Page 1

MANUAL OF THE
SERIAL
COMMUNICATION
SSW-05
Series SSW-05
SERIAL INTERFACE
CODE 0899.4895 E/4
Page 2

Page 3
Series: SSW
-
05
0899.4895 E/4
email: astec@weg.com.br
MANUAL OF THE
SERIAL
COMUNICATION
SSW-05
Software: Version 2.1X
ATTENTION!
It is very important to
check if the software
version is the same as
indicated above.
WEG AUTOMAÇÃO
Av. Pref. Valdemar Grubba, 3000
89256-900 Jaraguá do Sul, SC – Brasil
Tel.(047)372-4000 – Fax(047)372-4020
Page 4

Page 5

_______ Summary _______
1 1 2
3
7 7 7 8 8 8 8 9 9
10 10 11 13 13 14 15 16 16 17 17
18
SAFETY
NOTICES
1
1.1 Safety Notices in the Manual.......................................
1.2 Safety Notices on the Product ....................................
1.3 Preliminary Recommendations....................................
INTRODUCTION
2
COMMUNICATION
INTERFACES
3
DEFINITIONS
4
TELEGRAM
EXAMPLES
5
2.1 About this Manual........................................................
2.2 About WEG Protocol....................................................
3.1 RS-485 Interface..........................................................
3.2 RS-232 Interface.........................................................
3.2.1 RS-232 Electrical Characteristics........................
3.2.2 Cares with RS-232..............................................
3.2.3 RS-232 Connections...........................................
3.2.4 Description of the Soft-Starter Serial Connector.
3.2.5 Definition of the RS-232 Cable............................
3.2.6 Description of the Master Connector (RJ)...........
3.2.7 Definition of the RS-232 PC Cable......................
3.2.8 Description of the PC (DB9) Connector...............
4.1 Used Terms.................................................................
4.2 Block Diagram..............................................................
4.3 Variable Standardization..............................................
4.4 Character Format.........................................................
4.5 Protocol........................................................................
4.5.1 Reading Telegram...............................................
4.5.2 Writing Telegram.................................................
4.6 Execution and Test Telegram......................................
4.7 Telegram Sequence ....................................................
4.8 Variable Code..............................................................
4.9 Times...........................................................................
5.1 Example 1....................................................................
5.2 Example 2....................................................................
3
5
18
Page 6

19 20 22
23 23
24 24 24 24 24 24
24 25 25 26 26 27 30 30 30 32 32 33 33 33
34
34
VARIABLES OF THE
SERIAL
COMMUNICATION
6
ERRORS AND SERIAL
COMMUNICATION
PARAMETERS
7
DETAILED
PARAMETER
DESCRIPTION
8
TROUBLESHOOTING
9
6.1.1 V00 Indication of the Equipment Model...................
6.1.2 V01 Indication of the Soft-Starter Status...................
6.1.3 V02 Indication of the Soft-Starter Errors...................
6.1.4 V03 Logic Command Selection.................................
7.1 Parameters related to the Serial Communication .......
7.2 Errors Related to the Serial Communication ...............
8.1 P000 – Access Parameter...........................................
8.2 P002 – Motor Current Indication (%)...........................
8.3 P003 – Motor Current Indication (A)...........................
8.4 P023 – Software Version.............................................
8.5 P030 – R Phase Current..............................................
8.6 P030 – S Phase Current..............................................
8.7 P030 – T Phase Current..............................................
8.8 P050 – Status Indication of the Motor Thermal
Protection .......................................................
8.9 P101 – Initial Voltage (% Un).......................................
8.10 P102 – Time of Acceleration Ramp (s)......................
8.11 P104 – Time of Deceleration Ramp (s)......................
8.12 P105 – Motor Current Setting (%).............................
8.13 P106 – Protection Configuration...............................
8.14 P204 – Load Factory Setting.....................................
8.15 P206 – Auto-Reset Time............................................
8.16 P215 – Keypad Copy Function..................................
8.17 P220 – HMI / (Trimpots and Dip Switch) Selection....
8.18 P264 – Programmable Digital Input DI 1...................
8.19 P277 – Programmable Relay Output (14/23 – 24)....
8.20 P295 – Rated Current of the Soft-Starter..................
8.21 P308 – Network Address...........................................
8.22 P313 – Action of the Serial Communication
Verification.........................................................................
8.23 P314 – Verification Time of the Serial
Communication..................................................................
Problem and Corrective Action.......................................... 35
19
24
Page 7
1
SAFETY NOTICES 1
This Manual contains all necessary information for the correct use of the Serial
This Manual has been written for qualified personnel with suitable training or technical
qualification to operate serial interfaces and their respective communication protoco ls.
1.1 SAFETY
NOTICES
IN THE MANUAL
1.2 SAFETY
NOTICES ON THE
PRODUCT
Communication of the SSW -05 Soft-Starter.
The following Safety Notices will be used in this Manual:
DANGER!
If the Safety Instructions are not strictly observed, it can lead
to serious of fatal injuries of personnel and/or equipment
damage.
ATTENTION!
Failure to observe the recommended Safety Procedures can
lead to material damage.
NOTE!
The text aims at to provide important information for the
correct understanding and proper product performance.
The following symbols may be attached to the product,
serving as Safety Notice:
High Voltages.
Components sensitive to electrostatic discharge.
Do not touch them
Mandatory connection to ground protection (PE).
Shield connection to ground.
Page 8
1 SAFETY NOTICES
2
1.3 PRELIMINARY
RECOMMENDATIONS
DANGER!
Only qualified personnel should plan or implement the
installation, startup, operation and maintenance of serial
interfaces.
Read this manual before attempt any installation and
operation of the Soft-Starter by following ca refully all safety
notices here indicated.
Please follow the safety instructions indicated in this Manual,
in the Soft-Starter Manual and/or defined by local
regulations.
If personnel injuries or equipment damages can occurs due
to motors driven by motor starters, please provide always the
required electromechanical safety devices.
If remote control (via serial interface) is used, please take all
required precautions to avoid personnel injuries and
machine and installations damages.
Failure to comply with these instruction may result in
personnel injury and/or equipment damage.
DANGER!
Always disconnect the equipment from the power supply
before open it.
ATTENTION!
The electronic boards are fitted with components sensitive to
electrostatic discharges. Never touch any electrical
component or connector directly. If necessary to do so, touch
before the properly grounded metallic frame or use a suitable
ground strap.
NOTE!
In general, communication networks are sensitive to
interference generated by other equipment. In this case,
please follow all recommended instructions.
Page 9
3
INTRODUCTION 2
2.1 ABOUT THIS
MANUAL
This Manual describes how to install, start-up, operate and
identify problems related do the serial interface of WEG Soft Starters.
For more information, training or services, please contact:
WEG Service:
WEG AUTOMAÇÃO
Tel. (0800) 475767
Fax: (047) 372-4020
NOTE!
If you need information or services, please make available
following data:
þ model of WEG product;
þ serial number and manufacturing date as indicated on
WEG product nameplate;
þ version of installed software.
2.2 ABOUT WEG
PROTOCOL
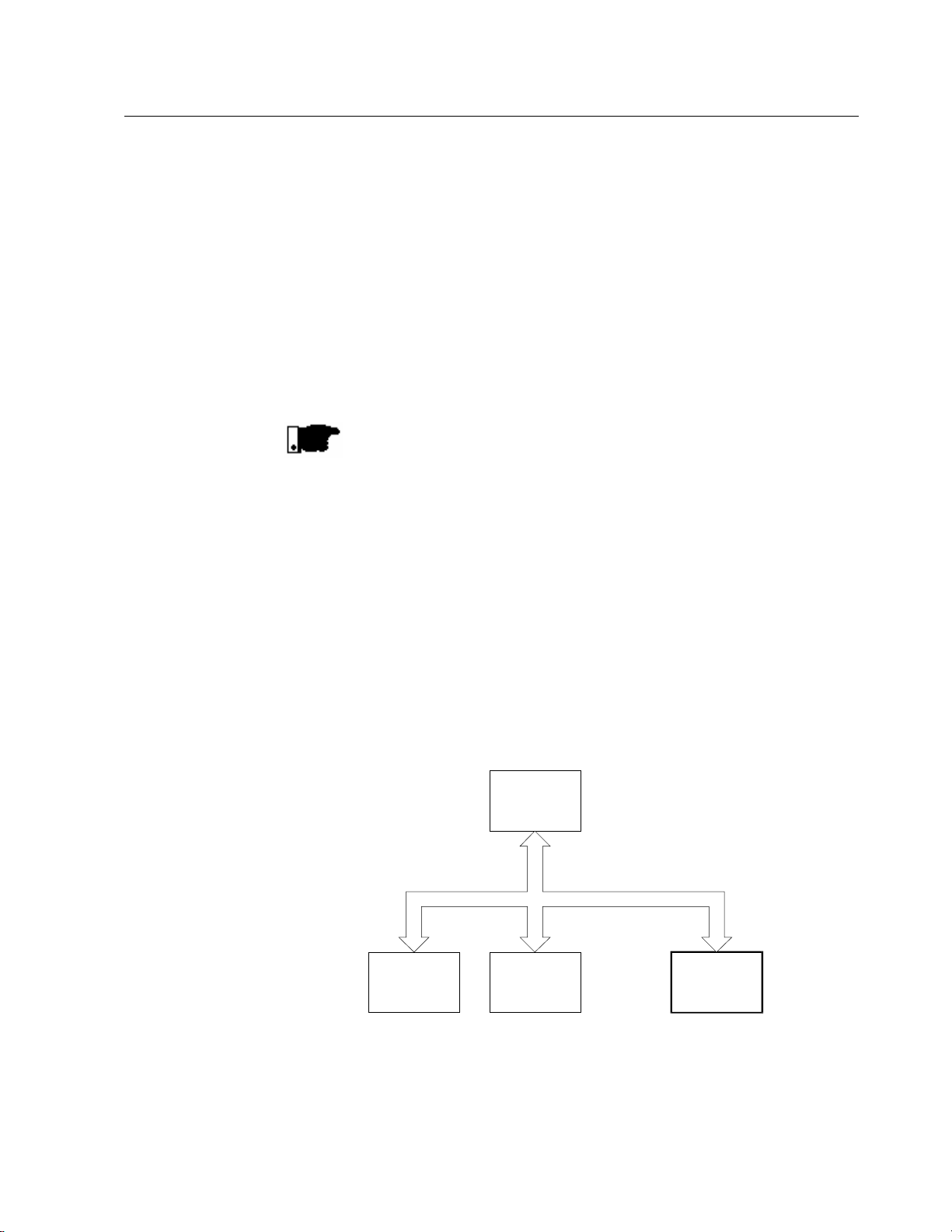
The main purpose of the serial network communication is
the physical connection of several equipment to one or more
masters connected to this network through only one or two
pair of wires:
Master
MESTRE
PC, CLP, etc.
Slave 1
ESCRAVO 1
(inverter)
(conversor)
Slave 2
ESCRAVO 2
(inverter)
(conversor)
. . .
Slave n
ESCRAVO n
(inverter)
(conversor)
n <= 30
WEG Soft-Starters are fitted with control software for the
transmission/reception of data through the serial interface to
enable the data reception sent by the master and the data
sending requested by the same.
Page 10

