Page 1

SmartSensor 105
USER GUIDE
Page 2

SmartSensor 105
USER GUIDE
www.wavetronix.com 78 East 1700 South Provo, Utah 84606 801.734.7200
Page 3

© 2012 Wavetronix LLC. All Rights Reserved.
Wavetronix, SmartSensor, Click, Command, and all associated product names and logos are trademarks of Wavetronix LLC. All
other products or brand names as they appear are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective holders.
Protected by U.S. Patent Nos. 6,556,916; 6,693,557; 7,426,450; 7,427,930; 7,573,400; 7,889,097; 7,889,098; 7,991,542; Canadian
Patent No. 2461411; and European Patent Nos. 1435036; 1438702; 1611458. Other U.S. and international patents pending.
e Company shall not be liable for any errors contained herein or for any damages arising out of or related to this document or the
information contained therein, even if the Company has been advised of the possibility of such damages.
is document is intended for informational and instructional purposes only. e Company reserves the right to make changes in the
specications and other information contained in this document without prior notication.
FCC Part 15 Compliance: e Wavetronix SmartSensor sensors comply with Part 15 of the Federal Communications Commission
(FCC) rules which state that operation is subject to the following two conditions: (1) this device may not cause harmful interference,
and (2) this device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause undesirable operation. FCC compliance statements for applicable optional modules are to be found in the module specications. Unauthorized changes or modications
not expressly approved by the party responsible for compliance with the FCC rules could void the user’s authority to operate this
equipment.
Disclaimer: e advertised detection accuracy of the Wavetronix SmartSensor sensors is based on both external and internal testing, as
outlined in each product’s specication document. Although our sensors are very accurate by industry standards, like all other sensor
manufacturers we cannot guarantee perfection or assure that no errors will ever occur in any particular applications of our technology.
erefore, beyond the express Limited Warranty that accompanies each sensor sold by the company, we oer no additional representations, warranties, guarantees or remedies to our customers. It is recommended that purchasers and integrators evaluate the accuracy of
each sensor to determine the acceptable margin of error for each application within their particular system(s).
WX-500-0050
12/2011
Page 4

Contents
Chapter 1 Introduction 5
SmartSensor 105 Package 6 • Selecting a Mounting Location
6
Part I Installing the SmartSensor 105
Chapter 2 Installing the SmartSensor 105 11
Selecting the Oset and Mounting Height 11 • Attaching the
Mount Bracket to the Pole 13 • Attaching the Sensor to the
Mount Bracket 14 • Aligning the Sensor to the Roadway 15 •
Applying Silicon Dielectric Compound 16 • Connecting the
SmartSensor Cable 16
Chapter 3 Connecting Power and Surge Protection 17
Connecting Lightning Surge Protection 17 • Connecting AC
Power Conversion 21 • Connecting DC Power 24 • Wiring
Communication 26
Part II Using SmartSensor Manager
Chapter 4 Getting Started with SmartSensor Manager 31
Installing SmartSensor Manager 31 • About Screen 32 • Table
of Contents 32
Chapter 5 Communication 35
Serial Connection 36 • Modem Connection 38 • Internet
Page 5

Connection 39 • Firmware Upload 41 • Connection Properties 43 • Address Book 44 • Communication Error 46
Chapter 6 Sensor Settings 49
Sensor Info 49 • Sensor Settings 50 • Sensor Date & Time 56
• Operating Mode 57
Chapter 7 Lane Setup 59
Lane Conguration – Automatic 59 • Lane Conguration –
Manual 62 • Verifying Lane Conguration 67
Chapter 8 Data Collection 73
Data Collection Setup 73 • Data Download 76 • Data Logs
78
Chapter 9 Tools 83
Hyperterminal 83 • Firmware Upload 84
Chapter 10 Contact Closure Communications 87
Selecting the Contact Closure Model 87 • Programming
Sensors for Use with Contact Closures 89 • Programming
Contact Closures 90
Chapter 11 Appendix 91
Appendix A – 9-conductor Cable Denitions 91 • Appendix
B – Old Cable Denitions 93 • Appendix C – Cable Lengths
95 • Appendix D – Direct Serial Connections 97
Page 6

Introduction
In this chapter
SmartSensor Package
Selecting a Mounting Location
e Wavetronix SmartSensor 105 utilizes patented Digital Wave Radar™ technology to
detect lane occupancy, trac volume and average speed in up to eight lanes of trac simul-
taneously. Classied as Frequency Modulated Continuous Wave (FMCW ) radar, SmartSensor collects data using a 10.525 GHz (X-band) operating radio frequency.
e installation and conguration process is quick and easy. Once installed, SmartSensor
congures automatically, requires little or no on-site maintenance and may be remotely recongured. is user guide provides the step-by-step process for installing and conguring
the SmartSensor, including mounting and alignment guidelines and instructions for both
automatic and manual sensor congurations. Any questions about the information in this
guide should be directed to Wavetronix or your distributor.
Caution
Do not attempt to service or repair this unit. This unit does not contain any components and/or parts serviceable in the field. Any attempt to open this unit, except
as expressly written and directed by Wavetronix, will void the customer warranty.
Wavetronix is not liable for any bodily harm or damage caused if service is attempted
or if the back cover of the SmartSensor unit is opened. Refer all service questions to
Wavetronix or an authorized distributor.
Page 7

6 INTRODUCTION SMARTSENSOR 105 USER GUIDE
SmartSensor 105 Package
A typical sensor package contains the following items:
10.525 GHz SmartSensor Radar Trac Sensor
SmartSensor mounting kit
SmartSensor cable
SmartSensor Manager software
SmartSensor User Guide
Caution
Check the packing slip for actual contents. If any of these items are missing, note the
serial number located on the back of the sensor and contact your distributor.
Additional products may be purchased through your distributor. e following optional
items are not included unless specically ordered (check packing list for actual inventory):
Click 172/174™ contact closure adapter
Click 200™ surge protector
Click 201/202™ AC to DC converter
Click 210™ circuit breaker and switch
Click 230™ AC surge module
Selecting a Mounting Location
Consider the following guidelines when selecting a mounting location:
Lane Coverage – Sensor mounting locations should be selected so that all monitored
lanes are within 10 to 200 ft. (3 to 61 m) and run parallel with each other. If more than
eight lanes need to be simultaneously monitored, consider using multiple sensors or
the SmartSensor HD, which can monitor up to 10 lanes simultaneously.
Parallel Lanes – When the sensor is used to collect both mainline and ramp data, the
pole position should be selected so that the on and o ramp lanes run parallel with the
mainline. If lanes are not parallel, installation of multiple SmartSensor units should be
considered to achieve the sensor’s ±2° side-to-side angle requirement.
Sensors on the Same Pole – When multiple sensors are mounted on the same pole,
they will not be subject to interference if they are congured to operating using different RF channels and are separated vertically by a few feet. e higher sensor would
typically be used for the lanes further from the pole in order to minimize occlusion.
Sensors on Opposing Poles – SmartSensor units facing each other on opposing poles
should operate on dierent RF channels and be separated by a 40-ft. (12.2-m) lateral
oset, if possible.
Page 8
INTRODUCTION SMARTSENSOR 105 USER GUIDE 7
Line of Sight – e SmartSensor is designed to work accurately in the presence of
barriers, but in general if there is an alternate mounting location that would avoid any
type of structural occlusion, this is preferred. Avoid occlusion by trees, signs, and other
roadside structures.
Neighboring Structures and Parallel Walls – It is also preferred that sensor locations
have a 30-ft. (9.1-m) lateral separation from overhead sign bridges, overpasses, tunnels,
parallel walls and parallel-parked vehicles in order to avoid multiple reection paths
from a single vehicle.
Mounting Height – e mounting height should be based upon the oset from the
lanes of interest. For each oset, the minimum, maximum and recommended range
of heights is shown in Table 1.1, found in chapter 1. In general, the range of recommended heights is between 9 and 50 ft. (2.7 to 15.2 m).
Mounting Oset – e minimum recommended oset from the edge of the rst lane
of interest is 10 ft. (3 m).
Arterial Locations – Sensor sites on arterials or other roadway segments with regu-
lated stop lines should be selected at mid-block positions to increase accuracy by increasing line of sight to stop-and-go vehicles.
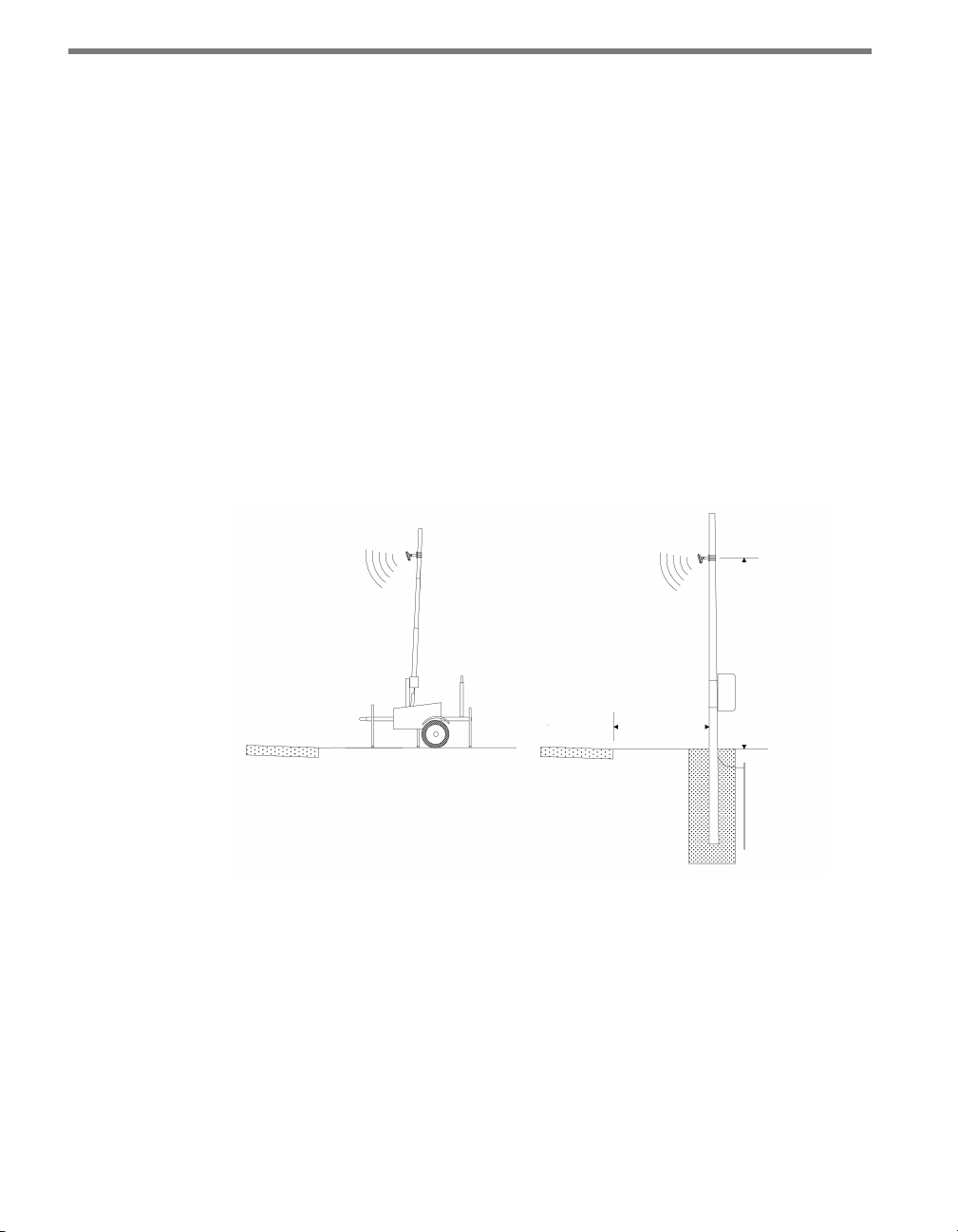
9 – 50 ft.
(see
mounting
guidelines)
10 ft. min.
Roadway Roadway
Figure I.1 – Portable (left) and Permanent (right) Sensor Stations
Freeway Locations – SmartSensor is often used at permanent ATR stations. e
number of stations along a single roadway and the distance between stations should
be selected to achieve adequate levels of statistical condence. Permanent ATR stations, which are selected to cover interstate, principal arterial and other national and
state highways, are used to establish seasonal adjustment factors for count data from
temporary collection sites (see Figure I.1).
Cable Lengths – Ensure that you have sucient homerun and sensor cabling. Cable runs
as long as 600 ft. (182.9 m) using 24 VDC operation and RS-485 communications. For
longer connections, alternate wired and wireless options should be considered.
Page 9

Page 10
Part 1
Installing the SmartSensor 105
Chapter 1 – Installing the SmartSensor 105
Chapter 2 – Connecting Power and Surge Protection
Page 11

