Page 1

wienet router
v2
configuration manual
Dok.-Nr. BA000819
Stand: 01/2012 (Rev. A)
Page 2
2
Wieland Electric | BA000819 | 01/2012 (Rev. A)
This work is copyright. The resulting rights remain with the company Wieland Electric Inc.
Any duplication of this document or parts thereof is permitted only within the limits of the
statutory provisions of the Copyright Act. Alteration or abridgement of without the express
written consent of Wieland Electric GmbH.
wienet is a trademark of Wieland Electric. Other names may in this assembly manual mentioned product and brand- trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective owners
could be used, whose use by third parties for their own purposes could violate the rights of
the owners.
Page 3

Wieland Electric | BA000819 | 01/2012 (Rev. A)
3
Page 4

Contents
4
Wieland Electric | BA000819 | 01/2012 (Rev. A)
Contents
1 About this docoment........................................................................................ 6
1.1 Function of this document .......................................................................................... 6
1.1 Scope and revision levelel ........................................................................................... 6
1.2 Target group ................................................................................................................ 6
1.3 Function and design of this installation manual.......................................................... 6
1.4 Symbols and notations................................................................................................ 7
2 Safety instructions ........................................................................................... 8
2.1 Qualified persons......................................................................................................... 8
2.2 Intended Use ............................................................................................................... 8
3 Configuration settings over web browser ........................................................ 9
3.1 Secured access to web configuration ....................................................................... 10
3.2 Network status .......................................................................................................... 10
3.3 DHCP status .............................................................................................................. 12
3.4 GPRS/UMTS status.................................................................................................... 13
3.5 IPsec status................................................................................................................ 16
3.6 DynDNS status .......................................................................................................... 17
3.7 System log................................................................................................................. 18
3.8 LAN configuration ..................................................................................................... 19
3.9 VRRP configuration ................................................................................................... 22
3.10 GPRS configuration ................................................................................................... 22
3.10.1 GPRS connection....................................................................................................... 22
3.10.2 DNS address configuration ....................................................................................... 22
3.10.3 Check PPP connection configuration ........................................................................ 22
3.10.4 Data limit configuration ............................................................................................. 22
3.10.5 Switch between SIM cards configuration ................................................................. 22
3.10.6 Dial-In access configuration ...................................................................................... 22
3.10.7 PPPoE bridge mode configuration ............................................................................ 22
3.10.8 PPPoE configuration.................................................................................................. 22
3.11 Firewall configuration................................................................................................ 22
3.12 NAT configuration ..................................................................................................... 22
3.13 OpenVPN tunnel configuration ................................................................................. 22
3.14 IPSec tunnel configuration ........................................................................................ 22
3.15 GRE tunnels configuration......................................................................................... 22
3.16 L2TP tunnel configuration ......................................................................................... 22
3.17 DynDNS client configuration..................................................................................... 22
3.18 NTP client configuration ............................................................................................ 22
3.19 SNMP configuration .................................................................................................. 22
3.20 SMTP configuration................................................................................................... 22
3.21 SMS configuration..................................................................................................... 22
3.21.1 Send SMS .................................................................................................................. 22
3.22 Expansion port configuration .................................................................................... 22
3.23 USB port configuration.............................................................................................. 22
3.24 Startup script .............................................................................................................. 22
3.25 Up/Down script ......................................................................................................... 22
4 Possible problems .......................................................................................... 22
5 FAQ ................................................................................................................ 22
Page 5

Contents
Wieland Electric | BA000819 | 01/2012 (Rev. A)
5
6 Customers support ......................................................................................... 22
7 List of figures ................................................................................................. 22
Page 6

About this docomen
t
Wieland Electric | BA000819 | 01/2012 (Rev. A)
1 About this docoment
Please read this chapter carefully before working with this users guide and the wienet
mobile router
1.1 Function of this document
In this wienet mobile router User's Guide the device and the functions of it are described.
Use the User's Guide, especially for the configuring of the mobile router.
1.1 Scope and revision levelel
This installation manual is valid for the products wienet VPN router, which are associated
with this installation manual. The installation instructions accompanying the product is
downloadable in the electronic catalog of Wieland. Be sure to always use the information
provided in the current version of this installation manual. The version and revision level
can be seen in the title page and the footer..
1.2 Target group
This manual is aimed at planners, engineers, installers and service personnel who are
planning a remote control or remote maintenance solution and put into operation.
1.3 Function and design of this installation manual
This installation manual guide the technical staff of router installer on installation, programming, operation and diagnosis of wienet router.
Chapter "Safety instructions" on side 8 contain basic safety instructions. Please read and
follow these instructions in each case.
You can also use our Internet site at http://eshop.wieland-
electric.com/catalog/de_*/Wieland-de/Netzwerktechnik%20$2F%20Feldbussysteme. You
can also download the following files:
Product informations wienet router and switches
Data sheets wienet router
Technical notes WIE-SERVICE24.com VPN Server portal
NOTICE
Page 7

About this docoment
Wieland Electric | BA000819 | 01/2012 (Rev. A)
7
1.4 Symbols and notations
The symbol "DANGER" means an imminent danger. If it is not avoided, can result in death
or serious injury.
"DANGER" is used to warn of dangers at the time of the warning are already existing (eg
hot surfaces, sharp edges, pinch points, etc.).
It is used exclusively in danger of personal injury!
The symbol "WARNING" indicates a possible threat. If it is not avoided, can result in death
or serious injury could result.
The symbol "CAUTION" indicates a possible threat. If it is not avoided, slight or minor injury can result.
Refer to notes for special features of a device.
Instructions also tell you about a potentially harmful situation. If it is not avoided, the system can be damaged or something in their environment.
DANGER
WARNING
CAUTION
NOTICE
Page 8

Safety instructions
8
Wieland Electric | BA000819 | 01/2012 (Rev. A)
2 Safety instructions
This chapter is for your safety and the safety of equipment operators. Please read this
chapter carefully before working with a VPN-Router.
General Safety
Personnel who makes installation, programming, makes operational or maintenance of
wienet router, must have read and understood this manual.
The personnel must be thoroughly familiar with all warnings, instructions and requirements contained in this manual.
The applicable local safety, protection and installation requirements must be observed.
The user is solely responsible for selecting the correct product and the technical design
in accordance with appropriate local regulations
2.1 Qualified persons
Wienet VPN router must be installed by competent persons only, configured in operation,
commissioned and maintained. Qualified is, who
has an appropriate technical training and
has access to the wienet VPN router installation manuals, and this has been read and
understood.
2.2 Intended Use
Please, observe the following instructions:
The router must be used in compliance with all applicable international and national laws
and in compliance with any special restrictions regulating the utilization of the router in
prescribed applications and environments.
To prevent possible injury to health and damage to appliances and to ensure that all the
relevant provisions have been complied with, use only the original accessories. Unauthorised modifications or utilization of accessories that have not been approved may result
in damage to the router and in a breach of applicable regulations. Unauthorized modifications or utilization of accessories that have not been approved may result in the termination of the validity of the guarantee.
The router can not be opened.
Caution! The SIM card could be swallowed by small children.
Voltage at the feed connector of the router must not be exceeded.
Do not expose the router to extreme ambient conditions. Protect the router against dust,
moisture and high temperature.
The router should not be used at petrol stations. We remind the users of the duty to
observe the restrictions concerning the utilization of radio devices at petrol stations, in
chemical plants, or in the course of blasting works in which explosives are used.
Switch off the router when travelling by plane. Utilization of the router in a plane may
endanger the operation of the plane or interfere with the mobile telephone network, and
may be unlawful. Failure to observe these instructions may result in the suspension or
cancellation of telephone services for the respective client, or, it may result in legal sanctions; it may also result in both eventualities.
When using the router in the close proximity of personal medical devices, such as car-
diac pacemakers or hearing aids, you must proceed with heightened caution.
If it is in the proximity of TV sets, radio receivers and personal computers, the telephone
may cause interference.
It is recommended that you should create an appropriate copy or backup of all the im-
portant settings that are stored in the memory of the device
For any other use, or changes to the equipment - even in the context of mounting and
installation - any warranty claim against Wieland Electric Gmb expired.
WARNING
WARNING
Page 9
Configuration settings over web browser
Wieland Electric | BA000819 | 01/2012 (Rev. A)
9
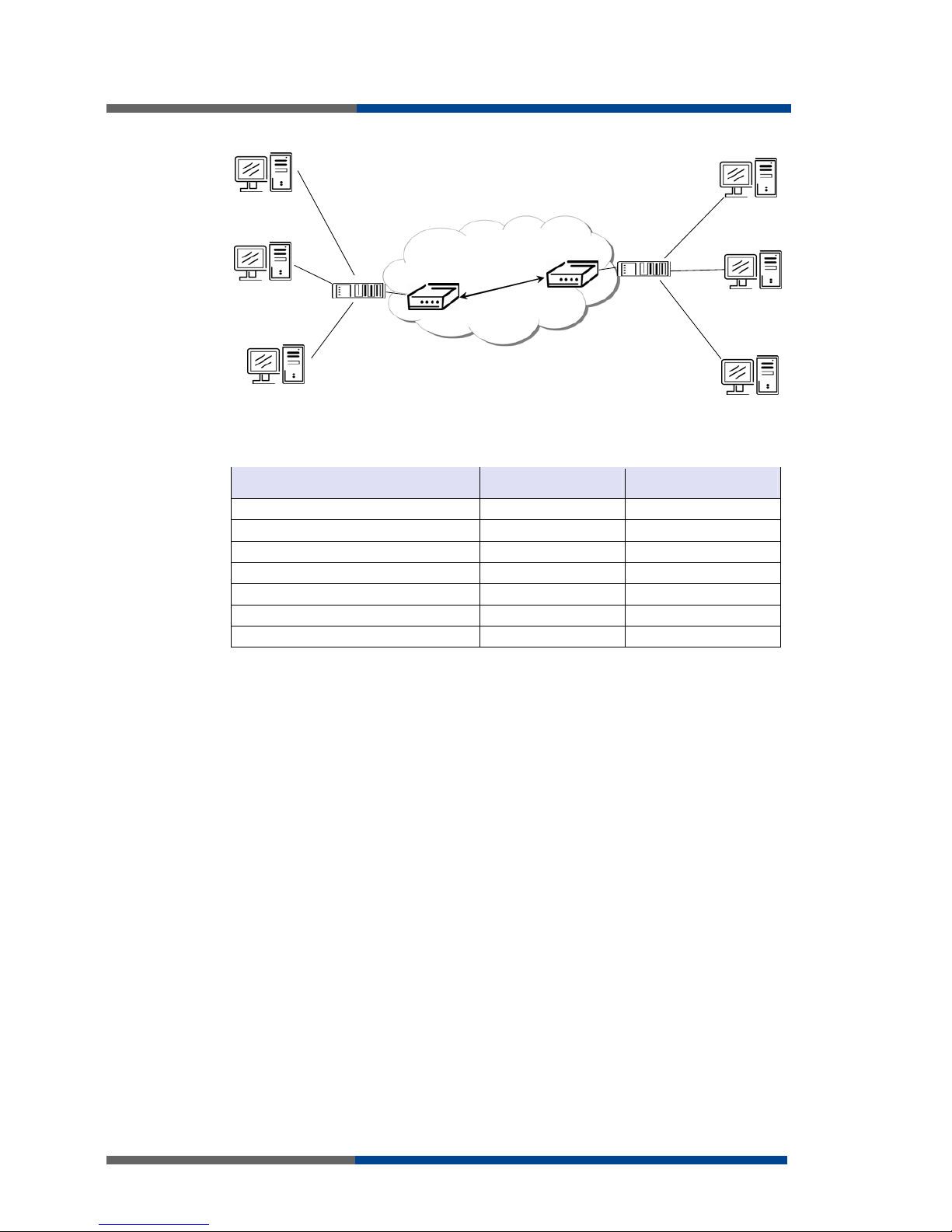
3 Configuration settings over web
browser
If the SIM card is not inserted in the router, then wireless transmissions will not work. The
inserted SIM card must have activated GPRS. Insert the SIM card when the router is switched-off.
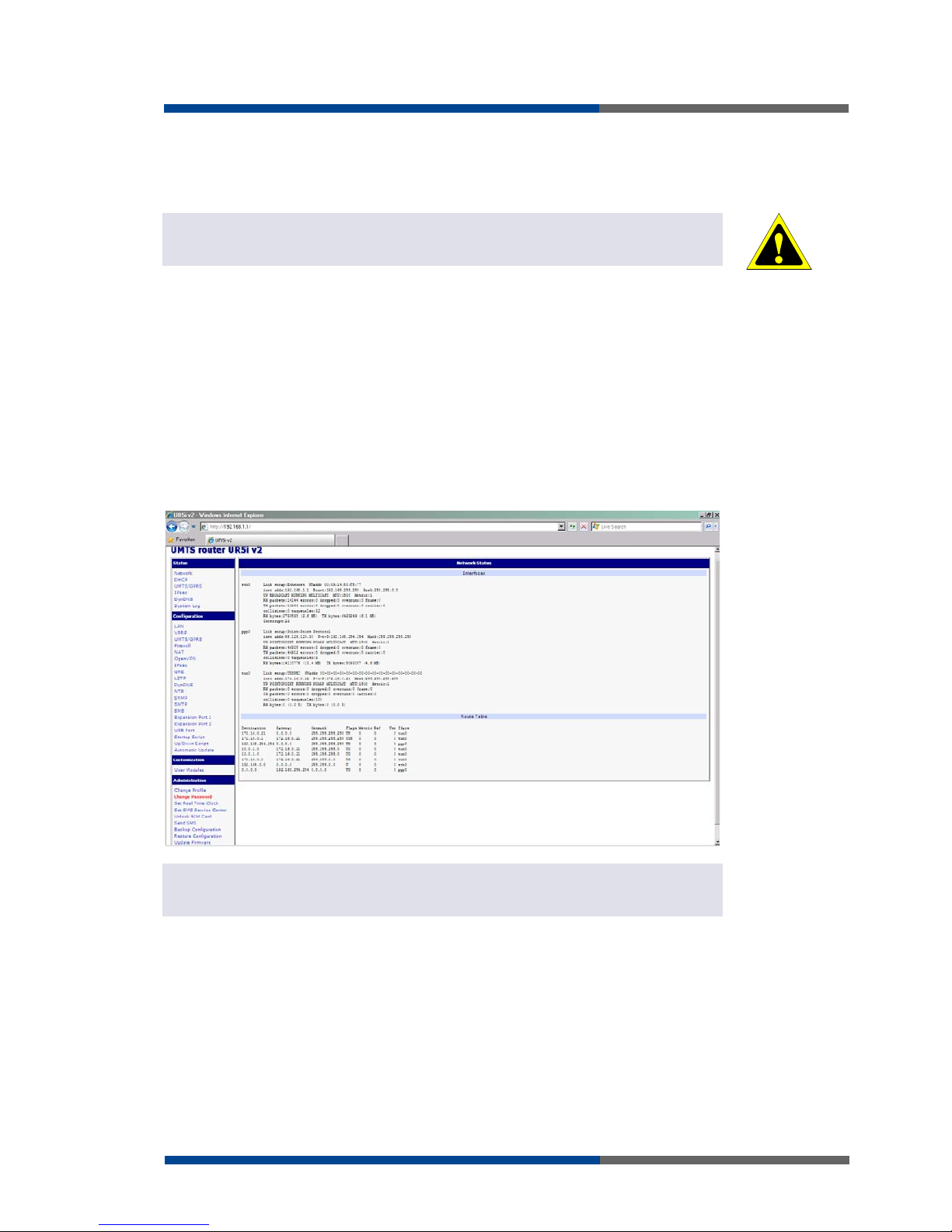
Monitoring of the status, configuration and administration of the router can be performed
by means of the web interface, which is available after insertion of IP address of the modem into the web browser. The default IP address of the modem is 192.168.1.1. Configuration may be performed only by the user "root" with initial password "root".
The left part of the web interface contains the menu with pages for monitoring of the Status, Configuration and Administration of the router.
Name of the router is displayed depending on type of your router. Items' Name and Location displays the name and location of the router filled in the SNMP configuration. (See
SNMP Configuration).
For enhanced security of network managed router is must change the default password
router. If the router's default password is set, the item "Change password" is highlighted in
red.
After green LED starts to blink it is possible to restore initial settings of the router by pressing button RST on front panel. If press button RST, configuration is restored to default
and it is reboot (green LED will be on).
CAUTION
F
ig 1: Web
configuration
NOTICE
Page 10