2 INTRODUCTION
4
The transfer rate is 9.600Bps, following an exchange
protocol, type question/answer, meeting ISO 1745 standard
for the data transmission in code.
The master is able to realize the following operations related
to each WEG equipment connected to the network:
þ Identification:
• Network number;
• Soft-Starter type (model);
• Software version.
þ Commands:
• general enabling/disabling;
• error reset.
þ Status Recognition:
• enabling/disabling;
• in acceleration;
• at rated voltage;
• in deceleration;
• in error.
þ Parameter Reading or Changing.
Typical examples of WEG network use:
• Supervisory monitoring at the same time several variables
of WEG Soft-Starters;
• PLC controlling the operation of several WEG SoftStarters WEG in an industrial process.
NOTE!
WEG protocol is the same for all WEG equipment, but the
logic command words, the basic variables and the
parameters can differ among equipment.
Page 11
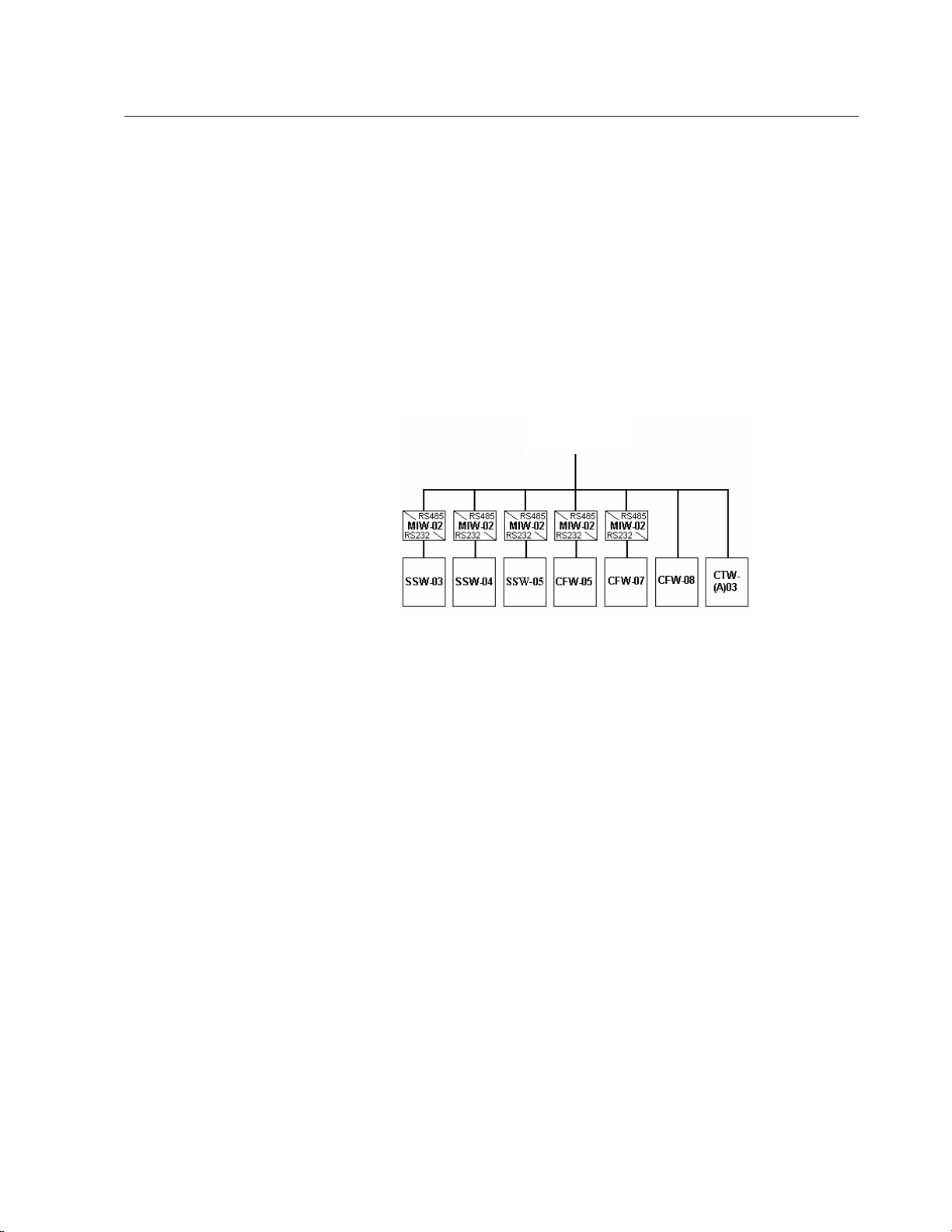
5
RS-485
COMMUNICATION INTERFACES 3
3.1 RS-485 INTERFACE
The physical connection between WEG Soft-Starters is
performed according to one of the standards below:
þ RS-232 point to point, up to 10m (32.8 ft);
þ RS-485 multipoint, with the use of the MIW-02 serial
interface module, with galvanic insulation, up to 1000m
(3280 ft).
For the serial communication of the Soft-Starters at WEG
network.
WEG Network
þ The interface allows the interconnection of up to 30 WEG
Soft-Starters to one master, attributing to each WEG
equipment one address (1 to 30) that has to be set.
þ In addition to these 30 addresses, two additional
addresses are at disposal to perform special tasks:
• Address 0: all WEG Soft-Starters are inquired,
independently of its address. On order to prevent shortcircuits in the interface lines, only one Soft-Starter can be
connected to the network (point-to-point).
• Address 31: a command can be transmitted to all SoftStarters on the network simultaneously, without
acceptance recognition.
Page 12
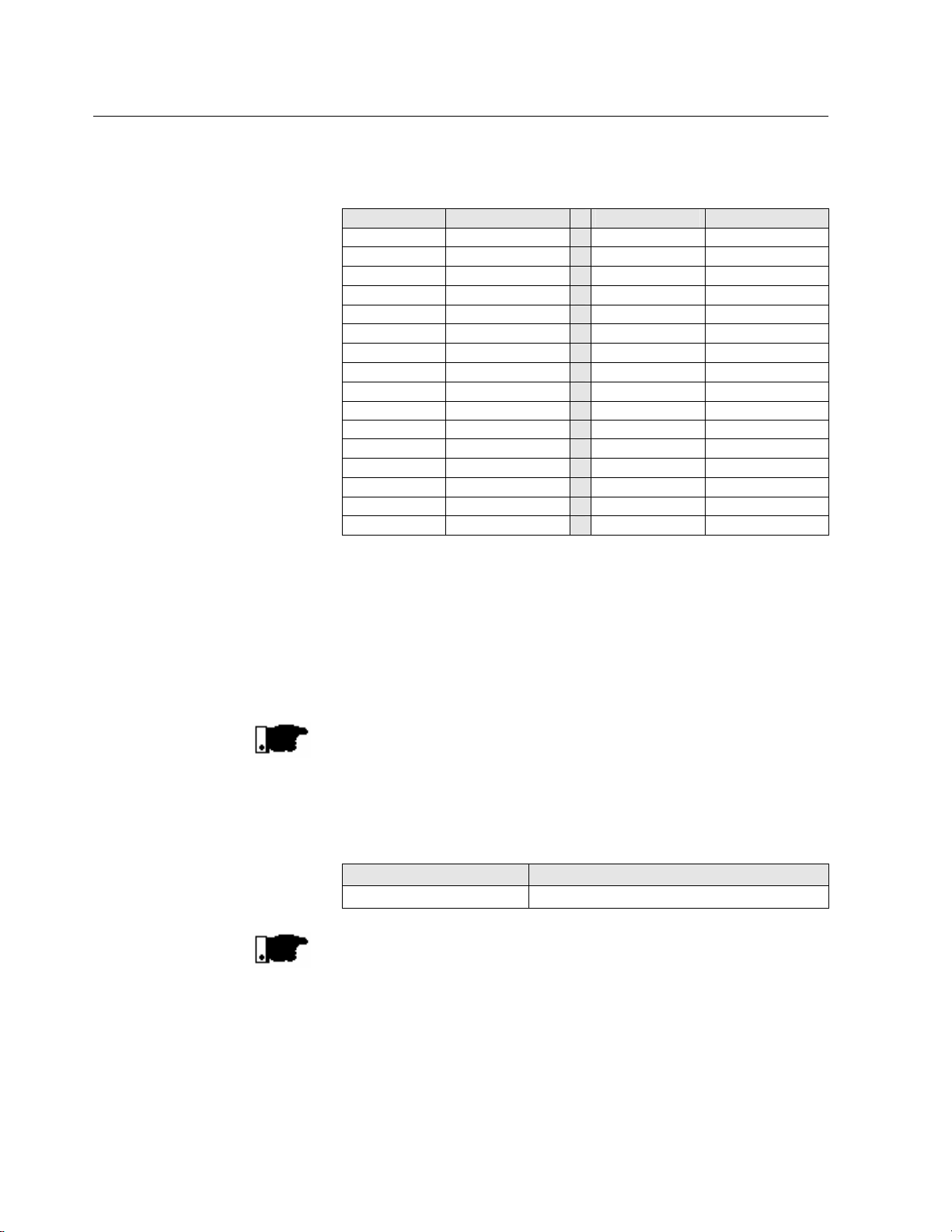
3 COMMUNICATION INTERFACES
6
þ List of addresses and corresponding ASCII characters:
Address ASCII Address ASCII
0 @ 16 P
1 A 17 Q
2 B 18 R
3 C 19 S
4 D 20 T
5 E 21 U
6 F 22 V
7 G 23 W
8 H 24 X
9 I 25 Y
10 J 26 Z
11 K 27 [
12 L 28 \
13 M 29 ]
14 N 30 ^
15 O 31 _
þ The connection between the network participants is
realized through a pair of wire.
þ The signal levels are according to EIA STANDARD RS -
485 with differential receivers and transmitters.
NOTE!
WEG SSW-05 Soft-Starter is only fitted with the RS-232
serial interface, thus requiring the use of a MIW-02 serial
interface module, when a RS-485 serial interface is applied.
Module Item WEG
MIW-02 417100543
NOTE!
If master is fitted with only one RS-232 standard serial
interface, you have to apply the serial MIW-02 interface
module, RS-232/RS-485, if fitted with RTS signal, Request
To Send. If the Master is not fitted with the RTS signal, you
must apply a module that is able to generate the RTS signal.
For more details, contact WEG.
Page 13
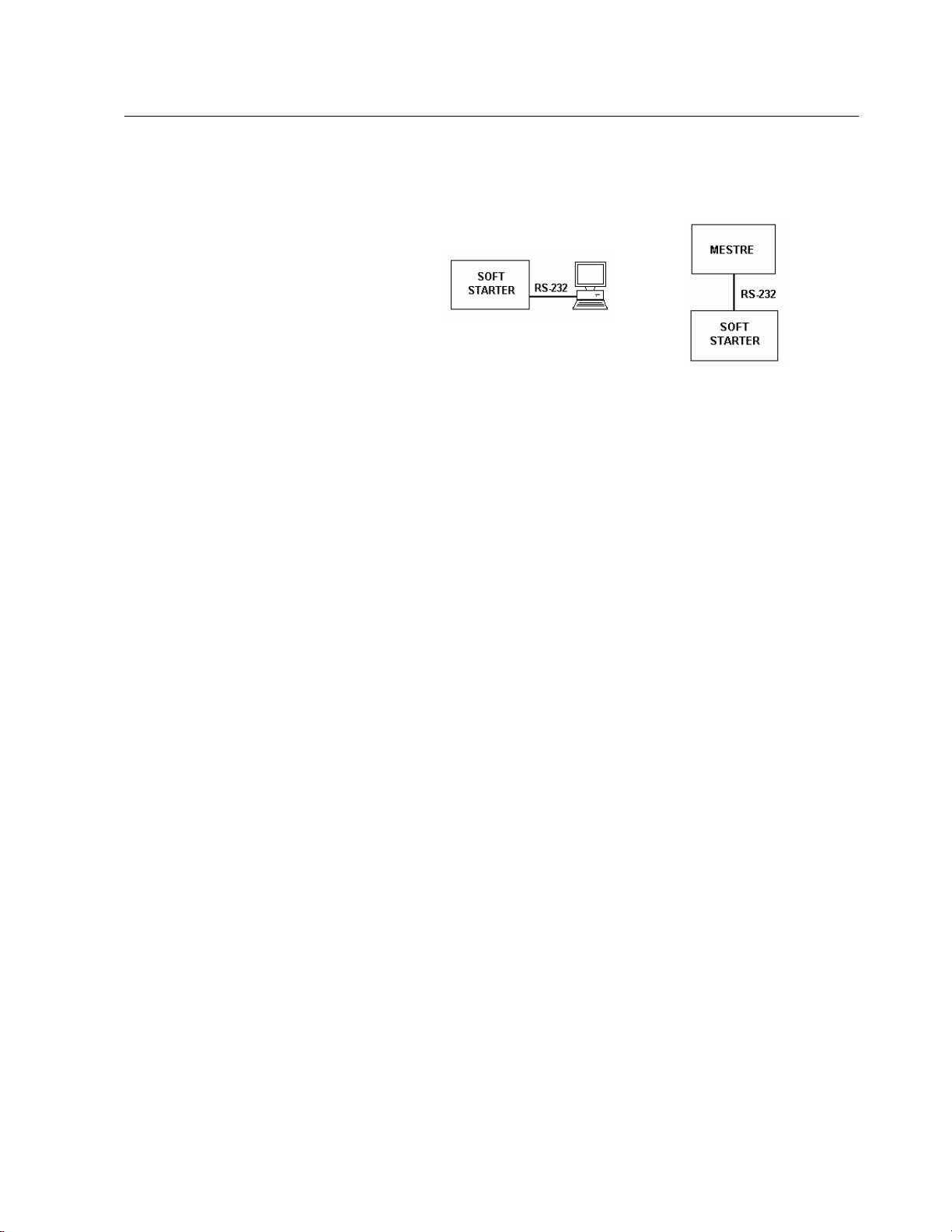
7
COMMUNICATION INTERFACES 3
3.2 RS-232 INTERFACE
For the point-to-point communication with WEG Soft-Starters.
þ In this case we have the connection of a Master to a Soft-
Starter WEG.
þ The logical levels meet EIA STANDARD RS-232C that
determines the use of balanced signals.
þ Use a connection cable for the RS-232 interface.
3.2.1 RS-232 Electrical
Characteristics
þ RS-232:
• Standard: EIA Standard RS-232C.
• Transmission speed: 9.600Bps.
• Max. Cable length: 10 m (32.8 ft).
þ Receiver:
Max. Input voltage: ± 25V;
Input resistance: > 3KΩ
Level 1 (MARK): < -3V;
Level 0 (SPACE): > +3V.
þ Transmitter:
Current limitation: ~ 10mA;
Output voltage at level 1: < -7V (RL = 3K);
Output voltage at level 0: > +7V (RL = 3K).
3.2.2 Cares with
RS-232
þ Ensure that the interface is not isolated against the
internal electronics of the equipment to which is
connected.
þ Thus you must plan carefully the wiring location by
separating it at least 10 cm (0.33 ft) from the power
wiring.
þ It is also recommended to install the master as near as
possible to RS-232 serial interface of WEG Soft-Starter.
Page 14

