Page 1

WTI Part No. 13513
Rev. B
MT5634/MT9234
Internal Modem
AT Command Set
Page 2

Page 3

Table of Contents
1. Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-1
2. AT Command Summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3. AT Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.1 Escape AT Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-16
4. S-Registers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5. Result Codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6. Remote Configuration and Country Code Configuration
6.1. Remote Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-1
6.1.1. Basic Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-1
6.1.2. Setup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-1
6.1.2.1. Changing the Setup Password . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-2
6.1.2.2. Changing the Remote Escape Character . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-2
6.2. Country Code Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-3
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-1
2-1
3-1
4-1
5-1
i
Page 4

MT5634/MT9234 Modem; AT Command Set
ii
Page 5

1. Introduction
The AT commands are used to control the operation of your modem. They are
called AT commands because the characters AT must precede each command
to get the ATtention of the modem.
AT commands can be issued only when the modem is in command mode or
online command mode.
• The modem is in command mode whenever it is not connected to another
modem.
• The modem is in data mode whenever it is connected to another modem
and ready to exchange data. Online command mode is a temporary state in
which you can issue commands to the modem while connected to another
modem.
• To put the modem into online command mode from data mode, you
must issue an escape sequence (+++) followed immediately by the AT
characters and the command, e.g., +++ATH to hang up the modem. To
return to data mode from online command mode, you must issue the
command ATO.
To send AT commands to the modem you must use a communications
program, such as the HyperTerminal applet in Windows 98 and NT 4.0, or
some other available terminal program. You can issue commands to the modem
either directly, by typing them in the terminal window of the communications
program, or indirectly, by configuring the operating system or communications
program to send the commands automatically. Fortunately, communications
programs make daily operation of modems effortless by hiding the commands
from the user. Most users, therefore, need to use AT commands only when
reconfiguring the modem, e.g., to turn auto answer on or off.
The format for entering an AT command is AT
and n is the specific value for the command, sometimes called the command
parameter. The value is always a number. If the value is zero, you can omit it
from the command; thus, AT&W is equivalent to AT&W0. Most commands
have a default value, which is the value that is set at the factory. The default
values are shown in Section 3.
You must press [Enter] (it could be some other key depending on the terminal
program) to send the command to the modem. Any time the modem receives a
command, it sends a response known as a result code. The most common result
codes are OK, ERROR, and the CONNECT messages that the modem sends
to the computer when it is connecting to another modem. See a table of valid
result codes at the end of this chapter.
Xn, where X is the command
1-1
Page 6

