Page 1

USER GUIDE
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
Reference: WI_DEV_CM52_UGD_001
Version: 001
Date: June 20, 2007
Page 2
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
Trademarks
®, WAVECOM®, WISMO®, Open AT®, Wireless CPU®, Wireless Microprocessor® and certain other trademarks and
logos appearing on this document, are filed or registered trademarks of Wavecom S.A. in France or in other
countries. All other company and/or product names mentioned may be filed or registered trademarks of their
respective owners.
Copyright
This manual is copyrighted by WAVECOM with all rights reserved. No part of this manual may be reproduced in
any form without the prior written permission of WAVECOM.
No patent liability is assumed with respect to the use of the information contained herein.
No Warranty
This document is provided “as is” without any warranty of any kind. WAVECOM makes no warranties of any kind,
either express or implied, including any implied warranties of merchantability, fitness for a particular purpose or
noninfringement.
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
WI_DEV_CM52_UGD_001-001
Page 2 of 53
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à des tiers sans son autorisation préalable
Page 3

CM52 Integrators’ Manual
Table of Contents
1 Introduction to the Integrator’s Manual............................................................ 9
1.1 OVERVIEW............................................................................................................................... 9
1.2 HOW TO READ THE MANUAL ................................................................................................... 9
1.3 SERVICE AND SUPPORT............................................................................................................ 9
1.3.1 WEB PAGES ......................................................................................................................... 9
1.4 RELATED DOCUMENTS .......................................................................................................... 10
1.5 ABBREVIATIONS..................................................................................................................... 10
2 Integrating the CM52 Wireless CPU®............................................................... 11
2.1 OVERVIEW............................................................................................................................. 11
2.2 MECHANICAL DESCRIPTION ................................................................................................... 11
2.2.1 MECHANICAL DIMENSIONS .......................................................................................... 11
2.2.2 HEAT-SINK REQUIREMENTS ......................................................................................... 16
2.2.3 MOUNTING HOLES ...................................................................................................... 16
2.2.3.1 MOUNTING CONFIGURATION A ................................................................................... 16
2.2.3.2 MOUNTING CONFIGURATION B.................................................................................... 17
2.2.4 RF CONNECTOR MOUNTING CONSIDERATIONS............................................................ 17
2.3 SYSTEM CONNECTOR INTERFACE........................................................................................... 18
2.3.1 MECHANICAL OVERVIEW.............................................................................................. 18
2.3.2 SYSTEM CONNECTOR INTERFACE PINOUT.................................................................... 19
2.3.3 LOGIC LEVELS ............................................................................................................. 21
2.3.3.1 LEAKAGE CURRENT FOR CMOS SIGNALS ...................................................................... 21
2.3.3.2 VALIDITY OF CMOS SIGNALS ....................................................................................... 21
2.4 POWER SUPPLY...................................................................................................................... 21
2.4.1 POWER SUPPLY INPUT CAPACITANCE ........................................................................... 22
2.4.2 POWER SUPPLY AND GROUND SIGNALS........................................................................ 23
2.4.2.1 POWER SUPPLY SIGNAL PINS ........................................................................................ 23
2.4.2.2 GROUND SIGNAL PINS ................................................................................................. 23
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
WI_DEV_CM52_UGD_001-001
Page 3 of 53
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à des tiers sans son autorisation préalable
Page 4

CM52 Integrators’ Manual
2.4.3 POWER CONSUMPTION................................................................................................ 23
2.4.3.1 VCC_MAIN SUPPLY POWER CONSUMPTION................................................................... 24
2.4.3.2 VCC_AUX SUPPLY POWER CONSUMPTION..................................................................... 24
2.4.3.3 POWER DOWN MODE (MINIMUM DC POWER CONSUMPTION) ........................................ 25
2.4.4 VREF SIGNAL DETAILS ................................................................................................. 25
2.5 REAL TIME CLOCK (RTC) CIRCUIT........................................................................................... 26
2.5.1 RTC INITIALIZATION.................................................................................................... 26
2.5.2 RTC FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM............................................................................. 26
2.6 AUDIO INTERFACE................................................................................................................. 27
2.6.1 DIGITAL AUDIO ........................................................................................................... 28
2.6.1.1 DATA FORMAT............................................................................................................ 28
2.6.1.2 TIMING ....................................................................................................................... 29
2.6.2 ANALOG AUDIO .......................................................................................................... 30
2.7 SERIAL DATA INTERFACE ....................................................................................................... 33
2.8 ANTENNA INTERFACE............................................................................................................ 33
2.8.1 ANTENNA CONNECTOR............................................................................................... 34
2.8.2 RF OUTPUT POWER...................................................................................................... 35
2.8.3 CARRIER APPROVAL .................................................................................................... 36
2.8.4 ANTENNA DIAGNOSTICS ............................................................................................. 36
3 Recommended Interface Circuitry................................................................... 38
3.1 STATUS GROUP RECOMMENDED CIRCUITRY........................................................................... 38
3.1.1 MODULE_PWR_EN_B .................................................................................................... 39
3.1.2 VREF ........................................................................................................................... 39
3.1.3 RI ............................................................................................................................... 40
3.1.4 HW_SD........................................................................................................................ 40
3.2 DATA GROUP RECOMMENDED CIRCUITRY.............................................................................. 42
3.2.1 VPPFLASH/DCD........................................................................................................... 42
3.3 PCM GROUP RECOMMENDED CIRCUITRY................................................................................ 43
3.4 ANALOG AUDIO GROUP RECOMMENDED CIRCUITRY .............................................................. 44
3.4.1 CREATING AN ANALOG GROUND................................................................................. 44
3.4.2 ANALOG GROUND VS. AGND....................................................................................... 45
3.4.3 MICROPHONE PATH .................................................................................................... 45
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
WI_DEV_CM52_UGD_001-001
Page 4 of 53
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à des tiers sans son autorisation préalable
Page 5

CM52 Integrators’ Manual
3.4.4 LOUDSPEAKER PATH ................................................................................................... 46
3.5 SYSTEM CONNECTOR IO FUNCTIONALITY .............................................................................. 47
4 Functional Description ................................................................................... 49
5 Hints for Integrating the Wireless CPU®.......................................................... 50
5.1 PRECAUTIONS ....................................................................................................................... 50
5.2 WHERE TO INSTALL THE WIRELESS CPU®................................................................................. 50
5.3 SAFETY STANDARDS.............................................................................................................. 50
5.4 ANTENNA.............................................................................................................................. 51
5.4.1 ANTENNA TYPE ........................................................................................................... 51
5.4.2 ANTENNA PLACEMENT ................................................................................................ 51
5.5 POSSIBLE COMMUNICATION DISTURBANCES .......................................................................... 51
6 Technical Data ............................................................................................... 52
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
WI_DEV_CM52_UGD_001-001
Page 5 of 53
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à des tiers sans son autorisation préalable
Page 6

CM52 Integrators’ Manual
List of Tables
TABLE 1: ABBREVIATION DEFINITIONS ................................................................................................ 10
TABLE 2: SYSTEM CONNECTOR AND MATING PART NUMBERS ..................................................................... 18
TABLE 3: PIN-OUT OF THE SYSTEM CONNECTOR HEADER........................................................................... 20
TABLE 4: CMOS OUTPUT / INPUT ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS .............................................................. 21
TABLE 5: MAXIMUM LEAKAGE CURRENT FOR CMOS SIGNALS ..................................................................... 21
TABLE 6: CM52 POWER SUPPLY REQUIREMENTS .................................................................................... 22
TABLE 7: POWER SUPPLY INPUT CAPACITANCE (0.6W VARIANTS) ............................................................. 22
TABLE 8: POWER SUPPLY INPUT CAPACITANCE (3W VARIANTS) ................................................................ 22
TABLE 9: CM52 POWER SUPPLY SIGNALS............................................................................................. 23
TABLE 10: CM52 GROUND SIGNALS.................................................................................................... 23
TABLE 11: VCC_MAIN SUPPLY POWER CONSUMPTION ........................................................................... 24
TABLE 12: VCC_AUX SUPPLY POWER CONSUMPTION ............................................................................. 25
TABLE 13: MODULE_PWR_EN_B SIGNAL PARAMETERS ........................................................................... 25
TABLE 14: VREF SUPPLY DETAILS ...................................................................................................... 26
TABLE 15: FREQUENCY CHARACTERISTICS OF THE RTC............................................................................. 26
TABLE 16: CM52 AUDIO SIGNALS ...................................................................................................... 27
TABLE 17: CM52 DIGITAL AUDIO SIGNALS .......................................................................................... 28
TABLE 18: PCM TIMING PARAMETERS ................................................................................................. 29
TABLE 19: CM52 ANALOG AUDIO SIGNALS........................................................................................... 30
TABLE 20: AUDIO CHARACTERISTICS ................................................................................................... 30
TABLE 21: SERIAL DATA CHANNELS..................................................................................................... 33
TABLE 22: ANTENNA CONNECTOR SUPPLIERS ........................................................................................ 35
TABLE 23: MOBILE STATION NOMINAL ANALOG POWER LEVELS ................................................................. 36
TABLE 24: MOBILE STATION CDMA MAXIMUM OUTPUT POWER................................................................. 36
TABLE 25: RANGE OF ADC READINGS FOR AN EXTERNAL ANTENNA .............................................................. 37
TABLE 26: PIN DIRECTION FOR GENERAL PURPOSE SIGNALS..................................................................... 48
TABLE 27: TECHNICAL DATA .............................................................................................................. 53
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
WI_DEV_CM52_UGD_001-001
Page 6 of 53
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à des tiers sans son autorisation préalable
Page 7

CM52 Integrators’ Manual
List of Figures
FIGURE 1: CM52 PRIMARY SIDE ........................................................................................................ 11
FIGURE 2: CM52 SECONDARY SIDE..................................................................................................... 11
FIGURE 3: MECHANICAL DIMENSIONS DRAWING (CM52003 VARIANT) ...................................................... 12
FIGURE 4: MECHANICAL DIMENSIONS DRAWING (CM52001 AND CM52004 VARIANTS)................................ 13
FIGURE 5: MECHANICAL DIMENSIONS DRAWING (CM52002 VARIANT) ...................................................... 14
FIGURE 6: KEEP-OUT DRAWING OF CM52 ............................................................................................. 15
FIGURE 7: MOUNTING CONFIGURATION A ............................................................................................. 16
FIGURE 8: MOUNTING CONFIGURATION B ............................................................................................. 17
FIGURE 9: APPLICATION HOUSING ...................................................................................................... 17
FIGURE 10: 40-PIN SYSTEM CONNECTOR ............................................................................................. 18
FIGURE 11: 40-PIN SYSTEM CONNECTOR PIN NUMBERING....................................................................... 18
FIGURE 12: RTC FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM ..................................................................................... 27
FIGURE 13: PCM TIMING DIAGRAM .................................................................................................... 29
FIGURE 14: BIAS DIAGRAM EXAMPLE ................................................................................................. 31
FIGURE 15: MICROPHONE IMPLEMENTATION EXAMPLE............................................................................. 32
FIGURE 16: DIFFERENTIAL IMPLEMENTATION EXAMPLE............................................................................ 32
FIGURE 17: COLOR AND KEYING FOR VARIOUS FAKRA CONNECTORS .......................................................... 34
FIGURE 18: SAMPLE SMA CONNECTOR AND MOUNTING HOLE.................................................................... 35
FIGURE 19: ANTENNA DIAGNOSTIC CIRCUIT ......................................................................................... 37
FIGURE 20: STATUS GROUP DIAGRAM.................................................................................................. 39
FIGURE 21: PIN 15 HW_SD DIAGRAM................................................................................................ 40
FIGURE 22: SHUT DOWN SEQUENCE TIMELINE ....................................................................................... 41
FIGURE 23: DATA GROUP DIAGRAM .................................................................................................... 42
FIGURE 24: PCM GROUP DIAGRAM ..................................................................................................... 43
FIGURE 25: CREATING AN ANALOG REFERENCE VOLTAGE (BIAS)................................................................ 44
FIGURE 26: BIAS/VANA REFERENCE ................................................................................................. 44
FIGURE 27: MICROPHONE IMPLEMENTATION EXAMPLE............................................................................. 45
FIGURE 28: LOUDSPEAKER IMPLEMENTATION EXAMPLE ............................................................................ 46
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
WI_DEV_CM52_UGD_001-001
Page 7 of 53
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à des tiers sans son autorisation préalable
Page 8
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
Revision History
Release Date Summary of Changes
PA1 05/07/2004 Initial Draft
PA2 09/01/2004 Formatting
PA3 11/17/2004 Updated Chapters 1 & 2
PA4 11/29/2004 Updated with review feedback
PA5 12/01/2004 Updated the List of Tables and Figures
PA6 06/16/2005 Current Consumption Table, RTC Block Diagram, Mechanical
Drawing
A 09/15/2005 Release version
PB1 11/30/2005 Updates for VREF sourcing capability, inrush current, mechanical
mounting, recommended application circuitry and CMOS leakage
current.
PB2 02/16/2006 Update to Power consumption section & Formatting updates
PB3 03/08/2006 Updated mechanical drawings, Re-formatted Table 2, Added RTC
Frequency Characteristics.
PB4 03/16/2006 Updated Sections: 2.5 - Real Time Clock Circuit, 2.8.2 – RF Output
Power. Added section 3.1.3 – RI
PB5 03/22/2006 Updated Table of Contents.
Updated Sections: 3.1.3 – RI and 3.1.4 – HW_SD.
Removed the Random Stationary Vibration information from
Section 6 – Technical Data.
B 03/24/2006 Release Version
PC1 06/02/2006 Updated Vibration Specification and add Minimum Off-Time
PC2 06/13/2006 Added RTC Initialization section and reformatted Technical Data
table
001 06/20/2007 Update product references, Wavecom format
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
WI_DEV_CM52_UGD_001-001
Page 8 of 53
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à des tiers sans son autorisation préalable
Page 9

