Page 1

OPERATORS
MANUAL
80N4/11
OT
MARINE
4 -120N6/170T6
01
PUBLICATION NO. 045139
FIRST EDITION
JULY 2000
L
ENGINES
WESTERBEKE CORPORATION
MYLES STANDISH INDUSTRIAL
150
JOHN
AIIT'-AIITAIIT
NMMA
..
UWW
HANCOCK ROAD, TAUNTON, MA 02780-7319
Member National Marine Manufacturers Association
PARK
Page 2

A
WARNING
Exhaust
colorless
unconsciousness
exposure
-
-Nausea
-Headache
-
IF
GET
seek
until
gasses
gas.
can
Dizziness
Weakness
YOU
OR
ANYONE
OUT
INTO
medical
it
has
contain
Carbon
include:
and
Sleepiness
THE
attention.
been
Carbon
Monoxide
and
death.
ELSE
EXPERIENCE
FRESH
AIR
Shut
inspected
Monoxide.
is
poisonous
Symptoms
-
-
-
- Inability
IMMEDIATELY.
down
and
repaired.
A
WARNING
WESTERBEKE
bulkhead
WESTERBEKE
CARBON
living/sleeping
They
obtainable
of
Throbbing
Muscular
Vomiting
to
ANY
the
unit
DECAL
and
near
also
MONOXIDE
are
inexpensive
at
your
Carbon
Twitching
OF
your
quarters
an
odorless
and
can
Monoxide
in
Temples
Think
Coherently
THESE
SYMPTOMS.
If
symptoms
and
do
not
is
provided
should
engine
recommends
DETECTORS
of
and
local
marine
and
cause
persist.
restart
be
fixed
or
generator.
your
easily
by
to
a
installing
in
the
vessel.
store.
CALIFORNIA
PROPOSITION
Diesel
engine
of
its
constituents
the
State
cancer,
birth
reproductive
exhaust
of
California
defects,
65
WARNING
and
some
are
known
to
cause
and
other
harm.
to
Page 3

SAFETY
INSTRUCTIONS
INTRODUCTION
Read this safety
by failure
Know when dangerous conditions exist
necessary precautions to protect yourself,
and
your
The following safety instructions are in compliance with the
American Boat
PREVENT
A
WARNING:
while
engine
power.
• Do not operate this machinery without electrical
enclosures and covers
• Shut off electrical power before accessing electrical
equipment.
• Use insulated mats whenever working
equipment.
• Make sure your clothing and skin are dry, not damp
(particularly shoes) when handling electrical equipment.
• Remove wristwatch and all jewelry when working on
electrical equipment.
• Do not connect utility shore power to vessel's AC
circuits, except through a ship-to-shore double throw
transfer switch. Damage to vessel's AC generator may
result
• Electrical shock results from handling a charged capacitor.
Discharge capacitor by shorting terminals together.
PREVENT
A
WARNING:
exhaust
very
hot!
• Always check the engine coolant level at the coolant
recovery tank.
A
WARNING:
•
In
case
before touching the engine
manual
to
follow
machinery.
and
ELECTRIC
is
Lethal
voltage
if
this procedure is not followed.
BURNS -HOT
system
of
an engine overheat, allow the engine to cool
carefully. Most accidents are caused
fundamental
Yacht Council (ABYC) standards.
rules
and
precautions.
and
talre
your
SHOCK
Do
not
touch
AC
electrical
running,
or
when
is
present
in
place.
connected
at
these
connections!
on
electrical
ENGINE
Do
not
touch
hot
engine
parts
components. A running
Steam
can
cause
or
checking the coolant.
engine
injury
or
the
personnel,
connections
to
shore
or
gets
death!
PREVENT
A
• Prevent flash fires.
sparks to occur near the carburetor, fuel line, filter, fuel
pump, or other potential sources of spilled fuel or fuel
vapors.
removing the fuel line, carburetor, or fuel filters.
• Do not operate with a Coast Guard Approved flame
arrester removed. Backfire can cause severe injury or
death.
• Do not operate with the air cleaner/silencer removed.
Backfire can cause severe injury or death.
• Do not smoke
fuel system. Keep the compartment and the engine/generator clean and free
fire.
• Be aware - diesel fuel will bum.
PREVENT
A
injury
• Follow re-fueling safety instructions. Keep the vessel's
hatches closed when fueling.
after fueling. Check below for fumes/vapor before running
the blower. Run the blower for four minutes before starting your engine.
• All
handling and storing fuels. Store fuel
area away from spark-producing equipment and out
reach
• Do not
• Shut off the fuel service valve at
the fuel system. Take care
spill.
sources of
Ensure proper ventilation exists when servicing the
system.
• Do not alter or modify the fuel system.
• Be sure all fuel supplies have a positive shutoff valve.
• Be certain fuel line fittings are adequately tightened and
free of leaks.
• Make sure a fire extinguisher is installed nearby and is
properly maintained. Be familiar with its proper use.
Extinguishers rated ABC by the
BURNS -FIRE
WARNING:
Use a suitable container to catch all fuel when
Wipe up all spilled fuel and engine oil.
Fire
can
cause
injury
or
death!
Do
not smoke or permit flames or
or
permit flames or sparks to occur near the
of
debris to minimize the chances of
BURNS -EXPLOSION
WARNING:
or
death!
fuel
vapors are highly explosive. Use extreme care when
of
children.
fill
DO NOT allow any smoking, open flames.
for all applications encountered
Explosions
the fuel tank(s) while the engine
fire
near the fuel system or engine when servicing.
from
fuel
vapors
Open and ventilate cabin
in
a well-ventilated
the
engine when servicing
in
catching any fuel that might
NFPA are appropriate
in
this environment.
can
is
running.
cause
of
or
other
fuel
the
Engines
& Generators
Page 4

SAFETY
INSTRUCTIONS
ACCIDENTAL
A
WARNING:
or
death!
• Disconnect the battery cables before servicing the engine/
generator. Remove the negative lead first and reconnect
it last.
• Make certain all personnel are clear
starting.
• Make certain all covers, guards, and hatches are reinstaIled before starting the engine.
BATTERY
A
WARNING:
or
death!
• Do not smoke
being serviced. Lead acid batteries emit hydrogen, a
highly explosive gas, which can be ignited by electrical
arcing or
equipment
servicing.
• Never connect the negative
(+) connection terminal
the battery condition
Sparks could ignite battery gases or fuel vapors. Ventilate
any compartment containing batteries to prevent accumu-
lation
the battery charger connections while the battery
charged.
• Avoid contacting the terminals with tools, etc., to prevent
burns or sparks that could cause an explosion. Remove
wristwatch, rings, and
the battery.
• Always turn the battery charger off before disconnecting
the battery connections. Remove the negative lead first
and reconnect it last when servicing the battery.
BATTERY
A
WARNING:
severe
STARTING
Accidental
starting
can
cause
of
the engine before
EXPLOSION
Battery
or
aIlow
by
lit tobacco products. Shut off all electrical
in
the vicinity to prevent electrical arcing during
of
explosive gases.
explosion
an
open flame near the battery
(-)
of
the starter solenoid. Do not test
by
shorting the terminals together.
To
any
other jewelry before handling
can
cause
battery cable to the positive
avoid sparks, do not disturb
ACID
injury
Sulphuric
or
death!
acid
in
batteries
injury
injury
is
can
being
cause
TOXIC
• Ensure that the exhaust system
• Be sure the unit and its surroundings are weIl ventilated.
.•
• For additional information refer to ABYC T-22 (educa-
• Do not use copper tubing
• Do not instaIl exhaust outlet where exhaust can be drawn
EXHAUST
A
WARNING:
discharged from the engine. Check the exhaust system
regularly for leaks and make sure the exhaust manifolds
are securely attached and no warping exists.
attention to the manifold, water injection elbow, and
exhaust pipe nipple.
In
addition to routine inspection
instaIl a carbon monoxide detector. Consult your boat
builder or dealer for instaIlation
tional information on Carbon Monoxide).
A
WARNING:
odorless
nausea
• Although diesel engine exhaust gases are not as toxic as
AVOID
gas.
or
fumes can rapidly destroy copper tubing
tems. Exhaust sulfur causes rapid deterioration
tubing resulting
through portholes, vents, or air conditioners. If the engine
exhaust discharge outlet is near the waterline, water could
enter the exhaust discharge outlet and close or restrict the
flow
of
exhaust. Avoid overloading the craft.
exhaust fumes from gasoline engines, carbon monoxide
is
present
gas
toms or signs
are:
Vomiting
Dizziness
Throbbing
Muscular twitching
Intense headache
Weakness and sleepiness
MOVING
GASES
Carbon
Inhalation
death!
in
in
diesel exhaust fumes. Some
of
carbon monoxide inhalation or poisoning
in
monoxide
Carbon
monoxide
produces
in
exhaust/water leakage.
temples
(CO)
is
adequate
of
the exhaust system,
of
approved detectors.
(CO)
flu-like
diesel exhaust systems. Diesel
is a deadly
is
in
PARTS
gas!
to
expel gases
Pay close
an
invisible
symptoms,
exhaust sys-
of
copper
of
the symp-
• When servicing the battery or checking the electrolyte
level, wear rubber gloves, a rubber apron, and eye protection. Batteries contain sulfuric acid which
it comes in contact with your skin, wash it off at once
with water. Acid may splash on the skin or into the eyes
inadvertently when removing electrolyte caps.
is
destructive. If
A
WARNING:
or
death!
• Do not service the engine/generator while
situation arises
Engines & Generators
ii
Rotating
in
which it
parts
can
cause
injury
it
is
running. If a
is
absolutely necessary to make
Page 5

SAFETY
INSTRUCTIONS
• Do not wear loose clothing or jewelry when servicing
equipment; avoid wearing loose jackets. shirts, sleeves.
rings. necklaces or bracelets that could be caught
moving parts.
• Make sure all attaching hardware
Keep protective shields and guards in their respective
places at all times.
• Do not check fluid levels or the drive belts' tension while
is
the engine/generator
• Stay clear
when the engine
be
HAZARDOUS
A
of
the drive shaft and the transmission coupling
caught
in
these rotating parts.
NOISE
WARNING:
operating.
is
running; hair and clothing can easily
High
noise
is
properly tightened.
levels
can
cause
in
hearing
loss!
• Never operate a generator without its muffler installed.
• Do not run
removed.
• Do not run engines or generators for long periods with
their enclosures open.
A
WARNING:
are
mentally
an
engine with the air intake (silencer)
00
not
work
on
machinery
or
physically
incapaCitated
by
when
you
fatigue!
ABYC,
INSTALLING
NFPA
AND
GASOLINE
USCG
PUBLICATIONS
AND
DIESEL
FOR
ENGINES
AND
GENERATORS
Read the following ABYC. NFPA and USCG publications
for safety codes and standards. Follow their recommendations when installing your WESTERBEKE engine/generator.
ABYC (American Boat and Yacht Council)
"Safety Standards for Small Craft"
From:
Order
ABYC
3069 Solomon's Island Rd.
Edgewater, MD 21037
NFPA (National Fire Protection Association)
"Fire Protection Standard for Motor Craft"
From:
Order
NFPA
1 Batterymarch Park
P.O.
Box 9101
Quincy, MA
USCG (United
"USCG 33CFR183"
From:
Order
U.S. Government Printing Office
. Washington, D.C. 20404
02269-9101
States Coast Guard)
OPERATORS
Many
of
in
your Operators Manual along with other cautions and
notes to highlight critical information. Read your manual
carefully. maintain your equipment, and follow all safety
procedures.
GASOLINE
MANUAL
the preceding safety tips and warnings are repeated
ENGINE
AND
GENERATOR
INSTALLATIONS
Preparations to install a gasoline engine
begin with a thorough examination
Yacht Council's (ABYC) standards. These standards are from
a combination
Sections
H-2 Ventilation
H-24 Gasoline fuel systems
P-l Exhaust systems
P-4 Inboard engines
E-9 DC Electrical systems
All installations must comply with the Federal Code
Regulations (FCR).
of
sources including the USCG and the NFPA.
of
the ABYC standards
or
generator should
of
the American Boat and
of
particular interest are:
of
Engines & Generators
iii
Page 6

INSTALLATION
When installing WESTERBEKE engines and generators it is important that strict
attention be paid to the following information:
CODES
Federal regulations, ABYC guidelines, and safety codes must be complied with when
installing engines and generators in a marine environment.
AND
REGULATIONS
SIPHON-BREAK
For installations where the exhaust manifold/water injected exhaust elbow
or will be below the vessel's waterline, provisions must be made to install a
break in the raw water supply hose to the exhaust elbow. This hose must be looped a
minimum
the exhaust
raw water damage to the engine
If
you have any doubt about the position
to the vessel's waterline under the vessel's various operating conditions,
siphon-break.
NOTE:
operation.
engine damage.
EXHAUST
The exhaust hose must be certified for marine use. The system must be designed
prevent water from entering the exhaust under any sea conditions and at any angle
of
of
20" above the vessel's waterline. Failure to
manifold
A siphon-break
Failure
Consult
SYSTEM
the vessels hull.
A
detailed
diesel,
engines
use
injection port
requires
to
properly maintain a siphon-break can result
the
siphon-break manufacturer for proper
40
page
Marine
and
generators,
is
at
or below the load waterline will result in
and
possible flooding
of
the water-injected exhaust elbow relative
periodic inspection and cleaning
Installation
Manual
is
available
of
covering
from
a siphon-break when
the boat.
to
in
gasoline
your
WESTERBEKE
dealer.
is
close to
siphon-
instaU a
ensure
proper
catastrophic
maintenance.
and
to
Engines & Generators
iv
Page 7

TABLE
Parts
Identification
Introduction .............................................................
Warranty
Serial Number Location ................................. ..4
Admiral
Fuel,
Oil Pressure ...................................................... 6
Preparations
Procedures ........................................
Control
Engine
Oil
for
Starting/Stopping
Warning
Engine
The
Starting the Engine .........................................
Maintenance
Cooling
Thermostat ......................................................
Raw Water Pump ............................................ 16
Heat Exchanger ..............................................
Air Intake Filter ..............................................
Fuel
Fuel Lift
Fuel Filters ......................................................
Fuel PumplFuel Bleeding ............................... 20
Engine
Oil Change .................... : .................................
Remote Oil Filter ............................................ 22
Water
DC
Alternator Troubleshooting ............................ 24
Battery ............................................................ 25
Glow
Lights,
Break-In
Daily
Routine
Schedule .....................................
System
System
......................................................
Pump ................................................ 19
Lubricating
Heater
Electrical
Plugs ..................................................... 26
................................................
Panel
Alarms
........................................
and
Coolant
Initial
Procedure
Procedure
..............................
Start-Up
.........................
...............................
and
Circuit
......................
Breaker
.............................................
.................................................
Oil
.......................................
.....................................................
System
..........................................
......
.........
OF
2
3
.3
.5
6
7
8
9
10
.
11
11
12
. 14
15
17
18
.
19
19
21
21
23
.24
CONTENTS
""
W
Engine
Tachometer
Engine
Hurth
Borg
Transmission
Lay-up
Metric
Specifications
Specifications
Specifications
Specifications
Suggested
0"
IFing
lagrams
Troubleshooting
................ ; ...............................
...
..................................
........................................................
Adjustments
Drive Belt Adjustment .................................... 32
Fuel Injectors ................................................. 32
Testing Engine Compression .......................... 33
Testing Oil Pressure ........................................ 33
Valve Clearance Adjustment ......................... .34
Injection Timing ............................................ 34
Transmissions
Changing Fluid ............................................... 37
Maintenance .................................................. 37
Cable Connections .......................................... 38
Shaft Couplings .............................................. 38
Warner
Changing Fluid ..............................................
Maintenance ..................................................
Transmission
Troubleshooting
and
Recommissioning
Conversions
Spares
...
..........................................
..........................................
.....
...........................
.........................
..........................
.........................................
80N4
........................................
11
OT4
........................................
120N6
170T6
........................................
.........................................
.............................................
27
29
31
32
36
39
.40
41
.42
.44
.46
..48
.49
50
51
52
Engines & Generators
1
Page 8
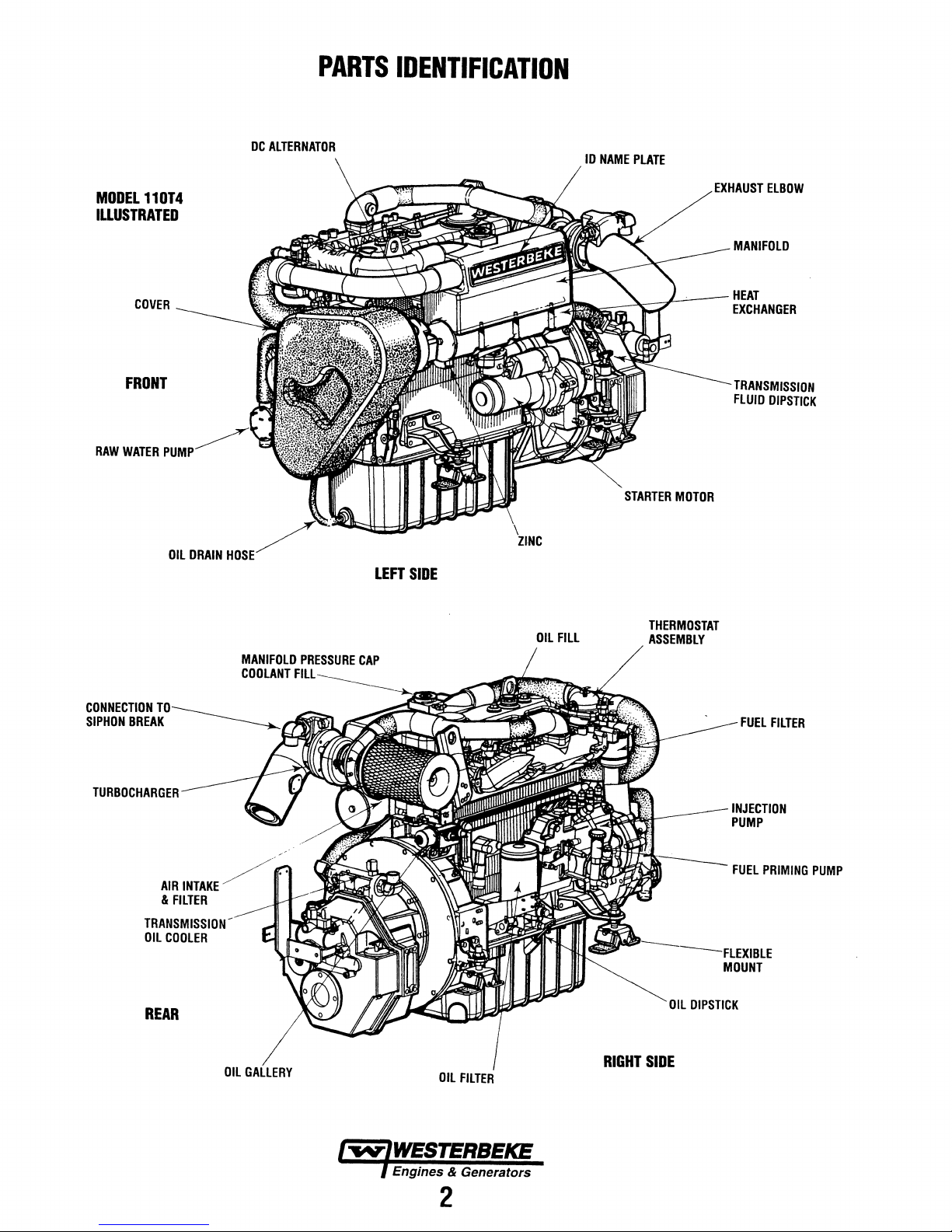
DC
ALTERNATOR
PARTS
IDENTIFICATION
ID
NAME
PLATE
MODEL
110T4
ILLUSTRATED
COVER
FRONT
RAW
WATER
OIL
DRAIN
HOSE
MANIFOLD
COOLANT
PRESSURE
FILL
CAP
LEFT
SIDE
OIL
FILL
EXHAUST
-~----;;I--'---
STARTER
MOTOR
THERMOSTAT
ASSEMBLY
ELBOW
MANIFOLD
HEAT
EXCHANGER
TRANSMISSION
FLUID
DIPSTICK
CONNECTION
SIPHON
BREAK
TURBOCHARGER
AIR
&
FILTER
TRANSMISSION
OIL
COOLER
REAR
INTAKE/"
//.
OIL
GALLERY
OIL
FILTER
RIGHT
OIL
SIDE
INJECTION
PUMP
FUEL
MOUNT
DIPSTICK
FUEL
BLE
FILTER
PRIMING
PUMP
Engines & Generators
2
Page 9

INTRODUCTION
These high perfonnance marine engines are products
WESTERBEKE's long years
technology.
dependable perfonnance
Thank you for selecting WESTERBEKE.
In
order to get the full use and benefit from your generator,
it
is
important that you operate and maintain it correctly.
This manual
manual carefully and observe all the safety precautions
throughout. Should your engine require servicing, contact
your nearest WESTERBEKE dealer for assistance.
This
provided and a technical manual is available from your
WESTERBEKE dealer.
equipment, contact your WESTERBEKE dealer for
WESTERBEKE'S installation manual.
WARRANTY
Your WESTERBEKE Warranty is included
folder. If. after
fonn you have not received a customer identification card
registering your warranty, please contact the factory in
writing with model infonnation, including the unit's
serial number and commission date.
Customer
We
take great pride in the superior durability and
is
designed to help you do this. Please read this
is
your operators manual. A parts catalog is also
PROCEDURES
60
days
Identification
of
experience and advanced
of
our engines and generators.
If
you are planning to install this
in
of
submitting the Warranty Registry
Card
of
a separate
l"WV"JWESTERBEKE
I
Customer Identification
USA
Ser.
I
OWNER
#UOOOO-E702
MR. WESTERBEKE
MAIN STREET
HOMETOWN,
Model80N4
Expires
2151200
PRODUCT
Product software, (technical data, parts lists, manuals,
brochures and catalogs), provided from sources other than
WESTERBEKE are not within WESTERBEKE's control.
WESTERBEKE CANNOT
CONTENT
RANTIES OR REPRESENTATIONS WITH RESPECT
THERETO, INCLUDING ACCURACY, TIMELINESS OR
COMPLETENESS
BE
LIABLE FOR
INCURRED IN CONNECTION WITH
OF
THE FURNISHING OR
WESTERBEKE customers should keep
span between printings
and the unavoidable existence
product software. The product software provided with .
WESTERBEKE products, whether from WESTERBEKE or
other suppliers, must not and cannot be relied upon exclu-
sively as the definitive authority on the respective product. It
not only makes good sense but
representatives
be consulted to detennine the accuracy and currentness
product software
NOTES,
As this manual takes you through the operating procedures.
maintenance schedules, and troubleshooting
engine, critical infonnation will be highlighted
CAUTIONS, and WARNINGS. An explanation follows:
NOTE:
A
observed,
your
SOFTWARE
BE
RESPONSIBLE FOR THE
OF
SUCH
SOFTWARE,
THEREOF
ANY
TYPE
USE
of
WESTERBEKE product software
of
WESTERBEKE
being consulted by the customer.
CAUTIONS
An
operating procedure essential to note.
CAUTION:
can
AND
Procedures
result
in
the
WARNINGS
engine.
MAKES
AND
WILL
OF
DAMAGE
OF
SUCH
of
earlier WESTERBEKE
is
imperative that appropriate
or
the supplier
which,
if
damage
NO
IN
NO
OR INJURY
OR
ARISING
SOFTWARE.
in
mind the time
of
your marine
by
not
strictly
or
destruction
WAR-
EVENT
OUT
in
question
NOTES,
of
of
the
The WESTERBEKE serial number
number that can assist in detennining the date
of
your WESTERBEKE engine
turer's date code is placed
number and consists
bers. The character indicates the decade (A=1960s, B=1970s,
C=1980s, D=1990s
in
the decade: and the second and third numbers repre-
year
of
sent the month
manufacture.
at
of
a character followed by three num-
E=2000s), the first number represents the
is
an
alphanumeric
or
generator. The manufac-
the end
of
the engine serial
of
manufacture
Engines & Generators
3
A
WARNING:
followed,
can
result
Procedures
in
personal
which,
injury
if
not
or
properly
loss
of
life.
Page 10