MT5634/MT9234 Modem; AT Command Set
You can issue several commands in one line, in what is called a command
string. The command string begins with AT and ends when you press [Enter].
Spaces to separate the commands are optional; the command interpreter
ignores them. The most familiar command string is the
initialization string,
which is used to configure the modem when it is turned on or reset, or when
your communications software calls another modem.
1-2
Page 7
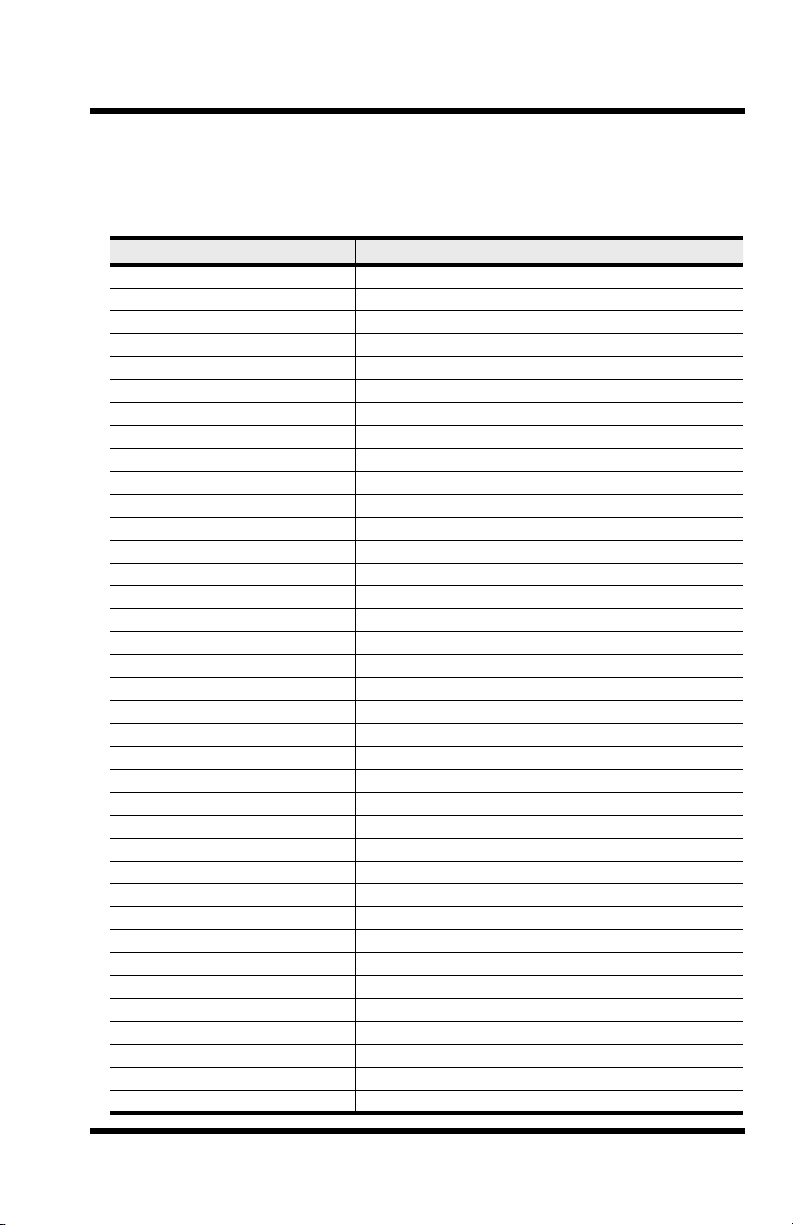
2. AT Command Summary
Organization of AT Commands on the following pages: 1st, by the initial
command character (&, +, %), 2nd, alphabetized by the second command
character (Except for listing of AT).
Command Description
AT Attention Code
A Answer
A/ Repeat Last Command
Bn Communication Standard Setting
Ds Dial
DS=y Dial Stored Telephone Number
En Echo Command Mode Characters
Fn Echo Online Data Characters
Hn Hook Control
In Information Request
Mn Monitor Speaker Mode
Nn Modulation Handshake
On Return Online to Data Mode
P Pulse Dialing
Qn Result Codes Enable/Disable
Sr=n Set Register Value
Sr? Read Register Value
T Tone Dialing
Vn Result Code Format
Wn Result Code Options
Xn Result Code Selection
Zn Modem Reset
&Cn Data Carrier Detect (DCD) Control
&Dn Data Terminal Ready (DTR) Control
&En XON/XOFF Pass-Through
&Fn Load Factory Settings
&Gn V.22bis Guard Tone Control
&Kn Flow Control Selection
&Ln Leased Line Operation
&Pn Pulse Dial Make-to-Break Ratio Selection
&Qn Asynchronous Communications Mode
&Sn Data Set Ready (DSR) Control
&Tn Loopback Test (V.54 Test) Commands
&V Display Current Settings
&Wn Store Current Configuration
&Zy=x Store Dialing Command
\An Select Maximum MNP Block Size
2-1
Page 8
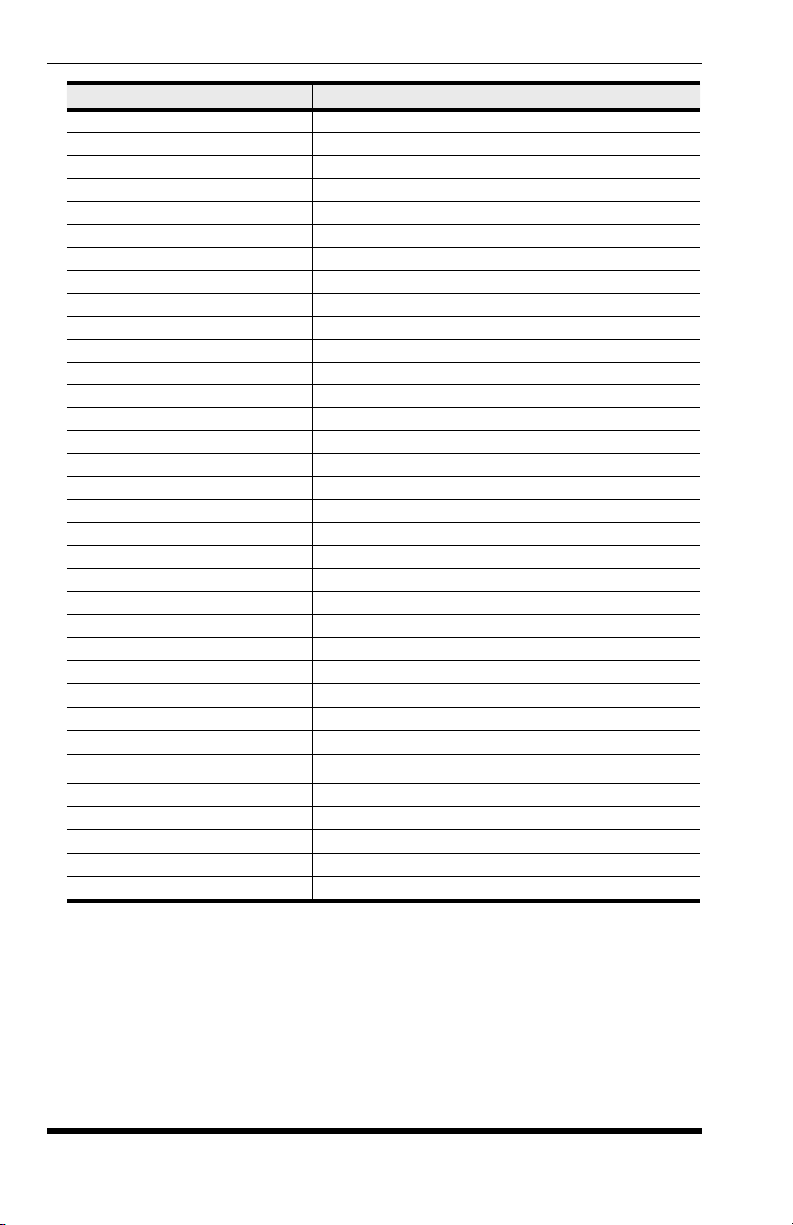
MT5634/MT9234 Modem; AT Command Set
Command Description
\Bn Transmit Break
\Kn Break Control
\Nn Error Correction Mode Selection
\Qn Flow Control Selection
\Tn Inactivity Timer
\Vn Protocol Result Code
-Cn Data Calling Tone
%An Adaptive Answer Result Code Enable
%B View Numbers in Blacklist
%Cn Data Compression Control
%DCn AT Command Control
%En Fallback and Fall Forward Control
%Hn Direct Connect Enable
%Rn Cisco Configuration
%Sn Command Speed Response
$EBn Asynchronous Word Length
$Dn DTR Dialing
$MBn Online BPS Speed
$SBn Serial Port Baud Rate
#CBAn Callback Attempts
#CBDn Callback Delay
# CBF? Callback Failed Attempts Display
# CBFR Callback Failed Attempts Reset
# CBIn Local Callback Inactivity Timer
# CBNy=n Store Callback Password
# CBPn Callback Parity
# CBRy Callback Security Reset
# CBSn Callback Enable/Disable
#Pn Set 11-bit Parity
#Sx Enter Setup Password
#S=x Store Setup Password
+VDR=x, y Distinctive Ring Report
+++AT<CR>
%%%ATMTSMODEM<CR> Remote Configuration Escape Sequence
Escape Sequence
2-2
Page 9