1 Introduction to the Integrator’s Manual
1.1 Overview
This manual is for use as a guide to the setup, installation, and use of the CM52 Wireless CPU® into
®
your application. The Wireless CPU
together with all the necessary tools in the Developer’s Kit.
1.2 How to Read the Manual
This manual is divided into six chapters:
Chapter 1 gives a general view of the integrator’s manual. A list of related documents as well as a
list of abbreviations used throughout the manual is also included. Information concerning service
and support is also presented.
may be tested using the developer’s board, which is supplied
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
Chapter 2 focuses on helping the hardware developer to integrate the CM52 hardware into their
application. An overview of the mechanical and electrical information is provided. Interface
specifications, RF output power, and power supply issues are included in this chapter.
Chapter 3 contains information on recommended circuitry needed to ensure proper performance
from the CM52 Wireless CPU
Chapter 4 describes several of the common cellular functions available with the CM52.
Chapter 5 provides some hints for integrating the Wireless CPU
Chapter 6 provides a summary of the technical data for the CM52 Wireless CPU®.
1.3 Service and Support
1.3.1 Web Pages
Visit our Web site for more information about where you can buy our products or for
recommendations for accessories and components. The address is:
http://www.wavecom.com
To register for product news and announcements or for product questions, work with your usual
Wavecom contact.
®
.
®
.
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
WI_DEV_CM52_UGD_001-001
Page 9 of 53
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à des tiers sans son autorisation préalable
Page 10
1.4 Related Documents
CM52 AT Command Manual – Details the AT command interface for the CM52
The CM52 is based upon the following mobile standards:
IS-2000 Release 0 (1XRTT), MOB_P_REV – CDMA protocol
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
TIA/EIA/IS-91 –
Cellular
TIA/EIA-98-D –
Spectrum Mobile Stations
1.5 Abbreviations
Abbreviation Definition
AGND Analog Reference
AMPS Advanced Mobile Phone System
AT Attention Command
CDMA Code Division Multiple Access
CTS Clear to Send
DCD Data Carrier Detect
DFMS Data from Mobile Station
DTMS Data to Mobile Station
DTR Data Terminal Ready
EMI Electromagnetic Interference
ESD Electrostatic Discharge
GND Chassis GrouND
IRA International Reference Alphabet
LSB Least Significant Bit
ME Mobile Equipment
MO Mobile Originated
MS Mobile Station
MT Mobile Terminated
OEM Original Equipment Manufacturer
PCB Printed Circuit Board
PCM Pulse Code Modulation
PIN Personal Identification Number
PSD Power Spectral Density
RD Receive Data, also known as DFMS
RF Radio Frequency
RI Ring Indicator
RTS Request to Send
SMS Short Message Service
TD Transmit Data, also know as DTMS
Mobile Station – Base Station Compatibility Standard for 800 MHz Analog
Recommended Minimum Performance Standards for Dual-Mode Spread
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
WI_DEV_CM52_UGD_001-001
Page 10 of 53
Table 1: Abbreviation Definitions
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à des tiers sans son autorisation préalable
Page 11
2 Integrating the CM52 Wireless CPU®
2.1 Overview
The CM52 is a dual band, dual mode CDMA transceiver Wireless CPU®. It operates in the 800 MHz
band for CDMA and AMPS and in the 1900 MHz band for CDMA. It is designed for consumer and
OEM industrial voice and data applications.
The CM52 Wireless CPU
provide wireless communication capability for the product. The target chassis could be in a wide
variety of forms such as a residential electric meter, a point of sale terminal, an alarm panel, or an
automobile console. All initial configuration, mode control, and operational commands are issued
to the Wireless CPU
®
circuitry has been designed to meet the environmental requirements of a large range of
CPU
commercial and industrial users.
2.2 Mechanical Description
®
is intended for mounting into an application developer’s chassis to
®
over an RS-232 serial port using a flexible AT command format. The Wireless
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
The CM52 has no mechanical elements other than the main PCB assembly. All critical electronic
components are shielded using six cans to prevent internal and external electromagnetic
®
interference from degrading the Wireless CPU performance and to prevent the Wireless CPU
®
interfering with other nearby devices. The Wireless CPU
is plugged into the fixed mating
from
connector and secured with four screws.
The antenna interface is provided via a board mounted RF connector at the opposite end of the
board from the system connector. See Section
2.8 for more information on antenna connector
options.
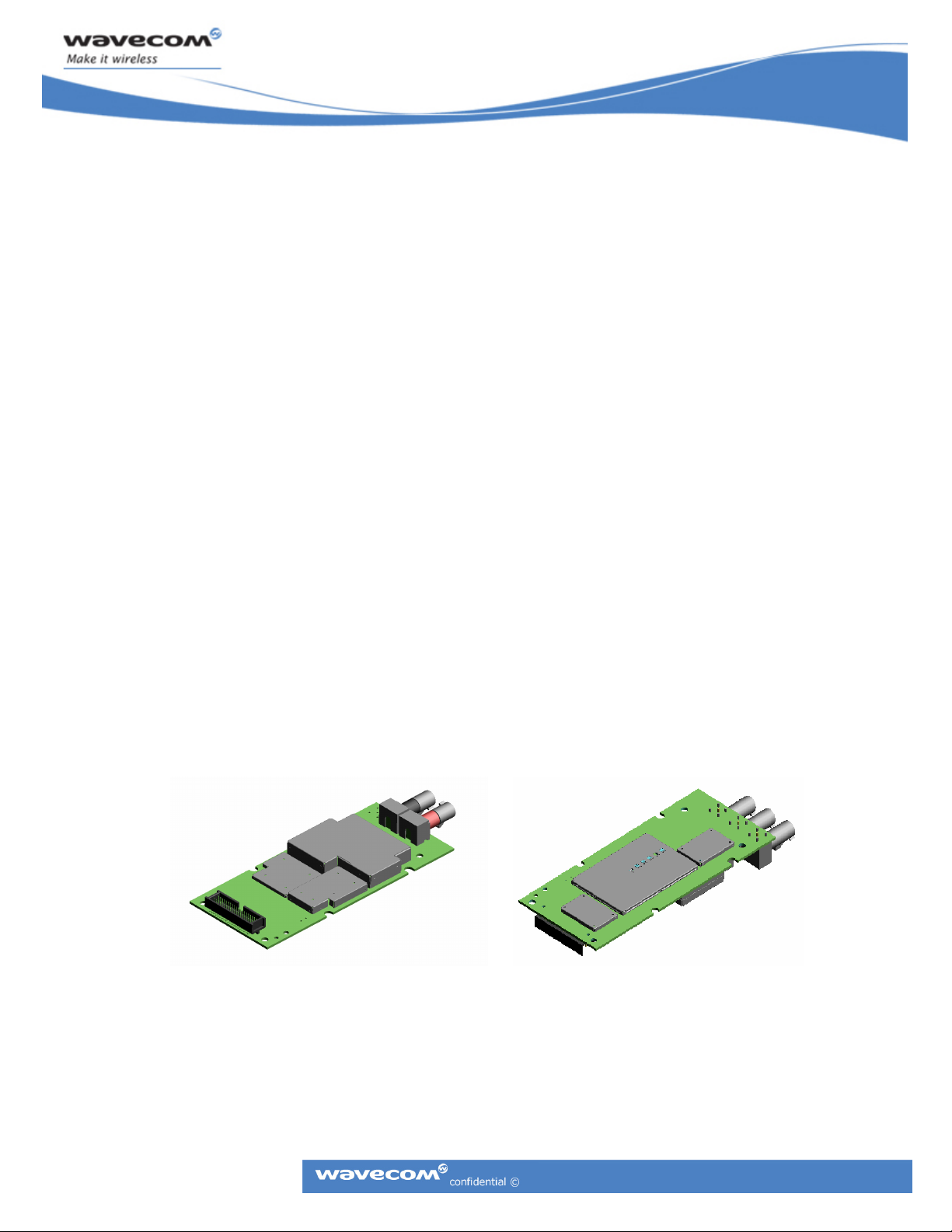
The Wireless CPU
show 3-D models of the Wireless CPU
Figure 1: CM52 Primary Side
®
has no keypad, display, microphone, speaker, or battery. The following figures
®
.
Figure 2: CM52 Secondary Side
2.2.1 Mechanical Dimensions
The following figures provide the mechanical dimensions for several CM52 variants (CM52002,
CM52003, and CM52004). There is also a drawing detailing the mechanical keep-out regions.
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
WI_DEV_CM52_UGD_001-001
Page 11 of 53
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à des tiers sans son autorisation préalable
Page 12
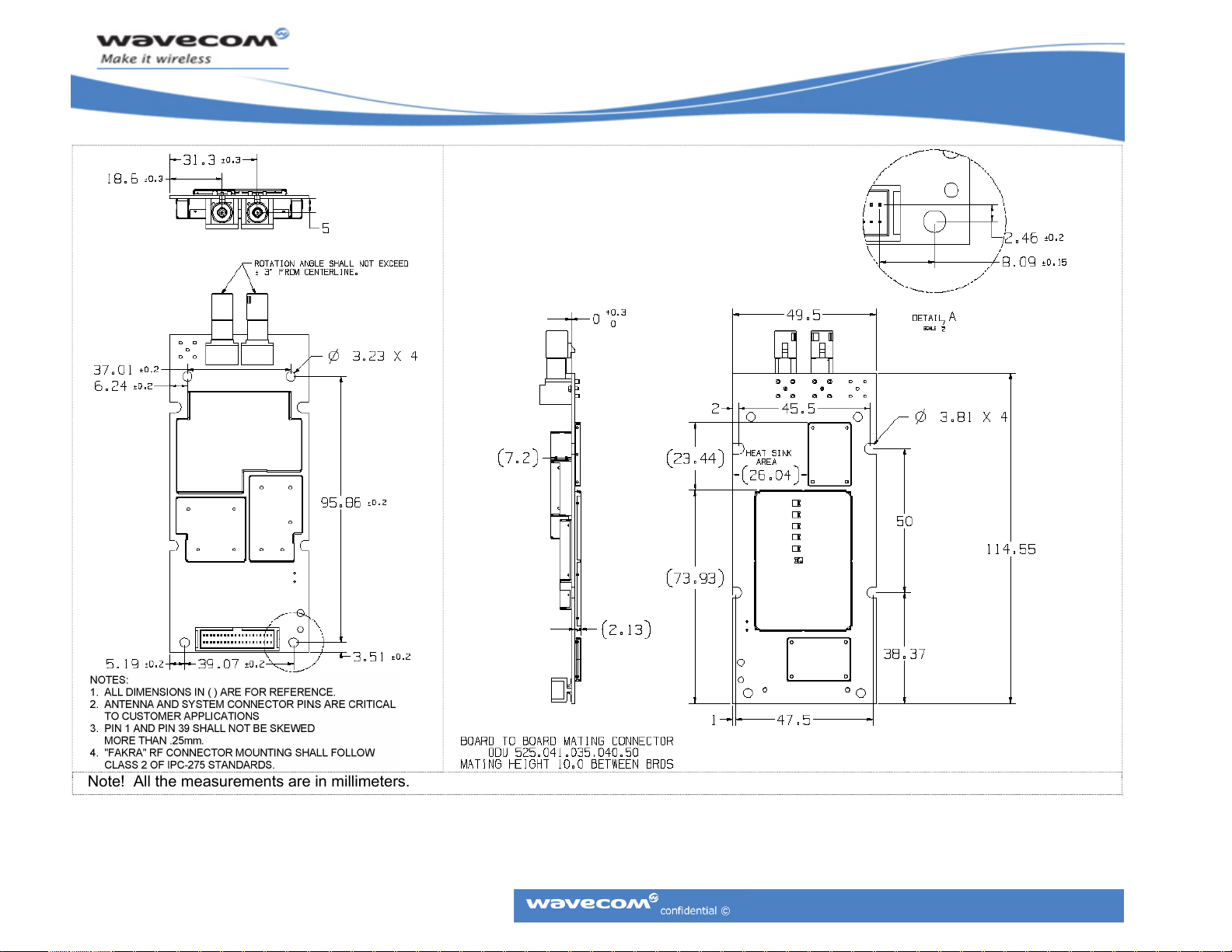
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
Note! All the measurements are in millimeters.
Figure 3: Mechanical Dimensions Drawing (CM52003 variant)
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à des tiers sans son autorisation préalable
WI_DEV_CM52_UGD_001-001
Page 12 of 53
Page 13
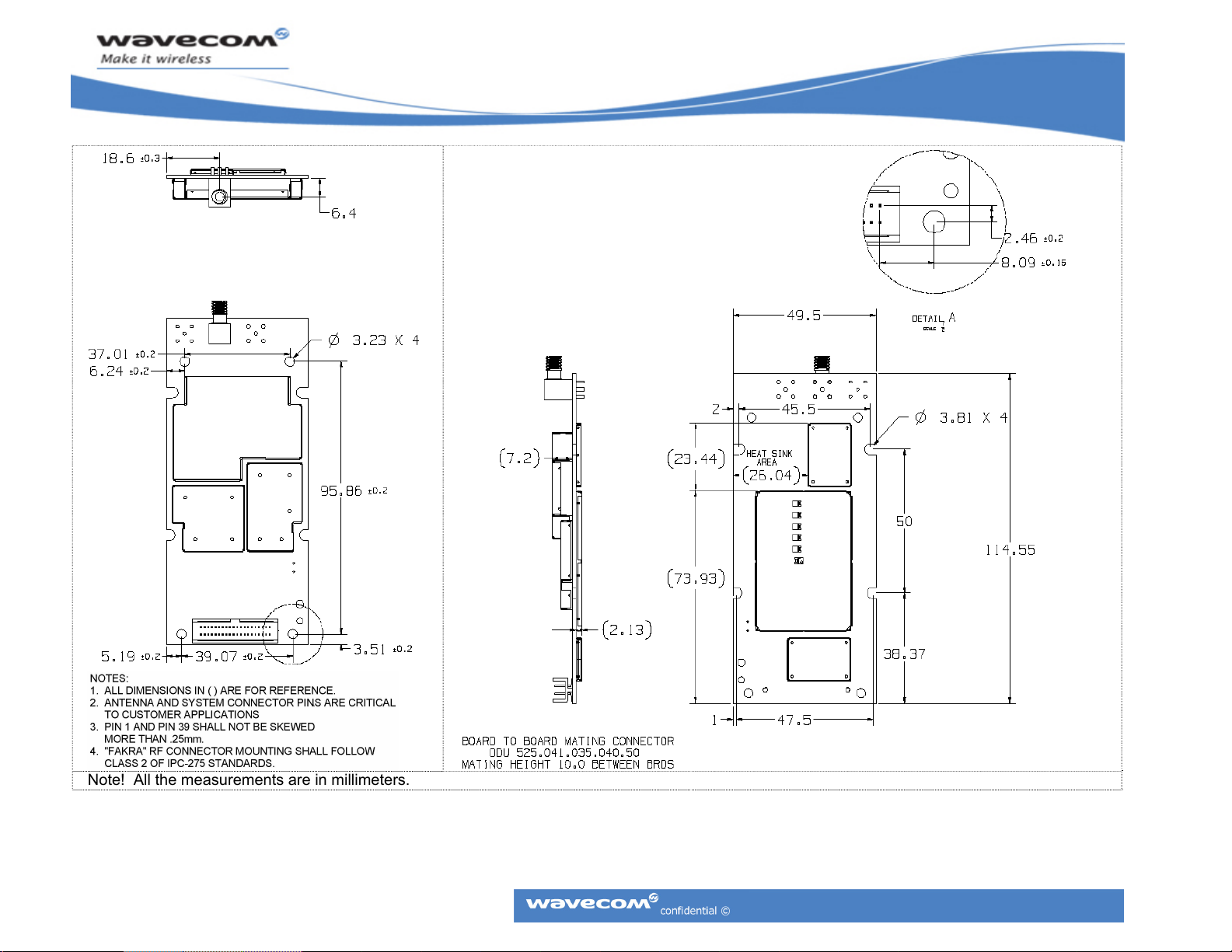
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
Note! All the measurements are in millimeters.
Figure 4: Mechanical Dimensions Drawing (CM52001 and CM52004 variants)
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à des tiers sans son autorisation préalable
WI_DEV_CM52_UGD_001-001
Page 13 of 53
Page 14
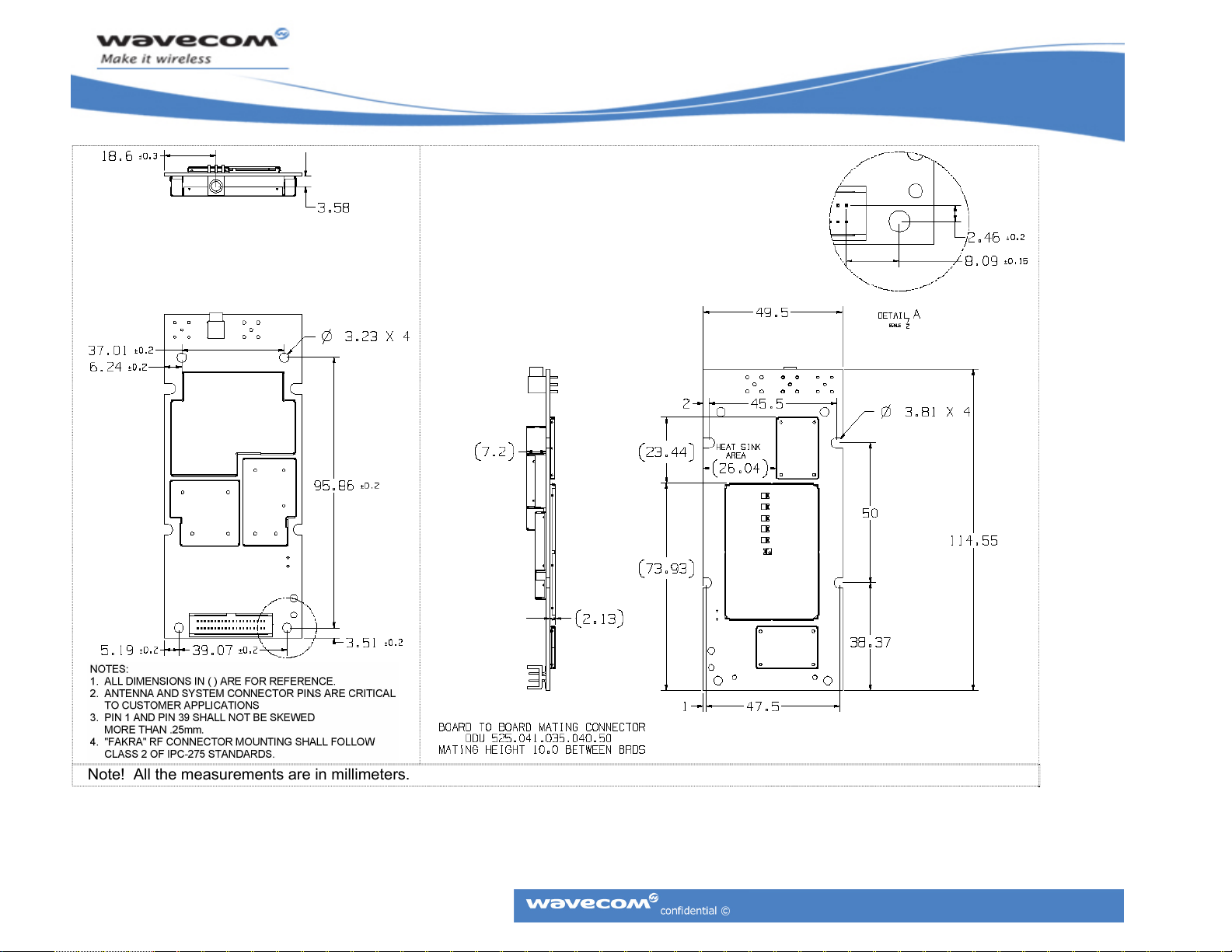
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
Note! All the measurements are in millimeters.
Figure 5: Mechanical Dimensions Drawing (CM52002 variant)
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à des tiers sans son autorisation préalable
WI_DEV_CM52_UGD_001-001
Page 14 of 53
Page 15
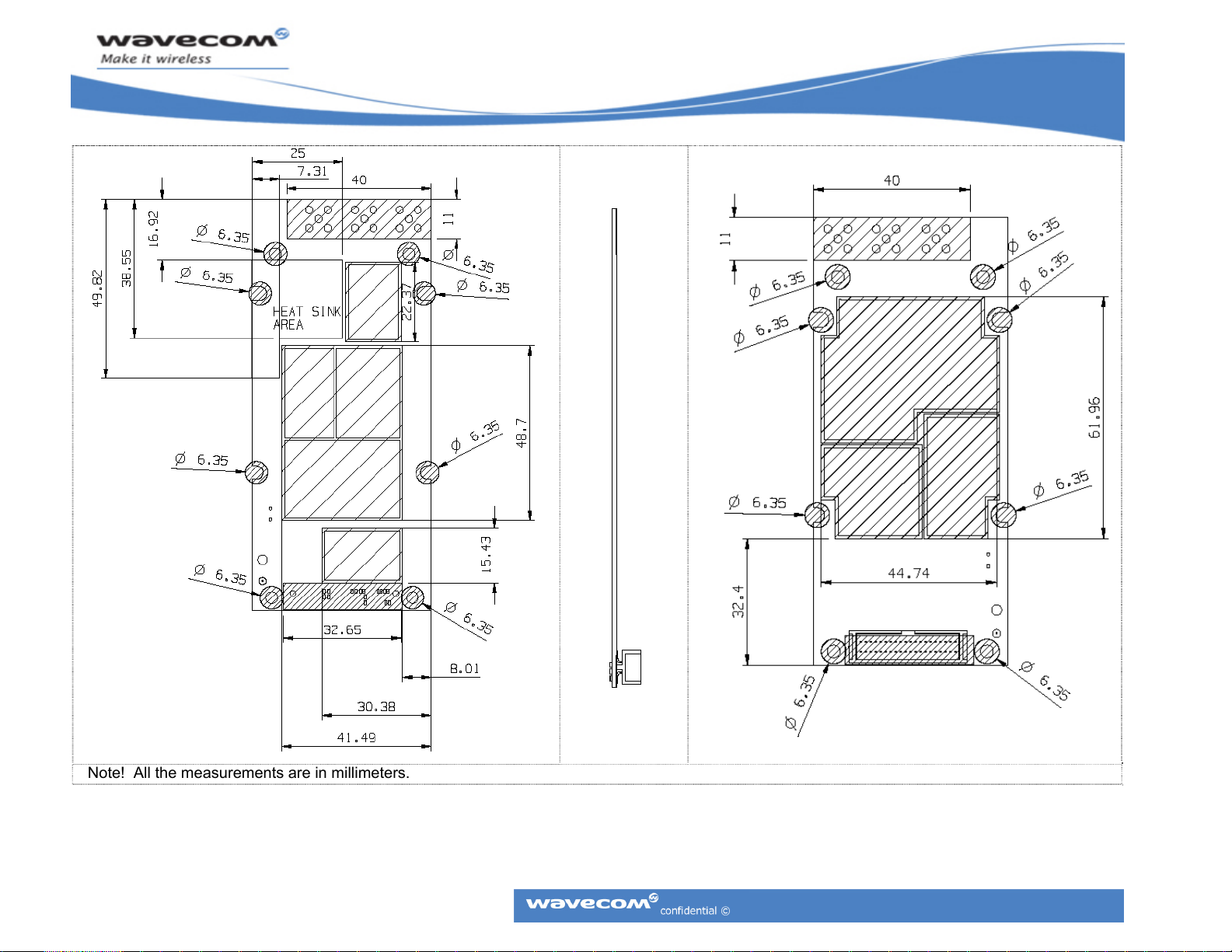
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
Note! All the measurements are in millimeters.
Figure 6: Keep-out drawing of CM52
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à des tiers sans son autorisation préalable
WI_DEV_CM52_UGD_001-001
Page 15 of 53
Page 16
2.2.2 Heat-Sink Requirements
The application is required to provide a heat-sink for the 3W AMPS capabilities of the CM52.
The application should be designed to provide a heat sink with a thermal resistance of 4.0
For applications that disable the 3W mode (Class I) and only operate in 0.6W mode (Class III) a
heat-sink is not required.
2.2.3 Mounting Holes
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
°
C/W.
Mounting holes and tabs are provided for proper mechanical support of the CM52 Wireless CPU
the customer’s application. The OEM’s application must provide sufficient mechanical retention
using the mounting holes and/or tabs or some other means. The system connector and RF
connector connections should not be used as a means of mechanical support. Also, please note
that the mounting holes may not substitute for the actual grounding pins provided via the system
connector.
Two mounting configurations are supported (A and B). Each has its own mechanical vibration
specification. Section 6 details the mechanical vibration specification for both configurations.
For machine screw mounting a wet torque of 8 in-lbs is recommended.
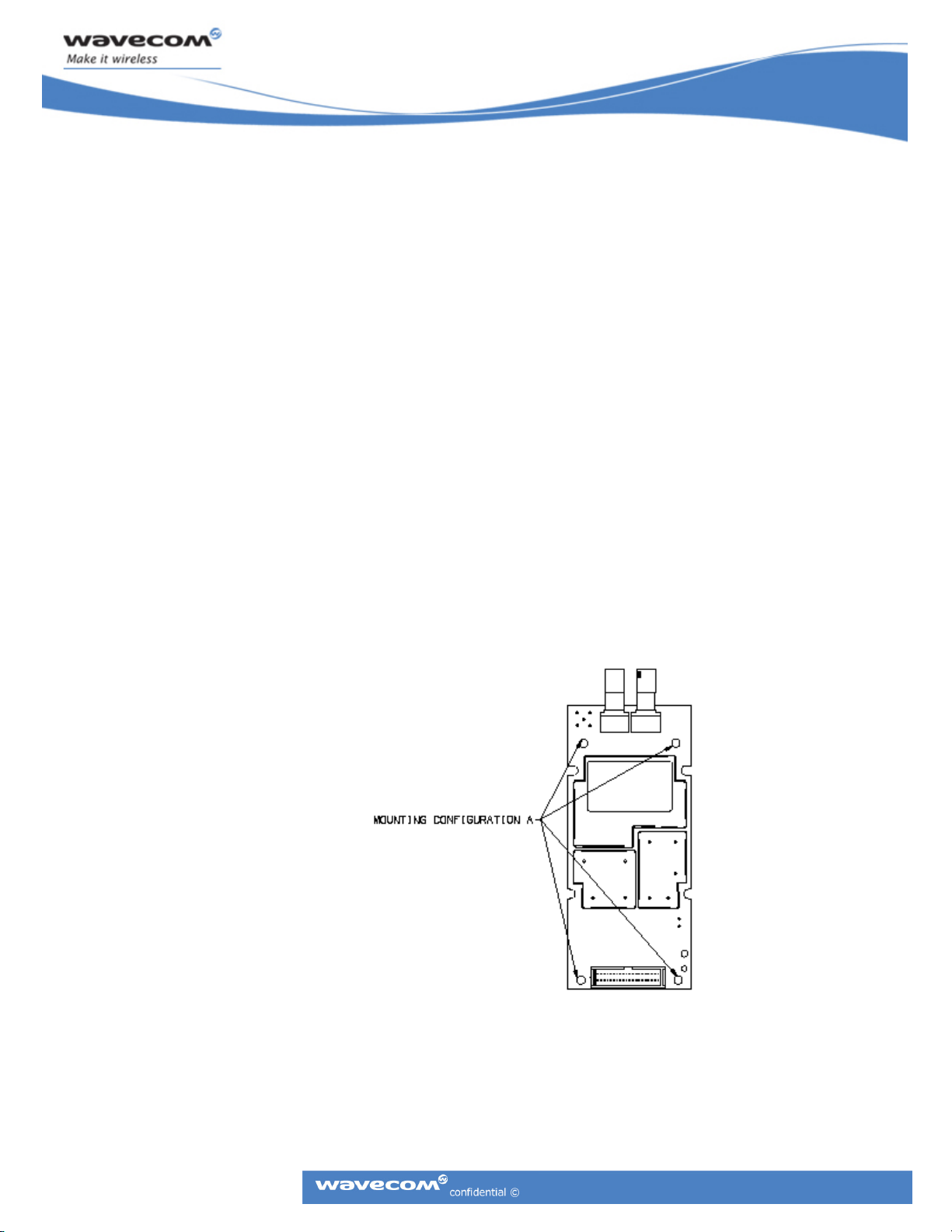
2.2.3.1 Mounting Configuration A
Mounting configuration “A” uses four exterior mounting holes that support #4 size screws.
®
in
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
WI_DEV_CM52_UGD_001-001
Page 16 of 53
Figure 7: Mounting Configuration A
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à des tiers sans son autorisation préalable
Page 17
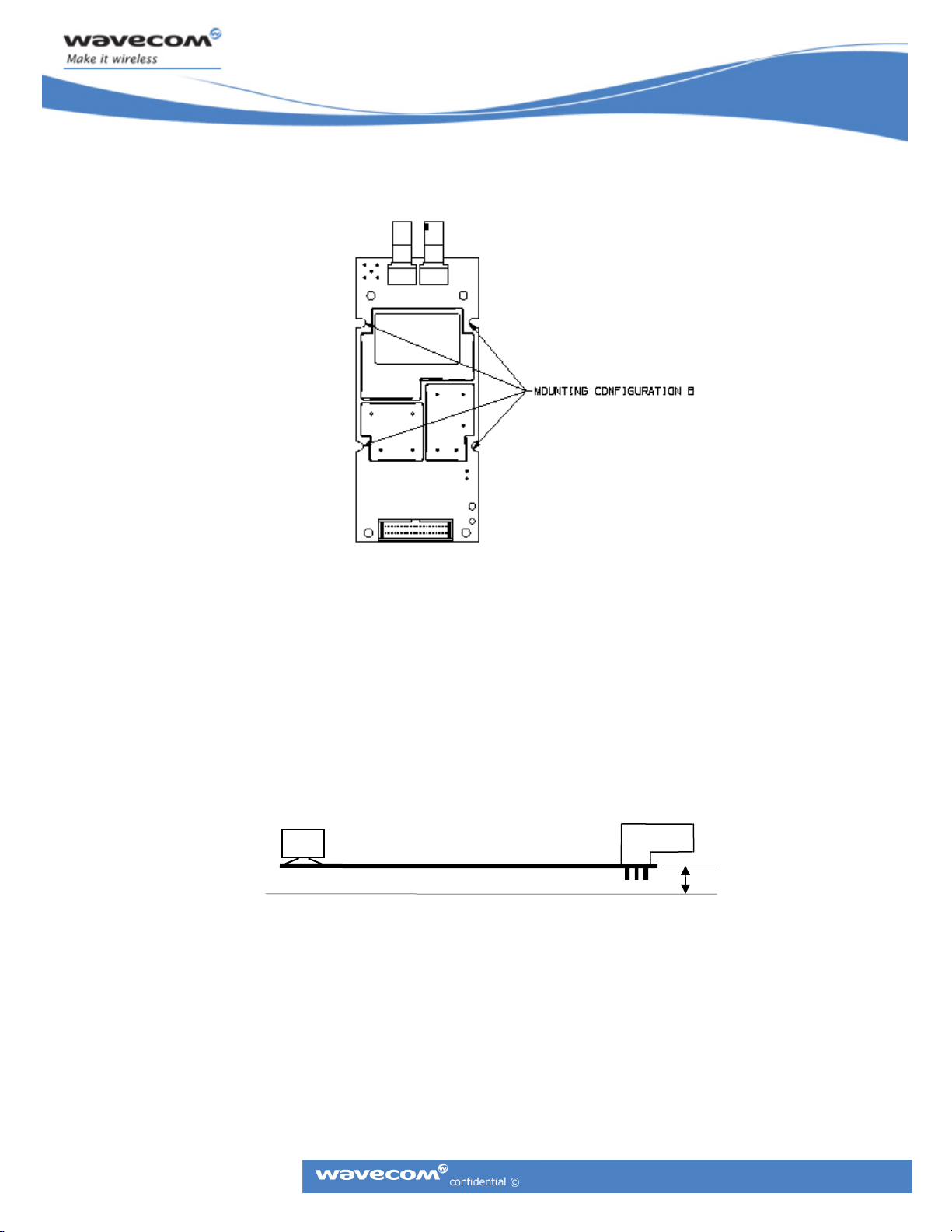
2.2.3.2 Mounting Configuration B
Mounting configuration “B” uses four 3/4 mounting holes that support #6 size screws.
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
Figure 8: Mounting Configuration B
Note: This is the recommend mounting configuration due to the higher mechanical vibration
specification supported.
2.2.4 RF Connector Mounting Considerations
When designing the application the designer should ensure that the housing does not degrade the
RF performance of the CM52. A minimum clearance of 4mm from the surface of the PCB to the
housing on the back side of the RF connectors should be provided.
Figure 9: Application Housing
4mm
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
WI_DEV_CM52_UGD_001-001
Page 17 of 53
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à des tiers sans son autorisation préalable
Page 18
2.3 System Connector Interface
2.3.1 Mechanical Overview
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
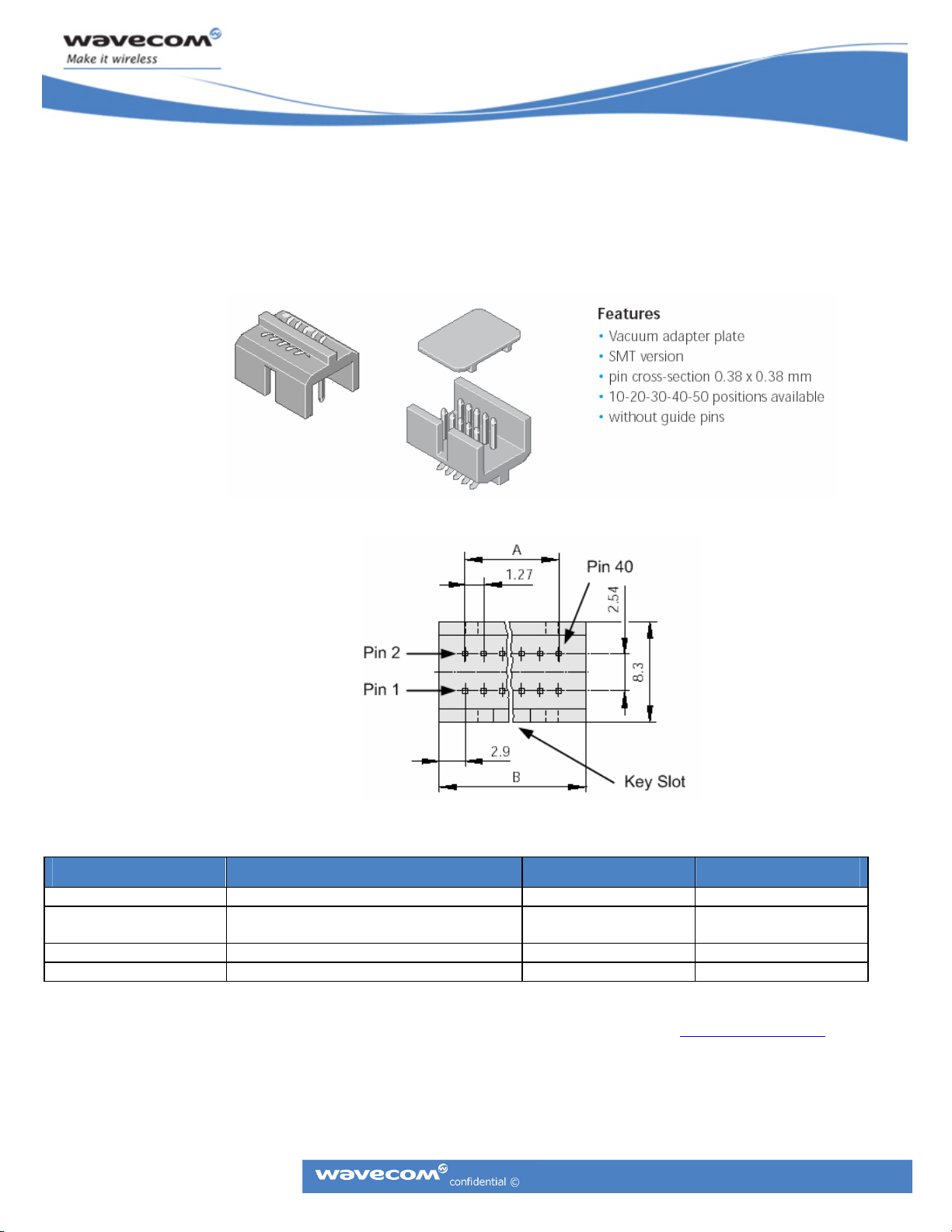
External interfaces to the Wireless CPU
pitch, ODU header show below.
Figure 10: 40-Pin System Connector
®
are made primarily through a 40 pin, standard 0.050-inch
Description ODU Part Number Dimension A Dimension B
System Connector 515.569.035.140.xxx 24.13 mm 22.86 mm
Mating Ribbon
Connector
SMT Mating Header 525.041.035.040.xxx
Ribbon cable, AWG 30 921.659.031.040.000
Please consult the ODU site for more information on mating options:
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
WI_DEV_CM52_UGD_001-001
Page 18 of 53
Figure 11: 40-Pin System Connector Pin Numbering
525.060.035.040.xxx
Table 2: System Connector and Mating Part Numbers
http://www.odu.de
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à des tiers sans son autorisation préalable
Page 19