INTRODUCTION
SERIAL
The engine's model number and serial number are located on
a nameplate mounted on the side
The engine's serial number
(left side) behind the alternator, below the manifold Take the
time
plate shown below, as this will provide a quick reference when
seeking technical information and/or ordering repair parts.
~~~~~~~~~
~1¥fii4il:1B3=t
o 0
• MODEL SPEC
UNDERSTANDING
The diesel engine closely resembles the gasoline engine,
since the mechanism
are arranged above a closed crankcase. The crankshaft
same general type as a gasoline engine, and the diesel engine
has the same type
rods and lubricating system.
Therefore, to a great extent, a diesel engine requires the same
preventive maintenance as a gasoline engine. The most
important factors are proper ventilation and proper mamtenance of the fuel, lubricating and cooling systems. Fuel and
lubricating filter elements must be replaced
ods specified, and frequent checking for contaminants (water,
sediment, etc.)
important factor
high detergent diesel lubrication oil designed specifically for
diesel engines.
The diesel
however,
carburetor and ignition systems are replaced
component - the fuel injection pump - which performs the
function
NUMBER
to
enter this information on the illustration
engine' does differ from the gasoline engine,
in
its
of
both.
LOCATION
of
the engine's manifold.
is
stamped into the engine block
AVO_
MA
USA
THE
DIESEL
is
essentially the same. The cylinders
of
valves, camshaft, pistons, connecting
in
the fuel system is also essential. Another
is
the consistent use
method
of
handling and firing
ENGINE
of
the same brand
of
the name-
SER.NO..
at
the time peri-
of
fuel. The
by
a single
ORDERING
Whenever replacement parts are needed, always provide the
engine model number and serial number as they appear on
the silver and black nameplate located on the manifold.
must provide
identify your engine. In addition, include a complete part
description and part number for each part needed (see the
separately furnished
packaged parts because
not made to the same specifications
SPARES
Certain spares will
WESTERBEKE engine. Your local WESTE.RBEKE dealer
will
a'ssist
the SPARE PARTS page
sories, see WESTERBEKE's
is
the
of
PARTS
us
with this information so
Parts List). Insist upon WESTERBEKE
will fit or generic parts are frequently
AND
ACCESSORIES
be
needed
you
in
preparing
in
we
may properly
as
original equipment.
to
support and maintain your
an
inventory
this manual. For engine acces-
ACCESSORIES brochure.
of
spare parts. See
You
Engines
4
& Generators
Page 11

ADMIRAL
CONTROL
PANEL
DESCRIPTION
This manually-operated control panel is equipped with a
KEY switch and RPM gauge with an ELAPSED
meter which measures the engine's running time
in
III 0 hours. The panel also includes a WATER TEMPERATURE gauge which indicates water temperature in degrees
Fahrenheit, an
engine's oil pressure
OIL PRESSURE gauge which measures the
in
pounds
per
square inch, and a DC
control circuit VOLTAGE gauge which measures the
tem's voltage. All gauges are illuminated when the key
switch is turned on and remain illuminated while the engine
in
operation. The panel also contains two rubber-booted
is
pushbuttons, one for PREHEAT and
WATER
GRADUATED
ILLUMINATED
TURNED
TEMPERATURE
RPM
GAUGE:
TERS
PER
ENGINE
RECALIBRATED
ACCURACY
REAR
REGIS-
REVOLUTIONS
MINUTE
OF
THE
AND
CAN
BE
FOR
FROM
THE
THE
PANEL.
OF
on,?
for START.
TEMPERATURE
IN
DEGREES
WHILE
ON.
THE
ENGINE'S
IS
170·
TIME
in
GAUGE:
FAHRENHEIT
THE
KEY
SWITCH
NORMAL
-190· F (n· -
hours and
sys-
THIS
GAUGE
AND
IS
OPERATING
SS·C).
IS
IS
When the engine is shut down with the key switch turned
off,
the water temperature gauge will continue to register the last
temperature reading indicated
power was turned
off
The oil pressure gauge will fall to zero
when the key switch is turned
by
the gauge before electrical
off
The temperature gauge
will once again register the engine's true temperature when
electrical power is restored to the gauge.
A separate alarm buzzer with harness is supplied with every
Admiral Panel. The installer
is
responsible for electrically con-
necting the buzzer to the four-pin connection on the engine's
is
electrical harness. The installer
the buzzer
in
a location where
be audible to the operator should
running. The buzzer will sound when the ignition
also responsib,le for installing
it
will
be
dry and where
it
sound while the engine
key
it
is
will
is
turned
on and should silence when the engine has started and the
engine's oil pressure rises above
OIL
PRESSURE
IN
POUNDS
ILLUMINATED
ON.
PRESSURE
THE
ENGINE'S
15
psi
GAUGE:
PER
SQUARE
WHILE
NORMAL
RANGES
(1.1
kg/cm2).
THIS
GAUGE
INCH
THE
KEY
SWITCH
OPERATING
BETWEEN
40 -85
(PSI)
IS
GRADUATED
AND
IS
IS
TURNED
OIL
pSi.
HOURMETER:
REGISTERS
TIME,
USED
THE
SCHEDULE.
PREHEAT
ALTERNATOR'S
FUEL
ENGINE'S
OIL
BUTTON
START
STARTER'S
THIS
UNLESS
AT
ELAPSED
AND
SHOULD
AS A GUIDE
MAINTENANCE
EXCITER,
SOLENOID
PRESSURE
BUTTON
THE
ON
GLOW
PLUGS.
ALARM
ENERGIZES
BUTTON:
WHEN
SOLENOID
WILL
THE
PREHEAT
SAME
TIME.
BE
FOR
THE
SWITCH.
THE
PRESSED,
WHICH
NOT
BUTTON
PRESSED,
THE
FUEL
INJECTION
IT
BYPASSES
IN
START
BUTTON.
ENERGIZES
CRANKS
OPERATE
ELECTRICALLY
IS
PRESSED
ENERGIZES
LIFT
PUMP,
PUMP,
AND
THE
ENGINE'S
ADDITION,
THE
THE
ENGINE.
AND
THE
THE
THE
THIS
HELD
I/<'
:
~...:
---
,
AUTOMATIC
SUPPLIED
REACHES
ALARM
OIL
LOCATED
THE
FALL
ING
SIGNAL.
ALARM
WITH
210· F (99·C),
WHICH
PRESSURE
OFF
ENGINE'S
TO 5 -10
THE
ALARM.
SYSTEM
THE
INSTRUMENT
THIS
WILL
EMIT A CONTINUOUS
ALARM:
AN
THE
OIL
psi
OIL
ENGINE'S
PRESSURE.
(0.4 -0.7
IN
THIS
EVENT,
OIL
kg/em'),
PANEL.
SWITCH
WILL
PRESSURE
GALLERY.
SHOULD
THE
THE
ALARM
IF
THE
CLOSE
SIGNAL.
ALARM
THIS
THE
ENGINE'S
SWITCH
WILL
SWITCH:
ONLY
THE
IS
BEING
SHOW
COOLANT
THE
IS
MONITORS
OIL
PRESSURE
CLOSE
PROVIDES
TO
PANEL
SOUND-
POWER
INSTRUMENT
CLUSTER.
DC
VOLTMETER:
INDICATES
BATTERY
SHOULb
ENGINE'S
SOUNDING
SWITCH
SWITCH
WILL
EMIT A PULSATING
THE
AMOUNT
CHARGED.
13V
TO
14V.
THE
Engines & Generators
5
Page 12

DIESEL
FUEL,
ENGINE
OIL
AND
ENGINE
COOLANT
DIESEL
Use fuel that meets the requirements
2-D (ASTM), and has a cetane rating
Care
Use only clean diesel fuel! The clearance
in your fuel injection pump
particles which might pass through the filter can damage
these finely finished parts. It
and keep it clean. The best fuel can be rendered unsatisfactory by careless handling or improper storage facilities.
assure that the fuel going into the tank for your engine's daily
use
Purchase a well-known brand
Install and regularly service a good, visual-type fuel
filter/water separator between the fuel tank and the engine.
The Raycor 445 or larger
ENGINE
80N41120N6
l1OT41170T6
Use the heavy duty engine oils as specified above. Change
the engine oil after
every
Engine oil viscosity largely affects engine startability, performance, oil consumption, speed
seizure, etc. Using lubricants whose viscosity
according to the atmospheric temperature
FUEL
or
of
Of
The
Fuel
Supply
is
very critical; invisible dirt
is
important to buy clean fuel,
is
clean and pure, the following practice
of
fuel.
is
a good example
OIL
API
100 hours
ENGINE
I
Grade CF
API
Grade CG-4
an
initial
of
operation thereafter.
ENGINE OIL VISCOSITY CHART
OIL
VISCOSITY GRADE -
I
I
SAE
lOW
or
CG-4
50
hour break-in period and
of
wearing and occurrence
AMBIENT
SAE
2020W
.1
specification
#45 or better.
of
the components
is
advisable:
of
such a filter.
is
selected
is
important.
TEMPERATURE
SAE
30
of
Class
To
of
_SA.
.I
40.501
OIL
PRESSURE
The engine's oil pressure, during operation, is indicated
by the oil pressure gauge on the instrument panel. During
normal operation, the oil pressure will range between 25 and
85 psi.
NOTE:
A newly staned, cold engine can have an oil pressure
85
reading up to
sure reading as low as
depending upon the temperature
placed on the engine,
ENGINE
WESTERBEKE recommends a mixture
and
chemicals that can corrode internal engine surfaces.
The antifreeze performs double duty. It allows the engine to
run at proper temperatures by transferring heat away from the
engine to the coolant, and lubricates and protects the cooling
circuit from rust and corrosion. Look for a good quality
antifreeze that contains Supplemental Cooling Additives
(SCAs) that keep the antifreeze chemically balanced, crucial
to long term protection.
The distilled water and antifreeze should be premixed before
being poured into the cooling circuit.
NOTE:
antifreeze that
Antifreeze mixtures will protect against an unexpected freeze
and they are beneficial to the engine's cooling system. They
retard rust and add to the life
Antifreeze
Freezing
COOLANT
50% distilled water. Distilled water
Look
Concentration
Temperature
psi. A warmed engine can have an oil pres-
25
psi. These readings will vary
of
the engine, the load
and
the RPM's.
of
50% antifreeze
is
free from the
for
the new environmentally-friendly long lasting
is now available.
of
the circulating pump seal.
ANTIFREEZE
PROTECTION
23%
14°F
(-10°C)
(-13°C)
30%
8°F
35%
50%
A
CAUTION:
engine
oil
additives
to
produce
Do
to
mix.
Each
of
different
properties
not
allow
brand
brands
harmful
two
or
more
contains
could
react
to
your
its
in
engine.
brands
own
additives;
the
mixture
COOLANT
A coolant recovery tank kit
WESTERBEKE diesel engine. The purpose
tank
during engine operation, without the loss
of
without introducing air into the cooling system. This
provided and must be installed before operating the engine.
NOTE:
located above the level
Engines & Generators
6
RECOVERY
is
to allow for engine coolant expansion and contraction
This tank, with its short run
TANK
is
supplied with each
of
plastic hose, must be
of
the engine's manifold.
\\
,
"
of
this recovery
of
coolant and
kit
is
Page 13

PREPARATIONS
FOR
INITIAL
START-UP
PRESTART
Before starting your engine for the first time or after a prolonged layoff, check the following items:
INSPECTION
D Check the engine oil level. Add oil to maintain the level
at the high mark on the dipstick.
D Turn on the fuel supply, then check the fuel supply and
examine the fuel filter/water separator bowl for contaminants.
D Check the transmission fluid leveL
NOTE:
Refer to the previous page
transmission fluid.
for
fuel, oil and
D Check the DC electrical system. Inspect wire connections
and battery cable connections. Make certain the positive
(+) battery cable is connected to the starter solenoid and
(-)
cable
is
the negative
stud (this location
D Check the coolant level
and at the manifold.
NOTE:
If
the
engine has not yet been filled with coolant,
refer
to the COOLING SYSTEM section
connected to the engine ground
is
tagged).
in
both the plastic recovery tank
of
this manual.
D Visually examine the engine. Look for loose or missing
parts, disconnected wires, and unattached hoses. Check
the threaded connections and engine attachments.
D Make certain there
engine. An ample supply
performance.
is
proper ventilation around the
is
necessary for proper engine
D Make sure the mounting installation is secure.
D Ensure the propeller shaft
transmission.
D Open the through-hull and make certain raw water
primed
to
the raw water strainer
is
securely attached to the
is
~
~
~
~
~
""-..',
DIPSTICK
PUSH
IN
TIGHT
'"
'I
I
\~
~/"
~
~
~,-~
Engines & Generators
"/',,----
..
'"
.,,,1:'
;,\\1''--
'~I
,,\)1
",'\l'l/
j
?CcC"r~
I
.
i/
MANIFOLD
COOLANT
PRESSURE
CAP
.'"
)
7
Page 14

STARTING/STOPPING
PROCEDURE
THE
STARTING
These marine diesel engine have
start circuitry
be depressed for the time specified in the preheat chart. Then,
while keeping the
button
is
depressed to crank the engine.
Starting
1. Place the transmission
control to slightly open.
A
in
neutral.
damage
vessels
2. Turn the KEY SWITCH to the
3. Depress the
lights, gauges, meters and fuel solenoid will be activated.
PREHEAT switch should be depressed
The
with the following chart:
SYSTEM
l2V
DC electric starters. The
is
designed so that the PREHEAT button must
PREHEAT button engaged, the START
Procedure
in
neutral and advance the throttle
CAUTION:
to
nearby.
Make
certain
Starting
your
PREHEAT switch. The voltmeter, panel
in
gear
transmission,
the
transmission
could
result
your
boat,
ON
position (2 o'clock).
in
is
serious
and
in
accordance
TemperatureJPreheat
Atmospheric
41°F(5°C)
41°F(5°C)
23°F(-5°C)
NOTE:
The START button will
HEAT
button
activates the glow plugs in the cylinder head so use the PRE-
HEAT
intem!ittently to avoid overheating the glow plugs.
4. While still depressing the
START switch. This will engage the starter solenoid.
Upon engine starting, release the START switch and
release the
NOTE:
When starting:
A voltage drop will occur
when the preheat button
is
depressed.
Temperature
or
higher
to
23°F
(-5°C)
or
lower
not
is
depressed. Depressing the PREHEAT button
PREHEAT switch, depress the
PREHEAT switch.
Preheating
Approx. 5 seconds
Approx.
Approx.
energize unless the PRE-
12
I
TIme
10
seconds
15
seconds
14
~6
\
",
~
'I,
L....J
\:i
VOLTS
5. Should the engine not start when the START button
depressed for 10 to 20 seconds, release both buttons and
wait
30 seconds; repeat the procedure above and preheat
longer. Never
A
CAUTION:
the
engine
system
the
pump
cooling
enter
the
filling
system
manifold
from
happening
through-hull
correcting
Engine
damage
warrantable
in
mind.
6. Once the engine starts, check the instruments for proper
oil pressure and battery charging voltage.
NOTE:
engine is running.
Starting
Make sure the lubricating oil
temperature. Use oil with
30. lOW-30, or 15W-40, or 20W-40.
SAE
The battery should be fully charged to minimize voltage drop.
Use a sufficient amount
Temperature/Preheat chart elsewhere in this section.
Stopping
To
stop the engine, bring the throttle to an idle position and
place the transmission
a
few
moments to stabilize temperatures. Turn the engine off
using the stop control cable.
NOTE:
Make certain this key switch is in the
(12 o'clock).
discharge.
operator
of
key from the key switch after stopping the engine.
of
preventing the battery from discharging is to remove the
ALTERNATOR
The Admiral Control Panel uses a voltmeter to monitor the
performance
run
the
starter
for
more
than
30
Prolonged
starting
wfth
raw
Is
pumping
during
engine's
once
cylinders
the
exhaust
by
closing
shutoff,
the
cause
resulting
issue;
the
Never attempt to engage the starter while the
Under
Cold
cranking
can
result
water.
raw
water
cranking.
by
system
the
draining
of
the
excessive
from
owner/operator
in
the
This
may
through
This
way
fills.
raw
water
the
exhaust
raw
water
Intervals
engine
happen
the
raw
water
of
the
exhaust
Prevent
supply
muffler,
engine
entry
should
exhaust
raw
Conditions
is
appropriate for the prevailing
an
API Specification
of
preheat to aid in starting. See the
of
Procedure
in
neutral. Allow the engine to idle for
OFF
If
the key switch is left
An
engine alarm buzzer is provided to warn the
this condition (key switch ON). The best method
ON,
the battery will
WARNINGS
of
the alternator.
is
seconds.
wfthout
because
water
can
this
and
cranking.
is not a
keep
this
CF
or
CG-4,
position
COOLANT
A coolant temperature switch
housing. This switch will activate a continuous alarm
coolant's operating temperature reaches approximately 210°F
(99°C).
Engines & Generators
8
TEMPERATURE
SWITCH
is
located on the thermostat
if
the
Page 15

WARNING
LIGHTS,
ALARMS & CIRCUIT
BREAKER
ALTERNATOR
The Admiral Control Panel uses a voltmeter to monitor the
performance
COOLANT
A coolant temperature switch
housing. This switch will activate a continuous alarm if the
coolant's operating temperature reaches approximately
(99°C).
COOLANT
SENDOR
WARNINGS
of
the alternator.
TEMPERATURE
TEMPERATURE
SWITCH
is
located on the thermostat
AIR
BLEED
PETCOCK
2IOOF
LOW
OIL
PRESSURE
A
low
oil pressure alarm switch is located off the engine's
oil gallery. This switch's sensor monitors the engine's oil
pressure.
(0.4 - 0.7 kg/cm2), this switch will activate a pulsating alarm.
ENGINE
The DC harness on the engine is protected by
mounted manual reset circuit breaker
Excessive current draw or electrical overload anywhere
instrument panel wiring or engine wiring will cause the
breaker to trip.
because the opened breaker disconnects the fuel supply.
this should occur, check and repair the source
After repairing the fault, reset the breaker and restart the
engine.
Should the engine's oil pressure fall to 5 -
CIRCUIT
In
ALARM
SWITCH
IO
BREAKER
an
engine-
(20 amps DC).
this event most engines will shut down
of
the problem.
OIL
PRESSURE
(NORMALLY
psi
in
If
the
I
SWITCH
OPEN)
THERMOSTAT
HOUSING
OIL
PRESSURE
SEND
OR
FROM
BLOCK
ENGINE
Engines & Generators
9
Page 16

ENGINE
BREAK-IN
PROCEDURE
DESCRIPTION
Although your engine has experienced a minimum
hour
of
test operations at the factory to make sure accurate
assembly procedures were followed and that the engine operated properly, a break-in time is required. The service life
your engine
and serviced during its initial
Breaking-in a new engine basically involves seating the piston rings to the cylinder walls. Excessive oil consumption
and smoky operation indicate that the cylinder walls are
scored, which is caused by overloading the engine during the
break-in period.
Your new engine requires approximately
conditioning operation to break in each moving part in
to maximize the performance and service life
Perform this conditioning carefully, keeping
lowing:
1. Start the engine according to the
DURE
that all systems (raw water
charging) are functioning.
2. Allow the engine to warm up (preferably by running at
fast idle) until the water temperature gauge moves into
the
is
dependent upon
section. Run the engine at fast idle while checking
130 - 140°F (55 - 60°C) range.
how
the engine is operated
50
hours
of
use.
50
STARTING PROCE-
pump,
oil pressure, battery
of
hours
of
of
the engine.
in
mind the fol-
one
of
initial
order
3. While using the vessel, run the engine at various engine
speeds for the first 25 hours. Avoid prolonged periods
idling.
4. Avoid rapid acceleration, especially with a
Use caution not to overload the engine. The presence
5.
grey
or
black exhaust and the inability
speed
reach its full rated
6. During the next 25 hours, the engine may be operated at
varying engine speeds, with short runs at full rated rpm.
Avoid prolonged idling during this break-in period.
CHECK
LIST
are signs
of
cold
of
the engine to
an
overload.
of
engine.
of
o Monitor the control panel gauges.
o Check for leaks
of
fuel and engine oil.
o Check for abnormal noise such as knocking, friction.
vibration and blow-back sounds.
o Confirm exhaust smoke:
cold
When the engine is
When the engine is
When the engine
NOTE:
See the TRANSMISSION section
break-in information on
is
- white smoke.
warm
- almost smokeless.
overloaded - some black smoke and soot.
of
this
manualfor
your
transmission.
a
Engines
10
& Generators
Page 17

THE
DAILY
ROUTINE
CHECK
Each day before starting your engine, take a few moments to
run this check list:
LIST
o Visually inspect the engine for fuel, oil, or water leaks.
o Check the oil level.
o Check the transmission fluid level.
o Check for loose wires at the alternator.
o Check the starting batteries (weekly).
o Check drive belts for wear and proper tension (weekly).
o Log your engine running time. These hours relate to
scheduled maintenance.
o Check fuel supply; always keep fuel tank(s) as full as
possible.
o Look for clean fuel
o Check the coolant level
NOTE:
Excessive loss
leak. Check the entire system.
pres'sure tester to pressurize the cooling system to locate
tem
the area
the svstem as outlined
secti~n
of
leakage.
of
this manual.
in
the fueVwater separator bowl.
in
the plastic recovery tank.
of
coolant indicates a cooling system
If
necessary, use a cooling sys-
III
cases
of
excessive coolant loss, refill
in
the ENGINE COOLANT CIRCUIT
STARTING
NOTE:
manual
1. Put the transmission
NOTE:
neutral safety switch through which the starter solenoid
energizing circuit passes. This switch
transmission
energize.
2. Tum the KEY to the ON position (2 o'clock).
3. Depress
4. While pressing PREHEAT, push
fires, release START and PREHEAT.
NOTE:
engine. This condition should abate
temperature
NOTE:
then repeat the above procedure, and PREHEAT
5. Allow a
fortable rpm (approximately
rpm, and get underway.
THE
ENGINE
See STARTING/STOPPING PROCEDURE
for
more detailed instructions.
in
neutral, throttle advanced.
Hydraulically operated transmissions have a
is
open when the
is
in gear so the starter solenoid will not
PREHEAT
Some unstable running may occur
is
Should the engine fail to start, wait 30 seconds,
few
(5
seconds).
START.
as
normal operating
reached and loads are applied.
minutes for the engine
to
warm at a com-
1200 rpm), then reduce the
As the engine
in
a cold
in
this
longer.
A
CAUTION:
reduce
the
sion
firmly
in
neutral
high
rpm
engine
from
will
will
damage
When
rpm
one
allow
shifting
to
direction
the
the
the
transmission,
idle,
then
shift
to
another. A slight
propeller
transmission/damper
to
slow.
the
transmis-
Shifting
plate.
always
pauSe
at
Engines & Generators
11
Page 18

MAINTENANCE
In
order to use this Maintenance Schedule, it will
to
log your engine hours. Use your engine hounneter or
sary
record your engine hours
NOTE:
Many
a/the/allowing
simple but others are more difficult
expert knowledge
0/ a service mechanic.
by
running time.
maintenance procedures are
and
may require the
be
neces-
SCHEDULE
A
WARNING:
while
the
equipment
correct
terminals
electrical
tools
Never
engine
is
running.
such
as
goggles
for
each
when
servicing
equipment.
job.
attempt
Wear
and
Disconnect
any
of
to
perform
the
proper
gloves,
the
engine's
and
the
any
service
safety
use
the
battery
DC
SCHEDULED
MAINTENANCE
Fuel
Supply
Fuel/Water
Engine
Coolant
Transmission
Drive
Visual
Fuel
Starting
(and
Engine
Heat
Fuel/Water
Exhaust
Engine
Throttle
Control
Raw
Separator
Oil
Level
Level
Fluid
Belts
Inspection
Filter
Batteries
House
Batteries)
Oil
and
Exchanger
Separator
System
Hoses
and
Transmission
Cable
Water
Pump
Level
of
Filter
Zinc
,
Engine
Anode
CHECK
EACH
DAY
0
0
0
0
0
0
weekly
0
0
weekly
HOURS
OF
OPERATION
50
100
250
500
750
1000
NOTE:
Keep
engine
surface
oil
will
cool.
inhibit
the
engine's
clean.
ability
to
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0
0
0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0
0 0 0
0 0
0 0
0 0 0 0
0 0
0 0
1250
Dirt
and'
remain
0 0
0
0
0
0
Diesel
No.2
Check
for
if
necessary).
Oil
level
should
dipstick.
Check
at
Add
coolant
Fluid
level
on
dipstick.
Inspect
for
and
adjust
Check
for
and
electrical
Check
for
Change
at
Check
electrolyte
and
make
excessive
Initial
engine
change
both
Inspect
zinc
exchanger
Change
filter
Initial
check
Inspect
for
tion.
Check
corrosion
replace
as
tight.
Check
Hose
should
spongy.
Check
Check
for
Lubricate
Remove
gasket,
cam
and
seals
Lubricate
MAINTENANCE
rating
of
45
cetane
water
and
dirt
in
indicate
between
recovery
the
tank;
if
needed.
should
indicate
proper
tension
if
needed.
fuel,
oil
and
connections.
loose
belt
50
hours
levels
sure
connections
corrosion.
oil & filter
every
100
anode,
end
of
zinc
every
at
50
hours,
leaks.
Check
the
exhaust
buildup
on
necessary.
casting
be
hard & tight.
and
loose
fittings,
with
WD-40
pump
and
cover
(the
shaft
when
reassembling.
if
Check
water
tension.
then
every
every
change
hours.
replace
anode
200
hours.
then
anti-siphon
elbow
inside
Check
integrity.
tighten
cotter
or
cover
for
can
turn,
DESCRIPTION
or
higher.
fuel
(drain/replace
MAX.
and
empty,
check
at
between
equivalent.
and
(3/8"
to
1/2"
belt
edges
leaks.
Keep
bolts & nuts
250
50
operating
are
very
at
50
if
needed.
debris.
every
for
carbon
passages;
that
all
Replace
all
hose
pins,
inspect
wear.
Check
but
not
MAX
deflection)
for
Inspect
hours.
tight.
hours,
Clear
250
valve
clean
connections
if
soft
clamps.
etc.
the
the
wobble).
filter
LOW
manifold.
and
LOW
wear.
wiring
tight.
hours
Clean
then
the
hours.
opera-
and/or
and
or
impeller,
bearings
on
off
heat
are
( continued)
--*
Engines & Generators
12
Page 19
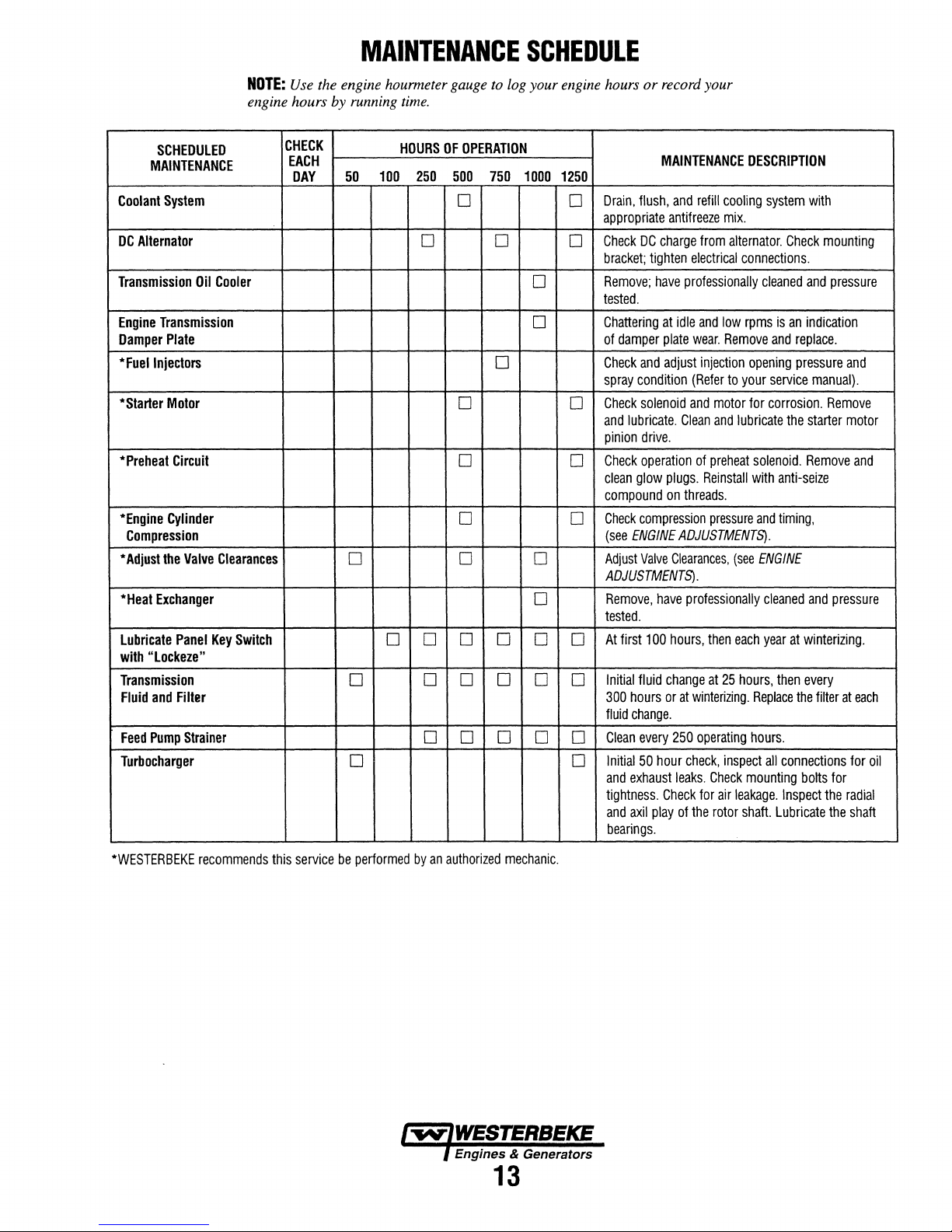
MAINTENANCE
NOTE:
Use the engine hourmeter gauge to log your engine hours
by
engine hours
running time.
SCHEDULE
or
record your
SCHEDULED
MAINTENANCE
Coolant
System
DC
Alternator
Transmission
Engine
Damper
*Fuellnjectors
*Starter
*Preheat
*Engine
Compression
*
Adjust
*Heat
Lubricate
with
"Lockeze"
Transmission
Fluid
Feed
Turbocharger
Oil
Transmission
Plate
Motor
Circuit
Cylinder
the
Valve
Exchanger
Panel
and
Filter
Pump
Strainer
Cooler
Clearances
Key
Switch
CHECK
EACH
DAY
HOURS
OF
OPERATION
100
250
500
750
50
1000
0
0 0
0
0
0 0
0
0 0 0
0 0 0
0
0 0 0
0
0 0 0 0 0
0
1250
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0 0
0 0
Drain,
flush,
appropriate
Check
bracket;
Remove;
tested.
Chattering
of
damper
Check
spray
condition
Check
and
lubricate.
pinion
Check
clean
glow
compound
Check
compression
(see
ENGINE
Adjust
ADJUSTMENTS).
Remove,
tested.
At
first
Initial
fluid
300
hours
fluid
change.
Clean
every
Initial
0
50
and
exhaust
tightness.
and
axil
bearings.
MAINTENANCE
and
refill
antifreeze
DC
charge
from
tighten
electrical
have
professionally
at
idle
and
plate
wear.
and
adjust
injection
(Refer
solenoid
drive.
operation
Valve
and
Clean
of
preheat
plugs.
Reinstall
on
threads.
pressure
ADJUSTMENTS).
Clearances,
have
professionally
100
hours,
then
change
at
or
at
winterizing.
250
operating
hour
check,
leaks.
Check
Check
for
play
of
the
rotor
DESCRIPTION
cooling
mix.
alternator.
connections.
cleaned
low
rpms
Remove
opening
to
your
motor
for
and
lubricate
solenoid.
with
and
(see
ENGINE
cleaned
each
year
25
hours,
Replace
hours.
inspect
mounting
air
leakage.
shaft.
system
with
Check
and
is
an
indication
and
replace.
pressure
service
manual).
corrosion.
the
starter
Remove
anti-seize
timing,
and
at
winterizing.
then
every
the
all
connections
bolts
Inspect
Lubricate
mounting
pressure
and
Remove
motor
and
pressure
filter
at
each
for
for
the
radial
the
shaft
oil
*WESTERBEKE
recommends
this
service
be
performed
by
an
authorized
Engines & Generators
13
mechanic.
Page 20

COOLING
DESCRIPTION
Westerbeke marine diesel engines are designed and equipped
for fresh water cooling. Heat produced in the engine
combustion and friction
which circulates throughout the engine. This circulating fresh
water coolant cools the engine block, its internal moving
parts, and the engine oil. The heat is transferred externally
from the fresh water coolant to raw water by means
exchanger, similar
water flows through the tubes
fresh water coolant flows around the tubes; engine heat
transferred to the fresh water coolant is conducted through
the tube walls to the raw water which
exhaust system where finally
other words, the engine
coolant
transferred heat overboard through the exhaust system. The
fresh water coolant and raw water circuits are independent
each other. Using only fresh water coolant within the engine
.allows the cooling water passages to stay clean and free from
harmful deposits.
FRESH
NOTE:
ommended antifreeze and water mixture to be used as the
fresh water coolant.
is
cooled by raw water, and the raw water carries the
WATER
Refer to the ENGINE COOLANT section
is
transferred to fresh water coolant
in
function to an automotive radiator. Raw
of
the heat exchanger while
is
then pumped into the
it
is
discharged overboard. In
is
cooled by fresh water coolant, this
COOLING
CIRCUIT
for
by
of
a heat
the rec-
of
SYSTEM
NOTE:
Periodically check the condition
sure cap. Ensure that the upper and lower rubber seals are
good
condition and check that the vacuum valve opens and
closes tightly. Carry a spare cap.
CHANGING
The engine's coolant must be changed according
MAINTENANCE SCHEDULE.
become contaminated, it can lead to overheating problems.
A
critical; a substantial
traced
Drain the engine coolant by loosening the drain plug on the
engine block and opening the manifold pressure cap. Flush
the system with fresh water, then start the refill process.
COOLANT
CAUTION:
back
Proper
to
cooling
cooling
number
system
of
If
the coolant
system
of
engine
corrosion.
the manifold pres-
to
the
is
allowed to
maintenance
fai/ures
can
ill
is
be
is
Fresh water coolant
circulating pump, absorbing heat from the engine. The
coolant then passes through the thermostat into the manifold,
to the heat exchanger where it