3. AT Commands
Command: AT Attention Code
Values: N/A
Description: The attention code precedes all command lines except
A: and escape sequences.
Command: [Enter] Key
Values: N/A
Description: Press the
commands.
[Enter] (RETURN) key to execute most
Command: A Answer
Values: N/A
Description: Answer call before final ring.
Command: A/ Repeat Last Command
Values: N/A
Description: Repeat the last command string. Do not precede this
command with AT. Do not press
[Enter] to execute.
Command: Bn Communication Standard Setting
Values: n = 0–3, 15, 16
Default: 0 and 15
Description: B0 Select ITU-T V.22 mode when modem is at 1200 bps.
B1 Select Bell 212A when modem is at 1200 bps.
B2 Deselect V.23 reverse channel (same as
B3 Deselect V.23 reverse channel (same as
B15 Select V.21 when the modem is at 300 bps.
B16 Select Bell 103J when the modem is at 300 bps.
A/,
B3).
B2).
3-1
Page 10

MT5634/MT9234 Modem; AT Command Set
Command: Ds Dial
Values: s = dial string (phone number and dial modifiers)
Default: none
Description: Dial telephone number
and include the 0–9, *, #, , B, C, and D characters, and the L, P, T,
V, W, S, comma (,), semicolon (;), !, @, ^ and $ dial string
modifiers.
Dial string modifiers:
L Redial last number. (Must be placed immediately
after ATD
number. Use ATH
(X2, X4, X5, X6, or X7 must be selected.)
of dial string.)
one-half second, then off-hook again.
ringback, then 5 seconds of silence, before
processing next part of command. If silence is not
detected, the modem returns a NO ANSWER code.
follow the phone number and precede the user’s call card
number: ATDT1028806127853500$123456789
P Pulse-dial following numbers in command.
T Tone-dial following numbers in command (default).
V Switch to speakerphone mode and dial the following
W Wait for a new dial tone before continuing to dial.
, Pause during dialing for time set in register S8.
; Return to command mode after dialing. (Place at end
! Hook flash. Causes the modem to go on-hook for
@ Wait for quiet answer. Causes modem to wait for a
^ Disable data calling tone transmission.
$ Detect AT&T call card “bong” tone. The character should
s, where s may up to 40 characters long
.)
command to hang up.
Command: DS=y Dial Stored Telephone Number
Values: y = 0–2 (0–1 for SMI-Parallel {internal})
Default: none
Description: Dial a number previously stored in directory number
&Zy=x command. Example: ATDS=2
y by the
Command: En Echo Command Mode Characters
Values: n = 0 or 1
Default: 1
Description: E0 Do not echo keyboard input to the terminal.
E1 Do echo keyboard input to the terminal.
Command: Fn Echo Online Data Characters
Values: n = 1
Default: 1
F0 Enable online data character echo. (Not supported.)
F1 Disable online data character echo (included for
backward compatibility with some software).
3-2
Page 11

AT Commands
Command: Hn Hook Control
Values: n = 0 or 1
Default: 0
Description: H0 Go on-hook (hang up).
H1 Go off-hook (make the phone line busy).
Command: In Information Request
Values: n = 0–5, 9, 11
Default: None
Description: I0 Display default speed and controller firmware version.
I1 Calculate and display ROM checksum (e.g., 12AB).
I2 Check ROM and verify the checksum, displaying
or
I3 Display default speed and controller firmware version.
I4 Display firmware version for data pump (e.g., 94).
I5 Display the board ID: software version, hardware
version, and country ID
I9 Display the country code.
I11 Display diagnostic information for the last modem
connection, such as link type, line speed, serial speed,
type of error correction/data compression, number
of past retrains, etc.
ERROR.
OK
Command: Mn Monitor Speaker Mode
Values: n = 0, 1, 2, or 3
Default: 1
Description: M0 Speaker always off.
M1 Speaker on until carrier signal detected.
M2 Speaker always on when modem is off-hook.
M3 Speaker on until carrier is detected, except while dialing.
Command: Nn Modulation Handshake
Values: n = 0 or 1
Default: 1
Description: N0 Modem performs handshake only at communication
standard specified by S37 and the
N1 Modem begins handshake at communication standard
specified by S37 and the
fallback to a lower speed can occur.
B command. During handshake,
B command.
Command: On Return Online to Data Mode
Values: n = 0, 1, 3
Default: None
Description: O0 Exit online command mode and return to data mode
(see +++AT<CR>
O1 Issue a retrain and return to online data mode.
O3 Issue a rate renegotiations and return to data mode.
escape sequence).
3-3
Page 12

MT5634/MT9234 Modem; AT Command Set
Command: P Pulse Dialing
Values: P, T
Default: T
Description: Configures the modem for pulse (non-touch-tone) dialing. Dialed
digits are pulsed until a
T command or dial modifier is received.
Command: Qn Result Codes Enable/Disable
Values: n = 0 or 1
Default: 0
Description: Q0 Enable result codes.
Q1 Disable result codes.
Q2 Returns an
some software.
OK for backward compatibility with
Command: Sr=n Set Register Value
Values: r = S-register number; n varies
Default: None
Description: Set value of register S
decimal format (e.g., S0=1).
r to value of n, where n is entered in
Command: Sr? Read Register Value
Values: r = S-register number
Default: None
Description: Read value of register Sr and display it in 3-digit decimal form
(e.g.,
S2? gives the response 043).
Command: T Tone Dialing
Values: P, T
Default: T
Description: Configures the modem for DTMF (touch-tone) dialing. Dialed
digits are tone dialed until a
is received.
P command or dial modifier
Command: Vn Result Code Format
Values: n = 0 or 1
Default: 1
Description: V0 Displays result codes as digits (terse response).
V1 Displays result codes as words (verbose response).
3-4
Page 13

AT Commands
Command: Wn Result Code Options
Values: n = 0, 1, or 2
Default: 2
Description: W0 CONNECT result code reports serial port speed, disables
protocol result codes.
W1 CONNECT result code reports serial port speed, enables
protocol result codes.
W2 CONNECT result code reports line speed, enables
protocol result codes.
Command: Xn Result Code Selection
Values: n = 0–7
Default: 4
Description: X0 Basic result codes (CONNECT); does not look for dial
tone or busy signal.
X1 Extended result codes (CONNECT 46000 V42bis); does
not look for dial tone or busy signal.
X2 Extended result codes with NO DIALTONE; does not
look for busy signal.
X3 Extended result codes with BUSY; does not look for
dial tone.
X4 Extended result codes with NO DIALTONE and BUSY.
X5 Extended result codes with NO DIALTONE and BUSY.
X6 Extended result codes with NO DIALTONE and BUSY.
X7 Basic result codes with NO DIALTONE and BUSY.
Command: Zn Modem Reset
Values: n = 0 or 1
Default: None
Description: Z0 Reset modem to profile saved by the last
Z1 Same as
Z0.
&W command.
Command: &Cn Data Carrier Detect (DCD) Control
Values: n = 0, 1, 2
Default: 1
Description: &C0 Forces the DCD circuit to be always ON.
&C1 DCD goes ON when the remote modem’s carrier signal
is detected, and goes OFF when the carrier signal is
not detected.
&C2 DCD turns OFF upon disconnect for time set by S18. It
then goes high again (for some PBX phone systems).
3-5
Page 14