2.3.2 System Connector Interface Pinout
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
Pin Signal Description Dir Pin Type Alternate
Function
1 Reserved
2 VREF Logic Voltage O Reference
3 Reserved
4 VRTC Supply pin for RTC
5 GND Chassis Ground
6 GND Chassis Ground
7 AFMS Analog Audio from Wireless CPU
8 GND Chassis Ground
9 AGND Analog Reference
10 ATMS Analog Audio to Wireless CPU
11 Reserved
12 MODULE_PWR_EN_B Switches the Wireless CPU® on/off
2
®
®
I Power GPS VRTC
Ground
Ground
O Audio
Ground
Audio
I Audio
I
(hardware-wise), active low
13 Reserved
14 Reserved
15 HW_SD Hardware shutdown I/O
16 Reserved
17 PCMCLK PCM Clock output O CMOS
18 PCMSYNC PCM Frame sync O CMOS
19 PCMULD PCM Voice input to Wireless CPU
20 PCMDLD PCM Voice output from Wireless CPU
21 GND Chassis Ground
22 GND Chassis Ground
23 DCD / VPPFLASH Data Carrier Detect & Flash programming
voltage input
24 Reserved
®
®
I CMOS
O CMOS
Ground
Ground
O / I CMOS /
Power
O
TIMEMARK
GPS Fix
1
UART3_RX
UART3_TX
RINGER O CMOS
Dir Pin
Type
1
O CMOS
1
1
1
O CMOS
I Supply
I CMOS
O CMOS
1
Default function if GPS option on board
2
Default function if RTC option on board
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
WI_DEV_CM52_UGD_001-001
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à des tiers sans son autorisation préalable
Page 19 of 53
Page 20
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
Pin Signal Description Dir Pin Type Alternate
Function
25 CTS Clear to send O CMOS
26 DTR Data Terminal Ready I CMOS
27 TD Transmit data, also known as DTMS I CMOS
28 RTS Request to Send I CMOS
29 VCC_AUX 13.8 VDC supply input I Power
30 RD Receive data, also known as DFMS O CMOS
31 VCC_AUX 13.8 VDC supply input I Power
32 VCC_AUX 13.8 VDC supply input I Power
33 VCC_MAIN 5 VDC regulated supply I Power
34 VCC_MAIN 5 VDC regulated supply I Power
35 SDA_SPI_IN Reserved
36 SCL_SPI_CLK Reserved
37 SYS_DTM_2 Transmit Data for UART2 I CMOS GPS TX Data
38 SPI_OUT Reserved
39 SYS_DFM_2 Receive Data for UART2 O CMOS GPS RX Data
40 RI Ring Indicator O CMOS
CMOS SDA_SPI_IN IO
CMOS SCL_SPI_CLK IO
CMOS SPI_OUT IO
1
1
Dir Pin
Type
I
O
Table 3: Pin-out of the System Connector Header
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
WI_DEV_CM52_UGD_001-001
Page 20 of 53
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à des tiers sans son autorisation préalable
Page 21

