, while they are on the ground and easy to access. Sweeping helps to ensure that
antennas and cables will operate as expected.
• Initially install equipment with flexibility—do not tie down cables, antennas should be free to move,
allow some slack in cables, avoid drilling and do not seal connections.
• Align antennas. (Two people are required, one at the base station and one at the remote unit. When
in the field, you may require binoculars and 2-way radios to communicate.) When aligning antennas,
adjust the orientation of the remote antenna while running a link monitor test between the remote
and the base station. Adjust the antenna until you achieve the highest fade margin with no bit errors
(BER = 0). See Performing the RSSI Test, page 59 and Performing Link Monitor Test (Normal Mode), page 54
for instructions. Repeat the antenna alignment procedure for each remote.
• When antennas are aligned and cables are secured, sweep the antennas with the Site Master test set
a final time before connecting to AWE.
• Install ferrite blocks on all 10/100BaseT Ethernet cables at the end of the cable that plugs into the
unit. See Performing Simple Network Tests, page 25.
• Perform diagnostic tests on the installed system. Compare field results to bench test results using
ping, ftp, fade margins, etc. Document your results (these results will be very useful when
troubleshooting and monitoring the system’s performance).
• When the system works as specified in the network plan, lock down and weatherproof all equipment
and connnections.
APR 2001 Rev 03
29

Installation
Point-to-Multipoint Installation
The procedure for installing a point-to-mulitpoint system is the same as the procedure for installing a pointto-point system. Treat each link in a point-to-multipoint system as a single, point-to-point wireless link.
Co-Location Installation
When you install a system with sectors and co-located base stations (see Creating a Network with Cells, page 5
for an example), you install and test sectors as if they were point-to-point systems; however, in this case you
must ensure that individual sectors are not interfering with each other.
• Align and test the first sector. Measure the fade margin and run the link monitor test. Document your
results, then turn off the radio in the first sector.
• Align and test the second sector. Measure the fade margin and run the link monitor test. Leave the
link monitor test running in the second sector.
• Turn on the radio in the first sector again and run the continuous tranmit test. See Performing Transmit
and Receive Tests, page 57.
• Observe the BER and fade margin of the second sector radio. Look for changes to determine if the
first sector is interfering with the second sector.
• Repeat the tests for all sector/pair combinations.
Test Network
Run the link monitor test and other tests such as ping and ftp file transfers to verify network operation when
the units are installed in the field. See Performing Link Monitor Test (Normal Mode), page 54.
Adding to a Network
Always add to your network one link or device at a time, working from a known base network. Measure and
document changes to the system and changes in performance. For example, you can transfer files with ftp
and measure the performance with LAN analyzer software. The key to a successful network is to proceed
one step at a time and to understand your network!
30 AWE 120-58 Installation & Configuration Guide

Network Test Setup
Preventative Maintenance and Monitoring
Indoor
Antenna
Base Unit
Air
Mode Wire Power
10/100 BaseT HUB
Preventative Maintenance
and Monitoring
Remote Unit
Air
PC
PC with LAN analyzer software
Mode Wire Power
Indoor
Antenna
LAN
You should set up a preventative maintenance schedule for your network. Wi-LAN recommends that the
following preventative maintenance be performed at least semi-annually.
• Regularly run link monitor tests across the network and measure BER and fade margin. You can also
test the network with ping, ftp and file transfers. Other resources are available on the Internet that
can help you monitor the performance of your link.
• If you have SNMP application software, you can check unit operation from a remote location. See
Appendix D: SNMP, page 133 for more information.
If you have SNMP application software, you can check unit operation remotely. See Appendix D: SNMP, page
133 for more information.
You should periodically perform a physical inspection of each site.
• Check that antennas and cables are secure and have not become loose.
• Check for physical obstructions in the line-of-sight radio path, such as trees and buildings.
• Sweep antennas and cables to ensure that antennas and cables are intact and operating properly.
• Check that there are no water leaks in cabinets.
• Check weatherproofing.
• Check for new sources of electromagnetic interference.
APR 2001 Rev 03
31

Installation
32 AWE 120-58 Installation & Configuration Guide

Configuration
Overview
This section explains how to use the Main Menu to configure and test your AWE unit, and to obtain useful
statistical and maintenance information.
Main Menu
In this section, each item in the Main Menu is described in the order that it appears in the menu. See Appendix
F: Menu Map, page 151 for a complete listing of submenus. Use the Main Menu and your keyboard keys to
select, view or change settings. Some items in the menu simply display information, while others ask you to
enter data or make a selection from a list.
Main Menu
Wi-LAN AWE 120-58 Main Menu
-> Unit Identification
Hardware/Software Revision
System Software ROM Images
Current System Status
Network Configuration
IP Filter Configuration
RF Station Configuration
Radio Module Configuration
RF/Ethernet Statistics
System Security
System Commands
Link Monitor Display
Logout
APR 2001 Rev 03 33

Configuration
Accessing the Main Menu
You can access the Main Menu of a AWE unit with a HyperTerminal® session (via the Serial port) or a telnet
session. Most instructions provided in this chapter assume that you have opened a HyperTerminal session.
You can also configure the AWE 120-58 remotely with the SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol).
See Appendix D: SNMP, page 133 for information about SNMP.
Accessing the Main Menu with HyperTerminal
To access the Main Menu with HyperTerminal
➧
1. Disconnect power from the AWE unit.
2. Connect a serial cable from a DB9 serial port on the PC to the Serial port on the AWE. See Configuring a
Base Station, page 16.
3. Start Hyperterminal or other a terminal emulation program on the PC. See Appendix B: Using
HyperTerminal.
4. Set the terminal emulation program to emulate a VT100 terminal with the following settings.
• COM port PC serial port connected to AWE unit
• Bits per second: 9600
• Data bits: 8
• Parity: none
• Stop bits: 1
• Flow control: none
5. Reconnect the power to the AWE unit.
6. Press Enter. The Wi-LAN AWE 120-58 Login menu is displayed.
®
Wi-LAN AWE 120-58 Login
Software: Rev 0.0.0 (May 25 2000 10:13:37)
Hardware: Rev 0.0.0 (4MB SDRAM, 4MB Intel Flash)
Enter Password:
7. Type a default password (user or supervisor) or type your personal password if already have one.
Login Account Default Password Privileges
User user Read Only
Supervisor supervisor Read and Write
The Main Menu is displayed.
34 AWE 120-58 Installation & Configuration Guide

Accessing the Main Menu
Accessing Units via telnet
To access units via telnet
➧
1. Ensure that the unit’s Internet IP address has been configured, the unit has a working Ethernet
connection, and wire and remote access has been enabled (see Allowing Remote Access and Configuration,
page 94).
2. Ensure that the VT100 Arrows feature in your telnet session is enabled. See Setting VT100 Arrows, page 35.
3. From the DOS prompt, type
C:>telnet <IP address>
where <IP address> is the IP address of the unit that you want to configure.
4. Press
Enter. The Login menu is displayed.
Wi-LAN AWE 120-58 Login
Software: Rev 0.0.0 (Aug 25 2001 10:13:37)
Hardware: Rev 0.0.0 (4MB SDRAM, 4MB Intel Flash)
Enter Password:
5. Type the default password (user or supervisor) or type your personal password.
The Main Menu is displayed.
Setting VT100 Arrows
To set the VT100 arrows in Microsoft telnet
➧
1. In the active Microsoft telnet 1.0 session, select Terminal, Preferences from the menu bar. The
Terminal Preferences window is displayed.
2. Click the VT100 Arrows checkbox.
3. Click OK. The VT100 arrows are enabled in the telnet session.
You can now use the keyboard arrow keys to navigate the configuration menus.
APR 2001 Rev 03
35

Configuration
Configuring with the Main Menu
This section describes how to configure units with the Main Menu. Menu items are presented in the order
they appear in the menu shown below.
Main Menu
How to Use the Main Menu
Wi-LAN AWE 120-58 Main Menu
• To select an item from the Main
Menu or a sub-menu, press the
-> Unit Identification
Hardware/Software Revision
System Software ROM Images
Current System Status
Network Configuration
IP Filter Configuration
RF Station Configuration
Radio Module Configuration
RF/Ethernet Statistics
System Security
System Commands
Link Monitor Display
Logout
keyboard arrow keys to
move the cursor –> next to the
item.
Press the
Enter key to
Enter
open the data entry field.
• To scroll through items in the data
entry field, press .
Press to select an item
Enter
from the field.
• To exit from a menu, press the
Esc
key.
Esc
36 AWE 120-58 Installation & Configuration Guide

Unit Identification
Unit Identification
Viewing Unit Identification
You can view a unit’s serial number, production date, and MAC address with the Unit Identification menu. The
fields are view only and are set at the factory.
You can also view the Unit Name/Description, Unit Location, and Contact Name. These fields are optional
and can be changed.
To view unit identification information
➧
1. From the Main Menu, select Unit Identification and press Enter. The Unit Identification menu is
displayed.
Unit Identification
Serial Number Serial-Number
Production Date Jun 07 2000
Ethernet MAC Address 001030000000
Unit Name/Description -> System Name
Unit Location System Location
Contact Name System Manager's Name
Serial Number Unique serial number of unit (Read Only)
Production Date Date unit was produced (Read Only)
Ethernet MAC Address Unique Internet MAC (Media Access Control)
address of the unit (Read Only)
Unit Name/Description Name of unit (optional)
Unit Location Location of unit (optional)
Contact Name Name of contact person (optional)
APR 2001 Rev 03
37

Configuration
Assigning Unit Identification Information
You can assign a name, location, and contact name to units. This information will help you to distinguish units
by physical location or by meaningful names rather than just station rank. Unit identification information is
optional.
To assign or change unit identification information
➧
1. From the Main Menu, select Unit Identification and press
displayed.
Unit Identification
Serial Number Serial-Number
Production Date 01-01-2000
Ethernet MAC Address 001030040502
Unit Name/Description -> System Name
Unit Location System Location
Contact Name System Manager's Name
2. Select Unit Name/Description and press
Enter. The data field highlights.
3. Type in a new name or description.
4. Press
5. Select Unit Location and press
Enter. The new name or description is displayed in the data field.
Enter. The data field highlights.
6. Type the location of the unit.
7. Press
8. Select Contact Name and press
Enter. The new location appears in the data field.
Enter. The data field highlights.
9. Type a contact or manager name.
10. Press
11. Press
Enter. The new name appears in the entry field.
Esc to exit to the Main Menu.
Enter. The Unit Identification menu is
38 AWE 120-58 Installation & Configuration Guide

Hardware/Software Revision
Hardware/Software Revision
Viewing System Revision Information
The System Revision Information window shows the revision information of the unit including memory
revision number, memory size, and software revision number.
To view system revision information
➧
1. From the Main Menu, select Hardware/Software Revision and press Enter. The System Revision
Information window is displayed. The menu is view only.
System Revision Information
Hardware Rev 0.0.0 (4MB SDRAM, 4MB Intel Flash)
ROM Size 0x400000
RAM Size 0x400000
2. Press
Software Rev 1.1.0 (Wi-LAN AWE 120-58 WEBII)
Oct 26 2000 10:13:37
329868 Bytes
File Name FACTORY-IMAGE
Hardware Revision number of the unit, and the amount SDRAM and
FLASH memory available in the unit
ROM Size Amount of Flash read-only memory in the unit = 4 MB
RAM Size Amount of random-access memory in the unit = 4MB
Software Revision number of the system image running on the unit,
the date of the revision, and the size of the image file (in
this example FACTORY-IMAGE is about 318 Kbytes)
File Name File name of the system image running on the unit
Esc to exit to the Main Menu.
APR 2001 Rev 03
39