Configuration settings over web browser
10
Wieland Electric | BA000819 | 01/2012 (Rev. A)
3.1 Secured access to web configuration
To the web configuration can be accessed via a secure HTTPS protocol.
In the event of a default router IP address is a secure router configuration accessed by
typing address https://192.168.1.1 in the web browser. The first approach is the need to
install a security certificate. If your browser reports a disagreement in the domain, this
message can be prevented use the following procedure.
Since the domain name in the certificate is given the MAC address of the router (such
separators are used dashes instead of colons), it is necessary to access the router under
this domain name. For access to the router via a domain name, it is adding a DNS record
in the DNS table, the operating system.
Editing /etc/hosts (Linux/Unix)
Editing C:\WINDOWS\system32\drivers\etc\hosts (Windows XP)
Configuring your own DNS server
In addition to configuring the router with MAC address 00:11:22:33:44:55 is accessed to
secure configuration by typing address https://00-11-22-33-44-55 in the web browser. The
first approach is the need to install a security certificate.
When using self signing certificate must upload your files and http_cert http_key directory
/etc/certs in the router.
3.2 Network status
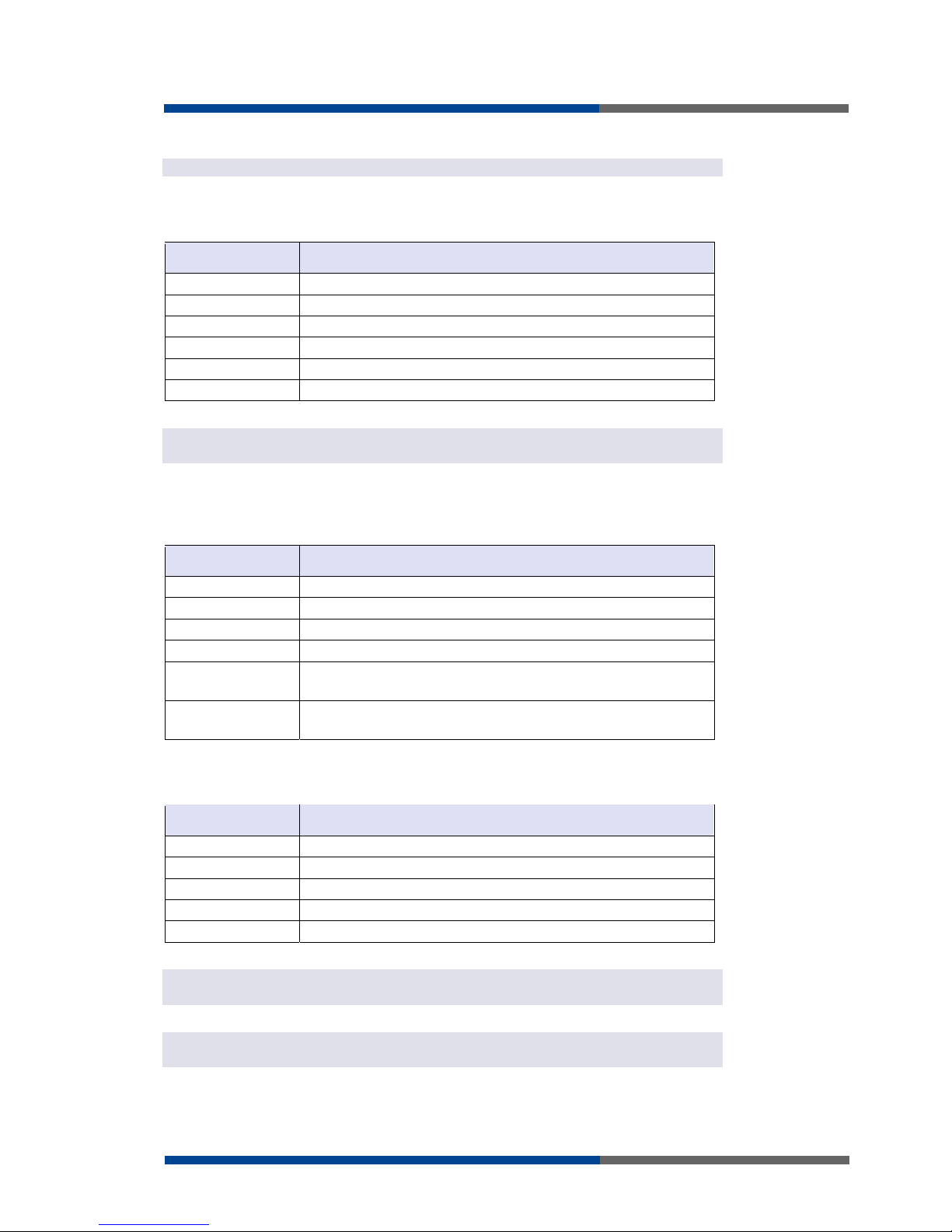
To view the system information about the router operation, select the Network menu item.
The upper part of the window displays detailed information about active interfaces.
Interface Desciption
eth0 Networks interface
ppp0 Interface (active connection to GPRS/EDGE)
tun0 OpenVPN tunnel interface
ipsec0 IPSec tunnel interface
gre1 GRE tunnel interface
NOTICE
Table 1: Description of
interface in network
status
Page 11
Configuration settings over web browser
Wieland Electric | BA000819 | 01/2012 (Rev. A)
11
By each of the interfaces is then shown the following information:
Item Desciption
HWaddr Hardware (unique) address of networks interface
inet IP address of interface
P-t-P IP address second ends connection
Bcast Broadcast address
Mask Mask of network
MTU Maximum size of packet, which is equipment able transmit
Metric Number of routers, over which packet must go trought
RX
packets received packets
errors number of errors
dropped dropped packets
overruns incoming packets lost because of overload
frame wrong incoming packets because of incorrect packet size
TX
packets transmit packets
errors number of errors
dropped dropped packets
overruns outgoing packets lost because of overload
carrier wrong outgoing packets with errors resulting from the
physical layer
collisions Number of collisions on physical layer
txqueuelen Length of front network device
RX bytes Total number of received bytes
TX bytes Total number of transmitted bytes
It is possible to read status PPP connection from the network information. If the PPP connection is active, then it is in the system information shown as ppp0 interface.
For industrial router XR5i v2, interface ppp0 indicates PPPoE connection.
Table
2
:
Description of
information in network
status
NOTICE
F
ig
2
:
Network status
Page 12

Configuration settings over web browser
12
Wieland Electric | BA000819 | 01/2012 (Rev. A)
3.3 DHCP status
Information on the activities of the DHCP server can be accessed by selecting the DHCP
status.
DHCP status informs about activities DHCP server. The DHCP server provides automatic
configuration of devices connected to the network managed router. DHCP server assigns
to each device's IP address, netmask, default gateway (IP address of router) and DNS server (IP address of router).
For each configuration, the DHCP status window displays the following information
Item Desciption
lease Assigned IP address
starts Time of assignation of IP address
ends Time of termination IP address validity
hardware ethernet Hardware MAC (unique) address
uid Unique ID
client-hostname Computer name
In the extreme, the DHCP status can display two records for one IP address. That could
have been caused by resetting of network cards.
Table
3
:
DHCP status
description
F
ig
3
: D
HCP status
NOTICE
Page 13
Configuration settings over web browser
Wieland Electric | BA000819 | 01/2012 (Rev. A)
13
3.4 GPRS/UMTS status
The industrial router XR5i v2 is not availability item GPRS/UMTS status.
GPRS menu item contains actual information about GPRS/UMTS connections.
Item Desciption
PLMN Code of operator
Cell The cell to which the router is connected
Channel The channel on which the router communicates
Level The signal quality of the selected cell
Neighbours Signal quality of neighboring hearing cells
Uptime Time to establish PPP connection
If the neighbor cell is highlighted in red, risk of often switching between neighbor and
actual cells.
The next section of this window displays information about the quality of the GPRS/UMTS
connection in each period.
Item Desciption
Today Today from 0:00 to 23:59
Yesterday Yesterday from 0:00 to 23:59
This week This week from Monday 0:00 to Sunday 23:59
Last week Last week from Monday 0:00 to Sunday 23:59
This period This accounting period. The interval must be set in the GPRS Con-
figuration
Last period Last accounting period. The interval must be set in the GPRS Con-
figuration
Item Desciption
Level Min. Minimal signal strength
Level Avg. Average signal strength
Level Max. Maximal signal strength
Cells Number of switch between cells
Availability Availability of PPP connection
Availability is information in percentage, that is calculated us ration of PPP connect time
and router power on time.
After you place your cursor on the maximum or minimum signal strength, will show the
last time when the signal strength reaching the router.
In the middle part of window is shows information about transferred data and number of
connection both SIM card, for each period
NOTICE
Table 4: Description of
GSM information item
NOTICE
Table 5: Description of
period
Table
6
:
Description of
GSM statistic
NOTICE
NOTICE
Page 14
Configuration settings over web browser
14
Wieland Electric | BA000819 | 01/2012 (Rev. A)
Item Desciption
RX data Total volume of received data
TX data The total volume of data sent
Connections Number of PPP connection establishment
Table 7: Description of
GSM traffic
Page 15
Configuration settings over web browser
Wieland Electric | BA000819 | 01/2012 (Rev. A)
15
The PPP Connection Log is in the bottom of window, where are information about the
make-up of the PPP connection and problems in establishment.
F
ig 4: GPRS status
Page 16

Configuration settings over web browser
16
Wieland Electric | BA000819 | 01/2012 (Rev. A)
3.5 IPsec status
Information on actual IPsec tunnel state can be called up in option IPsec in the menu.
After correct build the IPsec tunnel, status display IPsec SA established (highlighted in red)
in IPsec status information. Other information is only internal character.
F
ig 5: IPsec status
Page 17