2.3.3 Logic Levels
Many of the signals present in the interface are CMOS signals where the following levels apply.
The nominal voltage level for the CMOS signals is 2.9 V. Drive capability of the outputs is also
indicated.
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
High level output voltage (IOH = 800 µA) V
Low level output voltage (IOL = 800 µA) V
High level input voltage V
Low level input voltage V
Table 4: CMOS Output / Input Electrical Characteristics
Note: The maximum voltage that may be applied to any CMOS signal is 3.1V
2.3.3.1 Leakage Current for CMOS Signals
The following table defines the maximum leakage for the CMOS inputs of the CM52.
Parameter Max Units
High level drive for input signal with internal pull down 60 uA
Low level drive for input signal with internal pull up
Table 5: Maximum Leakage Current for CMOS signals
2.3.3.2 Validity of CMOS signals
The CMOS signals of the CM52 shall only be considered valid when the level of the VREF signal is
above 2.3V.
Conditions
OH
OL
IH
IL
3
Limits Parameter Test
Units
Min Max
2.45 3.1 Volts
0 0.45 Volts
1.9 3.1 Volts
0 0.9 Volts
60 uA
2.4 Power Supply
The CM52 requires a dual DC power supply implementation in the application. VCC_MAIN provides
power to the entire radio while VCC_AUX provides power for the 3-Watt functionality and biasing
for the RF switches.
Note: VCC_AUX must be present if the 3W option is provided even if it is not used. If the 3W
circuitry is not populated then VCC_AUX is not required or may be bussed together with
VCC_MAIN.
3
DTR is 90 uA and HW_SD is 350 uA
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
WI_DEV_CM52_UGD_001-001
Page 21 of 53
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à des tiers sans son autorisation préalable
Page 22

CM52 Integrators’ Manual
The following table summarizes the power supply requirements from the application.
(Volts DC)
VCC_MAIN 5.00 ± 10% 1.4 100mVpp 50mVpp
VCC_AUX 13.8 ± 20% 1.3 600mVpp 240mVpp
VRTC(no GPS) 1.8 to 3.9 1.2 uA
VRTC(with GPS) 3.4 to 3.9 500 uA
Table 6: CM52 Power Supply Requirements
2.4.1 Power Supply Input Capacitance
It should be noted that when applying power to the Wireless CPU
maximum input current specified in
electrical specification due to the transient current required to charge the de-coupling capacitors
®
of the Wireless CPU
(specified below as CIN). The magnitude and duration of the transient current
spike is solely dependent on the application power supply design. Any built-in short circuit
protection in the application power supply must take this in to account as well as all other "Power
Supply" specifications.
The maximum total input capacitance on VCC_MAIN is 100uF. However at “Contact”, 60uF will be
charged instantly by the application’s power supply. Then at “Wake” an additional 14.5uF will be
instantly charged. At that point internal regulators are activated and limit the charge rate of the
remaining capacitance. If VCC_MAIN and VCC_AUX are tied together (0.6W variants only) then the
input capacitance on VCC_AUX is negligible.
Max. Current
Max. Ripple (mVpp) Input Supply Voltage
(Amps)
Operation 0- 4KHz 4 KHz-
10MHz
®
, the current will exceed the
Table 6: CM52 Power Supply Requirements, or any other CM52
The “Wakeup” condition occurs when the MODULE_PWR_EN_B signal transitions from High to Low.
The “Contact” condition occurs when voltage is first asserted to VCC_MAIN, and or VCC_AUX.
Parameter Contact Wakeup Units
VCC_MAIN Input Capacitance (CIN) 60 14.5 uF
VCC_AUX Input Capacitance (CIN) 33 10 pF
Parameter Contact Wakeup 3W assertion
VCC_MAIN Input Capacitance (CIN) 60 uF 14.5 uF n/a
VCC_AUX Input Capacitance (CIN) 10 uF 10 pF 20 uF
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
WI_DEV_CM52_UGD_001-001
Page 22 of 53
Table 7: Power Supply Input Capacitance (0.6W variants)
Table 8: Power Supply Input Capacitance (3W variants)
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à des tiers sans son autorisation préalable
Page 23

