Page 1

WAVECOM Decoder
W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5
by WAVECOM ELEKTRONIK AG
Page 2

PUBLISHED BY
WAVECOM ELEKTRONIK AG
Hammerstrasse 8
CH-8180 Buelach
Switzerland
Phone +41-44-872 70 60
Fax +41-44-872 70 66
Email: info@wavecom.ch
Internet: http://www.wavecom.ch
© by WAVECOM ELEKTRONIK AG. All rights reserved.
Reproduction in whole or in part in any form is prohibited without written consent of the copyright owner.
The publication of information in this document does not imply freedom from patent or other protective rights of
WAVECOM ELEKTRONIK AG or others.
All brand names in this document are trademarks or registered trademarks of their owners.
Specifications are subject to change without further notice.
Printed: Wednesday, October 15, 2014
Page 3

Contents
General Information 2
Welcome ..................................................................................................... 2
Company Profile ........................................................................................... 2
Revisions ..................................................................................................... 2
Recommended WAVECOM Products and Services .............................................. 7
Setup 9
W61PC ........................................................................................................ 9
Software Uninstall....................................................................................... 18
W-BV BitView Tool ............................................................................. 7
W-Sat-email-Decoder ......................................................................... 8
W61PC Hardware Installation .............................................................. 9
W61PC Software Installation ............................................................. 10
W61PC Server Control ...................................................................... 12
W61LAN-MK3 .................................................................................. 12
W61PC/LAN Licensing ...................................................................... 16
First start 19
W61PC First Start ....................................................................................... 19
GUI ........................................................................................................... 20
Command Line Parameters .......................................................................... 20
Default Data and Program Folders (Paths) ..................................................... 21
Main Menu ................................................................................................. 22
File Menu ................................................................................................... 23
HF-Modes Menu .......................................................................................... 24
VHF/UHF-DIR Menu .................................................................................... 25
VHF/UHF-SUB Menu .................................................................................... 26
Satellite Menu ............................................................................................ 27
FAX & Modems Menu ................................................................................... 28
Options Menu ............................................................................................. 30
Alphabet......................................................................................... 30
Bit Inversion Mask ........................................................................... 30
CRC Recognition .............................................................................. 30
CRC Table....................................................................................... 31
Clear Screen ................................................................................... 31
Code Statistics ................................................................................ 31
Cycle... .......................................................................................... 32
Error Indication ............................................................................... 32
FAX & Modems Settings.................................................................... 32
Frame Format… ............................................................................... 32
IAS ................................................................................................ 33
Letters/Figures... ............................................................................. 33
Message Type... .............................................................................. 33
Modem Settings… ............................................................................ 35
MSI ............................................................................................... 35
Resync Mode ................................................................................... 35
Signal Polarity ................................................................................. 35
Symbol Definition ............................................................................ 35
SAT Settings… ................................................................................. 36
Toggle ............................................................................................ 37
Time Stamp... ................................................................................. 37
Demodulator Menu ..................................................................................... 38
WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5 Contents iii
Page 4

Auto .............................................................................................. 38
Mode... .......................................................................................... 38
PB Center... .................................................................................... 40
PB Bandwidth... ............................................................................... 40
Center............................................................................................ 40
Shift... ........................................................................................... 40
Baudrate... ..................................................................................... 40
Polarity... ....................................................................................... 40
Offset... ......................................................................................... 40
Input... .......................................................................................... 41
Gain... ........................................................................................... 41
Favorites Menu ........................................................................................... 42
Open... .......................................................................................... 42
Save As... ....................................................................................... 43
Configuration Menu ..................................................................................... 43
W61PC Card… ................................................................................. 43
Font... ............................................................................................ 44
Temp Files... ................................................................................... 44
Settings... ...................................................................................... 45
Receiver and Satellite Settings... ....................................................... 45
License... ........................................................................................ 46
Custom Inputs... ............................................................................. 47
Custom Alphabets… ......................................................................... 51
SR Fine Tuning ................................................................................ 52
SR Calibration ................................................................................. 53
View Menu ................................................................................................. 54
Window Menu............................................................................................. 55
Help Menu ................................................................................................. 55
Contents ........................................................................................ 55
WAVECOM on the Web ..................................................................... 55
About W61... .................................................................................. 55
Other GUI Elements .................................................................................... 55
Toolbar .......................................................................................... 55
WAVECOM Toolbar ........................................................................... 56
Level Indicator ................................................................................ 57
Spectrum Indicator .......................................................................... 57
Decoder Status Bar .......................................................................... 57
Demodulator Status Bar ................................................................... 57
SAT Frequency Tuning Bar ................................................................ 57
FFT / Sonagram Context Menu .......................................................... 59
Mode Selector ................................................................................. 61
Passband Filter Support .................................................................... 65
Analysis Tools 67
FFT ........................................................................................................... 67
FFT HF, FFT SUB, FFT DIR, FFT SAT ................................................... 68
Tuning FFT or Sonagram .................................................................. 68
FFT and Sonagram ...................................................................................... 69
Waterfall ................................................................................................... 70
Waterfall HF, Waterfall SUB, Waterfall DIR, Waterfall SAT ..................... 70
Sonagram .................................................................................................. 70
Sonagram HF, Sonagram SUB, Sonagram DIR, Sonagram SAT.............. 71
Oscilloscope ............................................................................................... 71
FSK Analysis .............................................................................................. 73
FSK Analysis Options ....................................................................... 74
FSK Code Check ......................................................................................... 75
FSK Code Check HF ......................................................................... 75
FSK Code Check DIR ........................................................................ 77
FSK Code Check SUB ....................................................................... 78
PSK Symbol Rate (HF, DIR, SUB, SAT) .......................................................... 80
PSK Phase Plane (HF, DIR, SUB, SAT) ........................................................... 81
PSK CODE CHECK (HF, DIR, SUB) ................................................................. 83
MIL-STANAG Code Check ............................................................................. 84
iv Contents WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5
Page 5

MFSK Analysis ............................................................................................ 84
MFSK Code Check HF .................................................................................. 85
Autocorrelation ........................................................................................... 86
BIT CORRELATION ...................................................................................... 88
BIT LENGTH ANALYSIS ................................................................................ 90
SELCAL ANALYSIS ...................................................................................... 92
Fundamentals of Radio Data Transmission 94
Telegraph Speed, Bit Rate, Baud Rate, Symbol Rate ....................................... 95
Formatting and Source Coding ..................................................................... 96
Encryption ................................................................................................. 98
Channel Coding .......................................................................................... 99
Equalization ............................................................................................. 100
Synchronization ........................................................................................ 100
Multiplexing and Multiple Access ................................................................. 101
Modulation ............................................................................................... 101
ASK (Amplitude Shift Keying) .......................................................... 102
FSK (Frequency Shift Keying) .......................................................... 102
PSK (Phase Shift Keying) ................................................................ 102
M-ary-FSK (MFSK), M-ary-PSK (MPSK) ............................................. 102
OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Modulation) ............................ 102
Bandwidth-efficient Modulation ........................................................ 103
INDIRECT FM ................................................................................ 103
INDIRECT AM ................................................................................ 103
FAX ......................................................................................................... 103
FAX Transmission Sequence ............................................................ 103
Transmission Modes 104
ACARS .................................................................................................... 104
AIS ......................................................................................................... 106
ALE-400 .................................................................................................. 107
ALF-RDS .................................................................................................. 108
ALIS ....................................................................................................... 108
ALIS-2 .................................................................................................... 109
AMSAT-P3D ............................................................................................. 110
APCO-25 ................................................................................................. 110
ARQ6-90 and ARQ6-98 .............................................................................. 111
ARQ-E ..................................................................................................... 111
ARQ-E3 ................................................................................................... 112
ARQ-M2-342 and ARQ-M2-242 ................................................................... 112
ARQ-M4-342 and ARQ-M4-242 ................................................................... 113
ARQ-N ..................................................................................................... 114
ASCII ...................................................................................................... 114
ATIS ....................................................................................................... 115
AUM-13 ................................................................................................... 116
AUTOSPEC ............................................................................................... 116
BAUDOT .................................................................................................. 117
BIIS ........................................................................................................ 118
BR-6028 .................................................................................................. 121
BULG-ASCII ............................................................................................. 122
CCIR ....................................................................................................... 123
CCITT ..................................................................................................... 124
CHU ........................................................................................................ 125
CIS-11 .................................................................................................... 125
CIS-12 .................................................................................................... 126
CIS-14 .................................................................................................... 126
CIS-36 .................................................................................................... 127
CIS-36-50 ............................................................................................... 128
CIS-50-50 ............................................................................................... 128
CLOVER-2 ................................................................................................ 128
CLOVER-2000 .......................................................................................... 129
CODAN-SELCAL ........................................................................................ 130
WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5 Contents v
Page 6

CODAN-9001 ........................................................................................... 131
COQUELET-13 .......................................................................................... 134
COQUELET-8 ............................................................................................ 135
COQUELET-80 .......................................................................................... 136
CTCSS ..................................................................................................... 137
CV-786 .................................................................................................... 138
CW-MORSE .............................................................................................. 139
DCS SELCAL ............................................................................................ 139
DGPS ...................................................................................................... 140
DMR ........................................................................................................ 141
dPMR ...................................................................................................... 142
DTMF ...................................................................................................... 142
DUP-ARQ ................................................................................................. 143
DUP-ARQ-2 .............................................................................................. 144
DUP-FEC-2............................................................................................... 144
DZVEI ..................................................................................................... 145
EEA ......................................................................................................... 146
EFR ......................................................................................................... 146
EIA ......................................................................................................... 147
ERMES .................................................................................................... 148
EURO ...................................................................................................... 150
FEC-A...................................................................................................... 150
FELDHELL ................................................................................................ 151
FLEX ....................................................................................................... 152
FM-HELL .................................................................................................. 152
FMS-BOS ................................................................................................. 153
GMDSS/DSC-HF ....................................................................................... 155
GMDSS/DSC-VHF ..................................................................................... 155
GOLAY/GSC ............................................................................................. 156
G-TOR ..................................................................................................... 157
GW-FSK .................................................................................................. 158
GW-OFDM................................................................................................ 158
GW-OFDM-Modulation and Protocol .................................................. 159
Decoder output ............................................................................. 159
GW-PSK .................................................................................................. 160
HC-ARQ ................................................................................................... 160
HF-ACARS ............................................................................................... 161
HNG-FEC ................................................................................................. 162
IAS Bitstream Output ................................................................................ 163
ICAO SELCAL ........................................................................................... 164
LINK-11 (CLEW) ....................................................................................... 165
MD-674 ASYNC ........................................................................................ 166
METEOSAT ............................................................................................... 166
MFSK-20 ................................................................................................. 167
MFSK-8 and MFSK-16................................................................................ 167
MIL-188-110-16Tone, (MIL-188-110A/B Appendix B) .................................... 168
MIL-188-110-39Tone, (MIL-188-110A/B Appendix C) .................................... 169
MIL-188-110A .......................................................................................... 170
MIL-188-110B (Appendix C), STANAG 4539 ................................................. 171
MIL-188-141A .......................................................................................... 173
MIL-188-141B (Appendix C) ....................................................................... 174
MIL-M-55529A NB/WB .............................................................................. 175
MOBITEX-1200 ......................................................................................... 176
MOBITEX-8000 ......................................................................................... 177
MODAT .................................................................................................... 177
Fax & MODEMS Half-Duplex ....................................................................... 178
FAX-G3-V.17 ................................................................................. 178
FAX-G3-V.27ter ............................................................................. 178
FAX-G3-V.29 ................................................................................. 179
FAX-G3-V34hdx ............................................................................ 179
V.21, BELL103 .............................................................................. 179
V.22 / V.22bis, BELL212A ............................................................... 179
V.23 ............................................................................................ 179
MPT-1327 ................................................................................................ 180
vi Contents WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5
Page 7

NATEL ..................................................................................................... 182
NMT-450 ................................................................................................. 182
NOAA-GEOSAT ......................................................................................... 183
NWR-SAME .............................................................................................. 184
OLIVIA .................................................................................................... 187
ORBCOMM ............................................................................................... 188
PACKET-1200 ........................................................................................... 189
PACKET-300 ............................................................................................ 190
PACKET-9600 ........................................................................................... 191
PACTOR ................................................................................................... 191
PACTOR-FEC ............................................................................................ 192
PACTOR-II ............................................................................................... 193
PACTOR-II-AUTO ...................................................................................... 194
PACTOR-II-FEC ........................................................................................ 194
PACTOR-III .............................................................................................. 195
PCCIR ..................................................................................................... 197
PDZVEI ................................................................................................... 197
PICCOLO-MK6 and PICCOLO-MK12 ............................................................. 198
POCSAG .................................................................................................. 199
POL-ARQ ................................................................................................. 201
PRESS-FAX .............................................................................................. 202
PSK-10 .................................................................................................... 202
PSK-31, PSK-63, PSK-125, PSK-250 ........................................................... 203
PSK-31-FEC ............................................................................................. 204
PSK-63F, PSK-125F, PSK-220F ................................................................... 204
PSK-AM ................................................................................................... 205
PZVEI ...................................................................................................... 205
ROBUST-PACKET ...................................................................................... 206
RUM-FEC ................................................................................................. 207
SAT-AERO-P ............................................................................................ 208
SAT-B ..................................................................................................... 208
SAT-B-C-TFC ............................................................................................ 209
SAT-C-TDM, SAT-C-TDMA, SAT-C-EGC ........................................................ 210
SAT-C TDM ................................................................................... 211
SAT-C-TDMA ................................................................................. 212
SAT-C-TDM-EGC ............................................................................ 212
SAT-M ..................................................................................................... 214
SAT-MINI-M ............................................................................................. 215
SI-ARQ .................................................................................................... 215
SI-AUTO .................................................................................................. 216
SI-FEC .................................................................................................... 216
SITOR-ARQ .............................................................................................. 217
SITOR-AUTO ............................................................................................ 217
SITOR-FEC............................................................................................... 217
SP-14 ...................................................................................................... 218
SPREAD-11, SPREAD-21 and SPREAD-51 ..................................................... 219
SSTV ....................................................................................................... 220
STANAG-4285 .......................................................................................... 222
STANAG-4415 .......................................................................................... 224
STANAG-4481-FSK ................................................................................... 225
STANAG-4481-PSK ................................................................................... 225
STANAG-4529 .......................................................................................... 227
STANAG-4539 .......................................................................................... 228
STANAG-5065-FSK ................................................................................... 229
SWED-ARQ .............................................................................................. 229
TETRA ..................................................................................................... 230
Constraints ................................................................................... 233
TWINPLEX ............................................................................................... 233
VDEW ..................................................................................................... 235
VDL-M2 ................................................................................................... 235
VISEL ...................................................................................................... 236
WEATHER-FAX ......................................................................................... 237
X.25........................................................................................................ 237
ZVEI-1 .................................................................................................... 239
WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5 Contents vii
Page 8

ZVEI-2 .................................................................................................... 239
ZVEI-3 .................................................................................................... 240
ZVEI-VDEW ............................................................................................. 241
Classifier (Optional) 244
Overview ................................................................................................. 244
Classifier ................................................................................................. 244
How the Classifier works................................................................. 244
Classifier User Interface ................................................................. 244
Caveats ........................................................................................ 249
Classifier Code Check HF (CCC) .................................................................. 249
How the Classifier Code Check works ............................................... 249
User Interface ............................................................................... 251
Decoding ...................................................................................... 255
Classifier Code Check (CCC) VHF/UHF ......................................................... 255
How the Classifier Code Check works ............................................... 255
User Interface ............................................................................... 257
Decoding ...................................................................................... 261
Classifier Code Check Editor ....................................................................... 261
Licensing ...................................................................................... 261
Installation ................................................................................... 261
CCC Editor GUI.............................................................................. 262
Data Base Fields ............................................................................ 267
SAT System 269
Overview ................................................................................................. 269
Systems .................................................................................................. 270
RF Channels .................................................................................. 271
Logical Channels............................................................................ 271
MES Identification .......................................................................... 272
Session Signaling .......................................................................... 272
SAT Operation .......................................................................................... 272
Traffic-Channel Decoder ................................................................. 274
The Sat Aero System ................................................................................ 274
Services ....................................................................................... 274
Channel types ............................................................................... 275
Trouble Shooting ........................................................................... 276
Modem and FAX modes 280
Overview ................................................................................................. 280
Line transmission .......................................................................... 280
Fax and data transmission ......................................................................... 281
Modem functionality ....................................................................... 281
Handshaking ................................................................................. 282
Modulation types ........................................................................... 283
Decoding ................................................................................................. 284
Input and interfacing ..................................................................... 286
Constraints ................................................................................... 286
Output ......................................................................................... 287
Additional Functions 288
License System, Software and Options ........................................................ 288
License System ............................................................................. 288
CmStick ....................................................................................... 288
WAVECOM Server ..................................................................................... 289
Introduction .................................................................................. 289
WAVECOM Server Control ............................................................... 290
Shortcut Manager ..................................................................................... 292
Adding a shortcut to an existing installation ...................................... 292
Alarm Monitor .......................................................................................... 292
viii Contents WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5
Page 9

Introduction .................................................................................. 292
Options ........................................................................................ 294
Settings ....................................................................................... 294
Run ............................................................................................. 296
Serial Link ............................................................................................... 296
Introduction .................................................................................. 296
Getting Started ............................................................................. 297
Status Information ........................................................................ 297
Remote Control ........................................................................................ 298
XML ........................................................................................................ 298
WAVECOM Data Formats 299
IP-CONF TCP/IP Data Format ..................................................................... 299
IP-PXGF TCP/IP Data Format ...................................................................... 299
OVERVIEW.................................................................................... 299
PXGF DESCRIPTION ....................................................................... 299
THE PXGF CHUNK STRUCTURE ........................................................ 299
APPLICATION NOTES ..................................................................... 300
DEFINITION OF CHUNKS ................................................................ 301
WAVECOM Data File Format ....................................................................... 303
File Header ................................................................................... 303
Data Structures ............................................................................. 304
File Headers and Data Structures for Individual File Types .................. 304
Appendix 312
Alphabets Details ...................................................................................... 312
Unicode ........................................................................................ 312
Questions & Answers................................................................................. 322
Signal Interference ................................................................................... 322
General ........................................................................................ 322
Antenna installation ....................................................................... 323
Receiver ....................................................................................... 323
HF cabling .................................................................................... 323
Grounding .................................................................................... 323
Location of decoder ....................................................................... 323
PCs and peripherals ....................................................................... 323
Video monitor ............................................................................... 323
LAN ............................................................................................. 323
Conditions of Sale ..................................................................................... 323
General ........................................................................................ 323
Prices ........................................................................................... 324
Delivery time ................................................................................ 324
Dispatch ....................................................................................... 324
Return of goods ............................................................................. 324
Payments ..................................................................................... 324
Reservation of ownership ............................................................... 324
Cancellation .................................................................................. 324
Changes of Order Quantities ........................................................... 324
Legal Domicile ............................................................................... 324
Warranty ...................................................................................... 325
Obligation ..................................................................................... 325
Copyright ..................................................................................... 325
Liability ........................................................................................ 325
Laws and Regulations ..................................................................... 325
Declaration of Conformity .......................................................................... 326
Conformity of W61PC ..................................................................... 326
Conformity of W61LAN ................................................................... 327
Manufacturer Address ............................................................................... 327
Glossary of Terms 329
Index 339
WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5 Contents ix
Page 10

x Contents WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5
Page 11

WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5 General Information 1
Page 12

