Page 1

WTI Part No. 12554
Rev. A
MDS Series
Multipurpose Data Switch
Models MDS-16 and MDS-8
Preliminary Draft
October 1995
User's Guide
Page 2

5Sterling
·
Irvine
·
California 92718
(949) 586-9950
·
Toll Free: 1-800-854-7226
Fax: (949) 583-9514
·
http://www.wti.com
Page 3

Table of Contents
1. Introduction
.........................................
1-1
2. Unit Description
......................................
2-1
2.1. Front Panel
.........................................
2-1
2.2. Back Panel
.........................................
2-2
3. Getting Started
.......................................
3-1
3.1. Communication Parameters
..........................
3-1
3.2. Connecting your PC to the MDS
......................
3-2
3.3. Apply Power to the MDS
............................
3-3
3.4. Communicating with the MDS Unit
...................
3-3
4. Hardware Installation
................................
4-1
4.1. Configure Setup Switches
............................
4-1
4.1.1. Default Baud Rate (Sw1, Sw2, Sw3) ...........4-2
4.1.2. Default Handshake (Sw4) .....................4-2
4.1.3. Default Response Message Format (Sw5) .......4-3
4.1.4. Default Command Echo (Sw7).................4-3
4.2. Initialize the Unit to Default Settings ..................4-4
4.3. Connecting Devices to the MDS ......................4-4
5. Configuration ........................................5-1
5.1. Access to the MDS Command Mode ...................5-1
5.2. Defining and Reading the Site I.D. ....................5-2
5.3. Port Configuration
..................................
5-2
5.3.1. Configuration Conventions
....................
5-2
5.3.2. Port Modes
..................................
5-3
5.3.3. Command Availability
........................
5-3
5.3.4. Port Configuration Command
..................
5-4
6. Operation
............................................
6-1
6.1. Any-to-Any Mode:
..................................
6-1
6.1.1. Port Connection and Disconnection
............
6-2
6.1.2. Defining Hunt Groups
........................
6-6
6.1.3. Port Buffers and Any-to-Any Mode Ports
.......
6-8
6.2. Buffer Mode
........................................
6-9
6.2.1. Reading Data from Buffer Mode Ports
..........
6-9
6.3. Mux Mode
........................................
6-10
6.3.1. Bi-directional Communication in Mux Mode
...
6-11
i
Page 4

7. Saving Configuration Parameters
......................
7-1
7.1. Sending Parameters to a File
.........................
7-1
7.2. Restoring Saved Parameters
..........................
7-2
8. Command Reference Guide
............................
8-1
8.1. Command Conventions
..............................
8-1
8.2. Command Response
.................................
8-2
8.3. Command Summary
.................................
8-3
8.4. Command Set
.......................................
8-4
Appendices
A. Description of System Interfaces
....................
Apx-1
A.1. RS-232 Ports
.....................................
Apx-1
A.2. Snap Adapters
...................................
Apx-2
A.3. Cables
..........................................
Apx-3
B. Specifications
......................................
Apx-4
C. FCC Notice ........................................Apx-5
D. Customer Service ..................................Apx-6
List of Figures
2.1. Instrument Front Panel
...................................
2-1
2.2. Instrument Back Panel
...................................
2-2
3.1. The MDS Help Screen
...................................
3-4
3.2. The Status Screen
.......................................
3-4
5.1. Port Configuration Menu (Port 2 Shown)
...................
5-4
6.1. The Any-to-Any Mode
...................................
6-1
6.2. The Buffer Mode
........................................
6-9
6.3. The Mux Mode
........................................
6-10
8.1. The Status Screen
.......................................
8-5
A.1. RS-232 Port Connectors
...............................
Apx-1
A.2. RS-232 Port Circuitry
.................................
Apx-1
A.3. Snap Adapter Interface
................................
Apx-2
A.4. Snap Adapters
........................................
Apx-2
A.5. Straight Cables
.......................................
Apx-3
ii
MDS Series Users Guide
Page 5

1. Introduction
WTI's MDS-16 and MDS-8 Multipurpose Data Switches provide
a convenient means for connecting devices running at dissimilar
baud rates, and collecting and multiplexing data from multiple
sources.
Versatile Connectivity
Up to 16 different devices can be connected to the MDS without
the need to select a common baud rate or parity. Each port can
be individually configured for specific baud rates, parity,
handshaking format, and various other parameters and options.
Collecting Data from Multiple Sources
The Buffer Mode allows the MDS to collect data from up to
fifteen different devices and store that data for later retrieval.
The MDS provides 256K or 512K (optional) of non-volatile
buffer memory. Buffer memory is dynamically allocated.
Multiplexing Data
The Mux Mode allows the MDS to receive data from up to
fourteen different devices and multiplex that data out a common
port. The Mux Mode also features a bi-directional
communication command, which allows data or commands to be
sent from an Output Port to an Input Port.
Easy Set-Up and Operation
Configuration of the MDS is simple. A menuing system is used
to select communications parameters, and enable or disable
options. The MDS can easily adapt to the requirements of almost
any data communications application.
Limited Command Access
The MDS is ideal for situations that require limited access to
important commands. Each port can be configured to allow
access to all commands (Administrator), or only allow access to
basic commands (User).
1-1
Page 6

Modular Design
RJ-11 jacks and RS-232 Modular Adapters provide quick, easy
connection to computers, modems, and other LAN hardware.
The MDS is compact and takes only one rack unit (1.75 inches)
of vertical rack space.
Modem Communication
The MDS can be controlled by a local PC that communicates
with the unit via cable, or controlled remotely via external
modem. ProComm® (or another communications program) is
used to send commands to connect ports or display status.
Configuration Backup
Once you have configured the MDS to fit your application,
parameters and options can be sent to an ASCII text file and
saved for future retrieval. If configuration is altered or deleted,
parameters can be reloaded using your communications program.
MDS-16 and MDS-8
This User's Guide discusses both the MDS-16 and MDS-8
Multipurpose Data Switches. The MDS-16 includes 16 ports,
and the MDS-8 includes eight ports. All other features function
identically.
Typographic Conventions
Throughout this manual, typefaces and characters have been used
to denote the following:
^ (e.g. ^E) Indicates a key combination used to invoke a
command. For example, the text "^A"
(Control A) indicates the [Ctrl] key and
the [A] key must be pressed simultaneously.
COURIER FONT Indicates characters typed on the keyboard.
For example, /^E or /P 02.
[Bold Font] Text set in bold face and enclosed in
square brackets, indicates a specific key.
For example, [Enter] or [Esc].
<> Indicates required keyboard entries:
For Example: /P <n>
[] Indicates optional keyboard entries.
For Example: /W [n]
1-2
MDS Series Users Guide
Page 7
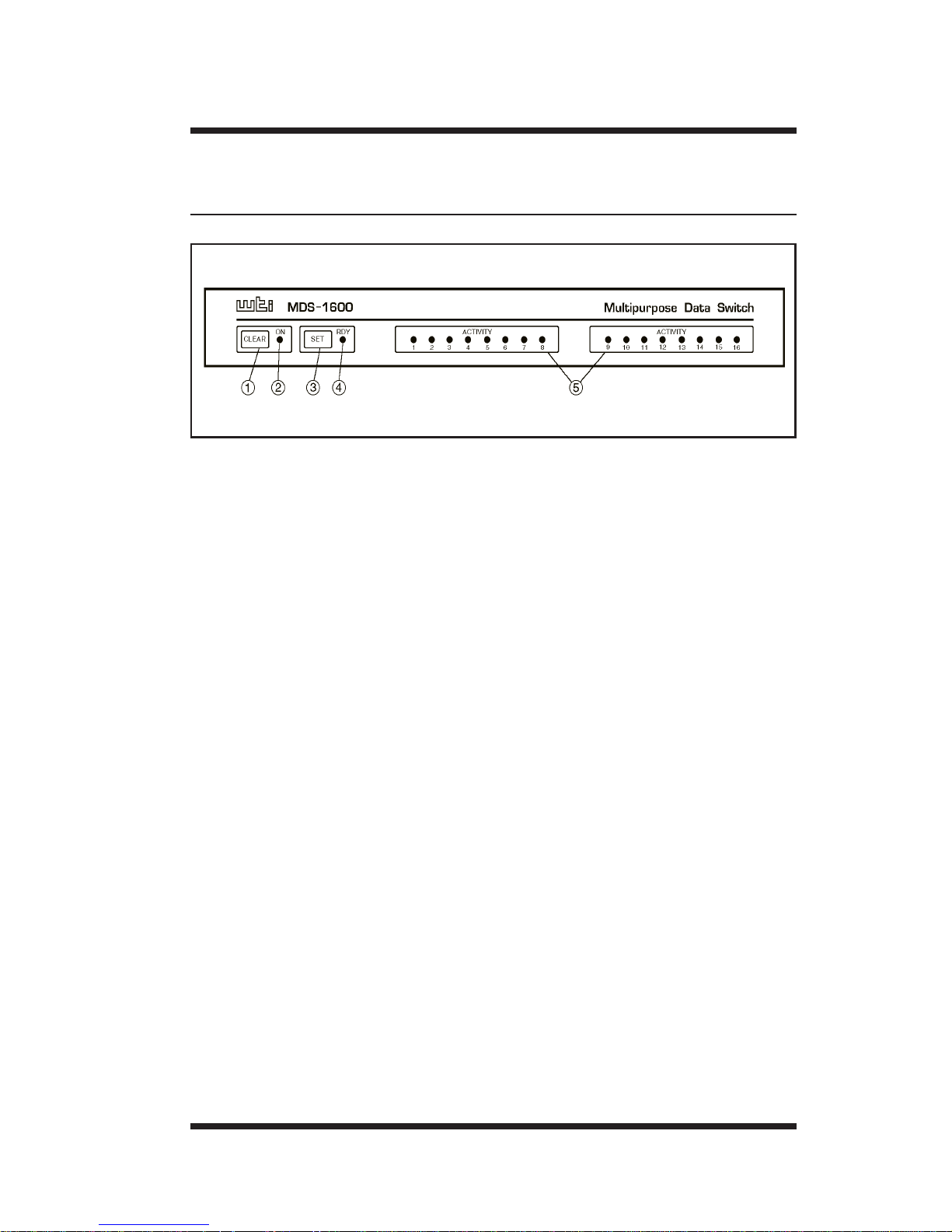
2. Unit Description
2.1. Front Panel
¬
CLEAR: Restarts the MDS operating program without
changing user-selected parameter settings or breaking
port connections.
ON: Lights when AC Power is applied to the unit.
® SET: Used to initialize the MDS to the defaults specified
by Setup Switch configuration. To initialize the MDS,
press and hold both the SET button and the CLEAR button,
release only the CLEAR button, and then release the
SET button.
Note:
When the MDS is initialized, all command-selected
parameters will be cleared, and the MDS will revert
to the default parameters specified by the current SetUp Switch configuration.
¯ RDY: Flashes to indicate the unit is operational.
° ACTIVITY: The Activity LEDs light to indicate that a
corresponding port is receiving data. Note that the model
shown here is the MDS-16 (16 ports), model MDS-8 has
eight Activity indicators.
2-1
Figure 2.1: Instrument Front Panel
Page 8

