Page 1

SmartSensor Matrix
USER GUIDE
www.wavetronix.com 78 East 1700 South Provo, Utah 84606 801.734.7200
Page 2

© 2013 Wavetronix LLC. All Rights Reserved.
Wavetronix, SmartSensor, Click, Command, and all associated product names and logos are trademarks of Wavetronix LLC. All other
products or brand names as they appear are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective holders.
Protected by US Patent Nos. 6,556,916; 6,693,557; 7,426,450; 7,427,930; 7,573,400; 7,889,097; 7,889,098; 7,924,170; 7,991,542;
8,248,272; Canadian Patent Nos. 2461411; 2434756; 2512689; and European Patent Nos. 1435036; 1438702; 1611458. Other US
and international patents pending.
e Company shall not be liable for any errors contained herein or for any damages arising out of or related to this document or the
information contained therein, even if the Company has been advised of the possibility of such damages.
is document is intended for informational and instructional purposes only. e Company reserves the right to make changes in the
specications and other information contained in this document without prior notication.
FCC Part 15 Compliance: e Wavetronix SmartSensor sensors comply with Part 15 of the Federal Communications Commission
(FCC) rules which state that operation is subject to the following two conditions: (1) this device may not cause harmful interference,
and (2) this device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause undesirable operation. FCC compliance statements for applicable optional modules are to be found in the module specications. Unauthorized changes or modications
not expressly approved by the party responsible for compliance with the FCC rules could void the user’s authority to operate this
equipment.
Disclaimer: e advertised detection accuracy of the Wavetronix SmartSensor sensors is based on both external and internal testing, as
outlined in each product’s specication document. Although our sensors are very accurate by industry standards, like all other sensor
manufacturers we cannot guarantee perfection or assure that no errors will ever occur in any particular applications of our technology.
erefore, beyond the express Limited Warranty that accompanies each sensor sold by the company, we oer no additional representations, warranties, guarantees or remedies to our customers. It is recommended that purchasers and integrators evaluate the accuracy of
each sensor to determine the acceptable margin of error for each application within their particular system(s).
WX-500-0053
1/2013
Page 3

Contents
Introduction 5
SmartSensor Matrix Package 6 • Selecting a Mounting Location 7
Part I Installing the SmartSensor Matrix
Chapter 1 Installing the SmartSensor Matrix 13
Sensor Mounting Guidelines 14 • Attaching the Mount
Bracket to the Pole 15 • Attaching the Sensor to the Mount
Bracket 16 • Aligning the Sensor to the Roadway 16 • Applying the Silicon Dielectric Compound 18 • Connecting the
SmartSensor 6-conductor Cable 18 • Grounding the Sensor
19
Chapter 2 Connecting Power and Surge Protection 21
Mounting the Backplate 22 • Connecting AC Power 22 •
Providing System Surge Protection 26 • Terminating Smart-
Sensor 6-conductor Cables 28
Chapter 3 Contact Closure Communication 31
Using the Click 112/114 DIP Switches 32 • Using the Click
104 Rotary Switch 34 • Attaching and Programming the
Click 112/114 35 • Attaching and Programming the Click
104 37 • Channel Mapping 39
Page 4

Part II Using SmartSensor Manager Matrix
Chapter 4 Installing SmartSensor Manager Matrix 45
Installing SSMM 47 • Microsoft .NET Framework 49
Chapter 5 Communication 51
Serial Connection 53 • Internet Connection 56 • Virtual
Connection 58 • Viewing Connection Information 60 • Up-
grading the Sensor’s Embedded Software 62
Chapter 6 Sensor Settings 65
General Sensor Settings 65 • Sensor Info Screen 67
Chapter 7 Lanes & Stop Bars 69
Display Options 70 • Menu Bar 73 • Automatic Conguration 76 • Manual Conguration 77
Chapter 8 Zones & Channels 81
Menu Bar 82 • Placing Zones 83 • Channel Type 84 • Mapping Zones to Channels 86 • Measuring Zones 89
Chapter 9 Verification 91
Channel Indicators 92 • Verication Menu Bar 93
Chapter 10 Tools 95
Backup/Restore 96 • Rack Cards Tools 97 • Sensor Self Tests
101
Appendix 103
Appendix A – Cable Connector Denitions 103 • Appendix
B – Cable Lengths 105 • Appendix C – Click 221 User Reference Guide 106 • Appendix D – Click 600 Installation 107
• Appendix E – Matrix Extended Range 111
Page 5

Introduction
In this chapter
SmartSensor Matrix Package
Selecting a Mounting Location
e Wavetronix SmartSensor Matrix™ is a stop bar presence detector designed for use at
signalized intersections (see Figure I.1). e SmartSensor Matrix detects vehicles through
the use of a 24.125 GHz (K band) operating radio frequency. Using what is classied as
frequency modulated continuous wave (FMCW) radar, SmartSensor Matrix detects and
reports vehicle presence in as many as 10 lanes simultaneously.
Figure I.1 – Wavetronix SmartSensor Matrix
SmartSensor Matrix is a rst-of-its-kind radar stop bar detector with Radar Vision™. It
delivers the reliability of radar and the simplicity of non-intrusive detection for stop bar
presence detection. In many situations, the sensor is installed on the roadside in order to
prevent the need for lane closures and trac control. Once the unit is installed, the congu-
Page 6

6 INTRODUCTION SMARTSENSOR MATRIX USER GUIDE
ration process is quick and easy. After installation, the sensor will require little or no on-site
maintenance and can be remotely congured.
is user guide outlines the step-by-step process of installing and conguring the SmartSensor Matrix. Any questions about the information in this guide should be directed to
Wavetronix or your distributor.
SmartSensor Matrix Package
A standard SmartSensor Matrix package may contain the following items:
SmartSensor Matrix SS225 detector(s) with installed sensor backplate
Sensor mounting kit(s)
SmartSensor 6-conductor cable(s)
Intersection preassembled backplate
Click 112/114 detector rack card(s) with patch cable(s)
Click 104 four-channel DIN rail contact closure module
SmartSensor Manager Matrix (SSMM) software
SmartSensor Matrix User Guide
Note
Instead of the intersection preassembled backplate, you may be using the Click 600
cabinet interface device, the preassembled 19-inch rack, or the segmented preassembled backplate. The coming chapters will note installation dierences between
these devices and the preassembled backplates where applicable.
SmartSensor Matrix system options include (see Figure I.2):
AC power conversion – Provides reliable power for the sensors and backplate com-
ponents. is option is normally recommended instead of the DC surge protection
because it will not burden the existing DC power modules.
Remote IP connection – Provides a way (via a Click 301 serial to Ethernet converter)
to connect to the sensor from a remote location. e Click 301 is recommended for
remote management.
Page 7

INTRODUCTION SMARTSENSOR MATRIX USER GUIDE 7
Control Bridge to Rack Cards
Configuration Toolkit
AC Power
Conversion
Option
Control Bridge
on T-bus
(attach to T-bus)
Control Bridge to Sensors
Figure I.2 – SmartSensor Matrix System Options
Remote IP Connection Option
(attach to T-bus)
Note
SmartSensor Matrix systems provide a control bridge to manage all connected
SmartSensor and Click devices. The control bridge is completely separate from the
dedicated channels used for communication of contact closure detection calls in real
time.
Selecting a Mounting Location
Consider the following guidelines when selecting a mounting location for each SmartSensor Matrix:
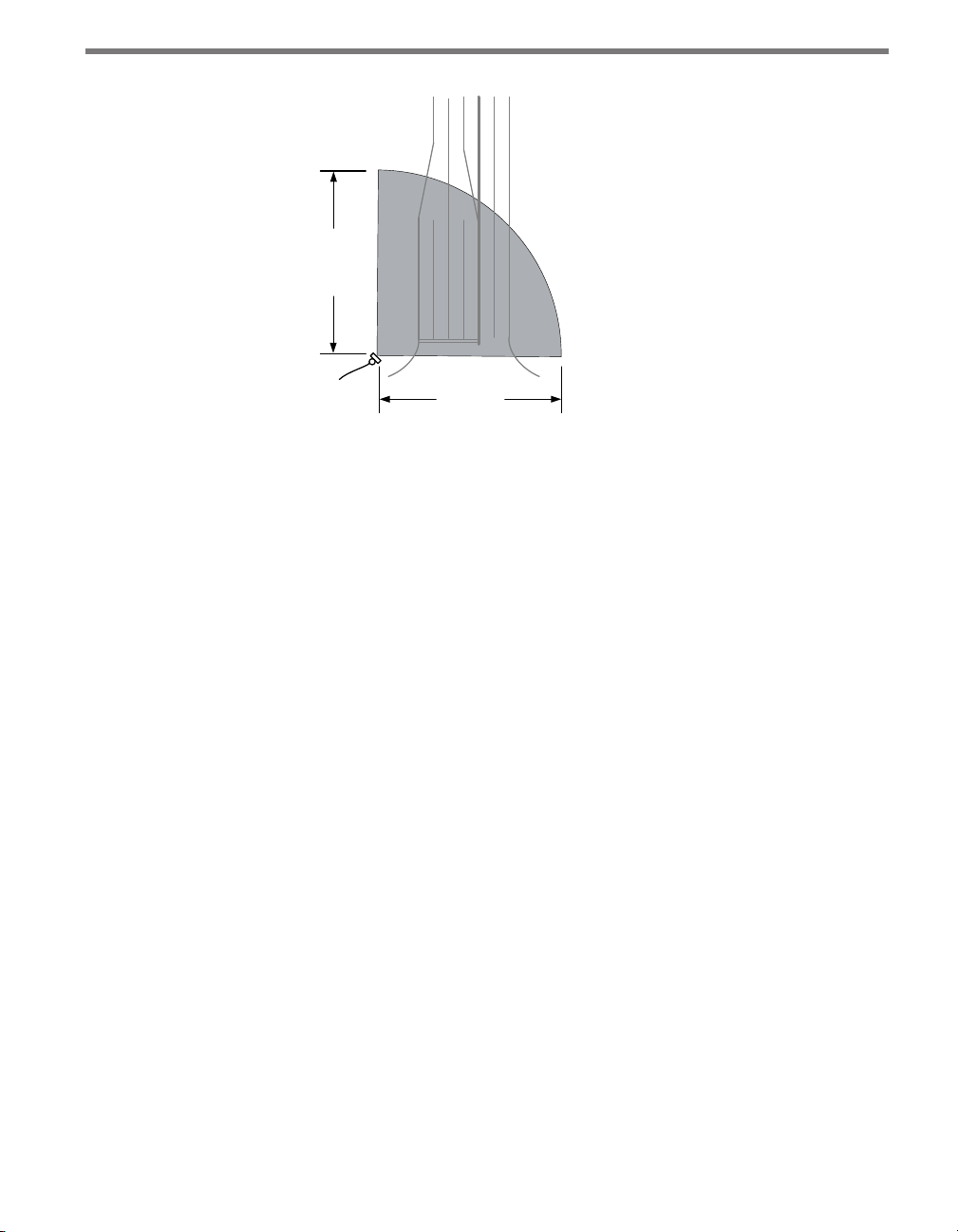
Corner radar – e SmartSensor Matrix is a corner radar device with a panoramic
90°, 140-ft. (42.7-m) view (see Figure I.3). e sensor’s mounting location should
be selected so that all stop bar detection zones on an approach are within a 6–140-ft.
(1.8–42.7-m) radial distance.
Page 8
8 INTRODUCTION SMARTSENSOR MATRIX USER GUIDE
140 ft
Sensor Pole
Figure I.3 – Corner Radar
140 ft
Line of sight – Position the sensor so that it will be able to detect the entire area
of interest. Avoid occlusion by installing the sensor away from trees, signs and other
roadside structures.
Detection coverage – Position the sensor so that it will be able to reach all the specied
stop bar detection zones. e sensor will often work better if you position it so that it
tracks vehicles for several feet before the rst zone in each lane. If the sensor has a view
several feet beyond the stop bar, it is more likely to accurately detect queue dissipation.
Closest roadside – Mount the sensor on the side of the road closest to the lanes of
primary interest. Always mount the sensor high enough to prevent trac from occluding approaching vehicles.
Mounting height – A minimum height of 12 ft. (3.6 m) is recommended. Mounting
the sensor higher will generally improve line of sight and decrease the possibility of
occlusion.
Mounting oset – A minimum oset of 6 ft. (1.8 m) to the rst lane of interest is
required.
Redundant detection – It is possible to have multiple sensors monitoring the same
approach. Multiple sensors are needed when zones are spread over more than 140 ft.
(42.7 m).
Sensor proximity – When multiple sensors are mounted at the same intersection,
interference can be avoided by conguring each sensor to operate on a unique RF
channel.
Departing lanes – ere is usually no need to view trac in departing lanes or to
congure departing lanes. However, if they are congured, then the stop bar should
not be congured.
Suspended electrical cables – e sensor is designed to work in the presence of sus-
pended power lines and other electrical cables. However, these cables should be at least
10 ft. (3 m) away from the front of the sensor.
Neighboring structures and parallel walls – e sensor should not be mounted with
Page 9
INTRODUCTION SMARTSENSOR MATRIX USER GUIDE 9
signs or other at surfaces directly behind it. is will help reduce multiple reection
paths from a single vehicle.
Cable length – Make sure that you have sucient homerun and sensor cabling. Cable
runs as long as 500 ft. (152.4 m) can be achieved using 24 VDC operation and the
system’s native RS-485 communications. If your application requires a cable length
longer than 500 ft. (152.4 m), contact Wavetronix Technical Services for assistance.
e SmartSensor Matrix should be mounted using one of the following options (see Figure
I.4):
➋
1 The back side of mast arm – is location allows the sensor to be placed near the lanes
of interest and may be the best location option for wide approaches. If you mount the
sensor on the back side of a mast arm, mount it near the end of the arm to reduce the
possibility of the mast arm or departing trac occluding approaching vehicles.
2 The far side of approach – e sensor is usually mounted on a corner vertical mast
pole or strain pole. If the sensor is mounted on a vertical pole with a mast arm, you
can usually avoid occlusion by mounting the sensor away from or below the mast arm.
3 The near side of approach – is mounting location is typically best if detecting the
left turn lane is less important. is location also allows you to mount the sensor high
enough to avoid occlusion.
Other mounting locations may be possible if these are not available at your intersection.
Contact Wavetronix Technical Services for assistance if you would like to use an alternative
mounting location.
➊
➌
Figure I.4 – Mounting locations
Page 10

Page 11
Part I
Installing the SmartSensor
Matrix
Chapter 1 – Installing the SmartSensor Matrix
Chapter 2 – Connecting Power and Surge Protection
Chapter 3 – Contact Closure Communication
Page 12