3 COMMUNICATION INTERFACES
8
TERMINAL
SYMBOL
DESCRIPTION
1 +5V
+5V
±5%
4 Rx Data recepti
on
6 Tx Data transmission
Length
WEG Item
Cable of serial RS
-
232
with 0.17m (0.56ft)
0307.4790
Cable of serial RS
-
232 with 1m (3.28ft)
0307.4820
Cable of serial RS
-
232 with 2m (6.56ft)
0307.4838
Cable of s
erial RS
-
232 with 3m (9.84ft)
0307.4846
TERMINAL
SYMBOL
DESCRIPTION
1 Rx Data reception
4 GND
0V
6 nc Not connecte
d
Connector of
Connector of
3.2.3 RS-232
CONNECTION
þ The RS-232 must be connected directly point-to-point.
þ There are two standard WEG cables, as described below.
3.2.4 Description of the
Soft-Starter Serial
Connector
3.2.5 Definition of the
RS-232 Cable
þ SSW-05 connector (Serial Port).
2 RTS Request To Send
3 GND 0V
5 GND 0V
þ The used cable is the standard one for WEG serial
communication, equipment x serial HMI of WEG
inverters (Human Machine Interface).
the SSW-05
Serial Port
the Master
Serial Interface
3.2.6 Description of the
Cable of serial RS-232 with 0,23m (0.75ft) 0307.4803
Cable of serial RS-232 with 0,32m (1.05ft) 0307.4811
þ Master connector with RJ.
Master Connector
(RJ)
2 GND 0V
3 Tx Data transmission
5 nc Not connected
Page 15