Configuration settings over web browser
Wieland Electric | BA000819 | 01/2012 (Rev. A)
17
3.6 DynDNS status
DynDNS up - dating entry result on server www.dyndns.org can be called up in option
DynDNS item in the menu.
In detecting the status of updates DynDNS record are possible following message:
Report
DynDNS client is disabled.
Invalid username or password.
Specified hostname doesn’t exist.
Invalid hostname format.
Hostname exists, but not under specified username.
No update performed yet.
DynDNS record is already up to date.
DynDNS record successfully update.
DNS error encountered.
DynDNS server failure.
For correct function DynDNS, SIM card of router must have assigned public IP address.
F
ig 6: DynDNS status
Table
8
:
Possibly
DynDNS report
NOTICE
Page 18
Configuration settings over web browser
18
Wieland Electric | BA000819 | 01/2012 (Rev. A)
3.7 System log
In case of any problems with connection to GPRS it is possible to view the system log by
pressing the System Log menu item. In the window, are displayed detailed reports from
individual applications running in the router. By the help of button
Save
it is possible to
save the system log to the computer.
Program syslogd can be started with two options that modifies its behavior. Option "-s"
followed by decimal number set maximal number of lines in one log file. Option "-r" followed by hostname or IP address enable logging to remote syslog daemon.
In the Linux must be enabled remote logging on the target computer. Typically running
syslogd with the parameter “-r”. On Windows must be installed the syslog server (for example Syslog Watcher).
For starting syslogd with these options you could modify script "/etc/init.d/syslog" or add
lines "killall syslogd" and "syslogd <options> &" into Startup Script.
Example of logging into the remote daemon at 192.168.2.115
F
ig 7: System log
NOTICE
F
ig
8
: E
xample
program syslogd start
with parameter
Page 19
Configuration settings over web browser
Wieland Electric | BA000819 | 01/2012 (Rev. A)
19
3.8 LAN configuration
To enter the network configuration, select the
LAN
menu item. ETH network set in
Pri-
mary LAN
configuration, expansion PORT ETH set in
Secondary LAN
configuration.
Item Desciption
DHCP Client disabled – The router does not allow automatic allocation IP
address from a DHCP server in LAN network.
enabled – The router allows automatic allocation IP address
from a DHCP server in LAN network.
IP address Fixed set IP address of network interface ETH.
Subnet Mask IP address of Subnet Mask.
Media type Auto-negation – The router selects the speed of communication
of network options.
100 Mbps Full Duplex – The router communicates at 100Mbps,
in the full duplex mode.
100 Mbps Half Duplex - The router communicates at 100Mbps,
in the half duplex mode.
10 Mbps Full Duplex - The router communicates at 10Mbps, in
the full duplex mode.
10 Mbps Half Duplex - The router communicates at 10Mbps, in
the half duplex mode.
Default Gateway IP address of Default gateway of router. When entering IP address
of default gateway, all packets for which the record was not found
in the routing table, sent to this address.
DNS server IP address of DNS server of router. Address where they are for-
warded to all DNS questions on the router.
DHCP server assigns IP address, gateway IP address (IP address of the router) and IP address of the DNS server (IP address of the router) to the connected clients.
DHCP server supports static and dynamic assignment of IP addresses. Dynamic DHCP
server assigns clients IP addresses from a defined address space. Static DHCP assigns IP
addresses that correspond to the MAC addresses of connected clients.
Item Desciption
Enable dynamic
DHCP leases
If this option is checked, can enable a dynamic DHCP server.
IP Pool Start Start IP addresses space to be allocated to the DHCP clients.
IP Pool End End IP addresses space to be allocated to the DHCP clients.
Lease time Time in seconds, after which the client can use IP address.
Item Desciption
Enable static DHCP
leases
If this option is checked, can enable a static DHCP server.
MAC Address MAC address of a DHCP client.
IP Address Assigned IP address.
Enable static DHCP
leases
If this option is checked, can enable a static DHCP server.
Table 9: Configuration
of network interface
Table 10
:
Configuration
of dynamic DHCP
server
Table 11
:
Configuration
of static DHCP server
Page 20
Configuration settings over web browser
20
Wieland Electric | BA000819 | 01/2012 (Rev. A)
It is important not to overlap ranges of static allocated IP address with address allocated by
the dynamic DHCP. Then risk collision of IP addresses and incorrect function of network.
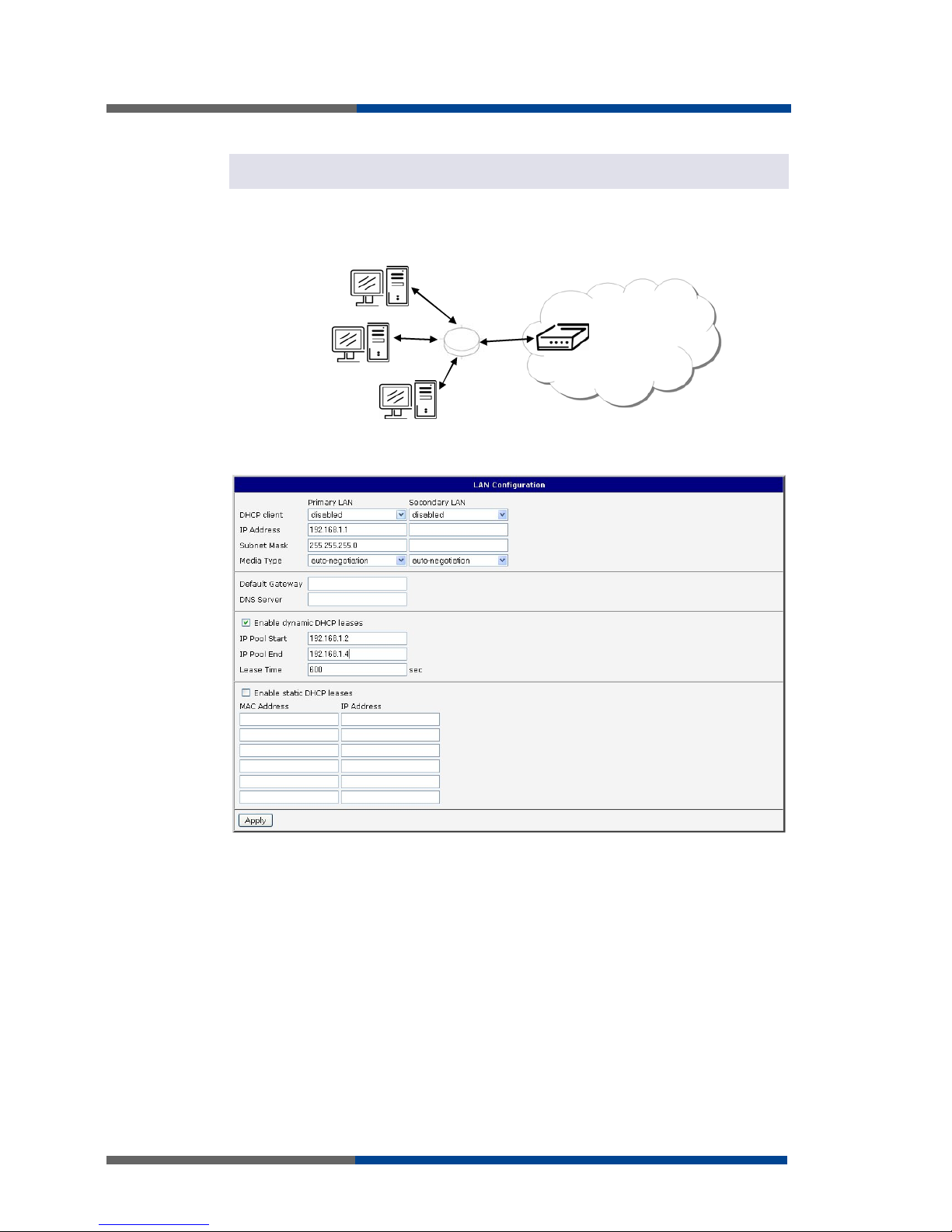
Example of the network interface with dynamic DHCP server:
The range of dynamic allocated addresses from 192.168.1.2 to 192.168.1.4.
The address is allocated 600 second (10 minutes).
192.168.1.3
192.168.1.4
ETH
192.168.1.2
GSM/GPRS
192.168.1.1
NOTICE
F
ig 9: Topology of
example LAN
configuration 1
F
ig 10: Example LAN
configuration
Page 21
Configuration settings over web browser
Wieland Electric | BA000819 | 01/2012 (Rev. A)
21
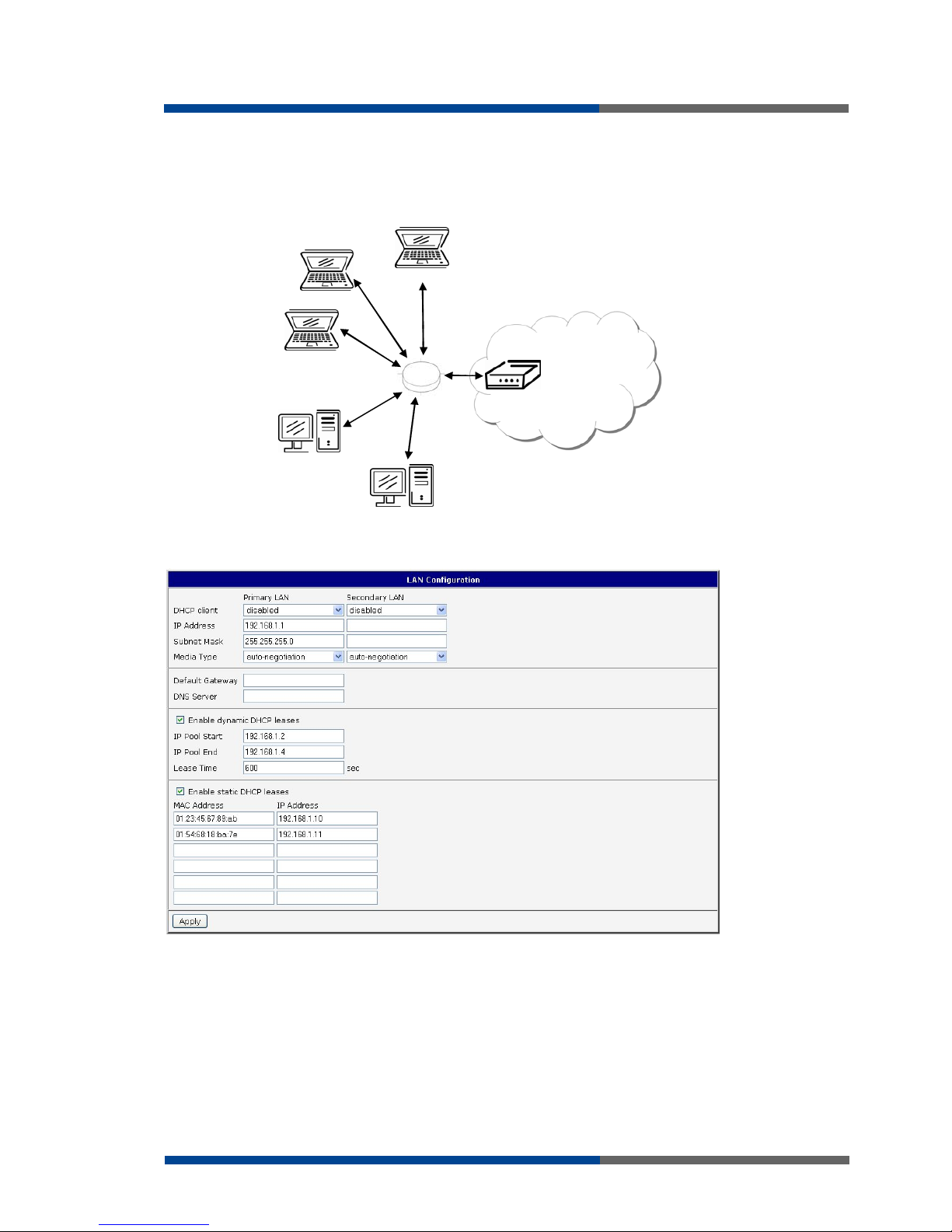
Example of the network interface with dynamic and static DHCP server:
The range of allocated addresses from 192.168.1.2 to 192.168.1.4.
The address is allocated 10 minutes.
Client's with MAC address 01:23:45:67:89:ab has IP address 192.168.1.10.
Client's with MAC address 01:54:68:18:ba:7e has IP address 192.168.1.11.
192.168.1.3
192.168.1.4
ETH
192.168.1.2
GSM/GPRS
192.168.1.10
01-23-45-67-89-ab
192.168.1.11
01-54-68-18-ba-7e
192.168.1.1
F
ig 11: Topology of
example LAN
configuration 2
F
ig 12:
E
x
ample LAN
configuration 2
Page 22
Configuration settings over web browser
22
Wieland Electric | BA000819 | 01/2012 (Rev. A)
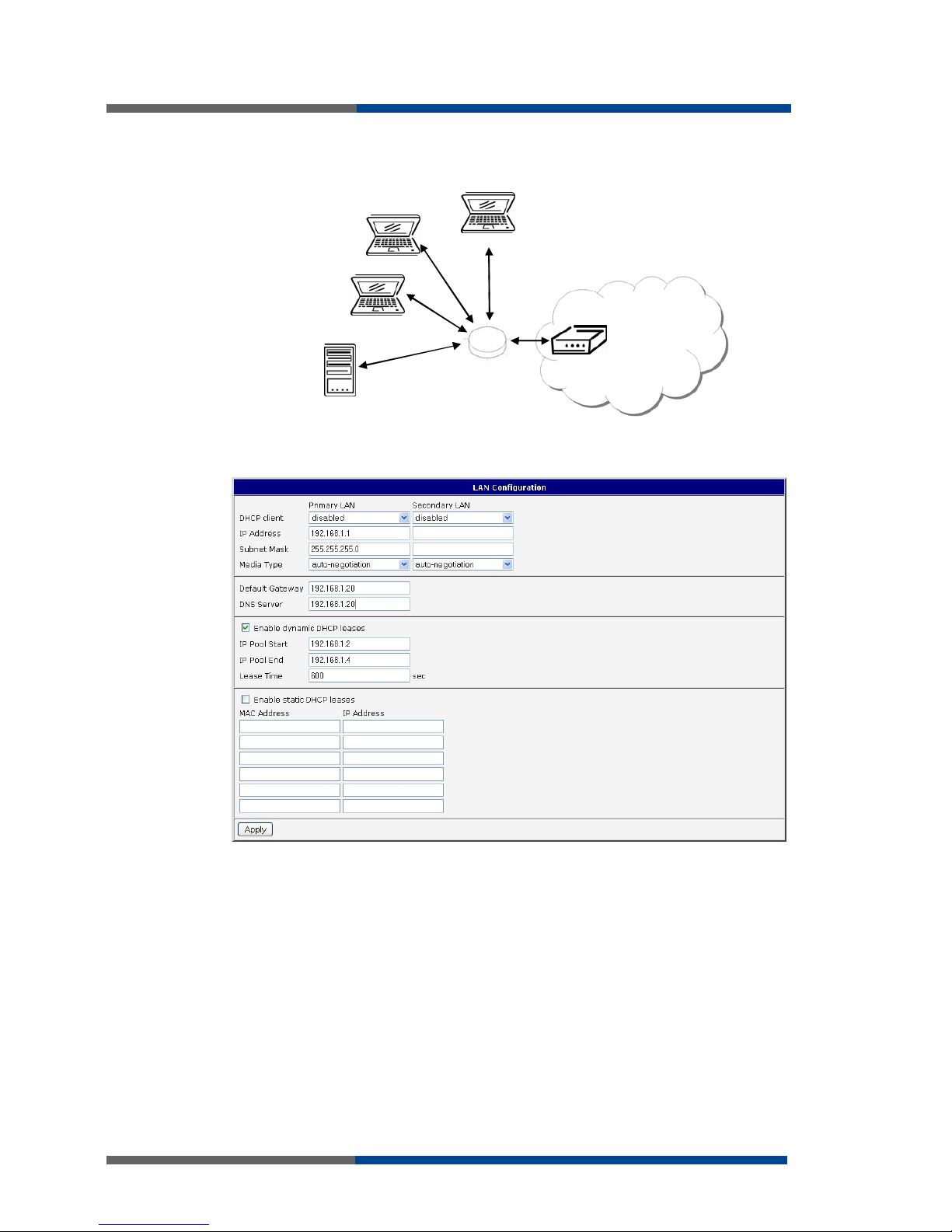
Example of the network interface with default gateway and DNS server:
Default gateway IP address is 192.168.1.20
DNS server IP address is 192.168.1.20
192.168.1.3
192.168.1.4
192.168.1.1
ETH
192.168.1.2
GSM/GPRS
192.168.1.20
F
ig 13: Topologie of
example LAN
configuration 3
F
ig 14: Example LAN
configuration 3
Page 23
Configuration settings over web browser
Wieland Electric | BA000819 | 01/2012 (Rev. A)
23
3.9 VRRP configuration
To enter the VRRP configuration select the VRRP menu item.
VRRP
protocol (Virtual
Router Redundancy Protocol) is a technique, by which it is possible to forward routing
from main router to backup router in the case of the main router failure. If the
Enable
VRRP
is checked, then it is possible to set the following parameters.
Item Desciption
Virtual Server IP
Address
This parameter sets virtual server IP address. This address should
be thesame for both routers. A connected device sends its data via
this virtual address.
Virtual Server ID
Parameter
Virtual Server ID
distinguishes one virtual router on the
network from others. Main and backup routers must use the same
value for this parameter.
Host Priority
The router, with higher priority set by the parameter
Host Priority
,
is the main router. According to RFC 2338 the main router has the
highest possible priority - 255. The backup router has priority in
range 1 – 254 (init value is 100). The priority value equals 0 is not
allowed.
Virtual Server IP
Address
This parameter sets virtual server IP address. This address should
be the same for both routers. A connected device sends its data
via this virtual address.
It is possible to set Check PPP connection flag in the second part of the window. The currently active router (main/backup) will send testing messages to defined Ping IP Address at
periodic time intervals (Ping Interval) with setting time of waiting for answer (Ping Timeout). The function check PPP connection is used as a supplement of VRRP standard with
the same final result. If there are no answers from remote devices (Ping IP Address) for a
defined number of probes (Ping Probes), then connection is switched to the other line.
Item Desciption
Ping IP Address Destinations IP address ping queries. Address can not specify as
domain name.
Ping Interval Time intervals between the outgoing pings.
Ping Timeout Time to wait to answer.
Ping Probes Number of failed ping requests, after which the route is considered
to be impassable.
Ping IP address is possible to use for example a DNS server of mobile operator as a test
message (ping) IP address.
There's an additional way for evaluating the state of the active line. It is activated by selecting Enable traffic monitoring parameter. If this parameter is set and any packet different
from ping is sent to the monitored line, then any answer to this packet is expected for Ping
Timeout. If Ping Timeout expires with no answer received then process of testing the active line continues the same way like in the case of standard testing process after first test
message answer drops out.
Table 12: VRRP
configuration
Table 13
:
Check PPP
connection
NOTICE
Page 24