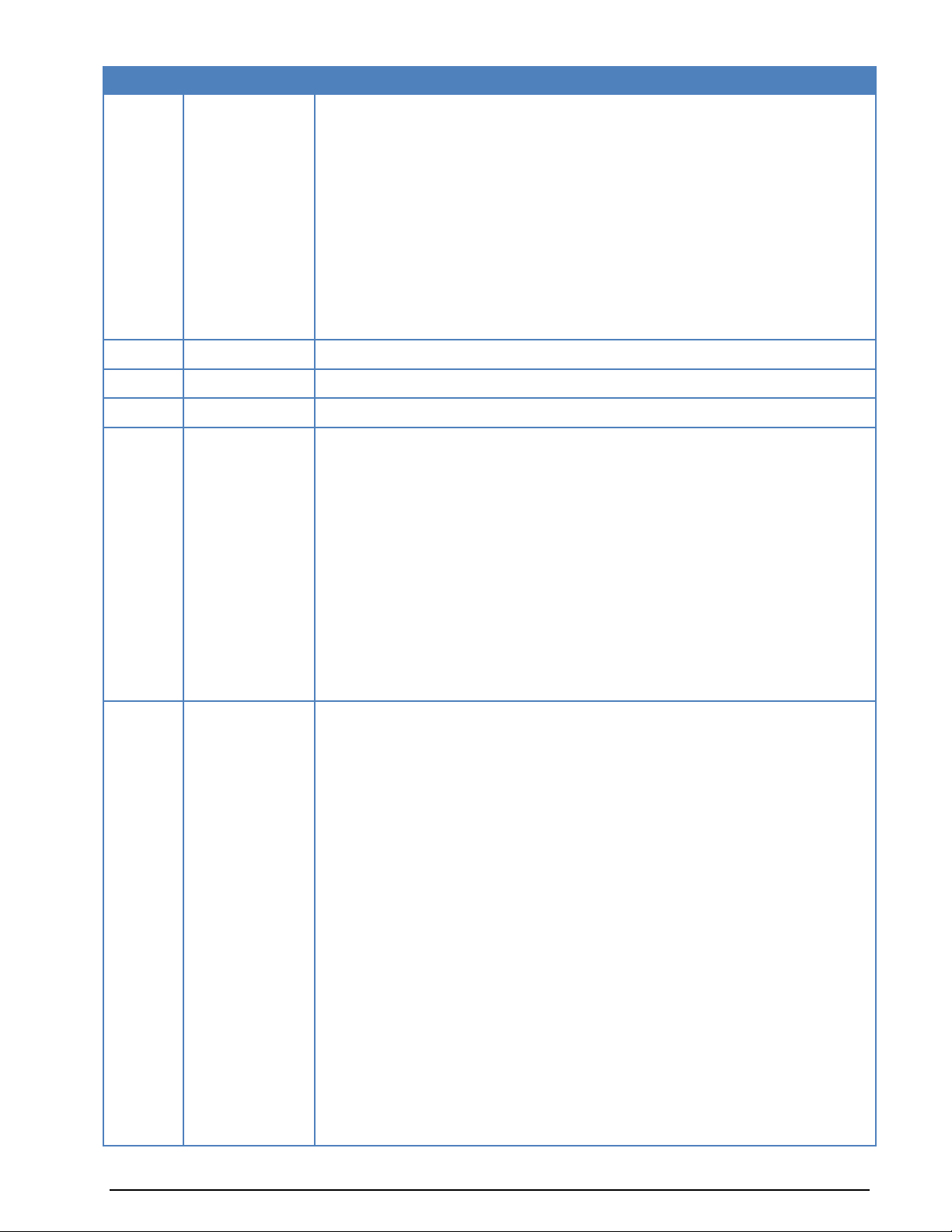
Version
Date
Changes
Beta
20-Dec-2005
Initial draft
6.3
15-Jan-2006
CMH files, index, installation
6.4
15-Jul-2006
New protocols:
- PSK-AM
- MIL-188-110-16Tone
- CIS-12
General Information
Welcome
Thank you for choosing a WAVECOM decoder. The product that you have purchased includes the latest
technology in data decoding, together with the latest software release available at the time of shipment.
Please check our website at http://www.wavecom.ch for software updates.
Before you install the product, please also check the latest documentation on the installation CD/DVD or
on our website.
WAVECOM ELEKTRONIK AG develops and sells products for wireless (HF/VHF/VHF/SHF) data monitoring
independent of frequency range.
Two decoder families are currently available:
W-CODE is a stand-alone application, which works with native host hardware.
W61PC/W61LAN consists of hardware (e.g., W61PC, W61LAN) and corresponding, integral soft-
ware (no additional order of the software required).
Company Profile
WAVECOM ELEKTRONIK GmbH was founded in 1985 in Hohentengen, Germany, close to the Swiss border.
In 1991 the company moved to Switzerland and established itself as WAVECOM ELEKTRONIK AG. Now located in Buelach, it is within close distance of Zurich airport.
The company has focused on decoding and analysis systems for wireless data transmissions. The wide
product range spans from professional, high performance systems to devices for private and amateur radio use.
Very high quality standards coupled with high system performance result in a high level of customer satisfaction worldwide. A global network of authorized sales partners ensures that local assistance and basic
level support can be provided in most places. More than 95% of all units sold are exported, and the majority of the customers are government agencies, defense organizations and the telecommunication industry.
About 40% of the turnover is invested in research and development. The employees at WAVECOM ELEKTRONIK AG are mainly engineers with experience in DSP technology, computer and RF hardware development, as well as software engineering and radio data transmission. Access to external know-how and
human resources increases the company’s capability to realize projects. Manufacturing is outsourced to
specialized companies within Switzerland which can handle today's needs for processing surface mount
components and fine-pitch structures.
WAVECOM ELEKTRONIK AG does not have any juridical or financial links or connections to other companies or official bodies, and is completely owned by Mr. Christian Kesselring.
Revisions
2 General Information WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5
Page 13
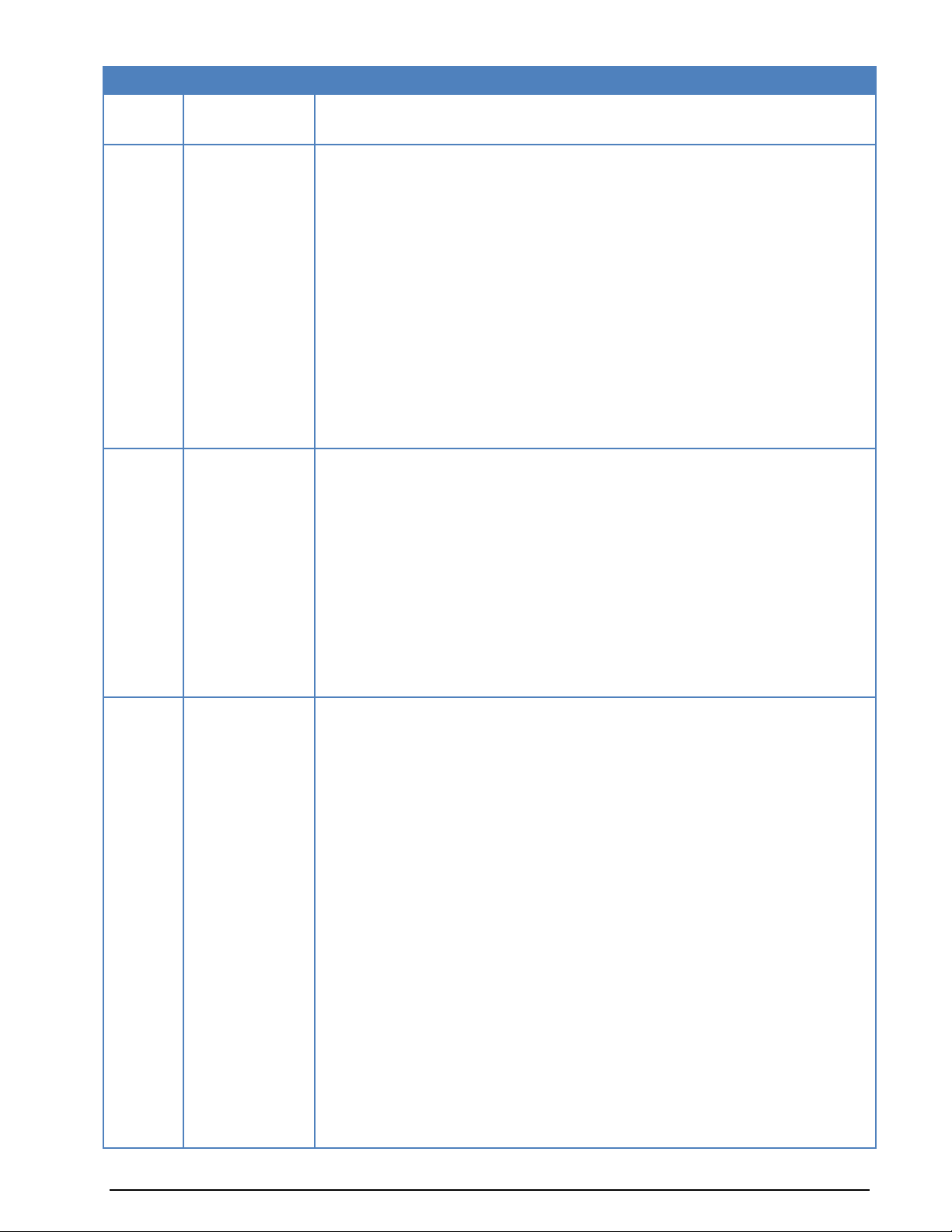
Version
Date
Changes
- PACTOR-III
- CLOVER-2
- CLOVER-2000
- CODAN-9001
Improvements and modifications:
HF PSK CODE CHECK
HF MFSK CODE CHECK
HF CLASSIFIER CODE CHECK
Tuning FFT
Installation for PACTOR-III/CODAN/CLOVER Modes
6.4
25-Aug-2006
W51PC added
6.4.01
4-Oct-2006
W61LAN added
6.4.02
4-Oct-2006
ServerControl
6.5.00
27-Apr-2007
New protocols:
- PACTOR-FEC
- CV-786
- MD-674
- MIL-M-55529a
- MOBITEX-1200
- VISEL
- STANAG-5066
Improvements and modifications:
Inputs added (streaming and user inputs)
Passband tuning added
6.6.00
23-Jan-2008
New protocols:
- CHU
- DZVEI
- MIL-188-110-39Tone
- MOBITEX-1200
- MODAT
- NWR-SAME
- PCCIR
- PDZVEI
- PZVEI
- SAT-AERO (Aero-I)
- ZVEI-3
- Stanag-5065-FSK
Improvements and modifications:
W51PC removed
ATIS changed
New chapter: WAVECOM TCP/IP Data File Format
WiNRADiO Setup
WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5 General Information 3
Page 14
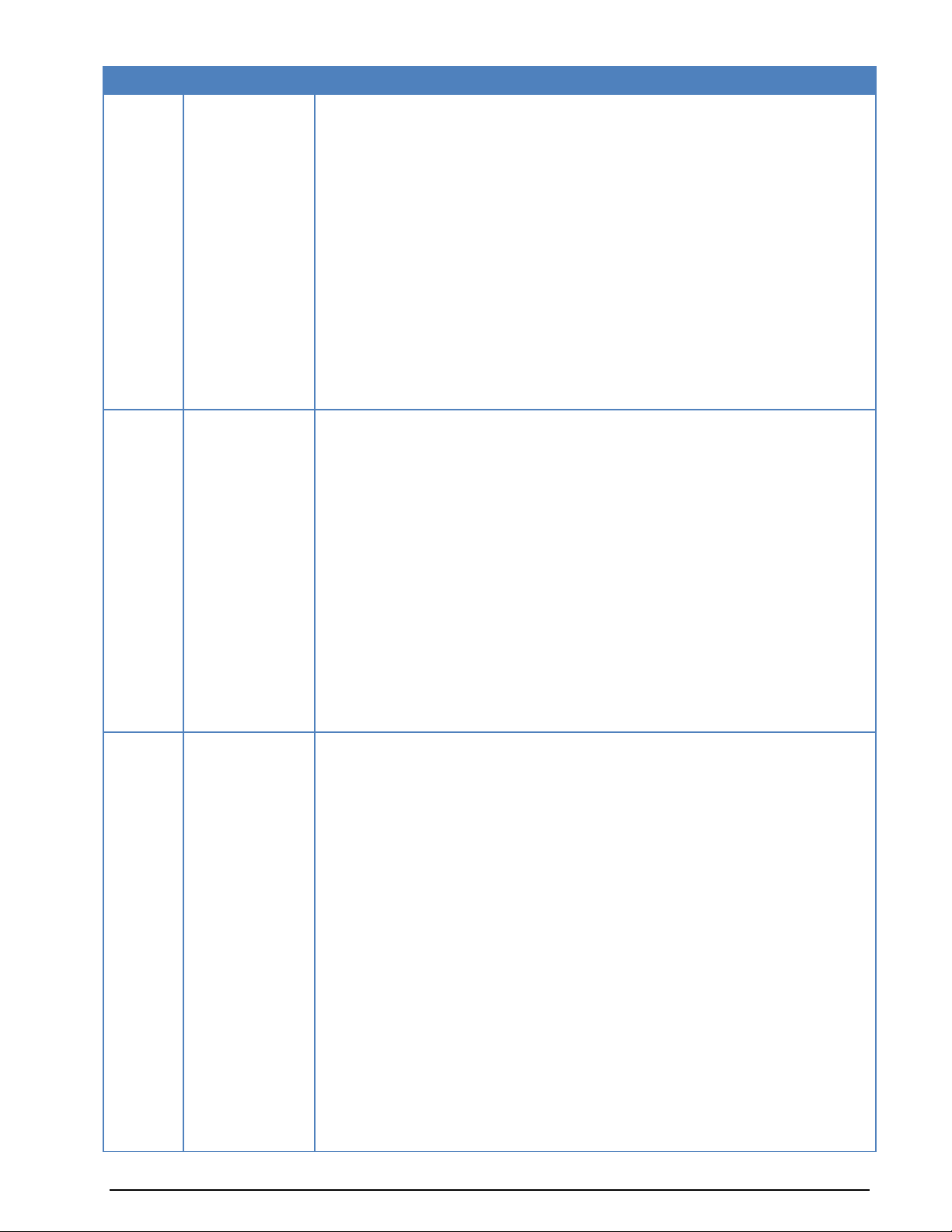
Version
Date
Changes
Time cursors in sonagram
New manual layout
6.6.5.0
2-Jul-2008
New protocols:
- OLIVIA
- BIIS-1200
Improvements and modifications:
Chapter: Professional version removed, as in the feature only one version is available
Phase plane “Sync/Async” replaced with “IQ demodulator”
"BITS" replaced by "BINARY" in ALF-RDS, CODAN 9001, INMARSAT-A, MIL188110A, -B, -16Tone, -39Tone, MIL 188-141B, STANAG 4285, -4415, -4529
"RAW" replaced by "HEX" in CIS36-50, CIS50-50,GW-FSK, GW-PSK, VISEL
STANAG4529 default center frequency changed to 1700 Hz
W-CODE added
CodeMeter added
6.6.6
22-Jan-2009
New protocols:
- SAT-B-C-TFC
- Robust Packet Radio
- ORBCOMM
Improvements and modifications:
User Manual split into a W-CODE and W-61 Manual.
FAX and Modem added
SAT-AERO improved
User defined alphabets added
Sample Rate Fine tuning added
6.6.7
14-Mai-2009
New protocols:
- FAX-G3-V.17
- FAX-G3-V.27ter
- FAX-G3-V.29
- FAX-G3-V34hdx
- V.21, BELL103
- V.22 / V.22bis, BELL212A
- V.23
- ALE-400 added
- Alternative Modes for CODAN-9001 (W-CODAN-9001), CLOVER-2 (WCLOVER-2) and CLOVER-2000 (W-CLOVER-2000)
Improvements and modifications:
“Modems” modes added (incl. new “Modem Settings...” and “Modem Input File…”
options):
OSI-Level removed
MIL-STD … tuning changed
OLIVIA changed
PACTOR-II: AFC ± 50 Hz, additional frame type detection, HEX (Binary output)
Sonagram added to FFT tuning window.
4 General Information WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5
Page 15
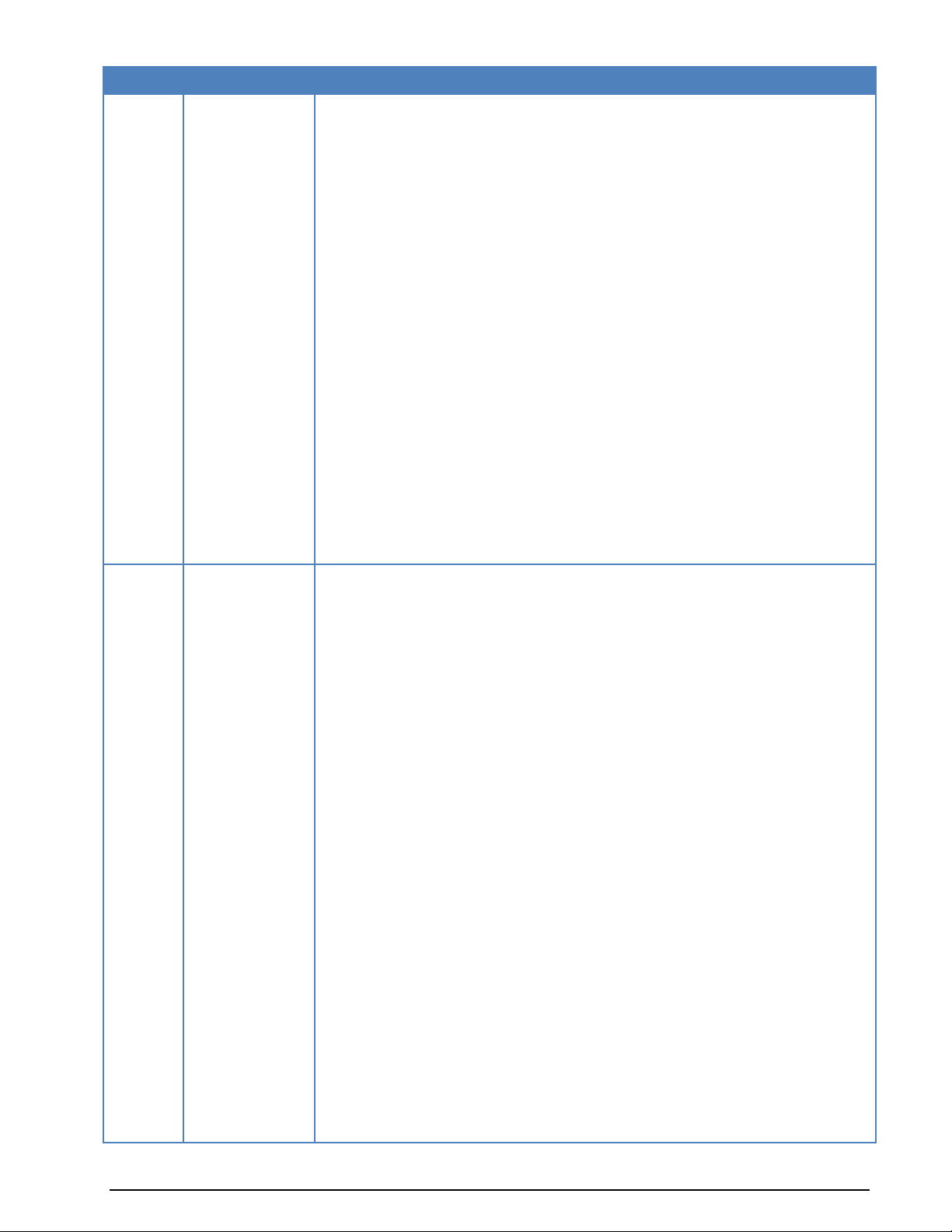
Version
Date
Changes
FFT and Sonagram tuning parameter moved from options to the new context menu.
“Pause Graphic” option for the sonagram tuning view
Passband display shows additional tuning information (shift mark, space frequency)
in a tooltip box, if the mouse is move over the cursors.
New “SAT Translation” frequency tuning bar added for “SAT-C-TDM” and “SAT-CTDM-EGC”
Number of “Custom Alphabets” and “Custom Inputs” limited to 16
“Message Type” dialog box. New parameter for Parity (MARK and SPACE)
“Message Type” dialog box. Display format “ ITA5” and “ASCII” merged to “ITA5
(ASCII)”
WAVECOM Data File Format, additional information added
Added: List of checked modes with FSK Code Check
Name of ROBUST-PACKET-RADIO changed to ROBUST-PACKET
Changed license manager.
6.8
15-Nov-2009
New protocols:
- VDL-M2 added
NMT-450 Center in the documentation changed to 1500 Hz
BIIS-1200 renamed to BIIS
CODAN-9001: LSR initialization changed from binary to hex
CLOVER-2 and CLOVER-2000, “CRC Recognition” added
Binary Output of PACTOR-I and PACTOR-II enhanced
MIL-39T enhanced
CIS-36-50, CIS-50-50 enhanced
AIS enhanced
CW improved
New installation software
XML: customer inputs configuration improved
6.8.1
17-Mar-2010
New protocols:
- DMR: New digital, TDMA based mobile radio mode
- W-CODE: Media Player/Recorder: This tool records signals directly to WAVfiles from the host sound card inputs. During playback of WAV files the signal is sent unprocessed to the W-CODE and a monitoring signal is played
through the sound card
- PSK-63, -125: Now independent amateur radio modes implementing the
FLARQ emergency messaging protocol
- PSK-250: New amateur radio modes implementing the FLARQ protocol
- VDL-M2: New digital, aeronautical data link mode
- W-PACTOR-III: Initial release of WAVECOM’s implementation of PACTOR-III
- IP-PXGF TCP/IP streaming data format added
Improvements and modifications:
- Installation: The procedure has been greatly improved and simplified, an
option to delete all settings before re- or new installation added
- CHU: Polarity now manually selected
- CW: New, much improved demodulator will decode speeds up to 90 wpm
- AIS: New “Inland AIS” interpretations of standard AIS message fields add-
WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5 General Information 5
Page 16
Version
Date
Changes
ed. Standard AIS, Inland AIS, St. Lawrence Seaway and PAWSS AIS binary
message decoding added
- Baudot: Reworked decoder with improved polarity detection and enhanced
performance
- PACTOR-I, PACTOR-II: ASCII 0x1E (idle) removed from hex output
- W-CODAN-9001: Output of demodulated multichannel symbols, derandomization of secure and unsecure modes, user selectable key for derandomization of secure modes, output of recognized key in secure mode,
output of status information, output of recognized frame type, decoding of
chat messages into readable output, decoding of text files into readable
output, decoding of data into hex output
- W-CLOVER-2, -2000: “CRC recognition” changed to “Display Mode” for se-
lection of error-free frames or all frames. Option for user defined table of
CRC added
- MIL-141A, CODAN-9001: Improved performance for Golay (24, 12) decoder
- MIL-39T: Display formats “ASCII” and “ITA-5” merged
- CIS-36-50, CIS-50-50: More fault-tolerant start and stop criteria, automatic default to Letter Shift after idle or a longer sequence of invalid data, synchronization to valid 3:4 characters without need for preamble
- DTMF: Character set changed (“*” and “#” replaces “E” and “F”)
- COQUELET-8, -13, -80: Bar graph range corrected
- STANAG, MIL modes: ITA-2 “U” character now printed
- FMS-BOS settings added to documentation
7.0
24-Nov-2010
New protocols:
- dPMR
- X.25
- TETRA
Improvements and modifications
- GUI, toolbars, menus etc. changed
- Wideband classifier (bandwidth 96 kHz)
- Adjustable “Classifier Code Check” with XML table lookup
- Classifier Code Check Table Editor
- CODAN-9001 extended with “Compressed Data” and “Secure Interactive
Packets” decoding. CODAN-9001 documentation extended
- SR Calibration added
- “SAT Translation Frequency Tuning Bar” changed to “SAT Frequency Tuning
Bar” and new functions added.
- PSK-mode tuning window cursors are now merged into one, single cursor
- Application notes removed from the user manual into separate documents
(available from www.wavecom.ch)
- BR-6028 is now a mode and no longer a demodulator
- CRC tables are changed from “\Config\CRCTABLE.TXT” to
“\Config\CRCTable.xml”
- Source code chapter removed (as the source is no longer available)
- INMARSAT-A and METOSAT removed
- Notation of “Translation frequency” changed to “Offset frequency”
- Notation of “INDIR” changed to “SUB”
- VDL-M2, “Display-Mode” added
6 General Information WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5
Page 17
Version
Date
Changes
- AMSAT-P3D: The file “amsatp3d.raw” is no longer available.
- Translation frequency replaced with offset frequency
- CW AFC: ON/OFF
- Automatic detection of the “Display Mode” for MIL-STD and STANAG signals
7.1
13-Apri-2011
- New WAVECOM install tool
- License Key no longer required for W61PC Professional version (but still
requiered for the SAT and Classifier options)
- W-CODE no longer supports MEDAV PACTOR-3, CLOVER-2000, CLOVER-2
and CODAN-9001.
- APCO25 added
- W-CODE: Name of SAT-Option and Classifier-Option changed
7.2
27-Jul-2011
- GW-OFDM protocol added
- LINK-11 protocol added
- SAT protocols, CLOVER2/2000, CODAN9001, PACTOR-III require no longer
an additional optional license. All functions are now contained in the WCODE or W61PC license.
- Better support of russian Windows (custom inputs)
- Wideband-Classifier works with VHF/UHF SUB Signals
- Wideband-Classifier works with VHF/UHF DIR Signals
- PxGF float support
- FSK Code Check SUB uses always the FM demodulator
- Classifier Code Check (CCC) VHF/UHF Direct added
- Classifier Code Check (CCC) VHF/UHF Sub added
- W-CODE: “Modem and Fax input file settings” removed. Direct support for
two analog input channels (stereo) added
- W-Sat-email-Decoder requres a dedicated license
7.3
12-Sept-2011
- VHF/UHF Classifier Codecheck DIR and SUB merged into one.
7.4
25-Feb-2014
- Custom Alphabet extended to 7 and 8 bits ASCII. Implemented in CLOVER2000 and CODAN-9001.
7.5.00
15-Oct-2014
- Significant enhancement of DMR: both slots are decoded. Full monitoring
especially of communication with a base station.
Recommended WAVECOM Products and Services
W-BV BitView Tool
The highly sophisticated BitView Tool is an external off-line, stand-alone .NET application for analysis of
unknown signals.
BitView has a number of features:
Bit manipulation tools
Bit display tools (text, graphics)
Simultaneous processing of multiple analysis sessions
Auto-update functionality
Report generator (parameters, data, ASCII, XML)
Drag and drop of functions
WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5 General Information 7
Page 18