Page 12

Installing the SmartSensor 105 1
In this chapter
Selecting the Oset and Mounting Height
Attaching the Mount Bracket to the Pole
Attaching the Sensor to the Mount Bracket
Aligning the Sensor to the Roadway
Applying Silicon Dielectric Compound
Connecting the SmartSensor Cable
1
Installing the SmartSensor 105 is quick and easy. Once installed, the SmartSensor requires
little or no on-site maintenance. is chapter will describe the installation process, including how to attach the sensor to the pole and how to correctly align the sensor.
Selecting the Oset and Mounting Height
After selecting a mounting location within the recommended range of osets (see intro-
duction), use Table 1.1 to select a mounting height. See Figure 1.1 for an illustration of
what is meant by oset and mounting height.
Page 13
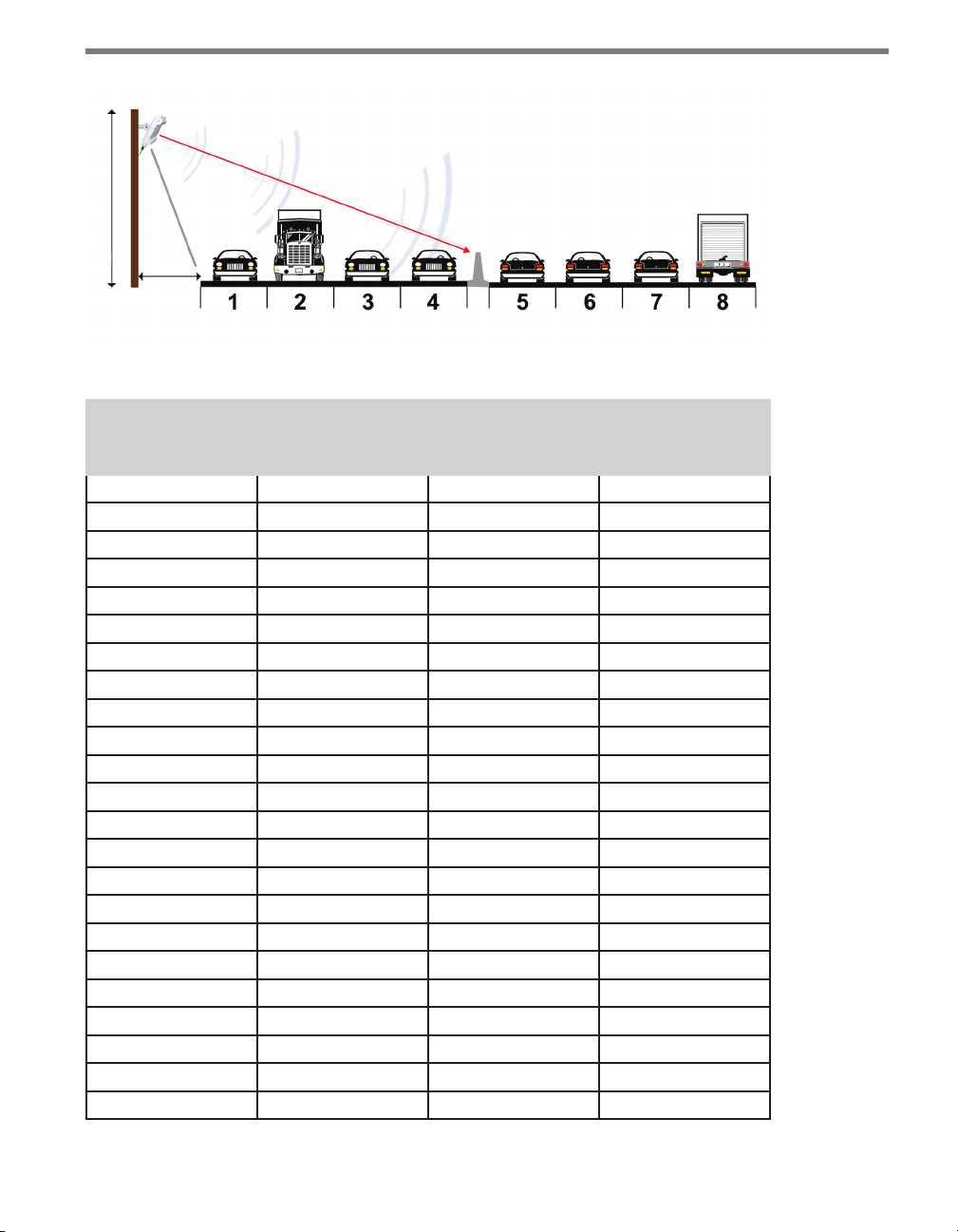
12 CHAPTER 1 INSTALLING THE SMARTSENSOR 105
Center Line
Mounting Height
Oset
Figure 1.1 – Mounting and Aiming a SmartSensor
Oset from 1st
Detection Lane (ft
/ m)
10 / 3 12 / 3.7 9 / 2.7 15 / 4.6
11 / 3.4 12 / 3.7 9 / 2.7 16 / 4.9
12 / 3.7 13 / 4 10 / 3 16 / 4.9
13 / 4 13 / 4 11 / 3.4 17 / 5.2
14 / 4.3 14 / 4.3 11 / 3.4 17 / 5.2
15 / 4.6 15 / 4.6 12 / 3.7 18 / 5.5
16 / 4.9 15 / 4.6 12 / 3.7 18 / 5.5
17 / 5.2 16 / 4.9 13 / 4 18 / 5.5
18 / 5.5 17 / 5.2 14 / 4.3 19 / 5.8
19 / 5.8 17 / 5.2 14 / 4.3 19 / 5.8
20 / 6.1 18 / 5.5 15 / 4.6 20 / 6.1
21 / 6.4 18 / 5.5 15 / 4.6 21 / 6.4
22 / 6.7 18 / 5.5 16 / 4.9 22 / 6.7
23 / 7 19 / 5.8 16 / 4.9 23 / 7
24 / 7. 3 19 / 5.8 16 / 4.9 24 / 7. 3
25 / 7.6 20 / 6.1 17 / 5.2 25 / 7.6
26 / 7.9 20 / 6.1 17 / 5.2 26 / 7.9
27 / 8.2 21 / 6.4 18 / 5.5 27 / 8.2
28 / 8.5 21 / 6.4 18 / 5.5 28 / 8.5
29 / 8.8 21 / 6.4 18 / 5.5 29 / 8.8
30 / 9.1 22 / 6.7 19 / 5.8 30 / 9.1
31 / 9.4 22 / 6.7 19 / 5.8 31 / 9.4
32 / 9.8 22 / 6.7 19 / 5.8 32 / 9.8
Recommended
Mounting Height
(ft / m)
Center of Roadway
Minimum Mounting Height (ft / m)
Maximum Mounting Height (ft / m)
Page 14
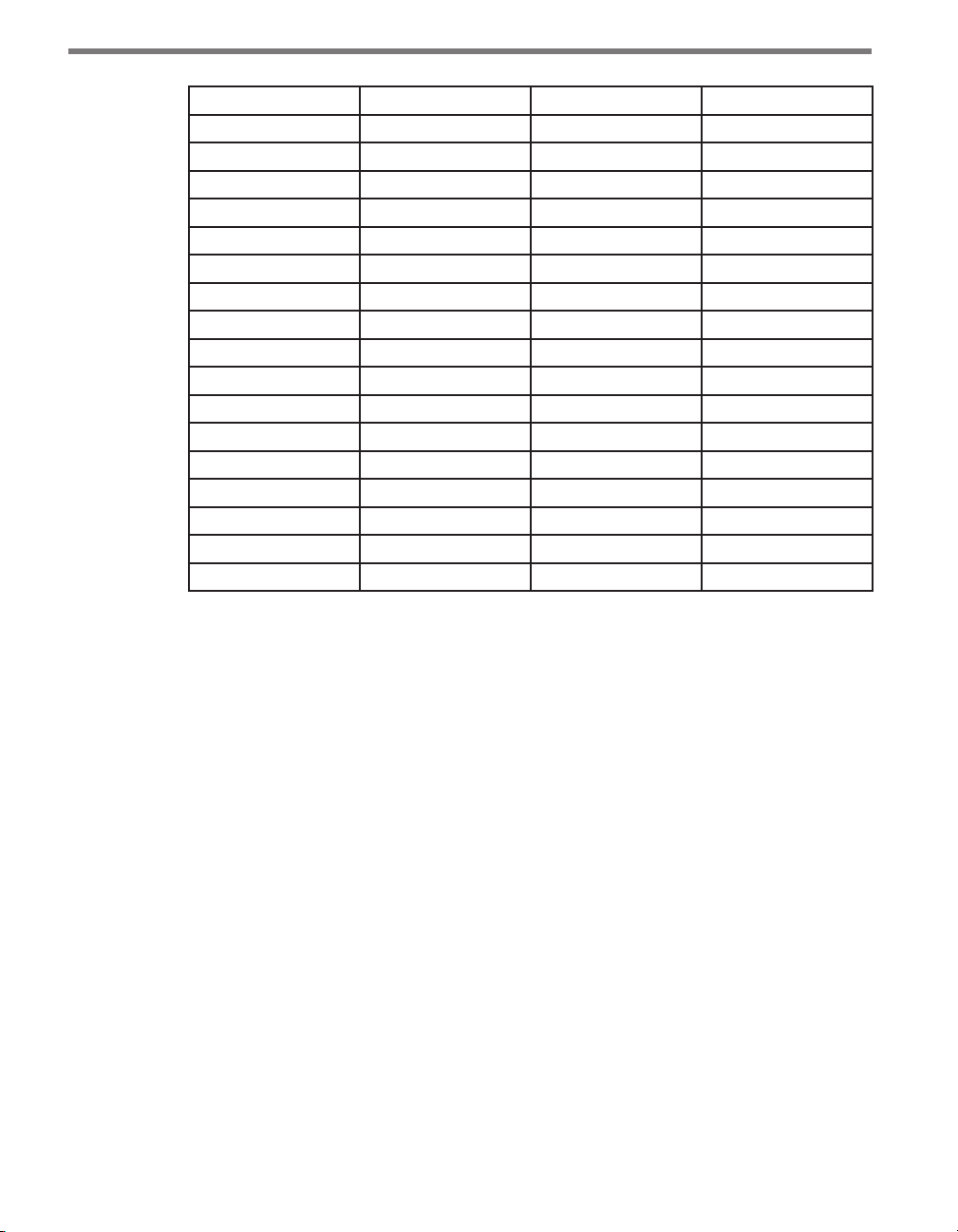
CHAPTER 1 INSTALLING THE SMARTSENSOR 105 13
33 / 10.1 23 / 7 19 / 5.8 33 / 10.1
34 / 10.4 23 / 7 19 / 5.8 34 / 10.4
35 / 10.7 23 / 7 20 / 6.1 35 / 10.7
36 / 11 23 / 7 20 / 6.1 36 / 11
37 / 11.3 23 / 7 20 / 6.1 37 / 11.3
38 / 11.6 24 / 7. 3 21 / 6.4 38 / 11.6
39 / 11.9 24 / 7.3 21 / 6.4 39 / 11.9
40 / 12.2 25 / 7.6 22 / 6.7 40 / 12.2
41 / 12.5 25 / 7.6 22 / 6.7 41 / 12.5
42 / 12.8 26 / 7.9 22 / 6.7 42 / 12.8
43 / 13.1 26 / 7.9 22 / 6.7 43 / 13.1
44 / 13.4 27 / 8.2 23 / 7 44 / 13.4
45 / 13.7 27 / 8.2 23 / 7 45 / 13.7
46 / 14 28 / 8.5 23 / 7 46 / 14
47 / 14.3 28 / 8.5 24 / 7. 3 47 / 14.3
48 / 14.6 29 / 8.8 24 / 7. 3 48 / 14.6
49 / 14.9 29 / 8.8 24 / 7.3 49 / 14.9
50–180 / 15.2–54.9 30 / 9.1 25 / 7.6 Must be < oset
Table 1.1 – Mounting Height Guidelines
Attaching the Mount Bracket to the Pole
Before attaching the mount bracket to the pole, rst make sure that your cables are long
enough to reach the sensor height and to stretch across the distance from the sensor to the
cabinet.
Follow the steps below to correctly attach the mount to the pole (see Figure 1.2):
1 Look up the recommended mounting height from Table 1.1.
2 Insert the stainless steel straps through the slots in the mount bracket.
3 Position the mount on the pole so that the head of the mount is pointing towards the
middle of the lanes of interest.
4 Tighten the strap screws.
Page 15
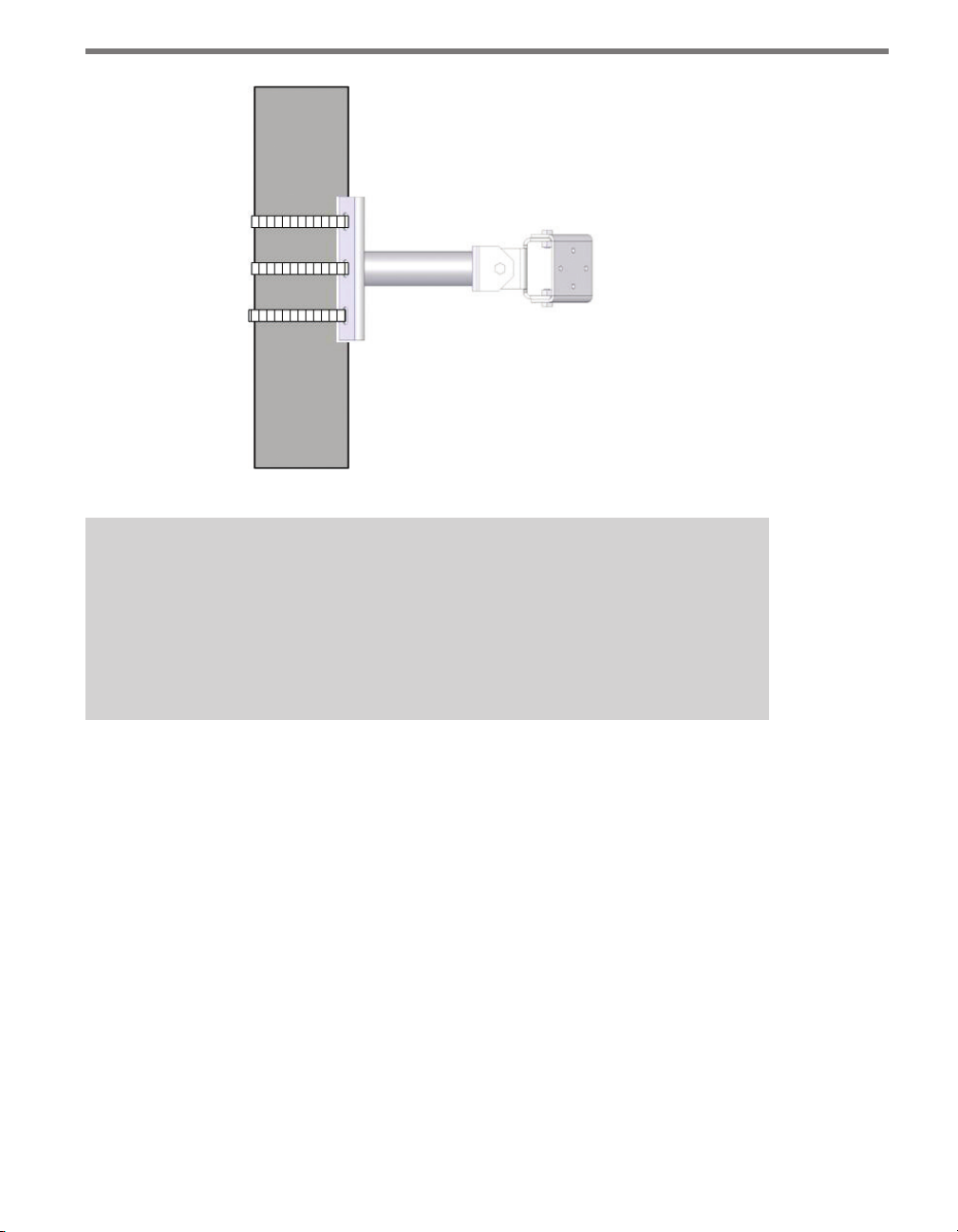
14 CHAPTER 1 INSTALLING THE SMARTSENSOR 105
Figure 1.2 – Attaching the Mount Bracket to the Pole
Caution
Depending on the site and type of trac, the sensor may tend to over or undercount.
If the sensor is overcounting, reduce the height of the sensor by three ft. (0.9 m) and
reconfigure the sensor. If the sensor is undercounting, increase the height of the sensor by three ft. (0.9 m) and reconfigure. Normally, reducing the height of the sensor
improves performance.
Attaching the Sensor to the Mount Bracket
Use the following steps to securely fasten the sensor to the mount bracket (see Figure 1.3).
1 Align the bolts on the back of the SmartSensor with the holes in the mounting brack-
et. e large 25-pin connector on the SmartSensor should be pointing towards the
ground.
2 Place the lock washers onto the bolts after the bolts are in the mounting bracket holes.
3 read on the nuts and tighten.
Page 16
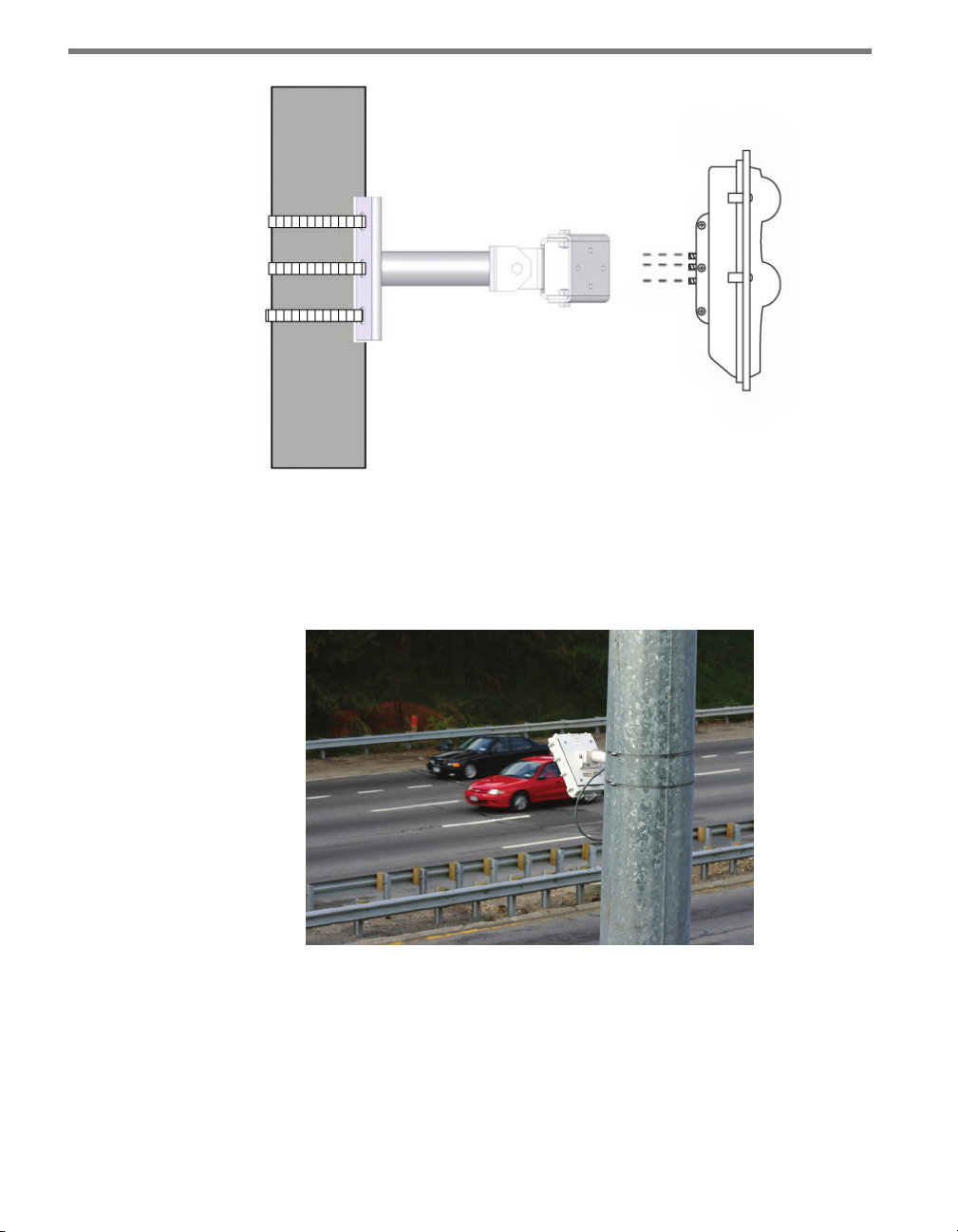
CHAPTER 1 INSTALLING THE SMARTSENSOR 105 15
Figure 1.3 – Attaching the Sensor to the Mounting Bracket
Aligning the Sensor to the Roadway
Follow the steps below to correctly align the SmartSensor (see Figure 1.4):
Figure 1.4 – Aiming the SmartSensor
1 Aim the front of the sensor at the center of the detection area. You may also refer to
Figure 1.1 as an illustration of where to aim the sensor.
2 Adjust the side-to-side angle to within approximately ±2° of perpendicular to the ow
of trac.
3 Tighten mounting bracket bolts.
Page 17
16 CHAPTER 1 INSTALLING THE SMARTSENSOR 105
Applying Silicon Dielectric Compound
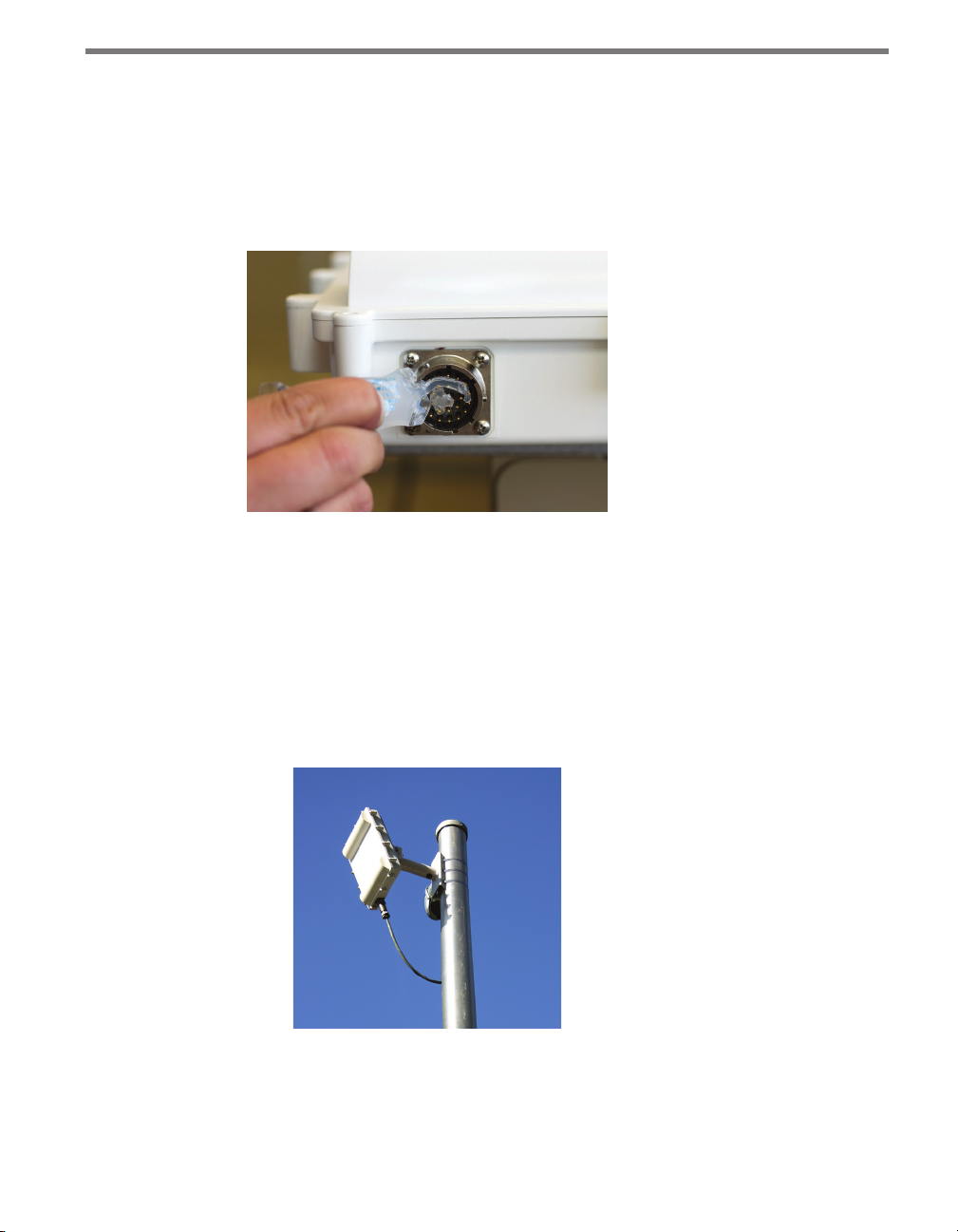
Use the following steps to correctly apply the silicon dielectric compound:
1 Tear the tab o the tube of silicon dielectric compound.
2 Squeeze about 25% of the silicon into the connector at the base of the SmartSensor as
shown in Figure 1.5. Be sure to wipe o any excess compound.
Figure 1.5 – Applying Silicon Dielectric Compound
Connecting the SmartSensor Cable
1 Attach the cable connector to the 25-pin connector at the base of the SmartSensor as
shown in Figure 1.6. e SmartSensor connector is keyed to ensure proper connection;
simply twist the connector clockwise until you hear it click into place.
2 Strap the cable to the pole or run it through a conduit to avoid undue movement from
wind and reduce cable strain.
Figure 1.6 – Attached Cable
Page 18