MT5634/MT9234 Modem; AT Command Set
Command: &Dn Data Terminal Ready (DTR) Control
Values: n = 0, 1, 2, or 3
Default: 2
Description: &D0 Modem ignores true status of DTR signal and responds
as if it is always on.
&D1 If DTR drops while in online data mode, the modem
enters command mode, issues an
remains connected.
&D2 If DTR drops while in online data mode, the modem
hangs up. If the signal is not present, the modem will not
answer or dial.
&D3 If DTR drops, modem hangs up and resets as if ATZ
command were issued.
OK, and
Command: &En XON/XOFF Pacing Control
Values: n = 12 or 13
Default: 12
Description: &E12 Disables XON/XOFF pacing.
&E13 Enables XON/XOFF pacing.
Command: &Fn Load Factory Settings
Values: n = 0
Default: None
Description: &F0 Load factory settings as active configuration.
Note: See also the Z command.
Command: &Gn V.22bis Guard Tone Control
Values: n = 0, 1, or 2
Default: 0
Description: &G0 Disable guard tone.
&G1 Set guard tone to 550 Hz.
&G2 Set guard tone to 1800 Hz.
Note: The &G command is not used in North America.
Command: &Kn Flow Control Selection
Values: n = 0, 3, or 4
Defaults: 3
Description: &K0 Disable flow control.
&K3 Enable CTS/RTS hardware flow control.
&K4 Enable XON/XOFF software flow control.
3-6
Page 15

AT Commands
Command: &Ln Leased Line Operation
Values: n = 0, 1, or 2
Defaults: 0
Description: &L0 The modem is set for standard dial-up operation.
&L1 The modem is set for leased line operation in
originate mode.
&L2 The modem is set for leased line operation in
answer mode.
power up and the starting of the leased line handshake. During
this time, you can turn off the command, if desired.
Note: For &L1 and &L2, there is a 30-second window between
Command: &Pn Pulse Dial Make-to-Break Ratio Selection
Values: n = 0, 1, or 2
Default: 0
Description: &P0 60/40 make-to-break ratio
&P1 67/33 make-to-break ratio
&P2 20 pulses per second
set to Japan.
Note: The &P2 command is available only if the country code is
Command: &Qn Asynchronous Communications Mode
Values: n = 0, 5, 6, 8, or 9
Default: 5
Description: &Q0 Asynchronous with data buffering. Same as
&Q5 Error control with data buffering. Same as
&Q6 Asynchronous with data buffering. Same as
&Q8 MNP error control mode. If MNP error control is not
established, the modem falls back according to the
setting in
&Q9 V.42 or MNP error control mode. If neither error control
is established, the modem falls back according to the
setting in
S36.
S36.
\N0.
\N3.
\N0.
Command: &Sn Data Set Ready (DSR) Control
Values: n = 0 or 1
Default: 0
Description: &S0 DSR is always ON.
&S1 DSR goes ON only during a connection.
3-7
Page 16

MT5634/MT9234 Modem; AT Command Set
Command: &Tn Loopback Test (V.54 Test) Commands
Values: n = 0, 1, 3, 6
Default: None
Description: The modem can perform selected test and diagnostic functions. A
test can be run only when the modem is operating in non-error correction mode (normal or direct mode). For tests 3 and 6, a
connection between the two modems must be established. To
terminate a test in progress, the escape sequence (+++AT
be entered.
&T0 Stops any test in progress.
&T1 Starts a local analog loopback, V.54 Loop 3, test. If a
connection exists when this command is issued, the
modem hangs up. When the test starts, a
message is displayed.
&T3 Starts local digital loopback, V.54 Loop 2, test. If no
connection exists,
&T6 Initiates a remote digital loopback, V.54 Loop 2, test
without self-test. If no connection exists,
is returned.
ERROR is returned.
CONNECT
ERROR
) must
Command: &V Display Current Settings
Values: N/A
Description: Displays the active modem settings.
Command: &Wn Store Current Configuration
Values: n = 0 or 1
Default: 1
Description: &W0 Stores current modem settings in non-volatile memory
and causes them to be loaded at power-on or following
the ATZ
See
&W1 Clears user default settings from non-volatile memory
and causes the factory defaults to be loaded at power-on
or following the ATZ
command instead of the factory defaults.
&F command.
command.
Command: &Zy=x Store Dialing Command
Values: y = 0–2 (0–1SMI-Parallel {internal})
Default: None
Description: Stores dialing command
number using the command ATDS=
command, a callback security command.
x = Dialing command
x in memory location y. Dial the stored
y. See Also the #CBS
3-8
Page 17

AT Commands
Command: \An Select Maximum MNP Block Size
Values: n = 0, 1, 2, or 3
Default: 3
Description: \A0 64-character maximum
\A1 128-character maximum
\A2 192-character maximum
\A3 256-character maximum
Command: \Bn Transmit Break
Values: n = 0–9 in 100 ms units
Default: 3
Description: In non-error-correction mode only, sends a break signal of the
specified length to a remote modem. Works in conjunction with
the
\K command.
Command: \Kn Break Control
Values: n = 0–5
Default: 5
Description: Controls the modem’s response to a break received from:
computer, remote modem, or
for each of three different states.
Data mode. Modem receives break from computer:
\K0 Enter online command mode, no break sent to the
remote modem.
\K1 Clear data buffers and send break to the remote modem.
\K2 Same as \K0.
\K3 Send break immediately to the remote modem.
\K4 Same as
\K5 Send break to the remote modem in sequence with the
transmitted data.
Data mode. Modem receives break from remote modem:
\K0 Clear data buffers and send break to the computer.
\K1 Same as
\K2 Send break immediately to the computer.
\K3 Same as
\K4 Send break to the computer in sequence with the
received data.
\K5 Same as
Online command mode. Modem receives \Bn command from
the computer:
\K0 Clear data buffers and send break to the remote modem.
\K1 Same as \K0.
\K2 Send break immediately to the remote modem.
\K3 Same as
\K4 Send break to the remote modem in sequence with the
transmitted data.
\K5 Same as
\K0.
\K0.
\K2.
\K4.
\K2.
\K4.
\B command. Response is different
3-9
Page 18