Email system
Recognize
Decode
se@comm
Y
N
AMOS
Y
Y
Blast
Y
N
Dualog
Y
Y
FidoNet
Y N GlobeWireless
Y
Y
GTMail
Y
Y
MS-RAS PPP
Y
Y
MS-RAS TCP/IP
Y N Rydex
Y Y SkyFile
Y Y UUCP
Y
N
Re-arrangement of functions in a tree view
Nested docking
Auto hide
Drag and drop of windows
Application and modification of alphabets
Persistent-to-XML file (screen layout is restored at start-up time)
.NET technology
No installation required, just run the executable
Data stream and data file import from W61PC/LAN and W-CODE
MatLab and C# user defined functions
W-Sat-email-Decoder
The W-Sat-email-Decoder takes as its input a session file and the corresponding text files, as produced by
a WAVECOM decoder, or any text file from an external source containing emails. It does protocol decoding
and possible decompression, the email(s) and possible attachment(s) are output as files. The following
email systems will be recognized and decoded respectively.
8 General Information WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5
Page 19
Input /
Output
Frequency Range Function
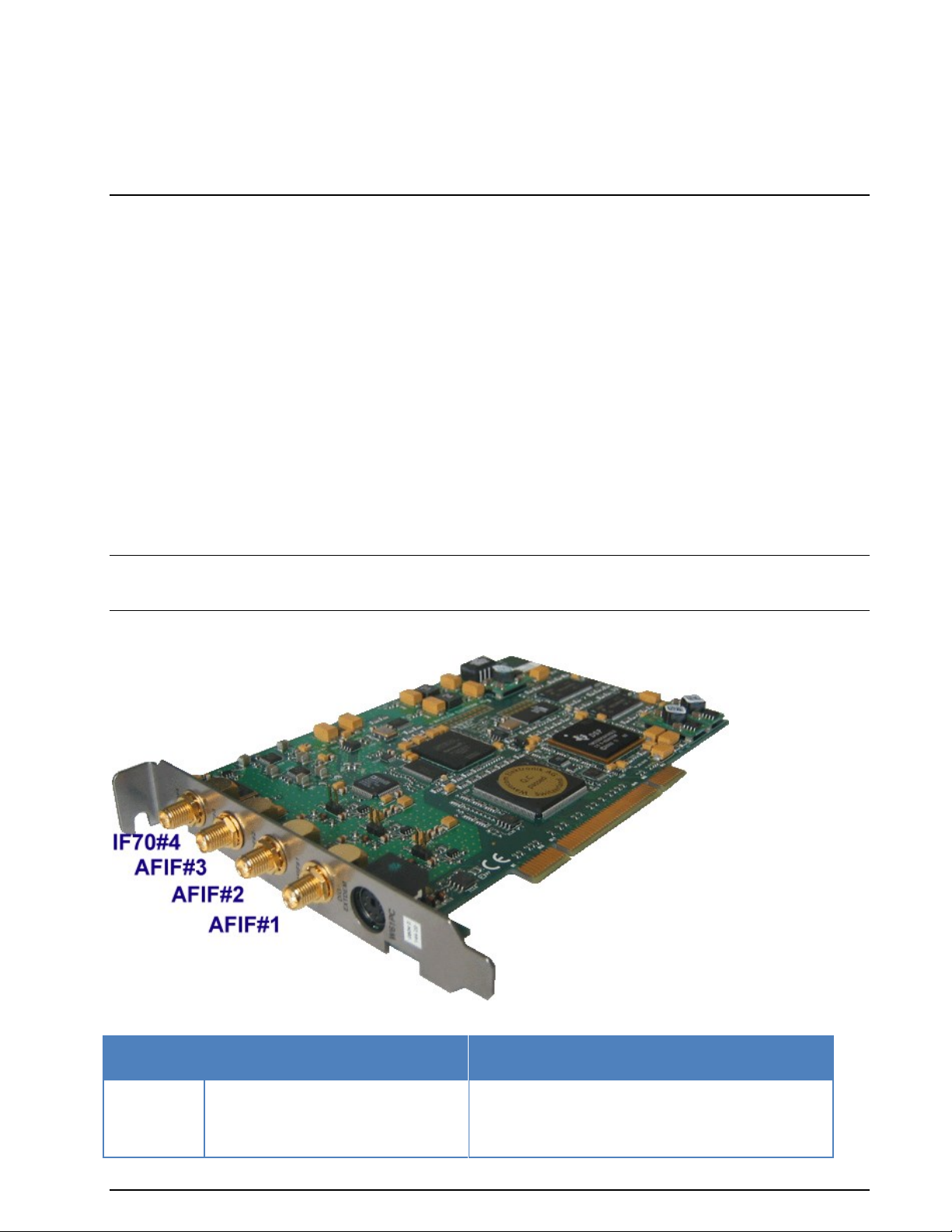
Input Voltage Range
AFIF#1- 3
50 Hz-25 MHz
AF or IF Input
2.0 mVrms – 0.5 Vrms
20 mVrms – 2.5 Vrms (with attenuator jumper)
Input impedance: 10 kOhm
Setup
W61PC
The powerful W61PC hardware includes a digital signal processor (DSP) and a fast 14-bit A/D converter.
Four signal inputs are available: AFIF#1-3, IF70MHz, and DIG/EXTDEM. An extremely stable direct digital
down-converter (DDC) translates all input signals to base band. The DSP demodulates the incoming data,
while the PC’s CPU provides the decoding and display of the data.
One PC can accommodate a maximum of eight W61PC cards. WAVECOM recommends that the number of
cards installed in a standard PC does not exceed four.
Plug-and-Play (PnP) automatic installation is provided.
W61PC Hardware Installation
Before unpacking the W61PC card or installing it in your PC ensure that your body is grounded, to avoid
damaging static sensitive components on the card or in the computer. You can reduce static electricity on
your body by touching the metal chassis of your computer or using a standard grounded wrist strap.
Power off your computer, unplug it from its power source and disconnect all peripherals. Then, carefully
remove the cover of the computer, and locate a free PCI slot. Carefully insert the card into the connector
and check that it is fully inserted. Replace the computer cover, and power on the machine.
WARNING: THE A/D CONVERTER ON THE W61PC CARD MAY DEVELOP ENOUGH HEAT TO PRODUCE BURNS OR START A FIRE IF PLACED NEAR FLAMMABLE OBJECTS. WAVECOM WILL NOT BE
RESPONSIBLE FOR ANY DAMAGES RESULTING FROM NON-COMPLIANCE WITH THIS WARNING.
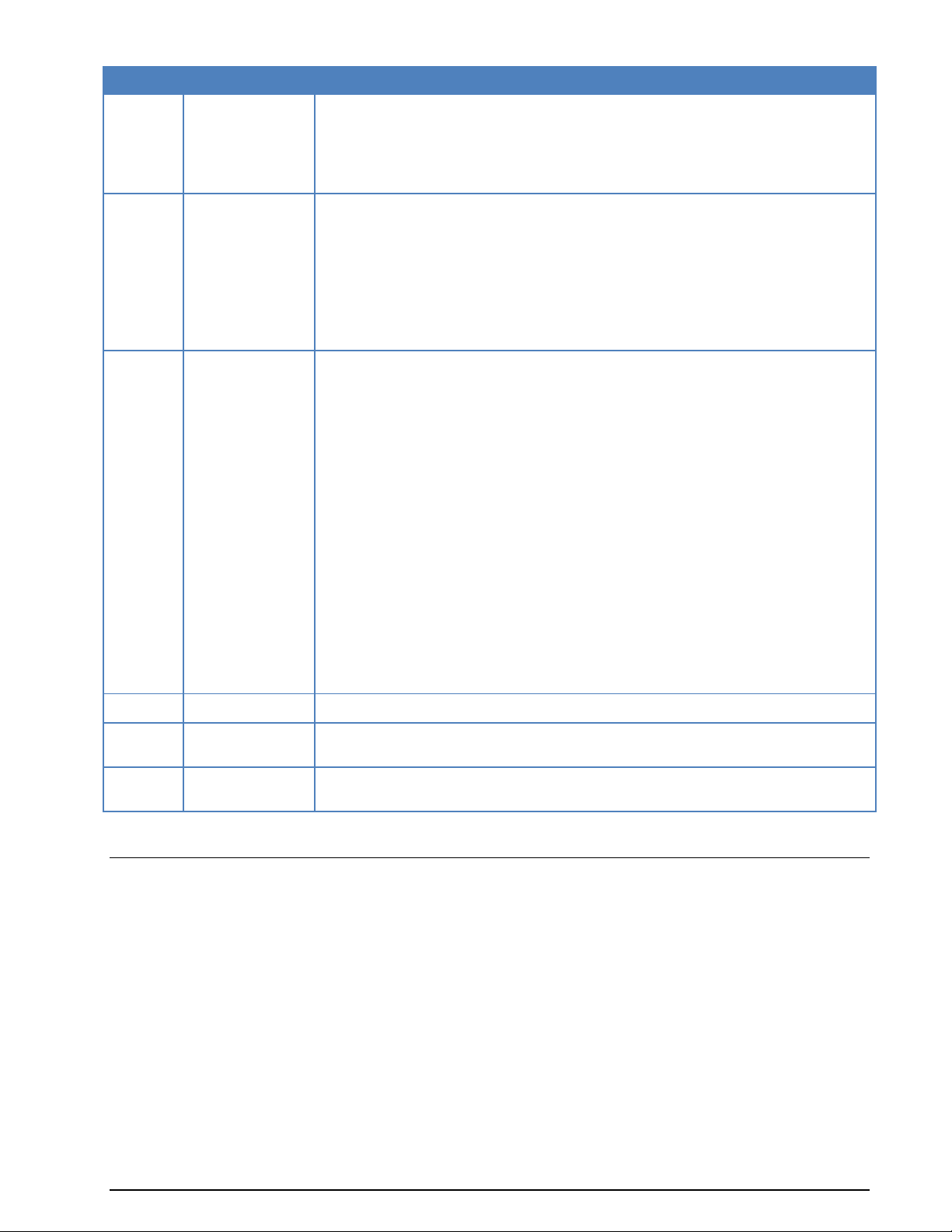
Connecting to a W61PC Card
The W61PC card has four SMA signal inputs and a Mini-DIN connector:
WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5 Setup 9
Page 20
IF70#4
52.5 MHz-87.5 MHz
IF input for SAT monitoring
50 mVrms - 5 Vrms
Input impedance: 50 Ohm
EXT-DEM
Max. 12 kbps
External Demodulator Input
[0 V, +5 V] to [-12 V, +12 V]
DIG
Max. 36 Mbps, Direct Input for DSP
receivers (not yet supported)
-0.5 to +6.5 V
AFOUT /
EXT-DEM
AF-IN
HF-IN
10.7MHz IN
W41PC
FSK
Demodulator Box
W61PC
Board
HF or VHF Receiver
Antenna
Personal Computer (PC)
21.4MHz IN
AFOUT /
EXT-DEM
AF-IN
HF-IN
10.7MHz IN
21.4MHz IN
ANT
AF
Out
455 kHz
Out
10.7 MHz
Out
One or more of these inputs must be connected to the signal source(s) using a coaxial cable or a similar
shielded cable. As an example a HF receiver may be connected to an AFIF connector and a satellite receiver to the IF70#4 connector.
To avoid distortion of the input signal the input voltage ranges listed above should be observed.
20 dB attenuation jumpers are located on the PCB close to the corresponding input connectors.
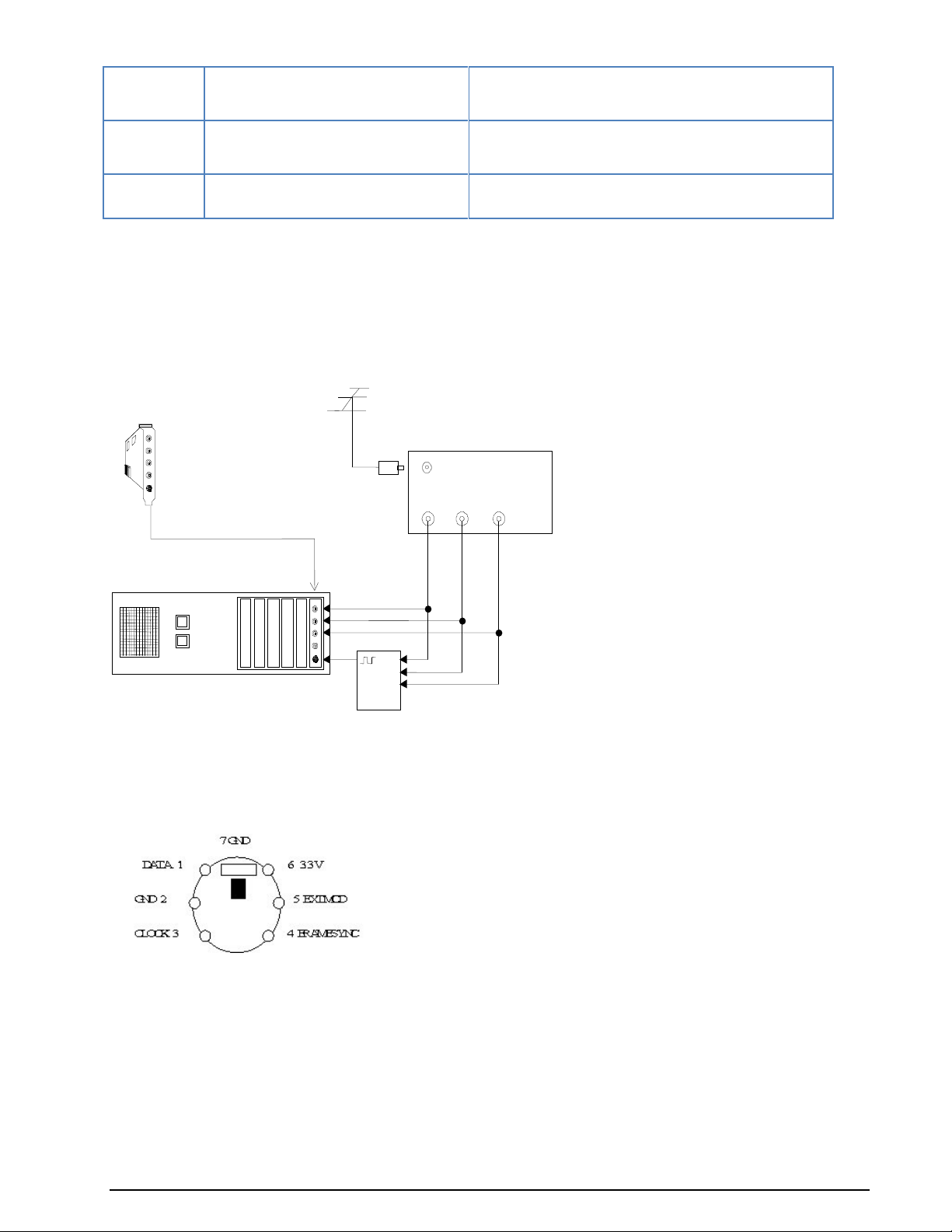
Below is an example configuration for a W61PC card setup:
The external FSK demodulator hardware is optional - it is only required if the customer wishes to use his
own demodulator hardware.
Mini-DIN Connector (EXT-DEM-IN/DIG)
W61PC Power Supply Ratings
The power supply ratings for a W61PC card are:
1.0A@+3.3V
0.4A@+12V
W61PC Software Installation
Windows’ hardware wizard can be used to install the software. Insert the WAVECOM installation disc in the
disc drive. When requested, point the wizard to the drive and start installation.
10 Setup WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5
Page 21
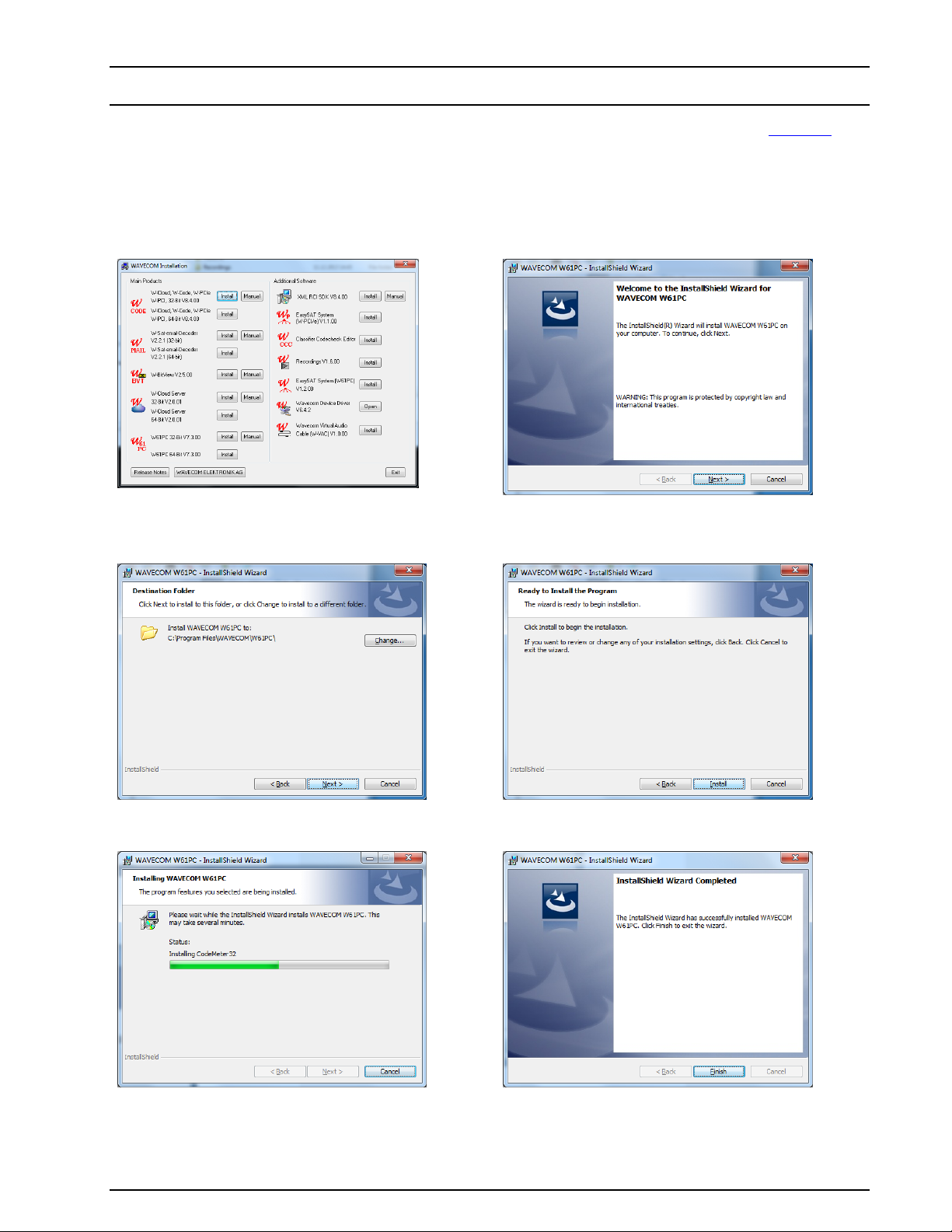
Click the W61PC button to start the installation
of the W61PC application.
First, you will see the welcome screen. Click
Next to continue the installation.
Change the destination folder and click Next to
continue the installation.
Click Next to continue the installation.
Wait until the installation is finished
If the installation was successful, click Finish to
complete the process.
Note: After installation you can run the W61PC application if you are a member of the Administrators,
Power Users or Users group.
If a software update is about to be undertaken, the old version must be uninstalled (see “Software ” on
page 18). After uninstallation has completed, insert the WAVECOM installation disc in the drive. The installation program will start automatically. Otherwise it can be started with Windows Explorer by doubleclicking Installation.exe. Now the welcome dialogue of the installation program is displayed:
If you are prompted to restart your computer, do so.
WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5 Setup 11
Page 22

Note: Check for hidden windows if the installation process seems to “hang” (this can be done by pressing
the Alt+Tab keys). Sometimes windows in the background are waiting for user input to allow the installation to proceed.
After rebooting, you may start the software even without any hardware installed. Click on the W61PC-1
icon to make a test start. However, starting a transmission mode is not possible without decoder hardware.
W61PC Drivers and Windows Logo Testing
Windows 2000/XP introduced a new feature called Driver Signing, in which drivers are certified by the Microsoft Logo testing program and a digital signature added to inform the operating system of a successful
certification.
As WAVECOM drivers are only used in a small number of computers, they are not submitted to Microsoft
for certification. As a result, during driver installation, a dialog box will be displayed to inform the user
that the driver is not signed.
This message does not indicate that a problem exists with the driver. It is a purely informational message
to notify the user that the driver does not contain a digital signature. To complete the driver installation,
users should select the Continue Anyway button.
W61PC Server Control
The WAVECOM Server and the WAVECOM Server Control applications are used to setup and monitor the
connections between decoder cards (clients) and the server. The server is responsible for managing the
decoders connected to the computer as well as all the connections made to that decoder. The WAVECOM
Server is started by the GUI for a local connection (GUI and card on the same machine). By default the
server is started as a Windows service, as opposed to a process.
W61LAN-MK3
Hardware Setup
The W61LAN delivery contains the following items,
A complete, single board computer system, running Windows XP
A Win7 installation CD
A W61PC card (integrated with the single board computer)
A power supply for 100-240VAC
A CD-ROM containing the drivers and the complete system documentation
A standard straight LAN cable (use with a switch or hub)
A cross-over LAN cable for direct connection of the W61LAN to a PC
The system is ready to go, but you should configure it according to your requirements regarding LAN setup, security etc.
Please allow enough space on each side and on top of the W61LAN to avoid overheating (max. 55 grad C
surface temperature). If necessary use an external fan.
For installation details, see “W61PC” on page 9.
12 Setup WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5
Page 23
BIOS
USB Keyboard
Enabled
Computer
Computer name
“W61LANnnn” (nnn is part of the W61PC serial number)
Workgroup
“WAVECOM-DECODER”
Remote desktop
Enabled for “user”
Remote assistance
Enabled, remote control on, Invitations 2 hours
Automatic updates
“Notify me but don't automatically download or install them”
Performance options
Adjust for best performance
Processor scheduling
Programs
Virtual memory
Automatically
Virus Checker
Microsoft Security Essential Installed
Firewall
Enabled, additional ports opened: 33233, 33234, 33235
Account
Name
User
Password
User
Member of
“remote desktop users”
“administrator” (the customer may change group membership according to his re-
quirements)
Name
“Administrator”
Password
No password set at the moment (the customer may change this according to his
requirements)
Member of
“administrator”
LAN
TCP/IP, DHCP
Alternate configuration IP address Lan1: 192.168.1.200
Lan2: 192.168.1.201
Important: If you have multiple CmSticks plugged into computers connected to the same local network,
consult “CmStick” on page 288
The standard W61LAN setup, when delivered from WAVECOM is:
You can use the W61LAN in different ways:
Remote mode with WAVECOM GUI
Windows Remote Desktop
Third party software
Stand alone
Important: Please, check the settings of your computers, firewalls and routers. It is important that all the
resources on the LAN are available, and that the required TCP ports are open.
WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5 Setup 13
Page 24
W61LAN Remote Mode with WAVECOM GUI
Install the W61PC software on the computer that you will use to control the W61LAN
Connect the W61LAN to the LAN
Check if the W61LAN computer is visible on your LAN (remember the firewall may block ping and
ICMP)
Start the W61PC application
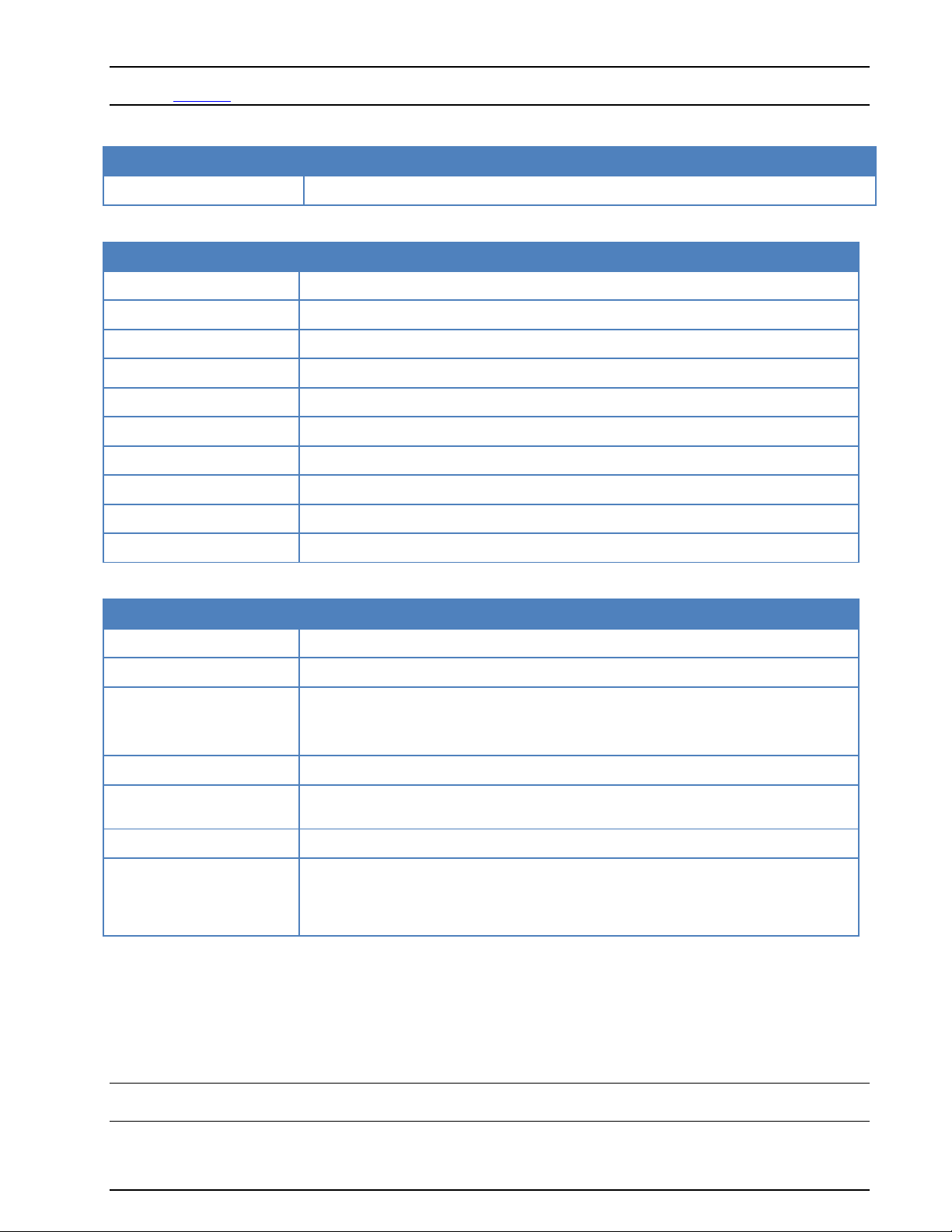
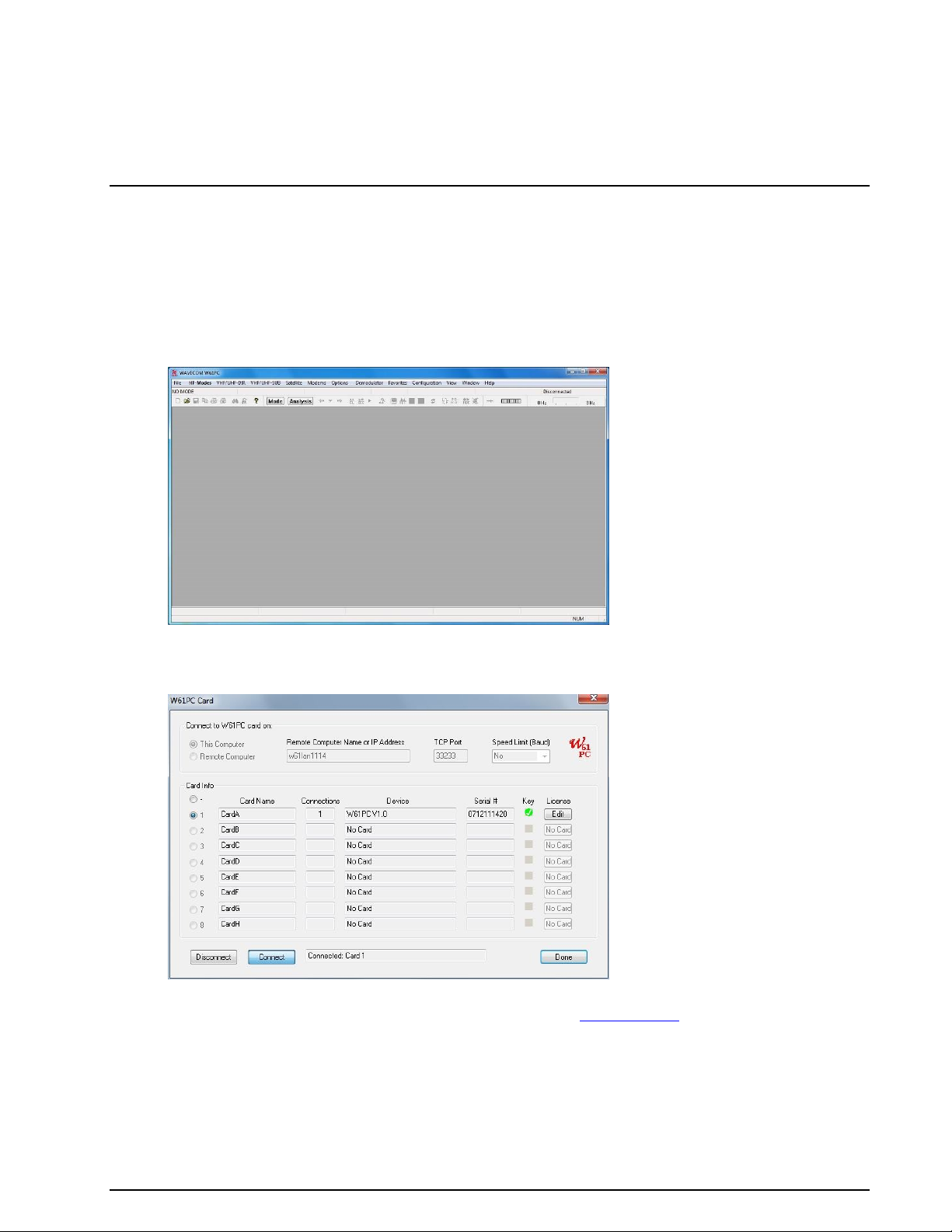
Select a W61PC card for remote control by using the Configuration | W61PC Card… menu
Disconnect, select Remote Computer and enter the name of the W61LAN remote computer
(“W61LANnnn”) or its IP address. Enter the port number (default is port 33233) and select the
speed (10M for LAN)
Click Connect
Select the card and close the “W61PC Card” window by pressing Done
Start a mode
The selected entry is stored in the card’s initialization file (*.ini file) and is available when the W61PC a pplication is restarted at a later time. The settings may be changed at any time.
Note: The version of the W61PC software on the controlling client computer must be the same as that on
the W61LAN.
W61LAN Remote Desktop Operation
Remote Desktop (RD) is a client-server application and part of the Windows XP Professional operating system, using port 3389. Remote Desktop can be used to remotely control a W61LAN, which acts as the RD
server, while the client resides on the controlling host.
To use Remote Desktop follow these steps:
Connect the W61LAN to the LAN
Check if the W61LAN computer is visible on your LAN (remember the firewall may block ping and
ICMP)
Start the RD client on the controlling computer by clicking Remote Desktop Connection in Start
| All Programs | Accessories | Communications
If the RD connection cannot be established check your firewall settings (port 3389 must be open)
14 Setup WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5
Page 25
Tip: Considerable time can be saved if a link to Remote Desktop Connection is placed on the desktop
When you are connected, the remote W61LAN computer will be represented by its own window on your
client computer. The W61PC on the remote W61LAN system may now be started.
Remote Desktop may also be used for software updates.
WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5 Setup 15
Page 26