2.2. Back Panel
¬
RS-232 PORTS: For connection to switched devices.
Accepts six wire RJ-11 cable. Note that the model shown
here is the MDS-16 (16 Ports), model MDS-8 has eight RS232 Ports.
·
Port 1 is used for communication with the MDS during
set-up and configuration. When the MDS is initialized to
the default state, Port 1 is the only port with access to
All (Administrator) MDS commands.
·
Port 1 can either be connected to a PC or modem.
Connection to a modem allows the MDS to be controlled
by a remote PC.
SETUP Switches: A bank of eight dip switches, used to
set baud rate, handshake, message type, and duplex mode.
® FUSE: Use only 250 V 1/8 amp slow blow fuse
¯ AC: 115/220 V AC Selector Switch
° Power Switch: Applies AC Power to unit.
± LINE: Receptacle for AC Power Cord (included).
2-2
MDS Series Users Guide
Figure 2.2: Instrument Back Panel
Page 9

3. Getting Started
This section provides a brief overview of the MDS's basic
capabilities, and describes tests that can be performed to
determine if the unit is operating properly.
3.1. Communication Parameters
The Setup Switches, located on the MDS Back Panel, are used to
select default settings for all MDS RS-232 ports. A label located
adjacent to the Setup Switches summarizes switch functions.
When the MDS is shipped from the factory, the Setup Switches
are configured for 9600 baud, 8 Bits-No Parity, DTR
handshaking, verbose command response, and no echo (all
switches down).
For the purpose of this overview, use the default Setup Switch
configuration. Set your communications program (e.g.
ProComm) to use the following parameters:
·
9600 Baud
·
8 Bits, No Parity
·
DTR Handshaking
·
Full Duplex
Using Other Parameters (Optional): If desired, the MDS can
be set to match the parameters used by the communications
program. Refer to the label on the bottom of the MDS, and
configure Setup Switches accordingly. After changing the SetUp Switches, initialize the MDS; press and hold the SET and
CLEAR keys, release CLEAR, and then release SET.
Note:
·
Section 4.1 describes procedures for setting the
MDS to match the parameters used by your
communications program.
·
If Setup Switches are changed, the new
configuration will not take effect until the MDS
is initialized.
3-1
Page 10

3.2. Connecting your PC to the MDS
In order to set-up the unit, a PC must be connected to Port 1.
Port 1 is always used for communication during set-up. This is
because Port 1 is the only MDS port that will allow access to All
(Administrator) commands when the unit has been initialized to
the default state.
Note that after the unit has been installed and configured, other
ports can also be granted access to All (Administrator) MDS
commands. This allows any MDS port to function as a "Control
Port" after configuration is complete.
The MDS can either be controlled by a local PC that
communicates via cable, or controlled by a remote PC that
communicates via external modem. For the purpose of this
overview, a local PC running ProComm (or a similar
communications program), will be cable connected to
MDS Port 1.
Note:
Communication via Modem (Optional): If desired,
this overview can also be performed via modem.
Section 4.3 describes the procedure for connecting a
modem to the MDS.
Perform the following procedure to connect a PC to Port 1.
1. Attach an appropriate Snap Adapter to your PC COM port.
Make certain to connect to the PC COM port used by your
communications program.
a) For 25 pin PC COM ports, use the SA-12F Snap
Adapter supplied with the MDS.
b) For nine pin PC COM ports, use the SA-9F Snap
Adapter supplied with the MDS.
c) For a description of the Snap Adapter interface, please
refer to Appendix A.2.
2. Use the RJ-11 cable included with the unit, to connect
MDS Port 1 to the Snap Adapter installed in your PC COM
port. Note that the cable used for connection must be a six
wire, straight wired RJ-11 cable. Standard crossover
(phone) cables cannot be used.
3-2
MDSSeriesUsersGuide
Page 11

3.3. Apply Power to the MDS
Connect the power cable to the MDS and plug the cable into an
AC power source. Press the Power Switch to ON. The ON LED
should light, and the RDY LED should begin to flash.
Note:
If all Port Activity LEDs flash upon power-up, this
may indicate a problem with the MDS unit. Please
contact WTI Technical Support as described in
Appendix D.
3.4. Communicating with the MDS Unit
Perform the following procedure to enter the MDS Command
Mode, explore the unit's basic features, and check for proper
operation.
1. If you have not already done so, start your communications
program (e.g. ProComm).
2. Issue the "Wake Port" command to access the MDS
Command Mode and make certain the port is ready to
receive commands. Type /, then simultaneously press the
[Ctrl] key and the [E] key, and then press [Enter]
(/^E [Enter]). The "MDS>" prompt should appear.
a) If the "MDS>" prompt is displayed, you have
successfully accessed the Command Mode. This
indicates the PC has contacted the MDS, and the unit is
operating properly.
b) If the "MDS>" prompt is not displayed, this may
indicate a problem in communicating with the MDS
unit. Check the following:
·
Cable Connection: Check the cable connection
between the MDS unit and the PC. Make certain the
Snap Adapter and RJ-11 cable connectors are
firmly seated.
·
Communication Parameters: Make certain the
MDS and ProComm are using the same
communication parameters.
3-3
Getting Started
Page 12