Page 13

Installing the SmartSensor Matrix 1
In this chapter
Sensor Mounting Guidelines
Attaching the Mount Bracket to the Pole
Attaching the Sensor to the Mount Bracket
Aligning the Sensor to the Roadway
Applying the Silicon Dielectric Compound
Connecting the SmartSensor 6-conductor Cable
Grounding the Sensor
1
e installation process includes attaching the mounting bracket to the pole; attaching the
sensor to the mounting bracket; aligning the sensor; applying a silicon dielectric compound
to the sensor connector; and connecting the SmartSensor 6-conductor cable to the sensor.
Caution
Do not attempt to service or repair this unit. This unit does not contain any components and/or parts serviceable in the field. Any attempt to open this unit, except
as expressly written and directed by Wavetronix, will void the customer warranty.
Wavetronix is not liable for any bodily harm or damage caused if service is attempted
or if the back cover of the SmartSensor unit is opened. Refer all service questions to
Wavetronix or an authorized distributor.
Page 14
14 CHAPTER 1 INSTALLING THE SMARTSENSOR MATRIX
Warning
Use caution when installing any sensor on or around active roadways. Serious injury
can result when installation is performed using methods that are not in accordance
with authorized local safety policy and procedures. Always maintain an appropriate
awareness of the trac conditions and safety procedures as they relate to specific
locations and installations.
Sensor Mounting Guidelines
e sensor is fairly insensitive to mounting height, but every site will vary based on lane
conguration and the presence of barriers and structures in and around the detection area.
e following table will help you determine how high to mount the sensor (see Table 1.1).
ese gures are only suggestions, but a good rule to follow is—the farther away the rst
lane is to the sensor, the higher you will want to mount the sensor to avoid occlusion.
Closest Lane Sensor Height
6–15 feet 12–25 feet
15–50 feet 15–25 feet
> 50 feet 25–60 feet
Table 1.1 – Suggested Mounting Guidelines
Note
In certain conditions, lanes that have stop bars or detection zones placed at extended
range may show some loss in performance, even with a proper mounting height. This
is more apparent at locations with many travel lanes or where detection zones are
placed near the far edges of detection. If you have any questions regarding the use
of SmartSensor Matrix at a particular location, please contact Wavetronix Technical
Services or your authorized Wavetronix dealer for more information.
Use the following guidelines to determine the best mounting height, then place your sensor
accordingly:
In general, the sensor should be placed at a height of roughly 20 ft. (6.1 m), give or
take 5 ft. (±1.5 m).
e maximum recommended mounting height for the SmartSensor Matrix is 60 ft.
(18.2 m). e minimum is 12 ft. (3.6 m). Placing the sensor above or below these limits
will adversely aect detection accuracy.
Page 15
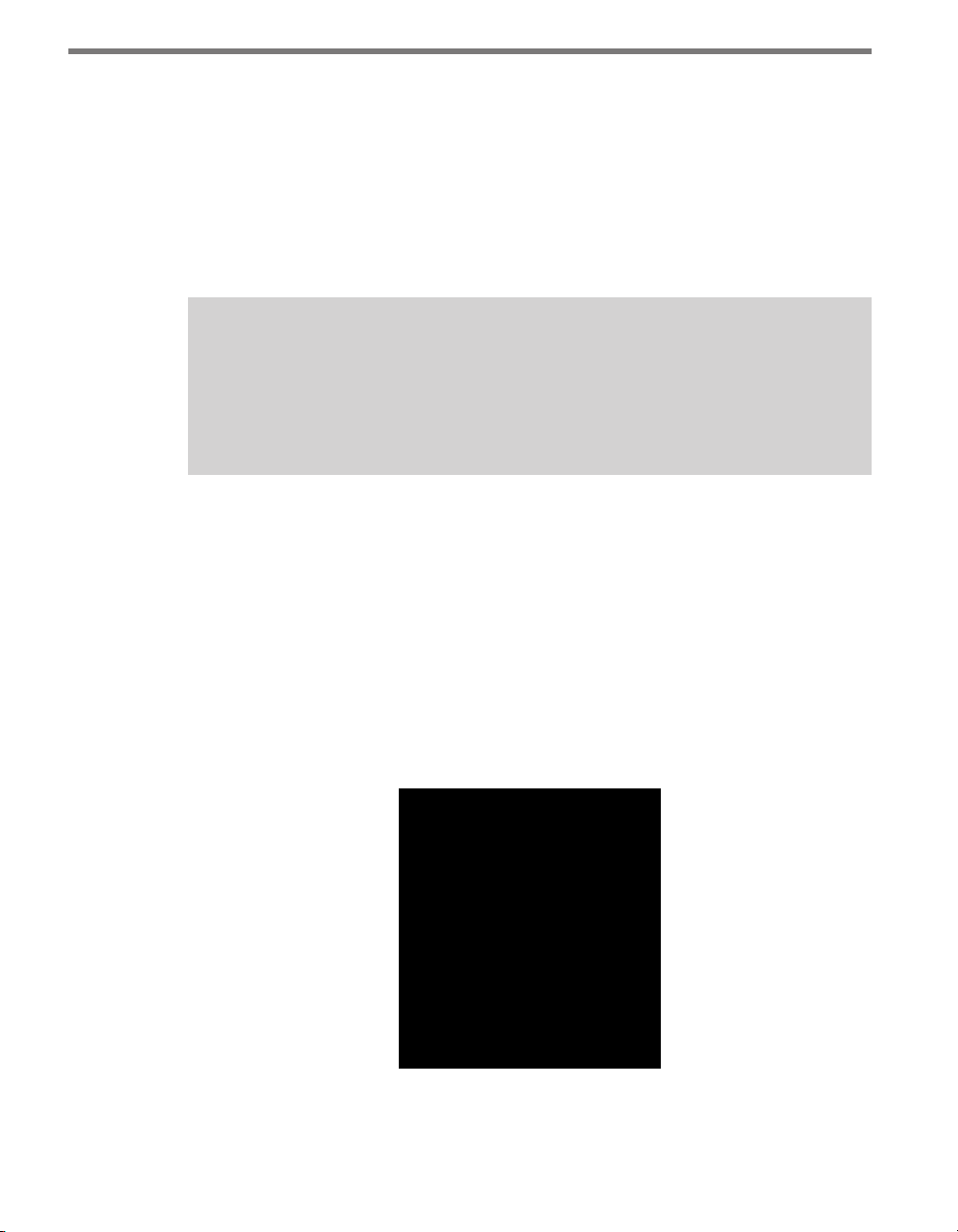
CHAPTER 1 INSTALLING THE SMARTSENSOR MATRIX 15
Take into consideration the sensor’s eld of view, which reaches 140 ft. (42.7 m) from
the sensor. Place the sensor so that the eld of view covers all the areas of interest.
e mast arm is frequently a good place to mount the sensor.
e mounting position should have a clear view of the detection area. Poles, mast arms,
signal heads, or other objects should not block the view of the detection area.
Placing the sensor higher will result in less occlusion. Placing it lower could result in
more occlusion. However, if the nearest detection area is less than about 20 ft. (6.1 m)
away, the sensor may perform better with a lower mounting position.
Note
It is possible to mount the sensor lower than 12 ft. (3 m) in some scenarios. The sen-
sor will continue to detect vehicles at lower heights, but missed detections due to
occlusion may become more prevalent or problematic in lanes that are farther away
from the sensor.
Attaching the Mount Bracket to the Pole
Before attaching the mount bracket to the pole, rst make sure that your cables are long enough
to reach the sensor height and to stretch across the distance from the sensor to the cabinet.
Follow the steps below to correctly attach the mount to the pole:
1 Insert the stainless steel straps through the slots in the mount bracket.
2 Position the mount on the pole so that the head of the mount is pointing toward the
lanes of interest at about a 45° angle.
3 Tighten the strap screws.
Figure 1.1 – Attach the Mount Bracket to the Pole
e sensor double-swivel mount may need to be adjusted later to ne-tune the alignment.
Page 16

16 CHAPTER 1 INSTALLING THE SMARTSENSOR MATRIX
One swivel joint is used to pan the sensor eld of view left or right and the other swivel
joint is used to tilt the sensor down towards the roadway. If you are not using the double
swivel-mount, make sure the pole straps are adjustable at this point in the installation
process.
Attaching the Sensor to the Mount Bracket
Use the following steps to securely fasten the sensor to the mount bracket:
1 Align the bolts on the sensor’s backplate with the holes in the mount bracket. e
eight-pin connector receptacle on the bottom of the sensor should be pointing towards
the ground.
2 Place the lock washers onto the bolts after the bolts are in the mount bracket holes.
3 read on the nuts and tighten (see Figure 1.2)
Figure 1.2 – Attach the Sensor to the Mount Bracket
Caution
Do not over-tighten the fasteners.
Aligning the Sensor to the Roadway
e sensor’s beams fan out 45° to the left and 45° to the right, creating a 90° corner radar
eld of view. In most applications, you will want to position the corner radar so that its 90°
footprint covers all lanes approaching the stop bar (see Figure 1.3).
Page 17
CHAPTER 1 INSTALLING THE SMARTSENSOR MATRIX 17
45°
45°
Edge of first lane of interest
Pan sensor
towards stop bar
Figure 1.3 – Corner Radar Field of View Position
Stop Bar
To visualize the extent of the sensor eld of view, the 90° eld of view is imprinted on the
top and bottom of the sensor case. If more of a visual indicator is needed, then a square
framing tool (e.g. rafter square) or other tool with a right angle can be held above the
sensor. By looking down both edges of the tool, you can visualize the extent of the radar’s
coverage.
Usually the front edge of the sensor’s eld of view is aligned to provide coverage beyond
the stop bar (see Figure 1.4). is allows you to place detection zones beyond the stop bar
to detect those vehicles that do not stop at or behind the stop line and will also allow the
sensor to see vehicles exiting queues. If the sensor pole is upstream from the stop bar, it is
recommended to pan in the direction of the stop bar.
Front edge of field of view
Figure 1.4 – Sensor Aligned by Rotating Towards the Stop Bar
Use the following steps to correctly align the SmartSensor Matrix:
Page 18
18 CHAPTER 1 INSTALLING THE SMARTSENSOR MATRIX
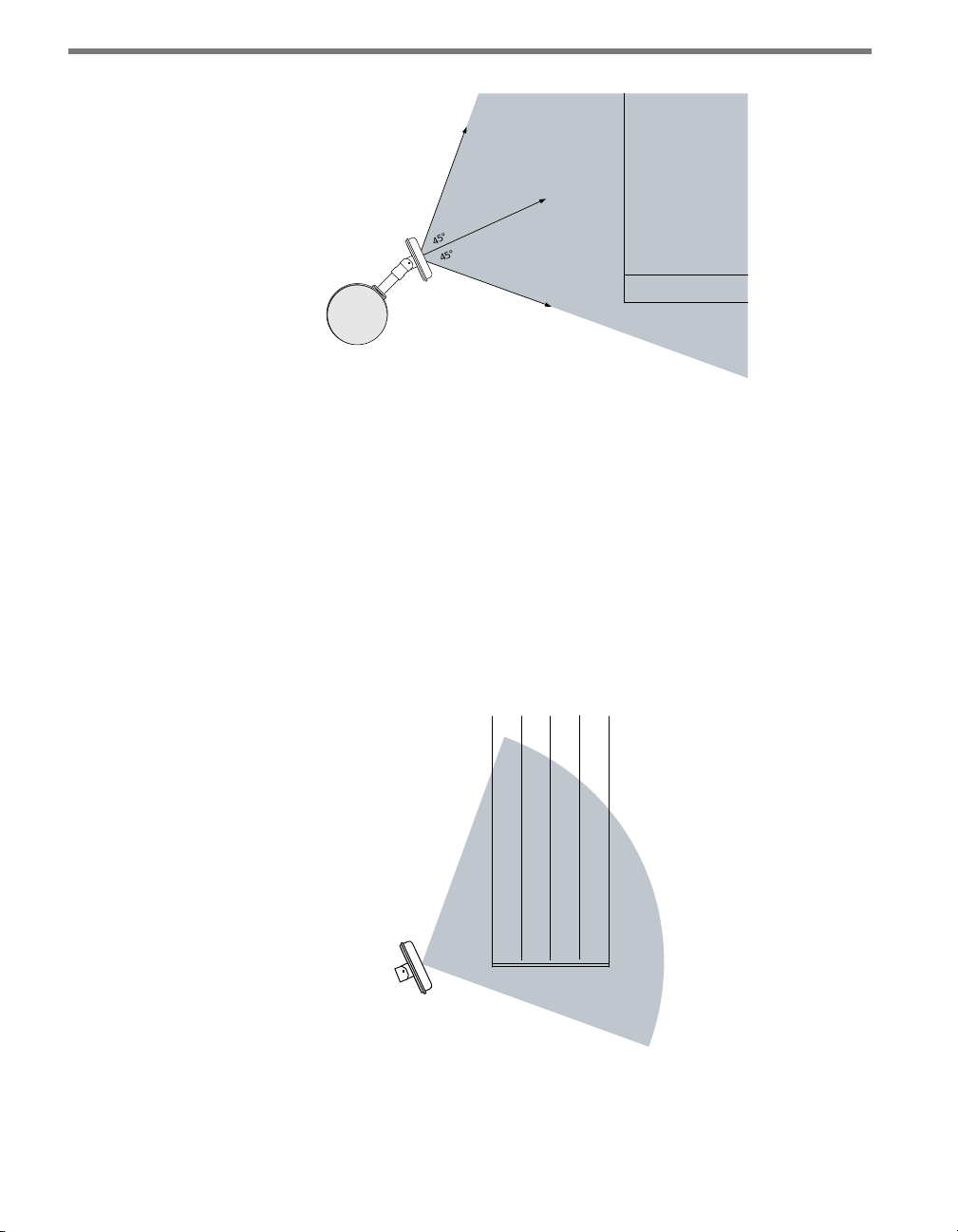
1 Adjust the side-to-side angle so that the front edge of the eld of view provides a view
downstream of the stop bar.
2 Tilt the sensor down so it is aimed at the center of the lanes of interest.
3 If necessary, rotate the sensor so that the bottom edge of the sensor is parallel with
the roadway. is is necessary where the intersection approach has a signicant grade.
Note
To fully complete sensor alignment, you will need to connect to the Matrix sensor
using SmartSensor Manager Matrix and verify that your alignment is detecting the
vehicles in the lanes of interest (see Chapter 8).
Applying the Silicon Dielectric Compound
Use the following steps to correctly apply the silicon dielectric compound to the cable connector:
1 Tear the tab o of the tube of silicon dielectric compound.
2 Squeeze about 25% of the silicon onto the pins of the receptacle side of the connector
at the base of the SmartSensor Matrix (see Figure 1.5). Be sure to wipe o any excess
compound.
Figure 1.5 – Connector Receptacle (left) and Grounding Lug (right)
Connecting the SmartSensor 6-conductor Cable
e next step is to plug the SmartSensor 6-conductor cable into the connector. e sensor
connector is keyed to ensure proper connection (see Figure 1.6); simply twist the plug end
of the connector clockwise until you hear it click into place. To avoid undue movement
from the wind, strap the 6-conductor cable to the pole or run it through a conduit, but leave
a small amount of slack at the top of the cable to reduce cable strain. Route the cable from
the sensor location back to the main trac cabinet.
Page 19
CHAPTER 1 INSTALLING THE SMARTSENSOR MATRIX 19
Figure 1.6 – Sensor 6-conductor Cable Connector
To set up your network in an orderly fashion, it is recommended that labeling be used on
the service end of each SmartSensor 6-conductor cable. A convenient way to label the
cables is to mark the last seven digits of the serial number on each sensor and the direction
of trac monitored (see Figure 1.7).
Figure 1.7 – Service End Labeling
Grounding the Sensor
e SmartSensor Matrix must now be grounded:
1 Connect a grounding wire to the grounding lug on the bottom of the sensor (see
Figure 1.5).
2 Connect the other end of the grounding wire to the earth ground for the pole that
the sensor is mounted on. Do not attempt to run the grounding wire back to the main
trac cabinet.
Page 20

