Page 1

SL-MOD-GW
Modbus/TCP Gateway
Usermanual
Page 2

SL-MOD-GW
Modbus/TCP Gateway: User manual
No part of this material may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means or used to make any derivative work without
express written consent from the copyright holders.
Weidmller is a registered trademark of Weidmller Interface GmbH & Co. KG. Modbus is a registered trademark of Schneider Automation
Inc. All other product and brand names mentioned in this document may be trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective owners.
Page 3

UMSLMODGW-1006 iii
Contents
Important user information .................................................................................................................... v
Safety Precautions ........................................................................................................................ v
Document conventions ................................................................................................................. vi
1 Introduction ....................................................................................................................................... 1
1.1 Features ................................................................................................................................ 2
1.2 Quick start checklist ............................................................................................................... 2
2 Description ........................................................................................................................................ 3
2.1 LED indicators ........................................................................................................................ 3
3 Installation ........................................................................................................................................ 5
3.1 Regulatory notes .................................................................................................................... 5
3.2 Unpacking, handling and storage ............................................................................................ 5
3.3 Before connecting anything ..................................................................................................... 5
3.4 DIN rail mounting and removal ................................................................................................ 6
3.5 Mounting rules ........................................................................................................................ 6
3.6 Powering the SL-MOD-GW ..................................................................................................... 7
3.7 Wiring the RS-485/422 interface .............................................................................................. 7
3.8 Wiring the RS-232 interface .................................................................................................... 8
3.9 Connecting Ethernet ............................................................................................................... 9
4 Ethernet & IP configuration .............................................................................................................. 11
4.1 IP setup using a terminal program like HyperTerminal ............................................................. 11
4.2 Temporarily changing the IP settings on your PC .................................................................... 12
5 Web browser based management .................................................................................................... 15
5.1 Connecting to the SL-MOD-GW ............................................................................................ 15
5.2 Monitoring and diagnostic ..................................................................................................... 16
5.2.1 Device status ............................................................................................................. 16
5.2.2 Modbus connection status .......................................................................................... 17
5.2.3 Finding the firmware version and serial number ........................................................... 18
5.3 Configuring and commissioning ............................................................................................. 19
5.3.1 Configuring Ethernet and IP ....................................................................................... 19
5.3.2 Configuring serial line Modbus .................................................................................... 20
5.3.3 Remote restarting the device ...................................................................................... 21
6 Decommissioning ............................................................................................................................ 23
6.1 Disconnecting ....................................................................................................................... 23
6.2 Disposal ............................................................................................................................... 23
A Specifications .................................................................................................................................. 25
A.1 Dimensions .......................................................................................................................... 27
Glossary ............................................................................................................................................. 29
Index .................................................................................................................................................. 31
Figures
2.1 Location of connectors .................................................................................................................... 3
5.1 Device management and configuration via the web browser ............................................................ 15
5.2 Overview page ............................................................................................................................. 16
5.3 Modbus status page ..................................................................................................................... 17
5.4 About page .................................................................................................................................. 18
5.5 Ethernet and IP settings page ....................................................................................................... 19
5.6 IP settings changed confirmation ................................................................................................... 20
5.7 Modbus settings page ................................................................................................................... 20
5.8 Restart device page ...................................................................................................................... 21
5.9 Restart confirmation page ............................................................................................................. 21
A.1 Enclosure dimensions ................................................................................................................... 27
Page 4

iv UMSLMODGW-1006
Tables
2.1 LED diagnostic codes ..................................................................................................................... 4
3.1 Power supply connector pinout ....................................................................................................... 7
3.2 RS-485/RS-422 connector pinout .................................................................................................... 7
3.3 Modbus RS-232 connector pinout ................................................................................................... 8
3.4 Ethernet connector pinout ............................................................................................................... 9
Page 5
UMSLMODGW-1006 v
Important user information
This manual explains how to install, operate and configure a SL-MOD-GW. This device may only be used for
the applications described in this document.
This manual is to be used with a SL-MOD-GW with firmware version 1.6.
These instructions are intended for use by trained specialists in electrical installation and control and automation
engineering, who are familiar with the applicable national standards and safety procedures.
Safety Precautions
ELECTRICAL HAZARD
• This equipment must be installed and serviced only by qualified personnel. Such work
should be performed only after reading this entire set of instructions.
• Before performing visual inspections, tests, or maintenance on this equipment, disconnect
all sources of electric power. Assume that all circuits are live until they have been completely
de-energized, tested, and tagged. Pay particular attention to the design of the power
system. Consider all sources of power, including the possibility of backfeeding.
• Apply appropriate personal protective equipment and follow safe electrical practices.
• Turn off all power supplying the equipment in which the SL-MOD-GW is to be installed
before installing, wiring or removing the SL-MOD-GW.
• Always use a properly rated voltage sensing device to confirm that power is off.
• The successful operation of this equipment depends upon proper handling, installation, and
operation. Neglecting fundamental installation requirements may lead to personal injury as
well as damage to electrical equipment or other property.
Failure to follow these instructions could result in death or serious injury!
Page 6

vi UMSLMODGW-1006
Document conventions
Throughout this manual we use the following symbols and typefaces to make you aware of safety or other
important considerations:
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation that, if not avoided, could result
in death or serious injury.
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation that, if not avoided, could result
in damage to equipment.
Indicates information that is critical for successful application and understanding of the product.
Provides other helpful user information that does not fall in above categories.
Provides supplemental user information.
Acronym This typeface is used to introduce acronyms or product names.
Command
This typeface is used to represent commands, prompts, input fields and filenames. In the context of programming it is used for functions, variable names,
constants or class names.
Placeholder
This typeface is used to represent replacable text. Replaceable text is a
placeholder for data you have to provide, like filenames or command line
arguments.
User input
This typeface is used to represent data entered by the user or buttons.
Screen output
Screen output or program listing
Page 7

UMSLMODGW-1006 1
1.Introduction
The SL-MOD-GW is a Modbus/TCP to Modbus RTU gateway.
The gateway features one serial port which can be configured as either RS-232, RS-485 or RS-422 and an
Ethernet port. It can be mounted on a DIN rail.
Usage and configuration of the gateway is simple and conveniently performed using a web browser which
connects to the embedded web server.
Possible areas of application are:
• PLC connection
• Operator panel interfacing
• HMIs
• SCADA integration
• Remote control & monitoring
• Data logging
Page 8