9
Length
WEG Item
Cable of the serial RS
-
232 PC with 3m (9.8
ft) 0307.5460
TERMINAL
SYMBOL
DESCRIPTION
1
Not connected
4
Not connected
5 0V
6
Not connected
7
Not connected
8
Not con
nected
9
Not connected
Connector of
Connector of the
3.2.7 Definition of the
RS-232 PC Cable
COMMUNICATION INTERFACES 3
þ The cable to be used is the standard one for WEG serial
communication, equipment x PC.
þ It must be connected directly to the serial PC interface.
3.2.8 Description of the
PC (DB9)
Connector
the SSW-05
Serial Port
PC Serial Interface
þ Serial Connector of the PC (DB9).
2 Data reception
3 Data transmission
NOTE!
Take care with equipment connected to different grounds,
since there can be different voltages among them, and as
they are connected through their serial interfaces they can be
damaged.
ATTENTION!
Do not use the neutral conductor for grounding purpose.
For long distances, use always serial interfaces at RS-485.
Page 16

4 DEFINITIONS
10
4.1 USED TERMS
4.2 BLOCK DIAGRAM
The protocol used for the serial communication between
WEG equipment.
þ Parameters: are those existing in WEG equipment, which
visualization or alteration is possible through the HMI
(Human x Machine Interface) or SuperDrive Software;
þ Variables: are values that have specific functions on
WEG equipment and that can be read and, in some
cases, changed by the Master;
þ Basic variables: are those that can be accessed only
through the serial interface.
Page 17

11
The variable exchange is subject to the following
4.3 VARIABLE
STANDARDIZATION
Value and Function Table of the Parameter of V2.1X software version to implement:
changing, and commands via serial communication.
Parameter
(2)
P000
P002
P003
P023
P030
P031
P032
P050
Parameter
P101
P102
P104
(1)
P105
(1)
P106
(1)
P204
P206
Parameter Function
Parameter Access
Motor Current Indication (%)
Motor Current Indication (A)
Software Version 24
R Phase Current
S Phase Current
T Phase Current
Status Indication of the motor
overload protection
Parameter Function
(Reading and Writing)
Time of the Acceleration Ramp
Time of the Deceleration Ramp
Motor Current Setting 30 ... 100 (%) 100 26
Protection Configuration
Load Factory Setting
Auto-Reset Time 1 ... 1200 s 900 30
DEFINITIONS 4
standardization.
Range of the
(Reading)
internal values
0 ... 4, 6... 9999
= Read
5 = Alteration
000,0 ... 999,9
(% In)
000,0 ... 999,9
(A)
000.0 ... 999,9
(A)
000.0 ... 999,9
(A)
000.0 ... 999,9
(A)
0 ... 250
250 = error
Range of the
internal values
Initial voltage 30 ... 80 (% Un) 30 25
1 ... 20 (s) 10 25
0 ... 20 (s) 0 = off 26
0 ... 3F
Hexadecimal
0 = No function
1 = No function
2 = No function
3 = No function
4 = No function
5 = Load factory
default
Factory
Setting
User
Setting
0 24
24
24
24
24
24
24
Factory
Setting
1F
User
Setting
Hex.
0
Page
Page
27
30
Page 18

4 DEFINITIONS
12
Parameter
(1)
P215
(1)
P220
(1)
P264
(1)
P277
(1) (2)
P295
P308
P313
P314
Parameter Function
(Reading and Writing)
Keypad Copy Function
HMI / (Trimpots and Dip Switch)
Selection
Programmable Digital Input
DI 1
Programmable relay output
(14/23 - 24)
Rated current of the Soft-
Starter
Network Address 1 ... 30 1 33
Action of the serial
communication verification
Verification Time of the Serial
Communication
Range of the
internal values
0 = Off
1 = Copy
(SSW -> keypad)
2 = Paste
(keypad -> SSW)
0 = Trimpots and
Dip Switch
1 = HMI
0 = Not used
1 = Enable /
Disable
2 = External
Fault
1 = Full voltage
2 = Error
3 = Serial Com.
0 = 3 A
1 = 10 A
2 = 16 A
3 = 23 A
4 = 30 A
5 = 45 A
6 = 60 A
7 = 85 A
1 = only Error
2 = ramp
disabling
3 = General
disabling
4 = P264 → 1
0 ... 5 (s)
0 = oFF
Factory
Setting
User
Setting
0 30
0 32
1
32
1 33
According
to the
model
33
1
0 = off
Page
34
34
(1)
These parameters can be changed only with stopped motor.
(2)
These parameters are not changed through the function “Loads Parameters with Factory Setting” (P204).
Page 19

13
according to ISO 646 and complemented for even parity
possible.
4.4 CHARACTER
FORMAT
4.5 PROTOCOL
DEFINITIONS 4
þ 1 start bit;
þ 8 information bits [they codify the text characters and
transmission characters, remove from the 7 bits code,
(eight bit)];
þ 1 stop bit;
After the start bit, follows the less significant bit:
start
bit
B2 B3 B4 B5 B6 B7 B8B1START
8 bits of information
STOP
stop
bit
The transmission protocol meets ISO 1745 standard for data
transmission in code.
Are used only text character sequences without headers.
The errors monitoring is made through transmission related
to the parity of the individual 7 bit characters, according to
ISO 646.
The parity monitoring is made according to DIN 66219 (even
parity). The master uses two type of messages:
þ READING TELEGRAM: for inquiring on the Soft-Starter
variable content;
þ WRITING TELEGRAM: to c hange the variable content or
to send controls to the Soft-Starters.
Note: No transmission between two inverters is
The master has the control of the bus access.
Page 20

4 DEFINITIONS
14
4.5.1 Reading
Telegram
The telegram permits the receive from the Soft-Starter the
content corresponding to the inquiry code.
In the answer telegram, the Soft-Starter transmits the data
requested by the master and it finishes the transmission with
EOT.
1) Master
1) Mestre:
EOT ADR ENQ
CÓDIGO
CODE
2) Soft Starter:
ADR STX = ETX BCC
CÓDIGO VAL
CODE
TEXT
TEXTO
þ Format of the reading telegram:
• EOT: control character of End Of Transmission;
• ADR: inverter address (ASCII@, A, B, C, ...) (ADRess);
• CODE: address of the 5-digit variable coded in ASCII;
• ENQ: control character of ENQuiry (enquiry)
þ Format of the Soft-Starter answer telegram:
• ADR: 1 character – Soft-Starter address;
• STX: control character - Start of TeXt;
• TEXT: consists in:
• CODE: Address of the variable;
• “ = “: separation character;
• VAL: 4 digit value (HEXADECIMAL);
• ETX: control character - End of TeXt;
• BCC: CheCksum Byte - EXCLUSIVE OR all the bytes
between STX (excluded) and ETX (included).
NOTE: In some cases there may be a soft-starter answer
with:
ADR
NAK
Page 21

15
DEFINITIONS 4
4.5.2 Writing Telegram
This telegram sends data to the Soft-Starter variables.
The Soft-Starter answers by indicating if the data have been
accepted or not.
1) Master
1) Mestre:
1) Mestre:
EOT ADR STX = ETX BCC
2) Soft Starter:
ADR ACK ADR NAK
CÓDIGO VAL
CODE
TEXTO
TEXT
OU
or
þ Format of the Writing Telegram:
• EOT: control character of End Of Transmission;
• ADR: Soft-Starter address;
• STX: Control Character of Start of TeXt;
TEXT: consists in:
• CODE: variable address;
• “ = “: separation character;
• VAL: 4 digit HEXADECIMAL value
• ETX: control character of End of TeXt;
• BCC: CheCksum Byte - EXCLUSIVE OR all bytes
between STX (excluded) and ETX (included).
þ Format of the Soft-Starter answer telegram:
Acceptance:
• ADR: Soft-Starter address;
• ACK: ACKnowledge control character;
Not acceptance:
• ADR: Soft-Starter address;
• NAK: Not AcKnowledge control character.
This means that the data were not accepted and the
addressed variables continue with its old value.
Page 22