Page 21

Connecting Power and
Surge Protection 2
In this chapter
Mounting the Backplate
Connecting AC Power
Providing System Surge Protection
Terminating SmartSensor 6-conductor Cables
2
After installation, each SmartSensor Matrix will need to be integrated into the main trafc cabinet for power and surge protection. is chapter contains information on how to
provide power and surge protection to a preassembled backplate that accommodates four
SmartSensor Matrix sensors (one for each stop bar of a common four-approach intersection).
Note
Also available to use are the intersection preassembled 19-inch rack for server racks,
the intersection segmented preassembled backplate for easier installation in trac
cabinets, and the Click 600 cabinet interface device (which combines all the function-
ality of the backplates in one module). Installation procedures for the rack and the
segmented backplate will be very similar to the instructions that follow; installation
procedures for the Click 600 can be found in Appendix D of this guide.
e standard four-approach preassembled backplate is 11 in. (28 cm) wide and 11.5 in.
(29.2 cm) high. All wiring on the rack and backplates is done using stranded wires with
wire ferrules for screw terminal connections (see Figure 2.1).
Page 22

22 CHAPTER 2 CONNECTING POWER AND SURGE PROTECTION
Figure 2.1 – Intersection Preassembled Backplate
Mounting the Backplate
Use the following steps to mount the backplate in the trac cabinet:
1 Locate the area planned for mounting the backplate. e backplate can usually be
mounted on the side panel of a NEMA-style cabinet.
2 Attach the backplate with the U-channel mounting screws.
Note
If you have a 330 series (170/2070 style cabinet) with a 19-inch EIA rack, please contact Wavetronix Technical Services for assistance. Wavetronix can provide modified
backplates that attach to a 19-inch rack.
Connecting AC Power
Since SmartSensor Matrix operates on 10–28 VDC, the standard preassembled backplates
provide an AC power conversion option. e backplate includes an AC to DC power converter, power surge and circuit breaker.
Page 23

CHAPTER 2 CONNECTING POWER AND SURGE PROTECTION 23
Warning
Make sure power to AC mains is disconnected while wiring the AC input. If your in-
stallation does not require AC power, you will need to use surplus DC power inside
the trac cabinet. In this case, Wavetronix recommends you use the Click 221 (8 A
DC surge protector) to protect the backplate and SmartSensor Matrix units from DC
surges. See Appendix C for information regarding the Click 221.
Figure 2.2 – Connecting AC Power to the Preassembled Backplate
Use the following steps to connect power to the AC terminal block on the bottom DIN
rail (see Figure 2.2):
1 Connect a neutral wire (usually a white wire) to the bottom side of the terminal block
labeled “N” for neutral.
2 Connect a ground wire (usually a green wire) to the bottom of the terminal block la-
beled “G” for ground. (see the Wiring Protective Earth Ground section below).
3 Connect a line wire (usually a black wire) to the bottom of the terminal block labeled
“L” for line.
4 Turn on AC mains power.
5 Press the circuit breaker switch on the left side of the top DIN rail to switch power to
the backplate. e switch is on if the button is below the level of the device housing;
the switch is o if the button is raised above the surface of the housing.
6 Verify that DC power is properly regulated by making sure the DC OK LEDs are il-
luminated on the Click 201/202/204.
Page 24
24 CHAPTER 2 CONNECTING POWER AND SURGE PROTECTION
Caution
An authorized electrical technician should install the preassembled backplate. Persons other than authorized and approved electrical technicians should NOT attempt
to connect the backplate to a power supply and/or trac control cabinet, as there is a
serious risk of electrical shock through unsafe handling of the power source. Extreme
caution should be used when connecting the backplate to an active power supply.
e AC power conversion section of the backplate will come pre-wired as shown in Figure
2.3. e main three components of the AC power conversion section include:
Click 201/202/204 AC to DC converter – A Click 201 provides 1 A of power and is
capable of powering a single sensor; a Click 202 provides 2 A and can power two sensors; a Click 204 provides 4 A and can power four sensors.
Click 210 circuit breaker – Interrupts power during overload conditions and provides
a convenient way to turn power on and o for the entire system.
Click 230 AC surge protector – Helps protect equipment from current surges on the
power lines.
Figure 2.3 – AC Power Conversion
Wiring Protective Earth Ground
All connections are surge protected when the protective earth ground is wired to the PE
terminal block on the backplate. Normally, the backplate should be mounted to the chassis
of the cabinet to provide a ground path. It is strongly recommended that you provide a low
impedance protective earth connection.
Page 25
CHAPTER 2 CONNECTING POWER AND SURGE PROTECTION 25
Follow the steps below to provide a low impedance protective earth connection:
1 Connect one end of a protective earth ground wire to the bottom of the PE terminal
block. A 10 AWG stranded wire is recommended for protective earth ground connec-
tions and is also the largest that will t in the terminal block.
2 Connect the other end of the protective earth ground wire to a protective earth screw
terminal within the main trac cabinet.
Controlling DC Power Distribution
e Click 210 circuit breakers provide a convenient way to turn power on or o for each
sensor independently (see Figure 2.4). To enable or disable DC power to the backplate,
switch the main circuit breaker (left side of upper DIN rail); to enable or disable DC power
to an individual sensor, switch the individual circuit breaker (left side of each sensor’s set
of terminal blocks).
Push this
button to
turn power
on or o
Figure 2.4 – DC Power Distribution
Note
The switch is ON when the switch button is level with the device housing; the switch
is OFF when the switch button is raised above the housing.
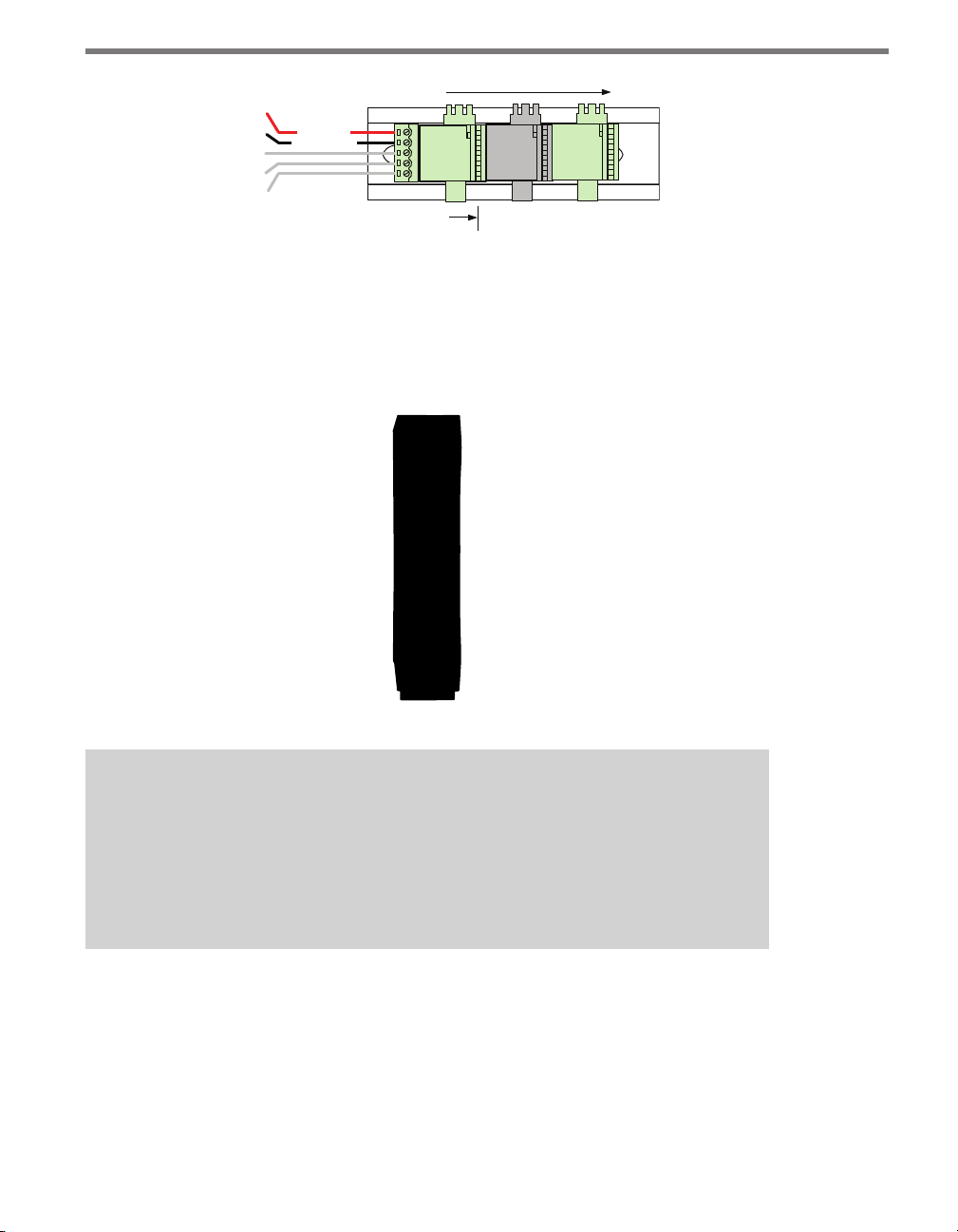
e four-approach preassembled backplate has 24 VDC power wired from the output of
the AC to DC converter into a 5-position screw terminal on the left side of the T-bus (see
Figure 2.5). e green T-bus conducts DC power and RS-485 communications from the
left to the right side of the modules; the gray T-bus conducts only DC power from the left
to the right side of the modules.
Page 26
26 CHAPTER 2 CONNECTING POWER AND SURGE PROTECTION
+24V DC
-DC
+RS-485
-RS-485
GND
red wire
( )
black wire
( )
Figure 2.5 – T-bus Pinout Diagram
Power
Green GreenGray
RS-485
Providing System Surge Protection
e Click 222 system surge protector is designed to prevent electrical surges conducted
along underground cables from damaging the cabinet equipment (see Figure 2.6).
Figure 2.6 – Click 222 Faceplate
Note
The SmartSensor Matrix has built-in surge protection and so there is no need to use
a pole-mount box for surge protection on the sensor side of the cable. However, it is
strongly recommended that the sensor be connected to a surge protection device in
the main trac cabinet. If you choose not to use surge protection in your main trac
cabinet, please contact Wavetronix Technical Services for assistance.
When a Click 222 is present, the power and RS-485 serial connections on the T-bus and
faceplate are protected from surges on the incoming SmartSensor 6-conductor cables.
e Click 222 faceplate has four activity indicator LEDs:
PWR – Indicates that the device has power.
DC Surge OK – Indicates that DC surge protection is operational.
Page 27