2.4.2 Power Supply and Ground Signals
2.4.2.1 Power Supply Signal Pins
Following is a list of the power supply pins:
Pin Signal Description
4 VRTC
29 VCC_AUX
31 VCC_AUX
32 VCC_AUX
33 VCC_MAIN
34 VCC_MAIN
For the power supply signals in the above table with multiple pins defined, the application shall
bus all defined pins together.
4
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
1.8 V to 3.9V ( 3.4V to 3.9V if GPS mounted)
13.8 volt ± 20%
13.8 volt ± 20%
13.8 volt ± 20%
5 volt ± 10% regulated
5 volt ± 10% regulated
Table 9: CM52 Power Supply Signals
2.4.2.2 Ground Signal Pins
The ground signal in the CM52 is Digital Ground, GND, connected to the system connector
interface through pin numbers 5, 6, 8, 21 and 22.
Following is a list of the ground pins:
Pin Signal Description
5 GND Digital Ground
6 GND Digital Ground
8 GND Digital Ground
21 GND Digital Ground
22 GND Digital Ground
Digital Ground (GND) is the logical reference of all digital signals in the System Interface as well as
the DC return of the power supply signal, VCC_MAIN and VCC_AUX (used for AMPS Class I
operation). All 5 ground pins in the Wireless CPU
ground. The PCB mounting holes may not to be used as substitute for the ground signal pins of
the system connector interface.
2.4.3 Power Consumption
Table 10: CM52 Ground Signals
®
need to be connected to the application
The following tables show typical and maximum values of current that can be expected from the
Wireless CPU
4
Only applicable to units with GPS or RTC functions
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
WI_DEV_CM52_UGD_001-001
Page 23 of 53
®
in different modes of operation.
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à des tiers sans son autorisation préalable
Page 24

2.4.3.1 VCC_MAIN Supply Power Consumption
Parameter Min Typical Max Units
Input Voltage 4.5 5 5.5 V
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
In AMPS Call on Power Level 0 (Power Class
0.62 0.82 A
I)
In AMPS Call on Power Level 2 0.94 1.4 A
In CDMA call-Cellular Mode 0.77 1.2 A
In CDMA call-PCS Mode 0.84 1.3 A
CDMA burst duration for Network update 1.2 s
Standby/Idle Current Draw in Slotted Mode
(CDMA)
1.28 sec slot 9.6 mA
2.56 sec slot 7.2 mA
5.12 sec slot 4.5 mA
Stand-by/Idle mode (AMPS) 45 mA
Powered Down Current Draw 1 5 uA
Table 11: VCC_MAIN Supply Power Consumption
Notes
1. The typical current measurements noted in CDMA mode are with the following settings:
a. CDMA-Cellular (800MHz): Band = IS-2000, Cell-Power = -104dBm,
Channel Number 358
b. CDMA-PCS (1900MHz): Band = IS-2000, Cell-Power = -104dBm,
Channel Number 563
Maximum Slot Cycle Index for both 800MHz and 1900MHz modes = 1
2. Measurements are based on worst case scenario—CM52 with 3W option. Values for CM52 with
no 3W option could be marginally lower.
3. A +10% tolerance is allowed for the listed maximum values.
2.4.3.2 VCC_AUX Supply Power Consumption
The VCC_AUX power supply is required for CM52 variants with 3W AMPS circuitry populated. This
requirement is regardless of whether the AMPS Power Class 1 is used.
The VCC_AUX power supply is not required for any CM52 Wireless CPU
AMPS circuitry populated, but it can be applied if desired. In this case, the VCC_AUX pins can be
supplied as 5V, 13.8V or Grounded.
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à des tiers sans son autorisation préalable
WI_DEV_CM52_UGD_001-001
Page 24 of 53
®
other than those with 3W
Page 25

Parameter Min Typical Max Units
Input Voltage 11 13.8 16.6 V
In a Call on Power Level 0 (Power Class I) 0.88 1.3 A
In a Call on Power Level 2 3.5 4.5 mA
AMPS Burst Duration for network update 0.16 S
Stand-by/Idle mode (Rx ON) 0.5 1 uA
Powered Down Current Draw 1 uA
Table 12: VCC_AUX Supply Power Consumption
Note: The typical values observed are made in AMPS call with voice channel set to 358.
2.4.3.3 Power Down Mode (Minimum DC Power Consumption)
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
In power down mode the Wireless CPU
®
is placed in a low power consumption state under the
control of host application. In this mode, the unit consumes approximately 1 uA of current as
measured from the VCC_MAIN supply input and 1 uA of current as measured from the VCC_AUX
supply input.
To activate this mode, the Module_PWR_EN_B signal on pin 12 of the system connector is pulled to
a logic level 1, which puts the Wireless CPU
®
into the low power state. The Wireless CPU® will stay in
the low power state until the Module_PWR_EN_B signal is driven low by an external open collector
transistor in the application circuitry. Turning the external open collector transistor off will cause
®
the Module_PWR_EN_B signal to float high and turn the Wireless CPU
off. The Module_PWR_EN_B
line is tied to VCC_MAIN through a 100kΩ pull-up resistor so the sink current in the external open
collector transistor is minimal.
Parameter Minimum Nominal Maximum Units
Internal Pull-up Resistance to
90 100 KΩ
VCC_MAIN
Off-Time 1 S
Table 13: Module_Pwr_EN_B Signal Parameters
In the Power Down Mode the radio is inactive and serial communication with the CM52 is
suspended.
2.4.4 VREF Signal Details
The following table defines the current sourcing capabilities and behavior of the VREF signal. This
signal is defined as a logic reference voltage, not a supply voltage to the application. Refer to
Recommend Circuitry for interface circuit implementation suggestions.
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
WI_DEV_CM52_UGD_001-001
Page 25 of 53
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à des tiers sans son autorisation préalable
3
Page 26
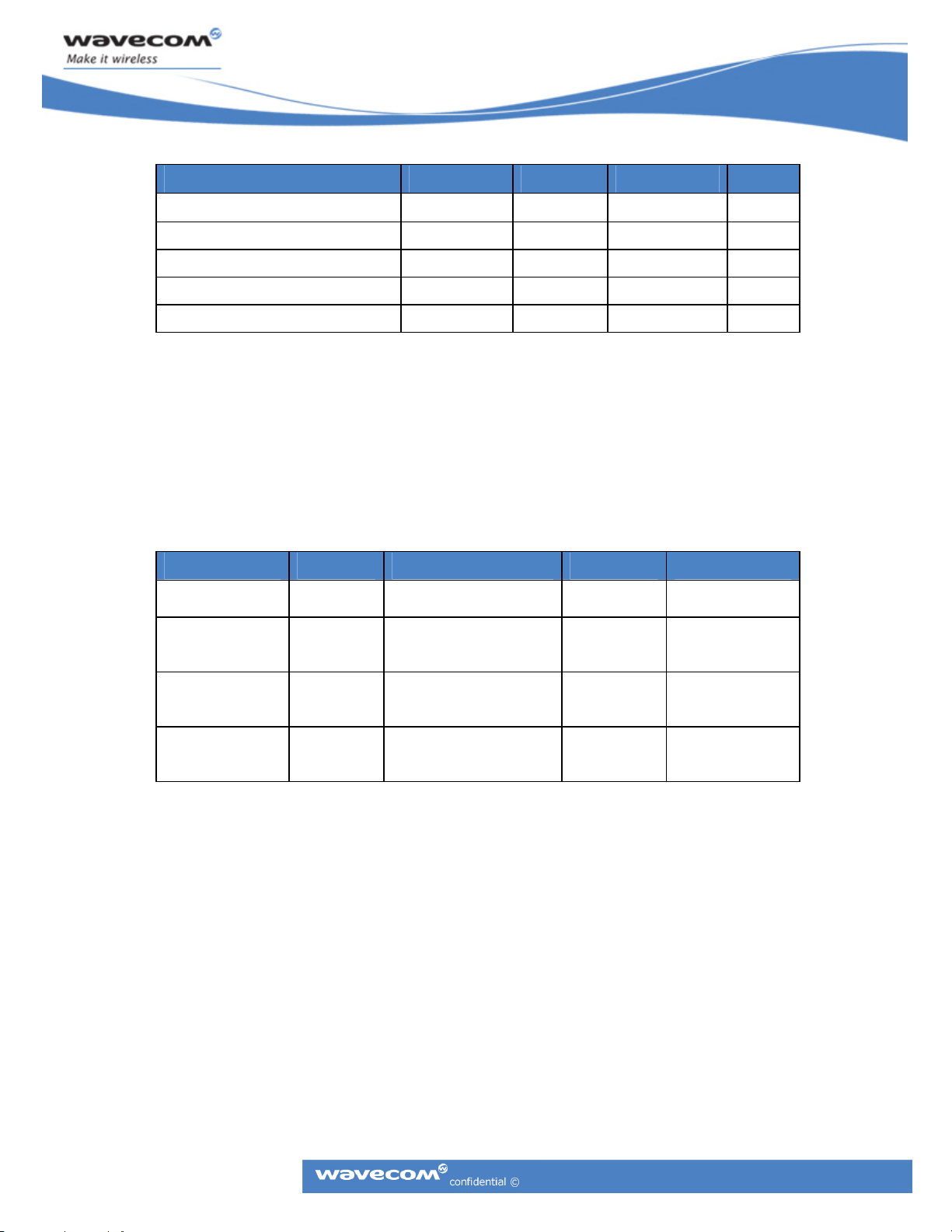
Parameter Minimum Typical Maximum Units
Supply Voltage Reference 2.45 2.9 3.1 V
Output Current 1000 uA
Application Load 10 100 KΩ
Rise Time 3300 us
Fall Time 0.8 ms
2.5 Real Time Clock (RTC) Circuit
The real time clock is a feature provided by the CM52 that allows the Wireless CPU® to sleep and
wakeup for a definable number of cycles, as configured by the host application. This feature is an
optional hardware feature. Please refer to the CM52 Software User’s Guide and AT Command
Manual for more details about usage scenarios and programming this feature.
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
Table 14: VREF Supply Details
The following table defines the Frequency Characteristics of the RTC:
Item Symbol Condition Rating Unit
Frequency
precision
Frequency /
voltage
characteristics
Frequency /
temperature
characteristics
Aging fa Ta = +25 °C,
(*1) precision gap per month: 1 minutes (excluding offset value)
2.5.1 RTC Initialization
When power is first applied to the RTC via the VRTC pin of the system connector it is necessary to
allow the CM52 to initialize the RTC. In order to initialize the RTC the CM52 must be powered up
while power is applied to the RTC. Once the Restart message is received the CM52 can be
shutdown via the normal procedures. If the supply to the VRTC input is interrupted then the CM52
must be allowed to power up to initialize the RTC again.
Δf / f Ta = +25 °C,
VDD = 3.0 V
f / V Ta = +25 °C,
VDD = 2.0 V to 5.0 V
Top Ta = -20 °C to +70 °C,
VDD = 3.0 V;
+25 °C reference
VDD = 3.0V,
first year
Table 15: Frequency characteristics of the RTC
5 ± 23 (*1) X 10-6
± 2 Max. X 10 -6 / V
+10 / -120 X 10 -6
± 5 Max. X 10 -6 / year
2.5.2 RTC Functional Block Diagram
The purpose of this section is to provide an overview of the Real Time Clock feature functional
block and interconnects that are shared with the application.
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
WI_DEV_CM52_UGD_001-001
Page 26 of 53
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à des tiers sans son autorisation préalable
Page 27

CM52 Integrators’ Manual
2.6 Audio Interface
The audio-related signals are: the analog audio signals
ATMS (Audio to Mobile Station),
AFMS (Audio from Mobile Station),
PCM (Pulse Code Modulation) signals (PCMULD, PCMDLD, PCMCLK, and PCMSYNC).
Pin Signal Description
7 AFMS Audio Output From Wireless CPU®.
10 ATMS Audio Input to Wireless CPU®.
9 AGND Analog Reference
17 PCMCLK PCM Clock Output from Wireless CPU®.
18 PCMSYNC PCM Frame Sync Output from Wireless CPU®.
19 PCMULD PCM Voice Input to Wireless CPU
20 PCMDLD PCM Voice Output from Wireless CPU®.
Figure 12: RTC Functional Block Diagram
®
Table 16: CM52 Audio Signals
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
WI_DEV_CM52_UGD_001-001
Page 27 of 53
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à des tiers sans son autorisation préalable
Page 28
2.6.1 Digital Audio
The CM52 provides digital audio capability over the system connector. The digital audio signals
enable the connection of a digital audio source. The receiver is bypassing the analog audio
processing functions performed within the Wireless CPU
following PCM signals:
Pin Signal Description
17 PCMCLK PCM Clock Output from Wireless CPU®.
18 PCMSYNC PCM Frame Sync from Wireless CPU
19 PCMULD PCM Voice Input to Wireless CPU®.
20 PCMDLD PCM Voice Output from Wireless CPU®.
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
®
. The digital audio interface includes the
®
Table 17: CM52 Digital Audio Signals
Already defined CMOS output/input electrical characteristics apply (see Section
signals are referenced to digital ground.
The PCM format (for PCMULD and PCMDLD) follows a linear PCM data format with 13-bit data
embedded in a 16-bit word. The data bits in PCMULD (input) and PCMDLD (output) are aligned so
that the MSB in each word occurs on the same clock edge. See timing diagram in
2.6.1.1 Data Format
The CM52 Wireless CPU
bit word as follows.
Each PCM word shall contain 16-bits D15 – D00. D15 – D03 is the 2´s-complement value of the
13-bit PCM, with D15 as the sign bit. D15 is the MSB while D03 is the LSB. Note that the MSB is
sent in first place. Ensure that the read data from PCMDLD is right shifted three times and sign
extended before being used
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
MSB LSB
1.1.1). The PCM
2.6.1.2.
®
implements a 13-bit linear PCM with the 13-bit data embedded in a 16-
13-bit linear
x x x
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
WI_DEV_CM52_UGD_001-001
Page 28 of 53
Bit Contents
D15 – D03 2’s complement of the 13-bit PCM.
D02 – D00 Bits are undefined.
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à des tiers sans son autorisation préalable
Page 29