Configuration
System Software ROM Images
Viewing System Software ROM Images
A ROM image is the software that a unit uses to operate. The System Software ROM Images window lists
software images currently available in the unit. New images can be loaded into a unit’s Flash ROM from an
outside source such as a PC. The example below shows that only the "Factory-Image" is available, however, in
the future other images may be available. If required, you can obtain a new image file from the Wi-LAN web
site and download it to your AWE unit–see Appendix G: Upgrading Software, page 153 for instructions. See
Setting Default System Image, page 97 for instructions about selecting a default image.
To view system software ROM images
➧
1. From the Main Menu, select System Software ROM Images and press Enter. The System Software
ROM Images window is displayed. The window is view only.
System Software ROM Images
File Name Revision Date Time Size Default Image
-------------------- -------- ----------- -------- ------ -------------
FACTORY-IMAGE 1.1.0 Aug 24 2001 10:13:37 306524 Current
File Name Name(s) of system image file(s) stored in the unit. To add or
delete images you must use ftp. See Appendix G: Upgrading
Software, page 151
Revision Revision number of the system image file. Each time the system
image is modified, the revision number increases by 1 unit. For
example, the first revision to the file would make the revision
number 0.0.1
Date Date image file was last revised
Time Time image file was last revised
Size Size of image file in bytes
Default Image Indicates which image file is the default. Default Image is used at
power up. See Setting Default System Image, page 97 to modify
default image
2. Press
Esc to exit to the Main Menu.
40 AWE 120-58 Installation & Configuration Guide

System Current Status
System Current Status
Viewing System Current Status
The System Current Status window provides administration information such as the amount of time a unit
has been running and login statistics.
To view system current status
➧
1. From the Main Menu, select System Current Status and press Enter. The System Current Status
window is displayed. The window is view only.
System Current Status
Cumulative Run-Time Days: 0 Hours: 16
Current Run-Time Days: 0 00:38:38
Successful Logins 35
Unsuccessful Logins 1
Local User Logged In Supervisor
Telnet User Logged In None
FTP User Logged In None
2. Press
Cumulative Run-Time Number of hours the system has been running since it
was manufactured
Information is required for maintenance purposes
Current Run-Time Time duration that has passed since the unit was last
reset or power cycled
Successful Logins Number of times that the configuration menus have
been successfully accessed
Unsuccessful Logins Number of times that access to the configuration
menus has failed
Local User Logged In Access level of the user currently logged into the
configuration menus via the RS-232
Telnet User Logged In Access level of the user currently logged into the
configuration menus via a telnet session
FTP User Logged In Access level of the user currently logged into the host
FTP server
Esc to exit to the Main Menu.
APR 2001 Rev 03
41

Configuration
Network Configuration
Each AWE 120-58 unit in a system must have a valid Internet IP address and subnet mask to communicate via
TCP/IP. You will need to know this information to remotely manage units.
Viewing Internet IP Addresses and Subnet Mask
To view the Internet IP addresses and subnet mask
➧
1. From the Main Menu, select Network Configuration and press Enter. The Network
Configuration menu is displayed.
Network Configuration
Internet IP Address 192.168.1.100
New IP Address (Reboot Reqd) -> 192.168.1.100
Internet IP Subnet Mask 255.255.255.0
Default Gateway IP Address 0.0.0.0
SNMP NMS Trap IP Address 0.0.0.0
MAC Filter Entry Age Time Minutes (1-60) 5
Internet IP Address IP address of unit
New Internet IP Address
(Reboot Reqd)
Internet IP Subnet Mask Number used to determine if a node is part of LAN or
Default Gateway IP Address
(future)
SNMP NMS Trap IP Address
(future)
MAC Filter Entry Age Time
Minutes
2. Press
Esc to exit to the Main Menu.
New IP address of unit
Required when changing IP address
whether a transmission must be handled by router (the
subnet mask is logically ANDed with the IP address)
Address of the main entry point into the network
NMS (network management system) trap address
Collects alarms and events and passes them to the
network administrator
Number of minutes after which the MAC (Media Access
Control) filter entry will expire
42 AWE 120-58 Installation & Configuration Guide

Setting the Internet IP Address
To set the new Internet IP address
➧
Network Configuration
1. From the Main Menu, select IP Network Configuration and press
Configuration menu is displayed.
Network Configuration
Internet IP Address 192.168.1.100
New IP Address (Reboot Reqd) -> 192.168.1.100
Internet IP Subnet Mask 255.255.255.0
Default Gateway IP Address 0.0.0.0
SNMP NMS Trap IP Address 0.0.0.0
MAC Filter Entry Age Time Minutes (1-60) 5
2. Select New IP Address and press
3. Type the unique Internet IP address for the unit.
4. Press the Enter key. The new Internet IP address appears in the New IP Address (Reboot
Reqd)field, but the old address remains in the upper field.
5. To save the changes, reboot the unit or power the unit down and up.
6. Press
Esc to exit to the Main Menu.
Enter. The data field highlights.
Enter. The Network
Setting the IP Subnet Mask
To set the default IP subnet address
➧
1. From the Network Configuration menu, select Internet IP Subnet Mask and press Enter. The
data field highlights.
2. Type the Internet IP subnet mask for the unit.
3. Press
4. Press
Enter. The Internet IP subnet mask appears in the field and is assigned to the unit.
Esc to exit to the Main Menu.
APR 2001 Rev 03
43

Configuration
Setting the Default Gateway IP Address (future)
You can define the IP address of the system gateway. This address designates the main entry point into the
network and is usually in the same subnetwork as the unit IP address.
To set the default gateway IP address
➧
1. From the Network Configuration menu, select Network Configuration. The Network
Configuration menu is displayed.
2. Select Default Gateway IP Address and press
3. Type the default gateway IP address for the unit.
4. Press
5. Press
Enter. The default gateway IP address for the unit appears in the field.
Esc to exit to the Main Menu.
Enter. The data field highlights.
Setting the SNMP NMS Trap IP Address (future)
The SNMP (System Network Management Protocol) NMS (Network Management System) Trap IP address
identifies the IP address of the network manager. This address passes alarms or events from the unit to the
network manager. The network manager can define the types of traps or alarms that will be forwarded to the
IP address.
To set the SNMP NMS trap IP address
➧
1. From the Network Configuration menu, select SNMP NMS Trap IP Address and press Enter. The
data field highlights.
2. Type the SNMP NMS Trap IP address for the unit.
3. Press
4. Press
Enter. The SNMP NMS Trap IP address appears in the entry field and is applied to the unit.
Esc to exit to the Main Menu.
Setting the MAC Filter Entry Age Time Minutes
The MAC Filter Entry Age Time Minutes setting enables you to control the number of minutes after which the
MAC (Media Access Control) filter will expire. This feature enables you to set the MAC time period of a unit
to a value that is most compatible with the MAC time period of other devices on a network.
To set the MAC Filter minutes
➧
1. From the Network Configuration menu, select MAC Filter Entry Age Time Minutes and
press Enter. The data field highlights.
2. Type a value from 1–60 and press Enter. The number of minutes appears in the entry field and is applied
to the unit.
3. Press Esc to exit to the Main Menu.
44 AWE 120-58 Installation & Configuration Guide

IP Filter Configuration
IP Filter Configuration
Two different IP filters are available: a packet filter, and an address filter. The IP packet filter determines which
type of packets are allowed to pass through a unit. If the IP Packet Filter is OFF, the unit passes all packets. If
the IP Packet Filter is ON, the unit passes only IP and ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) packets.
IP address filters are actually tables that contain lists of IP addresses. If an address is listed in the table, the
unit will pass data packets to other IP addresses. If it is not listed, the unit will not pass data packets.
IP Address Filter Table
xxx.xx.xx.x
xxx.xx.xx.x
xxx.xx.xx.x
IP
Addresses
WireAir
Data packets pass only
if the IP address is
listed in the IP filter table
When IP address filtering is enabled, all IP packet are sorted according to the following conditions:
1. If the source IP address is contained in one of the IP address lists, IP packets coming from the wire will
be forwarded to the air. If not, IP packets are dropped.
2. If the destination IP address is contained in one of the IP address lists, IP packets coming from the air
will be forwarded to the wire. If not, IP packets are dropped.
Each IP address filter is defined by a range and a base value. IP address filtering improves system security and
helps manage data throughput.
Viewing IP Filter Configuration
To view current IP filter configuration
➧
1. From the Main Menu, select IP Filter Configuration and press Enter. The IP Filter
Configuration menu is displayed.
APR 2001 Rev 03
IP Filter Configuration
IP Packet Filtering -> off
IP Address Filtering off
Filter 1 Range (0-255) 0
Filter 1 Base Address 0.0.0.0
Filter 2 Range (0-255) 0
Filter 2 Base Address 0.0.0.0
Filter 3 Range (0-255) 0
Filter 3 Base Address 0.0.0.0
Filter 4 Range (0-255) 0
Filter 4 Base Address 0.0.0.0
Filter 5 Range (0-255) 0
Filter 5 Base Address 0.0.0.0
45

Configuration
IP Packet
off (disabled) All packets are passed
Filtering
on (enabled) Only IP (Internet Protocol) packets and ARP packets can pass
IP Address
off (disabled) Packets from all IP addresses pass
Filtering
on (enabled) Only packets whose IP addresses listed in at least one IP filter
pass. Up to five IP filters are available; each filter lists up to 255
IP addresses
Filter n Range n = 0–5 Defines how many contiguous IP addresses are in the filter’s list
of addresses
Filter n Base
Address
n = lowest IP
Address
Lowest numbered address on the filter’s list of IP addresses
Example: To configure a unit to pass only IP data packets from the IP addresses in the list below,
192.168.2.10
192.168.2.11
192.168.2.12
192.168.2.13
194.120.3.51
194.120.3.52
194.120.3.254
194.120.3.255
194.120.4.0
194.120.4.1
you would configure the unit as follows:
IP Packet Filtering = on
IP Address Filtering = on
Filter 1 Range (0 - 255) = 4
Filter 1 Base Address = 192.168.2.10
Filter 2 Range (0 - 255) = 2
Filter 2 Base Address = 194.120.3.51
Filter 3 Range (0 - 255) = 4
Filter 3 Base Address = 194.120.3.254
46 AWE 120-58 Installation & Configuration Guide

IP Filter Configuration
Enabling IP Packet Filtering
IP Packet filtering should initially be set to off so you can start from a known state and observe changes that
result from using the IP packet filter.
To enable IP packet filtering
➧
1. From the IP Filter Configuration menu, select IP Packet Filtering and press
highlights.
IP Filter Configuration
IP Packet Filtering -> off
IP Address Filtering off
Filter 1 Range (0-255) 0
Filter 1 Base Address 0.0.0.0
Filter 2 Range (0-255) 0
Filter 2 Base Address 0.0.0.0
Filter 3 Range (0-255) 0
Filter 3 Base Address 0.0.0.0
Filter 4 Range (0-255) 0
Filter 4 Base Address 0.0.0.0
Filter 5 Range (0-255) 0
Filter 5 Base Address 0.0.0.0
2. Scroll to on.
3. Press
4. Press
Enter to make the change.
Esc to exit to the Main Menu.
Enter. The data field
Enabling IP Address Filtering
To enable IP address filtering
➧
1. From the IP Filter Configuration menu, select IP Address Filtering and press Enter. The data
field highlights.
2. Scroll to on and press
3. Press
APR 2001 Rev 03
Esc to exit to the Main Menu.
Enter.
47