CHAPTER 2 CONNECTING POWER AND SURGE PROTECTION 27
TD – Indicates when data is transmitted over the T-bus or over the control bridge. is
LED does not indicate data transmitted on the A or B ports.
RD – Indicates when data is received over the T-bus or over the control bridge. is
LED does not indicate data received on the A or B ports.
Note
If the DC Surge OK LED is not on when the Click 222 is powered, call Wavetronix Technical Services for assistance.
e Click 222 provides the following three independent serial connections:
Topmost jack: control bridge
Middle jack: dedicated communications for sensor 2 detection calls
Lowest jack: dedicated communications for sensor 1 detection calls
e control bridge enables a multi-drop shared communication bus between all sensors
connected to the backplate. is allows control of all SmartSensor Matrix sensors, rack
cards and other connected Click devices. e remaining two serial connection ports provide
communications to only one sensor each, as outlined above.
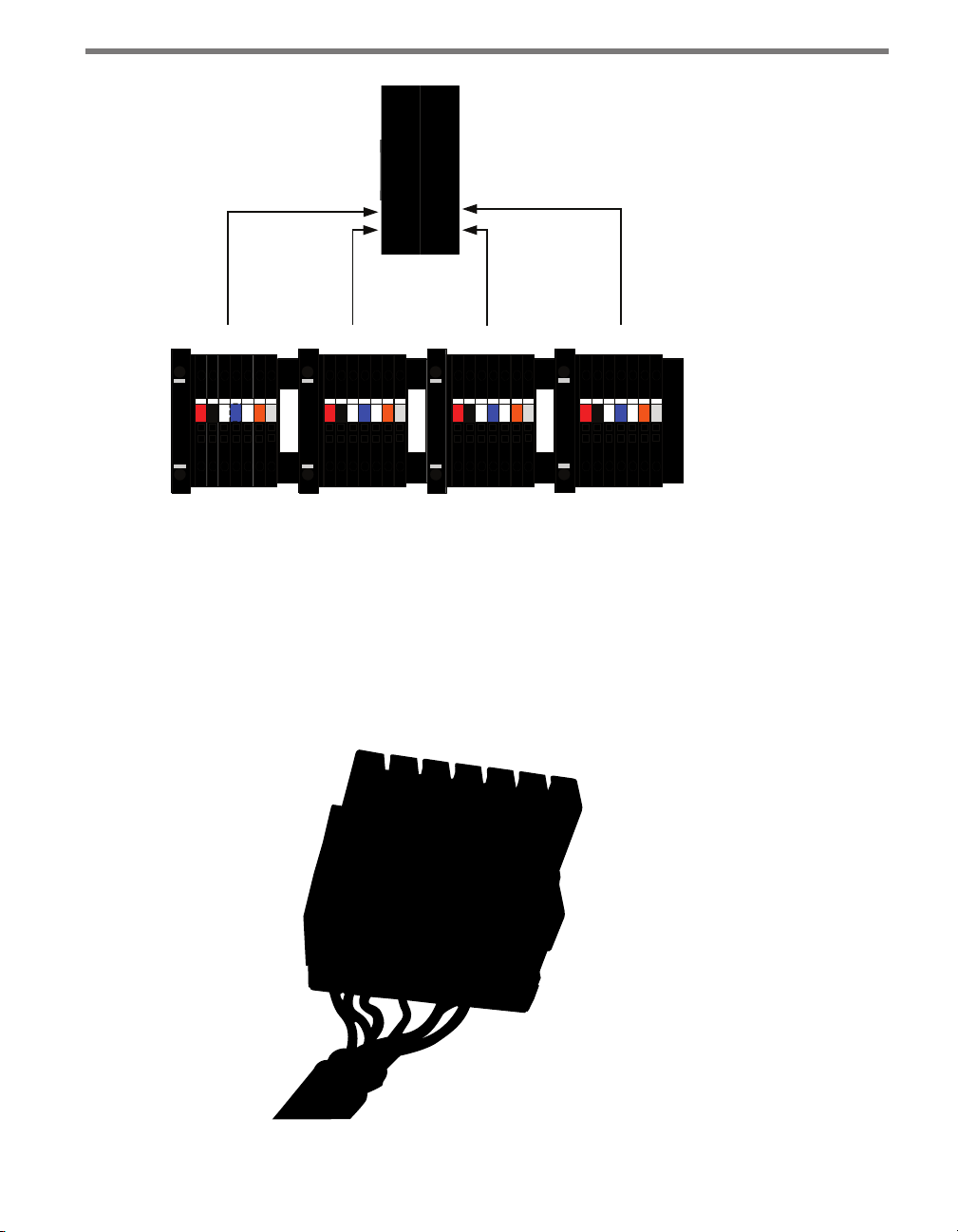
On a four-sensor preassembled backplate (see Figure 2.7):
e sensor wired into the left-most terminal blocks will be connected to ports A and
C on the Click 222 on the left. Port A is for detection calls and port C is connected
to the control bridge.
e sensor wired to the second set of terminal blocks will be wired to ports B and D
on the Click 222 on the left. Port B is for detection calls and port D is connected to
the control bridge.
e sensor wired to the third set of terminal block from the left will be wired to ports
A and C on the Click 222 on the right.
e sensor wired to the right-most terminal block will be wired to ports B and D on
the Click 222 on the right.
Page 28
28 CHAPTER 2 CONNECTING POWER AND SURGE PROTECTION
Port A & Port C Port B & Port D Port A & Port C Port B & Port D
x
x
x
x
x
OUT
x
PWR
GND
485+
485-
485+
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
OUT
SSMatrix #2
DRN
485-
x
PWR
GND
485+
485-
485+
x
x
x
DRN
485-
x
x
x
x
x
OUT
SSMatrix #3
PWR
x
GND
485+
485-
485+
485-
x
x
x
DRN
x
OUT
SSMatrix #4
PWR
GND
x
x
x
x
x
DRN
485+
485-
485+
485-
IN
x
x
x
x
x
x
IN
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
IN
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
IN
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
Figure 2.7 – Click 222 Ports A, B, C and D
Terminating SmartSensor 6-conductor Cables
e SmartSensor Matrix will receive power once each SmartSensor 6-conductor cable is
correctly landed into the plug-in terminals on the backplate (see Figure 2.8 and Table 2.1).
Each 6-conductor cable has one DC power wire pair, two RS-485 communication pairs,
and a drain wire. e service end of the cable connects to plug-in terminals on the preassembled backplate (see Figure 2.8).
Figure 2.8 – Color Label on Plug-in Terminals
Page 29

CHAPTER 2 CONNECTING POWER AND SURGE PROTECTION 29
Note
Do not strip the service end of the cable until after it has been routed through conduit. The cable should be one continuous run without any splices.
Use the steps below to land the sensor cables:
1 After routing your SmartSensor 6-conductor cable into the cabinet, carefully strip
back the cable jacket and shielding on the service end of the cable.
2 Open the insulation displacement connectors on the plug by inserting a small screw-
driver into each square slot and rocking it back.
3 Insert the wire leads into the bottom side of the plug-in terminal according to the
color code shown in Table 2.1 and Figure 2.8. Make sure the wires are completely
inserted in the terminal.
4 Close the insulation displacement connector by reinserting the screwdriver into the
square slot and rocking it forward. e plug-in terminals will automatically complete
the electrical connection. ere is no need to manually strip the insulation on the end
of each wire.
ere are two measures in place to ensure that the plugs are always returned to their correct
terminal block sections.
First, for visual conrmation, one part of the plug is blue (see Figure 2.8) and must be
visually matched up to a blue terminal block. e location of the blue piece rotates in the
dierent plugs and terminal block sections: in the rst, the rst block is blue, in the second,
the second is blue, etc.
Second, the plugs are keyed (see the blue piece in Figure 2.8) so they will only t into their
correct terminal block sections.
Wire Color Signal
Red (PWR) DC+
Black (GND) DC-
White with Blue stripe (485+) Control bridge 485+ (port1)
Blue (485-) Control bridge 485 - (port 1)
White with Orange stripe (485+) Data bus 485+ (port 2)
Orange (485-) Data bus 485- (port 2)
Bare metal (DRN) Drain
Table 2.1 – Cable Wiring Color Code
Page 30

Page 31

Contact Closure Communication 3
In this chapter
Using the Click 112/114 DIP Switches
Using the Click 104 Rotary Switch
Attaching and Programming the Click 112/114
Attaching and Programming the Click 104
Channel Mapping
3
Each SmartSensor Matrix communicates with standard trac cabinets using either the
Click 104 DIN rail contact closure module or the Click 112/114 detector rack cards (see
Figure 3.1). During real-time operations, up to four channels from each sensor can be signaled to a Click 114 or Click 104 (or to a pair of Click 112 cards daisy-chained together).
Figure 3.1 – Click 104 (left) and Click 112/114 Rack Cards (right)
Page 32

32 CHAPTER 3 CONTACT CLOSURE COMMUNICATION
14356781234
56782
Note
See the Click 100–400 Series User Guide for complete information on how to connect and configure the Click 104 DIN rail contact closure module and the Click 112/114
detector rack cards.
Each SmartSensor Matrix could potentially use up to 16 channels using a combination of
Click 104/112/114 contact closure modules. is means that a standard four-approach stop
bar detection system can be accommodated by a 64-channel detector rack.
e Click 112/114 cards can be congured using DIP switches on the circuit board, the
front panel menu on the faceplate or Click Supervisor. e Click 104 can be congured
using the rotary switch, the front panel menu on the faceplate or Click Supervisor.
Using the Click 112/114 DIP Switches
e DIP switches allow you to program the baud rate and input mapping using the hardware. If the Click 112/114 cards are programmed using the DIP switches, the settings can
be viewed, but not modied, using the front panel menu or Click Supervisor.
If you are planning to use either the front panel menu or Click Supervisor to program the
device settings, then you will need to rst make sure that the DIP switches are set to allow for software conguration; to set this, simply make sure that all relevant switches are
turned o (see Figure 3.2).
Input Mapping Switches
S4
Channel
Group
Makes channel group selection software configurable
Figure 3.2 – DIP Switch Setting for Software Configuration Mode (left)
Baud Rate Switches
S5
On
O
Bus 1 Bus 2
ere is no need to change the baud rate of the Click 112/114 cards from the factory default of 9600 baud. e settings for the input mapping, however, will need to be set. is
process is explained in the following sections.
Page 33

CHAPTER 3 CONTACT CLOSURE COMMUNICATION 33
123456781
234
567
8
Note
An advantage of using the DIP switches for configuration is that if you ever need to
replace a Click 112/114, you can simply set the DIP switches on the new card to match
the pattern of the DIP switches on the card you are replacing, then slide the new one
into the same slot in the detector rack.
Click 114 Input Mapping DIP Switch Settings
On a Click 114, channel group 1 comprises input channels 1–4. When this channel group
is selected; sensor channel 1 will be mapped to output channel 1; sensor channel 2 will be
mapped to output channel 2; sensor channel 3 will be mapped to output channel 3; and
sensor channel 4 will be mapped to output channel 4.
Use Figure 3.3 below to set the DIP switch settings to select channel group 1:
Input Mapping Switches Baud Rate Switches
S4 S5
On
O
Channel
Group
Click 114 – Selects Matrix channels 1 through 4 for output
Figure 3.3 – Click 114 DIP Switch Settings
Bus 1 Bus 2
Click 112 DIP Switch Settings
On a Click 112, channel group 1 comprises input channels 1 and 2, where sensor channel 1
will be mapped to output channel 1 and sensor channel 2 will be mapped to output channel 2. In order to map sensor channel 3 to output channel 1 and sensor channel 4 to output
channel 2, you will need to select channel group 2.
If you are using two Click 112 devices, you will need to set the DIP switches dierently for
each card and daisy-chain the cards together using bus 1.
Figure 3.4 below shows how to set the DIP switches on the Click 112 card on the left. is
will select Matrix output channels 1 and 2 for output.
Page 34

34 CHAPTER 3 CONTACT CLOSURE COMMUNICATION
123456781
234
567
8
124356781
234
567
8
Input Mapping Switches Baud Rate Switches
S4 S5
On
O
Channel
Group
Bus 1 Bus 2
Click 112 –Selects channels 1 & 2
Figure 3.4 – Click 112 DIP Switches for Channels 1 and 2
Figure 3.5 shows how to set the DIP switches on the Click 112 on the right. is will assign sensor output channels 3 and 4 for output.
Input Mapping Switches Baud Rate Switches
S4
S5
On
O
Channel
Group
Bus 1 Bus 2
Click 112 – Selects channels 3 & 4
Figure 3.5 – Click 112 DIP Switches for Channels 3 and 4
For information on how to use other DIP switch conguration options, as well as the front
panel menu and Click Supervisor, see the Click 112/114 chapter in the Click Series User
Guide.
Using the Click 104 Rotary Switch
e rotary switch is located on the lower part of the faceplate and can be used to change
the channel input mapping. e switch can be twisted by inserting a small screwdriver into
the arrow slot.
If you use this switch to set the channel input mapping, you won’t be able to use the Click
Supervisor software or the front panel menu to change this particular parameter (although
you will still be able to use them to change other parameters).
If the switch is set to 0, the device is in Software mode. is means that all parameters are
set by the front panel menu or Click Supervisor. If the switch is set to any other number,
the device is in Hardware mode, meaning that the channel input mapping is set by the
rotary switch.
e Click 104 has four output channels; if you need more than this, you’ll need to use multiple devices daisy-chained together.
Page 35

CHAPTER 3 CONTACT CLOSURE COMMUNICATION 35
As shown in the table below, the outputs are mapped sequentially—that is, they can only
be mapped in numerically ordered groups of four (1–4, 5–8, etc.). If you set the switch to 3,
for 9–12, then sensor channel 9 would be mapped to output 1, sensor channel 10 would be
mapped to output 2, sensor channel 11 would be mapped to output 3, and sensor channel
12 would be mapped to output 4.
Switch Channels
0 Software mode
1 1–4
2 5–8
3 9–12
4 13–16
5 17–20
6 21–24
7 25–28
8 29–32
9 33–36
Table 3.1 – Click 104 Rotary Switch Channel Input Map Settings
Attaching and Programming the Click 112/114
Use the following steps to set up the contact closure rack cards for each sensor:
1 Make sure the DIP switches are set according to Figure 3.3 for a Click 114 and Fig-
ures 3.4 and 3.5 for Click 112 cards.
2 Power all the cards by plugging them into the detector rack.
Figure 3.6 – Wiring the Click 112/114 Rack Cards
3 Connect a 6-ft. (1.8-m) patch cord from the Click 222 RS-485 A port to a bus 1 port
on the appropriate rack card (see Figure 3.6).
Page 36

36 CHAPTER 3 CONTACT CLOSURE COMMUNICATION
4 Connect a 6-ft. (1.8-m) patch cord from the Click 222 RS-485 B port to a bus 1 port
on another rack card.
5 If you are using Click 112 cards, use an 6-in. (15-cm) patch cord to share bus 1 be-
tween cards dedicated to the same sensor. Also, congure one card to use Matrix channels 1 and 2 and congure the other card to use Matrix channels 3 and 4. If you have
more than two sensors in your system, repeat steps 2–4 to connect bus 1 for all remaining rack cards.
6 Connect a 5-ft. (1.5-m) patch cord from one of the Click 222 bridge ports to bus 2 of
the rack cards.
7 Use the 6-in. (15 cm) patch cords to create a daisy-chain that shares bus 2 between all
of the rack cards. Bus 2 will be used for device conguration.
Click 112/114 LEDs
Once you have completed the wiring, check the Menu Level 1 LEDs, which have both
menu-indicating and general status–indicating functions. e list below contains information on the general status–indicating functions of the LEDs:
PWR (red) – Indicates the device is powered.
PU (blue) – is LED is not associated with any general status function and should
remain o while the card is in normal operating mode.
TD (green) – Indicates the card is transmitting serial communication.
RD (yellow) – Indicates the card is receiving serial communications.
e red LED should be on, showing the card is powered and operating normally.
e list below contains additional information about the rest of the LEDs:
Detection Channel LEDs (red) – Indicates when a call is placed on the corresponding
contact closure output channel.
Menu Level 2 – Used for the conguration menu that is activated using the Mode
switch.
General Status (Menu Level 1) – In addition to the functions listed above, these are
used to cycle through and select options from the front panel menu.
Page 37

CHAPTER 3 CONTACT CLOSURE COMMUNICATION 37
Detection
Channel
Menu Level 2
Menu Level 1
Mode Switch
Figure 3.7 – Click 112/114 Menu
Normally, a SmartSensor Matrix sensor will send 10 contact closure messages each second.
If a rack card does not receive communications from a sensor within 10 seconds, the rack
card will go into fail-safe mode and all of the contact closures will be activated and the corresponding detection channel LEDs on the faceplate will turn on.
Attaching and Programming the Click 104
Use the following steps to set up the DIN rail contact closure module for each sensor:
1 Mount the Click 104 on a DIN rail over a T-bus connector. is connects the device’s
control bus (bus 2) to the installation’s shared communication bus; you can connect
your computer to another device on this shared bus, such as the Click 305 USB converter, to access the Click 104 to congure it using Click Supervisor. Mounting the
Click 104 on the T-bus also connects it to the power source.
Figure 3.8 – Wiring the Click 104 Module
2 Send detection data to the data bus (bus 1). Connect a Click 222 to the Click 104 by
connecting jumper cables from the RJ-11 jacks on the faceplate of the Click 222 to the
RJ-11 jacks on the faceplate of the Click 104 (see Figure 3.8).
Page 38