3. Type /H and press [Enter]. The MDS Help Screen will
appear as shown in Figure 3.1. The Help Screen lists all
available MDS commands, along with a brief description of
each command.
4. Type /S and press [Enter]. The MDS Status Screen will
appear (Figure 3.2). The Status Screen summarizes
conditions at all MDS Ports. The various fields of the
Status Screen are explained in Section 8.4.
3-4
MDS Series Users Guide
/^E Wake-Up Port
/X Sleep - Only Accepts Wake-Up Command
/H Help - Displays Command List ------------------
/S Status - Displays Status Screen n Port # or Name
/W [n] Who - Displays Port Parameters N Port #
/C <n> [n] Connect - Local [Remote] | "or"
/D <n> |...| * Disconnect * "all"
/R[/C] <n> Read Buffer and [Clear] <> Required Entry
/E <n> | * Erase Buffer [] Optional Entry
/I Initialize / Test Unit
/F Enter Site ID
/J Read Site ID
/P <n> Set Port Parameters
/U Read Port Parameters
/L-[n] Load Port Parameters
/G-00 Reset All Ports
/D, /E, /I Commands: Add /Y to bypass "SURE? (Y/N)"
Figure 3.1: The MDS Help Screen
SYSTEM STATUS VERSION 1.4 MEMORY 512KB
PORT | NAME | STATUS | BAUD | B/P | HS | MODE | TIMEOUT | BUFF | CTS
------+----------+--------+------+-----+------+--------+---------+------+----
01 | |*FREE | 9600 | 8N | DTR | ANY | OFF | ---- | H
02 | | FREE | 9600 | 8N | DTR | ANY | OFF | ---- | L
03 | | FREE | 9600 | 8N | DTR | ANY | OFF | ---- | L
04 | | FREE | 9600 | 8N | DTR | ANY | OFF | ---- | L
05 | | FREE | 9600 | 8N | DTR | ANY | OFF | ---- | L
06 | | FREE | 9600 | 8N | DTR | ANY | OFF | ---- | L
07 | | FREE | 9600 | 8N | DTR | ANY | OFF | ---- | L
08 | | FREE | 9600 | 8N | DTR | ANY | OFF | ---- | L
| | |||| | ||
09 | | FREE | 9600 | 8N | DTR | ANY | OFF | ---- | L
10 | | FREE | 9600 | 8N | DTR | ANY | OFF | ---- | L
11 | | FREE | 9600 | 8N | DTR | ANY | OFF | ---- | L
12 | | FREE | 9600 | 8N | DTR | ANY | OFF | ---- | L
13 | | FREE | 9600 | 8N | DTR | ANY | OFF | ---- | L
14 | | FREE | 9600 | 8N | DTR | ANY | OFF | ---- | L
15 | | FREE | 9600 | 8N | DTR | ANY | OFF | ---- | L
16 | | FREE | 9600 | 8N | DTR | ANY | OFF | ---- | L
Figure 3.2: The Status Screen
Page 13

5. Port Connection: The MDS can perform two different
types of port connections; Resident Connections and Third
Party Connections.
a) Resident Connection: This type of connection occurs
when your resident port issues a /C command to
connect to a second port.
i. To connect Port 1 to Port 2, type /C 2 [Enter].
Note that while Port 1 is connected, the MDS will
not recognize commands received via Port 1.
However, the MDS will recognize a Resident
Disconnect Sequence issued at Port 1 or Port 2.
ii. Issue the Resident Disconnect Sequence; type
[Enter]+++[Enter].
b) Third Party Connection: This type of connection
occurs when your resident port issues a /C command to
create a connection between two other ports.
i. To connect Port 2 to Port 3, type /C23[Enter].
ii. While Ports 2 and 3 are connected, Port 1 will still
recognize MDS commands. Type /S [Enter], the
Status Screen will appear. Note that the "STATUS"
column now lists Ports 2 and 3 as connected, while
Port 1 is listed as "FREE".
iii. Issue a Third Party Disconnect command; type
/D 2 [Enter].
iv. Type /S [Enter] to display the Status Screen.
The "STATUS" column now lists Ports 2 and 3
as "FREE".
3-5
Getting Started
Page 14

6. Define the Site I.D. message. The Site I.D. allows the user
to denote the location or name of the MDS unit. The Site
I.D. cannot include non-printable ASCII codes such as
NULS and Line Feeds.
a) Type /F [Enter]. The MDS will prompt the user to
enter the Site I.D.. Key in the desired Site I.D. and
press [Enter]. Up to 32 characters long.
b) To display the Site I.D., type /J [Enter].
c) The Site I.D. will be cleared when the MDS is
initialized.
This completes the introductory overview of the MDS unit.
After you have determined that the unit is operating properly,
configure the MDS as described in Sections 4 and 5.
3-6
MDS Series Users Guide
Page 15

4. Hardware Installation
This section describes the procedures for installing the MDS and
connecting devices to the unit.
4.1. Configure Setup Switches
When the MDS is shipped from the factory, the Setup Switches
are configured for 9600 baud, 8 Bits-No Parity, DTR
handshaking, verbose command response, and no echo (all
switches down). These switch settings are compatible with most
applications. If the default settings are not compatible with your
application, change the switch settings as described in the
following subsections.
Setup Switches should be configured to match the
communication parameters used by the device attached to Port 1.
This allows access to the MDS if the unit is initialized to default
parameters.
Note:
Communication parameters (baud rate, parity, etc.)
can also be individually selected for each MDS port
by accessing the Command Mode and invoking the /P
command as described in Section 5.3.4. However, if
the MDS is initialized, parameters will return to the
settings specified by the current Set-Up Switch
configuration.
4-1
Page 16

4.1.1. Default Baud Rate (Sw1, Sw2, Sw3)
Setup Switches one through three select the default baud rate for
all MDS Ports. The default baud rate must match the rate your
control device will use when communicating with the MDS. If
the control device will communicate via modem, select a default
baud rate that is compatible with the modem.
After the MDS has been installed, the /P command can be used to
select individual baud rates for each port.
SW
Baud Rate123
D D D 9600*
UDD300
D U D 1200
U U D 2400
D D U 4800
U D U 9600
D U U 19.2K
U U U 38.4K
* = Factory Default
4.1.2. Default Handshake (Sw4)
The default handshake format should be set to match the device
attached to Port 1. Setup Switch 4 can select either DTR
(hardware) or XON/XOFF handshaking.
After the MDS has been installed, the /P command can be used to
select both DTR and XON/XOFF handshaking, or no
handshaking. The /P command can select a different
handshaking format for each port.
Switch 4 Handshake
Down DTR *
Up XON/XOFF
* = Factory Default
4-2
MDS Series Users Guide
Page 17

4.1.3. Default Response Message
Format (Sw5)
The MDS can respond with either verbose (English text) or terse
(numeric / abbreviated ) messages. Terse and verbose response
messages are summarized in Section 8.2.
After the unit has been installed, the /P command can also set the
response message format to "none" (Quiet Mode). When the
Quiet Mode is selected, the MDS will not send messages in
response to commands. The /P command can select a different
Response Message Format for each port.
Switch 5 Response Message Type
Down Verbose (English Text) *
Up Terse (abbreviated / numeric)
* = Factory Default
4.1.4. Default Command Echo (Sw7)
Switch Seven enables or disables the Command Echo. When
enabled, characters sent to the MDS will be echoed back to the
control device.
After the MDS is installed, the /P command can individually
select the Command Echo Mode for each port.
Switch 7 Command Echo
Down Disable*
Up Enable
* = Factory Default
Note:
·
If the Setup Switch configuration is changed while
the unit is powered on, the new configuration will
not take effect until the MDS is initialized. The
MDS can be initialized by invoking the /I
command, or by pressing and holding the CLEAR
and SET keys, releasing the CLEAR key, and then
releasing the SET key.
·
Setup Switches 6 and 8 are not used.
4-3
Hardware Installation
Page 18

4.2. Initialize the Unit to Default
Settings
If Setup Switch configuration has been changed while the MDS
is powered on, the unit must be initialized in order for the new
switch configuration to take effect.
Caution:
When the MDS is initialized, the unit will revert to
the parameters specified by the current Set-Up
Switch configuration. Any command-selected
parameters will be lost.
1. Simultaneously press the SET and CLEAR buttons, located
on the face of the MDS unit.
2. Release the CLEAR button, wait one second, and then
release the SET button.
4.3. Connecting Devices to the MDS
Many different types of devices can be connected to the MDS.
To physically connect a device to the MDS, proceed as follows.
1. Access the Command Mode.
2. Determine which MDS port will be used for connection to
the new device (e.g. Port 3).
3. Attach an appropriate Snap Adapter to an RS-232 serial
port on the device you intend to connect. Refer to
Appendix A.2 for more information on WTI Snap Adapters.
a) Modem: An external modem can be connected to any
MDS port, providing the modem does not require
password protection, or an externally generated reset
message or hang-up message. Connect an SA-25M
Snap Adapter to the modem's serial port.
4-4
MDS Series Users Guide
Page 19

Note:
·
The SA-25 Snap Adapter allows correct
transfer of DCD and handshaking signals.
When using the SA-25, the DSR signal from
the modem must be high in order to pull up
the DTR signal.
·
When a modem is connected to the MDS,
other connected devices can use the modem
for calling out. To call out from the modem,
invoke the /C command to connect to the
port, and access the modem as you normally
would.
b) PC: Any MDS RS-232 Port can be used for connection
to a PC. For 25 pin PC COM ports, use an SA-12F
Snap Adapter. For 9 pin PC COM ports, use an SA-9F
Snap Adapter.
c) Printer: Any MDS RS-232 Port can be used for
connection to a printer. Use an SA-12M Snap Adapter.
d) Other Devices: For a description of the MDS Port
interface, please refer to Appendix A.1.
4. Connect a 6 wire, straight wired RJ-11 cable from the Snap
Adapter to a vacant MDS RS-232 port.
5. Select communication parameters for each port as
described in Section 5.
4-5
Hardware Installation
Page 20