Configuration
Setting IP Address Filter Range
To set IP address filter range
➧
1. From the IP Filter Configuration menu, select Filter 1 Range (0 - 255) and press
data field highlights.
2. Type in the number of contiguous addresses in the filter list (0 - 255) and press
3. Press
Esc to exit to the Main Menu.
Enter.
Setting the IP Filter Base Address
To set IP filter base address
➧
1. From the IP Filter Configuration menu, select Filter 1 Base Address and press
field highlights.
2. Type the IP address and press
3. Press
Esc to exit to the Main Menu.
Enter. The data field highlights.
Enter. The data
Enter. The
48 AWE 120-58 Installation & Configuration Guide

RF Station Configuration
RF Station Configuration
The RF Station Configuration menu enables you to choose the operating mode, run some tests and optimize
the RF link. Four tests can be run from this menu: link monitor test, transmit test, receive test and RSSI test.
You can optimize a link by setting the maximum remote distance to a remote and by controlling the rate of
data throughput (throttling). You can also block a unit so that it cannot pass any data.
Viewing Current RF Station Configuration
To view current RF station configuration
➧
1. From the Main Menu, select RF Station Configuration and press Enter. The RF Station
Configuration menu is displayed.
RF Station Configuration
Operating Mode -> Normal Mode
RF Transmit Status unblocked
Link Monitor Period (0=OFF, 1-10000) 0
Test Mode Timer Minutes (1-1000) 20
Base Station Only Parameters
Maximum Remote Distance 5 Km
Link Monitor Remote Station Rank 1
Remote Station Only Parameters
Throttle Enable off
Throttle Level (1-50) 1
Operating Mode Four modes are available: Normal Mode, Receive Test,
Transmit Test, and RSSI Test
RF Transmit Status Determines if data transmissions through the unit will be
blocked or passed
Link Monitor Period Period determines the amount of test data that is used to
test the link. The smaller the number, the larger the
amount of test data and test data overhead. A non-zero
value starts the link monitor test
Test Mode Timer
Minutes
Maximum Remote
Distance
Maximum time in minutes that a unit will be allowed to
stay in test mode
Distance value compensates for polling delay due to large
distances
Link Monitor Remote
Station Rank
APR 2001 Rev 03
Rank (or ID number) of the remote that you want to test
49

Configuration
Throttle Enable Turns throttling (data throughput control) on or off
Throttle Level Determines the data rate of a remote unit. When
2. Press Esc to exit to the Main Menu.
throttling is enabled, the data rate passed is equal to the
throttling level times 128 kbps
50 AWE 120-58 Installation & Configuration Guide

Setting the Operating Mode
Four modes are available: Normal Mode, Receive Test, Transmit Test, and RSSI Test.
Normal Mode Normal operating mode of a unit. Unit transmits and receives data in
both directions across the RF link.
Link Monitor test is run with the unit set to Normal mode. (You can
view the link statistics with Link Monitor Display.)
RF Station Configuration
Receive
Test
Receives test data only. Processes expected packet data and displays
statistics on RS-232 monitor. Use this mode to test a unit’s ability to
receive data.
Transmit
Test
Transmits test data only. Sends known packet data to the receiving unit.
Use this mode to test a unit’s abilty to transmit data.
RSSI Test RSSI (Received Signal Strength Indicator) test–indicates signal strength.
Unit receives known data packets and displays fade margin data on the
Air LED. Use this mode to get a quick visual indication of the signal
strength. See Performing the RSSI Test, page 59 for more information.
To set the operating mode
➧
1. From the Main Menu, select RF Station Configuration and press Enter. The RF Station
Configuration menu is displayed.
RF Station Configuration
Operating Mode -> Normal Mode
RF Transmit Status unblocked
Link Monitor Period (0=OFF, 1-10000) 0
Test Mode Timer Minutes (1-1000) 20
Base Station Only Parameters
Maximum Remote Distance 5 Km
Link Monitor Remote Station Rank 1
Remote Station Only Parameters
Throttle Enable off
Throttle Level (1-50) 1
2. Select Operating Mode and press
Enter. The data field highlights.
3. Press the arrow keys to select the desired mode: Normal mode, Transmit mode, Receive mode or RSSI
mode.
4. Press
Enter. The screen clears, and the Mode LED on the unit is ON. The color of the Mode LED
indicates the current mode: Normal Mode = off, Transmit Test = red, Receive Test = green and
RSSI Test = orange.
APR 2001 Rev 03
51

Configuration
5. To exit a mode, briefly disconnect the power or press and hold the Mode button on the rear panel of the
unit. The Mode LED goes off (normal mode) and the Login menu is displayed.
Note: The operating mode can also be set with the Mode button on the back of the AWE. See Setting
Operating Mode with the Mode Button, page 102 for more information.
General Equipment Setup for Performing RF Tests
The general equipment setup is shown below. The specific setup depends on the test you want to run.
• To perform the Normal Mode (Link Monitor) test you need to connect a PC to either the base
station or a remote unit.
• To perform the Transmit Test or Receive Test you need at least one base station with PC, a remote
station with PC, and an RF link between units. See Establishing a Basic RF Link, page 21 for instructions
about establishing an RF link.
• To perform the RSSI test you need a PC for the unit that will transmit. The receiving unit does not
require a PC. You can also run this test with the Mode button.
General Equipment Setup
Base Unit
Air
Mode Wire Power
RS-232
Serial
Cable
2 m
minimum
Remote Unit
Air
Mode Wire Power
To Serial PortTo Serial Port
RS-232
Serial
Cable
COM
Por t
PC PC
COM
Por t
Before you run any tests, you should set the number of test minutes, as descibed below in Setting Test Mode
Timer Minutes, page 53.
52 AWE 120-58 Installation & Configuration Guide

RF Station Configuration
Setting Test Mode Timer Minutes
Before you run any of these tests, you should set the maximum time, in minutes, that a unit will be allowed to
stay in test mode. When this time period expires, the AWE unit performs an automatic software reboot and
returns to Normal mode. (Test mode timer minutes setting applies only to Transmit Test, Receive Test, and
RSSI Test modes.)
Note: The test mode timer minutes can be changed only with this menu. This time period does not apply to
Normal mode or the Link Monitor test. See Setting Operating Mode with the Mode Button, page 102.
To set test mode timer minutes
➧
1. From the Main Menu, select RF Station Configuration and press
Enter. The RF Station
Configuration menu is displayed.
RF Station Configuration
Operating Mode Normal Mode
RF Transmit Status unblocked
Link Monitor Period (0=OFF, 1-10000) 0
Test Mode Timer Minutes (1-1000) -> 20
Base Station Only Parameters
Maximum Remote Distance 5 Km
Link Monitor Remote Station Rank 1
Remote Station Only Parameters
Throttle Enable off
Throttle Level (1-50) 1
2. Select Test Mode Timer Minutes and press Enter. The data field highlights.
3. Type the desired time in minutes (1-1000). (20 minutes is a suggested starting value.)
4. Press
5. Press
Enter.
Esc to exit to the Main Menu.
APR 2001 Rev 03
53

Configuration
Performing Link Monitor Test (Normal Mode)
The link monitor test can be run from either a base station or a remote unit that is set to Normal Mode. The
test operates in parallel with the message stream, so it consumes some of the link’s total data capacity. You
can control the ratio of test data to message data (and thereby control the amount of test data overhead) by
setting the link monitor period. See Setting the Link Monitor Period, page 61 for more information.
Note: Link monitor test stays in effect even if you power cycle or reboot units, so you must turn it off using
the Link Monitor Period (0 = OFF) setting.
To perform Link Monitor test from a base station
➧
1. Connect the test PC to the Serial port of the base station. See General Equipment Setup for Performing RF
Tests, page 52.
2. Log in to the unit and go to the Main Menu.
3. Select RF Station Configuration and press
displayed.
RF Station Configuration
Enter. The RF Station Configuration menu is
Operating Mode -> Normal Mode
RF Transmit Status unblocked
Link Monitor Period (0=OFF, 1-10000) 0
Test Mode Timer Minutes (1-1000) 20
Base Station Only Parameters
Maximum Remote Distance 5 Km
Link Monitor Remote Station Rank 1
Remote Station Only Parameters
Throttle Enable off
Throttle Level (1-50) 1
4. Select Operating Mode and press
5. Press the arrow keys to select Normal mode and press
6. Select RF Transmit Status and press
7. Press the arrow keys to select unblocked and press
8. Select Link Monitor Remote Station Rank and press
9. Type the rank of the remote unit that you want to link to and press
Enter. The data field highlights.
Enter.
Enter. The data field highlights.
Enter.
Enter. The data field highlights.
Enter. (The rank is the identification
number of the remote unit. The rank of a remote can be any number from 1 – 1000. See Setting the
Station Rank, page 69.)
10. Select Link Monitor Period and press
11. Type a link monitor period (1) and press
Enter. The data field highlights.
Enter. Link Monitor starts as soon as a non-zero value is
entered in the field. (A setting of 1 means that 50% of all data is test data.)
54 AWE 120-58 Installation & Configuration Guide

RF Station Configuration
12. View the link statistics. From the Main Menu select Link Monitor Display and press Enter. The RF
Link Monitor Statistics window is displayed.
RF Link Monitor Statistics
Link Monitor Rank 1
Base to Remote BER 0.0E+00
Remote to Base BER 0.0E+00
Missed Packet Count 0
Base to Remote Env Power 27
Base to Remote Corr Power 28
Remote to Base Env Power 29
Remote to Base Corr Power 30
13. Check for BER = 0.0E+00 and Corr Power between 15 – 50 dB. If the Corr Power is <15 dB the
receive signal is probably too weak. If the power is >55 dB the receiving unit is probably saturated. See
Viewing Link Monitor Statistics, page 101 for more information about Link Monitor Statistics.
If you have problems, ensure that the unit is configured to its basic default settings (see Restoring Factory
Configurations, page 99) and reconfigure the unit, or contact Wi-LAN Technical Assistance Center.
14. When finished viewing link monitor statistics, disable Link Monitor to remove the test overhead data
from the RF link. Select RF Station Configuration from the Main Menu and press
Enter. The RF
Station Configuration menu is displayed.
15. Select Link Monitor Period and press
16. Type 0 in the field and press
17. Press
Esc to exit.
Enter. The link monitor test ends.
Enter. The field is highlighted.
To perform Link Monitor test from a remote unit
➧
1. Connect the test PC to the Serial port of the remote unit. See General Equipment Setup for Performing RF
Tests, page 52.
2. Log in to the unit and go to the Main Menu.
APR 2001 Rev 03
55