engine block via the suction side
When the engine is started cold, external coolant flow
prevented
flow
manifold from overheating). As the engine warms up, the
thermostat gradually opens, allowing full flow
coolant
cooling system.
Coolant
A coolant recovery tank allows for engine coolant expansion
and contraction during engine operation, without any
significant loss
the cooling system. This tank should be located at
the engine manifold level and should be easily accessible.
TO
TANK
)I-
by
the closed thermostat (although some coolant
is
bypassed around the thermostat to prevent,. the exhaust
to
flow unrestricted to the external portion
Recovery
COOLANT
RECOVERY
pumped through the engine by a
is
cooled, and returned to the
of
the circulating pump.
of
the engine's
of
Tank
of
coolant and without introducing air into
or
~
COOLANT
RETRACTION
is
the
above
A
WARNING:
Wear
protective
Beware
gloves.
DRAIN
DRAIN
of
PLUG
PETCOCK
the
hot
engine
coolant.
COOLANT
EXPANSION
Engines & Generators
14
SOME
ENGINE
TO
BE
MODELS
ATTACHED
WITH A PETCOCK
A
HOSE
THAT
...........
ARE
EQUIPPED
ALLOWS
'\-
...
,
I
FOR
Page 21

COOLING
SYSTEM
Refilling
After closing the engine block drain, pour clean, premixed
coolant into the manifold and when the coolant
the manifold, start the engine and run it at slow idle.
the air bleed petcocks
housing.
Monitor the coolant
the
from
install the pressure cap.
Remove the cap
coolant mix to halfway between
the cap. Run the engine and observe the coolant expansion
flow
thermostat housing
After checking for leaks, stop the engine and allow it to cool.
Coolant should draw back into the cooling system
engine cools down. Add coolant to the recovery tank if
needed. Clean
the
Coolant
is
on
the manifold and the thermostat
in
the manifold and add
manifold
the
into the recovery tank. When the petcock on the
~'
to
the filler neck and when the coolant flowing
petcock
is
free
of
on
the coolant recovery tank and
is
free
up
any spilled coolant. . /
..---'
"\
AIR
BLEED
PETCOCK,
y--..
air bubbles, close the petcock and
LOW and MAX and replace
of
air bubbles, close that petcock.
/
~.,.
Q
.~,
~~~0:r~:1!~
"'\j
~\}~"
_<\11'
as
needed. Fill
visible in
Open
fill
with
as
the
Replacing
Remove the cap screws and disassemble the thermostat housing as shown. When installing the new thermostat and gasket,
apply a thin coat
pressing it into place. Do
Run the engine and check for normal temperatures and that
there are
the
Thermostat
of
sealant on both sides
not over-tighten the cap screws.
no
leaks at the thermostat housing.
of
the gasket before
TEMPERATURE
'.ij,j
//
https://manualmachine.com/-
THERMOSTAT
A thennostat, located near the manifold at the front
engine, controls the coolant temperature as the coolant
continuously flows through the closed cooling circuit.
When the engine
vents coolant from flowing (some coolant
through a hole in the thermostat to prevent the exhaust
manifold from overheating). As the engine warms up, the
thermostat gradually opens. The thermostat
and can be checked, cleaned, or replaced easily. Carry a
spare thermostat and gasket.
is
first started, the closed thermostat pre-
I'
is
by-passed
is
accessible
of
the
THE
GASKET
FITS
EDGE
IS
AROUND
OF
THE
GROOVED
THE
OUTER
THERMOSTAT
CHANGING
THE
THERMOSTAT
Engines & Generators
15
Page 22
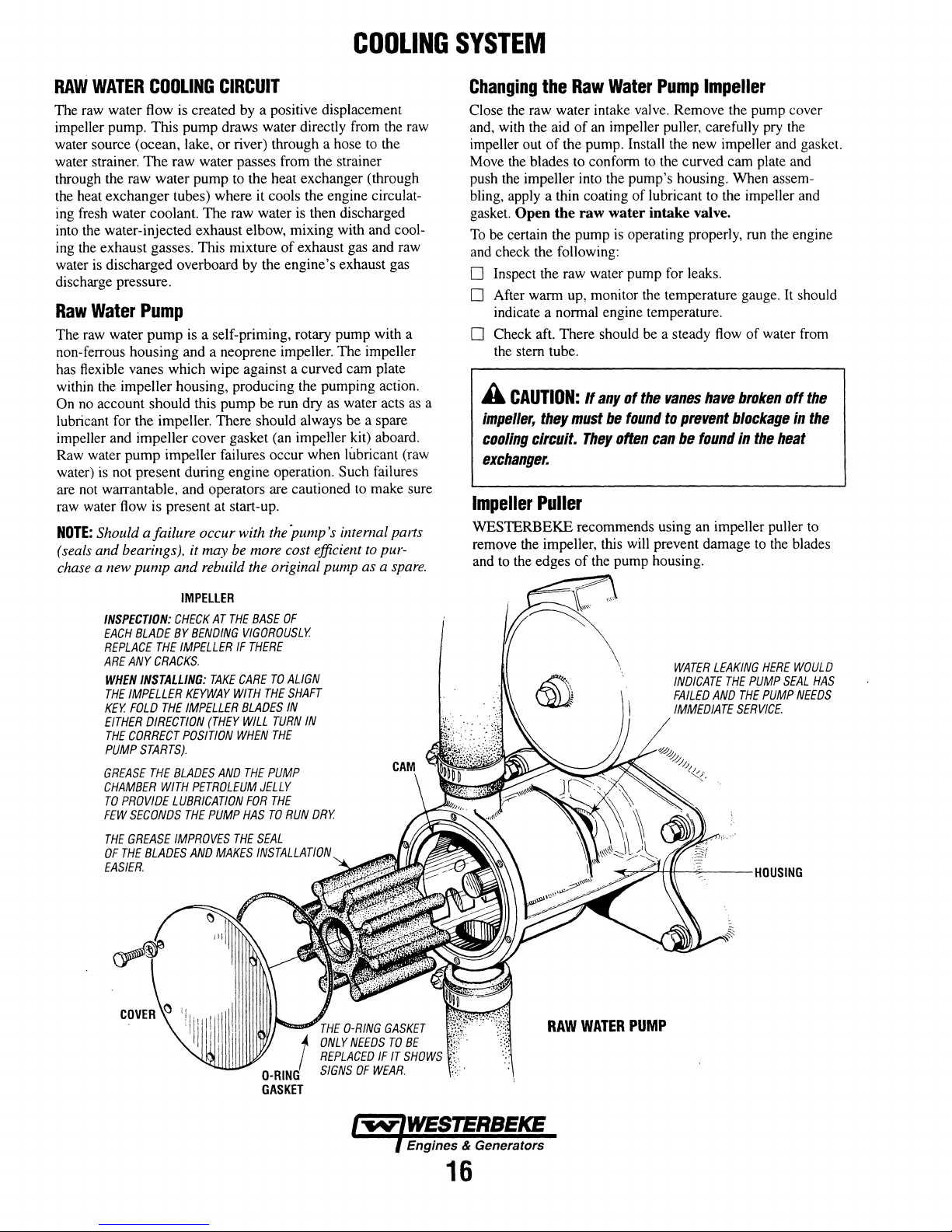
COOLING
RAW
WATER
The raw water flow is created by a positive displacement
impeller pump. This pump draws water directly from the raw
water source (ocean, lake,
water strainer.
through the raw water pump to the heat exchanger (through
the heat exchanger tubes) where it cools the engine circulating fresh water coolant. The raw water is then discharged
into the water-injected exhaust elbow, mixing with and cooling the exhaust gasses. This mixture
water
is
discharge pressure.
Raw
Water
The raw water
non-ferrous housing and a neoprene impeller. The impeller
has flexible vanes which wipe against a curved cam plate
within the impeller housing, producing the pumping action.
On no account should this pump be run dry as water acts
lubricant for the impeller. There should always be a spare
impeller and impeller cover gasket (an impeller kit) aboard.
Raw water pump impeller failures occur when lubricant (raw
water)
is
are not warrantable, and operators are cautioned to make sure
raw water flow is present at start-up.
NOTE:
Should a failure occur with the
(seals and bearings). it
chase a new
COOLING
The
raw water passes from the strainer
discharged overboard by the engine's exhaust gas
CIRCUIT
or
river) through a hose to the
of
exhaust gas and raw
Pump
pump
is a self-priming, rotary pump with a
not present during engine operation. Such failures
pump
pump's
may be more cost efficient to pur-
and
rebuild the original pump
internal parts
as
a spare.
as
SYSTEM
Changing
Close the raw water intake valve. Remove the pump cover
and, with the aid
impeller out
Move the blades to conform to the curved cam plate and
push the impeller into the pump's housing. When assembling, apply a thin coating
gasket.
To
be certain the pump
and check the following:
o Inspect the raw water pump for leaks.
o After warm up, monitor the temperature gauge. It should
indicate a normal engine temperature.
o Check aft. There should be a steady flow
the stem tube.
a
A
impeller,
cooling
exchanger.
Impeller
WESTERBEKE recommends using an impeller puller to
remove the impeller, this will prevent damage to the blades
and to the edges
the
Raw
of
an
of
the pump. Install the new impeller and gasket.
Open the
CAUTION:
circuit.
they
raw
If
any
must
They
Puller
of
the pump housing.
Water
Pump
impeller puller, carefully pry the
of
lubricant to the impeller and
Impeller
water intake valve.
is
operating properly, run the engine
of
the
vanes
have
broken
be
found
to
onen
can
prevent
be
blockage
found
in
of
water from
the
heat
off
in
the
the
INSPECTION:
EACH
BLAOE
REPLACE
ARE
WHEN
THE
KEY.
EITHER
THE
PUMP
GREASE
CHAMBER
TO
FEW
THE
OF
EASIER.
THE
ANY
CRACKS.
INSTALLING:
IMPELLER
FOLD
THE
DIRECTION
CORRECT
STARTS).
THE
WITH
PROVIDE
SECONDS
GREASE
THE
BLADES
LUBRICATION
IMPELLER
CHECK
AT
BY
IMPELLER
BLADES
IMPROVES
THE
BENDING
TAKE
KEYWAY
IMPELLER
(THEY
POSITION
AND
PETROLEUM
THE
PUMP
AND
MAKES
BASE
OF
VIGOROUSLY.
IF
THERE
CARE
TO
WITH
WHEN
THE
ALIGN
THE
SHAFT
BLADES
IN
WILL
TURN
THE
THE
PUMP
JELLY
FOR
THE
HAS
TO
RUN
SEAL
INSTALLATION
IN
DRY.
THE
O-RING
ONLY
REPLACED
SIGNS
NEEDS
IF
OF
WEAR.
GASKET
TO
BE
IT
SHOWS
WATER
LEAKING
INDICATE
FAILED
AND
IMMEDIATE
~~~ft-*""---HOUSING
RAW
.
WATER
..
PUMP
THE
PUMP
THE
SERVICE.
HERE
SEAL
PUMP
WOULD
HAS
NEEDS
Engines & Generators
16
Page 23

COOLING
HEAT
EXCHANGER
The heat exchanger
large number
through the small copper tubes and the fresh water coolant
from
the engine
raw water removes heat from the fresh water coolant.
Heat
Exchanger
After approximately 1000 hours
and pressure test the engine's heat exchanger. (A local automotive radiator shop should
exchanger.)
NOTE:
Operating
that a heat exchanger cleaning be perfonned more often than
every
1000 hours.
Zinc
Anode
A zinc anode, or pencil,
circuit within the heat exchanger. The purpose
zinc anodes
place
effects
The condition
and the anode cleaned or replaced as required. Spare anodes
should be carried on board.
NOTE:
installation and vessel location; not that
is
in
the raw water cooling circuit, thereby reducing the
of
electrolysis on other components
Electrolysis action is the result
is
a copper cylinder which encloses a
of
small copper tubes. Raw water
is
circulated around the copper tubes. The
is
pumped
Service
of
operation, remove, clean
be
able to clean and test the heat
in
silty and/or tropical waters may require
is
located
to sacrifice them to electrolysis action taking
of
the zinc anode should be checked monthly
in
the raw water cooling
of
having
of
the system.
of
each particular
of
the engine.
SYSTEM
ZINC
ANODES
NEW
If the zinc anodes need replacement, hold the hex boss into
which the zinc anode
ening the anode with another wrench. This prevents the hex
boss from possibly tearing off the exchanger shell. After
removing the zinc, note the condition
poor condition, there are probably a lot
the exchanger. Remove the end
clean the inside
exchanger end gasket
aged when removing the end cover. Replace the gasket (refer
to
your engine model's heat exchanger end gasket part num-
ber),
O-ring and cover, and install a new zinc anode.
NOTE:
The threads
do
not require sealant. Sealant should not be used as it may
insulate the zinc from the metal
ing preventing electrolysis action on the zinc.
of
REPLACE
is
threaded with a wrench while loos-
of
of
the heat exchanger and
all zinc debris. Always have a spare heat
in
case the present one becomes dam-
of
the zinc anodes are pipe threads and
of
the heat exchanger hou;-
CLEAN & REUSE
it.
If
the zinc
of
zinc flakes within
is
in
CLEAN
OUT
BOTH
ENDS
ZINC
ANODE
ALSO
SERVES
FOR
THE
RAW
AS A DRAIN
WATER
SYSTEM
HEAT
EXCHANGER
TO
REMOVE
HEAT
EXCHANGER
17
CLEAN
GASKET
OUT
ACCUMULATED
DEBRIS
Page 24

COOLING
Raw
Water
NOTE:
the strainer will always be self-priming.
A clean raw water intake strainer is a vital component
engine's cooling system. Include a visual inspection
strainer when making your periodic engine check. The water
in the glass should be clear.
Perform the following maintenance after every
operation:
1.
Close the raw water seacock.
2. Remove and clean the strainer filter.
3. Clean the glass.
4. Replace the washer if necessary.
5. Reassemble and install the strainer.
6.
Open the seacock.
7. Run the engine and check for leaks.
Intake
Always install the strainer
Strainer
at
or
below the waterline so
100 hours
of
of
this
the
of
SYSTEM
NOTE:
Also follow the above procedure after having run hard
aground.
If
the engine temperature gauge ever shows a higher than
normal reading, the cause may be that silt, leaves or grass
may have been caught up in the strainer, slowing the
raw water through the cooling system.
WASHER
STRAINER
FILTER
flow
of
AIR
INTAKE
DESCRIPTION
A marine diesel engine will typically consume
6,000 cubic feet
be
room
unrestricted. The air intake filter/cleaner should be inspected
every
100
of
air per hour. Not only must the engine
well ventilated, the air flow into the engine must be
operating hours. Clean/replace when needed.
AIR
INTAKE
FILTER
as
much
as
TYPICAL
FILTER
RAW
WATER
tOwner
........
--CONNECTS
INTAKE
Installed]
ARM
COVER
STRAINER
TO
ROCKER
Engines & Generators
18
Page 25

FUEL
SYSTEM
DIESEL
Use
use
FUEL
A primary fuel filter
installed between the fuel tank and the engine to remove
water and other contaminants from the fuel before they can
be carried to the fuel system on the engine.
Most installers include a type
the installation package as they are aware
that contaminants in the fuel can cause.
A typical fuel filter/water separator is iIIustrated below. This
is
separator type filter is not installed between the fuel supply
tank and engine-mounted fuel system, any water in the fuel
will affect the fuel pump, engine filter, and injection
equipment. The owner/operator is responsible for making
certain the fuel reaching the engine's injection equipment
free
and maintaining a proper filtration/separation system.
FUEL
WATER
[Owner
FUEL
No.2 diesel
kerosene or home heating
WATER
the Raycor Model 445. Keep in mind that
of
impurities. This process is accomplished by installing
FILTER!
SEPARATOR
Installed]
fuel
with a cetane rating of 45 or
fuel.
SEPARATOR
of
the water separating type must be
of
filter/water separator with
higher.
of
the problems
if
a water
Do
not
is
FUEL
FILTERS
The
fuel injection pump and the fuel injectors are precisely
manufactured and they must receive clean diesel fuel, free
of
valve
Take
fire
near
clean fuel, the
at
the
care
in
catching
any
smoking,
the
fuel
ventilation
from water and dirt. To ensure this flow
must pass through at least two fuel filters. a fuel/water separator and the engine's spin-on fuel filter. Visually inspect,
clean. and change these filters according to the maintenance
schedule in this manual.
A
WARNING:
when
servicing
any
fuel
that
open
flames
system
when
when
servicing
Shut
the
fuel
may
spill.
or
other
sources
servicing.
the
fuel
off
the
system.
DO
NOT
Ensure
system.
fuel
allow
of
proper
tank
exists
LIGHTLY
WITH
fuel
CLEAN
WIPE
FUEL
FUEL
INJECTION
The
fuel
injection pump
diesel
engine. requiring the utmost care
injection pump
owner-operator
requires servicing, remove
injection pump service facility. Do not attempt
and
repair
it.
The
only
adjustment the servicing mechanic should make to
fuel
injection pump
FUEL
LIFT
The
fuel
lift
pump
PUMP
is a very
has
been thoroughly bench-tested
is
cautioned not
is
the adjustment for engine idle speed.
important component of the
in
to
attempt
it
and take
it
to
PUMP
is
an
integral part of
the
handling. The
to
an
fuel
fuel
and
the
service
it.
If
authorized
to
disassemble
injection pump.
it
fuel
the
TO
LlFTPUMP
AND
INCOMING
FUEL
TO
INJECTION
PUMP
Changing
1.
Shut
2. Loosen the fuel filter, turning counterclockwise with a
filter wrench. Place the used filter in a container for proper
disposal.
3.
Using a rag, wipe clean the sealing face on the housing
bracket so the new filter can
4. Lightly oil the sealing O-ring on the new filter. To rein-
stall, turn the filter assembly counterclockwise carefully
until the O-ring contacts the sealing surface
bracket. Turn 2/3 further with the filter wrench.
NOTE:
during disassembly.
the
Fuel
Filter
the fuel supply off.
be
The cartridge contains fuel.
seated properly.
of
Take
care not to spill it
the housing
Engines & Generators
19
Page 26
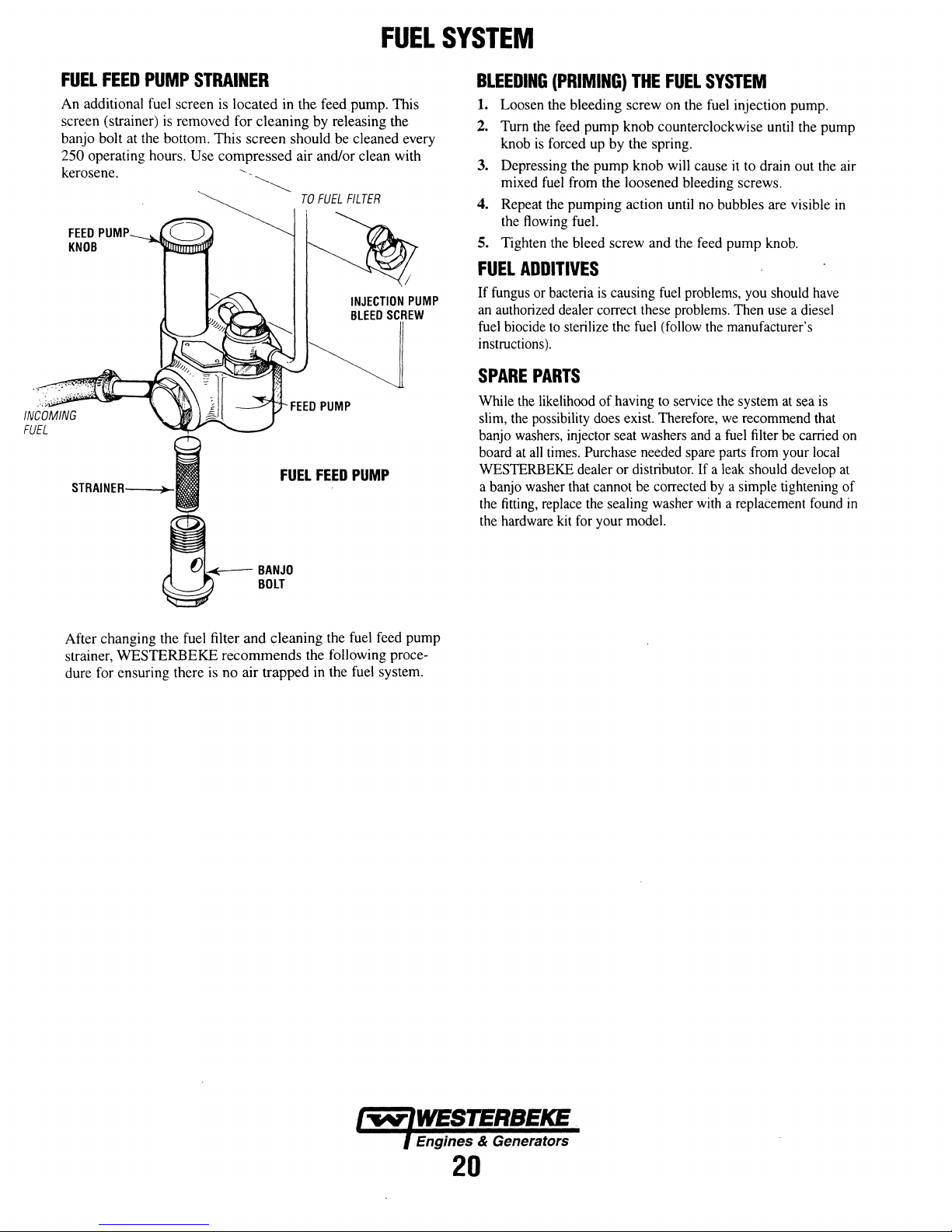
FUEL
FUEL
FEED
PUMP
An additional fuel screen is located in the feed pump. This
screen (strainer)
banjo bolt at the bottom. This screen should be cleaned every
250 operating hours. Use compressed air and/or clean with
kerosene.
STRAINER
is
removed for cleaning by releasing the
TO
FUEL
FILTER
INJECTION
BLEED
PUMP
SCREW
SYSTEM
BLEEDING
1. Loosen the bleeding screw on the fuel injection pump.
2. Tum the feed pump knob counterclockwise until the pump
knob
3. Depressing the
mixed fuel from the loosened bleeding screws.
4. Repeat the pumping action until no bubbles are visible
the flowing fuel.
5. Tighten the bleed screw and the feed pump knob.
FUEL
If
fungus or bacteria
an authorized dealer correct these problems. Then use a diesel
fuel biocide
instructions
(PRIMING)
is
forced up by the spring.
THE
FUEL
SYSTEM
pump
knob will cause it to drain out the air
ADDITIVES
is
causing
to
sterilize the fuel (follow the manufacturer's
).
fuel
problems, you should have
in
FEED
PUMP
FUEL
FEED
PUMP
1.4---
After changing the fuel filter
strainer, WESTERBEKE
dure for ensuring there is no air trapped in the fuel system.
BANJO
BOLT
and
cleaning the fuel feed pump
recommends
the following proce-
SPARE
While the likelihood
slim, the possibility does exist. Therefore,
banjo washers, injector seat washers
board at
WESTERBEKE dealer or distributor.
a banjo washer that cannot be corrected by a simple tightening of
the fitting, replace the sealing washer with a replacement found
the hardware kit for your model.
PARTS
of
having to service the system
we
and a fuel
all
times. Purchase needed spare parts from your local
If
a leak should develop
at
recommend that
filter
be
sea is
carried on
at
in
Engines & Generators
20
Page 27

ENGINE
LUBRICATING
DESCRIPTION
The lubricating system
oil pump. The engine oil
oil pump, which drives the oil, under pressure, through the
filter, oil cooler and various lubricating points
oil
engine. The oil then returns to the oil sump to repeat the
continuous cycle. When the oil pressure exceeds the
specified pressure, the oil pushes open the relief valve
oil pump and returns to the oil sump, keeping the oil pressure
within its specified range.
Oil
Pressure
The engine's oil pressure, during operation,
by the oil pressure gauge on the instrument panel. During
normal operation, the oil pressure will range between 25 and
85
psi.
is
a pressure feeding system using
is
drawn from the oil sump by the
in
is
indicated
the .
in
an
the
OIL
NOTE:
Generic filters are not recommended. as the mater-
ial standards
parts might
Immediately after an oil filter change
engine to make sure the oil pressure is normal
there are no oil leaks around the new oilfilter.
3.
Filling the Oil Sump. Add new oil through the oil filler
cap on the top
engine for a few moments while checking the oil
pressure. Make sure there
oil filter or from the oil drain system, and stop the engine.
Then check the quantity
Fill to, but not over the high mark on the dipstick, should
the engine require additional oil.
or
diameters
be
entirely different from genuine parts.
of
the engine. After refilling, run the
of
important items on generic
and
oil fill.
is
no
leakage around the new
of
oil with the lube oil dipstick.
and
run
the
that
ENGINE
1.
2.
OIL
CHANGE
Draining the Oil Sump. Discharge the used oil through
of
the sump drain hose (attached to the front
while the engine is wann. Drain the used oil completely,
in
replace the hose
=urely.
SUMP
DRAIN
HOSE-
Always observe the used oil as it
yellow/gray emulsion indicates the presence
the oil. Although this condition
prompt attention to prevent serious damage. Call a
qualified mechanic should water be present
Raw water present
the exhaust system attached to the engine and/or a
siphoning
circuit into the exhaust, filling the engine. This problem
often caused by the absence
poor location
of
Draining the Oil
flows from the drain (into an appropriate container). After
draining, remove the filter and wipe off any excess oil.
Tighten the
When installing the new oil filter element, wipe the
filter's O-ring gasket's sealing surface free
apply a thin coat
on the
new
oil filter. Screw the filter onto the threaded oil
filter nipple on the oil filter bracket, and then tighten the
filter firmly by hand.
its bracket, and replace the end cap
.
1\
~
__
~
in
the oil can be the result
raw water through the raw water cooling
or
lack
of
maintenance.
Filter.
Back off the drain plug until oil
drain
plug.
of
clean engine oil to the rubber O-ring
'~~~
is
removed. A
is
rare, it does require
of
an
anti-siphon valve, its
the engine)
of
water in
in
the oil.
of
of
oil and
6"0.0.
a fault
FOR
EXTENSION
1/4"
NPT
in
is
SPIN
ON
OIL
FILTER
TURN
HAND
O-RING.
THEN
2/3
OF A TURN.
O-RING
APPLY
CLEAN
ENGINE
OIL
WHEN
INSTALLING
CUSTOMER
THIS
WIRE
USED
TO
GAUGE
OEVICE
THE
THE
WIRE
BUNDLED
WIRING
CHANGING
ATTACH
OR
ALARM
TO
MONITOR
CONDITION
OIL
FILTER.
IS
CURRENTLY
INTO
HARNESS.
THE
TIGHT
AGAINST
TIGHTEN
OPTION
CAN
BE
A
OF
THE
THE
ENGINE
OIL
Engines
21
& Generators
Page 28

REMOTE
OIL
INSTALLATION
This popular accessory
ter from the engine to a more convenient location such as an
engine room bulkhead.
NOTE:
Refer to ENGINE OIL CHANGE in this manualfor
instructiollS on removing the oil filter.
A
CAUTION:
correctly.
by-pass
from
failure.
immediately
If
the
valve
reaching
If
there
and
In
the
Is
It
011
the
is
used to relocate the engine's oil fil-
Is
Ifltal
to
Install
the
oill/nes
flows
In
filter
engine
no
011
check
themvelSB
assembly
causing
pmssuTB
the
hose
dlmctlon,
will
prevent
an
Intemal
reading,
shutdown
connections.
the
the
011
engine
NOTE
THE
ON
THE
ADAPTER
REMOVED
WILL
BE
RECONNECTED
"IN"
FOR
FILTER
AND
"OUT"
WHEN
INSTALLATION
(OPTIONAL)
To
install, simply remove the engine oil filter and thread on
WESTERBEKE's remote oil filter kit as shown. Always
install this kit with the oil filter facing down as illustrated.
Contact your WESTERBEKE dealer for more information.
NOTE:
Westerbeke is not responsible
incorrect installation
MARKINGS
THE
HOSES
ARE
SO
THEY
CORRECTLY.
of
the Remote Oil
for
engine failure due to
Filter.
FASTEN
SECURelY
(SCREWS
ARE
OWNER
TO A BULKHEAD
SUPPLIED)
APPLY A COAT
INSTALLING
TIGHTEN
AN
CONTACTS
OF
THIS
KIT.
ADDITIONAL
THE
BASE.
CLEAN
THREAD
3/4
TURN
OIL
THE
TO
THE
KIT
ON,
AFTER
O-RING
THEN
THE
O-RING
WHEN
HAND
Engines & Generators
22
APPLY A THIN
TER
GASKET
FILTER
CONTACTS
ADDITIONAL
I
COAT
WHEN
3/4
TURN.
THE
OF
CLEAN
BASE,
OIL
TIGHTEN
INSTALLING.
TO
THE
AFTER
THE
IT
AN
FIL-
Page 29
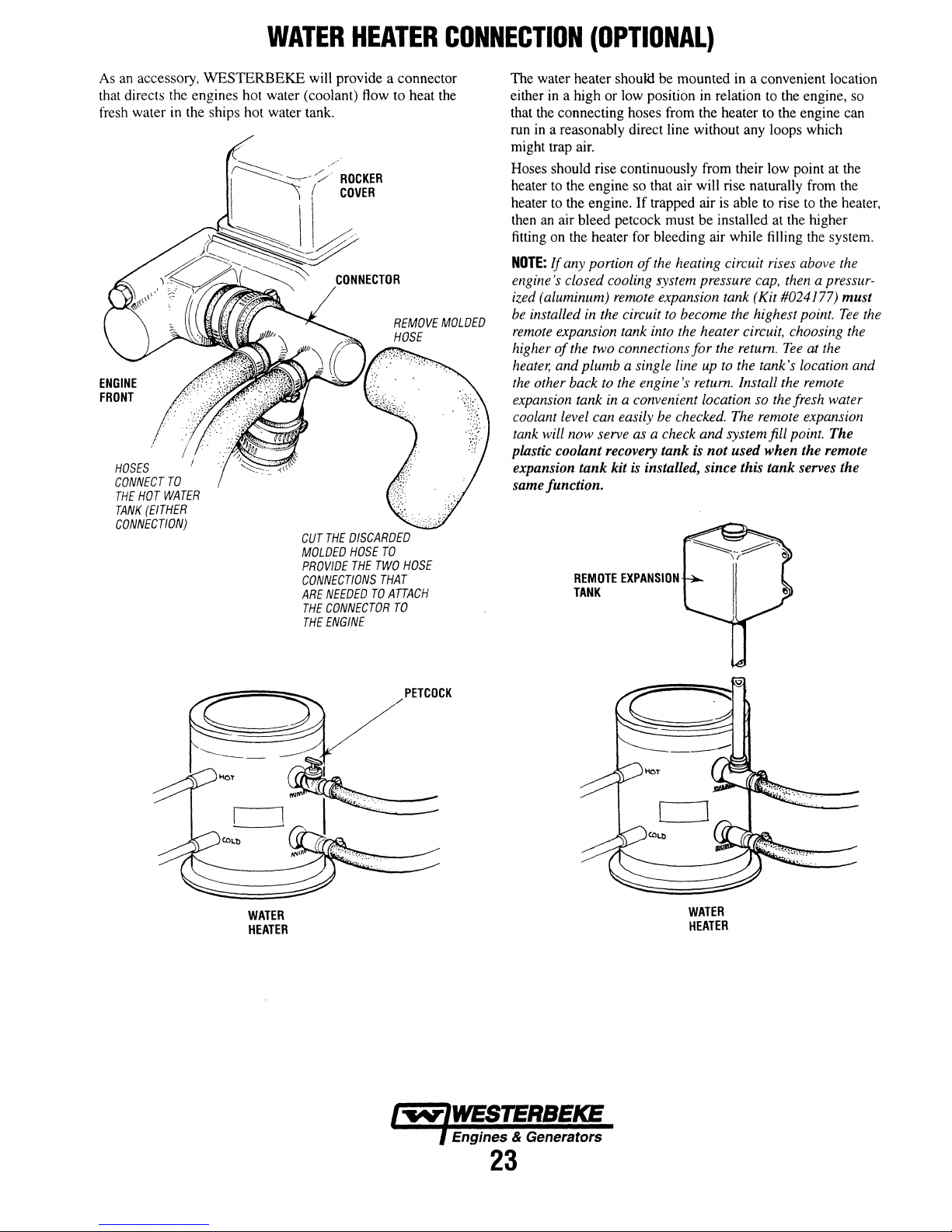
WATER
As
an
accessory, WESTERBEKE
that directs the engines hot water (coolant) flow to heat the
fresh water
ENGINE
FRONT
HOSES
CONNECT
THE
TANK
CONNECTION)
TO
HOT
WATER
(EITHER
in
the ships hot water tank.
CUT
MOLDED
PROVIDE
CONNECTIONS
ARE
THE
THE
HEATER
wiJI
provide a connector
ROCKER
COVER
THE
DISCARDED
HOSE
TO
THE
TWO
NEEDED
CONNECTOR
ENGINE
THAT
TO
ATTACH
TO
CONNECTION
HOSE
(OPTIONAL)
The water heater shouKl be mounted
either
in
a high or low position
that the connecting hoses from the heater to the engine can
run
in
a reasonably direct line without any loops which
might trap air.
Hoses should rise continuously from their low point at the
heater to the engine so that air will rise naturally from the
heater to the engine.
then
an
air bleed petcock must be installed at the higher
fitting on the heater for bleeding air while filling the system.
NOTE:
If
any portion
engine's closed cooling system pressure cap, then a pressurized (aluminum) remote expansion tank (Kit #024177)
be installed in the circuit to become the highest point.
remote expansion tank into the heater circuit, choosing the
of
higher
heater;
the other back to the engine's return. Install the remote
expansion tank in a convenient location so the fresh water
coolant level can easily be checked. The remote expansion
tank will now serve as a check
the two connections
and
plumb a single line up
plastic coolant recovery
expansion
tank
If
trapped air is able to rise
of
the heating circuit rises above the
tank
kit
is
installed, since this
same function.
REMOTE
TANK
EXPANSION
in
a convenient location
in
relation to the engine, so
to
for
the return.
to
and
system fill point. The
is
not
used
Tee
the tank's location and
when the remote
tank
serves the
the heater,
must
Tee
at the
the
WATER
HEATER
WATER
HEATER
Engines & Generators
23
Page 30
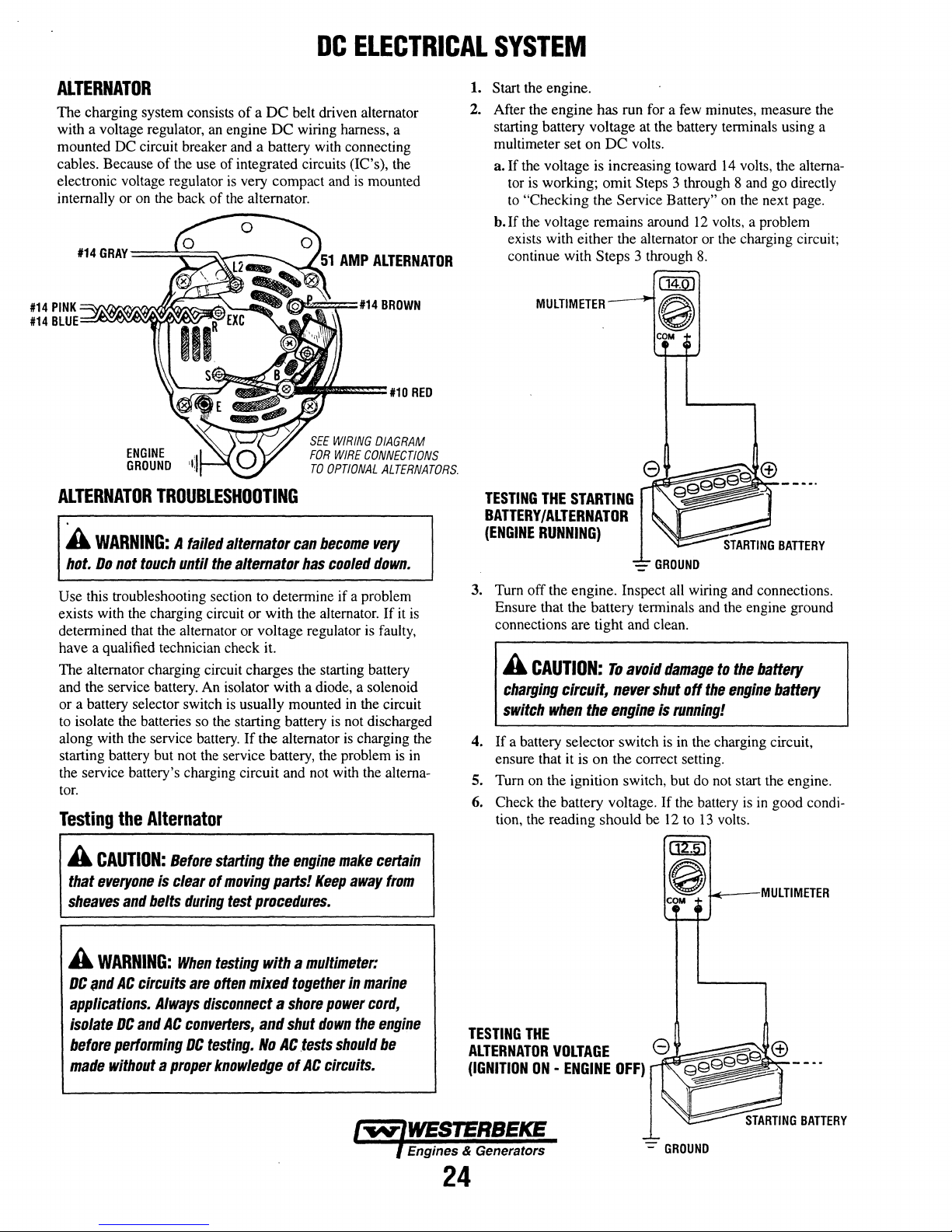
DC
ELECTRICAL
SYSTEM
ALTERNATOR
The charging system consists
with a voltage regulator, an engine
mounted DC circuit breaker and a battery with connecting
cables. Because
electronic voltage regulator
internally or
#14
GRAy==#=w
#14
PINK
#14
~~~~~~~fiC--
BLUE=
of
the use of integrated circuits (lC's), the
on
the back
of a DC
DC
is
very compact and
of
the alternator.
__
......
belt driven alternator
wiring harness, a
is
(9)~~=#14
iB@lillili====
SEE
ENGINE
GROUND
ALTERNATOR
A
WARNING:
hot.
00
not
touch
Use this troubleshooting section to determine if a problem
exists with the charging circuit
determined that the alternator or voltage regulator
have a qualified technician check it.
The alternator charging circuit charges the starting battery
and the service battery. An isolator with a diode, a solenoid
or a battery selector switch
to
isolate the batteries so the starting battery
along with the service battery.
starting battery but not the service battery, the problem
the service battery's charging circuit and not with the alternator.
Testing
the
,':1
TROUBLESHOOTING
A
failed
alternator
until
the
alternator
or
with the alternator.
is
usually mounted
If
the alternator
Alternator
FOR
TO
can
has
WIRING
WIRE
OPTIONAL
become
cooled
in
is
not discharged
is
charging the
mounted
BROWN
#10
REO
DIAGRAM
CONNECTIONS
ALTERNATORS.
very
down.
If
it
is
is
faulty,
the circuit
is
in
1. Start the engine.
2. After the engine has run for a few minutes, measure the
starting battery voltage at the battery terminals using a
multimeter set on
a.
If
the voltage is increasing toward 14 volts, the alternator is working; omit Steps 3 through 8 and go directly
to
"Checking the Service Battery" on the next page.
h.If
the voltage remains around
exists with either the alternator or the charging circuit;
continue with Steps 3 through
DC
volts.
12
volts, a problem
8.
CIDJ
MULTIMETER
o
COM
TESTING
BATTERY
(ENGINE
3. Turn off the engine. Inspect all wiring and connections.
4.
S.
Turn
6. Check the battery voltage.
THE
STARTING
IALTERNATOR
RUNNING)
-=
GROUND
Ensure that the battery terminals and the engine ground
connections are tight and clean.
A
CAUTION:
charging
switch
when
If
a battery selector switch is in the charging circuit,
ensure that it is on the correct setting.
on
the ignition switch, but do not start the engine.
tion, the reading should be
circuit,
the
To
avoid
never
engine
damage
shut
off
is
running!
If
the battery
12 to
the
13
to
the
engine
volts.
is
battery
battery
in good condi-
A
CAUTION:
that
everyone
sheaves
A
DC
applications.
iso/ate
before
made
and
WARNING:
and
AC
DC
performing
without a proper
Before
is
clear
belts
circuits
Always
and
AC
starting
of
moving
during
test
procedures.
When
are
testing
often
with a multimeter:
mixed
disconnect a shore
converters,
DC
testing.
and
No
know/edge
the
parts!
together
shut
AC
of
engine
Keep
down
.tests
AC
make
away
in
marine
power
cord,
the
should
circuits.
certain
from
engine
be
TESTING
ALTERNATOR
(IGNITION
Engines & Generators
24
THE
VOLTAGE
ON -ENGINE
OFF)
Cl2ID
~W---MULTIMETER
-=
GROUND
Page 31
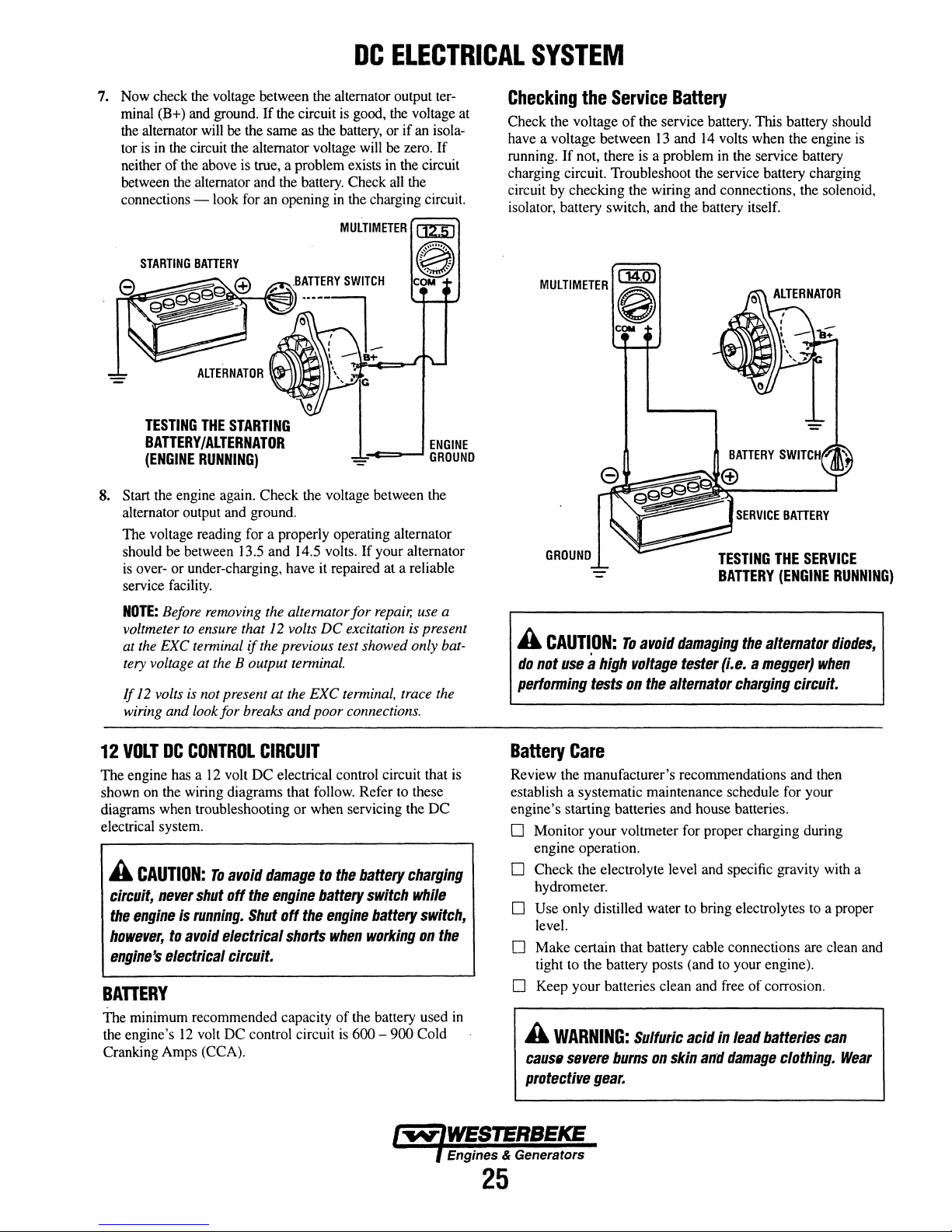
DC
ELECTRICAL
SYSTEM
7. Now check the voltage between the alternator output terIf
minal (B+) and ground.
the alternator will
tor
is
in the circuit the alternator voltage will be zero.
neither
of
between the alternator and the battery. Check all the
connections - look for an opening
TESTING
BATTERY
(ENGINE
8. Start the engine again. Check the voltage between the
alternator output and ground.
The voltage reading for a properly operating alternator
should be between 13.5 and 14.5 volts.
is
over- or under-charging, have it repaired at a reliable
service facility.
NOTE:
Before removing the alternator
voltmeter to ensure that
at
the EXC terminal
tery voltage
If
12
volts is not present
wiring
and
be the same as the battery, or
the above
THE
STARTING
IALTERNATOR
RUNNING)
at
the B output terminal.
look
for
the circuit
is
true, a problem exists in the circuit
12 volts
if
the previous test showed only bat-
at
the
breaks
and
is
good, the voltage at
in
the charging circuit.
M
ULTIMETER
WITCH
~~a+"
I
If
your alternator
for
repair;
DC
excitation is present
EXC
terminal, trace the
poor
connections.
if
an isola-
CI2ID
0
COM
I'
"\..
use a
If
ENGIN
GROUND
Checking
Check the voltage
have a voltage between
running.
charging circuit. Troubleshoot the service battery charging
circuit by checking the wiring and connections, the solenoid,
isolator, battery switch, and the battery itself.
E
A
do
performing
the
Service
If
not, there
MumMETER
GROUND
i
COM
CAUTI,ON:
not
use a high
tests
Battery
of
the service battery. This battery should
13
and 14 volts when the engine
is
a problem in the service battery
SERVICE
TESTING
BATTERY
To
avoid
voltage
on
the
damaging
tester
alternator
the
alternator
(i.e. a megger)
charging
BATTERY
THE
SERVICE
(ENGINE
when
circuit.
is
RUNNING)
diodes,
12
VOLT
DC
CONTROL
The engine has a 12 volt DC electrical control circuit that
shown on the wiring diagrams that follow. Refer to these
diagrams when troubleshooting or when servicing the
electrical system.
A
CAUTION:
circuit,
the
however,
engine's
never
engine
To
shut
is
running.
to
avoid
electrical circuit.
CIRCUIT
avoid
damage
off
the
engine
Shut
electrical
off
the
shorts
to
the
battery
engine
when
battery
switch
battery
working
DC
charging
while
SWitch,
on
BAnERY
The minimum recommended capacity
the engine's
Cranking Amps (CCA).
12
volt DC control circuit
of
the battery used
is
600 - 900 Cold
Battery
is
Review the manufacturer's recommendations and then
establish a systematic maintenance schedule for your
engine's starting batteries and house batteries.
o Monitor your voltmeter for proper charging during
engine operation.
o Check the electrolyte level and specific gravity with a
hydrometer.
o Use only distilled water to bring electrolytes to a proper
the
in
Engines & Generators
level.
o Make certain that battery cable connections are clean and
tight to the battery posts (and to your engine).
o Keep your batteries clean and free
A
WARNING:
cause
protective
25
Care
severe
gear.
Sulfuric
bums
on
acid
skin
in
and
of
corrosion.
lead
batteries
damage
can
clothing.
Wear
Page 32