MT5634/MT9234 Modem; AT Command Set
Command: \Nn Error Correction Mode Selection
Values: n = 0–5, or 7
Default: 3
Description: \N0 Non-error correction mode with data buffering
(buffer mode; same as
\N1 Direct mode.
\N2 MNP reliable mode. If the modem cannot make an
MNP connection, it disconnects.
\N3 V.42/MNP auto-reliable mode. The modem attempts first
to connect in V.42 error correction mode, then in MNP
mode, and finally in non-error correction (buffer) mode
with continued operation.
\N4 V.42 reliable mode. If the modem cannot make a V.42
connection, it disconnects.
\N5 V.42, MNP, or non-error correction (same as
\N7 V.42, MNP, or non-error correction (same as
&Q6).
\ N3).
\ N3).
Command: \Qn Flow Control Selection
Values: n = 0, 1, or 3
Default: 3
Description: \Q0 Disable flow control (same as
\Q1 XON/XOFF software flow control (same as
\Q2 CTS-only flow control. Not supported.
\Q3 RTS/CTS hardware flow control (same as
&K0).
&K4).
&K3).
Command: \Tn Inactivity Timer
Values: n = 0, 1–255
Default: 0
Description: Sets the time (in minutes) after the last character is sent or
received that the modem waits before disconnecting. A value of
zero disables the timer. Applies only in buffer mode.
value of
Note: You can also set the inactivity timer by changing the
S30.
Command: \Vn Protocol Result Code
Values: n = 0, 1, or 2
Default: 1
Description: \V0 Disables the appending of the protocol result code to
the DCE speed.
\V1 Enables the appending of the protocol result code to
the DCE speed.
\V2 Same as
\V1.
3-10
Page 19

AT Commands
Command: \Xn XON/XOFF Pass-Through
Values: n = 0 or 1
Default: 0
Description: \X0 Modem responds to and discards XON/XOFF characters.
\X1 Modem responds to and passes XON/XOFF characters.
Note: This is also controlled via &E6 and &E7.
Command: -Cn Data Calling Tone
Values: n = 0 or 1
Defaults: 1
Description: -C0 Disable V.25 data calling tone to deny remote
data/fax/voice discrimination.
-C1 Enable V.25 data calling tone to allow remote
data/fax/voice discrimination.
Command: %An Adaptive Answer Result Code Enable
Values: n = 0 or 1
Default: 0
Description: The %A command controls whether the DATA or FAX result
codes will be sent by the modem. The modem must be in fax
mode for this command to work. Also, the modem must be set
to +FAA=1
a fax and a data call. When these commands are enabled, the
modem sends DATA to the computer when it detects data tones
and FAX when it detects fax tones. These strings are used by
some servers to select the appropriate communication program.
%A0 Disables adaptive answer result codes.
%A1 Enables adaptive answer result codes.
, which enables the modem to distinguish between
Command: %B View Numbers in Blacklist
Values: N/A
Description: If blacklisting is in effect, AT%B
which the last call attempted in the previous two hours failed.
In countries that do not require blacklisting, the
result code appears.
displays the numbers for
ERROR
Command: %Cn Data Compression Control
Values: n = 0 or 1
Default: 1
Description: %C0 Disable V.42bis/MNP 5 data compression.
%C1 Enable V.42bis/MNP 5 data compression.
3-11
Page 20

MT5634/MT9234 Modem; AT Command Set
Command: %DCn AT Command Control
Values: n = 0 or 1
Default: 0
Description: %DC0 The modem responds to AT commands.
%DC1 The modem ignores AT commands.
Note: The modem will respond to AT%DC for 10 seconds
after power-up.
Command: %En Fallback and Fall Forward Control
Values: n = 0, 1, or 2
Default: 2
Description: %E0 Disable fallback and fall forward.
%E1 Enable fallback, disable fall forward.
%E2 Enable fallback and fall forward.
Command: %Hn Direct Connect Enable
Values: n = 0, 1
Default: 0
Description: %H0 Sets callback security to normal operation.
%H1 All callback security calls will be direct connect
regardless of whether the password or phone number
has the
- character.
Command: %Rn Cisco Configuration
Values: n = 0, 1
Default: 0
Description: %R0 Disables Cisco configuration.
%R1 Sets E0, Q1, &D0, \N0, $SB9600, and %S1 for
operation with a Cisco router.
Command: %Sn Command Speed Response
Values: n = 0, 1
Default: 0
Description: %S0 Sets modem to respond to AT commands at all
normal speeds.
%S1 AT commands accepted at 115200 bps only.
Commands at other speeds are ignored.
Command: $Dn DTR Dialing
Values: n = 0 or 1
Default: 0
Description: $D0 Disables DTR dialing.
$D1 Dials the number in memory location 0 when
DTR goes high.
3-12
Page 21