4-6
MDS Series Users Guide
Page 21

5. Configuration
This section describes procedures that are used to configure the
MDS to fit the requirements of your application.
5.1. Access to the MDS Command Mode
When the Command Mode is active, the user can invoke
commands to configure the unit, display status, and connect or
disconnect ports. The Command Mode can be accessed from a
local PC that communicates with the MDS via cable, or accessed
by a remote PC that communicates via modem.
Note:
·
The Command Mode can only be accessed from a
"Free" Any-to-Any Mode Port.
·
The Command Mode cannot be accessed via a
Buffer Mode Port, Mux Mode Port, or an Any-toAny Mode Port that is currently connected to
another MDS port.
1. Start the communications program (e.g. ProComm) on your
local or remote PC. Make certain the MDS and ProComm
are set for the same communication parameters (e.g. baud,
parity, etc.).
2. Access the MDS Command Mode.
a) Local Access: To access the command mode from a
local PC, type /^E and press [Enter]. The MDS
Command Mode is now active.
b) Remote Access: To access the command mode from a
remote PC, proceed as follows:
i. Dial the number for the modem connected to
the MDS.
ii. Type /^E and press [Enter] to make certain the
Command Mode is active, and the unit is ready to
receive commands.
5-1
Page 22

5.2. Defining and Reading the Site I.D.
When your application involves communication with several
MDS units, the Site I.D. can indicate the location or name of
each unit. If you have already defined the Site I.D. in Section 3,
and have not re-initialized the MDS, skip this section.
Note:
·
The Site I.D., cannot include non-printable ASCII
characters, such as NULS and Line Feeds.
·
The Site I.D. will be cleared when the MDS is
initialized to default settings.
1. Access the Command Mode.
2. Type /F [Enter]. The MDS will prompt the user to enter
the Site I.D.. Key in the desired Site I.D. and press
[Enter]. Up to 32 characters long.
3. To display the Site I.D., type /J [Enter].
5.3. Port Configuration
5.3.1. Configuration Conventions
When responding to prompts, invoking commands, and selecting
items from the port configuration menu, note the following:
·
To select an item from the Port Configuration menu, key in
the number for the item and press [Enter].
·
When defining the Port Name, do not use ASCII Control
Codes, the slash character (/), quotation marks ("), the
asterisk character (*), or blank spaces.
·
The Port Name cannot begin with a number.
·
Refer to the instructions in each screen for additional
functions available under that screen.
·
To exit a menu or prompt without changing its current
configuration, press [Esc].
·
Note that Port Names are case sensitive. When defining
Port Names, take care to note the exact text, including the
case of each character.
5-2
MDS Series Users Guide
Page 23

5.3.2. Port Modes
The MDS offers three port operation modes; the Any-to-Any
Mode, the Buffer Mode, and the Mux Mode. The MDS Port
Modes function as follows:
·
Any-to-Any Mode: Allows communication between
connected devices. Any-to-Any Ports can be connected to
other Any-to-Any Ports by accessing the Command Mode
and issuing ASCII commands. The Any-to-Any Mode is
available to all MDS ports.
·
Buffer Mode: Allows collection and storage of data
received from connected devices. Collected data can be
retrieved by accessing the Command Mode from an Any-toAny Port, and issuing the Read Buffer (/R) Command. The
Buffer Mode is not available to Port 1.
·
Mux Mode: Allows data from several sources to be
multiplexed to a common port. During port configuration,
Mux Input Ports are assigned to a common Mux Output Port.
Data can then be collected from connected devices and sent
to a device connected to the Mux Output Port. The Mux
Mode is not available to Port 1.
MDS Port Modes are discussed in detail in Section 6.
5.3.3. Command Availability
The "Commands" field in the Port Configuration menu allows the
user to specify which MDS commands will be available to each
port. The user can either select "All" commands or only "Basic"
commands. The "All" option is normally selected for
administrator ports, and allows access to all MDS commands.
The "Basic" option is normally selected for user ports, and
allows limited access to MDS commands. Section 8.3
summarizes "All" and "Basic" commands.
In the default state, Port 1 is the only port with access to "All"
MDS commands. When ports are configured, at least one port
should be granted access to "All" MDS commands.
5-3
Configuration
Page 24

5.3.4. Port Configuration Command
The following section describes the procedure for using the Port
Configuration Menu to select options for each port.
Note that parameters and options selected via the Port
Configuration Menu will stay in effect until the MDS is
initialized using the /I command or the CLEAR and SET buttons.
When the unit is initialized, parameters will revert to the defaults
specified by the Setup Switch configuration.
After parameters have been selected, the configuration can be
saved to an ASCII file on your PC. Later, if the MDS
configuration is altered or deleted, the file with the saved
parameters can be sent to the MDS to automatically reconfigure
the unit without the need to manually select each parameter.
Section 7 provides a description of the procedure for saving and
restoring configuration parameters.
To select port parameters, proceed as follows:
1. Access the MDS Command Mode.
2. Type /P, followed by the number of the port to be
configured, and press [Enter]. For example, to configure
Port 2, type /P 02 [Enter]. The Port Configuration
menu will appear as shown in Figure 5.1.
5-4
MDS Series Users Guide
PORT PARAMETERS #02
1. PORT NAME:
2. BAUD RATE: 9600
3. BITS/PARITY: 8-None
4. STOP BITS: 1
5. HANDSHAKE: DTR
6. MODE: Any-to-Any
7. COMMANDS: All
8. LOGOFF CHAR: +
9. DISCONNECT
SEQ: On
TIMEOUT: Off
10. TIMEOUT: 5 Sec
11. MESSAGE TYPE: Verbose
12. ECHO: On
Enter: "<" previous port,
">" next port,
"##" change parameter
<ESC> exit ...
Figure 5.1: Port Configuration Menu (Port 2 Shown)
Page 25

The Port Configuration menu offers the following options:
·
1. Port Name: Allows the user to assign a name to this
port (for example, "PRINTER"). Up to eight characters.
·
2. Baud Rate: Defines the baud rate for this port.
The Baud rate can be set to any standard rate from
300 to 38.4K bps.
·
3. Bits/Parity: Defines the data bits and parity for
this port.
·
4. Stop Bits: Defines the stop bits for this port.
·
5. Handshake: Defines the handshake format for this
port. The handshake can be set to XON/XOFF, DTR
(hardware), Both, or None.
·
6. Mode: Defines the operation mode for this port. The
user can select the Any-to-Any Mode, Buffer Mode, or
Mux Mode. Note that Port 1 cannot be configured for
the Buffer Mode or the Mux Mode.
·
When the Mux Mode is selected, the port will be
assigned as a Mux Input Port, and the MDS will display
an additional menu which is used to select the following
parameters.
n
1. Common Port: Specifies the Mux output port for
this Mux Input Port. The Common Port can be any
port except Port 1, or a port already specified as a
Mux Port or Buffer Port. Note that if the Common
Port is not specified, the Mux feature will not
function.
n
2. End Character: Specifies the End-of-Record
character that will delineate the end of each data
record. The default EOR character is ^J (Line Feed).
n
3. Block Size: Specifies the block size that can also
be used to determine the end of each data record. The
default Block Size is 128 characters.
n
4. Port I.D.: Enables or disables the Port I.D.
option. When enabled, the MDS will label each data
record with the number of the port that received the
record. The Port I.D. label uses the format "#nn_",
where nn is the port that received the record. In the
default state, this feature is disabled.
5-5
Configuration
Page 26

·
7. Commands: Determines which commands will be
available to this port. The port can be configured to
recognize only Basic commands (user), or All
Commands (Administrator). When the MDS is
configured, at least one port (typically Port 1) should be
granted access to All MDS commands.
·
8. Logoff Char.: Defines the Logoff Character for this
port. The Logoff Character determines the disconnect
sequence that must be issued at this port in order to
disconnect from a second port (Resident Disconnect).
When defining the Logoff Character, note the following:
n
The default Logoff Character is "+". As a result, the
default Resident Disconnect Sequence is
[Enter]+++[Enter].
n
The Resident Disconnect Sequence uses the format
[Enter]###[Enter], where # is the currently defined
Logoff Character.
n
The Logoff Character should only be re-defined when
the default Resident Disconnect Sequence is not
compatible with your application.
n
The Resident Disconnect Sequence is not used when
performing a Third Party Disconnect. The /D
command is used to initiate a Third Party Disconnect.
·
9. Disconnect: Enables or disables the Resident
Disconnect Sequence and/or Timeout Disconnect
·
10. Timeout: Selects the Timeout Period for this port.
When the Timeout Disconnect is enabled, and the port
does not receive or transmit data for the specified
Timeout Period, the port will disconnect from the
associated port.
·
11. Message Type: Defines the type of response
messages that will be sent when the MDS responds to
commands. The user can select Verbose Messages
(English Text Response), Terse Messages (Numeric /
Abbreviation), or Quiet Mode (No Response).
·
12. Echo: Enables or Disables the command echo.
3. (Optional) After all ports have been configured, save the
user-selected configurations parameters to an ASCII file as
described in Section 7.
5-6
MDS Series Users Guide
Page 27