W61LAN with Third Party Software
The W61LAN can be used from third party software in the same manner as a standard W61PC. For use
and installation follow the instructions of the third party software.
W61LAN Stand-alone
Connect a monitor, keyboard and mouse to the W61LAN.
W61PC/LAN Licensing
Software Updates
WAVECOM provides the W61PC software with all future updates included - updates that are released for
the rest of the life of the product are provided free of charge.
For customers who have purchased a 12 months software update period, an additional upgrade to receive
all future updates can be ordered.
Note: No License Key must be entered as long as no software option must be enabled.
W61LAN Software Updates
For software updates a DVD-drive or a memory stick can be connected to a USB socket on the W61LAN. It
is also possible to map a DVD ROM to a remote desktop connection.
Order Software Options
Additional functions may be enabled and licensed to work with your decoder.
Options are marked with (Option) in this manual.
Follow this procedure to order options:
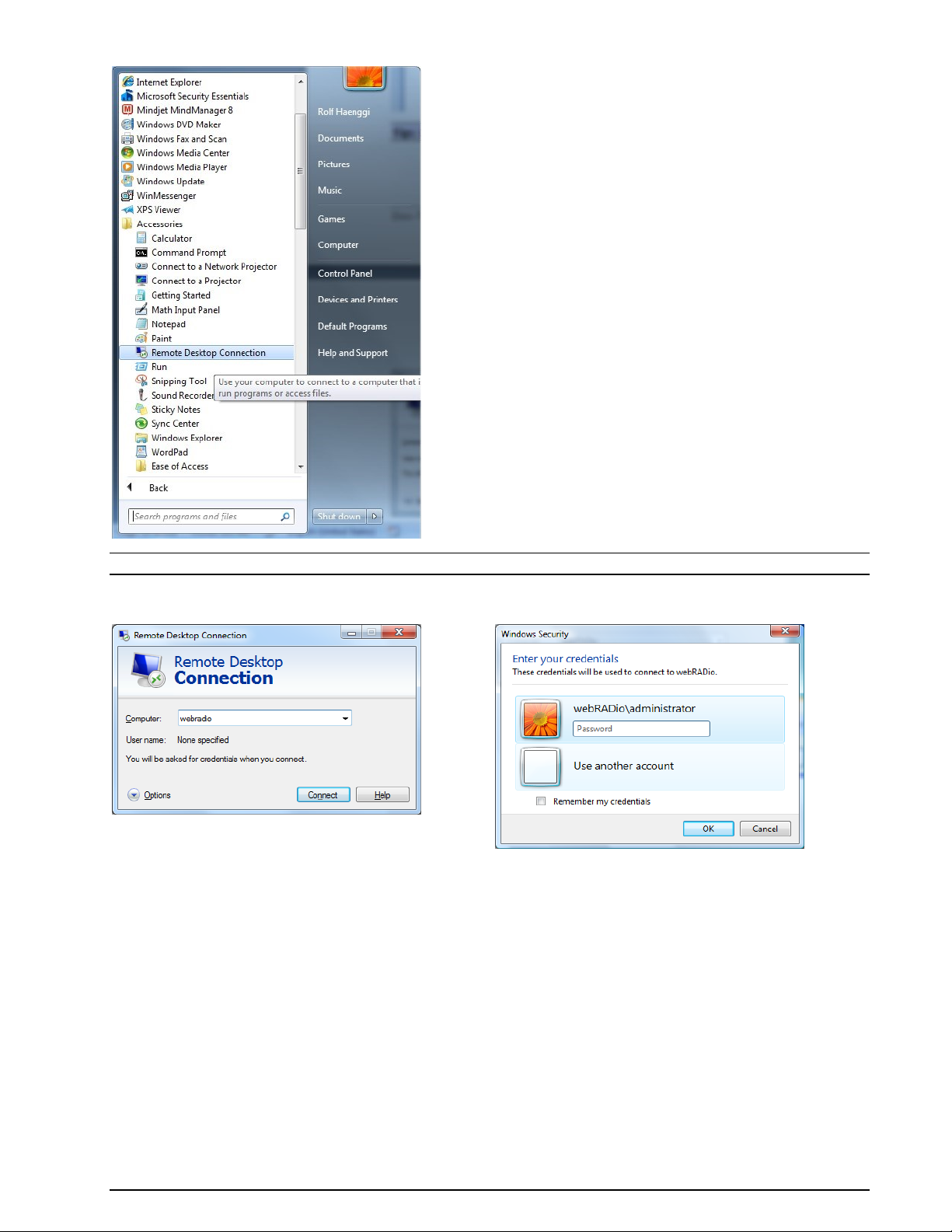
The serial number of your card or device must be provided. You can get the serial number from:
a. The W61PC GUI Configuration | W61PC Card… screen.
b. The W61 Server Control All Program | WAVECOM | W61PC | WAVECOM Server Control.
16 Setup WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5
Page 27
c. The label on the W61PC card.
List the required options you would like to order and mail the information to WAVECOM
WAVECOM will process your order and forward an invoice
After the payment has been received, a new key will be sent
Enter or Change a License Key (W61PC, SAT, CL, BV)
A key will only work with a W61PC card that has exactly the same serial number that was provided during
registration, or forwarded with the order.
New keys can be entered using:
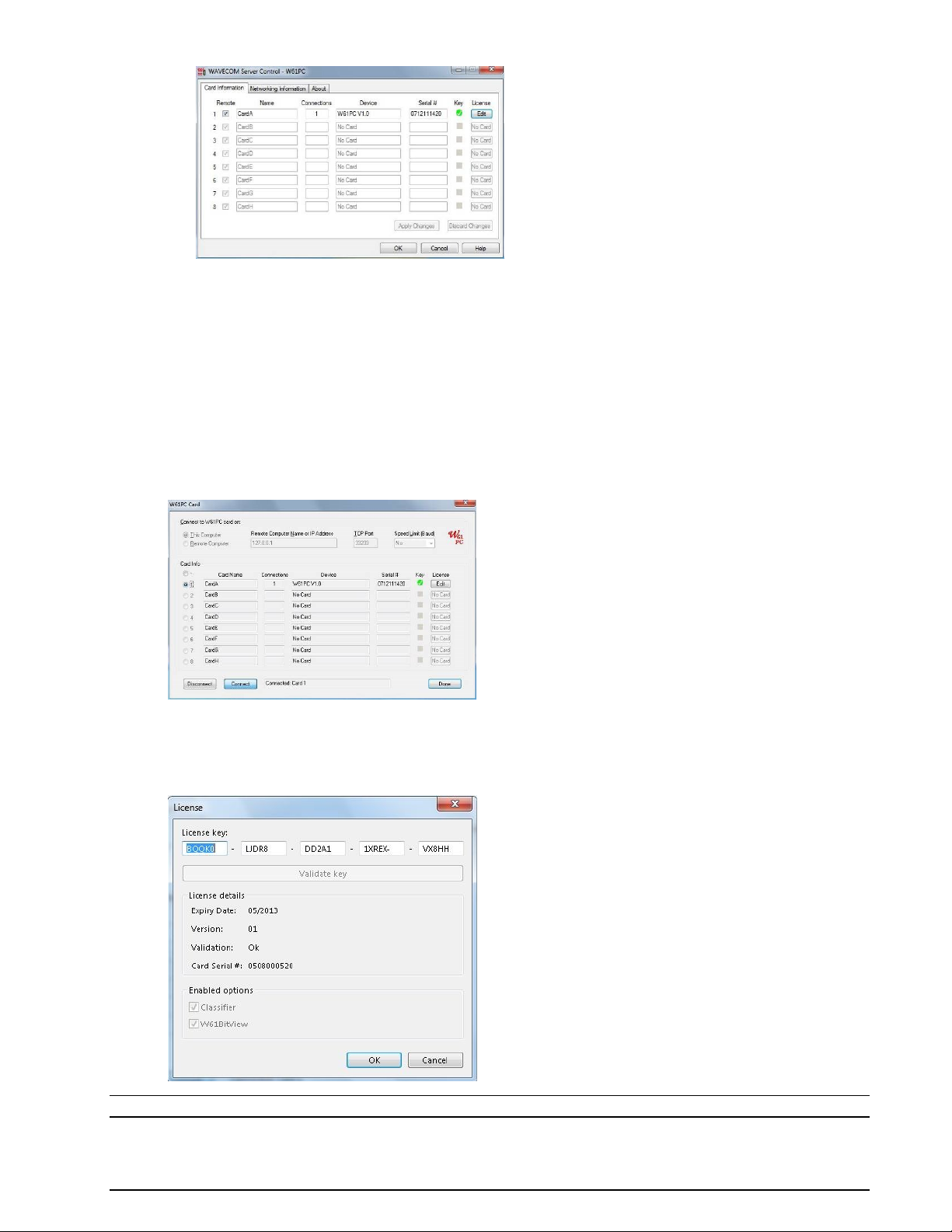
The W61PC GUI (Configuration | W61PC Card… screen. Click License Edit
The WA61 Sever Control All Program | WAVECOM | W61PC | WAVECOM Server Control.
Click License Edit
Enter the key in the Key fields and press the OK button. If you validate the key, the enabled op-
tions and the expiry date will be visible.
Note: A software version released before the expiry date will still work.
WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5 Setup 17
Page 28
VISTA
XP
Click on Start, go to the Computers menu
and click the Uninstall or change a pro-
gram button
Select WAVECOM W-[XX] from the list
Click Uninstall
Click on Start, go to the Settings menu
and open Control Panel
Select the Add/Remove Programs icon
Select Install/Uninstall
Choose WAVECOM W-[XX] from the list
Click Add/Remove
Enter or Change a License Key
You can find information regarding “License System, Software and Options” on page 288.
Software Uninstall
In certain situations, e.g., when updating the application, it is necessary to uninstall the software. Use the
following commands:
The application has now been removed from the PC - it is possible, however, that the shortcut icons may
have to be removed manually.
18 Setup WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5
Page 29
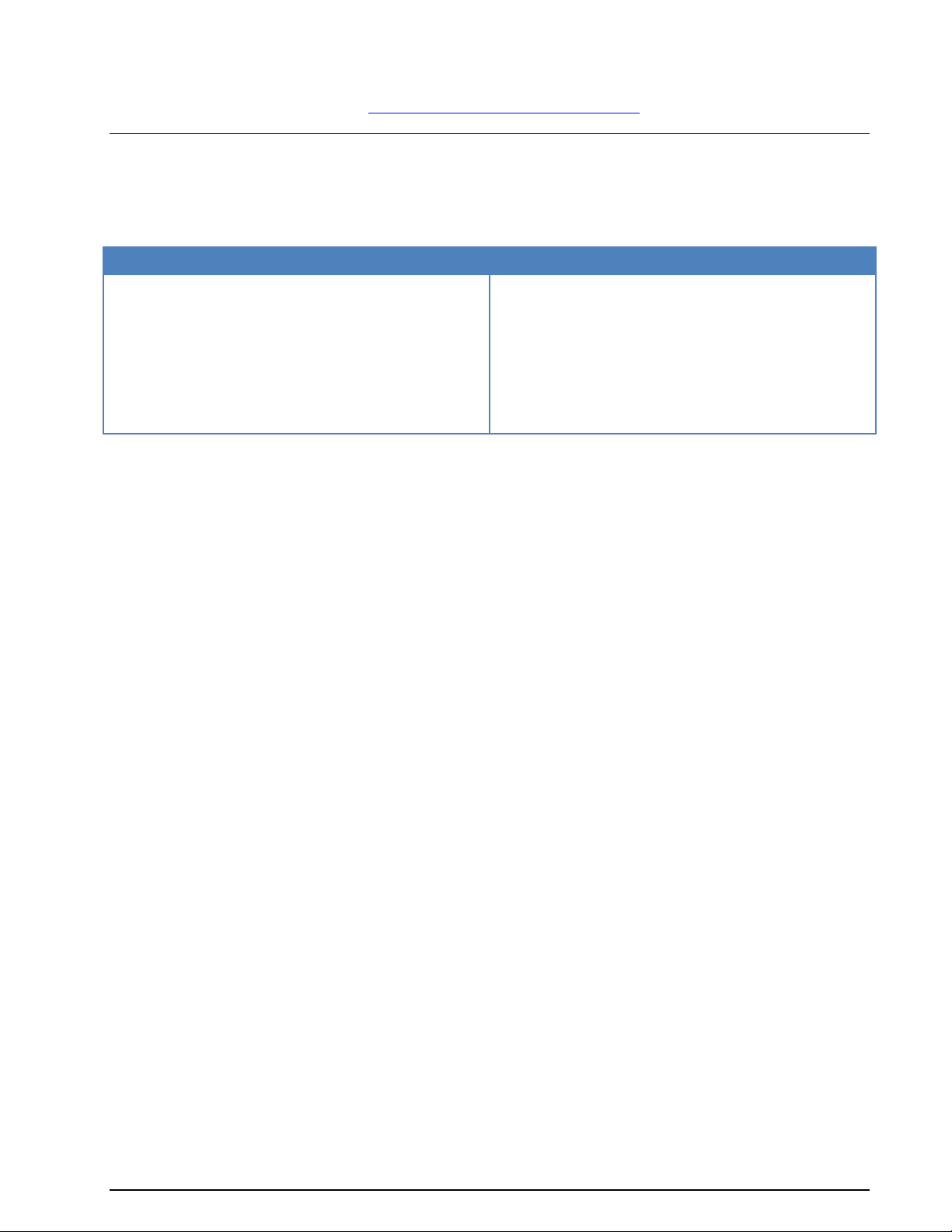
First start
W61PC First Start
After the software and the W61PC card have been successfully installed, the decoder program can
be started either from the WINDOWS Start menu or by double-clicking the program icon on your
desktop.
Proper operation of the decoder is indicated by the WAVECOM Server Control icon in the Windows
system tray. If the traffic light in the icon is green, then the server is operating normally. You may
also move the mouse over the icon and check that you get this status message: WAVECOM
Server (running).
The first time the software is used after the installation, you will have to set the decoder device
manually. From the menu bar, go to Configuration. A drop-down menu will appear. Click on the
W61PC Card… menu item. A setup window appears.
Select a device number and click Done to save the entry. If you require more details regarding
remote connections and connection parameters then see “W61PC Card…” on page 43.
The decoder is now ready for use. Apply a signal to the selected input (from a receiver) or from a
played back file.
From the HF-Modes, VHF/UHF-Modes or Satellite menus, a mode may be selected, e.g.,
PACTOR-II if a PACTOR-II signal is played back.
WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5 First start 19
Page 30

Tune the demodulator to the correct center frequency and set the correct level.
GUI
The user interface of the application conforms to standard WINDOWS interface guidelines. The main program window is shown in this section. This is the window you will see after setup has been completed as
described in the preceding paragraphs.
The WINDOWS elements TOOLBAR, WAVECOM TOOLBAR, LEVEL INDICATOR and SPECTRUM INDI-
CATOR may be moved anywhere in the screen as required. In the View menu the user may show or hide
all window elements. By default, all elements are visible.
Please be aware that the appearance of the GUI will vary depending on the product, software version and
operating system.
Command Line Parameters
You can pass information to the application by adding command line parameters.
The following commands are valid:
/i <ini file name>
The name of the INI file that is located in the same directory as the decoder application. Alternatively a
path may be entered.
/n <card number>
The number of the card to be connected (a value between 1 and 8).
/c <computer>
The name of the computer to be used for the connection
localhost (not case sensitive) or 127.0.0.1 means that you work with cards on the local comput-
er.
Computer name or the IP address plus the port number to connect to another computer. The port
number must be entered on the WAVECOM Server Control screen. If a port number is not provided, then default port 33233 is used.
/l <speedlimit>
Speed limit of the connection to the server. This attribute is a choice of “9600”, “14400”, “19200”,
“56k”, “64k”, “128k”, “512k”, “1M”, “2M”, “5M”or “10M”. If no /l option is used, the speed is un-
limited.
Examples (for W61PC):
W61PC.EXE /i config1.ini
W61PC.EXE /i "\configuration\setupAB.ini"
W61PC.EXE /n 2 /c W61Server:5800
20 First start WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5
Page 31
Folder
XP
Vista
Program
Folder (RO)
C:\Program Files\WAVECOM\<Product>\
C:\Program Files\WAVECOM\<Product>\
Global Data
(RO)
C:\Documents and Settings\All Users\Application Data\ WAVECOM\<Product>\
C:\ProgramData\WAVECOM\<Product>\
Global Data
(RW)
C:\Documents and Settings\All Users\Documents\ WAVECOM\<Product>\
C:\Users\Public\Public Documents\
WAVECOM\<Product>\
User Specific
Roaming Data
C:\Documents and Settings\\<Username>\\Application Data\
WAVECOM\<Product>\
C:\Users\<Username>\AppData\Roaming\
WAVECOM\<Product>\
User Specific
Non-Roaming
Data
C:\Documents and Settings\<Username>\Local Settings\Application
Data\ WAVECOM\<Product>\
C:\Users\<Username>\AppData\Local\
WAVECOM\<Product>\
W61PC.EXE /n 1 /c 192.168.1.12:8080
W61PC.EXE /n 3 /c 192.168.2.5
W61PC.EXE /n 3 /c 192.168.2.5 /l 56k
Default Data and Program Folders (Paths)
To see all folders, select Folder Options in the Control Panel
Enable Show all folders.
Enable Show hidden files, folders and drives
Path names can vary if you use a non- English language operating system or if you are not using the Microsoft “Windows Explorer”
WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5 First start 21
Page 32

Program Folder
Global Data(RO)
Global Data(RW)
Graphical User Interface (GUI)
Main Menu
The main menu includes all submenus relating to operating modes, as well as analysis and setup functions.
The WINDOWS operating system is based on a multitasking kernel and can handle several tasks simultaneously, and therefore interaction with the menu system will not interrupt the execution of an active function. This allows, for example, the shift and center frequency to be set in the Demodulator submenu
without disrupting the currently active operating mode.
Main Menu Screen Display
This window is displayed without any mode started.
As a standard WINDOWS procedure a left-click on a menu item will display the corresponding drop-down
menu.
22 First start WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5
Page 33

Open…
Open previously saved files.
Save
Save received text to an already open text file. If no file is open “Save As...” will be started
to ask for a valid path and file name
Save As…
You can specify a path and file name and save the received text to this file
Save As Text...
Save received text as an ASCI or Unicode file
Save As Bitmap…
Save the main window as a BMP file
Save As Bitstream...
Save a bit stream e.g. from an auto-correlation session as a text file of ASCII 0’s and 1’s
Save Selection as...
Select a block of text and save it to a text file
Save Continuously
Save continuously all output to a file
Media Player/Recorder
Record and play back WAV files
Find
Search for every occurrence of a specific word or phrase in the received text
Find Next
Find the next occurrence of a specific word or phrase in the received text
Clear Screen
Prompts the user to clear the screen
Print
Send the received text to a printer.
Print Continuously
Send continuously all output to a printer
Print Preview
Preview the output before sending it to the printer.
Print Setup…
Open the printer setup dialog.
Recent File
Displays a list of recently opened files
The functions of the File, View and Window menus are general system functions in accordance with the
WINDOWS standard.
File Menu
Using the File menu, files may be saved and opened. Other functions such as the Media Player/Recorder,
find, printing, print preview and printer setup are also available.
WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5 First start 23
Page 34