AT Commands
Command: $EBn Asynchronous Word Length
Values: n = 0 or 1
Default: 0
Description: $EB0 Enables 10-bit mode.
$EB1 Enables 11-bit mode.
Command: $MBn Online BPS Speed
Values: n = speed in bits per second
Default: 28,800
Description: $MB75 Selects CCITT V.23 mode
$MB300 Selects 300 bps on-line
$MB1200 Selects 1200 bps on-line
$MB2400 Selects 2400 bps on-line
$MB4800 Selects 4800 bps on-line
$MB9600 Selects 9600 bps on-line
$MB14400 Selects 14400 bps on-line
$MB19200 Selects 19200 bps on-line
$MB28800 Selects 28800 bps on-line
$MB33600 Selects 33600 bps on-line
Command: $RPn Ring Priority vs. AT Command Priority
Values: n = 0 or 1
Default: 1
Description: $RP0 The AT command will have priority over the ring. S1 will
be reset to 0 if an AT command is received. This
command is storable to memory.
$RP1 The ring will have priority over the AT command. S1 will
increment even if an AT command and ring are received
together and the incoming call will be answered when S1
is equal to S0.
telephone line simulators as a valid ring.
Note: SocketModems do not detect ring cadence of TelTone
Command: $SBn Serial Port Baud Rate
Values: n= speed in bits per second
Default: 57600
Description: $SB300 Sets serial port to 300 bps
$SB1200 Sets serial port to 1200 bps
$SB2400 Sets serial port to 2400 bps
$SB4800 Sets serial port to 4800 bps
$SB9600 Sets serial port to 9600 bps
$SB19200 Sets serial port to 19200 bps
$SB38400 Sets serial port to 38400 bps
$SB57600 Sets serial port to 57600 bps
$SB115200 Sets serial port to 115200 bps
$SB230400 Sets serial port to 230400 bps
3-13
Page 22

MT5634/MT9234 Modem; AT Command Set
Command: +VDR=x, y Distinctive Ring Report
Values: x = 0, 1 Distinctive Ring report control.
See description.
See description.
Default: 0, 0
Description: Enables reporting of ring cadence information to the
DTE and specifies the minimum ring cadence that will
be reported. The report format is one line per silence
period and one line per ring period. The length of the
silence period is in the form DROF=number in units of
100 ms<CR><LF>, and the length of the ring is in the
form DRON=number in units of 100 ms<CR> <LF>.
The modem may produce a Ring event code after the
DRON message if enabled by the y parameter. The y
parameter must be set to a value equal to or smaller than
the expected ring cadence in order to pass the report to
the DTE.
+VDR=0, N/A Disables Distinctive Ring
cadence reporting.
+VDR=1, 0 Enables Distinctive Ring cadence
reporting. Other call progress result
codes (including RING) are reported
as normal.
+VDR=1, >0 Enables Distinctive Ring cadence
reporting. The RING result code is
reported after the falling edge of the
ring pulse (i.e., after the DRON report).
+VDR=? Displays the allowed values.
+VDR? Displays the current value.
y = 0–255 Minimum ring interval in 100 ms units.
Command: #CBAn Callback Attempts
Values: n = 1–255
Default: 4
Description: Sets the number of callback attempts that are allowed after
passwords have been exchanged between modems.
Command: #CBDn Callback Delay
Values: n = 0–255
Default: 15
Description: Sets the length of time (in seconds) that the modem waits
before calling back the remote modem.
3-14
Page 23

AT Commands
Command: #CBF? Callback Failed Attempts Display
Values: N/A
Default: N/A
Description: Requests the number of failed callback passwords since reset
or power-up. This number can be stored to nonvolatile memory
using the &W command.
Command: #CBFR Callback Failed Attempts Reset
Values: N/A
Default: N/A
Description: Resets the number of failed callback passwords to 0. This does
not reset the number stored in nonvolatile memory.
Command: #CBIn Local Callback Inactivity Timer
Values: n = 1–255
Default: 20
Description: Sets the time (in minutes) that the modem waits for a command
before forcing the user to enter the setup password again.
Command: #CBNy=x
Store Callback Password
Values: y = 0–29
Defaults: None
Description: Sets the callback security password for the y memory location.
The password must have 6 to 10 characters, and cannot include
the + or - ¬characters.
x = password
Command: #CBPn Callback Parity
Values: n = 0, 1, or 2
Default: 0
Description: Sets parity for the callback security messages.
#CBP0 No parity.
#CBP1 Odd parity.
#CBP2 Even parity.
Command: #CBRy Callback Security Reset
Values: y = 0–29
Default: None
Description: Clears the password and phone number in the y memory location.
3-15
Page 24

MT5634/MT9234 Modem; AT Command Set
Command: #CBSn Callback Enable/Disable
Values: n = 0, 1, 2, or 3
Default: 0
Description: #CBS0 Disables callback security.
#CBS1 Enables local and remote callback security.
#CBS2 Enables remote callback security only.
#CBS3 Disables callback security until local hang-up or reset.
Command: #Pn Set 11-bit Parity
Values: n = 0 or 1
Default: 2
Description: #P0 No parity.
#P1 Odd parity.
#P2 Even parity.
Command: #Sx Enter Setup Password
Values: x= password (1–8 characters, case sensitive)
Default: MTSMODEM
Description: Enters the remote configuration setup password.
Command: #S=x Store Setup Password
Values: x= password (1–8 characters, case sensitive)
Default: MTSMODEM
Description: Stores a new remote configuration setup password.
3.1 Escape AT Commands
Command: +++AT<CR> Escape Sequence
Values: N/A
Description: Puts the modem in command mode (and optionally
issues a command) while remaining online. Type
+++AT
then press
command: +++ATH<CR>
Command: %%%ATMTSMODEM<CR>
Remote Configuration Escape Sequence
Values: N/A
Description: Initiates remote configuration mode while online
with remote modem. The remote configuration
escape character (%) is defined in register
3-16
and up to six optional command characters;
[Enter]. Used mostly to issue the hang-up
.
S13.
Page 25