2.6.1.2 Timing
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
Timing shall be according to the following diagram (see
Figure 13: PCM Timing Diagram). The
signals in the diagram shall be interpreted according to the following relation.
Figure 13: PCM Timing Diagram
The meaning and value of the timing parameters are described in
Name Description Min Typical Max Unit
SYNC
PCM_SYNC cycle time. 125 Us t
PCM_SYNC frequency 8.0 kHz
t
SYNCA
t
SYNCD
t
SU(SYNC)
PCM_SYNC asserted time. 62.4 62.5 Us
PCM_SYNC de-asserted time. 62.4 62.5 Us
PCM_SYNC setup time to PCM_CLK
rising.
t
H(SYNC)
PCM_SYNC hold time after PCM_CLK
falling.
CLK
PCM_CLK cycle time. 7.8 us t
PCM_CLK frequency 128 kHz
t
CLKH
t
CLKL
t
PDLD
PCM_CLK high time. 3.8 3.9 us
PCM_CLK low time. 3.8 3.9 us
Propagation delay from PCM_CLK
rising to PCM_DLD valid.
T
SU(ULD)
PCM_ULD setup time to PCM_CLK
falling.
T
H(ULD)
PCM_ULD hold time after PCM_CLK
falling.
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
WI_DEV_CM52_UGD_001-001
Page 29 of 53
Table 18.
1.95 us
1.95 us
50 ns
70 ns
20 ns
Table 18: PCM Timing Parameters
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à des tiers sans son autorisation préalable
Page 30

2.6.2 Analog Audio
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
ATMS is the analog audio input to the Wireless CPU
via the audio processing stages in the Wireless CPU
The AFMS is the analog audio output from the Wireless CPU
the radio via the audio processing stages in the Wireless CPU
®
. When it is active, it is connected to the radio
®
.
®
. When it is active it is connected to
®
.
The AGND is the analog reference signal. ATMS and AFMS are referenced to this signal, which is
®
connected to GND in one place inside the Wireless CPU
.
Pin Signal Description
7 AFMS Audio Output From Wireless CPU
10 ATMS Audio Input To Wireless CPU
®
®
9 AGND Analog Reference
Table 19: CM52 Analog Audio Signals
Signal Parameter
AFMS
Wireless CPU® audio output 300 – 3400 Hz
Output Impedance
Drive capacity into 10 kΩ
External Device audio input
Rout 100 Ω
3.77 V
max. or 2.5 dBV
P-P
Zin ≥ 10 kΩ
impedance
Volume control -81 dB from maximum > - 81 dB (mute)
Sensitivity 1004 Hz tone at 8kHz deviation
rms
.
ATMS
Sources are preferably AC
generates 900+100 mV
Cout ≥ 2.2uF
coupled.
External Device audio source
Rout ≤ 1.0 kΩ
Output resistance
Wireless CPU® audio input
Zin ≥ 10 kΩ
impedance
Levels from external audio source
3.77 V
max. or 2.5 dBV
P-P
(maximum)
Sensitivity 1004 Hz tone at 900+100 mV
rms
generates 8kHz deviation.
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
WI_DEV_CM52_UGD_001-001
Page 30 of 53
Table 20: Audio Characteristics
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à des tiers sans son autorisation préalable
Page 31

CM52 Integrators’ Manual
Analog Reference (AGND)
The AGND lead is the analog audio reference ground. It is the return signal for Audio To Mobile
Station (ATMS), Audio From Mobile Station (AFMS).
Electrical characteristics: Imax < 40 mA (peak)
The AGND is connected to the chassis Ground (GND) in the CM52 Wireless CPU
there. The application should be connected to GND and only use AGND as reference for the
audio lines ATMS and AFMS.
AGND and GND are not to be connected together in the application.
Application Implementation:
BIAS:
An analog ground plane should be generated which connects to GND in one point so that
high frequency digital current is not floating through the analog ground. Connecting the analog
ground in only one point also avoids ground currents from power supplies and other high current
circuitry from creating noise in the analog circuitry. The voltage supply for the analog circuitry
should connect its ground pin as close as possible to the point where the analog ground connects
to GND. The BIAS reference is generated from this supply voltage and analog ground and shall be
used as a reference for all analog circuitry in the application. Note that
are two different signals.
Analog Ground
is the ground plane used by the application. It should be
Analog Ground
connected to the application’s GND in one point preferably at the regulator that generates the
AGND
analog supply voltage.
signal with the intent to be used together with
between the Wireless CPU
is the analog audio reference received from the phone. This is a
ATMS
and
AFMS
as a semi differential interface
®
and the application.
®
, and only
and
AGND
ATMS:
internal BIAS to AGND. The figure below shows an example of a microphone implementation.
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
WI_DEV_CM52_UGD_001-001
Page 31 of 53
Figure 14: BIAS Diagram Example
An application using the analog audio interface must re-reference the signal from its own
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à des tiers sans son autorisation préalable
Page 32

CM52 Integrators’ Manual
Figure 15: Microphone Implementation Example
The microphone should preferably be connected to its pre-amplifier differentially which will
minimize noise pickup from possible ground current.
AFMS:
An application using the analog audio interface must re-reference the AFMS-signal from
AGND to its own internal BIAS. The figure shows a differential implementation. C1 is chosen to
create the correct HP frequency response. R1 and R2 determine the gain; C2 and R2 determine the
LP frequency response.
Figure 16: Differential Implementation Example
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
WI_DEV_CM52_UGD_001-001
Page 32 of 53
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à des tiers sans son autorisation préalable
Page 33

2.7 Serial Data Interface
The serial channels are used as asynchronous communication links between the application system
and the Wireless CPU
Pin Signal Description Dir
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
®
. The following table shows the serial data channels related signals:
23 DCD Data Carrier Detect
O
This signal is set default high. It goes low indicating that a data
call is established (CONNECT received from the remote modem).
The signal goes high when the data connection is disconnected.
25 CTS Clear To Send
This signal is initially set high indicating that the Wireless CPU® is
not ready to receive data. It is set low after the Wireless CPU
®
is
O
done performing its startup procedure indicating that it is ready to
receive data.
26 DTR Data Terminal Ready
I
This signal should be set low by the application during a data call.
A low to high transition will terminate the data call.
27 TD Transmit Serial Data To Wireless CPU® (DTMS)
I
The application shall set this signal high at startup.
28 RTS Request To Send
I
The application shall set this pin low when it is ready to receive
data.
30 RD Receive Serial Data From Wireless CPU® (DFMS)
O
The Wireless CPU® will set this signal high at startup.
Table 21: Serial Data Channels
The common CMOS electrical specifications defined in Section
1.1.1 are valid for all these signals.
The standard character format is 1 start bit, 8 data bits, non-parity and 1 stop bit. In all there are
10 bits per character.
Note! The signal levels do not match the standard RS-232 (V.28). If the application signal levels
are not compatible with the CMOS levels described in
Characteristics
necessary between the CM52 Wireless CPU
2.8 Antenna Interface
The antenna interface of the CM52 consists of a single or dual RF connector for the radio with
optional antenna diagnostics and a single RF connector for the optional GPS function.
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
WI_DEV_CM52_UGD_001-001
Page 33 of 53
Table 4: CMOS Output / Input Electrical
, then electrical protection level limiters or level conversion hardware will be
®
and the application.
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à des tiers sans son autorisation préalable
Page 34

2.8.1 Antenna Connector
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
A variety of antenna connectors are available for the CM52 Wireless CPU
®
including SMA, SMB, and
MCX. A standard 5-pin, thru-hole pattern has been selected because of the wide variety of
compatible connectors available and also for the maximum mechanical strength.
For automotive applications, a FAKRA-type connector is available which provides a double locking
mechanism as well as a keyed, color-coded interface as shown below:
A
Black
G
Gray
B
Natural
H
Violet
C
Blue
Beige
I
D
Violet
K
Curry
E
Green
Z
F
Brown
Waterblue
Figure 17: Color and Keying for various FAKRA connectors
The physical dimensions of a sample SMA connector and mounting hole are shown in the drawing
below.
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
WI_DEV_CM52_UGD_001-001
Page 34 of 53
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à des tiers sans son autorisation préalable
Page 35

CM52 Integrators’ Manual
Figure 18: Sample SMA Connector and Mounting Hole
Electrical performance parameters are valid
only when the terminating impedance at the output of
the antenna connector exhibits a VSWR of less than 2:1 for all phase angles in the frequency band
of operation. High VSWR loads at the antenna connector adversely affect current consumption,
®
linearity, and power efficiency of the Wireless CPU
and may degrade operation; however, internal
protection circuitry has been added to the design to prevent damage.
The performance of the Wireless CPU
®
as defined in Section 2.8.2, RF Output Power, is referenced
to the antenna connector. The antenna connectors must not negatively affect the performance of
the CM52. For this reason, all options are discrete connectors and thus do not include cable
assemblies.
The table below lists several suppliers of antenna connectors that are available.
Description Vendor / Part # Additional Information
RF Connectors and cabling ITT Cannon /
http://www.ittcannon.com
Various
RF Connectors and cabling Amphenol RF /
http://www.amphenolrf.com
Various
RF Connectors and cabling Hirschmann /
http://portal.hirschmann.com
Various
Table 22: Antenna Connector Suppliers
2.8.2 RF Output Power
The CM52 is able to operate in several modes and different output power level. Applications may
require output power levels similar to those in a handheld cellular phone or higher levels
commonly required in rural areas.
A CM52 that is a 0.6W variant is an AMPS Power Class III device. A 3W variant will be an AMPS
Power Class I device. The following tables show the nominal power provided by the CM52.
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
WI_DEV_CM52_UGD_001-001
Page 35 of 53
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à des tiers sans son autorisation préalable
Page 36

CM52 Integrators’ Manual
Mobile Station Power Level (dBm)
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
Class I, AMPS
Class III, AMPS
Note: These numbers represent the Nominal Output Power
the antenna connector. Analog output power levels are as defined for a Power Class I device in
Industry Specification EIA/TIA IS-91.
Class III, CDMA Band Class 0
Class II, CDMA Band Class 1
2.8.3 Carrier Approval
The CM52 has undergone carrier qualification and has been approved referencing the antenna
connector. Any application intending to use the CM52 will likely be required to undergo similar
testing with the CM52 integrated into the application. For this reason it is strongly recommended
that the application is designed to accommodate exposing the antenna connector(s) of the CM52.
This will help insure that the qualification of the application with the carrier will be successful.
34.8 31 26.3 24 20 16 12 8
26.3 26.3 26.3 24 20 16 12 8
Table 23: Mobile Station Nominal Analog Power Levels
5
in AMPS mode and are referenced to
Mobile Station Power Level (dBm)
Lower Limit Upper Limit
23 dBm (0.2 Watts) 30 dBm (1.0 Watts)
23 dBm (0.2 Watts) 30 dBm (1.0 Watts)
Table 24: Mobile Station CDMA Maximum Output Power
2.8.4 Antenna Diagnostics
The antenna diagnostics function consists of one antenna detection circuit per RF connector. Each
detection circuit can support antenna resistance (RL) values of 1 KΩ to 20 KΩ and 49.9 KΩ.
Internal resistance (R) value is either 10 KΩ or 49.9 KΩ, as required by the customer’s application.
AT commands are provided to query the status, query the limits and set the limits for the status:
GOOD, OPEN, or SHORTED. These commands are detailed in the CM52 Software User’s Guide and
AT Command.
The drawing below is a high level description of the antenna diagnostics circuit.
5
PL0 and PL1 require VCC_AUX = 13.8V
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à des tiers sans son autorisation préalable
WI_DEV_CM52_UGD_001-001
Page 36 of 53
Page 37

CM52 Integrators’ Manual
Figure 19: Antenna Diagnostic Circuit
The current antenna status is based on a comparison between the voltage measured at the antenna
connector and the limits set by the application for OPEN and SHORT.
Because of the tolerances associated with Wireless CPU
ADC itself, there will be a correction factor in the ADC reading as listed below in
®
power supply, ADC power supply and the
Table 25.
Lower Limit Nominal Higher Limit
ADC Reading Correction (%) -5 4 11
ADC Correction (Multiplying Factor) 0.95 1.04 1.1
Table 25: Range of ADC readings for an external antenna
Example: The multiplying factors shown above are used to establish the ADC limits values for an
antenna OPEN, SHORT and nominal conditions of a known antenna resistance value. These limits
can be calculated using the formula below:
ADC Reading = 255 * Multiplying Factor * RL/(R+ RL)
The following example shows calculation using internal resistance (R) = 49.9K and antenna
resistance (RL) = 10K.
Lower Limit of ADC Reading = 255 * 0.95 * 10k/ (49.9k + 10k) = 41
Nominal Value of ADC Reading = 255 * 1.04 * 10k/ (49.9k + 10k) = 45
Upper Limit of ADC Reading = 255 * 1.1 * 10k/ (49.9k + 10k) = 47
Note: All ADC values should be rounded up to next integer value.
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
WI_DEV_CM52_UGD_001-001
Page 37 of 53
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à des tiers sans son autorisation préalable
Page 38