2 UMSLMODGW-1006
1.1 Features
The SL-MOD-GW gateway provides the following key features:
• Modbus/TCP protocol (Ethernet)
• Modbus RTU protocol (either RS-232, RS-485 or RS-422, software configurable)
• Embedded web server for easy configuration and commissioning using a web browser
• Firmware upgradeable via Ethernet
• DIN rail mountable
• 24 V DC (10-30 V) power supply
• Status LEDs for power, Ethernet link, device status and communication status
1.2 Quick start checklist
• Read this set of instructions properly and in its entirety.
• Mount the unit.
• Connect the power. Do not connect yet serial ports.
• Configure the Ethernet communications settings with a web browser (using an Ethernet crossover cable) or
with a terminal program like HyperTerminal (using a null modem cable)
• Configure the serial line communication settings.
• Configure the operational aspects of the device.
• Wire serial line interfaces.
Page 9
UMSLMODGW-1006 3
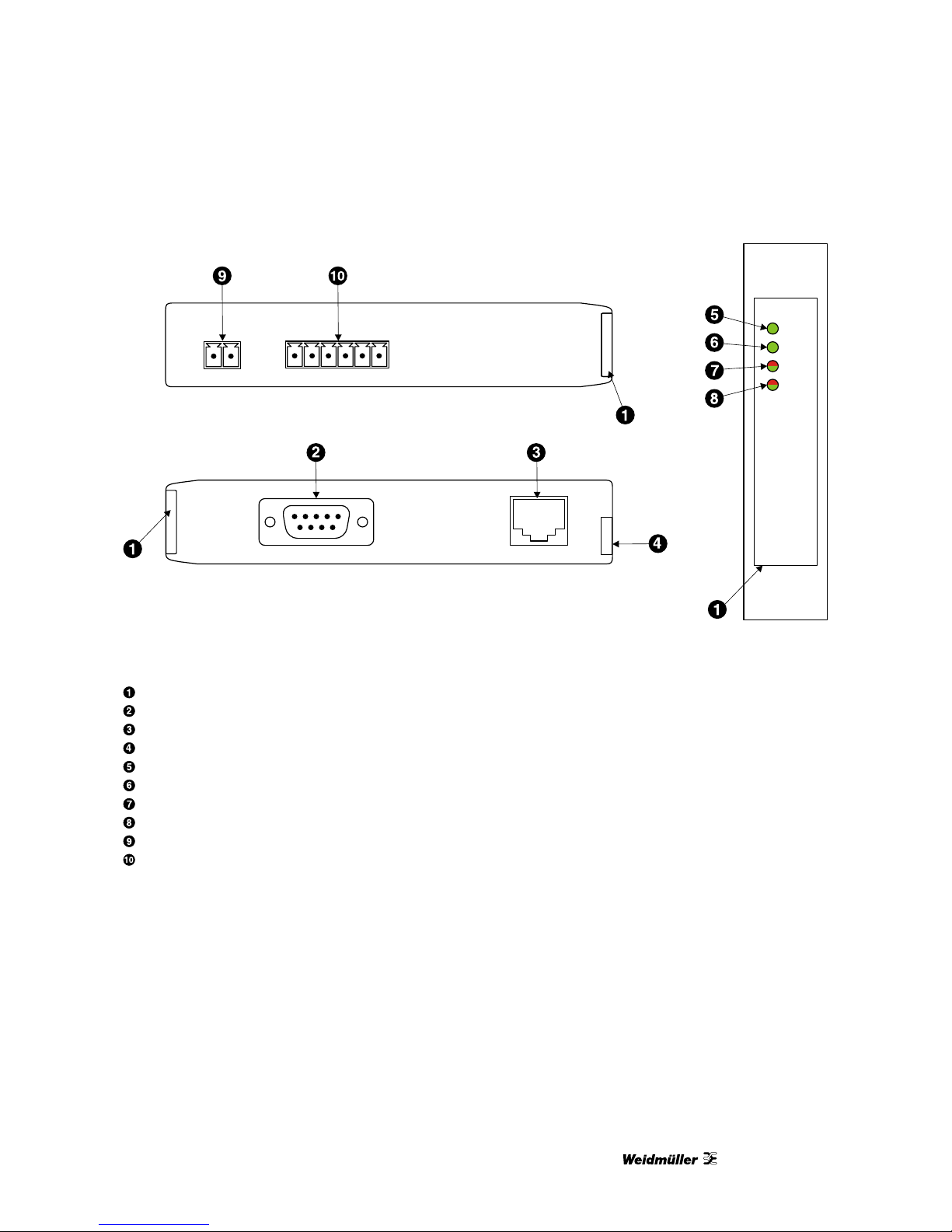
2.Description
The power and RS-485/RS-422 terminals are placed on the top side of the unit. The RS-232 and Ethernet
connectors are placed on the bottom side of the unit as shown in the following illustration:
TOP VIEW
BOTTOM VIEW
FRONT VIEW
Illustration 2.1: Location of connectors
Clear front cover
RS-232 connector
Ethernet connector
DIN rail clip
Power LED
Ethernet link LED
Device status LED
Communication status LED
Power terminals
RS-485/RS-422 terminals
2.1 LED indicators
Four LEDs located at the front panel indicate the status of the device. The LEDs assist maintenance personnel
in quickly identifying wiring or communication errors.
A LED test is exercised at power-up, cycling each LED off, green and then red for approximately 0.25 seconds.
At the same time the power-on self test of the device is performed.
Page 10
4 UMSLMODGW-1006
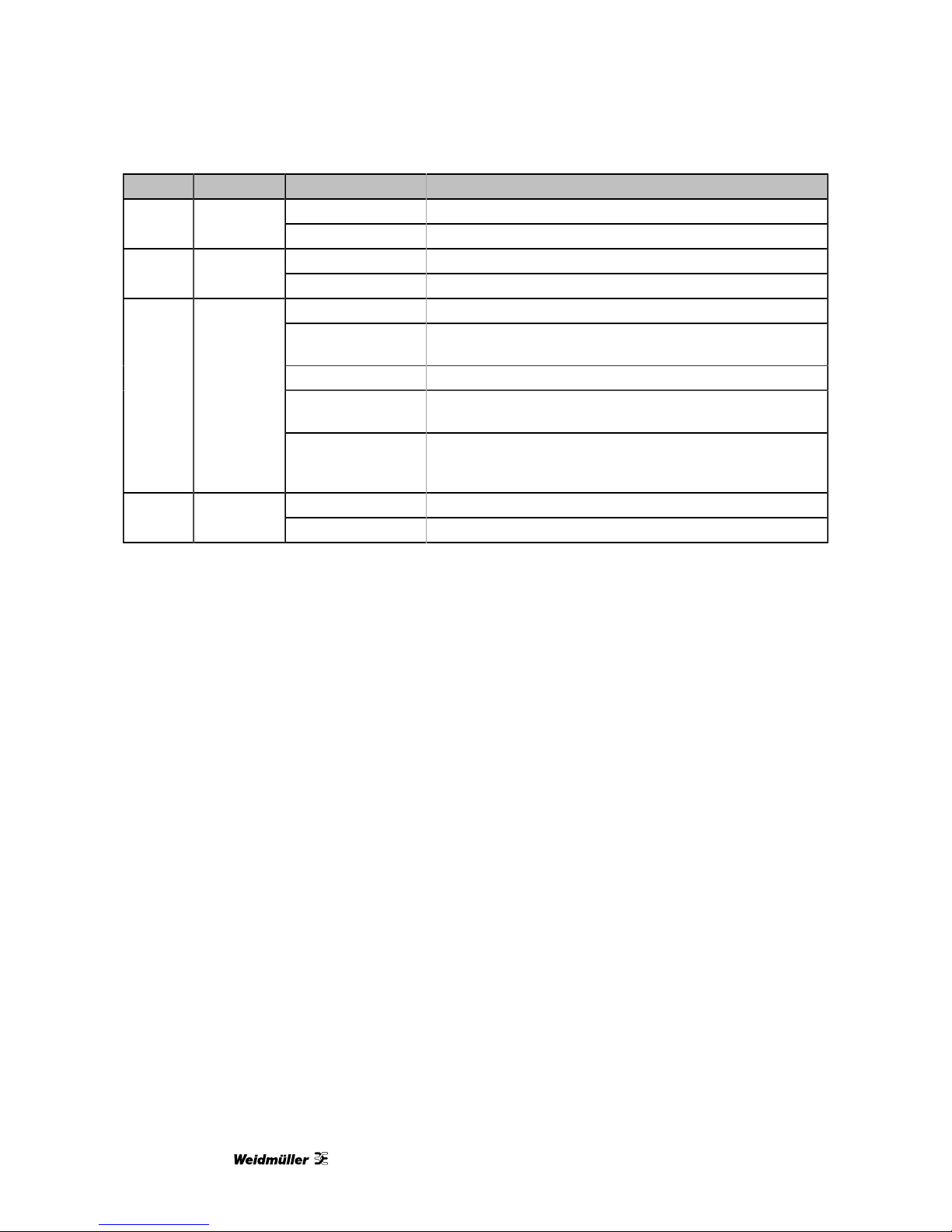
The following table outlines the indicator condition and the corresponding status after the power-on self test
has been completed:
LED Function Condition Indication
Off No power applied to the device.
Power Power
Green Power supply OK
Off No Ethernet link
Link Ethernet link
Green Ethernet link OK
Off The device has an unrecoverable fault; may need replacing.
Flashing green
1 s rate
Device operational but needs commissioning due to configuration missing, incomplete or incorrect.
Green The device is operating in normal condition.
Flashing red
1 s rate
Device operational but has a fault listed which requires acknowledgment.
Status1
Device status
Red
The device has an unrecoverable fault; may need replacing.
Flashing sequence and rate of Status2 LED indicates fault
class.
Off No Modbus/TCP connection.
Status2
Communication status
Green Modbus/TCP connection established.
Table 2.1: LED diagnostic codes
Page 11
UMSLMODGW-1006 5
3.Installation
3.1 Regulatory notes
1. The SL-MOD-GW is suitable for use in non-hazardous locations only.
2. The SL-MOD-GW is not authorized for use in life support devices or systems.
3. Wiring and installation must be in accordance with applicable electrical codes in accordance
with the authority having jurisdiction.
4. This is a Class A device and intended for commercial or industrial use. This equipment may
cause radio interference if used in a residential area; in this case it is the operator’s responsibility
to take appropriate measures.
5. The precondition for compliance with EMC limit values is strict adherence to the guidelines
specified in this set of instructions. This applies in particular to the area of grounding and
shielding of cables.
FCC Notice (USA only)
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital device, pursuant to Part
15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference
when the equipment is operated in a commercial environment. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate
radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instruction manual, may cause
harmful interference to radio communications. Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely to cause
harmful interference in which case the user will be required to correct the interference at his own expense.
Industry Canada Notice (Canada only)
This Class A digital apparatus complies with Canadian ICES-003.
3.2 Unpacking, handling and storage
1. Please read this set of instructions. carefully before fitting it into your system.
2. Keep all original packaging material for future storage or warranty shipments of the unit.
3. Do not exceed the specified temperatures.
3.3 Before connecting anything
1. Before installing or removing the unit or any connector, ensure that the system power and
external supplies have been turned off.
2. Check the system supply voltage with a multimeter for correct voltage range and polarity.
3. Connect the power supply cable and switch on the system power. Check if the Power LED is lit.
4. Turn off system power.
5. Connect all I/O cables.
Page 12
6 UMSLMODGW-1006
6. Once you are certain that all connections have been made properly, restore the power.
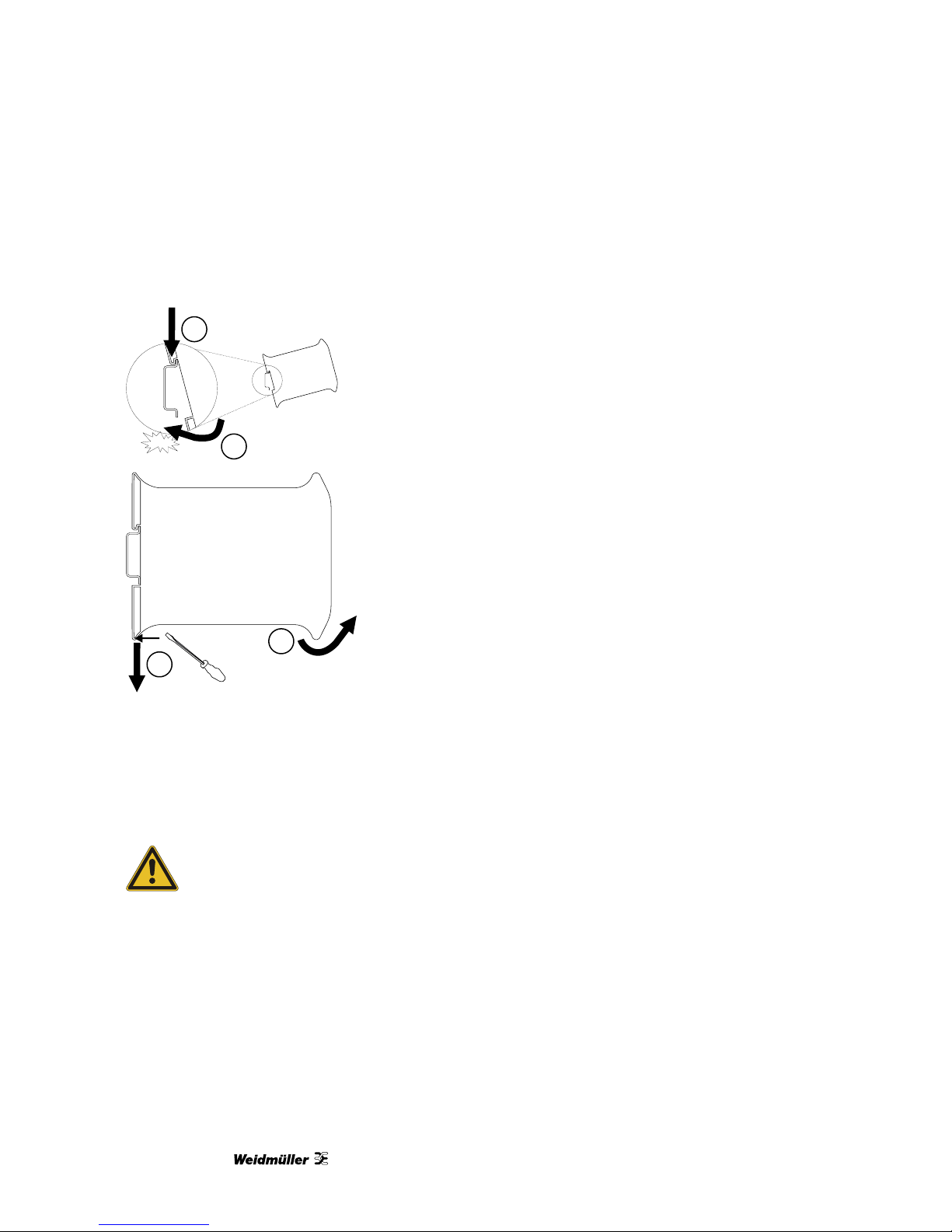
3.4 DIN rail mounting and removal
The SL-MOD-GW gateway is designed to be mounted on a 35 mm DIN rail according to DIN/EN 50022. The
enclosure features a 35 mm profile at the back which snaps into the DIN rail. No tools are required for mounting.
Please observe the rules outlined in Section 3.5, “Mounting rules”.
2
1
Click
DIN rail
To mount the unit on a DIN rail, slot the top part of the
SL-MOD-GW into the upper guide of the rail and lower the enclosure until the bottom of the red hook clicks into place.
Slide down
2
1
To remove the SL-MOD-GW from the DIN rail, use a screw driver
as a lever by inserting it in the small slot of the red hook and push
the red hook downwards. Then remove the unit from the rail by
raising the bottom front edge of the enclosure.
3.5 Mounting rules
The enclosure provides protection against solid objects according to IP 20 / NEMA Type 1 protection rating.
When mounting the unit observe the following rules:
• No water splash and water drops
• No aggressive gas, steam or liquids
• Avoid dusty environments.
• Avoid shock or vibration
• Do not exceed the specified operational temperatures and humidity range.
• Mount inside an electrical switchboard or control cabinet.
• Make sure there is sufficient air ventilation and clearance to other devices mounted next to the
unit.
• Observe applicable local regulations like EN60204 / VDE0113.
Page 13