GLOW
PLUGS
DESCRIPTION
The glow plugs are wired through the preheat solenoid.
When PREHEAT
should
"click" on and the glow plug should begin to get hot.
is
pressed at the control panel this solenoid
INSPECTION
To
inspect the plug, remove the electrical terminal connections, then unscrew or unclamp each plug from the cylinder
head. Thoroughly clean each plug's tip and threads with a
soft brush and cleaning solution to remove all the carbon and
oil
deposits. While cleaning, examine the tip for wear and
burn erosion;
if
it has eroded too much, replace the plug.
TESTING
An accurate way
Touch one prod to the glow plug's wire connection, and the
other
to
the body of the glow plug,
plug will have a
used with the plug
an ammeter
A
WARNING:
to
the
touch.
testing
the
to
test glow plugs is with an ohmmeter.
as
shown. A good glow
0.4 - 0.6 ohm resistance. This method can be
in
or out
of
the engine.
to
test the power drain (5 - 6 amps per plug).
These
glow
plugs
Be
careful
not
to
burn
will
your
You
can also use
become
fingers
very
plugs.
hot
when
~
Re-install the plugs
plugs should get very hot (at the terminal end) within 7
seconds.
circuit. When reinstalling the glow plugs, use anti-seize
pound
A
Glow
If
the plugs don't heat
on
the threads.
WARNING:
than
30
seconds.
Plug
Tightening
~=:::::;IC;;;;==;;;:;):="""",!~
in
the engine and test them again. The
up
quickly, check for a short
Do
not
keep a glow
Torque
19.5
TESTING A GLOW
WITH
AN
OHMMETER
KEYIPREHEAT-QPi
H-Ib
PLUG
(2.7
plug
m-kg)
on
for
more
TERMINAL
END
TIP
to
15
com-
GLOW
FROM
PREHEAT
TERMINAL
PLUGS
/;
TESTING A GLOW
USING A TEST
LIGHT
PLUG
+
Engines & Generators
26
Page 33