4. S-Registers
Certain modem values, or parameters, are stored in memory locations called
S-Registers. Use the S command to read or to alter the contents of S-Registers
(see previous section).
Register Unit Range Default Description
S0 1 ring 0, 1–255 1 Sets the number of rings until the modem answers.
ATS0=0 disables auto answer completely.
S1 1 ring 0–255 0 Counts the rings that have occurred.
S2 decimal 0–127 43 (+) Sets ASCII code for the escape sequence character.
128–255 Values greater than 127 disable escape.
S3 decimal 0–127 13 (^M) Sets the ASCII code for the carriage return character.
S4 decimal 0–127 10 (^J) Sets the ASCII code for the line feed character.
S5 decimal 0–32 8 (^H) Sets the ASCII code for the backspace character.
33–127 Values greater than 32 disable backspace.
S6 seconds 2–65* 2* Sets the time the modem waits after it goes off-hook
before it begins to dial the telephone number.
S7 seconds 35-65* 50* Sets the time the modem waits for a carrier signal
before aborting a call. Also sets the wait for silence
time for the @ dial modifier.
S8 seconds 0–65 2 Sets the length of a pause caused by a comma
character in a dialing command.
S9 decimal 0, 1–127 37 (%) Sets ASCII code for remote configuration escape
character. S9=0 disables remote configuration.
S10 100 ms 1–254 20 Sets how long a carrier signal must be lost before the
modem disconnects.
S11 1 ms 50–150* 95* Sets spacing and duration of dialing tones.
S28 decimal 0, 1–255 1 0 disables, 1–255 enables V.34 modulation.
S30 1 minute 0, 1–255 0 Sets the length of time that the modem waits before
disconnecting when no data is sent or received.
A value of zero disables the timer. See also
the \T command
S35 decimal 0–1 1 0 disables, 1 enables the V.25 calling tone, which
allows remote data/fax/voice discrimination.
S36 decimal 0–7 7 Specifies the action to take in the event of a
negotiation failure when error control is
selected. (See S48.)
4-1
Page 26

MT5634/MT9234 Modem; AT Command Set
Register Unit Range Default Description
S37 decimal 0–19 0 Sets the maximum V.34 "upstream" speed at which
the modem attempts to connect.
0 = maximum speed
1 = reserved
2 = 1200/75 bps
3 = 300 bps
4 = reserved
5 = 1200 bps
6 = 2400 bps
7 = 4800 bps
8 = 7200 bps
9 = 9600 bps
10 = 12000 bps
11 = 14400 bps
12 = 16800 bps
13 = 19200 bps
14 = 21600 bps
15 = 24000 bps
16 = 26400 bps
17 = 28800 bps
18 = 31200 bps
19 = 33600 bps
S38 decimal 0–23 1 Sets "downstream" data rate where V.90 provides
rates of 28,000 to 56,000 bps in increments of
1,333 bps.
0 = V.90 disabled
1 = V.90 auto rate
2 = 28,000 bps
3 = 29,333 bps
4 = 30,666 bps
5 = 32,000 bps
6 = 33,333 bps
7 = 34,666 bps
8 = 36,000 bps
9 = 37,333 bps
10 = 38,666 bps
11 = 40,000 bps
12 = 41,333 bps
13 = 42,666 bps
14 = 44,000 bps
15 = 45,333 bps
16 = 46,666 bps
17 = 48,000 bps
18 = 49,333 bps
19 = 50,666 bps
20 = 52,000 bps
21 = 53,333 bps
22 = 54,666 bps
23 = 56,000 bps
Upstream data rates: Upstream V.90 data rates are
4800 to 33,600 bps in 2400 bps increments.
S43 decimal 0–1 1 For testing and debugging only. Enables/disables
V.32bis start-up auto mode operation. 0 = disable;
1 = enable.
4-2
Page 27

S-Registers
Register Unit Range Default Description
S48 decimal 7 or 128 7 Enables (7) or disables (128) LAPM negotiation.
The following table lists the S36 and S48
configuration settings for certain types of connections.
S48=7 S48=128
S36=0, 2 LAPM or hang up Do not use
S36=1, 3 LAPM or async Async
S36=4, 6 LAPM, MNP, MNP or hang up
or hang up
S36=5, 7 LAPM, MNP, MNP or async
or async
S89 seconds 0, 5–255 10 Sets the length of time in the off-line command mode
before the modem goes into standby mode or
"sleep mode". A value of zero prevents standby
mode; a value of 1–4 sets the value to 5. Standby
mode (sleep mode or low power mode) is controlled
by S89. It programs the number of seconds of
inactivity before the modem will go to sleep. The
default value is 0. A value of 0 disables standby
mode. The modem will wake on an incoming ring
or an AT command.
S108 decimal 0–3, 6, 7 6 Selects the 56K digital loss if using the modem
through a PBX line. The default value is -6 dB loss,
the value used when calling from a typical POTS
line long distance.
0 = -0 dB digital loss, no robbed-bit signaling
1 = -3 dB PBX digital loss
2 = -2 dB digital loss
3 = -3 dB digital loss
6 = -6 dB digital loss
7 = -0 dB digital loss with robbed-bit signaling
4-3
Page 28

MT5634/MT9234 Modem; AT Command Set
4-4
Page 29

5. Result Codes
In command mode your modem can send responses called Result Codes to
your computer. Result codes are used by communications programs and can
also appear on your monitor.
Terse Verbose Description
0 OK Command executed
1 CONNECT Modem connected to line
2 RING Ring signal detected
3 NO CARRIER Carrier signal lost or not detected
4 ERROR Invalid command
5 * CONNECT 1200 Connected at 1200 bps
6 NO DIALTONE No dial tone detected
7 BUSY Busy signal detected
8 NO ANSWER No answer at remote end
9 CONNECT 75 Connected at 75 bps
10* CONNECT 2400 Connected at 2400 bps
11* CONNECT 4800 Connected at 4800 bps
12* CONNECT 9600 Connected at 9600 bps
13* CONNECT 14400 Connected at 14400 bps
14* CONNECT 19200 Connected at 19200 bps
18 CONNECT 57600 Connected at 57600 bps
24* CONNECT 7200 Connected at 7200 bps
25* CONNECT 12000 Connected at 12000 bps
28 CONNECT 38400 Connected at 38400 bps
40* CONNECT 300 Connected at 300 bps
55* CONNECT 21600 Connected at 21600 bps
56* CONNECT 24000 Connected at 24000 bps
57* CONNECT 26400 Connected at 26400 bps
58* CONNECT 28800 Connected at 28800 bps
59* CONNECT 31200 Connected at 31200 bps
60* CONNECT 33600 Connected at 33600 bps
70 CONNECT 32000 Connected at 32000 bps
71 CONNECT 34000 Connected at 34000 bps
72 CONNECT 36000 Connected at 36000 bps
73 CONNECT 38000 Connected at 38000 bps
74 CONNECT 40000 Connected at 40000 bps
75 CONNECT 42000 Connected at 42000 bps
76 CONNECT 44000 Connected at 44000 bps
77 CONNECT 46000 Connected at 46000 bps
78 CONNECT 48000 Connected at 48000 bps
79 CONNECT 50000 Connected at 50000 bps
5-1
Page 30