Connecting Power and
Surge Protection 2
In this chapter
Connecting Lightning Surge Protection
Connecting AC Power Conversion
Connecting DC Power
Wiring Communication
2
Once the sensor is installed, it will need to be wired for power and surge protection. is
chapter will explain how to connect lightning surge protection, AC power conversion, DC
power and basic communication.
Wavetronix Click products allow you to quickly and easily connect power and surge protection to your sensor application. Please refer to the Click quick-start guides for more comprehensive product instructions. Chapter 9 contains information on how Click products
make the sensor compatible with all standard control cabinets.
A pinout diagram showing the sensor cable’s pinout and appropriate connection points can
be found in Appendix A of this document.
Connecting Lightning Surge Protection
It is strongly recommended that the sensor be connected to a surge protection device. e
Wavetronix Click 200 and equivalent devices are designed to prevent electrical surges conducted along underground cables from damaging the sensor and/or the cabinet. e service
end of the sensor cable should be connected to the PROTECTED side of the Click 200
in a cabinet mounted on the sensor pole. is will help protect the sensor when lightning
strikes the ground in the vicinity of the cabinet (see Figure 2.1).
Page 19
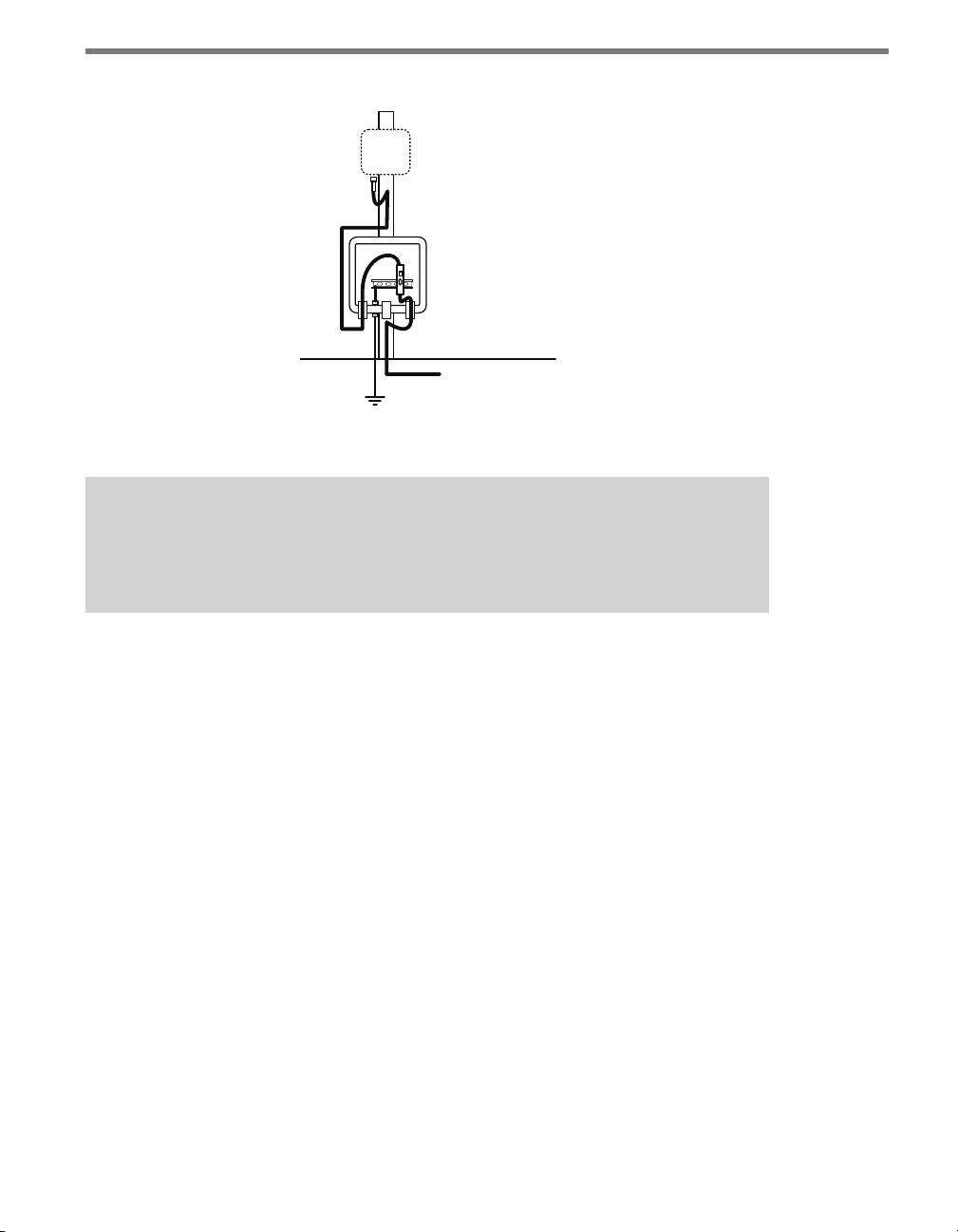
18 CHAPTER 2 CONNECTING POWER AND SURGE PROTECTION
Sensor
Underground
Cable
Figure 2.1 – Protecting the Sensor
Note
If you choose not to use surge protection in your installation, please contact Wavetronix Technical Services for assistance.
In many installations, the pole-mount cabinet is also connected to a main trac cabinet
via an underground homerun cable. To protect the trac cabinet, a second surge device is
strongly recommended. Follow the steps below to include surge protection using Click 200
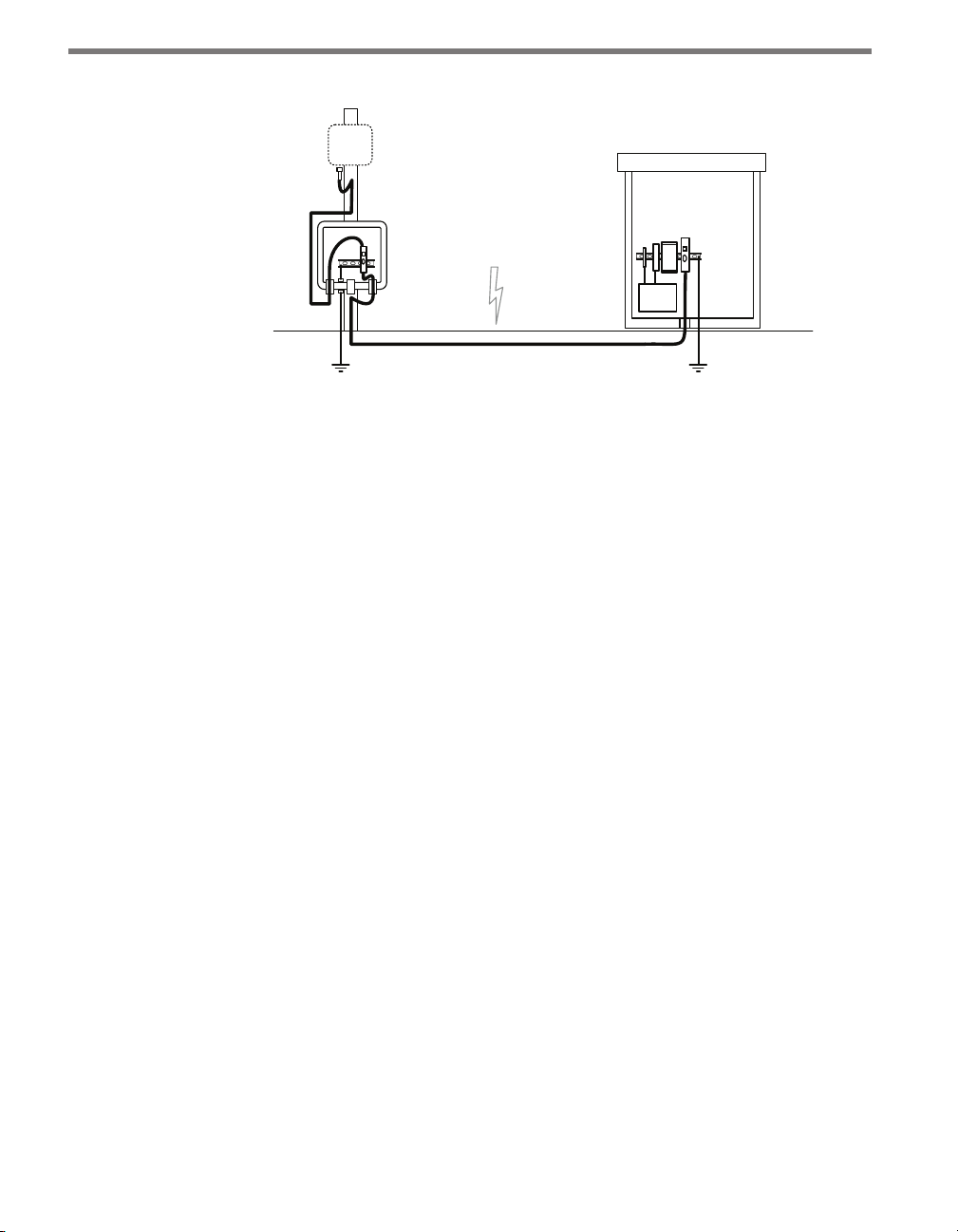
devices (see Figure 2.2):
1 Install one Click 200 device in a pole-mount box on the same pole as the sensor being
protected.
2 Install another Click 200 in the main trac cabinet.
3 Connect the SmartSensor cable from the sensor to the PROTECTED side of the
Click 200 in the pole-mount cabinet. e SmartSensor cable should be kept as short
as possible.
4 Connect a SmartSensor cable from the UNPROTECTED side of the Click 200 on
the pole to the UNPROTECTED side of the Click 200 in the main trac cabinet.
Page 20
CHAPTER 2 CONNECTING POWER AND SURGE PROTECTION 19
Main Trac Cabinet
Pole
Mount
Trac
Cabinet
Sensor
Both ends of the home-
run cable connect to the
UNPROTECTED side of the
surge modules
Figure 2.2 – Typical Cable Run
e Click 200 contains three terminal connectors on both the top and the bottom of the
module (see Figure 2.3). e terminal connectors are removable and are red-keyed, allowing the connector to plug into only one specic jack. is both simplies the wiring process
and reduces the possibility of wiring errors.
e back four terminals consist of one +DC power, -DC and two surge ground connections; the middle four terminals are for RS-485 communication and consist of a +485 connection, a -485 connection, an RS-232 ground connection and a surge ground connection;
the front four terminals are for RS-232 communication and consist of TD, RD, CTS and
RTS.
Page 21

20 CHAPTER 2 CONNECTING POWER AND SURGE PROTECTION
GND/-DC (Black)
+DC (Red)
+485 (White)
-485 (Blue)
CTS (Brown)
RTS (Orange)
Figure 2.3 – Surge Protected Terminal Connections (Top)
Power Drain
232 Drain
485 Drain
Ground (Gray)
TD (Yellow)
RD (Purple)
Figure 2.3 above shows the PROTECTED side of the Click 200. e UNPROTECTED
side of the Click 200 contains the same screw terminal connections, but are reversed from
left to right.
Note
See Appendix B for a description of how to wire the Click 200 using the old SmartSensor cable as well as for a cable connector pin out diagram.
Wiring to Earth Ground
ALL Click 200 devices should be mounted on a DIN rail that is connected to earth ground
either through an earth-grounded chassis or a 16 AWG or larger grounding wire attached
to a 7-ft. (2.1-m) grounding rod. Follow the steps below to correctly wire to earth ground:
1 Connect the grounding wire from either the DIN rail or a GND screw terminal on
the UNPROTECTED side of the Click 200 to the lug bolt on the inside of the pole-
mount box.
2 Connect another grounding wire from the exterior lug bolt to earth ground (see Figure
2.4).
Page 22

CHAPTER 2 CONNECTING POWER AND SURGE PROTECTION 21
Figure 2.4 – Earth Ground Connections
Connecting AC Power Conversion
Since the sensor operates on 10-30 VDC, it is necessary to provide AC power conversion
when reliable DC power is not already available. Wavetronix recommends using the following three Click components:
Click 201/202 AC to DC converter
Click 230 AC surge module
Click 210 circuit breaker and switch
Warning
Make sure power to AC mains is disconnected while wiring the AC input.
A Click 201 provides 1 amp of power and is capable of powering a single sensor, while a
Click 202 provides 2 amps and can power two sensors. e Click 230 helps limit current
surges on the power lines; the Click 210 interrupts power during overload conditions and
provides a convenient way to turn power on and o.
Depending on your conguration, these Click modules may be mounted in the pole-mount
cabinet or the main trac cabinet. When mounted in the main trac cabinet, a homerun
cable is used to conduct DC power and communication signals to the pole-mount cabinet.
For connections shorter than 600 ft. (182.9 m), use the SmartSensor cable as your homerun
cable. is will simplify the wiring process and ensure reliable connections.
Page 23
22 CHAPTER 2 CONNECTING POWER AND SURGE PROTECTION
Caution
An authorized electrical technician should perform installation and operation of this
unit. Persons other than authorized and approved electrical technicians should NOT
attempt to connect this unit to a power supply and/or trac control cabinet, as there
is a serious risk of electrical shock through unsafe handling of the power source. Extreme caution should be used when connecting this unit to an active power supply.
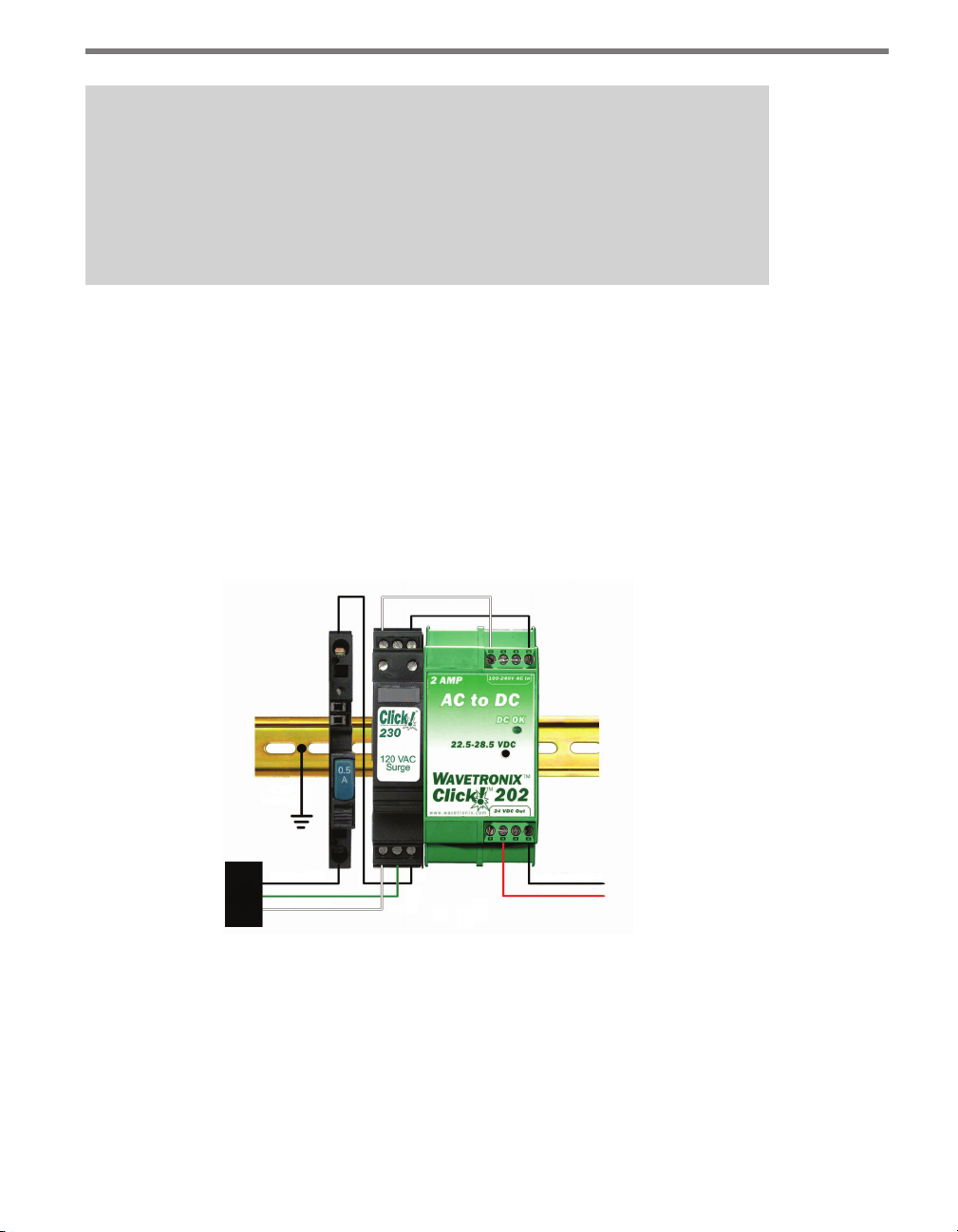
Wiring a Circuit Breaker and Switch
e Click 210 is a compact circuit breaker DIN rail device designed to interrupt an electric
current under overload conditions. e breaker is trip-free and can be easily reset after a
current interruption by pushing the reset button.
To add a Click 210 circuit breaker and switch (see Figure 2.5):
1 Mount the Click 210 onto the DIN rail.
2 Connect power in to either side of the module.
3 Connect power out to the other side.
Earth
Ground
Black (Line)
Green (Ground)
White (Neutral)
Figure 2.5 – AC Surge Protection
Black (Ground)
Red (+24 VDC)
Wiring AC Surge Protection
To include AC surge protection in your installation (see Figure 2.3):
1 Mount the Click 230 onto the DIN rail.
2 Connect the line conductor (hot) from the Click 210 to terminal 5 on the IN side of
the Click 230.
Page 24

CHAPTER 2 CONNECTING POWER AND SURGE PROTECTION 23
3 Connect the neutral wire from the AC terminal block or cord to the terminal marked
1 on the Click 230.
4 Connect the ground wire from the AC terminal block or cord to the terminal marked
3 on the Click 230.
5 Connect the outgoing and protected line wire to the terminal marked 2 on the Click
230.
6 Connect the outgoing and protected neutral wire to the terminal marked 6 on the
Click 230.
e terminal blocks 3 and 4 are directly bonded via the metal mounting foot of the base
element to the DIN rail. ere is no need for any additional grounding between terminals
3 and 4 and the DIN rail.
Wiring AC Power Into the Click 201/202
Follow the steps below to properly wire an AC to DC power conversion module (see Figure
2.6):
1 Mount the Click 201/202 onto the DIN rail.
2 Connect the line (hot) wire from the Click 230 into the L screw terminal on the top
of the Click 201/202. e line wire is usually black.
3 Connect the neutral wire from the Click 230 to the N screw terminal to the top of the
Click 201/202. e neutral wire is usually white.
Figure 2.6 – Wiring AC Power into the Click 201/202
Note
The NC screw terminal is not connected internally. Connecting a wire to a no connect
(NC) terminal simply gives it a convenient termination point.
Page 25

24 CHAPTER 2 CONNECTING POWER AND SURGE PROTECTION
Wiring DC Power Out of the Click 201/202
1 Connect a +DC conductor (usually a red wire) to the + screw terminal on the bottom
of the Click 201/202 (see Figure 2.7).
2 Connect a -DC conductor (usually a black wire) to either of the - screw terminals on
the bottom of the Click 201/202.
Figure 2.7 – Wiring DC Power Out of the Click 201/202
Note
Do not use the screw terminal marked DCOK; it provides only 20 mA and should be
used only for monitoring the power supply.
e screw terminal connectors on the top and bottom of the module are removable to simplify wiring and are red-keyed, allowing the connector to plug into only one correct jack.
Connecting DC Power
To power the sensor, 10-30 VDC needs to be connected to the Click 200 in the pole-
mount cabinet. Additionally, if there is a main trac cabinet connected by a homerun cable,
you will need to connect DC power to the Click 200 in that cabinet.
In the Pole-Mount Cabinet
Whether DC voltage comes from a homerun cable or from a Click 201/202 within the polemount cabinet, you can always wire the DC wires to the last screw terminal on the UNPRO-
TECTED side of the Click 200 module. is will protect your sensor from surges.
To wire DC power into the Click 200:
1 Connect +DC (usually a red wire) to the +DC screw terminal.
Page 26
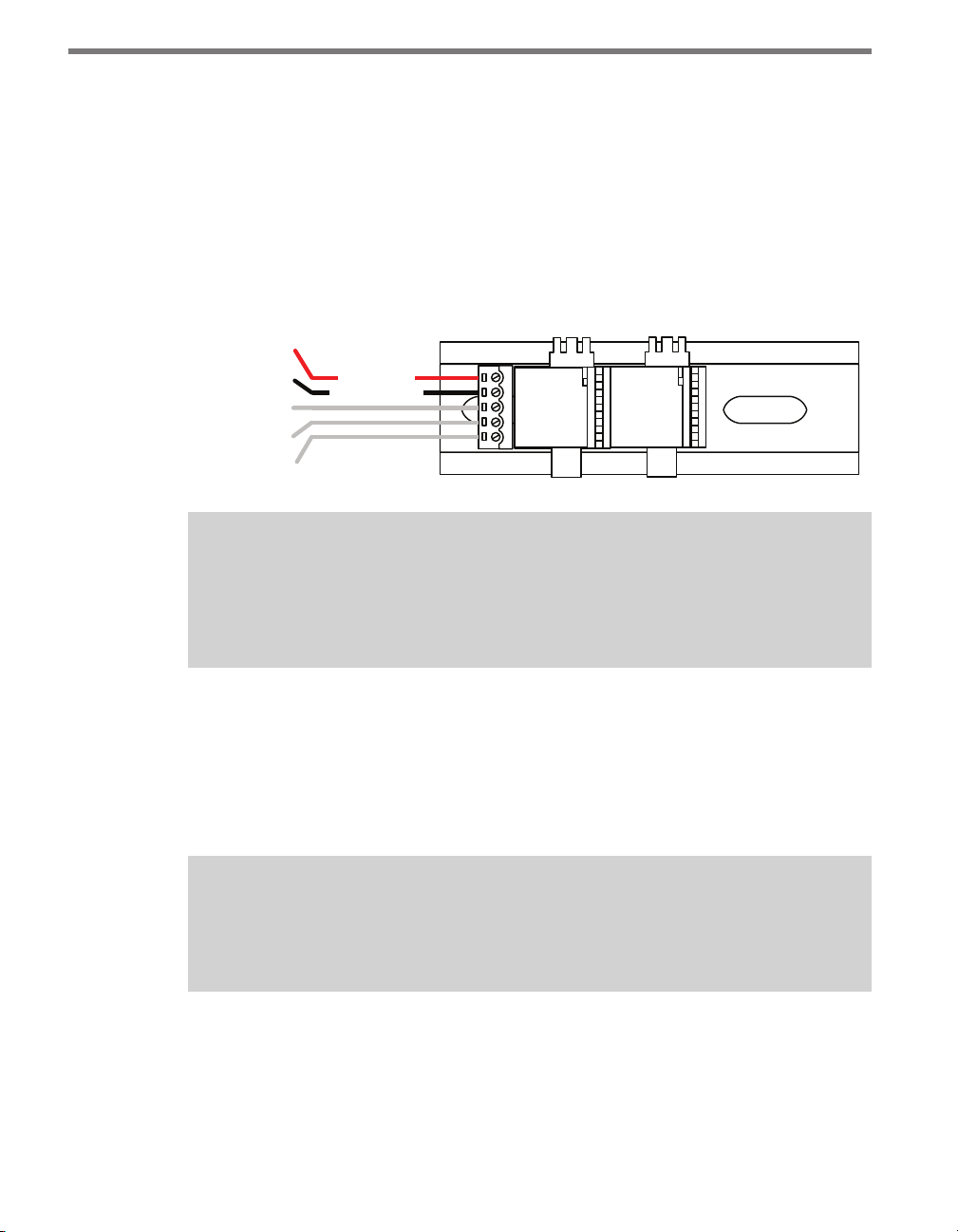
CHAPTER 2 CONNECTING POWER AND SURGE PROTECTION 25
2 Connect -DC (usually a black wire) to the GND screw terminal next to the +DC
terminal.
If the DC power comes from a Click 201/202 in the pole-mount cabinet that is surge pro-
tected using a Click 230, you can also connect power to the T-bus using a 5-position screw
terminal. To wire DC power directly into a 5-position screw terminal (see Figure 2.8):
1 Connect +DC (24 VDC) to the top screw terminal.
2 Connect –DC to the second screw terminal.
3 Connecting Power Directly to the T-bus
+24 VDC
-DC
+485
-485
GND
(red wire)
(black wire)
(Green)
(Gray)
Note
Green T-bus connectors provide power and communication connectivity on the DIN
rail backplane; gray T-bus connectors only provide power connectivity and are used to
distribute power without connecting communication.
In the Main Trac Cabinet
If DC voltage is sent across a homerun connection, AC power conversion is provided in the
main cabinet. In the main cabinet, the DC wires out of the Click 201/202 should be wired
to the PROTECTED side and the homerun cable should be connected to the UNPROTECTED side of the Click 200.
Note
The purpose of the Click 200 in the main cabinet is not to protect the sensor, but the
electrical equipment inside of the main cabinet.
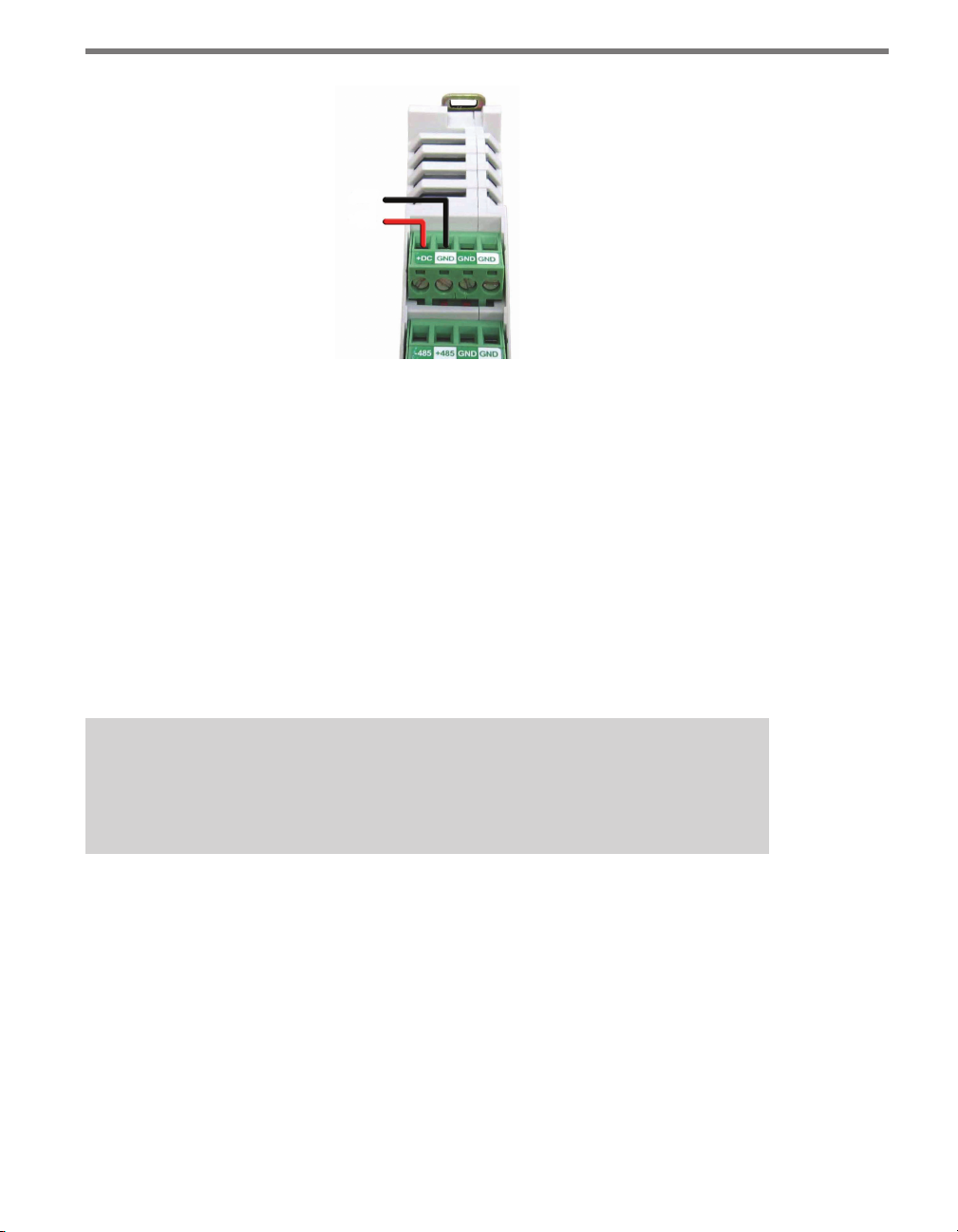
e last screw terminal block on the PROTECTED side of the Click 200 module contains
a +DC, -DC and two surge ground connections (see Figure 2.9).
1 Connect +DC (usually a red wire) to the +DC screw terminal.
2 Connect -DC (usually a black wire) to the GND screw terminal next to the +DC
terminal.
Page 27
26 CHAPTER 2 CONNECTING POWER AND SURGE PROTECTION
GND
+DC
Figure 2.8 – Wiring DC Power into the Click 200
Wiring Communication
After wiring the sensor cable into the PROTECTED side of the Click 200 in the pole
mount cabinet, two isolated serial connections are available. e sensor’s native RS-232
port is available via the DB-9 connector on the faceplate.
In addition, the sensor’s native RS-485 connection is available in the pole mount cabinet
via the following three ports on the Click 200:
Screw terminals on the bottom
RJ-11 connector on the faceplate
T-bus backplane
Note
The Click 200 does not convert RS-232 communication to RS-485. It simply provides
surge protection for these two independent connections.
One common way to connect communications back to a main cabinet is to use a SmartSensor cable as your homerun cable. See Appendix C for information about maximum
cable lengths for wired communication. Wavetronix Click products facilitate a wide variety
of additional wired and wireless communication options. Contact a Wavetronix-authorized
technical representative to nd out which options are best suited for your application.
Contact Closure Connections
While any of the RS-485 ports on the Click 200 can be connected to contact closure modules, it is often easiest to connect from the RJ-11 port. In some cases, several contact closure
cards can be daisy-chained together. However, the chain should not be connected until each
Page 28