Configuration
3. Select RF Station Configuration and press Enter. The RF Station Configuration menu is
displayed.
RF Station Configuration
Operating Mode -> Normal Mode
RF Transmit Status unblocked
Link Monitor Period (0=OFF, 1-10000) 0
Test Mode Timer Minutes (1-1000) 20
Base Station Only Parameters
Maximum Remote Distance 5 Km
Link Monitor Remote Station Rank 1
Remote Station Only Parameters
Throttle Enable off
Throttle Level (1-50) 1
4. Select Operating Mode and press
5. Press the arrow keys to select Normal mode and press
6. Select RF Transmit Status and press
7. Press the arrow keys to select unblocked and press
8. Select Link Monitor Remote Station Rank and press
Enter. The data field highlights.
Enter.
Enter. The data field highlights.
Enter.
Enter. The data field highlights and the
remote automatically connects with the base station.
9. Select Link Monitor Period and press
10. Type a link monitor period (1) and press
Enter. The data field highlights.
Enter. Link Monitor starts as soon as a non-zero value is
entered in the field. (A setting of 1 means that 50% of all data is test data.)
11. View the link statistics. From the Main Menu select Link Monitor Display and press
Link Monitor Statistics window is displayed.
RF Link Monitor Statistics
Link Monitor Rank 1
Base to Remote BER 0.0E+00
Remote to Base BER 0.0E+00
Missed Packet Count 0
Base to Remote Env Power 27
Base to Remote Corr Power 28
Remote to Base Env Power 29
Remote to Base Corr Power 30
Enter. The RF
12. Check for BER = 0.0E+00 and Corr Power between 15 – 50 dB. If the Corr Power is <15 dB the
receive signal is probably too weak. If the power is >55 dB the receiving unit is probably saturated. See
Viewing Link Monitor Statistics, page 101 for more information about Link Monitor Statistics.
56 AWE 120-58 Installation & Configuration Guide

RF Station Configuration
If you have problems, ensure that the unit is configured to its basic default settings (see Restoring Factory
Configurations, page 99) and reconfigure the unit or contact Wi-LAN customer support.
13. When you finish viewing link monitor statistics, disable Link Monitor to remove the test overhead data
from the RF link. Select RF Station Configuration from the Main Menu and press
Station Configuration menu is displayed.
14. Select Link Monitor Period and press
15. Type 0 in the field and press
16. Press
Note: When testing, it is possible to run the link monitor in both directions over one link by enabling link
Esc to exit.
monitor on the base and the remote at the same time. This situation should be avoided during normal
operation because it causes needless overhead.
Enter. The link monitor test ends.
Enter. The field is highlighted.
Enter. The RF
Performing Transmit and Receive Tests
When performing transmit or receive tests, one unit is set up to operate in Transmit Test mode and the other
unit is set up to operate in Receive Test mode. The transmitting unit sends packets of known data to the
receiving unit. The receiving unit analyzes the data and displays link statistics on the PC connected to the
Serial port.
To set up the transmit unit
➧
1. Connect a PC to the Serial port of the unit.
2. Log in to the unit and go to the Main Menu.
3. From the Main Menu, select RF Station Configuration and press
Configuration menu is displayed.
4. Select Operating Mode and press
5. Select Transmit Test and press
transmitting.
To set up the receive unit
➧
1. Connect a PC to the Serial port of the unit.
2. Log in to the unit and go to the Main Menu.
3. From the Main Menu, select RF Station Configuration and press
Configuration menu is displayed.
4. Select Operating Mode and press
5. Select Receive Test and press
receiving. The link statistics are displayed on the receiving unit. Alternating lines of statistics across the
screen indicate that data is incoming. See the following example.
Enter. The field highlights.
Enter. The Mode LED on the unit is red, indicating that the unit is
Enter. The field highlights.
Enter. The Mode LED on the turns green, indicating that the unit is
Enter. The RF Station
Enter. The RF Station
APR 2001 Rev 03
57

Configuration
Link Statistics Example
Previous
Sample
Current
Sample
- BER = 0.0E+00, MPC = 0, EnvP = 63, CorrP = 63
| BER = 0.0E+00, MPC = 0, EnvP = 63, CorrP = 63
BER Bit Error Rate
MPC Missed Packet Count
EnvP Envelope Power—the power of the received signal inlcuding noise,
CorrP Correlation Power—the power of the received signal, excluding noise,
Bit Error Rate
measured in dB (0–63)
measured in dB (0–63)
Missed
Packet
Count
Envelope Power
Correlation Power
6. Check for BER = 0.0E+00 and CorrP between 15 – 50 dB. If the CorrP is <15 dB the receive signal is
probably too weak. If the power is >55 dB the receiving unit is probably saturated.
If you have problems ensure that the unit is configured to its basic default settings (see Restoring Factory
Configurations, page 99) and reconfigure the unit, or contact Wi-LAN customer support.
7. To end the test, briefly disconnect power from the unit or press and hold the Mode button to return to
Normal mode.
58 AWE 120-58 Installation & Configuration Guide

RF Station Configuration
Performing the RSSI Test
RSSI mode is used to measure the signal strength (fade margin) of a system. When running the test between
two units, the transmit unit is set to Transmit Test mode (using either the RF Station Configuration menu or
the Mode button). The receive unit is put into RSSI Test mode (using either the RF Station Configuration
menu or the Mode button). The Air LED on the receiving unit indicates the fade margin.
To run the RSSI test
➧
1. Put the receiving unit into RSSI mode. See Setting the Operating Mode, page 51 or Setting Operating Mode
with the Mode Button, page 102. The Mode LED is orange when the unit is in RSSI mode.
2. Put the transmiting unit into Transmit Test mode. The Mode LED on the unit is red, indicating that
the unit is in transmit mode. See Setting the Operating Mode, page 51 or Setting Operating Mode with the
Mode Button, page 102.
3. Observe the color of the Air LED on the receiving unit. The Air LED is green when the signal strength is
acceptable.
Air LED Color Signal Strength
Green Reliable signal—greater than 15 dB fade margin
Orange Marginal signal—between 11 and 15 dB fade margin
Red Poor signal—less than 10 dB fade margin
Blank No signal at all
4. To exit from the test, briefly disconnect power from the unit or press and hold the Mode button to
return to Normal mode.
APR 2001 Rev 03
59

Configuration
Setting the RF Transmit Status
This setting can block a unit (or link) from carrying data traffic. It is used to disable units and to discontinue
service to customers, if necessary.
To set RF transmit status
➧
1. From the Main Menu, select RF Station Configuration and press
Configuration menu is displayed.
RF Station Configuration
Operating Mode Normal Mode
RF Transmit Status -> unblocked
Link Monitor Period (0=OFF, 1-10000) 0
Test Mode Timer Minutes (1-1000) 20
Base Station Only Parameters
Maximum Remote Distance 5 Km
Link Monitor Remote Station Rank 1
Remote Station Only Parameters
Throttle Enable off
Throttle Level (1-50) 1
2. Select RF Transmit Status and press
Enter. The data field highlights.
3. Select a setting.
Enter. The RF Station
unblocked Unit passes data in both directions (default setting)
blocked Does not pass data in either direction
4. Press
5. Press
Enter.
Esc to exit to the Main Menu.
60 AWE 120-58 Installation & Configuration Guide

RF Station Configuration
Setting the Link Monitor Period
The Link Monitor Period determines the ratio of test data to message data that is sent when you run the link
monitor test. The higher the period number, the smaller the ratio of test data to message data. The following
diagram shows the ratios of test data to link data
Link Monitor Period Settings
Period Setting
Packet Ratio
(Test/Link)
1
2
3
Test Msg
Test Msg Msg
Test Msg Msg Msg
Test = test data
Msg = message data
50% (1/2)
33.3% (1/3)
25% (1/4)
See Performing Link Monitor Test (Normal Mode), page 54 for information about running the Link Monitor test.
To set Link Monitor Period
➧
1. From the Main Menu, select RF Station Configuration and press
Enter. The RF Station
Configuration menu is displayed.
RF Station Configuration
Operating Mode Normal Mode
RF Transmit Status unblocked
Link Monitor Period (0=OFF, 1-10000) -> 1
Test Mode Timer Minutes (1-1000) 20
Base Station Only Parameters
Maximum Remote Distance 5 Km
Link Monitor Remote Station Rank 1
Remote Station Only Parameters
Throttle Enable off
Throttle Level (1-50) 1
2. Select Link Monitor Period and press
3. Type the period setting (0=OFF, 1-10000)
4. Press
5. Press
APR 2001 Rev 03
Enter. The test starts as soon as a non-zero value is entered.
Esc to exit to the Main Menu.
Enter. The data field highlights.
61

Configuration
Setting Maximum Remote Distance (Base Station Only)
The Maximum Remote Distance setting is used to optimize dynamic polling by compensating for time delays
caused by long distances between the sending unit and the receiving unit.
IMPORTANT
In the base unit, the Maximum Remote Distance should always be set to the distance
between the base and the farthest remote.
To set the maximum remote distance
➧
1. From the Main Menu, select RF Station Configuration and press Enter. The RF Station
Configuration menu is displayed.
RF Station Configuration
Operating Mode Normal Mode
RF Transmit Status unblocked
Link Monitor Period (0=OFF, 1-10000) 0
Test Mode Timer (1-1000)mins 20
Base Station Only Parameters
Maximum Remote Distance -> 5 Km
Link Monitor Remote Station Rank 1
Remote Station Only Parameters
Throttle Enable off
Throttle Level (1-50) 1
2. Select Maximum Remote Distance and press
Enter. The data field highlights.
3. Press the arrow keys to set the distance of the furthest remote unit (5 km increments are used).
4. Press
5. Press
Enter.
Esc to exit to the Main Menu.
62 AWE 120-58 Installation & Configuration Guide

RF Station Configuration
Setting Link Monitor Remote Station Rank
When you run the Link Monitor Test from a base station, you need to specify the rank (ID number) of the
remote that you want to test. When you run the link monitor test from a remote, there is only one base, so
the rank number does not need to be entered.
To set the link monitor remote station rank
➧
1. From the Main Menu, select RF Station Configuration and press
Configuration menu is displayed.
RF Station Configuration
Operating Mode Normal Mode
RF Transmit Status unblocked
Link Monitor Period (0-OFF, 1-10000) 0
Test Mode Timer Minutes (1-1000) 20
Base Station Only Parameters
Maximum Remote Distance 5 Km
Link Monitor Remote Station Rank -> 1
Remote Station Only Parameters
Throttle Enable off
Throttle Level (1-50) 1
2. Select Link Monitor Remote Station Rank and press
Enter. The data field highlights.
3. Type the station rank (ID#) of the remote to test.
4. Press
5. Press
Enter.
Esc to exit to the Main Menu.
Enter. The RF Station
APR 2001 Rev 03
63