WIRING
MARINE
SCHEMATIC
ENGINES
#44781
+ ~ • .-______________
IZV ( 24V
20A
C.B C.B
lOA
e:
....
c
~
~
'"'
u
'"
....
.;
~8~AT~T~E~RT~I~2~·2~.~V~O~C~
START
SOl.
________________
STARTER
•
OPTIONAL
ALTERNATORS
ADMIRAL
PANEL
KEY
SW.
PREHEAT
SWITCH
TACHOMETER
$
VOLTMETER
PRESlOLllE 12
AMP
PRESlOLllE\LEECE-NEVILLE
DISCONNECT JUMPER
USE
WITH
TWO
BATTERIES.
90
fOR
ALl
AMP
ALl
LESTEK
Engines & Generators
27
135
160.
190
AMP.
ALT.
~l"
!-ZUlli
Page 34

WIRING
MARINE
ENGINES
DIAGRAM
#44781
ALTERNATOR.
21Y
12A
I----~~~~~t-w_----_rt_------t_--J_--~
"'~"
,~
I
I
+~
~-===-
BATTERY
12-21
VDC
(USED
NEUTRAL
rTY
a
WI
H
DELSI
NOTES:
•
'NIS
'IOOUCI IS
ITAnn.
SMUT
DOI'IiI.
£IIG'I£
2.
'II
all-orr
DISCOI"I[(T
WITH
A COITIIIUGUS
$1.
TeM
J.
THE
"11'
..
TME
, •
5
co
..
lcr
nSTUS
IUISTOI
AlE
'MOULD
.,.
rill
OIU.
[attallV[
'HE
,.STALUD
SWITCH
THE
1.1It[
II.I[
CIICUIl
.,lIl
'.onenD
CUIIUT
IUILO[l/o.III[l
I!tOULD
,aTTU'
IU"IG
lOT
IE
AT
'LUG Z
AT
'"UG 1 IS
IIURU
FOt
Z4
ro
rill
TO
"II(VUT
IE
UI
uUD
VOLT
.. 4 LT
IT
,..
or
TO
IS
nSTtMs
.Iusn
u.usn
"
1iI
..
Will
MUST
COII"CT
IUTALUI
(MUGUel
115
Allrs
MAil
".0
USIUOt
ILU
IiIUAL
UUS[
01
".D
....
I[MOVI
WillS
Sf
IU.ElI
.I[AI
0
!tun
Ttll
SUII[
en.EU
"liD
AT
12
SHOULD
SMOULD
.'I[
rill
"ID
ClIltUIl
.ltUl.lII
THU
THE
[lECTlICAL
THE
I"HUr
,,"£II
LlAWl1IG
"DC
WILL
THE C !leUIT
IE U'SULATED.
liE
IIilSULun,
ro
'"l
Clleulr
rill.
GlOUID
.RUln
LOCATED
..
I'
TME
rUII''''L
AIID
p"ln,
OUlets
STAUn
10AT
THIS
CAPU'I
ADlIIIAL
"10
.,"
THE
[II&III(
AIID
...
rUIICTlOI.
"un
'un
rOt
co.l[er
rUM
..
IIUI
SWnCM
TO
nIP
.IISTIUIiIUT
I[lV[
.
","
IIUIII'
rll[
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I,--_~~
I
I
I
I
I
L
__
W.IIIIG.
sUlun
TO
12
"l
TME
OIlU
Gell'
WOlf
rill
Will
IMIS
,toIO
SI
PI
II
110
ADMIRAL
PANEL
-,
REO
Engines & Generators
28
Page 35

ENGINE
TROUBLESHOOTING
The following troubleshooting table describes certain problems
relating to engine service, the probable causes
of
these prob-
lems, and the recommendations to overcome these problems.
No
panel
indications;
or
fuel
pump
is
on
and
PREHEAT
START
button
engagement.
Engine
cranks,
start.
Engine
can't
Battery
runs
Battery
not
charging
Engine
slows
Problem
fuel
is
not
working
button
is
depressed,
but
does
be
stopped.
down.
and·
stops.
solenoid
(key
is
depressed).
no
starter
not
switch
1.
Battery
20-amp
2.
10-amp
3.
preheat
4.
Loose
Preheat
5.
Connection
1.
2.
Gear
Faulty
3.
4.
Faulty
5.
Loose
Low
6.
Faulty
1.
Preheat
2.
Low
3.
1.
Disconnect
off
Oil
1.
2.
High
Low
3.
Poor
4.
DC
5.
(tachometer
Alternator
1.
1.
Fuel
20
2.
Exhaust
3.
4.
Water
Air
5.
Probable
switch
circuit
breaker
solenoid
battery
solenoid
to
shift
not
switch.
solenoid.
battery
battery.
fueling
solenoid
battery
fuel
the
fuel
pressure
resistance
resistance
battery
alternator
drive.
starvation.
Amp
circuit
system
in
fuel.
intake
obstruction.
Cause
not
on.
breaker
tripped.
tripped
connections.
not
operating.
solenoid
faulty.
in
neutral.
connections.
system.
faulty.
power.
shut-off
switch.
leak
to
ground.
leak.
connections.
not
charging
not
operating).
breaker
is
restricted.
NOTE:
The engine's electrical system is protected by a
ampere manual reset circuit breaker located on a bracket
the back
of
the engine. The preheat solenoid is mounted on
the same bracket.
VerificationJRemedy
Check
switch
and/or
battery
connections.
trips
again.
for
shorts
at
and
after
for
it
to
to
starter
Check
battery
terminal
for
in
neutral
(see
are
present
state.
are
open.
system.
Bleed
Replace
filters
house
and
shut-off
lever.
panel
lights
the
oil
pressure
sensitive
engine.)
Remove
temperature
at
battery
check
belt
alternator
Check
Exc.
terminal.
valves,
overly
sensitive
button
to
collapsed
tank(s);
cartridge.
output
draw
the
fuel
amperage
fuel
to
the
cool
then
solenoid
cable
voltage.
NEUTRAL
at
the
air
and
start
batteries.
Pull
are
(0 -.25
rise
for
tension,
should
fuel
lift
during
reset.
hose,
change
on
cable.
tripping.
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
1.
1a.
1
2.
3.
3a.
1.
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
1.
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
b.
Reset
circuit
Check
preheat
Check
engine
Check
Check
Gear
HURTH
Check
Check
Check
Check
Check
Check
Fuel
fuel
Check
Switch
Replace
Check
Observe
is
Check
lines.
after
Check
Check
corrosion
Check
DC
Check
for
volts
Check
Check
Ensure
cause
Check
exhaust
Pump
bleed
Check
breaker;
if
and
the
(+)
ground
solenoid
connection.
shift
switch
that
battery
battery
that
for
filters
system.
solenoid.
connection
not
running.
wiring.
(Do
short
all
cable
connections,
ELECTRICAL
drive
loose
are
tripping.
fuel
breaker
check
circuit
voltage
solenoid -wait
connection
stud.
"S"
must
be
TRANSMISSIONS).
with
12
volts
connections.
charge
fuel
valves
air
in
fuel
clogged.
to
combine
batteries.
if
gauges
Test
Insert
not
start
is
located.
wires
for
connections
SYSTEM/ALTERNATOR.
belt
tension;
connections.
present
fuel
supply,
for
high
DC
breaker
is
Push
for
blockage,
elbow.
water
from
system.
air
intake
filter
both
ohmmeter.
at
and
at
not
check
preheat
ground.
breaker
on
res~t.
and
(-)
connections.
SWITCH
solenoid
connection.
from
fuel
bleed
air
lever
back
activated
switch.
amp)
meter
connections
to
locate
the
loose
connections,
test
alternator.
turn
with
voltmeter.
pump.
operation.
to
heat
which
carbon
buildup
filters
and
20
solenoid
the
connection
under
system.
from
to
close
when
engine
in
battery
and
replace
fault.
See
freely.
Check
Ensure
would
at
at
to
12
(continued)
Engines & Generators
29
Page 36
ENGINE
TROUBLESHOOTING
Engine
Engine
Engine
Exhaust
Problem
overheats.
alarm
sound
alarm
sounds
smoke
problems
pulsates.
continuously.
1.
2.
1.
2.
1.
2.
1.
2.
3.
Probable
Raw
water
Coolant
Loss
of
Oil
pressure
Engine
High
temperature
too
Iowa
Blue
smoke.
White
Black
smoke.
not
circulating.
not
circulating.
oil.
switch.
coolant.
temperature.
smoke.
Cause
switch
opens
at
Verification/Remedy
1.
Raw
water
pump
failure.
Check
impeller -replace.
2.
Obstruction
2a.
Thermostat -remove
Replace
2b.
Loss
lor
2c.
Broken
2d.
Air
bleed
Check
1.
oil
Replace
2.
1.
Check
.
2.
Check
check
Incorrect
1.
1a.
Crankcase
through
2.
Engine
2a.
Faulty
3.
Improper
3a.
Fuel
insufficient
exhaust
3b.
Improperly
3c.
Lack
ventilation.
3d.
Overload.
at
thermostat.
of
coolant -check
leaks.
or
loose
leak
in
system;
air.
Add
dipstick,
drain
hose
oil
pressure
engine
for
satisfactory
with
ohmmeter,
grade
is
overfilled
the
exhaust).
is
running
injector
grade
burn
incomplete
air
system;
timed
of
air -check
raw
water
intake
or
raw
and
test
in
hot
hoses,
hose
belts -tighten/replace.
run
engine
and
coolant
as
look
for
oil
connection.
switch.
coolant
level.
operation
replace
of
engine
with
cold.
or
incorrect
of
fuel.
due
for
proper
check
air
injectors
air
intake
open
needed.
leaks
at
oil
with
if
faulty.
oil.
engine
oil
injector
timing.
to
high
back-pressure
combustion
intake).
or
valves,
and
air
water
water.
clamps,
the
filter
switch
(oil
is
(check
or
poor
filter.
filter.
drain
plug,
pressure
cap
and
at
bypassed,
blowing
out
in
exhaust
for
restrictions
compression.
Check
for
proper
etc.
to
or
in
TROUBLESHOOTING
If
the
gauge reading
by
the
gauge when the instrument panel
step
is
to
check for
and
the
Negative
Assuming that there is
is
other than what is nonnally indicated
12
volts DC between the ignition (B+)
(B-)
tenninals
12
of
the gauge.
volts as required, leave the
COOLANT
is
energized, the first
TEMPERATURE
instrument panel energized and perfonn the following steps:
1.
Disconnect the sender wire at the gauge and see if the
is
gauge reads zero, which
the nonnal reading for this
situation.
2.
Remove the wire attached to the sender tenninal at the
sender and connect it
full
scale, which
to
ground. See if the gauge reads
is
the nonnal reading for this situation.
Engines & Generators
AND
OIL
PRESSURE
If
both
of
the above gauge tests are positive, the gauge
undoubtedly
conductor from the sender
If
either
OK
and the problem lies either with the
of
the above gauge tests are negative, the gauge
GAUGES
to
the gauge or with the sender.
probably defective and should be replaced.
Assuming the gauge
to
sender
the sender tenninal at the gauge for continuity.
Check that the engine block
is
OK, check the conductor from the
is
connected
to
the ground.
Some starters have isolated ground tenninals and if the
battery
is
connected
to
the starter (both plus and minus
tenninals), the ground side will not necessarily be connected
to the block.
30
is
is
Page 37

TACHOMETER
TACHOMETER/HOUR
The tachometerlhour meter used in propulsion engine instrument panels contains two separate electrical circuits with a
common ground.
other the tachometer. The hour
volts alternator charging voltage supplied to the (+) terminal
on
the back
The tachometer circuit operates on AC voltage 6-8 volts, fed
from one
tachometer input terminal while the engine is running, and
the alternator producing battery charging voltage 13.0-14.8
volts DC.
The following are procedures to follow when troubleshooting
a fault in either
meter.
Hour
Check for the proper DC voltage between (+) and (-)
terminals.
1.
Voltage present - meter is defective - repair or replace.
2.
Voltage not present - trace (+)
nections for fault. (Jump
terminal to verify the operation.)
Tachometer
Check for the proper AC voltage between tachometer input
terminal and (-) terminal with the engine running.
1.
Voltage present - attempt adjusting meter through calibration access hole. No results, repair or replace meter.
2.
AC
output voltage.
3. Check for
ground.
4. Check electrical connections from tachometer input terminal to alternator connection.
of
the instrument.
of
the diodes
of
meter
Inoperative
Inoperative
voltage not present - check for proper alternator DC
AC
METER
One circuit operates the hour meter and the
meter
circuit operates on
in
the alternator and supplied to the
the two circuits in a tachometerlhour
and
(-) electrical con-
12
volts
DC
to meter (+)
voltage at tach terminal on alternator to
12
NOTE:
Current model tachometers use a coarse adjustment
dial to set the tachometer to the crankshaft pulley rpms. The
calibrating screw is then used
COARSE
ADJUSTMENT
TACHOMETER
NOTE:
In a new installation having new instrument panels.
the tachometer may not always be correctly calibrated to the
engine's rpm. This calibration should be checked
installations.
1.
Warm up the engine to normal operating temperature.
Remove any specks on the crankshaft pulley with a clean
cloth and place a piece
pulley to facilitate use
2. Start and idle the engine.
3. Aim the light
confirm the engine speed. Check the instrument panel
tachometer reading. Adjust the tachometer in the panel by
using the instrument coarse adjustment to calibrate the
instrument reading to the closest R.P.M. that the photo tach
is showing. Then use the fine calibration adjustment
bring the instrument to the exact reading
CHECK
of
the tachometer onto the reflecting tape to
for
fine tuning.
TACH
INP
AC
VOLTAGE
(New
Installation)
in
all new
of
suitable reflecting tape on the
of
a photoelectric type tachometer.
as
the photo tach.
TERMINAL
to
Tachometer
1.
Check for proper AC voltage between "tach inp."
terminal and (-) terminal.
2.
Check for good ground connection between meter (-)
terminal and alternator.
3. Check that alternator is well grounded to engine block at
alternator pivot bolt.
Tachometer
a. With a hand-held tach on the front
pulley retaining nut or with a strobe-type tach, read the
front crankshaft pulley rpm at idle.
b.
Adjust the tachometer with a small Phillips type screwdriver through the calibration access hole in the rear
the tachometer. Zero the tach
indicated by the strobe
idle and at high speed and adjust the tach as needed).
Sticking
Inaccurate
or
of
the crankshaft
of
and
bring it to the rpm
hand tach. (Verify the rpm at
Engines & Generators
31
Page 38

ENGINE
ADJUSTMENTS
DRIVE
Proper inspection, service and maintenance
is
Drive Belts under MAINTENANCE SCHEDULE).
Drive belts must be properly tensioned. Loose drive belts win
not provide proper alternator charging and will eventually
damage the alternator. Drive belts that are too tight will pun
the alternator out
wear out prematurely. Excessive drive belt tension can also
cause rapid wear
coolant pump's bearing. A slack belt or the presence
the belt can cause belt slipping, resulting
temperatures and tachometer variations.
The drive belt
no less than 3/8 inch (lOmm) and no more than
(12mm)
point between the two pulleys on the longest span
A spare belt or belts should always be carried on board.
Adjusting
1.
2.
3.
4. Tighten the base mounting bolt and the adjusting strap
5. Run the engine for about 5 minutes, then shut down and
BELT
ADJUSTMENT
of
the drive belts
important for the efficient operation
of
alignment and/or cause the alternator to
of
the belt and reduce the service life
is
properly adjusted
as
the belt
A
WARNING:
drive
belt's
Loosen the alternator adjusting strap bolt and the base
mounting bolt.
With the belt loose, inspect for
edges.
Pivot the alternator on the base mounting bolt to the left
or right as required, to loosen
bolt.
recheck the belt tensions.
tension
Belt
is
depressed with the thumb at the mid-
Never
attempt
while
the
Tension
of
your engine (see
in
high operating
if
the belt can be deflected
112
to
check
Dr
adjust
engine
is
in
operation.
wear,
cracks and frayed
or
tighten.
inch
of
of
the
of
oil on
the belt.
the
FUEL
INJECTOR
HOLOOWN
FUEL
In case
injectors checked and overhauled
injection service center.
loss
in injector faults. Since fuel injectors must
clean room environment, it
injector as a spare should a problem occur.
Before removing the old injector, clean the area around the
base
falling down into the injector hole.
out easily and is held in by carbon build-up
the injector side-to-side with the aid
free
The injector seats in the cylinder head on a copper sealing
washer. This washer should be removed with the injector and
replaced with a new washer when the new injector
The fuel injectors should be pressure tested after
hours.
INJECTION
INJECTION
NUTS
INJECTORS
of
severe vibrations and detonation noise, have the
by
an authorized fuel
Poor fuel quality, contaminants and
of
positive fuel pressure to the injection pump can result
be
serviced
is
best to carry at least one extra
of
the injector to help prevent any rust
If
it,
and then lift it out.
STARTING
HOLDDOWN
PRESSURE
NUTS
TORQUE
2630
psi
13.7 ± 1.5
or
debris from
the injector will not lift
or
the like, work
of
the socket wrench
is
750 operating
(18.1
Mpa)
(185
Kg/em')
It-Ib
(1.9 ± 0.2
in
a
to
installed.
Kg-m)
STARTER
The starter and the alternator should be serviced every 1200
operating hours.
Starter
Alternator slip ring cleaning.
Carbon
Refer to your WESTERBEKE SERVICE MANUAL.
AND
ALTERNATOR
commentator cleaning.
brushes
and
the
brush
SERVICE
contact check.
Engines & Generators
32
Page 39

NOTE:
ments
below
ENGINE
WESTERBEKE
be
performed
is
provided
to
ADJUSTMENTS
recommends
by
a competent engine
assist
the
that
mechanic.
the
following engine adjust-
mechanic.
The
information
TESTING
Make certain the oil level (dipstick)
and the air intake filter
must also be
1.
2.
3.
ENGINE
Warm the engine to normal operating teITiperature.
Move the control lever to a position for shutting off the
fuel. (Disconnect the wires
is
used).
Remove all the glow plugs from the engine and install
the compression gauge/adapter combination to the
cylinder on which the compression
COMPRESSION
is
clean. The battery and starter motor
in
good condition.
is
at the correct level
if
a fuel shutdown solenoid
is
to be measured.
MEASURING
COMPRESSION
DIAL
GAUGE
OIL
PRESSURE
The engine's oil pressure, during operation,
by
the oil pressure gauge on the instrument panel. During
normal operation, the oil pressure will range between
85
psi.
NOTE:
A newly started, cold engine can
reading
pressure
depending upon
placed
Low
The specified safe minimum oil pressure
gradual loss
For additional information on low oil pressure readings, see
the ENGINE
Testing
To
install a mechanical oil pressure gauge in it's place. After
warming up the engine, set the engine speed at idle and read
the oil pressure gauge.
OIL
SENDER
up
to
85
psi.
A warmed engine can have
reading
on
Oil
Pressure
as
low
as 40 psi.
the
temperature
the
engine,
of
and the RPM's.
oil pressure usually indicates worn bearings.
These
of
the
TROUBLESHOOTING
Oil
Pressure
test the oil pressure, remove the oil pressure sender, then
PRESSURE
AND
SWITCH
15 -20
psi
TORQUE
at
idle
9 -
speed.
13
n-Ib
have
engine,
chart.
(1.2 -1.8
is
indicated
an
readings
the
is
5 -
10
oil
an
psi. A
m -
40 and
pressure
oil
will
vary
load
Kg).
4.
Close the raw water seacock (thru-hull).
5.
Crank the engine and allow the gauge to reach a
maximum reading, then record that reading.
6.
Repeat this process for each cylinder.
COMPRESSION
ALLOWABLE
MAXIMUM
28.44
psi
NOTE:
Jfthe readings
PRESSURE
LIMIT
PERMISSIBLE
(2.0
Kg/em')
are
441
psi
(31.0
370psi
(26.0
DIFFERENCE
below
the
Kg/em')
Kg/em').
BETWEEN
limit,
CYLINDERS
the
at
200
engine
rpm.
needs
overhaul.
7.
Re-install the glow plugs and reset the fuel shut-off
run position.
S.
Open the
Low
Compression
When low compression
applying a small amount
plug hole. Allow the oil to settle.
Install the pressure gauge and repeat the above test. If the
compression reading rises dramatically, the fault is with the
rings. If the compression valve does not rise, the problem
with the valves.
A slight rise
both the rings and the valves.
raw
water
seacock (thru-hull).
is
found, determine the cause
of
oil
in
the cylinder thru the glow
in
compression would indicate a problem with
to
by
an
the
is
PREHEAT
OIL
PRESSURE
SWITCH
SOLENOID
20A
BREAKER
Engines & Generators
33
Page 40

ENGINE
NOTE:
WESTERBEKE recommends that the following engine adjustments be performed by a competent engine mechanic. The information
below is provided
to
ADJUSTMENTS
assist the mechanic.
VALVE
The valve clearance must
hours. or whenever the valve rocker
Valve adjustment should only be done when engine
Cold engine valve clearance
CLEARANCE
ADJUSTMENT
be
adjusted every 200 operating
is
abnormally noisy.
is
is
0.0157
in
(0.40 mm).
~..J
~D.D1571N
'D.4DMMI
~VE
~
NOTE:
The head bolts have been tightened with the
"Angular Tightening Method". Therefore, it
to
retighten the cylinder head bolts before adjusting the valve
clearances.
ADJUSTMENT
Chart
shows
Cylinder
Valve
arrangement
PROCEDURE
six
cylinder
model
No.
1
I
E I E I E I E I E
~~EARANCE
is
not necessary
2
4
3
5
cold.
CRANKSHAFT
6
I
E
3. After adjusting the valves with piston No. I at
rotate the crankshaft 3600 again aligning the TDC mark
and the pulley mark. This brings piston
TDC, then adjust the remaining valves.
INJECTION
Improper injection timing can cause engine failure. In normal
servicing, this check and adjustment
it
might be necessary in conjunction with other related work
such as
PUllEY
TIMING
an
engine overhaul.
CHECK/ADJUSTMENT
in
unnecessary, however,
.........
'~::7'l'---TDC
No.6
IDC,
or
No.4
TIMING
MARKS
MARK
PULLEY
to
MARK
When
No.1
TOC
in
stroke
No.6
in
the
stroke
No.4
four
No.
arrangement
No.1
TDC
in
stroke
No.4
TOC
in
the
stroke
cylinder
the
com-
cylinder
com-
cylinder
cylinder
the
cylinder
com-
O 0
is
to
the top dead center
piston (four cyl.)is on
model
1
I E
com-
O 0
is
0
No.6
I E I E I
0 0 0
@ @ @ @ @ @
piston (six cyl.)
in
the compression
in
is
in the
IDC
in
No.6
IDC
in the
2 3
4
E
0 0
@ @
@
@
is
at
pression
When
at
TOC
pression
1.
In
order to bring No. I or
piston (four cyl.)
stroke, align the TDC mark and the crank shaft pulley
mark.
2.
Do the adjustment on the circle marked valves
above table where No. I piston
compression stroke. After these steps, do the adjustment
on the double circle marked valves where the
(six cyl.)
compression stroke.
Chart
shows
Cylinder
Valve
I-
When
Z
is
at
=
a::
pression
II.
When
at
pression
No.4
the
the
piston
CHECK
Bring No. 1 piston to the top dead center on the compression
stroke. Turn the crankshaft pulley
engine front) and align the mark on the crankshaft pulley
with the
Remove the access cover at the front
and check the alignment between the pointer
injection pump gear lock plate and the projected pointer
the timing gear case.
is
If they are
the compression stroke.
turning the crankshaft pulley one more tum to repeat the
procedure to make sure that it
PROCEDURE
IDC
mark.
set correctly.
in
alignment, No. 1 cylinder
INJECTION
PUMP
MARKS
If
A and B are
If
it
c1ockwi~e
(viewed at
of
the injection pump
A on the
in
alignment, the timing
is
at the TDC on
is
in
misalignment, recheck by
is
in
alignment.
B on
Engines & Generators
34
Page 41