UMSLMODGW-1006 7
3.6 Powering the SL-MOD-GW
Before connecting power please follow the rules in the section called “Safety Precautions” and
Section 3.3, “Before connecting anything”.
Power is supplied via a 3.81 mm 2-pin pluggable terminal block located at the top side of the mounted unit
(refer to Figure 2.1, “Location of connectors”). The following table and picture shows the power terminal socket
pinout:
V+
V-
1
Pin Signal Function
1 V+ Positive voltage supply (10 - 30 V DC)
2 V- Negative voltage supply, DC power return
Table 3.1: Power supply connector pinout
Caution
Make sure that the polarity of the supply voltage is correct before connecting any device to
the serial ports! A wrong polarity can cause high currents on the ground plane between the
V- power supply pin and the serial port ground pins, which can cause damage to the device.
3.7 Wiring the RS-485/422 interface
The RS-485/422 port is used for integrating the SL-MOD-GW into a two-wire or four-wire Modbus over Serial
Line network. The use of either the RS-485 or RS-422 interface must be configured using the web interface
(See Section 5.3.2, “Configuring serial line Modbus”). The SL-MOD-GW is a Modbus Master device on this
interface.
The RS-485 and RS-422 signals are located at the 3.81 mm 6-pin pluggable terminal block on the top side of the
mounted unit (refer to Figure 2.1, “Location of connectors”). The following table and picture shows the pinout:
1
GND
D-
D+
RS-485
GND
TX-
TX+
GND
RX-
RX+
1
RS-422
Pin RS-485
signal
RS-422
signal
Description
3 GND GND Modbus Common
4 D+ TX+ Modbus D1 or TXD1
5 D- TX- Modbus D0 or TXD0
6 GND Modbus Common
7 RX+ Modbus RXD0
8 RX- Modbus RXD1
Table 3.2: RS-485/RS-422 connector pinout
• Line termination is required and is typically done with a 120 Ohm 1/4 W resistor. For RS-485 operation the
bus must be terminated at both ends. For RS-422 operation a termination resistor must be inserted between
the RX+/RX- signals.
• Maximum number of RS-485 nodes without repeater is 32.
Page 14