Configuration
Adjusting Throttling (Remote Station Only)
Throttling enables you to control the rate that data passes though a remote, so data throughput can be
adjusted to make the data rate compatible with the rest of the system. Throttling restricts the flow of data
from air to wire or from wire to air. When throttling is enabled, the amount of data passed is equal to the
throttling level times 128 kbps, to a maximum of 6.4 Mbps. Throttling applies to both down link and up link
traffic, so a throttle level of 1 means the unit will pass 128 kbps in each direction. A throttle level of 50 means
that 50 x 128 kbps will be passed. When throttling is disabled, the unit uses the maximum available bandwidth.
The default setting is to disable throttling.
To enable throttling
➧
1. From the Main Menu, select RF Station Configuration and press
Configuration menu is displayed.
RF Station Configuration
Operating Mode Normal Mode
RF Transmit Status unblocked
Link Monitor Period (0=OFF, 1-10000) 0
Test Mode Timer (1-1000)mins 20
Base Station Only Parameters
Maximum Remote Distance 5 Km
Link Monitor Remote Station Rank 1
Remote Station Only Parameters
Throttle Enable -> off
Throttle Level (1-50) 1
2. Select Throttle Enable and press
3. Scroll to select on or off, and press
4. Press
Esc to exit to the Main Menu.
Enter. The data field highlights.
Enter.
Enter. The RF Station
To set the throttle level
➧
1. Set Throttle Enable to on, then select Throttle Level from the RF Conguration menu and press
Enter. The data field highlights.
2. Type a value from 1–50 to select the data throughput rate (where 1 = 1 x 128 kbps, 50 = 50 x 128 kbps)
and press
3. Press
Enter.
Esc to exit to the Main Menu.
64 AWE 120-58 Installation & Configuration Guide

Radio Module Configuration
Radio Module Configuration
The Radio Module Configuration menu is used to change several key parameters, including station type,
station rank, and security passwords. Because these settings can affect service, they are changed in three
progessive stages: new, current, and flash. (New and current are for temporary storage, while flash is for
long-term storage.) The general procedure for changing settings with the Radio Module Configuration menu
follows.
1. View the current Radio Module Configuration menu. See Viewing the Radio Module Configuration, page 65.
2. Select Config Test Minutes. To begin, enter a time of 15–20 minutes. See Setting Config Test
Minutes, page 67.
3. Select a parameter and, if necessary, change the value in the "New" column.
4. After making changes, select Reboot New RF Configuration and press Enter. The unit reboots
and the "New" settings become the "Current" settings of the unit. See Rebooting and Saving RF Module
Configurations, page 84.
5. If the unit operates as expected, you can save the current settings to "Flash". See Rebooting and Saving
RF Module Configurations, page 84.
If current settings do not operate as expected, do not save them to "Flash". Either change the current
settings or wait for the Config Test Minutes time period to expire. At expiry, the unit will
automatically reboot and revert to the last-saved flash memory settings. See Rebooting and Saving RF
Module Configurations, page 84.
Viewing the Radio Module Configuration
To view the current radio module configuration
➧
1. From the Main Menu, select Radio Module Configuration and press
Configuration menu is displayed.
Radio Module Configuration
New Current Flash
Station Type -> Remote Unit Remote Unit Remote Unit
Station Rank (1-1000) 1 1 1
Center Frequency (57410-58338) 5.7874 GHz 5.7874 GHz 5.7874 GHz
Security Password 1 (Hex) 1 1 1
Security Password 2 (Hex) 10 10 10
Security Password 3 (Hex) 100 100 100
Security Password 4 (Hex) 1000 1000 1000
Security Password 5 (Hex) 10000 10000 10000
Scrambling Code (Hex) 0 0 0
Acquisition Code (0-15) 1 1 1
Config Test Minutes (1-120) 30 30 30
Tx Power Level Adjust 0 dB 0 dB 0 dB
Base Station Only Parameters
Repeater Mode off off off
System Symmetry Type Asymmetric Asymmetric Asymmetric
Dynamic Polling Level (1-100) 1 1 1
Remote Station Only Parameters
Remote Unit RF Group (0-63) 0 0 0
Enter. The Radio Module
Reboot New RF configuration Press Enter to Execute
Save Current Config to Flash Press Enter to Execute
APR 2001 Rev 03
65

Configuration
Station Type Defines unit as either a base station or a remote station
Station Rank For a base station, the number of remotes that the base polls
For a remote, the polling ID # of the remote
Center Frequency Defines the channel the unit uses to transmit and receive
Security Password n Password(s) for the unit
Scrambling Code Code used to scramble messages
Acquisition Code Code used to reduce system-induced interferance in a multi-
sector system
Config Test Minutes Amount of time before unit returns to its pre-configuration state
Tx Power Level Adjust Reduces the power below maximum Tx power by the specified
amount in dB.
Repeater Mode Sets up a base station to pass data to and from remotes rather
than function as a control unit
System Symmetry Type Defines the amount of priority the base unit has when polling the
remotes
Dynamic Polling Level Number of polling cycles that inactive remote units are ignored by
the base station
Remote Unit RF Group Identifies the goup number of the remote unit
Remote units with same RF group number can communicate
directly with each other
Reboot new RF
Reboots unit to save New settings as Current settings
configuration
Save Current Config
Stores current settings in flash memory
to Flash
2. Press Esc to exit to the Main Menu.
66 AWE 120-58 Installation & Configuration Guide

Radio Module Configuration
Setting Config Test Minutes
When changing Radio Module Configuration settings, you may enter settings that cause a unit or system to
not function as expected. If this happens, you can return to the last-saved settings if you first set the Config Test
Minutes test period. When this test period expires, the unit automatically reboots and returns to its last-saved
flash memory settings. The time period can be fixed from 1 to 120 minutes.
Tip: To begin, enter a time period of 30 minutes. If the time period is too short, you will not have enough
time to make configuration changes and save them to flash ROM. If the time period is long, you will have to
wait a long time before the unit automatically reboots and restores the settings to the original flash ROM
state.
To set the config test timeout period
➧
1. From the Main Menu, select Radio Module Configuration and press
Configuration menu is displayed.
Radio Module Configuration
New Current Flash
Station Type Remote Unit Remote Unit Remote Unit
Station Rank (1-1000) 1 1 1
Center Frequency (57410-58338) 5.7874 GHz 5.7874 GHz 5.7874 GHz
Security Password 1 (Hex) 1 1 1
Security Password 2 (Hex) 10 10 10
Security Password 3 (Hex) 100 100 100
Security Password 4 (Hex) 1000 1000 1000
Security Password 5 (Hex) 10000 10000 10000
Scrambling Code (Hex) 0 0 0
Acquisition Code (0-15) 0 0 0
Config Test Minutes (1-120) -> 30 30 30
Tx Power Level Adjust 0 dB 0 dB 0 dB
Base Station Only Parameters
Repeater Mode off off off
System Symmetry Type Asymmetric Asymmetric Asymmetric
Dynamic Polling Level (1-100) 1 1 1
Remote Station Only Parameters
Remote Unit RF Group (0-63) 0 0 0
Reboot New RF configuration Press Enter to Execute
Save Current Config to Flash Press Enter to Execute
Enter. The Radio Module
2. Select Config Test Minutes and press Enter. The data field highlights.
3. Type the number of minutes (1-120) and press
4. Select Reboot New RF Configuration and press
Enter. The number of minutes is stored in the New state.
Enter. The unit reboots and the AWE 120-58
Login menu is displayed. The unit will now use the current settings to operate, for the length of time
specified by Config Test Minutes.
5. To save the current setting(s) to flash memory, log in, go to the Main Menu, and select Radio Module
Configuration, Save Current Config to Flash. See Rebooting and Saving RF Module
Configurations, page 84.
6. Press
APR 2001 Rev 03
Esc to exit to the Main Menu.
67

Configuration
Setting the Station Type
Each unit must be set up as either a base station or a remote station. In a given system there is only one base
station, but there can be numerous remote stations. (A base station can also be set up as a repeater base.)
You define the unit as a base station or remote unit by setting the Station Type.
To set the station type
➧
1. From the Main Menu, select Radio Module Configuration and press
Configuration menu is displayed.
Radio Module Configuration
New Current Flash
Station Type -> Remote Unit Remote Unit Remote Unit
Station Rank (1-1000) 1 1 1
Center Frequency (57410-58338) 5.7874 GHz 5.7874 GHz 5.7874 GHz
Security Password 1 (Hex) 1 1 1
Security Password 2 (Hex) 10 10 10
Security Password 3 (Hex) 100 100 100
Security Password 4 (Hex) 1000 1000 1000
Security Password 5 (Hex) 10000 10000 10000
Scrambling Code (Hex) 0 0 0
Acquisition Code (0-15) 1 1 1
Config Test Minutes (1-120) 30 30 30
Tx Power Level Adjust 0 dB 0 dB 0 dB
Base Station Only Parameters
Repeater Mode off off off
System Symmetry Type Asymmetric Asymmetric Asymmetric
Dynamic Polling Level (1-100) 1 1 1
Remote Station Only Parameters
Remote Unit RF Group (0-63) 0 0 0
Reboot New RF configuration Press Enter to Execute
Save Current Config to Flash Press Enter to Execute
Enter. The Radio Module
2. Select Station Type and press
Enter. The data field highlights.
3. Scroll to select the Station Type (base station or remote unit).
4. Press
5. Select Reboot New RF Configuration and press
Enter. The new setting is displayed in the "New" column.
Enter. The unit reboots and the AWE 120-58
Login menu is displayed. The unit now runs using the "Current" station type for the amount of time
specified by Config Test Minutes.
6. To save the current setting(s) to flash memory, log in, go to the Main Menu, and select Radio Module
Configuration, Save Current Config to Flash. See Rebooting and Saving RF Module
Configurations, page 84.
7. Press
Esc to exit to the Main Menu.
68 AWE 120-58 Installation & Configuration Guide

Radio Module Configuration
Setting the Station Rank
Station Rank is defined two different ways, which depend on the station type: For a base station, rank is the
total number of remotes that a base will poll. For a remote unit, rank is a unique polling ID number that identifies
a remote to a base station.
When it polls remotes, the base station begins polling at the remote with rank number 1, then proceeds to
the remote with rank number 2, then goes to the remote with rank number 3, and so on. The base continues
polling remotes until it reaches the remote with the highest rank number. The base then repeats the polling
cycle.
Note: Dynamic polling gives you some control over the polling process. See Setting Dynamic Polling Level (Base
Station Only), page 80.
To set the station rank
➧
1. From the Main Menu, select Radio Module Configuration and press
Configuration menu is displayed.
Radio Module Configuration
New Current Flash
Station Type Remote Unit Remote Unit Remote Unit
Station Rank (1-1000) -> 1 1 1
Center Frequency (57410-58338) 5.7874 GHz 5.7874 GHz 5.7874 GHz
Security Password 1 (Hex) 1 1 1
Security Password 2 (Hex) 10 10 10
Security Password 3 (Hex) 100 100 100
Security Password 4 (Hex) 1000 1000 1000
Security Password 5 (Hex) 10000 10000 10000
Scrambling Code (Hex) 0 0 0
Acquisition Code (0-15) 1 1 1
Config Test Minutes (1-120) 30 30 30
Tx Power Level Adjust 0 dB 0 dB 0 dB
Base Station Only Parameters
Repeater Mode off off off
System Symmetry Type Asymmetric Asymmetric Asymmetric
Dynamic Polling Level (1-100) 1 1 1
Remote Station Only Parameters
Remote Unit RF Group (0-63) 0 0 0
Reboot New RF configuration Press Enter to Execute
Save Current Config to Flash Press Enter to Execute
Enter. The Radio Module
2. Select Station Rank (1-1000).
3. Type the rank (a number from 1–1000) of the station.
4. Press
5. Select Reboot New RF Configuration and press
Enter. The new setting is displayed in the "New" column.
Enter. The unit reboots and the AWE 120-58
Login menu is displayed. The unit now runs using the "Current" rank for the amount of time specified
by Config Test Minutes.
6. To save the current setting(s) to flash memory, log in, go to the Main Menu, and select Radio Module
Configuration, Save Current Config to Flash. See Rebooting and Saving RF Module
Configurations, page 84.
7. Press
APR 2001 Rev 03
Esc to exit to the Main Menu.
69