38 CHAPTER 3 CONTACT CLOSURE COMMUNICATION
3 If needed, daisy-chain multiple Click 104 devices together by utilizing both RJ-11
jacks on each device’s faceplate.
Click 104 LEDs
e front panel of the device features a push-button and three banks of LEDs for on-device
conguration and monitoring. e rst bank of LEDs, labeled Channel, displays the state
of the contact closure outputs (see Figure 3.8).
Channel
1 2 3 4
Menu
PWR OK TD RD
Figure 3.9 – Click 104 LEDs
e two lower banks of LEDs, labeled Menu, and the push-button, labeled Mode Switch,
are used for navigating through Menu mode.
e lower bank of LEDs will be referred to as Level 1 and is used in selecting menu options. e upper bank will be referred to as Level 2 and is used in conguring the menu options. Level 2 LEDs only light up when a menu selection is made using the Level 1 LEDs.
e mode switch push-button is used to enter Menu mode (see Figure 3.9). To use the
menu:
1 2 3 4
Menu
Level 2
Level 1
PWR
OK TD RD
Mode Switch
Figure 3.10 – Click 104 LED Menu
1 Press and hold the mode switch to enter Menu mode. e Level 1 LEDs will start to
light up to indicate that the device is cycling through all menu options.
2 Release the mode switch when you reach the desired menu option. (Pressing and hold-
ing again will resume cycling through menu options.)
3 Quickly press and release the mode switch to select the current menu option. Once it’s
selected, the Level 2 LEDs will start to let you congure the options for the selected
Page 39

CHAPTER 3 CONTACT CLOSURE COMMUNICATION 39
2
5
1
6
4
7
3
menu option.
4 Press and hold the mode switch to cycle through the submenu. e Level 2 LEDs will
light to indicate that the device is cycling though all conguration options.
5 Release the mode switch once the desired conguration option is reached.
6 Quickly press and release the mode switch to select the current conguration option.
e device will exit Menu mode, and either the selected function will run or the selected conguration will be set and saved to the device.
Channel Mapping
Once the Click 104/112/114 devices are installed, make sure that each detector rack channel is properly mapped to the correct trac phase in the trac controller. e general
NEMA standard for 8-phase numbering is presented in Figure 3.8. Many intersections
will not have eight phases, and in some cases they may not even follow the NEMA convention. Check the plans in the trac signal cabinet to verify how the phases are numbered at
each intersection.
Figure 3.11 – Standard NEMA 8-phase Number Scheme
Phases 1, 2, 5 and 6 are often used for the “main” street, and phases 3, 4, 7 and 8 are often
used for the “side” street as shown in Figure 3.8.
Note
Chapter 10 contains a section about Rack Card Tools which explains how the channelto-phase mapping can be verified with or without the sensors installed.
Since each Matrix sensor often detects both the left-turn phase and the through-movement phase for a single approach, the associated rack card will have often have channels
that correspond to one of the following phase (ф) pairs: ф2 and ф5; ф6 and ф1; ф4 and ф7;
ф8 and ф3.
Page 40

40 CHAPTER 3 CONTACT CLOSURE COMMUNICATION
C1
↓
Φ
1
C2
↓
Φ
6
C3
↓
Φ
6
C4
↓
Φ
6
C5
↓
Φ
5
C6
↓
Φ
2
C7
↓
Φ
2
C8
↓
Φ
2
C9
↓
Φ
3
C10
↓
Φ
8
C11
↓
Φ
8
C12
↓
Φ
8
C13
↓
Φ
7
C14
↓
Φ
4
C15
↓
Φ
4
C16
↓
Φ
4
NEMA TS2, 2070 and other advanced trac cabinet systems usually allow software programming of the detector card channel outputs to trac phases via a channel-to-phase
mapping grid in the controller menu. Figure 3.9 illustrates how the detector channels 1 to
16 of a NEMA TS-2 rack can be assigned to the standard eight phases using four Click
114 cards. e rack card slots are numbered across the top and the controller’s detection
channels are represented by the gray labels C1–C16.
Slot 1 Slot 2 Slot 3 Slot 4 Slot 5 Slot 6 Slot 7 Slot 8
Figure 3.12 – NEMA TS-2 Type 1 Rack Channel to Trac Phase Example
In Figure 3.9, four channels are used from each SmartSensor Matrix. In this example,
channel 1 from the rst sensor is mapped to trac phase 1 (left-turn phase on main street).
Channels 2, 3 and 4 from the rst sensor are mapped to trac phase 6. is represents a
case where detections from three through-movement lanes are brought in separately. is
type of lane-by-lane detection can be benecial in some situations. Wavetronix typically
recommends the use of 4-channel cards because it oers greater exibility of signaling
contact closures.
Note
With NEMA TS1 and other legacy systems, the programming is often done via a wiring panel on the side of the controller cabinet. With wired systems, you will need to
verify that the wiring on the detector programming panel provides the proper mapping from the rack channel outputs to the controller input wires dedicated for ф1–ф8
detector calls.
Page 41

Page 42

Page 43

Part II
Using SmartSensor Manager
Matrix
Chapter 4 – Installing SmartSensor Manager Matrix
Chapter 5 – Communication
Chapter 6 – Sensor Settings
Chapter 7 – Lanes & Stop Bars
Chapter 8 – Zones & Channels
Chapter 9 – Verification
Chapter 10 – Tools
Page 44

Page 45

Installing SmartSensor
Manager Matrix 4
In this chapter
Installing SSMM
Microsoft .NET Framework
4
e SmartSensor Manager Matrix (SSMM) software enables you to congure and interact
with the SmartSensor Matrix. SSMM can be run on a Windows® PC and on a Socket
Mobile 650 handheld computer.
e software can be downloaded on other computers by going to www.wavetronix.com.
is chapter explains how to download and install the SSMM software.
Using the Click 421
e Click 421 converts wired or wireless serial data to RS-485 communication and sends
it to all devices on a shared multi-drop communication bus on the backplate. is allows
control of all SmartSensor Matrix units from a single access point.
You can make a wired connection using a USB-to-serial converter and a USB adapter
cable; alternatively, you can make a wireless connection using a precongured Bluetooth
link. A whip antenna can be attached to the Click 421 to increase the distance and reliability of the wireless link.
Follow the steps below to use the Click 421 to communicate with the SmartSensor Matrix:
1 Rock the Click 421 device onto the green T-bus to the left of the gray T-bus connector
on the second DIN rail on the backplate.
Page 46

46 CHAPTER 4 INSTALLING SMARTSENSOR MANAGER MATRIX
2 Make a wired (using the serial port on the front of the device) or wireless (Bluetooth)
connection between the Click 421 and the handheld computer.
If you wish to establish a wired connection with a laptop computer instead of the handheld
device, use the laptop’s native RS-232 serial port to connect to the Click 421, or a USBto-serial converter if the laptop does not have an RS-232 serial port. You can also establish
a Bluetooth connection from your laptop to the Click 421. To do so, consult your laptop’s
software guidelines on how to discover Bluetooth devices and congure a Bluetooth serial
connection.
An RJ-11 patch cord with a pigtail on one end can be wired to the RS-485 screw terminal
on the Click 421 and used to patch into RJ-11 sockets on the rack cards or backplate for
troubleshooting.
Once you’ve connected to the Click 421, you can connect to the sensor using SmartSensor
Manager Matrix, as outlined in the next chapter.
Installing SSMM
You can install SSMM to your PC or laptop. Everything needed for this installation is
contained in the SSMM Setup.exe le.
Note
You must have Administrator rights to run the setup program.
Follow these steps to install SSMM on a PC or laptop:
1 To download the install le, go to the Wavetronix website at www.wavetronix.com.
2 Click the Support link near the top of the page and follow the controls to nd the
correct link for the SmartSensor Manager Matrix install le.
3 Once you’ve downloaded the le, double-click on it. Opening it executes a setup pro-
gram that will copy all the necessary les to the hard drive and place icons in the Start
menu and on the desktop of the PC or laptop (see Figure 4.2).
Page 47

CHAPTER 4 INSTALLING SMARTSENSOR MANAGER MATRIX 47
Figure 4.1 – SSMM Setup Wizard
4 Select an installation location. e default location provided is normally “C:\Program
Files\Wavetronix.” If desired, click Browse to choose another location (see Figure 4.3).
Figure 4.2 – Location to be Installed
5 Click the Install Now button.
6 After SSMM is installed, you can create shortcuts to the SSMM software on the desk-
top and in the Start menu using the corresponding checkboxes (see Figure 4.4). If no
shortcuts are desired, uncheck the corresponding boxes.
Figure 4.3 – Shortcut Options
7 Click the View release notes when nished checkbox to view the SSMM release
notes. e release notes contain additional information about the current version of
Page 48

48 CHAPTER 4 INSTALLING SMARTSENSOR MANAGER MATRIX
the SSMM software. A PDF reader program (i.e. Adobe Acrobat Reader) is required
to view the release notes.
8 Click Finish to complete the setup process.
Note
SSMM is designed for the 96 DPI display setting. The application may not display text
properly, and may not function properly in general, if the display is not set to 96 DPI.
Installing SSMM on a Handheld Computer
SSMM can also be installed and on a handheld computer. Use these steps to install SSMM
on a handheld computer running Windows Mobile:
1 Ensure the handheld computer is connected to the PC and synced.
2 Click on the SSMM Setup.exe le to run the setup program on the host computer.
e SSMM Setup Wizard will automatically check the host computer to see if Microsoft ActiveSync is installed (ActiveSync is a program that is used to communicate
with a handheld device). If the ActiveSync program is found, the option of installing
SSMM to a handheld device will become available.
3 Click the Pocket PC checkbox and then the Next>> button to install SSMM on a
connected handheld device (see Figure 4.5). If both the Computer and Pocket PC
boxes are checked, the setup program will rst install the SSMM software to the PC.
Figure 4.4 – Destination Selection
4 Click Continue>> to start the handheld computer installation process. e setup pro-
gram runs the Add/Remove Programs application for Windows handheld devices. If
a handheld device is connected to the computer, Add/Remove Programs will immediately begin installing SSMM on the handheld device. If a handheld device is not connected to the computer, SSMM will be downloaded the next time a handheld device
is connected to the computer.
Page 49

CHAPTER 4 INSTALLING SMARTSENSOR MANAGER MATRIX 49
5 Click OK once the download is complete.
Microsoft .NET Framework
e SSMM setup program will automatically detect whether Microsoft .NET Compact
Framework v3.5 is installed on your PC. If it is not installed, you will be prompted to install
it (see Figure 4.7).
Figure 4.5 – Microsoft .NET Framework V2.0 Prompt
Click the Install Framework button and you will be taken to the Microsoft Website where
you can install the latest version of Microsoft .NET Framework.
Page 50

Page 51

Communication 5
In this chapter
Serial Connection
Internet Connection
Virtual Connection
Viewing Connection Info
Upgrading the Sensor’s Embedded Software
5
Once the sensors are installed, use the SSMM software to change settings, view data and
congure the sensors to the roadway.
Launch SSMM by either clicking on the icon that was placed on your desktop or clicking
the icon found in the Start menu. e SSMM splash screen and then main screen shown
in Figure 5.1 will appear.
Page 52

52 CHAPTER 5 COMMUNICATION
Figure 5.1 – SSMM Splash Screen (left) and Main Screen (right)
You can always view the version of SSMM you are using by right-clicking (click and hold
on handheld) on the main screen and then clicking SSM Matrix Version. To see the ver-
sion, date and timestamp of the individual components that make up the program, select
Component Version (see Figure 5.2).
Figure 5.2 – Matrix Version (top) and Component Version (bottom)
After you are connected to a sensor, you can also view the dates the rmware components
were created by clicking Firmware Versions. Information on the two main hardware components, the DSP and RF board, can be viewed by clicking Hardware Version (see Figure 5.3).
Page 53

CHAPTER 5 COMMUNICATION 53
Figure 5.3 – Firmware Versions (left) and Hardware Versions (right)
If you are using SSMM on a computer, you can use the panel in the lower left of the main
screen to change the size of the user interface on your computer. Click any of the three
squares to increase or decrease the size of the user interface.
e rst step is to make a connection to the sensor. e following three types of connections can be made:
Serial connection – Made using Bluetooth, RS-232, or RS-485 communication.
Internet connection – Made using an IP address and a serial to Ethernet converter.
Virtual connection – Made for convenience in learning and demonstrating SSMM
functionality.
Communication settings are stored in the system registry each time a connection is established. After the rst connection is made to the SS225, the SSMM software will save the
connection settings that were used. Click the magnifying glass icon on the right side of
the communication link to connect using the most recently used parameters stored in the
registry.
Serial Connection
1 Click on Communication to access the Communication window (see Figure 5.2).
2 Select the Serial tab.
3 Set Port and Timeout to the desired settings.
4 Select the type of search (Full or Quick) you would like to perform. A full search will
nd all SmartSensor Matrix units on the selected RS-485 control bus and can take
up to 30 seconds; a quick search can be used after the rst time a full search has been
performed.
Page 54

54 CHAPTER 5 COMMUNICATION
Note
A quick search should not be used the first time you connect to sensors on an RS-485
control bus. If you add or replace a sensor on an existing control bus, a full search will
need to be performed before a quick search can be made.
Note
If you perform a full search and then cancel before the search is complete, the sensors not discovered before the full search was terminated will also not be visible after
a quick search. You will then need to perform a full search to completion before all
sensors can be discovered using a quick search.
5 Click the Search button.
6 Click on the desired sensor row from the list to select a sensor (see Figure 5.4). e
sensor list shows the sensor ID, location, and approach of each discovered sensor.
7 Click the Connect button. You will be directed back to the home page once a connec-
tion is established.
Figure 5.4 – Serial Connection
After you have connected to a sensor, the next time you would like to connect you
can simply click the magnifying glass icon in the upper right corner of the screen.
is will take you to the last connection settings you used to connect to a sensor.
e rst time you connect to a sensor, the default Sensor ID will be the last seven digits of
the sensor’s serial number. However, the names in the Location and Approach elds will
Page 55