8 UMSLMODGW-1006
• Stub connections off the main line should be avoided if possible or at least be kept as short as possible. Stub
connections must not have terminating resistors.
• Maximum cable length to 1200 m (4000 ft).
• To assure a high degree of electromagnetic compatibility and surge protection the cable should be twisted
pairs and shielded. An additional cable conductor or pair may be used for the GND reference.
Caution
Do not connect the cable shield to the GND pins! Use an external chassis ground connection
to terminate the shield.
3.8 Wiring the RS-232 interface
The RS-232 port can alternativly be used for serial communication to a Modbus Slave device instead of RS-485.
The use of the RS-232 interface must be configured using the web interface (See Section 5.3.2, “Configuring
serial line Modbus”). The SL-MOD-GW is a Modbus Master device on this interface.
The Modbus RS-232 connector is a male 9-pin D-sub type located at the bottom side of the mounted unit (refer
to Figure 2.1, “Location of connectors”). It has industry standard EIA-574 data terminal equipment (DTE) pinout
as shown in the following table and picture:
GND
TDX
CTS
DTR
RI
RXD
RTS
1
6
CD
Pin Signal Function Direction
1 DCD (unused) in
2 RXD Receive data in
3 TXD Transmit data out
4 DTR (unused) out
5 GND Signal ground
6 DSR (unused) in
7 RTS (unused) out
8 CTS (unused) in
9 RI (unused) in
Table 3.3: Modbus RS-232 connector pinout
• Maximum cable length is 15 m (50 ft) or a length equal to a line capacitance of 2500 pF, both at the maximum
standard bit rate of 20 kbps. If operating at higher bit rates the maximum cable length drops to 3 m (10 ft)
at a bit rate of 57.6 kbps.
• To assure a high degree of electromagnetic compatibility and surge protection the RS-232 cable should
shielded. The shield shall be connected to an external chassis ground at the either or both ends, depending
on the application.
• The shield must not be connected to the GND pin.
Note
To connect the SL-MOD-GW to a PC (Personal Computer) or any other device with data
terminal equipment (DTE) pinout you need a null-modem or cross-over cable.
Page 15