4 DEFINITIONS
16
4.6 EXECUTION AND
TEST TELEGRAM
4.7 TELEGRAM
SEQUENCE
The Soft-Starters and the master test the telegram syntax.
The answers for the respective verified conditions are
defined as follows:
þ Reading Telegram:
• No answer: with wrong telegram structure, control
characters were received incorrectly of Soft-Starter
address in wrong;
• NAK: CODE corresponding to a no-existing variable or
write only variable;
• TEXT: with valid telegrams.
þ Writing Telegram:
• No answer: with wrong telegram structure, control
characters received incorrectly or wrong Soft-Starter
address;
• NAK: code corresponding to a non-existing variable,
wrong BCC (checksum byte), read-only variable, VAL out
of permitted range for the concerned variable, operation
parameter out of the alteration mode;
• ACK: with valid telegrams;
The Soft-Starters process the telegrams in determined
intervals. Therefore, a larger pause than the times of the
involved telegrams should be ensured between two
telegrams addressed to the same Soft-Starter (see item
4.9).
Page 23

17
address and the basic variables formed by 5 digits (ASCII
Starters WEG is
4.8 VARIABLE CODE
DEFINITIONS 4
The filed designated with CODE contains the parameter
characters) as follows:
Equal to zero (0)
4.9 TIMES
þ The transmission speed of WEG Soft-
9600bps.
þ WEG protocol times:
Data reception/transmission speed is 9600bps 1bit / 104.2us
Each data word has 10bits 1.04ms
An enquiry telegram has 8 words 8.33ms
An answer telegram to an enquiry has 14 words 14.58ms
A changing telegram has 15 words 15.63ms
An answer telegram to a changing has 2 words 2.08ms
Updating to a requested variable (with prompt answer) 22.91ms
Changing of a write variable (with prompt answer) 17.71ms
Page 24

5 TELEGRAM EXAMPLES
18
5.1 EXAMPLE 1 þ Changing of the rated SSW-05 current (P295) to 4 = 30A,
at the Soft-Starter 7 (“>” = SSW-05).
5.2 EXAMPLE 2 þ Output Current Reading of (P002) of the Soft-Starter 10,
by supposing that the same current was equal to 100.0%
of In at the moment of the enquiry (“>” = SSW-05).
Page 25

VARIABLES OF THE SERIAL COMMUNICATION 6
19
0 =
0 =
0 =
0 =
0 =
0 =
0 =
0 =
0 =
independently of the P294 programming (DI 1 programmable
6.1 BASIC VARIABLES
6.1.1 V00
6.1.2 V01
LSB
MSB
(code 00>00)
þ Indication of the equipment model.
þ Read Variable;
(code 00>01)
þ Indication of the Soft-Starter status.
þ Read variables which bits have the following meaning:
0 0 = disabled 1 = enabled
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
general disabled 1 = general enabled
reserved
not used 1 = at acceleration
reserved
not used 1 = at rated voltage
reserved
not used 1 = at deceleration
DI 1 opened 1 = DI 1 closed
reserved
reserved
reserved
relay output disabled 1 = relay output enabled
not used 1 = with hardware error
without power supply 1 = with power supply
without error 1 = with error
NOTE!
The bit 8 of V01 indicates the status of the DI 1 digital input,
digital input).
Page 26

6 VARIABLES OF THE SERIAL COMMUNICATION
20
6.1.3 V02
Errors:
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
MSB LSB
Error code: hexadecimal error number
Ex.: E03 Ü 03H
E06 Ü 06H
E10 Ü 0AH
(code 00>02)
þ Indication of the Soft-Starter errors.
þ Read variable which bits have following meaning:
Serial error (byte-high)
Hardware error (byte-low)
Serial Error Hardware error
Page 27

VARIABLES OF THE SERIAL COMMUNICATION 6
21
Error code and description:
DISPLAY DESCRIPTION
E03
E05
E06
E10
E2x
E22
E24
E25
E26
Phase loss
Output overload (Ixt function)
External fault
Error in the copy function
Serial communication error
Longitudinal parity fault
Parameterization fault
Variable or parameter not existing
Expected value out of the allowed limits
E27
E29
E31
E63
E64
E66
E67
E70
E71
E72
E73
E75
Writing attempt in a read only variable or logical control disabled
Error of the cyclic serial communication interrupted
Keypad conection fault
Locked rotor
Thyristor overload
Overcurrent
Incorrect phase sequence
Undervoltage in the control supply
Internal By-pass relay contact is open
Overcurrent before the By-pass
Overcurrent of the SSW-05 By-pass relay
Frequency out of tolerance
Page 28

6 VARIABLES OF THE SERIAL COMMUNICATION
22
0 =
0 =
0 =
0 =
1 =
1 =
1 =
6.1.4 V03
LSB
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8 1 = enabling/disabling
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
MSB
(code 00>03)
þ Logic command selection.
þ Write variable, whose bits have following meanings:
disabling 1 = enabling
general disabling 1 = general enabling
reserved
reserved
opens relay output
contact
reserved
reserved
Not used 1 = reset
general enabling/disabling
reserved
reserved
opens/closes relay output contact
reserved
reserved
Soft-Starter “ reset “ when in error
þ BYTE HIGH (8-15): desired action mask. The
corresponding bit should be set to 1, so the action
happens.
þ BYTE LOW (0-7): logical level of the desired action.
NOTE!
Reset acts only if Soft-Starter has hardware error.
1 = closes relay output
contact
Page 29

23
7.1 PARAMETERS
RELATED TO
THE SERIAL
COMMUNICATION
7.2 ERRORS RELATED
TO THE SERIAL
COMMUNICATION
ERROS E PARÂMETROS DA SERIAL 7
þ P264 - Commands via HMI and Serial or via Digital
Inputs.
þ P308 – Address of the Soft-Starter at the communication
network.
þ P313 – Action of the Serial Communication Verification.
þ P314 – Time of the Serial Communication Verification.
þ They do not disable WEG Soft-Starters;
þ They do not disable the defective relay;
þ They are informed in the word of the logical status.
Fault Types:
• E22: longitudinal parity fault (BCC);
• E24: parameterization fault;
• E25: variable or parameter not existing;
• E26: expected value out of the permitted limits;
• E27: writing attempt in a read only variable or logical
control disabled;
• E29: error of the cyclic serial communication interrupted.
Note:
These errors can be noted by reading the status variable of
WEG equipment.
NOTE!
The fault E29 can disable the Soft-Starters.
This protection is used in installations, where the Soft-Starter
has to take a decision in case of a communication fault
between the master and the Soft-Starter.
NOTE!
Please take care of the function incompatibilities between the
parameters as indicated in WEG Soft-Starter Manual.
Page 30