Configuration
Setting the Center Frequency
A center frequency defines the RF channel that a unit uses to transmit and receive. The AWE 120-58 can
operate at a center frequency ranging from 5.7410 GHz to 5.8338 GHz, in 400 kHz steps. All units in the
same system must be set to the same center frequency.
If you plan to co-locate AWE 120-58 systems, you will need to use more than one center frequency.You will
choose center frequencies that are well-separated from each other. The following section Choosing Center
Frequencies explains how to choose center frequencies.
Choosing Center Frequencies
A simplified diagram of the spectrum around a center frequency (when transmitting) is shown below.
Center Frequency Spectrum
66 MHz
16 MHz16 MHz 33 MHz
Data
Region
SideSide
LobeLobe
5.7410 GHz 5.8338 GHz
Center Frequency
Only the 33 MHz data region of the 66 MHz spectrum contains data; the remaining 16 MHz side lobes
contain no useful information (frequency ranges given are approximate).The side lobes operate at a much
lower power than the data region.
If only one center frequency is required, simply choose a frequency between 5.7410 GHz and 5.8338 GHz (in
400 kHz increments). You will probably choose a center frequency where the 5.8 GHz ISM band is cleanest,
meaning a frequency where no other people are transmitting.
If two or more AWE 120-58 systems must be co-located, center frequencies are selected that have as much
separation as possible so different systems do not interfere with each other. It is very important that the 33
MHz data regions of adjacent systems do not overlap. System performance is also better if the side lobes of
one system do not overlap the data region of another system. It does not matter if the side-lobes of two
systems overlap.
70 AWE 120-58 Installation & Configuration Guide

Radio Module Configuration
Some examples of center frequency separation and performance ratings are provided below.
Excellent
Fair
Good
Poor
These examples show that there is no benefit to separating the center frequencies of adjacent systems by
more than 66 MHz. 48 MHz of center frequency separation is more than adequate in most cases. Separation
of 33MHz is adequate for strong RF links, but weak signals will be degraded by the overlap of the side-lobes
into the data region. Overlapping of data regions is not recommended and will cause problems.
The following diagram shows seven different center frequencies in the 5.8 GHz ISM band that are spaced as
far apart as possible. If you wish, you can choose your center frequencies from these sample schemes.
Sample Center Frequency Schemes for Co-located Systems
1 System
2 Systems
Choose any one center frequency
Choose any two center frequencies
3 Systems
4 Systems
ABCDEFG
5.7250
5.7410
5.7562
5.7718
5.7874
5.7803
5.8182
5.8338
5.8500
Center Frequency (GHz)
Three co-located system could use the A,D and G center frequencies. Frequencies B, D and F would
probably work equally as well. Four co-located systems could use the A, C, E and G frequencies. Having
more than four co-located systems would require careful radio network planning to ensure the proper
operation of each system.
APR 2001 Rev 03
71

Configuration
To set the center frequency
➧
1. From the Main Menu, select Radio Module Configuration and press
Configuration menu is displayed.
Radio Module Configuration
New Current Flash
Station Type Remote Unit Remote Unit Remote Unit
Station Rank (1-1000) 1 1 1
Center Frequency (57410-58338) -> 5.7874 GHz 5.7874 GHz 5.7874 GHz
Security Password 1 (Hex) 1 1 1
Security Password 2 (Hex) 10 10 10
Security Password 3 (Hex) 100 100 100
Security Password 4 (Hex) 1000 1000 1000
Security Password 5 (Hex) 10000 10000 10000
Scrambling Code (Hex) 0 0 0
Acquisition Code (0-15) 1 1 1
Config Test Minutes (1-120) 30 30 30
Tx Power Level Adjust 0 dB 0 dB 0 dB
Base Station Only Parameters
Repeater Mode off off off
System Symmetry Type Asymmetric Asymmetric Asymmetric
Dynamic Polling Level (1-100) 1 1 1
Remote Station Only Parameters
Remote Unit RF Group (0-63) 0 0 0
Reboot New RF configuration Press Enter to Execute
Save Current Config to Flash Press Enter to Execute
Enter. The Radio Module
2. Select Center Frequency and press
Enter. The data field highlights.
3. Type the value of the RF center frequency. The value can range from 57410 GHz to 53338 GHz in steps
of 400 kHz. (Numbers are automatically rounded down to the nearest step.) All units in a system must
have the same center frequency.
4. Press
5. Select Reboot New RF Configuration and press
Enter. The new setting is displayed in the "New" column.
Enter. The unit reboots and the AWE 120-58
Login menu is displayed. The unit now runs using the "Current" center frequency for the amount of
time specified by Config Test Minutes.
6. To save the current setting(s) to flash memory, log in, go to the Main Menu, and select Radio Module
Configuration, Save Current Config to Flash. See Rebooting and Saving RF Module
Configurations, page 84.
7. Press
Esc to exit to the Main Menu.
72 AWE 120-58 Installation & Configuration Guide

Radio Module Configuration
Setting Security Passwords
Passwords are always exchanged between units when they communicate with each other. A set of five
security passwords is assigned to each unit. The set of passwords must be exactly the same for all units in a
system. (A convenient, but non-secure option is to set all passwords to "0".) The more password levels you
use, the greater the security of your system. For example, using a set of five different passwords will result in
a highly secure system. All units in the same network must use the same set of security passwords.
To set security passwords
➧
1. From the Main Menu, select Radio Module Configuration and press Enter. The Radio Module
Configuration menu is displayed.
Radio Module Configuration
New Current Flash
Station Type Remote Unit Remote Unit Remote Unit
Station Rank (1-1000) 1 1 1
Center Frequency (57410-58338) 5.7874 GHz 5.7874 GHz 5.7874 GHz
Security Password 1 (Hex) -> 1 1 1
Security Password 2 (Hex) 10 10 10
Security Password 3 (Hex) 100 100 100
Security Password 4 (Hex) 1000 1000 1000
Security Password 5 (Hex) 10000 10000 10000
Scrambling Code (Hex) 0 0 0
Acquisition Code (0-15) 1 1 1
Config Test Minutes (1-120) 30 30 30
Tx Power Level Adjust 0 dB 0 dB 0 dB
Base Station Only Parameters
Repeater Mode off off off
System Symmetry Type Asymmetric Asymmetric Asymmetric
Dynamic Polling Level (1-100) 1 1 1
Remote Station Only Parameters
Remote Unit RF Group (0-63) 0 0 0
Reboot New RF configuration Press Enter to Execute
Save Current Config to Flash Press Enter to Execute
2. Select Security Password 1 and press
3. Enter a password in Hex code and press
4. Select Security Password 2 and press
5. Enter a different password in Hex code and press
Enter. The data field highlights.
Enter. The password is stored in the New state.
Enter. The data field highlights.
Enter. The password is stored in the New state.
6. Repeat this process until you complete all five password levels.
7. Select Reboot New RF Configuration and press
Enter. The unit reboots and the AWE 120-58
Login menu is displayed. The unit now runs using the "Current" set of passwords for the amount of
time specified by Config Test Minutes.
8. To save the current setting(s) to flash memory, log in, go to the Main Menu, and select Radio Module
Configuration, Save Current Config to Flash. See Rebooting and Saving RF Module
Configurations, page 84.
9. Press
APR 2001 Rev 03
Esc to exit to the Main Menu.
73

Configuration
Setting the Scrambling Code
To protect the privacy of a wireless link, units can scramble messages—the message content is rearranged so
that messages are difficult to read by unintended receivers. The scrambling code determines how messages
are scrambled by a unit. Only units with the same scrambling code as the originating unit can de-scramble and
read the message. The scrambling code can be 0-32 bits long. All units in the same wireless network must
have this setting set to the same value.
To set scrambling codes
➧
1. From the Main Menu, select Radio Module Configuration and press Enter. The Radio Module
Configuration menu is displayed.
Radio Module Configuration
New Current Flash
Station Type Remote Unit Remote Unit Remote Unit
Station Rank (1-1000) 1 1 1
Center Frequency (57410-58338) 5.7874 GHz 5.7874 GHz 5.7874 GHz
Security Password 1 (Hex) 1 1 1
Security Password 2 (Hex) 10 10 10
Security Password 3 (Hex) 100 100 100
Security Password 4 (Hex) 1000 1000 1000
Security Password 5 (Hex) 10000 10000 10000
Scrambling Code (Hex) -> 0 0 0
Acquisition Code (0-15) 1 1 1
Config Test Minutes (1-120) 30 30 30
Tx Power Level Adjust 0 dB 0 dB 0 dB
Base Station Only Parameters
Repeater Mode off off off
System Symmetry Type Asymmetric Asymmetric Asymmetric
Dynamic Polling Level (1-100) 1 1 1
Remote Station Only Parameters
Remote Unit RF Group (0-63) 0 0 0
Reboot New RF configuration Press Enter to Execute
Save Current Config to Flash Press Enter to Execute
2. Select Scrambling Code and press
Enter. The data field highlights.
3. Type the code (hexidecimal number).
4. Press
5. Select Reboot New RF Configuration and press
Enter. The new setting is displayed in the "New" column.
Enter. The unit reboots and the AWE 120-58
Login menu is displayed. The unit now runs using the "Current" scrambling code for the amount of time
specified by Config Test Minutes.
6. To save the current setting(s) to flash memory, log in, go to the Main Menu, and select Radio Module
Configuration, Save Current Config to Flash. See Rebooting and Saving RF Module
Configurations, page 84.
7. Press
Esc to exit to the Main Menu.
74 AWE 120-58 Installation & Configuration Guide

Radio Module Configuration
Setting the Acquisition Code
An acquisition code is a unique code contained within the preamble of a transmitted message. Units search
the air for messages that begin with a particular acquisition code. Messages without the correct code are
treated as interference and are rejected by a unit. Messages with the correct code are accepted and
processed. Acquisition codes serve to isolate units from each other, especially when several units operate in
close proximity or at the same frequency in a multiple-sector or multi-cell environment. All units in the same
network must have the same acquisition code in order to communicate with each other.
To set the acquisition code
➧
1. From the Main Menu, select Radio Module Configuration and press Enter. The Radio Module
Configuration menu is displayed.
Radio Module Configuration
New Current Flash
Station Type Remote Unit Remote Unit Remote Unit
Station Rank (1-1000) 1 1 1
Center Frequency (57410-58338) 5.7874 GHz 5.7874 GHz 5.7874 GHz
Security Password 1 (Hex) 1 1 1
Security Password 2 (Hex) 10 10 10
Security Password 3 (Hex) 100 100 100
Security Password 4 (Hex) 1000 1000 1000
Security Password 5 (Hex) 10000 10000 10000
Scrambling Code (Hex) 0 0 0
Acquisition Code (0-15) -> 0 0 0
Config Test Minutes (1-120) 30 30 30
Tx Power Level Adjust 0 dB 0 dB 0 dB
Base Station Only Parameters
Repeater Mode off off off
System Symmetry Type Asymmetric Asymmetric Asymmetric
Dynamic Polling Level (1-100) 1 1 1
Remote Station Only Parameters
Remote Unit RF Group (0-63) 0 0 0
Reboot New RF configuration Press Enter to Execute
Save Current Config to Flash Press Enter to Execute
2. Select Acquisition Code and press
Enter. The data field highlights.
3. Type the Acquisition code (0-15).
4. Press
5. Select Reboot New RF Configuration and press
Enter. The new setting is displayed in the "New" column.
Enter. The unit reboots and the AWE 120-58
Login menu is displayed. The unit now runs using the "Current" acquisition code for the amount of time
specified by Config Test Minutes.
6. To save the current setting(s) to flash memory, log in, go to the Main Menu, and select Radio Module
Configuration, Save Current Config to Flash. See Rebooting and Saving RF Module
Configurations, page 84.
7. Press
APR 2001 Rev 03
Esc to exit to the Main Menu.
75