ENGINE
NOTE:
WESTERBEKE recommends that the following engine adjust-
ments be
below is provided to assist the mechanic.
Check the crankshaft position for the start
1.
Turn
the crankshaft pulley counterclockwise viewed from pulley mark. The timing mark
the
engine front about 30°. pulley mark indicates the degrees before
2.
Remove No. I high pressure injection line.
1'1
~DELIVERY
e
::-~~~~*-----
3. Remove the injection pump No. I delivery valve holder,
delivery valve and spring and reinstall the delivery valve
holder back into the pump.
DELIVERY
39 -44
4. Slowly turn the crankshaft pulley clockwise and at the
same time, feed fuel to the injuection pump by slowly
pumping the feed pump. When the fuel stops to
from
shaft pulley and pumping. This is
injection. .
VALVE
HOLDER
Nm
(4 -4.5
No. I delivery valve holder, stop tut;ning the crank-
TIGHTENING
Kg-m!28.9 -32.5
TORQUE:
ft-Ib)
th~
peiformed
of
fuel injection. 5. Notice which injection timing mark
VALVE
HOLDER
DELIVERY
VALVE
beginning
ADJUSTMENTS
by a competent engine mechanic. The information
of
fuel
injection
The degrees before TDC differs depending on the engine
model. Refer to the specifications
for
the respective model engine.
do the following adjustment.
flow
of
fuel
out
ADJUSTMENT
1.
Align the pulley mark and the specified timing mark.
(Refer
2.
Loosen the four injection pump attachment nuts.
3.
To advance
pump drive shaft away from the engine.
To
retard
pump drive shaft toward the engine.
NOTE:
on
the crankshaft pulley correspond
angle.
4.
Recheck the timing, following procedures I through
5. Tighten the four injection pump attachment nuts.
6.
Again remove No. I delivery valve holder, and reinstall
the delivery valve, spring and the valve holder.
DELIVERY
39 -44
7.
Reinstall the No. I high pressure injection line.
LOOSEN
(80TH
PROCEDURES
to
the injection timing specifications.)
the
timing, pivot the injection pump
the
timing, pivot the injection pump at the
The 1
mm
misalignment between the timing marks
VALVE
HOLDER
Nm
(4 -4.5
FOUR
SIDES)
TIGHTENING
Kg-m!28.9 -32.5
NUTS
is
aligned with the
in
alignment with the
(IDC),
on
the injection timing
If
the timing
to
about r
TORQUE:
ft-Ib)
the start
is
incorrect,
at
in
the
crank
5.
"
PULLEY
MARK
Engines & Generators
35
TIMING
CASE
GEAR
Page 42
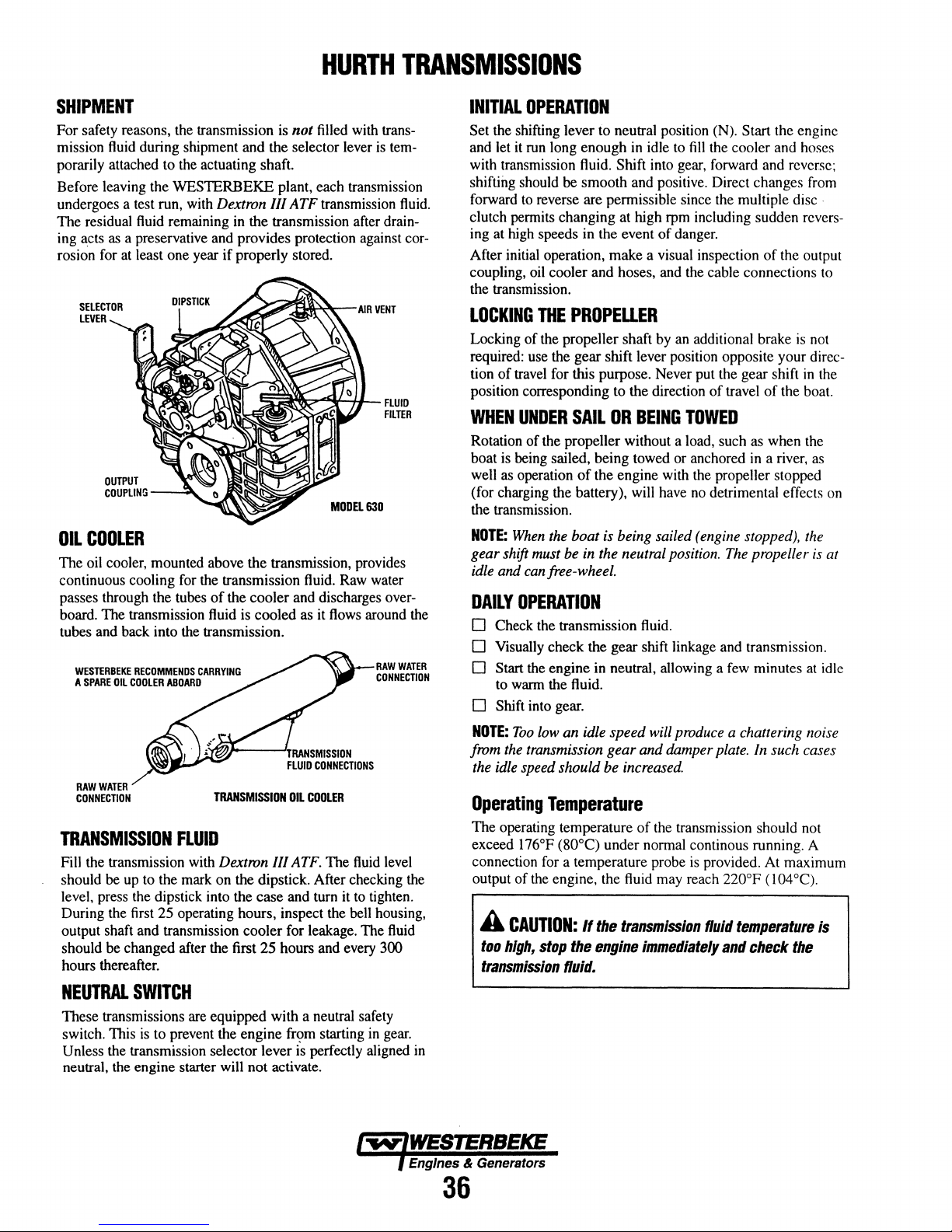
HURTH
TRANSMISSIONS
SHIPMENT
For safety reasons, the transmission is not filled with trans-
mission fluid during shipment and the selector lever
porarily attached to the actuating shaft.
Before leaving the WESTERBEKE plant, each transmission
undergoes a test run, with Dextron III
The residual fluid remaining in the transmission after draining acts as a preservative and provides protection against corrosion for at least one year
DIPSTICK
OUTPUT
COUPLING --.....
OIL
COOLER
The oil cooler, mounted above the transmission, provides
continuous cooling for the transmission fluid. Raw water
passes through the tubes
board. The transmission fluid is cooled as it flows around the
tubes and back into the transmission.
WESTERBEKE
A
SPARE
RECOMMENDS
OIL
COOLER
ABOARD
if
properly stored.
\l:I....e3IN
of
the cooler and discharges over-
CARRYING
ATF
transmission fluid.
~;;iJ#N~k--AIR
~~IJt,
........
is
tem-
VENT
~.JJ--
MODEL
FLUID
FIlTER
630
RAW
WATER
CONNECTION
INITIAL
Set the shifting lever to neutral position (N). Start the engine
and let it run long enough in idle to
with transmission fluid. Shift into gear, forward and reverse;
shifting should be smooth and positive. Direct changes from
forward to reverse are permissible since the mUltiple
clutch permits changing at high rpm including sudden reversing at high speeds in the event
After initial operation, make a visual inspection
coupling, oil cooler and hoses, and the cable connections to
the transmission.
LOCKING
Locking
required: use the gear shift lever position opposite your direction
position corresponding to the direction
WHEN
Rotation
boat
well as operation
(for charging the battery), will have
the transmission.
NOTE:
gear shift must be in the neutral position. The propeller
idle
DAILY
OPERATION
fill
the cooler and hoses
of
danger.
THE
PROPELLER
of
the propeller shaft by an additional brake
of
travel for this purpose. Never put the gear shift
of
travel
UNDER
of
is
being sailed, being towed or anchored in a river,
When the
and
can free-wheel.
SAIL
OR
BEING
the propeller without a load, such as when the
of
the engine with the propeller stopped
boat
is being sailed (engine stopped), the
TOWED
no
detrimental effects on
OPERATION
disc·
of
the output
is
of
the boat.
in
not
the
as
is
at
o Check the transmission fluid.
o Visually check the gear shift linkage and transmission.
o Start the engine in neutral, allowing a few minutes
to warm the fluid.
at
idle
o Shift into gear.
RAW
WATER
CONNECTION
TRANSMISSION
Fill the transmission with Dextron
should be up to the mark on the dipstick. After checking the
level, press the dipstick into the case and turn it to tighten.
During the first 25 operating hours, inspect the bell housing,
output shaft and transmission cooler for leakage. The fluid
should be changed after the first 25 hours and every
hours thereafter.
NEUTRAL
These transmissions are equipped with a neutral safety
switch. This
Unless the transmission selector lever is perfectly aligned
neutral, the engine starter will not activate.
SWITCH
is
to prevent the engine
TRANSMISSION
FLUID
OIL
COOLER
l/l
ATF. The fluid level
fr<,Jrn
starting
300
in
gear.
in
Engines & Generators
NOTE:
Too
Iowan
idle speed will produce a chattering noise
from the transmission gear and damper plate. In such cases
the idle speed should be increased.
Operating
The operating temperature
exceed 176°F
connection for a temperature probe
output
A
too
transmission
Temperature
of
the transmission should not
(80°C) under normal continous running. A
is
provided. At maximum
of
the engine, the fluid may reach 220°F (l04°C).
CAUTION:
high,
stop
If
the
fluid.
the
transmission
engine
immediately
fluid
temperature
and
check
is
the
36
Page 43

HURTH
TRANSMISSIONS
CHANGING
ACTUATING
LEVER
16mm
(8")
THE
SCREW
TRANSMISSION
O-RINGS
FILTER
ELEMENT
FLUID
MODEL
450
Replacing
Pour in new
with the dipstick.
Transmission fluid quantities will vary with the use
ers, length
Reinsert the filter assembly into the housing. Press it
and tighten the Allen screw.
NOTE:
screw
After running the engine, shut down and recheck the fluid
A
engine
hole.
the
Fluid
Dextron
of
HURTH 45 - 2.12 quarts (2.0 Liters)
HURTH 63 - 3.2 quarts (3.0 Liters)
Some
transmissions
on
their filter assemblies.
WARNING:
Is
ronnlng.
This
could
1Il
ATF fluid and check the quantity
hoses and the angle
Approximate Quantities
use
a "T" handle
Neller
pull
out
Hot
nuld
will
cause
sell
ere
bums.
of
the transmission.
the
splash
dipstick
from
in
place
while
the
of
cool-
in
place
of
a
level.
the
dipstick
MAINTENANCE
Transmission maintenance is minimal. Keep the exterior
housing clean, check the fluid level as part
routine, and change the fluid every
Periodically inspect the transmission and the cooler for leaks
and corrosion. Make certain the
checking the fluid level look for signs
(fluid will appear as strawberry cream).
300 operating hours.
air vent is clear and when
of
your regular
of
water contamination
Filter
Element
The Hurth transmission has a filter element located opposite
the dipstick. This filter must be replaced whenever the fluid
changed.
Remove the filter
6mm Allen wrench.
Twist and pull out the filter and remove the element.
the new filter onto the cover and lock it into place
it clockwise. Check the
necessary. Replacement filters can be obtained from your
local WESTERBEKE dealer or
Removing
Push a suction pump hose down through the pipe hole (under
the filter) to the bottom
Remove the oil return line from the cooler and allow the oil
to drain into a container, then reconnect the oil return line.
Wipe down the transmission and properly dispose
fluid.
the
by
loosening the screw on the cover using a
Place
by
O-rings for damage and replace if
ZF
(Hurth
dealer).
Fluid
of
the housing and suck out the fluid.
of
turning
the used
Lay-upJWinterize
Storage requires special care. Follow these procedures:
D Drain water from the transmission oil cooler and replace
is
with a proper mixture
NOTE:
This
operation will normally occur
engine
raw
water cooling system
D Clean up the transmission and touch up unpainted areas
(use heat resistant paint).
D Fill the transmission with
vent internal corrosion (extended storage only, twelve
months
or
more).
D Loosen attaching hardware from the transmission output
flange and propeller shaft coupling flange before
ing the boat from the water. Separate the flanges and
spray with lubricant.
D Inspect the gear shift cable, linkage, and attachments.
Look for corrosion
the conduit, and bending
all moving parts.
NOTE:
If
the
transmission
(twelve
months or
fluid
to
prevent internal
before
putting
of
more),
the
engine back
of
antifreeze coolant.
when
the
is
properly
Dextron
the end fittings, cracks or cuts
of
is
1Il
the actuator rods. Lubricate
to
be
stored for a
it should be topped off
corrosion.
Reduce the fluid
into
service.
winterized.
ATF fluid to pre-
remov-
10llg
with
in
time
level
Engines & Generators
37
Page 44

HURTH
TRANSMISSIONS
CABLE
. The transmission is suitable for a single lever gear shift.
Upon loosening the retaining screw, the actuating lever (see
illustration) can be moved to any position required for the
control elements (cable or rod linkage). Make certain that the
actuating lever does not contact the lever hub: the minimum
distance between the lever and
The control cable
to
tral position
should coincide with the neutral position
transmission.
Shifting
NOTE:
shift lever travel is sufficient
its stop.
CONNECTIONS
hub
should be 0.02in(0.5mm).
or
rod should
the actuating lever when in the neutral position. The neu-
of
the gear shift lever
Positions:
A= Propeller rotation opposite
N= Neutral position
B=
Propeller rotation same as engine rotation.
When shifting to
CABLE
BRACKET
"A"
be
arranged at a right angle
on
the control console
of
the lever on the
of
engine rotation.
or
"B"
positions. make sure the
for
the actuating lever to contact
N
SHAn
WESTERBEKE recommends a flexible connection between
the transmission and the propeller shaft
bly mounted, in order to compensate for angular deflections.
The installation
required, since the propeller thrust will be absorbed
transmission bearing, provided the value specified under
SPECIFICATIONS is not exceeded. However, the output
shaft should be protected from additional loads. Special care
should be taken to prevent torsional vibration. When using a
universal joint shaft, make certain to observe the manufacturer's instructions.
Even with the engine solidly mounted,the use
coupling
bearings caused by hull distortions, especially
boats
coupling and stern gland is less than about
NOTE:
shifting is
or
small a bending radius
mount
two threaded holes located
the gear housing. Refer to the WESTERBEKE parts
COUPLINGS
if
the engine
of
a special propeller thrust bearing
or
"DRIVESAVER" will reduce stress
or
where the distance between the transmission output
800mm.
When installing the transmission, make certain that
not
impeded
rod linkage, by unsuitably positioned guide sheaves, too
a support
by
restricted movability
or
other
restrictions.
for
shift control cable connections, use the
on
the cable bracket mounted
In
is
by
of
a flexible
in
the gearbox
in
wooden
of
the cable
order to
list.
is
flexi-
not
the
011
8
ACTUATING
LEVER
A greater amount
detrimental and is recommended. However,
is shorter, proper clutch engagement might be impeded
which,
in
turn, would mean premature wear, excessive heat
generation and clutch plate failure. This would be indicated
by slow clutch engagement or
CONTROL
TROUBLESHOarING)
NOTE:
Check
season.
A
CAUTION:
the
actuating
shift
lever
this
mechanism
transmlsslDn
of
actuating lever travel is in no way
no
engagement at all (see
CABLES
for
travel
under TRANSMISSION
proper actuating lever travel
The
position
lever
Is
from
Is
In
any
wananty
of
factory-adjusted
neutral
will
position
way
tampered
be'
vDld.
the
mechanism
to
to A and
with.
if
ensure
ACTUATING
LEVER
LEVER
1-
0.021n
r(0.5mm)
the lever travel
at
least each
behind
equal
B.
If
the
HUB
GEAR
SHIFT
LEVER
For additional information contact:
HURTH MARINE
ZF
Industries
Marine
3131
Fort Lauderdale,
Tel.: (954)
Fax: (954) 581-4077
US Headquarters
SW
42nd Street
581-4040
GEAR
FL
33312
TYPICAL
STEERING
STATION
Engines & Generators
38
Page 45

BORG
WARNER
OIL
COOLER
VELVET
DRIVE
SHIFT
The gear shift control mechanism and linkage must position
the actuating lever on the transmission exactly
(F), Neutral
ball located behind the transmission lever must work freely
to center the lever in each position.
the helm must
actuating lever through shift mechanism adjustments. An
improperly adjusted shift mechanism can cause damage
the transmission. The shifting mechanism and transmission
actuating lever should be free
ensure proper operation.
TRANSMISSION
LEVER
POSITION
in
Forward
(N), and Reverse (R) shifting positions. A detent
The
gear shift positions at
be coordinated with those
of
dirt and well lubricated to
of
the Velvet Drive
to
SHIPMENT
For safety reasons, the transmission is not filled with transmission fluid during shipment and the selector lever is temporarily attached to the actuating shaft.
Before leaving the WESTERBEKE plant, each transmission
III
ATF
undergoes a test run, with Dextron
The residual fluid remaining in the transmission after drain-
ing acts as a preservative and provides protection against
corrosion for at least one year
TRANSMISSION
Check the transmission fluid level on the dipstick.
transmission has not been filled, fill with Dextron
continue
tion, keep a lookout for any leakage at the bell housing, output shaft and transmission cooler. This fluid should be
changed after the first 25 hours and approximately every
operating hours thereafter and/or at winter lay-up.
A
to
CAUTION:
and
the
correct
staffing
the
FLUID
use this fluid. During the first 25 hours
Be
ceffaln
slzs
cooler
engine.
if
properly stored.
the
transmission
Is
properly
transmission fluid.
If
the
III and
of
opera-
Is
filled
Installed
before
300
Shifting
Place the gear shift in Neutral before starting the engine.
Shifting from one selector position to another selector position may be made at any time below
order.
speed.
allow the transmission fluid to warm up for a few minutes.
Into
Gear
1000 rpm and
Shifts should be made at the lowest practical engine
Start the engine and set the throttle at idle speed;
in
any
Neutral
Move the gear shift lever to the middle position.
feel the detent. This centers the actuating lever on the transmission. With the control in this position, hydraulic power is
completely interrupted and the output shaft
sion does not tum.
NOTE:
Some transmissions are equipped with a neutral safety
switch.
aligned in neutral, the engine starter will not activate.
Unless the transmission actuating lever is perfectly
You
of
the transmis-
should
Forward
Move the gear shift lever to the forward position.
The
feel the detent.
the forward position. The output shaft and the propeller shaft
move the boat in a forward direction.
actuating lever on the transmission
You
should
is
in
Reverse
Move the gear shift lever to the reverse position.
feel the detent.
the reverse position. The output shaft and the propeller
should move the boat
NOTE:
Moving the transmission actuating lever from Neutral
Position to Forward is always toward the engine. Reverse is
always away from the engine.
the gear shift control in the forward position, shut
engine! This problem
of
the actuating lever by the gear shift lever.
The
actuating lever on the transmission is
in
a reverse direction (astern).
If
boat
moves backwards with
may
be
a result
of
incorrect movement
You
off
should
in
the
Engines & Generators
39
Page 46
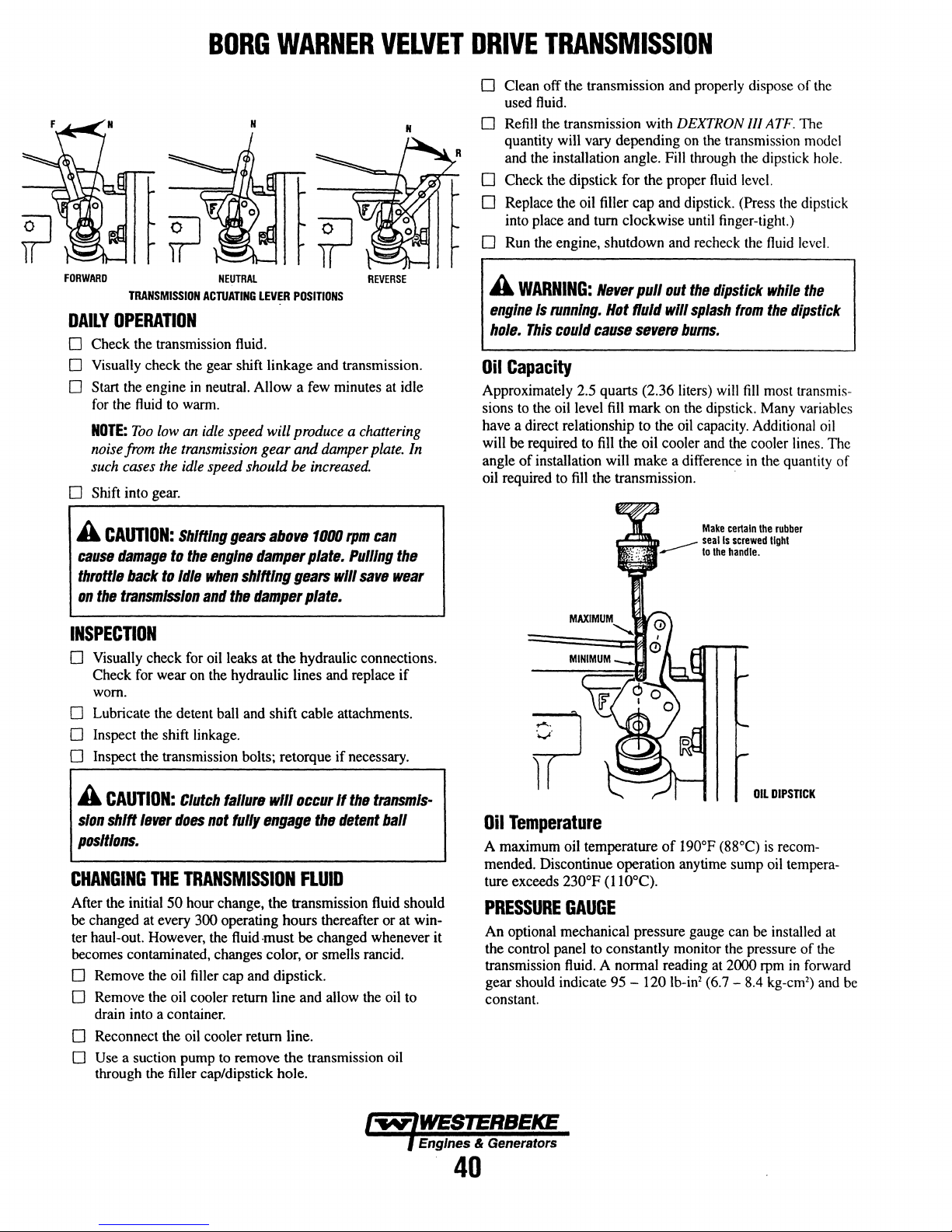
BORG
WARNER
VELVET
DRIVE
TRANSMISSION
FORWARD
DAILY
OPERATION
TRANSMISSION
NEUTRAL
AC11JATING
LEVER
REVERSE
POSITIONS
o Check the transmission fluid.
o Visually check the gear shift linkage and transmission.
o Start the engine
for the fluid to warm.
NOTE:
Too
noise
from
such
cases
in
Iowan
idle
the
transmission
the
idle
neutral. Allow a few minutes at idle
speed will
speed
should
produce a chattering
gear and
damper
be
increased.
plate.
o Shift into gear.
A
CAUTION:
cause
damage
throttle
on
back
the
transmission
Shifting
to
to
Idle
the
and
gears
engine
when
the
above
damper
shifting
damper
1000
plate.
gears
plate.
rpm
Pulling
will
can
save
the
wear
In
o Clean off the transmission and properly dispose
used fluid.
o Refill the transmission with
quantity will vary depending on the transmission model
and the installation angle. Fill through the dipstick hole.
DEXTRON
/II
of
ATF. The
the
D Check the dipstick for the proper fluid level.
D Replace the oil filler
into place and tum clockwise until finger-tight.)
cap
and dipstick. (Press the dipstick
D Run the engine, shutdown and recheck the fluid level.
A
WARNING:
engine
Is
hole.
This
Oil
Capacity
Approximately 2.5 quarts (2.36 liters)
sions to the oil level fill
have a direct relationship to the oil capacity. Additional oil
will
be required to fill the oil cooler and the cooler lines. The
of
angle
oil required to fill the transmission. .
installation will make a difference
Never
running.
could
cause
Hot
pull
out
the
dipstick
nuld will
severs
mark
splash
bums.
will
on the dipstick. Many variables
Make
____
seal
to
the
from
certain
Is
screwed
handle.
fill
in
while
the
most transmis-
the quantity
the
tight
the
dipstick
rubber
of
INSPECTION
o Visually check for oil leaks
Check for wear on the hydraulic lines and replace
worn.
at
the hydraulic connections.
if
o Lubricate the detent ball and shift cable attachments.
o Inspect the shift linkage.
o Inspect the transmission bolts; retorque
A
CAUTION:
sion
shift
plISltlons.
CHANGING
After the initial
be
changed at every 300 operating hours thereafter or at win-
ter haul-out. However, the fluid
becomes contaminated, changes color,
Clutch
fallurs will
lellSr
does
not
fully
THE
TRANSMISSION
50
hour change, the transmission fluid should
engage
must
if
necessary.
occur
If
the
transmis-
the
detent
ball
FLUID
be changed whenever it
or
smells rancid.
o Remove the oil filler cap and dipstick.
o Remove the oil cooler return line and allow the oil to
drain into a container.
o Reconnect the oil cooler return line.
D Use a suction pump to remove the transmission oil
through the filler cap/dipstick hole.
OILDIPsnCK
Oil
Temperature
A maximum oil temperature
mended. Discontinue operation anytime sump oil tempera-
ture exceeds 2300P (1lO
PRESSURE
An
optional mechanical pressure gauge can be installed
the control panel to constantly monitor the pressure
transmission fluid. A normal reading at
gear should indicate 95 -
constant.
GAUGE
of
1900P (88°C) is recom-
D
C).
2000 rpm
120 Ib-in2 (6.7 - 8.4 kg-cm
of
in
forward
2
)
at
the
and be
EngInes & Generators
40
Page 47