6. Operation
This section describes the capabilities that are available to Anyto-Any Mode Ports, Buffer Mode Ports, and
Mux Mode Ports.
6.1. Any-to-Any Mode:
Allows communication between connected devices, regardless of
dissimilarities between baud rate, parity, and etc.. Any-to-Any
Mode Ports can be connected to other Any-to-Any Ports by
accessing the Command Mode and issuing ASCII commands.
All MDS ports can be configured for the Any-to-Any Mode.
Any-to-Any Mode Ports cannot be connected to Buffer Mode
ports, Mux Mode ports, or Mux Output Ports. Note however,
that Any-to-Any ports can use the /R command to read data from
Buffer Mode Ports.
6-1
Figure 6.1: The Any-to-Any Mode
Page 28

6.1.1. Port Connection and Disconnection
The MDS allows communication between devices without the
requirement that both devices use the same communication
parameters. This enables the user to connect devices that use
dissimilar baud rates, parity, handshake, and etc.. The MDS
converts data rates and other communications parameters,
eliminating the need to select common parameters for all
connected devices.
6.1.1.1. Using ASCII Commands to Connect Ports
Two different types of connections can be made between MDS
ports; Resident Connections and Third Party Connections.
In a Resident Connection, your resident port issues a /C
command to connect to a second port. For example, if Port 4
issues the /C command to connect to Port 5, this is a Resident
Connection.
In a Third Party Connection, your resident port issues a /C
command to create a connection between two other ports. For
example, if Port 1 is your resident port, and Port 1 issues a
command to connect Port 2 to Port 3, this is a Third Party
Connection.
Note:
·
Port Names are case sensitive. When invoking the
/C command, note the case of each letter of the
Port Name.
·
Ports that have been granted Basic (User)
command capability, can only use the /C command
to perform a Resident Connection. Ports with
Basic command capability cannot initiate a Third
Party Connection.
6-2
MDS Series Users Guide
Page 29

To Connect MDS ports, proceed as follows:
1. Access the MDS Command Mode.
2. Invoke the /C command to connect the desired ports.
a) Resident Connection: To connect your resident port to
another port, type /C nn [Enter]. Where nn is the
number or name of the port you want to connect.
Examples:
·
To connect your resident port to Port 8, type
/C 08 [Enter].
·
To connect your resident port to a port named
"MODEM", type /C MODEM [Enter].
b) Third Party Connection: To connect any two ports
(other than your resident port), type /C nn NN
[Enter]. Where nn and NN are two MDS port numbers
or port names.
Examples:
·
To connect Port 5 and Port 6, go to a third port with
"All" command capability, and type /C 05 06
[Enter].
·
To connect a Port named "SALES" to a Port named
"MODEM", go to a third port with "All" command
capability, and type /C SALES MODEM [Enter].
When the /C command specifies the port name, it is only
necessary to enter enough letters to differentiate the desired port
from other ports. For example, to connect your resident port to a
port named "SALES", the connect command can be invoked as
/C S, providing no other port names begin with the letter "S".
6-3
Operation
Page 30

6.1.1.2. Disconnecting Ports
There are three different methods for disconnecting ports, the
Resident Disconnect, the Third Party Disconnect, and the No
Activity Timeout. Providing the timeout feature has been
enabled, a No Activity Timeout can be used to disconnect
resident ports or third party ports.
Note:
·
Port Names are case sensitive. When invoking the
/D command, note the case of each letter of the
Port Name.
·
In the DTR mode, the DTR signal will drop for
approximately 250 ms after a disconnect has
occurred.
To disconnect MDS ports, proceed as follows:
1. Resident Disconnect: A Resident Disconnect disconnects
your resident port from another port. For example, if you
are communicating via Port 3, and Port 3 is connected to
Port 4, a Resident Disconnect would be used to
disassociate the two ports. A Resident Disconnect is
initiated by invoking the Resident Disconnect Sequence.
a) The default Resident Disconnect Sequence is
[Enter]+++[Enter].
b) If the default Resident Disconnect Sequence is not
compatible with your application, the Logoff Character
can be redefined using the /P (Port Configuration)
command. For example, if the Logoff Character is
defined as @, the new Resident Disconnect Sequence
would be [Enter]@@@[Enter].
6-4
MDS Series Users Guide
Page 31

2. Third Party Disconnect: A Third Party Disconnect is
used to disconnect two ports by invoking the /D command
at a third port. For example, if you are communicating via
Port 1, and you wish to disconnect Port 3 from Port 4, a
Third Party Disconnect would be used.
a) The /D (Disconnect) command can be invoked by any
port that has been granted access to "All" commands
(Administrator).
b) The /D command line can specify both connected ports,
or either of the two connected ports. For example, if
Port 3 is connected to Port 4, and Port 1 has access to
"All" commands, the user can invoke one of the
following commands at Port 1:
/D 03 04 [Enter]
or
/D 03 [Enter]
or
/D 04 [Enter]
3. No Activity Timeout: Providing the Timeout Disconnect
feature has been enabled for either connected port, the No
Activity Timeout can disconnect Resident Ports, or Third
Party Ports.
a) The Timeout Feature is enabled and defined by
invoking the /P command to access the Port
Configuration Menu for the desired port. Option 9
enables or disables the Timeout Feature, and Option 10
defines the Timeout Period.
b) When the Timeout Feature has been enabled, the port
will automatically disconnect when no additional data
is received for the defined Timeout Period. The default
Timeout Period is 5 seconds.
6-5
Operation
Page 32

6.1.2. Defining Hunt Groups
A Hunt Group creates a situation where the MDS will scan a
group of Any-to-Any Mode Ports, and connect to the first
available port in the group. Hunt Groups are created by
assigning identical or similar port names to two or more Any-toAny Mode Ports.
Note:
Port Names are case sensitive. When invoking the /C
command, note the case of each letter of the Port
Name.
1. Access the MDS Command Mode.
2. Invoke the /P command to access the Port Configuration
Menu for the desired Port(s). For example, to configure
Port 4, type /P 4 [Enter].
3. From the Port Configuration Menu, select item 1. to define
the Port Name.
4. Repeat steps 2 and 3 above to assign similar or identical
names to the other Any-to-Any Mode Port(s) you wish to
include in the Hunt Group. For example, a series of ports
in a Hunt Group could be named "PRINTER1",
"PRINTER2", "PRINTER3", and etc., or all ports in the
group could be assigned the same name (e.g. "PRINTER").
5. To connect to the next available port in the hunt group,
invoke the /C (Connect) command using the port name to
specify the desired group of ports. For example,
/C PRINTER [Enter].
6. The MDS will connect to the first available port in the
Hunt Group. If all ports in the specified Hunt Group are
already connected, the MDS will respond with "BUSY".
Note that it is only necessary to enter enough letters of the port
name to differentiate the ports in the Hunt Group from other
MDS ports. For example, to connect your resident port to the
first available port in a group of ports named "SALES1",
"SALES2", "SALES3", and etc., the connect command can be
invoked as /C S [Enter], providing no other port names begin
with the letter "S".
6-6
MDS Series Users Guide
Page 33

The names of ports in Hunt Groups must be unique. Otherwise
ports with names that are similar or identical to the Hunt Group,
will also be included in the Hunt Group.
Hunt Group Example 1:
1. Assume MDS Ports 1 and 2 have been configured in the
Any-to-Any Mode, and modems have been installed at both
ports.
2. Assume Port 1 has been named "MODEM1" and Port 2 has
been named "MODEM2".
3. If your resident port is Port 4, and you want to connect to
the first available Modem, access the MDS Command
Mode, type /C MODEM [Enter].
Hunt Group Example 2:
1. Assume Ports 3, 4, and 5 have been configured in the Anyto-Any Mode and printers are attached to each port.
2. Assume all three ports have been named "PRINTER".
3. If your resident port is Port 1, and you want to connect
Port 2 to the first available printer, access the MDS
Command Mode, type /C 02 PRINTER [Enter].
6-7
Operation
Page 34

6.1.3. Port Buffers and Any-to-Any
Mode Ports
The MDS provides 256K or 512K (optional) of non-volatile
buffer memory that can be shared by all MDS ports. Buffer
memory is dynamically allocated in blocks of 2K characters.
The Status Screen lists the amount of Buffer Memory currently
used by each port.
The MDS uses buffer memory in three different ways, depending
on the user-selected port mode.
·
Any-to-Any Mode Ports, Mux Input Ports: When two
ports are communicating at dissimilar baud rates, the buffer
memory prevents data overflow at the slower port.
·
Mux Output Ports: The MDS reserves 8K of buffer
memory for multiplexing purposes.
·
Buffer Mode Ports: Stores data received from connected
devices. The user issues a read command (/R) to retrieve
data from each port buffer.
If data is allowed to accumulate in a port buffer, this will
decrease the amount of buffer memory available to other ports.
If the Status Screen indicates an accumulation of data, the /E
(Erase Buffer) or /R/C (Read and Clear Buffer) commands can be
invoked to clear the buffer.
6-8
MDS Series Users Guide
Page 35