HF-Modes | Analysis
HF-Modes | FSK
Note: Files that are saved with Save and Save as... are stored in the WAVECOM *.WDA format. This
format is used to save decoded text together with time stamps in a text file. The import of old *.W40
(W40PC), *.W41 (W41PC) and *.W51 (W51PC) files is also supported. For more details see “WAVECOM
Data File Format” on page 303.
HF-Modes Menu
The various HF protocols are displayed in the HF-Modes menus and are divided into different groups. To
select the modes of a group, left-click or let the mouse rest briefly on the group item to be selected. Now,
the modes of the group are displayed in a separate menu. Start decoding the desired mode by another
left-click.
It may be difficult to guess or remember to which group a particular mode belongs. To facilitate an overview, a full-screen menu may be opened by clicking the menu item Mode Selector. To start a mode, click
on the appropriate menu field. Leaving the full-screen menu will not terminate an active mode.
The various analysis tools available are displayed in the Analysis menus.
Descriptions of the operating modes in a separate section of this manual are arranged in alphabetical order.
The Mode Selector is available from the HF-Modes menu and from the WAVECOM Toolbar.
HF-Modes are organized as follows:
24 First start WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5
Page 35

HF-Modes | MFSK
HF-Modes | PSK
HF-Modes | MIL-STANAG & HF-ACARS
HF-Modes | Graphic Modes and CW
HF-Modes | Mode Selector...
See “Mode Selector” on page 61.
VHF/UHF-DIR Menu
DIRECT modes can only be demodulated at the intermediate frequency level IF (analogue or IQ). The
various VHF/UHF-DIR protocols are displayed in the VHF/UHF-DIR menu. To start decoding of the desired mode, click on it.
The various analysis tools are displayed in the Analysis menus.
The descriptions of the operating modes in a separate section of this manual are arranged in alphabetical
order.
The Mode Selector is available from the VHF/UHF-DIR menu and from the WAVECOM Toolbar.
WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5 First start 25
Page 36

VHF/UHF-DIR | Analysis
VHF/UHF-DIR | Modes
VHF/UHF-DIR | Mode Selector...
See “Mode Selector” on page 61.
VHF/UHF-SUB | Analysis
VHF/UHF-SUB | Modes
VHF/UHF-SUB Menu
INDIRECT modes require additional AM or FM demodulation in the receiver. If the signal is demodulated
from an IF-IQ signal (offset frequency <> 0), then a standard AM or FM software demodulator is automatically added to the signal processing path.
The various VHF/UHF-SUB protocols are displayed in the VHF/UHF-SUB menu. To start decoding of the
desired mode, click on it.
The various analysis tools are displayed in the Analysis menus.
The descriptions of the operating modes in a separate section of this manual are arranged in alphabetical
order.
The Mode Selector is available from the VHF/UHF-DIR menu and from the WAVECOM Toolbar.
26 First start WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5
Page 37

VHF/UHF-SUB | Selcal Analog
VHF/UHF-SUB | Mode Selector...
See “Mode Selector” on page 61.
Satellite | Analysis
Satellite | Modes
Satellite Menu
The various satellite protocols are displayed in the Satellite menu. To start decoding of the desired mode,
click on it or to select the modes of a group, left-click or let the mouse rest briefly on the group item to be
selected. Now, the modes of the group are displayed in a separate menu. Start decoding the desired mode
by another left-click.
The various analysis tools are displayed in the Analysis menus.
The descriptions of the operating modes in a separate section of this manual are arranged in alphabetical
order.
The Mode Selector is available from the Satellite menu and from the WAVECOM Toolbar.
WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5 First start 27
Page 38

Satellite | INMARSAT-B
Satellite | INMARSAT-C
Satellite | INMARSAT-M
Satellite | INMARSAT-mM
Satellite | Mode Selector...
See “Mode Selector” on page 61.
FAX & Modems Menu
The various modem protocols are displayed in the FAX & Modems menu. To start decoding of the desired
mode, click on it or to select the modes of a group, left-click or let the mouse rest briefly on the group
item to be selected. Now, the modes of the group are displayed in a separate menu. Start decoding the
desired mode by another left-click.
The various analysis tools are displayed in the Analysis menus.
The descriptions of the operating modes in a separate section of this manual are arranged in alphabetical
order.
The Mode Selector is available from the FAX & Modems menu and from the WAVECOM Toolbar.
28 First start WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5
Page 39

FAX & Modems | Analysis
FAX & Modems | Modes
Fax & Modems | Mode Selector...
See “Mode Selector” on page 61.
WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5 First start 29
Page 40

Options Menu
In the Options menu all supported functions for a particular mode or functionality are collected - the
menu is adapted to each individual mode. The Options menu will therefore appear with different contents
depending on the mode or functionality selected.
Alphabet...
The Alphabet menu has options for transparent and normal output. The normal output includes fonts for
e.g. Latin, Greek, Cyrillic, Hebrew, Arabic alphabets.
The ASCII character sets for output in German, Bulgarian, US, Swedish, Danish-Norwegian, Chinese
or other alphabets may also be selected.
Skyper, an alphabet which is used in POCSAG mode in Germany, is also available.
The transparent alphabet includes output of non-printable characters of a data transmission, e.g. ITA-2
control characters like Letter Shift and Figure Shift, or undefined upper case characters. In normal alphabets these characters are not output.
Bit Inversion Mask
One or several data bits may be inverted by using the Bit Inversion Mask item in the Options menu.
The Bit Inversion Mask can be entered in three different ways:
In the top input box a decimal number between 0 and 31 may be entered
In the center input box the same number may be entered in binary format with the least signifi-
cant bit to the right
In the bottom check boxes a logical "1" is entered with the mouse by clicking in the check box
Bit Inversion is only implemented for ITA-2 (Baudot) based bit streams.
CRC Recognition
An automatic detection of the CRC can be switched on/off with Options | CRC Recognition. The detected CRC is displayed in the decoder status bar.
30 First start WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5
Page 41
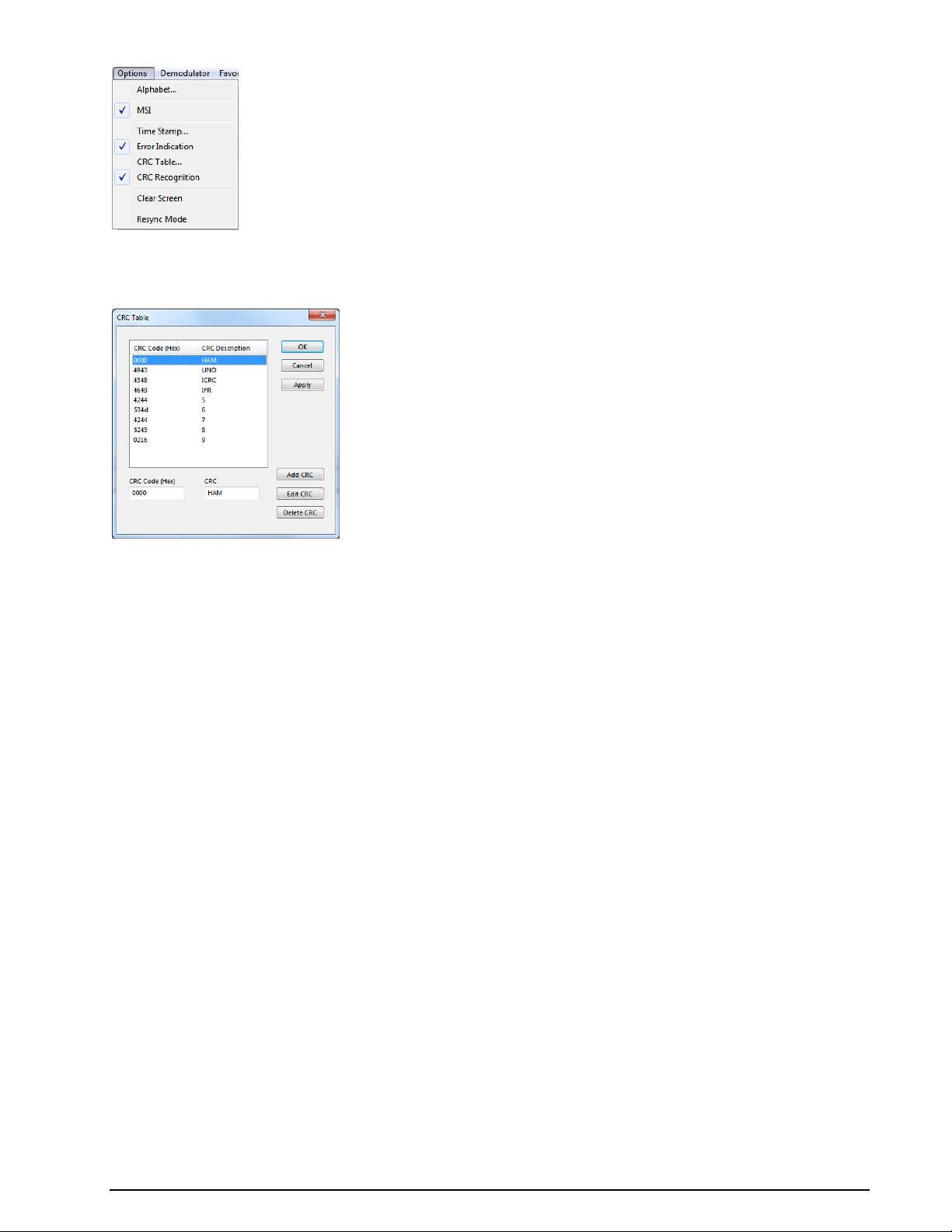
CRC Table
Using Option | CRC Table a certain CRC mask can be defined.
A table of CRC's is stored in \Config\CRCTable.xml.
Clear Screen
This function will clear the screen contents. All data will be lost.
Code Statistics
For five bit alphabets a code statistics window can be shown below the text window. In the Options menu
chose Code Statistics to switch the statistic window on or off.
The bottom row shows the decimal value of the characters. The row above displays the number of characters as a percentage.
The statistics are displayed as a 3D bar graph, with the height of the bars proportional to the number of
instances of a given character.
Click on the Reset button to reset all counters to zero.
Press the Enabled button to toggle sampling of the received characters for the statistics on and off.
Using the Statistics button the data can be showed ordered by quantity.
WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5 First start 31
Page 42
Cycle...
In some modes, the character repetition cycle may be manually selected.
Error Indication
If Error Indication is switched on, then characters containing errors are marked in red color. If possible,
the error correction will correct the erroneous data.
FAX & Modems Settings
For the FAX & Modems modes, additional parameters regarding the output location can be set in the Options | FAX & Modem Settings dialog box.
These settings are:
Server: The path to the specific output directory has to be specified
Client: The path to the specific output directory has to be specified. This option is only enabled in
remote mode
Frame Format…
32 First start WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5
Page 43

IAS
IAS is the abbreviation for ISO-ASYNCHRONOUS and SYNCHRONOUS modes. Iso-asynchronous modes
have start and stop elements like Baudot, but the code words have an integral number of elements. The
IAS function is utilized for the extremely accurate baud rate determination of a synchronous or isoasynchronous bit stream.
The automatic phase correction for the ideal bit center sampling (bit synchronism) is completely independent of the IAS function and is always active. The extremely accurate baud rate determination uses
the number of necessary phase correction steps for the baud rate determination.
In modes working with an interrupted data stream such as PACKET-300, it may be advantageous to be
able to switch off the baud rate correction to prevent drifting of the pre-selected baud rate. When the IAS
function is disabled, any pre-selected variable baud rate will be treated in the same way as a fixed baud
rate.
In most of the VHF/UHF modes the IAS is permanently disabled. This is due to the lack of phase coherence between successive data blocks. An exact measurement of the phase shift is not possible for an extended period of time.
In the event of adverse HF reception conditions (fading), enabling IAS may offer substantial advantages.
The software will decrease the size of the phase correction steps in accordance with the verified, reduced
phase errors, and thus prevent bit glitches and the resulting loss of synchronism. It is therefore recommended to enable IAS as a default.
Tick the IAS menu item to enable IAS.
Letters/Figures...
This option is only available for ITA-2 based modes.
The Letters/Figures dialog box contains the options Normal, Letters Only, Figures Only and Unshift
on Space (UOS). Letters and Figures designates the ITA-2 lower (letters) and upper (figures) cases.
For reception under normal conditions the selection of one case or the other is controlled by the reception
of the shift characters.
Special alphabets, e.g. Chinese, comprise only letters so forcing a shift into lower case mode may be an
advantage (Letters Only). Selecting this function may also be advantageous when searching for a bit inversion pattern, as the pattern may be more easily recognized.
In weather code transmissions five figure groups are used - in this case one may force a shift into upper
case (Figures Only).
The Unshift on Space (UOS) function forces a shift into lower case after a space character has been received. In this manner the readability of the transmission may be enhanced under poor conditions (weak
signals or interference).
Compared to the Letters Only mode, UOS has the advantage that single, upper case characters like periods/full-stops and commas are correctly printed. The drawback is that the software will incorrectly shift to
lower case when receiving figure groups separated by space characters.
Message Type...
Mode specific parameters can be selected
WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5 First start 33
Page 44

Message Type is used to apply terminal specific settings like:
SYNC / ASYNC
Number of databits
Parity bits
- NONE
- EVEN
- ODD
- MARK
- SPACE
Number of stop bits
Bit Sequence order
- MSB
- LSB
Display format
- ITA5 (ASCII)
- ITA2
- HEX
- BINARY
- S5066. The STANAG5066 parser can be used with the NATO and MIL-STD modems (like
STANAG4285, STANAG4539, MIL-STD-110…).
- Display format
If you press the Activate Button, the software tries to evaluate the following parameters:
- SYNC/ASYNC
- Number of databits
- Parity bits
- Number of stop bits
- Display format
34 First start WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5
Page 45

Modem Settings…
For the modem modes additional parameters can be set in the Options | Modem Settings... dialog box.
These settings are:
Path server: Set the Windows directory for the output files on the server
Path client: Set the Windows directory for the output files on the client computer. This setting is
only enabled on a remote GUI.
MSI
MSI (Multiple Scroll Inhibit) is a function which will suppress multiple linefeeds (LF). In addition, a
software generated Line Feed (LF) is inserted when a carriage return is received.
Using this menu item, the function may be separately toggled on and off for the video output.
Using the MSI function has several advantages. During disturbances in reception a carriage return character may be lost – using MSI prevents lines being overwritten and text being lost. It should also be considered that some stations do not transmit carriage returns: in this case the MSI function will automatically
generate the missing carriage return. To clearly divide a message into paragraphs, many carriage returns
are often transmitted.
Resync Mode
This function forces a re-synchronization of the current mode.
Signal Polarity
If you select a FSK or PSK demodulator in Bitstream Output or Autocorrelation mode, then signal polarity definition is available.
Pressing Change Order will reverse the polarity of the signal and pressing Default ST will restore the default value.
Symbol Definition
If you select a PSK demodulator in Bitstream Output or Autocorrelation mode, then a symbol definition is available.
WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5 First start 35
Page 46

Pressing Change Order will reverse the polarity of the signal and pressing Default ST will restore the default value.
By right-clicking on the display a menu appears.
SAT Settings…
For the SAT Modes, additional parameters can be set in the Options | SAT Settings dialog box.
These settings are:
Service: Select the service to monitor. Choose between:
FAX/DATA/TEL/HSD/TELX_SM/TELX_MM. There are two different possibilities for monitoring
telex:
36 First start WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5
Page 47

- TELX_SM: Single Message monitoring: only the Telex of the MES found in the Control
Channel will be recorded
- TELX_MM: Multi Message monitoring, the Mode stays on the TDM channel until there are
no more Telex transmissions on this channel
Server: Set the Windows directory for the output files on the server
Client: Set the Windows directory for the output files on the client computer. This setting is only
enabled on a remotely-connected GUI.
Watchlist: Click the All MES IDs box, if all MESs must be monitored; leave this box empty if only
specific MESs should be monitored. Enter these MES IDs into the combo box. If ranges of MES IDs
should be monitored, enter and enable each range.
See “SAT System” on page 269.
Toggle
Clicking the Toggle function will immediately switch from the current case to its opposite – i.e., from Letters to Figures or vice-versa. Thus an incorrect case shift caused by a character received in error may be
corrected at once and the proper case restored.
Time Stamp...
Clicking Time stamp offers a selection of different time zones for time stamping text output. Time stamping may also be disabled at a later time through this menu.
To display the time stamp a new window is opened on the left hand side of the screen. When a text line
has been displayed, date and time is displayed in this window. This function is available for all text output
modes.
WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5 First start 37
Page 48

Demodulator Menu
Using the Demodulator menu all parameters for decoding may be edited. In addition to baud rate, the
options and values for mode, shift, center frequency, offset frequency, input and input gain may be manually entered.
The availability of the functions depends on the active mode.
Auto
Click on the Auto button to enable a mode. Shift, center frequency and baud rate is automatically calculated and adjusted. The new value is selected by double-clicking on the preset value or by clicking OK.
Mode...
In the Mode menu the demodulator mode may be selected.
Most HF, VHF or UHF modes feature a pre-selected demodulator mode for optimum performance, but
sometimes different demodulators may be chosen.
AM
Satellite weather charts are transmitted using AM. This demodulator uses the quadrature I/Q demodulation method.
The level displayed by the level indicator corresponds to the AM modulation depth of the signal. The gain
and the amplitude offset may be set using the Demodulator menu.
BPSK
BPSK shifts the carrier phase ±180 degrees. For carrier recovery a Costas loop is used - this is a PLL with
a special phase comparator, which removes the payload data from the PLL loop. The input signal is then
down-converted to base band by mixing the carrier in a complex mixer, and the resulting signal is the data signal.
BPSK is almost exclusively used for satellite data links.
CW
The CW demodulator utilizes a steep, adaptive band pass filter and automatic amplitude control. The AGC
attack time may be adjusted according to the propagation conditions. The filter response may be set to
Slow, Normal or Fast. This demodulator produces high quality CW decoding. It is important to select the
appropriate receiver AGC response (normal or slow).
DSP
The DSP mode utilizes an I/Q demodulator (Hilbert transformation). The received signal is split into an inphase component and a quadrature component. Next, amplitude normalization takes place and the resultant signal is used for the frequency conversion. This method is characterized by a linear relationship between the received frequency and the output voltage of the demodulator.
The DSP demodulator has a good signal-to-noise ratio and yields very good results under most conditions.
DPSK
In differential PSK the absolute carrier phase cannot be used for data recovery as is the case with BPSK
and QPSK. To decode multiphase DPSK (up to 16DPSK) the input signal is mixed with a complex, phase
regulated reference signal. The resulting data reduced signal is then filtered in a low pass filter. The fol-
38 First start WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5
Page 49

lowing phase comparator calculates the phase difference between the signal from the integrator and the
delayed signal.
A variant of DPSK is used almost exclusively when phase modulation is employed on short wave data
links.
DBPSK
Similar to DPSK, but has two phase shifts at ± 180 degrees.
DQPSK
Similar to DPSK, but has four phase shifts at ± 90 and ± 180 degrees.
DTMF
This demodulator handles multi-frequency signals. Filters are switched in on the various frequencies of the
signal and the amplitude is then calculated for each frequency. Next the amplitudes are evaluated. Two
simultaneous tones are demodulated. The SNR is the same as for the mark-space demodulator.
DXPSK
Adaptive DPSK demodulator for PACTOR-II. This demodulator will automatically adapt itself to DBPSK,
DQPSK, D8PSK or D16PSK.
D8PSK
Similar to DPSK, but has eight phase shifts at ±45, ±90, ±135 and ± 180 degrees.
D16PSK
Similar to DPSK, but has sixteen phase shifts at ±22.5, ±45, ±67.5, ±90, ±112.5, ±135, ±157.5 and
±180 degrees.
FFSK and GFSK
Depending on the mode, the FFSK (Fast Frequency Shift Keying) and GFSK (Gaussian Frequency Shift
Keying) demodulator is automatically selected. Basically this demodulator utilizes the I/Q principle (Hilbert). However, filters are adjusted to accommodate the special demands of these modes.
MFSK
This demodulator handles multi-frequency signals. Filters are switched in on the various frequencies of the
signal and the amplitude is then calculated for each frequency. Next the amplitudes are evaluated. Depending on the number of tones used, the filters are configured as phase linear FIR filters or as IIR filters.
The SNR is the same as for the mark-space demodulator. Simultaneous multi-tone decoding (e.g. DTMF)
is not possible with this demodulator.
MS (Mark-Space)
The mark-space demodulator processes the two keying frequencies of a FSK signal. These are fed to two
phase linear FIR filters and the amplitude is then calculated. The mark-space demodulator exhibits an extremely good noise distance and should be used for all FSK modes utilizing a speed of less than 300 Baud.
OQPSK
Carrier recovery is mandatory to demodulate OQPSK. As OQPSK has phase shifts at ±90 degrees, the signal must be squared two times to produce a carrier at four times the original frequency. A PLL recovers
the carrier in frequency and phase with ambiguities at ±90 and ±180 degrees. A complex mixer down
converts the signal to base band and the resulting signal is the data signal. In contrast to QPSK, OQPSK
has only phase steps of ±90 degrees in one step. First the in-phase part is switched, then after half a
symbol duration the quadrature part is switched. The advantage of this process is a smaller amplitude variation.
OQPSK is used almost exclusively for satellite data links.
QPSK
Carrier recovery is mandatory to demodulate QPSK. As QPSK has phase shifts at ±90 and ±180 degrees,
the signal must be squared two times to produce a carrier at four times the original frequency. A PLL recovers the carrier in frequency and phase with ambiguities at ±90 and ±180 degrees. A complex mixer
down converts the signal to base band, and the resulting signal is the data signal.
QPSK is almost exclusively used for satellite data links.
WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5 First start 39
Page 50

SUBTONE
The same as DSP, but the parameters are optimized for low frequencies.
PB Center...
Click on the PB Center menu item to adjust the center frequency of the passband filter.
For more details see “Passband Filter Support” on page 65.
PB Bandwidth...
Click on the PB Bandwidth menu item to adjust the bandwidth of the passband filter.
For more details see “Passband Filter Support” on page 65.
Center...
Click on the Center menu item to adjust the demodulator center frequency within 1 Hz accuracy. For
modes utilizing direct FSK this button is not available: in this case the offset frequency is equal to the effective center frequency.
Shift...
Click on the Shift menu item to adjust the frequency shift in 1Hz steps. In HF modes the range is 50 Hz –
3500 Hz, and in VHF-UHF modes using direct FSK the range is 50 Hz – 16000 Hz.
Baudrate...
Click on the Baudrate menu item to enter a new value. Depending on the mode, the baud rate dialog box
contains preset values which may be directly selected. The new value is selected by double-clicking on the
preset value or clicking on OK.
Polarity...
Click the Polarity menu item to toggle between normal and inverse polarity.
Offset...
Adjusting the offset frequency and the center frequency will adapt the decoder input to a receiver IF output.
The minimum offset frequency resolution available with the decoder is 1 Hz. The effective center frequency is the sum of the offset frequency and the center frequency. The function is similar to the mixing of the
signal frequency and BFO of a receiver.
An exception is the FFSK demodulator for direct frequency modulation: in this case the indicated offset
frequency is equal to the effective center frequency.
An example for an HF receiver and ARQ-E mode:
Receiver IF 455,000 Hz
Offset 453,300 Hz
Center 1700 Hz
The advantage of this method is that the user only needs to know the center frequency.
Another example for a VHF-UHF receiver and POCSAG mode:
Receiver IF 455,000 Hz
Offset 455,000 Hz
Center 0 Hz
In this case the offset frequency is equal to the center frequency.
40 First start WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5
Page 51

Input...
The decoder supports a number of inputs:
AFIN#1-3 have a range of 50 Hz–25 MHz. These inputs should be used when the source is an AF
output (line or speaker), or an IF output of a communication receiver or digital recorder
IF70#4 has a range of 52.5 MHz - 87.5 MHz. This IF is common for satellite equipment
EXT-DEM will accommodate voltage levels from TTL to RS-232C, [0 V, +5 V] to [-12 V, +12 V].
Use this input for input from an external demodulator
STANAG4285 is a file “Custom Input”
VAC1 is a sound card “Custom Input”
PXGF1 is a sound card “Custom Input”
For details regarding “Custom Inputs...” see on page 47.
AF(xxx) These inputs are used when you work with the sound card. The frequency range depends
on the sound card specification. You can also apply IF to this input, as long as your signal is within
the supported bandwidth of the selected sound card input.
IQ is used for analogue IQ signals, with the I and Q channels sent to the left and right channel of
the soundcard respectively.
STANAG4285 is a file “Custom Input”
PXGF1 is a sound card “Custom Input”
For details regarding “Custom Inputs...” see on page 47.
Gain...
For manual gain adjustment, use the slider. The input gain can be adjusted between 0 and 100 % of the
nominal input sensitivity of the selected input. When the gain has been adjusted to the desired level,
press OK to save the setting.
The adjustment is valid only for the selected input. The gain setting for each input is separately saved in
the application initialization file.
Gain adjustment should never cause the red bars of the level indicator to be lit.
WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5 First start 41
Page 52