CHAPTER 5 COMMUNICATION 55
be set to default values.
Note
It is recommended that you label the service end of each SmartSensor Matrix cable
when the cable is pulled so that the approach the sensor is monitoring can be documented. You may need to power down all sensors except for the one you are configuring in order to determine which approach it is monitoring.
If you have problems connecting:
1 Make sure that all power and communication wiring is correct.
2 Check the port settings (Port ID).
Connection failure can occur for various reasons; if a failure occurs repeatedly, call Wavetro-
nix Technical Support at 801-734-7200 for assistance.
Once you have selected a sensor from the device list, you can click again on that
row to bring up a Sensor Info pop-up (see Figure 5.5). To bring up the Sensor Info
pop-up, you can also click on the sensor icon that appears in the upper right corner
of the screen (see Figure 5.4). e information in the Sensor Info screen cannot be edited.
Figure 5.5 – Sensor Info Screen
e Sensor Info screen lists the following sensor settings and version information:
Sensor ID – e last seven digits of the sensor serial number. is eld is not editable.
Description – Used to describe the application (e.g. stop bar detection); can also be
used for GPS coordinates. is eld is not editable from this screen.
Location – Used to describe the intersection where the sensor is located. is eld is
Page 56

56 CHAPTER 5 COMMUNICATION
not editable from this screen.
Approach – Used to indicate which approach of the intersection the sensor monitors.
is eld is not editable from this screen.
Sensor Version – Overall sensor product version, which represents a released combi-
nation of the DSP, Algorithm, FPGA and FPAA subcomponent versions.
DSP Rev – DSP code version date (YYYY-MM-DD).
Algorithms Rev – Algorithm code version date (YYYY-MM-DD).
FPGA Version – FPGA version date (YYYY-MM-DD).
FPAA Version – FPAA version date (YYYY-MM-DD).
Signal Rack Cards – When the switch is on, any rack cards connected to this sensor’s
data port will identify themselves by ashing a blink sequence on the main menu
LEDs of the rack card.
Internet Connection
e SmartSensor Matrix can be connected to the Internet, allowing access to the sensor
from anywhere with Internet access. e following is a list of ways to connect the SmartSensor Matrix to the Internet:
Serial to Ethernet Converter – e SmartSensor Matrix can be connected to a local
area network (LAN) by using a Click 301 serial to Ethernet converter.
Serial to 802.11b Wireless – e SmartSensor Matrix can be connected using a Click
420 serial to 802.11b converter. e Click 420 provides serial devices with an IP address on a wireless 802.11b network.
Internet Service Providers – e SmartSensor Matrix can be equipped with optional
external modems (CDMA, GMS or GPRS) and assigned an Internet address on these
networks. (Please contact Wavetronix Technical Services for assistance.)
Note
The Internet connection is made to the control bridge and NOT to the data ports.
Use the steps below to connect to the SmartSensor Matrix using an Internet connection:
1 Click on Communication.
2 Click the Internet tab and the Internet setting options will appear (see Figure 5.6).
Page 57

CHAPTER 5 COMMUNICATION 57
Figure 5.6 – Internet Connection Screen
3 Enter the IP address or URL of the sensor of interest. Enter the IP address assigned to
either the CDMA modem or the Click 301 serial to Ethernet converter.
4 Enter the port number assigned to the CDMA modem or the Click 301 serial to Eth-
ernet converter in the Port eld. is will be an integer value in the range of 0–65536.
e Click 301 port number automatically defaults to 10001.
5 Set the Timeout value to 1000.
6 Select the type of search (Full or Quick) you would like to perform (see the Serial
Connection section of this chapter for more on these two searches).
7 Click the Search button. is may take up to 30 seconds while the sensors on your
control bus are discovered and listed. (You can click Cancel as soon as the sensor of
interest is listed.)
8 Click on the desired row from the list to select a sensor (see Figure 5.7).
Figure 5.7 – Internet Connection Screen
Page 58

58 CHAPTER 5 COMMUNICATION
9 Click the Connect button. When a connection is established you will be directed back
to the home page.
If you have problems connecting:
1 Make sure that all power and communication wiring is correct.
2 Check the address and port number.
Connection failure can occur for various reasons; if a failure occurs repeatedly, call Wa-
vetronix Technical Support at 801-764-0277 for assistance.
Address Book
e Address Book is available on the Internet connection tab and allows you to save IP
connection settings for future use.
Click the Address Book button located at the bottom of the Communication page to add
new connection settings to the Address Book (see Figure 5.8).
Deletes an
Address Book
Edits the
Selected Device
Adds a Device to
the Address Book
Deletes a Device from
the Address Book
Figure 5.8 – Address Book
Imports an
Address Book
Exports an
Address Book
Virtual Connection
A virtual connection allows you to use the SSMM software without being connected to an
actual sensor. Making a virtual connection can be useful for the following reasons:
To view a saved sensor setup le
To play back previously logged trac
To demonstrate functionality for dierent trac applications
Page 59

CHAPTER 5 COMMUNICATION 59
To review how the software works
Use the following steps to make a virtual connection:
1 Click the Communication button.
2 Select the Virtual tab (see Figure 5.9).
Figure 5.9 – Virtual Connection Screen
3 Select or create a virtual sensor le (.vsf ) by clicking the magnifying glass icon.
4 Click the Search button. is may take up to 30 seconds while the sensors on your
virtual control bus are discovered and listed. (You can click Cancel if the sensor of
interest has already been listed.)
5 Click on the desired row from the list to select a sensor.
6 Click the Connect button. When a connection is established you will be directed back
to the home page.
Virtual Sensor File
Since a virtual connection is not made to an actual sensor, a virtual sensor le (.vsf ) is used
to save the conguration settings much like an actual sensor’s ash memory. SSMM comes
with default virtual les that you can see once you click the Search button. If you create
your own virtual sensor le, you will have to nd it in the virtual les directory by clicking
the magnifying glass icon under the Virtual Sensor Files Location heading.
Note
When you are connected using a virtual sensor file, changes that would normally be
saved to a sensor’s flash memory will automatically be saved to the virtual sensor
file.
Page 60

60 CHAPTER 5 COMMUNICATION
Virtual sensor les can be converted to sensor setup les and can be restored to an actual
sensor; sensor setup les that have been backed up from a sensor can also be converted
to virtual sensor les. To convert a sensor setup le to a virtual sensor le, make a virtual
connection and then use the Restore Sensor Setup tool in the Tools menu. To convert a
virtual sensor le to a sensor setup le, use the Back-up Sensor Setup tool.
Note
To configure channels for a future installation, connect using a virtual connection,
create a virtual sensor file and then back up the configuration settings that you created. After the file is successfully backed up, the virtual sensor file will change to a
sensor setup file and can be restored to any sensor in the field.
When a connection is made to the SmartSensor Matrix, the main menu will appear and all
conguration options will become available (see Figure 5.10).
Figure 5.10 – Main Menu (Connected)
Viewing Connection Information
Once connected, you can view additional information about the connection you have established by clicking on the moving arrows icon on the top right of the main menu page or
on the bottom right of the Communication screen (see Figure 5.11). ese arrows are only
visible when there is an established connection.
Page 61

CHAPTER 5 COMMUNICATION 61
Figure 5.11 – Connection Info Screen
Below is a list of the information available on the Connection Info screen:
Status – Shows that you are connected.
Sensor – Shows the subnet and sensor ID.
Type – Shows the type of connection.
Duration – Shows how long you have been connected.
Failures – Shows the amount of failures during the connection, the percentage rate of
failure and a link to the communication error log.
Communication Error Log
e error log contains all errors stored in the sensor’s memory buer. If you are having
trouble connecting, using the error log may be helpful in the troubleshooting process. If you
continue having trouble, save the error log le and contact Wavetronix Technical Services.
Note
The error log is cleared every time you close SSMM, so if you need to save the file, do
so before shutting the program down.
Click the View Error Log link to view the communications error log (see Figure 5.12).
e error log can also be accessed by clicking on the Error Log icon at the bottom of the
Communication screen.
Page 62

62 CHAPTER 5 COMMUNICATION
Figure 5.12 – Error Log
Upgrading the Sensor’s Embedded Software
After clicking the Connect button, the software will check to see if your software version
matches the version of the sensor’s embedded software. If a discrepancy is detected, the
Version Control screen may appear asking you to install rmware upgrades (see Figure
5.13). If you think you have reached this screen in error, clicking the Recheck button will
have the software retry and ensure that there has not been a communication issue. Clicking the Details button will display the current sensor and software information. Click the
UPLOAD FIRMWARE button to upgrade the software.
Checking the Upload to all sensors checkbox will broadcast the upgrade to all the sensors
on the control bridge. Check the Disable fast pacing checkbox if you are connected using
Bluetooth or other devices with a slow connection speed (see Figure 5.13).
Figure 5.13 – Sensor’s Embedded Software Upgrade (left) and Details Table (right)
Page 63

CHAPTER 5 COMMUNICATION 63
Click the Details button to view the rmware versions of both the SSMM software and
the SmartSensor Matrix.
Once the Version Control screen appears, you can do one of the following:
Upgrade the sensor’s embedded software by clicking the UPLOAD FIRMWARE
button.
Click the Close button and continue the conguration process.
Find the version of SSMM software that is compatible with the sensor’s embedded
software.
Note
Clicking the Close button and continuing configuration without upgrading may cause
problems with functionality.
If any row is highlighted in red, the rmware upgrade may need to be installed. Compare
the sensor number with the SSMM number in the Digital row of the details table. If the
SSMM rmware version date is more recent than the sensor rmware version date, the
newer rmware will need to be installed; if the sensor’s rmware date is more recent than
the SSMM rmware version date, a warning will appear notifying you that older rmware
will be uploaded to the sensor (see Figure 5.14).
Figure 5.14 – Sensor Firmware Downgrade (left) Back Up Configuration (right)
If the downgrade message appears, it means that the sensor rmware is newer than the version of SSMM that was used to connect to the sensor. e newest version of SSMM can
be downloaded from www.wavetronix.com.
If you are upgrading from certain versions of SSMM, the upgrade may cause you to lose
Page 64

64 CHAPTER 5 COMMUNICATION
your sensor conguration. Follow the steps in the back up message to back up your sensor’s
conguration.
Note
If you are upgrading the software, it is always a good idea to back up your sensor configuration. There is always a chance that the sensor conguration could be lost after
upgrading. You can create a back up file by going to the Tools screen (see Chapter 10).
Click the UPLOAD FIRMWARE button to install the rmware embedded in SSMM
onto the SmartSensor Matrix. e Recheck button will query the sensor to see if the rmware bundled in SSMM is dierent than the version running on the sensor.
Page 65

Sensor Settings 6
In this chapter
Sensor Settings Screen
Sensor Info Screen
6
Click the Sensor Settings link on the main menu to change and save settings on the sensor.
General Sensor Settings
e General tab of the Sensor Settings screen allows you to change the sensor description,
RF channel, wash-out time, and other settings (see Figure 6.1).
Figure 6.1 – Serial Settings Window
Page 66

66 CHAPTER 6 SENSOR SETTINGS
e General tab contains the following elds:
Serial Number – Contains the sensor serial number and cannot be edited.
Sensor ID – Contains the ID used to uniquely identify all sensors on a multi-drop bus.
is ID is the last seven digits of the sensor’s serial number and cannot be edited.
Description – Allows you to enter a description for each sensor. Limited to 64 char-
acters.
Location – Allows you to enter the intersection location of the sensor. Limited to 64
characters.
Approach – Allows you to enter information about the direction of trac the sensor is
detecting (e.g. NB, SB, EB, WB). Limited to 32 characters.
RF Channel – Lets you set which one of the eight radio frequency channels the sensor
is using. Using multiple sensors in close proximity will require each sensor to be set
to a dierent RF channel (see the introduction for more information about mounting
the sensor).
Sensor Height – e height of the sensor in feet. is value aects the sensor’s detec-
tion algorithms. Entering an approximate height measurement for the sensor allows
detections to be placed correctly on the roadway.
Wash-out Time – Used to set the time the sensor has to see a tracker before it gets
washed out into the background.
Units – Allows sensor height, zone dimensions and road objects to be viewed in metric
mode rather than standard units.
Comm Sensor Settings
e Comm tab allows you to change the response delay, and other settings (see Figure 6.2).
Figure 6.2 – Comm Tab
Response Delay – Used to congure how long the sensor will wait before responding
to a message received. is is useful for some communications devices that are unable
Page 67

CHAPTER 6 SENSOR SETTINGS 67
to quickly change transmission direction. e default value is 10 milliseconds. is
value can be selected for both of the sensor’s ports independently.
Note
In many cases, SSMM will be connected over port 1. A green arrow is used to show the
port over which SSMM is connected to the sensor. During troubleshooting or other
special cases, you may want to connect to the sensor over port 2. Port 2 is connected
to the orange RS-485 wire pair and is typically used for detection calls.
Data Push – Data can be pushed over port 1, port 2 or both. To disable data push,
select None. In many cases, data push will only occur over port 2.
If you would like to change which port is used to push data, please contact Wavetronix
Technical Services rst, as changing this setting can aect how the sensor, and other
devices connected to it, are wired.
Note
If for some reason SSMM connects over the same port that SmartSensor Matrix is
using to push data, the software will continue to poll the sensor for detection call
messages. This will help keep the intersection operating normally during the configuration process.
Source – In normal use, the source is always the radar antenna. However, in some
cases, other sources may be used for demonstrations or evaluations. When the source
is switched to Diagnostic, the antenna is no longer used. Instead, a predetermined
sequence of trac will appear.
Sensor Info Screen
Some of the Sensor Settings information can be viewed on the Sensor Info screen. After
searching for sensors, select a sensor from the list and either click on the sensor icon in the
upper right corner of the Communication screen or click again on the sensor row and the
Sensor Info screen will appear (see Figure 6.3).
Page 68

68 CHAPTER 6 SENSOR SETTINGS
Figure 6.3 – Sensor Info Screen
Page 69

Lanes & Stop Bars 7
In this chapter
Display Options
Menu Bar
Automatic Configuration
Manual Configuration
7
After Sensor Settings, the next option available from the main menu is Sensor Setup.
When you click this option, the rst screen that appears is Lanes & Stop Bars.
e Lanes & Stop Bars screen shows the sensor’s 100-ft. (30.5-m), 90° degree view and
provides automatic and manual controls to quickly and easily congure the sensor to the
roadway. e sensor’s view has the appearance of a baseball ineld with the sensor icon
shown at the position where home plate would be (see Figure 7.1).
Figure 7.1 – Lanes & Stop Bars Tab
Page 70

70 CHAPTER 7 LANES & STOP BARS
Vehicle detections are represented by tracks (a series of dots) along the sensor’s view. e
vehicle tracks show where the sensor is detecting trac and will later help you congure
lanes. Vehicle track history can be cleared from the screen by clicking the Clear Tracks
button below the sensor view.
Note
Vehicle tracks are not constrained to lanes, even after you have saved a lane configuration to the sensor.
Display Options
e Lanes & Stop Bar tab has the following display options:
Edit Area
Edit Area with Saved Conguration Overlay
Edit Area with Automatic Conguration Overlay
Edit Area
e edit area is where manual changes to the sensor’s conguration are made (see Figure
7.2). e changes you make in the edit area will only be saved if you click on the Save Con-
g button or click on another tab.
Edit Area
Figure 7.2 – Edit Area
You can copy elements from the saved and automatic conguration, which will be described
later.
Page 71