3 Recommended Interface Circuitry
Abbreviations:
VCC - Represents the logic supply voltage used by the application.
VREF_CA- Current amplified reference voltage used for all logic interface circuitry to the CM52.
Component proposals:
Transistors not showing a base resistor should be interpreted as a BRT (Built in Resistor
Transistor) i.e. Toshiba RN1308.
The inverting buffers should preferably be Schmitt-Triggered, i.e. Toshiba TC7S14 or similar.
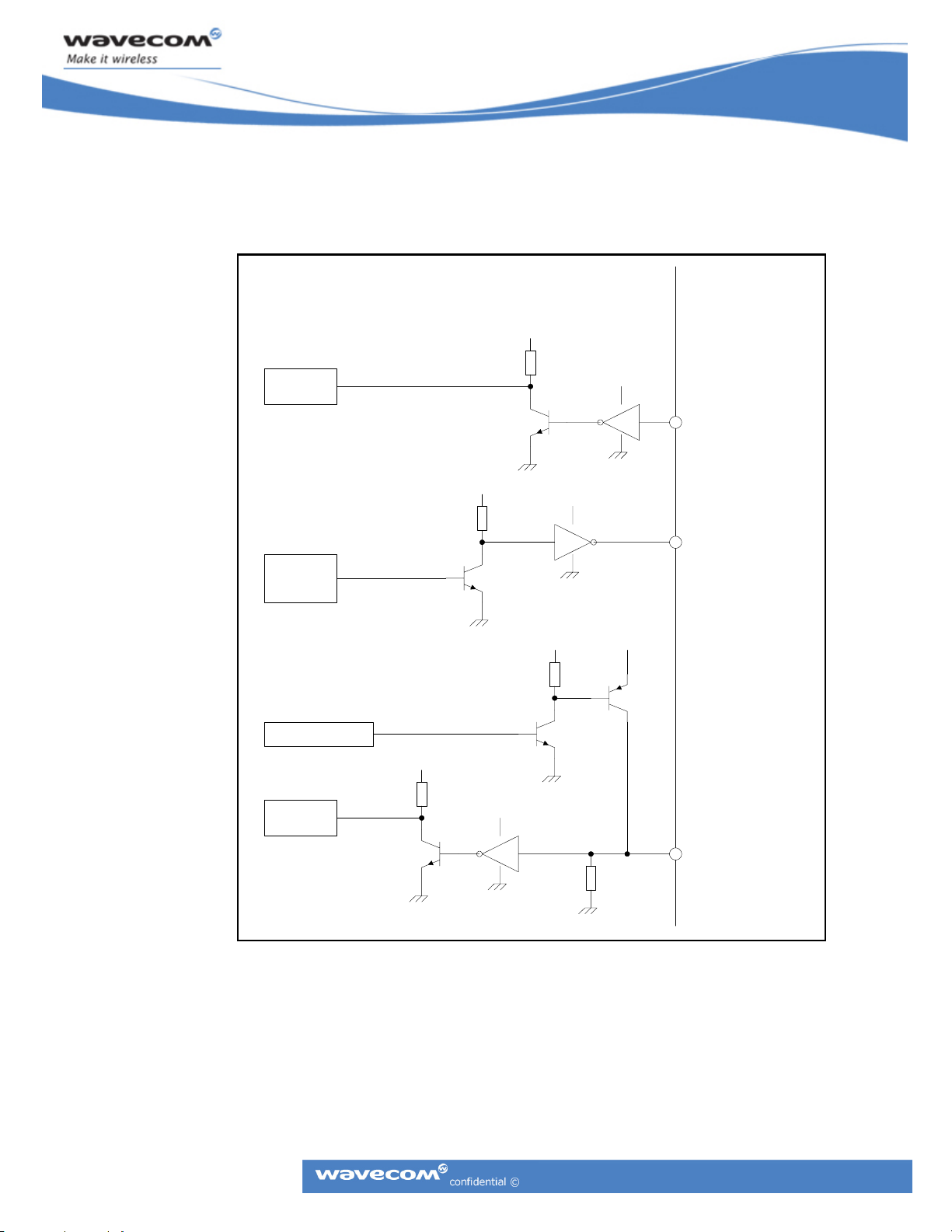
3.1 Status Group Recommended Circuitry
The status group contains four signals, one output signal from the application and three input
signals to the application.
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
WI_DEV_CM52_UGD_001-001
Page 38 of 53
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à des tiers sans son autorisation préalable
Page 39

CM52 Integrators’ Manual
Phone ModuleApplication
0 = Phone Module Power OFF
1 = Phone Module Power ON
5V
0 -10 ohm
VREF_CA
10uF
Shutdown Indicate
Shutdown Request
Ring Indicator
0 - 1k
1 - 100k
5V
0
VCC
12, MODULE_PWR_EN_B
+
-
100
VREF_CA
2, VREF
1M
15, HW_SD
40, RI
3.1.1 MODULE_PWR_EN_B
This signal, located on pin 12 in the system connector, enables the main 5V supply in the phone
®
Wireless CPU
so that it powers on. This is an open collector input to the phone Wireless CPU®. Its
reference voltage is the VCC_MAIN supply.
3.1.2 VREF
This signal, located on pin 2 in the system connector, provides the application with its logic supply
voltage. The application shall current-amplify this signal to use it as a supply (VREF_CA) for its
interface circuitry to the Wireless CPU
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
WI_DEV_CM52_UGD_001-001
Page 39 of 53
Figure 20: Status Group Diagram
®
.
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à des tiers sans son autorisation préalable
Page 40

3.1.3 RI
3.1.4 HW_SD
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
This signal, located on pin 40 in the system connector, provides the application with notification of
an incoming call or SMS. Please refer to the CM52 Software User’s Guide and AT Command Manual
for more details about what events can toggle this signal.
It takes approximately three seconds for the Wireless CPU
®
to be ready to receive data after it is
powered ON by pulling the MODULE_PWR_EN_B signal low. The application should not rely on the
ring indicator signal at power up, until the ‘Restart’ message is received via the RD signal.
This signal, located on pin 15 in the system connector, provides the ability to perform a hardware
shutdown of the Wireless CPU
®
. It is a bi-directional signal that is pulled up inside the phone
module.
Application Phone Module
VREF
Shutdown
Indicate
Shutdown
Request
15, HW_SD
Shutdown
Detect
Shutdown
Confirm
Figure 21: Pin 15 HW_SD Diagram
The following sequence and diagram illustrate a proper shutdown sequence initiated by the
application via the HW_SD pin.
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
WI_DEV_CM52_UGD_001-001
Page 40 of 53
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à des tiers sans son autorisation préalable
Page 41

CM52 Integrators’ Manual
Shut down sequence
1. To request a shutdown of the phone module, the application should provide an active low
pulse of 100 ± 25 ms on the HW_SD pin through an open collector output.
2. This pulse is detected by the Wireless CPU
HW_SD output, setting it active low.
3. The application waits for the HW_SD pin to become inactive high.
4. The Wireless CPU
®
has performed its power down sequence and disables its output
resulting in HW_SD becoming inactive high.
5. The application shuts down, disabling MODULE_PWR_EN_B.
HW_SD
®
, which confirms the request by enabling its
Shutdown
Request
Shutdown
Confirm
MODULE_
PWR_EN_B
1423
Figure 22: Shut Down Sequence Timeline
5
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
WI_DEV_CM52_UGD_001-001
Page 41 of 53
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à des tiers sans son autorisation préalable
Page 42
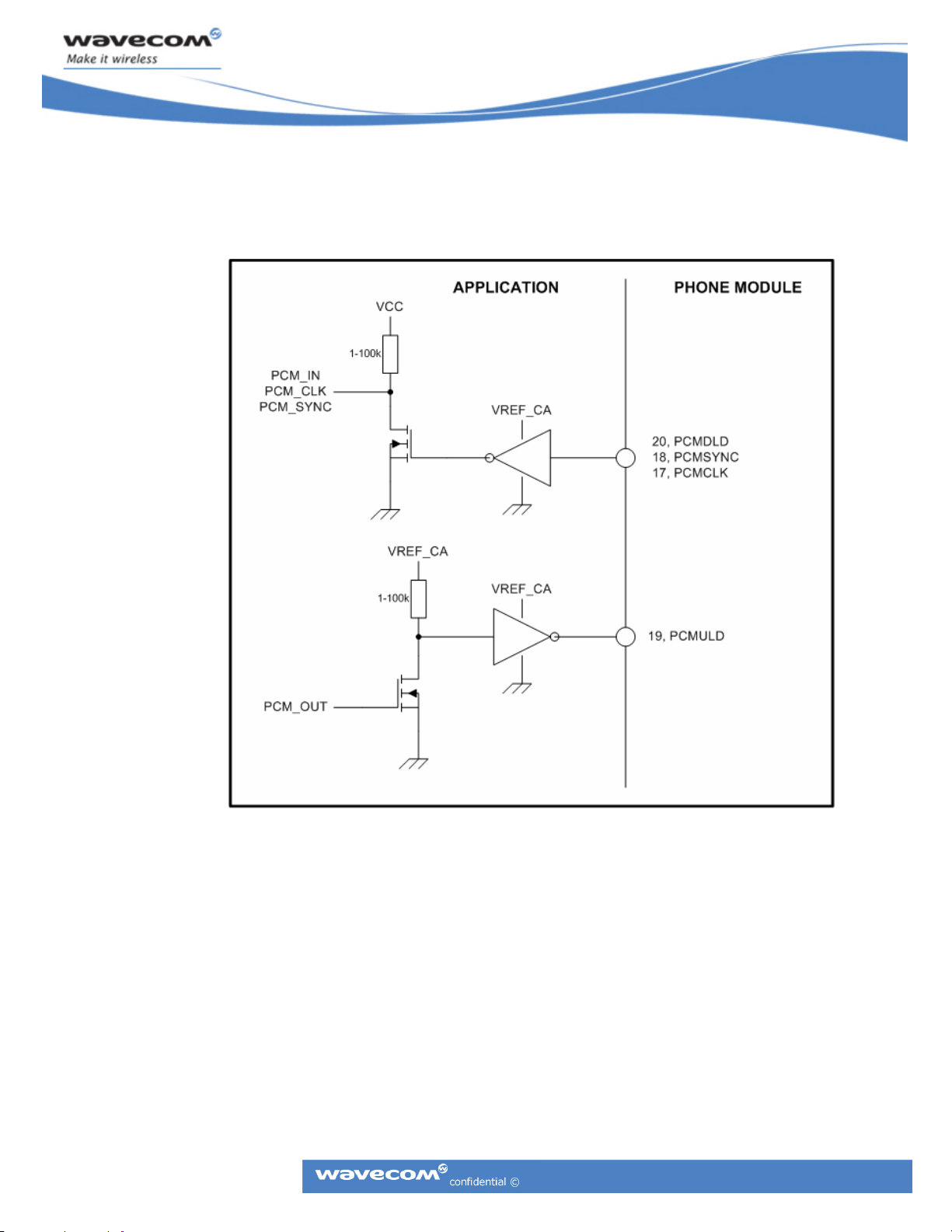
3.2 Data Group Recommended Circuitry
The data group contains six signals: three output signals from application, two input signals to
application, and one I/O signal.
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
RxD
CTS
TxD
RTS
DTR
VPPFLASH_EN
Application
1 - 100k
VREF_CA
1 - 100k
VCC
VREF_CA
1 - 100k
Phone Module
VREF_CA
30, RD (DFMS)
25, CTS
VREF_CA
27, TD (DTMS)
28, RTS
26, DTR
VREF_CA
3.2.1 VPPFLASH/DCD
This signal, located on pin 23 in the system connector, can be used by the application to enable
flashing of the phone module. To enter flash-mode, the application shall set VPPFLASH_EN active
high, then enable the MODULE_PWR_EN_B pin.
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
WI_DEV_CM52_UGD_001-001
Page 42 of 53
VCC
1 - 100k
DCD
VREF_CA
23, VPPFLASH/DCD
100k
Figure 23: Data Group Diagram
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à des tiers sans son autorisation préalable
Page 43
3.3 PCM Group Recommended Circuitry
The PCM group contains four signals, three input signals to the application, and one output signal
from the application.
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
WI_DEV_CM52_UGD_001-001
Page 43 of 53
Figure 24: PCM Group Diagram
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à des tiers sans son autorisation préalable
Page 44

3.4 Analog Audio Group Recommended Circuitry
3.4.1 Creating an analog ground
An analog ground plane should be generated which connects to GND in one point so that high
frequency digital current is not floating through the analog ground. Connecting the analog ground
in only one point avoids ground currents from power supplies and other high current circuitry from
creating noise in the analog circuitry. This common point should be located where the analog
supply voltage (VANA) is generated (at filter (A), or regulator (B) depending on implementation).
5V
VANA
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
BA
12V
Regulator
VANA
Figure 25: Creating an analog reference voltage (BIAS)
The BIAS reference should be generated from the analog supply voltage (VANA) and be referenced
to the analog ground. This reference shall be used to bias all analog circuitry in the application.
VANA
100k
0
-
BIAS
+
100k
Figure 26: BIAS/VANA Reference
The bias can be tapped directly from the resistor voltage divider, but the amplifier will make the
bias more stable and less susceptible to noise.
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
WI_DEV_CM52_UGD_001-001
Page 44 of 53
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à des tiers sans son autorisation préalable
Page 45
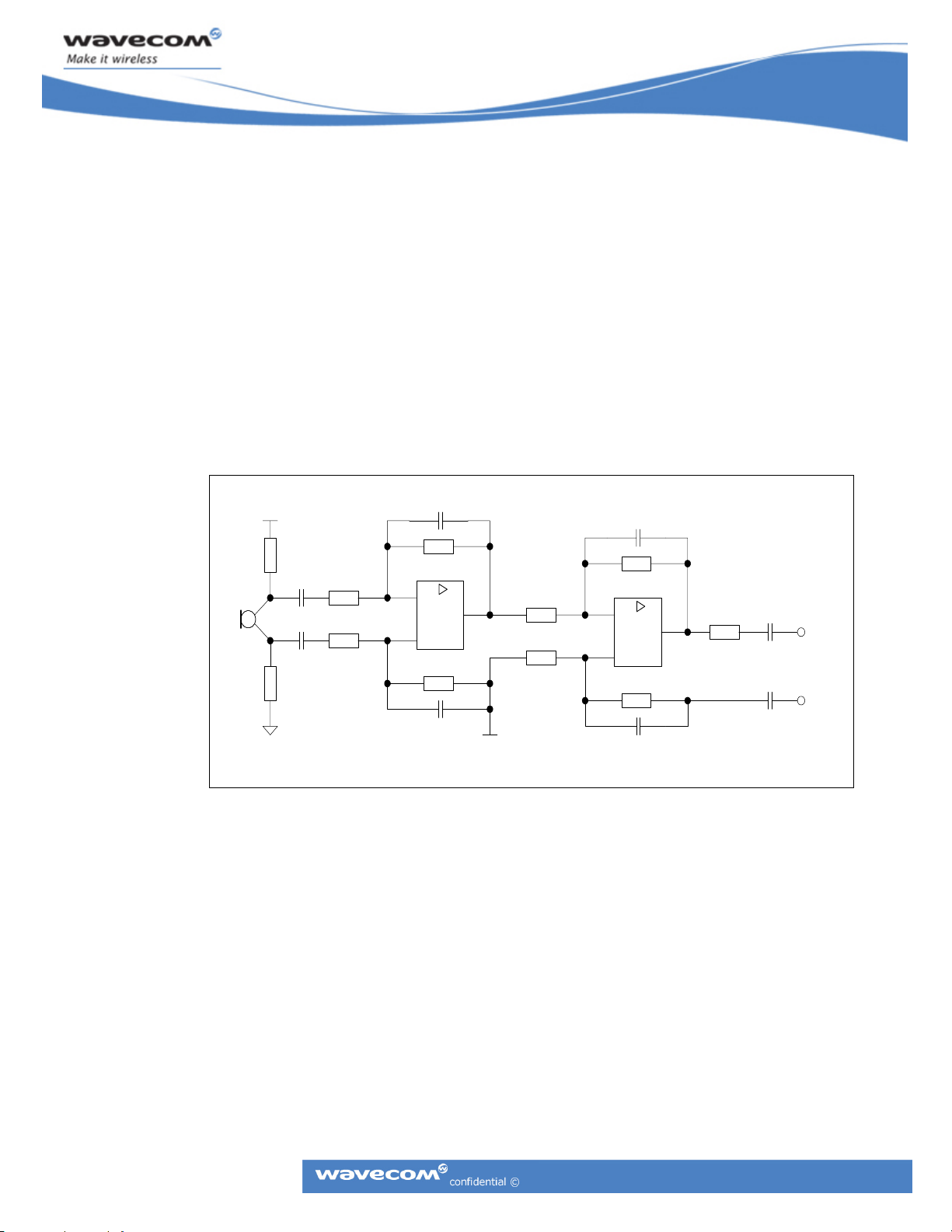
3.4.2 Analog ground vs. AGND
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
The AGND signal output from the Wireless CPU
connected to the main ground and used by the Wireless CPU
Under any circumstances it should not be used as a ground or connected to application’s ground.
AGND must be treated as a signal. Together with ATMS and AFMS it creates a semi differential
interface. The analog ground shall be used as ground plane for the analog circuitry of the
application. It should not be connected to the AGND signal output from the phone module.
3.4.3 Microphone path
An application using the analog audio interface must re-reference the signal from its own internal
BIAS to AGND received from the Wireless CPU
The figure below shows an example of a microphone implementation.
VCC
®
is not a ground. It is an analog reference,
®
in one place inside the Wireless CPU®.
®
.
C3
C5
R1
C2
R2
C2
R2
R1
R3
0
-
0
+
R3
C3
BIAS
R4
R4
R5
0
-
0
<=1k
>=2.2uF
+
ATMS
+
R5
C5
>=2.2uF
+
AGND
The microphone should preferably be connected to its pre-amplifier differentially which will
minimize noise picked up along the way from the microphone to its amplifier. If the impedance is
the same on both microphone lines, and the lines are run in parallel, the same amount of noise is
picked up on both lines. This noise is then removed in the differential amplifier stage.
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
WI_DEV_CM52_UGD_001-001
Page 45 of 53
Figure 27: Microphone Implementation Example
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à des tiers sans son autorisation préalable
Page 46