Configuration settings over web browser
24
Wieland Electric | BA000819 | 01/2012 (Rev. A)
Example of the VRRP protocol:
Main router
Vir tual server ID 5
Host priority 255
192.168.1.1
192.168.1.2
192.168.1.3
Backup router
Virtual server ID 5
Host priority 100
ETH
10.0.1.3
APN 1
APN 2
F
ig 15: Topology of
example VRRP
configuration
F
ig 1
6
: :
Example
VRRP configuration –
main router
F
ig 17: : Example
VRRP configuration –
backup router
Page 25

Configuration settings over web browser
Wieland Electric | BA000819 | 01/2012 (Rev. A)
25
3.10 GPRS configuration
The industrial router wienet XR5i v2 is not availability item GPRS Configuration.
To enter the GPRS connection configuration select the GPRS menu item.
3.10.1 GPRS connection
If the Create GPRS connection option is selected, the modem automatically tries to establish GPRS connection after switching-on.
Item Desciption
APN Network identifier (Access Point Name)
Username User name to log into the GSM network.
Password Password to log into the GSM network.
Authentication Authentication protocol in GSM network
PAP or CHAP – Router is chosen one of the authentication methods.
PAP – It is used PAP authentication method.
CHAP – It is used CHAP authentication method.
IP Address IP address of SIM card. The user sets the IP address, only in the
case IP address was assigned of the operator.
Phone Number Telephone number to dial GPRS or CSD connection. Router as a
default telephone number used *99***1 #.
Operator This item can be defined PLNM preferred carrier code
Network type Automatic selection – The router automatically selects a specific
transmission method according to the availability of transmission
technology.
Furthermore, according to the type of router - it is also possible to
select a specific method of data transmission (GPRS, EDGE, UMTS
…).
PIN PIN parameter should be set only if it requires a SIM card router.
SIM card is blocked in case of several bad attempts to enter the
PIN.
MRU Maximum Receiving Unit) – it is the identifier of the maximum size
of packet, which is possible to receive in a given environment.
Default value is 1500 bytes. Other settings may cause incorrect
transmission of data.
MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) – it is the identifier of the maximum
size of packet, which is possible to transfer in a given environment. Default value is 1500 bytes. Other settings may cause incorrect transmission of data.
If the IP address field is not filled in, the operator automatically assigns the IP address
when it is establishing the connection. If filled IP address supplied by the operator, router
accelerate access to the network.
If the APN field is not filled in, the router automatically selects the APN by the IMSI code of
the SIM card. If the PLMN (operator number format) is not in the list of APN, then default
APN is “internet“. The mobile operator defines APN.
NOTICE
Table 14: GPRS
connection
configuration
NOTICE
NOTICE
Page 26

Configuration settings over web browser
26
Wieland Electric | BA000819 | 01/2012 (Rev. A)
If only one SIM card is plugged in the router, router switches between the APN. Router
with two SIM cards switches between SIM cards.
Correct PIN must be filled. For SIM cards with two APN’s there will be the same PIN for
both APN`s. Otherwise the SIM card can be blocked by false SIM PIN.
Items marked with an asterisk must be filled only if the information required by the operator.
In the case of a failed build a PPP connection is recommended to check the accuracy of
entered data. Alternatively, try a different authentication method or network type.
3.10.2 DNS address configuration
The choice Get DNS address from operator is given for easier configuration on client side.
If this field is filled in, then the router tries to get an IP address of primary and secondary
DNS server from the operator automatically.
3.10.3 Check PPP connection configuration
If the Check PPP connection option is selected, it has active control of connection over
PPP. The modem will automatically send the ping question to the selected domain name
or IP address in periodic time intervals. If the PING failed, new ping be sent immediately.
After three unsuccessfully pings on appropriate IP address the router terminates connection and tries to establish a new connection. It is possible to use, for example, the DNS
server of a mobile operator as the ping IP address.
Item Desciption
Ping IP Address Destinations IP address or domain name of ping queries.
Ping Interval Time intervals between the outgoing pings.
If the Enable Traffic Monitoring option is selected, then the router stops sending ping
questions to the Ping IP Address and it will watch traffic in PPP connection. If PPP connection is without traffic longer than the Ping Interval, then the router sends ping questions to
the Ping IP Address.
We recommend checking the GPRS connection in case of uninterrupted running.
3.10.4 Data limit configuration
Item Desciption
Data limit With this parameter you can set the maximum expected amount
of data transmitted (sent and received) over GPRS in one billing
period (month).
Warning Threshold Parameter Warning Threshold determine per cent of Data Limit in
the range of 50% to 99%, which if is exceeded, then the router
sends SMS in the form Router has exceeded (value of Warning
Threshold) a data limit.
Accounting Start Parameter sets the day of the month in which the billing cycle
starts SIM card used. Start of the billing period defines the operator, which gives the SIM card. The router begin to count the transferred data since that day
CAUTION
Table 15
:
Check PPP
connection
configuration
CAUTION
Table 16
:
Data limit
configuration
Page 27

Configuration settings over web browser
Wieland Electric | BA000819 | 01/2012 (Rev. A)
27
If the parameter Switch to backup SIM card when data limit is exceeded (see next) or Send
SMS when datalimit is exceeded (see SMS configuration) are not selected the data limit
will not count.
3.10.5 Switch between SIM cards configuration
At the bottom of configuration it is possible to set rules for switching between two APN’s
on the SIM card, in the event that one SIM card is inserted or between two SIM cards, in
the event that two SIM cards are inserted.
Item Desciption
Default SIM card This parameter sets default APN or SIM card, from which it will try
to establish the PPP connection. If this parameter is set to none,
the router launches in off-line mode and it is necessary to establish
PPP connection via SMS message.
Backup SIM card Defines backup APN or SIM card, that the router will switch the
defining one of the following rules.
If parameter Backup SIM card is set to none, then parameters Switch to other SIM card
when connection fails, Switch to backup SIM card when roaming is detected and Switch
to backup SIM card when data limit is exceeded switch the router to off-line mode.
Item Desciption
Switch to other SIM
card when connection fails
If PPP connection fails, then this parameter ensures switch to
secondary SIM card or secondary APN of the SIM card. Failure of
the PPP connection can occur in two ways. When I start the router, when three fails to establish a PPP connection. Or if it is checked Check the PPP connection, and is indicated by the loss of a
PPP connection.
Switch to backup
SIM card when roaming is detected
In case that the roaming is detected this parameter enables switching to secondary SIM card or secondary APN of the SIM card.
Switch to backup
SIM card when data
limit is exceeded
This parameter enables switching to secondary SIM card or secondary APN of the SIM card, when the data limit of default APN
is exceeded.
Switch to backup
SIM card when binary input is active
This parameter enables switching to secondary SIM card or secondary APN of the SIM card, when binary input ‘bin0’ is active.
Switch to primary
SIM card after timeout
This parameter defines the method, how the router will try to
switch back to default SIM card or default APN.
NOTICE
Table 17: Default and
backup SIM
configuration
NOTICE
Table 1
8
:
Switch
between SIM card
configuration
Page 28

Configuration settings over web browser
28
Wieland Electric | BA000819 | 01/2012 (Rev. A)
The following parameters define the time after which the router attempts to go back to the
default SIM card or APN.
Item Desciption
Initial timeout The first attempt to switch back to the primary SIM card or APN
shall be made for the time defined in the parameter Initial Timeout,
range of this parameter is from 1 to 10000 minutes.
Subsequent Timeout In an unsuccessful attempt to switch to default SIM card, the rou-
ter on the second attempt to try for the time defined in the parameter Subsequent Timeout, range is from 1 to 10000 minutes.
Additive constants Any further attempt to switch back to the primary SIM card or
APN shall be made in time computed as the sum of the previous
time trial and time defined in the parameter Additive constants
range is 1-10000 minutes.
Example:
If parameter Switch to primary SIM card after timeout is checked and parameters
are set as follows Initial Timeout – 60min. Subsequent Timeout 30min a Subsequent
Timeout - 20min.The first attempt to switch the primary SIM card or APN shall be carried
out after 60 minutes. Switched to a failed second attempt made after 30 minutes. Third
after 50 minutes (30 +20). Fourth after 70 minutes (30 +20 +20).
3.10.6 Dial-In access configuration
Dial in access configuration is supported only for routers ER75i, UR5, ER75i v2 UR5 v2 and
v2.
In the bottom part of the window it is possible to define access over CSD connection by
Enable Dial-In Access function. Access can be secured by used the Username
and Password. In the event that this function is enabled and the router does not have a
PPP connection is granted access to the router via dial-up connections CSD. The router
waits 2 minutes to accept connections. If the router during this time nobody logs on, the
router will try again to establish a GPRS connection.
Item Desciption
Username User name for secured Dial-In access.
Password Password for secured Dial-In access.
3.10.7 PPPoE bridge mode configuration
If the Enable PPPoE bridge mode option selected, it activate the PPPoE bridge protocol
PPPoE (point-to-point over ethernet) is a network protocol for encapsulating Point-to-Point
Protocol (PPP) frames inside Ethernet frames. Allows you to create a PPPoE connection
from the device behind router. For example from PC which is connected to ETH port
router. There will be allot Ip address of SIM card to PC.
Table 19: Switch
between SIM card
configurations
CAUTION
Table
20:
Dial-In
access configuration
Page 29

Configuration settings over web browser
Wieland Electric | BA000819 | 01/2012 (Rev. A)
29
The changes in settings will apply after pressing the Apply button.
F
ig 1
8
: :
GPRS
configuration
Page 30

Configuration settings over web browser
30
Wieland Electric | BA000819 | 01/2012 (Rev. A)
Example of setting controls the PPP connection to the address 8.8.8.8 in the time interval
of 60s for primary SIM card and to the address www.google.com in the time interval 80s
for secondary SIM card. In the case of traffic on the PPP control pings are not sent, but the
traffic on PPP is observed:
Example of switching to a backup SIM card after exceeding the data limits of 800MB
Sending SMS warning when reaching 400MB. With the beginning billing day of the 18th
of the month:
Example: Primary SIM card switch to offline modes, after router detection roaming. The
first attempt to switch back to the default SIM card is done after 60 minutes, the second
after 40 minutes, the third after 50 minutes (40 +10)...
F
ig 19: : Example of
GPRS configuration
F
ig 20: : Example of
GPRS configuration 2
F
ig 21: : Example of
GPRS configuration 3
Page 31

Configuration settings over web browser
Wieland Electric | BA000819 | 01/2012 (Rev. A)
31
3.10.8 PPPoE configuration
PPPoE configuration item is available only on the industrial router XR5i v2.
PPPoE for industrial router works in client mode. Router using connection to the PPPoE
server or PPPoE bridge (for example ADSL modem).
To enter the PPPoE configuration select the
PPPoE
menu item. If the Create PPPoE connection option is selected, the router tries to establish PPPoE connection after switchingon. PPPoE (Point-to-Point over Ethernet) is a network protocol, which PPP frames encapsulating to the Ethernet frames. PPPoE client to connect devices that support PPPoE
bridge or a server (typically ADSL router). After connecting the router obtains the IP address of the device to which it is connected. All communications from the device behind
the PPPoE server is forwarded to industrial router.
Item Desciption
Username Username for secure access to PPPoE
Password Password for secure access to PPPoE
Authentication Authentication protocol in GSM network
PAP or CHAP – Router is chosen one of the authentication methods.
PAP – It is used PAP authentication method.
CHAP – It is used CHAP authentication method.
MRU (Maximum Receiving Unit) – it is the identifier of the maximum
size of packet, which is possible to recese in given environment.
Default value is set to 1492 bytes. Other settings may cause incorrect data transmission.
MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) – it is the identifier of the maximum
size of packet, which is possible to transfer in given environment.
Default value is set to 1492 bytes. Other settings may cause incorrect data transmission.
CAUTION
NOTICE
Table 21: PPPoE
configuration
F
ig 22: : PPPoE
configuration
Page 32