Configuration
Adjusting the Tx Power Level
Tx Power Level Adjust enables you to reduce the transmit power output level by up to 31 dB. For example,
selecting a value of 0 sets the transmit power to maximum power, while selecting a value of –31 sets the
transmit power to 31 dB below maximum power.
To adjust the Tx power output level
➧
1. From the Main Menu, select Radio Module Configuration and press
Configuration menu is displayed.
Radio Module Configuration
New Current Flash
Station Type Remote Unit Remote Unit Remote Unit
Station Rank (1-1000) 1 1 1
Center Frequency (57410-58338) 5.7874 GHz 5.7874 GHz 5.7874 GHz
Security Password 1 (Hex) 1 1 1
Security Password 2 (Hex) 10 10 10
Security Password 3 (Hex) 100 100 100
Security Password 4 (Hex) 1000 1000 1000
Security Password 5 (Hex) 10000 10000 10000
Scrambling Code (Hex) 0 0 0
Acquisition Code (0-15) 0 0 0
Config Test Minutes (1-120) 30 30 30
Tx Power Level Adjust -> 0 dB 0 dB 0 dB
Base Station Only Parameters
Repeater Mode off off off
System Symmetry Type Asymmetric Asymmetric Asymmetric
Dynamic Polling Level (1-100) 1 1 1
Remote Station Only Parameters
Remote Unit RF Group (0-63) 0 0 0
Reboot New RF configuration Press Enter to Execute
Save Current Config to Flash Press Enter to Execute
Enter. The Radio Module
2. Select Tx Power Level Adjust and press
3. Scroll through the list and press
Enter to select a power attenuation level. Choose a value between 0
Enter. The data field highlights.
and –31, where 0 means no Tx power attenuation and –31 means Tx power is attenuated by 31 dB.
4. Press
5. Select Reboot New RF Configuration and press
Enter. The new setting is displayed in the "New" column.
Enter. The unit reboots and the AWE 120-58
Login menu is displayed. The unit now runs using the "Current" acquisition code for the amount of time
specified by Config Test Minutes.
6. To save the current setting(s) to flash memory, log in, go to the Main Menu, and select Radio Module
Configuration, Save Current Config to Flash. See Rebooting and Saving RF Module
Configurations, page 84.
7. Press
Esc to exit to the Main Menu.
76 AWE 120-58 Installation & Configuration Guide

Radio Module Configuration
Setting a Base to Repeater Mode (Base Station Only)
When repeater mode is enabled at a base station (Repeater Mode = on), the base acts as a repeater in
addition to performing its normal base station functions. As a repeater, the base station receives incoming
messages from remotes, stores them and broadcasts them to all remotes within RF range. Remotes belonging
to the same RF group (with the same RF Group number) can communicate via the repeater. (See Setting
Remote Unit RF Group, page 81 for information about RF groups.) The diagram below expains the process.
Repeater Mode
Message is sent from
1
originating remote
Wired Network
RF Group n
n = 1–63
Rank = 1
(ID # of remote)
Wired Network
RF Group n
n = 1– 63
Rank = 2
(ID # of remote)
Remote
Remote
Message is stored
2
and broadcast
to all remotes in
RF Group n
Base
Repeater Mode = on
(number of remote units)
Rank = 4
Remote
(ID # of remote)
3
Remote
(ID # of remote)
Wired Network
RF Group n
n = 1– 63
Rank = 3
Message is
received by
destination remote
Wired Network
RF Group n
n = 1– 63
Rank = 4
When repeater mode is disabled (Repeater Mode = off), the base station functions normally (it polls remotes
and links the various segments of the network). By definition, Repeater Mode does not apply to units of RF
Group = 0.
APR 2001 Rev 03
77

Configuration
To set base to repeater mode
➧
1. From the Main Menu, select Radio Module Configuration and press
Configuration menu is displayed.
Radio Module Configuration
New Current Flash
Station Type Remote Unit Remote Unit Remote Unit
Station Rank (1-1000) 1 1 1
Center Frequency (57410-58338) 5.7874 GHz 5.7874 GHz 5.7874 GHz
Security Password 1 (Hex) 1 1 1
Security Password 2 (Hex) 10 10 10
Security Password 3 (Hex) 100 100 100
Security Password 4 (Hex) 1000 1000 1000
Security Password 5 (Hex) 10000 10000 10000
Scrambling Code (Hex) 0 0 0
Acquisition Code (0-15) 0 0 0
Config Test Minutes (1-120) 30 30 30
Tx Power Level Adjust 0 dB 0 dB 0 dB
Base Station Only Parameters
Repeater Mode -> off off off
System Symmetry Type Asymmetric Asymmetric Asymmetric
Dynamic Polling Level (1-100) 1 1 1
Remote Station Only Parameters
Remote Unit RF Group (0-63) 0 0 0
Reboot New RF configuration Press Enter to Execute
Save Current Config to Flash Press Enter to Execute
Enter. The Radio Module
2. Select Repeater Mode and press
Enter. The data field highlights.
3. Scroll to select the desired setting where:
off Base unit does not re-transmit messages
Default setting
on Base unit re-transmits messages received from one remote to other
remotes in the same RF group
4. Press
5. Select Reboot New RF Configuration and press
Enter. The new setting is displayed in the "New" column.
Enter. The unit reboots and the AWE 120-58
Login menu is displayed. The unit now runs using the "Current" repeater mode for the amount of time
specified by Config Test Minutes.
6. To save the current setting(s) to flash memory, log in, go to the Main Menu, and select Radio Module
Configuration, Save Current Config to Flash. See Rebooting and Saving RF Module
Configurations, page 84.
7. Press
Esc to exit to the Main Menu.
78 AWE 120-58 Installation & Configuration Guide

Radio Module Configuration
Setting System Symmetry Type (Base Station Only)
System symmetry type fixes the priority of the base unit when it polls remotes. The default "asymmetric"
setting alots the base one time slot for each time a remote is polled—this setting is useful when the base is
the access point to a large network. The "symmetric" setting alots the base one time slot per polling cycle. A
symmetric system gives the base station the same polling priority as a remote unit.
To set system symmetry type
➧
1. From the Main Menu, select Radio Module Configuration and press
Configuration menu is displayed.
Radio Module Configuration
New Current Flash
Station Type Remote Unit Remote Unit Remote Unit
Station Rank (1-1000) 1 1 1
Center Frequency (57410-58338) 5.7874 GHz 5.7874 GHz 5.7874 GHz
Security Password 1 (Hex) 1 1 1
Security Password 2 (Hex) 10 10 10
Security Password 3 (Hex) 100 100 100
Security Password 4 (Hex) 1000 1000 1000
Security Password 5 (Hex) 10000 10000 10000
Scrambling Code (Hex) 0 0 0
Acquisition Code (0-15) 0 0 0
Config Test Minutes (1-120) 30 30 30
Tx Power Level Adjust 0 dB 0 dB 0 dB
Base Station Only Parameters
Repeater Mode off off off
System Symmetry Type -> Asymmetric Asymmetric Asymmetric
Dynamic Polling Level (1-100) 1 1 1
Remote Station Only Parameters
Remote Unit RF Group (0-63) 0 0 0
Reboot New RF configuration Press Enter to Execute
Save Current Config to Flash Press Enter to Execute
2. Select System Symmetry Type and press
Enter. The data field highlights.
3. Scroll to the desired setting where:
Enter. The Radio Module
asymmetric Base unit has higher priority than remotes: the base unit has one time slot
after every remote time slot
Default setting
symmetric Base unit has the same priority as all remotes: the base unit has one time
slot for every polling cycle
4. Press
5. Select Reboot New RF Configuration and press
Enter. The new setting is displayed in the "New" column.
Enter. The unit reboots and the AWE 120-58
Login menu is displayed. The unit now runs using the "Current" symmetry type for the amount of time
specified by Config Test Minutes.
6. To save the current setting(s) to flash memory, log in, go to the Main Menu, and select Radio Module
Configuration, Save Current Config to Flash. See Rebooting and Saving RF Module
Configurations, page 84.
7. Press
APR 2001 Rev 03
Esc to exit to the Main Menu.
79

Configuration
Setting Dynamic Polling Level (Base Station Only)
Dynamic polling improves system performance by reducing overhead due to idle remote units. A base station
automatically learns which remote stations are active and which are idle. The base station waits a brief time
period for a remote to respond to a poll. If the remote doesn’t respond within the time period, the base
considers the remote to be idle. (This process is called dynamic time allocation or DTA.) Idle remote units
are ignored by the base station for the number of polling rounds entered in the Dynamic Polling Level field.
The higher the dynamic polling level, the more efficient the throughput and the longer it takes to move a
subscriber from an inactive state to an active state. Dynamic Polling improves system performance whenever
there is more than one remote. When there are a large number of remotes system performance improves
significantly.
Note: Polling level is set only at the base station.
To set the dynamic polling level
➧
1. From the Main Menu, select RF Station Configuration and press
Configuration menu is displayed.
Radio Module Configuration
New Current Flash
Station Type Remote Unit Remote Unit Remote Unit
Station Rank (1-1000) 1 1 1
Center Frequency (57410-58338) 5.7874 GHz 5.7874 GHz 5.7874 GHz
Security Password 1 (Hex) 1 1 1
Security Password 2 (Hex) 10 10 10
Security Password 3 (Hex) 100 100 100
Security Password 4 (Hex) 1000 1000 1000
Security Password 5 (Hex) 10000 10000 10000
Scrambling Code (Hex) 0 0 0
Acquisition Code (0-15) 0 0 0
Config Test Minutes (1-120) 30 30 30
Tx Power Level Adjust 0 dB 0 dB 0 dB
Base Station Only Parameters
Repeater Mode off off off
System Symmetry Type Asymmetric Asymmetric Asymmetric
Dynamic Polling Level (1-100) -> 1 1 1
Remote Station Only Parameters
Remote Unit RF Group (0-63) 0 0 0
Reboot New RF configuration Press Enter to Execute
Save Current Config to Flash Press Enter to Execute
Enter. The RF Station
1. Select Dynamic Polling Level and press
Enter. The data field highlights.
2. Type the desired polling level (1-60).
3. Press
4. Select Reboot New RF Configuration and press
Enter. The new setting is displayed in the "New" column.
Enter. The unit reboots and the AWE 120-58
Login menu is displayed. The unit now runs using the "Current" dynamic polling level for the amount of
time specified by Config Test Minutes.
5. To save the current setting(s) to flash memory, log in, go to the Main Menu, and select Radio Module
Configuration, Save Current Config to Flash. See Rebooting and Saving RF Module
Configurations, page 84.
6. Press
Esc to exit to the Main Menu.
80 AWE 120-58 Installation & Configuration Guide