BORG
WARNER
VELVET
DRIVE
TRANSMISSION
MAINTENANCE
Transmission maintenance is minimal. Keep the exterior
of
housing clean, check the fluid level as part
routine, and change the fluid every 300 operating hours.
Periodically inspect the transmission and the cooler for leaks
and corrosion. Make certain the air vent is clear and when
checking the fluid level look for signs
(fluid will appear as strawberry cream).
your regular
of
water contamination
Lay-up/Winterize
Storage requires special care. Follow these procedures:
o Drain the water from the transmission oil cooler and
replace it with a proper mixture
NOTE:
This
operation will usually occur
raw
water cooling system
of
antifreeze coolant.
when
is
properly winterized.
the
engine
o Clean up the transmission and touch-up unpainted areas
(use heat resistant paint).
o Fill the transmission with Dextron III ATF fluid to pre-
vent internal corrosion.
o Loosen attaching hardware from the transmission
output flange and propeller shaft coupling flange before
removing the boat from the water. Separate the flanges
and spray with lubricant.
o Inspect the gear shift cable, linkage, and attachments.
Look for corrosion
the conduit, and bending
all moving parts.
of
the end fittings, cracks
of
the actuator rods. Lubricate
or
cuts in
WARRANTY
Service manuals are available from your
dealer.
For assistance, contact:
BORG
200 Theodory Rice Blvd.
New Bedford,
Tel.: (508) 979-4881
BORG
placed
ation
or
Therefore torque loads and directional changes should be
made at low engine speeds.
caused by a shock load, any warranty claim
A
CAUTION:
occur
resulting
BORG
related
If
any problems occur with the transmission, see
TRANSMISSION
NOTES
WARNER
MA
WARNER
on
fully reversing
at
WARNER
torsional
is aware
its gears as the result
System-related
low
engine
In
damage
Is
speeds
to
not
vibration
TROUBLESHOOTING
BORG
WARNER
02745
of
the shock loads that can
of
mechanical propeller oper-
of
the propeller blades while shiftIng.
If
it
is
found that a failure was
wiJI
be denied.
noises
or
vibrations
which
can
cause
gear
the
engine
and/or
transmission.
responsible
of
this
for
total
type.
system-
in
this manual.
be
can
rattle
NOTE:
(twelve
fluid
to
before
If
the
transmission
months or
prevent internal corrosion. Reduce the fluid level
putting
the
is
to
be stored for a long
more),
it should
engine back into
be
topped
service.
off
time
with
Engines & Generators
41
Page 48
TRANSMISSION
TROUBLESHOOTING
CONTROL
The majority
CABLES
of
transmission difficulties arise as a result
of
improper clutch adjustments (manual transmissions) or problems with control cables (hydraulic transmissions) rather than
from problems with the transmission itself.
HURTH clutches,
in
particular, are very sensitive to improper
cable adjustments.
If
you experience operating problems with the transmission,
shut the engine down. First check the transmission-oil level,
then have a helper move the cockpit shift lever through the
full range - from neutral to full forward, back to neutral,
into full reverse, and back to neutral - while you observe
the actuating lever on the transmission.
to operate, break the cable loose
again.
If
it is still stiff, check the cable for kinks
If
the remote
at
the transmission and try
or
exces-
is
stiff
sively tight bends, and check any linkage for binding. A new
cable and perhaps a new linkage mechanism may be needed.
While the cable is loose, shift the transmission in and out
gear using the lever on the side
of
the transmission to make
of
sure there's no binding inside the case.
If the transmission passes these tests, crank the engine and
have a helper put it in forward and reverse while you observe
the propeller shaft;
needs professional attention.
thrust, check to see you still have a propeller on the end
the shaft or,
it
isn't
stuck in the
if
the shaft
if
you have a folding
"no
pitch" position.
isn't
turning, the transmission
If
it does tum but there's no
or
feathering propeller, that
of
OIL
COOLERS
The continued flow
time, erode the inside
occur. These internal cooler leaks will cause one
of
raw water through the cooler will,
of
the cooler causing cross leaks to
of
in
the fol-
lowing two problems:
1.
Transmission fluid will leak into the flow
of
raw water
and be discharged overboard through the engine exhaust.
A loss
of
transmission fluid will cause the transmission to
fail.
2. The raw water will leak into the transmission fluid causan
increase in transmission fluid. This contaminated
ing
fluid will appear as strawberry cream.
The transmission
will eventually fail.
Either case requires an immediate response:
1. Install a new oil cooler.
2. Refill the transmission with
If
water has contaminated the fluid, the transmission fluid
DEXTRON
III
ATF.
needs to be cleaned out and replaced with fresh fluid. It will
of
take several fluid changes to get rid
the contamination.
Check your dipstick each time until it appears as pure transmission fluid. Change the transmission filter and clean out
the fluid lines that connect to the cooler.
If
the transmission fails to shift properly, it will most likely
need the attention
of
a qualified transmission service facility.
A transmission cooler may last ten years or more but, in
some circumstances, depending on operating hours, tropical
waters, maintenance, etc. it might only last half that time.
WESTERBEKE recommends having a spare cooler aboard.
Transmission
Shifting
pressure
Transmission
Problem
gears
cannot
too
low.
noise
becomes
be
shifted.
louder.
Probable
1.
Shifting
Shifting
2.
unattached.
Loss
of
3.
4.
Water
Improper
1.
Filter
is
2.
3.
Water
Transmission
4.
Air
vent
5.
Fluid
1.
so
that
Damage
2.
to
wear
ment
Beginning
3.
mission
without
transmiSSion,
lever
is
loose.
cable
is
transmission
in
transmission
fluid.
dirty
(if
applicable).
in
transmission
fluid
is
clogged.
level
too
low,
pump
sucks
starting
or
fatigue,
between
engine.
damage
due
to
torsional
fluid,
overload,
or
Cause
broken,
bent
fluid.
fluid.
fluid.
too
low.
in
air.
on
flexible
possibly
and
of
bearings
wrong
excessive
or
coupling
due
to
misalign-
transmission.
in
trans-
vibrations,
alignment
engine
running
output.
due
of
TIghten
1.
Check
2.
3.
Check
Tighten
Oil
cooler
4.
Replace
compartment,
item
2.
1.
Replace
Replace
2.
Replace
3.
Add
fluid.
4.
Remove
5.
Top
up
1.
Replace
2.
and
transmission.
Transmission
3.
VerlflcatlonJRemedy
damping
bolt
on
shifting
the
cable,
reattach
or
replace.
for
leaks
at
case
leak -see
cooler
remedy
DEXTRON
filter.
oil
cooler -see
painVdirt
fluid
to
flexible
coupling.
needs
transmission
bolts.
Check
OIL
COOLER.
(see
OIL
COOLER).
cause.
1/1
ATF.
OIL
from
vent.
marking
on
Check
professional
gear
oil
with
with
lever.
seal
and
all
oil
hoses
High
Shifting
pressure
COOLER.
dipstick.
alignment
attention.
output
for
water
between
shaft.
leaks.
in
engine
too
low,
see
engine
(continued)
Engines & Generators
42
Page 49

TRANSMISSION
TROUBLESHOOTING
Chattering
mainly
at
low
Transmission
fails
to
propel
NOTE:
If
you
Problem
transmission
engine
shifts
the
speed.
into
boat.
noise,
gear,
but
suspect a major problem
The
1.
vibrations
a
1.
Output
Propeller
2.
Output
Output
3.
propeller
in
your
Probable
engine
or
in
"chattering"
coupling
shaft
coupling
coupling
shaft
transmission,
immediately contact your WESTERBEKE dealer or
authorized marine transmission facility.
Cause
propeller
the
drive
noise
Is
not
is
not
is
tuming.
and
are
turning.
an
generates
unit
which
in
the
transmission.
tuming.
turning.
torsional
produces
Mount a flexible
1.
between
a
higher
1.
Transmission
The
coupling
2.
on
the
propeller
pins
and
Inspect
3.
A
folding
Variable
VerlficatlonJRemedy
coupling
with
the
engine
stiffness
needs
bolts
coupling
the
propeller;
propeller
pitch
propeller
and
factor
professional
are
shaft.
bolts
may
another
transmission; a coupling
might
be
sheared
or
Tighten
or
as
necessary.
it
may
be
missing
be
jammed.
may
be
in
stiffness
sufficient.
attention.
the
coupling
replace
set
or
"no
pitch"
factor
with
is
slipping
screws,
damaged.
position.
keys,
Engines
43
& Generators
Page 50

LAY-UP & RECOMMISSIONING
GENERAL
Many owners rely on their boatyards to prepare their craft,
including engines and generators, for lay-up during the offseason or for long periods of inactivity.
accomplish lay-up preparation themselves.
The procedures which follow will allow you to perform your
own lay-up and recommissioning, or you may use them as a
check list if others do the procedures.
These procedures should afford your engine protection
during a lay-up and also help familiarize you with the
of
maintenance needs
If
you have any questions regarding lay-up procedures, call
your local servicing dealer; he will be more than willing to
provide assistance.
Propeller
The transmission and propeller half couplings should always
be
opened up and the bolts removed when the boat
out
of
storage
severe strain on the propeller shaft or coupling or both, while
the boat
shaft has actually been bent
apply
not
in
period of time.
Fresh
A 50-50 solution
recommended for use in the coolant system at all times.
This solution may require a higher concentration
antifreeze, depending on the area's winter climate. Check the
solution
Should more antifreeze
amount from the engine block and add a more concentrated
mixture.
and mixture
cooling system. Now recheck the antifreeze solution's strength.
Shaft
the water or moved from land to water, and during
in
the cradle. The flexibility
is
taken out or put
to
small boats that are hauled out
use, unless they have been dry for a considerable
Water
to
make sure the antifreeze protection
Operate the engine
of
Lubrication
With
the
engine warm, drain all the engine oil from the oil
sump. Remove and replace the oil filter and fill the sump
with
new
oil. Use the correct grade
ENGINE LUBRICATING OIL pages
oil
changing procedure. Run the engine and check for proper
oil
pressure and make sure there are no leaks.
A
CAUTION:
oil
in
the
sump
combustion
chemicals
internal
which
parts.
your engine.
Coupling
Cooling
of
antifreeze and distilled water
the antifreeze concentration throughout the
[Propulsion
in
the water. In some cases, the
by
these strains. This does not
Circuit
be
needed, drain
to
ensure a complete circulation
System
Do
not
leave
over
the
lay-up
deposits
combine
can
reduce
Others prefer to
of
the boat often puts a
of
the water when
an
appropriate
of
oil. Refer to the
in
this manual for the
the
engine's
period.
to
the
Engine
produce
life
of
your
Engine]
is
hauled
is
of
is
adequate.
old
engine
oil
and
harmful
engine's
Fuel
System
Top off your fuel tanks with unleaded gasoline
of
higher. A fuel conditioner ·such as STABIL gasoline
stabilizer should be added. Change the element
gasoline/water separator and clean the metal bowl.
Re-install and make certain there are no leaks. Clean
up any spilled fuel.
Fuel
System
Top off your fuel tanks with
such as
control algae and condition the fuel. Care should
that the additives used are compatible with the primary
filter/water separator used
in
has one, and clean the separator sediment bowl.
Change the fuel filter elements on the engine and bleed the
fuel system, as needed. Start the engine and allow
for 5
system. Check for any leaks that may have been created
the fuel system during this servicing, correcting them as
needed.
allow movement
equipment on the engine.
Raw
Close the through-hull seacock. Remove the raw water intake
hose from the seacock.
gallon bucket
check the zinc anode found
the engine and clean or replace it
any zinc debris from inside the heat exchanger where the
zinc anode
Start the engine and allow the raw water pump
fresh water through the system. When the bucket
stop the engine and refill the bucket with
solution slightly stronger than needed for winter freeze
protection
Start the engine and allow all
through the raw water system.
the engine. This antifreeze mixture should protect the raw
water circuit from freezing during the winter lay-up,
as providing corrosion protection.
Remove the impeller from your raw water pump (some
antifreeze mixture will accompany it, so catch it
Examine the impeller. Acquire a replacement, if needed, and
BlOB
your primary fuel filter/water separator, if the
- 10 minutes to make sure no air
Water
a cover gasket. Do not replace the impeller (into the pump)
until recommissioning, but replace the cover and gasket.
Cylinder
With the engine running, remove the flame arrester and spray
fogging oil into the open air intake. The fogging
out the engine as
plugs for winter protection.
[Gasoline]
[Diesel]
No.2
diesel fuel. Fuel additiyes
OR and STABIL should be added
in
the system. Change the element
Operating the engine for 5 -
of
the treated fuel through the injection
Cooling
of
is
located. Clean the raw water strainer.
in
your area.
Lubrication
Circuit
Place the end
clean fresh water. Before starting the engine,
in
[Gasoline]
it
coats the valves, cylinders and spark
10
of
the primary heat exchanger on
as
required, and also clean
of
this mixture
Once the bucket
of
89
octane
in
your
at
this time
be
taken
fuel
system
it
to run
is
left
in
the fuel
minutes will help
this hose into a
to
draw the
is
empty,
an
antifreeze
to
be
drawn
is
empty, stop
as
in
a bucket).
oil
will stall
to
fuel
in
five
well
Engines & Generators
44
Page 51

LAY-UP
&
RECOMMISSIONING
Starter
Lubrication and cleaning
able,
sure the battery connections are
remove the starter. Take care in properly replacing any elec-
trical connections removed from the starter.
Cylinder
If
WESTERBEKE recommends removing
fuel injectors for access to the cylinders. Squirt light
lubricating oil into the cylinders to prevent the piston rings
from sticking to the cylinder walls. Rotate the engine by hand
two revolutions then replace the glow plugs
Make sure you have a replacement
sealing washer for the injector and fuel line return.
NOTE:
months
complete turns every additional 4 months to allow the injection pump components to move. This will help prevent their
sticking during extended storage periods.
Intake
Place a clean cloth, lightly soaked in lubricating oil.
opening
shove the cloth out
recommissioning, and an attempt is
you may need the assistance
note to remove the cloth prior to start-up.
exhaust port
Intake
Clean the filter screen in the flame arrester, and place a clean
cloth lightly soaked in lube oil around the flame arrester to
block any opening. Also place an oil-soaked cloth
through-hull exhaust port. Make a note to remove cloths prior
to
Transmission
Check
engine
sion
its nonnaI
and touch up unpainted areas.
flange with an anticorrosion coating,
TRANSMISSION SECTION in this manual for additional
information.
Motor
of
the starter drive pinion
if
access to the starter permits its easy removal. Make
shut
off
before attempting to
Lubrication
you anticipate a long lay-up period (12 months or more)
[Diesel]
the
if
removing the injector
If engine storage is going to be a lengthy one, 12
or
beyond, it is wise to rotate the engine by hand two
Manifold
of
the intake manifold to block the opening.
Manifold
start-up!
or
change fluid in the transmission as required.
is
to be layed up 12 months
to
the very top to prevent corrosion.
at
and
Thru-Hull
of
sight.
(If
can
be blocked in the
[Gasoline]
[Propulsion
recommissioning.
Exhaust[Diesel]
it is not visible at
made
to start the engine,
of
a servicing dealer.) Make a
The
same
manner.
Engine]
or
more, fill the transmis-
Lower
Wipe
off
grime and grease
Protect coupling and output
Refer
is
advis-
glow plugs or
or
injectors.
in
the
Do
through-hull
in
the
If
the
fluid
to the
not
the
to
SPARE
Lay-up time provides a good opportunity to inspect your
WESTERBEKE
belts
spares kit and order items not on hand, or replace those items
used during the lay-up, such as filters and zinc anodes. Refer
to the
PARTS
engine to see
or
coolant hoses need replacement. Check your basic
SPARE PARTS section
if
external items such as drive
of
this manual.
RECOMMISSIONING
The
recommissioning
seasonal lay-up generally follows the same procedures as
those described in the
section regarding preparation for starting and normal starts.
However, some
counteracted before starting the engine.
1. Remove any rags that were placed in the exhaust. intake
manifold,
2. Remove the raw water
the old gasket. Install the raw water pump impeller
removed during lay-up (or a replacement, if required).
Install the raw water
3. Reinstall the batteries that were removed during the lay-
up, and reconnect the battery cables, making sure the
terminals are clean and that the connections are tight.
Check to make sure that the batteries are fully charged.
4. Remove the spark plugs, wipe clean, re-gap, and install
to proper tightness.
5. Check the condition
circuit and clean
that it is not necessary to flush the antifreeze/fresh water
solution from the raw water coolant system. When the
engine
a short period
up the heat exchanger ends and clear out any accumulated debris.
6. Check the transmission fluid,
during the lay-up, lower the level
or
is
put into operation, the system will self-flush in
[Propulsion
7. Make certain all electrical connections and switches are
in the correct position and there are no-loads on the
generator at start up.
8. Start the engine
described in the
section
of
of
your
WESTERBEKE
PREPARATIONS FOR STARTING
of
the lay-up procedures will need to be
flame arrester.
pump
cover and gasket and discard
pump
cover with a new cover gasket.
[Gasoline]
of
the zinc anode in the raw water
or
replace the anode as needed. Note
of
time with
no
adverse affects. Also open
if
it had been topped off
of
the fluid to normal.
Engine]
[Generator]
in
accordance with the procedures
PREPARATIONS FOR STARTING
this manual.
engine after a
Batteries
If
batteries are to be left on board during the lay-up period,
make sure they are fully charged, and will remain that way,
to
prevent them from freezing.
the batteries will not remain fully charged,
be
subjected to severe environmental conditions, remove
the batteries and store them in a warmer, more compatible
environment.
If
there exists any doubt that
or
that they will
Engines
45
& Generators
Page 52

METRIC
CONVERSIONS
INCHES TO MILLIMETERS
Inches
1 25.40
2 50.80 20 508.00 2 0.0787 20
3 76.20 25 635.00 3
4 101.60 30 762.00 4 0.1575 30 1.1811
5
10
10
mm
127.00 35 889.00 5 0.1969 35
254.00 40
MILLIMETERS
Inches
15
= 1
CENTIMETER,
mm
381.00 1 0.0394
1016.00
100
CENTIMETERS
INCHES TO METERS
Inches
1 0.0254
2
3
4
5
6
TO
CONVERT
Meters
0.0508 8
0.0762
0.1016
0.1270
0.1524
METERS
Inches
10
11
12
TO
CENTIMETERS,
Meters
7 0.1778
0.2032 0.2 7.874 0.8 31.496
9 0.2286 0.3 11.811 0.9 35.433
0.2540 0.4 15.748 1.0 39.370
0.2794 0.5 19.685 1.1 43.307
0.3048 0.6
MOVE
YARDS TO METERS
Yards
1 0.91440 6
2
3
4 3.65760
5
Meters
1.82880 7 6.40080 2 2.18723 7 7.65529
2.74320 8
4.57200
MOVE
DECIMAL
Yards
9 8.22960 4 4.37445 9 9.84252
10
POINT
FOR
Meters
5.48640
7.31520
9.14400 5 5.46807
HIGHER
VALUES -e.g.
MILLIMETERS TO INCHES
mm
10
= 1
Meters
0.1
DECIMAL
Meters
1 1.09361 6
3
Inches
0.1181 25 0.9843
0.3937 40 1.5748
METER = 39.37
METERS
Inches
POINT
METERS
3.28084
6,000
METERS = 6,561.68
TO INCHES
3.937 0.7 27.559
23.622 1.2 47.244
TWO
PLACES
TO YARDS
Yards
mm
15
INCHES
Meters
TO
Meters
8
10
(3.3
FEET)
THE
RIGHT
YARDS
10.93614
Inches
0.5906
0.7874
1.3780
Inches
Yards
6.56168
8.74891
POUNDS TO KILOGRAMS KILOGRAMS TO POUNDS
Ib
1 0.454
2
3 1.361 8
4 1.814
5 2.268
kg
0.907
GALLONS
Gallons
1 3.79
2 7.57
3 11.36
4 15.14
5 18.93
Liters
PINTS TO LITERS
Pints
1
2
3 1.42 8
4 1.89 9
5
Liters
0.47 6
0.95
2.37
32 40 50
I I
I I
0 5
I
I
10 15
Ib
6 2.722 1 2.205
7 3.175
9
10 4.536
TO
LITERS LITERS
Gallons
10
20 75.71 2 0.53 90 23.77
30 113.57 5 1.32 120 31.32
40 151.42
50 189.28 20
kg kg
3.629
4.082
Liters
37.86
Ib
2
3 6.614 8 17.637
4 8.818 9 19.842
5
4.409 7 15.432
11.023
TO
Liters
1
10
Gallons
0.26 60 15.66
2.64 150 39.62
5.28 180 47.54
kg
6 13.228
10
GALLONS
Liters
Gallons
LITERS TO PINTS
Pints
7 3.31 2 4.23 7 14.79
10
Liters Liters
2.84
3.79 3 6.34 8 16.91
4.26 4 8.45 9
4.73
1
5
Pints
2.11 6 12.68
10.57
Liters
10
TEMPERATURE
60
70
75
85
95 105
140
I I I I I I I I
I I I I I
I
175 212
I I
I
I
20 25 30 35 40 60 80 100 °C
Ib
22.046
Pints
19.02
21.13
OF
Engines & Generators
46
Page 53