Configuration settings over web browser
32
Wieland Electric | BA000819 | 01/2012 (Rev. A)
3.11 Firewall configuration
By the help of a firewall it is possible to set IP addresses from which are possible to remotely access the router and internal network connected behind a router. The choice Allow remote access only from specified hosts is given for easier configuration of hosts. In
this firewall configuration it is possible to set up to four remote accesses by the help of
Source, Source IP Address, Protocol and Target Port.
Item Desciption
Source single address - access allowed a single IP address defined in the
Source IP Address
any address – allowed access to any IP address
Source IP address IP address from which it is allowed to access the router.
Protocol Specify protocol for remote access
all – access is allowed by all
TCP – access is allowed by TCP
UDP - access is allowed by UDP
ICMP access is allowed by ICMP
Target Port The port number on which it is allowed to access the router.
Caution! Firewall doesn’t filter via Ethernet.
Table 22: Firewall
configuration
CAUTION
Page 33

Configuration settings over web browser
Wieland Electric | BA000819 | 01/2012 (Rev. A)
33
Example of the firewall configuration:
The router has allowed the following access:
from address 171.92.5.45 using any protocol
from address 10.0.2.123 using TCP protocol on any ports
from address 142.2.26.54 using ICMP protocol
10.0.2.123
171.92
.5.45
142.2.26.54
TCP/1000
ICMP
ALL
F
ig 23: : Topology of
example firewall
configuration
F
ig 24: : Example of
firewall configuration
Page 34

Configuration settings over web browser
34
Wieland Electric | BA000819 | 01/2012 (Rev. A)
3.12 NAT configuration
To enter the Network Address Translation configuration, select the NAT menu item. NAT
(Network address Translation / Port address Translation - PAT) is a method of adjusting the
network traffic through the router default transcript and/or destination IP addresses often
change the number of TCP/UDP port for walk-through IP packets. The window contains
sixteen entries for the definition of NAT rules.
Item Desciption
Public Port Public port
Private Port Private port
Type Protocol selection
Server IP address IP address which will be forwarded incoming data.
If necessary set more than sixteen rules for NAT rules, then is possible insert into start up
script following script:
iptables -t nat -A napt -p tcp --dport [PORT_PUBLIC] -j DNAT --to-destination
[IPADDR]:[PORT1_PRIVATE]
Concrete IP address [IPADDR] and ports numbers [PORT_PUBLIC]
and [PORT1_PRIVATE] are filled up into square bracket.
The following items are used to set the routing of all incoming traffic from the PPP to the
connected computer.
Item Desciption
Send all incoming
packets to default
server
By checking this item and setting the Default Server item it is possible to put the router into the mode in which all incoming data
from GPRS will be routed to the computer with the defined IP
address.
Default Server Send all incoming packets to this IP addresses.
Enable the following options and enter the port number is allowed remote access to the
router from PPP interface.
Item Desciption
Enable remote HTTP
access on por
t
If this item field and port number is filled in, then configuration of
the router over web interface is possible.
Enable remote
HTTPS access on
port
If this item field and port number is filled in, then configuration of
the router over web interface is possible.
Enable remote FTP
access on port
Choice this item and port number makes it possible to access over
FTP.
Enable remote SSH
access on port
Choice this item and port number makes it possible to access over
SSH.
Enable remote Telnet access on port
Choice this item and port number makes it possible to access over
Telnet.
Enable remote
SNMP access on
port
Choice this item and port number makes it possible to access to
SNMP agent.
Masquerade outgoing packets
Choice Masquerade (alternative name for the NAT system) item
option turns the system address translation NAT.
Enable remote HTTP
access on port
If this item field and port number is filled in, then configuration of
the router over web interface is possible.
Table 23: NAT
configuration
Table
24:
Configuration
of send all incoming
packets
Table
25:
Remote
access Configuration
Page 35

Configuration settings over web browser
Wieland Electric | BA000819 | 01/2012 (Rev. A)
35
Example of the configuration with one connection equipment on the router:
162.209.13.222
IP 192.168 .1. 2
Defau lt gat e way
192.168.1.1
ppp0 10 .0.0.1
eth0 192.168.1.1
In these configurations it is important to have marked choice of Send all remaining incoming packets it default server, IP address in this case is the address of the device behind the
router. Connected equipment behind the router must have set Default Gateway on the
router. Connected device replies, while PING on IP address of SIM card.
F
ig 25: : Topology of
example NAT
configurations
F
ig
26
: : E
xample NAT
configuration 1
Page 36

Configuration settings over web browser
36
Wieland Electric | BA000819 | 01/2012 (Rev. A)
Example of the configuration with more connected equipment:
162.209.13.222
192.168.1.2:80
192.168.1.3:80
192.168. 1.4:80
ppp0 10.0.0.1
SWITCH
10.0.0.1:81
10.0.0.1:82
10.0.0.1:83
F
ig 27: : Topology of
example NAT
configuration 1
F
ig
28
: : E
xample of
NAT configuration 2
Page 37

Configuration settings over web browser
Wieland Electric | BA000819 | 01/2012 (Rev. A)
37
In this configuration equipment wired behind the router defines the address Server IP Address. The router replies, while PING on address of SIM card. Access on web interface of
the equipment behind the router is possible by the help of Port Forwarding, when behind
IP address of SIM is indicating public port of equipment on which we want to come up. At
demand on port 80 it is surveyed singles outer ports (Public port), there this port isn't defined, therefore at check selection Enable remote http access it automatically opens the
web interface router. If this choice isn't selected and is selected volition Send all remaining
incoming packets to the default server fulfill oneself connection on induction IP address. If
it is not selected selection Send all remaining incoming packets to default server and Default server IP address then connection requests a failure.
3.13 OpenVPN tunnel configuration
OpenVPN tunnel configuration can be called up by option OpenVPN item in the menu.
OpenVPN tunnel allows protected connection of two networks LAN to the one which looks
like one homogenous. In the OpenVPN Tunnels Configuration window are two rows, each
row for one configured OpenVPN tunnel.
Item Desciption
Create This item enables the individual tunnels.
Description This item displays the name of the tunnel specified in the configu-
ration of the tunnel.
Edit Configuration OpenVPN tunnel.
Item Desciption
Description Description of tunnel.
Protocol Protocol, by which the tunnel will communicate.
UDP:
TCP server:
TCP client:
OpenVPN will communicate using UDP.
OpenVPN will communicate using TCP in server
mode.
OpenVPN will communicate using TCP in client
mode.
UDP/TCP port Port, by which the tunnel will communicate.
Remote IP Address IP address of the opposite side of the tunnel. Can be used domain
name.
Remote Subnet Network IP address of the opposite side of the tunnel.
Remote Subnet
Mask
Subnet mask of the opposite side of the tunnel.
Redirect Gateway By this parameter is possible to redirect all traffic on Ethernet.
Local Interface IP
Address
IP address of the local side of tunnel.
Remote Interface IP
Address
IP address of interface local side of tunnel.
Ping Interval This parameter defines the time period after which router sends a
message to opposite side of tunnel, for check the existence of the
tunnel.
Ping Timeout Ping Timeout waits on message from off-side tunnel. For
OpenVPN tunnel right verifies parameter Ping Timeout has to be
Table 26: Overview
OpenVPN tunnels
F
ig 29: : OpenVPN
tunnels configuration
Table
27:
OpenVPN
configuration
Page 38

Configuration settings over web browser
38
Wieland Electric | BA000819 | 01/2012 (Rev. A)
bigger than Ping Interval.
Renegotiate Interval This parameter sets renegotiate period (reauthorization) of the
OpenVPN tunnel. This parameter is possible to set only at username/password authentication or at X.509 certificate using. After
this time period, the router changes the encryption tunnel to ensure the continued safety of the tunnel.
Max Fragment Size By parameter Max Fragment Size it is possible to define maximum
sending packet size.
Compression Sending data is possible compress
none No compression is used.
LZO Are used lossless LZO compressions. Compression
has to be on both tunnel ends.
NAT Rules By parameter NAT Rules it is possible to apply set NAT rules to
OpenVPN tunnel.
not applied NAT rules to OpenVPN is not applied.
applied NAT rules to OpenVPN is applied.
Authenticate Mode This parameter can be set authentication mode.
none is used any authentication mode
Pre-shared secret - enables authentication using Pre-shared sec-
ret. This authentication set shared key for both offside tunnel
Username/password – enables authentication using CA Certifica-
te, Username and Password
X.509 Certificate (multiclient) – enables authentication by CA
Certificate, Local Certificate and Local Private Key
X.509 Certificate (client) – enables authentication by CA Certifica-
te, Local Certificate and Local Private Key
X.509 Certificate (server) - enables authentication by CA Certifica-
te, Local Certificate and Local Private Key
Pre-shared Secret Authentication using Pre-shared secret can be used in all offered
authentication mode.
CA Certificate This authentication certificate can be used in authentication mode
Username/password and X.509 certificate.
DH Parameters Protocol for exchange key DH parameters can be used in authenti-
cation mode X.509 server.
Local Certificate This authentication certificate can be used in authentication mode
X.509 certificate.
Local Private Key Local private key can be used in authentication mode X.509 certi-
ficate.
Username
Password
Authentication using a login name and password authentication
can be used in the Authenticate Mode Username/Password.
Extra Options By the help of parameter Extra Options it is possible to define addi-
tional parameters of the OpenVPN tunnel, for example DHCP options etc.
Page 39

Configuration settings over web browser
Wieland Electric | BA000819 | 01/2012 (Rev. A)
39
The changes in settings will apply after pressing the Apply button.
F
ig 30: : OpenVPN
tunnel configuration
Page 40

Configuration settings over web browser
40
Wieland Electric | BA000819 | 01/2012 (Rev. A)
Example of the OpenVPN tunnel configuration:
192.168.1.4
192.168.1.3
192.168.1.2
192.168.2.2
192.168.2.3
192.168.2.4
ppp0 10.0.0.1
192.168.1.0
tun0 19.16.1.0
ppp0 10.0.0.2
192.168.2.0
tun 0 19.16.2.0
OpenVPN tunnel
Default Gateway 192.168. 1.1
Default Gateway 192.168.2.1
A
B
OpenVPN tunnel configuration:
Configuration A B
Protocol UDP UDP
UDP Port 1194 1194
Remote IP Address 10.0.0.2 10.0.0.1
Remote Subnet 192.168.2.0 192.168.1.0
Remote Subnet Mask 255.255.255.0 255.255.255.0
Local Interface IP Address 19.16.1.0 19.16.2.0
Remote Interface IP Address 19.16.2.0 19.18.1.0
Compression LZO LZO
Authenticate mode none none
Examples of different options for configuration and authentication of OpenVPN can be
found in the configuration manual OpenVPN tunnel.
F
ig 31: : Topology of
example OpenVPN
configuration 2
Table
28
:
Example
OpenVPN
configuration
Page 41

Configuration settings over web browser
Wieland Electric | BA000819 | 01/2012 (Rev. A)
41
3.14 IPSec tunnel configuration
IPsec tunnel configuration can be called up by option IPsec item in the menu. IPsec tunnel
allows protected (encrypted) connection of two networks LAN to the one which looks like
one homogenous. In the IPsec Tunnels Configuration window are four rows, each row for
one configured one IPSec tunnel.
Item Desciption
Create This item enables the individual tunnels.
Description This item displays the name of the tunnel specified in the configu-
ration of the tunnel.
Edit Configuration IPsec tunnel.
Table 29: Overview
IPsec tunnels
F
ig 32: : IPsec tunnels
configuration
Page 42

Configuration settings over web browser
42
Wieland Electric | BA000819 | 01/2012 (Rev. A)
Item Desciption
Description Description of tunnel.
Remote IP Address IP address of opposite side tunnel. Can be used domain main.
Remote ID Identification of opposite side tunnel. Parameters ID contain two
parts: hostname and domain-name.
Remote Subnet Address nets behind off - side tunnel
Remote Subnet
Mask
Subnet mask behind off - side tunnel
Local ID Identification of local side. Parameters ID contain two parts: host-
name and domain-name.
Local Subnet Local subnet address
Local subnet mask Local subnet mask
Key Lifetime Lifetime key data part of tunnel. The minimum value of this para-
meter is 60s. The maximum value is 86400 s.
IKE Lifetime Lifetime key service part of tunnel. The minimum value of this
parameter is 60s. The maximum value is 86400 s.
Rekey Margin Specifies how long before connection expiry should attempt to
negotiate a replacement begin. The maximum value must be less
than half the parameters IKE and Key Lifetime.
Rekey Fuzz Specifies the maximum percentage by which should be randomly
increased to randomize re-keying intervals
DPD Delay Defines time after which is made IPsec tunnel verification
DPD Timeout By parameter DPD Timeout is set timeout of the answer
NAT traversal If address translation between two end points of the IPsec tunnel
is used, it needs to allow NAT Traversal
Aggressive mode If this parameter is enabled, establishing of IPsec tunnel will be
faster, but encryption will set permanently on 3DES-MD5.
Authenticate Mode Authentication is possible to set by parameter Authenticate mode,
at choice are following possibilities:
Pre-shared key - shared key for both off-side tunnel.
X.509 Certificate -
Pre-shared Key sharable key for both parties tunnel
CA Certificate This certificate is necessary to insert Authentication mode x.509.
Remote Certificate This certificate is necessary to insert Authentication mode x.509.
Local Certificate This certificate is necessary to insert Authentication mode x.509.
Local Private Key This private key is necessary to insert Authentication mode x.509.
Local Passphrase This Local Passphrase is necessary to insert Authentication mode
x.509.
Extra Options By the help of this parameter it is possible to define additional
parameters of the IPsec tunnel, for example secure parameters
etc.
The certificates and private keys have to be in PEM format. As certificate it is possible to
use only certificate which has start and stop tag certificate.
Random time, after which it will re-exchange of new keys are defined:
Lifetime - (Rekey margin + random value in range (from 0 to Rekey margin * Rekey
Fuzz/100))
Table 30: IPsec tunnel
configuration
NOTICE
NOTICE
Page 43