CHAPTER 7 LANES & STOP BARS 71
e Edit Area also contains the approach name in a small window outside of the sensor’s
view (see Figure 7.3) If needed, click on the name box to see the entire approach name. is
allows you to always know which approach is being congured. e approach name can be
edited in the Sensor Settings window.
Figure 7.3 – Approach Name
Saved Configuration Overlay
e Saved Conguration overlay shows everything that has been saved to the sensor (see
Figure 7.4). e purpose of this feature is to compare what is currently saved to the sensor
with the changes you are making in the edit area. To show or hide this overlay, click the
Saved Cfg button.
Figure 7.4 – Saved Configuration Overlay
Automatic Configuration Overlay
e Automatic Conguration overlay shows lanes and stop bars that have been automatically discovered (see Figure 7.5). To show or hide this overlay, click the Auto Cfg button.
Page 72

72 CHAPTER 7 LANES & STOP BARS
Figure 7.5 – Automatic Configuration Overlay
SmartSensor Matrix is constantly running the auto-conguration process in order to nd
undiscovered lanes and stop bars. During this process, lanes will appear in the Auto Cfg
overlay. You will need to select and capture auto-congured lanes in order to save them to
the sensor (see the Capturing Lanes and Stop Bars section below). Wait at least 2–3 cycles
of the intersection to accurately detect the lanes and stop bars.
Capturing Lanes and Stop Bars
Lanes that appear in the Saved Conguration Overlay or in the Automatic Conguration
Overlay can be captured by clicking on them. Once a lane is captured, it becomes part of
the edit area. Captured lanes are only copied to the edit area and are NOT saved to the
sensor until after clicking on the Save Cong button.
To capture lanes:
1 Select a lane by clicking on it once.
2 Click on the lane a second time to bring up the Capture window (see Figure 7.6).
3 Click on the Capture Lane button to capture the selected lane. If you want to capture
all the congured lanes, click the Capture All button.
Figure 7.6 – Capture Window
Page 73

CHAPTER 7 LANES & STOP BARS 73
Note
If a stop bar is found for a lane during the auto-configuration process, it will be captured with the lane.
Menu Bar
e menu bar at the bottom of the screen allows you to perform a variety of operations
during sensor conguration. Click the button at the right side of the menu bar to open
a window that shows descriptions for the various menu icons (see Figure 7.7).
Figure 7.7 – Sensor Setup Menu Window
e Menu Bar contains the following options:
To Main Menu – Returns you to the main menu.
Save Config – Saves the lanes and stop bars to the sensor.
Undo Last Edit – Undoes the last change in the edit area.
Clear Edit Area – Deletes all lanes from the edit area.
Move Sensor – Moves the sensor to a dierent corner of the edit area and rotates the
view accordingly.
Restart/Reboot – Gives you the option to restart automatic conguration or reboot
the sensor.
Edit Thresholds – Allows you to edit the sensor’s thresholds.
Pause Trac – Suspends or resumes movement of vehicle tracks on the screen.
Saving the Configuration
After automatic and manual conguration is complete, click the Save Cong button to
save the changes to the sensor. If you attempt to leave the Lanes & Stop Bar view before
saving your changes, the following prompt will appear (see Figure 7.8).
Page 74

74 CHAPTER 7 LANES & STOP BARS
Figure 7.8 – Save Changes Dialog
Moving the Sensor View
e SSMM software shows the position of the SmartSensor Matrix and the view is drawn
from the perspective of the sensor. e sensor’s default position is in the bottom-left corner
of the display. If the perspective in the software does not match your perspective of the
roadway, click the Rotate View button until the sensor position matches the approach you
are conguring.
Note
Moving the sensor in the software will have no eect on the sensor’s performance.
Its purpose is to facilitate the configuration process.
Restarting Auto Lane Config/Rebooting the Sensor
Restarting the automatic lane conguration will erase any auto-conguration information
that may have been gathered and will start the auto-conguration process over again.
Rebooting the sensor will also erase any auto-conguration information, but in addition
will clear and recongure the sensor thresholds.
Follow the steps below to restart the automatic lane conguration process or reboot the
sensor:
1 Click the Restart/Reboot button and the Restart or Reboot window will appear (see
Figure 7.9).
2 Select the appropriate radio button and click OK.
Figure 7.9 – Restart or Reboot Window
Page 75

CHAPTER 7 LANES & STOP BARS 75
Note
After you have mounted and aligned the sensor, you should always reboot the sensor
so that thresholds can adjust to the current view.
Editing Thresholds
You should only edit the Matrix thresholds under the direction of Wavetronix Technical
Services.
Warning
If you believe that you need to adjust the thresholds, please call Wavetronix at 801734-7200 for assistance.
1 Click on the Edit resholds button. is will turn the sensor’s view green and allow
you to change the sensitivity of certain areas in the view.
2 Click anywhere within the sensor’s view and the Sensitivity window will appear (see
Figure 7.10).
Figure 7.10 – Sensitivity Window
e Sensitivity window contains the following options:
Adjust All – Allows you to edit all of the sensor thresholds.
Adjust Region – Allows you to adjust thresholds in a selected region of the sensor view.
Zoom In – Allows you to zoom in and change thresholds of selected areas in the sensor
view (see Figure 7.11).
Reset Region – Allows you to reset only a selected region of thresholds to default set-
tings.
Reset All – Allows you to reset all the sensor thresholds to default settings.
Page 76

76 CHAPTER 7 LANES & STOP BARS
Figure 7.11 – Zoom In Feature
After you click on Adjust Bins or Adjust All, the Sensitivity Slider window will appear
(see Figure 7.12). Click on the up/down buttons to change the sensitivity (in decibels).
Negative values will lower the rejection threshold in order to increase sensitivity; positive
values will increase the rejection threshold in order to decrease sensitivity.
Figure 7.12 – Sensitivity Slider Window
Automatic Configuration
Use the following steps to auto-congure the SmartSensor Matrix:
1 Move the sensor to the appropriate location by clicking the button.
2 Click the button to clear the edit area.
3 If necessary, restart Automatic Lane Conguration by clicking the button and
selecting Restart Auto Lane Cfg from the window. Allow the intersection to cycle at
least twice before proceeding (this will take approximately 5 to 10 minutes).
4 Capture lanes & stop bars to edit area.
5 Make any necessary manual adjustments.
6 Save the desired changes to the sensor.
Note
Lanes have a direction shown by white arrows on top of the lane. To switch the lane
direction, simply click on the arrows. (To be able to change lane direction, there must
not be any display overlays on.) Before you save the configuration, make sure that all
the arrows are pointing in the correct direction.
Page 77

CHAPTER 7 LANES & STOP BARS 77
Manual Configuration
After the automatic conguration process is complete, manual adjustments can be made to
ne-tune the sensor conguration. In some cases, it will be easier to congure the sensor
manually than to use the auto-congured lanes and stop bars. e following manual operations can be performed:
Adding/deleting a lane
Inserting/deleting/moving a stop bar
Inserting/deleting a lane node
Moving a lane node
Adjusting the width of a lane node
Adding/Deleting/Moving a Lane
To add a new lane:
1 Click in the edit area where you would like to add a lane and the Edit Area window
will appear (see Figure 7.13).
2 Click on the Add Lane button. You are allowed to have a maximum of ten lanes and
you will not be able to save your conguration if any lanes overlap.
Figure 7.13 – Edit Area Window
To delete a lane:
1 Click in the edit area to select the lane you would like to delete and the Edit Lane
window will appear (see Figure 7.14).
2 Click the Delete Lane button.
Figure 7.14 – Edit Lane Window
To move a lane, simply click and drag the lane wherever you need. If you move a lane outside the edit area, a window will appear asking you if you would like to delete the lane (see
Figure 7.15).
Page 78

78 CHAPTER 7 LANES & STOP BARS
Figure 7.15 – Moving Lane Outside Edit Area
Inserting/Deleting/Moving a Stop Bar
To insert a lane stop bar:
1 Select a lane in the edit area.
2 Click on the selected lane again to bring up the Edit Lane window (see Figure 7.14).
3 Click on the Insert Stop Bar option of the Edit Lane window.
To delete a lane stop bar:
1 Select a lane in the edit area.
2 Click on the Delete Stop Bar option of the Delete Stop Bar window (see Figure 7.16).
Figure 7.16 – Deleting a Stop Bar
Additionally, you can click and drag or click on the arrows to move the stop bar in the
desired direction. e number between the arrows indicates the distance in feet from the
lane’s end node.
Inserting/Deleting a Lane Node
A lane node is a point, placed within a lane, that can be used to adjust a lane by moving
its trajectory, adding turns or corners, or widening part or all of a lane. Each lane starts out
with two nodes, one on each end. More can be added as needed.
To insert a lane node:
1 Select a lane in the edit area.
2 Click on the selected lane in the vicinity of the desired node to bring up the Edit Lane
window (see Figure 7.14).
3 Click on the Insert Node option. A lane can have a maximum of six nodes.
Page 79

CHAPTER 7 LANES & STOP BARS 79
To delete a lane node:
1 Select a lane in the edit area.
2 Click on the selected lane in the vicinity of the desired node to bring up the Node
Adjustment window (see Figure 7.17).
3 Click on the Delete Node option.
Figure 7.17 – Node Adjustment Window
Moving a Lane Node
1 Select a lane in the edit area.
2 Click and drag the lane node to the desired location (see Figure 7.18). Additionally,
you can click on the selected lane in the vicinity of the desired node to bring up the
Node Adjustment window (see Figure 7.17). e numbered pair (x,y) between the arrows indicates the distance within the sensor’s view. Click on the arrows to move the
node in the desired direction.
Figure 7.18 – Moving a Lane Node
Adjacent lane nodes can be placed to follow the curve of a lane. However, the lane curve
cannot exceed 45°. While you will be able to move the node anywhere on the screen, when
you try to save, a message will appear notifying you that the lane conguration is invalid if
the allowable limits are exceeded.
Page 80

80 CHAPTER 7 LANES & STOP BARS
Adjusting the Width of a Lane Node
Adjusting the width of a lane node will adjust the width of the lane.
1 Select a lane in the edit area.
2 Click on the selected lane and then click again on the node that will be adjusted and
the Edit Node window will appear.
3 Change the width (in feet) of the node, by clicking the Width up/down buttons or
enter the desired node width in the Width eld. Adjusting the node width will impact
detection search area for that lane.
Changing the Lane Arrows
You can change the arrows on the lanes to represent exactly what is present at the intersection.
1 Select a lane in the edit area.
2 Click on the arrow in the lane to toggle through the dierent arrow options (see Figure
7.19).
Figure 7.19 – Changing Lane Arrows
Page 81

Zones & Channels 8
In this chapter
Menu Bar
Placing Zones
Measuring Zones
8
After you have congured the lanes and stop bars, click on tab 2 to congure the zones and
channels. e Zones & Channels screen allows you to place zones and congure detection
channels (see Figure 8.1).
Figure 8.1 – Zones & Channels Tab
Each Matrix sensor supports up to 16 zones and 16 channels. If unused, the 16 zones are
stacked outside the sensor view and labeled Z1–Z16.
Page 82

82 CHAPTER 8 ZONES & CHANNELS
When you enter the Zones & Channels tab and you haven’t yet congured any zones, you
will be prompted to add auto zones (see Figure 8.2). If you click Yes, a zone will be placed
in each congured lane. Lanes and stop bars must be dened before you can add auto zones.
Note
Lanes and stop bars must be defined and saved before you will be able to add auto
zones.
Figure 8.2 – Auto Zones
If you enter a negative number in the Distance from stop bar: eld, the zone will be placed
after the stop bar. To add a negative distance from the stop bar, make the distance 0, highlight the whole eld and then click the down arrow once.
You can add a zone up to 100 ft. past the stop bar and a zone can be anywhere from 5 to
100 ft. long.
Menu Bar
e menu bar on the bottom of the screen allows you to make changes to the zones and
channels. Click the button at the right side of the menu bar to see a window with menu
descriptions (see Figure 8.3).
Page 83

CHAPTER 8 ZONES & CHANNELS 83
Figure 8.3 – Zones & Channels Menu Bar
e Zones & Channels menu bar contains the following options:
To Main Menu – Returns you to the main menu.
Save Config – Saves the zones and channel mapping to the sensor.
Undo Changes – Undoes changes made to the zones and channels.
Edit Zone – Allows you to move a zone and specify the channels to which it is mapped.
Zone/Channel Map – Allows you to map zones to channels.
Edit Channel – Allows you to map channels and change extend and delay settings.
Output Settings – Allows you to change extend and delay settings for each channel.
Place AutoZones – Allows you to easily place one zone per lane at each stop bar.
How to use these menu options will be covered in the next section.
After the conguration is complete, click the Save Cong button to save the changes to
the sensor. If you attempt to leave the Zones & Channels view before saving your changes,
you will be presented with the following prompt:
Figure 8.4 – Save Changes Dialog
Placing Zones
Zones can also be placed by dragging them from the stack on the edge of the view to a
location within the view. e boundaries of the zones can be moved by selecting the zone,
clicking on one of the corners and dragging it to a new location. e rst ten automatically
placed zones are also mapped to the rst ten detection channels respectively.
Page 84

84 CHAPTER 8 ZONES & CHANNELS
Editing Zones
Click the Edit Zone button to adjust the currently selected zone. An entire zone can be
moved by clicking and dragging or by using the arrow buttons on the Edit Zone window
(see Figure 8.5). Zones can overlap each other.
Figure 8.5 – Edit Zone Window
Placing AutoZones
Click the Place Auto Zones button if you would like to replace your manually congured
zones with auto zones. Placing auto zones requires you to insert the distance from the stop
bar and also the auto zone width (see Figure 8.6). Clicking Yes will add a zone to each
automatically congured lane.
Figure 8.6 – Placing Auto Zones Prompt
If zones are too long for the SSMM view, the zones will be cropped so that the entire zone
can be seen. For more information on auto zones, see the auto zone information at the
beginning of this chapter.
Note
Please note that all existing zones will be removed before new zones are placed automatically.
Channel Type
ere are three dierent types of channels to choose from: Normal, Counting and Pulse.
Page 85