UMSLMODGW-1006 9
3.9 Connecting Ethernet
The following table describes the 10BASE-T Ethernet RJ-45 connector pinout:
TX+
TX-
RX-
RX+
1
Pin Signal Function
1 TX+ Non-inverting transmit signal
2 TX- Inverting transmit signal
3 RX+ Non-inverting receive signal
4 Internal termination network
5 Internal termination network
6 RX- Inverting receive signal
7 Internal termination network
8 Internal termination network
Table 3.4: Ethernet connector pinout
• We recommend to use Category 5 UTP network cable.
• Maximum cable length is 100 m (3000 ft).
Page 16

10 UMSLMODGW-1006
Page 17

UMSLMODGW-1006 11
4.Ethernet & IP configuration
Before configuring the SL-MOD-GW, obtain a unique static IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway
address from your network administrator.
The factory default IP address of the SL-MOD-GW is 192.168.1.130.
There are several methods of configuring the unit’s IP address:
1. Via the Serial Port 1 and a terminal program like HyperTerminal (see Section 4.1, “IP setup using a terminal
program like HyperTerminal”).
2. Leaving your PC connected to your corporate network and temporarily changing the IP settings on your
PC to match the subnet of the SL-MOD-GW (see Section 4.2, “Temporarily changing the IP settings on
your PC”).
Note
In order to connect to the SL-MOD-GW via TCP/IP, your PC must be on same IP subnet as
the gateway. In most situations this means that the first three numbers of the IP address have
to be identical.
4.1 IP setup using a terminal program like HyperTerminal
1. Connect a null modem RS-232 cable between your PC and the SL-MOD-GW's Serial Port 1.
2.
In Windows XP, click Start, point to All Programs, point to Accessories, point to Communications,
and then click HyperTerminal.
3. When HyperTerminal starts, it opens a dialog box and asks for a name for the new connection. Enter a
name (for example, deviceconfig) then click OK.
4.
The Connect to dialog opens. Select the COM port you will be using in the Connect using drop-down
list box, then click OK.
5.
Select 9600, 8, None, 1, None in the COM Properties dialog, then click OK.
6. HyperTerminal is now connected to the serial line.
7.
Keep the space bar pressed in HyperTerminal and power-cycle your device at the same time.
8. A menu should appear after one or two seconds showing device information, the current IP configuration
and a > prompt.
Page 18

12 UMSLMODGW-1006
9.
Type SETIP, then press Enter within 10 seconds after the prompt is shown:
DIAG MODE
Ver: x.y
S/N: 1234
MAC: 00:50:C7:67:71:97
IP Address: 192.168.1.130
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
Gateway Address: 0.0.0.0
>SETIP
IP Address (192.168.1.130): 10.0.0.100
Subnet Mask (255.255.255.0): 255.255.255.0
Gateway Address (0.0.0.0): 0.0.0.0
RUN MODE
10.The device will show current values and prompt for new values for IP address, net mask and gateway
address. Enter the new values and press Enter. A key press must be received at least every 10 seconds
otherwise the device will go back to RUN MODE and resume normal operation.
11.
The gateway will return to the main prompt. Type X and press Enter to leave DIAG MODE and resume
normal operation indicated with RUN MODE.
4.2 Temporarily changing the IP settings on your PC
This method involves manually assigning an IP address to your PC in the same subnet as the gateway. The
default subnet of the gateway is 192.168.1.0/8.
1. Connect the SL-MOD-GW to your Ethernet network.
2.
On a Windows PC, open the Control Panel and double-click on Network Connections. Right-click
on the Network Connection associated with your network adapter and select Properties:
Page 19