6.2. Buffer Mode
Ports configured for the Buffer Mode will collect data from the
connected device and store it in the MDS's dynamically allocated
memory. Any Buffer Port can use the maximum available
memory. Handshake commands control the flow of data to buffer
memory. The Buffer Mode is not available to MDS Port 1.
The Buffer Mode allows collection of data from various devices
without the requirement that all devices use the same
communication parameters (e.g. baud rate, parity, etc.).
6.2.1. Reading Data from
Buffer Mode Ports
To retrieve data from Buffer Mode Ports, the user must first
determine which port buffers contain data. To check port buffers
for stored data, type /S [Enter] to display the Status Screen.
The Status Screen includes a column that indicates the amount of
data currently stored in the buffer memory for each port.
6-9
Operation
Figure 6.2: The Buffer Mode
Page 36

To retrieve data from buffer memory, issue the /R (Read Buffer)
command at any port that is configured for the Any-to-Any
Mode. The /R command uses the following format:
/R[/C] nn [Enter]
Where:
nn Is the number or name of the port buffer to be read.
/C (Optional) Causes data to be deleted from the port buffer
after it has been read. Note that the /R/C option is only
available to ports that have All (Administrator)
Command Availability.
6.3. Mux Mode
The Mux Mode allows data from several sources to be
multiplexed to a common output port, regardless of
dissimilarities between baud rate, parity, and etc..
Ports that are configured for the Mux Mode will send data to a
user specified Mux Output Port. Data records will be terminated
by the user defined End-of-Record character, and/or by user
defined block size. The Mux Mode is not available to MDS
Port 1. Note that data collected by a Mux Input Port will not be
released until the End-of-Record character is sent, or the block
size requirement is met.
6-10
MDS Series Users Guide
Figure 6.3: The Mux Mode
Page 37

6.3.1. Bi-directional Communication
in Mux Mode
A bi-directional link can be temporarily established between a
Mux Output Port and its assigned Mux Input Port. This allows
commands or data to be sent from the Mux Output Port to a userspecified Mux Input Port. To send a command from a Mux
Output Port to a linked Mux Input Port, invoke the following
command at the Mux Output Port.
#nn_
Where nn is the port number of the desired Mux Input Port.
Note that the bi-directional link will remain intact until the
Resident Disconnect Sequence, or another #nn_ command is
issued from the Mux Output Port.
Example: Assume Port 5 has been designated as a Mux Input
Port and linked to Port 3, which has been configured as a Mux
Output Port. To send data from Port 3 to Port 5, issue the
following command at Port 3:
#05_
Note that while the bi-directional connection is active, data from
other Mux Input Ports will be stored in buffer memory until the
Mux Output Port disconnects from the Mux Input Port.
To disconnect the Mux Output Port from the Mux Input Port,
issue the Resident Disconnect Sequence (default =
[Enter]+++[Enter]) from the Mux Output Port. Any data
collected at other Mux Input Ports will then be sent to the Mux
Output Port.
6-11
Operation
Page 38

6-12
MDS Series Users Guide
Page 39

7. Saving Configuration
Parameters
After you have configured the MDS for your application,
parameters can be downloaded to your PC and saved as an ASCII
text file. Later, if the configuration is accidentally altered, the
file with the saved parameters can be uploaded to automatically
re-configure the MDS without the need to manually define each
parameter.
The saved parameters can also be uploaded to other MDS units.
This allows rapid set-up when several MDS units will be
configured with the same parameters.
This section describes the procedure for using ProComm to save
and load MDS parameters. Note that this procedure can also be
applied to other communications programs.
7.1. Sending Parameters to a File
1. Start Procomm and access the MDS Command Mode.
2. Use the /P command to disable the MDS's echo feature as
described in Section 5. When the Port Configuration menu
is displayed, option 12 is used to enable or disable the echo
feature.
3. Press the [Page Down] key.
4. ProComm's Download Menu will appear. Select (A)
ASCII. ProComm will display a prompt which reads
"ASCII DOWNLOAD - Please enter file name".
5. Type in a name for the file that will contain the saved MDS
parameters using the full path and drive designation. For
example, "C:\MDS.PAR".
7-1
Page 40

6. At the ProComm screen, type /U and press [Enter]. The
MDS will send a series of command lines to the file
specified in Step 5. Each line describes parameters for an
individual Port.
a) The /U command must be invoked before ProComm's
download timeout is reached. The download timeout
can be redefined using ProComm's set-up menu.
b) ProComm will emit a Beep when the download timeout
period has elapsed.
7. When the MDS has finished sending parameters, press
[Esc] to terminate ProComm's Download mode.
7.2. Restoring Saved Parameters
This section describes the procedure for using ProComm to send
stored parameters to the MDS unit.
1. Start ProComm and access the MDS Command Mode.
Press the [Page Up] key to activate ProComm's Upload
menu.
2. Select (A) ASCII. The system will display a prompt which
reads "ASCII UPLOAD - Please enter the file name".
3. Key in the name of the ASCII text file with the stored
parameters using the full path and drive designation and
press [Enter]. For example, C:\MDS.PAR [Enter].
4. ProComm will send the ASCII text file to the MDS and
saved parameters will be restored. When ProComm has
finished sending parameters to the MDS, press [Esc] to
terminate ProComm's Upload mode.
5. Type /S and press [Enter], the MDS's Status Screen will
be displayed. Check the Status Screen to make certain the
MDS has been configured with the saved parameters.
7-2
MDS Series Users Guide
Page 41

8. Command Reference Guide
This section describes the MDS command set and explains
options available to each command.
8.1. Command Conventions
The commands described in this section conform to the following
conventions:
·
Slash Character: All MDS commands begin with the Slash
Character (/). The only exception is Resident Disconnect
Sequence (Default = [Enter]+++[Enter]).
·
Asterisk Character: When the asterisk character is entered
as the argument of the /D command (Disconnect Port), or
the /E command (Erase Buffer) the command will be
applied to all ports. For example, to erase all port buffers,
type /E * [Enter].
·
Suppress "SURE (Y/N)?" Prompt: When the /D
(Disconnect Port), /E (Erase Buffer), or /I (Initialize Unit)
commands are invoked, the /Y option can be included in the
command line to override the "SURE (Y/N)?" prompt. For
example, to disconnect Port 8 without displaying the
"SURE? (Y/N)" prompt, type /D/Y 8 [Enter].
·
Enter Key: All commands are invoked by pressing the
[Enter] key.
·
Command Mode: MDS Ports will only recognize
commands when the Command Mode has been accessed.
The Command Mode can only be accessed from an Any-toAny Mode Port. To access the Command Mode, type /^E
and press [Enter].
·
Connected Ports: When the /C command has been issued to
connect two ports, most MDS commands will not be
recognized by either of the two connected ports. The only
exception is the Resident Disconnect Sequence (Default =
[Enter]+++[Enter]) which will cause the two ports to
disconnect.
8-1
Page 42

8.2. Command Response
When commands are sent to the MDS, the unit can respond with
either verbose (English Text) or terse messages (numeric /
abbreviated). The default message type for all MDS ports can be
set to either terse or verbose by configuring Setup Switch Five.
After the MDS has been installed and configured, the Port
Configuration (/P) command can be used to specify an individual
response message format for each port. In addition to the Terse
and Verbose response modes, the /P command can also select the
Quiet Mode. When the Quiet Mode is selected, the port will not
send messages in response to commands.
The table below summarizes the various response messages for
both the Terse and Verbose modes.
Terse Verbose
0
OK
1
PORT CONNECT
2
BUSY
3
PORT DISCONNECT
4
INVALID COMMAND
5
SURE ? (Y/N)
6
INVALID PARAMETER
7
INVALID SYNTAX
8
INVALID ACCESS
9
INVALID PORT TYPE
A
COMMAND ABORTED
8-2
MDS Series Users Guide
Page 43