Configuration settings over web browser
Wieland Electric | BA000819 | 01/2012 (Rev. A)
43
By default, the repeated exchange of keys held in the time range:
• Minimal time: 1h - (9m + 9m) = 42m
• Maximal time: 1h - (9m + 0m) = 51m
When setting the times for key exchange is recommended to leave the default setting in
which tunnel has guaranteed security. When set higher time, tunnel has smaller operating
costs and smaller the safety. Conversely, reducing the time, tunnel has higher operating
costs and higher safety of the tunnel.
The changes in settings will apply after pressing the Apply button.
F
ig 33: : IPsec tunnel
configuration
Page 44
Configuration settings over web browser
44
Wieland Electric | BA000819 | 01/2012 (Rev. A)
Example of the IPSec Tunnel configuration:
192.168.1.4
192.168.1.3
192.168.1.2
192.168.2.2
192.168.2.3
192.168.2.4
ppp0 10.0.0.1
192.168.1.0
ppp0 10.0.0.2
192.168.2.0
IPS ec tunel
Defau lt Gateway 192.168. 1.1
Default Gateway 192.168.2.1
A
B
IPsec tunnel configuration:
Configuration A B
Remote IP Address 10.0.0.2 10.0.0.1
Remote Subnet 192.168.2.0 192.168.1.0
Remote Subnet Mask 255.255.255.0 255.255.255.0
Local Subnet 192.168.1.0 192.168.2.0
Local Subnet Mas: 255.255.255.0 255.255.255.0
Authenticate mode pre-shared key pre-shared key
Pre-shared key test test
Examples of different options for configuration and authentication of IPsec can be found in
the configuration manual IPsec tunnel.
F
ig 34: : Topology of
example IPsec
configuration 2
Table
31:
Example
IPsec configuration
Page 45

Configuration settings over web browser
Wieland Electric | BA000819 | 01/2012 (Rev. A)
45
3.15 GRE tunnels configuration
To enter the GRE tunnels configuration, select the GRE menu item. The GRE tunnel is used
for connection of two networks to one that appears as one homogenous. It is possible to
configure up to four GRE tunnels. In the GRE Tunnels Configuration window are four rows,
each row for one configured GRE tunnel.
Item Desciption
Create This item enables the individual tunnels.
Description This item displays the name of the tunnel specified in the configu-
ration of the tunnel.
Edit Configuration GRE tunnel.
Item Desciption
Description Description of tunnel.
Remote IP Address IP address of the remote side of the tunnel
Local Interface IP
Address
IP address of the local side of the tunnel
Remote Interface IP
Address
IP address of the remote side of the tunnel
Remote Subnet IP address of the network behind the remote side of the tunnel
Remote Subnet
Mask
Mask of the network behind the remote side of the tunnel
Pre-shared Key An optional value that defines the 32b shared key, through which
the filtered data through the tunnel. This key must be defined on
both routers as same, otherwise the router will drop received packets. Using this key, the data do not provide a tunnel through.
GRE tunnel doesn’t connect itself via NAT.
The changes in settings will apply after pressing the Apply button.
Table 32: Overview
GRE tunnels
F
ig 35: : GRE tunnels
configuration
Table
33:
GRE tunnel
configuration
CAUTION
F
ig
36
: :
GRE tunnel
configuration
Page 46

Configuration settings over web browser
46
Wieland Electric | BA000819 | 01/2012 (Rev. A)
Example of the GRE Tunnel configuration:
192.168.1.4
192.168.1.3
192.168.1.2
192.168.2.2
192.168.2.3
192.168.2.4
ppp0 10.0.0.1
eth0 192. 168.1.1
ppp0 10.0.0.2
eth 0 192.168.2.1
GRE tunnel
Default Gatewa
y
192.168.1.1 Default Gateway 192.168.2.1
A
B
GRE tunnel Configuration:
Configuration A B
Remote IP Address 10.0.0.2 10.0.0.1
Remote Subnet 192.168.2.0 192.168.1.0
Remote Subnet Mask 255.255.255.0 255.255.255.0
F
ig 37: : Topology of
GRE tunnel
configuration
Table
34:
Example GRE
tunnel configuration
Page 47

Configuration settings over web browser
Wieland Electric | BA000819 | 01/2012 (Rev. A)
47
3.16 L2TP tunnel configuration
To enter the L2TP tunnels configuration, select the
L2TP
menu item. L2TP tunnel allows
protected connection by password of two networks LAN to the one which it looks like one
homogenous. The tunnels are active after selecting Create L2TP tunnel.
Item Desciption
Mode L2TP tunnel mode on the router side
L2TP server:
L2TP client:
in the case of a server must define the start and
end IP address range offered by the server
in case of client must define the IP address of the
server
Server IP Address IP address of server
Client Start IP Address
Start IP address in range, which is offered by server to clients
Client End IP Address
End IP address in range, which is offered by server to clients
Local IP Address IP address of the local side of the tunnel
Remote IP Address IP address of the remote side of the tunnel
Remote Subnet Address of the network behind the remote side of the tunnel
Remote Subnet
Mask
The mask of the network behind the remote side of the tunnel
Username Username for login to L2TP tunnel
Password Password for login to L2TP tunnel
The changes in settings will apply after pressing the
Apply
button.
Table 35: L2TP tunnel
configuration
F
ig
38
: : L
2TP tunnel
configuration
Page 48

Configuration settings over web browser
48
Wieland Electric | BA000819 | 01/2012 (Rev. A)
Example of the L2TP Tunnel configuration:
192.168.1.4
192.168.1.3
192.168.1.2
192.168.2.2
192.168.2.3
192.168.2.4
ppp0 10.0.0.1
192.168.1.1
ppp0 10.0.0.2
192.168.2.1
L2TP tunel
Default Gateway 192.168.1.1
Default Gateway 192.168.2.1
A
B
Configuration of the L2TP tunnel:
Configuration A B
Mode L2TP Server L2TP Client
Server IP Address --- 10.0.0.1
Client Start IP Address 192.168.1.2 ---
Client End IP Address 192.168.1.254 ---
Local IP Address 192.168.1.1 ---
Remote IP Address --- ---
Remote Subnet 192.168.2.0 192.168.1.0
Remote Subnet Mask 255.255.255.0 255.255.255.0
Username username username
Password password password
F
ig 39: : Topology of
example L2TP tunnel
configuration
Table
36:
Example
L2TP tunnel
configuration
Page 49

Configuration settings over web browser
Wieland Electric | BA000819 | 01/2012 (Rev. A)
49
3.17 DynDNS client configuration
DynDNS client Configuration can be called up by option DynDNS item in the menu. In the
window can be defined a third order domain registered on server www.dyndns.org
Item Desciption
Hostname Third order domain registered on server www.dyndns.org
Username Username for login to DynDNS server
Password Password for login to DynDNS server
Server If you want to use a different server than www.dyndns.org, fill in
his address to the item server (Server). If this item is left blank, the
default server is used.
Example of the DynDNS client configuration with domain wieland.dyndns.org, username
wieland, password wieland and default server http://members.dyndns.org:
Table 37: DynDNS
configuration
F
ig 40: : Example of
DynDNS configuration
Page 50

Configuration settings over web browser
50
Wieland Electric | BA000819 | 01/2012 (Rev. A)
3.18 NTP client configuration
NTP client Configuration can be called up by option NTP item in the menu. NTP (Network
Time Protocol) allows set the exact time to the router from the servers, which provide the
exact time on the network.
By parameter
Enable local NTP service
router is set to a mode in which it operates as an
NTP server for other devices in the LAN behind the router.
By parameter
Enable local NTP service
it is possible to set the router in mode, that it can
serve as NTP server for other devices.
Item Desciption
Primary NTP Server
Address
IP or domain address primary NTP server.
Secondary NTP Server Address
IP or domain address secondary NTP server.
Timezone By this parameter it is possible to set the time zone of the router
Daylight Saving
Time
By this parameter is possible to define time shift:
No - time shift is disabled
Yes - time shift is allowed
Example of the NTP configuration with set primary (ntp.cesnet.cz) and secondary
(tik.cesnet.cz) NTP server and with daylight saving time:
Table
38
:
NTP
configuration
F
ig 41: : Example of
NTP configuration
Page 51

Configuration settings over web browser
Wieland Electric | BA000819 | 01/2012 (Rev. A)
51
3.19 SNMP configuration
To enter the SNMP Configuration it is possible with SNMP agent ver.1 configuration which
sends information about the router, eventually about the status of the expansion port CNT
or M-BUS.
SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) provides status information about network
elements such as routers or end computers.
Item Desciption
Community Password for access to the SNMP agent.
Contact Person who manages the router together with information how to
contact this person.
Name Designation of the router.
Location Placing of the router.
By choosing Enable I/O extension
it is possible to monitor binary inputs I/O on the router.
By choosing Enable XC-CNT extension it is possible to monitor the expansion port CNT
inputs and outputs status.
By choosing Enable M-BUS extension and enter the
Baudrate, Parity
and
Stop Bits
it is
possible to monitor the meter status connected to the expansion port M-BUS status.
Item Desciption
Baudrate Communication speed.
Parity Control parity bit:
none – Data will be sent without parity.
even – Data will be sent with even parity.
odd - Data will be sent with odd parity.
Stop Bits Number of stop bit.
Parameters Enable XC-CNT extension and Enable M-BUS extension can not be checked
together.
Table 39: SNMP
configuration
Table 40
:
SNMP
configuration
CAUTION
Page 52

Configuration settings over web browser
52
Wieland Electric | BA000819 | 01/2012 (Rev. A)
Every monitor value is uniquely identified by the help of number identifier OID -
Object
Identifier
. For binary input and output the following range of OID is used:
OID Desciption
.1.3.6.1.4.1.30140.2.3.1.0 Binary input BIN0 (values 0,1)
.1.3.6.1.4.1.30140.2.3.2.0 Binary output OUT0 (values 0,1)
For the expansion port CNT the following range of OID is used:
OID Desciption
.1.3.6.1.4.1.30140.2.1.1.0 Analogy input AN1 (range 0-4095)
.1.3.6.1.4.1.30140.2.1.2.0 Analogy input AN2 (range 0-4095)
.1.3.6.1.4.1.30140.2.1.3.0 Counter input CNT1 (range 0-4294967295)
.1.3.6.1.4.1.30140.2.1.4.0 Counter input CNT2 (range 0-4294967295)
.1.3.6.1.4.1.30140.2.1.5.0 Binary input BIN1 (values 0,1)
.1.3.6.1.4.1.30140.2.1.6.0 Binary input BIN2 (values 0,1)
.1.3.6.1.4.1.30140.2.1.7.0 Binary input BIN3 (values 0,1)
.1.3.6.1.4.1.30140.2.1.8.0 Binary input BIN4 (values 0,1)
.1.3.6.1.4.1.30140.2.1.9.0 Binary output OUT1 (values 0,1)
For the expansion port M-BUS the following range of OID is used:
OID Desciption
.1.3.6.1.4.1.30140.2.2.<address>.1.0 IdNumber – meter number
.1.3.6.1.4.1.30140.2.2.<address>.2.0 Manufacturer
.1.3.6.1.4.1.30140.2.2.<address>.3.0 Version – specified meter version
.1.3.6.1.4.1.30140.2.2.<address>.4.0 Medium – type of metered medium
.1.3.6.1.4.1.30140.2.2.<address>.5.0 Status – errors report
.1.3.6.1.4.1.30140.2.2.<address>.6.0 0. VIF – value information field
.1.3.6.1.4.1.30140.2.2.<address>.7.0 0. measured value
.1.3.6.1.4.1.30140.2.2.<address>.8.0 1. VIF – value information field
.1.3.6.1.4.1.30140.2.2.<address>.9.0 1. measured value
…
.1.3.6.1.4.1.30140.2.2.<address>.100.0 47. VIF – value information field
.1.3.6.1.4.1.30140.2.2.<address>.101.0 47. measured value
The meter address can be from range 0..254 when 254 is broadcast.
Table 41: Object
identifier for binary
input and output
Table 42
:
Object
identifier CNT port
Table 43: Object
identifier for M-BUS
port
Page 53

Configuration settings over web browser
Wieland Electric | BA000819 | 01/2012 (Rev. A)
53
Example of SNMP settings and readout:
It is important to set the IP address of the SNMP agent (router) in field
Remote SNMP
agent
. After enter the IP address is in a
MIB tree
part is possible show object identifier.
The path to objects is:
iso->org->dod->internet->private->enterprises->wieland->protocols.
The path to information about router is:
iso
->
org->dod->internet->mgmt->mib-2->system
F
ig 42: : Example of
SNMP configuration
F
ig 43: : Example of
the MIB browser
Page 54

Configuration settings over web browser
54
Wieland Electric | BA000819 | 01/2012 (Rev. A)
3.20 SMTP configuration
To enter the SMTP it is possible configure SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) client,
which is set by sending emails.
Item Desciption
SMTP Server Address
IP or domain address of the mail server.
Username Name to email account.
Password Password to email account.
Own Email Address Address of the sender.
Example settings SMTP client:
E-mail can be send from the Startup script. This command is used to email with following
parameters.
-t receiver Email address
-s subject
-m message
-a appendix
-r number of attempts to send email (default set 2 attempts)
Commands and parameters can be entered only in lowercase.
Example to send email:
email –t name@domain.com –s “subject“ –m “message“ –a c:\directory\abc.doc –r 5
This command sends e-mail to address
jack@google.com
with the subject “
subject”
, body
message “message” and annex “abc.doc” right from the directory c:\directory\ and 5 attempts to send.
Table 44: SMTP client
configuration
F
ig 44: : SNMP
configuration
CAUTION
Page 55