UMSLMODGW-1006 13
This will show the Local Area Connection Properties Dialog:
3.
Select the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) entry and click on Properties to open the TCP/IP
Properties dialog as shown below:
4. Write down your current settings so they can be restored later.
5.
Select Use the following IP address and configure a static IP address in the same subnet as the
device, for example 192.168.1.1 and the subnet mask 255.255.255.0. Click OK to save the changes.
6. Start Internet Explorer.
7.
In the address box, type 192.168.1.130 and then press Enter.
8.
Click Configuration… and then Ethernet & IP in the menu on the left side of the page.
9.
Enter the IP address, subnet mask, and gateway address assigned to your SL-MOD-GW, then click Save.
10.Restore your computer’s original settings.
Page 20

14 UMSLMODGW-1006
Page 21

UMSLMODGW-1006 15
5.Web browser based management
The SL-MOD-GW incorporates an embedded web server. This allows you to connect to the device and monitor
and configure it using a web browser. Most browsers should work, provided they support JavaScript. We
recommend Internet Explorer 6.0 or higher.
5.1 Connecting to the SL-MOD-GW
Once you made sure that your PC is configured to be on the same subnet as the SL-MOD-GW, start your web
browser. In the address box, type the IP address of your device (192.168.1.130 is the default), and then press
Enter. (See Chapter 4, Ethernet & IP configuration)
The web browser will establish communication with the embedded web server and an overview page similar
to the following picture will appear:
Illustration 5.1: Device management and configuration via the web browser
Gateway IP address
Main menu
Configuration sub-menu
Information area
Page 22

16 UMSLMODGW-1006
Use the menu bar shown on the left side to navigate the different pages.
Note
In order to connect to the SL-MOD-GW via TCP/IP, your PC must be on same IP subnet as
the gateway. In most situations this means that the first three numbers of the IP address have
to be identical.
5.2 Monitoring and diagnostic
The SL-MOD-GW offers several web pages which allow monitoring of the status of the different communication
networks and the device performance.
5.2.1 Device status
The Overview page shows the principal device status as shown in the following picture:
Illustration 5.2: Overview page
The value shown in the Device row represents the device status register which keeps track of run-time faults.
All run-time faults are latched and must be reset by the user. The following faults can be listed here:
OK
The device is fault free.
Watchdog reset
This warning indicates that the device was reset by it’s internal watchdog supervision circuit.
Brown out reset
This warning indicates that the device was reset by it’s internal supply voltage monitoring circuit. This fault
occurs when the supply voltage drops below the lower limit.
Device out of memory
This warning indicates that the internal dynamic memory has been exhausted and due to this a certain
function could not be completed.
Device configuration data write failure
This alarm indicates that the configuration data could not be written to the non-volatile memory.
Configuration data changes will be lost once the device is power-cycled or reset.
Page 23

UMSLMODGW-1006 17
Reset to factory defaults
This alarm indicates that the device' configuration data was reset to factory defaults. The device requires
re-commissioning.
5.2.2 Modbus connection status
The Modbus Status page shows status and statistics about the Modbus traffic. These values provide
valuable information used to troubleshoot Modbus network problems. This page is automatically updated every
5 seconds.
Illustration 5.3: Modbus status page
Note
This page shows accumulated readings since the SL-MOD-GW was last activated or reset.
If power to the SL-MOD-GW is lost, all cumulative values are reset to zero.
The following statistics are maintained:
TCP status
Status of the TCP/IP connection as per TCP finite state machine (refer to RFC 793). If no client is connected
the status indicates LISTEN. If a client is connected, it’s IP address is shown.
Accumulative connections
A counter that increments each time a client opens a Modbus/TCP connection.
Requests
A counter that increments each time an inbound request message is successfully received.
Replies
A counter that is incremented each time a reply message is sent back to the master. This includes exception
replies.
Page 24

18 UMSLMODGW-1006
CRC errors
A counter that increments each time a message is received that has a CRC that does not match what is
calculated. Typically the result of wiring issues. Messages with CRC errors are discarded and not replied to.
Invalid frames
A counter that increments each time a malformed Modbus frame is detected. Malformed frames are for
example messages larger than the allowed maximum PDU size defined in the Modbus standards. This
can be caused by non-Modbus traffic on the network.
Rx time-outs (Modbus serial line)
A counter that increments each time an inter-character time-out occurred during the reception of an inbound
message.
Rx time-outs (Modbus/TCP)
A counter that increments if the master connection has timed out. Subsequently the connection is
terminated by the SL-MOD-GW. A time-out occurs if no Modbus request is received from a connected
client within a 10 second period.
Tx time-outs
Number time-outs occurred when attempting to send a reply message.
The cumulative diagnostic data is reset when the device is power cycled or reset. The data is also reset by
pressing the Clear Counter button.
5.2.3 Finding the firmware version and serial number
Click on the About menu entry on the menu bar to show the product information as shown below:
Illustration 5.4: About page
This product information is important for service and support inquiries. The following product information is
provided:
Product name
The name of the product.
Hardware version
SL-MOD-GW hardware version.
Firmware version
The firmware version that is installed on the SL-MOD-GW.
Page 25

UMSLMODGW-1006 19
Serial number
The serial number of the SL-MOD-GW. The serial number is specific to your device.
5.3 Configuring and commissioning
The configuration pages are accessed by clicking on the Configuration… menu entry on the menu bar which
then expands a configuration sub-menu. All configuration settings are kept in the device' non-volatile memory.
Note
If you make changes to any settings, remember to save each page before changing to a
different page!
5.3.1 Configuring Ethernet and IP
Select the Configuration→Ethernet & IP sub-menu from the menu bar to open the Ethernet and
IP settings which are shown below:
Illustration 5.5: Ethernet and IP settings page
The following Ethernet parameters are shown:
MAC address
The device' unique MAC address. This number is hard coded and cannot be changed.
The following Internet protocol (IP) settings can be entered:
IP address
The IP address assigned to this device.
Subnet mask (also known as indexterm2:[network mask])
If you have a router, enter the subnet mask for the segment to which this device is attached.
Gateway address
If your network segment has a router, enter its IP address here. Otherwise leave the address as 0.0.0.0.
Page 26