Manual gain adjustment will not optimize the combined input sensitivity setting and the internal gains of
the demodulator. To optimize input sensitivity and internal gain, press Autoset. This will start Automatic
Level Setting (ALS), initiate the calculation of the optimized settings and display ALS running.... When
the calculation has completed, ALS finished will be displayed. Press OK to accept the result.
Note: ALS does not apply to input from virtual sound cards, e.g. the WiNRADiO VSC.
Favorites Menu
The Favorites menu lets the user save and reload a mode and its corresponding settings, i.e. mode, alphabet, center frequency, baud rate etc. The settings are saved in a *.WFV file.
Open...
Select Open to reload the settings.
42 First start WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5
Page 53

Save As...
Select Save to save the settings.
Configuration Menu
In the Configuration menu all general setup functions are available.
W61PC Card…
The first time the decoder application is started with the decoder card installed, the location of the decoder
devices must be set.
WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5 First start 43
Page 54

When a W61PC card is detected, the card selection dialog shows the type of product found, as well as the
hardware version and serial number.
In the example above, the W61PC software is looking for W61PC cards in a local computer. The process
should only take a few seconds.
Each device is identified by a unique serial number. Thus the application is able to search for devices automatically; this functionality is available for local as well as remote computers - pressing the Connect
button will start the process.
The selected entry is stored in the initialization file (*.INI file) for the card or device and no further entry
is necessary, when the application is restarted. The settings may be changed at any time.
The system can be used in a network configuration. This allows the system to be remotely controlled.
Font...
Clicking Font opens a configuration window.
Important: Please, note that changing the font and changing the alphabet are two different actions. If
you change the alphabet, then you select a table in a Unicode Font. If you change the font, then you
change the graphical representation (Arial, Courier etc.) of the characters of an alphabet. You may run into problems if you select a non-Unicode font and change the alphabet.
For some types of transmission it will make sense to change the font - this depends on the software that
was used for the transmission.
Temp Files...
Clicking Temp Files opens a configuration window.
You can set the number of lines to be saved to temporary files during a session. These limits allow a user
to leave his computer on for days, while not exhausting hard drive space.
44 First start WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5
Page 55

If the temporary files are larger than 50% of free disk space, it will not be possible to save your recording
as a new copy of the temporary file(s) is made when you perform a save operation.
You can select different values for:
Text modes
Fax modes
FSK analysis
Sonagram analysis
Selecting high values allows the user to scroll back over a longer time, but requires more memory and
hard disk space.
Settings...
Clicking Setttings... opens a configuration window.
You can enable or disable different options, to control the behavior of the application:
When selecting "Print" include front page containing all mode settings. Enable or disable
the printing of a status page with all mode settings if you use the Print command.
When selecting "Clear Screen" show warning before deleting all data. Enable or disable
the display of a warning window before the screen is cleared when you use the Clear Screen
command.
When selecting "Exit" save last mode. Enable or disable storing of settings from the last
mode. If enabled, the decoder will start again in the latest mode used.
When selecting "FFT" and "PSK Symbol Rate" pause graphics while cursors are active.
Enable or disable the automatic freezing of the graphic as long as the cursors are displayed.
Enable the Backspace support. Sometimes in modes like PSK-31, the operator is sending back-
space characters. If backspace support is enabled, backspace will work as for an ordinary terminal
program.
Enable reconnect to cards on remote computer. Enable or disable the GUI to reconnect to a
card on a remote computer. If enabled, the decoder will reconnect to the card on the remote computer.
Enable relative frequency display. You can select if, in the FFT, sonagram etc displays, the “re-
al frequency” (center frequency+offset) or the “relative frequency” is displayed.
Receiver and Satellite Settings...
These settings are used for satellite modes and analysis, and give the operator the possibility to configure
receiver or down-converter frequencies, and to select a satellite and receiver type. The receiver or downconverter control interface to be controlled is connected to a serial port of the computer. Receiver center
frequency is preconfigured to 1542 MHz for the L-Band settings and 3544.5 MHz for the C-Band settings
WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5 First start 45
Page 56

The GUI displays a number of input fields:
Ocean Region. Select the ocean region satellite pointed to by the monitoring antenna.
Oscillator Frequency. Set this parameter to the frequency of the local oscillator used, or set it to
0 if an external converter or mixer is not used.
Frequency Offset. Find out how accurately the receiver sets its frequency. Use the real-time FFT
item in the Analysis DIRECT menu and select a bandwidth of 24 kHz to find out the frequency
offset of the receiver. Adjust the receiver to the NCSC frequency of the appropriate ocean region.
Following this, the NCSC signal should be centered exactly in the FFT display. The adjustment applied to centre the NCSC signal is the offset (make it accurate to 500 Hz or less).
L Band and C-Band Center Frequency. Exact value of the L or C-band frequency that is con-
verted to 70.000 MHz.
License...
To activate the additional software options, a valid activation key is required from WAVECOM.
The key enables the decoder application to
Check if a customer is entitled to receive certain software updates
46 First start WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5
Page 57

Enable certain optional functions
Select Configuration | License... from the menu bar.
To validate the key, press Validate.
The license key is normally printed on your invoice or on your CD/DVD.
Custom Inputs...
To add a customer defined Input, all other decoder windows must be closed. The number of custom inputs
is limited to 16.
Streaming and custom inputs belong together. A new custom input has to be defined before streaming can
be used to acquire a specific data stream for decoding. At the moment, streaming can be defined for
TCP/IP data, sound card devices (real or virtual) and for .WAV-files. If a custom input is selected as the
input source, the data stream is read from the specific input.
For defining, editing and deleting a custom input, the dialog Custom Inputs is used. The properties of
the custom input are stored in a XML file. The defined custom inputs are selectable like any other input
sources.
In the screen shot below two user-defined inputs appear.
In the left table, the user defined custom inputs are listed.
In the right table, the parameters of the currently selected custom input are displayed. The Pa-
rameter column contains the names of the parameters, and the Value column shows the related
parameter values.
The Add button is used to create a new custom input. The Apply button saves the parameter set-
tings of a newly created or an edited custom input. Pressing the Delete button removes a selected
custom input.
WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5 First start 47
Page 58

The following picture shows the Custom Inputs dialog after pressing the Add button.
The Input Name can be edited in the right table by typing a new name into the Value field if desired.
Next, the device type has to be specified. Sound card, File or TCP/IP can be chosen from the list box
that appears by clicking on the Choose a device type.
Add a new WAV-File Custom Input
Select the Configuration | Custom Inputs... menu entry to open the configuration dialog for the custom
inputs.
To use a WAV-File as signal input source, the following parameters have to be set via the Custom Inputs
dialog:
48 First start WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5
Page 59

File Input Parameter
Value
Input Name
The name of the custom input
Device
Select File in the list
File Path
The path to the specific WAV-file has to be specified
Channel
In the list box the channel(s) to be used are displayed: Left, Right, Left + Right. For
mono files, only Left is displayed
If IQ is selected, only Left + Right can be selected. If PCM is selected all three channel
configurations are available
If you start by entering the filename, then the file is analyzed and the correct settings are
automatically selected
Type
PCM or IQ (A-law, mu-law or other codecs are not supported), 16 bit, sampling rate up to
192 kHz (min. 8 kHz recommended)
Play Continuous
Indicates if the files are played in repeat mode. Select On to switch on the repeat mode or
Off to switch off the repeat mode
Soundcard Input Parameter
Value
Input Name
The name of the custom input
Device
Select Soundcard in the list
Name
The names of all the sound cards installed on the computer which hosts the decoder
are displayed in a list box. Select the desired sound card
Channel
In the list box the channel(s) to be used are displayed: Left, Right, Left + Right
Type
PCM or IQ
Sampling Rate [Hz]
The sampling rate is fixed at 48 kHz
The file can be selected from any available directory on the LAN. The specified WAV-file is copied to the
Data-Input directory (on the computer hosting the decoder) and stored under the name
<SerialNumberOfW[xx]Card>_<InputName>.wav.
Note: The WAV-file is reloaded each time the Apply button is pressed. The Apply button must also be
used to save the configuration of a new custom input. Pressing the OK button only closes the dialog. The
XML file Inputs.xml, located in the Config directory, is updated by pressing the Apply button.
Add a New Sound Card (Real or Virtual) Custom Input
Select the Configuration | Custom Inputs... menu entry to open the configuration dialog for the custom
inputs.
To use a sound card as the signal input source, the following parameters have to be set via the Custom
Inputs dialog:
WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5 First start 49
Page 60

TCP/IP Input Parameter
Value
Input Name
The name of the custom input
Device
Select TCP/IP in the list
IP address
Set the source IP address (at the moment this menu item is not enabled, all traffic sent
to the enabled port is processed by the decoder)
Port number
Enter the a port number. The data source must be configured with the same port number
Format
IP-CONV or IP-PXGF (for more information, see “WAVECOM Data Formats” on page
299)
Sampling Rate (Hz)
The sampling rate used by the data source
Number of channels
Number of channels
Channel
In the list box the channel(s) to be used are displayed: Left, Right, Left + Right.
If IQ is selected, only Left + Right can be selected. If PCM is selected all three chan-
nel configurations are available
Type
PCM or IQ
Note: If the GUI is running in remote mode, the names of the sound cards installed on the remote com-
puter which hosts the WAVECOM decoder are listed.
Add a new TCP/IP Custom Input
Select the Configuration | Custom Inputs... menu entry to open the configuration dialog for the custom
inputs.
To use a TCP/IP stream as signal input source, the following parameters have to be set via the Custom
Inputs dialog:
Edit a Custom Input
Select the custom input from the input list on the left in the Custom Inputs dialog. For instance, select
the NewInput 3 entry, which is a file input.
Now it is possible to modify the parameter values in the parameter table on the right.
For instance, the Input Name or the Channel parameter value can be modified.
Even the Device value can be changed from File to Sound card. By changing the Device, the new device-related parameters will appear in the parameter list and the parameters of the old device will disappear.
By pressing the Apply button, the changes will be saved for the specific custom input.
The XML file Inputs.xml, located in the Config directory, is updated by pressing the Apply button.
50 First start WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5
Page 61

Important: After modifying custom input parameters, press the Apply button; otherwise the changes will
be lost.
Delete a Custom Input
Select the custom input to delete in the Input list (left table) and press the Delete button. This will remove the custom input from the XML file Inputs.xml, located in the Config directory.
Selecting a Custom Input
The user defined custom inputs can be selected via the Signal Input dialog. The dialog can be opened via
the Demodulator menu’s entry Input... or by double-clicking the Input status bar field at the right bottom of the GUI.
The screen shot below shows the Signal Input dialog including two user defined custom inputs at the end
of the list.
Custom Alphabets…
Custom defined alphabets are also available. This feature allows the user to add alphabets of his own creation that are not defined by WAVECOM, and to add variants of existing alphabets.
Custom alphabets are implemented for 5-bit, 7-bit and 8-bit alphabets, and the number of custom alphabets is limited to 16.
The Custom Alphabets… dialog box displays a number of input fields:
Clicking Save As… opens a dialog box, in which to enter a name for the newly created translation
table. Press OK to close the dialog box and save the new translation table. The translation table
contains the actual values set in the Alphabet Translation Table dialog. The name of the new
table appears in the Alphabet combo box and a new .xml file with the name of the table is created containing the table data.
Pressing Save stores the current dialog settings to the translation table that is active as shown in
the Alphabet combo box. The data is stored in the related .xml file.
Clicking Delete deletes the active translation table.
WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5 First start 51
Page 62

Pressing Undo will replace the new, user selected values in the dialog box with the values stored
for the current alphabet.
The Update List is used to add the user created alphabets to the list of alphabets. By pressing the
Update List button, the Alphabet directory is searched for .xml files related to new alphabet. If a
new one is found the list and the Alphabet combo box are updated.
The Alphabet combo box shows the names of all translation tables. By selecting an entry the
stored data for the specific translation table are displayed. Note that the most recent changes to
the current alphabet are not saved until Save is pressed.
Select the font that is used to display the translation tables by pressing Font.
The Alphabet list control (left list) displays the characters defined for the current alphabet. The
first column shows the position index in the alphabet for the characters. The second column (Current) shows the currently defined value of the character at the selected position. The third column
(New) shows the user defined character value. By pressing the Save button, the Current value
becomes the New value.
The Font list control (right list) displays all the characters defined in the selected font. The first
column shows the decimal or hex character value. The second column (Symbol) shows the character. Selected characters are copied to the selected rows in the Alphabet list by pressing the Ar-
row () button.
Using the Writing Direction radio buttons, a LeftToRight or RightToLeft output direction of the
decoded text may be selected
The System combo list is used to set the length of the codeword for a user defined alphabet.
Click Transparent to select if control characters are to be displayed in the decoded text.
Depending on which radio button, i.e. Letters, Figures or Third, is selected, the letters, figures
or third shift control characters of the current 5-bit custom alphabet are displayed in the list control.
The Control Characters combo box contains the control characters that can be added to an al-
phabet, i.e. the Letters Shift, Figures Shift, Third Shift, Unperforated Tape, Space,
Linefeed and Carriage Return characters. Select a character, then press the Arrow () button
to copy the selected character to the selected row in the custom Alphabet list.
The Arrow () button is used to move characters to the translation table. Press this button to
copy the selected character in the Font table, or the selected entry in the Control Characters
combo box to the selected position in the Alphabet table.
The Find button and the edit box to the left of the button are used to find a character (decimal or
hex value) in the Alphabet or Font table.
Press Reset to replace all character values in the custom Alphabet list with ‘0’ .
Press Refresh to reload all characters of the current font and update the display. This feature is
useful when the font has been changed.
Pressing Hex View to display the hex value for all characters; otherwise, decimal values are used.
When Show All is enabled, the positions of undefined characters are displayed in the Font char-
acter table.
Press the OK button to close the window. Recent changes are not saved - if the latest changes
have to be saved, press the Save button before pressing OK.
SR Fine Tuning
Sound card sampling frequency accuracy is much more critical for sophisticated digital modes compared to
the simple BAUDOT or SITOR modes. The built-in SR Fine Tuning feature can be used to correct errors
that are introduced by an inaccurate soundcard sampling frequency (the tolerance of soundcards can be a
few hundred parts per million).
52 First start WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5
Page 63
SR Calibration
To check the error of you soundcard, use analysis software that is able to calculate the deviation of the
sample rate in ppm. Try to avoid sound cards that are completely out of tolerance.
When W-CODE uses low-cost sound cards as a signal source, sampling frequency errors will most likely
occur. For commonly available sound cards, the sampling frequency may vary up to one percent of the
nominal value. This behavior prevents decoding or introduces additional errors. Complex signals like the
MIL-Standard and STANAG waveforms are heavily affected.
In previous versions of W-CODE the “SR Fine Tuning” feature was used to correct the sampling rate, but
adjusting the rate was very difficult due to a substantial time lag between the adjustment taking place and
the display being updated. To remedy this problem, a new feature has been introduced under “Configura-
tion | SR Calibration”. The new feature utilizes an AM demodulator, which demodulates the pulses of a
reference signal - the output, which resembles a fax image, is displayed in a calibration window. The degree and the direction of slanting of vertical lines are a measure of the amount and the sign of the deviation between the sound card sampling frequency and the reference signal. The values are stored and used
for all future decoding.
Signal thresholds can be set with a tunable band pass filter, which may be placed anywhere in the spectrum with the desired bandwidth. The settings affect the blurring of pulse edges.
Reference signals which may be used include weather fax transmissions and time signals, e.g. CHU,
DCF77, MSF, HBG etc. For instance, CHU transmits a short tone pulse every second. If the band pass filter
is tuned to the frequency of this tone, a straight, vertical line will be visible if the sampling rate of the
sound card is correct. If the line is slanted to either side the sampling rate is offset. To adjust the sampling rate, use “Options | Fine Tune” until the vertical line representing the reference signal is straight.
Example: CHU signal
First adjust the center frequency and the bandpass filter settings. You will notice that the vertical lines are
skewed.
Press “Options | Fine Tune…” and use the slider to adjust the vertical lines so they become perpendicular
to the time axis of the calibration window.
WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5 First start 53
Page 64

Note: The full range of the“Fine Tune” process is 0.1 % deviation. For deviations larger than this use “Fine
Tune” repeatedly until the desired effect has been achieved.
If you succeeded in correcting the sampling rate, i.e. the vertical lines have been straightened and are
perpendicular to the time axis, press “OK” to save the measured value.
As the sampling rate calibration feature utilizes an AM demodulator, input level should be as high as pos-
sible, resulting in a high level of contrast which facilitates the adjustments. If necessary use the “Demodu-
lator” menu to adjust the AM gain and offset.
View Menu
54 First start WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5
Page 65

In the View menu the visibility of each individual status and indicator element may be enabled or disabled. A checkmark indicates that the element is enabled. A disabled element is not deleted, but may be
made visible at any time.
Window Menu
Using the Window menu new output windows may be opened and organized.
Help Menu
For context sensitive help on a menu item, use F1 on the item.
Contents
Selecting Contents opens the online help system.
Help on clicked buttons, menus and windows are then available.
WAVECOM on the Web
Contents access the decoder help file.
www.wavecom.ch links to website of WAVECOM.
About W61...
Displays information on software version, build number, and release date for the installed application.
Other GUI Elements
Toolbar
Allows access to file, print and search operations. Most functions on this toolbar are also available from the
File menu.
If the mouse is resting for more than approximately half a second on a button, a label with the name of
the function is displayed (tool tip). In addition a short help text is displayed on the system status bar.
Depending on the active mode, buttons for which the corresponding function is not available are grayed.
WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5 First start 55
Page 66

Mode Selector
Analysis Selector
Back - go to last decoding or analysis mode
History - select one of the last decoding or analysis modes from this drop down menu.
Go Forward in the history list after going back in the history list
Classifier
Classifier Code Check
Start/Stop Classifer
FSK Auto Tuning
FSK Analysis
FFT Analysis
Sonagram Analysis
Waterfall Analysis
Resync Mode
Toggle Letter/Figure
Maximize Passband
Media Player/Recorder
Live Voice
WAVECOM Toolbar
The selection of the most important decoder functions is facilitated by toolbar buttons. Operation is identical to the use of the menu bar.
If the mouse is resting for more than approximately half a second on a button, a label with the name of
the function is displayed (tool tip). In addition a short help text is displayed on the system status bar.
Depending on the active mode, buttons for which the corresponding function is not available are grayed.
56 First start WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5
Page 67

Frequency
User entry field for the real frequency.
In modes with automatic frequency setting the automatically set
frequency is shown
Step
Spinner to increase or decrease the frequency.
List box to select the frequency step for the spinner
Level Indicator
Click on the Gain icon to adjust the input to the correct level. Gain adjustment must never turn on the
red bars of the level indicator.
Spectrum Indicator
The Spectrum Indicator is a tuning tool consisting of a bar graph, increasing frequency from the left to
the right, which displays the frequencies of the incoming signal. For FSK signals the mark and space frequencies are displayed. For PSK signals the carrier is displayed.
Decoder Status Bar
The Status Bar displays decoder status information.
Double-Clicking on Status Bar Fields
Double-clicking the status bar fields will open the corresponding dialog box. This facilitates the use of the
decoder software.
A double-click on the shift field, baud rate field, frequency shift field, etc. of the demodulator status bar
opens the corresponding dialog box.
Selecting a field will not terminate the active mode. As far as possible, value changes will be implemented
immediately, without the interruption of data acquisition.
Demodulator Status Bar
The Demodulator Status Bar displays information about the status of the DSP demodulator
Double-Clicking on Status Bar Fields
Double-clicking various status bar fields will activate the corresponding dialog boxes. This facilitates the
use of the decoder software.
A double-click on the shift field, baud rate field, frequency shift field etc. of the demodulator status bar
opens the corresponding dialog boxes.
Selecting a field will not terminate the active mode. As far as possible changed values will be immediately
used without interrupting data acquisition.
SAT Frequency Tuning Bar
The SAT Frequency Tuning Bar simplifies frequency selection for the satellite modes. In Receiver and
Satellite Settings the user has the ability to store the center frequency of the down converter.
The SAT Frequency Tuning Bar box displays a number of inputs and controls:
WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5 First start 57
Page 68

Memory
Retrieve a frequency from the selected memory entry
Store the current frequency to memory. You will be prompted for
a name. The current frequency will be replaced by the new frequency
Delete the contents of the selected memory position
Edit the name of the memory entry
List box containing memory entries
Sort buttons for numerical or alphabetical sort of the list box entries
NCSC-Auto
Only available in SAT-C-TDM mode. Please, refer the manual section on SAT-C-TDM
The SAT Frequency Tuning Bar display elements are mode dependent.
There are three different variations of the frequency bar:
SAT-B, SAT-M, SAT-mM
Display of the real frequency. Direct tuning is disabled.
SAT-B-C-TFC, SAT-AERO-P, SAT-C-TDM-EGC, SAT-C-TDMA
Display of the real frequency, frequency memory and step. Direct tuning is enabled.
SAT-C-TDM
Display of the real frequency, frequency memory and step. Direct tuning is enabled. NCSC-Auto tuning
can be selected.
Waterfall SAT, FFT SAT, Sonagram SAT
Display of the real frequency and step. Direct tuning is enabled.
The C-band or L-band frequency range depends on the system context set up in the Receiver and Satellite
Settings
XML Frequency Memories File
All frequencies are stored in XML files c:\Users\Public\Documents\WAVECOM\<Product>\. Each mode has
a XML file containing its corresponding settings. In addition to frequency entries, the watch list, desired
services, NCSC-Auto status (only for SAT-C-TDM) and demodulators used (only for SAT-AERO-P) are
stored in these files.
58 First start WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5
Page 69
The illustration below shows an example of a XML file for the SAT-C-TDM mode, including watch list and
memory positions.s
For SAT-AERO-P a frequency entry contains the demodulator used on a particular frequency.
In multi-card systems, each card has its own section in the XML file.
The user may edit these files by hand, however it is recommended to use the SAT Frequency Tuning Bar.
The installation package contains example XML files for each mode.
FFT / Sonagram Context Menu
Pause Graphic
Freeze the FFT or Sonagram Window.
Bandwidth...
To select a display bandwidth use Bandwidth from the context menu or double-click on the Bandwidth:
field on the demodulator status bar. For the Tuning Sonagram / FFT bandwidths of 0.5, 1.0, 2.0, and
4.0 kHz are available. For the Analysis FFT/Sonagram bandwidths of 0.5, 1.0, 2.0, 4.0, 24, 48 and 96 kHz
are available.
WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5 First start 59
Page 70

Window Type
Signal Type
Frequency Resolution
Spectral Leakage
Amplitude Accuracy
Blackman
Random
Poor
Best
Poor
Hamming
Random
Good
Fair
Fair
Hanning
Random
Good
Good
Fair
Rectangular
Transient
Best
Poor
Poor
Average Factor
After choosing an Average Factor from the context menu, the average of up to 64 measurements may
be displayed at each step. A value of "1" turns averaging off. The averaged display of several measurements is very helpful when monitoring MFSK and FDM transmissions or during heavy fading. The averaging function may also be selected by double-clicking the Avg: field in the upper status bar.
Window Type…
Four window functions Rectangle, Hamming, Hanning and Blackman may be selected. The selection of
a window type influences the accuracy of the signal spectrum measurement. Good frequency resolution is
obtained using the rectangular window, however the rectangular window also causes heavy distortion due
to its poor side-lobe suppression characteristics. A window should be chosen according to the user’s requirements; each window type has its own characteristics as listed below.
The user should be aware that changes in the received signal can cause the display of spurious spectral
lines or aliasing ("false" frequency display) in FFT measurements. Depending on the keying frequency and
the magnitude of the frequency shift, the aliased frequencies may even be stronger than the desired signal.
Period...
From the Period menu the time unit per measurement may be selected. The lowest value is 50 ms corre-
sponding to 20 FFT’s/s. For the highest value of 10,000 ms a measurement is done once every 10 seconds.
Peak Hold…
For easy tuning, switch on Peak Hold in the Options menu on. The tone spectrum appears in the FFT
window after a short delay and the frequency range can be changed as required using the cursors as
shown below.
If you select max Decay, then a decay value can be set. This allows to use the peak hold functions during
thunderstorms or if tuning the receiver.
60 First start WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5
Page 71

Color schemes
Select between Grey, Hot, Cool, Cooper and RGB.
Mode Selector
Full-screen menus are available for modes and analysis tools. Click on the Mode Selector Button in the
toolbar to open this menu. Modes are available in alphabetical order. Click on a mode to start it. From the
top row tabs analysis tools may also be selected.
If a mode is already active it will not be terminated or halted by opening the full-screen menu. Click on
Cancel or the Close button to leave the menu.
The descriptions of the operating modes in another section of this manual are arranged in alphabetical order.
HF Mode Selector
WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5 First start 61
Page 72