Radio Module Configuration
Setting Remote Unit RF Group
The RF Group setting enables you to determine which units in a system can communicate with each other.
For example, in a system consisting of a base station and associated remotes, you can: 1) assign units to
different groups so that only members of the same group can communicate with each other and the base (an
open system); 2) isolate remotes so they cannot talk to other remotes, but can talk only to the base (a closed
system); 3) assign remote units to groups and configure the base station as a repeater (a closed system); and
4) combine closed units with open units in the same system. These configurations are explained below.
Remote units with the same RF group number (RF Group = 1– 63) can communicate directly with each other
and with the base station (if there is a line-of-sight RF path between units and base station Repeater Mode =
off.) An example is a company where the Human Resources department needs direct access to the Payroll
department, but the two departments must be isolated from other departments. Since HR and Payroll are in
the same RF group 14, they can talk directly to each other, but they cannot talk directly to other groups such
as R&D, which belongs to RF Group 20.
Example 1: Open System
Repeater
Mode = off
Base
Remote
RF Group = 20
R&D
Remote
RF Group = 14
Human Resources
Remote
RF Group = 14
Payroll
RF Group = n
n = 1 – 63
Remote units configured as RF Group = 0 are independent, closed units. Closed units cannot talk directly to
each other, they can only talk directly to the base station. This setup acts to isolate remote units and the
associated LANs from each other. Example 2 shows a situation where independent companies are connected
wirelessly to a single base station and communication between the companies is prevented.
Example 2: Closed System
Repeater
Mode = off
Base
Remote
RF Group = 0
Company 1
Remote
RF Group = 0
Company 2
Remote
RF Group = 0
Company 3
RF Group = 0
APR 2001 Rev 03
81

Configuration
A repeater is used to bypass obstacles that block the RF path (for example, a mountain). When a base station
is set to repeater mode (Repeater Mode = on), it can pass data from remotes in an RF group to other
remotes in the same group. A system with a repeater is a closed system. Example 3 shows a repeater with
four remotes. All the remotes are in the same RF Group 4, so they can talk to each other via the repeater
base.
Example 3: Repeater Configuration (Closed System)
Repeater
Mode = on
Base
Closed
System
Remote
RF Group = 4
n = 1 – 63
Remote Remote
RF Group = 4
n = 1 – 63
Mountain
No direct communcation
possible due to obstacle
RF Group = 4
n = 1 – 63
Remote
RF Group = 4
n = 1 – 63
Closed remote units (RF Group = 0) can be combined with open remote units (RF Group = non-zero) within
the same system. In this case each group in the system behaves according to its RF Group characteristics:
closed remotes could communicate only with the base, remotes with the same (non-zero) group number
could communicate with each other, and remotes with different (non-zero) group numbers could not
communicate with each other. A base or repeater would not pass packets originating from a closed remote.
The following table summarizes the first three situations.
Repeater Mode
(Base only)
Repeater Mode =
off
RF Group
(Remote only)
1–63 Open Remotes can communicate directly with
System
Type
System Characteristics
the base and each other if remotes that
have the same non-zero RF group number
(if a LOS RF path can be established)
Repeater Mode =
off
0 Closed Remotes can communicate only with the
base station—they cannot talk to each
other
Repeater Mode = on1–63 Closed Remotes cannot communicate directly with
each other, they can only communicate via
the repeater base with other remotes that
have the same RF group number
In a mixed system, each RF group behaves according to the RF Group charactersitics assigned to it (0 =
closed , 1–63 = open; same non-zero group number = communication, different non-zero group number =
no communication).
82 AWE 120-58 Installation & Configuration Guide

To set remote unit RF group
➧
Radio Module Configuration
1. From the Main Menu, select RF Module Configuration and press
Radio Module Configuration
New Current Flash
Station Type Remote Unit Remote Unit Remote Unit
Station Rank (1-1000) 1 1 1
Center Frequency (57410-58338) 5.7874 GHz 5.7874 GHz 5.7874 GHz
Security Password 1 (Hex) 1 1 1
Security Password 2 (Hex) 10 10 10
Security Password 3 (Hex) 100 100 100
Security Password 4 (Hex) 1000 1000 1000
Security Password 5 (Hex) 10000 10000 10000
Scrambling Code (Hex) 0 0 0
Acquisition Code (0-15) 1 1 1
Config Test Minutes (1-120) 30 30 30
Tx Power Level Adjust 0 dB 0 dB 0 dB
Base Station Only Parameters
Repeater Mode off off off
System Symmetry Type Asymmetric Asymmetric Asymmetric
Dynamic Polling Level (1-100) 1 1 1
Remote Station Only Parameters
Remote Unit RF Group (0-63) -> 0 0 0
Reboot New RF configuration Press Enter to Execute
Save Current Config to Flash Press Enter to Execute
2. Select Remote Unit RF Group and press
Enter. The data field highlights.
Enter. The g menu is displayed.
3. In the Remote Unit RF Group entry field, type the RF group number, using the following table as a guide.
4. Press
5. Select Reboot New RF Configuration and press
Enter. The new setting is displayed in the "New" column.
Enter. The unit reboots and the AWE 120-58
Login menu is displayed. The unit now runs using the "Current" remote unit RF group for the amount
of time specified by Config Test Minutes.
6. To save the current setting(s) to FLASH, log in, go to the Main Menu, and select Radio Module
Configuration, Save Current Config to Flash. See Rebooting and Saving RF Module
Configurations, page 84.
7. Press
Esc to exit to the Main Menu.
APR 2001 Rev 03
83

Configuration
Rebooting and Saving RF Module Configurations
Because changes to radio module configuration settings can affect service in a wireless system, changes are
made in three progessive stages: new, current, and flash.
New Intended configuration changes. Temporary memory storage.
Current Configuration actually running on the unit. Temporary memory storage.
Flash Configuration stored in FLASH memory. Long-term memory storage.
A reboot of a unit is required to save New settings as Current settings. If Current settings are valid (and do
not disrupt the system), they can be saved to Flash memory. If the changes disrupt the system, the original
configuration will be restored automatically when the Config Test Minutes period expires.
To reboot a unit
➧
1. From the Main Menu, select Radio Module Configuration and press Enter. The Radio Module
Configuration menu is displayed.
Radio Module Configuration
New Current Flash
Station Type Remote Unit Remote Unit Remote Unit
Station Rank (1-1000) 1 1 1
Center Frequency (57410-58338) 5.7874 GHz 5.7874 GHz 5.7874 GHz
Security Password 1 (Hex) 1 1 1
Security Password 2 (Hex) 10 10 10
Security Password 3 (Hex) 100 100 100
Security Password 4 (Hex) 1000 1000 1000
Security Password 5 (Hex) 10000 10000 10000
Scrambling Code (Hex) 0 0 0
Acquisition Code (0-15) 1 1 1
Config Test Minutes (1-120) 30 30 30
Tx Power Level Adjust 0 dB 0 dB 0 dB
Base Station Only Parameters
Repeater Mode off off off
System Symmetry Type Asymmetric Asymmetric Asymmetric
Dynamic Polling Level (1-100) 1 1 1
Remote Station Only Parameters
Remote Unit RF Group (0-63) 0 0 0
Reboot New RF configuration -> Press Enter to Execute
Save Current Config to Flash Press Enter to Execute
2. Select Reboot New RF configuration and press
Enter. The unit reboots with the with new
settings and with the Config Test Minutes timeout period in effect. The new settings can be viewed in the
"Current" column of the Radio Module Configuration menu. The old, last-saved configuration remains
in Flash memory.
If the configuration is the one you want and the unit operates as intended, you can save the current
changes to "permanent" flash memory by selecting Save Current Config to Flash from the
Radio Module Configuration menu. When you save the current settings to "Flash" the new settings
overwrite the old flash memory settings.
84 AWE 120-58 Installation & Configuration Guide

To save current configuration to FLASH
➧
Radio Module Configuration
1. From the Main Menu, select Radio Module Configuration and press
Configuration menu is displayed.
Radio Module Configuration
New Current Flash
Station Type Remote Unit Remote Unit Remote Unit
Station Rank (1-1000) 1 1 1
Center Frequency (57410-58338) 5.7874 GHz 5.7874 GHz 5.7874 GHz
Security Password 1 (Hex) 1 1 1
Security Password 2 (Hex) 10 10 10
Security Password 3 (Hex) 100 100 100
Security Password 4 (Hex) 1000 1000 1000
Security Password 5 (Hex) 10000 10000 10000
Scrambling Code (Hex) 0 0 0
Acquisition Code (0-15) 1 1 1
Config Test Minutes (1-120) 30 30 30
Tx Power Level Adjust 0 dB 0 dB 0 dB
Base Station Only Parameters
Repeater Mode off off off
System Symmetry Type Asymmetric Asymmetric Asymmetric
Dynamic Polling Level (1-100) 1 1 1
Remote Station Only Parameters
Remote Unit RF Group (0-63) 0 0 0
Reboot New RF configuration Press Enter to Execute
Save Current Config to Flash -> Press Enter to Execute
Enter. The Radio Module
2. Select Save Current Config to Flash.
3. Press
Enter. The current configuration is saved to flash memory. A reboot is not required. The new flash
memory values are displayed in the "Flash" column of the Radio Module Configuration menu.
APR 2001 Rev 03
85

Configuration
RF/Ethernet Statistics
Ethernet and RF statistics are useful for troubleshooting, monitoring link performance, and measuring
throughput. Ethernet and RF statistics are cumulative and increment until reset. The window is view only. See
Resetting Radio and Ethernet Statistics, page 100 for information about resetting RF/Ethernet statistics.
Viewing RF/Ethernet Statistics
To view RF and Ethernet statistics
➧
1. From the Main Menu, select RF/Ethernet Statistics and press Enter. The RF/Ethernet Statistics
window is displayed. The window is view only.
RF/Ethernet Statistics
Ethernet Receive Statistics Ethernet Transmit Statistics
Total Packets Received 0 Total Packets Transmitted 0
Packets For Local Host 0 Packets From Local Host 0
Receive Errors 0 Packets Dropped 0
Packets Dropped 0 Total KBytes Transmitted 0
Packets Discarded 0 Broadcast KBytes Transmitted 0
Total KBytes Received 0
Broadcast KBytes Received 0
RF Receive Statistics RF Transmit Statistics
Total Packets Received 0 Total Packets Transmitted 0
Packets For Local Host 0 Frames From Local Host 0
Packets Dropped 0 Packets Dropped 0
Packets Discarded 0
RF Super Frame Rx Statistics RF Super Frame Tx Statistics
Super Frames Received 0 Super Frames Transmitted 0
Receive Overrun Errors 0
Frame Control Word Errors 0
Header Checksum Errors 0 Throughput Statistics
Packet Control Word Errors 0 Ethernet-to-RF Throughput 0
Super Frame Length Errors 0 RF-to-Ethernet Throughput
0
86 AWE 120-58 Installation & Configuration Guide
 Loading...
Loading...