3.4.4 Loudspeaker path
An application using the analog audio interface must re-reference the AFMS-signal from AGND to
its own internal BIAS. The figure shows a differential implementation. C1 is chosen to create the
correct HP frequency response. R1 and R2 determine the gain, and C2 and R2 determine the LP
frequency response.
AFMS
AGND
C1
C1
R1
>=10k
R1
>=10k
-
+
C2
R2
R2
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
0
0
Internal App +
Internal App -
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
WI_DEV_CM52_UGD_001-001
Page 46 of 53
C2
Figure 28: Loudspeaker Implementation Example
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à des tiers sans son autorisation préalable
BIAS
Page 47
3.5 System connector IO functionality
Note 1: The application IO can be one of the following listed types:
I Logic input (no pull up or pull down resistors required).
IOC Logic open-collector input.
O Logic output (no pull up or pull down resistors required).
OOC Logic open-collector output.
I/O Logic I/O.
The pin direction in this table is referenced from the application’s point of view.
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
Group Pin
Name Application Requirements App
No
HW flow control is by default enabled in the phone module.
27 TD (DTMS) Logic output to phone module. The application shall set this
30 RD (DFMS) Logic input from phone module. I
28 RTS Logic output to phone module. Pulled down by the phone module
25 CTS Logic input from phone module. This signal is initially set high,
26 DTR Logic output to phone module. This signal is pulled up in the
Data
23 VPPFLASH/DC
D
PCM
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
WI_DEV_CM52_UGD_001-001
Page 47 of 53
19 PCMULD Logic output to phone module. O
20 PCMDLD Logic input from phone module. I
18 PCMSYNC Logic input from phone module. I
output high upon start-up.
(R > 20k). The application shall set this pin low when ready to
receive data.
indicating that the phone module is not ready to receive data. It is
set low when the phone module is ready to receive data.
phone module (R > 20k).
This signal should be set low by the application during a data call.
A low to high transition will terminate the data call.
This signal is asserted by the application when it wishes to open a
communications channel. The phone module then prepares the
modem to be connected to the telephone circuit, and, once
connected, maintains the connection. When DTR is de-asserted,
the phone module is switched to "on-hook" to terminate the
connection.
DCD: Logic input from phone module. This signal is set default
high. It goes low indicating that a data call is established,
(CONNECT) received from remote modem. The signal goes high
when data connection is disconnected.
Sent from the phone module (DCE) to the application (DTE) to
indicate that it has received a basic carrier signal from a (remote)
DCE.
VPPFLASH: The application shall not apply a voltage to this pin
unless they intend to use it as VPPFLASH in which case it
becomes a power output.
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à des tiers sans son autorisation préalable
I/O
O
O
I
O
I/O
Page 48

Group Pin
Analog
Audio
Status
Unused
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
Name Application Requirements App
No
17 PCMCLK Logic input from phone module. I
9 AGND Analog reference. This signal is an analog reference output by the
phone module. This signal is connected to GND in one place in
the phone module. Under no circumstances shall it be connected
to any ground or be used as ground in the application.
See 2.4 for more detailed information.
10 AUX1(ATMS) Single ended audio output to phone module. O
7 AUX0(AFMS) Single ended audio input from phone module. I
12 MODULE_PWR
_EN_B
2 VREF Phone module logic voltage sense input to application. This signal
40 RI This signal is used to indicate to the application of an incoming
24 RINGER
6
15 HW_SD Bi-directional signal, default set to be an open collector output from
39 CFMS No termination. Leave open. I
37 CTMS No termination. Leave open. O
36 Reserved No termination. Leave open. IOC
35 Reserved No termination. Leave open. IOC
38 Reserved No termination. Leave open. O
4 IO_4_VRTC No termination. Leave open. I/O
3 IO_3_GPS_FIX No termination. Leave open. I/O
1 IO_1_TIMEMARK No termination. Leave open. I/O
Logic open collector output that is set low by the application to
enable power to the phone module. The pull-up resistor resides in
the phone module.
provides the application with the logic system voltage level used
by the phone module.
voice or data call or SMS. The event is indicated by the signals
falling edge and remains low for 100 ms.
Pulse Modulated logic input from phone module. The application
must provide power amplification if the current draw is expected to
exceed 1mA.
the application.
I/O
I
OOC
I
I
I
OOC
I
Reserved
13 OUTPUT1 No termination. Leave open. I
16 INPUT2 No termination. Leave open. O
11 INPUT1 No termination. Leave open. O
14 OUTPUT2 No termination. Leave open. I
6
Not currently Implemented in the CM52.
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
WI_DEV_CM52_UGD_001-001
Page 48 of 53
Table 26: Pin Direction for General Purpose Signals
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à des tiers sans son autorisation préalable
Page 49

4 Functional Description
The CM52 Wireless CPU® performs a set of telecom services according to TIA/EIA-IS-2000. The
functions of the display and keypad, usually used to make calls, are implemented by issuing AT
Commands over the serial interface.
See the CM52 Software User's Guide and AT Command Manual for a complete functional
description and user scenarios for the CM52.
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
WI_DEV_CM52_UGD_001-001
Page 49 of 53
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à des tiers sans son autorisation préalable
Page 50

5 Hints for Integrating the Wireless CPU®
This section, which gives you advice and helpful hints on how to integrate the CM52 with the
application, should be taken as a guide.
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
Note!
The circuits on the test board are not shielded. Therefore take proper precautions for
avoiding ESD and EMI.
5.1 Precautions
Following is a list of preparations that you should make before beginning the integration work that
is described in this section.
Where to install the Wireless CPU
®
Safety standards
Network and subscription
Antenna
5.2 Where to Install the Wireless CPU®
Make sure that the Wireless CPU® is installed in proper environmental conditions such that
temperature, humidity, vibration, etc., are not beyond the limits specified for it.
Make sure that the signal strength is sufficient. To improve signal strength, move the antenna to
another position. Signal strength may depend on how close the Wireless CPU
station. Degradation in signal strength could be a result of disturbance from another source, for
example, an electronic device nearby.
®
is to a radio base
You can verify signal strength by issuing the AT command AT+CSQ. See the CM52 Software User’s
Guide and AT Command Manual for a description of this and other useful AT commands.
Tip! Before installing the Wireless CPU®, use an ordinary mobile telephone to check a possible
location for it. Consider signal strength as well as cable length in determining the location for the
®
Wireless CPU
and antenna. That way you will find out if it is practical to install the Wireless CPU
where you intended.
5.3 Safety Standards
You are responsible for observing your country’s safety standards and the relevant wiring rules,
where applicable.
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
WI_DEV_CM52_UGD_001-001
Page 50 of 53
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à des tiers sans son autorisation préalable
®
Page 51

5.4 Antenna
5.4.1 Antenna Type
When choosing an antenna for your application you must consider the following requirements:
The antenna must be designed for the AMPS/CDMA 800 and CDMA 1900 MHz frequency band
(dual band) for the CM52.
The impedance of the antenna and antenna cable must be 50 Ω.
The VSWR value should be less than 2:1.
5.4.2 Antenna Placement
Always follow the instructions supplied by the antenna manufacturer.
You should place the antenna away from electronic devices or other antennas. The recommended
minimum distance between adjacent antennas operating in a similar radio frequency band is at
least 50 centimeters.
If the Wireless CPU
centimeters must be maintained between the radiating antenna and the user or nearby persons. In
this mode of operation, the combined connection cable path loss and antenna gain must be no
greater than 1 dBi.
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
®
is used in the Class I AMPS mode, a separation distance of at least 23
5.5 Possible Communication Disturbances
Noise can be caused by electronic devices and radio transmitters.
Free Space
distance from the transmitter.
Shadowing is a form of environmental attenuation of radio signals that is caused by hills,
buildings, trees or even vehicles. Inside buildings this can cause problems, especially if the walls
are thick and reinforced.
Multi-path fading is a sudden decrease or increase in the signal strength. This is the result of
interference caused when direct and reflected signals reach the mobile phone simultaneously. Flat
surfaces such as buildings, streets, vehicles, etc, can reflect signals.
Path-loss occurs as the strength of the received signal steadily decreases with the
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
WI_DEV_CM52_UGD_001-001
Page 51 of 53
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à des tiers sans son autorisation préalable
Page 52

6 Technical Data
Mechanical specifications
Maximum length: 114 mm
Maximum width: 49.50 mm
Maximum thickness: 18.97 mm
Weight: 68.2 g
Power supply voltage, normal operation VCC_MAIN VCC_AUX
Nominal Voltage: 5.00 Volts 13.8 Volts
Voltage range: 4.50 – 5.50 Volts 11.0 – 16.5 Volts
Radio specifications AMPS CDMA (BC-0) CDMA (BC-1)
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
Frequency range: TX: 824 – 849
RX: 869 – 894
Antenna impedance:
50 Ω 50 Ω 50 Ω
TX: 824 – 849
RX: 869 – 894
TX: 1850-1910
RX: 1930-1990
VSWR (Maximum): 2:1 2:1 2:1
Environmental specifications
Operating temperature range:
-30°C to +70°C: EIA/TIA/IS-2000
+70°C to +85°C: –3dB Degradation beyond +70°C Spec
Storage temperature range: -40
Relative humidity:
0
C to +85 0C
85% ± 3% at +85
0
C
Stationary Vibration Profile:
Mounting Configuration “A” Frequency (Hz) PSD (G2 / Hz)
Profile:
5 – 10 0.00998
10 – 200 0.029946
200 – 500 0.00998
Total Grms: 2.95
Mounting Configuration “B” Frequency (Hz) PSD (G
Profile:
10 0.02936
2
/ Hz)
170 0.00489
200 0.00978
350 0.00978
400 0.01958
750 0.000978
950 0.00978
2000 0.000048
Total Grms: 2.86
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
WI_DEV_CM52_UGD_001-001
Page 52 of 53
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à des tiers sans son autorisation préalable
Page 53

CM52 Integrators’ Manual
Non-stationary vibration, including shock Shock response spectrum I, peak acceleration:
- 4 shocks in each axis and direction: 300 m/s2, 11 ms
Bump: Acceleration 250 m/s2
Free fall transportation: 1.0 m
Rolling pitching transportation: Angle: 35 degrees, period: 8s
Static load: 10 kPa
Low air pressure/high air pressure: 70 kPa / 106 kPa
Table 27: Technical Data
CM52 Integrators’ Manual
WI_DEV_CM52_UGD_001-001
Page 53 of 53
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged without prior written agreement.
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à des tiers sans son autorisation préalable
Page 54

APPLICATION NOTE
GR/GS64 Charging Interface
Page: 1/1
WAVECOM S.A. - 3 esplanade du Foncet - 9 2442 Issy-les-Moulineaux Cedex - France - Tel: +33(0)1 46 29 08 00 - F ax: +33(0)1 46 29 08 08
This document is the sole and exclusive property of WAVECOM. Not to be distributed or divulged without prior written agreement.
Wavecom, Inc. - 430 Davis Drive - Suite 300 - Research Triangle Park, N C 27709 - USA - Tel: +1 919 237 4000 - Fax: +1 919 237 4140
Ce document est la propriété exclusive de WAVECOM. Il ne peut être communiqué ou divulgué à des tiers sans son autorisation préalable
WAVECOM Asia Pacific Ltd. - Unit 201-207, 2
Shatin - New Territories, Hong Kong - Tel: +852 2824 0254 - Fax: +852 2824 0255
nd
P
P
Floor - Bio-Informatics Centre - No. 2 Science Park West Avenue - Hong Kong Science Park,
 Loading...
Loading...