8.3. Command Summary
The chart below summarizes all available MDS Commands:
Command Availability
Function Command Syntax
All
(Admin.)
Basic
(User)
Wake-up
/^E
[Enter]
XX
Sleep
/X
[Enter]
XX
Help
/H
[Enter]
XX
Status
/S
[Enter]
XX
Who (View Port
Parameters
/W [n]
[Enter]
XX
Connect
/C <n> [n]
[Enter]
X
X
Ê
Resident
Disconnect
Ë
[Enter]
+++
[Enter]
XX
Third Party
Disconnect
Ì
/D[/Y] <n> [n]
[Enter]
/D[/Y] *
[Enter]
X
Read Buffer
/R[/C] <n>
[Enter]
X
X
Í
Erase Buffer
/E[/Y] <n>
[Enter]
/E[/Y] *
[Enter]
X
Initialize
/I[/Y]
[Enter]
X
Enter Site ID
/F
[Enter]
X
Read Site ID
/J
[Enter]
XX
Set Port
Parameters
/P <n>
[Enter]
X
Read Port
Parameters
/U
[Enter]
X
Ê
A port with "Basic" command capability
can
perform a Resident
Connect, but
cannot
perform a Third Party Connect.
Ë
Resident Disconnect: Used to disconnect your resident port from
another port. Note that the Resident Disconnect Sequence can be
redefined via the Port Configuration Menu.
Ì
Third Party Disconnect: Used to disconnect two or more non-
resident ports. Must be issued from a third port with "All"
command capability.
Í
A port with "Basic" (User) command capability cannot use the /C
option to clear a port buffer after reading data.
8-3
Command Reference Guide
Page 44

8.4. Command Set
Wake Up (Access Command Mode) (/^E)
Waking an Any-to-Any Mode Port will provide access to the
Command Mode, allowing the user to enter commands to connect
ports, display status and etc.. When the Command Mode is
inactive (Port Asleep), /^E is the only MDS command that will
be recognized.
Command Availability: All (Administrator) / Basic (User)
Command Format: /^E [Enter]
MDS Response: The "MDS>" prompt will appear.
Sleep (Exit Command Mode) (/X)
Puts an Any-to-Any Mode Port to sleep and exits the Command
Mode. While a port is sleeping, the unit will not recognize any
MDS commands except the /^E (Wake Up) command. Note that
exiting from the Command Mode will not terminate port
connections.
Command Availability: All (Administrator) / Basic (User)
Command Format: /X [Enter]
MDS Response: (Terse and Verbose) PORT ASLEEP
Help (/H)
Displays a Help Screen, which lists all MDS commands along
with a brief description of each command.
Command Availability: All (Administrator) / Basic (User)
Command Format: /H [Enter]
MDS Response: Displays Help Screen
8-4
MDS Series Users Guide
Page 45

Status (/S)
Displays the Status Screen (Figure 8.1), which lists current
conditions and parameters for all MDS ports.
Command Availability: All (Administrator) / Basic (User)
Command Format: /S [Enter]
MDS Response: Status screen (Figure 8.1).
The Status Screen lists the following parameters:
Port: The Port Number.
Name: The user-defined Port Name.
Status: Indicates the current status of each port:
*: Indicates the port has accessed the MDS Command Mode.
FREE: Indicates the port is not in use.
C-nn: Indicates the port is connected to Port Number "nn".
MUXOUT: Indicates the port has been designated as a Mux
Output Port.
Baud: Lists the Port's baud rate.
B/P: Lists the port's data bits and parity settings.
HS: Lists the port's handshaking setting: XON/XOFF, DTR,
BOTH, or NONE.
8-5
Command Reference Guide
STATUS SCREEN VERSION 1.4 MEMORY 512KB
PORT | NAME | STATUS | BAUD | B/P | HS | MODE | TIMEOUT | BUFF | CTS
------+----------+--------+------+-----+------+--------+---------+------+----
01 | SYSADMIN |*FREE | 9600 | 8N | DTR | ANY | OFF | ---- | H
02 | SENSOR1 | C-16 | 9600 | 8N | XON | MUX | OFF | ---- | H
03 | SENSOR2 | C-16 | 9600 | 8N | NONE | MUX | OFF | ---- | H
04 | SENSOR3 | C-16 | 4800 | 8N | XON | MUX | OFF | ---- | H
05 | SENSOR4 | C-16 | 9600 | 8N | XON | MUX | OFF | ---- | H
06 | SENSOR5 | C-16 | 9600 | 8N | NONE | MUX | OFF | ---- | L
07 | SENSOR6 | C-16 | 9600 | 8N | NONE | MUX | OFF | ---- | H
08 | SENSOR7 | C-16 | 2400 | 8N | XON | MUX | OFF | ---- | H
| | |||| | ||
09 | REGISTR1 | FREE | 4800 | 8N | XON | BUFFER | 1 SEC | 2K | H
10 | REGISTR2 | FREE | 9600 | 8N | NONE | BUFFER | 1 SEC | ---- | L
11 | REGISTR3 | FREE | 9600 | 8N | XON | BUFFER | 1 SEC | 10K | H
12 | REGISTR4 | FREE | 9600 | 8N | XON | BUFFER | 1 SEC | ---- | H
13 | REGISTR5 | FREE | 4800 | 8N | NONE | BUFFER | 1 SEC | 4K | H
14 | REGISTR6 | FREE | 9600 | 8N | NONE | BUFFER | 1 SEC | 6K | H
15 | SERVER |*FREE | 9600 | 8N | DTR | ANY | BOTH | ---- | H
16 | DATABASE | MUXOUT | 9600 | 8N | XON | MUX | OFF | --2K | H
Figure 8.1: The Status Screen
Page 46

Mode: Lists the user-selected port mode. The Mode column
will list either the Any-to-Any Mode, Buffer Mode,
or Mux Mode.
Timeout: Indicates the status of the Timeout Feature. When the
Timeout feature is disabled, this column will read "OFF".
When the Timeout feature is enabled, this column will list the
user-defined Timeout period.
Buff: Lists the amount of data currently stored in the buffer for
this port. The MDS will allocate buffer memory in blocks of
2K characters. If necessary, the /E command can be issued
from a port with "All" command capability to clear data from
port buffers.
CTS: Lists the status of the port's input hardware signal.
H (high) = active, L (low) = inactive.
Who (View Port Parameters) (/W)
Displays the current configuration of an individual port, but does
not allow the user to change port parameters.
Command Availability: All (Administrator) / Basic (User)
Command Format: /W [n] [Enter]
Where "n" is the number or name of the desired port.
MDS Response: Displays port parameters.
Examples:
To display parameters for your resident port, access the MDS
Command Mode and type the following:
/W [Enter]
To display parameters for Port 7, access the MDS Command
Mode and type the following:
/W 07 [Enter]
To display parameters for a port named "SALES", access the
MDS Command Mode and type the following:
/W SALES [Enter]
8-6
MDS Series Users Guide
Page 47

Connect (/C)
Establishes a bi-directional connection between two Any-to-Any
Mode Ports. The /C command can perform two different types of
port connections:
·
Resident Connect: If the /C command specifies one port
name or number, the MDS will connect your resident port
with the specified port.
·
Third Party Connect: If the /C command specifies two
port numbers or names, the MDS will connect the two ports
indicated by the command. Note that a Third Party Connect
command must be issued from a third port, which has been
granted access to "All" MDS commands. Ports which have
been configured for "Basic" command capability cannot
perform a Third Party Connect.
Note:
The /C command can only be used to connect Any-toAny Mode Ports. The /C command cannot be used to
connect Buffer Mode Ports or Mux Mode Ports.
Command Availability: All (Administrator) / Basic (User)
Command Format: /C <n> [n] [Enter]
Where n is the number or name of the port(s) to be connected.
MDS Response:
Verbose: PORT CONNECT
Terse: 1
Examples:
Resident Connect: To connect your resident port to Port 16,
access the MDS Command Mode and type:
/C 16 [Enter]
Third Party Connect: To connect Port 12 to Port 14, access the
MDS Command Mode from a third port with "All" command
capability and type the following:
/C 12 14 [Enter]
8-7
Command Reference Guide
Page 48

Third Party Disconnect (/D)
When two ports are connected, the /D command can be invoked
at a third port with "All" command capabilities. Note that the /D
command cannot disconnect your resident port. To disconnect
your resident port, issue the Resident Disconnect Sequence
(Default = [Enter]+++[Enter]) or wait for the Timeout Period to
elapse (if enabled).
Command Availability: All (Administrator)
Command Format: /D[/Y] <n> [n] [n] [Enter]
Where:
/Y (Optional) suppresses the "SURE? (Y/N)" prompt.
n Is the number or name of the port(s) to be disconnected.
To Disconnect all ports, enter an asterisk.
MDS Response:
Verbose: SURE? (Y/N), if Y is entered, the MDS will respond
with "PORT DISCONNECT".
Terse: 5, if Y is entered, the MDS will respond with 3.
Examples:
To disconnect Port 2 from Port 3, invoke either of the following
commands from a third port with "All" Command Capability:
/D 2 [Enter] or /D 3 [Enter]
To disconnect Port 2 from Port 3 without the "SURE? (Y/N)"
prompt, access the MDS Command Mode from a third port with
"All" command capability and type one of the following
commands:
/D/Y 2 [Enter] or /D/Y 3 [Enter]
To disconnect a group of ports with similar names (e.g. PC1,
PC2, PC3), access the MDS Command Mode from another port
with "All" command capability and type the following:
/D PC [Enter]
To disconnect all ports, access the MDS Command Mode from a
port with "All" command capability and type the following:
/D * [Enter]
8-8
MDS Series Users Guide
Page 49