Configuration settings over web browser
Wieland Electric | BA000819 | 01/2012 (Rev. A)
55
3.21 SMS configuration
The industrial router XR5i v2 is not availability item SMS Configuration.
SMS Configuration can be called up by option SMS item in the menu. SMS configuration
defines the options for sending SMS messages from the router at different defined events
and states of the router. In the first part of window it configuration send SMS.
Item Desciption
Send SMS on power
up
Automatic sending of SMS messages after power up
Send SMS on PPP
connect
Automatic sending SMS message after PPP connection.
Send SMS on PPP
disconnect
Automatic sending SMS message after PPP disconnection.
Send SMS when
datalimit exceeded
Automatic sending SMS message after datalimit exceeded.
Send SMS when
binary input on I/O
port (BIN0) is active
Automatic sending SMS message after binary input on I/O port
(BIN0) is active. Text of message is intended parameter BIN0.
Send SMS when
binary input on expansion port (BIN1BIN4) is active
Automatic sending SMS message after binary input on expansion
port (BIN1-BIN4) is active. Text of message is intended parameter
BIN1 - BIN4.
Phone Number 1 Telephone numbers for sending automatically generated SMS.
Phone Number 2
Phone Number 3
Unit ID The name of the router that will be sent in an SMS.
BIN0 - SMS SMS text messages when activate the binary input on the router.
BIN1 - SMS SMS text messages when activate the binary input on the expan-
sion port.
BIN2 - SMS SMS text messages when activate the binary input on the router.
BIN3 - SMS SMS text messages when activate the binary input on the router.
BIN4 - SMS SMS text messages when activate the binary input on the router.
In the second part of the window it is possible to set function
Enable remote control via
SMS
. After this it is possible to establish and close PPP connection by SMS message.
Item Desciption
Phone Number 1
Phone Number 2
Phone Number 3
This control can be configured for up to three numbers. If is set
Enable remote control via SMS,
all incoming SMS are processed
and deleted. In the default settings this parameter is turned on.
If no phone number is filled in, then it is possible to restart the router with the help
of SMS in the form of Reboot from any phone number. While filling of one, two or three
numbers it is possible to control the router with the help of an SMS sent only from these
numbers. While filling of sign “*” it is possible control the router with the help of an SMS
sent from every numbers.
Control SMS message doesn’t change the router configuration. If the router is switched to
offline mode by the SMS message the router will be in this mode up to next restart. This
behavior is the same for all control SMS messages.
CAUTION
Table 45
: S
end SMS
configuration
Table 46
:
Control via
SMS configuration
CAUTION
NOTICE
Page 56

Configuration settings over web browser
56
Wieland Electric | BA000819 | 01/2012 (Rev. A)
It is possible to send controls SMS in the form:
SMS Desciption
go online sim 1 Switch to SIM1 card
go online sim 2 Switch to SIM2 card
go online Switch router in online mode
go offline PPP connection termination
set out0=0 Set output I/O connector on 0
set out0=1 Set output I/O connector on 1
set out1=0 Set output expansion port XC-CNT on 0
set out1=1 Set output expansion port XC-CNT on 1
set profile std Set standard profile
set profile alt1 Set alternative profile 1
set profile alt2 Set alternative profile 2
set profile alt3 Set alternative profile 3
reboot Router reboot
get ip Router send answer with IP address SIM card
By choosing
Enable AT-SMS protocol on expansion port 1
and
Baudrate
it is possible to
send/receive an SMS on the serial Port 1.
Item Desciption
Baudrate Communication speed expansion port 1
By choosing
Enable AT-SMS protocol on expansion port 2
and
Baudrate
it is possible to
send/receive an SMS on the serial Port 2.
Item Desciption
Baudrate Communication speed expansion port 2
By choosing
Enable AT-SMS protocol on TCP port
and enter the
TCP port
it is possible to
send/receive an SMS on the TCP port. SMS messages are sent by the help of a standard
AT commands.
Item Desciption
TCP Port TCP port on which will be allowed to send/receive SMS messages.
3.21.1 Send SMS
The SMS is possible to do for example in HyperTerminal program. After establishing connection with the router via serial interface or Ethernet, it is possible to do with SMS by the
help of the next AT commands.
AT command Desciption
AT+CMGF=1 Set the text mode for SMS writing
AT+CMGS=”tel.
number”
Commands enables to send SMS on entered tel. number
AT+CMGL=ALL List of all SMS messages
AT+CMGR=<index> Read of the definite SMS (all SMS has our index)
AT+CMGD=<index> SMS delete according to index
AT+CMGL=ALL List of all SMS messages
AT+CMGR=<index> Read of the definite SMS (all SMS has our index)
Table 47: Control SMS
Table 4
8
: S
end SMS
on serial PORT1
configuration
Table 49
: S
end SMS
on serial PORT2
configuration
Table 50
: S
MS TCP
Port configuration
Table 51
:
AT
commands for work
with SMS
Page 57

Configuration settings over web browser
Wieland Electric | BA000819 | 01/2012 (Rev. A)
57
For the text mode for SMS writing is used command
AT+CMGF=1
.
AT+CMGF=1 Enter
OK
The SMS message is created by the help of command
AT+CMGS=<tel. number>
. After
Enter
button is pressed is displayed mark >, behind this mark it is possible to write your
own SMS message. The SMS message is sent by the help of
CTRL+Z
(SMS sending takes
a few minutes). SMS writing is possible to cancel by pressing
Esc
.
AT+CMGS=”1604758944” Enter
>Hello World! CTRL+Z (keys combination)
OK
It is possible to find the new SMS by the help of command
AT+CMGL=ALL
. This command reproaches all SMS messages.
AT+CMGL=”ALL” Enter
+CMGL: <index>, <status>,<sender number>, ,<date>,<time>
SMS text.
+CMGL: 1,“REC UNREAD“,“+491604758944“, ,“12/01/12, 10:33:26+04“
Hello World!
where <index> is ordinal number of the SMS,
<status> is SMS status:
REC UNREAD – SMS unread
REC READ – SMS read
STO UNSENT – stored unsent SMS
STO SENT – stored sent SMS
ALL – all SMS messages
<sender number> is tel. number from which the SMS was receive,
<date> is date of SMS received,
<time> is time of SMS received.
It is possible to read the new SMS message by command AT+CMGR=<index>.
AT+CMGR=1
Enter
+CMGL: <index>, <status>,<sender number>, ,<date>,<time>
SMS text.
+CMGL: 1,“REC READ“,“+491604758944“, ,“12/01/12, 9:48:04+04“
Hello World!
Received SMS is possible to delete by command AT+CMGD=<index>.
AT+CMGD=1
Enter
OK
Page 58
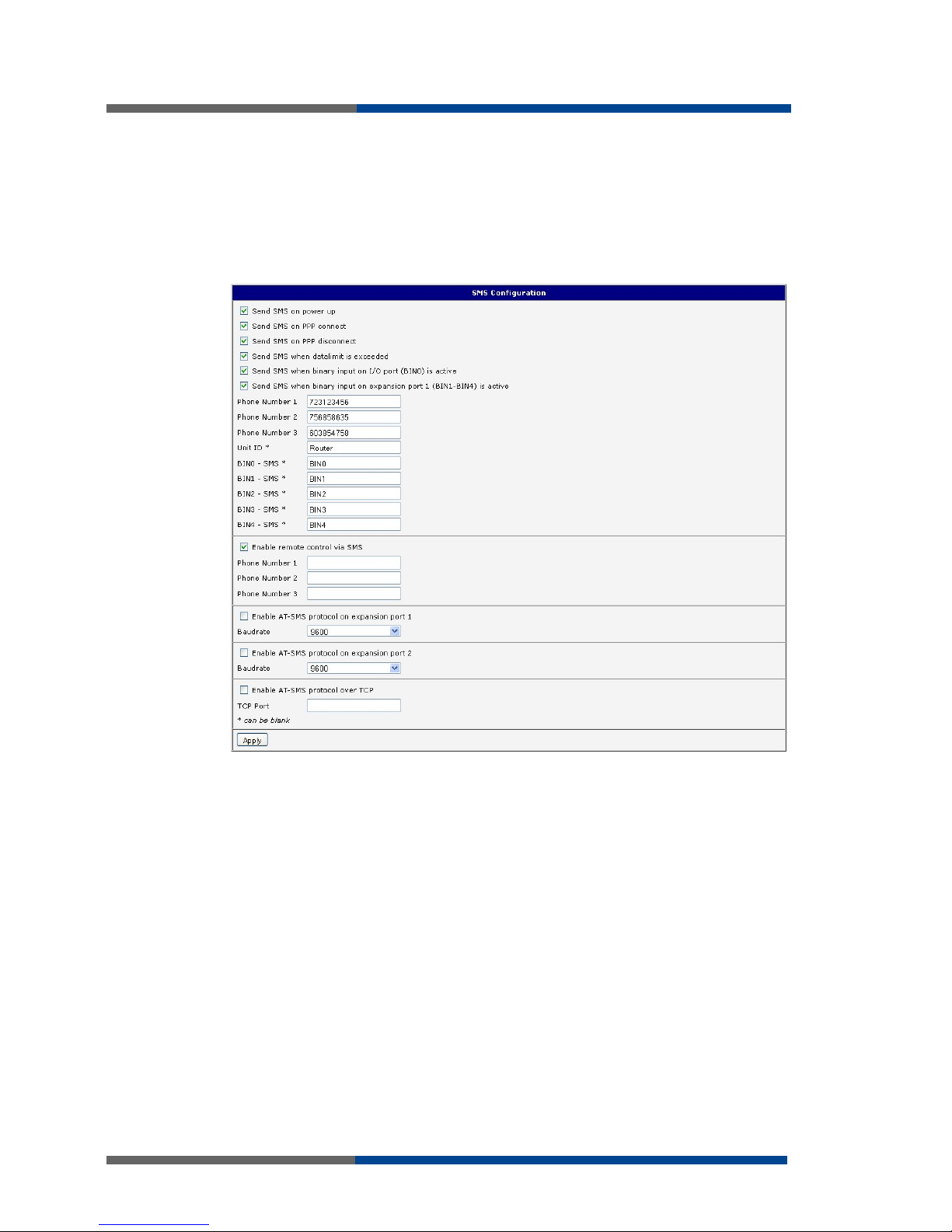
Configuration settings over web browser
58
Wieland Electric | BA000819 | 01/2012 (Rev. A)
After powering up the router, at introduction of the telephone number comes SMS in the
form of:
Router (Unit ID) has been powered up.GSM signal strength –xx dBm.
After PPP connect, at introduction of the telephone number comes SMS in the form:
Router (Unit ID) has established PPP connection. IP address xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
After PPP disconnect, at introduction of the telephone number comes SMS in the form:
Router (Unit ID) has lost PPP connection. IP address xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
Configuration of sending this SMS is following:
F
ig 45: : Example of
SMS configuration 1
Page 59

Configuration settings over web browser
Wieland Electric | BA000819 | 01/2012 (Rev. A)
59
Example of the router configuration for SMS sending via serial interface on the PORT1:
F
ig 4
6
: : E
xample of
SMS configuration 2
Page 60

Configuration settings over web browser
60
Wieland Electric | BA000819 | 01/2012 (Rev. A)
Example of the router configuration for controlling via SMS from every phone numbers:
F
ig 47: : Example of
SMS configuration 3
Page 61

Configuration settings over web browser
Wieland Electric | BA000819 | 01/2012 (Rev. A)
61
Example of the router configuration for controlling via SMS from two phone numbers:
F
ig 4
8
: : E
xample of
SMS configuration 4
Page 62

Configuration settings over web browser
62
Wieland Electric | BA000819 | 01/2012 (Rev. A)
3.22 Expansion port configuration
Configuring of the expansion ports PORT1 and PORT2 can cause selecting Expansion Port
1 or Expansion Port 2.
Item Desciption
Baudrate Applied communication speed.
Data Bits Number of data bits.
Parity Control parity bit
none - Will be sent without parity.
even - Will be sent with even parity.
odd - Will be sent with odd parity.
Stop Bits Number of stop bit.
Split Timeout Time to rupture reports. If you receive will identify the gap bet-
ween two characters, which is longer than the parameter value in
milliseconds. Then all of the received data compiled and sent the
message.
Protocol Protocol
TCP - communication using a linked protocol TCP
UDP - communication using a unlinked protocol UDP
Mode Mode of connection:
TCP server - The router will listen to incoming requests about
TCP connection.
TCP client - The router will connect to a TCP server on the speci-
fied IP address and TCP port.
Server Address In mode
TCP client
it is necessary to enter the
Server address
and
final
TCP port.
TCP Port In both modes of connection is necessary to specify the TCP port
on which the router will communicate TCP connections.
At
Check TCP connection
it activates verification of coupled TCP connection.
Item Desciption
Keepalive Time Time, after which it will carry out verification of the connection
Keepalive Interval Waiting time on answer
Keepalive Probes Number of tests
When you select items Use CD as indicator of the TCP connection is activated function
indication TCP connection using signal CD (DTR on the router).
CD Desciption
Active TCP connection is on
Nonactive TCP connection is off
Table 52: Expansion
PORT configuration 1
Table 53
: E
xpansion
PORT configuration 2
Table 54
:
CD signal
description
Page 63

Configuration settings over web browser
Wieland Electric | BA000819 | 01/2012 (Rev. A)
63
When you select items Use DTR as control of TCP connection is activated function control TCP connection using signal DTR (CD on the router).
DTR Description server Desciption client
Active The router allows establishing a
TCP connection.
Router starts TCP connection.
Nonactive The router does not permit estab-
lishing a TCP connection.
Router stops TCP connection.
The changes in settings will apply after pressing the
Apply
button.
Table 55: DTR signal
description
F
ig 49: : Expansion
port configuration
Page 64

Configuration settings over web browser
64
Wieland Electric | BA000819 | 01/2012 (Rev. A)
Example of external port configuration:
192.168.1.100
ppp0 10.0. 0.1
192.168.1.1
ppp0 10.0.0.2
Settings in application on PC:
TCP connection on 10.0.0.2:2000
Settings in the router
Mode: TCP server
Server Address: TCP Port: 2000
ETH
RS232
PC
PLC
Default Gateway 192.168.1.1
ppp0 10.0.0.1
ppp0 10.0.0.2
Settings in the router
Mode: TCP server
Server Address: TCP Port: 2000
RS232
RS232
PC
PLC
Settin gs in th e ro ute r
Mode: TCP client
Server Address: 10.0.0.2
TCP Port: 2000
F
ig 50: : Example of
expansion port
configuration 1
F
ig 51: : Example of
expansion port
configuration 2
Page 65