8 DETAILED PARAMETER DESCRIPTION
24
8.1 -
8.2 -
8.3 -
8.4 -
8.5 -
8.6 -
8.7 -
8.8 -
P000 – Access
Parameter
P002 – Motor
Current Indication
(%)
P003 – Motor
Current Indication
(A)
P023 – Software
Version
P030 – R Phase
Current
P023 – S Face
Current
P023 – T Face
Current
P050 – Status
Indication of the
Motor Thermal
protection
þ Releases the access to change the parameter values.
þ The password is 5.
þ Indicates the In-% output current of the Soft-Starter.
þ Accuracy of ± 10% @ 1xIn of the SSW-05.
þ Indicates directly in A the Soft-Starter output current.
þ Is necessary to program P295 correctly. This is important
in the correct indication value in amperes
þ Accuracy of ± 10% @ 1xIn of the SSW-05.
þ Indicates the version of the software installed in the CPU.
þ It indicates the current of the R Phase.
þ Accuracy of ± 10% @ 1xIn of the SSW-05.
þ It indicates the current of the R Phase.
þ Accuracy of ± 10% @ 1xIn of the SSW-05.
þ It indicates the current of the T Phase.
þ The indicated value is estimated from the instantaneous
current of the R and S Phases.
þ Indicates in percentage the status of the thermal motor
protection (0 ... 250). 250 is the point where the thermal
motor protection is activated, E05.
Page 31

25
8.9 - P101 – Initial
Voltage (%Un)
8.10 - P102 – Time of the
Acceleration Ramp
(s)
DETAI LED PARAMETER DESCRIPTION 8
þ It sets the start voltage (%Un) that will be applied to the
motor according to Figure 8.1.
þ When P220 = 0, the parameter content indicates the
value that has been set through the trimpot. When the
trimpot has been set to the maximum value, the value
indicated at the Parameter may be lower than expected.
This is due to mechanical limits variations. The
parameter content cannot be changed through the
keypad when P220 = 0.
þ With P220=1, the content of the parameter indicates the
value programmed through the communication or HMI.
þ It defines the ramp time of the voltage increment, as
shown in Fig. 8.1.
þ When P220 = 0, the parameter content indicates the
value that has been set through the trimpot. When the
trimpot has been set to the maximum value, the value
indicated at the Parameter may be lower than expected.
This is due to mechanical limits variations. The
parameter content cannot be changed through the
keypad when P220 = 0.
þ With P220=1, the content of the parameter indicates the
value programmed through the communication or HMI.
NOTE!
Due to the back-EMF (electromotive Force) generated by the
motor, motors without load or with small loads will have a
shorter acceleration time than the time that has been
programmed at P102.
Page 32

8 DETAILED PARAMETER DESCRIPTION
26
8.11 - P104 – Time of the
Deceleration
Ramp (s)
8.12 - P105 – Motor
Current Setting (%)
þ Used on pump application.
þ Defines the ramp time of the voltage decrement
þ When P220 = 0, the parameter content indicates the
value that has been set through the trimpot. When the
trimpot has been set to the maximum value, the value
indicated at the Parameter may be lower than expected.
This is due to mechanical limits variations. The
parameter content cannot be changed through the
keypad when P220 = 0.
þ With P220=1, the content of the parameter indicates the
value programmed through the communication or HMI.
NOTE!
This function is used to delay the normal deceleration time of
a load and in that way to not force a shorter time than that
imposed by the own load.
þ It sets the motor current in percent relating to the rated
Soft-Starter current.
þ The indica ted value is related directly to the activation
levels of the following motor protection devices: phase
loss, overload, overcurrent and locked rotor.
þ When P220 = 0, the parameter content indicates the
value that has been set through the trimpot. When the
trimpot has been set to the maximum value, the value
indicated at the Parameter may be lower than expected.
This is due to mechanical limits variations. The
parameter content cannot be changed through the
keypad when P220 = 0.
þ With P220=1, the content of the parameter indicates the
value programmed through the communication or HMI.
Page 33

27
8.13 - P106 – Protection
configuration
Example:
P106 = 13 Hex
1 - Enabled
1 - Enabled
0 - Disabled
0 - Disabled
1 - Enabled
0 - Disabled
13Hex = 010011bin
DETAI LED PARAMETER DESCRIPTION 8
þ With P220=0, the content of the parameter indicates the
value programmed through Dip Switch. In this case the
alteration of the content of the parameter through HMI is
not possible.
þ With P220=1, the content of the parameter indicates the
value programmed through the communication or HMI.
þ It configures the protections that are enabled.
þ The value is indicated as Hexadecimal value. Please find
below the protection and the corresponding bit.
LSB
0 Overcurrent
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8 -
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
MSB
Phase loss
Incorrect phase sequence
Locked rotor
Motor overload
Automatic reset
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- Overcurrent
- Phase loss
- Incorrect phase sequence
- Locked rotor
- Motor overload
- Automatic reset
Page 34

8 DETAILED PARAMETER DESCRIPTION
28
þ The Table below shows the combination of the enabled
protections and the corresponding value to be
programmed at P106.
Protection Configuration
Value
programmed
at P106
(hexadecimal)
Automatic Reset
Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
Motor Overload
Stall
Incorrect
Phase sequence
Phase Loss
þ
þ þ
þ
þ
4
þ þ
þ þ þ
þ
þ
þ
þ
þ þ
þ þ
8
þ
þ þ
C
þ þ þ
þ þ þ þ
þ
þ
þ
þ
þ
þ
þ
þ
þ þ
þ þ
þ þ
þ þ
þ þ þ
þ þ þ
10
þ
þ
þ þ
þ þ þ
18
þ
þ þ
14
þ
þ þ
1C
þ þ þ þ
Overcurrent
þ
2
þ
6
þ
A
þ
E
þ
12
þ
16
þ
1A
þ
1E
1
3
5
7
9
B
D
F
11
13
15
17
19
1B
1D
Page 35

29
DETAI LED PARAMETER DESCRIPTION 8
Protection Configuration
Value
programmed
at P106
(hexadecimal)
Automatic Reset
Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
þ
þ
þ
þ
þ
þ
þ
þ
þ
þ
þ
þ
þ
þ
þ
þ
þ þ
þ þ
þ þ
þ þ
þ þ
þ þ
þ þ
þ þ
þ þ þ
þ þ þ
þ þ þ
þ þ þ
þ þ þ þ
þ þ þ þ
þ þ þ þ þ
þ þ þ þ þ þ
Motor Overload
Stall
Incorrect
Phase sequence
Phase Loss
Overcurrent
þ þ þ þ þ
20
þ
þ
þ
þ
þ þ
þ þ
þ þ þ
þ þ þ þ
30
þ
þ
þ þ
þ þ þ
þ
þ
þ þ
þ þ þ
28
38
þ
þ þ
þ
þ þ
þ
þ þ
þ
þ þ
24
2C
34
3C
þ
22
þ
26
þ
2A
þ
2E
þ
32
þ
36
þ
3A
þ
3E
1F
21
23
25
27
29
2B
2D
2F
31
33
35
37
39
3B
3D
3F
þ = proteção habilitada
Page 36