CHAPTER 8 ZONES & CHANNELS 85
Pulse
Pulse
Normal Channel
e normal channel detects presence in the zone. is means that as soon as the leading
edge of the vehicle breaks the plane of the leading edge of the zone, the channel will be
activated (see Figure 8.7).
Channel LED
Channel LED
Channel LED
Figure 8.7 – Normal Channel
If there are no delay or extend settings, the zone will remain activated until all cars have
exited the zone.
Counting Channel
A counting channel counts each vehicle that passes through the zone. e channel is activated once the middle of the vehicle crosses the leading edge of the zone (see Figure 8.8).
Note
If you use a counting channel, you need to position the zones so that the vehicle is
detected and tracked before it arrives at the zone. Also, fast-traveling vehicles may
not be counted as accurately as slow-moving vehicles.
Channel LED
Channel LED
Channel LED
Figure 8.8 – Counting Channel
Once you select a counting channel type, the delay and extend settings will be disabled.
Page 86

86 CHAPTER 8 ZONES & CHANNELS
Pulse
Pulse Channel
A pulse activates the channel for a very short period of time once the front edge of the vehicle crosses the leading edge of the zone (see Figure 8.9). You can congure how long you
would like the pulse to be by changing the pulse channel width setting (see Figure 8.13). A
new pulse will only be sent after a car enters a zone when the zone is empty.
Channel LED
Channel LED
Channel LED
Figure 8.9 – Pulse Channel
Even though the zone stays activated, the contact closure call will only stay on for the time
specied in the pulse channel width setting. You can verify the duration of the pulse channel calls by viewing the virtual LEDs in the SSMM software. Once you have selected the
pulse channel type, the extend setting will be disabled.
Note
A pulse channel may be dicult to view in the SSMM software. The default pulsed
channel width is 200 ms. To better view the pulse channel activation, increase the
pulsed channel width in the output settings window (see the Output Settings section below).
Mapping Zones to Channels
After the zones are placed, the zones must be mapped to output channels. Channel mapping is described in the following sections.
Zone/Channel Map
e Zone/Channel map allows you to map or un-map zones to channels (see Figure 8.10).
To map a zone to a channel, determine which zone you want to map to which channel and
click on the gray indicator in the Zones/Channels table. A zone is mapped to a channel
only if the corresponding indicator is green. To see Channels 9–16, click and drag anywhere
inside the table.
Page 87

CHAPTER 8 ZONES & CHANNELS 87
Figure 8.10 – Zone/Channel Map Window
Each channel column contains channel number and channel type (N=normal, C=count,
P=pulse). Click on the individual zones in the zone column to highlight the zones in the
edit area.
Editing Channels
e Edit Channel button will allow you to choose the channel type, map/un-map zones
to a selected channel, and change delay/extend settings (see Figure 8.11). Click on the
Z1–Z16 indicators to map a zone/zones to the channel (only the congured zones will be
visible). Click on the channel indicator in the top-left corner or the Edit Channel button
to quickly cycle through channels.
Figure 8.11 – Edit Channel Window
e Edit Channel window also allows you to do the following:
AND/OR – Channels support AND and OR logic for all zones. Using the AND logic
means that all the selected zones have to be active for the channel to be triggered; the
OR logic means that any activity in any zone will trigger the channel. Click on the
AND or OR button to change the logic.
Delay/Extend Settings – Delay and extend settings can be viewed and then edited for
a selected channel. e channel delay is used to ignore alert outputs that are shorter
than the specied delay time. e extend feature is used to continue a channel output
after the required conditions have been met. e delay and extend settings will be
disabled for all counting channels and the extend setting will be disabled for all pulse
channels.
To edit the extend and delay, click anywhere in the white box with the D and E, and
the corresponding box will appear (see Figure 8.12). Manually edit or use the up/down
buttons to change the delay/extend settings.
Page 88

88 CHAPTER 8 ZONES & CHANNELS
Figure 8.12 – Output Settings (Normal, Counting, Pulse)
Detector Input – e Detector Input number provides a way for you to map inputs
to the intersection phase in the controller. By default, the Detector Input will be set
to “00;” if the input is left at “00,” then it is unassigned. is setting is for reference
purposes only and does not actually change the sensor.
Phase – Since the SmartSensor Matrix is capable of monitoring more than one phase,
this setting allows you to enter the phase number that most closely represents the
phase the sensor is monitoring. By default, the Phase will be set to “00;” if the phase is
left at “00,” then it is unassigned. is setting is for reference purposes only and does
not actually change the sensor.
Channel Type – is drop-down list allows you to select the type of channel (Normal,
Counting or Pulse). A normal channel is presence detection; a counting channel is
a special pulse based on counting algorithms; and a pulse channel is a generic pulse
based on zone presence.
Output Settings
e extend and delay settings can also be specied using the Output Settings button.
is button will open a window that will allow you to select individual channels to edit
and also to specify the minimum pulse width and pulsed channel width (Figure 8.13). e
minimum pulse width is the minimum duration a presence detection will be signaled via
the contact closure rack cards. e pulsed channel width is the duration the contact closure
message lasts for a pulse or counting channel. All output settings are specied in seconds.
Figure 8.13 – Output Settings Pop-up
Page 89

CHAPTER 8 ZONES & CHANNELS 89
e dashes in the table mean that those particular settings are disabled due to the selected
channel type. Double click on any channel row to change the output settings for that channel.
Measuring Zones
e SSMM software contains a feature that allows you to see how large a zone is as well as
a number of other distance measurements. Click on the ruler icon at the top of the Zones
& Channels window and then click on the zone you would like to measure and the zone’s
dimensions will appear (see Figure 8.14).
Figure 8.14 – Zone Measurements
Flags
A red and blue ag will also appear once a zone is selected. ese ags can be used to
measure the distance from that zone to anywhere in the edit area. ese ags will be saved
to the sensor.
Two additional ags are also available near the ruler icon. ese ags can be dragged anywhere on the edit area and used to measure anything in the sensor’s view (see Figure 8.15).
ese ags will NOT be saved to the sensor.
Page 90

90 CHAPTER 8 ZONES & CHANNELS
Figure 8.15 – Using Flags
Page 91

Verification 9
In this chapter
Channel Indicators
Verification Menu Bar
9
After the conguration is complete, you will need to verify that the sensor was congured
correctly. To verify lane conguration and channel mapping, click on tab 3. is will bring
up the Verication window (see Figure 9.1).
Figure 9.1 – Verification View
In the Verication window, vehicle detections will appear as light blue rectangles. e extent of these detections will vary based upon the length of the detected vehicle and the
length of queued trac.
Page 92

92 CHAPTER 9 VERIFICATION
Vehicle detections in a stopped queue are represented by a stationary light blue rectangle.
Channel Indicators
When detections enter a zone, they will cause the indicators for the channel mapped to
that zone to turn red. To see the zones mapped to a particular channel, select that channel by clicking on its indicator (see Figure 9.2). Active zones for the selected channel will
be red; inactive zones for the selected channel will be gray. Click on the yellow button on
either side of the channel indicators to see channels 9–16.
Figure 9.2 – Channel Verification
Note
Only the zones for selected channels will appear. If zones are not mapped to any
channel, they will not be seen in the Verification window.
To see the delay/extend, logic and detector input/phase settings for a single zone, click and
hold on a channel indicator and the following window will appear (see Figure 9.3).
Page 93

CHAPTER 9 VERIFICATION 93
Figure 9.3 – Delay and Extend Zone Settings
When vehicles stop before and after a zone, the stopped vehicle queue is extended to ll
the space between the two vehicles. is ensures that a queue of vehicles that extends in
front and behind a zone will always activate the zone even if the vehicles are not directly
over it (see Figure 9.4).
Stopped
Vehicle
Stopped Vehicle
Queue Extension
Stopped
Vehicle
Figure 9.4 – Two Vehicles Stopped With a Zone in Between
If a vehicle stops within 30 feet of the stop bar, then the stopped vehicle queue will be extended to the stop bar. is ensures that a vehicle will activate a zone even if it stops behind
the zone (see Figure 9.5).
Stopped
Vehicle
Figure 9.5 – A Vehicle Stopped Behind the Stop Bar
Stopped Vehicle
Queue Extension
Verification Menu Bar
As on the Edit Lanes & Stop Bar screen, you can use the menu bar to save a conguration,
Page 94

94 CHAPTER 9 VERIFICATION
undo your last edit, edit thresholds and pause/play trac (see Figure 9.6). Click the
button at the right side of the menu bar to see a window with menu descriptions.
Figure 9.6 – Verification View Menu Bar
e Verication menu bar contains the following options:
To Main Menu – Returns you to the main menu.
Save Config – Saves the zones and channel mapping to the sensor.
Channel Info – is screen will show you presence counts and channel information in
table form (see Figure 9.7). ese counts are not saved on the sensor, but this shows
how many times the channel has been actuated since you opened the Channel Info
window.
Figure 9.7 – Channel Info Screen
Edit Thresholds – Allows you to edit sensor thresholds (see Chapter 7 for more infor-
mation about editing thresholds).
Pause Trac – Suspends or resumes movement of vehicle detections on the screen.
Note
The SSMM interface cannot accurately show all pulsed outputs unless the pulsed
channel width is greater than 500 ms. If the SSMM software misses a counting
pulse, the counts will not be accurate. The software only reports what it receives
through its messages.
Page 95

Tools 10
In this chapter
Backup/Restore
Rack Cards Tools
Tracker Logging
Sensor Self Tests
10
e Tools screen allows you to back up or restore your sensor conguration, log vehicle detections, and perform several other functions (see Figure 10.1). When connected to a sensor, all
the options will be active except for the Rack Card Tools option. When a sensor connection
is not active, the Rack Card Tools option will be available but the other options will not.
Figure 10.1 – Tools Screen
Page 96

96 CHAPTER 10 TOOLS
Backup/Restore
To back up or restore the sensor settings that you have changed, click the Backup/Restore
button on the Tools screen (see Figure 10.2).
Figure 10.2 – Backup/Restore
To create a backup, click on the magnifying glass icon in the Back-up File section. Choose
a destination, type in a lename for your new backup and click OK, then click the Back-up
Sensor Setup button.
Note
The backup will appear as an .mxc file. While this file can be opened as a text file by
using Notepad, do not edit the file, as it will change the settings you backed up.
e restore function allows you to restore a set of sensor settings you have backed up. To
restore, click on the magnifying glass icon in the Restore File section. Select the backup le
you wish to restore and click OK, then click the Restore Sensor Setup button.
Warning
Restoring sensor settings will cause you to lose the settings previously on the sensor,
unless they are backed up.
To restore the sensor to factory defaults, click the Restore Factory Setup button on the
bottom of the screen.
Page 97

CHAPTER 10 TOOLS 97
Rack Cards Tools
Access tools for working with rack cards and other contact closure devices by clicking the
Rack Card Tools button on the Tools screen when a sensor connection is NOT active (see
Figure 10.3).
Figure 10.3 – Rack Card Tools
e Rack Card Tools screen allows you to verify that you have the correct channel mapping
into the trac controller, without being connected to a sensor. Serial data messages sent by
the rack card tool reach the rack cards via a T-bus and the patch cord connections from the
Click 222 control bridge to the contact closure cards.
Since this tool can be used without a sensor, it can reduce the amount of time spent on-site
when installing a SmartSensor Matrix system. You can use the rack card tool to verify rack
card connections while cable is being pulled through conduit or the sensors are being installed.
Note
When used with SmartSensor Matrix, the rack cards should be configured to communicate at the default 9600 bps. If you are having communication issues, you may
want to verify that the rack cards are configured to communicate at 9600 bps.
Using the Rack Card Tool
To search for Click 112/114 rack cards or a Click 104 contact closure device using the rack
card tool:
1 Click on the Settings button and select the correct communications port and baud
rate (see Figure 10.4).
Page 98

98 CHAPTER 10 TOOLS
Figure 10.4 – Rack Card Tool Serial Settings
2 After you have entered the correct settings, close the Serial Settings window and click
the Search button.
3 Once a list of devices appears, click on the desired row. You can identify a device by its
ID, Device, Description or Location elds. If you would like to communicate to all the
devices, select All Rack Cards in the device column.
Status
e Status eld indicates whether the rack card is operating normally or whether it is in
fail-safe mode. If the device is in fail-safe mode, the text message may help you understand
why the device is in fail-safe. For example, if the text reads “Failsafe Initializing,” this indicates that the rack card has never seen any detection call messages since it was rebooted.
If the message reads “Failsafe Timeout (No Data),” this indicates that the rack card was
previously receiving detection calls, but hasn’t received any in the last 10 seconds or more.
e message will always say "Timeout: (No Data)” when you are connected to the Rack
Card Tools.
Firmware Version
e Firmware Version eld lists the version of the rack card rmware. When you would
like to refresh the status of these elds, click the associated Refresh button. If you are communicating with all devices, the status and rmware version elds are not applicable (N/A).
Signal Cards Switch
You can use the Signal Cards toggle switch to help single out devices. When the switch is
ON, all main menu LEDs on the selected devices will begin ashing. If you have selected
All Rack Cards, then the main menu LEDs of every card connected on the bus will begin
ashing.
Page 99

CHAPTER 10 TOOLS 99
Channel Outputs Switch
e Channel Outputs toggle switch and 1–16 checkboxes are used to help assist in testing
of the rack card outputs.
If the Channel Outputs switch is ON, all the selected channel outputs on the Click 112/114
rack card or Click 104 contact closure device will be active. e LEDs that indicate an active output channel will light up accordingly. An output will only be active when the corresponding box is checked.
Note
It is recommended that you disable pushing by sensors or disconnect the detection
call bus patch cord for each sensor before using this tool. Otherwise, the rack card
may be receiving conflicting calls on its other bus.
e Channel Outputs switch can be very helpful in verifying the I/O channel mapping
from the rack card outputs to the trac controller inputs. By sequentially checking boxes
1–16, you should be able to quickly verify the mapping of each channel, even in the absence
of trac.
Tracker Logging
Access the Tracker Logging tool by clicking on the Tracker Logging button on the Tools
screen. is tool will allow you to log vehicle detections as they are tracked through the
sensor’s view (see Figure 10.5). is tool can be used to record trackers and replay them at
a later time for demonstration purposes.
Figure 10.5 – Tracker Logging Tool
Page 100

100 CHAPTER 10 TOOLS
is tool records vehicle detections as shown on the Verication page. Recorded vehicle
detections can be used later for playback using a virtual connection.
Click on the open folder icon to select a log le. e Select Tracker Log File screen allows
you to specify the name of an existing log le or to create a new le (see Figure 10.6).
Figure 10.6 – Select Detection Log File Screen
Click the ON/OFF toggle switch icon to the ON position to begin logging vehicle detections. Once activated, the duration of the logging session is displayed on the timer display.
Click the toggle switch to the OFF position to end a logging session.
e vehicle detection log le is an ASCII text le and can be viewed using a standard text
editor. Click on the View Log icon to view the current log le using the system’s default
text editor (see Figure 10.7).
Figure 10.7 – Log File
 Loading...
Loading...