20 UMSLMODGW-1006
Once you click Save the new settings are stored and applied instantly. The new settings are confirmed with
the following page:
Illustration 5.6: IP settings changed confirmation
Important
Please write down the new IP address so you are able to communicate with the device in
the future!
5.3.2 Configuring serial line Modbus
The Modbus settings for serial line can be configured to match the network configuration of your Modbus master
device. Select the Configuration→Modbus sub-menu from the menu bar to open the Modbus settings which
are shown below:
Illustration 5.7: Modbus settings page
The following Modbus settings can be entered:
Physical layer
Can be set to two-wire RS-485, RS-422 or RS-232 mode. RS-485 is the default. Depending on this setting
either the D-sub (RS-232) connector or the terminal block connector (RS-485/422) of the SL-MOD-GW is
utilized. The (RS-485 + RS-422) mode is a special mode which allows operating one RS-422 device
and a RS-485 bus one the same serial interface.
Transmission mode
Only RTU mode can be selected here.
Baud rate
9600 and 19200 are the most common baud rates for Modbus. 19200 is the default setting.
Page 27

UMSLMODGW-1006 21
Data bits
Only 8 data bits can be selected here which is a requirement for RTU.
Stop bits
Can be configured to be 1 or 2. The Modbus standard mandates that 2 stop bits are configured when
using no parity.
Parity
Changes parity mode to either none, even or odd. The default parity mode for Modbus is even parity.
Slave ID for RS-422 node
This setting is only valid for the combined RS-485 + RS-422 mode which allows operating one RS-422
device and a RS-485 bus one the same serial interface. This setting determines based on the slave ID
whether a Modbus message is transmitted onto the RS-485 bus or the RS-422 interface. Configure here
the slave ID of the RS-422 device.
Once you click Save the new settings are stored and applied instantly. A confirmation message is shown.
5.3.3 Remote restarting the device
You can perform a remote restart of the device from the web interface. A remote restart is similar to power
cycling the device. Possibly connected clients are disconnected and communication is interrupted until the
device has rebooted.
To perform a remote restart, click on the Configuration sub-menu and then click on the Restart menu
entry. This will open the device restart page as shown below:
Illustration 5.8: Restart device page
Click on the Restart button to perform a restart of the device. The restart is confirmed with the following
notification:
Illustration 5.9: Restart confirmation page
Please allow a few seconds before continuing working with the device as it has to fully start-up first, before
being able to respond to further web browser requests.
Note
After a remote restart a Watchdog reset alarm is shown on the device' home page. This is a
side-effect of the remote restart procedure and the alarm shall be ignored and cleared.
Page 28

22 UMSLMODGW-1006
Page 29

UMSLMODGW-1006 23
6.Decommissioning
Before disconnecting the unit please follow the rules in the section called “Safety Precautions”.
6.1 Disconnecting
1. Ensure that the system power and external supplies have been turned off.
2. Disconnect power supply plug.
3. Disconnect all I/O cables.
4. Remove the SL-MOD-GW from the DIN rail following the procedure described in Section 3.4,
“DIN rail mounting and removal”.
6.2 Disposal
This product must be disposed of at a specialized electronic waste recycling facility. Do not
dispose of in domestic waste.
Page 30

24 UMSLMODGW-1006
Page 31

UMSLMODGW-1006 25
AppendixA.Specifications
SL-MOD-GW Modbus/TCP Gateway
Interfaces
Ethernet 1
Serial ports 1, software configurable as either 1 x RS-232 or 1 x RS-485 or 1 x
RS-422
User interface
LED indicators Power (green), Ethernet link (green), 2 status (bi-color red/green)
Monitoring & configuration Web browser based
Diagnostic
High availability features Watchdog supervision, brown-out detection
Serial Port 1 RS-232 interface
Connector male 9-pin D-sub, DTE, EIA-574 pin-out
Physical layer EIA-232-F
Isolation non-isolated
Signals RXD, TXD, RTS, CTS, DTR, DSR, DCD, RI
Speed 300, 600, 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 19200, 57600, 115200 bps
Protocols Modbus RTU master
Serial Port 1 RS-485/RS-422 interface
Connector 3.81 mm 6-pin pluggable terminal block header
Physical layer EIA-485-A, 2-wire or 4-wire
Isolation non-isolated
Speed 300, 600, 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 19200, 57600, 115200 bps
Max. number of nodes 32
Protocols Modbus RTU master
Ethernet port
Connector 8-pin RJ-45 socket for Cat 5 UTP
Physical & Data Link Layer Layer IEEE 802.3i 10BASE-T
Isolation 1.5 kV galvanic
Speed 10 Mbit/s
Max. cable length 100 m (328 ft)
Ethernet frame types 802.3
Protocols Modbus/TCP slave, HTTP, IP, TCP, ARP
Concurrent connections 4 Modbus/TCP slave, 2 HTTP
Power supply
Connector 3.81 mm 2-pin pluggable terminal block header
Voltage 10-30 V DC
Current 30 mA typical @ 24 V DC
Intrinsic consumption 750 mW
Electromagnetic compatibility
Page 32

26 UMSLMODGW-1006
Emissions (radiated and conducted) AS/NZS CISPR 22 / EN 55022 (Class A)
Immunity EN 55024
Electrostatic discharge EN 61000-4-2
Radiated RF EN 61000-4-3
Fast transients EN 61000-4-4
Conducted RF EN 61000-4-6
Enclosure
Material Self-extinguishing PC/ABS blend (UL 94-V0)
Mounting 35 mm DIN rail (EN 60715)
Classification / Type rating IP 20 / NEMA Type 1
Cooling Convection
Environmental
Operating temperature 0 to 60 °C / 32 to 140 °F
Storage temperature -25 to 85 °C / -13 to 185 °F
Humidity rating 10 to 95% relative humidity, non condensing
Operating ambience Free from corrosive gas, minimal dust
Physical
Dimensions 101 x 22.5 x 120 mm / 3.98 x 0.886 x 4.72 in
Weight 0.12 kg / 0.265 lb
Compliance
Australia C-Tick
Europe CE, RoHS
USA FCC Part 15 (Class A)
Canada ICES-003 (Class A)
Page 33

UMSLMODGW-1006 27
A.1 Dimensions
101.0 mm
120.0 mm
3.98 in
4.72 in
0.89 in
22.5 mm
101.0 mm
3.98 in
Illustration A.1: Enclosure dimensions
Page 34