Configuration settings over web browser
Wieland Electric | BA000819 | 01/2012 (Rev. A)
65
3.23 USB port configuration
The USB port configuration can be called up by airbrush option
USB Port
in menu. Con-
figuration can be done, if we have USB/RS232 converter.
Item Desciption
Baudrate Applied communication speed.
Data Bits Number of data bits.
Parity Control parity bit
none - Will be sent without parity.
even - Will be sent with even parity.
odd - Will be sent with odd parity.
Stop Bits Number of stop bit.
Split Timeout Time to rupture reports. If you receive will identify the gap bet-
ween two characters, which is longer than the parameter value in
milliseconds. Then all of the received data compiled and sent the
message.
Protocol Communication protocol:
TCP - communication using a linked protocol TCP
UDP - communication using a unlinked protocol UDP
Mode Mode of connection:
TCP server - The router will listen to incoming requests about
TCP connection.
TCP client - The router will connect to a TCP server on the speci-
fied IP address and TCP port.
Server Address In mode TCP client it is necessary to enter the Server address and
final TCP port.
TCP Port In both modes of connection is necessary to specify the TCP port
on which the router will communicate TCP connections.
At
Check TCP connection
it activates verification of coupled TCP connection.
Item Desciption
Keepalive Time Time, after which it will carry out verification of the connection
Keepalive Interval Waiting time on answer
Keepalive Probes Number of tests
When you select items Use CD as indicator of the TCP connection is activated function
indication TCP connection using signal CD (DTR on the router).
CD Desciption
Active TCP connection is on
Nonactive TCP connection is off
Table 56: USB port
configuration 1
Table 57
:
USB port
configuration 2
Table 5
8
:
CD signal
description
Page 66

Configuration settings over web browser
66
Wieland Electric | BA000819 | 01/2012 (Rev. A)
When you select items Use DTR as control of TCP connection is activated function control TCP connection using signal DTR (CD on the router).
DTR Description server Desciption client
Active The router allows establishing a
TCP connection.
Router starts TCP connection.
Nonactive The router does not permit estab-
lishing a TCP connection.
Router stops TCP connection.
Supported USB/RS232 converters:
FTDI
Prolific PL2303
Silicon Laboratories CP210× (Podporován od firmware verze 3.0.1)
The changes in settings will apply after pressing the
Apply
button
Table 59: DTR signal
description
NOTICE
F
ig 52: : USB
configuration
Page 67
Configuration settings over web browser
Wieland Electric | BA000819 | 01/2012 (Rev. A)
67
Example of USB port configuration:
192.168.1.100
ppp0 10.0. 0.1
192.168.1.1
ppp0 10.0.0.2
Settings in applica ti on on PC:
TCP connection on 10.0.0.2:2000
Sett ings in the router
Mode: TCP server
Server Address: TCP Port: 2000
ETH
USB/RS232
PC
Equipment
De fault Gateway 192.168.1.1
ppp0 10.0.0.1
ppp0 10.0.0.2
Settings inthe r outer
Mode: TCP server
Server Address: TCP Port: 2000
ETH
USB/RS232
PC
Equipment
Settings in the router
Mode: TCP client
Server Address: 10.0.0.2
TCP Port: 2000
F
ig 53: : Example USB
port configuration 1
F
ig 54: : Example USB
port configuration 2
Page 68

Configuration settings over web browser
68
Wieland Electric | BA000819 | 01/2012 (Rev. A)
3.24 Startup script
In the window S
tartup Script
it is possible to create own scripts which will be executed
after all initial scripts.
The changes in settings will apply after pressing the
Apply
button.
Change take effect after shut down and witch on router by the help of button
Reboot
in
web administration or by SMS message.
Example of Startup script: When start the router, stop syslogd program and start syslogd
with remote logging on address 192.168.2.115 and limited to 100 entries listing.
F
ig 55: : Startup script
NOTICE
F
ig 5
6
: : E
xample of
Startup script
Page 69

Configuration settings over web browser
Wieland Electric | BA000819 | 01/2012 (Rev. A)
69
3.25 Up/Down script
In the window
Up/Down Script
it is possible to create own scripts. In the item
Up script
is
defined scripts, which begins after establishing a PPP/WAN connection. In the item
Down
Script
is defines script, which begins after lost a PPP/WAN connection.
The changes in settings will apply after pressing the
Apply
button.
Example of UP/Down script: After establishing or lost a PPP connection, the router sends
an email with information about establishing or loss a PPP connection.
F
ig 57: : Up/Down
script
F
ig 5
8
: : E
xample
Up/Down script
Page 70

Configuration settings over web browser
70
Wieland Electric | BA000819 | 01/2012 (Rev. A)
3.26 Automatic update configuration
In the window
Automatic update
it is possible to set automatic configuration update. This
choice enables that the router automatically downloads the configuration and the newest
firmware from the server itself. The configuration and firmware are stores on the server.
By
Enable automatic update of configuration
it is possible to enable automatic configu-
ration update and by
Enable automatic update of firmware
it is possible to enable firm-
ware update.
Item Desciption
Source In the item source can be set, where new firmware download:
HTTP/FTP server -
new firmware or configuration look at ad-
dress in the Base URL item
USB flash drive -
Router finds current firmware or configuration
in the root directory of the connected USB device.
Both -
looking for the current firmware or configuration from both
sources.
Base URL By parameter
Base URL
it is possible to enter base part of the
domain or IP address, from which the configuration file will be
downloaded.
Unit ID Name of configuration. If the Unit ID is not filled, then as the file
name used the MAC address of the router. (The delimiter is a colon is used instead of a dot.)
Update Hour Automatic configuration update starts 5 minutes after turning on
the router and then every 24 hours or it is possible to set the time
of automatic configuration in parameter
Update Hour.
If the entered URL is different configuration than in the router then the
router downloads this configuration and restarts itself.
The configuration file name is from parameter
Base URL
, hardware MAC address of ETH0
interface and
cfg
extension. Hardware MAC address and
cfg
extension is connected auto-
matically and it isn’t needed to enter this. By parameter
Unit ID
enabled it defines the con-
crete configuration name which will be download to the router. When using parameter
Unit ID
, hardware MAC address in configuration name will not be used.
The firmware file name is from parameter
Base URL,
type of router and bin extension.
Table 60: Automatic
update configuration
NOTICE
NOTICE
Page 71
Configuration settings over web browser
Wieland Electric | BA000819 | 01/2012 (Rev. A)
71
The following examples find if there is a new firmware or configuration each day at 1:00 in
the morning. An example is given on the type of router ER75i v2.
Firmware: http://router.cz/er75i-v2.bin
Configuration file: http://router.cz/temelin.cfg
The following examples find if there is a new firmware or configuration each day at 1:00 in
the morning. An example is given on the type of router ER75i v2 with MAC address
00:11:22:33:44:55.
Firmware: http://router.cz/er75i-v2.bin
Configuration file: http://router.cz/00.11.22.33.44.55.cfg
3.27 User modules
Custom configuration of modules can be accessed by selecting the Users Modules. In the
menu is possible add new software modules, remove them and move into their configuration. Programming, compiling and upload of user modules are described in the application
programming guide.
F
ig 59: : Example
automatic update 1
F
ig 60: : Example
automatic update 2
F
ig 61: : User modules
Page 72

Configuration settings over web browser
72
Wieland Electric | BA000819 | 01/2012 (Rev. A)
3.28 Change profile
To open the dialog box for changing profile select the
Change Profile
menu item. Profile
switch is making by press the button
Apply
. Change take effect after restarting router by
the help of button
Reboot
in web administration or by SMS message. It is possible select
the standard profile or up to three alternative profiles. It is possible to copy actual configuration to selected configuration by selecting
Copy settings from current profile to se-
lected profile
.
Example of usage profiles: Profiles can be used for example to switch between different
modes of operation of the router (router has compiled a PPP connection, the router has not
compiled a PPP connection and the router creates a tunnel to the service center). Change
the profile can then be done using a binary input, SMS or Web interface of the router.
Page 73

Possible problems
Wieland Electric | BA000819 | 01/2012 (Rev. A)
73
4 Possible problems
Some network cards are able to be set in situation, when it is not possible to connect the
router. It is possible to solve this problem in the following steps:
hand by selection communication rates 10 MB/s in property network cards,
connect router over switch,
start computer only after finalizing the start of the router.
NOTICE
Page 74

FAQ
74
Wieland Electric | BA000819 | 01/2012 (Rev. A)
5 FAQ
I can’t get from internet on equipment, which is connected to router and I have NAT
enabled.
The device's gateway has to be configured as the router.
Router resets itself, connection on Ethernet fails.
It is necessary to use an antenna, which will be situated far from power supply.
I don’t get on web server at NAT.
The remote http access of the router has to be disabled, default server address has to
be your web server and the gateway of the web server has to be the IP of router.
PPP connection fails.
Check signal power. If signal power is weak, you will have to use a better antenna. If
the environmental cells have a similar signal it will be necessary to use a directive antenna. Signal levels have to be in the range -50dBm and -90dBm.
It is necessary to set ping, which will check the connection and, in the case of fail
ping, restart connection.
PPP connection won't be established.
Recheck GPRS settings - APN, name, password and IP address.
Try to enter PIN – verification if the SIM card hasn’t set PIN code.
In private APN it is appropriate to switch the DNS server send off.
Switch log system on and observe where the error turns up.
Connection fails on Ethernet or connection isn’t establishing.
On ethernet interface of the router it is possible to switch auto negotiation off and set
a rate and duplex by hand.
DynDNS not function.
In private APN not functional.
If the same IP address is recorded in your canonic name as dynamically assign address, it means that the operator is using NAT or firewall.
NAT is possible to verify by the help of the ping on address of your server with static
IP address and by the help of the router address verify and address in ping.
Firewall is possible to verify, for example by remote access on web interface.
The operator doesn’t give out address DNS servers and without DNS server’s it is impossible to connect to server dyndns.org. In log system will be this message:
o DynDNS daemon started,
o Error resolving hostname: no such file or directory,
o Connect to DynDNS server failed.
IPSec tunnel is establishing but communication doesn’t function.
Probably it is badly set up route conditionals of connected equipment or it is bad set
up GW.
FTP doesn’t function.
Router doesn’t support the active FTP mode, supports the passive mode only.
RS232 doesn’t function.
It is necessary to verify present the expansion port RS232.
Verify present the expansion port RS232 in router configuration in menu „external
port“, or verify connection locally by the help Telnet-Hyper terminal.
L2TP or IPSec isn’t establishing.
Verify the reason in the log system.
I switched the router to offline mode by the SMS message, but the router is in online
mode after restart.
Control SMS message doesn’t change the router configuration. If the router is switched to offline mode by the SMS message the router will be in this mode up to next
restart. This behaviour is the same for next all control SMS messages.
Page 75

Customers support
Wieland Electric | BA000819 | 01/2012 (Rev. A)
75
6 Customers support
Up to date information about the product is on website:
http://www.wieland-electric.com/
Upkeep-advices:
The SIM-card must be handled carefully as with a credit card. Do not bend, do not scratch
onthis and do not expose to static electricity.
During cleaning of the router do not use aggressive chemicals, solvents and abrasive
cleaners!
Admission:
Wieland Electric hereby declares that the router narrated in this user’s guide fits all basic
demands of directive 1999/5/EC (R&TTE).
NOTICE
Page 76

List of figures
76
Wieland Electric | BA000819 | 01/2012 (Rev. A)
7 List of figures
Fig 1: Web configuration........................................................................................................9
Fig 2: Network status ...........................................................................................................11
Fig 3: DHCP status ............................................................................................................... 12
Fig 4: GPRS status ................................................................................................................ 15
Fig 5: IPsec status................................................................................................................. 16
Fig 6: DynDNS status ........................................................................................................... 17
Fig 7: System log.................................................................................................................. 18
Fig 8: Example program syslogd start with parameter ........................................................ 18
Fig 9: Topology of example LAN configuration 1................................................................. 20
Fig 10: Example LAN configuration...................................................................................... 20
Fig 11: Topology of example LAN configuration 2 .............................................................. 21
Fig 12: Example LAN configuration 2 .................................................................................. 21
Fig 13: Topologie of example LAN configuration 3.............................................................. 22
Fig 14: Example LAN configuration 3 .................................................................................. 22
Fig 15: Topology of example VRRP configuration ............................................................... 22
Fig 16: : Example VRRP configuration – main router ........................................................... 22
Fig 17: : Example VRRP configuration – backup router ....................................................... 22
Fig 18: : GPRS configuration ................................................................................................ 22
Fig 19: : Example of GPRS configuration ............................................................................. 22
Fig 20: : Example of GPRS configuration 2 .......................................................................... 22
Fig 21: : Example of GPRS configuration 3 .......................................................................... 22
Fig 22: : PPPoE configuration............................................................................................... 22
Fig 23: : Topology of example firewall configuration ........................................................... 22
Fig 24: : Example of firewall configuration........................................................................... 22
Fig 25: : Topology of example NAT configurations.............................................................. 22
Fig 26: : Example NAT configuration 1 ................................................................................ 22
Fig 27: : Topology of example NAT configuration 1 ............................................................ 22
Fig 28: : Example of NAT configuration 2 ............................................................................ 22
Fig 29: : OpenVPN tunnels configuration............................................................................. 22
Fig 30: : OpenVPN tunnel configuration............................................................................... 22
Fig 31: : Topology of example OpenVPN configuration 2.................................................... 22
Fig 32: : IPsec tunnels configuration .................................................................................... 22
Fig 33: : IPsec tunnel configuration...................................................................................... 22
Fig 34: : Topology of example IPsec configuration 2 ........................................................... 22
Fig 35: : GRE tunnels configuration...................................................................................... 22
Fig 36: : GRE tunnel configuration ....................................................................................... 22
Fig 37: : Topology of GRE tunnel configuration ................................................................... 22
Fig 38: : L2TP tunnel configuration ...................................................................................... 22
Fig 39: : Topology of example L2TP tunnel configuration ................................................... 22
Page 77

Wieland Electric | BA000819 | 01/2012 (Rev. A)
 Loading...
Loading...