8 DETAILED PARAMETER DESCRIPTION
30
8.14 - P204 - Load
Factory Setting
8.15 - P206 – Auto-Reset
Time
8.16 - P215 – Keypad
Copy Function
Note: The Keypad
Copy Function is
only available when
using HMI-SSW05RS
þ Programs all parameters to the standard factory default,
when P204=5.
þ The parameters P000 and P295 are not changed when
the factory default parameters are loaded through
P204=5.
þ When any fault is detected, excepting E10, E24, E29,
E31 e E67, the Soft-Starter SSW-05 can cause an
automatic reset after the time programmed at P206 has
elapsed
þ If after an “auto-reset” the same fault is repeated three
times consecutively, the Auto-Reset function will be
disabled. A fault is considered consecutive if it happens
again within 30 second after an auto-reset has been
executed.
þ This is fault is repeated four times consecutively, it will be
displayed permanently and the Soft-Starter will be
disabled.
þ Auto-Reset Enable/Disable is executed through the Dip
Switch (Man Auto) or by means of P106 and P220.
þ The keypad copy function is used to transfer the content
of the parameters from one SSW to another.
P215 Action Notes
0 Off -
1
2
(SSW -> Keypad)
(Keypad -> SSW)
Copy
Paste
Transfers the current
parameter values of the SSW
to non volatile memory
(EEPROM) of the HMISSW05-RS Keypad. The
current SSW parameters are
not changed.
Transfers the content of the
non volatile memory of the
keypad (EEPROM) to the
current SSW parameters.
Page 37

31
DETAI LED PARAMETER DESCRIPTION 8
þ Procedure is as follows:
1. Connect the keypad (HMI-SSW05-RS) to the inver ter
from which the parameters will be copied (SSW A –
source Soft-Starter).
2. Set P215=1 (copy) to transfer the parameter values
from the SSW A to the keypad. Press key.
During running of the copy function, display will show
. P215 resets automatically to 0 (Off) after
transfer has been completed.
3. Disconnect the keypad from the SSW (A).
4. Connect the same keypad to the SSW to which the
parameters will be transferred (SSW B – target SoftStarter).
5. Set P215=2 (paste) to transfer the content of the
keypad (EEPROM has the SSW A parameters) to
SSW B. Press the key. While the keypad is
running the paste function, the display shows ,
an abreviation for paste. When P215 returns to 0, the
parameter transfer has been concluded. Now SSWs
A and B will have the same parameter values.
To copy the parameter content of the SSW A to other
SSW(s), repeat steps 4 to 5 above.
Fig. 8.2 – Copying the parameters from the SSW A to the SSW B, by using the
Copy Function and the HMI-SSW05-RS keypad
Page 38

8 DETAILED PARAMETER DESCRIPTION
32
8.17 - P220 –
HMI / (Trimpots
and Dip Switch)
Selection
8.18 - P264–
Programmable
Digital Input DI 1
þ It configures the operation mode of the Soft-Starter, in
“Trimpot and Dip Switch” mode or “HMI” mode.
0 - “(Trimpot and Dip Switch)” – the programming of the initial
voltage, ramp time, motor current setting and enabling of
the protection devices is performed by means of the
trimpots and dip switch. The values programmed through
the serial communication is not used.
1 - “HMI” – the programming is performed through the serial
communication. The values programed through trimpots
and dip switch is not used.
NOTE !
In “HMI” mode (P220=1) the trimpots and dip switch
programming is ignored. The start voltage, ramp times, motor
current setting and the protection enabling is programmed
through the parameters P101, P102, P104, P105 and P106.
þ It configures the DI 1 digital input to operate according to
the codes described below.
0 - “Not used”, DI 1 digital input is disabled. The enabling
commands are only accept via serial communication
(V03).
1 - “Enable/Disable”, enabling only via digital input. The
enabling commands via serial communication are
ignored.
2 - “External Fault”, it acts only if the DI 1 digital input is
open. It can also be used as additional load protection.
Example: thermal protection of the motor through dry
contact (without voltage) of a protection relay
(Thermostat).
The enabling commands are only accepted via serial
communication (V03).
Page 39

33
8.19 - P277 –
Programmable
Relay Output
(14/23 – 24)
DETAI LED PARAMETER DESCRIPTION 8
þ It enables the relay (14/23 – 24) to operate according to
the following parameter setting:
1 - Function “Full voltage” – the relay closes the contact only
after the Soft-Starter reached 100% of Un (By-pass), and
opens the contact when the Soft -Starter has received a
switch-Off order.
2 - Function “Error”, the relay closes the NO contact when
the SSW-05 is with no error.
3 - Function “Logic Command”, the relay opens and closes
the relay contact according to the BIT 5 status of the V03
basic variable.
8.20 - P295 – Rated
Current of the
Soft-Starter
8.21 - P308 - Network
Address
þ Configures the SSW-05 models.
þ Its function is to set the software so the current indication
in Ampere (P003) is correct.
The possible configurations of the SSW-05 model are:
0 = 3A
1 = 10A
2 = 16A
3 = 23A
4 = 30A
5 = 45A
6 = 60A
7 = 85A
þ It defines the address at which the Soft-Starter will
respond on the communication network between all
equipment connected to this network.
Page 40

8 DETAILED PARAMETER DESCRIPTION
34
8.22 - P313 – Action of
the Serial
Communication
Verification
þ This parameter has the purpose to set the action to be
taken when an error indication occurs.
NOTE!
To attribute a function to this parameter, set P314 different
from 0 = Off.
Values for P313: 1- It indicates only error.
2- Indicates error and disables the Soft-
3- Indicates error and causes general
4- Indicates error and program P264 with
Starter by ramp. If the programmed
deceleration time is equal to 0 sec, the
motor driven by the Soft-Starter will be
stopped by inertia.
disabling of the Soft-Starter. It can be
used as emergency stopping.
the value 1. The bit 0 of V03 is reseted.
8.23 - P314 – Verification
Time of the Serial
Communication
þ This parameter has the function to enable or disable, as
well as to set the verification time of the serial
communication. This protection acts when the serial
communication between the master and the Soft-Starter
is interrupted generating the respective indication or
introducing an action as set at parameter P313.
NOTE!
Enable this function only if there is a cyclic serial
communication with a master.
Set the verification time according to the time of the
telegrams sent by the master.
Page 41

35
485 is applied and the master is using a
TROUBLESHOOTING 9
Problem
Corrective Action
þ Check if the telegrams are assembled correctly.
• Equipment code;
• Byte of correct BCC;
• Parity;
• Word length.
No communication to the
Soft-Starter:
þ Check if all connections of the serial communication
cables and required power cables are correct.
þ Check if the master transfer rate is 9600bps.
þ Check if the address of the Soft-Starter (P308) is the
same to which the master is sending the telegrams.
þ When RS-
RS-232/RS-485 inverter, check if RTS signal is present.
þ Check if the changing telegrams are assembled
Master reads but does not
change the Soft-Starter
parameters:
correctly.
þ Check if there is no write attempt on a read-only variable.
þ Check if the variable can be changed with running motor.
Random indication of serial
errors in the serial
communication:
þ When connected in communication network with RS-485:
• Check if all serial cable connection at the network and
their respective shields were performed correctly
• Check if all grounding points are grounded correctly.
• Check if only the network terminals have terminating
connectors.
þ Check if all cables of the RS-232 connections are as
short as possible and laid at the recommended distances
from the power cables.
 Loading...
Loading...