MT5634/MT9234 Modem; AT Command Set
Terse Verbose Description
80 CONNECT 52000 Connected at 52000 bps
81 CONNECT 54000 Connected at 54000 bps
82 CONNECT 56000 Connected at 56000 bps
83 CONNECT 58000 Connected at 58000 bps
84 CONNECT 60000 Connected at 60000 bps
86 CONNECT 16800 Connected at 16800 bps
87 CONNECT 115200 Connected at 115200 bps
88 DELAYED Delay is in effect for the dialed number
89 BLACKLISTED Dialed number is blacklisted
90 BLACKLIST FULL Blacklist is full
91 CONNECT 230400 Connected at 230400 bps
100 CONNECT 28000 Connected at 28000 bps
101 CONNECT 29333 Connected at 29333 bps
102 CONNECT 30666 Connected at 30666 bps
103 CONNECT 33333 Connected at 33333 bps
104 CONNECT 34666 Connected at 34666 bps
105 CONNECT 37333 Connected at 37333 bps
106 CONNECT 38666 Connected at 38666 bps
107 CONNECT 41333 Connected at 41333 bps
108 CONNECT 42666 Connected at 42666 bps
109 CONNECT 45333 Connected at 45333 bps
110 CONNECT 46666 Connected at 46666 bps
111 CONNECT 49333 Connected at 49333 bps
112 CONNECT 50666 Connected at 50666 bps
113 CONNECT 53333 Connected at 53333 bps
114 CONNECT 54666 Connected at 54666 bps
115 CONNECT 25333 Connected at 25333 bps
116 CONNECT 26666 Connected at 26666 bps
* EC is added to these result codes when the extended result codes
configuration option is enabled. EC is replaced by one of the following
codes, depending on the type of error control connection:
• V42bis – V.42 error control (LAP-M) and V.42bis data compression
• V42 – V.42 error control (LAP-M) only
• MNP5 – MNP 4 error control and MNP 5 data compression
• MNP4 – MNP 4 error control only
• NoEC – No error control protocol
5-2
Page 31

6. Remote Configuration and
Country Code Configuration
6.1. Remote Configuration
Remote configuration is a network management tool that allows you to
configure modems anywhere in your network from one location. With
password-protected remote configuration, you can issue AT commands to a
remote modem for maintenance or troubleshooting as if you were on-site.
6.1.1. Basic Procedure
The following steps are valid regardless of whether the connection is
established by the local or the remote modem.
1. Establish a data connection with a remote modem.
2. Send three remote configuration escape characters followed by AT and
the setup password and press [Enter].
• Example: %%%ATMTSMODEM.
• You have four tries to enter the correct password before being
disconnected. If the password is correct, the remote modem responds
with OK.
3. You can now send AT commands to configure the remote modem.
4. When you have finished configuring the remote modem, save the new
configuration by typing AT&W0
5. Type ATO. Press [Enter] to exit remote configuration. You can now
break the connection.
6.1.2. Setup
MT5634/MT9234 Modems are shipped with a default setup password
(MTSMODEM). Because anyone who has the User Guide knows the default
setup password, you should change the password and possibly also the remote
configuration escape character.
. Press [Enter].
6-1
Page 32

MT5634/MT9234 Modem; AT Command Set
6.1.2.1. Changing the Setup Password
1. Open a data communications program such as HyperTerminal.
2. In the terminal window, type AT#SMTSMODEM
(or AT#Syyyyyy if
you have replaced the MTSMODEM password with yyyyyy) and press
[Enter]. The modem responds with OK if the setup password is correct
and ERROR if it is wrong.
3. To change the password, type AT#S=yyyyyy, where yyyyyy stands for
the password and press [Enter]. The password can include any keyboard
character and can be up to eight characters long. The modem responds
with OK.
4. The new password is saved automatically. You can now either enter more
AT commands or exit the data communications program. The next time
you remotely configure the modem you must use the new setup password.
Note: You can only change the setup password locally; you cannot do
it remotely. Also, passwords are case sensitive. The next time you enter
the password, it must be in the same case as you set it up.
6.1.2.2. Changing the Remote Escape Character
To further improve security, you can change a remote modem’s remote
configuration escape character. The remote configuration escape character is
stored in register S9. The factory default is 37, which is the ASCII code for the
percent character (%). Setting S9 to 0 (zero) disables remote
configuration entirely.
Caution: If you do this remotely, you won’t be able to change it
back remotely!
1. Establish a remote configuration link with the remote modem as described
in Basic Procedure.
Note: This command can be executed locally as well as remotely.
2. Type ATS9=n, where n is the ASCII code for the new remote
configuration escape character and press
[Enter].
3. Save the new value by typing AT&W and pressing [Enter].
4. Type ATO and press [Enter] to exit remote configuration.
6-2
Page 33

Remote Confi guration and Country Code Confi guration
6.2. Country Code Configuration
Different countries have different requirements for how modems must
function. Therefore, before you use the modem, you must configure it to match
the defaults of the country in which you are using it.
If you are comfortable using AT commands, you can configure your modem
using AT commands. You must enter these commands in your communication
program’s terminal window.
To configure the modem for a specific country, execute the following AT
commands:
1. Type AT%T19,0,nn (nn stands for country code). Press [Enter]. OK is
displayed.
2. Then save the changes by issuing the following command:
AT&F&W
3. To verify that the correct country has been configured, issue the following
command:
ATI9
4. The country code is then displayed in decimal format.
The following is an example of country, AT commands, and result codes.
AT Command
Country
Euro/NAM AT%T19,0,34 (default) 52
Australia AT%T19,0,01 1
Czech Republic AT%T19,0,25 37
Japan AT%T19,0,10 16
New Zealand AT%T19,0,9 9
(Hexadecimal) Result Code (Decimal)
6-3
Page 34

MT5634/MT9234 Modem; AT Command Set
6-4
Page 35

Page 36

5 Sterling • Irvine • California 92618
(949) 586-9950 • Toll Free: 1-800-854-7226
Fax: (949) 583-9514 • http://www.wti.com
 Loading...
Loading...