CHAPTER 2 CONNECTING POWER AND SURGE PROTECTION 27
card has been independently programmed (see Figure 2.10).
Figure 2.9 – Connecting Contact Closure Modules
Note
Wait to connect contact closure communications until after the sensor is programmed using the configuration software.
See Chapter 9 for more information on contact closure communications.
Page 29

Page 30
Part II
Using SmartSensor Manager
Chapter 3 – Getting Started with SmartSensor Manager
Chapter 4 – Communication
Chapter 5 – Sensor Settings
Chapter 6 – Lane Setup
Chapter 7 – Data Collection
Chapter 8 – Tools
Chapter 9 – Contact Closure Communications
Page 31

Page 32

Getting Started with SmartSensor
Manager 3
In this chapter
Installing SmartSensor Manager
About Screen
Table of Contents
3
After the SmartSensor is installed, it must be congured to the roadway for proper opera-
tion. e SmartSensor Manager (SSM) software is used to perform this conguration.
SmartSensor Manager brings increased user-friendliness and improved functionality to
the ITS industry’s only patented auto-conguration and auto-calibration process. e new
features found in SmartSensor Manager 2.2.8 include a redesigned New Connection page,
a reorganized menu bar with new options, and expanded help capabilities to assist you in
navigating SmartSensor Manager and performing basic operations.
Installing SmartSensor Manager
Follow these steps to install SSM on a PC:
1 To download the install le, go to the Wavetronix website at www.wavetronix.com.
2 Click the Support link near the top of the page. is will bring up a page with icons
from the three dierent Wavetronix product lines.
3 Click the SmartSensor icon. is will bring up drop-down menus allowing you to
select a product by name or part number.
4 Select SmartSensor 105 or WX-SS-105. A list of links will appear.
5 Select the SmartSensor Manager link (it will be near the top) to download the SSM
install le.
Page 33

32 CHAPTER 3 GETTING STARTED WITH SMARTSENSOR MANAGER
6 A File Download window will pop up. Click Save.
7 In the Save As window, select where you would like the le to be saved, then click Save.
8 Once you’ve downloaded the le, double-click on it to open SmartSensor Manager.
About Screen
To access information about the version of SmartSensor Manager you are using, as well as
copyright information, go to Help>About SmartSensor Manager (see Figure 3.1).
Figure 3.1 – About SmartSensor Manager
Note
The newest version of SSM is always available on the Wavetronix website.
Table of Contents
is user guide presents the features of SmartSensor Manager in the order that they should
be used when setting up and using your sensor. If you’d like to access information about
features organized according to the way the software is laid out, however, you can use the
Table of Contents feature.
To access the Table of Contents, go to Help > Table of Contents. is will open the Table
of Contents, which is a list of help subjects organized according to the layout of the SSM
menu bar. e list is divided into the following three columns (see Figure 3.2):
Page 34

CHAPTER 3 GETTING STARTED WITH SMARTSENSOR MANAGER 33
Figure 3.2 – Table of Contents Page
Topic – Lists the available topics according to the setup of the software.
Availability – Shows whether the information is available. If it is available, this column
will show a Y. If it is not, this column and the one to the right of it will be blank.
Type – Shows the type of information contained on the page. Pages marked Tutorial
provide overview information; pages marked Context Sensitive have information specic to a particular function or operation.
Open the desired information from the Table of Contents by either double-clicking on the
subject in the list, or by highlighting the item and clicking the Display Help Topic button
(see Figure 3.3).
Figure 3.3 – Help Screen
Page 35

34 CHAPTER 3 GETTING STARTED WITH SMARTSENSOR MANAGER
Note
You can also access the Table of Contents help information for a given page by pressing the F1 key while on that page. Additionally, some pages have question marks in
the upper right-hand corner that lead to their Table of Contents help pages.
You can access the Table of Contents page from anywhere in SmartSensor Manager; an
active sensor connection is not needed. is enables you to get help information at any time,
especially if information about connecting to a sensor is needed.
Release Notes
e last entry in the Table of Contents is Release Notes, which, when selected, displays
information on the current and previous versions of SSM. is information includes the
version number, date of release (in YY/MM/DD format), and the new features added and
issues resolved in each release.
Page 36

Communication 4
In this chapter
Serial Connection
Modem Connection
Internet Connection
Firmware Upload
Connection Properties
Address Book
Communication Error
4
When the SmartSensor Manager application is opened, you will be taken to the New
Connection page, where you will be able to connect using one of three connection options:
serial, modem, or Internet. Choose the desired method of connection and click OK. e
Serial (COM Port) radio button will be selected by default (see Figure 4.1).
You can also access the three connection options at any time by going to File > New Con-
nection.
Note
Selecting a connection type under File > New Connection while you are already onnected will terminate your current connection. You can also end a connection by going
to File > Close Connection.
Page 37

36 CHAPTER 4 COMMUNICATION
Figure 4.1 – New Connection Page
Clicking OK opens a connection page unique to each connection option. Each connection
page contains three function buttons: Advanced, Cancel and one that allows you to con-
nect or dial. e advanced functions for each connection option are specic for each option.
Serial Connection
To make a serial connection, click the Serial (COM Port) radio button and then OK. e
message below will appear (see Figure 4.2):
Figure 4.2 – Serial Connection
e three action buttons appear near the bottom of the page. e CONNECT button will
attempt to connect to the sensor using the current settings. e Cancel button cancels the
action and returns you to the New Connection page.
A message bar at the bottom, identied by the icon, displays the serial settings being
used for this connection. If the default settings are used, then the message bar will display
the following:
COM - Auto; Baud - Auto; ID - Simple; Synchronize - Yes; Wait - 0
Page 38

CHAPTER 4 COMMUNICATION 37
Advanced Serial Settings
Click the Advanced button to change the Advanced Connection settings (see Figure 4.3).
Figure 4.3 – Advanced Connection Settings
PC Com Port Settings – By default, SSM is set to automatically detect PC com port
& baud rate settings. To manually congure these settings, click the Specify PC com
port & baud rate settings radio button. is will activate the Port # and Baud Rate
(bps) drop-down lists.
Additional Response Wait Time – By default, SmartSensor Manager waits a few mil-
liseconds to receive a response from the sensor before timing out and displaying a
communication error message. You can add additional milliseconds to the response
wait time to give the program more time to make a connection. Click the Use an addi-
tional: check box to activate the milliseconds text eld and enter the number of addi-
tional milliseconds SmartSensor Manager should wait for a response from the sensor.
SmartSensor Network Protocol – ese options can be used to identify sensors that
are part of a multi-drop network. e Simple protocol option refers to sensors that are
not part of a multi-drop environment. If the sensor is part of a multi-drop network,
SmartSensor Manager can either auto-detect the multi-drop ID, or you can enter the
four-digit ID. Clicking the Use Multidrop Protocol… Connect Directly to ID: radio
button will activate the text box so you can enter the ID number.
Time Synchronization – Click the check box to have SmartSensor automatically syn-
chronize with the PC clock.
Click on the check box at the bottom of the Advanced Connection Settings page to use
the new settings as default. Click OK to save the new settings or Cancel to return to default; both buttons will return you to the Serial Connection page. e new settings will be
reected in the message bar at the bottom of the page.
Page 39

38 CHAPTER 4 COMMUNICATION
Modem Connection
Clicking the Modem (Phone #) radio button on the New Connection page and then clicking OK will allow you to connect to the SmartSensor using a modem. e Modem Connection page has a text box in which you can enter the phone number for the sensor’s
modem (see Figure 4.4).
Figure 4.4 – Modem Connection
e phone book icon to the right of the text eld allows you to browse for numbers pre-
viously saved in the SmartSensor Manager address book (for more information, see the
Address Book section later in this chapter). If you’d prefer to dial manually, click the Dial
Manually check box beneath the text eld, then click on Dial. At this point you will need
to pick up the telephone receiver and manually dial the phone number.
Note
When this window is first opened, the modem connection phone number you used
most recently will automatically appear in the text field.
Once the number is entered, click Dial to make a connection. Click Cancel to stop the
action and return to the New Connection page.
e message bar at the bottom of the page, identied by the icon, shows the modem
settings being used. If the default settings are used, the message bar will display the following:
ID - Simple; Synchronize - Yes; Wait - 0
Advanced Modem Settings
e following settings are part of the modem connection’s advanced functions and can be
found by clicking the Advanced button (see Figure 4.5):
Page 40

CHAPTER 4 COMMUNICATION 39
Figure 4.5 – Advanced Modem Settings
Local Modem Settings – e initialization string and auto-nd command can be en-
tered in their respective text elds in the Local Modem Settings section. e Restore
Defaults button will return these functions to their default settings. e port number
and baud rate will be automatically detected by SmartSensor Manager, so these settings cannot be changed.
Additional Response Wait Time – By default, SmartSensor Manager waits a few mil-
liseconds to receive a response from the sensor before timing out and displaying a
communication error message. You can add additional milliseconds to the response
wait time to give the program more time to make a connection. Click the Use an addi-
tional: check box to activate the milliseconds text eld and enter the number of addi-
tional milliseconds SmartSensor Manager should wait for a response from the sensor.
SmartSensor Network Protocol – ese options can be used to identify sensors that
are part of a multi-drop network. e Simple protocol option refers to sensors that are
not part of a multi-drop environment. If the sensor is part of a multi-drop network,
SmartSensor Manager can either auto-detect the multi-drop ID, or you can enter the
four-digit ID. Clicking the Use Multidrop Protocol… Connect Directly to ID: radio
button will activate the text box so you can enter the ID number.
Time Synchronization – Click the check box to have SmartSensor automatically syn-
chronize with the PC clock.
Click the check box near the bottom of the Advanced Connection Settings page to use
the new settings as default. e OK button saves the new settings and the Cancel button
cancels the changes; both buttons return you to the Modem Connection page. e new
settings will be displayed in the message bar at the bottom of the page.
Internet Connection
e Internet (TCP/IP) option will allow you to connect to the SmartSensor using the
Page 41
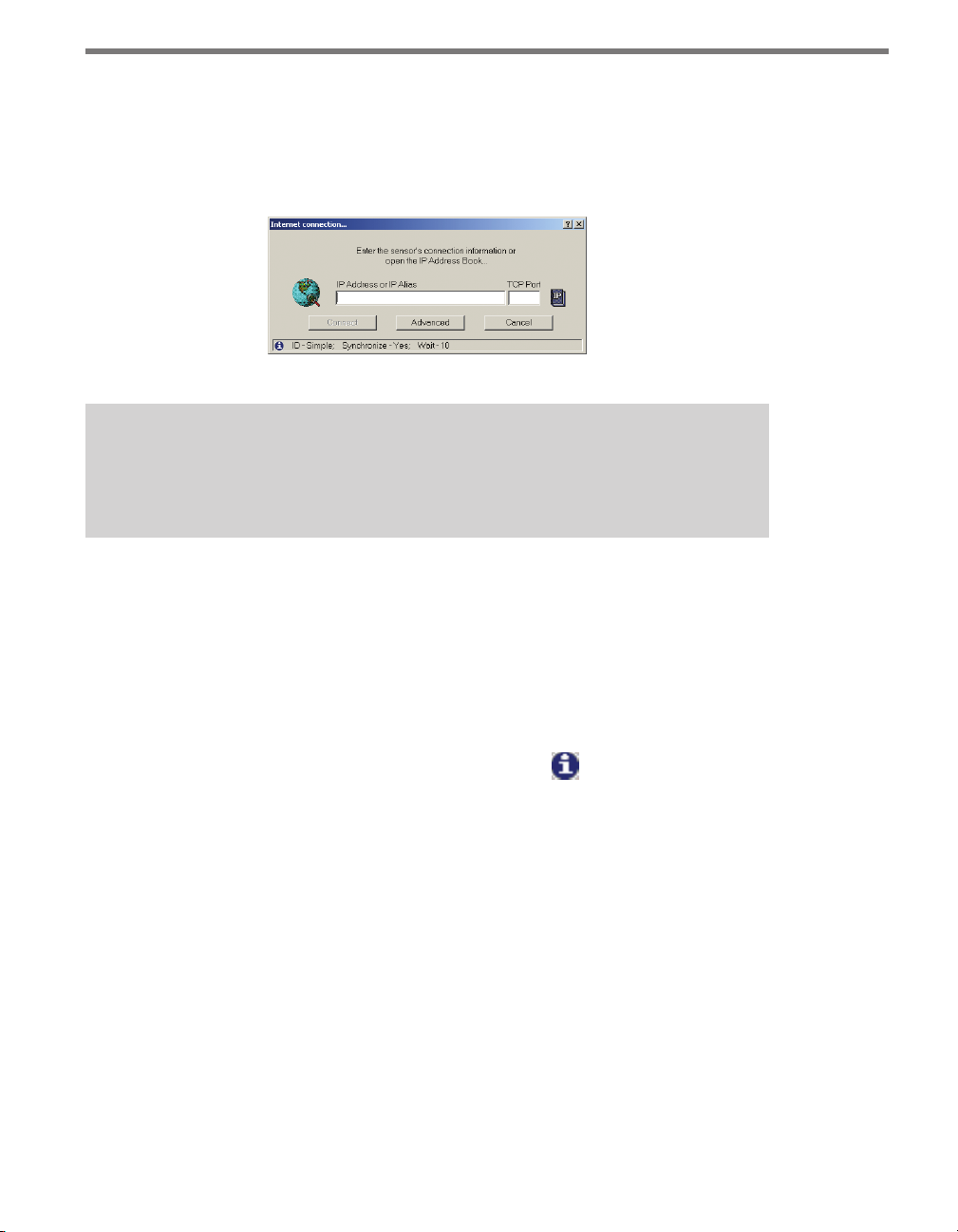
40 CHAPTER 4 COMMUNICATION
sensor’s IP address. e Internet Connection page has two text boxes in which you can
enter the sensor IP address and port number (see Figure 4.6). e Connect button does
not become active until both the IP address and port number boxes are lled. You can also
establish an Internet connection using a domain name by entering that domain name in
the IP address text eld.
Figure 4.6 – Internet Connection
Note
When this window is first opened, the connection properties for the Internet connection you used most recently will automatically appear in the text fields.
e IP icon next to the text elds allows you to browse through previously saved addresses
in the SSM address book, which is especially useful if you are connecting to more than one
sensor using an Internet connection. For more information, see the Address Book section
of this chapter.
Once the IP address and port number are entered, click Connect to make a connection.
Click Cancel to stop the action and return to the New Connection page.
e message bar at the bottom of the page, identied by the icon, shows the Internet
settings being used. If the default settings are used, the message bar will display the following:
ID - Simple; Synchronize - Yes; Wait - 0
Advanced Internet Settings
e following settings are part of the Internet connection advanced functions and can be
found by clicking the Advanced button (see Figure 4.7):
Page 42

CHAPTER 4 COMMUNICATION 41
Figure 4.7 – Advanced Internet Settings
Additional Response Wait Time – By default, SmartSensor Manager waits a few mil-
liseconds to receive a response from the sensor before timing out and displaying a
communication error message. You can add additional milliseconds to the response
wait time to give the program more time to make a connection. Click the Use an addi-
tional: check box to activate the milliseconds text eld and enter the number of addi-
tional milliseconds SmartSensor Manager should wait for a response from the sensor.
SmartSensor Network Protocol – ese options can be used to identify sensors that
are part of a multi-drop network. e Simple protocol option refers to sensors that are
not part of a multi-drop environment. If the sensor is part of a multi-drop network,
SmartSensor Manager can either auto-detect the multi-drop ID, or you can enter the
four-digit ID. Clicking the Use Multidrop Protocol… Connect Directly to ID: radio
button will activate the text box so you can enter the ID number.
Time Synchronization – Click the check box to have SmartSensor automatically syn-
chronize with the PC clock.
Click the check box near the bottom of the Advanced Connection Settings page to use
the new settings as default. e OK button saves the new settings and the Cancel button
cancels the changes; both buttons return you to the Internet Connection page. e new
settings will be displayed in the message bar at the bottom of the page.
Firmware Upload
If the rmware installed onboard the SmartSensor is not the same as the rmware bundled
with the SSM software, the Firmware/Software Compatibility screen may appear after
you’ve nished connecting. is screen gives you four options: Upload, Exit SmartSensor
Manager, Continue w/o upload, and View Details (see Figure 4.8).
Page 43

42 CHAPTER 4 COMMUNICATION
Figure 4.8 – Firmware/Software Compatibility Screen
Upload
Selecting Upload will upload the bundled rmware to the sensor, thereby eliminating any
compatibility problems. e amount of time it takes to complete the upload depends primarily on your connection speed, but usually varies from 1 to 10 minutes.
During the upload process, you can cancel at any time. However, if the FPGA rmware was
incompatible and the new version was not fully loaded before you clicked Cancel, the sensor will revert back to a factory-installed version of the FPGA rmware upon reboot of the
sensor. e factory-installed version of the FPGA rmware may not be the same as the last
version you were running on the sensor. In this case, you will need to re-upload the version
of FPGA rmware you’d like to have on the sensor (see chapter 8 for information on how
to do this). is does not occur when you cancel an upload of DSP rmware.
If the upload completes successfully, the sensor will need to reboot and restart before the
new rmware will take eect. e restart should take about 15 seconds.
Exit SmartSensor Manager
If you are unsure what to do, you should click the Exit SmartSensor Manager button.
When you have decided what to do, you can reconnect to the sensor.
In some cases, you may have simply connected to the sensor with the wrong version of
SmartSensor Manager. Click the Exit SmartSensor Manager button to close your current
connection and quit the program. Once you have quit this version of SmartSensor Man-
ager, you can then connect up with the version you originally intended.
Continue w/o upload
If you are determined to continue using this version of SmartSensor Manager to interact
with the sensor, but have good reason not to upload the bundled rmware, you can click
the Continue w/o Upload button. With this choice, SmartSensor Manager nishes estab-
lishing the connection and continues normal execution. However, depending on the nature
of incompatibilities between the sensor’s rmware and SmartSensor Manager, unexpected
errors may result.
Page 44