Read Buffer (/R)
Reads data from the buffer for a specified port. After reading
data from the buffer, the unit will wait for the Resident
Disconnect Sequence or timeout period, and then return to the
"MDS>" prompt. To terminate the Read Buffer command before
it is complete, issue the Resident Disconnect Sequence
(Default = [Enter]+++[Enter]).
When the /R command is issued from a port with "All"
(Administrator) command capability, the MDS can also be
instructed to read and then clear the buffer by including the /C
option in the command line.
Command Availability: All (Administrator) / Basic (User)
Command Format: /R[/C] <n> [Enter]
Where:
/C (Optional) Instructs the MDS to clear the buffer after
reading. Note that the /C option can only be issued by a
port with "All" command capability.
n Is the number or name of the port buffer to be read.
Command Response: MDS releases data from the buffer. If the
command line includes the /C option, the port buffer will also be
cleared.
Examples:
To Read data from the buffer for Port 3, access the Command
Mode from an Any-to-Any Mode Port and type the following:
/R 3 [Enter]
To Read and Clear data from the buffer for Port 3, access the
Command Mode from an Any-to-Any Mode Port with access to
All MDS commands and type the following:
/R/C 3 [Enter]
To Read data from the buffer for a port named DEVICE1, go to
an Any-to-Any Mode Port and type the following:
/R DEVICE1 [Enter]
8-9
Command Reference Guide
Page 50

Erase Buffer (/E)
Erases data from the buffer for a specified port.
Note:
Buffered data which has been cleared by the /E
command cannot be recovered.
Command Availability: All (Administrator)
Command Format: /E[/Y] <n>
Where:
n is the number or name of the port buffer to be cleared.
To erase buffers for all ports, enter an asterisk in place
of the port number.
/Y suppresses the "SURE? (Y/N)" prompt
MDS Response:
Verbose: SURE? (Y/N), if Y is entered, the MDS will respond
with "OK".
Terse: 5, if Y is entered, the MDS will respond with 0.
Examples:
To clear the buffer for Port 3, access the MDS Command Mode
from an Any-to-Any Mode port with "All" command capability,
and type the following:
/E 3 [Enter]
To clear the buffer for a port name DEVICE1, access the MDS
Command Mode from an Any-to-Any Mode port with "All"
command capability, and type the following:
/E DEVICE1 [Enter]
To clear all port buffers, without displaying the "SURE? (Y/N)"
prompt, access the MDS Command Mode from an Any-to-Any
Mode Port with "All" command capability, and type the
following:
/E/Y * [Enter]
8-10
MDS Series Users Guide
Page 51

Initialize (/I)
Tests the MDS's internal memory and initializes the system with
the default parameters specified by the Setup Switch
configuration. While the memory test is in progress, the Activity
LEDs will flash in sequence.
Caution:
When the /I command is invoked, the MDS will
revert to the parameters specified by the Set-Up
Switch configuration. Any command selected
parameters will be lost.
Command Availability: All (Administrator)
Command Format: /I[/Y] [Enter]
Where /Y is a command option used to suppress the "SURE?
(Y/N)" prompt.
MDS Response:
Verbose: SURE? (Y/N), if Y is entered, the MDS will begin
the memory test and initialization sequence.
Terse: 5, if Y is selected, the MDS will begin the memory test
and initialization sequence.
Enter Site ID (/F)
When your application involves communication with several
MDS units, the Site I.D. can indicate the location or name of
each unit. The Site I.D. message can be up to 32 characters long,
and cannot include non-printable ASCII codes such as NULS and
Line Feeds.
Command Availability: All (Administrator)
Command Format: /F [Enter]
MDS Response: (Verbose and Terse) ENTER SITE ID.
8-11
Command Reference Guide
Page 52

Read Site ID (/J)
Displays the user-defined Site I.D. message.
Command Availability: All (Administrator) / Basic (User)
Command Format: /J [Enter]
MDS Response: Displays Site I.D. Message
Set Port Parameters (/P)
Displays a menu which allows the user to select options and
parameters for an individual port.
Note:
When the unit is initialized (using the /I command or
the SET and CLEAR buttons), parameters selected
via the /P command will revert to the defaults
specified by the Setup Switch configuration.
Please refer to Section 5 for a detailed description of the
procedure for defining Port Parameters.
Command Availability: All (Administrator)
Command Format: /P <n> [Enter]
Where n is the number or name of the port to be configured.
MDS Response: The Port Parameters Menu will be displayed.
Read Port Parameters (/U)
Sends configuration parameters to an ASCII text file as described
in Section 7. When the /U command is invoked, the system will
send a series of command lines describing current port
configuration.
Command Availability: All (Administrator)
Command Format: /U [Enter]
MDS Response: The MDS will send a series of command lines.
8-12
MDS Series Users Guide
Page 53

A. Description of System
Interfaces
A.1. RS-232 Ports
Apx-1
Figure A.1: RS-232 Port Connectors
Figure A.2: RS-232 Port Circuitry
Page 54

A.2. Snap Adapters
Figures A.4 and A.5 below describe several WTI Snap Adapters
commonly used with the MDS unit. The MDS uses the AT&T
wiring standard.
Apx-2
MDS Series Users Guides
Figure A.3: Snap Adapter Interface
Figure A.4: Snap Adapters
Page 55

A.3. Cables
The following 6-wire, straight wired RJ-11 cables are available
from WTI.
Part No. Length Part No. Length
AC-5 5 ft. AC-50 50 ft.
AC-10 10 ft. AC-100 100 ft.
AC-15 15 ft. AC-150 150 ft.
AC-25 25 ft. RJC-6 Extension Cable Coupler
The MDS will accept any 6-wire, straight wired RJ-11 cables.
Do not use standard crossover (phone) cables. Refer to the
Figure below to determine if your cable is straight wired, or
crossover.
Note:
Make sure your baud rate / cable combinations do not
exceed the speed / lengths shown below:
Baud
9600 19.2K 38.4K
Feet
750 500 300
Apx-3
Appendices
Figure A.5: Straight Cables
Page 56

B. Specifications
Interface: 16 RS-232C serial inputs use RJ-11 connectors,
which require 4-wire straight RJ-11 cables and modular
adapters and 6-wire cable if using CTS/DTR flow control.
Distance: 750 feet maximum at 9600 baud, for each port.
Coding: Asynchronous, 7/8 bits ASCII.
Parity: Even, Odd, None
Stop Bits: 1or2.
Data Rate: 300 to 38.4K BPS (all standard rates).
Flow Control: XON/XOFF, CTS/DTR, Both, or None.
Timeout: No activity timeout disconnects port. None, 1, 5, 10,
15 seconds, 1, 5, 15, 30 minutes.
Memory: Non-volatile 256K (512K optional) battery-backed
SRAM. Auto configuring, dynamically allocated.
Setup Switch: 8 position, sets default parameters for baud rate,
flow control and port mode.
LEDs: Power On, Ready, Data Activity for Ports 1-16.
Temperature: 0°Cto50°C (operating)
Power: Internal 115/230 VAC 50/60 Hz, 5 watts
Size: 1.75" x 17.0" x 6.5" (HxWxD)
Weight: 6 lbs. shipping weight
Apx-4
MDS Series Users Guides
Page 57

C. FCC Notice
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the
limits for a Class A digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the
FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable
protection against harmful interference when the equipment is
operated in a commercial environment. This equipment
generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if
not installed and used in accordance with the instruction manual,
may cause harmful interference to radio communications.
Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely to
cause harmful interference in which case the user will be
required to correct the interference at his own expense.
Apx-5
Appendices
Page 58

D. Customer Service
Customer Service hours are from 8:00 AM to 5:00 PM, PST,
Monday through Friday. When calling, please be prepared to
give the name and make of the unit, its serial number and a
description of its symptoms. If the unit should need to be
returned for factory repair it must be accompanied by a Return
Authorization number from Customer Service.
WTI Customer Service
5 Sterling
Irvine, California 92618
949-586-9950
Toll Free: 1-800-854-7226
Fax: 949-583-9514
Trademark and Copyright Information
WTI and Western Telematic are trademarks of Western Telematic
Inc.. All other product names mentioned in this publication are
trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective
companies.
Information and descriptions contained herein are the property of
Western Telematic Inc.. Such information and descriptions may
not be copied, disseminated, or distributed without the express
written consent of Western Telematic Inc..
© Copyright Western Telematic Inc. 1995.
Printed in the United States of America.
October 1995
Part Number: 12554 Revision: A
Apx-6
MDS Series Users Guides
 Loading...
Loading...