Waukesha Bearings CQ Tilting Pad Thrust Bearings User Manual
- 1 -
CQ Tilting Pad Thrust Bearings
Installation and Maintenance Instructions
1. Introduction
The following notes provide installation and assembly instructions for Waukesha
Bearings CQ tilting pad thrust bearings.
Reference should be made to the specific contract drawing for operational information
and special features which may be provided.
2. General Description
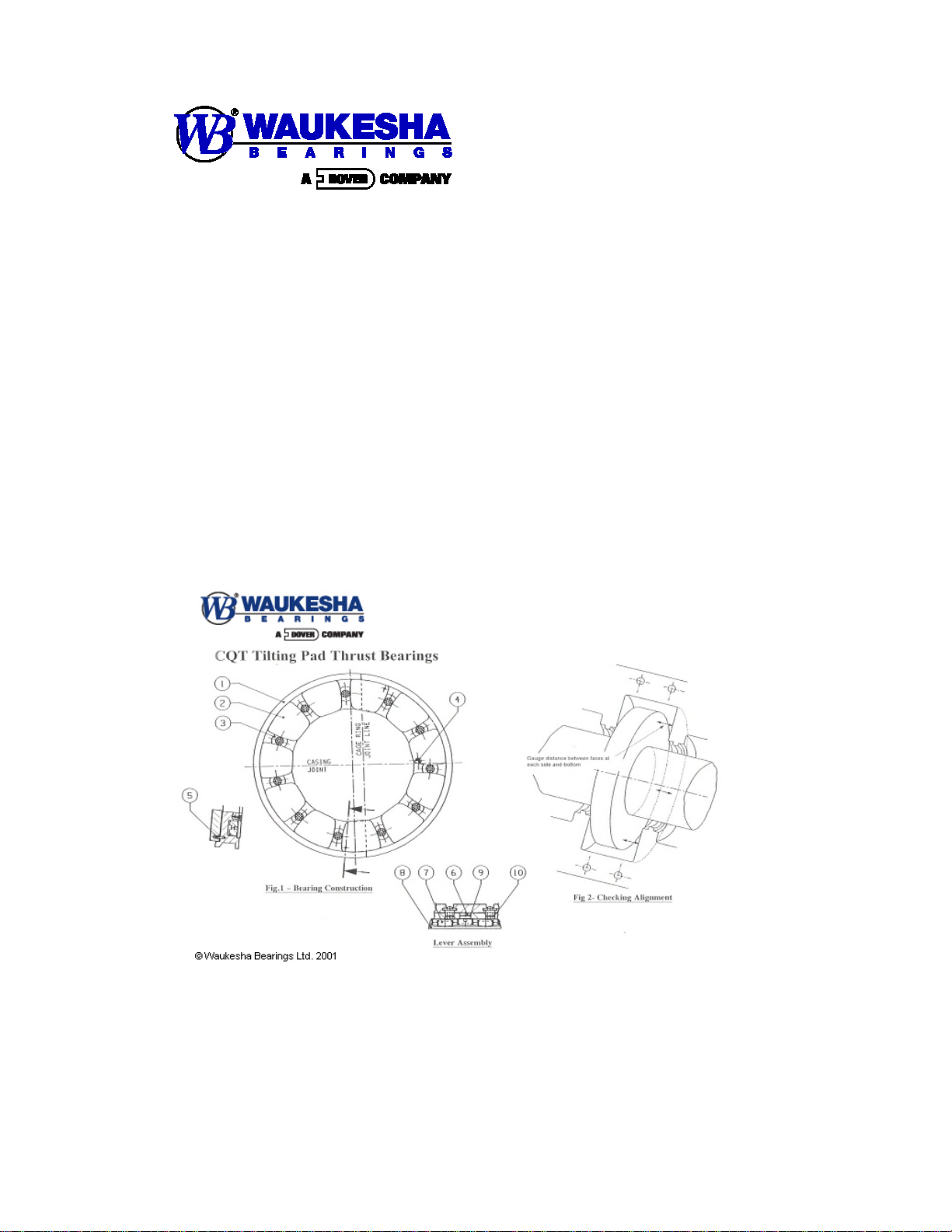
The Waukesha Bearings CQ bearing is shown in Fig 1, and reference is made to this
drawing in the following comments.
The CQ tilting pad thrust bearing consists of a number of thrust pads (item 2)
supported in a cage ring (item 1). Each pad is loosely retained by pad stops (item 3)
so that each pad is free to tilt and it is supported on a system of levers (item 7) to
equalise load sharing between the pads. A screw held spacer plate (item 8) is fixed to
the back face of the cage ring, securing the levers within the cage ring.

- 2 -
The spacer plate, normally supplied with a machining allowance, acts as an adjustable
spacer (for adjusting axial bearing clearance and/or rotor position).
The cage ring can be supplied in a one piece, or in halves construction, with an annular
groove around the bearing outside diameter to receive lubricating oil from the casing.
On bearings with rings in halves, pins (item 5) are provided near the joint line to ensure
security of the pad and levers whilst the two halves of the bearing are separated. 'O' rings
(items 9 and 10) are provided on the pillars and pad stops to retain their position in the
cage ring.
The thrust bearing is prevented from rotating in the casing by an anti-rotation pin
(item 4) situated in the back face of the cage ring.
3. Lubrication
The bearings are designed to be lubricated by a pressurised oil system, with oil supplied
into the cage ring annular groove. The oil then feeds from the annulus to the thrust
bearing chamber via a number of radial holes in the cage ring (which can also be used
for rotating the ring in the casing).
With flooded lubrication
wall of the cage ring, through to the shaft space, providing a continuous flow of oil
which fills the whole bearing chamber.
, oil from the lever chamber is fed via radial holes in the inside
For Directed Lubrication (DL) bearings, the oil feeds from the lever chamber to the
bearing face via spray pad stops. With Directed Lubrication, the bearing housing
should be provided with large drains to prevent an accumulation of oil (see contract
drawing).
4. Pad Design
The thrust pads are normally manufactured from steel lined with a tin based whitemetal
and are either offset pivot (single direction of rotation), or centre pivot (for both
directions of shaft rotation).
NB: In the case of double thrust bearings with an offset pivot arrangement, note that the
main and reverse pads are identical and interchangeable, as the pivot is built into the
cage ring assembly, not the pads.
Pads can be removed from the cage ring by sufficiently raising each pad stop with a
screwdriver or similar lever, whereby each pad can be withdrawn radially outwards.
5. Dismantling
Should it be necessary to completely dismantle the thrust bearing parts from the cage
ring, the procedure is as follows:
 Loading...
Loading...