CHAPTER 4 COMMUNICATION 43
View Details
Dierences between the sensor’s rmware and the rmware bundled with SmartSensor
Manager can be viewed by clicking on View Details. e dierences between the two ver-
sions will be highlighted in red. Knowing the details of the detected dierences may help
you make a more informed decision about how to proceed (see Figure 4.9).
Figure 4.9 – View Details
Version – Shows the software version.
Programmable Hardware – Shows the FPGA version.
Year – Shows the year of of the version’s release in YY format.
Algorithm/Month – Shows the month of the version’s release in MM format, as well
as the operating mode; this will appear as an S for side re mode and an F for forward
re mode.
Day.Application – Shows the day of the version’s release in DD format as well as the
current application; this will appear as an S for sensor or a D for diagnostic.
Connection Properties
Information about the current connection can be accessed on the Current Connection
Properties page, which is found under File > Properties (see Figure 4.10).
Figure 4.10 – Current Connection Properties
Page 45

44 CHAPTER 4 COMMUNICATION
e page shows the following information about your connection:
Type – Shows the type of connection (serial, modem or Internet). is will say Discon-
nected if the software is not currently connected to a sensor.
Port / Phone # / Address – Displays information about the connection endpoint. is
will vary based on the kind of connection made.
Protocol – Indicates whether sensor is on a multi-drop network or a simple sensor
network.
Response Wait Time – Shows the wait time information for each sensor. e rst box
shows the number of milliseconds SmartSensor Manager will automatically wait for
a response from a specic sensor. SmartSensor Manager determines this number by
averaging recent sensor response times, so this number may uctuate slightly when
the Re-calculate button is clicked. e second box shows the number of additional
seconds you have added under the Advanced Settings page for your connection; this
number can be changed on this screen. e third box shows the total number of seconds SSM will wait for a response. Click the Save As Default button to save the new
settings as default.
Click OK to close the window.
Address Book
e address book can save connection information for both modem and Internet connections, allowing you to access this information later and connect quickly without reentering
IP addresses, modem numbers and so on.
Accessing the Address Book
e address book can be accessed in two ways:
1 Go to File > Address Book. is will give you two options: New and Open. Selecting
New will open a directory box where you can create a new address book le (.abf ).
Creating an address book le will not immediately open the new le.
Select Open to access the most recently created or accessed address book le. is
option is divided into two choices, Modem Entries and Internet Entries (see Figure
4.11). Selecting these will allow you to access all the modem or Internet entries in the
address book. If you have not yet created an address book le, you will be prompted to
do so now.
Figure 4.11 – Accessing Address Book through the Menu Bar
Page 46

CHAPTER 4 COMMUNICATION 45
2 Begin to make a new modem or Internet connection, either through File > New Con-
nection or the New Connection screen. In the connection screen that comes up, click
the book icon next to the text eld. is will access the address book specic to that
type of connection. If you have not yet created an address book le, you will be asked
to do so.
Note
By default, accessing the address book will open the address book file (.abf) that you
most recently had open. As a single .abf can store both modem and Internet connection information, it will usually not be necessary to have multiple address book files
stored on your computer. If you do have more than one file, however, you can switch
back and forth by going to File > Address Book > New. Instead of creating a new file,
however, select the file you wish to access and click OK. Now when you go to File >
Address Book > Open or you select the address book icon on a connection screen, it
will default to this most recently opened file.
Using the Address Book
No matter how you access the address book, using it is the same. e information available
and visible will dier, however, based on what kind of connection you’re making. If you’re
looking at modem entries, the screen will display three columns: Phone Number, Sensor
ID and Description (see Figure 4.12). e Internet entries have ve columns: IP Alias, IP
Address, TCP Port, Sensor ID and Description.
Figure 4.12 – Address Book for Modem Entries
Use the buttons in the address book to work with entries and make connections:
Select – Selects an entry to use to connect. When you have chosen the entry you would
like to use to connect, highlight it in the list and click Select. is will close the address
book and enter the desired information into the connection page.
Page 47

46 CHAPTER 4 COMMUNICATION
Note
When accessing the Address Book screen using the menu options, the Select button
is disabled. You will be able to edit the address book entries, but will not be able to
connect unless you use the Modem or Internet Connection Screens.
New – Creates a new entry. Select New and enter the desired information. In a modem
connection, this is the phone number of the modem, the sensor ID number and a description of the connection for your own information.
If you are adding an Internet connection entry, you have two options for the address:
an IP address or a domain name. With both options you must also specify the TCP
port number. If you use a domain name, the domain name must be entered as the IP
alias and you should not enter an IP address, since the domain name may resolve to
one or more dynamic IP addresses. When you enter both an IP address and an IP
alias, SmartSensor Manager will add an entry to the Windows HOSTS le on your
computer. In this case, the IP alias can be a simple text string (or a domain name that
is tied to a xed IP address). You may want to use a simple text string to help identify
IP addresses that do not have a domain name.
Edit – Allows you to edit the information contained in a highlighted entry.
Delete – Deletes the selected entry.
Close – Exits out of the address book.
Communication Error
e Communication Error screen will appear if SmartSensor Manager can no longer communicate with the sensor. If such an error occurs, the Communication Error screen will
give you the following options (see Figure 4.13):
Retry – Tells SSM to try to communicate with the sensor again.
Cancel – Stops the current operation as well as other operations that may be in process.
Details – Shows error details.
Figure 4.13 – Communication Error with Details Screen
Page 48

CHAPTER 4 COMMUNICATION 47
Clicking the Details button will access additional information specic to this problem:
Operation – Shows the operation SSM is trying to accomplish.
Response Error – Shows the response error SSM has encountered.
Error Code – Gives the error code related to the specic error.
Reliability – Indicates the percentage of communication attempts that were success-
fully completed.
Automatic Retries – Shows the number of times the SSM automatically attempts to
reconnect before showing the communication error screen.
Response Timeout – Displays the total number of milliseconds that SSM waited
before timing out the requested operation.
If you retry multiple times to communicate with the sensor and it still doesn’t work, the
problem can often be xed by editing the additional response wait time, found in the Advanced Settings page for your connection.
Page 49

Page 50

Sensor Settings 5
In this chapter
Sensor Info
Sensor Settings
Sensor Date & Time
Operating Mode
5
ere are several ways to access and change sensor settings using SSM.
Sensor Info
Going to File > Sensor Info opens the Sensor Information page, which displays the properties unique to each sensor (see Figure 5.1).
Figure 5.1 – Sensor Information
Page 51

50 CHAPTER 5 SENSOR SETTINGS
Although the information cannot be edited, there must be an active connection to view
the Sensor Information page. e page is divided into two sections, Identication and
Firmware Versions.
e Identication section information includes the following:
Serial Number – Shows the 16-digit serial number given to the sensor by the manu-
facturer. It can be used to uniquely identify the sensor.
Description – Shows the 32-character, user-created sensor description as set using the
Sensor Settings screen (for more information, see the Sensor Settings section later in
this chapter). It is used to describe the sensor and/or the installation site.
Location – Displays the 32-character, user-created location description as set using the
Sensor Settings screen (for more information, see the Sensor Settings section later in
this chapter). It is used to describe the location of the sensor.
Sensor ID – Shows the 4-digit numeric string used to identify the sensor on a multi-
drop network. You can set this ID number using the Sensor Settings screen (for more
information, see the Sensor Settings section later in this chapter). e SmartSensor
Multi-drop protocol uses the sensor ID to uniquely address sensors on a shared bus.
Serial Interface – Indicates which of the sensor’s four ports it is using to communicate.
e four ports are RS-232, RS-485, EXP-A, and EXP-B.
Note
The two expansion ports (EXP-A and B) are currently not available for use.
e Firmware Versions section shows on which versions of DSP (Digital Field Processing)
and FPGA (Field Programmable Gain Amplier) the sensor is operating.
Sensor Settings
You can both view and change certain sensor options and information in the Sensor Settings page. To access this page, go to Edit > Sensor Settings. If no sensor connection is
active, selecting this will open a directory box, allowing you to nd SmartSensor conguration (.ssc) les that are saved on your computer. You can also use this directory box to create
a new .ssc le.
e Sensor Settings page is divided into three tabs: General, Communication and Data
Collection. Only the General and Communication tabs will be discussed here; the Data
Collection tab will be discussed in chapter 7.
General Tab
e General tab allows you to edit the following settings (see Figure 5.2):
Page 52

CHAPTER 5 SENSOR SETTINGS 51
Figure 5.2 – General Tab
Serial Number – Shows the 16-digit serial number given to the sensor by the manu-
facturer, used to uniquely identify the sensor. is is the only setting on this screen that
cannot be edited.
SmartSensor (Multidrop) ID – Allows you to enter a 4-character ID number. is
number is used to identify the sensor on a multi-drop network. Each sensor on such
a network must have a unique ID number. is number is referred to on the Sensor
Information page as the sensor ID.
RTMS ID – Lets you change the RTMS ID. e SmartSensor has been designed to
utilize other protocols for those cases when there might already be a project built
around another type of sensor. If you choose to communicate using the RTMS protocol, all you need is the RTMS ID.
Note
The RTMS ID number 13 cannot be used for polled communications.
Description – Allows you to create a description of the sensor and/or installation site
for identication purposes. e description may be up to 32 characters long and will
be displayed on the Sensor Information page.
Location – Allows you to enter the location of the sensor for identication purposes.
e location may be up to 32 characters long and will be displayed on the Sensor Information page.
Orientation – Lets you select, from a drop-down menu, the direction the sensor is
facing. e orientation does not aect sensor operation or alignment and is simply for
your information.
Measurement Units – Allows you to choose between English and metric measure-
Page 53

52 CHAPTER 5 SENSOR SETTINGS
ments. Metric units are entered in decimeters so that the metric and English units can
be converted more accurately.
RF Channel – is allows you to assign specic RF channels to sensors that are in-
stalled in close proximity to each other to prevent the sensors from interfering with
each other.
Communication Tab
e Communication tab allow you to change the following settings (see Figure 5.3):
Figure 5.3 – Communications Tab
Baud Rates – Allows you to set the baud rate for the each of the sensor’s four connec-
tion ports. To change the baud rate, simply click on the drop-down menu and select
the desired rate. Besides the standard RS-232 and RS-485 ports, there are also two
other expansion ports. ese expansion ports are currently not available for use.
Response Delays (milliseconds) – Allows you to change the number of milliseconds
that the sensor will delay before responding. is is useful if you ever attach the sensor to communication equipment that cannot handle the speed with which the sensor
responds to message requests. You can change the response delay for each of the four
connection ports separately by entering the desired number of milliseconds. If you are
not able to determine the amount of delay required by consulting the communication
equipment’s documentation, you will need to determine this number by trial and error.
Note
If you increase the response delay, you should also increase the additional response
wait time that SmartSensor Manager uses when communicating to the sensor.
Page 54

CHAPTER 5 SENSOR SETTINGS 53
Advanced Comm Register – e Advanced Comm Register on the SmartSensor
holds two settings: Simple Protocol and Flow Control.
e rst setting selects whether Simple SmartSensor protocol is enabled or disabled.
By default Simple protocol is enabled. Networks comprised of simply one sensor can
use the Simple protocol. However, if there is more than one sensor on the network, this
protocol can cause communication messages to be broadcast unintentionally. ese
messages can result in collisions and even ongoing chatter between sensors on a multidrop network. If you are setting up a multi-drop network of sensors, you should con-
nect to them one by one and disable Simple protocol. To disable Simple protocol,
select Disabled from the drop-down list. Simple protocol must also be disabled if you
plan on using RTMS protocol.
e second setting selects whether ow control handshaking is enabled or disabled on
the sensor. Flow control is a hardware handshaking protocol used by some communication equipment. If your communication equipment requires handshaking, you will
need to enable this by selecting RTS/CTS from the drop down menu.
Note
If you have established a serial connection, enabling RTS/CTS handshaking will cause
you to lose communication with SmartSensor Manager unless you first short the
RTS/CTS lines on the sensor.
Data Push Setup – Allows you to enable and congure data push. SmartSensor com-
municates trac data in either Data Polled mode or Data Push mode. By default the
SmartSensor is in Data Polled mode. In Data Polled mode, a trac data collection
device must periodically poll the sensor to retrieve the most recent information. Data
Polled mode is preferred if multiple sensors share the same data bus, so that the data
transmitted over the connection will not be corrupted or lost by collisions.
In Data Push mode, the sensor is set up to transmit any new data it generates automatically (without any prompting by the collection device). In Data Push mode there
is no arbitration of the data bus, and data messages sent by dierent sensors can collide,
causing information to be lost. However, if there is only one sensor connected to the
data bus, there should be no collisions in data push mode.
Before you change to Data Push mode, select the desired port and data type from the
drop-down lists provided. You can set the sensor up to push data over more than one
port. You can also set it up to push multiple types of data over the same port. To change
to Data Push mode, click on the Enabled checkbox next to each one of the four ports
you wish to enable.
Data Collection Tab
e Data Collection tab allows you to edit the following settings (see Figure 5.7):
Page 55

54 CHAPTER 5 SENSOR SETTINGS
Figure 5.4 – Data Collection Tab
Interval Data – Allows you to specify the length of your intervals as well as how those
intervals are stored. e interval refers to the time (in seconds) that trac data is aggregated (minimum interval is ve seconds). Interval data is stored directly into the
sensor’s SRAM memory, which is volatile and will not persist after a power cycle. e
number of intervals is limited to 246. You can also tell the sensor to move the data
from SRAM to the sensor’s ash memory by clicking the Store in Flash Memory
check box. is protects the data because ash memory persists after power cycles. e
capacity in ash is about ten times greater than SRAM. If the Store in Flash Memory
box is not checked, the interval data will remain in SRAM until it is overwritten. Flash
storage management features are explained in greater depth in the Data Collection
Setup section of chapter 7.
Vehicle Classification – Lets you customize vehicle classications by length. Enter the
maximum length amounts for small and medium class vehicles in the active text boxes
and SmartSensor Manager will automatically determine the minimum lengths.
Lane Setup – Allows you to change specic lane information such as lane name and
direction of travel, for your own information and for identication.
You can also change scale occupancy (loop size) and scale speed (loop spacing). e
entry in these columns for each lane represents the manual scaling applied to the occupancy/duration and speed data. e occupancy scale factor is the ratio of each lane’s
loop size to the default loop size. e speed scale factor is the ratio of each lane’s loop
spacing to that of the default loop spacing. You can modify the scale factors by clicking
on the arrows to the right of each box.
Page 56

CHAPTER 5 SENSOR SETTINGS 55
Note
Interval occupancy is derived from event duration, so the occupancy scale factor
scales both the duration and the occupancy. Additionally, the length-based event
classification is derived from the event duration and the event speed, so scaling either the speed or the duration will impact the classification results.
e Show Loop Values button allows you to toggle quickly between the loop values
and the corresponding scale factors.
Default Loop Size & Spacing – Lets you enter default values which, when applied, will
automatically update the information for each lane. e terms “loop size” and “loop
spacing” are used since in many cases you will be using these values to scale the occupancy and speed to match those of dual loops. e loop size and loop spacing (space
between loops) are specied in inches or centimeters.
Extension Time – Allows you to increase the time, in milliseconds, on the countdown
timer that the sensor uses in detection. Adding time can help reduce the occurrence of
vehicles with trailers being detected twice. However, increasing the time also increases
the likelihood that one vehicle being tailgated by another will result in a single detection.
Note
The lane name, lane direction, and interval data settings on this page can also be
changed on other pages. The rest of the settings can only be changed here.
Saving and Restoring Sensor Settings
Once you have made changes to your settings, use the four buttons at the bottom of the
screen to save the changes from all three tabs. You can also use these buttons to discard all
your changes and return to the old settings.
Save to Sensor – Saves the changes you’ve just made to the sensor. If you do not push
this button after making changes, they will be lost when you navigate away from this
page.
Open from Sensor – Returns all settings to those currently saved on the sensor.
Save to File – Saves the settings currently entered in the Sensor Settings screens to
a SmartSensor conguration le (.ssc) on your computer. is setting can be used
to back up your settings; additionally, if you’re not connected to your sensor, you can
change settings, save them to a le, and use the le to update your sensor once you’re
connected again.
Page 57

56 CHAPTER 5 SENSOR SETTINGS
Note
Using the Save to File function does not save the changes to your sensor. If you want
to update and then back up your sensor, you need to use both Save to File and Save
to Sensor.
Open from File – Restores settings from an existing .ssc le. Once the settings have
been restored, you must click Save to Sensor if you want the sensor updated with the
restored settings.
Note
Return to this page to back up your sensor after you’ve completed the steps to configure your lanes and data collection.
Sensor Date & Time
To ensure that the data collected is timestamped correctly, use the Sensor Date & Time
screen, located at Edit > Sensor Date & Time (see Figure 5.5).
Change the date by selecting the correct date from the drop-down lists (month, day, and
year) or use the calendar to scroll to the correct date. Change the time by selecting the correct time (hour, minutes, and seconds) from the drop-down lists.
Click the check box below the calendar to automatically adjust for local computer time and
daylight savings time settings. e check box at the bottom of the page will automatically
synchronize sensor to PC UTC time at a certain interval you can dene in the text eld.
Page 58

CHAPTER 5 SENSOR SETTINGS 57
Figure 5.5 – Sensor Date & Time
e Sensor Date & Time page includes the following three function buttons:
Clocks icon – Performs a one-time synch of the sensor to the PC’s UTC time.
Disk icon – Saves the new settings.
Arrow icon – Undoes the changes.
Operating Mode
Selecting Edit > Operating Mode allows you to switch between Side Fire and Forward
Fire operation modes. While Side Fire mode is standard, Forward Fire mode allows you
to detect trac from a forward-facing position, such as when the sensor is mounted on a
bridge across the road. With this setup, however, the sensor can only detect one lane at a
time and cannot detect cars until after they’ve passed the mounting location. If you’re interested in a forward-facing sensor, consider the SmartSensor Advance, which can detect
vehicles in multiple lanes up to 500 ft. (152.4 m) in advance.
If you would like to use the SmartSensor 105 in Forward Fire mode, call Wavetronix Technical Services at 801-764-0277 for assistance and further instruction.
Page 59

58 CHAPTER 5 SENSOR SETTINGS
Page 60

Lane Setup 6
In this chapter
Lane Configuration – Automatic
Lane Configuration – Manual
Verifying Lane Configuration
6
Setting up lanes is simple in SmartSensor Manager because the software will do it for you
with the click of a button. Additionally, if SmartSensor Manager is unable to correctly
congure due to barriers, obstacles or irregular lanes, you can use the Manual Congura-
tion mode to adjust.
Note
Free-flowing trac in each lane is required for proper configuration. Light or sporadic
trac may result in slower configurations.
Lane Configuration – Automatic
Follow the steps below to automatically congure lanes in SmartSensor Manager:
1 Select Edit > Lane Conguration.
2 Once the Lane Conguration page opens, click on the Automatic button.
3 If you would like to set constraints on the conguration through the Edit Range
Blinders or Manage Gain buttons, do so now. For more information on these options
see the sections on them in the following pages.
Page 61

60 CHAPTER 6 LANE SETUP
4 Click the Restart button at the lower right.
5 Conrm the conguration restart by clicking Yes in the box that appears (see Figure
6.1). SmartSensor Manager will now automatically begin detecting and conguring
lanes, and the screen will show a visual depiction of the lanes and vehicle detections
in real time.
Figure 6.1 – Confirming Automatic Lane Configuration
6 After the lanes have been detected and congured correctly, save the conguration
by clicking the Finished button. e time required for conguration depends on the
volume of trac present in the lanes, but is typically only a few minutes.
Note
After clicking the Finished button, wait for one minute before turning o the sensor.
During this time the sensor is completing adjustments of the configuration thresholds. Typically this is not a problem because verification may be needed in Trac
View after clicking Finished. The verification process will normally be longer than
one minute.
Edit Range Blinders
Range blinders are an optional setting available in Automatic mode. Using range blinders
will narrow the search area of the automatic lane conguration process (range blinders
have no eect in Manual Conguration mode), allowing you to congure faster and avoid
conguring undesired lanes such as frontage roads. Use the steps below to successfully edit
the range blinders:
1 Click the Range Blinders button. Red bars (range blinders) will appear at the top and
bottom of the roadway display and any previously displayed roadways will be cleared.
Page 62