28 UMSLMODGW-1006
Page 35

UMSLMODGW-1006 29
Glossary
10BASE-T
10 Mbit/s twisted pair Ethernet standard.
Standardized in IEEE 802.3i
APIPA
Automatic Private IP Addressing
Class A
Class A equipment is that used in commercial or
light industrial environments.
DCE
Data communications equipment. DTE and
DCE devices have different pinouts for RS-232
connectors. A Modem for example is a DCE.
DIN rail
35 mm wide mounting bracket standardized in
DIN/EN 50022.
DTE
Data terminal equipment. DTE and DCE devices
have different pinouts for RS-232 connectors. A
PC for example is a DTE.
EIA-232
Standard for serial transmission of data between
two devices, also known as RS-232 and V.24.
EIA-422
ANSI/TIA/EIA-422 standard for serial
transmission of data between two devices, also
known as RS-422 and V.11.
EIA-485
ANSI/TIA/EIA-485 standard for serial
transmission of data between multiple devices,
also known as RS-485.
EIA-574
Standard for the pinout of serial D-sub connectors.
EMC
Electromagnetic compatibility
EMI
Electromagnetic interference
ESD
Electrostatic discharge. ESD can damage
electronic equipment.
Ethernet
The standard for local area networks developed
jointly by Digital Equipment Corp., Xerox, and
Intel. Ethernet is used as the underlying transport
vehicle by several upper-level protocols, including
TCP/IP.
Gateway
A network device that passes data between
different networks or fieldbusses.
Gateway address
The IP address of the gateway or router used to
access the Internet from the local are network.
IEEE
Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers
IP
Ingress Protection Rating standardized in IEC
60529. Standard for various grades of electrical
enclosures.
IP address
A numeric address used by computer hosts to
transmit and receive information over the Internet.
ISO
International Standards Organisation
MAC address
Every piece of Ethernet hardware has a unique
number assigned to it called it’s MAC address.
MAC addresses are administered and assigned
by the IEEE organization.
Modbus
Fieldbus protocol used in the process automation
industry. It uses a master and slave structure.
Originally developed by Modicon, now part of
Schneider Automation.
NEMA
National Electrical Manufacturers Association.
NEMA defines standards for various grades of
electrical enclosures.
Node
A communications device on the network.
PC/ABS
Polycarbonate-ABS. Widely used thermoplastic
material.
PLC
Programmable Logic Controller
RS-232
See EIA-232.
Page 36

30 UMSLMODGW-1006
RS-422
See EIA-422.
RS-485
See EIA-485.
Subnet mask
A numeric address used in conjunction with an
IP address to segment network traffic; used to
restrict transmissions to certain subnets.
Switch
A device that facilitates transmissions between
nodes in a star-formed network.
TCP/IP
Transport Control Protocol/Internet Protocol.
Connection-orientated transfer protocol.
Telnet
A network protocol (RFC 854) for character based
terminal access to remote machines.
UL 94
Plastics flammability standard released by
Underwriters Laboratories of the USA.
Page 37

UMSLMODGW-1006 31
Index
A
About, 18
Accumulative connections, 17
B
Baud rate, 20
Brown out reset, 16
C
cable
RS-232, 8
RS-422, 8
RS-485, 8
cable length
Ethernet length, 9
RS-232, 8
RS-485, 8
Class A, 5
connector
Ethernet, 9
location, 3
power, 7
RS-232, 8
RS-422, 7
RS-485, 7
CRC errors, 18
D
Data bits, 21
default IP address, 11
Device configuration data write failure, 16
Device out of memory, 16
device status register, 16
DIN rail
mounting, 6
removal, 6
Disconnecting, 23
Disposal, 23
E
electronic waste, 23
embedded web server, 15
EMC, 5
enclosure
DIN rail clip, 3
front cover, 3
mounting, 6
red hook, 6
removal, 6
Ethernet, 9, 19
settings, 19
F
faults, 16
features, 2
Firmware version, 18
G
Gateway address, 19
grounding, 5
H
Hardware version, 18
HyperTerminal, 11
I
Invalid frames, 18
IP
settings, 11, 19
IP address, 19
J
JavaScript, 15
L
LED, 3, 3
M
MAC address, 19
Modbus
settings, 20
status, 18
mounting, 6
rules, 6
N
nodes
maximum
RS-485, 7
P
Parity, 21
Physical layer, 20
pinout
Ethernet, 9
power, 7
RS-232, 8
RS-422, 7
RS-485, 7
power, 7
Product name, 18
R
recycling, 23
remote restart, 21
Page 38

32 UMSLMODGW-1006
removal, 6
Replies, 17
Requests, 17
Reset to factory defaults, 17
restart, 21
RJ-45, 9
RS-232, 8
RS-422, 7
RS-485, 7
run-time faults, 16
Rx time-outs, 18
S
Serial number, 19
settings
Ethernet, 19
IP, 11, 19
Modbus, 20
shield, 8, 8
shielding, 5
shock, 6
Slave ID for RS-422 node, 21
Specifications, 25
Stop bits, 21
storage, 5
Stub connections, 8
Subnet mask, 19
supply voltage, 7
T
TCP status, 17
temperature
operating, 6
terminal program, 11
termination
RS-422, 7
RS-485, 7
Transmission mode, 20
twisted pairs, 8
Tx time-outs, 18
U
Unpacking, 5
V
ventilation, 6
vibration, 6
W
Watchdog reset, 16
Watchdog reset alarm, 21
Page 39

UMSLMODGW-1006 33
References
Name: Weidmller
Company: Weidmller Australia Pty Ltd
Street Address: 43 Huntingwood Drive,
Postcode: 2148
Suburb: Huntingwood, NSW
Tel: +61 2 9671 9999
Fax: +61 2 9671 9900
Version: 1.0, October 2010
Software-Version: 1.6
Model: SL-MOD-GW
Description: Modbus/TCP Gateway
Document Type: User manual
IP-Address: 192.168.1.130
WebSite: www.weidmuller.com.au
Warenzeichen1: Ethernet is a trademark of Xerox Corporation.
Warenzeichen2: Weidmller® is a registered trademark of Weidmller
Interface GmbH & Co. KG
Page 40

34 UMSLMODGW-1006
 Loading...
Loading...