HF Analysis Selector
VHF/UHF-DIR Mode Selector
VHF/UHF-DIR Analysis Selector
62 First start WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5
Page 73

VHF/UHF-SUB Mode Selector
VHF/UHF-SUB Analysis Selector
Satellite Mode Selector
WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5 First start 63
Page 74
Satellite Analysis Selector
FAX & Modem Mode Selector
FAX & Modem Analysis Selector
64 First start WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5
Page 75

Passband Filter Support
Perfect signal processing (filtering) is essential for best decoding results, which are achieved by using the
correct filters in the receiver. Doing so prevents blocking effects from strong nearby signals. However correctly processed signals may be unavailable, e.g. when a receiver does not offer optimum filters or when
using recorded signals. To overcome these obstacles additional passband filters are included in the
WAVECOM decoders to assist the operator in separating signals within the analyzed frequency spectrum.
In the WAVECOM GUI a passband (PB) tuning bar is placed below the tuning FFT window. If tuning FFT is
not available, as is the case for some modes, the parameters can be set in the Demodulator Menu.
For many modes the parameters PB Center, PB Bandwidth and Center can be individually controlled
(see the table below).
WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5 First start 65
Page 76

Item
PB Conf.
Remarks
DSP
+
Freely configurable
AM + Freely configurable
CW + Freely configurable
GFSK
+
PB center frequency controlled from offset frequency setting
FFSK
+
PB center frequency controlled from offset frequency setting
MARK-SPACE
-
PB automatically adjusted depending on center, shift and speed
MFSK
-
Individual tones are filtered and PB automatically adjusted depending on tone spacing, center and speed
DTMF
-
Individual tones are filtered and PB automatically adjusted depending on tone spacing, center and speed
BR6028
-
Preconfigured filters that cannot be changed. The location of the pilot tone can be manually set
BPSK
+
Freely configurable
QPSK
+
Freely configurable
OQPSK
+
Freely configurable
DPSK
-
PB bandwidth automatically adjusted depending on center, shift and
speed. The center frequency can be manually set
DXPSK
-
PB bandwidth automatically adjusted depending on center, shift and
speed. The center frequency can be manually set
DBPSK
-
PB bandwidth automatically adjusted depending on center, shift and
speed. The center frequency can be manually set
DQPSK
-
PB bandwidth automatically adjusted depending on center, shift and
speed. The center frequency can be manually set
D8PSK
-
PB bandwidth automatically adjusted depending on center, shift and
speed. The center frequency can be manually set
D16PSK
-
PB bandwidth automatically adjusted depending on center, shift and
speed. The center frequency can be manually set
IQ + Freely configurable
ANALYSE
+
Freely configurable
FFT - No filtering implemented
TIME
-
No filtering implemented
OFDM
-
No filtering implemented
SUBTONE
-
No filtering implemented
DISCRIMINATOR
-
No filtering implemented
EXT-DEM
-
No filtering implemented
BYPASS
-
No filtering implemented
The PB parameters can be set to maximum bandwidth (switched off) with the Maximize Passband button.
66 First start WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5
Page 77

Analysis Tools
FFT
The real-time FFT analysis is a powerful spectrum analysis tool based on Fast Fourier Analysis (FFT), operating in real time with a 4096-point resolution. The signal is digitized, saved and its frequency spectrum
calculated and displayed.
The measurement is started by selecting a bandwidth. The display of the frequency spectrum has a linear
scale and covers a dynamic range of 60 dB. (The internal dynamic range is considerably higher due to the
16 bit A/D converter used, but the configured display resolution performs better in practical use.)
The frame refresh rate averages 10 to 20 pictures per second, allowing even fast signal changes to be displayed. The frame refresh rate is however dependent on the speed of the PC and its video card.
To start the FFT, click on the FFT button or use Analysis | Real-time FFT from one of the menus.
To activate the measurement cursors, click inside the FFT graphics window. The left and right cursors may
be moved around using the mouse. The cursor positions are displayed as absolute frequency values; the
center cursor automatically displays the center value.
To remove the cursors, click on the graphics window again.
When the cursors have been placed in the desired positions they may be moved right or left by moving
the center cursor. By doing this, the measurement of frequency spacing in MFSK and FDM systems is possible.
Adjustment of the Offset Frequency
An FFT spectrum calculation can be done from 0 Hz, up to the selected maximum frequency.
The offset frequency for decoding of VHF/UHF-DIR transmissions e.g. POCSAG, GOLAY/GSC, or ERMES
must be adjusted to the effective center frequency of the signal, e.g. 455 kHz.
A bandwidth of 24 kHz from 455 kHz to 479 kHz is sufficient for the measurement range of the FFT.
therefore the offset frequency must be offset to half of the bandwidth. The offset frequency adjustment is
WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5 Analysis Tools 67
Page 78

FFT Type
Start Frequency
End Freqeuncy
FFT HF
Offset Frequency
Bandwidth
FFT SUB
Offset Frequency
Bandwidth
FFT DIR
Offset Frequency – Bandwidth/2
Offset Frequency + Bandwidth/2
FFT SAT
Offset Frequency – Bandwidth/2
Offset Frequency + Bandwidth/2
calculated as the IF output frequency (455 kHz) minus half of the selected FFT bandwidth (24/2 kHz) =
Offset (443 kHz). The measurement range is now 443 kHz - 467 kHz.
For the 455 kHz receiver IF output of a shortwave receiver (e.g. HF-1000), the offset frequency is first adjusted to 453.3 kHz to obtain the standard center frequency of 1,700 Hz. The HF-1000 BFO must now be
adjusted to 1,700 Hz.
FFT HF, FFT SUB, FFT DIR, FFT SAT
Tuning FFT or Sonagram
In some modes a Tuning FFT or Sonagram is available. The FFT or Sonagram can be used to set the
center frequency, shift, and passband filter.
Tuning FSK Signals
Mark and Space are selected with the right and left cursor. The precision of the center frequency is
very important and directly influences the performance of the decoder.
After every change, the center frequency and shift are automatically updated.
Automatic tuning is also available. It works perfectly as long as there is only one input signal present in
the spectrum. To apply a filter, see “Passband Filter Support” on page 65.
Options can be set using the right mouse button or the context menu (see “FFT / Sonagram Context
Menu” on page 59). It is possible to remove the tuning FFT or Sonagram in the View Menu.
Tuning MFSK Signals
68 Analysis Tools WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5
Page 79

The highest and lowest tone of the signal is selected with the right and left cursor. The precision of the
center frequency is very important and directly influences the performance of the decoder.
After every change, the center frequency and shift are automatically updated.
Options can be set using the right mouse button or the context menu (see “FFT / Sonagram Context
Menu” on page 59). It is possible to remove the tuning FFT or Sonagram in the View Menu.
Tuning PSK Signals
The upper and lower frequency boundaries of the signal is selected with the right and left cursor. With the
center cursor, the center frequency may be set more precisely. The precision of the center frequency
is very important and directly influences the performance of the decoder.
After every change, the center frequency is automatically updated and the bandwidth of the signal is set
according to the received mode.
Options can be set using the right mouse button or the context menu (see “FFT / Sonagram Context
Menu” on page 59). It is possible to remove the tuning FFT or Sonagram in the View Menu.
FFT and Sonagram
This analysis tool combines real-time FFT and sonagram analysis modes.
Detailed information for each of the analysis tools can be found in the corresponding descriptions, see
“FFT” on page 67 and “Sonagram” on page 70.
WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5 Analysis Tools 69
Page 80

FFT Type
Start Frequency
End Freqeuncy
Waterfall HF
Offset Frequency
Bandwidth
Waterfall SUB
Offset Frequency
Bandwidth
Waterfall DIR
Offset Frequency – Bandwidth/2
Offset Frequency + Bandwidth/2
Waterfall SAT
Offset Frequency – Bandwidth/2
Offset Frequency + Bandwidth/2
Options can be set using the right mouse button or the context menu (see “FFT / Sonagram Context
Menu” on page 59). It is possible to remove the tuning FFT or Sonagram in the View Menu.
Waterfall
The waterfall analysis produces a three dimensional display of FFT spectra over time, frequency and amplitude. The waterfall display aggregates many single measurements to 40 displayed spectra. An updated
measurement in the two-dimensional real-time FFT display only shows a fraction of the data, depending
on the modulation method. In contrast the FFT waterfall display also displays data in the time domain
A time histogram is displayed on the left-hand side of the display.
By clicking on the graph, the display will be paused and measurement cursors appear.
Options can be set using the right mouse button or the context menu (see “FFT / Sonagram Context
Menu” on page 59). It is possible to remove the tuning FFT or Sonagram in the View Menu.
Waterfall HF, Waterfall SUB, Waterfall DIR, Waterfall SAT
Sonagram
A second widespread method for FFT display is the real-time sonagram, which displays the amplitude and
frequency values produced by the FFT over time. In the sonagram, the signal amplitude is displayed by
colour, with different colours representing different amplitudes. Sometimes this display is also called
“Spectrogram”.
70 Analysis Tools WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5
Page 81

FFT Type
Start Frequency
End Freqeuncy
Sonagram HF
Offset Frequency
Bandwidth
Sonagram SUB
Offset Frequency
Bandwidth
Sonagram DIR
Offset Frequency – Bandwidth/2
Offset Frequency + Bandwidth/2
Sonagram SAT
Offset Frequency – Bandwidth/2
Offset Frequency + Bandwidth/2
This amplitude related spectrum analysis mode offers many hints to the distribution of a signal spectrum.
The operation is numerically identical to the real-time waterfall analysis, and is simply a different method
of visualisation.
Options can be set using the right mouse button or the context menu (see “FFT / Sonagram Context
Menu” on page 59). It is possible to remove the tuning FFT or Sonagram in the View Menu.
Making measurements
With the four cursors it is possible to make measurements in the frequency and time domain. To enable
the time cursors, click into the sonagram to freeze the screen. Then click with the right mouse button to
get the menu to set the time cursors.
T1 Add first cursor to the actual mouse position
T2 Add second cursor to the actual mouse position
Move Move T1 cursor and T2 cursor simultaneously
It is also possible to drag the cursor to a new location. If the cursor line gets in the upper our lower part of
the window, then the window will scroll automatically.
Sonagram HF, Sonagram SUB, Sonagram DIR, Sonagram SAT
Oscilloscope
In general, an oscilloscope is used to measure voltage over time. However, the oscilloscope displays a relative and un-calibrated value. After obtaining the measurement time, frequency can be determined.
WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5 Analysis Tools 71
Page 82

The Trigger Mode option allows the real-time
oscilloscope to trigger on the Positive or the
Negative slope or to be switched Off.
The Trigger Level option allows conventional
level driven triggering to be set. The uncalibrated input voltage range is from +99%
to –99%.
The vertical sensitivity may be set with the
option Time/Div. Nine predefined values are
available covering a range from 200 s to 100
ms per division.
Using the Oscilloscope Gain option, the horizontal un-calibrated input voltage sensitivity
may be adjusted from 0% to 100%.
By clicking on the graph, the display will be paused and measurement cursors appear for both axis.
Several Color schemes are available through the right-click menu.
72 Analysis Tools WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5
Page 83

FSK Analysis
The FSK analysis mode is an important tool to measure the baud rate and frequency shift of FSK transmissions. The magnitude of these property values may help to identify the transmission being monitored.
To open the FSK analysis window go to the HF-Modes menu and select Analysis/FSK Analysis, or use
the FSK Analysis button. The baud rate and spectrum window will open, but NOT the waterfall window.
After a few seconds the baud rate and spectrum window are updated.
The FSK analysis window consists of four panes:
A spectrum graph pane
A spectrum waterfall pane
A baudrate graph pane
A baudrate waterfall pane
Baudrate and Spectrum Window
The baudrate and spectrum window are two-dimensional displays of the monitored baud rate, measured in
Baud, and the spectrum of the transmission, measured in Hz, on a relative scale from 0 to 100. The displays are updated around every 5 seconds. The calculated baud rate, center frequency and frequency shift
values of the latest sample are stored to be used whenever a decoding mode is selected.
Two pairs of cursors may be placed in the baudrate and spectrum graph windows, to assist in manual
measurements. The values to which they point, and the difference between the two cursor values, are
shown above the cursors. When a pair of cursors is placed in one of these windows, graph display updating is halted, but signal sampling continues and is displayed in the waterfall window. The time cursor in
the waterfall window is placed on the selected sample.
Methods exclusively based on bit length measurement are unreliable for baud rate measurements. The
baud rate measuring process employed by the decoder is therefore based on a new method employing auto-correlation and subsequent Fast Fourier Transformation (FFT) presentation. Using this method, FSK
transmissions may be analyzed without problems. Be aware that when measuring the baud rate of codes
using code words which have a non-integer number of bits, e.g. asynchronous 7.5-bit ITA-2, the indicated
baud rate will increase by a factor two.
WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5 Analysis Tools 73
Page 84

Waterfall Window
To open the waterfall window, move the mouse to the left of the extreme right of the graph window. The
normal cursor will turn into a splitter - two parallel lines with arrows perpendicularly attached. Now, hold
and drag to place the boundary between the windows where you wish, when the mouse button is released.
The waterfall windows are two-dimensional displays of baud rate and spectrum versus time. The color intensity of the displays represents the energy density of the spectrum, and the value of the relative occurrence of a baud rate - for gray scale values, white is the highest intensity and black the lowest. A time
stamp points to the latest sample taken. The latest sample is color inverted to distinguish it from the previous samples.
If the user wishes to examine a particular sample, it may be selected in the waterfall window. The sample
is marked with the time cursor, cursors are placed in the graph window and updating is halted in that window.
FSK Analysis Options
To assist in the measurement of noisy signals, a peak measurement function and an averaging function
are available. When one of these options is selected the last five samples will be used for calculations. The
result is displayed in the graph window. The user may also select a larger time span as basis for calculations from anywhere in the waterfall window.
MEASURE PEAK AND AVERAGE VALUES
Select the function you wish to use from the Options menu. A checkmark is shown to the left of the option selected and five samples are inverted in the waterfall window selected to indicate the number of
samples used for the calculations.
If you wish to use a different number of samples in the calculation, place the mouse on the waterfall sample from which calculation should start, and hold and drag the mouse over as many samples as you want
to use.
The marked samples will be color inverted, cursors will appear in the graph window and the graph display
will show the average or peak value of the marked samples.
To disable peak or average measurement, uncheck it in the Options menu: the cursors will disappear, only one sample is marked in the waterfall window, and updating of the graph window will resume.
EXAMINE SAMPLE, DISPLAY CURSORS
Click on the baudrate or the spectrum graph window to display the cursors, or click on the sample in the
waterfall window that you wish to examine. Graph window updates will stop and a pair of cursors will appear. You may move the cursors along the x-axis in normal Windows fashion. The matching waterfall
sample is marked with the time cursor.
Click on the graph window again to remove the cursors and resume graph window updates.
74 Analysis Tools WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5
Page 85

Right-click with the mouse into the spectrum
or baudrate graph pane (upper panes) and select if you like to Zoom 2X or or to Zoom 4X.
To adjust the frequency scale, move the cursor into the range of the frequency scale. If
you see the “Hand”, press the left mouse button and move the frequency slider.
Zoom
FSK Code Check
The purpose of the FSK Code Check is to automatically identify the mode of transmission, baud rate, frequency shift and center frequency.
FSK Code Check HF
FSK code check is started in automatic mode by selecting the Analysis | Code Check button or from HFModes | Analysis | FSK Code Check. This function has a high degree of accuracy when determining
baud rate, frequency shift and center frequency of HF FSK systems.
As an additional aid, FSK code check also offers an option to start the analysis manually after user entry of
baud rate, frequency shift and center frequency. To utilize this option the Auto button must be deselected. The software will then start data acquisition using the pre-selected parameters. If a pre-selected parameter has been changed data acquisition is atomatically restarted.
The selection of baud rate, frequency shift or center frequency is done by clicking on the status bar fields
or using the Demodulator menu.
If the FSK code check cannot identify a mode, the code check should be repeated. Data acquisition is continuously performed as a background task. Heavy fading or other disturbances during data acquisition
may prevent the identification of a mode.
You can also restart data acquisition by pressing the Resync button
The 1.5 stop elements used in many Baudot transmissions will often prevent the correct determination of
the signal baud rate, or the baud rate will be calculated as twice its actual value. Distorted stop elements
may also lead to completely erroneous baud rate calculations. To prevent this malfunction, measurements
of Baudot transmissions take place using the standard speeds of 45.45, 50, 75, 100, 150 and 180 Baud, in
addition to the measured baud rate.
WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5 Analysis Tools 75
Page 86

Steps:
After starting the FSK code check the frequency shift, center frequency and baud rate are deter-
mined. The values of these parameters are displayed in the appropriate fields after measurement
has finished.
The software then proceeds with code and system analysis. The incoming bit stream is tested
against known modes. For some modes using a high interleaving depth (e.g. RUM-FEC) large
quantities of input data are required. These modes therefore require longer to test and are tested
last.
The name of each identified system is displayed in the output window. An identified system may
be immediately started by double-clicking the system in the output window - for instance doubleclicking BAUDOT ITA-2 in the figure above will interrupt FSK code checking and immediately start
BAUDOT ITA-2.
The Hits-Checks will show you how often during checking a mode was successfully determined. If
multiple modes are listed this will indicate which mode should be tried.
Some modes are very difficult to distinguish, especially when the system is in idle mode. The de-
coded text including text representations of the special characters IDLE ALFA, IDLE BETA and RQ
are important additional classification aids in determining the mode under examination.
If a mode is uniquely identified, the software will switch to the identified mode and decoding is ini-
tiated with the measured values of mode, baud rate, shift, and center frequency.
If two or more different systems are identified or if too many transmission errors occur, an auto-
matic switch to a mode will not take place.
Fast Scan / Full Scan
The Scan Mode can be selected by Options | Scan Mode… or by double-clicking the Scan Mode field in
the Status Bar.
76 Analysis Tools WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5
Page 87

The software proceeds to create a list of modes to check, which is displayed in the Code Check window.
The content of this list depends on the selection of the Fast Scan or Full Scan options.
In Fast Scan mode, the list only contains the modes which are known to use the measured baud
rate, to reduce the evaluation time.
In Full Scan every mode which is suitable for an FSK code check is listed, and all possible combi-
nations are checked.
FSK Code Check DIR
FSK code check is started in automatic mode by selecting the Analysis | Code Check button or from
VHF/UHF-DIR | Analysis | FSK Code Check. This function has a high degree of accuracy when determining baud rate, frequency shift and center frequency of HF FSK systems.
As an additional help FSK code check also offers an option to start the analysis manually after user entry
of baud rate, frequency shift and center frequency. To utilize this option the Auto button must be deselected. The software will then start data acquisition using the pre-selected parameters. If a pre-selected
parameter has been changed data acquisition is atomatically restarted.
The selection of baud rate, frequency shift or center frequency is done by clicking on the status bar fields
or using the Demodulator menu.
If the FSK code check cannot identify a mode, the code check should be repeated. Data acquisition is continuously performed as a background task. Heavy fading or other disturbances during data acquisition
may prevent the identification of a mode.
You can also restart data acquisition by pressing the Resync button.
Because this kind of signal is not continuous, there is a need for a Noise Gate. The status of the noise
gate is displayed in the status bar; it examines the input signal and tries to determine if a valid signal is
available which can be processed, or if the input consists only of noise.
Steps:
After starting the FSK code check the frequency shift, center frequency and the baud rate are de-
termined. The values of these parameters are displayed in the appropriate fields after the measurement has completed.
The software then proceeds with code and system analysis. The incoming bit stream is tested and
compared against known modes.
WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5 Analysis Tools 77
Page 88

The name of each identified system is displayed in the output window. An identified system may
be immediately started by double-clicking the system in the output window - for instance doubleclicking ACARS in the figure above will interrupt FSK code checking and immediately start ACARS.
The Hits-Checks will show you how often during checking a mode was successfully determined. If
multiple modes are listed this will indicate which mode should be tried.
If a mode is uniquely identified, the software will switch to the identified mode and decoding is ini-
tiated with the measured values of mode, baud rate, shift, and center frequency.
If two or more different systems are identified or if too many transmission errors occur, an auto-
matic switch to a mode will not take place.
Noise Gate Mode…
The Noise Gate Mode can be selected by Options | Noise Gate Mode… or by double-clicking the Noise
Gate Mode field in the Status Bar.
In Enabled mode, a Noise Gate is used. This is necessary as this kind of signal is not continuous.
The noise gate examines the input signal and tries to determine if a valid signal is available which
can be analyzed, or if the input consists only of noise.
In Disabled mode the Noise gate is switched off.
FSK Code Check SUB
FSK code check is started in automatic mode by selecting the Analysis | Code Check button or from
VHF/UHF-SUB | Analysis | FSK Code Check. This function has a high degree of accuracy when determining baud rate, frequency shift and center frequency of HF FSK systems.
As an additional help FSK code check also offers an option to start the analysis manually after user entry
of baud rate, frequency shift and center frequency. To utilize this option the Auto button must be deselected. The software will then start data acquisition using the pre-selected parameters. If a pre-selected
parameter has been changed data acquisition is atomatically restarted.
The selection of baud rate, frequency shift or center frequency is done by clicking on the status bar fields
or using the Demodulator menu.
If the FSK code check cannot identify a mode, the code check should be repeated. Data acquisition is continuously performed as a background task. Heavy fading or other disturbances during data acquisition
may prevent the identification of a mode.
You can also start a new data acquisition by pressing the Resync button.
As this kind of signal is not continuous, a Noise Gate is required. The status of it is displayed in the status
bar. The noise gate examines the input signal and tries to find out, if a valid signal is available which can
be processed or if the input consists only of noise.
78 Analysis Tools WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5
Page 89

Steps:
After starting the FSK code check, the frequency shift, center frequency and the baud rate are de-
termined. The values of these parameters are displayed in the appropriate fields after the measurement has completed.
The software then proceeds with code and system analysis. The incoming bit stream is tested and
compared against known modes.
The name of each identified system is displayed in the output window. An identified system may
be immediately started by double-clicking the system in the output window - for instance doubleclicking ACARS in the figure above will interrupt FSK code checking and immediately start ACARS.
The Hits-Checks will show you how often during checking a mode was successfully determined. If
multiple modes are listed this will indicate which mode should be tried.
If a mode is uniquely identified, the software will switch to the identified mode and decoding is ini-
tiated with the measured values of mode, baud rate, shift, and center frequency.
If two or more different systems are identified or if too many transmission errors occur, an auto-
matic switch to a mode will not take place.
Noise Gate Mode…
The Noise Gate Mode can be selected by Options | Noise Gate Mode… or by double-clicking the Noise
Gate Mode field in the Status Bar.
In Enabled mode, a Noise Gate is used. This is necessary as this kind of signal is not continuous.
The noise gate examines the input signal and determines if a valid signal is available which can be
analyzed, or if the input consists only of noise .
In Disabled mode the Noise gate is switched off.
WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5 Analysis Tools 79
Page 90

PSK Symbol Rate (HF, DIR, SUB, SAT)
When starting PSK signal analysis, one is trying to determine the characteristics of an unknown signal.
The normal starting point for this is the FFT.
The FFT is used to determine an estimate of the signal center frequency and signal bandwidth. This should
be done by adjusting the measurement cursors. The phase analysis tools inherits the information determined by the measurement cursors, and uses this information to configure the center frequency and
bandwidth. This in turn sets up a pre-filter, allowing the tools to be used for signals disturbed by out-ofband interference, or when more concurrent channels are present.
To determine the symbol rate, a PSK symbol rate analysis tool is provided. This tool provides a spectrum
display (with three zoom levels) and allows the measurement of the symbol rate using cursors. A PSK signal will normally produce multiple peaks. Normally (but not always) the symbol rate (or baud rate) will be
a distinct peak at the highest amplitude. The other peaks are normally fractions of the true symbol rate.
Zoom
For signals with low symbol rates, select a different zoom factor by using the menu which appears when
right-clicking the display. Note that the lower scales have a higher precision, but at the expense of a lower
display rate.
Filter
The filter adjusts the smoothing filtering applied to the display. Depending on the signal data content, it
may be found that more filtering is required to clearly observe the peaks.
80 Analysis Tools WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5
Page 91