CHAPTER 6 LANE SETUP 61
2 Click on one of the range blinders and drag its edge to the desired range (refer to the
range markers on the left side of the screen).
3 Repeat Step 2 for the other range blinder if necessary.
4 Click the Restart button to apply the range blinders. When the range blinders are ap-
plied, they will turn from a red color to a dark khaki color. To cancel and use the default
ranges, or to start over, or click the Range Blinders button again.
5 After the lanes are detected and congured correctly, save the conguration by clicking
the Finished button. After clicking the Finished button, the SmartSensor will begin
storing vehicle data. e time required for conguration depends on the volume of
trac present in the lanes, but is typically only a few minutes.
Note
After clicking the Restart button, detected vehicles (represented by moving blue
rectangles) will be displayed only if a range blinder does not cover the lane center. If
the edge of a range blinder lies between two lanes of the same road, some manual
adjustment of the gray line (usually reserved to indicate a road shoulder) may need to
be made. The edge of the road shown in the display is really a lane divider.
Manage Gain
Managing gain is an optional setting available in Automatic mode. During the automatic
conguration process, the sensor’s gain is automatically adjusted in order to best process
the radar signal at that particular installation site. In some locations the reections from
vehicles may be stronger than in other locations, and the gain will need to be lowered in
order to optimize detection accuracy.
For the gain to be optimally adjusted by the automatic process, the sensor needs to be:
Aligned almost exactly perpendicular to all the lanes of the roadway.
Still conguring while several large vehicles (that return strong reections) pass
through the beam in the lanes closest to the sensor.
In some locations, and at particular times of the day, it may be dicult to meet these two
requirements. In these cases, click the Manage Gain button to change the starting point of
the automatic gain adjustment process. e default starting point is a gain value of 5. e
adjustment process never increases the gain value; it only decreases it. e starting point is
therefore also the maximum gain value.
A new starting point will only be applied after clicking the Restart button. During the
automatic conguration process, the sensor’s current gain value is displayed in the status
bar at the bottom of the screen.
No adjustments to the gain can be made once the conguration is saved to the sensor.
Page 63
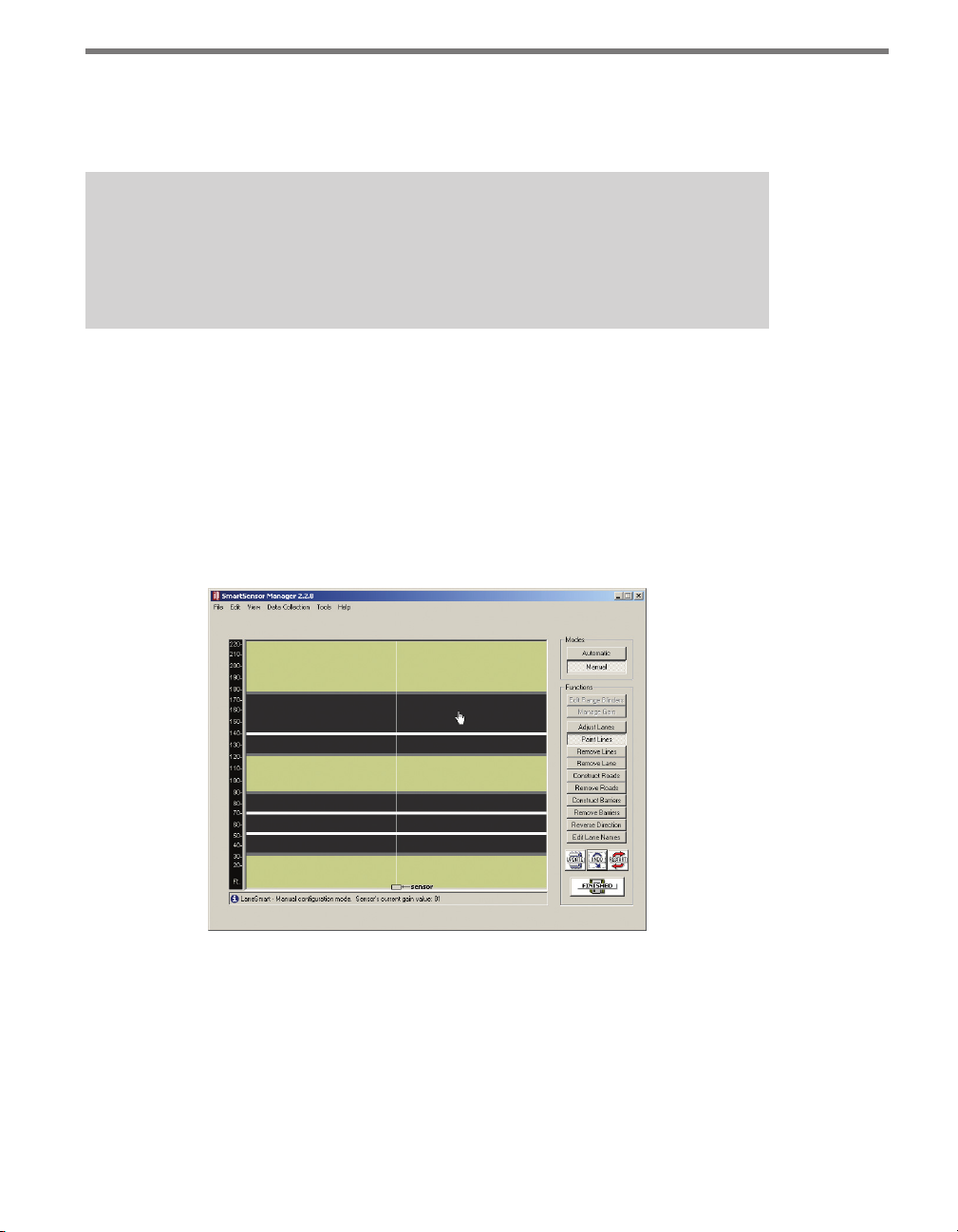
62 CHAPTER 6 LANE SETUP
However, the detection thresholds congured for the sensor during the automatic conguration process are based upon the current level of the gain and will continue to adapt for up
to one minute after clicking the Finished button.
Note
The default starting point of 5 is also the largest starting point allowed. If you enter
a value larger than 5 the default starting point of 5 will be used. If you are managing
the gain, you should generally change the starting point to a 3 or 4.
Lane Configuration – Manual
If the sensor is unable to automatically congure itself to your satisfaction, you can manually congure it by adding, removing or adjusting lanes, lane dividers and lane centers.
To make changes in Manual mode:
1 With the Lane Conguration page open, select the Manual button; the buttons in
the toolbar on the right of the screen will change from gray to black (see Figure 6.2).
Figure 6.2 – Manual Lane Configuration
2 Selecting a button in the toolbar will allow you to make changes using the roadview
window on the left.
3 Once you’ve made the necessary adjustments, hit Finished to save your changes.
Adjust Lanes
e Adjust Lanes button allows you to click your cursor on any visible shoulder (gray line),
Page 64
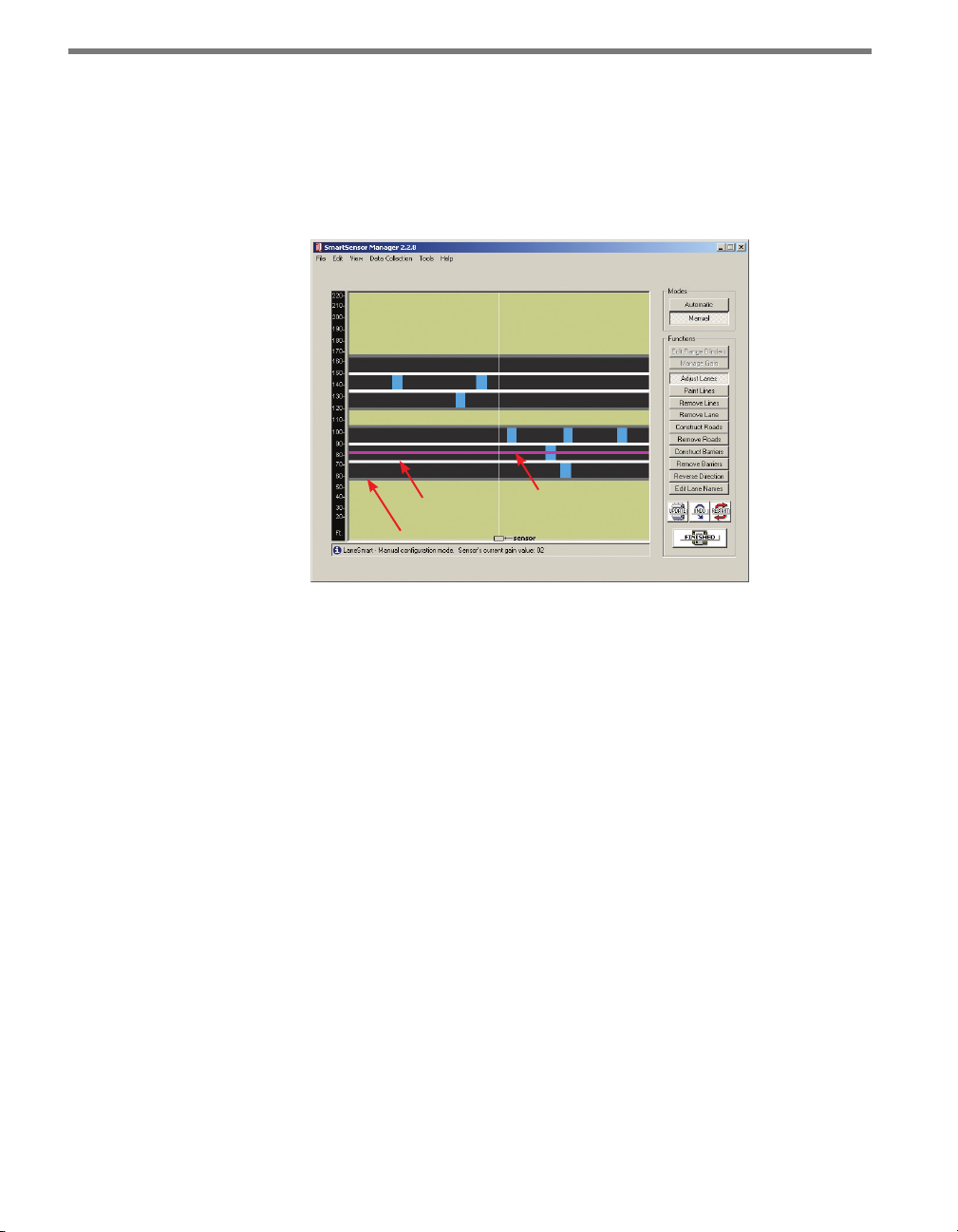
CHAPTER 6 LANE SETUP 63
lane divider (white line) or lane center (pink line) and drag it to the desired position (see
Figure 6.3). e cursor will change from an arrow to a hand when it is positioned over a
“draggable” line. Lane centers (pink lines) only appear when the cursor is placed directly
over them. To adjust the lane center, click and hold the mouse and move the line up or
down on the screen, but only within the area between the shoulders. Notice that shoulders,
dividers, or centers cannot be dragged past each other.
Lane Divider
Shoulder
Figure 6.3 – Adjusting Lanes
Lane Center
Paint and Remove Lines
e Paint Lines button allows you to add new lanes by inserting lane dividers in paved
(black) areas. SmartSensor Manager allows a maximum of eight lanes.
Again, the cursor will change from an arrow to a hand when it is positioned directly over
a location where it is possible to paint a lane divider. When the cursor appears as a hand,
click and a white line will appear.
To remove a lane divider, click on the Remove Lines button, select the white line you want
to remove and click the left mouse button (again, wait for the cursor to become a hand).
Remove Lane
e Remove Lane button allows you to remove entire lanes by moving the cursor to the
desired lane. When the arrow changes to a hand, click and the selected lane will disappear.
Construct and Remove Roads
To insert a new road, click on the Construct Roads button and select a location anywhere
in the background (khaki-colored) area. Make sure the cursor appears as a hand and then
click to draw the road.
Page 65

64 CHAPTER 6 LANE SETUP
Because new roads are initially drawn with an upper shoulder line, a centerline and a lower
shoulder line, you will usually need to adjust your road to the desired width using the Adjust Lanes function.
To remove an entire road, including all lanes, click on the Remove Roads button and click
on the road you wish to remove.
Construct and Remove Barriers
Constructing a barrier or median is essentially the act of dividing a single road into two
separate roads. SmartSensor Manager denes a barrier or median as two adjacent shoulder
lines or two shoulder lines with only background (khaki-colored) areas in between them.
To construct a barrier or median, click on the Construct Barriers button and move the
cursor to the paved area where you want to insert the barrier. When the cursor changes
from an arrow to a hand, click and the barrier will appear.
Initially, the new barrier is only two shoulder lines wide. To widen the barrier, use the Adjust Lanes feature as explained earlier.
You may also remove a barrier, or convert two roads into a single road, by clicking on the
Remove Barrier button and selecting the barrier you wish to delete.
Reverse Direction
Once the conguration process has been completed, you will notice that SmartSensor
Manager shows all detected vehicles moving in the same direction. e Reverse Direction
button enables you to change the direction of travel depicted in SmartSensor Manager so
that each lane reects the actual direction traveled by detected vehicles.
To do this, click the Reverse Direction button and move the cursor over the lane you wish
to change. Once the cursor is in place, the cursor will again change from an arrow to a hand
and a tiny arrow will appear below the hand to indicate the current direction of that lane
(see Figure 6.4).
Page 66
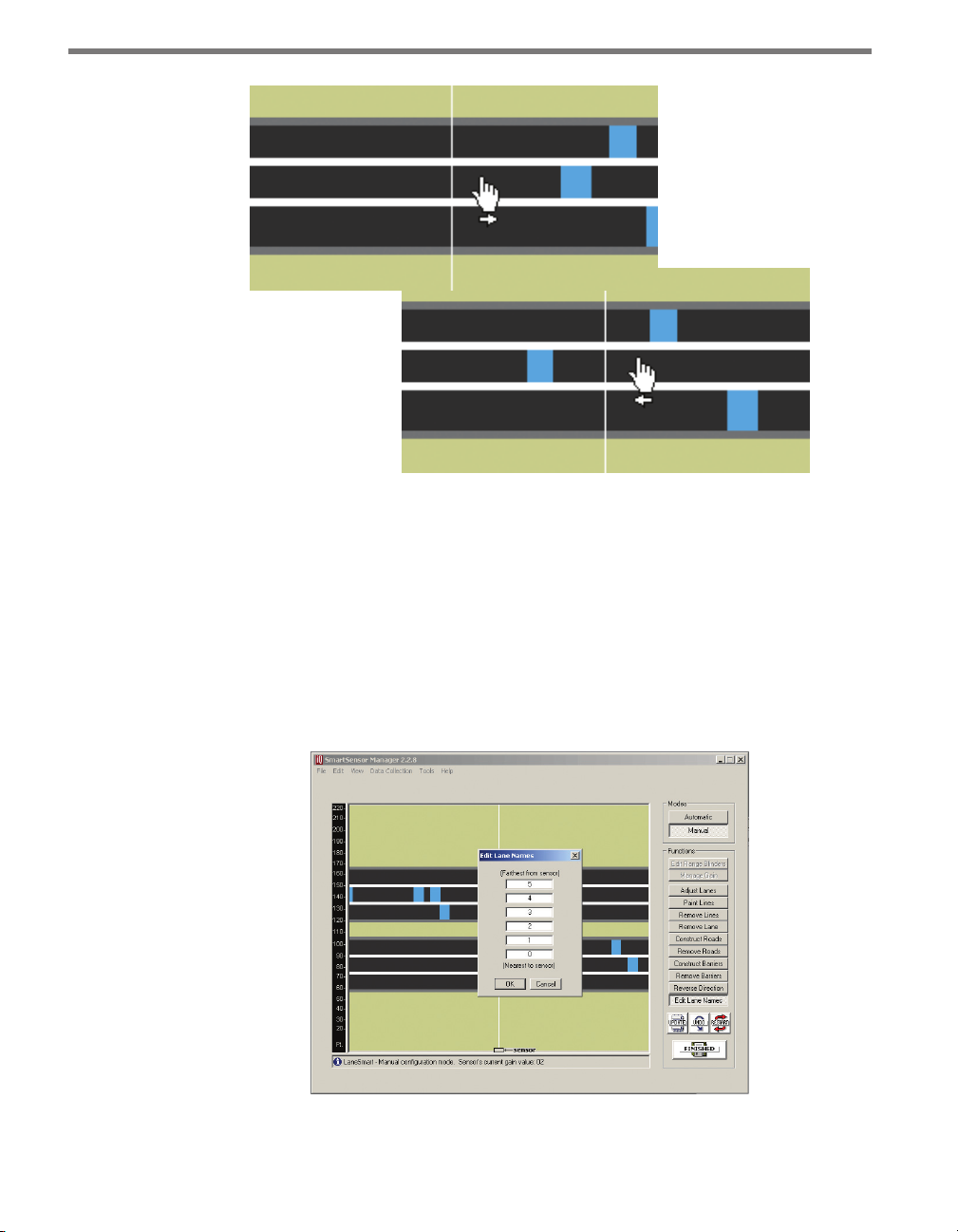
CHAPTER 6 LANE SETUP 65
Before
After
Figure 6.4 – Reverse Direction
Click the mouse, and the arrow will reverse direction to verify the change has occurred. Using the Reverse Direction button only aects the SmartSensor Manager display, not the
sensor or any detections, and is useful for verifying performance.
Edit Lane Names
By default, the SmartSensor identies the lanes it congures as lane 1 up to lane 8, where
lane 1 is located closest to the sensor. However, you may wish to assign lane numbers dif-
ferently with the Edit Lane Names window (see Figure 6.5).
Figure 6.5 – Editing Lane Names
Page 67

66 CHAPTER 6 LANE SETUP
To do this, click on the Edit Lane Name button and the Edit Lane Names window will
appear. Highlight the current lane name by double-clicking on it, then type in the lane’s
new alphanumeric identication of up to eight characters.
To reorder the lanes, you will rst need to enter a “#” sign and then the lane number. Once
you enter “#1,” for example, you can add “NB” or any other name with the remaining char-
acters.
Note
The RTMS protocol can report up to eight lanes. By default, the first zone is associated with the lane closest to the sensor; the second zone is associated with the
next closest lane and so on. .To map the lanes in a dierent order, enter the “#”
sign followed by a unique number character between 1 and 8. (Unused lanes do not
need to be named.) The other characters are ignored but may be used for clarification
purposes. Remember, a lane with the name “#1” will be reported first in the RTMS
protocol, corresponding to zone 1; a lane with the name “#2” will be reported second,
corresponding to zone 2.
Lane names can also be changed by going to Sensor Settings and clicking on the Data
Collection tab (see chapter 7 for more information).
Saving the Configuration
Once all congurations are completed, the changes must be updated in the SmartSensor’s
ash memory (lane changes won’t take eect until after the sensor has been updated). Update all manual changes by clicking the Update button located below the manual tool buttons (see Figure 6.6). e process of updating the conguration takes only seconds. Once
the process is completed, SmartSensor Manager will remain on the Lane Conguration
page so that any manual changes made may be viewed and easily changed if needed.
Figure 6.6 – Update, Undo, and Restart Buttons
Undoing Manual Changes
Unsaved changes may be undone without repeating the manual conguration process.
Click on the Undo button found below the manual tool buttons (see Figure 6.6). is
tool retrieves the last saved conguration from the SmartSensor, eectively undoing any
unsaved changes that were made.
Page 68
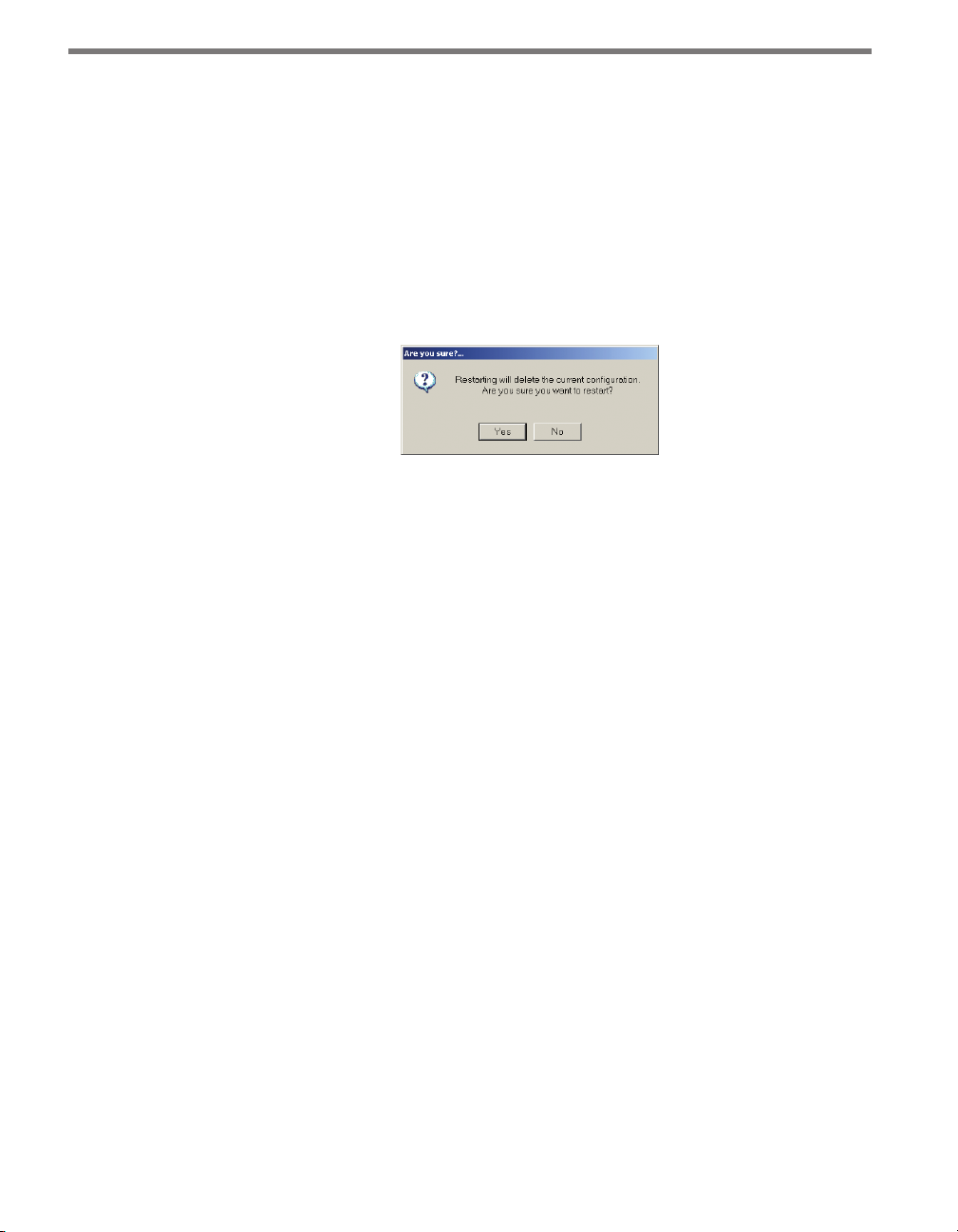
CHAPTER 6 LANE SETUP 67
Restarting Lane Configurations
To completely erase the SmartSensor’s current conguration and restart the lane conguration routine, change from Manual back to Automatic mode by clicking on the Automatic
button and then clicking on the Restart button located near the Update and Undo buttons
below the Manual toolbar (see Figure 6.6).
is erases all manual changes that have been made, and the SmartSensor Manager will
automatically recongure the road for you. After clicking on the Restart button, a window
will be displayed asking whether you want to proceed (see Figure 6.7). Click on Yes to
continue or on No to quit this procedure.
Figure 6.7 – Confirmation of Restart
Exiting the Lane Configuration Page
Once all automatic and manual congurations have been completed, you may perform a
nal save and exit the Lane Conguration page by clicking on the Finished button located
at the bottom right of the screen.
A window will appear indicating that the changes are being saved to the SmartSensor.
After the changes have been saved, SmartSensor Manager will automatically change from
Lane Conguration to Trac (Event) Data View mode so that you can verify lane con-
guration.
Verifying Lane Configuration
After you click Finished on the Lane Conguration page, SmartSensor Manager will take
you immediately to the View Trac (Event Data) page. Here you can view your saved lane
conguration and see trac in real time, allowing you to verify that the lanes have been
congured correctly.
e other way to view data is the Interval Data screen, which shows numerical data gathered per lane by the sensor. You can switch back and forth between the two screens with
the toggle button in the lower right corner of each screen; this button will be marked with
the name of the screen you’re going to switch to.
e Trac (Event) Data and Interval Data screens can both also be accessed through the
View menu.
Page 69
68 CHAPTER 6 LANE SETUP
Note
If the connection’s additional response wait time is greater than 500 ms, event and
actuation information is not displayed on the screen.
Trac (Event) Data
In Event mode, this screen allows you to verify the SmartSensor’s conguration by comparing the trac on the road to event information shown in the window (see Figure 6.8). In
order to keep a record of your verication results, the event data can also be saved to a log
le while you remain on this screen.
Figure 6.8 – View Trac (Event) Data
e window can also be used to verify true presence information by switching to Actuation
mode (click the A icon).
Note
A status bar below the Trac View window indicates whether you are in Event mode
or Actuation mode.
By default, Trac View launches in Event mode. In Event mode, the vehicles (represented
by the blue rectangles) appear after having passed through the radar detection zone.
e four icons located at the bottom of the screen are active in this mode. ey are, from
left to right:
Page 70
CHAPTER 6 LANE SETUP 69
View Event Counter – Brings up a real-time volume counter lane by lane (see Figure
6.9). Each time a vehicle enters and leaves the radar detection zone, the volume for
the corresponding lane will increment accordingly. If counting needs to be paused for
any reason, click on the Pause button; click the Play button to resume counting. Any
vehicles that were detected by the SmartSensor while the event counter was paused
will not be shown in Volume. Clicking the Reset button will clear the volume count
and will begin a fresh count.
Figure 6.9 – Event Counter
Turn Event Logging On and O – Allows you to log the information you’re currently
seeing. When you switch event logging on, you will be prompted to create a new log
le if there is not already an existing one. With event logging turned on, all of the event
data is written to a log le on the computer that can then be viewed later. To turn
event logging o, click on the icon again. No other visible changes occur while turning
event logging on and o. Event logging remains on as long as you are in the Trac
View screen. If you switch to another screen of SmartSensor Manager, and then come
back to the Trac View window, event logging will have been turned o.
View Event Log – Opens the current event log le in a text editor, such as Notepad
(see Figure 6.10).
Figure 6.10 – Event Log
e event log le breaks down each event and reports back the event Timestamp, Lane
Name, Duration, Event Speed, Class, and Count. e timestamp, which is formatted using the local time zone settings on your computer in hours, minutes, seconds
and milliseconds, is the time the vehicle entered the detection zone. e lane name
is a string of eight alphanumeric characters that describe the lane. e duration is the
number of 2.5ms ticks that elapsed while the vehicle was in the sensor’s detection
zone. e event speed represents the speed of the vehicle, displayed either in miles per
Page 71