STANDARD
AND
LENGTH-DISTANCE
Inches
(in) x 25.4 = Millimeters
Feet
(ft) x .305 = Meters
Miles x 1.609 = Kilometers
METRIC
(mm) x .0394 = Inches
(m) x 3.281 = Feet
(km) x .0621 = Miles
CONVERSION
DATA
VOLUME
Cubic
Inches
(inJ) x 16.387 = Cubic
Imperial
Imperial
Imperial
Imperial
Imperial
Fluid
US
US
US
Pints
(IMP
Quarts
Gallons
Quarts
Gallons
Ounces x 29.573 = Milliliters x .034 = Ounces
Pints
(US
pt) x .473 = Liters(L) x 2.113 = Pints
Quarts
(US
Gallons
(US
MASS-WEIGHT
Ounces
Pounds
(oz) x 28.35 = Grams
(Ib) x .454 = Kilograms
PRESSURE
Pounds
Inches
Inches
Inches
Inches
Inches
Per
of
Mercury
of
Mercury
of
Water
of
Water
of
Water
Sq
Centimeters x .061
pt) x .568 = Liters
(IMP
qt) x 1.137 = Liters
(IMP
gal) x 4.546 = Liters
(IMP
qt) x 1.201 = US
(IMP
gal) x 1.201 = US
qt) x .946 = Liters
gal) x 3.785 = Liters
(g) x .035 = Ounces
In
(psi) x 6.895 = Kilopascals
(Hg) x .4912 = psi x 2.036 = Hg
(Hg) x 3.377 = Kilopascals
(H20) x .07355 = Inches
(H20) x .03613 = psi x 27.684 = H20
(H20) x .248 = Kilopascals
(L) x 1.76 = IMP
(L)
x.88 = IMP
(L) x .22 = IMP
Quarts
(US
Gallons
(L) x 1.057 = Quarts
(L) x .264 = Gallons
(kg) x 2.205 = Pounds
(US
(kPa) x .145 = psi
(kPa) x .2961 = Hg
of
Mercury x 13.783 = H20
(kPa) x 4.026 = H20
3
=in
pt
qt
gal
qt) x .833 = IMP
gal) x .833 = IMP
qt
gal
TORQUE
Pounds-Force
Pounds-Force
Inches
Feet
VELOCITY
Miles
Per
Hour
(MPH) x 1.609 = Kilometers
POWER
Horsepower
FUEL
CONSUMPTION
Miles
Kilometers
Miles
Kilometers
(Hp) x .745 = Kilowatts
Per
Hour
IMP
Per
Liter
Per
Gallons
Per
Liter
TEMPERATURE
Degree
Degree
Fahrenheit
Celsius
(OC) = (OF -32) x .56
(in-Ib) x .113 = Newton
(ft-Ib) x 1.356 = Newton
(Kw) x 1.34 = MPH
(MPG) x .354 = Kilometers
(Km/L) x 2.352 = IMP
US
(MPG) x .425 = Kilometers
(Km/L) x 2.352 = US
(OF) = (OC X 1.8) + 32
Engines
& Generators
Meters
Meters
Per
MPG
MPG
(Nm) x 8.85
(Nm) x .738
Hour
(KPH) x .621 = MPH
Per
Liter
(Km/L)
Per
Liter
(Km/L)
=in-Ib
= ft-Ib
47
Page 54
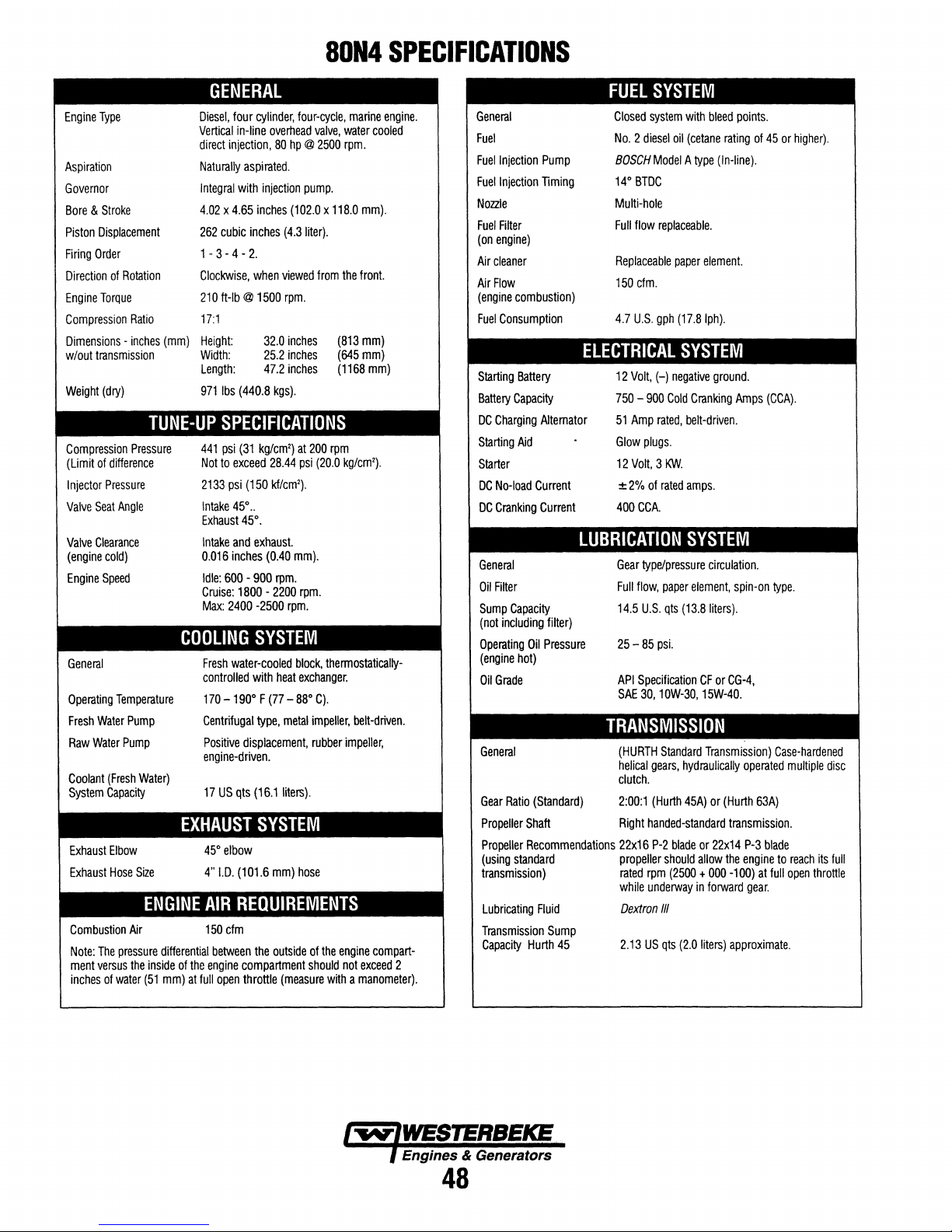
80N4
SPECIFICATIONS
Engine
Type
Aspiration
Govemor
Bore & Stroke
Piston
Displacement
Firing
Order
Direction
of
Rotation
Engine
Torque
Compression
Dimensions -inches
w/out
Weight
Ratio
transmission
(dry)
TUNE-UP
Compression
(Limit
Injector
Valve
Valve
(engine
Engine
General
Operating
Fresh
Raw
Coolant
System
Exhaust
Exhaust
Pressure
of
difference
Pressure
Seat
Angle
Clearance
cold)
Speed
Temperature
Water
Pump
Water
Pump
(Fresh
Water)
Capacity
Elbow
Hose
Size
ENGINE
Combustion
Note:
ment
inches
The
pressure
versus
of
water
Air
the
inside
(51
GENERAL
Diesel,
Vertical
direct
Naturally
Integral
4.02 x 4.65
262
1-3-4-2.
Clockwise,
210
17:1
(mm)
Height
Width:
Length:
971
441
Not
2133
Intake
Exhaust
Intake
0.Q16
Idle:
Cruise:
Max:
COOLING
Fresh
controlled
170
Centrifugal
Positive
engine-driven.
17
US
EXHAUST
45°
4"
I.D.
AIR
150
differential
mm)
of
the
at
full
between
engine
open
four
cylinder,
in-line
overhead
injection,
aspirated.
with
injection
inches
cubic
inches
when
ft-Ib @ 1500
32.0
25.2
47.2
Ibs
(440.8
kgs).
four-cycle,
80
hp @ 2500
(102.0 x 118.0
(4.3
viewed
rpm.
inches
inches
inches
valve,
pump.
liter).
from
marine
water
rpm.
mm).
the
front.
(813
mm)
(645mm)
(1168
SPECIFICATIONS
psi
(31
kg/cm')
at
200
to
exceed
psi
(150
45°
..
45°.
and
exhaust.
inches
600 -900
1800 -2200
2400
-2500
28.44
kf/cm').
(0.40
rpm.
psi
mm).
rpm.
rpm.
rpm
(20.0
kg/cm').
SYSTEM
water-cooled
-190° F
displacement,
Qts
with
(77 -88°
type,
(16.1
block.
heat
exchanger.
metal
liters).
thermostatically-
C).
impeller,
belt-driven.
rubber
impeller,
SYSTEM
elbow
(101.6
mm)
hose
REQUIREMENTS
cfm
the
outside
of
the
compartment
throttle
(measure
engine
should
not
exceed
with a manometer).
engine.
cooled
mm)
compart-
2
General
Fuel
Fuel
Injection
Fuel
Injection
Nozzle
Fuel
Filter
(on
engine)
Air
cleaner
AirFlow
(engine
combustion)
Fuel
Consumption
Starting
Battery
Battery
Capacity
DC
Charging
Starting
Aid
Starter
DC
No-load
DC
Cranking
General
Oil
Filter
Sump
Capacity
(not
including
Operating
(engine
Oil
General
Oil
hot)
Grade
Gear
Ratio
(Standard)
Propeller
Shaft
Propeller
Recommendations
(using
standard
transmission)
Lubricating
Transmission
Capacity
Hurth
FUEL
Pump
Timing
ELECTRICAL
A1temator
Current
Current
LUBRICATION
filter)
Pressu
re
TRANSMISSION
Fluid
Sump
45
SYSTEM
Closed
system
No.2
diesel
BOSCH
Model A type
WBTDC
Multi-hole
Full
flow
replaceable.
Replaceable
150
efm.
4.7
U.S.
gph
12
Volt,
(-)
negative
750 -900
51
Glow
12
±
400
Gear
Full
14.5
25-85
API
SAE
(HURTH
helical
clutch.
2:00:1
Right
22x16
propeller
rated
while
Cold
Amp
rated,
plugs.
Volt, 3 KW.
2%
of
rated
CCA.
type/pressure
flow,
paper
U.S.
QIs
psi.
Specification
30,
10W-30,
Standard
gears,
(Hurth
handed-standard
P-2
blade
should
rpm
(2500 + 000
underway
Dextron
III
2.13
US
qts
with
bleed
oil
(cetane
rating
(In-line).
paper
element.
(17.8
Iph).
SYSTEM
ground.
Cranking
belt-driven.
amps.
SYSTEM
circulation.
element,
(13.8
liters).
CF
or
CG-4,
15W-40.
Transmission)
hydraulically
45A)
or
(Hurth
transmission.
or
22x14
allow
the
-100)
in
forward
(2.0
liters)
approximate.
points.
of
Amps
spin-on
operated
63A)
P-3
engine
at
gear.
45
(CCA).
blade
or
higher).
type.
Case-hardened
multiple
disc
to
reach
its
open
full
throttle
full
Engines & Generators
48
Page 55

110T 4 SPECIFICATIONS
Engine
Type
Aspiration
Govemor
Bore & Stroke
Piston
Displacement
Firing
Order
Direction
of
Rotation
Engine
Torque
(max.)
Compression
Dimensions -inches
w/out
Weight
Ratio
transmission
(dry)
TUNE-UP
Compression
(Limit
Injector
Valve
Valve
(engine
Engine
General
Operating
Fresh
Raw
Coolant
System
Exhaust
Exhaust
Pressure
of
difference
Pressure
Seat
Angle
Clearance
cold)
Speed
Temperature
Water
Pump
Water
Pump
(Fresh
Capacity
Elbow'
Hose
Water)
Size
GENERAL
Diesel,
marine
water
cooled
rpm.
Turbo
charged.
Integral
4.02 x 4.65
202
cubic
1 - 3 -4 -
Clockwise,
280
ft-Ib @ 1500
17:1.
(mm)
Height:
Width:
Length:
987
Ibs
SPECIFICATIONS
441
psi
Not
to
2133
psi
Intake
Exhaust
Intake
0.016
Idle:
600 -900
Cruise:
Max:
2300
COOLING
Fresh
water-cooled
controlled
180
-190° F
Centrifugal
Positive
engine-driven.
17
US
EXHAUST
45°
elbow
4"
1.0.
four
cylinder,
engine.
Vertical
direct
with
injection
inches
inches
(4.3
2.
when
viewed
rpm.
32.0
inches
28.3
inches
47.2
inches
(448.0
kgs).
(31
kg/cm')
exceed
28.44
(150
kf/cm').
45°
45°
and
exhaust
inches
(0.40
rpm.
1800 -2200
-2400
rpm.
SYSTEM
with
heat
(77 -88°
type,
metal
displacement,
Qts
(16.1
liters)
SYSTEM
(101.6
mm)
four-cycle,
injection,
pump.
(102.0 x 118.0
at
psi
mm).
rpm.
block,
exchanger.
hose
turbocharged
in-line
overhead
110
liter).
from
the
(813
(719
(1168
200
rpm
(20.0
kg/cm').
thermostatically-
C)
impeller,
belt-driven.
rubber
impeller,
valve,
hp @ 2400
mm).
front.
mm)
mm)
mm)
General
Fuel
Fuel
Injection
Fuel
Injection
Nozzle
Fuel
Filter
(on
engine)
Air
cleaner
Air
Flow
(engine
combustion)
Fuel
Consumption
Starting
Battery
Battery
Capacity
DC
Charging
Starting
Aid
Starter
DC
No-load
Current
DC
Cranking
General
Oil
Filter
Sump
Capacity
(not
including
Operating
(engine
Oil
General
Gear
Propeller
Propeller
(using
transmission)
Lubricating
Transmission
Capacity
Oil
hot)
Grade
Ratio
(Standard)
Shaft
Recommendations
standard
Fluid
Hurth
FUEL
Closed
No.2
Pump
liming
BOSCH
12°
Multi-hole.
Full
Replaceable
230
6.1
ELECTRICAL
12
750 -900
Altemator
Current
51
Glow
12
±
400
LUBRICATION
Gear
Full
filter)
Pressure
14.5
25-85
API
SAE
TRANSMISSION
(HURTH
helical
clutch.
2:00:1
Right
24x18
propeller
rated
while
Dextron
Sump
45A
2.13
SYSTEM
system
with
diesel
oil
(cetane
Model A type
BTDC.
flow
replaceable.
paper
cfm.
U.S.
gph
(23.1
SYSTEM
Volt,
(-)
negative
Cold
Cranking
Amp
rated,
belt-driven
plugs
Volt, 3 KW
2%
of
rated
amps
CCA.
SYSTEM
type/pressure
flow,
paper
element,
U.S.
Qts
(13.8
psi
Specification
30,
10W-30,
Standard
gears,
hydraulically
(Hurth
45A)
handed-standard
P-2
blade
should
rpm
underway
US
allow
(2400 + 000
in
III
Qts
(2.0
bleed
pOints.
rating
of
(In-line).
element.
Iph).
ground
Amps
circulation
spin-on
liters)
CF
or
CG-4,
15W-40
Transmission)
operated
or
(Hurth
63A)
transmission.
or
24x16
P-3
the
engine
-100)
forward
liters)
at
gear.
approximate.
45
or
higher).
(CCA)
type.
Case-hardened
multiple
disc
blade
to
reach
open
its
throttle
full
full
Combustion
Note:
ment
inches
The
pressure
versus
of
water
Air
the
(51
differential
inside
of
mm)
the
at
full
230
cfm
between
engine
open
the
outside
compartment
throttle
of
should
(measure
the
engine
compart-
not
exceed
with a manometer).
2
Engines & Generators
49
Page 56
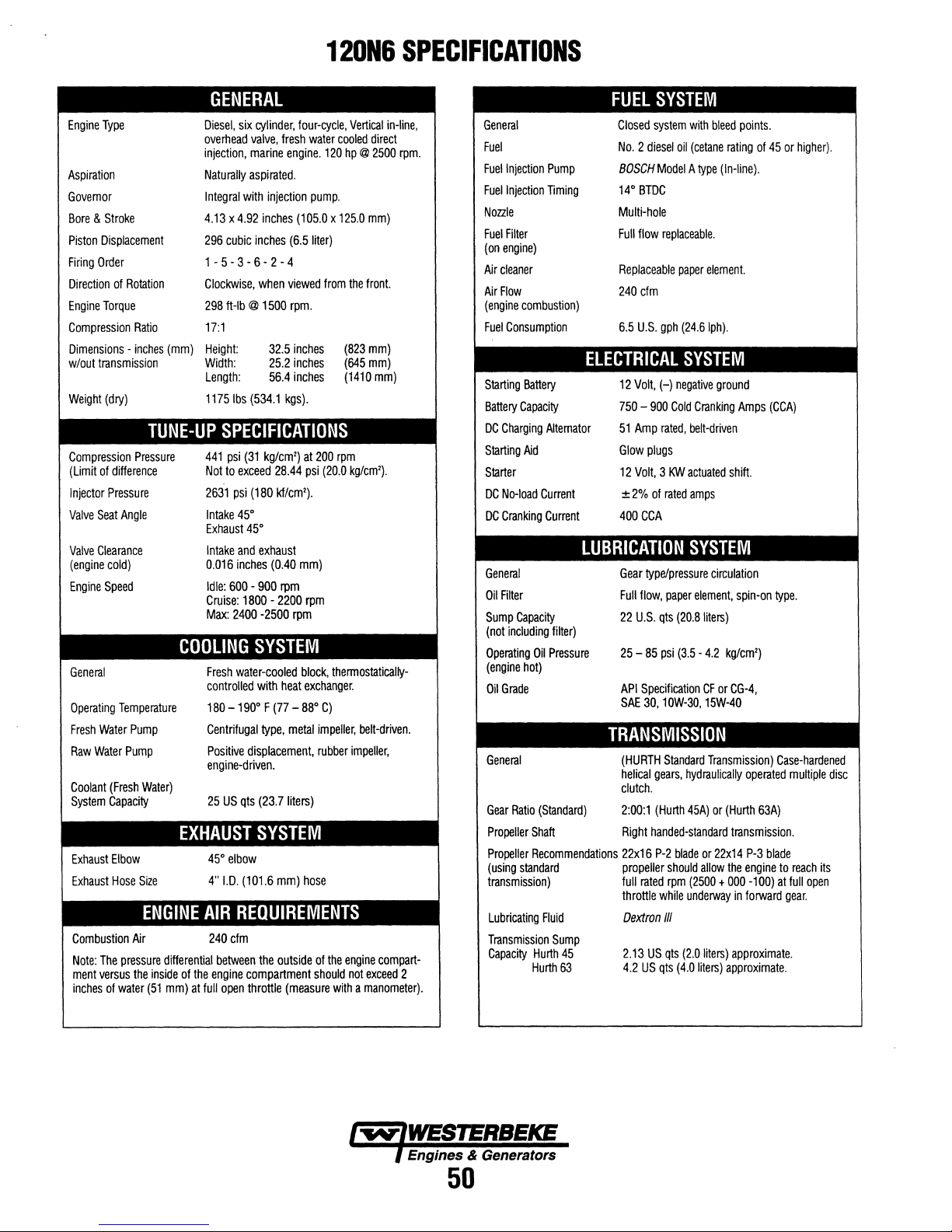
120N6
SPECIFICATIONS
Engine
Type
Aspiration
Governor
Bore & Stroke
Piston
Displacement
Firing
Order
Direction
of
Rotation
Engine
Torque
Compression
Dimensions -inches
w/out
Weight(dry)
Ratio
transmission
TUNE-UP
Compression
(Limit
Injector
Valve
Valve
(engine
Engine
General
Operating
Fresh
Raw
Coolant
System
Exhaust
Exhaust
Pressure
of
difference
Pressure
Seat
Angle
Clearance
cold)
Speed
Temperature
Water
Pump
Water
Pump
(Fresh
Capacity
Elbow
Hose
Water)
Size
ENGINE
Combustion
Note:
ment
inches
The
pressure
versus
of
water
Air
the
inside
(51
GENERAL
Diesel,
overhead
injection,
Naturally
Integral
4.13 x 4.92
296
cubic
1-5-3-6-2-4
Clockwise,
298
ft-Ib @ 1500
17:1
(mm)
Height:
Width:
Length:
1175
SPECIFICATIONS
441
psi
Not
to
2631
Intake
Exhaust
Intake
0.016
Idle:
Cruise:
Max:
COOLING
Fresh
controlled
180 -1900 F
Centrifugal
Positive
engine-driven.
25
US
EXHAUST
45°
4"
I.D.
AIR
240cfm
differential
mm)
of
the
at
full
between
engine
open
six
cylinder,
valve,
marine
aspirated.
with
injection
inches
inches
when
32.5
25.2
56.4
Ibs
(534.1
(31
kg/cm')
exceed
psi
(180
45°
45°
and
exhaust
inches
600 -900
1800 -2200
2400
-2500
four-cycle,
fresh
engine.
(105.0 x 125.0
(6.5
viewed
rpm.
inches
inches
inches
kgs).
28.44
kf/cm').
(0.40
mm)
rpm
rpm
water
pump.
liter)
at
200
psi
rpm
cooled
120
from
rpm
(20.0
Vertical
hp
the
(823mm)
(645mm)
(1410
kg/cm').
SYSTEM
water-cooled
displacement,
qts
with
heat
(77 -880 C)
type,
metal
(23.7
liters)
block,
thermostatically-
exchanger.
impeller,
rubber
impeller,
SYSTEM
elbow
(101.6
mm)
hose
REQUIREMENTS
the
outside
of
the
compartment
throttle
(measure
engine
should
not
with a manometer).
in-line,
direct
@2500
rpm.
mm)
front.
mm)
belt-driven.
compart-
exceed
2
General
Fuel
Fuel
Injection
Fuel
Injection
Nozzle
Fuel
Filter
(on
engine)
Air
cleaner
Air
Flow
(engine
combustion)
Fuel
Consumption
Starting
Battery
Battery
Capacity
DC
Charging
Starting
Aid
Starter
DC
No-load
Current
DC
Cranking
General
Oil
Filter
Sump
Capacity
(not
including
Operating
(engine
Oil
General
Gear
Propeller
Propeller
transmission)
Oil
hot)
Grade
Ratio
(Standard)
Shaft
Recommendations
(using
standard
Lubricating
Transmission
Capacity
Fluid
Hurth
Hurth
FUEL
Closed
No.2
Pump
TIming
BOSCH
WBTDC
Multi-hole
Full
Replaceable
240
6.5
ELECTRICAL
12
750 -900
Alternator
Current
51
Glow
12
±2%
400
LUBRICATION
Gear
Full
filter)
Pressure
22
25 -85
API
SAE
TRANSMISSION
(HURTH
helical
clutch.
2:00:1
Right
22x16
propeller
full
throttle
Dextran
Sump
45
63
2.13
4.2
SYSTEM
system
with
diesel
oil
(cetane
Model A type
flow
replaceable.
paper
cfm
U.S.
gph
(24.6Iph).
SYSTEM
Volt,
(-)
negative
Cold
Cranking
Amp
rated,
belt-driven
plugs
Volt,
3
I<N{
actuated
of
rated
amps
CCA
SYSTEM
type/pressure
flow,
paper
element.
U.S.
qts
(20.8
psi
(3.5 -4.2
Specification
30,
1
OW-3~,
Standard
gears,
hydraulically
(Hurth
45A)
handed-standard
P-2
blade
should
rated
rpm
(2500 + 000
while
underway
/11
US
qts
(2.0
US
qts
(4.0
liters)
bleed
pOints.
rating
of
(In-line).
element.
ground
Amps
shift.
circulation
spin-on
liters)
kg/cm')
CF
or
CG-4,
15W-40
Transmission)
operated
or
(Hurth
63A)
transmission.
or
22x14
P-3
allow
the
engine
-100)
in
forward
liters)
approximate.
approximate.
45
or
higher).
(CCA)
type.
Case-hardened
multiple
disc
blade
to
reach
its
at
full
open
gear.
Engines & Generators
50
Page 57

170T6
SPECIFICATIONS
Engine
Type
Aspiration
Govemor
Bore & Stroke
Piston
Displacement
Firing
Order
Direction
of
Rotation
Engine
Torque
(max.)
Compression
Dimensions -inches
w/out
Weight
Ratio
transmission
(dry)
TUNE-UP
Compression
(Limit
Injector
Valve
Valve
(engine
Engine
General
Operating
Fresh
Raw
Coolant
System
Exhaust
Exhaust
Pressure
of
difference
Pressure
Seat
Angle
Clearance
cold)
Speed
Temperature
Water
Pump
Water
Pump
(Fresh
Capacity
Elbow
Hose
Water)
Size
GENERAL
Diesel,
marine
fresh
water
2500
rpm.
Turbocharged.
Integral
4.13 x 4.92
423
cubic
1-5-3-6-2-4
Clockwise,
423
ft-Ib @ 1800
17:1
(mm)
Height:
Width:
Length:
12451bs
SPECIFICATIONS
441
psi
Not
to
2631
Intake
Exhaust
Intake
0.016
Idle:
600 -900
Cruise:
Max:
2400
COOLING
Fresh
controlled
180
-190° F
Centrifugal
Positive
engine-driven.
25
US
EXHAUST
45°
elbow
4"
1.0.
six
cylinder,
engine.
Vertical
cooled
with
injection
inches
inches
(6.5
when
viewed
rpm.
33.5
28.0
57..5
(565.23
kgs).
(31
kg/cm')
exceed
28.44
psi
(185
kf/cm').
45°
45°
and
exhaust
inches
(0.40
rpm
1800 -2200
-2500
SYSTEM
water-cooled
with
heat
(77 -88°
type,
metal
displacement,
qts
(23.7
liters)
SYSTEM
(101.6
mm)
four-cycle,
direct
(105.0 x 125.0
inches
inches
inches
mm)
rpm
block,
hose
turbocharged
in-line
overhead
injection,
pump.
liter)
from
the
(823
(711
(1410mm)
at
200
rpm
psi
(20.0
kg/cm')
rpm
thermostatically-
exchanger.
C)
impeller,
rubber
impeller,
valve,
170
hp
@
mm)
front.
mm)
mm)
belt-driven.
General
Fuel
Fuel
Injection
Fuel
Injection
Nozzle
Fuel
Filter
(on
engine)
Air
cleaner
Air
Flow
(engine
combustion)
Fuel
Consumption
Starting
Battery
Battery
Capacity
DC
Charging
Starting
Aid
Starter
DC
No-load
Current
DC
Cranking
General
Oil
Filter
Sump
Capacity
(not
including
Operating
(engine
Oil
General
ened
Gear
Propeller
Propeller
(using
transmission)
Transmission
Oil
hot)
Grade
Ratio
Shaft
Recommendations
standard
Lubricating
Capacity
Hurth
(Standard)
Fluid
FUEL
Closed
No.2
Pump
TIming
BOSCH
12°
Multi-hole
Full
Replaceable
365
9.3
ELECTRICAL
12
750 -900
Alternator
51
Glow
12
±
Current
400
LUBRICATION
Gear
Full
filter)
Pressure
22
25-85
API
SAE
TRANSMISSION
(HURTH
helical
disc
2:00:1
Right
24x18
propeller
full
throttle
Dextran
Sump
63
4.2
SYSTEM
system
with
diesel
oil
(cetane
Model A type
BTDC
flow
replaceable.
paper
cfm.
U.S.
gph
(35.2
SYSTEM
Volt,
(-)
negative
Cold
Cranking
Amp
rated,
belt-driven
plugs
Volt,
3
I<m
2%
of
rated
amps
CCA
SYSTEM
type/pressure
flow,
paper
element,
U.S.
qts
(20.8
psi
Specification
30,
10W-30,
Standard
gears,
hydraulically
clutch.
(Hurth
45A)
handed-standard
P-2
blade
should
rated
rpm
(2500 + 000
while
underway
III
US
qts
(4.0
liters)
bleed
points.
rating
of
(In-line).
element.
Iph).
ground
Amps
circulation
spin-on
liters)
CF
or
CG-4,
15W-40
Transmission)
operated
or
(Hurth
63A)
transmission.
or
24x16
P-3
allow
the
engine
-100)
in
forward
approximate.
45
or
higher).
(CCA)
type.
Case-hard-
multiple
blade
to
reach
at
full
gear.
its
open
Combustion
Note:
ment
inches
The
pressure
versus
of
water
Air
the
differential
inside
(51
mm)
of
the
at
365
between
engine
full
open
cfm
the
compartment
throttle
outside
of
the
should
(measure
with a manometer).
engine
not
exceed
compart-
2
Engines & Generators
51
Page 58

SUGGESTED
SPARE
PARTS
CONTACT
YOUR
WESTERBEKE
WESTERBEKE
DEALER
MARINE
FOR
DIESEL
ADDITIONAL
ENGINES
SUGGESTIONS
AND
INFORMATION
FUEL
FILTERS
I
, i
::
FUEL
STRAINER
The
red
18"
handles,
and
long
with a full
and a carrying
black
duffel
zipper,
bag
dual
strap.
OIL
FILTERS
is
'-,
-,
:./(\
"":,.,./
'
~
WESTERBEKE
Kit A has
offers
the
basic
Kit
A
Impeller
Heat
Exchanger
Fuel
Filter
Oil
Filter
Drive
Belts
Zincs
Thermostat
Engines & Generators
Spare
spares.
Gasket
TRANSMISSION
FILTER
HARDWARE
J:P~~
~
SPARE
Parts
Kits
Kit B is
PARTS
in
two
for
more
KitB
Impeller
Heat
Fuel
Oil
Drive
Zincs
Thermostat
Complete
Injector
Air
Transmission
Filter
KITS
versions
complete
Exchanger
Filter
Belts
Gasket
Filter
(separate)
KIT
each
for
Gasket
Filter
packaged
offshore
Kit
THERMOSTATS
AND
GASKETS
in a canvas
cruising.
duffel
bag.
52
Page 59

Page 60

Engines & Generators
1041WM/DW612000
 Loading...
Loading...