PSK Phase Plane (HF, DIR, SUB, SAT)
The phase analysis tool is used for analyzing the characteristics of phase modulated signals, and to a limited extent, m-ary PAM (Phase Amplitude Modulation) signals.
If the symbol rate is known (for details see “PSK Symbol Rate (HF, DIR, SUB, SAT)” on page 80), start the
PSK phase plane analysis tool.
The display can be started and stopped by clicking on it. If stopped, a Paused message is displayed.
You can use an existing demodulator (BPSK, QPSK or DPSK) or IQ to decode the signal, and produce a
phase plane display of the output of the demodulator. For BPSK and QPSK, this provides a check of the
quality of the signal. When using DPSK, this provides an indication of the level of phase modulation which
is being used, i.e. 2-PSK to 16-PSK. As the symbol rate is equal to the baud rate of the signal, the baud
rate must be known to configure the demodulator.
Center
The Center allows the center frequency for the demodulator to be adjusted. A center frequency error normally results in a phase plane that is rotating with a speed proportional to the frequency error.
Hold Time
The Hold Time adjusts the number of points displayed on the screen. Increasing the hold time increases
the amount of time a dot will remain in the image before being overwritten by a new value.
WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5 Analysis Tools 81
Page 92
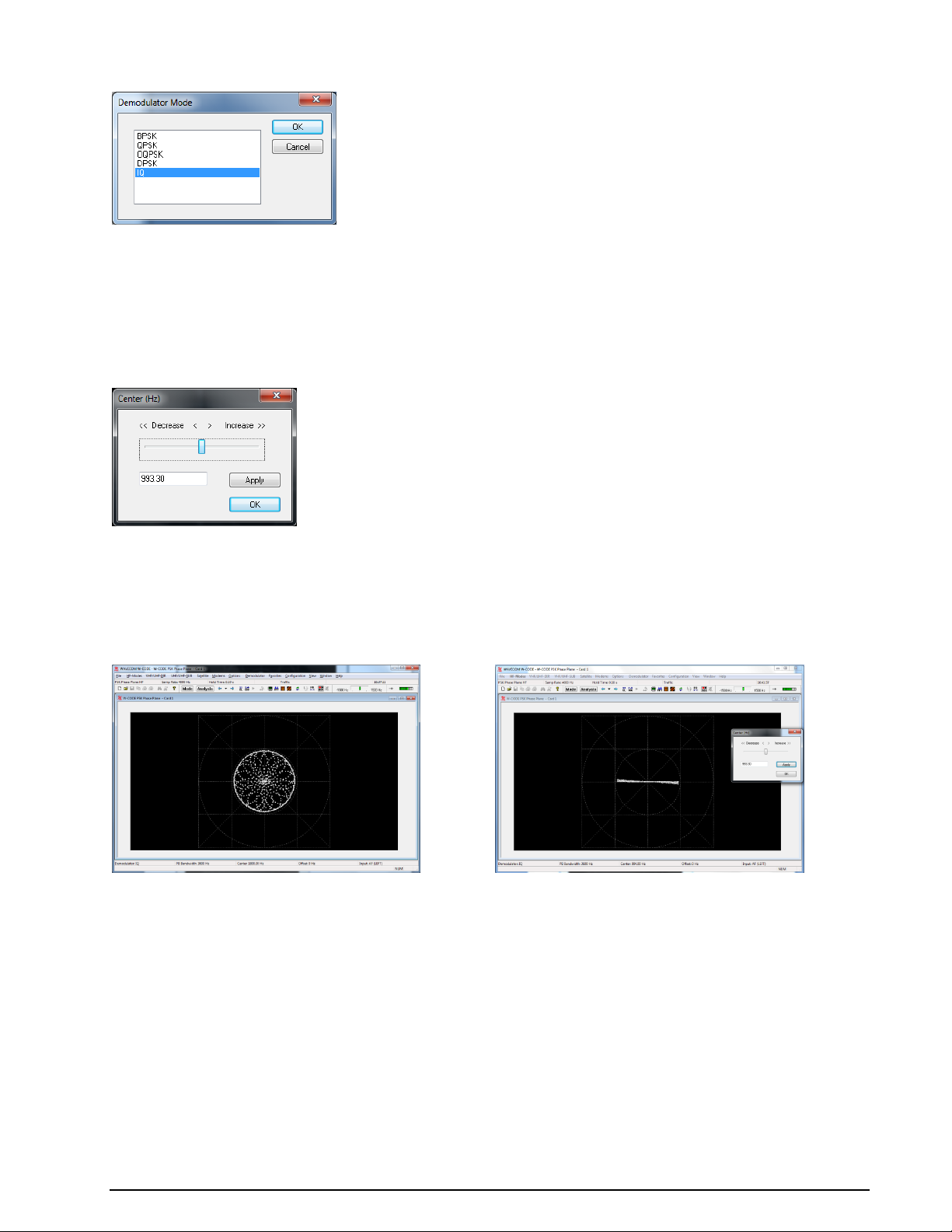
Incorrect settings
Correct settings
Demodulator Mode
If you select IQ as the demodulator, the signal is not demodulated at all. Instead, the phase of the signal
is visually 'compared' with a reference signal. Providing the correct reference signal is selected, this will
result in a phase display that provides an indication of the type of PSK or PAM signal. The points will trace
the path taken as the signal phase change. At the nominal signal mapping points, there is normally an accumulation of data points, providing a visual clue to the overall signal mapping.
Multi-channel DPSK signals often have a very narrow channel signal bandwidth. This results in the phase
of the signal never remaining constant, and so the accumulation of signal points in the phase plane is not
visible. To quantify such signals use the IQ demodulator mode.
The frequency of the reference signal is set using the Center option. Note that if the reference frequency
is incorrect, the display rotates at a rate that is the difference between the reference frequency and the
true carrier frequency of the signal. When adjusting the reference signal, the changes are 'live'. This
means that changes you make immediately take effect, and the resulting change in the phase display is
immediately visible on the display.
Several Color schemes for both tools are available through the right-click menu.
In summary, the basic steps for analyzing a suspected (D)PSK signal are as follows:
Use the FFT in the PSK Symbol Rate analysis tool to characterize the signal. Use the cursors to
configure the estimate of the center frequency and bandwidth.
Use the PSK Symbol Rate analysis tool to measure and select the symbol rate of the signal.
Try and view the phase plane of the signal using the DPSK demodulator. If the signal is a PSK sig-
nal, the phase plane should be visible.
If the DPSK demodulator failed to produce a meaningful display, try the IQ demodulator. This re-
quires accurate adjustment of the reference signal to produce a meaningful display.
82 Analysis Tools WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5
Page 93

PSK CODE CHECK (HF, DIR, SUB)
PSK code check is started by selecting the PSK Code Check button or from HF-Modes | Analysis | PSK
Code Check.
The PSK code check is initialized with default values. In many cases the user needs to set up the following
values:
center frequency
baudrate
number of channels
bandwidth (use the pb tuning to enter the correct bandwidth
The center frequency can be set by using the cursors in the FFT Window as shown below, or by selecting
Center in the Demodulator menu. The baud rate can also be configured.
The number of channels is set to one for all single channel modes and to two for two channel modes like
PACTOR II/II-FEC. Modes with more than one channel need the shift settings in addition to the center frequency.
Note: The accuracy of the center frequency and shift settings is very important and directly influences the
performance of the decoding.
After each configuration change, the PSK code check automatically restarts with the new values. The values of these parameters are displayed in the appropriate fields after the setting has completed.
If two or more different systems are identified, or if more than five proven transmission errors occur, an
automatic switch to a mode will not take place.
The software then proceeds with code and system analysis. The incoming bit stream is tested and compared against known PSK modes.
The name of each identified system is displayed in the output window. An identified system may be immediately started by double-clicking the system in the output window – for instance double-clicking PSK-31
in the figure above will interrupt PSK code checking and immediately start PSK-31.
Hits-Checks shows how many times a mode was successfully identified during the code check. If multiple
modes are listed, the mode with most hits should be tried first.
Some modes are very difficult to distinguish, especially when the system is in idle mode.
WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5 Analysis Tools 83
Page 94

MIL-STANAG Code Check
The MIL/STANAG code check analysis tool is used to determine whether a signal is one of the following
MIL/STANAG and related transmission modes:
HF-ACARS
MIL-188-110A
MIL-188-110B
MIL-188-141B
STANAG-4285
STANAG-4529
STANAG-4415 is a sub-mode of MIL-188-110A and is detected as this mode. STANAG-4481 is a sub-mode
of STANAG-4285 and is detected as this mode.
This analysis feature can be started from the HF-Modes | Analysis | MIL-STANAG Code Check menu,
from the Analysis Selector.
The center frequency can be set by the user. The default value for the code check is 1800 Hz, as shown in
the user interface. The center frequency of HF-ACARS (1440 Hz) can be selected from a list. After the center frequency is set, the code check searches for the mode within a range of ± 100 Hz of the center frequency. Although HF-ACARS may have a center frequency of 1440 Hz, it can also be detected when the
code check is set with center 1800 Hz.
Apart from HF-ACARS, which has a baud rate of 1800, all other MIL and STANAG modes operate at 2400
baud. However, the code check can automatically determine modes with different baud rates.
After the code check has determined a mode, the mode name is displayed in the text window. The confidence parameter shows how good the match is, the highest possible value being 100%. When confidence
is greater than 90%, the code check automatically switches to the corresponding mode decoder using the
corrected center frequency.
MFSK Analysis
The MFSK analysis for the HF signal range employs a graphical display in two dimensions, frequency (yaxis) and time (x-axis). Both values may be preset. This tool was originally developed for the analysis of
analogue tone call systems, but is equally suitable for evaluation of FSK and MFSK systems. In particular
the frequency and element duration is well displayed.
84 Analysis Tools WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5
Page 95
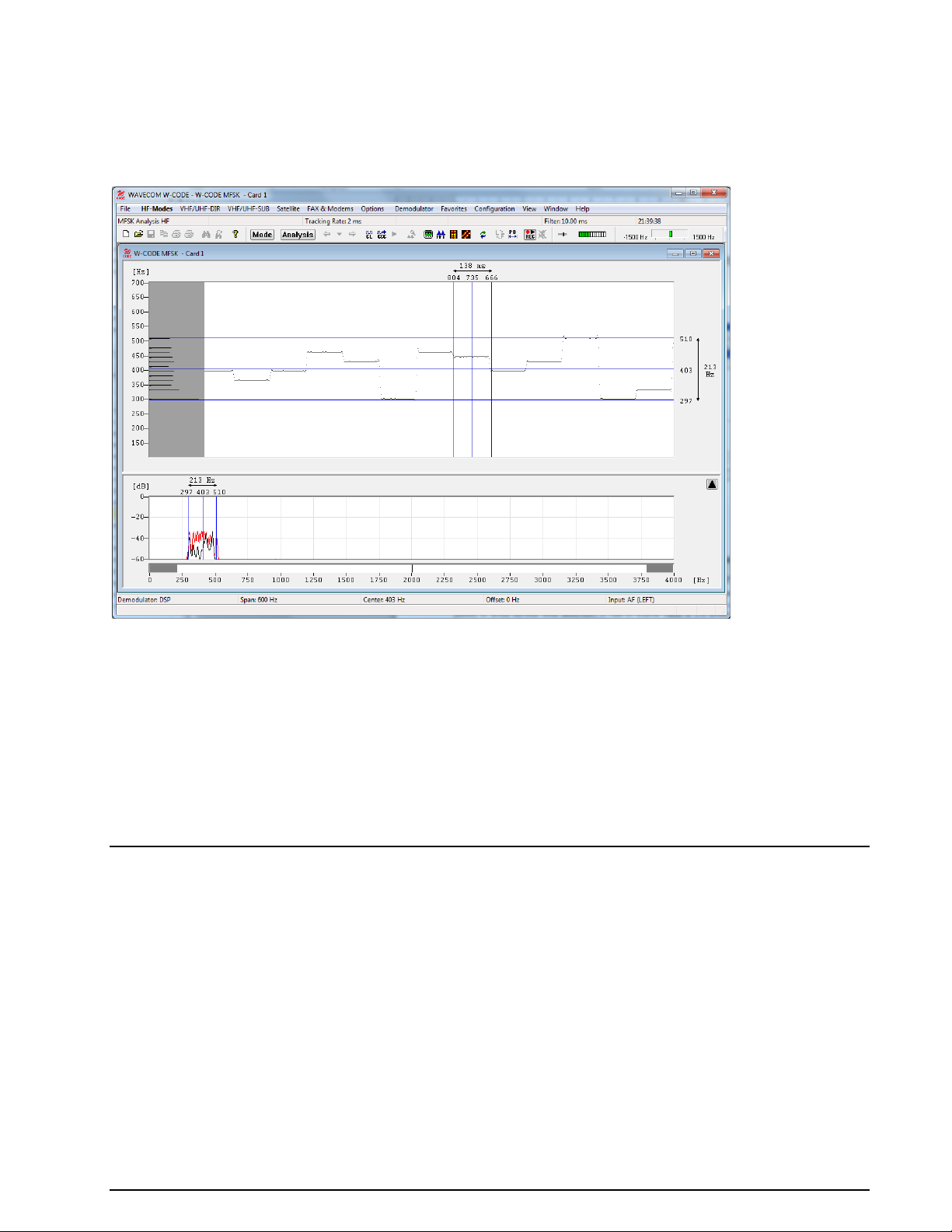
After starting MFSK Analysis the detected frequency values are displayed as pixels.
A monitored MFSK signal is easily recognized as stable lines. To stop the display from scrolling horizontally, click on the display. Measurement cursors for both the time axis and the frequency axis appear. The
display may be scrolled backwards, with a maximum range of 15 seconds when tracking rate is set to 1
ms, and 225 seconds when the tracking rate is set to 15ms. The scroll-back range for all tracking rate settings in between varies accordingly.
Tracking rate determines the sampling rate. The range is 1 - 15 ms; the default is 2 ms.
Double-clicking Filter inserts a low pass filter for filtering the tones. The value of the filter should be adjusted to avoid serious tone distortion. A rule-of-thumb value is 1.6 times the baud rate.
The filter range is 1 - 100 ms.
Using the Span menu, the resolution of the frequency axis may be increased. The steps are 3000 Hz (for
analogue selective calling systems), 1500, 600 and 300 Hz.
From the Center menu, the center frequency may be adjusted. It is important to readjust the center frequency whenever the frequency (Span) axis is increased.
Several Color schemes are available through the right-click menu.
MFSK Code Check HF
MFSK code check is started by selecting the Analysis | MFSK Code Check button or from HF-Modes |
Analysis | MFSK Code Check.
The MFSK code check starts with default values.
In many cases the user needs to set the following values:
center frequency
baudrate (1/tone length)
number of channels
bandwidth (use the PB tuning to enter the correct bandwidth)
WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5 Analysis Tools 85
Page 96

The center frequency and bandwidth can be set by using the cursors in the FFT Window, as shown below
or by selecting Center, in the Demodulator menu. The baud rate and the Number of Channels/Tones
can also be configured.
Note: The accuracy of the center frequency and shift settings are critical, and directly influence the quality
of the decoding.
After each configuration change, the MFSK code check automatically restarts with the new values. The
values of these parameters are displayed in the appropriate fields after changes have been made.
If two or more different systems are identified, or if more than five proven transmission errors occur, an
automatic switch to a mode will not take place.
The software then proceeds with code and system analysis. The incoming bit stream is tested and compared against known MFSK modes.
The name of each identified system is displayed in the output window. An identified system may be immediately started by double-clicking the mode name in the output window – for instance double-clicking
COQUELET-13 in the figure above will interrupt MFSK code checking and immediately start COQUELET-13.
Hits-Checks shows how many times a mode was successfully identified during the code check. If multiple
modes are listed, the mode with most hits should be tried first.
Some MFSK modes are very difficult to distinguish, especially when the system is in idle mode.
Autocorrelation
Autocorrelation is used for determining the periodicity of bit patterns. Periodicity implies a constant repetition of a specific bit pattern. If a station transmits the idle pattern 0010011011 0010011011..., the periodicity is said to be 10 bits. HNG-FEC and RUM-FEC have a periodicity of 15 and 16 bits respectively. The
periodicity could also be 11250 bits, i.e. after 11250 bits the same constantly repeated pattern occurs
again. Periodicity becomes very important in the classification of unknown transmissions and the analysis
of unknown modes and systems.
First of all, the Auto option from the Demodulator menu field or the Auto button should be used to determine the exact baud rate and frequency shift. If the exact baud rate is unknown, the IAS measurement
86 Analysis Tools WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5
Page 97

function can be used for this purpose with an accuracy of 0.001 Bd. This is done by activating the IAS setting in the Demodulator menu field. Autocorrelation is then initiated by selecting and programming the
baud rate menu field. If the baud rate deviates by more than 0.5 Baud, a bit slip may occur and therefore
the autocorrelation must be restarted with the exact baud rate.
To start the sampling process, press the Start button. The number of sampled bits is continuously displayed. Autocorrelation can currently process up to 200,000 bits.
By pressing the Correlate button, the actual computation of the autocorrelation is started. Results are
displayed graphically. If a large number of bits have been sampled and the graph indicates a low periodicity, the computation may be stopped by pressing the Stop button. Periodicity is indicated by distinct peaks
in the graphic display, which may exhibit various characteristics:
A large number of closely spaced vertical lines indicates a very small period (7 to 15 bits).
Small and asymmetric peaks indicate that a distinct periodicity is not present. The presence of
such small peaks may however be an indication of a very long period.
In the case of a very "noisy" graph, periodicity cannot be determined without the zoom function.
Such measurements indicate the fact that the system is transmitting data (traffic state). The user
should then wait for an idle state or for some request (RQ) cycles for closer examination.
The graphic display only shows approximate wave forms. This peculiarity is often evident in the
case of simplex systems, however an approximate determination is still possible.
In the case of a horizontal line without any peaks or deviations, no periodicity may be deduced, or
the period is much larger than the total number of sampled data bits.
Each mode and each signal can produce very different displays. Often, it is possible to determine a periodicity with the zoom function.
For FSK signals the polarity is changed from the menu Options | Signal Polarity, and then using the
buttons in the window shown. For more information see “Signal Polarity” on page 35.
For PSK signals the configuration of the symbol definition is in the menu Options | Symbol Definition.
For more information see “Symbol Definition” on page 35.
By selecting Zoom In, the mouse cursor changes its shape. By clicking and dragging, a field can be enlarged or reduced horizontally and vertically. The field should be sized in such a way that the peaks fill out
the zoom field optimally.
WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5 Analysis Tools 87
Page 98
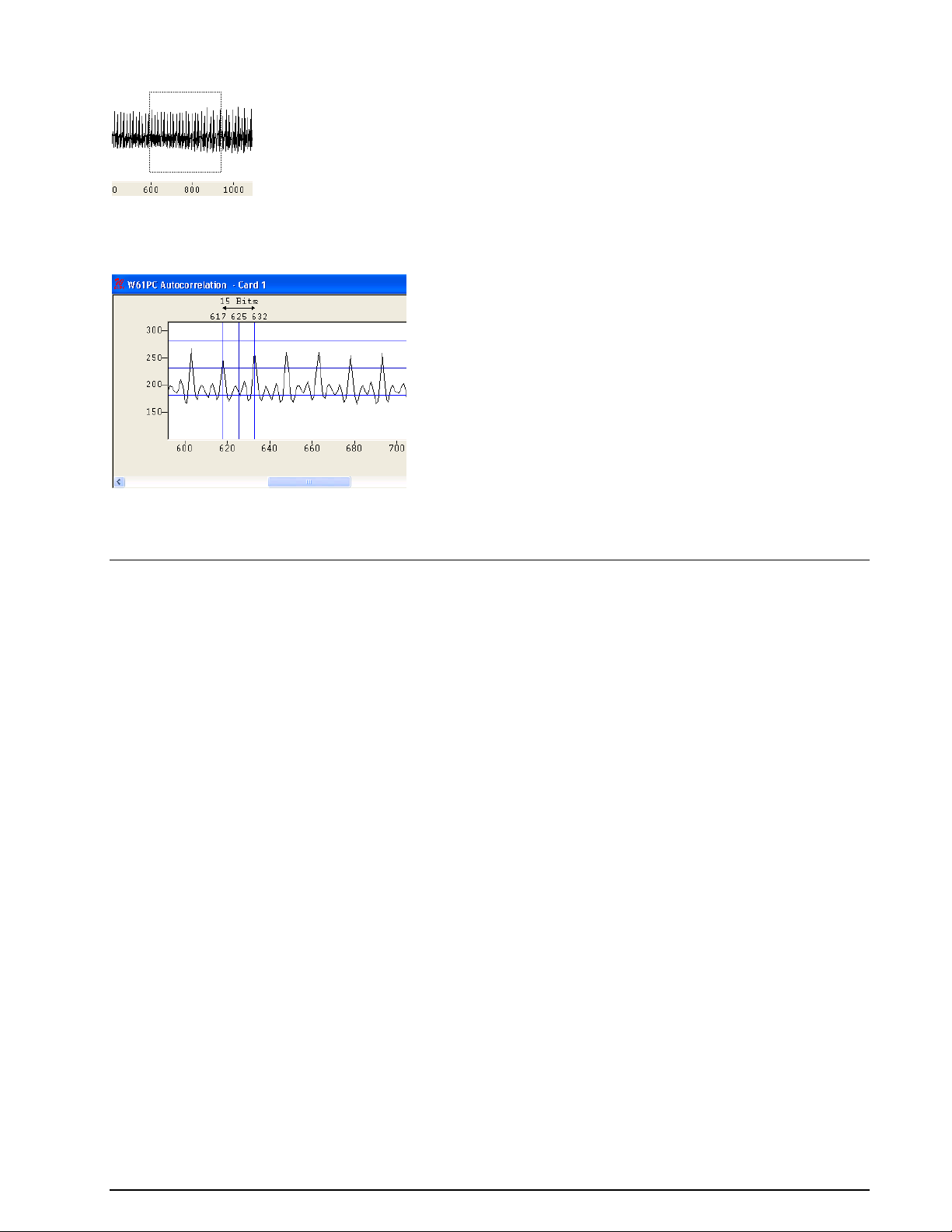
After the zoom field has been sized, release the mouse button. An enlarged section of the autocorrelation
trace is displayed.
The distance between recurring, equidistant peaks gives the periodicity of the signal under investigation.
By selecting Zoom 100% the full screen display will reappear.
Several Color schemes are available through the right-click menu.
BIT CORRELATION
The bit correlation and bit length analysis tools allow the measurement of bit length. Bit length analysis
relies on a statistical evaluation of many individual measurements, whereas the bit correlation function
displays the data of the V1 channel graphically.
The data for bit correlation is sampled and displayed with respect to time. Thus pulse and tone duration
lengths as well as bit bias may be measured. The bit correlation analysis also allows the accurate determination of baud rates in the case of asynchronous systems with bit errors and propagation dependent distortions.
88 Analysis Tools WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5
Page 99

The time duration of a video line, and thus the display resolution, is set with the sliders in Time per Line.
The range is 20,000 s (0.02 s) to 10,000,000 s (10 s) per graphical line and sampling takes place in
steps of 14 s. One graphical display line corresponds to the preset time.
Selecting the Start/Stop button controls the effective data sampling.
By moving the mouse cursor a text field is displayed. The value of the positioned segment is continuously
displayed in microseconds (s) and in Baud (Bd) with the graphical cursor. The graphical representation of
V1 channel polarity (mark or space) corresponds to the value of the displayed time and the converted
baud rate.
Also the correlation can be determined by using bit correlation. The number of time units per line set in
Time per Line in addition to the baud rate, constitute the preset values for the correlation.
The following example shows a correlation of 111 bits. The baud rate is 228.66 Bd. Hence the calculation
of the total system cycle length is (1/228.66) x 111 = 0.4854369 s.
By right-clicking on the display a menu appears. By selecting Zoom In, the mouse cursor changes its
shape. By clicking and dragging a field can be enlarged or reduced horizontally and vertically. After the
zoom field has been sized, release the mouse button. An enlarged section of the bit correlation is now displayed.
WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5 Analysis Tools 89
Page 100

Additionally, several Color schemes are available through the right-click menu.
BIT LENGTH ANALYSIS
Bit length analysis serves to determine baud rate distributions, tone duration or bit length distributions.
The resolution offered by the sampler option is 14 s (72,000 samples per second). After the demodulator
has been correctly set up either manually or by using the auto function, sampling is initiated by pressing
the Start button. To stop sampling, the Stop button is pressed. Captured data may then be further analyzed.
A screen with two graphs is displayed. The following example shows a typical bit length display screen.
90 Analysis Tools WAVECOM Decoder W61PC/LAN Manual V7.5
 Loading...
Loading...