70 CHAPTER 6 LANE SETUP
hour (mph) or kilometers per hour (kph). e class indicates into which one of three
length-based classication groupings (0=Small, 1=Medium, and 2=Large) the vehicle
ts. e count is the time the vehicle entered the detection zone encoded as the num-
ber of 2.5ms ticks counted on the sensor since the beginning of the day (UTC time).
Note
Each time the Turn Event Logging On and O button is clicked, a new header is cre-
ated in the log file.
Actuation/Event Toggle – Changes between Actuation and Event modes. Clicking on
the icon when an “A” is displayed changes the mode from Event to Actuation. Clicking
on the icon when an “E” is displayed changes the mode from Actuation to Event mode.
In Actuation mode, the three leftmost icons are inactive, and the vehicles are displayed as
long as they are present in the detection zone.
Interval Data
is screen allows you to verify interval data accuracy. e most recent interval data is displayed on the screen (see Figure 6.11). In order to keep a record of your verication results,
the interval data can also be saved to a log le while you remain on this screen.
Figure 6.11 – View Interval Data
Before interval data verication is performed, do the following:
1 Specify the desired interval length in the Interval (Bin) Size edit box. To do this,
enable the edit box by clicking Edit, then type the desired length of the interval in
seconds and click Submit. e minimum interval allowed is ve seconds. If you must
Page 72

CHAPTER 6 LANE SETUP 71
cancel your changes, click Cancel and Refresh. Clicking Refresh button will restore
the current interval length.
2 Synchronize the sensor time to your computer’s UTC time. is will ensure that inter-
vals will begin and end at the expected time. Intervals are timestamped at the end of
the interval. To synchronize the sensor time, click the Synchronize icon, which shows
two overlapping clocks.
e other two icons near the bottom of the page are for logging data:
Turn Interval Data Logging On/O – Turns event logging on and o. Click on the icon
(it shows a clock and light switch) to toggle the switch on and o. Once you’ve turned
it on, you will be prompted to create a new log le if there is not already an existing
one. Now all of the data shown on the screen will be written to a standard text le that
can be viewed at any time.
View Interval Data Log – Opens the log le in a text editor such as Notepad (see Fig-
ure 6.12). e icon shows a clock and paper.
Figure 6.12 – Interval Data Log
e interval data in the Interval Data Screen is displayed in a table that contains the lane
name, volume, speed, occupancy, and class. e lane at the top of the table is the lane closest to
the sensor. At the bottom of the screen is a status bar that indicates the time the interval data
table was last updated. It also displays the amount of time that has elapsed since this update.
Lane Name – Displays the string of eight alphanumeric characters that describes the
lane.
Volume – Shows the number of events during the interval.
Interval Lane Speed – Represents the average speed of the lane during the time of the
interval. e speed is displayed either in miles per hour (mph) or kilometers per hour
(kph), depending on your settings.
Occupancy – Displays the percentage of time vehicles occupied the sensor’s detection
zone during the selected interval.
Class – Represents the percentage of vehicles detected as tting in one of three length-
based classication groupings (Small, Medium, and Large).
Note
To open data logs from anywhere in the SmartSensor Manager program, go to File
> Data Logs . . . > Open and select the type of log. This will open the most recently
used log.
Page 73

Page 74

Data Collection 7
In this chapter
Data Collection Setup
Data Download
Data Logs
7
Once you’ve set up your sensor and lanes, you can collect data for studies. is chapter
outlines the steps necessary for data collection
Data Collection Setup
Go to Data Collection > Setup to prepare your sensor for a study. e screen that appears
is divided into two steps: Congure Data Storage and Congure the Sensor (see Figure
7.1).
Page 75

74 CHAPTER 7 DATA COLLECTION
Figure 7.1 – Data Collection Setup
Step 1: Configure Data Storage
e Interval (Bin) Size option species the interval of time over which trac variables
like volume, speed, occupancy and classication are aggregated. is type of data is called
interval data. e minimum interval allowed is ve seconds.
By default, the checkbox next to Memory Overwrite is checked. is means that your
study will run indenitely and repeatedly overwrite the ash memory onboard storage.
is means that in order to not lose collected data, you must download it to a log on your
computer before it is overwritten.
Alternatively, you can uncheck the Memory Overwrite checkbox. In this case, the study
will run only until the sensor’s ash memory has been lled with interval data.
Note
Once the flash memory buer is full, it must be erased before it can be reused. Before
you erase the stored data, you will want to download the data to a log file on your
computer.
e third line under Step 1 displays the Flash Storage Time. is shows the duration of
interval data that a full ash buer holds, calculated for you as a number of days and hours.
Because of the way ash memory is managed, the Flash Storage Time will vary based on
whether or not you have Memory Overwrite enabled.
Page 76

CHAPTER 7 DATA COLLECTION 75
Step 2: Configure the Sensor
When you are ready to begin the study, click on the Start button to:
Enable ash storage
Save the selected settings to the sensor
Synchronize the sensor date and time
Erase stored data from both SRAM and ash memory
It will take several seconds before the study actually begins. When the study does begin, the
start time will be displayed in the status bar at the bottom of the screen.
Note
If the start time does not coincide directly with the beginning of an interval, the first
interval in memory will contain a partial aggregation of data.
Interval Data Buer Status
As soon as the study begins, the View Interval Data Buer Status window will appear. is
window shows you how much of the guaranteed onboard storage space is lled with interval data. If the data collection setup process has just nished, the storage space should be
mostly unused. If you leave this window open, the status will be updated every 30 seconds.
e blue bars indicate the amount of memory that contains data (see Figure 7.2).
Figure 7.2 – View Interval Data Buer Status
Note
This screen can be accessed via the Data Collection Download screen by clicking on
the View Data Buer Status button.
Page 77

76 CHAPTER 7 DATA COLLECTION
e sensor’s SRAM buer contains up to 246 of the most recent interval data records.
is type of storage is temporary because SRAM is volatile—its contents will be lost if the
sensor’s power supply is interrupted. e sensor’s ash memory buer contains up to 2975
interval data records. is type of storage is permament because ash memory is nonvola-
tile—it will retain its contents even if the sensor’s power supply is interrupted.
Note
The smallest amount of flash memory that can be erased at one time represents
several interval data records. As a result, if you are collecting data with the Memory
Ovewrite feature enabled, you will not typically see the buer fill up 100%. In fact,
you may see the usage fall from near 100% to something near 80%. This is because
as usage approaches 100%, a portion of the oldest contents are erased in order to
make room for newer data.
If you want to force the contents of the sensor’s SRAM buer to be written to ash memory, click the Transfer>> button.
Data Download
To download interval data stored on the sensor in the SRAM and ash memory buers—
such as data collected in a study—go to Data Collection > Download. e screen that
comes up is divided into two sections, Download Interval Data and Interval Data Buers
(see Figure 7.3).
Figure 7.3 – Data Download
Page 78

CHAPTER 7 DATA COLLECTION 77
Download Interval Data
Under the Download Interval Data section, click the Browse button. is will open a directory box where you can either create a new data download le log or locate an existing
download le log. Once you’ve selected an existing le or entered the name of the new le,
select Open.
Next, select the type of download to perform. e following types of download sessions are
available:
Normal – Retrieves all interval data from the beginning of the study to the most recent
record. e number of lanes per record is determined by the number of lanes currently
congured on the sensor.
Incremental – Retrieves only the interval data that was recorded after the indicated
date and time. e number of lanes per record is determined by the number of lanes
currently congured on the sensor.
Error Recovery – Retrieves the entire contents of the ash memory buer. e ash
memory buer contains 2976 records and each record has data for eight lanes. e
contents of SRAM are not retrieved in this mode. You can perform this type of download to verify the contents of the ash memory buer in the event that a normal or
incremental download does not retrieve all the data that you expect to receive.
Once you have selected the type of download, click Download.
Note
Each time a data download is performed, a header is inserted into the log file that
indicates the date of the download.
Data in the SRAM buer contains the most recent information and will be downloaded
rst. If there is any data in the ash buer, it will be downloaded second. However, before
the data is written to the log le it will be reordered, so that the oldest data intervals will
be near the top of the le.
If you want to cancel the download or if you only want to download a certain number of
intervals, click the Stop button as soon as the desired number of interval data records are
downloaded. Once the download process has stopped, a window is displayed that indicates
number of interval data records that were downloaded.
Page 79

78 CHAPTER 7 DATA COLLECTION
Note
If your sensor experienced power cycles during the study, it may have been impossible for SmartSensor Manager to determine the timestamp of some of your intervals. The timestamp entry for these intervals will appear blank. If you have detailed
knowledge about the length of the study and when the power cycles occurred (and
for how long), you may be able to reconstruct the unknown timestamps. Periodic
connection to the sensor is recommended in order to resynchronize the sensor time
in case of a power cycle.
Interval Data Buers
e second section of the download screen is Interval Data Buers. is section has two
options, View Data Buer Status and Erase Data Buers.
Selecting View Data Buer Status takes you to the Interval Data Buer Status screen; see
the Data Collection Setup section of this chapter for more information.
Note
If you are not sure when your storage space will completely fill up with data; you can
click on the View Data Buer Status button and monitor its progress. You can also
look at the Flash Storage Time entry on the Data Collection Setup screen to see how
long you have before the flash memory fills up. Multiply the percentage of remaining
storage space by the total Flash Storage Time to approximate the remaining amount
of time before the storage space will completely fill up.
Selecting Erase Stored Data clears the sensor’s memory and starts fresh. If the storage
space is full, data must be downloaded or erased in order for the study to continue.
Note
If intervals expire during (or immediately after) your download, you will be prompted to
download the new intervals before you erase. If you are presented with the option to
download and erase, it is recommended that you do so in order to prevent losing data.
Data Logs
Going to File > Data Logs . . . allows you to create new data logs, open existing ones, and
Page 80

CHAPTER 7 DATA COLLECTION 79
export logs into 3 Card format.
Selecting New and then the type of log—Download, Interval or Event—opens a directory box where you can create a new log. is le will then be used to log data. If you created an event log, going to View > Trac (Event) Data and turning logging on will ll the
log. If you created an interval log, going to View > Interval Data and turning logging on
will ll the log. If you created a download log, going to Data Collection > Download and
downloading data will ll the log.
Note
If you haven’t created a log file when you go to start logging, the program will prompt
you to create one then.
Selecting Open and then the type of log will open the most recently used log in a text editor such as Notebook.
Note
You can also open event and interval logs by going to View > Trac (Event) Data or
View > Interval Data and clicking the View Log button; you can view download logs by
selecting the View data file when this window is closed button after downloading.
Export
Select File > Data Logs . . . > Export to export an interval log or download log to another
le format (see Figure 7.4).
Page 81

80 CHAPTER 7 DATA COLLECTION
Figure 7.4 – Export Data Logs
First, select the le to export by clicking the “. . .” button next to the Export File text eld.
is will open a directory where you can select the log to be exported. Next is a spot to
select the format for export. Currently the only supported destination le format is 3 Card
(for more information about this format, see the FHWA’s Trac Monitoring Guide, available
from fhwa.dot.gov). Click Continue.
On the following screen, ll out the requested information, which includes a starting and
ending date, a station ID number, the functional classication of the sensor site, the state
you’re located in, and any restrictions. Click Continue when you’re done.
Note
The starting date and ending date will generally be the first and last day of data in your
interval log file. However, you may wish to set your starting date and ending date so
that you export only certain days.
On the third page, specify the lane assignment number and lane direction. So that you can
tell which lane you’re working with, the lanes are numbered under the Sensor Log File
heading, with the lane closest to the sensor at the top of the list. While multiple lanes may
have the same direction, no two lanes may have both the same direction and number, unless
that number is 0. You can call multiple lanes 0 in order to group them together (see Figure
7.5).
Page 82

CHAPTER 7 DATA COLLECTION 81
Figure 7.5 – Step 3 of Export Process
Click Finish to create the 3 Card le. (To see the le immediately, click the Open 3 Card
export le when nished box.) SmartSensor Manager will take the entered information
and format the le according to 3 Card standards.
Page 83

Page 84

Tools 8
In this chapter
Hyperterminal
Firmware Upload
8
e Tools menu allows you to view and send messages to and from the sensor, as well as to
upload rmware.
Hyperterminal
Hyperterminal allows you to send message requests and view message responses for any
commands in either Simple or Multi-drop protocols (see Figure 8.1). Enter the request
in the text eld marked Command Line located near the top of the screen. Click on the
appropriate radio button to either transmit information all at once after you’ve hit Enter
on the keyboard or to automatically transmit each character as it is typed. e message
response will be returned in the gray scrollable area below the Command Line.
You may also use binary mode to verify operation of binary protocols supported by SmartSensor by clicking the Binary Mode button.
Page 85

84 CHAPTER 8 TOOLS
Figure 8.1 – Hyperterminal
Firmware Upload
When you rst connect, the program will prompt you to update your rmware if it sees a
discrepancy between the software and rmware versions, but you can also go at any time
to Tools > Firmware Upload and select a rmware le (.hex) stored on your computer to
upload to your sensor (see Figure 8.2).
Before using something other than the most current rmware version, please contact Wavetronix Technical Services for assistance.
To upload rmware, click the appropriate radio button for either DSP or FPGA rmware.
Click the Browse . . . button to locate the rmware stored on your computer; click the
UPLOAD button to transfer the rmware to the sensor.
Page 86

CHAPTER 8 TOOLS 85
Figure 8.2 – Firmware Upload
Page 87

Page 88

Contact Closure Communications 9
In this chapter
Selecting the Contact Closure Model
Programming Sensors for Use with Contact Closures
Programming Contact Closures
9
In many applications, you will not need to use your SmartSensor with contact closure cards.
Often trac data is collected directly from the sensor via a serial, modem or Internet con-
nection. However, a contact closure module is often needed to use a SmartSensor with a
trac controller, trac data recorder or other type of data logger.
Selecting the Contact Closure Model
In some applications, all of the contact closure modules listed in Table 9.1 below could be
used, but one model may have major advantages over the others; for example, the Click 101
is better for midblock applications.
Model Number Form Factor Major Advantages
Click 100 Din rail Screw terminals for easy wiring to automatic trac
recorders or data loggers
Click 101 Din rail Collection from multiple sensors
Click 172/174 Rack card Works with standard ITS and intersection detector
racks (NEMA TS1/TS2, 170, 2070)
Click 500 Din rail User-programmable contact closure development
platform for virtually any application.
Table 9.1 – Advantages of Contact Closure Models
Page 89
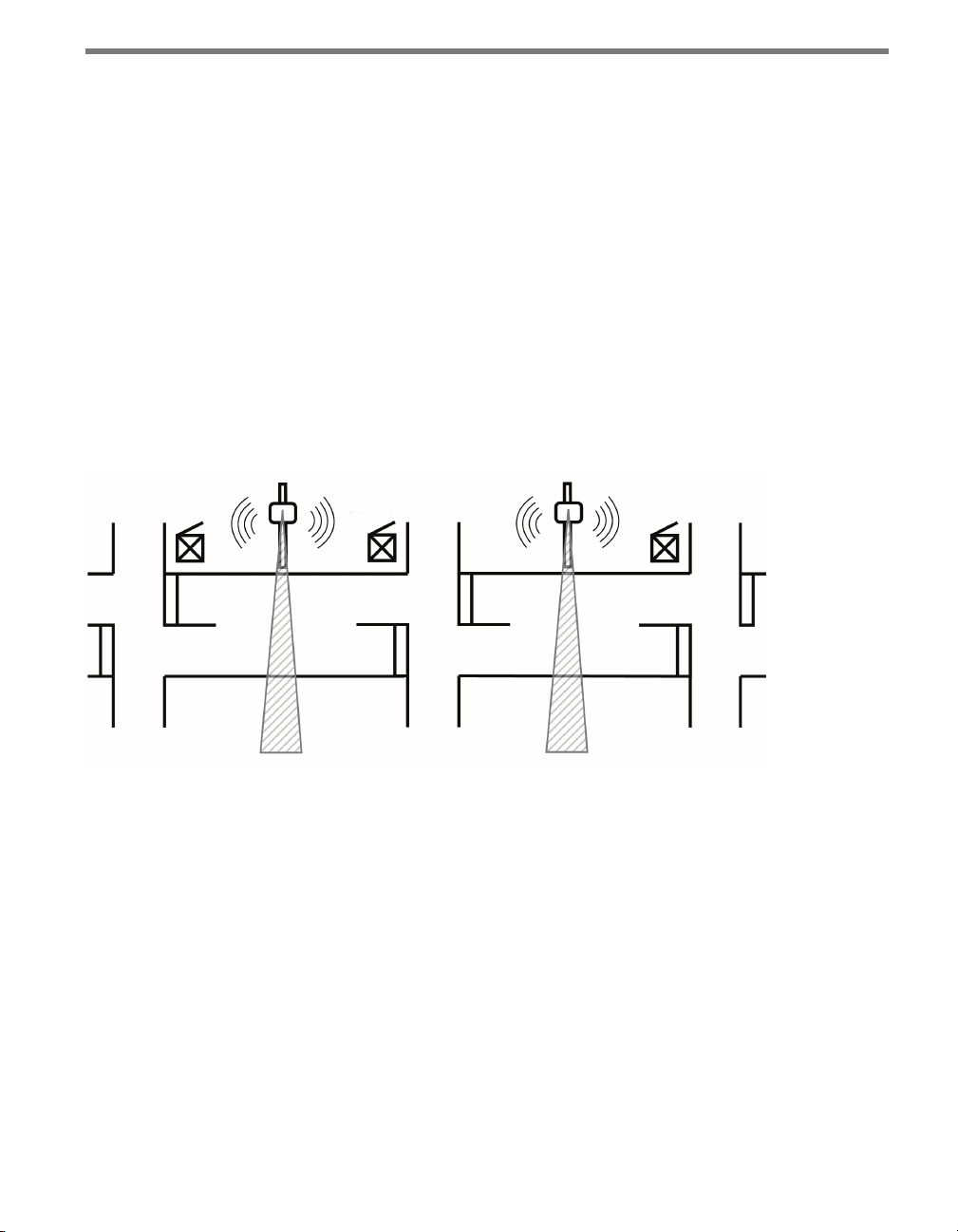
88 CHAPTER 9 CONTACT CLOSURE COMMUNICATIONS
Click 100 – e Click 100 is a din rail–mounted contact closure that can be used in
cabinets without detector racks and simplies integration into automatic data recorders and data loggers. e wiring harness of the automatic data recorders can connect
directly to the screw terminals of the Click 100. Application notes for wiring to common automatic trac recorders can be obtained by contacting your authorized Wa-
vetronix dealer or Wavetronix Technical Services.
Click 101 – e Click 101 has the built-in capability of collecting from multiple Smart-
Sensor units simultaneously, making it an excellent choice for midblock applications.
is allows one Click 101 to collect trac data from all the SmartSensor stations
pertaining to an intersection. For arterial management, the resulting system is very
cost-eective and can be rapidly deployed, especially when wireless communications
is included.
Each SmartSensor uses its two communication ports to send real-time trac data to
both cabinets for which it is collecting data (see Figure 9.1). e real-time data is used
to control the intersection using either local control strategies or closed-loop control
systems like ACS-lite.
Trac
Controller
Figure 9.1 – SmartSensor Sending Real-time Data to Multiple Approaches Using Dual Ports
Click 172/174 – e Click 172/174 are contact closure cards that allow the SmartSen-
sor to integrate into standard ITS and intersection detector racks. e Click 172 has
two contact closure outputs and the Click 174 has four. e Click 172/174 are com-
monly used in legacy ITS cabinets or for midblock intersection detection. Multiple
modules can be daisy-chained together to collect data from all eight lanes possible
with SmartSensor.
Unlike the Click 101, which actively collects information from multiple sensors, each
Click 172/174 is dedicated to a single sensor. During programming, the Click 172/174
cards transmit conguration information to SmartSensor to set up the mode of operation. Once the mode is set up, the rack cards stop transmitting messages and passively
listen for data pushed by the sensor.
Page 90

CHAPTER 9 CONTACT CLOSURE COMMUNICATIONS 89
Tip
In many cases, the trac data detected by SmartSensor is valuable to both operations
and planning departments. However, when legacy systems are used, often there is no
mechanism to directly share the data. Even with the limitations of legacy systems,
contact closures can sometimes provide a way for operations and planning to both get
what they need from a single sensor. For example, the operations department can collect trac data into a trac controller via a Click 172/174 over one of the SmartSensor’s
two ports. Then the planning department can use the second port to send data to an
automatic trac data recorder via a Click 100.
Click 500 – e Click 500 is a user-programmable contact closure platform for vir-
tually any application. For example, the Click 500 can be programmed to activate a
contact closure output when vehicles over a specied speed and length are detected.
To accelerate development, the Click 500 will provide developers with SmartSensor
communication drivers.
For a full description of each module refer to the Click quick-start guides, user manuals and
bid specications. Or contact your authorized Wavetronix dealer or Wavetronix Technical
Services for more information.
Programming Sensors for Use with
Contact Closures
Click 100 – e Click 100 supports baud rates from 9600 to 57600 bps. When using
a Click 100, make sure your SmartSensor is set to operate at a baud rate in this range.
Click 101 – e Click 101 modules support baud rates from 9600 to 115200 bps. e
Click 101 identies each sensor by its sensor ID. Before you congure the Click 101,
you can retrieve the sensor ID using SmartSensor Manager over communication link.
Click 172/174 – e Click 172/174 modules support baud rates from 9600 to 57600
bps. When using a Click 172/174 device, make sure SmartSensor is set to operate at
a baud rate in this range. To select which SmartSensor lanes are mapped to the Click
172/174 outputs, the lane names of the SmartSensor need to be set up correctly using
SmartSensor Manager. e rst character of the lane name should take on the value 0
to 9. e second character can take on a value R or L to represent the direction trac
is owing. For example, lane names could be 1R (right to left) or 1L (left to right).
Page 91

90 CHAPTER 9 CONTACT CLOSURE COMMUNICATIONS
Note
The SmartSensor default loop size and spacing will change the values of SmartSensor
data. The default loop size is used in the calculation of lane occupancy, vehicle duration
and vehicle length. The default loop spacing is used in the calculation of vehicle speed
and length. The Click 100 and 172/174 also use these settings to change the duration
and spacing of contact closures signaled on their output pins. If your SmartSensor is
connected to a contact closure device and you are also retrieving data serially, first adjust the default loop size and spacing to match the inductive loop setup that you’re trying to emulate, then adjust the individual lane size and spacing values used to calculate
the per lane scale factors.
Click 500 – e Click 500 modules support baud rates from 9600 to 115200 bps. Any
special programming of SmartSensor for an application running on the Click 500 will
be explained in the documentation for that application.
Programming Contact Closures
e contact closure modules have several modes of operation explained in their respective
quick-start guides and user manuals. Consult this documentation to determine the mode
appropriate for your application. is documentation will explain how to program each
mode.
Page 92

Appendix
In this chapter
Appendix A – 9-conductor Cable Definitions
e 9-conductor cable is composed of three groups of wires, each containing color-coded
wires and a drain wire and surrounded by a shield. Table A.1 details the pinout of the cable
and the appropriate connection inside the cabinet for each wire:
A – 9-conductor Cable Definitions
B – Old Cable Definitions
C – Cable Lengths
D – Direct Serial Connections
Wire Description
Red +DC
Black -DC
Drain GND
Blue -485
White +485
Drain 485 GND
Yellow 232 (TD)
Violet 232 (RD)
Drain GND
Orange RTS
Page 93

92 APPENDIX SMARTSENSOR 105 USER GUIDE
Brown CTS
Gray 232 GND
Table A.1 – 9-conductor Cable and Cabinet Connection
Figure A.1 shows a diagram of the 9-conductor cable’s 26-pin socket assignment. e
codes listed in the diagram are to be used to solder wires into the back of the plug where
the letters represent the individual solder cups.
Figure A.1 – SmartSensor 105 Plug Connector Socket Assignment
Figure A.2 shows the 9-conductor cable wire connections into a Click 200 surge protector.
Page 94
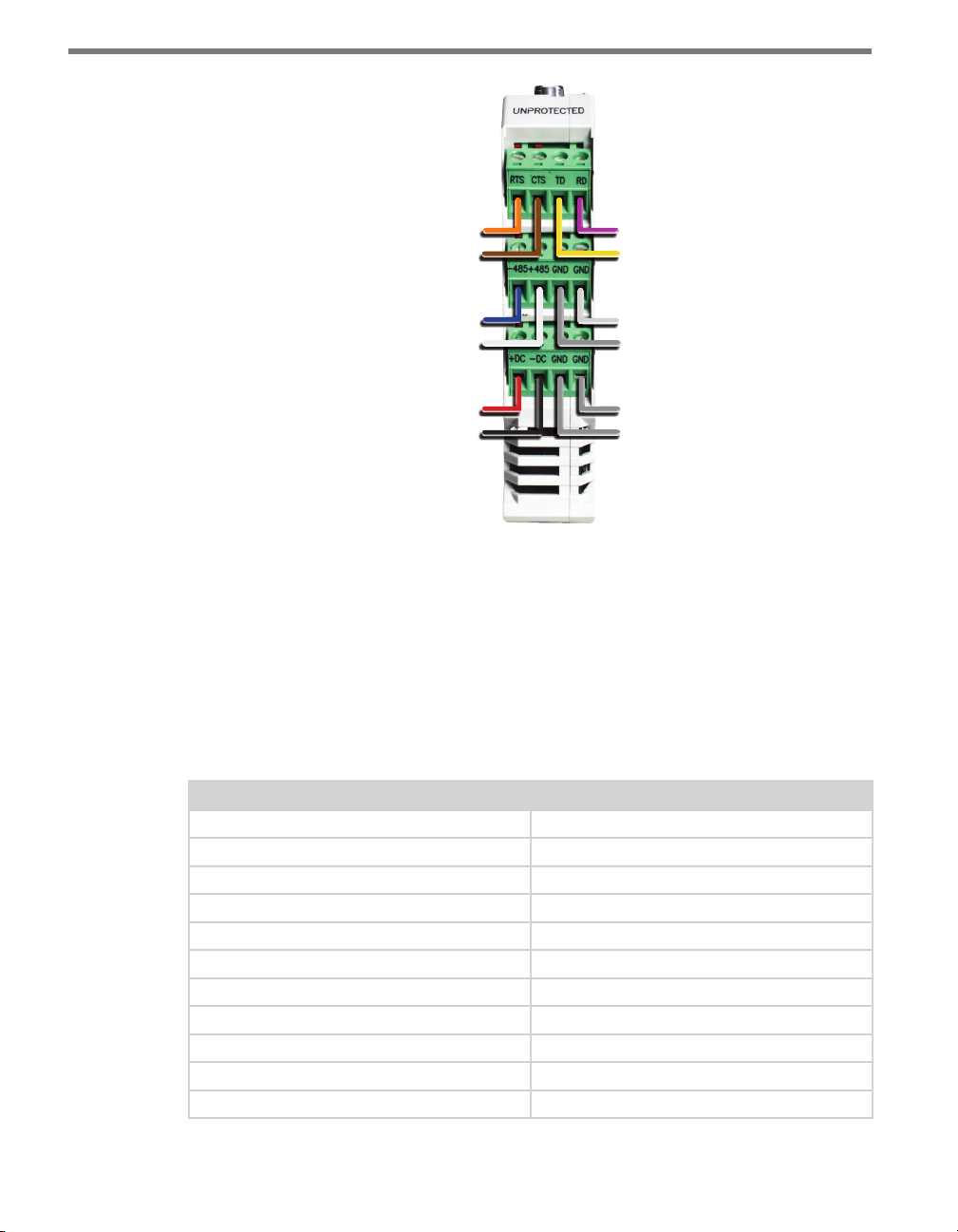
APPENDIX SMARTSENSOR 105 USER GUIDE 93
RTS (Orange)
CTS (Brown)
-485 (Blue)
+485 (White/Blue)
+DC (Red)
-DC (Black)
Figure A.2 – 9-conductor Cable into the Click 200
RD (Purple)
TD (Yellow)
GND (Gray)
RS-485 Drain
RS-232 Drain
Power Drain
Appendix B – Old Cable Definitions
e previously used SmartSensor cable is composed of six twisted pairs of wire. Each pair
is composed of a black and a red wire, accompanied by a drain wire and surrounded by a
shield. A numeric label (1 through 6) identies each pair of black and red wires. Table B.1
details the pinout of the cable and the appropriate connection inside the cabinet for each
wire:
Cable Description
Red 1 +DC
Black 1 -DC
Drain of Pair 1 GND
Red 2 +DC
Black 2 -DC
Drain of Pair 2 GND
Red 3 +485
Black 3 -485
Drain of Pair 3 485 GND
Red 4 232 (TD) output from sensor
Black 4 232 (RD) input to sensor
Page 95
94 APPENDIX SMARTSENSOR 105 USER GUIDE
Drain of Pair 4 232 GND
Pair 5 Reserved for future use
Red 6 CTS flow for 232
Black 6 RTS flow for 232
Table B.1 – Old Cable Description
Figure B.1 shows a diagram of the old SmartSensor cable’s 26-pin socket assignment. e
codes listed in the diagram are to be used to solder wires into the back of the plug where
the letters represent the individual solder cups.
A=1
N=13
232 CTS
(R6)
M=12
232 TD
(R4)
L=11
232 RD
(B4)
P=14
232 RTS
(B6)
K=10
232 GND
(Drain 4)
a=24
RSVD
Z=23
RSVD
R=15
RS_DFM2
(R5)
Y=22
RSVD
+DC
(R1)
S=16
RS_DTM2
b=25
NC
c=26
NC
X=21
GND
(Drain 5)
J=9
RSVD
T=17
GND
(Drain 1)
H=8
-485
(B3)
B=2
-DC
(B1)
RSVD
W=20
RSVD
U=18
V=19
RSVD
G=7
485 GND
(Drain 3)
C=3
+DC
(R2)
D=4
-DC
(B2)
E=5
GND
(Drain 2)
F=6
+485
(R3)
Figure B.1 – Old SmartSensor Plug Connector Socket Assignment
Figure B.2 shows the old SmartSensor cable wire connections into a Click 200 surge protector.
Page 96

APPENDIX SMARTSENSOR 105 USER GUIDE 95
(Black 6)
RTS
(Red 6)
CTS
(Black 3)
-485
(Red 3)
+485
+DC
(Red 1 & Red 2)
GND/-DC
(Black 1 & Black 2)
(Black 4)
RD
(Red 4)
TD
Ground
Ground
Ground
Ground
(Drain 4)
(Drain 3)
(Drain 2)
(Drain 1)
Figure B.2 – Old SmartSensor Cable into the Click 200
Appendix C – Cable Lengths
e recommendations in Table C.1 below allow you to provide reliable power to the SmartSensor. e SmartSensor cable’s red and black wires provide a 20 AWG wire pair. e other
pairs on the SmartSensor cable are 22 AWG and are normally used for communication.
Cable Gauge 24 Volts 12 Volts
20 AWG (8-conductor Cable) 600 ft. (182.9 m) 110 ft. (33.5 m)
Additional 22 AWG Add 400 ft. (121.9 m) Add 75 ft. (22.9 m)
22 AWG (9-conductor Cable) 400 ft. (121.9 m) 75 ft. (22.9 m)
Additional 22 AWG Add 400 ft. (121.9 m) Add 75 ft. (22.9 m)
14 AWG 2500 ft. (762 m) 450 ft. (137.2 m)
12 AWG 3900 ft. (1188.7 m) 700 ft. (213.4 m)
10 AWG 6000 ft. (1828.8 m) 1050 ft. (320 m)
8 AWG 9900 ft. (3017.5 m) 1750 ft. (533.4 m)
6 AWG 14,000 ft. (4267.2 m) 2500 ft. (762 m)
Table C.1 – Maximum Cable Length for Power
If the cable length is longer than 600 ft. (182.9 m) when operating at 24 V, it is possible
to increase the maximum cable length by wiring a pair of lines normally used for RS-232
communications with the red and black wires.
Page 97

96 APPENDIX SMARTSENSOR 105 USER GUIDE
If the cable length is 200 ft. (61 m) or greater you cannot reliably use RS-232 communi-
cations. To add 400 ft. (121.9 m) and achieve a maximum cable length of 1000 ft. (304.8
m), connect the orange wire (normally RTS) to the red wire and the brown wire (normally
CTS) to the black wire.
If your cable run is longer than 1000 ft. (304.8 m), it is possible to sacrice additional com-
munication pairs to increase the maximum cable length for power. However, you may desire
to communicate to the sensor over two independent channels, in which case you will need
to consider an alternate cable for power. e AWG for wire pairs that achieve a 2000 ft.
(609.6 m) maximum cable length or greater at 12 and 24 V are listed in Table A.5.
To achieve reliable wired communications, the selected baud rate must be compatible with
the length of the cable run. Table C.2 below shows the cable length recommendations for
wired communications:
Baud Rate (bps) RS-232 RS-485
115200 40 ft. (12.2 m) 300 ft. (91.4 m)
57600 60 ft. (18.3 m) 600 ft. (182.9 m)
38400 100 ft. (30.5 m) 800 ft. (243.8)
19200 140 ft. (42.7 m) 1000 ft. (304.8 m)
9600 200 ft. (61 m) 2000 ft. (609.6 m)
Table C.2 – Maximum Cable Length for Wired Communications
To provide two independent communication channels with a homerun cable length over
200 ft. (61 m), convert the RS-232 data into RS-485 using a Click 304 in a pole-mount
cabinet mounted next to the sensor. In this case, the homerun connection establishes one
RS-485 channel over the normal white/blue wire pair and another RS-485 channel over
the yellow/violet wire pair. An additional Click 304 is needed to convert the data sent over
the yellow/violet wire pair back to RS-232 before connecting to surge protection.
If you elect to use an alternate cable for power, you may also want to select an alternate
cable for RS-485 communications. Some options include the Belden 3105A (Paired – EIA
Industrial RS-485 PLTC/CM) or Alpha Wire 6010C 3PR 22 AWG.
ere are many reliable options available for wired power and communications connections
(see Table C.3).
Length Cable Comm. Channel 1 Comm. Channel 2
0–200 ft. (0–61 m) 8-conductor Cable Native RS-485 Native RS-232
200–1000 ft.
(61–304.8 m)
1000–1400 ft.
(304.8–426.7 m)
8-conductor Cable Native RS-485 Click conversion of
RS-232 to RS-485
8-conductor Cable Native RS-485 N/A
Page 98
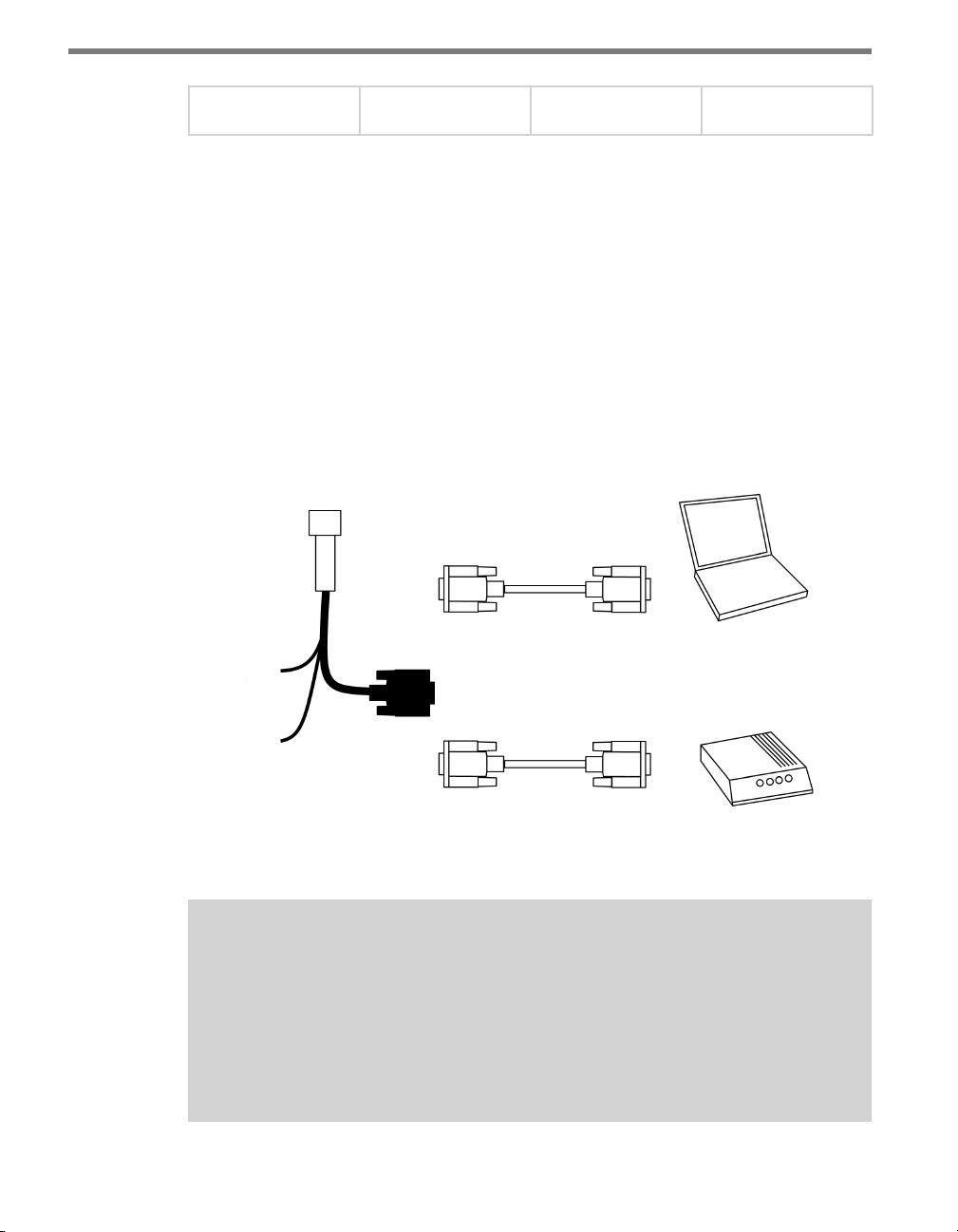
APPENDIX SMARTSENSOR 105 USER GUIDE 97
1400–2000 ft.
(426.7–609.6 m)
Table C.3 – Cable Length Options
Alternate power and
communications cable
Native RS-485 Click conversion of
RS-485 to RS-232
Appendix D – Direct Serial Connections
For most applications, the service end of the SmartSensor cable terminates in a surge protection device. However, during demonstrations, troubleshooting, and certain other situations, it is sometimes convenient to bypass surge protection and connect directly to a
personal computer or communications device such as a modem.
e sensor is congured as an RS-232 DTE device. To connect the SmartSensor cable’s
RS-232 wires directly to another DTE device (such as a PC), you can use a standard 9-pin
“D” connector and a null modem cable. To connect directly to a DCE device (such as a
modem), you will need a straight-through cable. Figure D.1 illustrates both of these cases.
SmartSensor
Connector
Null Modem Cable
Power Wires
or
DTE Device (PC)
Straight-through Cable
RS-485 Wires
DCE Device (Modem)
Figure D.1 – Direct Serial Connections
Note
If you do not have the right type of RS-232 physical connection you will not be able
to connect using the SmartSensor Manager software. Since null modem cables and
straight-through cables look similar, you may want to label them. Alternatively, you
may want to use a null modem adapter instead of a null modem cable. If you do, you
can turn your straight-through cable into a null modem cable by attaching the adapter
on one end.
Page 99

98 APPENDIX SMARTSENSOR 105 USER GUIDE
If you wish to connect the SmartSensor cable’s RS-485 wires directly to a PC or modem,
this will require that these devices natively support RS-485 communications. Often, mod-
ern personal computers do not support RS-485 communications and support USB communications instead. If your computer only supports USB communications, you may want
to use a Click serial to USB converter to make a direct connection.
 Loading...
Loading...